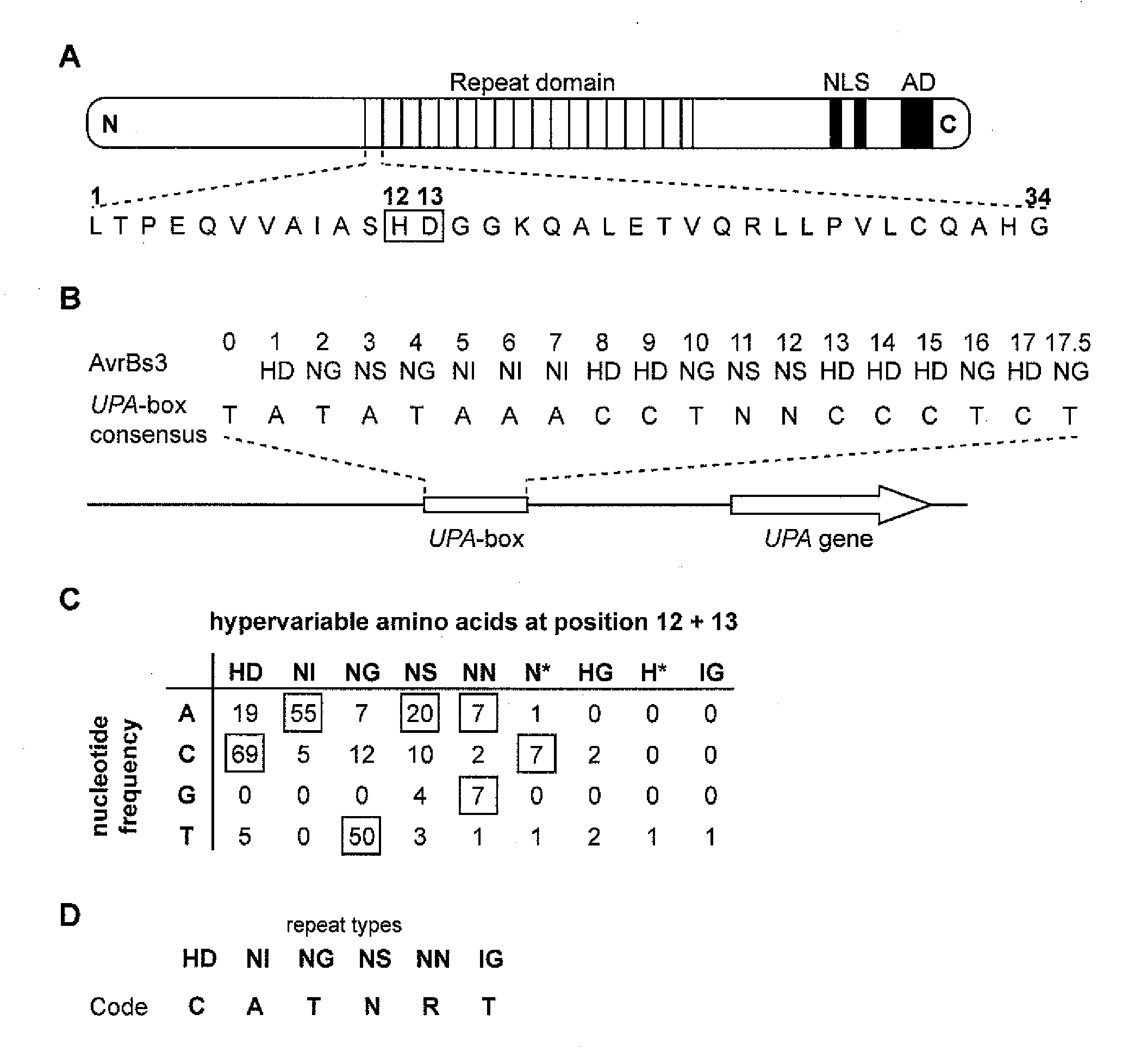
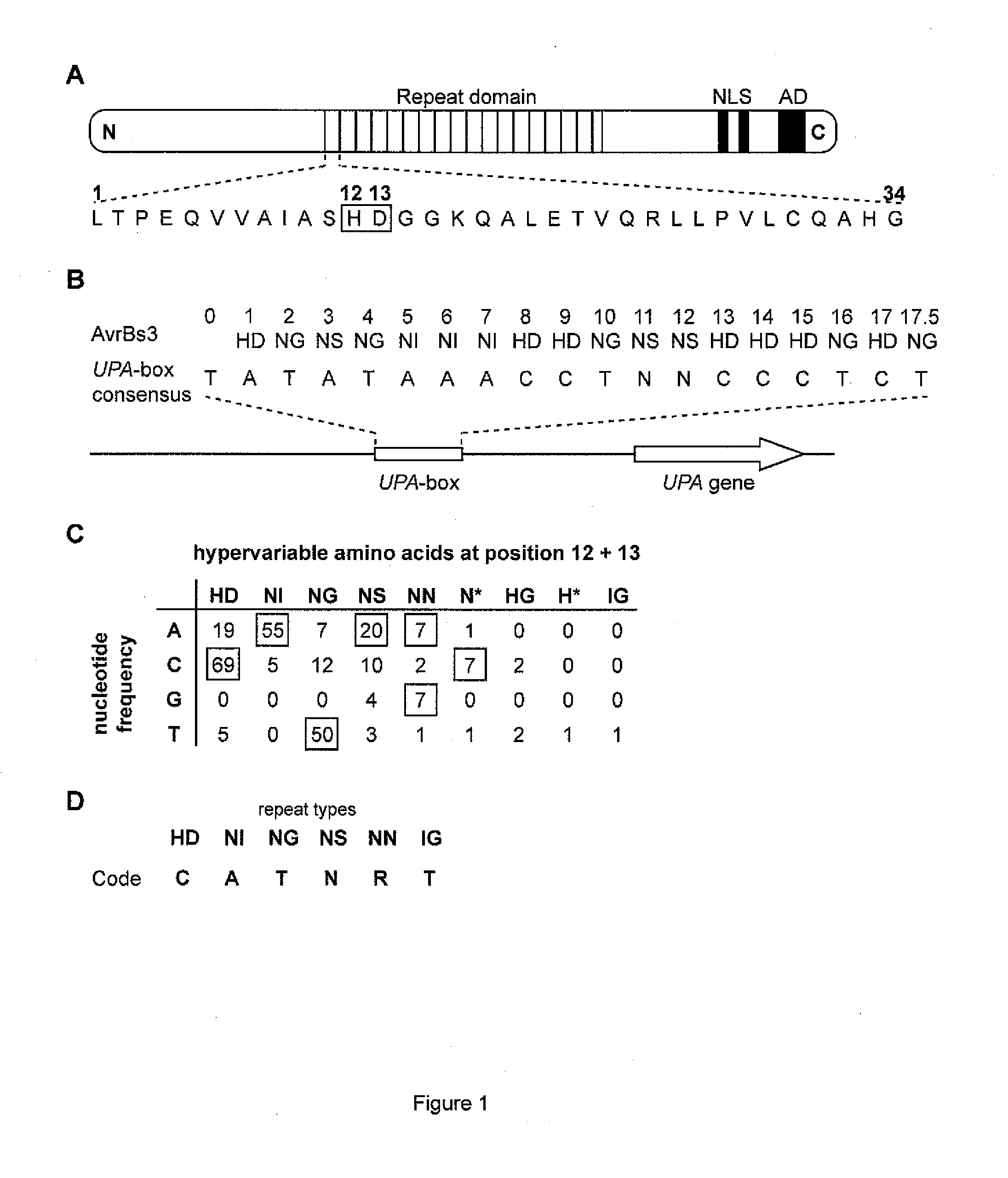
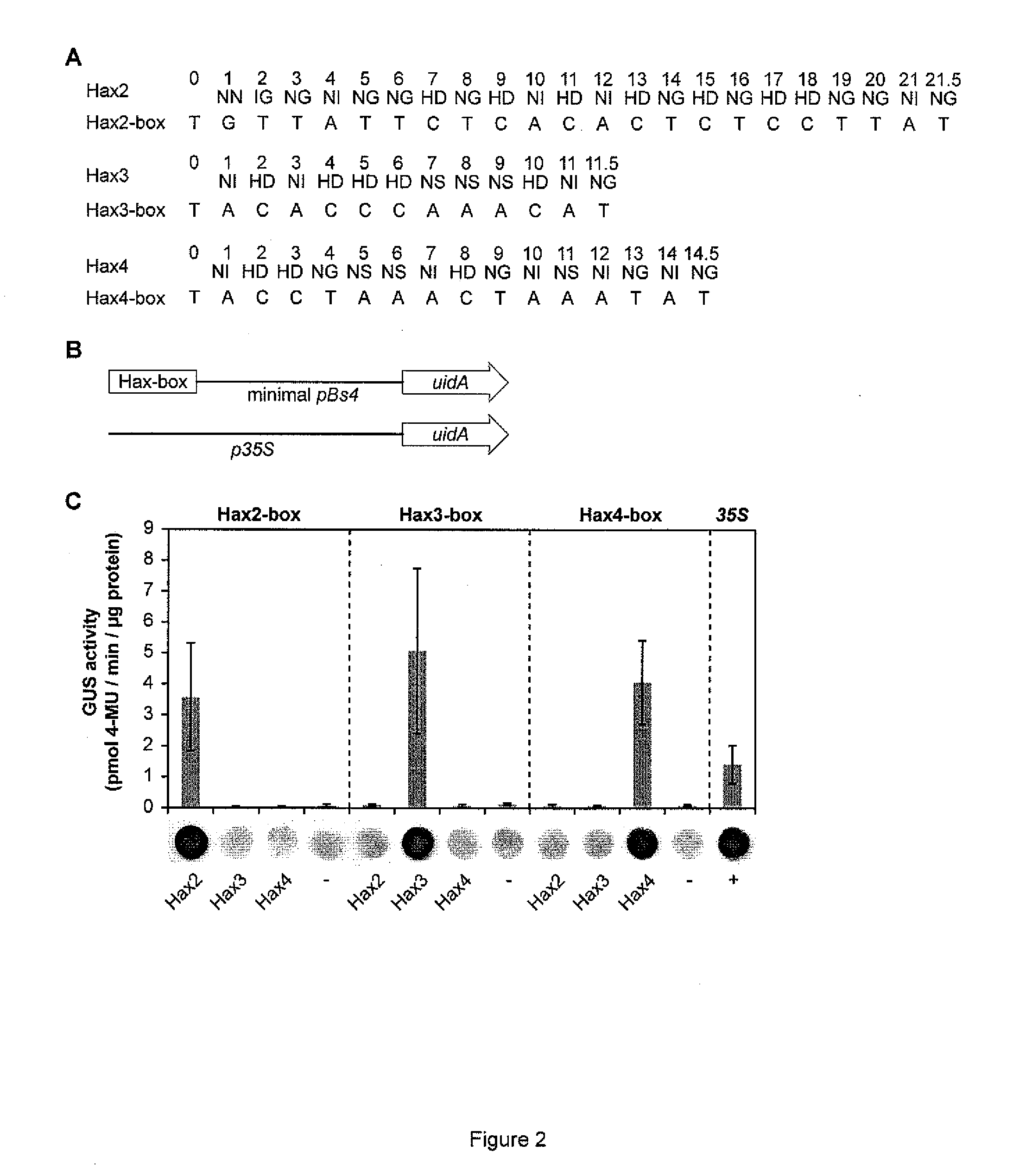
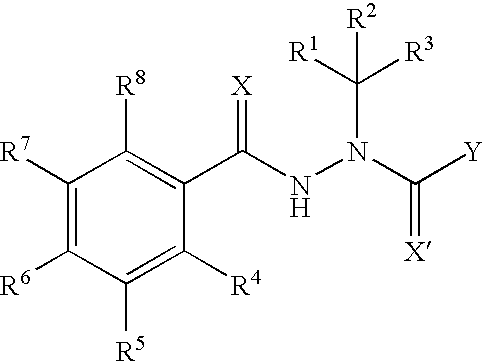
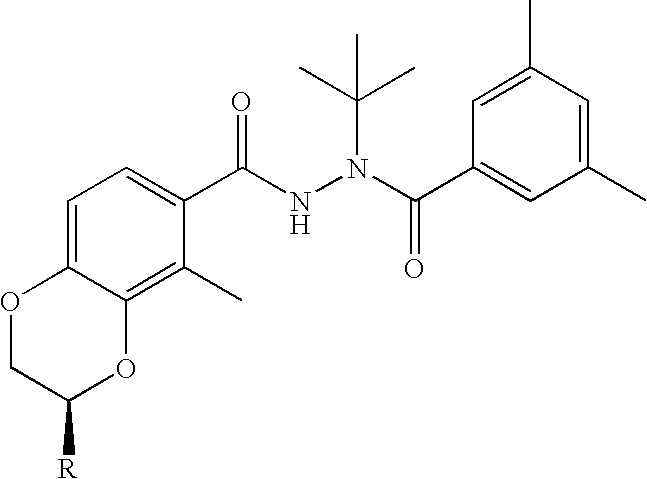
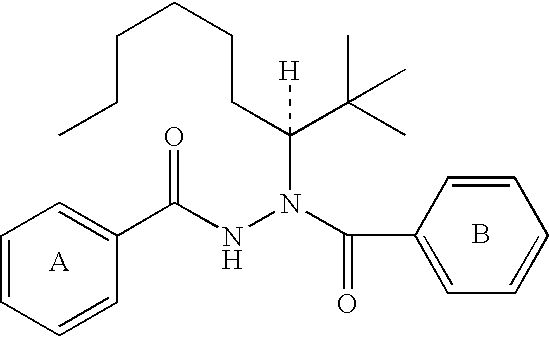
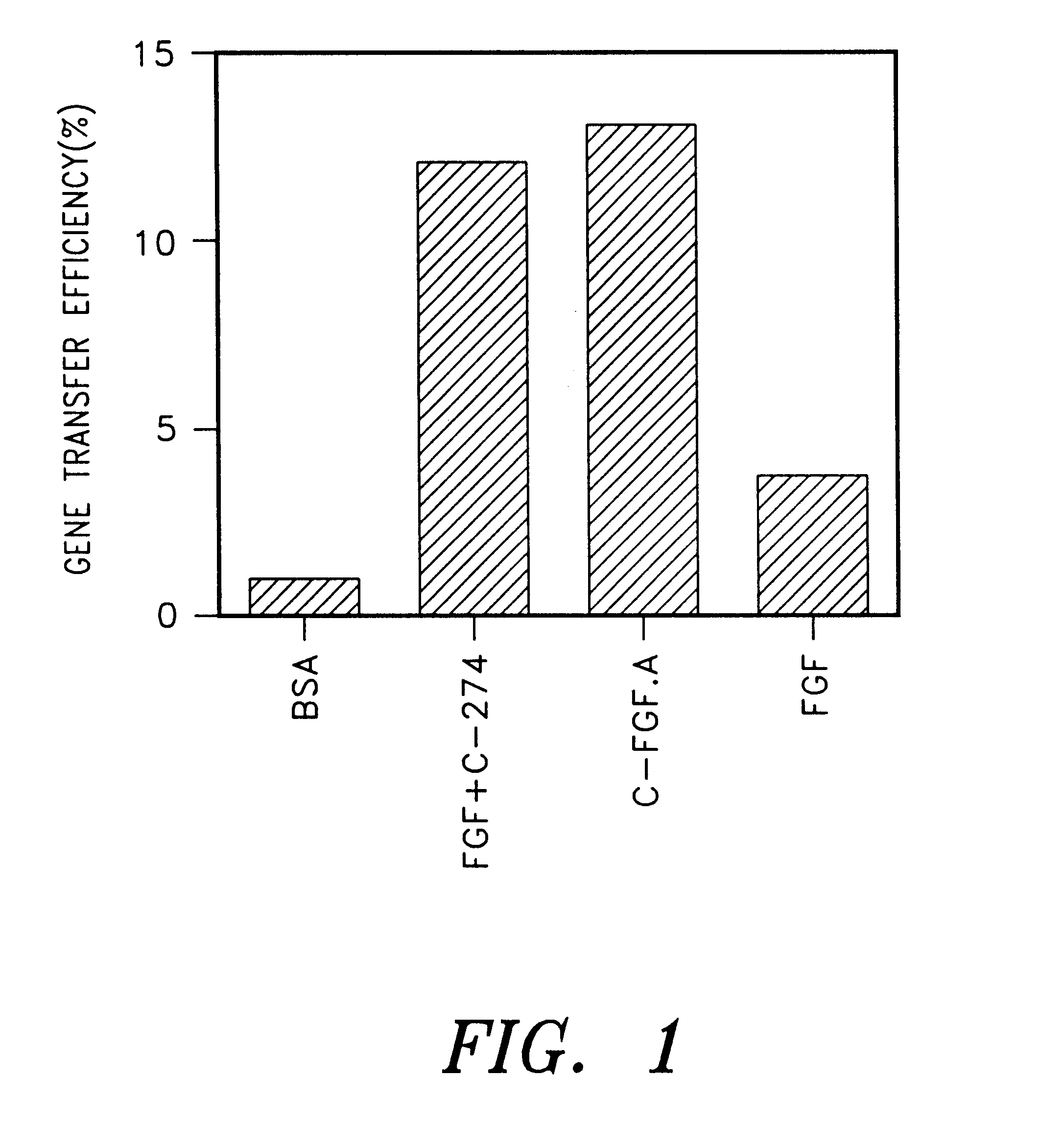
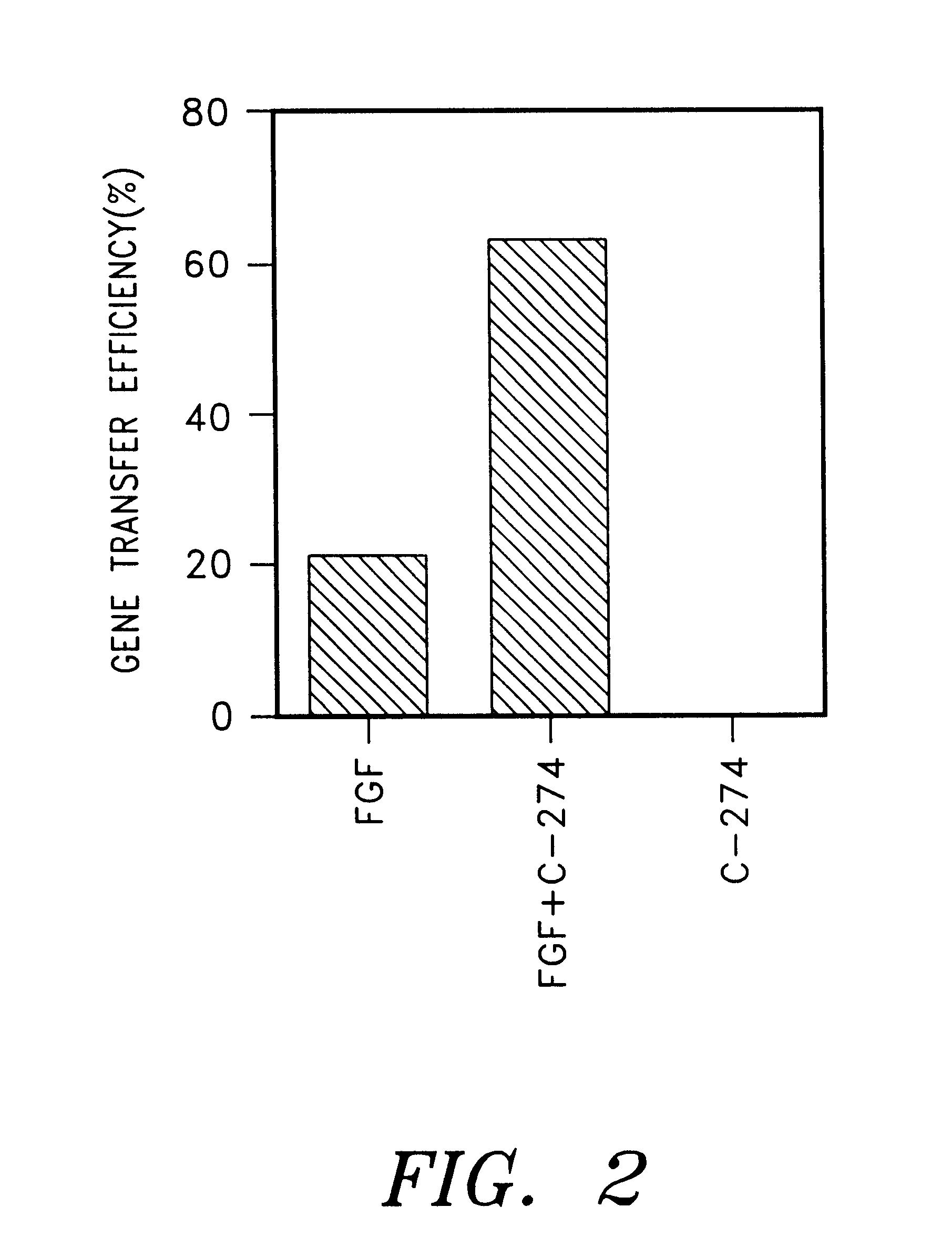
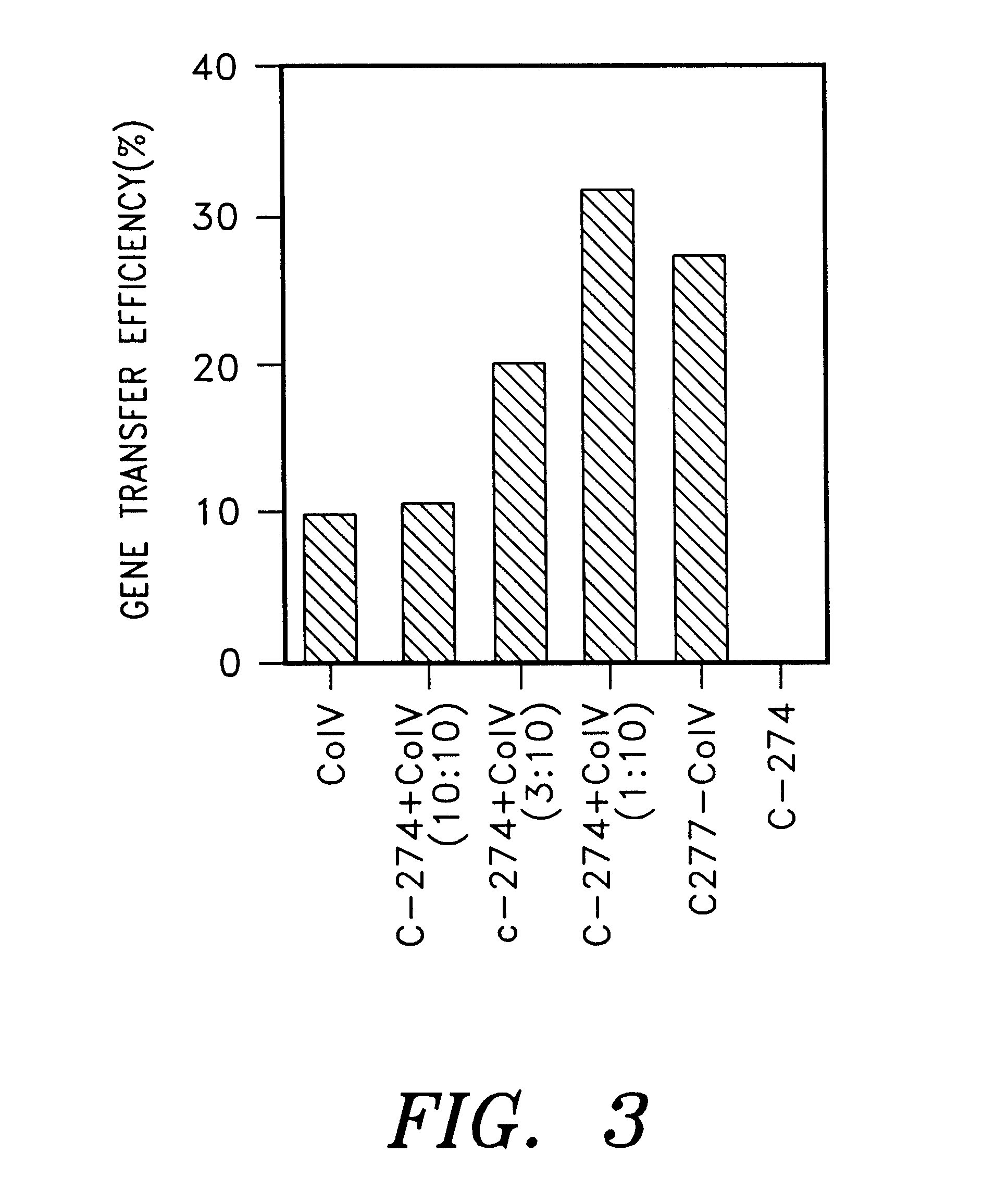
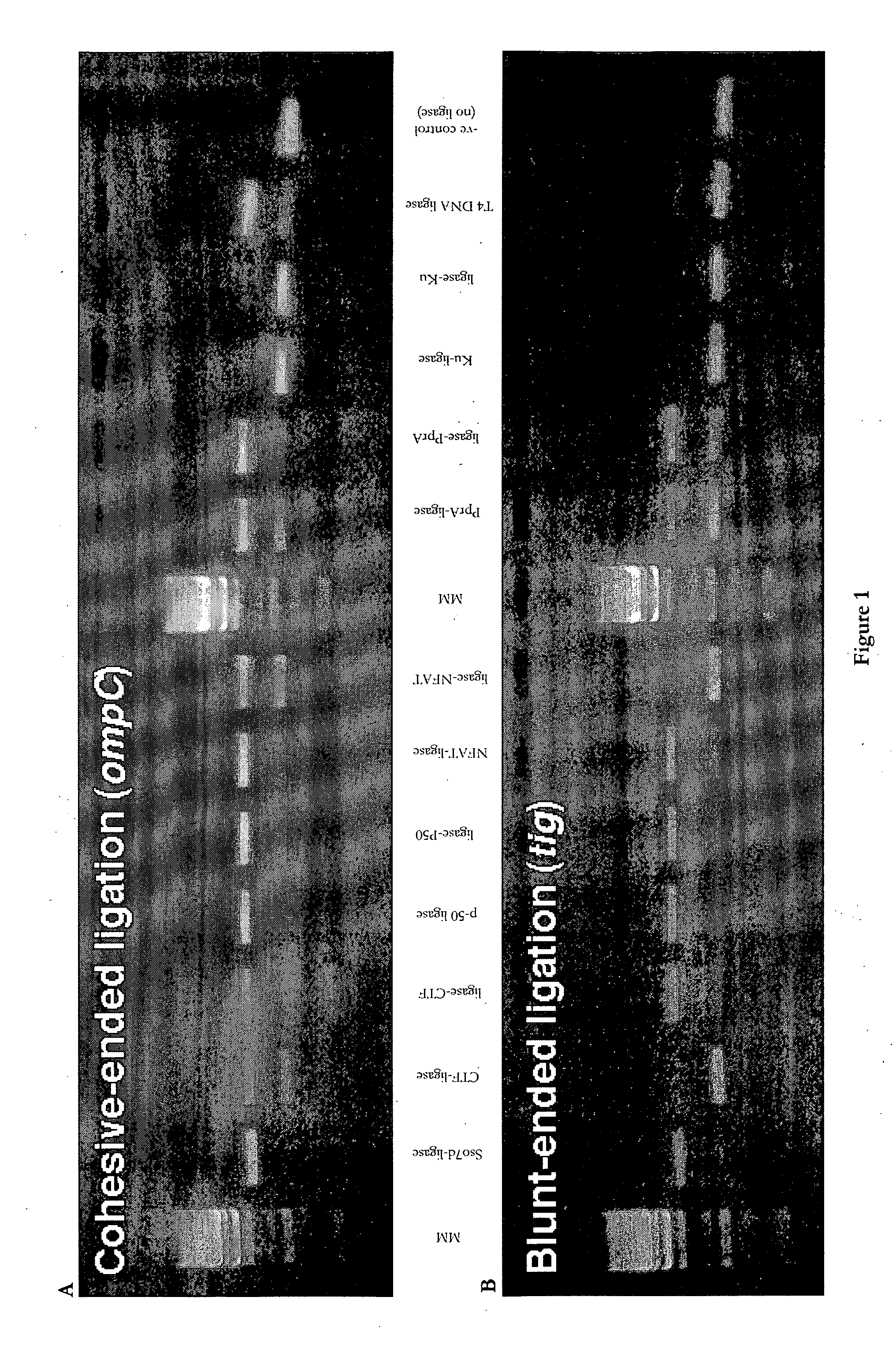
