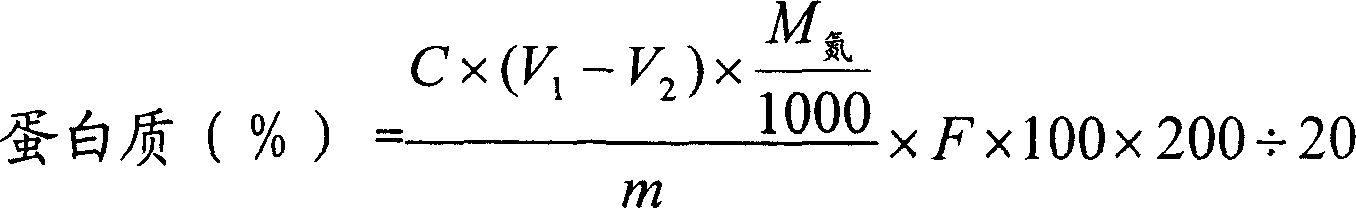Patents
Literature
69 results about "Test protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
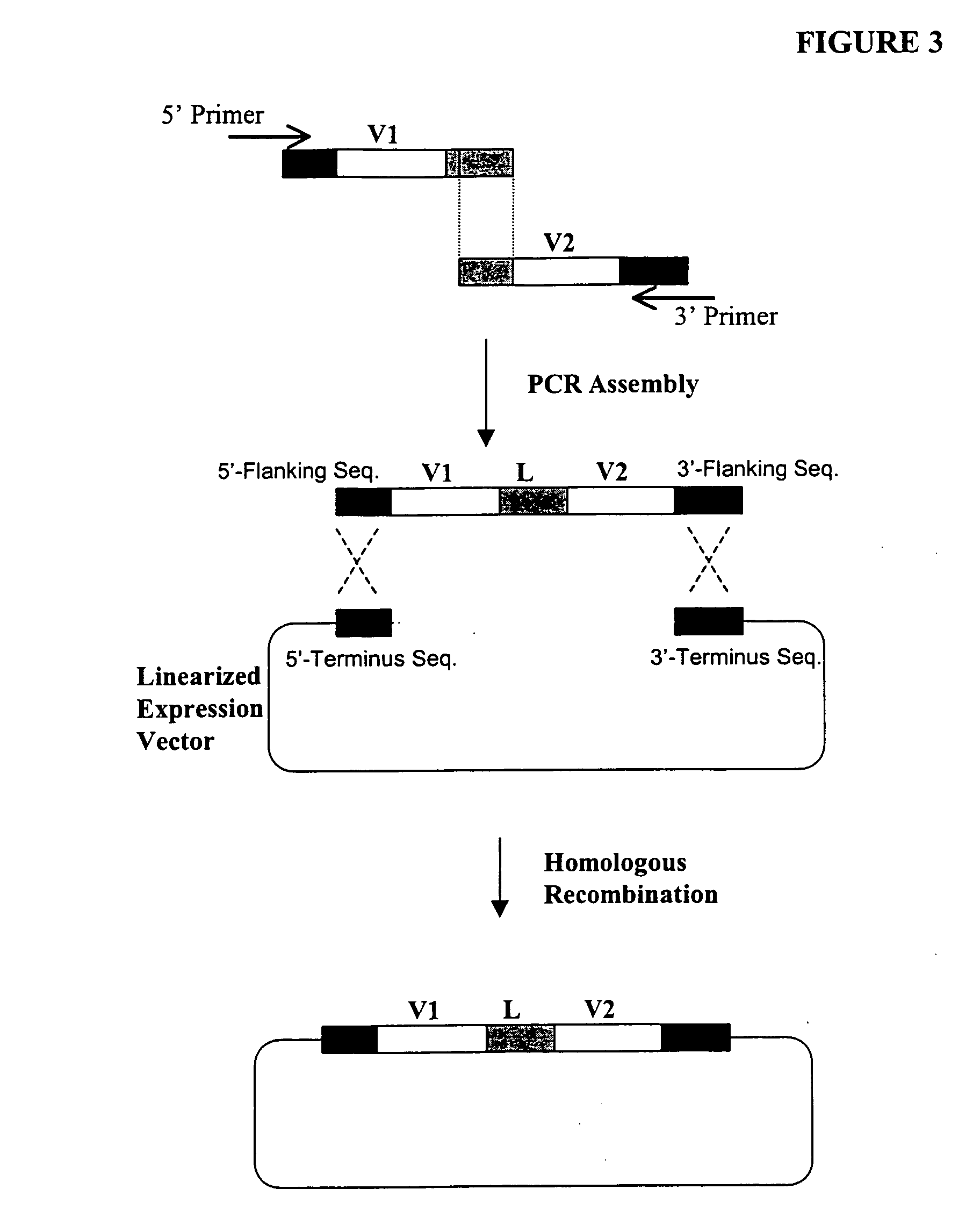
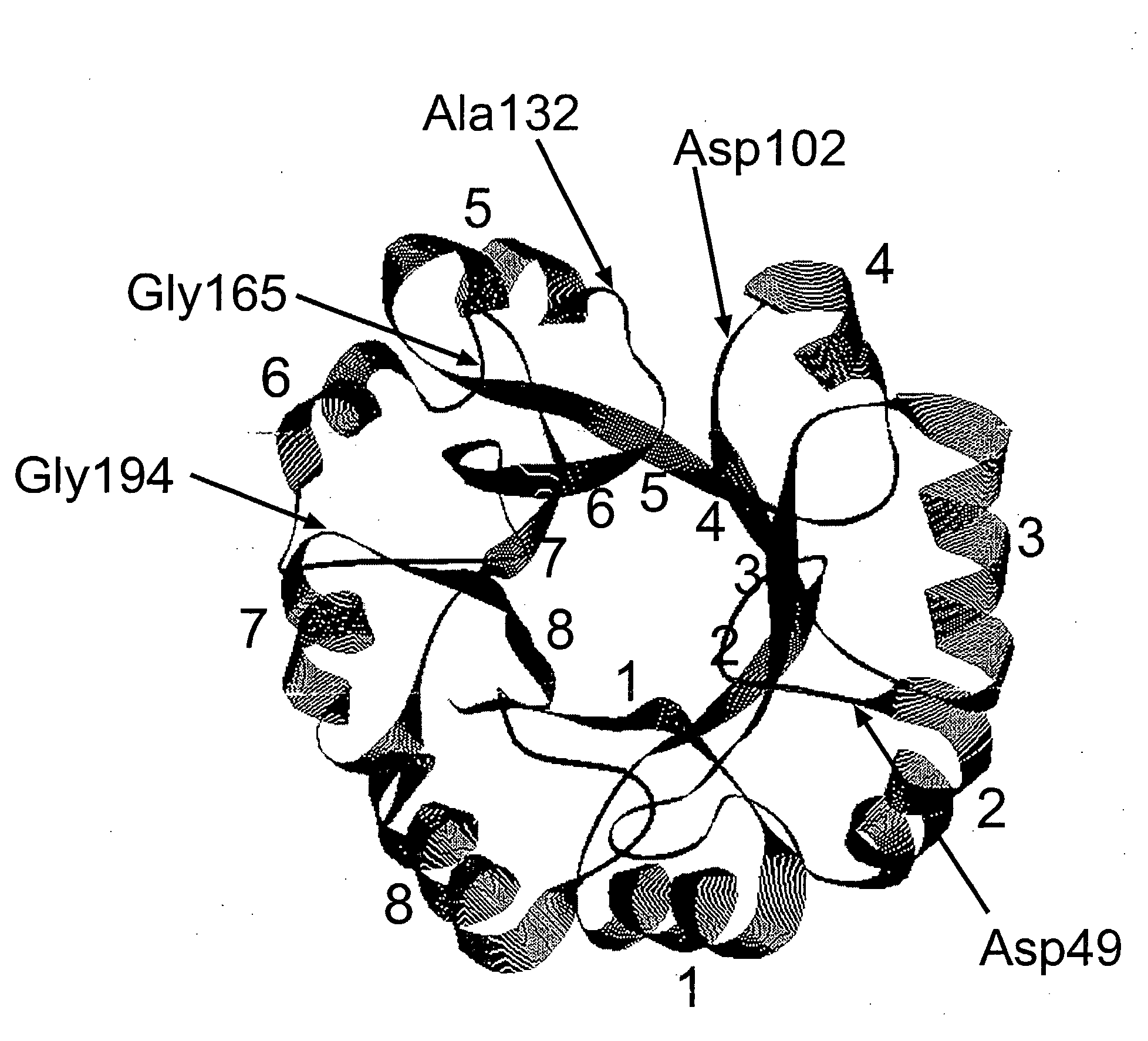
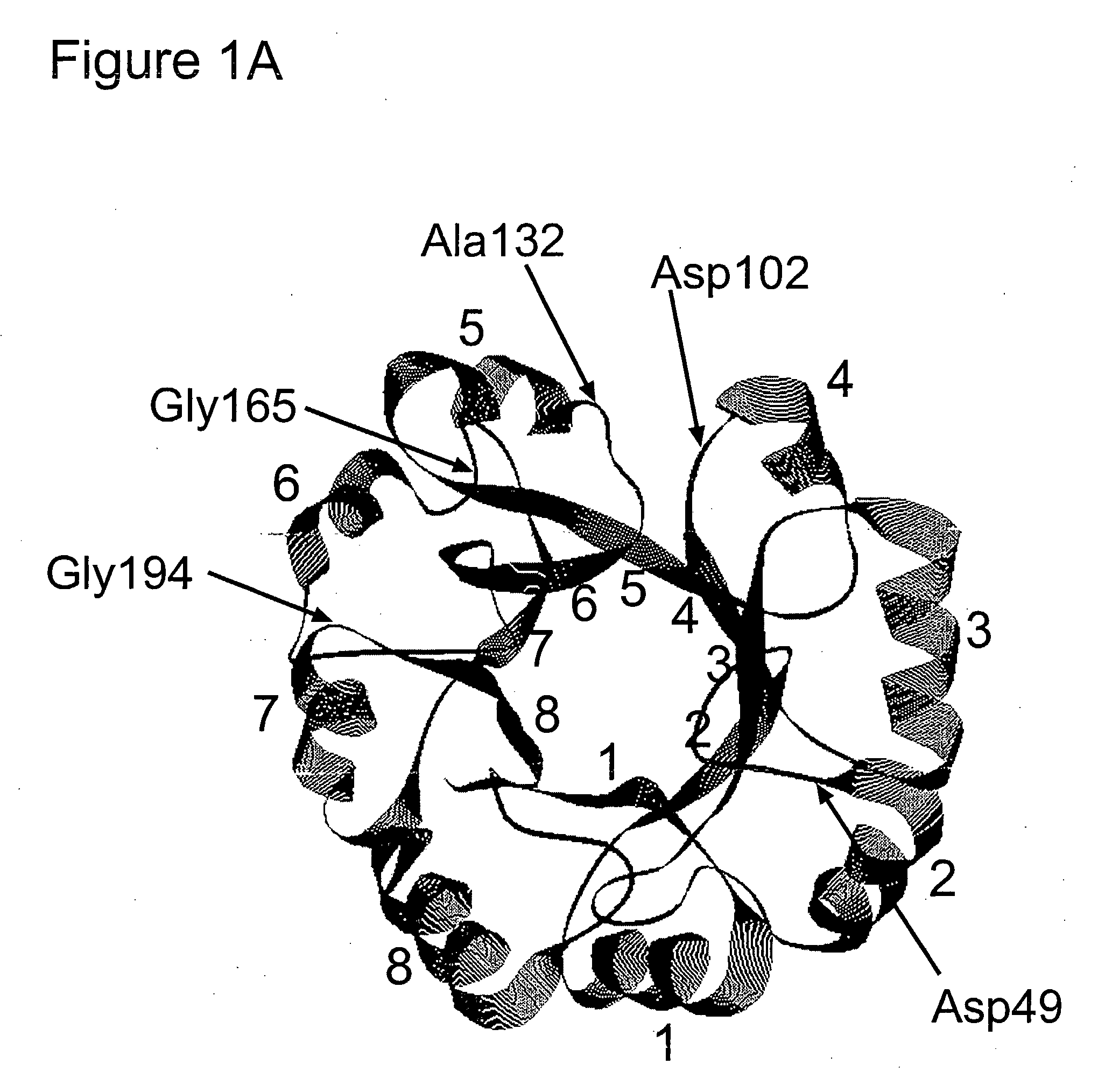
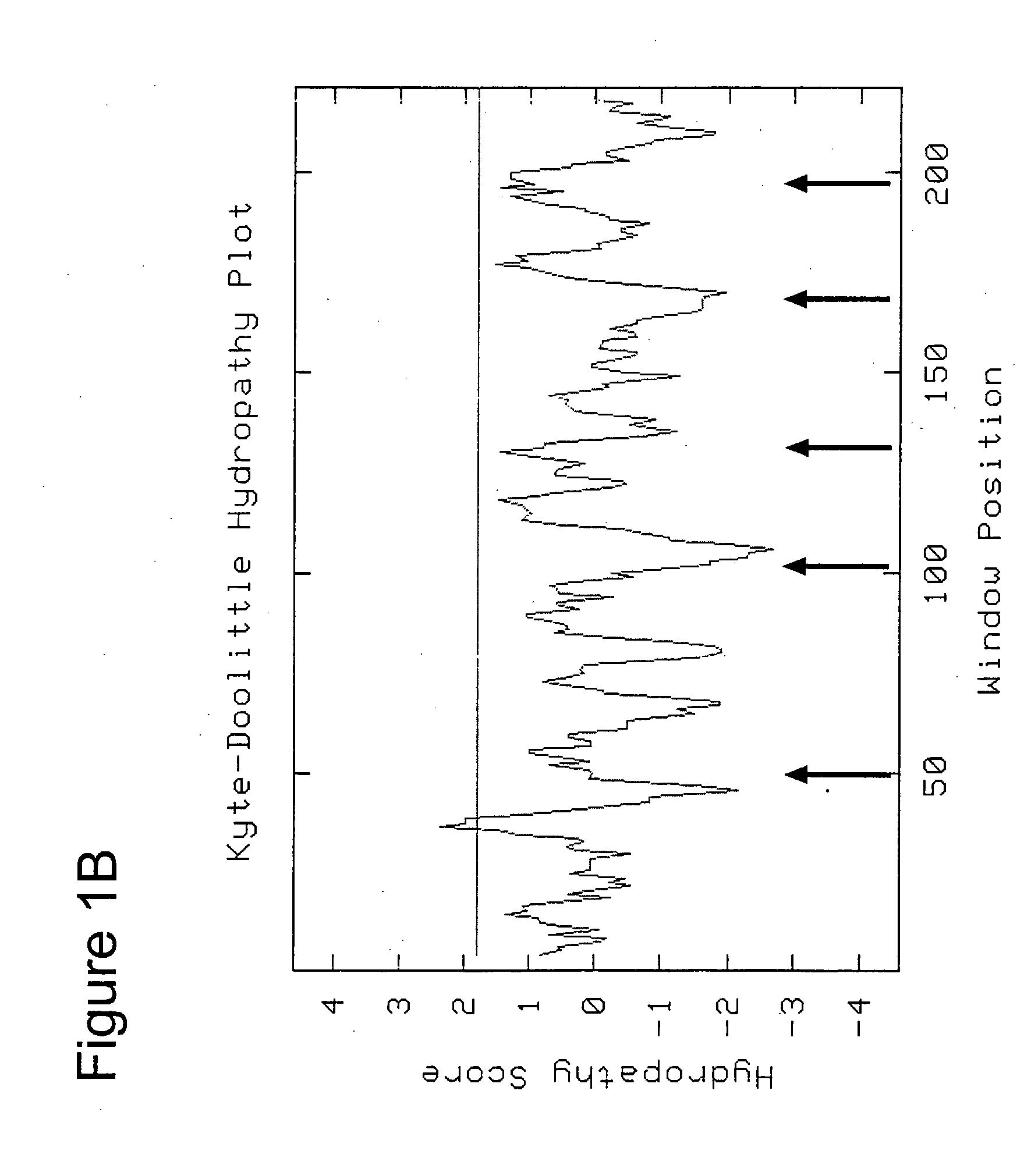
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
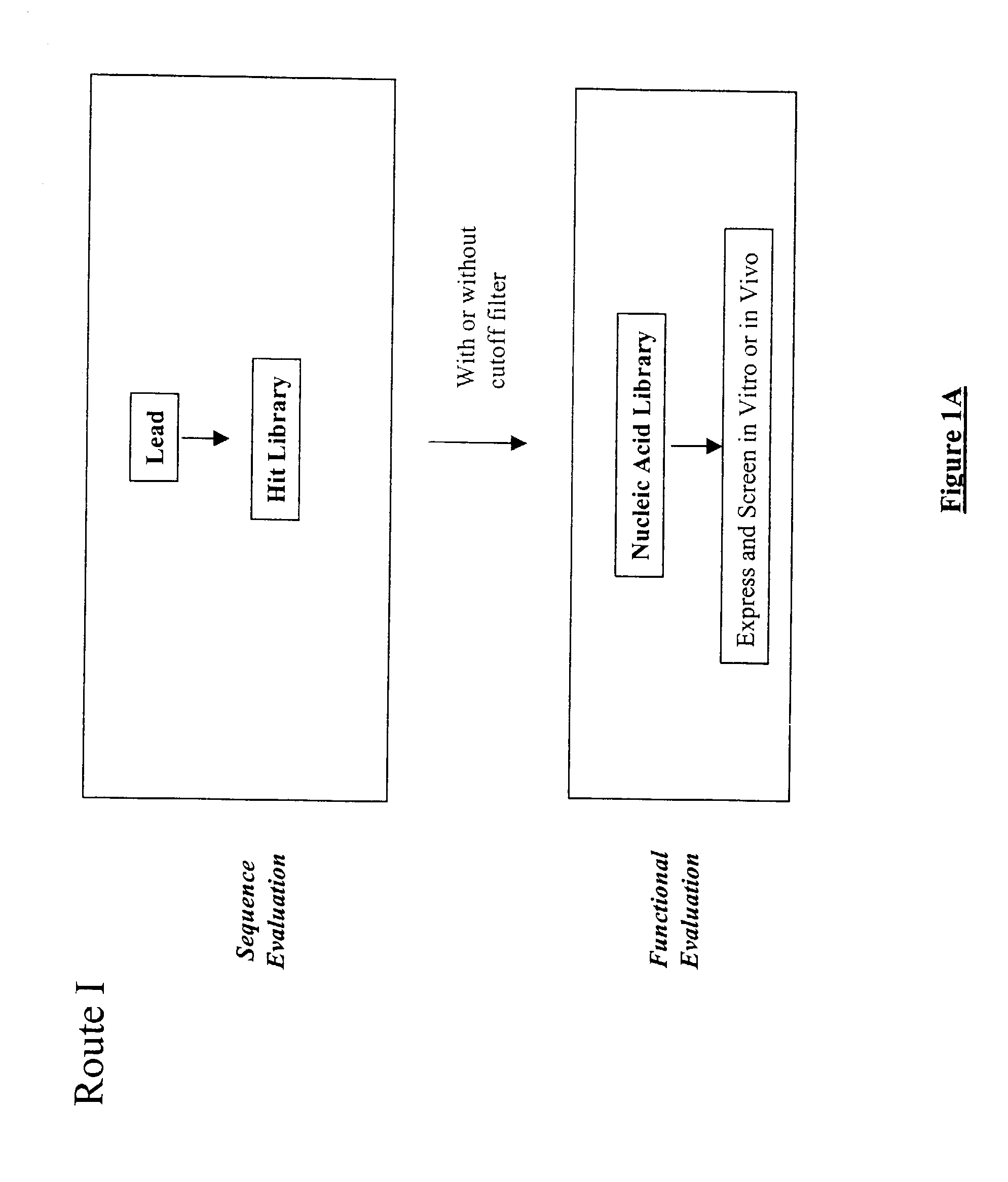
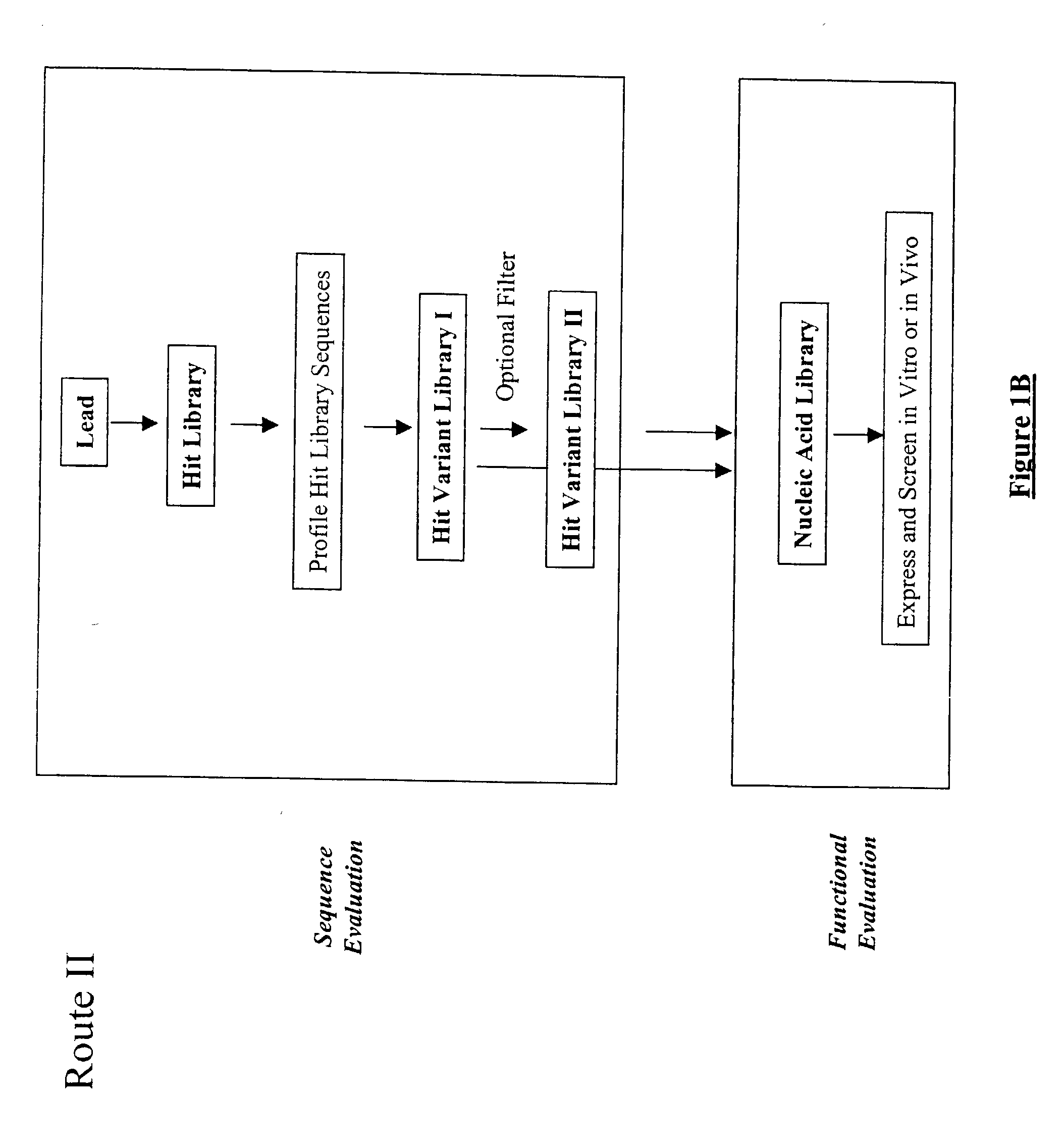
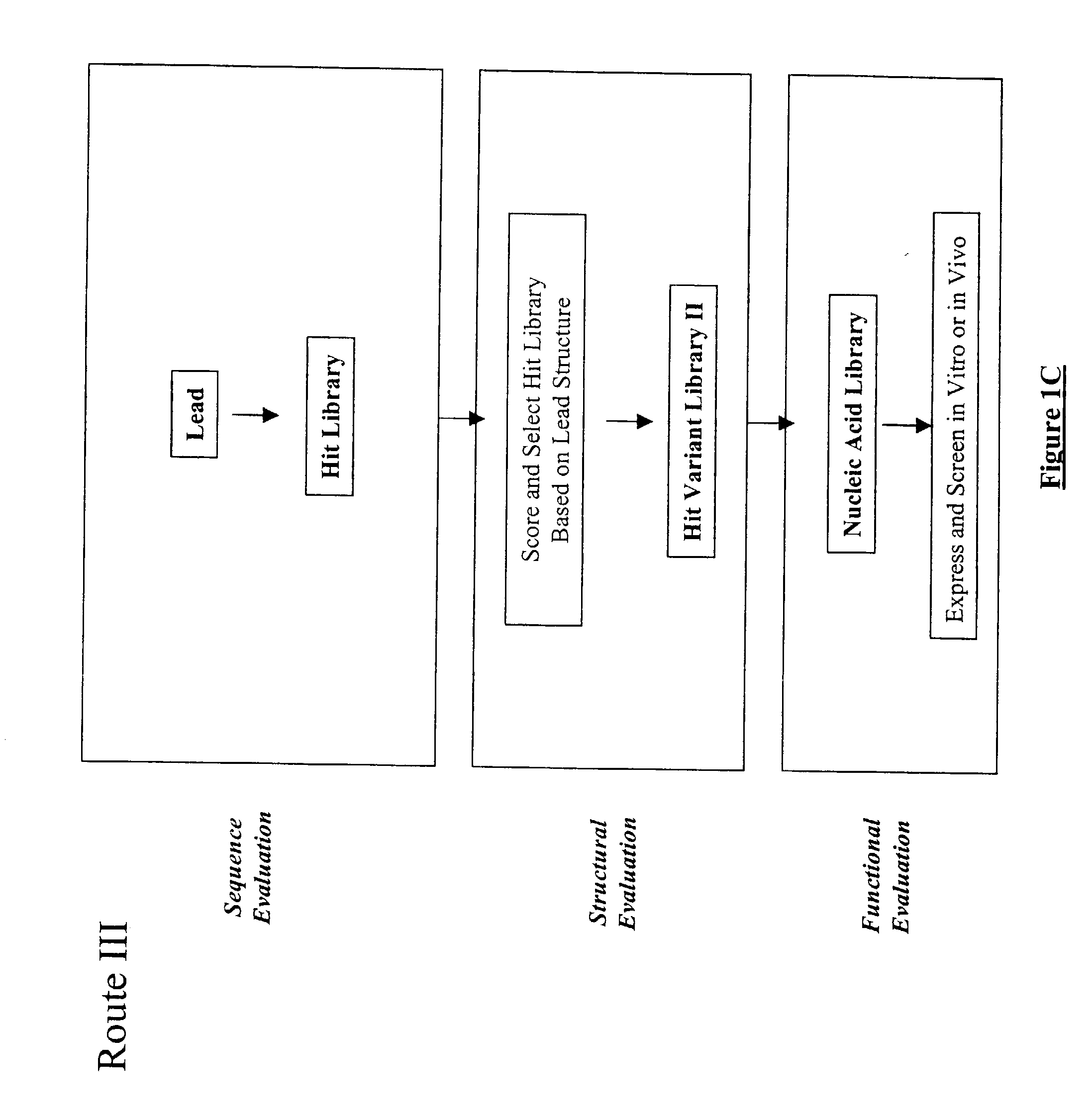
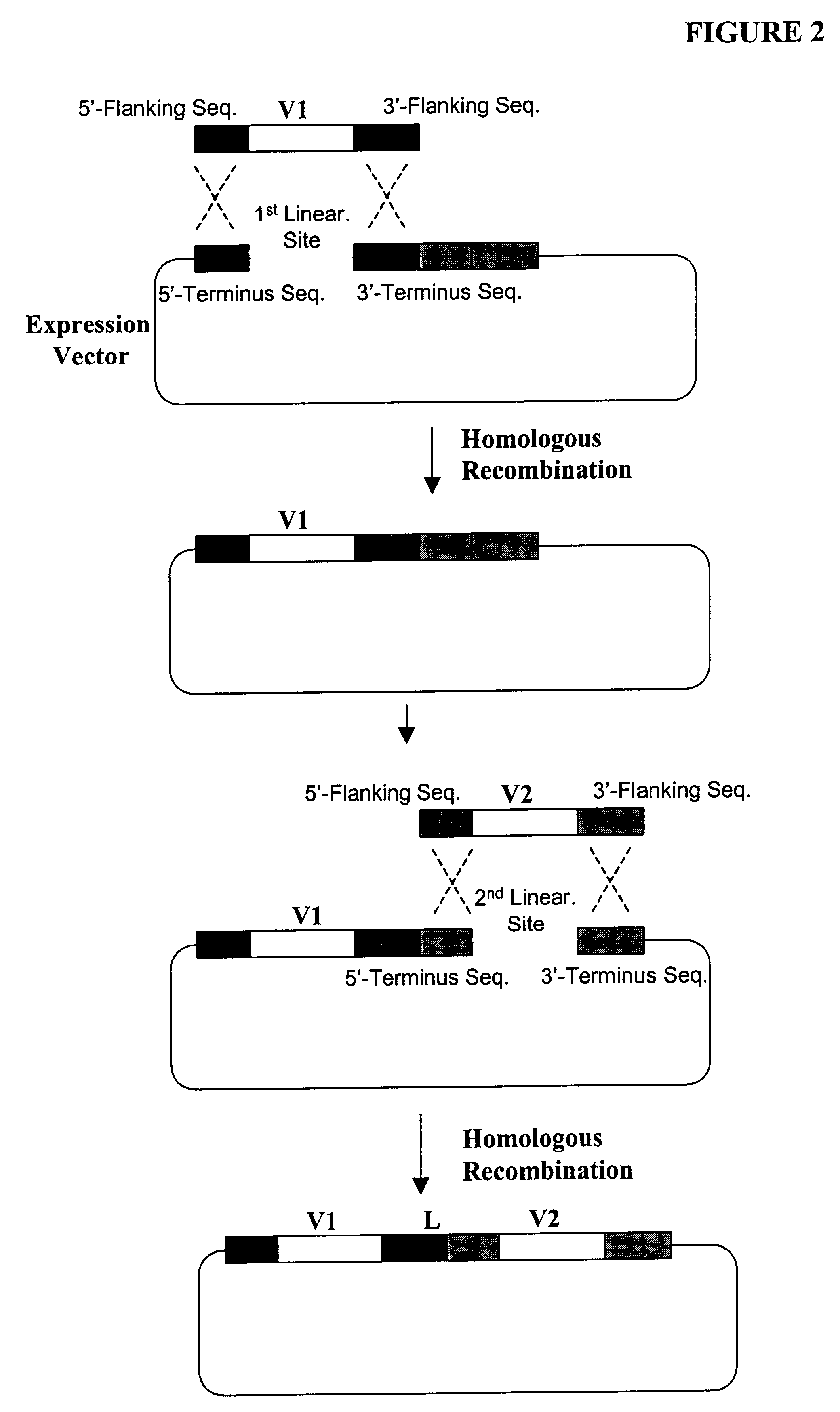
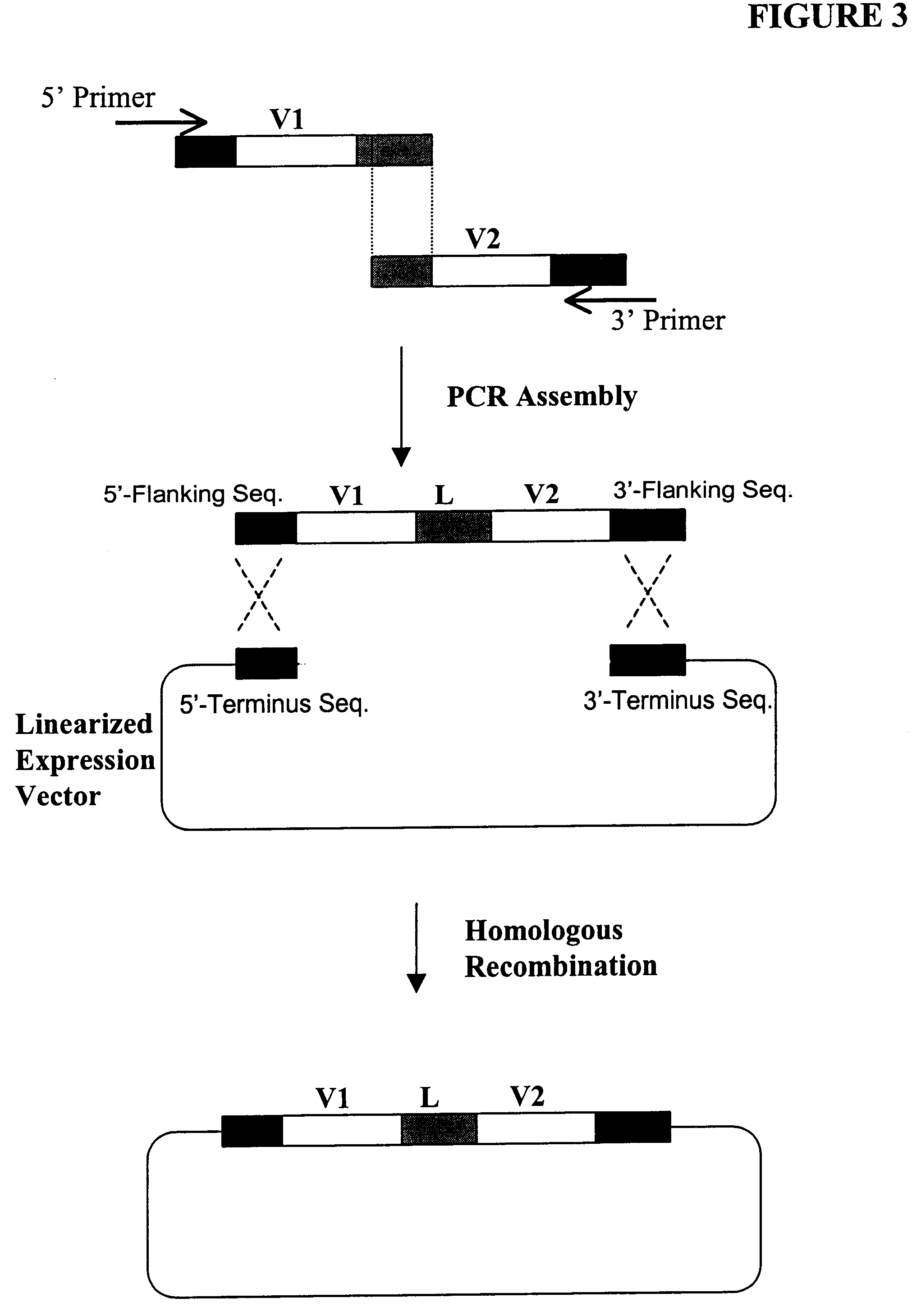
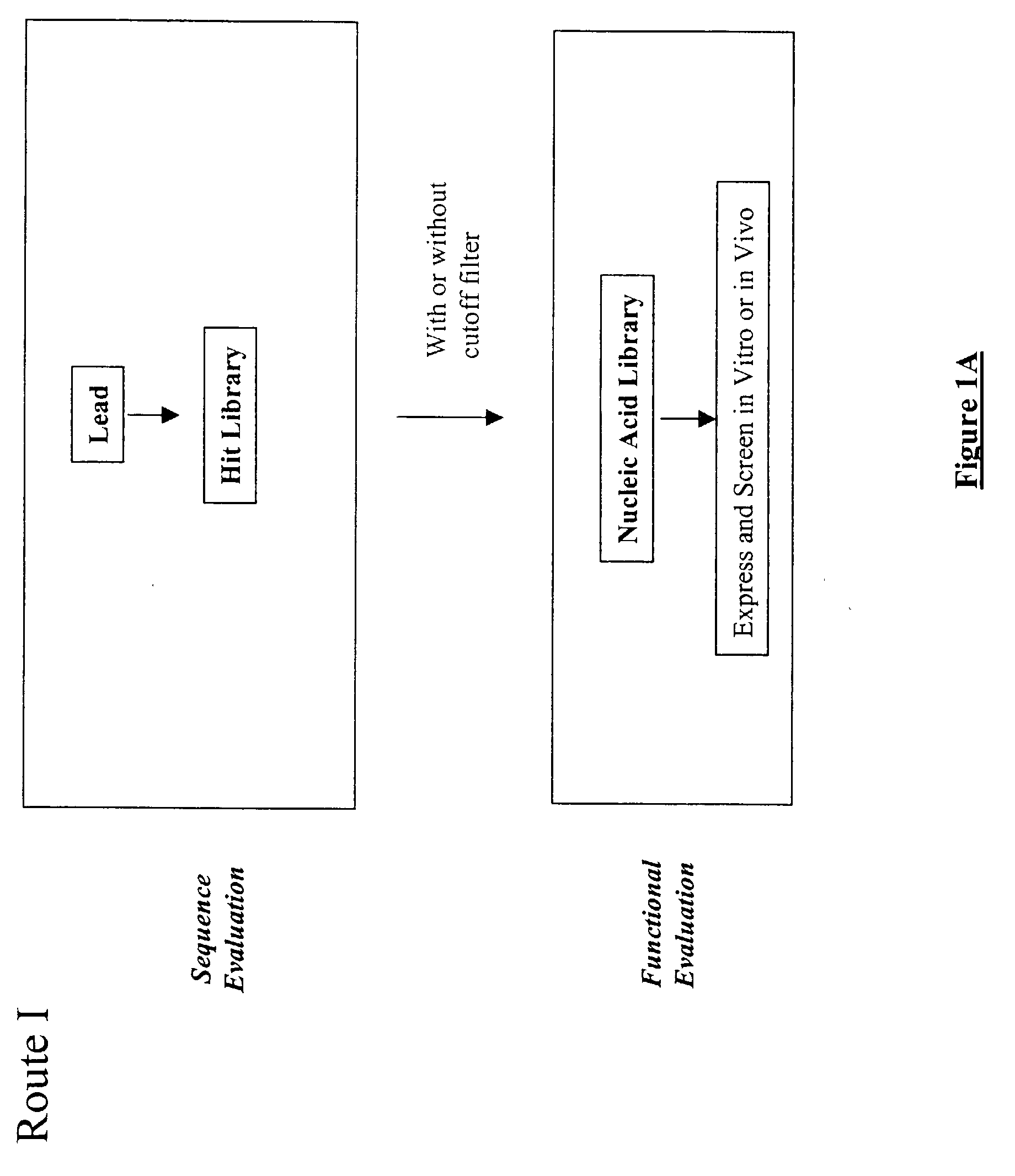
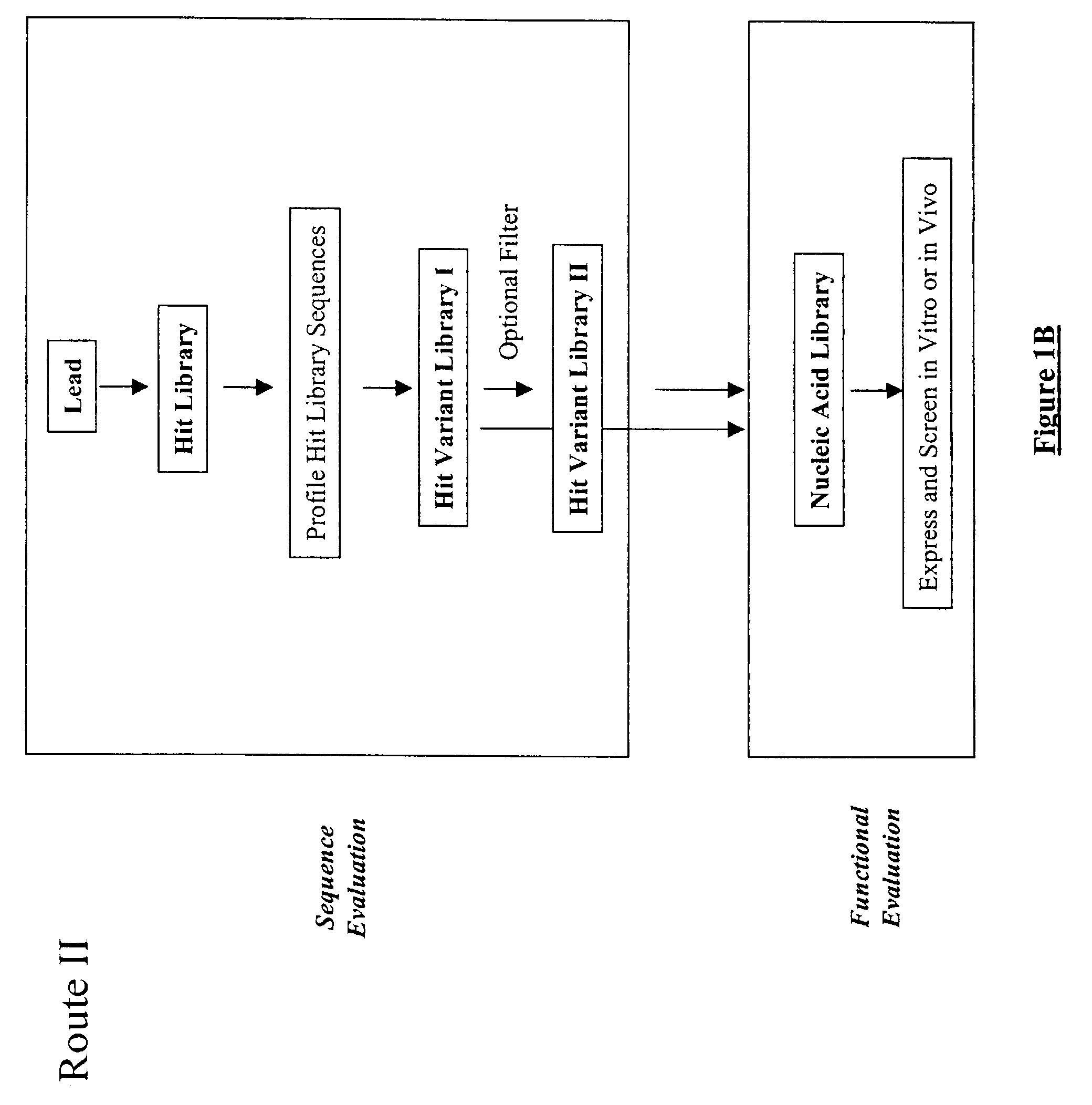
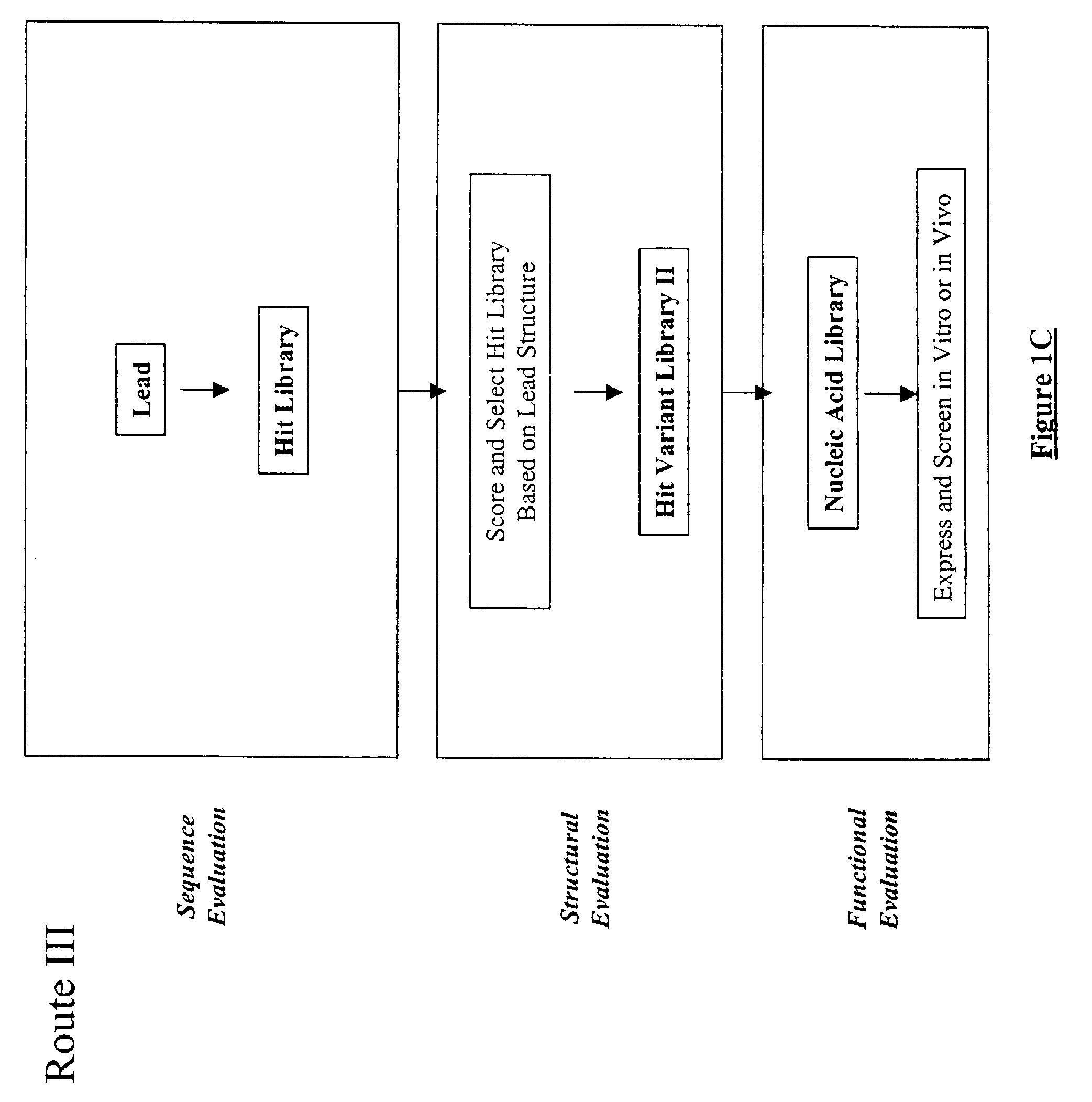
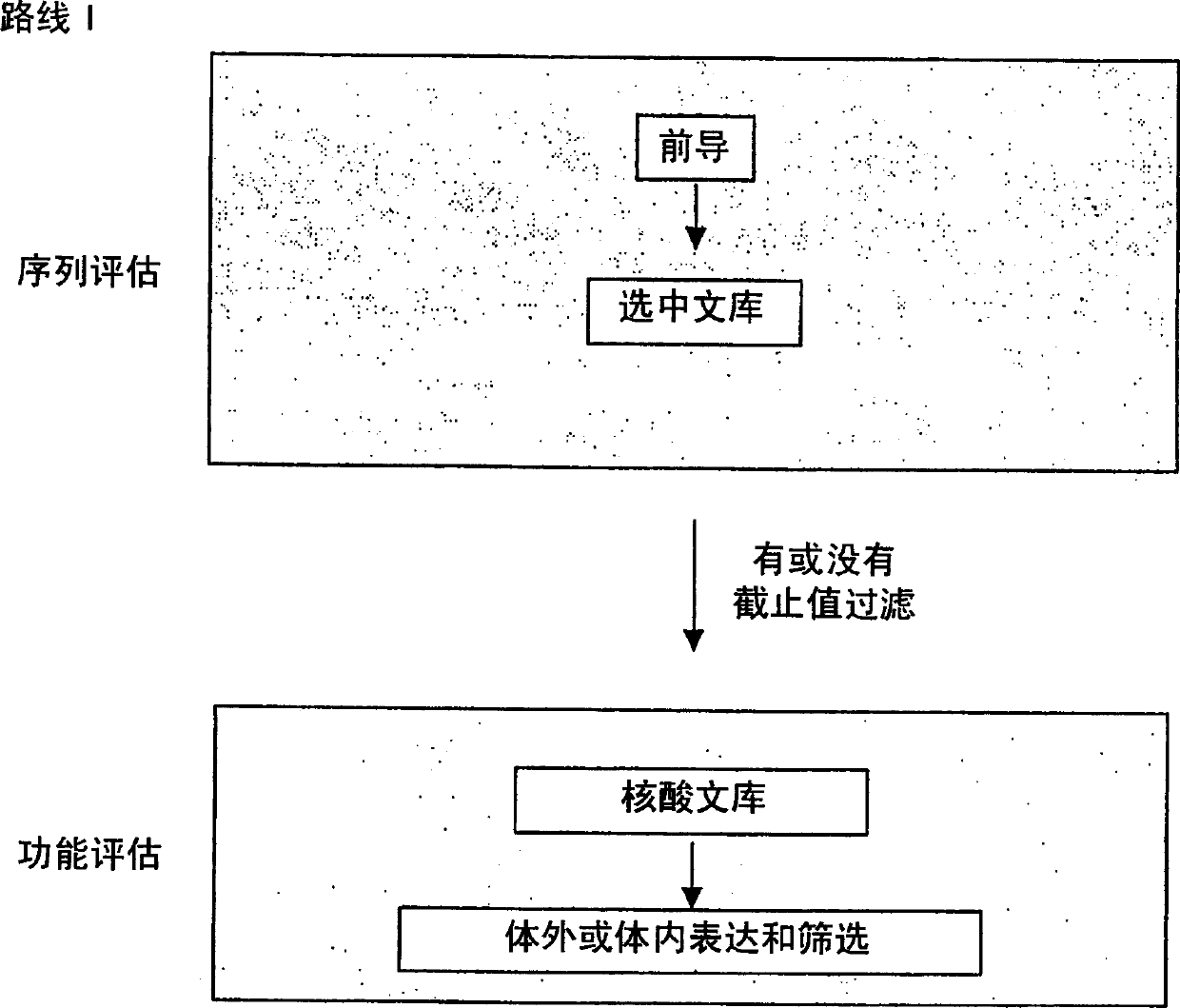
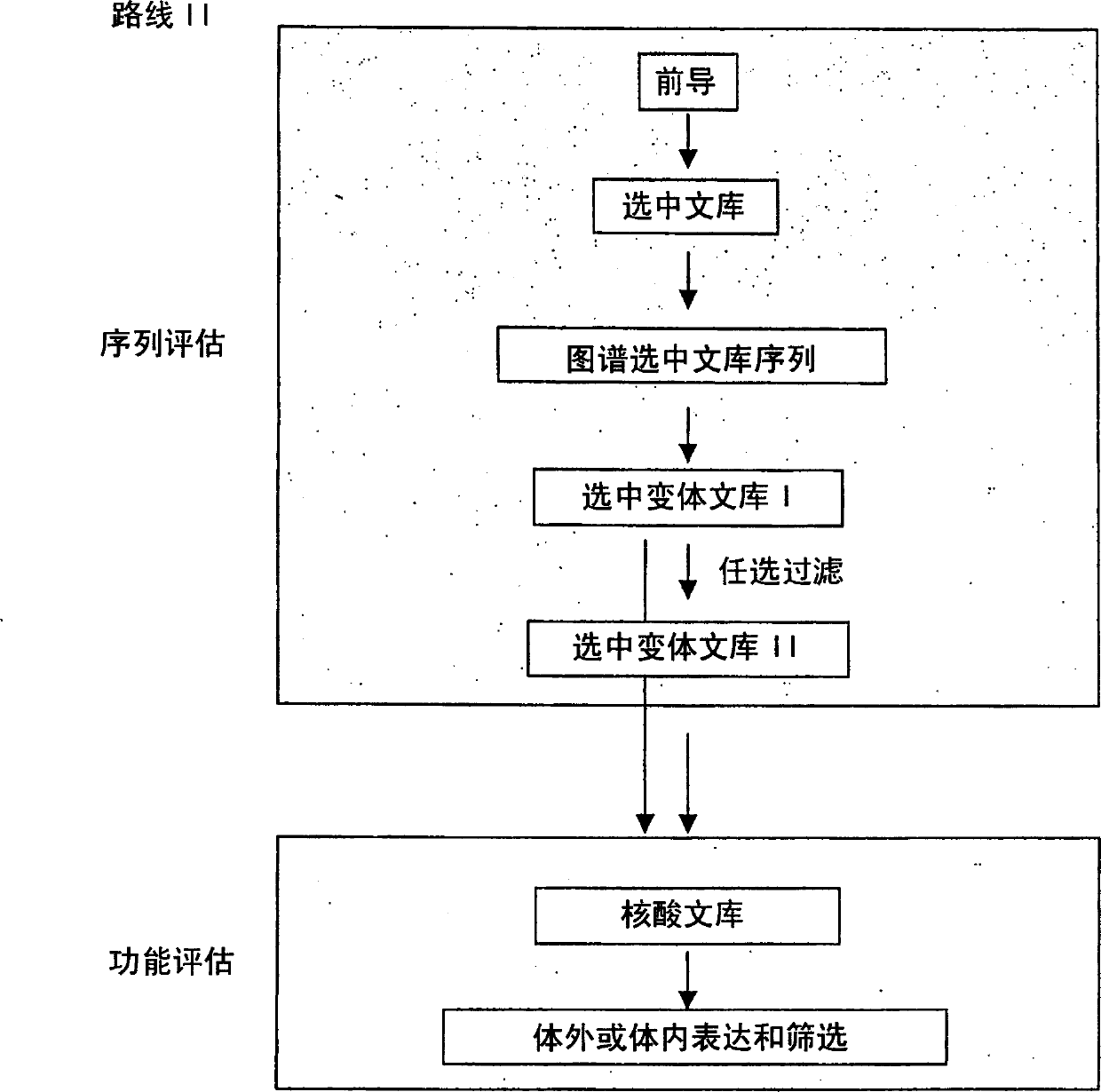
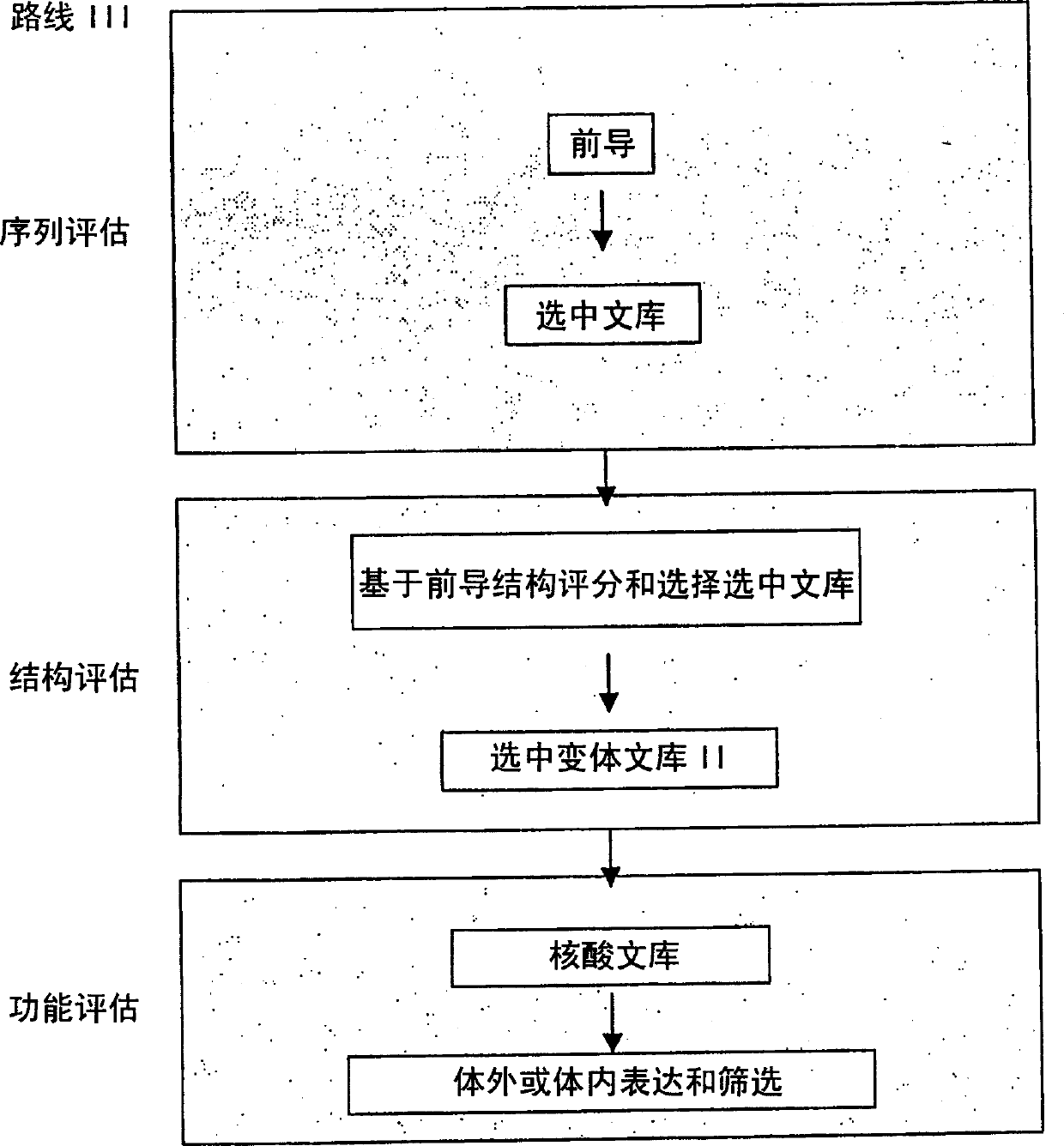
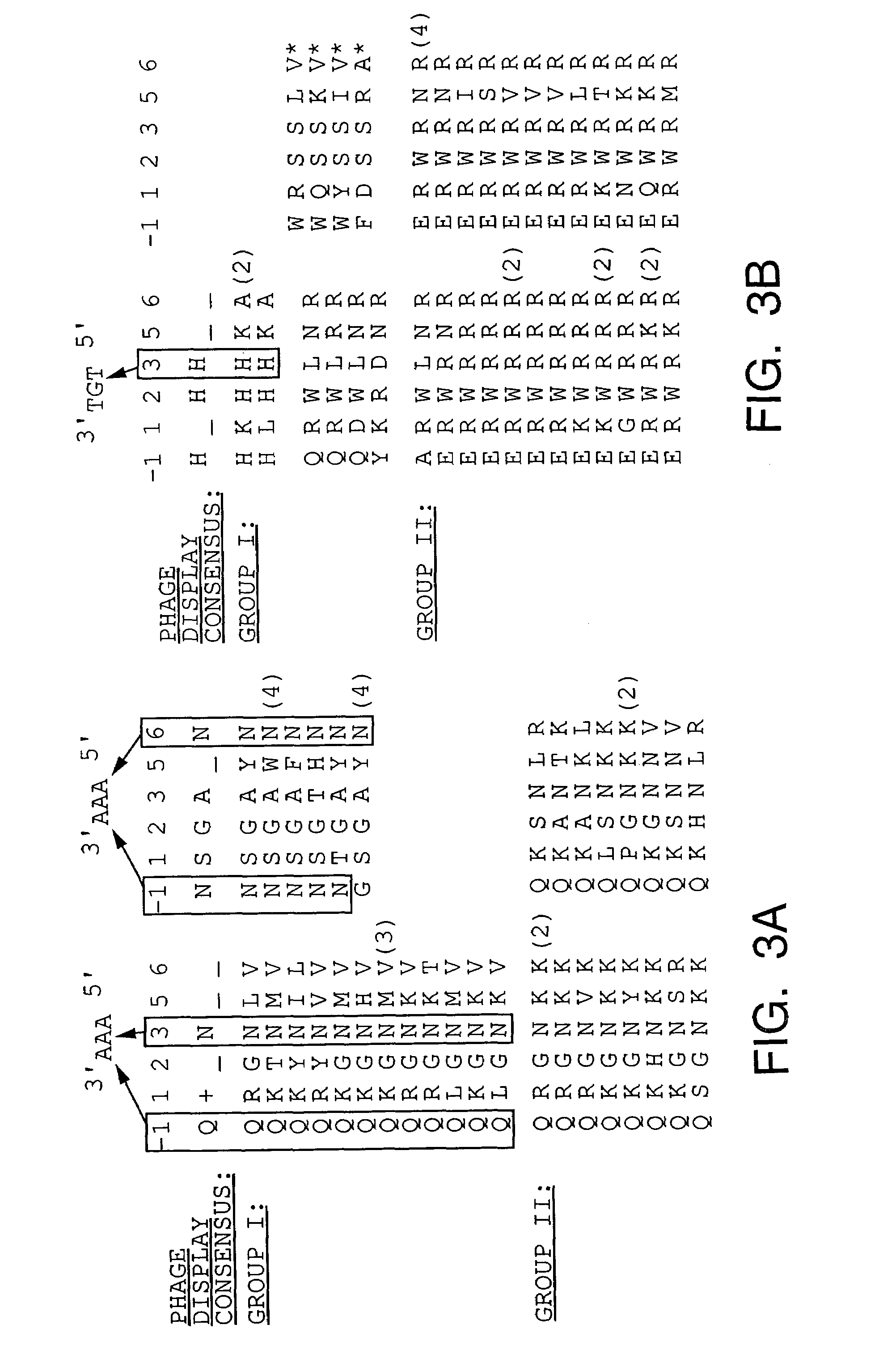
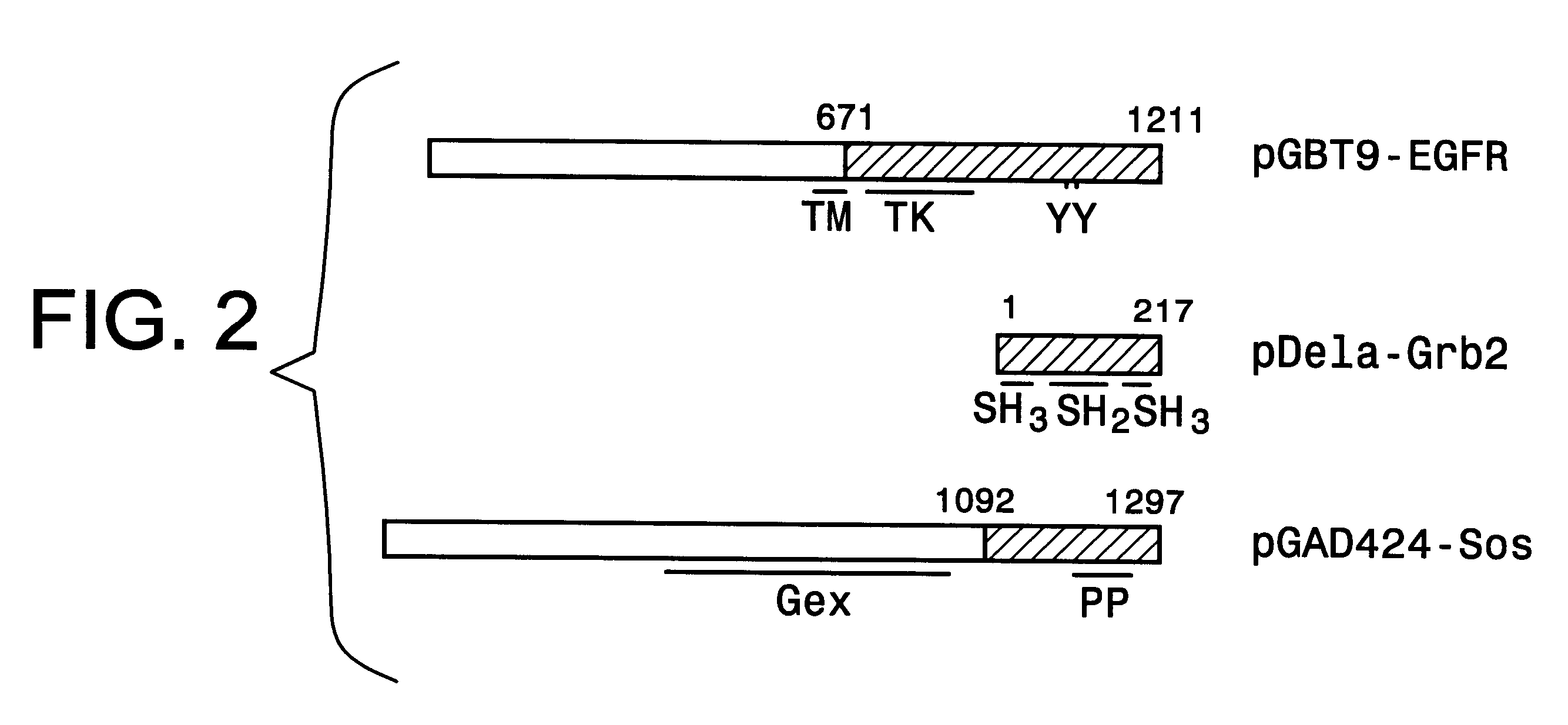
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6406863B1High affinityEasy to assembleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsTarget peptideIn vivo