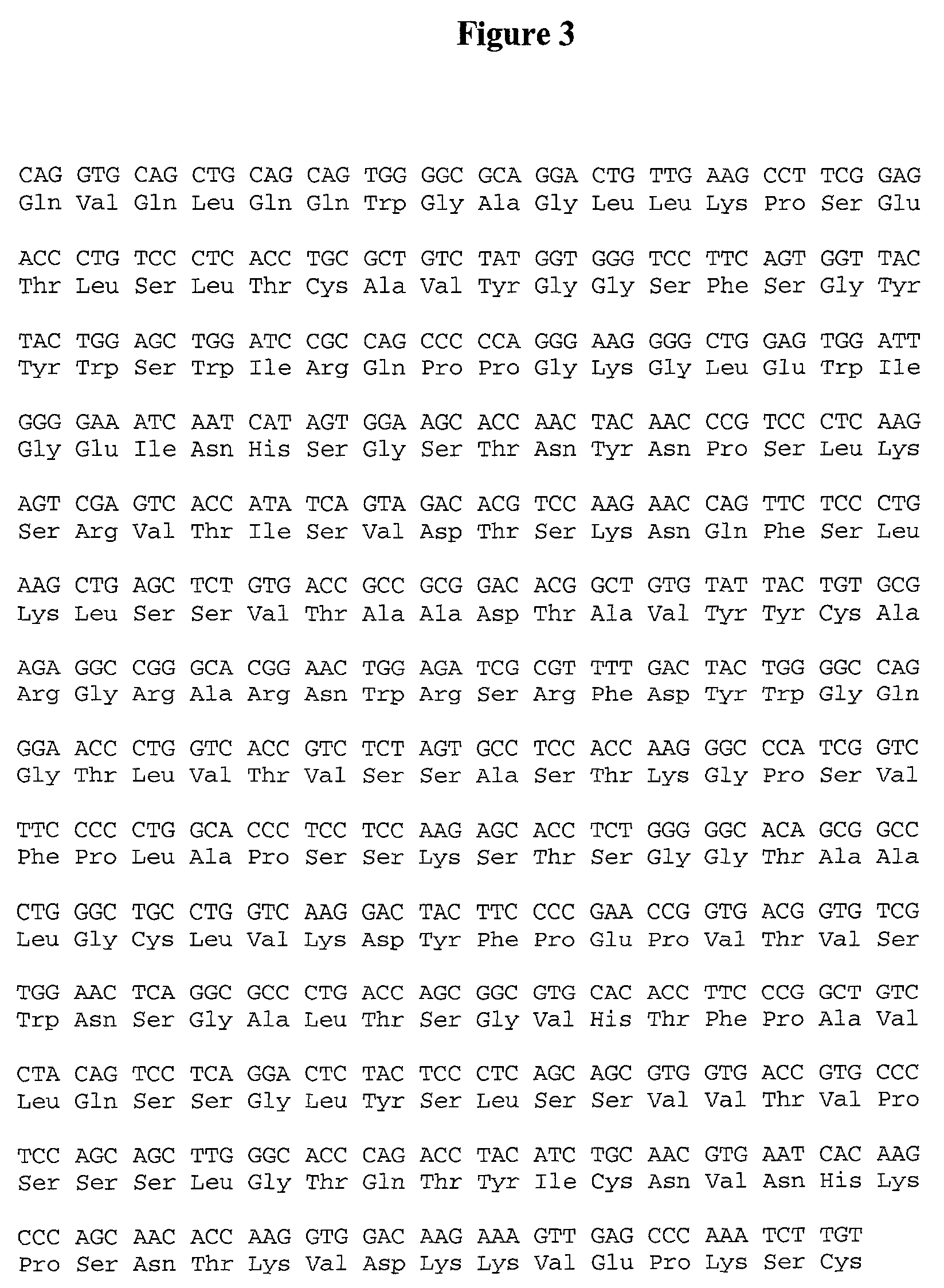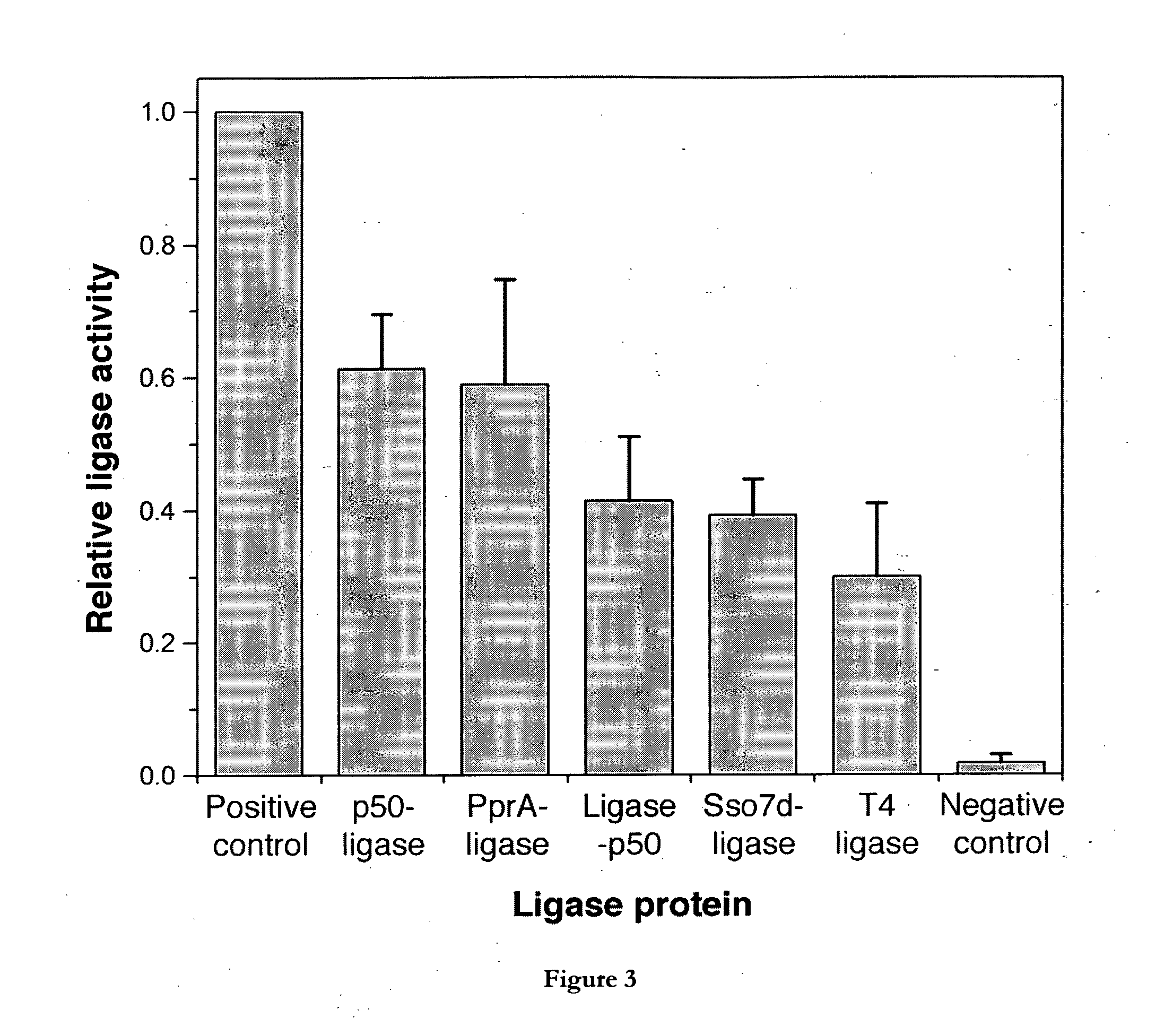Patents
Literature
136 results about "DNA-binding domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
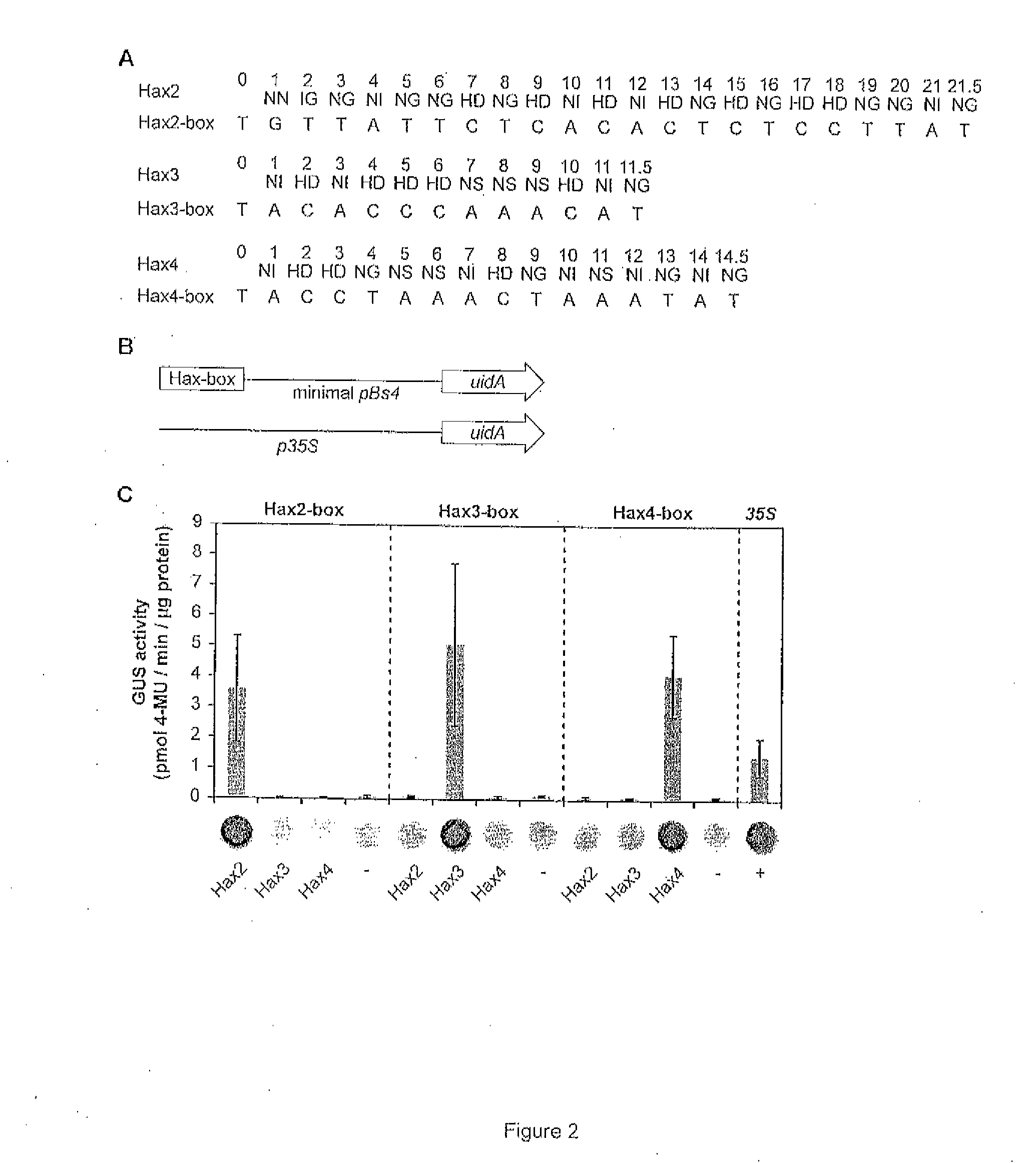
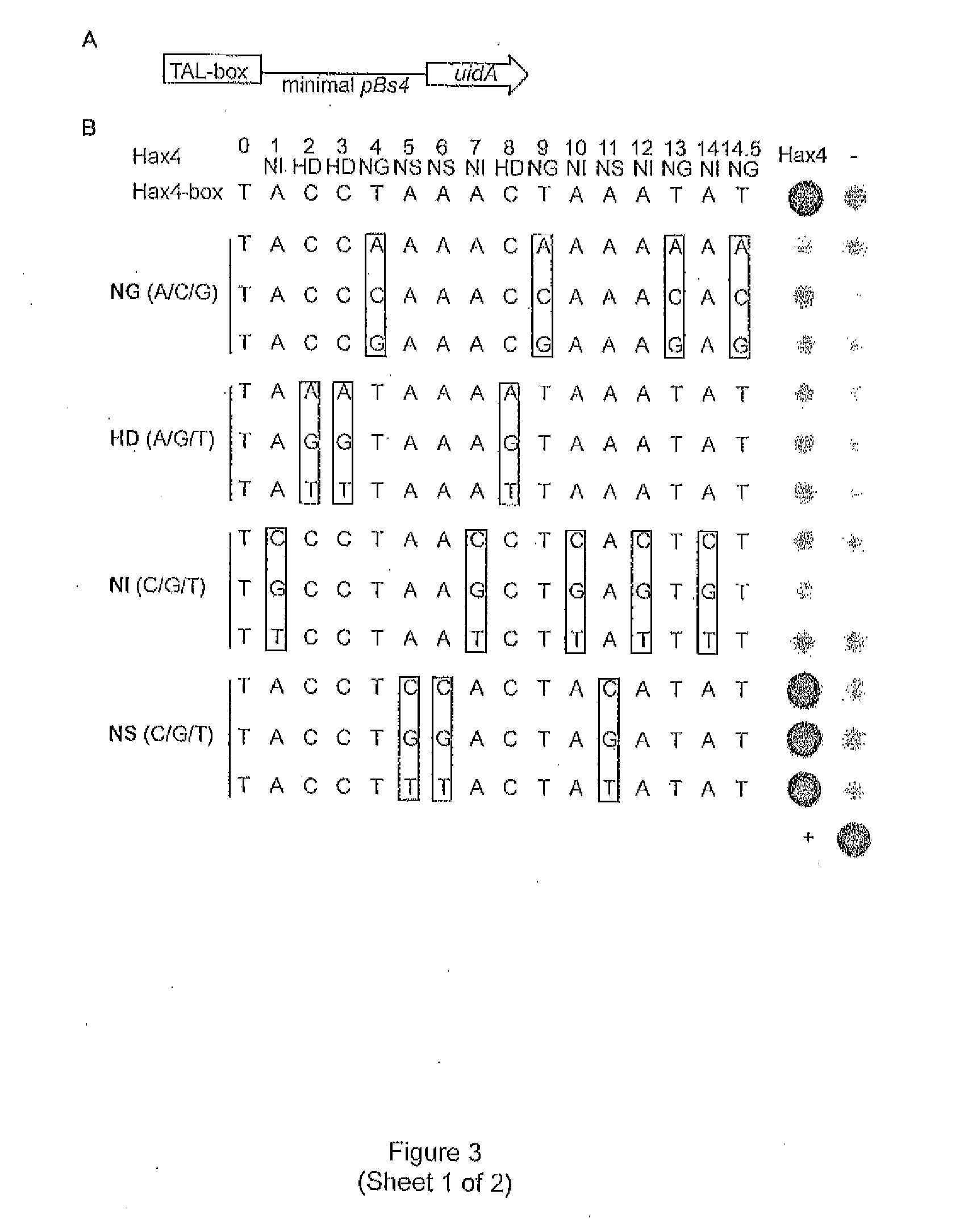
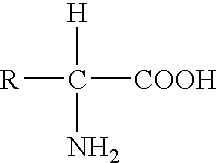
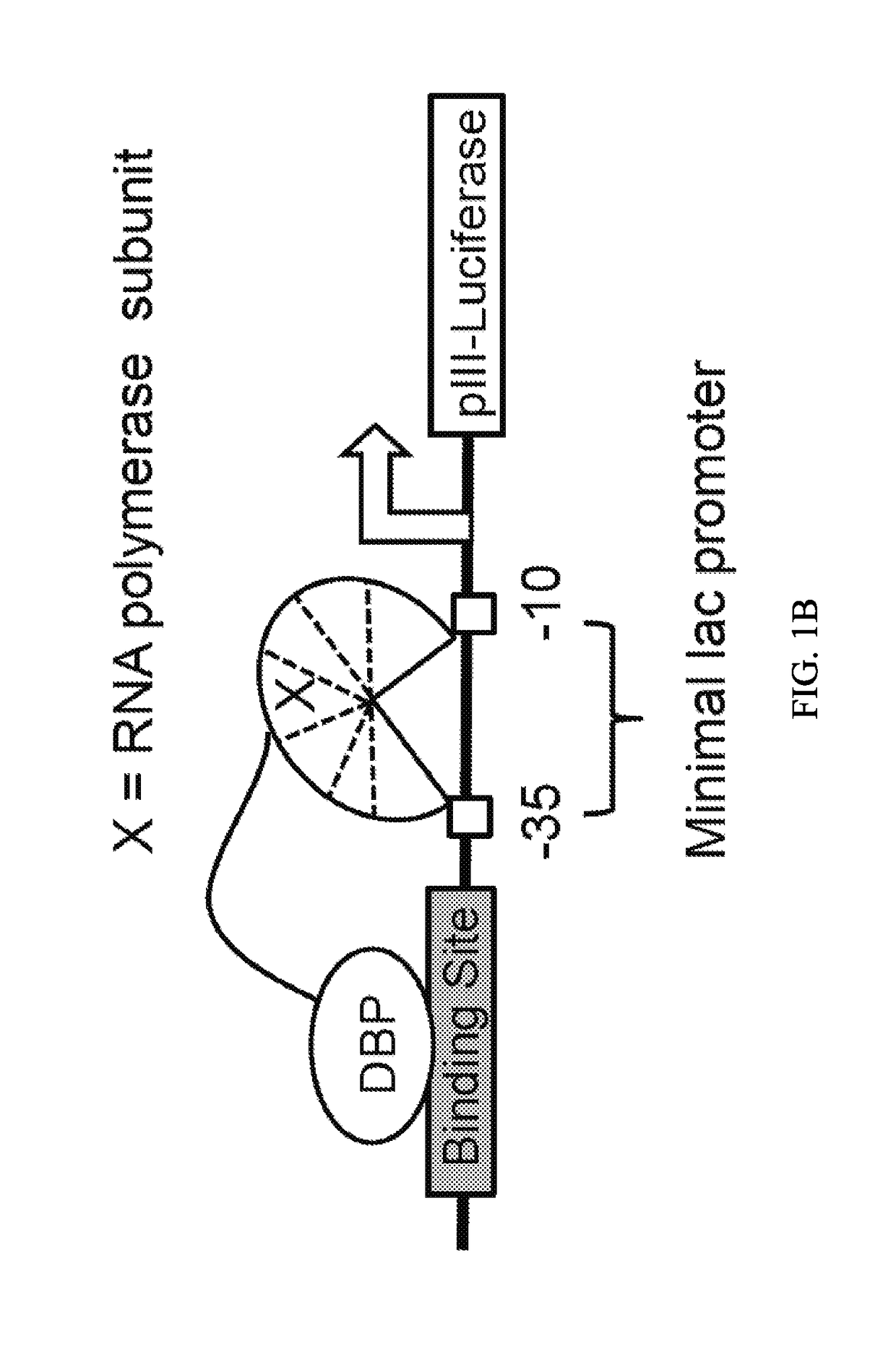
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure.
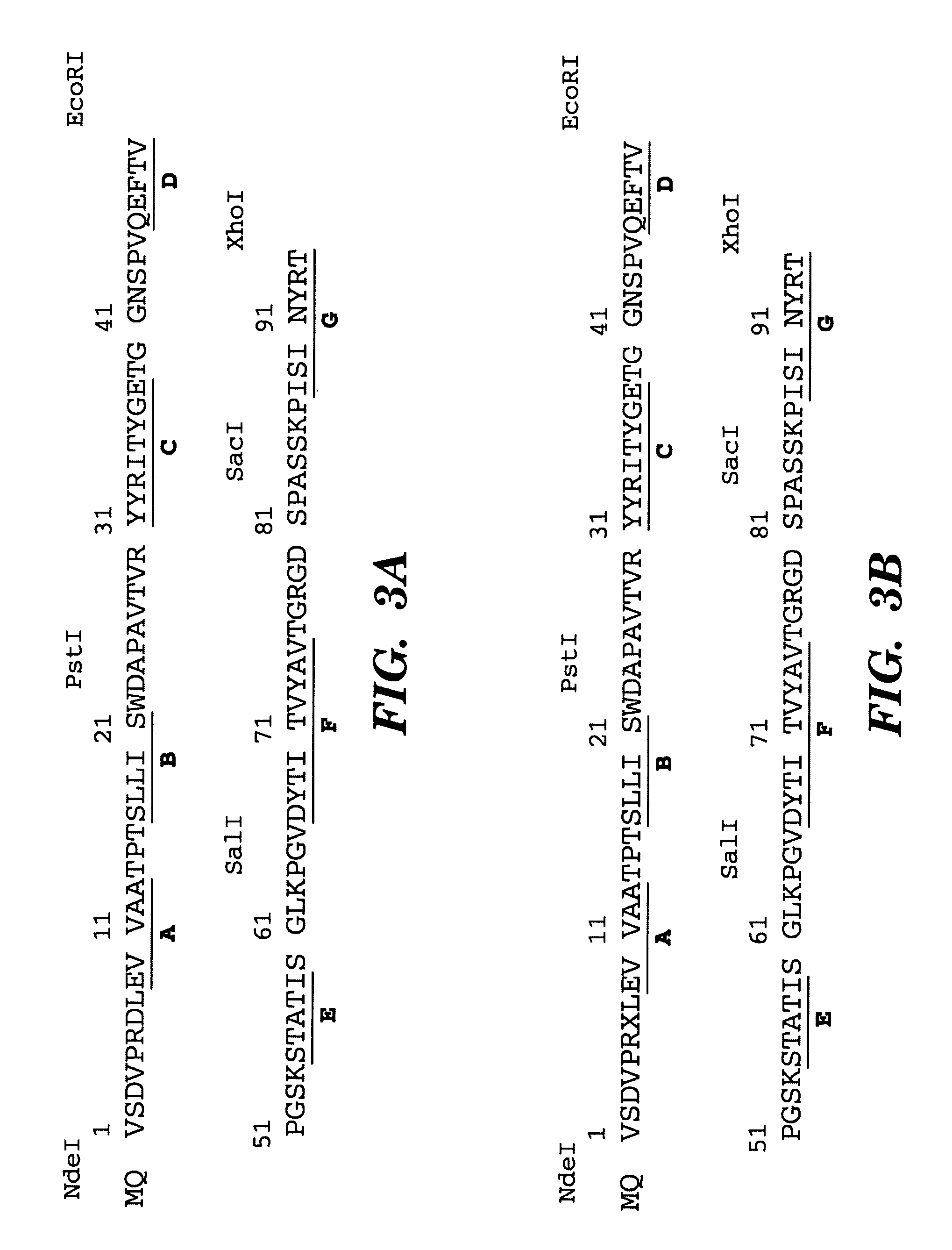
Nucleic acid encoding poly-zinc finger proteins with improved linkers
InactiveUS7153949B2Enhanced affinity and specificityImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainNucleotide
Polynucleotides encoding chimeric proteins, and methods for their production and use are disclosed. The chimeric proteins comprise a flexible linker between two zinc finger DNA-binding domains, wherein the linker contains eight or more amino acids between the second conserved histidine residue of the carboxy-terminal zinc finger of the first domain and the first conserved cysteine residue of the amino-terminal zinc finger of the second domain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
InactiveUS20110239315A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFungiBacteriaDNA-binding domainDna targeting
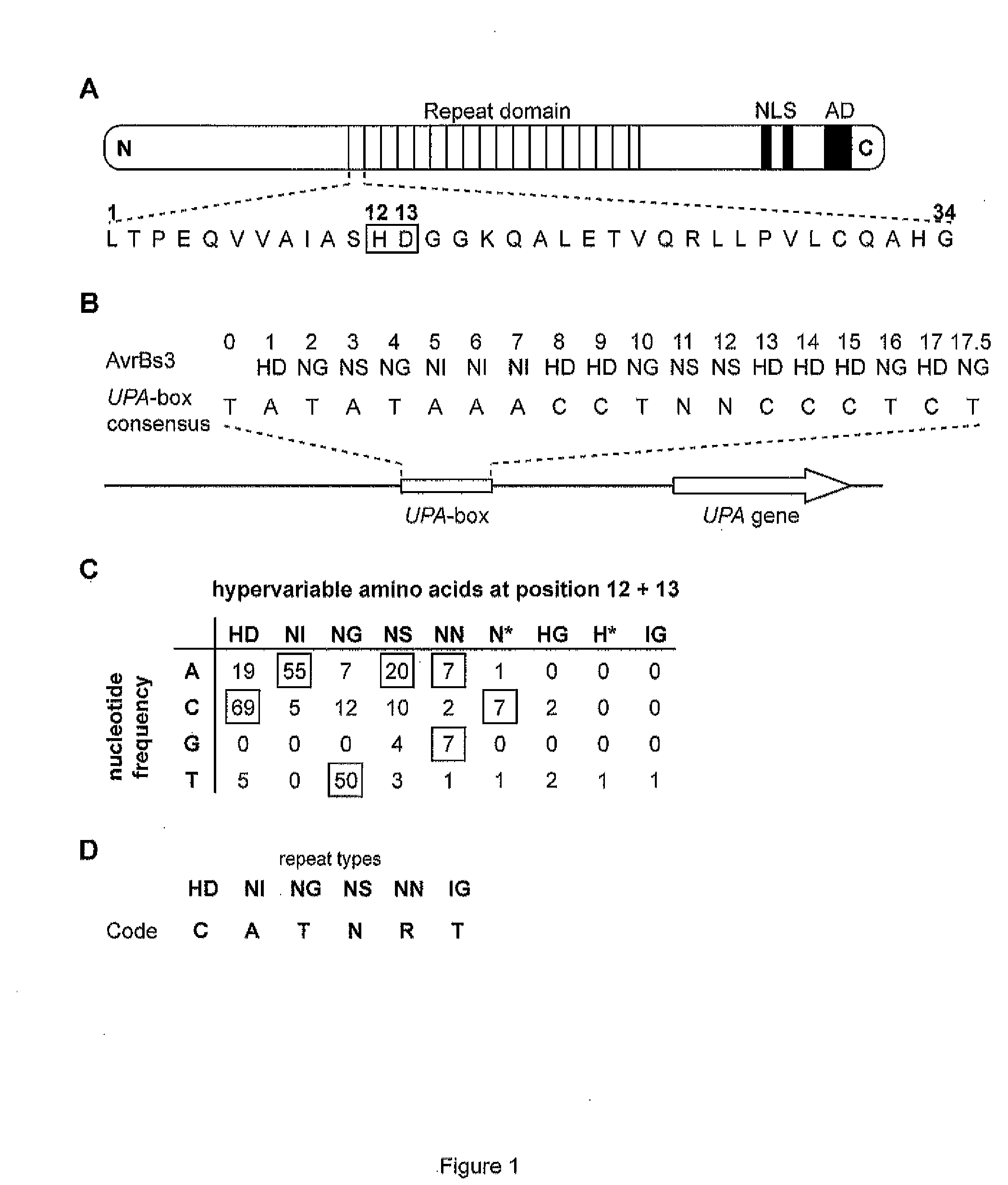
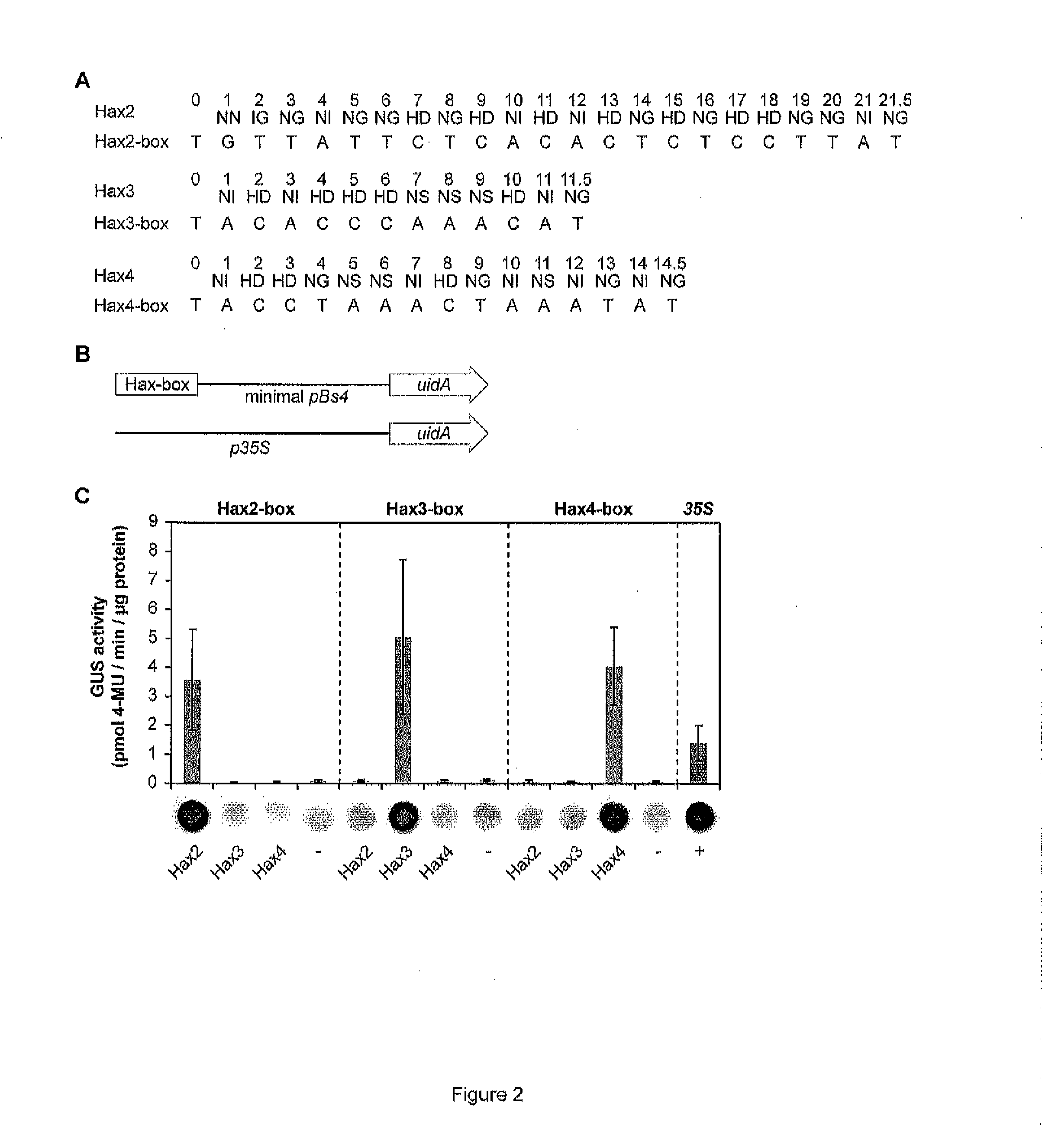
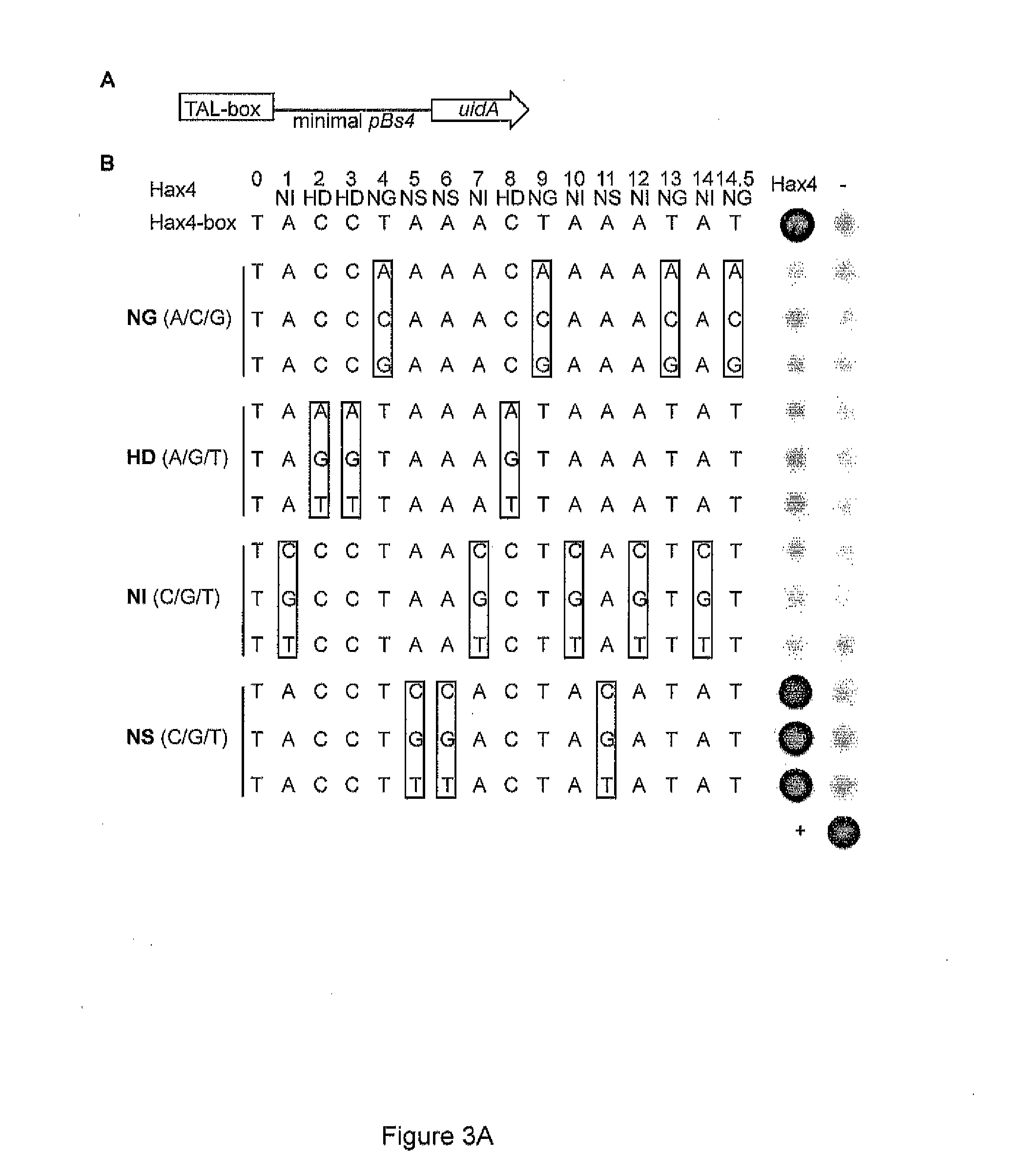
The present invention refers to methods for selectively recognizing a base pair in a DNA sequence by a polypeptide, to modified polypeptides which specifically recognize one or more base pairs in a DNA sequence and, to DNA which is modified so that it can be specifically recognized by a polypeptide and to uses of the polypeptide and DNA in specific DNA targeting as well as to methods of modulating expression of target genes in a cell.