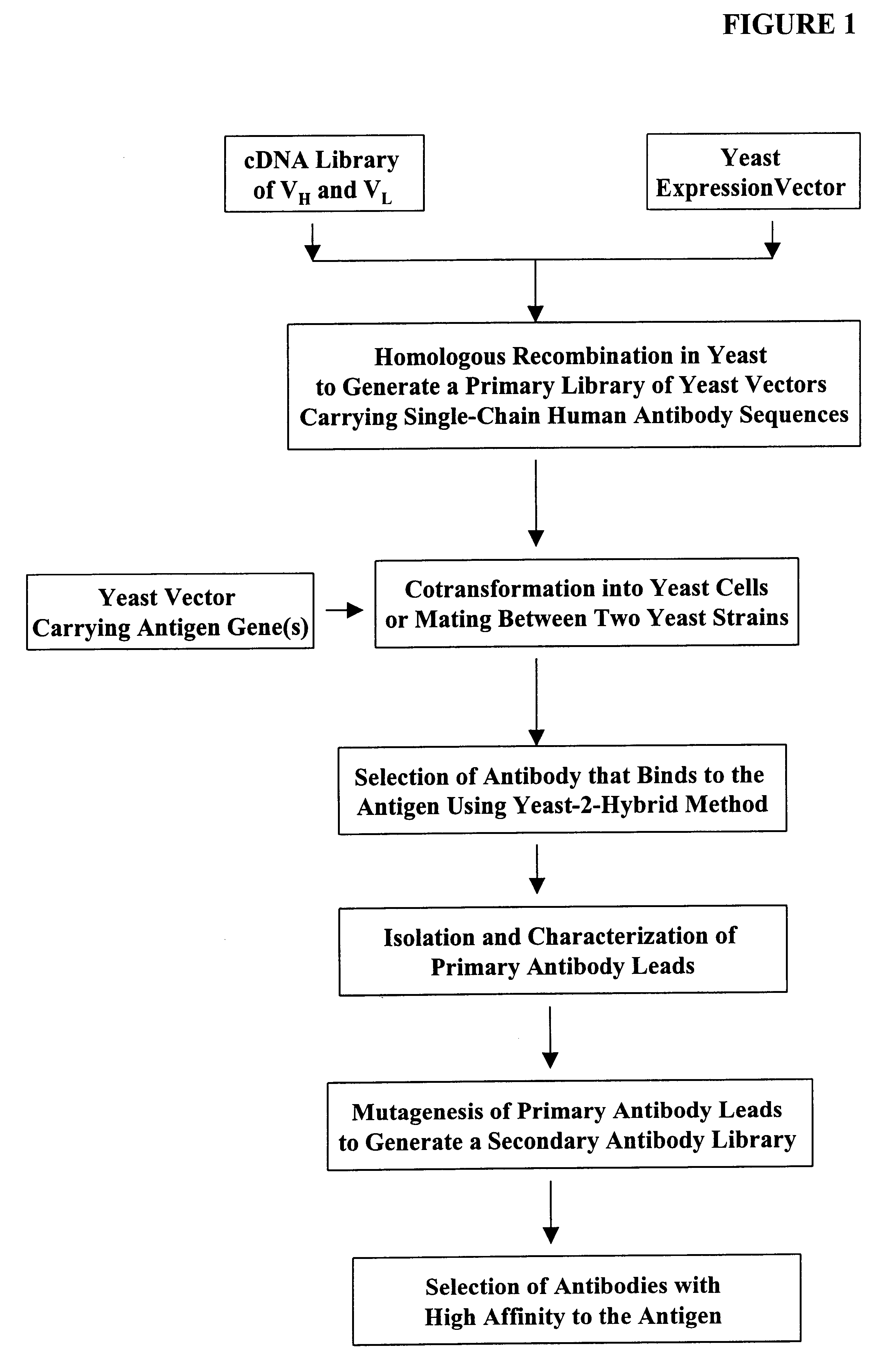
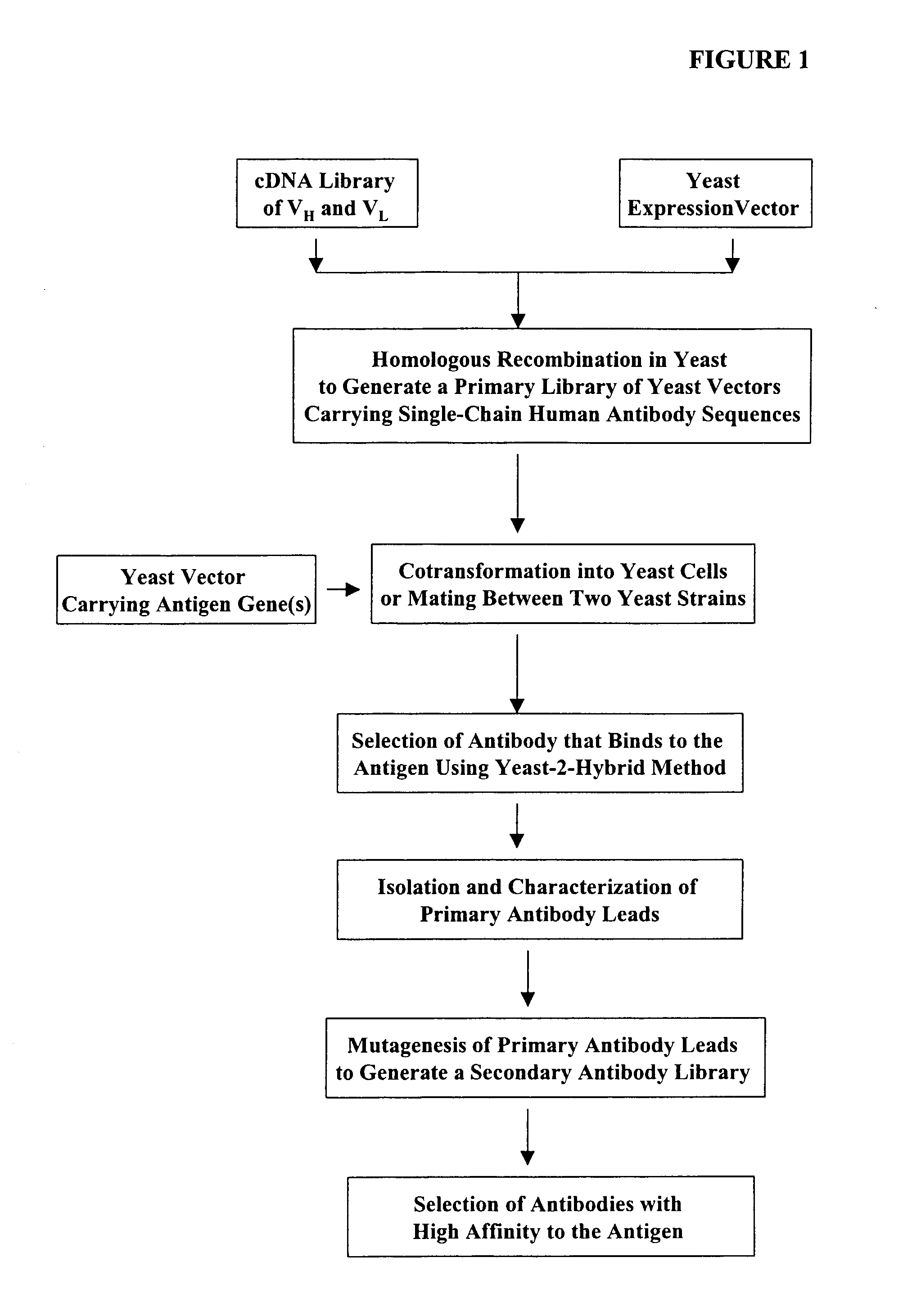
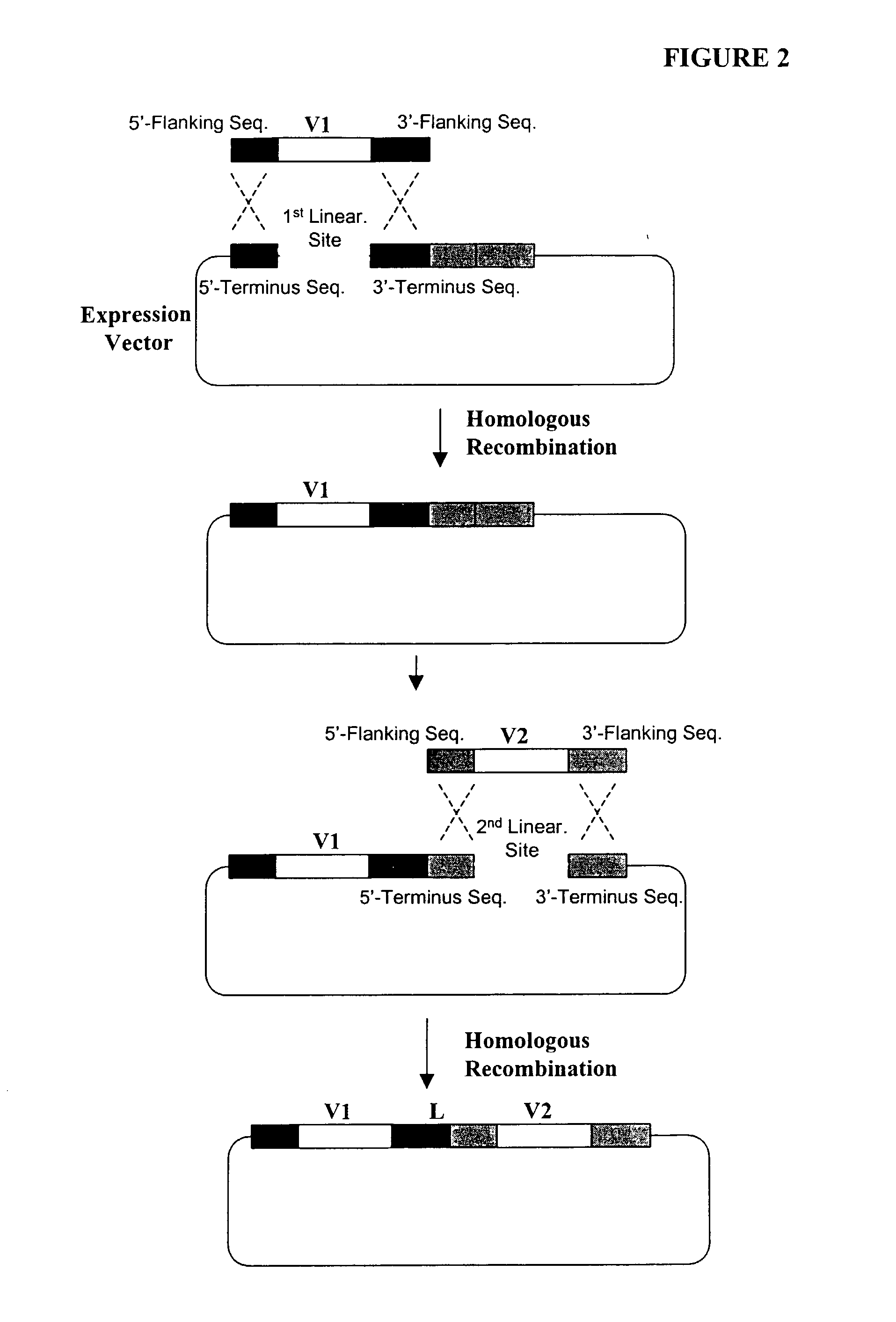
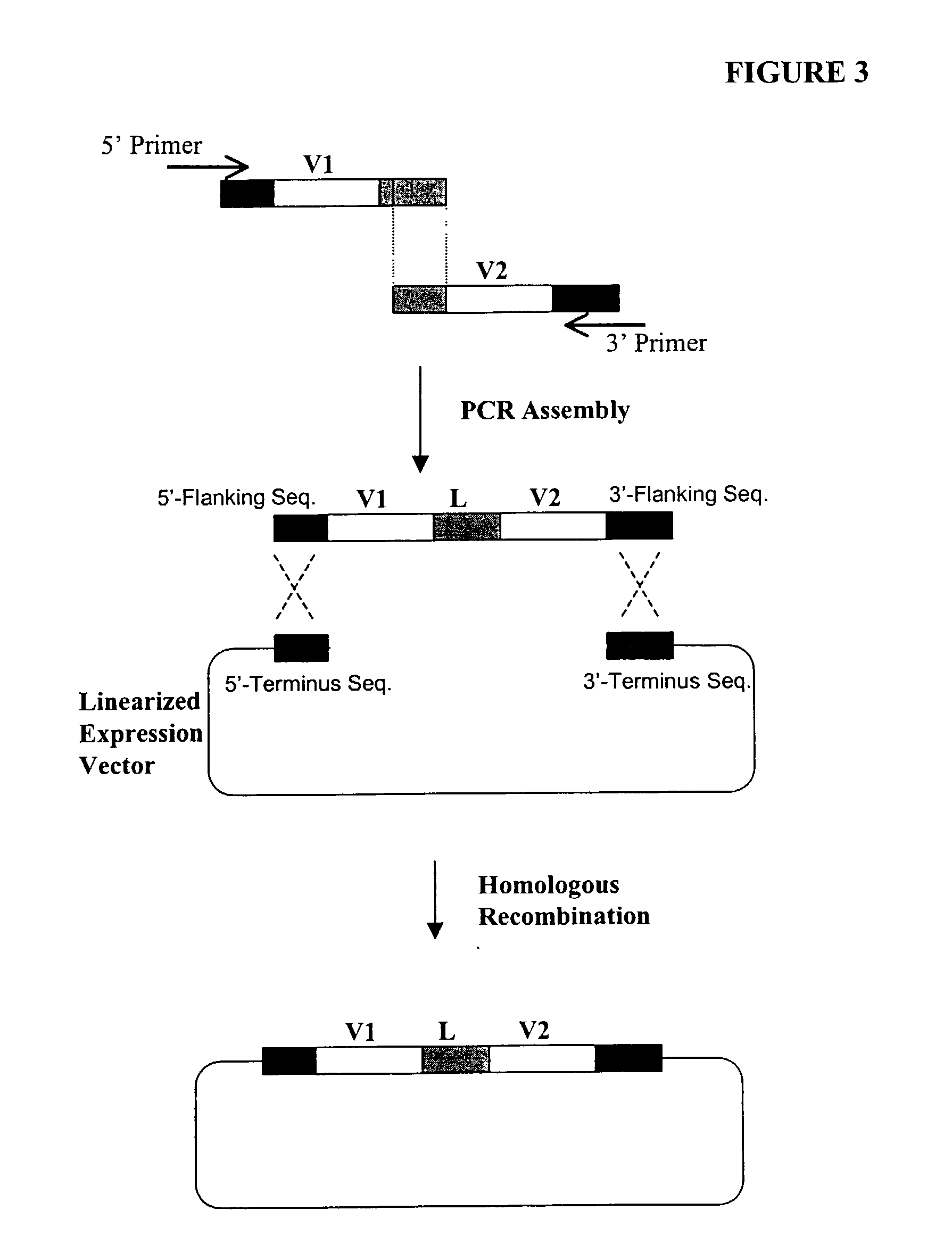
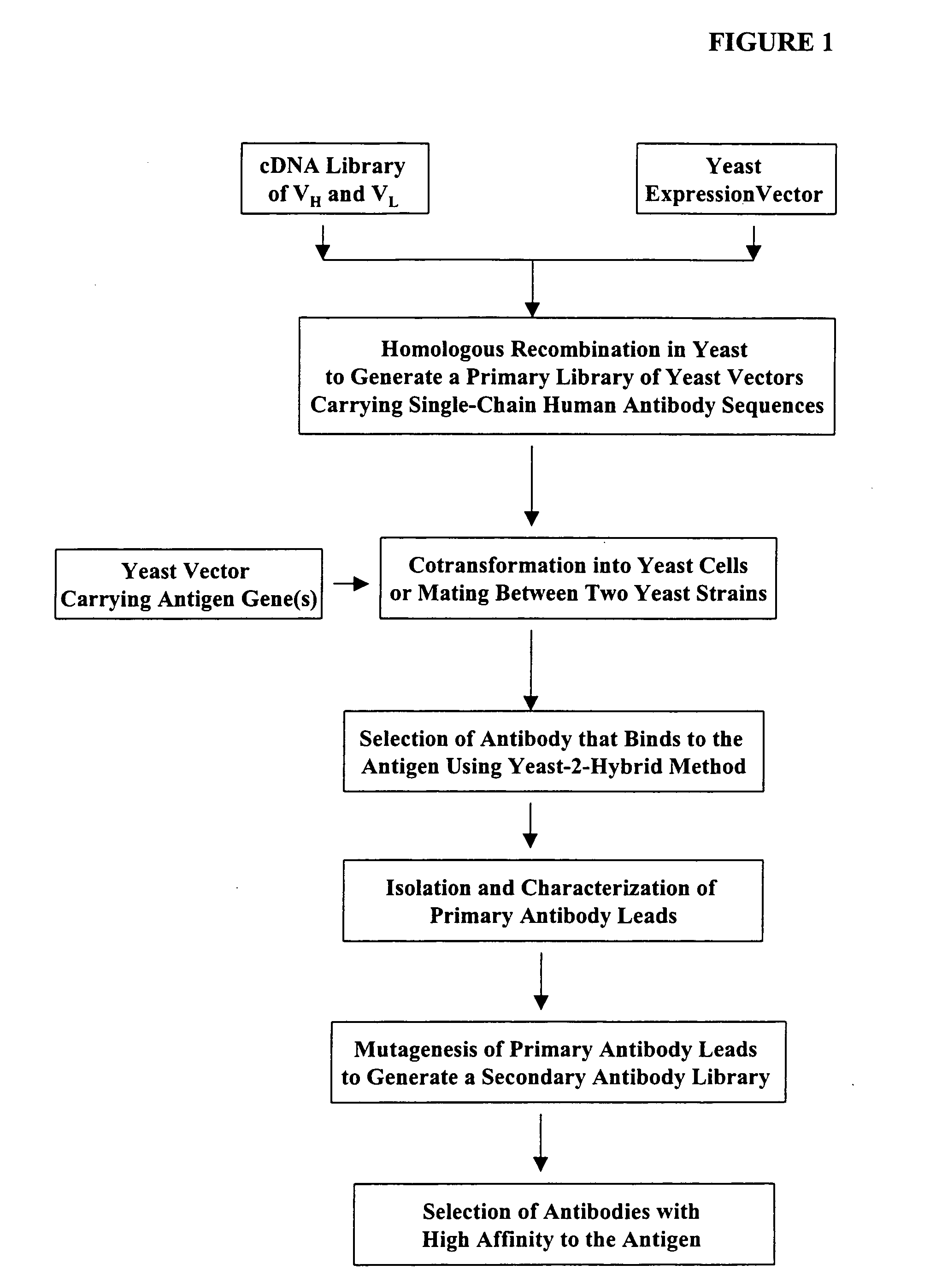
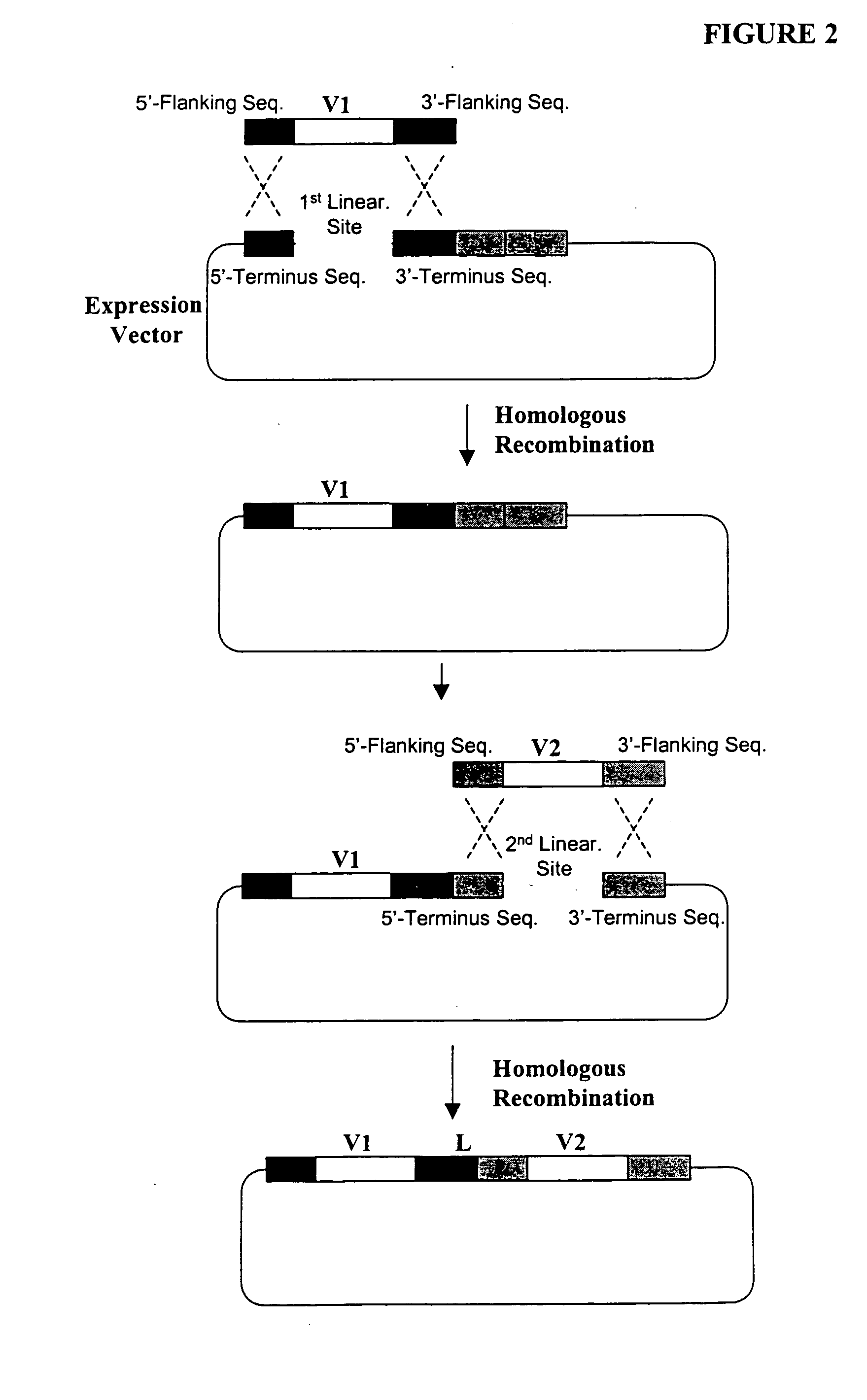
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Generation and affinity maturation of antibody library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on the amino acid sequence of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library. The hit library of antibody sequences can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Haploid yeast cells transformed with a library of expression vectors encoding a fully human antibody repertoire
InactiveUS20030027213A1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetTarget peptide
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides methods for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimal proteins with desired biological functions, such as improved binding affinity for biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The method is performed in silico in a high-throughput fashion by mining the ever-expanding database of protein sequences in all living things, especially humans. In one embodiment, a method of constructing a designer protein library comprises the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, referred to as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of test protein sequences; Select at least two peptide fragments having at least 15% sequence identity with the leader sequence from each test protein sequence, and the selected peptide fragments form a selection library; a library of designed proteins is formed by replacing the leader sequence with the selection library. Libraries of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to generate libraries of recombinant proteins that can be screened for new or improved functions relative to lead proteins, such as antibodies against a therapeutically important target.