Owner:BONAS ULLA +2
Method for the generation of compact tale-nucleases and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130117869A1Simple processSimple and efficient vectorizationFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesDNA-binding domainNuclease
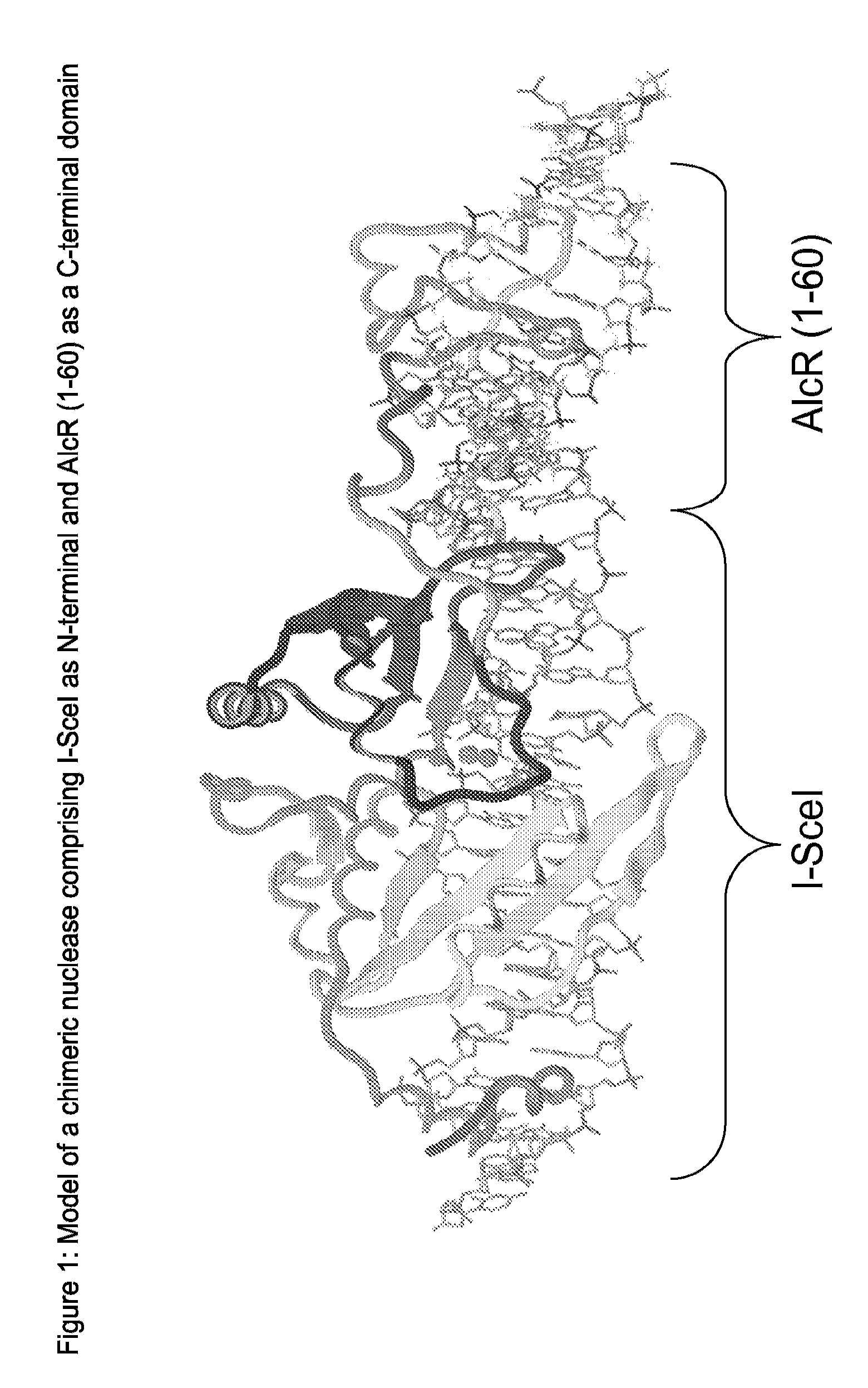
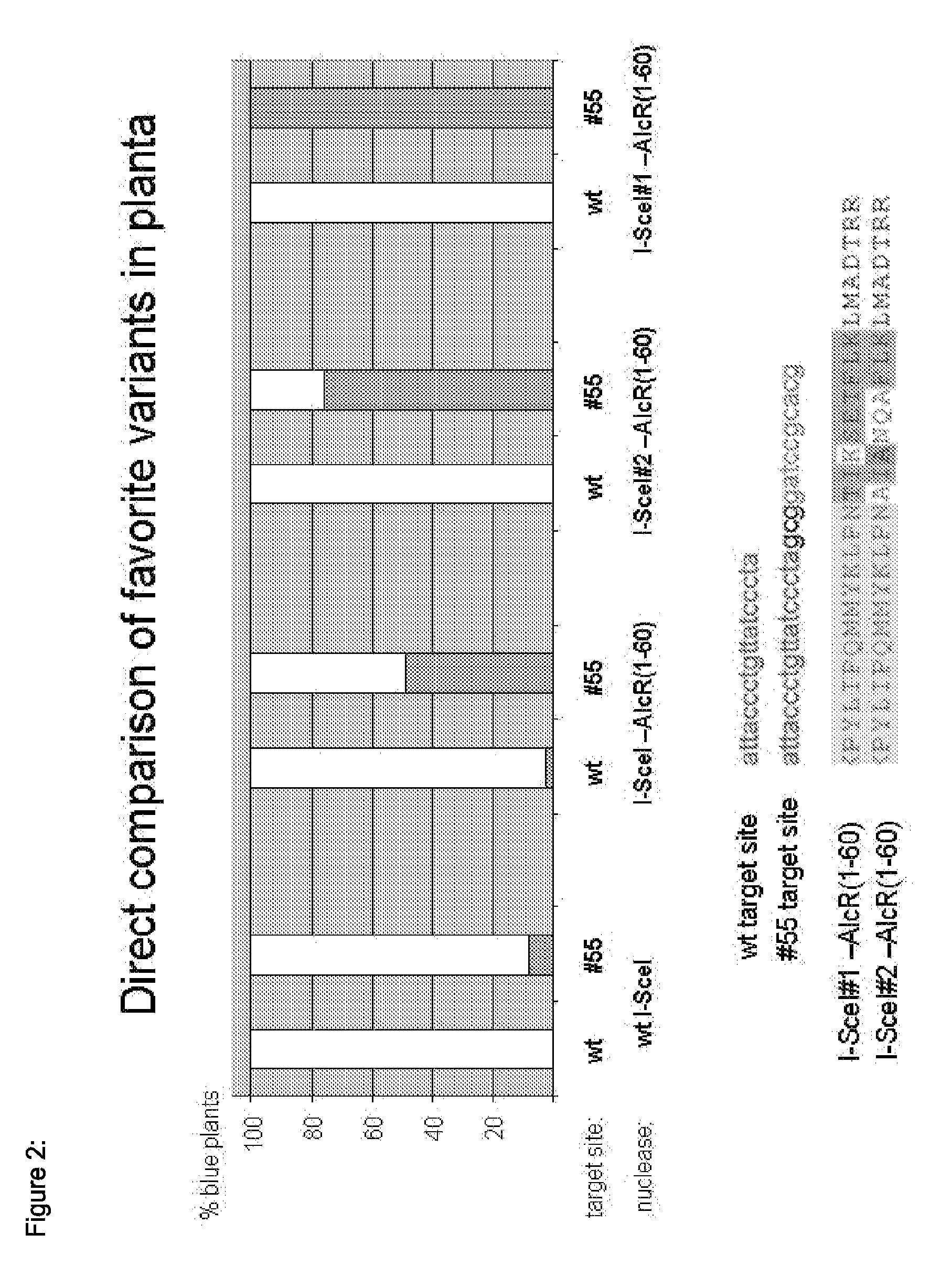
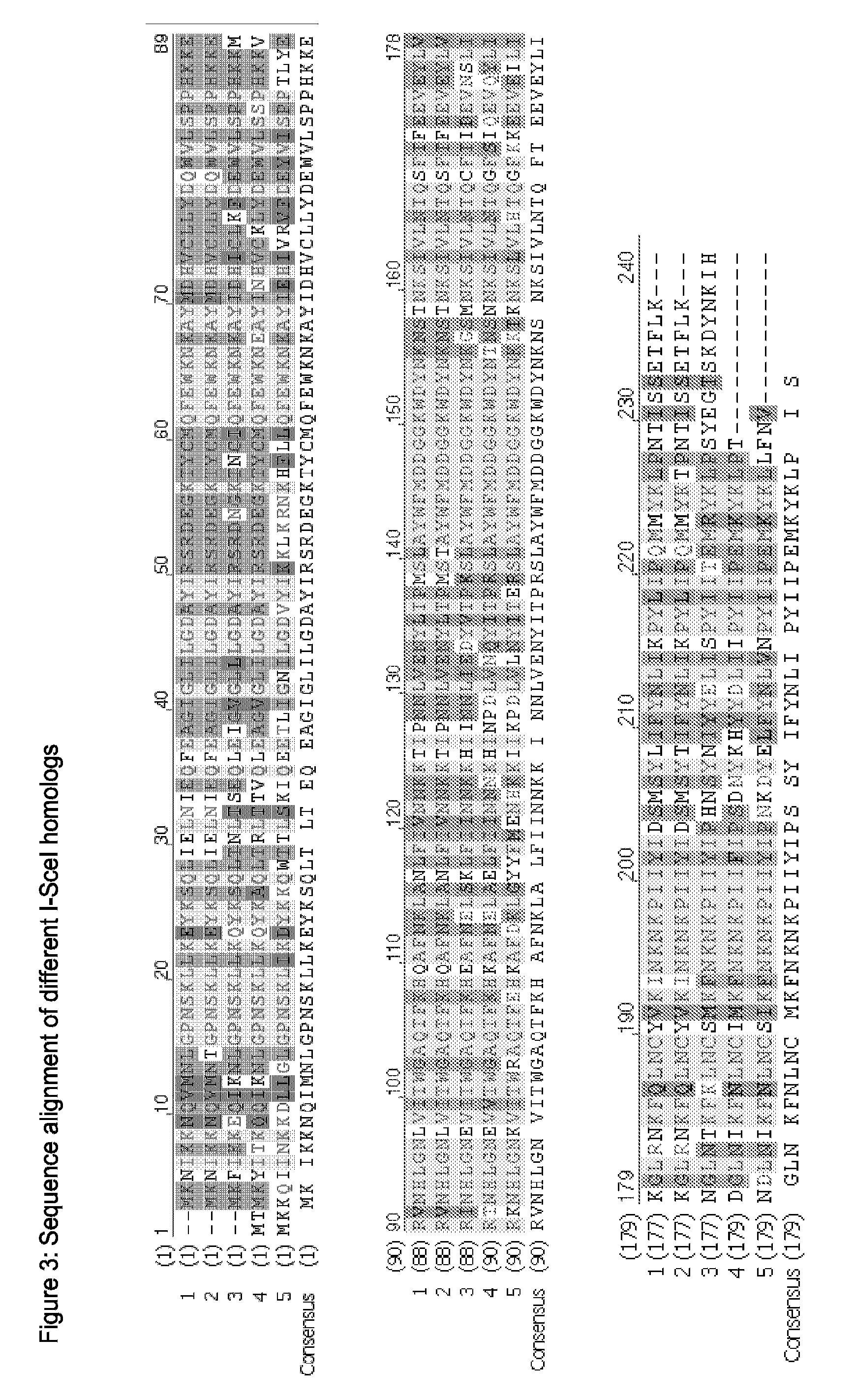
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of compact Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs) that can efficiently target and process double-stranded DNA. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for the creation of TALENs that consist of a single TALE DNA binding domain fused to at least one catalytic domain such that the active entity is composed of a single polypeptide chain for simple and efficient vectorization and does not require dimerization to target a specific single double-stranded DNA target sequence of interest and process DNA nearby said DNA target sequence. The present invention also relates to compact TALENs, vectors, compositions and kits used to implement the method.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Fully human antibody Fab fragments with human interferon-gamma neutralizing activity
InactiveUS7084257B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsDNA-binding domainAntigen binding
Selective binding agents of interferon-gamma (IFNγ) are provided by the invention. More particularly, the invention provides for antibodies and antigen binding domains which selectively bind to IFNγ and may be used to prevent or treat conditions relating to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis. Nucleic acid molecules encoding said antibodies and antigen binding domains, and expression vectors and host cells for the production of same are also provided.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
ActiveUS20120064620A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesDNA-binding domainDna targeting
The present invention refers to methods for selectively recognizing a base pair in a DNA sequence by a polypeptide, to modified polypeptides which specifically recognize one or more base pairs in a DNA sequence and, to DNA which is modified so that it can be specifically recognized by a polypeptide and to uses of the polypeptide and DNA in specific DNA targeting as well as to methods of modulating expression of target genes in a cell.
Owner:BONAS ULLA +3
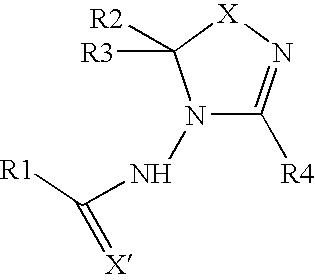
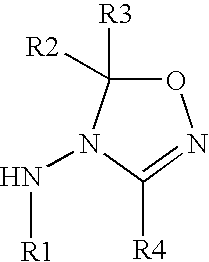
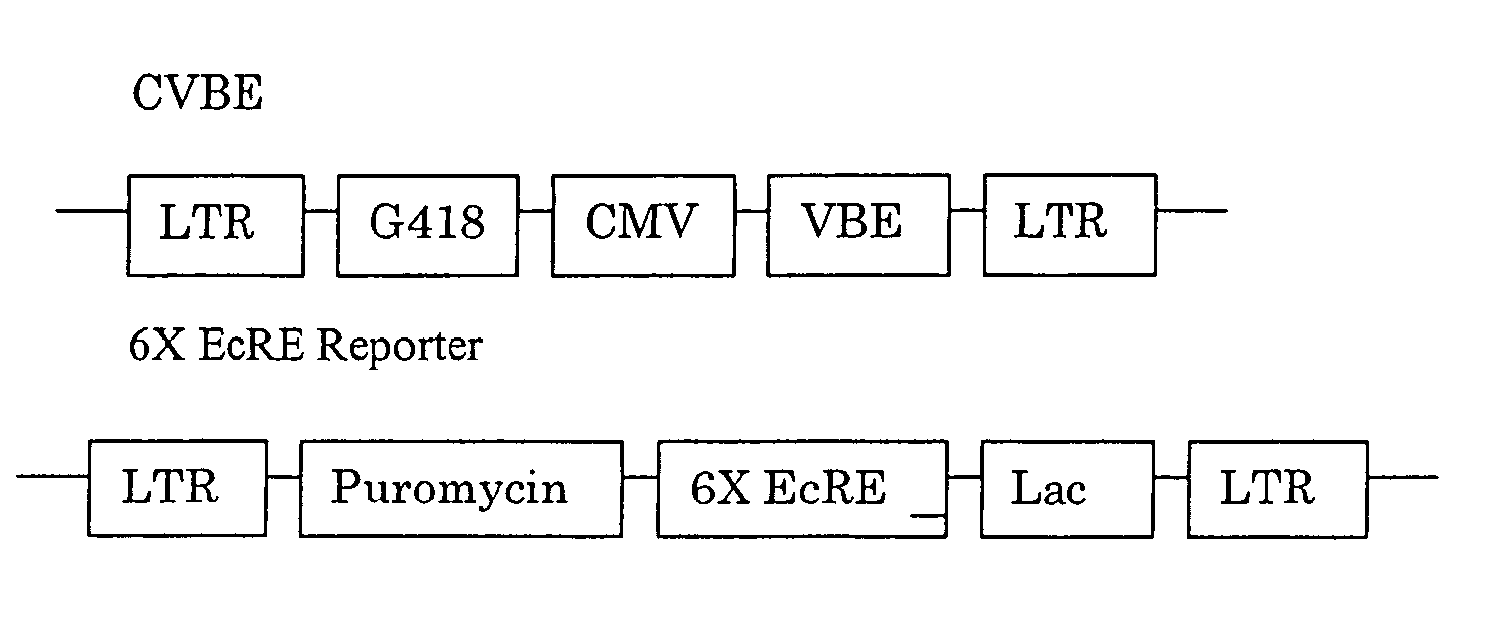
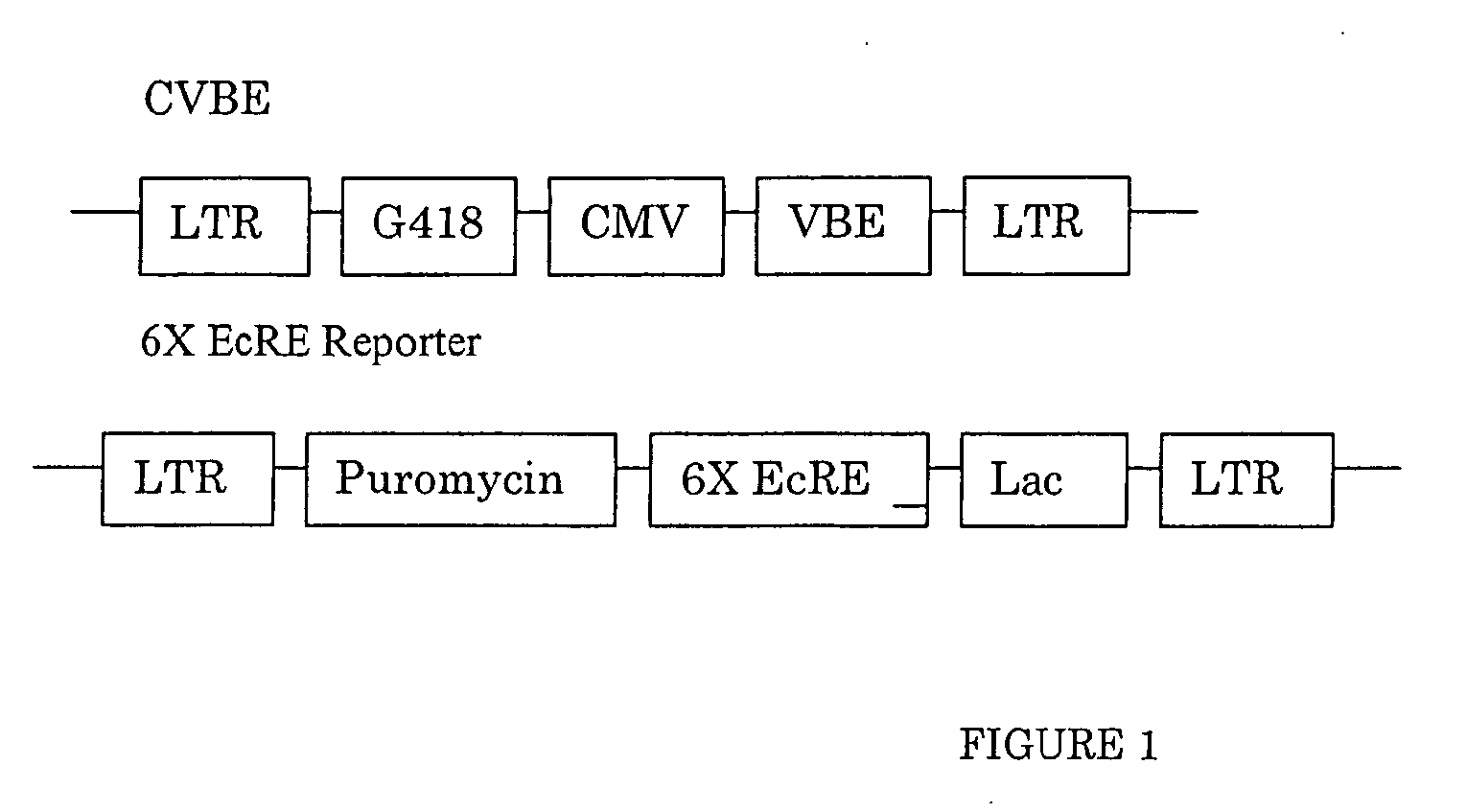
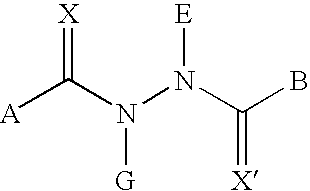
Diacylhydrazine ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes in mammalian systems via an ecdysone receptor complex
The present invention relates to non-steroidal ligands for use in nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system, and a method to modulate exogenous gene expression in which an ecdysone receptor complex comprising: a DNA binding domain; a ligand binding domain; a transactivation domain; and a ligand is contacted with a DNA construct comprising: the exogenous gene and a response element; wherein the exogenous gene is under the control of the response element and binding of the DNA binding domain to the response element in the presence of the ligand results in activation or suppression of the gene.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Method of identifying polypeptide monobodies which bind to target proteins and use thereof