Owner:埃博马可西斯公司
Methods and compositions for interaction trap assays
InactiveUS7029847B2Increase opportunitiesEnhanced interactionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods and compositions for interaction trap assays for detecting protein-protein, protein-DNA, or protein-RNA interactions. The methods and compositions of the invention may also be used to identify agents which may agonize or antagonize a protein-protein, protein-DNA, or protein-RNA interaction. In certain embodiments, the interaction trap system of the invention is useful for screening libraries with greater than 107 members. In other embodiments, the interaction trap system of the invention is used in conjunction with flow cytometry. The invention further provides a means for simultaneously screening a target protein or nucleic acid sequence for the ability to interact with two or more test proteins or nucleic acids.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods and compositions for interaction trap assays
InactiveUS7297491B2Increase opportunitiesEnhanced interactionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetAssay
The present invention provides methods and compositions for interaction trap assays for detecting protein-protein, protein-DNA, or protein-RNA interactions. The methods and compositions of the invention may also be used to identify agents which may agonize or antagonize a protein-protein, protein-DNA, or protein-RNA interactions. In certain embodiments, the interaction trap system of the invention is useful for screening libraries with greater than 107 members. In other embodiments, the interaction trap system of the invention is used in conjunction with flow cytometry. The invention further provides a means for simultaneously screening a target protein or nucleic acid sequence for the ability to interact with two or more test proteins or nucleic acids.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Rapid assay, method and system for detecting biowarfare agents
InactiveUS20050238535A1Promote solubilizationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsBurette/pipette supportsTest proteinSugar
Provided herein are methods for preliminary analysis of suspect samples, which can be used in triaging possible contaminated sites (e.g., sites contaminated or thought to be contaminated by biowarfare agents). In some embodiments, the methods involve testing for the presence of protein in the suspect sample; optionally, the sample can also be tested for the presence of sugar, and / or for pH determination. Specific embodiment methods are carried out in tubes or other reaction vessels, others are carried out in a pad format, and still others are carried out in a test strip format. Kits for carrying out the described methods are also provided.
Owner:20 20 GENESYSTEMS INC
Development of Protein-Based Biotherapeutics That Penetrates Cell-Membrane and Induces Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect - Improved Cell-Permeable Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (iCP-SOCS3) Proteins, Polynucleotides Encoding the Same, and Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Compositions Comprising the Same
InactiveUS20160060310A1Good effectImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityHepatocellular carcinoma
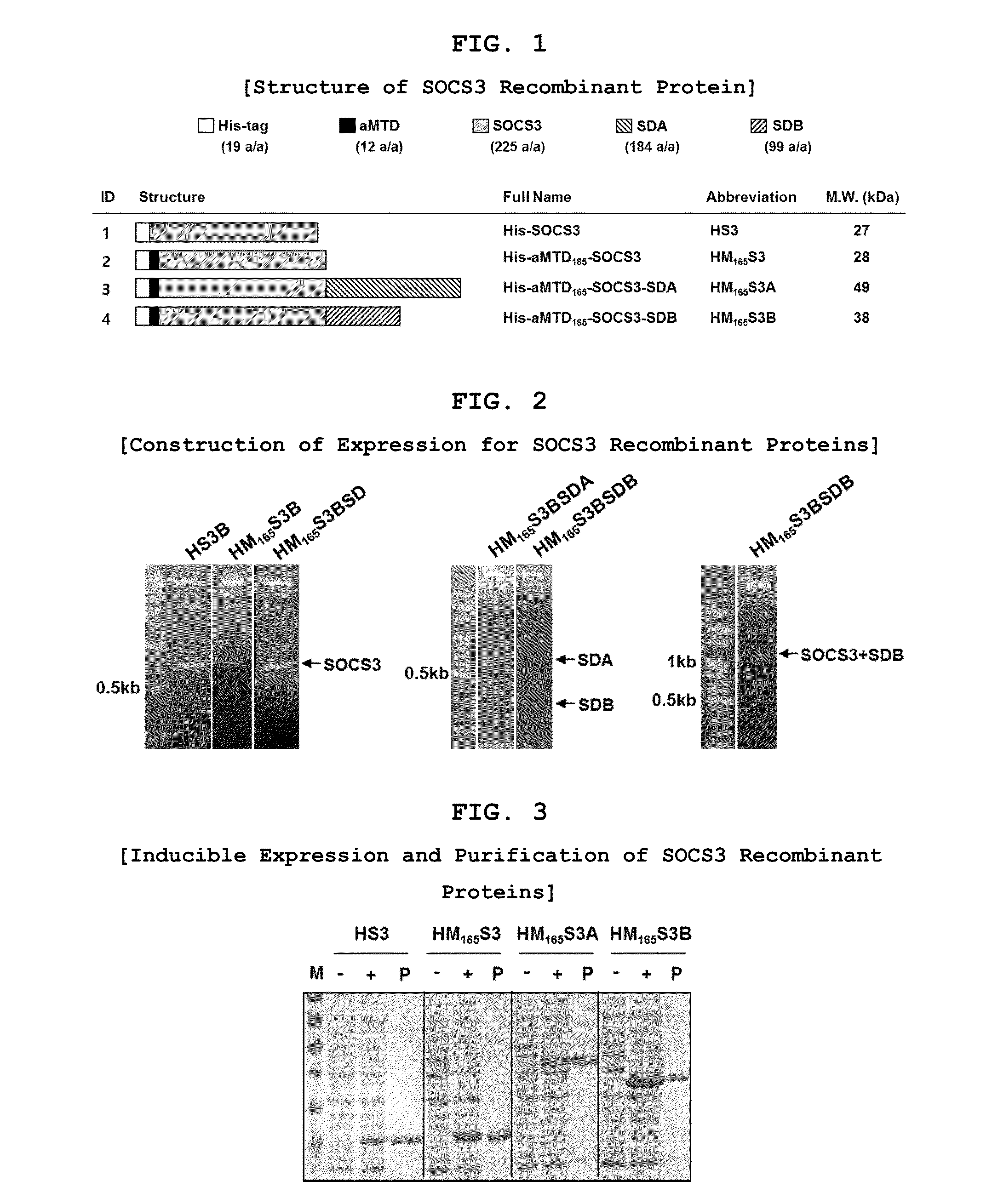
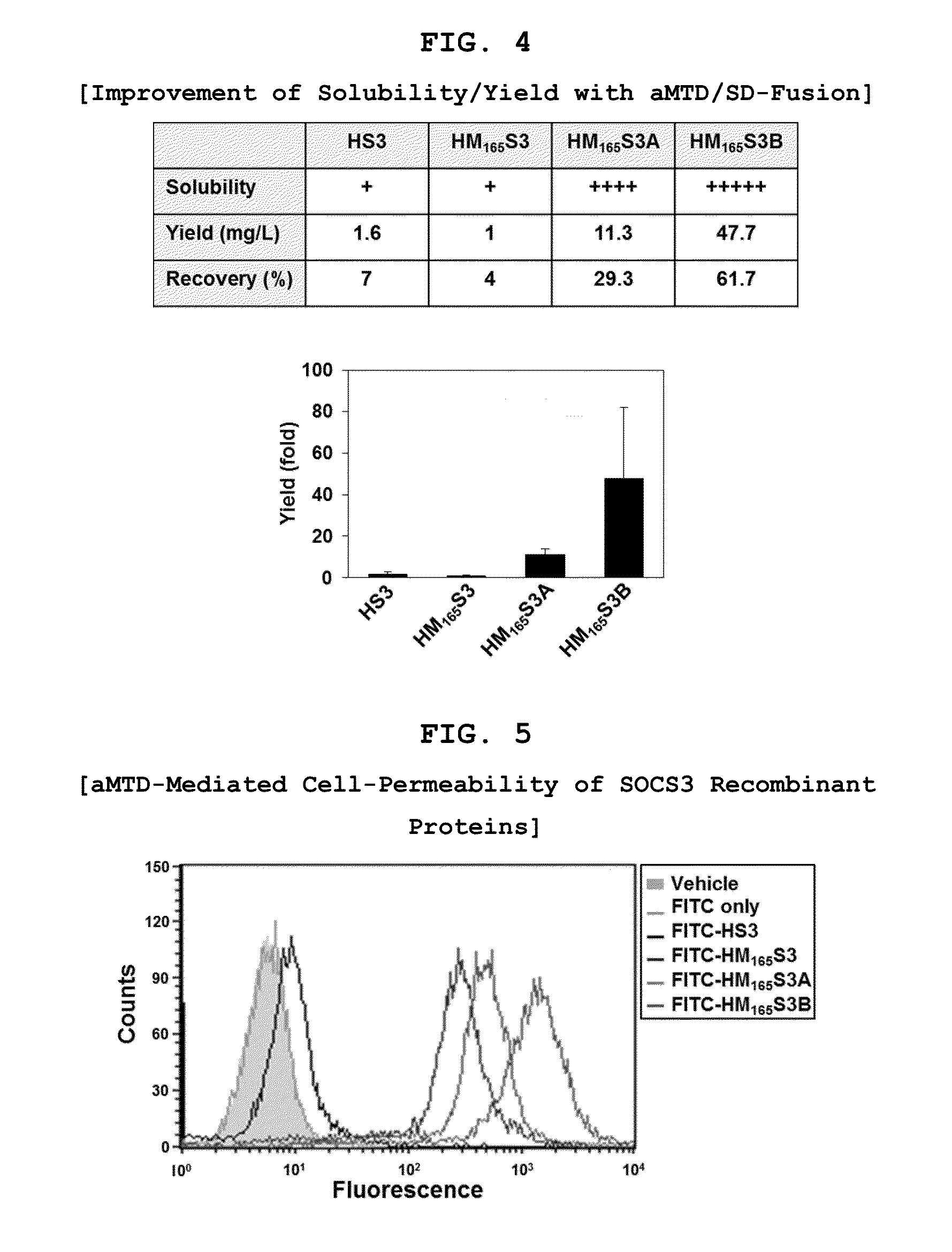
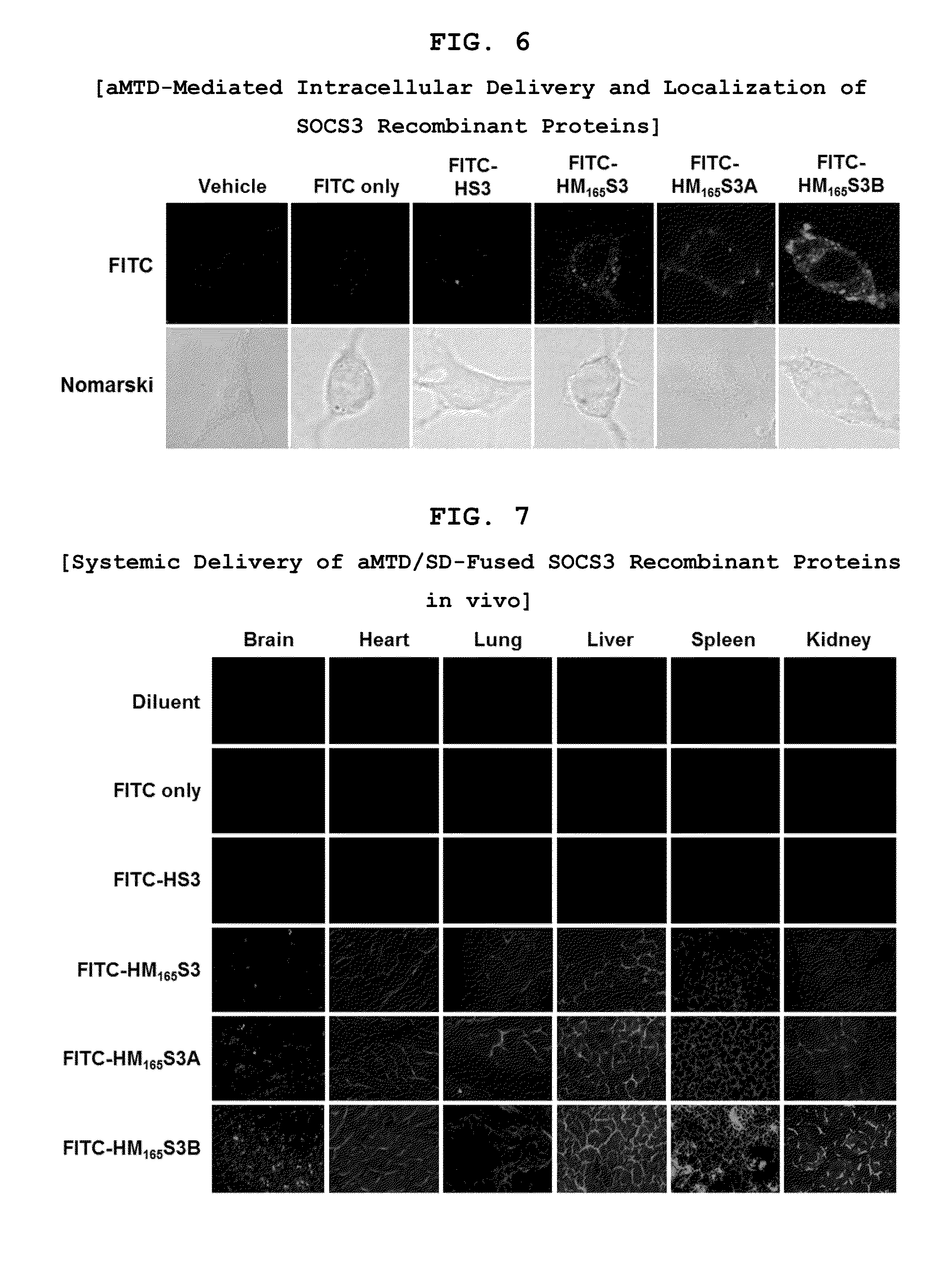
Protein transduction exploits the ability of some cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) sequences to enhance the uptake of proteins and other macromolecules by mammalian cells. Previously developed hydrophobic CPPs, named membrane translocating sequence (MTS), membrane translocating motif (MTM) and macromolecule transduction domain (MTD), are able to deliver biologically active proteins into a variety of cells and tissues. Various cargo proteins fused to these CPPs have been used to test the functional and / or therapeutic efficacy of protein transduction. For example, recombinant proteins consisting of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 protein (CP-SOCS3) fused to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 4-derived MTM were developed to inhibit inflammation and apoptosis. However, CP-SOCS3 fusion proteins expressed in bacteria were hard to purify in soluble form. To address these critical limitations, CPP sequences called advanced MTDs (aMTD) have been developed in this art. This is accomplished by (i) analyzing previous developed hydrophobic CPP sequences to identify specific critical factors (CFs) that affect intracellular delivery potential and (ii) constructing artificial aMTD sequences satisfied for each critical factor. In addition, solubilization domains (SDs) have been incorporated into the aMTD-fused SOCS3 recombinant proteins to enhance solubility with corresponding increases in protein yield and cell- / tissue-permeability. These recombinant SOCS3 proteins fused to aMTD / SD having much higher solubility / yield and cell- / tissue-permeability have been named as improved cell-permeable SOCS3 (iCP-SOCS3) proteins. Previously developed CP-SOCS3 proteins fused to MTM were only tested or used as anti-inflammatory agents to treat acute liver injury. In the present art, iCP-SOCS3 proteins have been tested for use as anti-cancer agents in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Since SOCS3 is frequently deleted in and loss of SOCS3 in hepatocytes promotes resistance to apoptosis and proliferation, we reasoned that iCP-SOCS3 could be used as a protein-based intracellular replacement therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. The results support this reasoning: treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma cells with iCP-SOCS3 results in reduced cancer cell viability, enhanced apoptosis and loss of cell migration / invasion potential. Furthermore, iCP-SOCS3 inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in a subcutaneous xenografts model. In the present invention with iCP-SOCS3 fused to an empirically determined combination of newly developed aMTD and customized SD, macromolecule intracellular transduction technology (MITT) enabled by the advanced MTD may provide novel protein therapy against hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:CELLIVERY THERAPEUTICS
Protein -protein interaction detection system using fluorescent protein microdomains
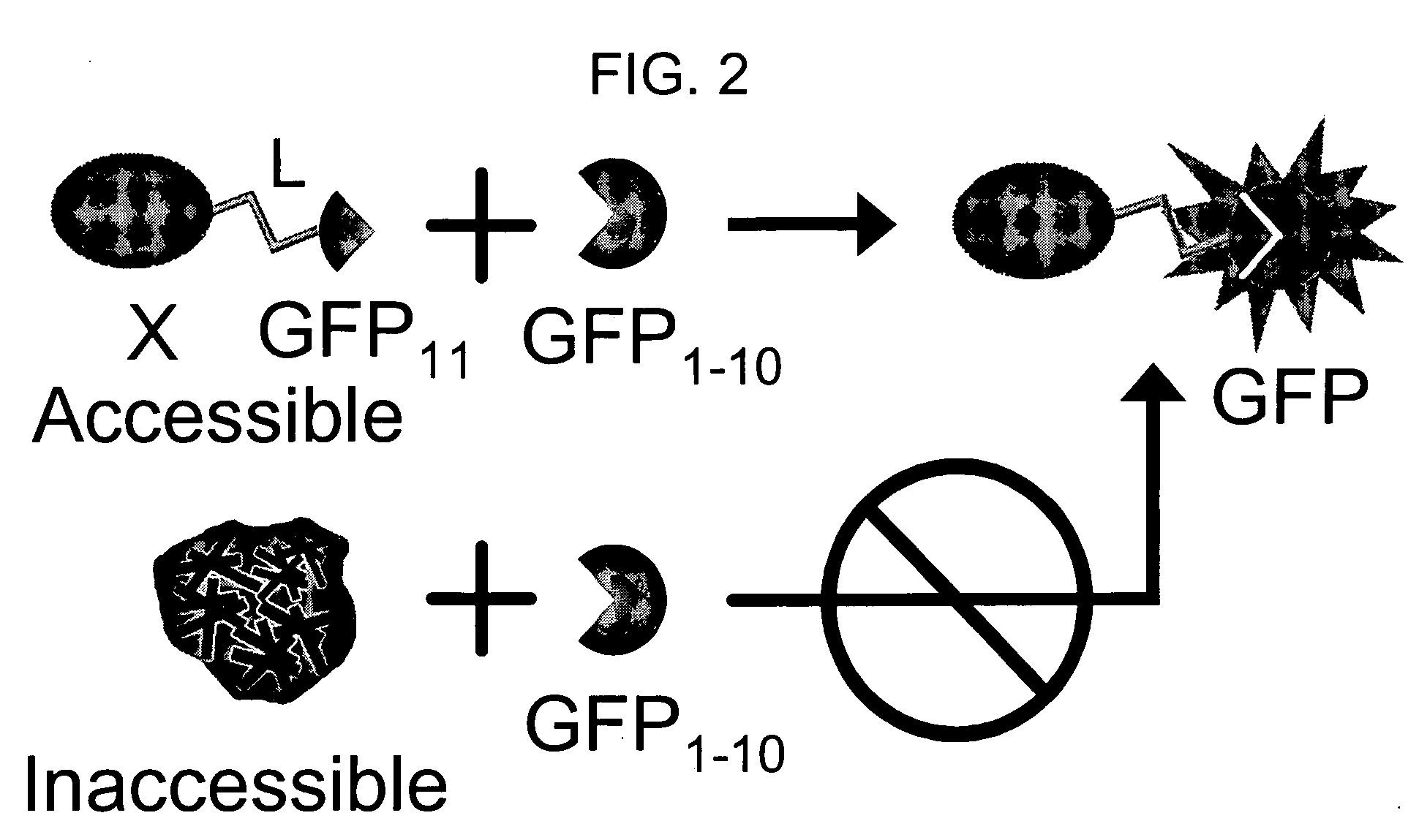
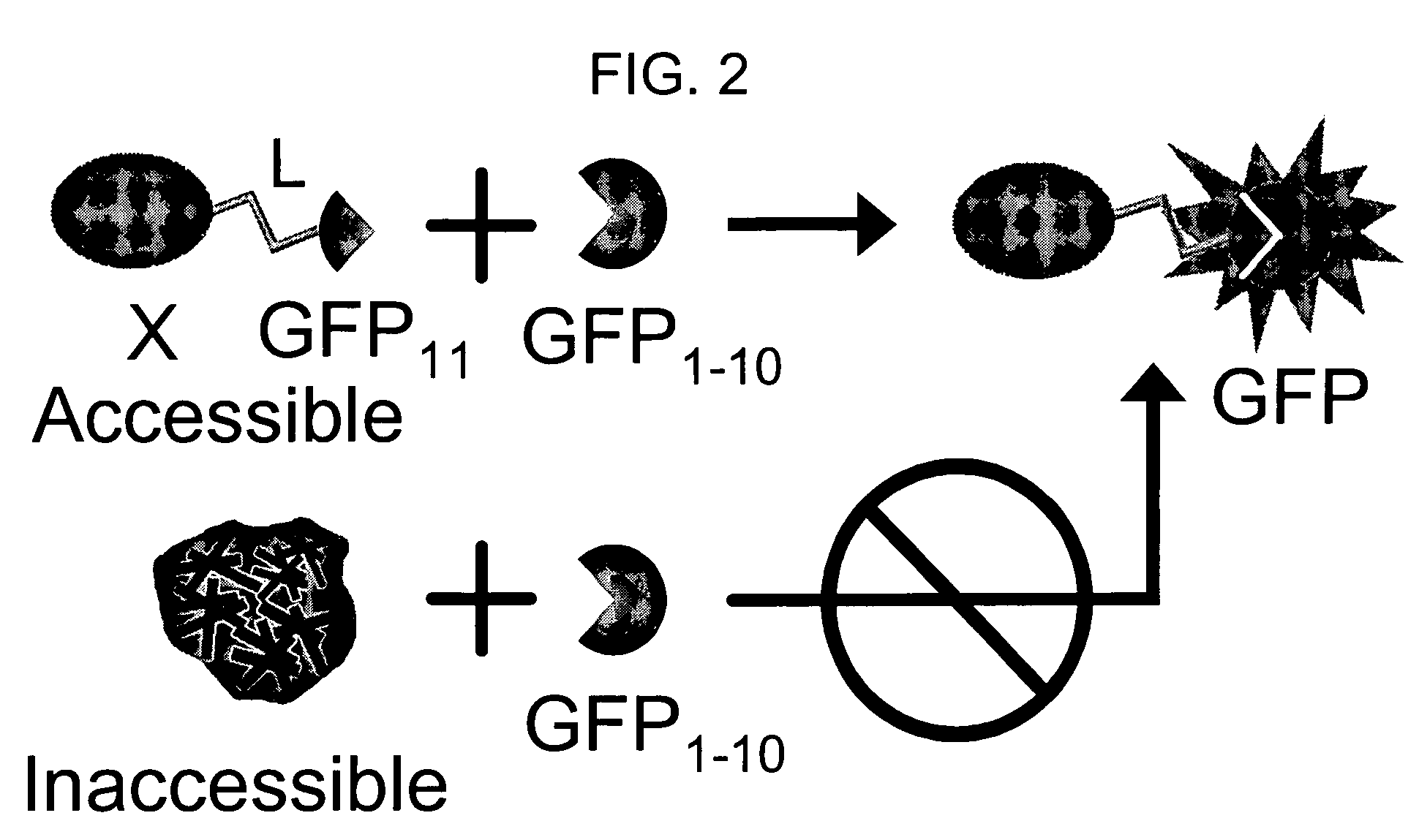
ActiveUS20060257887A1Signal sensitiveImproving foldingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSolubilityProtein labeling
The invention provides a protein labeling and interaction detection system based on engineered fragments of fluorescent and chromophoric proteins that require fused interacting polypeptides to drive the association of the fragments, and further are soluble and stable, and do not change the solubility of polypeptides to which they are fused. In one embodiment, a test protein X is fused to a sixteen amino acid fragment of GFP (β-strand 10, amino acids 198-214), engineered to not perturb fusion protein solubility. A second test protein Y is fused to a sixteen amino acid fragment of GFP (β-strand 11, amino acids 215-230), engineered to not perturb fusion protein solubility. When X and Y interact, they bring the GFP strands into proximity, and are detected by complementation with a third GFP fragment consisting of GFP amino acids 1-198 (strands 1-9). When GFP strands 10 and 11 are held together by interaction of protein X and Y, they spontaneous association with GFP strands 1-9, resulting in structural complementation, folding, and concomitant GFP fluorescence.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Protein- protein interaction detection system using fluorescent protein microdomains
ActiveUS7666606B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein markersProtein labeling
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for analysis of protein interaction using fluorescent protein
InactiveUS20070031912A1Time obtainedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTest proteinFluorescent light
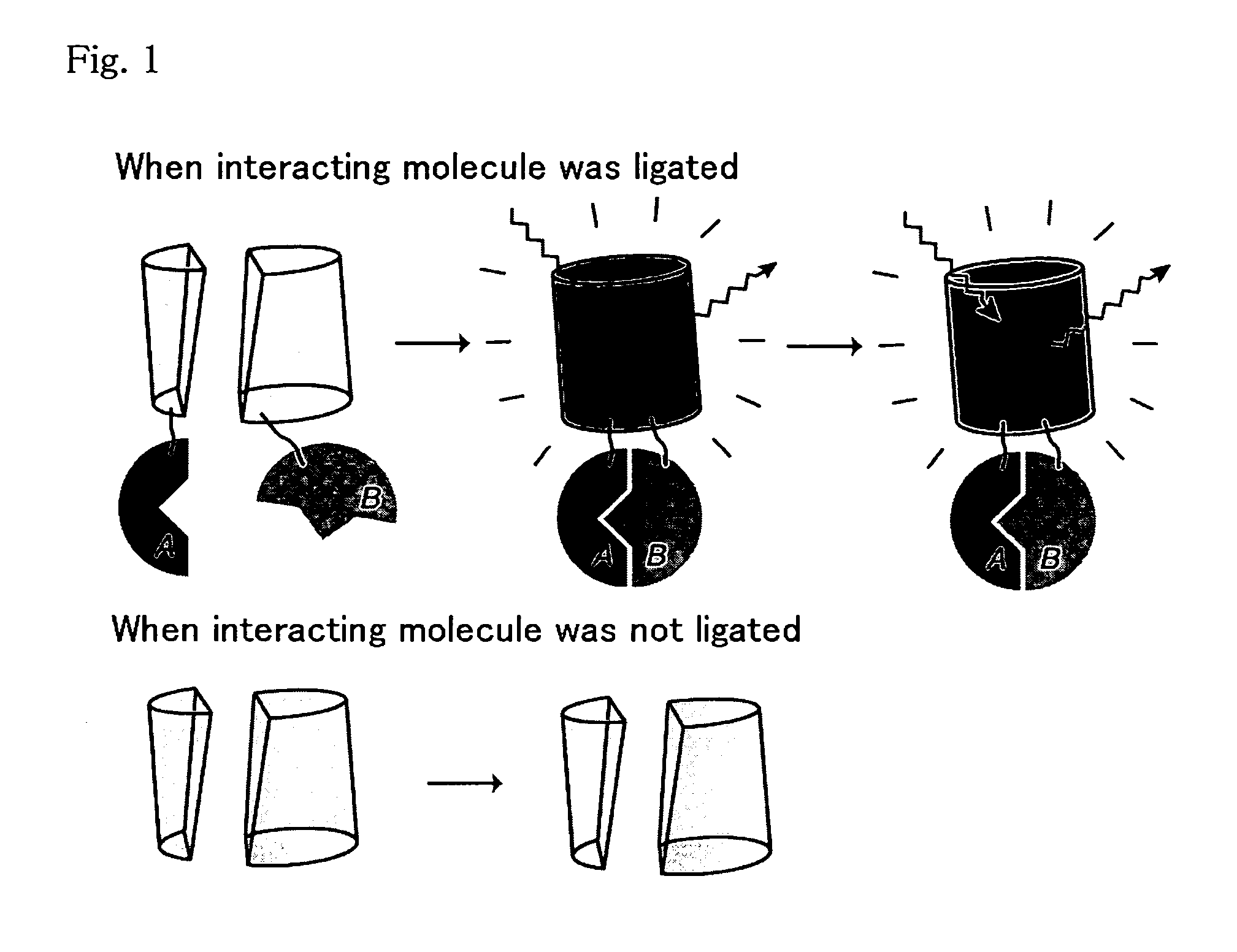
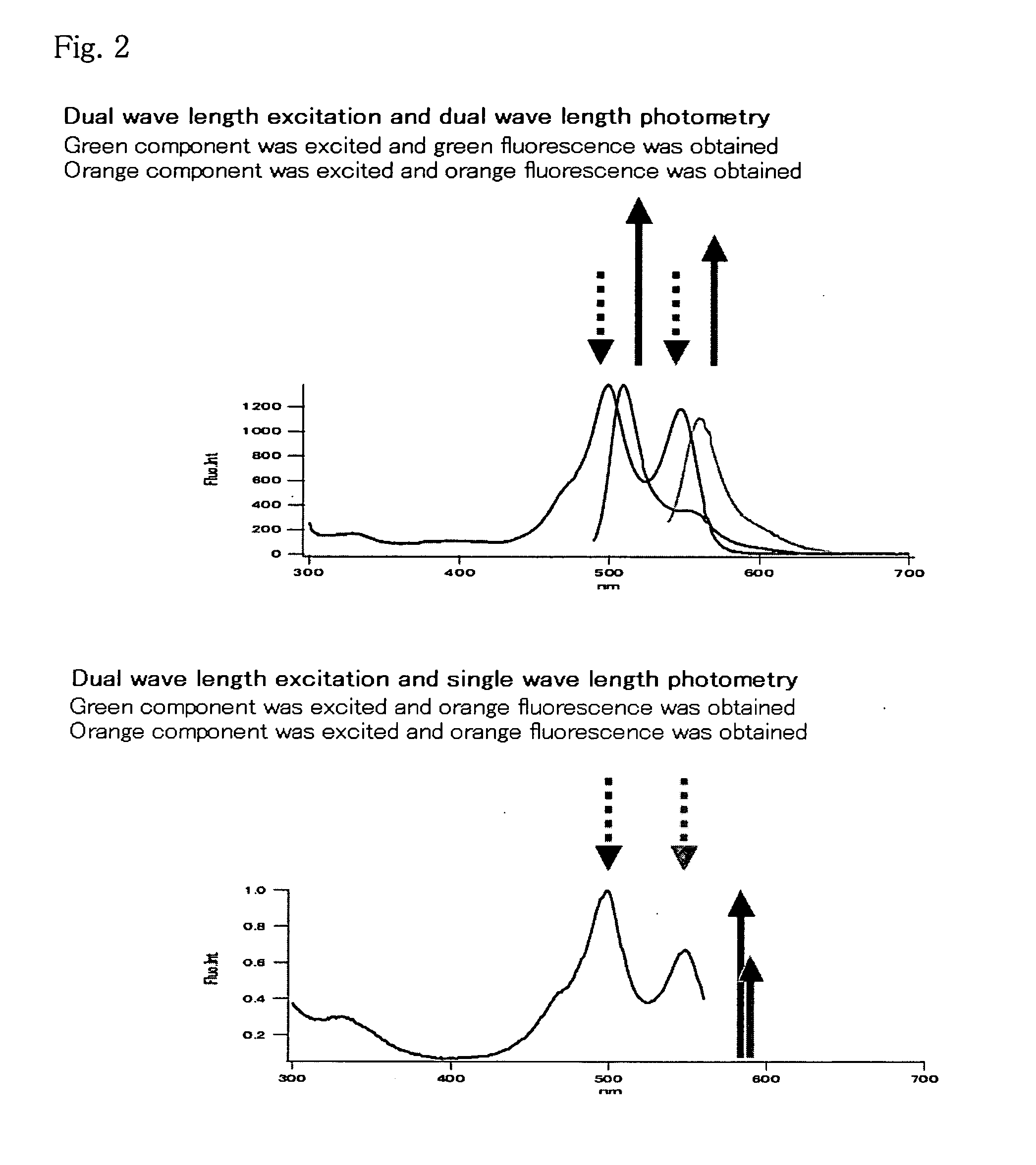
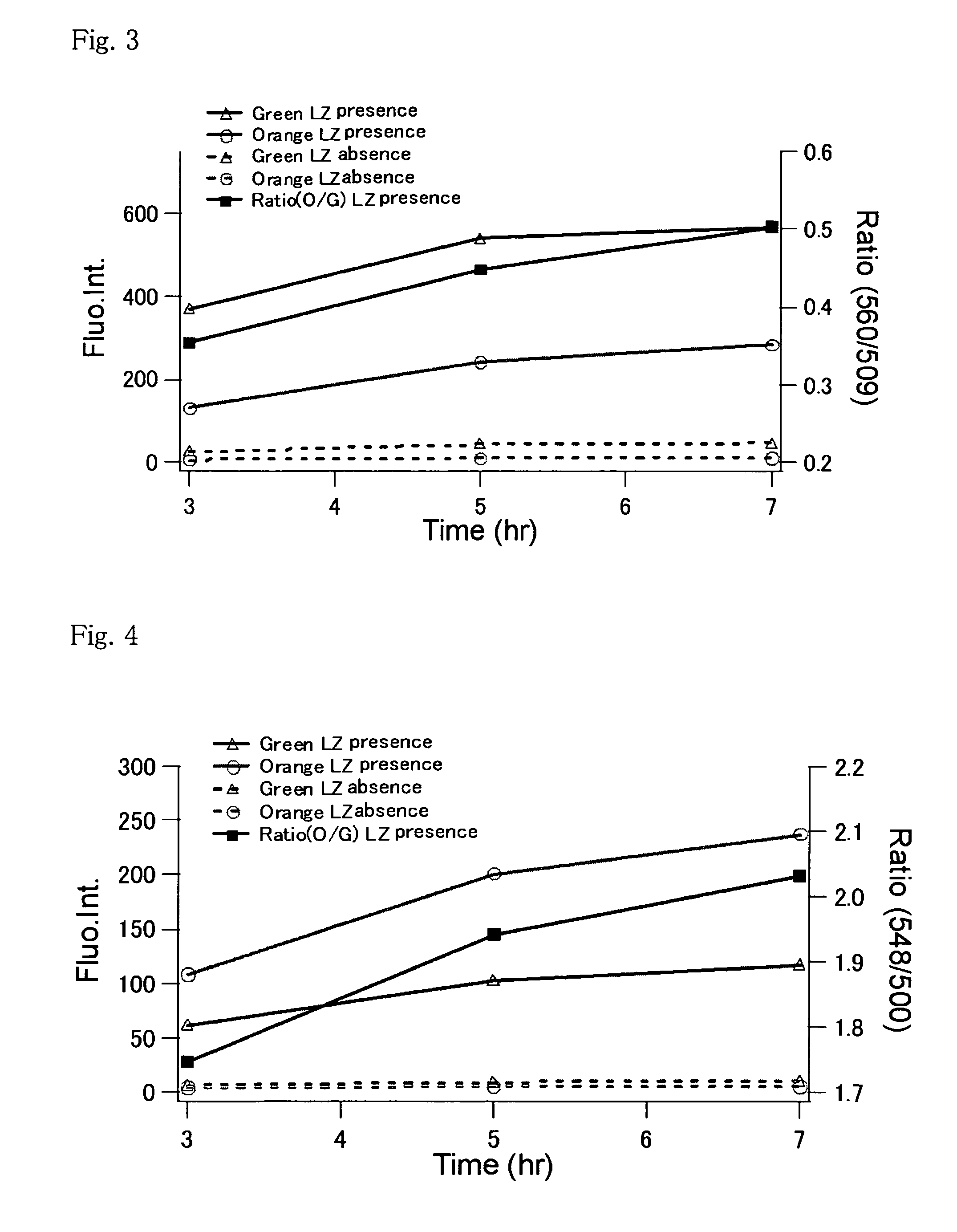
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for analyzing the protein interaction, wherein the information about time can be obtained and the movement of protein can be monitored. The present invention provides a method for analyzing interaction between a first test protein and a second test protein which comprises the steps of: splitting a fluorescent protein capable of emitting different color of fluorescence according to passage of time into an N-terminal fragment and a C-terminal fragment; allowing the first test protein to interact with the second test protein by making coexist a fusion protein of the N-terminal fragment with the first test protein and another fusion protein of the C-terminal fragment with the second test protein; and detecting the change in the fluorescent light due to the interaction.
Owner:RIKEN +1
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS20050142562A1High affinityHighly efficient homologous recombinationFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget peptideIn vivo
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
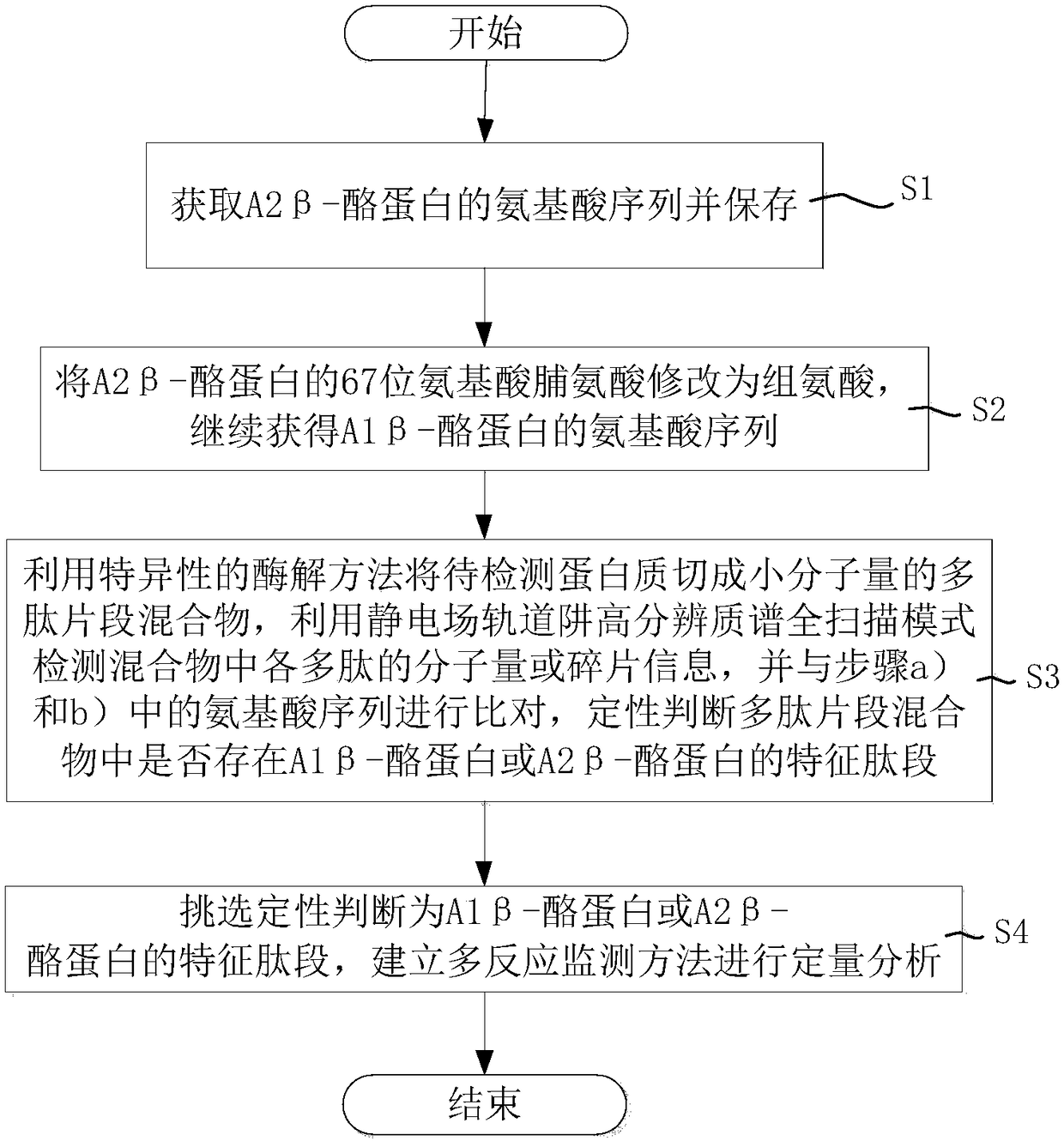
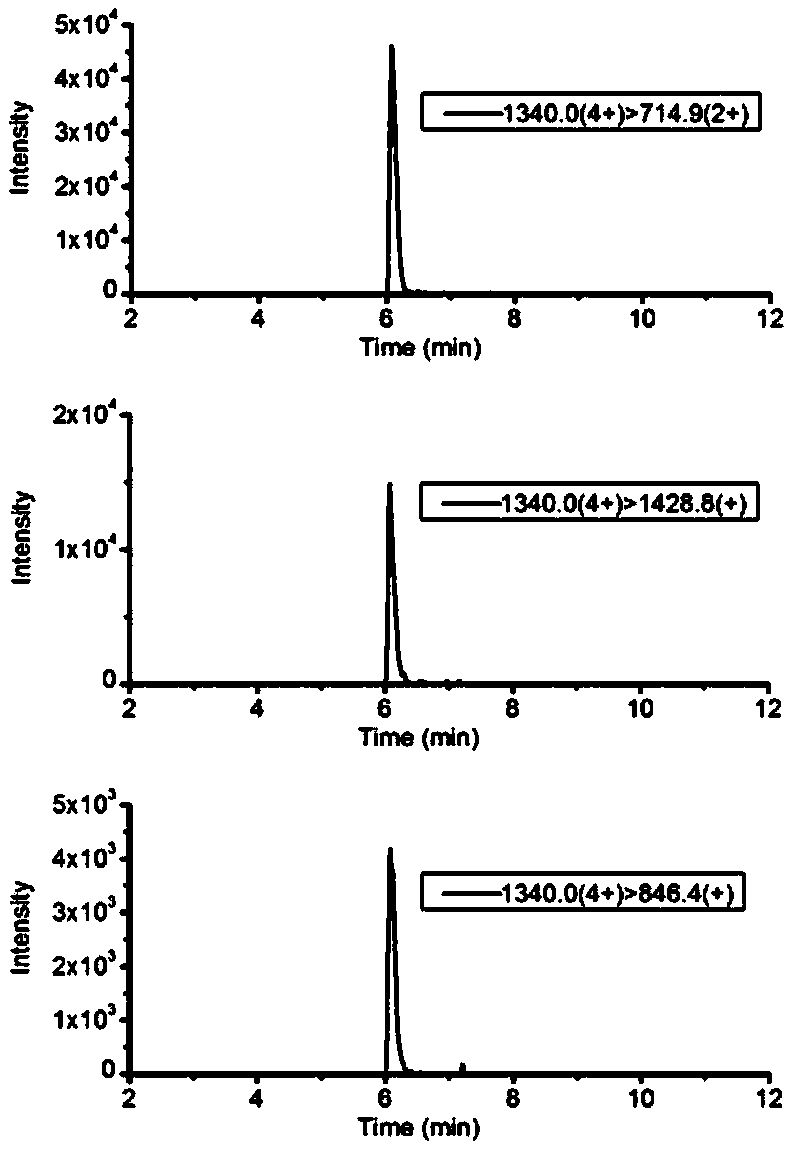
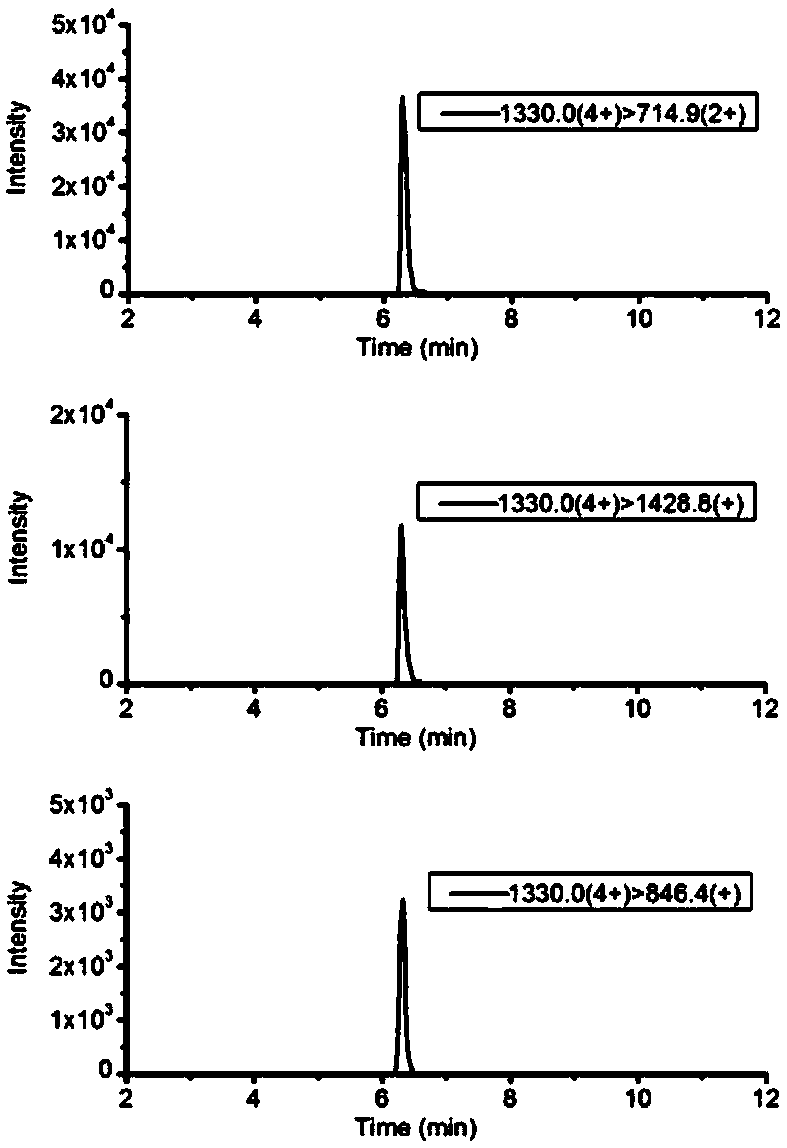
Mass spectrometric detection method of A1/A2 beta-casein
ActiveCN108519485AExtensive corroborationBroad detectabilityComponent separationBiological testingIsotopeHistidine
The invention discloses a mass spectrometric detection method of A1 / A2 beta-casein. The mass spectrometric detection method comprises the following steps that a) the amino acid sequence of A2 beta-casein is obtained; b) 67-site amino acid proline of A2 beta-casein is modified to be histidine, and the amino acid sequence of A1 beta-casein is obtained; c) a to-be-tested protein is cut to be a polypeptide segmented mixture with the low molecular mass by using a specific enzymolysis method, the molecular mass and segment information of polypeptides in the mixture are detected by utilizing an electrostatic field orbitrap high resolution mass spectrum full scanning mode and compared with the previous amino acid sequence, and whether the feature peptide fragment of A1 or A2 beta-casein exists ornot is determined qualitatively; and d) the fragment determined to be the feature peptide fragment of A1 or A2 beta-casein is selected to synthesize the isotope internal standard peptide fragment, andquantitative analysis is conducted by utilizing tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry to build a multiple reaction monitoring method. The mass spectrometric detection method can achieve qualitative identification and quantitative research of A1 and A2 beta-casein simultaneously, is high in sensitivity, precision and anti-interference capability, and can be widely applied to confirmation and detection of A2 milk products.