InactiveUS7598352B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainProtein target
A method of identifying a polypeptide monobody having target protein binding activity, said method comprising: providing a host cell comprising (i) a reporter gene under control of a 5′ regulatory region operable in the host cell, (ii) a first chimeric gene which encodes a first fusion polypeptide comprising a target protein, or fragment thereof, fused to a C-terminus of a DNA-binding domain which binds to the 5′ regulatory region of the reporter gene, and (iii) a second chimeric gene which encodes a second fusion polypeptide comprising a polypeptide monobody fused to a transcriptional activation domain; and detecting expression of the reporter gene, which indicates binding of the polypeptide monobody of the second fusion polypeptide to the target protein such that the transcriptional activation domain of the second fusion polypeptide is in sufficient proximity to the DNA-binding domain of the first fusion polypeptide to allow expression of the reporter gene.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Diaclhydrazine ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes in mammalian systems via an ecdysone receptor complex
The present invention relates to non-steroidal ligands for use in nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system, and a method to modulate exogenous gene expression in which an ecdysone receptor complex comprising: a DNA binding domain; a ligand binding domain; a transactivation domain; and a ligand is contacted with a DNA construct comprising: the exogenous gene and a response element; wherein the exogenous gene is under the control of the response element and binding of the DNA binding domain to the response element in the presence of the ligand results in activation or suppression of the gene.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
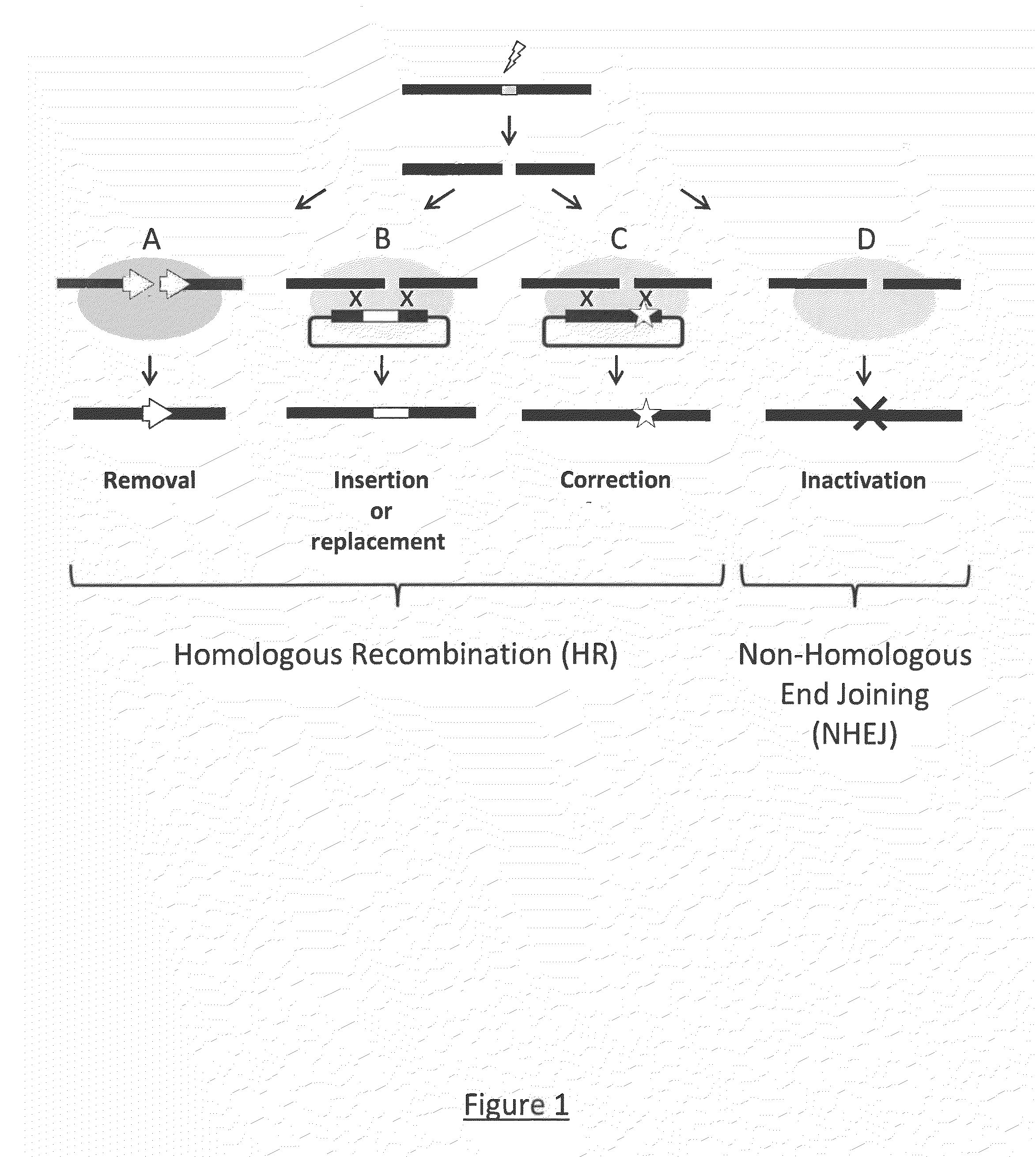
Chimeric Endonucleases and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20120324603A1Reduce contentFacilitate homologous recombinationFungiFusion with DNA-binding domainBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention relates to chimeric endonucleases, comprising an endonuclease and a heterologous DNA binding domain, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of polynucleotides using chimeric endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
ActiveUS20120110685A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFungiBacteriaDNA-binding domainModular design
The present invention refers to methods for selectively recognizing a base pair in a DNA sequence by a polypeptide, to modified polypeptides which specifically recognize one or more base pairs in a DNA sequence and, to DNA which is modified so that it can be specifically recognized by a polypeptide and to uses of the polypeptide and DNA in specific DNA targeting as well as to methods of modulating expression of target genes in a cell.