Owner:PLANTS & ANIMALS & FOOD TESTING QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
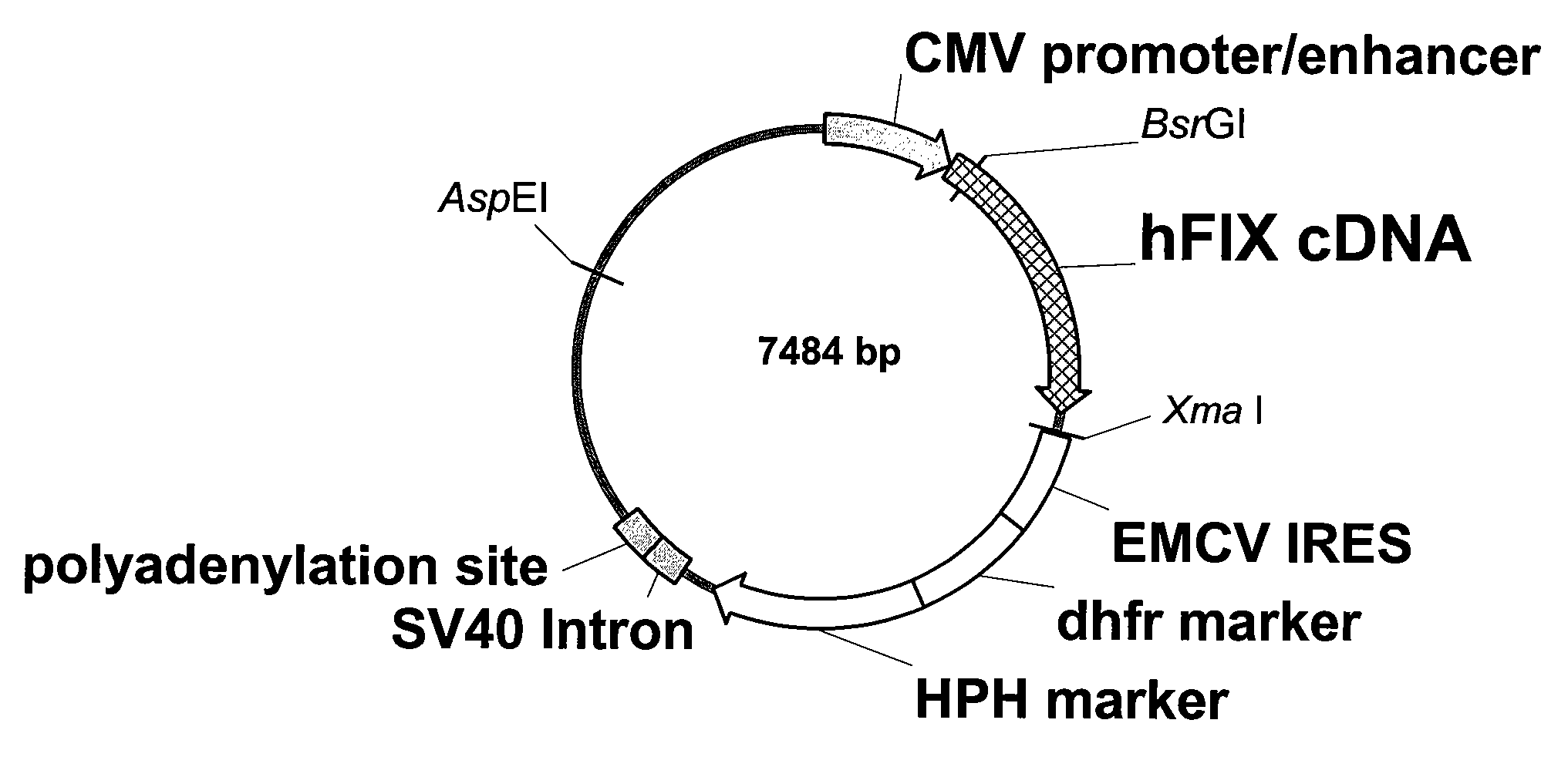
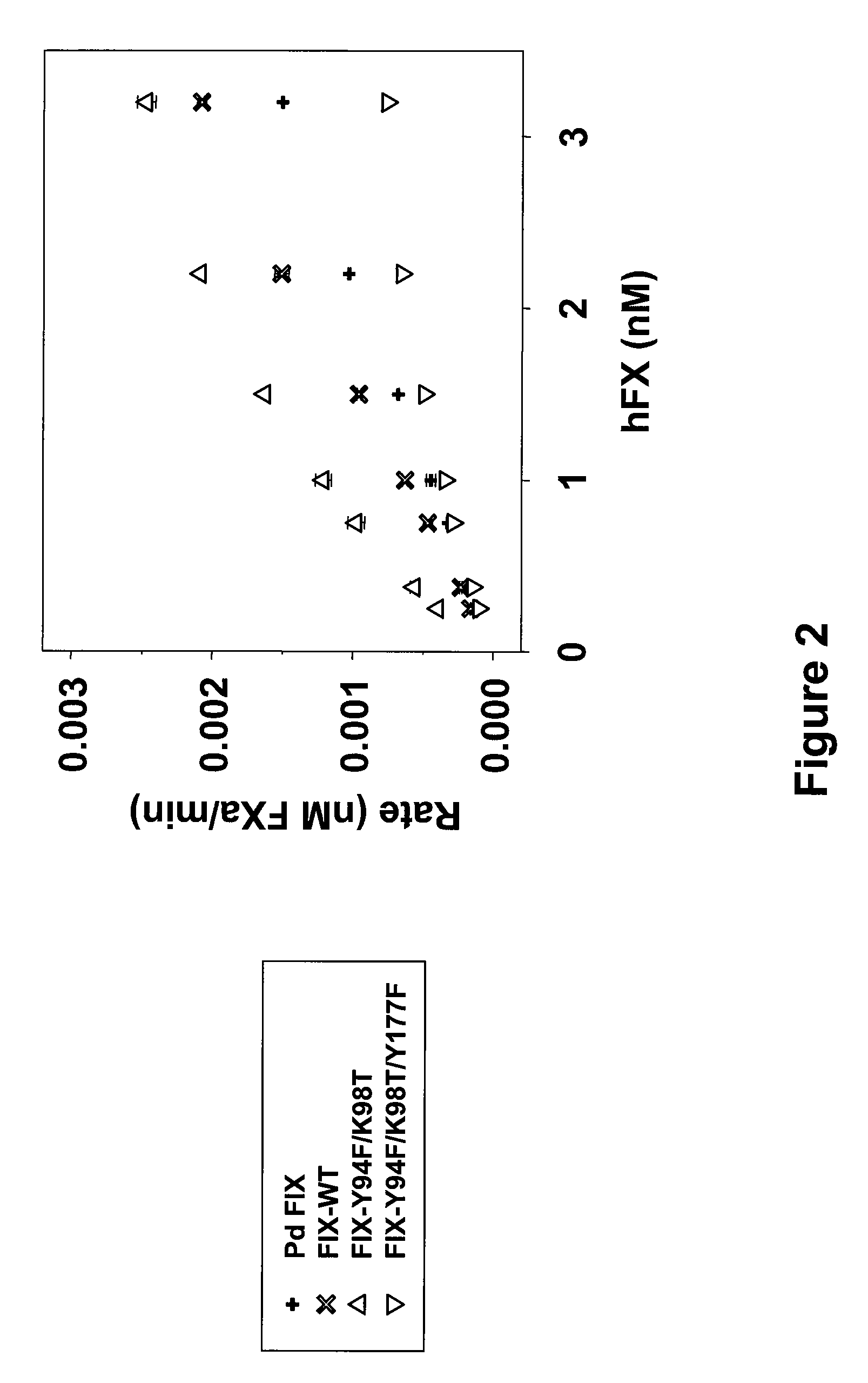
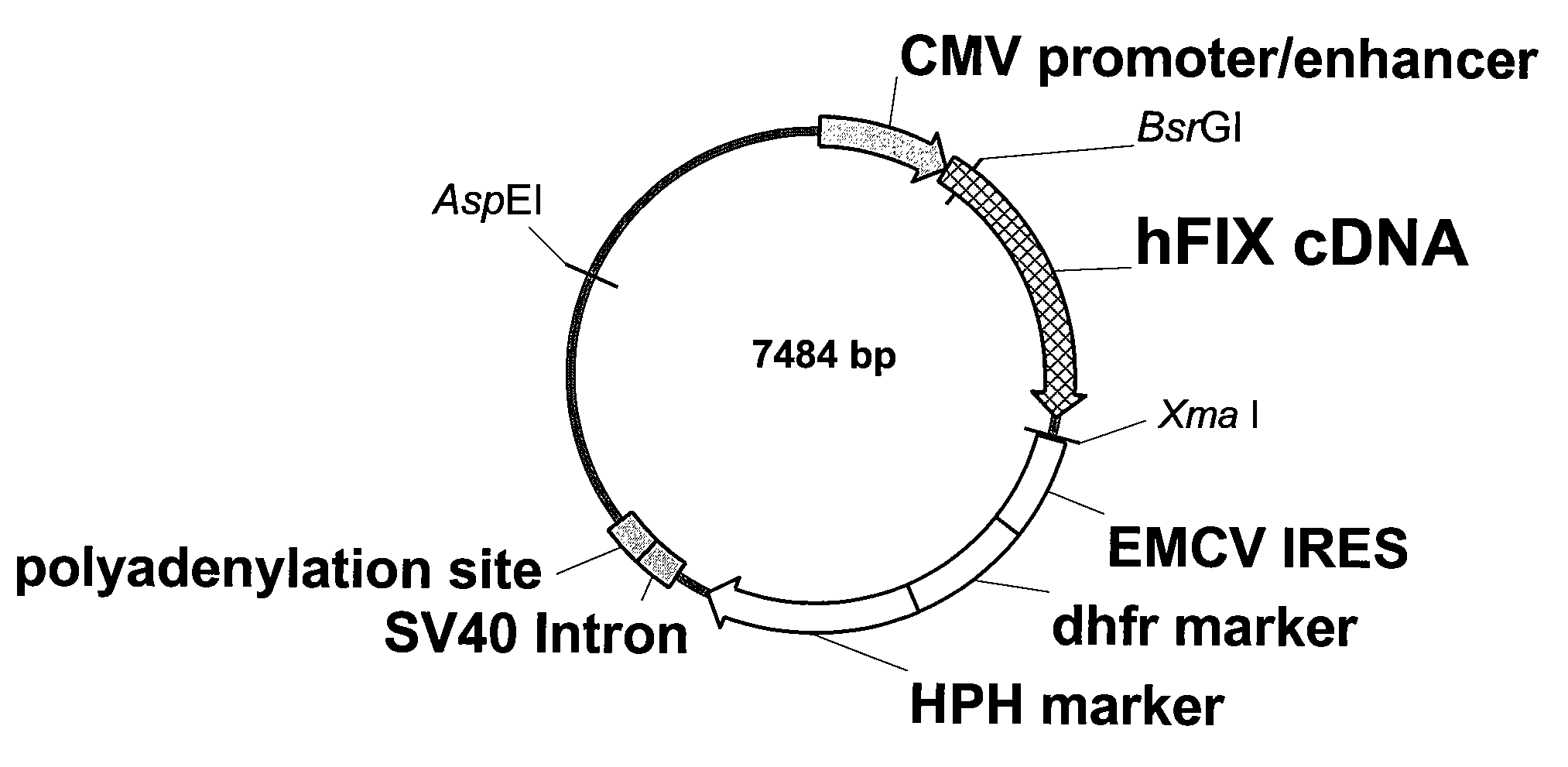
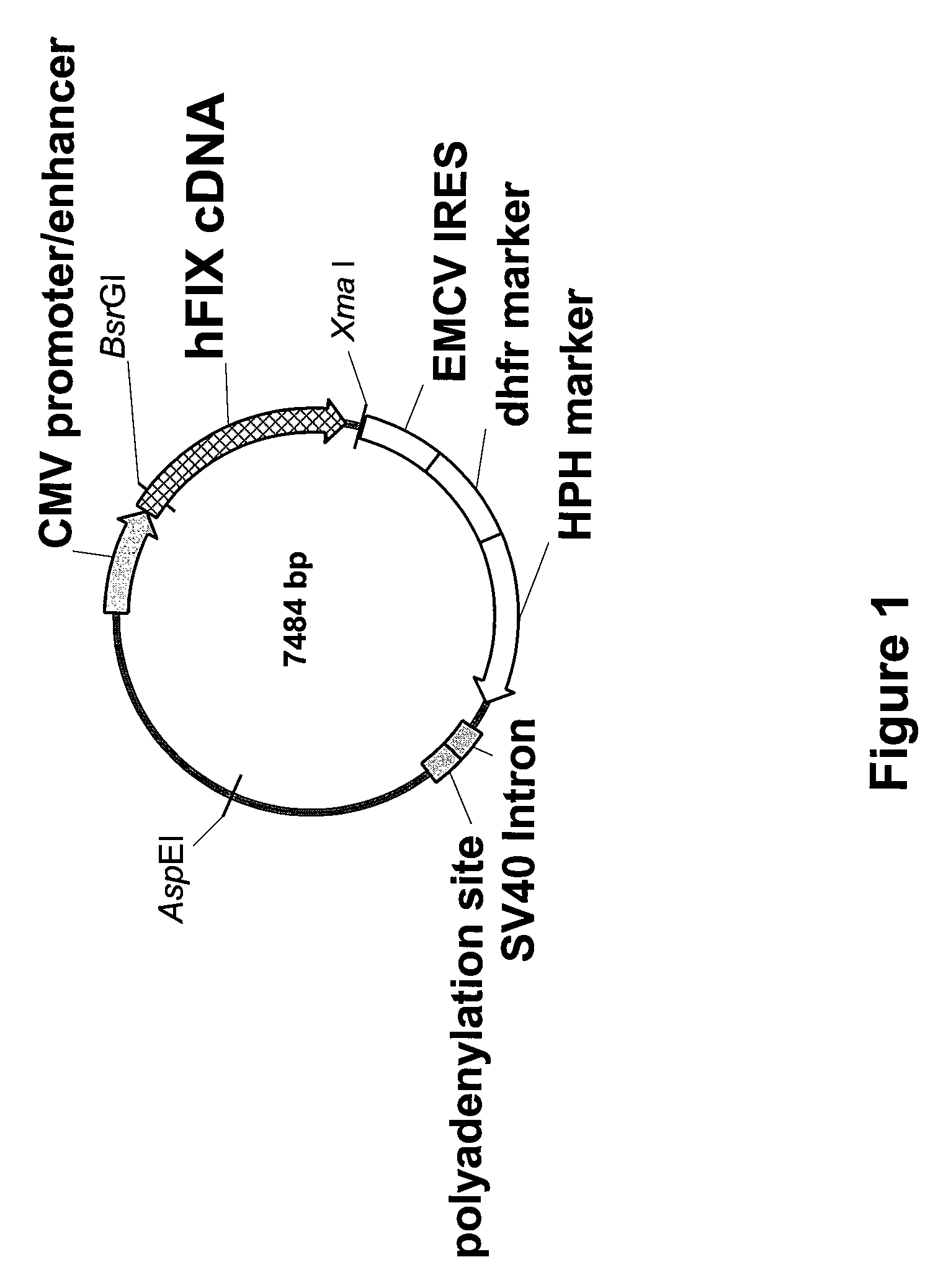
FIX-Mutant Proteins for Hemophilia B Treatment
InactiveUS20080214462A1Improved clot activityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHEK 293 cellsDisease
The present invention relates to recombinant blood coagulation factor IX (rFIX) mutants having improved FIX clotting activity. Three full length FIX proteins with combinations of mutations of amino acids important for functional activity of FIX and FIX wild type were cloned and expressed in HEK 293 cells. The proteins were tested by an activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) assays in FIX-depleted plasma. Two mutant proteins had increased specific FIX activity. Furthermore, a pre-activated FIX protein had an increased activity in FIX-depleted plasma. Therefore these FIX mutants can be used for the treatment of FIX associated bleeding disorders.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Micro fluid control array protein chip and its usage method
ActiveCN101165486AImprove capture abilityImprove handlingBiological testingControl layerFluid control
Said protein chip comprises a micro flow control channel layer and a chip substrate; at least one of both above is made of soft substance. It features: the micro flow control layer comprises two layers respectively having a first micro flow control channel and a second micro flow control channel; the first micro flow control channel is used for assembling the capturing probes; the second micro flow control channel is used for adding the tested protein sampler and the detection probes; said first micro flow channel layer and the second micro flow control channel layer are located on the chip substrate and forms 2D micro-array pattern on the chip.
Owner:HANGZHOU JINCHENGYIBANG TECH CO LTD
FVIII-Independent FIX-Mutant Proteins for Hemophilia A Treatment
ActiveUS20080214461A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHEK 293 cellsMutated protein
The present invention relates to recombinant blood coagulation factor IX (rFIX) mutants having factor VIII (FVIII) independent factor X (FX) activation potential. Five full length FIX proteins with combinations of mutations of amino acids important for functional activity of FIX and FIX wild type were cloned and expressed in HEK 293 cells. The proteins were tested by an activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) assay in FVIII-depleted plasma as well as in FVIII-inhibited patient plasma. In FVIII-depleted plasma functional activity of the FIX mutants was calculated as increased FVIII equivalent activity. The mutant proteins had increased FVIII equivalent activity. In FVIII-inhibited patient plasma the FEIBA equivalent activity was calculated for analysis of FVIII independent FX activation potential. The proteins had also increased FEIBA equivalent activity. Furthermore, the pre-activated FIX proteins had an increased activity in FIX-depleted plasma containing FVIII inhibitors. Therefore these FIX mutants are alternatives as bypassing agents for treatment of FVIII inhibitor patients.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Reagent kit for quickly testing protein content of milk powder and method for making same
InactiveCN101034065ASimple equipmentEasy to carryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsProtein solutionImage processing software
This invention relates to a kind of milk powder protein content detection kit, includes milk powder protein content standard color grade, sampler, transparence graduated vessels and biuret coloration liquid. The invention also open the manufacturing method of this kit, includes the step of make milk powder protein content standard color grade which as follows: use milk powder of given protein content and standard protein agent to prepare standard protein solution series contain milk powder; add biuret reagent into above series standard protein solution to obtain mixed liquor; shot mixed liquor;with image processing software to process photo, obtain color strip and output. This kit lends itself to carry. When detect milk powder protein content it not needs other supplementary instrument and equipment, detection cost low, testing time short. It has no special requirement to detection staff.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIYUNDA TECH CO LTD
Reverse protein chip
InactiveCN1335506ALess quantitySimple detection operationBiological testingProtein insertionHybridization reaction
Owner:GENETECH BIOTECH SHANGHAI
Fluorescent labeling of specific protein targets in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS20060147948A1High sensitivityReduced flexibilityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceIn vivo
New methods are provided for the post-genomic era that will permit the analysis of the dynamic expression and localization of gene products in living cells. Herein we propose the development of such a method from a bioorganic approach involving organic synthesis and protein engineering. Specifically, novel compounds bearing two maleimide groups attached directly to fluorescent cores will be prepared, whose latent fluorescence is quenched until their maleimide groups undergo a specific thiol addition reaction. Complementary a-helical proteins are designed bearing two cysteine residues appropriately positioned to react with our novel fluorogens. Genetically fusing our helical probe peptides to test proteins of interest, we can selectively label the target sequence in living cells with our small synthetic fluorogenic molecules. The scope of this technique is described in the context of studying protein localization and protein-protein interactions in living cells.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP +1
Transcription-based assay for identification of post-translational modification and its application in proteomics
InactiveUS7052843B2Simple and rapid assayLess time-consumingAnimal cellsSugar derivativesProtein targetPost translational
The present invention relates to a method for detecting the post-translational modification of a target protein by a post translational modifier polypeptide molecule; a method for screening a candidate protein for E3 ligase activity; a method of screening a test compound for the ability to regulate the post-translational modification of a target protein by a post-translational modifier polypeptide molecule; and a method for the large-scale detection of candidate target proteins of post-translational modification by a modifier polypeptide molecule. The present invention also relates to a kit for determining whether a test protein is post-translationally modified by a modifier polypeptide molecule; a kit for screening a test compound for the ability to regulate the post-translational modification of a target protein by a post-translational modifier peptide molecule, and another kit for determining whether a test protein is post-translationally modified by a modifier polypeptide molecule.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method and kit for detection of multiple protein interactions
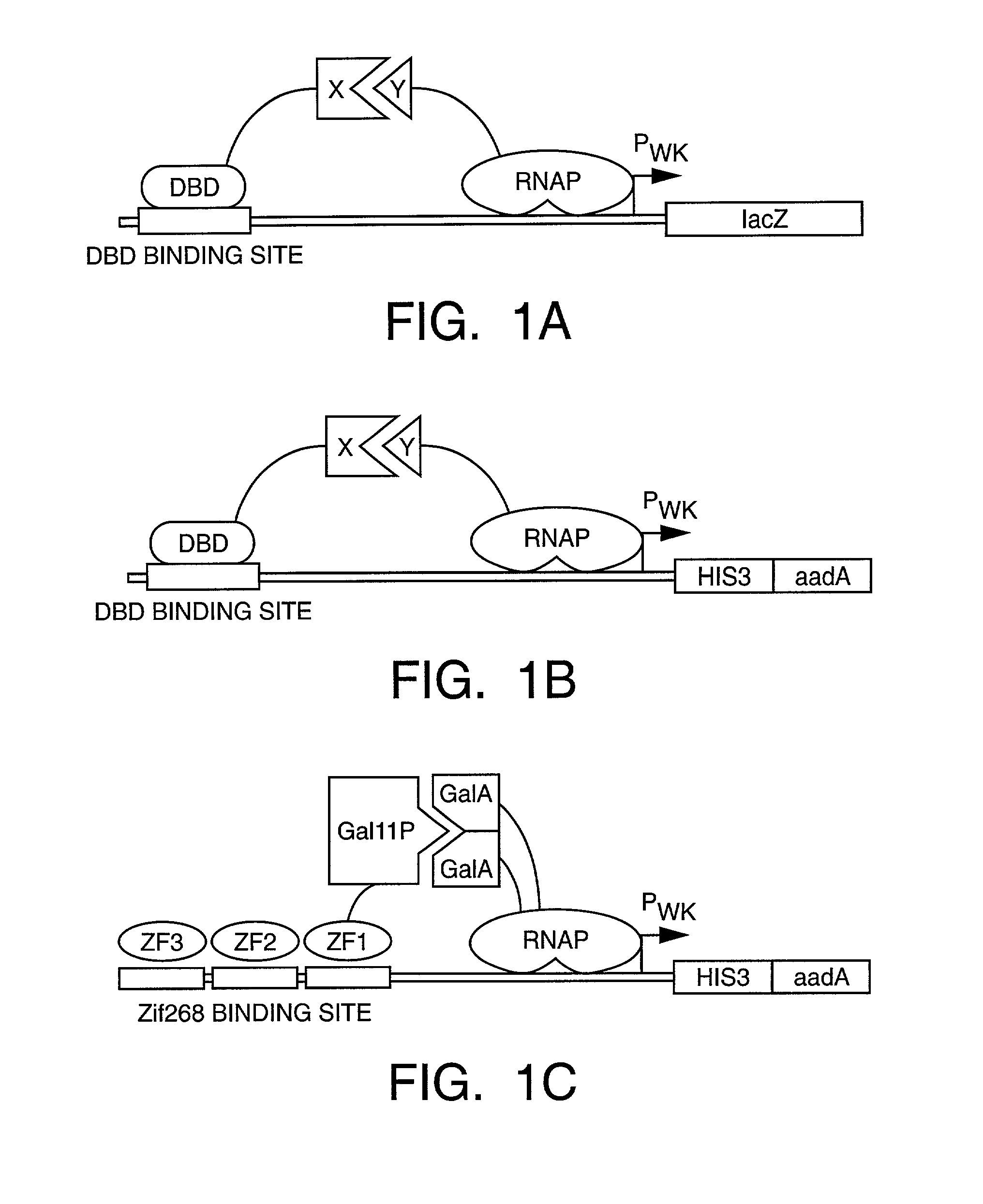
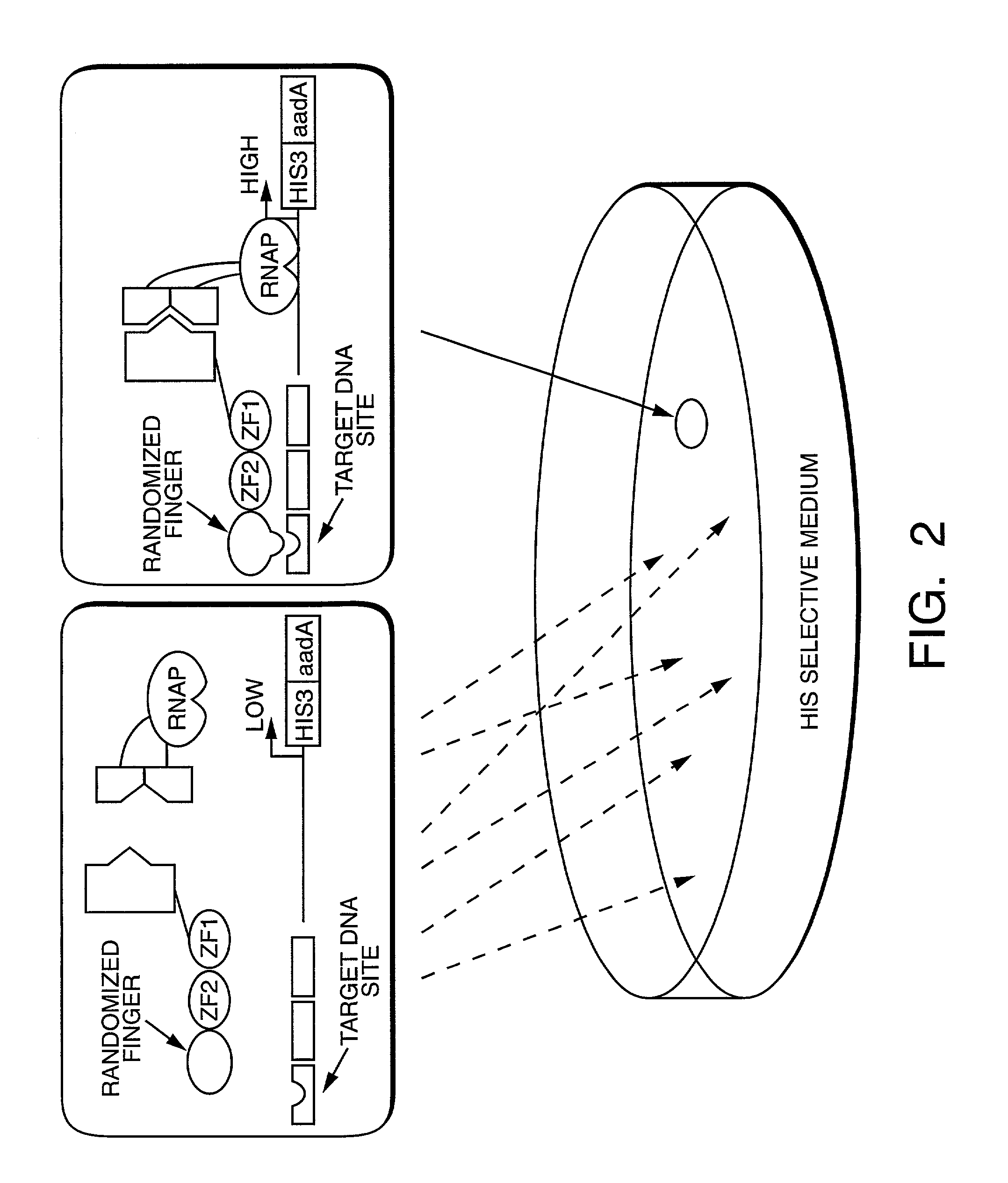
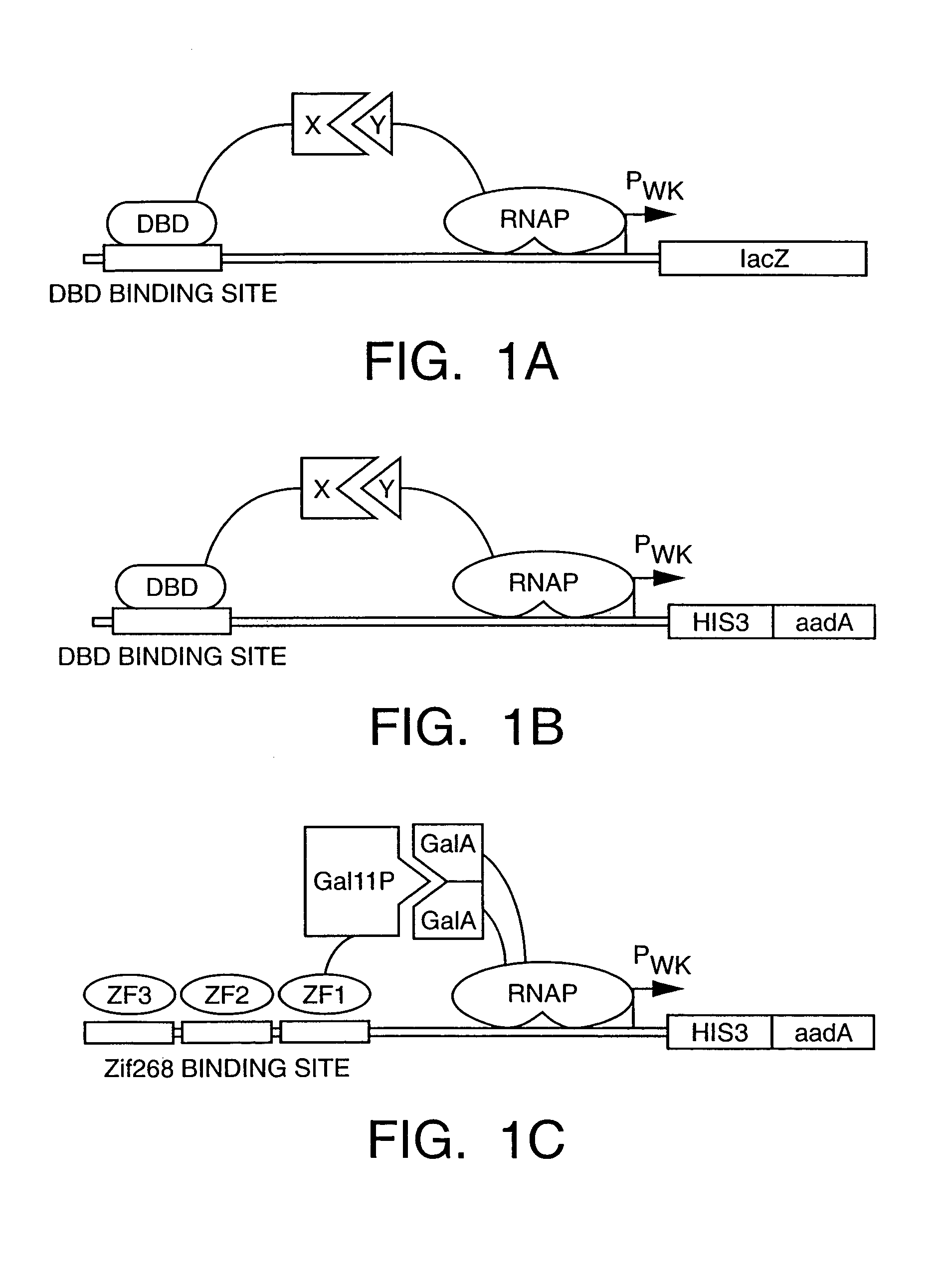
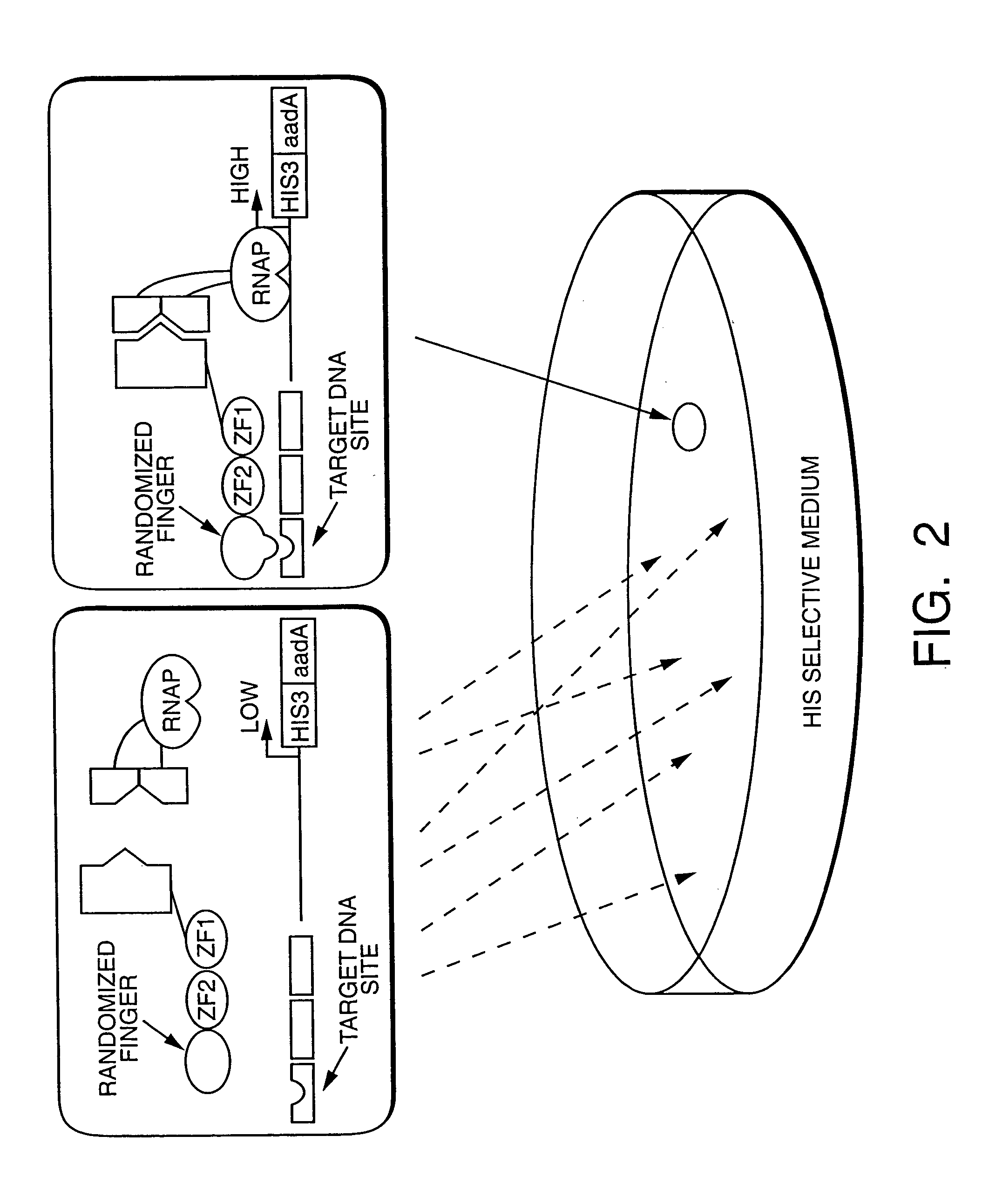
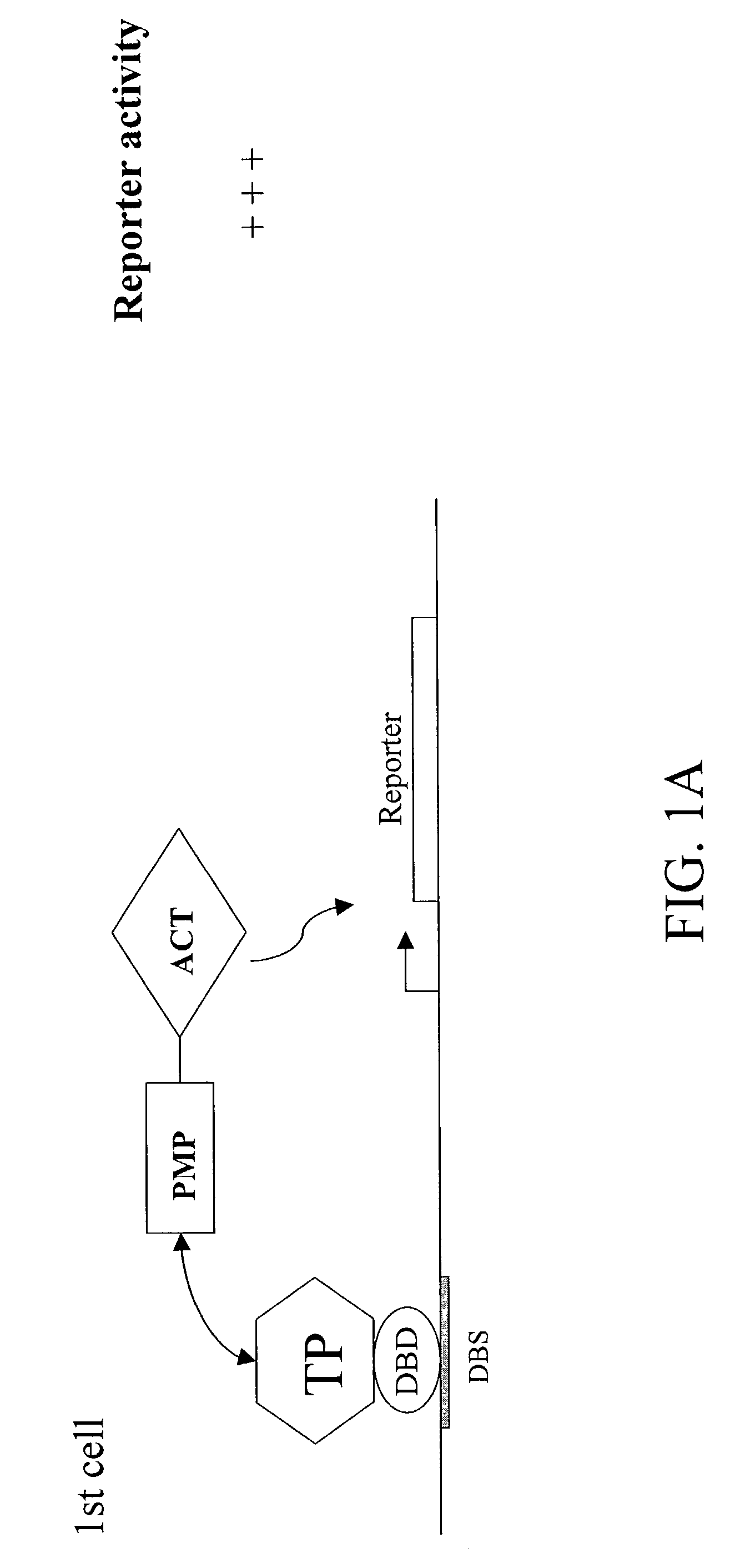
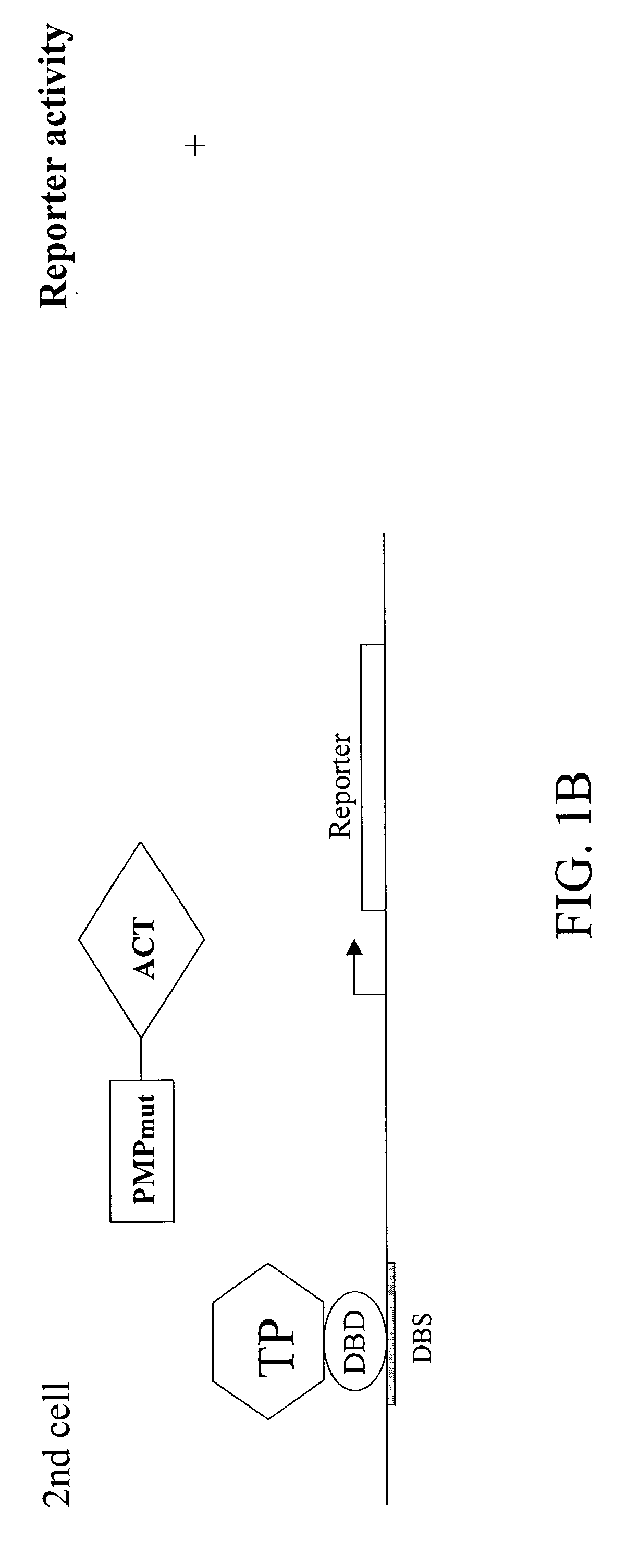
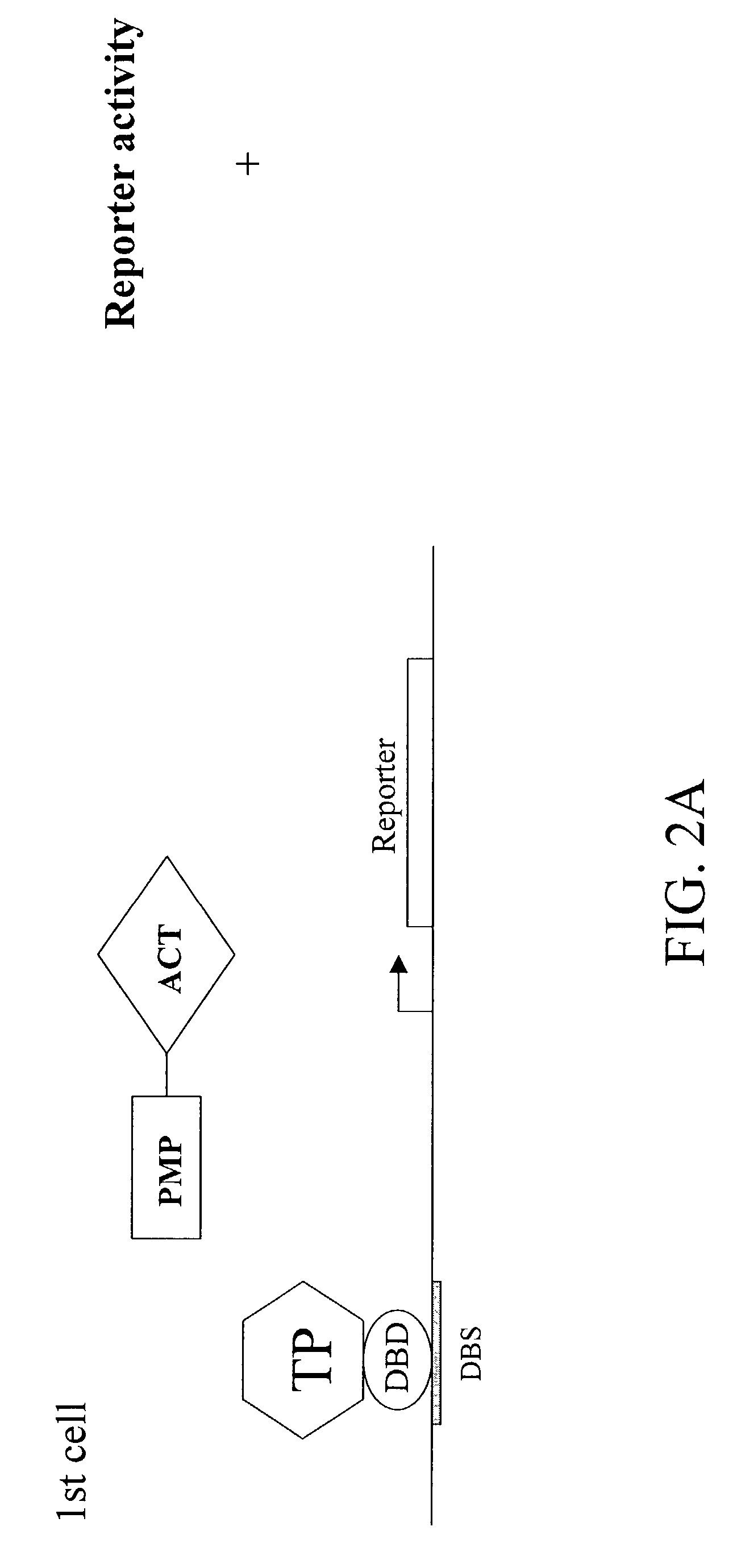
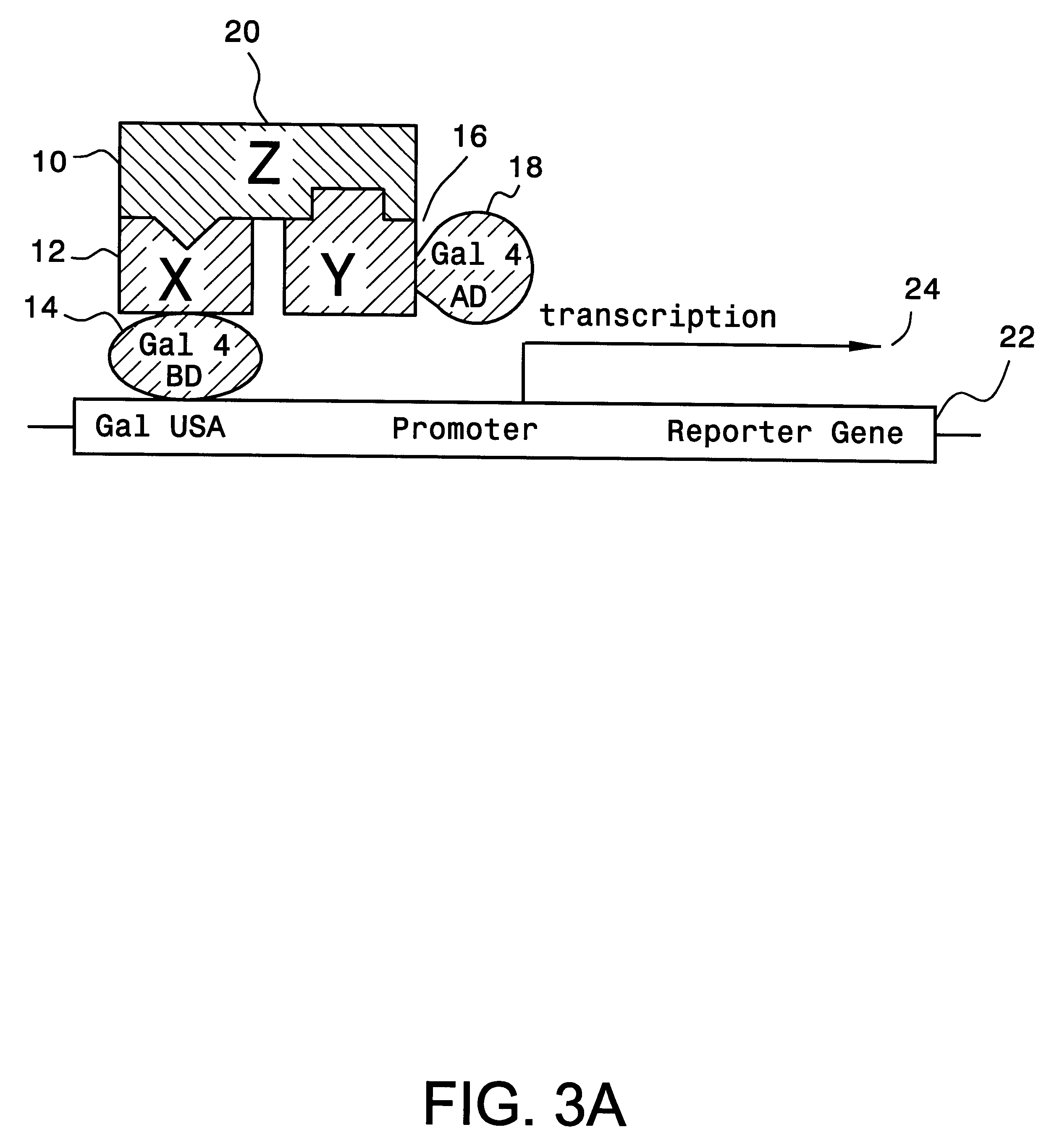
A method and a kit for detecting interactions between three or more proteins, in vivo, using reconstitution of the activity of a transcriptional activator is provided. Reconstitution of the transcriptional activator makes use of chimeric genes which express hybrid proteins. In one embodiment, three types of hybrid proteins are prepared. The first hybrid contains the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator fused to the first test protein. The second hybrid protein contains a transcriptional activation domain fused to the second test protein. The third hybrid protein contains a nuclear localization peptide fused to a third test protein and mediates assembly of the three-protein complex involving the three hybrids. If the three test proteins are able to interact, they bring into close proximity the two domains of the transcriptional activator. This proximity is sufficient to cause transcription, which can be detected by the activity of a marker gene that contains a binding site for the DNA-binding domain.
Owner:GUILFORD PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Quantitative, high-throughput screening method for protein stability
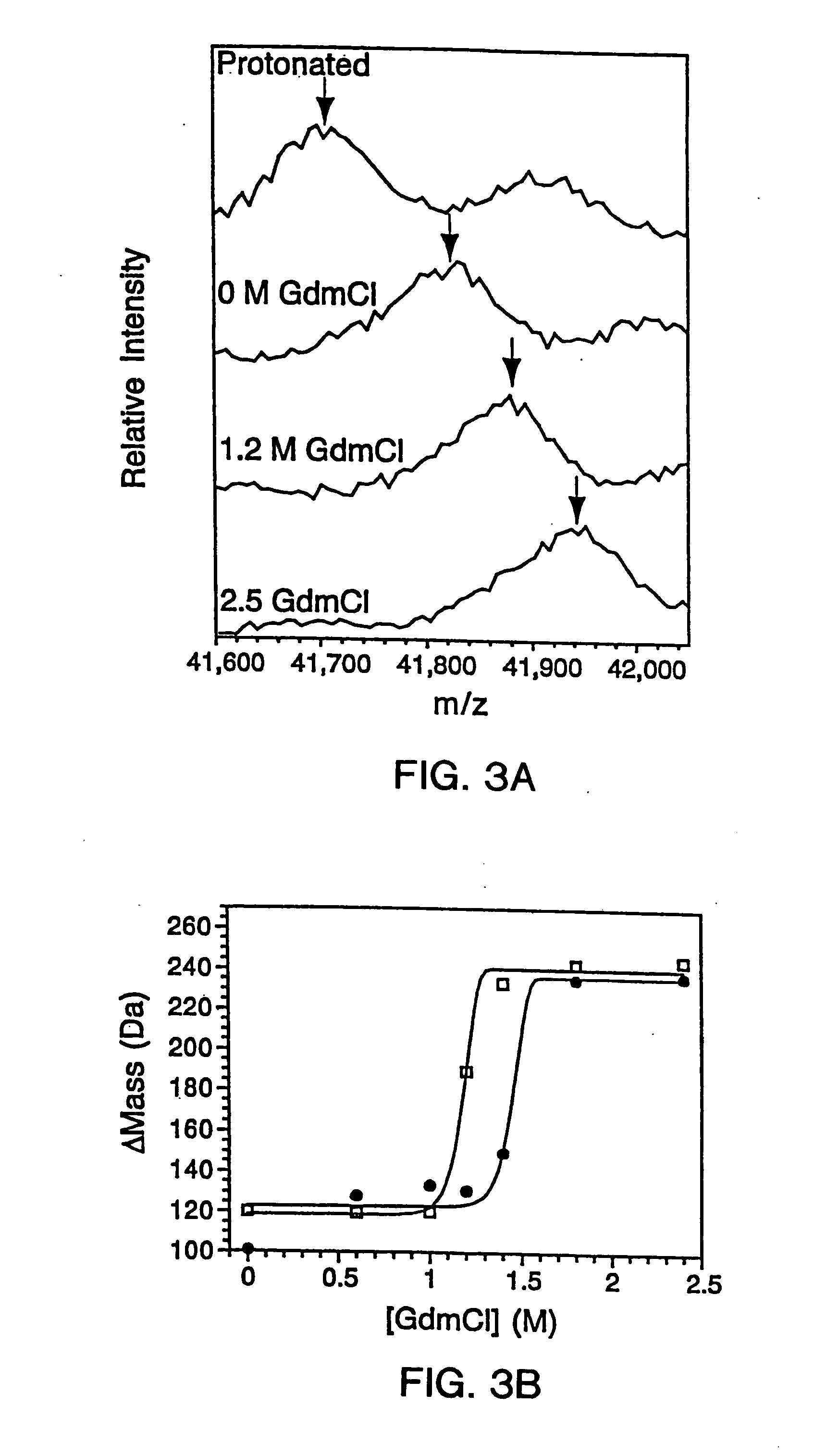
InactiveUS20070099305A1Improve completenessImprove stabilityDisease diagnosisBiological testingLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
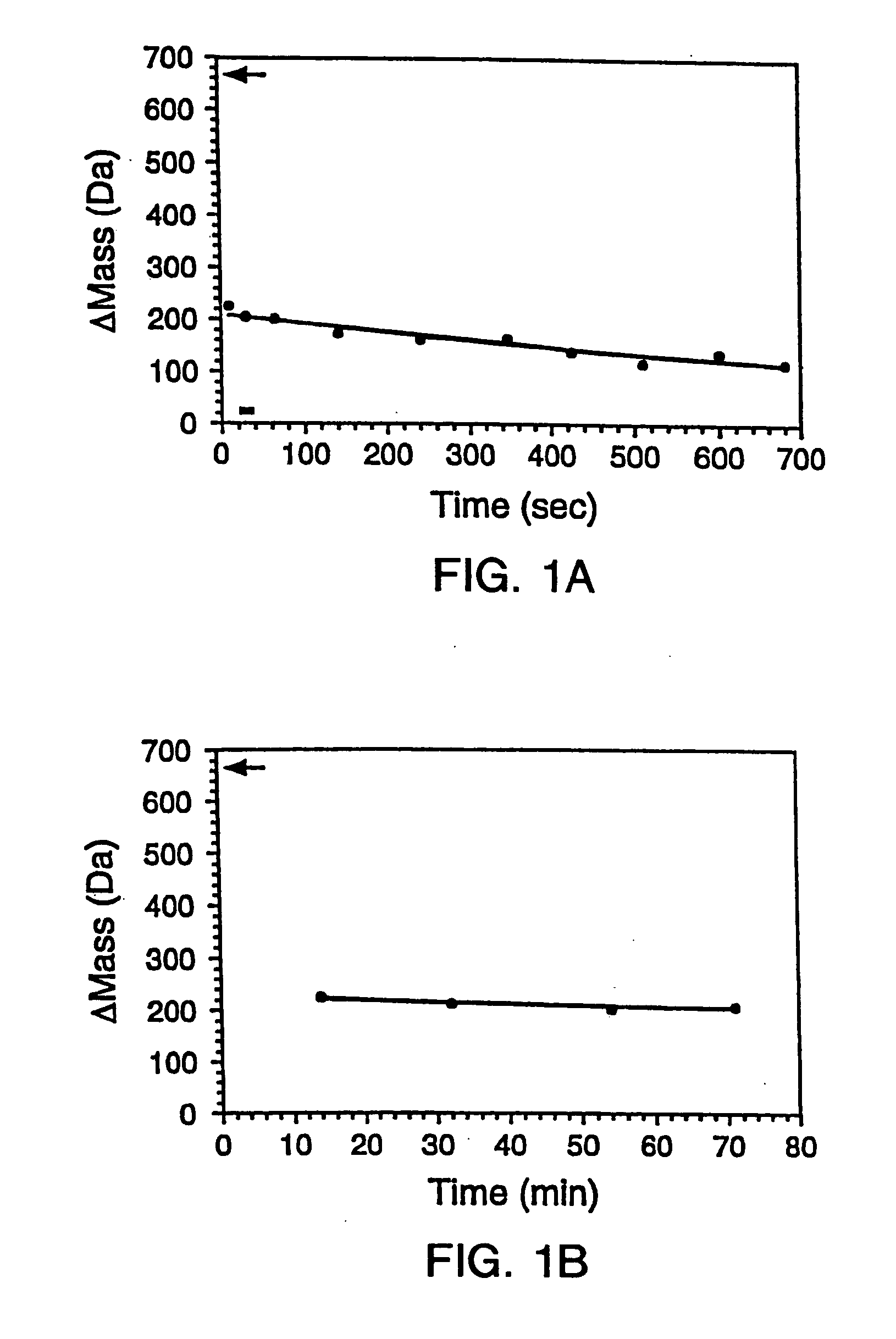
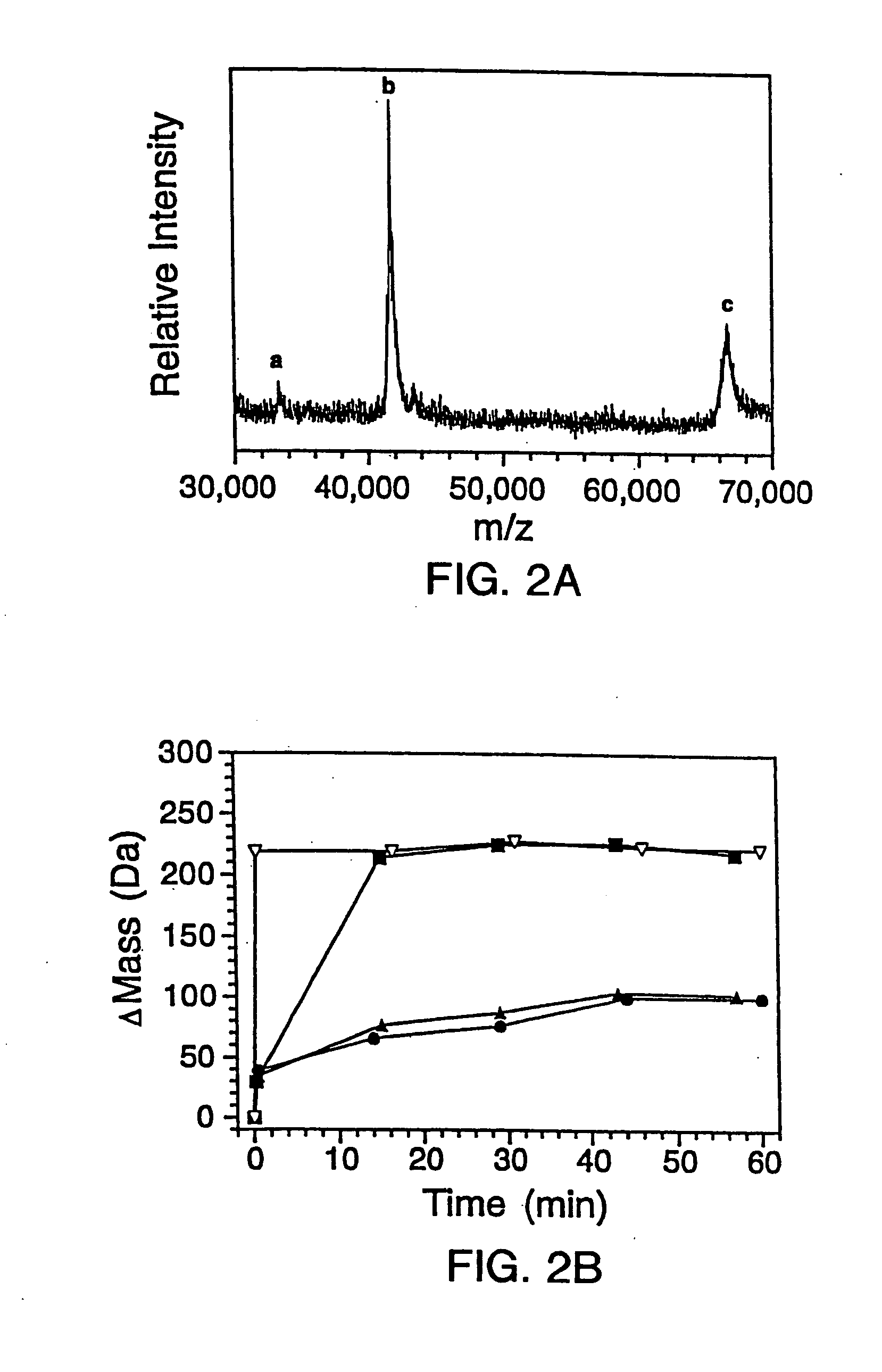
In proteomic research, it is often necessary to screen a large number of polypeptides for the presence of stable structure. Described herein are methods (referred to as MALDI MS-HX and SUPREX) for measuring the stability of proteins in a rapid, high-throughput fashion. The method employs hydrogen exchange to estimate the stability of quantities of unpurified protein extracts, using matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry. A method of quantitatively determining the stability of a test protein under native conditions is disclosed. The method includes the steps (a) providing a test protein; (b) contacting the protein with an exchange buffer comprising a denaturant and deuterium, the exchange buffer having a denaturant concentration; (c) contacting the test protein with a mass spectrometry matrix medium; (d) determining a change in mass of the test protein by mass spectrometry; (e) varying the denaturant concentration of the exchange buffer; (f) repeating steps (a)-(e) a desired number of times; and (g) quantitatively determining protein stability based on the change in mass of the test protein as a function of denaturant concentration, whereby the stability of a test protein under native conditions is quantitatively determined.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Protein chip used for detecting functional injury of central nervous system and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveCN101008644AHigh speedSpeed up the processMaterial analysisTOR activityBiological activation
This invention relates to one functional central neutral damage dialogue test protein chip and its process method, which comprises the following steps: using protein chip to fix multiple central neutral system damage generation development key function abnormal protein factor antigen and its array; the said protein antigen and its array abnormal protein factors act as key property protein factors in the neutral system for inflammation and activation reaction and cell ion balance adjust and signal transmission.
Owner:陈云 +3
Method and system for identifying protein
InactiveCN109425662AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyImprove identification efficiencyComponent separationProteomics methodsProteomic Profile
The invention relates to a method and system for identifying a protein, especially to a proteomic method and system for efficiently identifying polyclonal antibodies. The method includes the followingsteps: (1) a step of sample treatment, namely a step of performing enzymatic hydrolysis treatment on a to-be-tested protein sample by using multiple enzymes in series; (2) a step of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry detection, namely a step of performing liquid chromatography separation and mass spectrometric detection on peptide fragments after the enzymatic hydrolysis treatment; and (3) astep of data analysis, namely a step of filtering mass spectrometry original down data, performing database searching identification of the mass spectrometry data according to a constructed databaseto obtain identified peptide fragment information, and performing merging according to the identified peptide fragment information to obtain the reliable to-be-tested protein. The method and system for identifying a protein provides a standard bioinformation analysis process for proteomics analysis of the polyclonal antibodies, and can effectively, simply and reliably obtain specific antibodies with high specificity and good immunoreactivity from the polyclonal antibodies.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
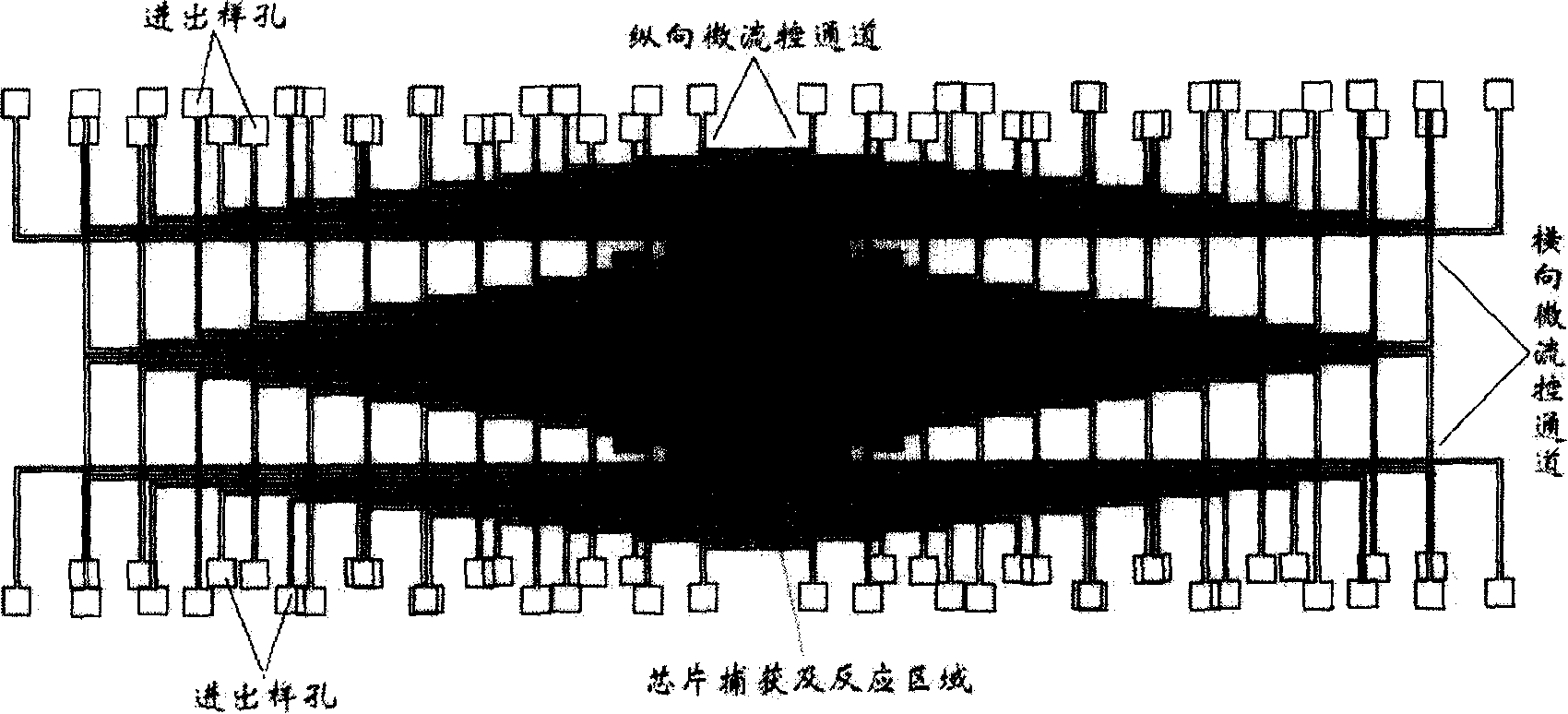
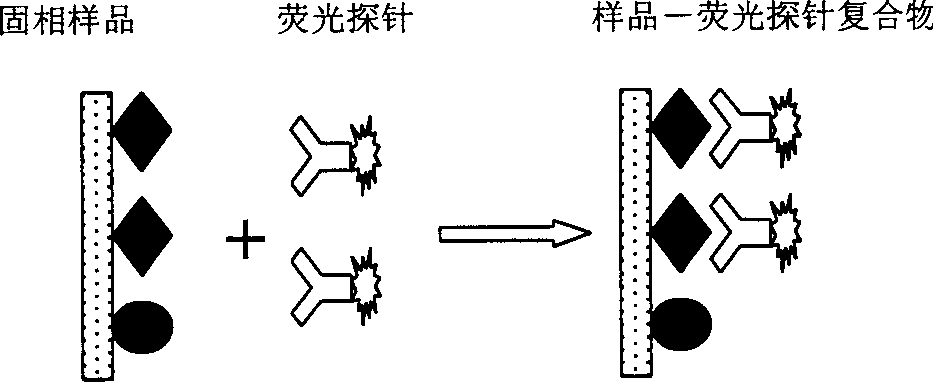
Micro-fluidic chip, protein detecting method, protein detecting device and protein detecting system
PendingCN110646493AEliminate the problem of unstable responseHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseProtein detection
The invention discloses a protein detecting system which aims at improving the consistency and repeatability of trace protein detection. The protein detecting system comprises a micro-fluidic chip, anambipolar electrode chip and a concentration determining assembly, wherein the micro-fluidic chip comprises a plurality of micropits in array distribution; the micropits are used for capturing solid-phase carriers in a tested sample; the tested sample comprises solid-phase carriers combined with tested protein and an electrochemical luminescent material, solid-phase carriers not combined with thetested protein and the electrochemical luminescent material, and an electrochemical reaction solution; the ambipolar electrode chip comprises a plurality of electrode units in array distribution; when being activated in the tested sample, the electrode units take an electrochemical reaction with the electrochemical luminescent material and give out light; and the concentration determining assembly determines the concentration value of the tested protein in the tested sample according to the total quantity of the solid-phase carriers in the micropits and the quantity of the luminescent solid-phase carriers. In addition, the embodiment of the invention also provides the micro-fluidic chip, the ambipolar electrode chip, a protein detecting method and a protein detecting device.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Fluorescent labeling of specific protein targets in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS7700375B2High sensitivityReduced flexibilityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementCysteine thiolateProtein insertion
New methods are provided for the post-genomic era that will permit the analysis of the dynamic expression and localization of gene products in living cells. Herein we propose the development of such a method from a bioorganic approach involving organic synthesis and protein engineering. Specifically, novel compounds bearing two maleimide groups attached directly to fluorescent cores will be prepared, whose latent fluorescence is quenched until their maleimide groups undergo a specific thiol addition reaction. Complementary a-helical proteins are designed bearing two cysteine residues appropriately positioned to react with our novel fluorogens. Genetically fusing our helical probe peptides to test proteins of interest, we can selectively label the target sequence in living cells with our small synthetic fluorogenic molecules. The scope of this technique is described in the context of studying protein localization and protein-protein interactions in living cells.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP +1
Genetic selection system to identify proteases, protease substrates and protease inhibitors
The present invention concerns a tester protein for identifying and / or monitoring protease activity in a cellular assay suitable for high throughput screenings by growth selection, wherein the tester polypeptide is a non-regulatory protein carrying a protease cleavage sequence. Upon co-expression of the protease recognizing said cleavage sequence the tester protein is inactivated, which influences the growth and / or survival of the host cells under the chosen conditions. However, in the presence of protease inhibitor the growth phenotype is reversed. The system can be used to identify proteases, protease inhibitors, and protease cleavage sites.
Owner:ONCALIS
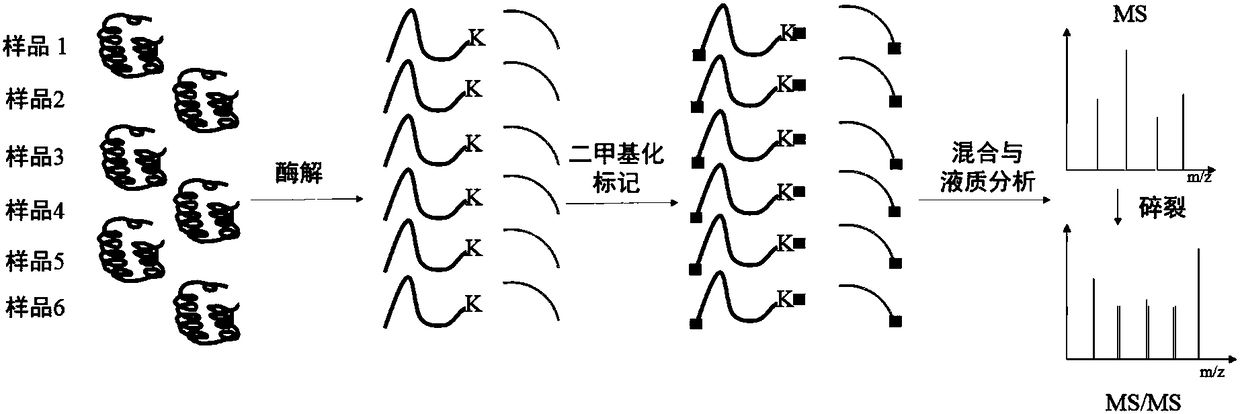
Absolute quantification method based on dimethylated multiple labeling and characteristic fragment ions
ActiveCN108088945ARealize simultaneous quantificationAchieve precise absolute quantificationComponent separationProtein targetLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
The present invention relates to a multiple-sample multiple-target high-throughput accurate absolute quantification method of proteomes. A N-terminal and a lysine amino group of a peptide fragment canbe labeled by dimethylation reaction, and by organic combination of various isotopic forms of a dimethylation labeling reagent, multiple labeling of a to-be-tested protein and / or peptide fragment sample and a protein and / or peptide fragment in a target internal standard substance with a known amount can be realized. The labeled sample is analyzed by a LC / MS system. Peak areas of characteristic fragment ions in the secondary spectrum of the sample and the internal standard substance are extracted for quantifying to obtain the absolute amount of a target protein in the to-be-tested sample. Themethod has the advantages of high analysis throughput, great saving of analysis time, cheap labeling reagent, strong practical application, high quantitative accuracy, good precision, and wide dynamicrange, and can meet the needs of multiple-sample analysis based on the internal standard substance or multiple-target analysis based on a standard curve.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
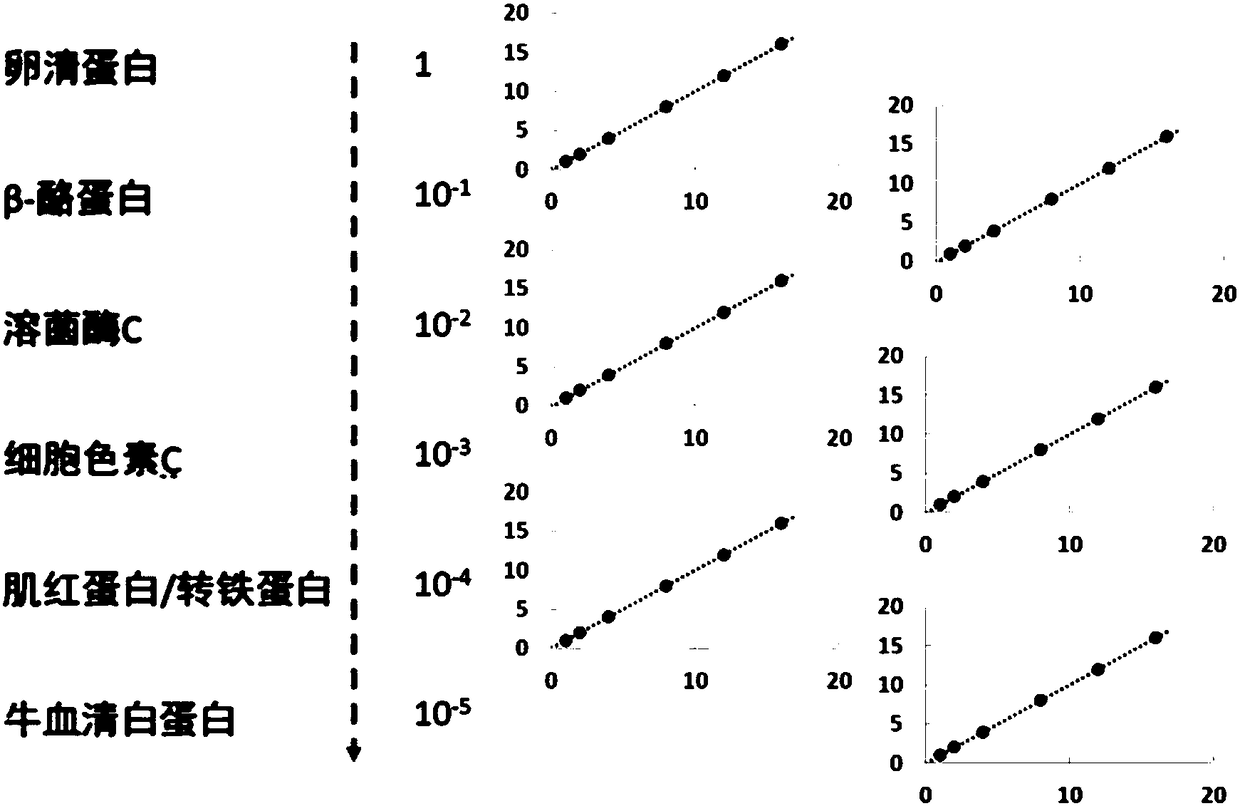
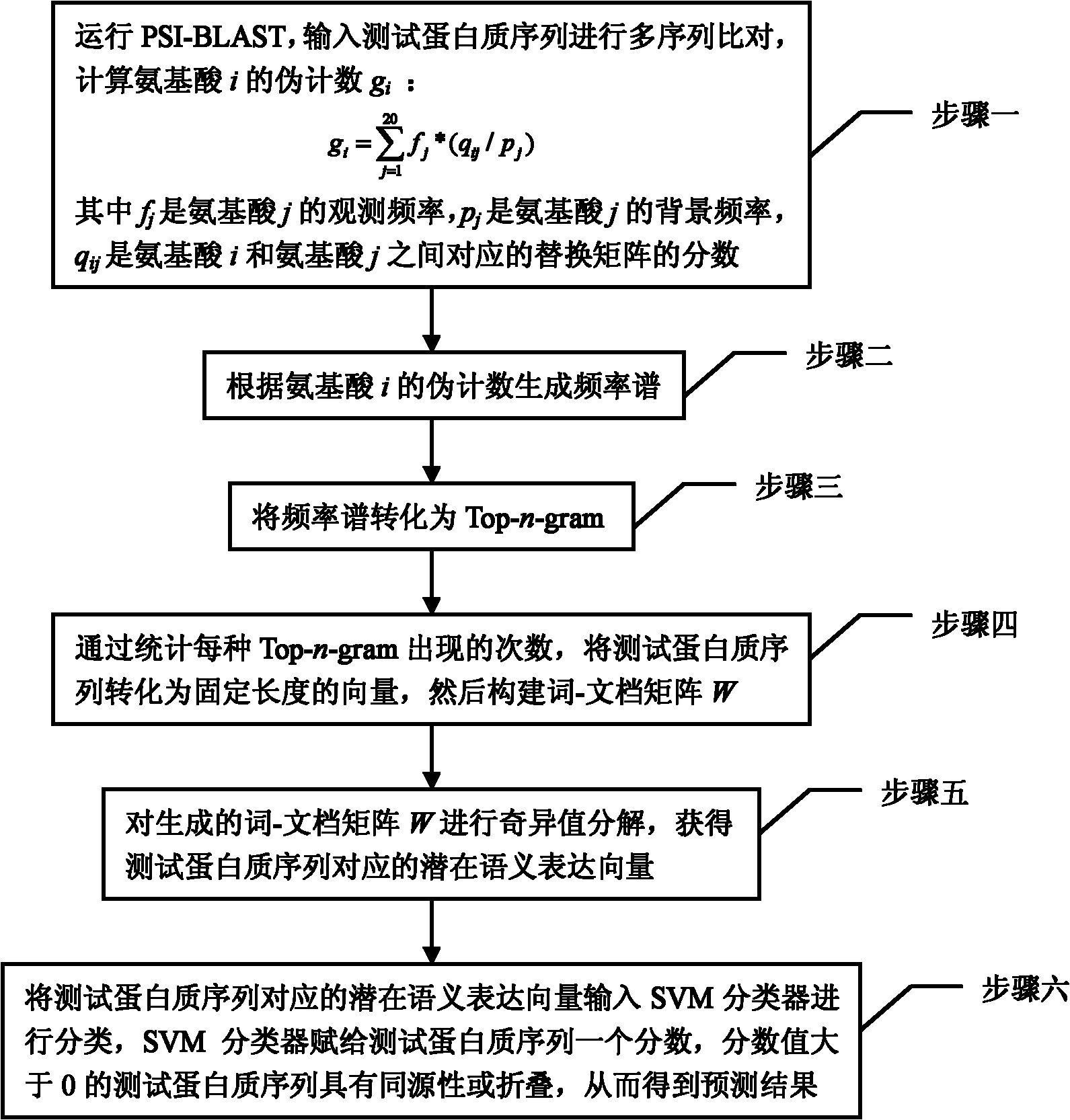
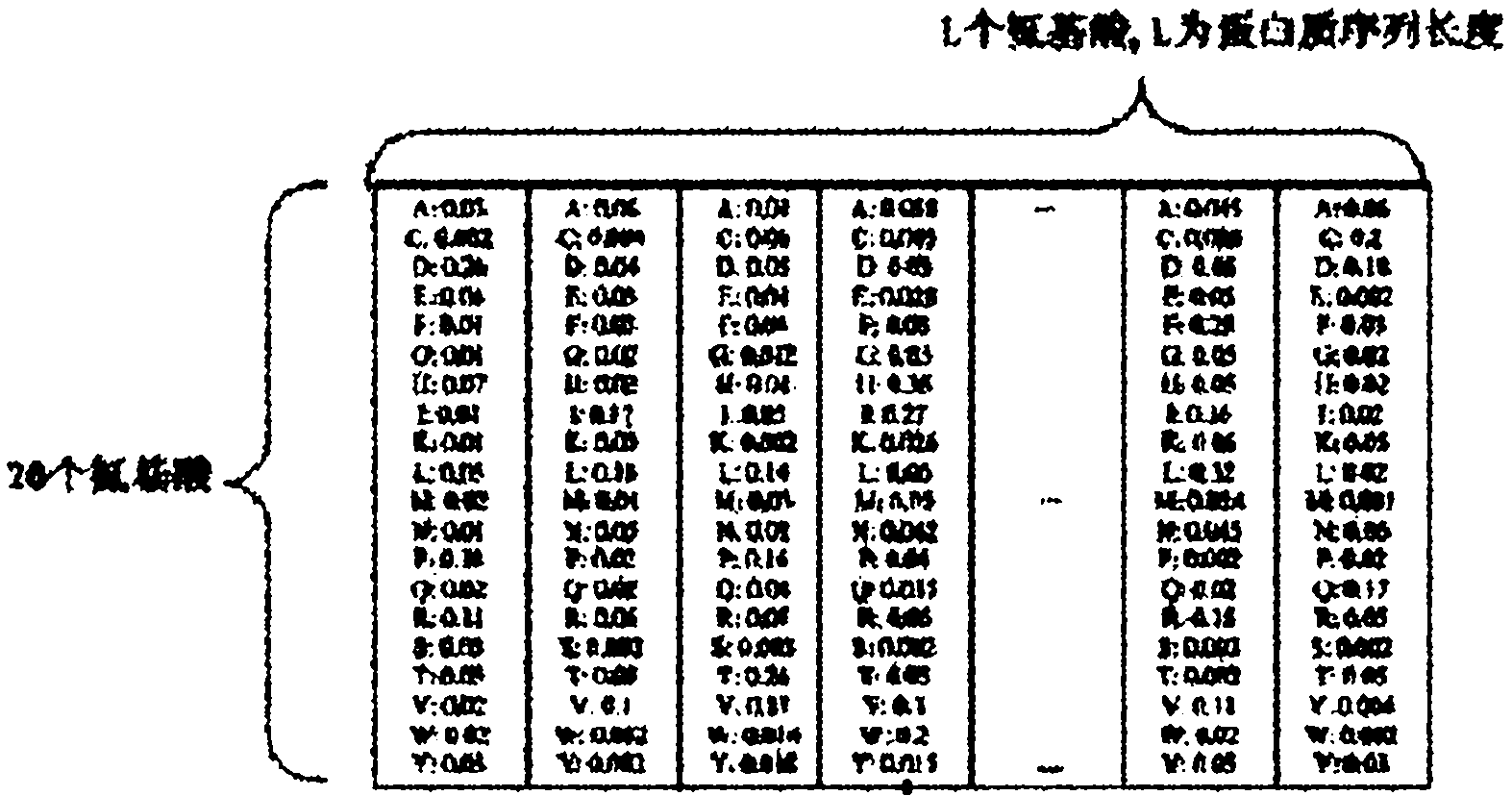
Remote protein homology detection and fold recognition method based on Top-n-gram
InactiveCN102043910AImprove predictive performanceEmphasize the importanceSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a remote protein homology detection and fold recognition method based on a Top-n-gram, and relates to a remote protein homology detection and fold recognition method. The method is used for solving a problem that a binary spectrum cannot find out an optimal threshold and cannot distinguish difference of frequency of occurrences of amino acid in the prior protein remote homology detection and fold recognition method, and comprises the following steps: 1, operating a PSII-BLAST, inputting a tested protein sequence for multiple sequence alignment, and calculating a pseudocount of an amino acid i; 2, generating a frequency spectrum; 3, transforming the frequency spectrum into the Top-n-gram; 4, obtaining a latent semantic expression vector corresponding to the tested protein sequence; 5, inputting the latent semantic expression vector corresponding to the tested protein sequence into an SVM sorter for sorting, and obtaining a forecasting result. The protein remotehomology detection and fold recognition method based on the Top-n-gram is used in the filed of protein homology detection and fold recognition.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com