Owner:BONAS ULLA +3
Oxadiazoline ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes via an ecdysone receptor complex
The present invention relates to non-steroidal ligands for use in nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system, and a method to modulate exogenous gene expression in which an ecdysone receptor complex comprising: a DNA binding domain; a ligand binding domain; a transactivation domain; and a ligand is contacted with a DNA construct comprising: the exogenous gene and a response element; wherein the exogenous gene is under the control of the response element and binding of the DNA binding domain to the response element in the presence of the ligand results in activation or suppression of the gene.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Modular dna-binding domains and methods of use
ActiveUS20120122205A1Enabling targeted DNA modificationFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA-binding domainModular design
Owner:BONAS ULLA +3
Chimeric Endonucleases and Uses Thereof
The invention relates to chimeric endonucleases, comprising a endonuclease and a heterologous DNA binding domain comprising one or more Zn2C6 zinc fmgers, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of polynucleotides using chimeric endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Nuclear receptor ligands and ligand binding domains
The present invention provides new methods, particularly computational methods, and compositions for the generation of nuclear receptor synthetic ligands based on the three dimensional structure of nuclear receptors, particularly the thyroid receptor (herein referred to as "TR"). Also provided are crystals, nuclear receptor synthetic ligands, and related methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
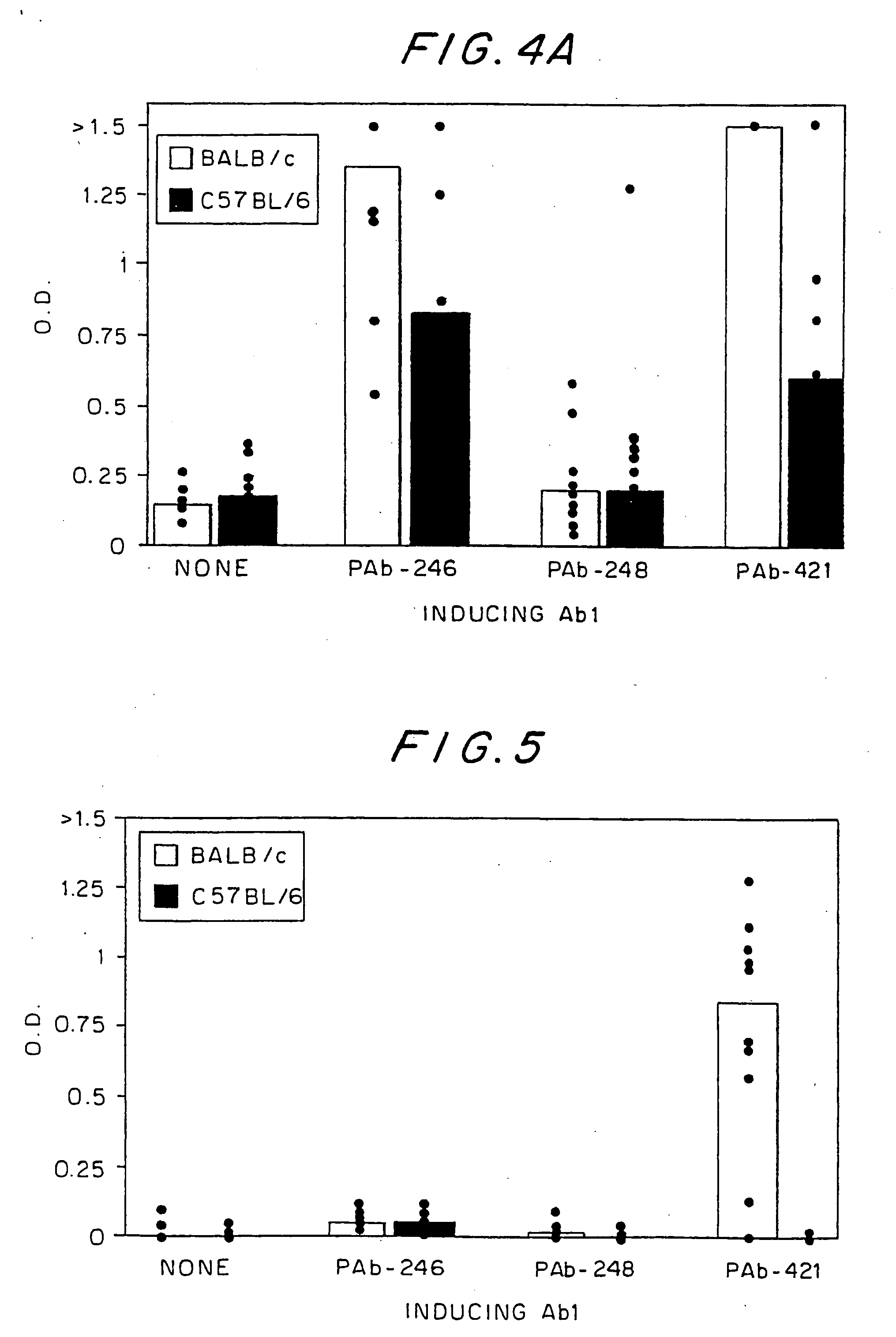
Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus by down-regulating the autoimmune response to autoantigens
InactiveUS20060030524A1Improving immunogenicityEasily raisedAntipyreticGenetic material ingredientsAntigenDNA-binding domain
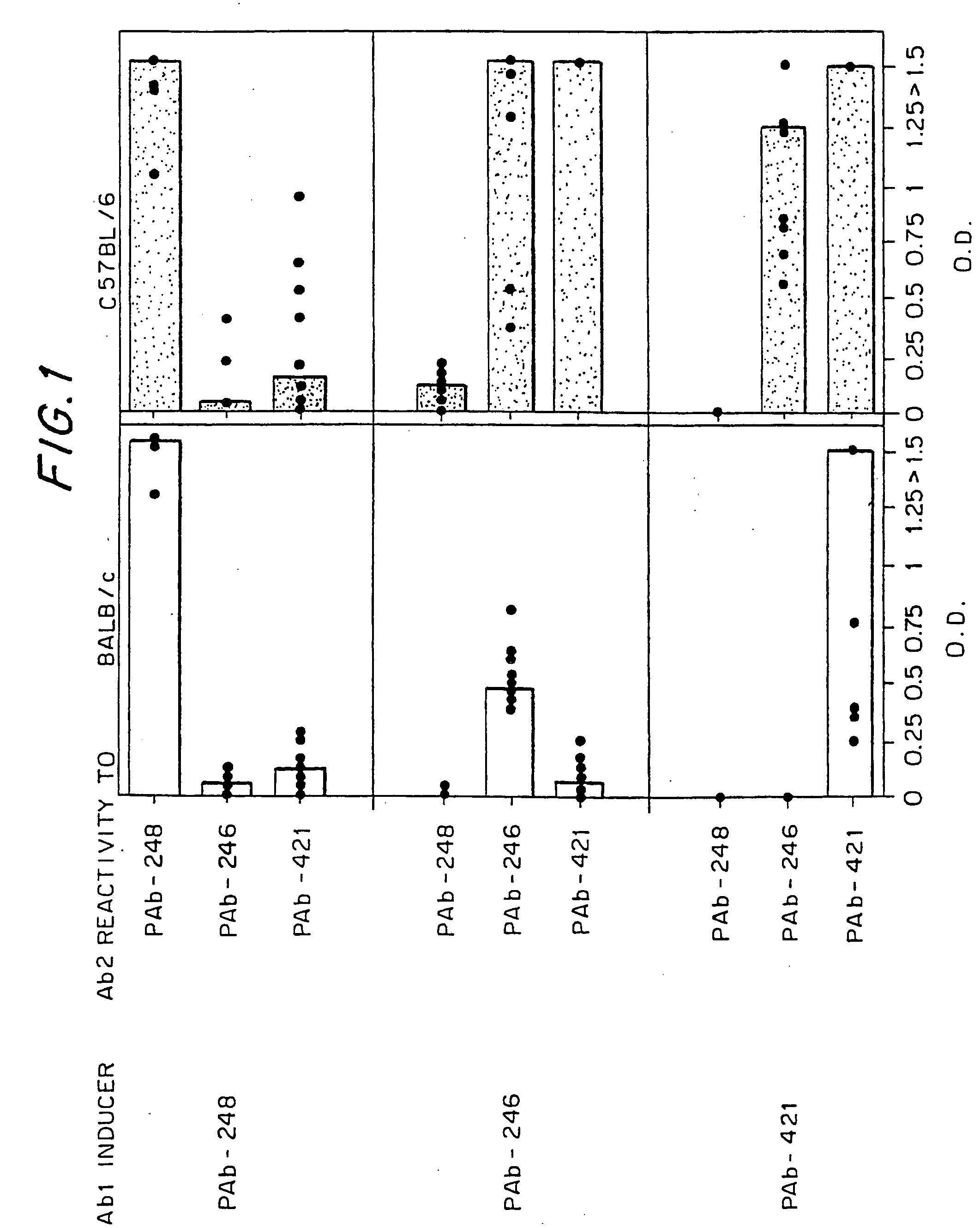
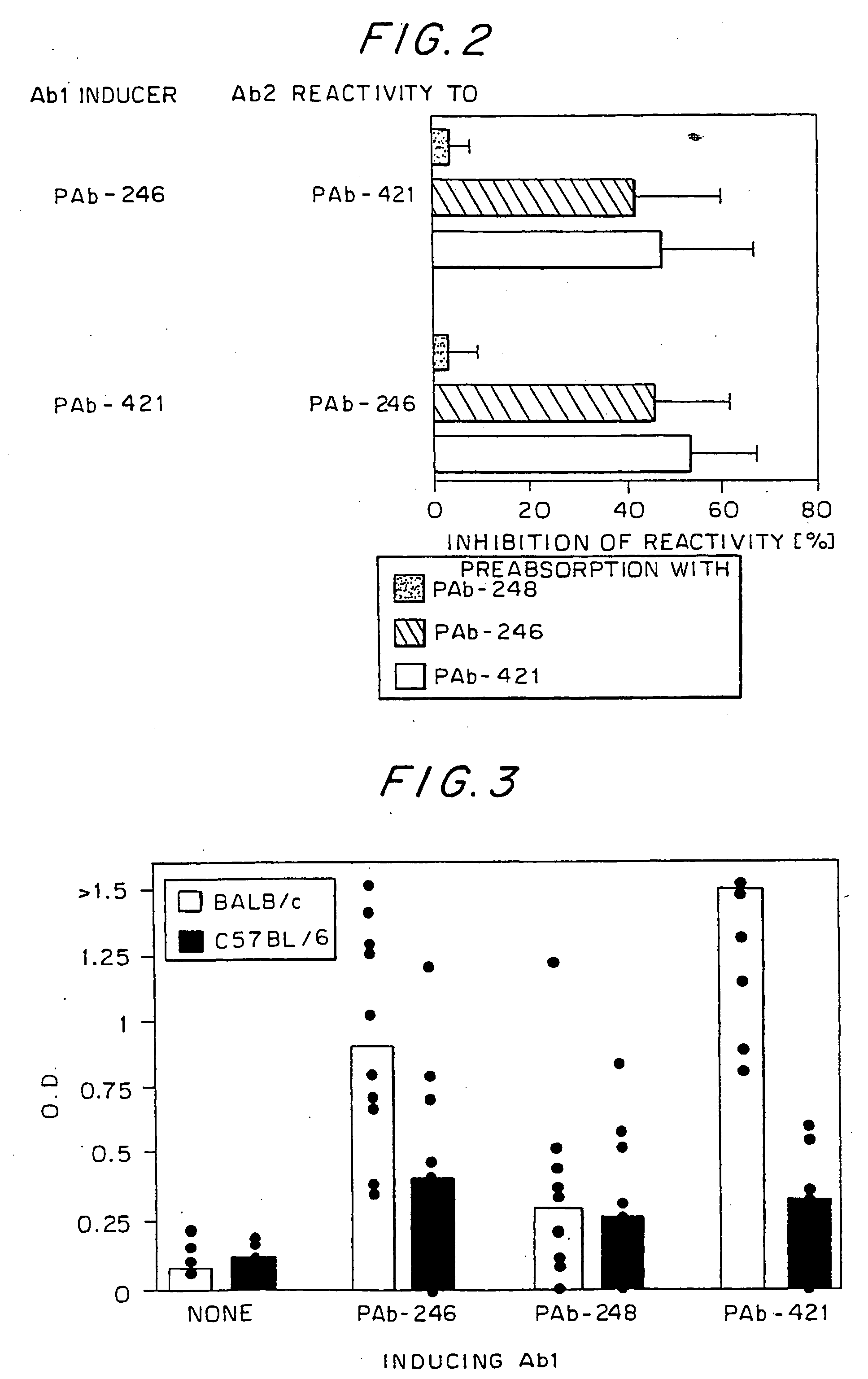
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) can be prevented or treated by down-regulating the autoimmune response to the C-terminal-DNA-binding domain of the p53 protein (p53) by an active principle selected from the group consisting of: (i) a peptide of, or comprising, the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of the p53 protein; (ii) a monoclonal antibody (mAb) specific for said domain of p53 (Ab1), and fragments thereof; (iii) an mAb specific for Ab1 (hereinafter Ab2), and fragments thereof; (iv) a peptide based on a complementarity determining region (CDR) of the heavy or light chain of said Ab1 or Ab2; (v) a DNA molecule coding for (i) and (iv) of for the variable region of said Ab1 and Ab2 of (ii) and (iii); and (vi) T cells specific for (i) to (iv), fragments thereof, T cell receptor (TCR) thereof and peptides comprising the variable region of said TCR. SLE can also be diagnosed by assaying for antibodies (Ab1) against the C-terminal DNA-binding domain of p53 or antibodies (Ab2) specific to the Ab1 antibodies.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
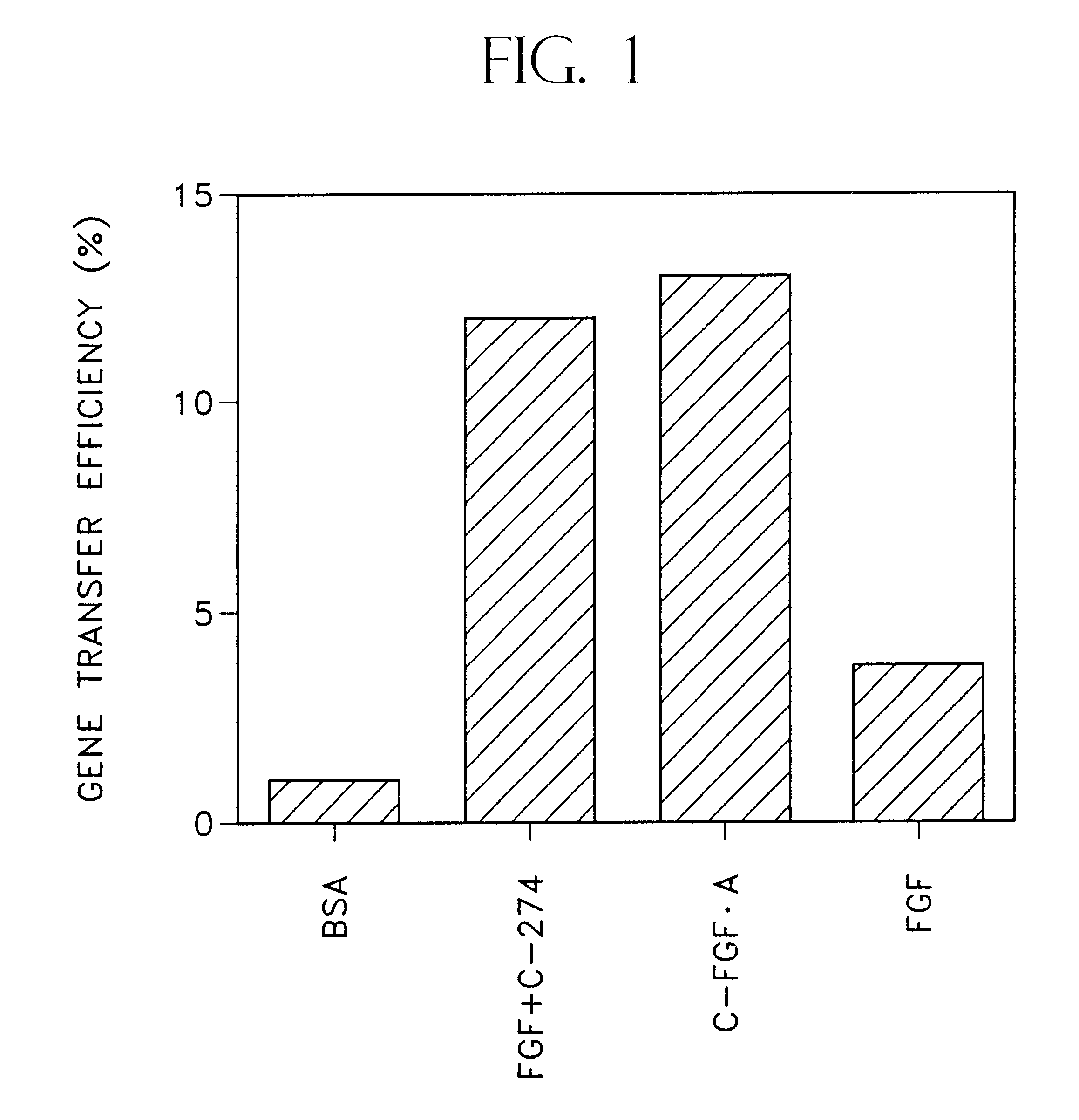
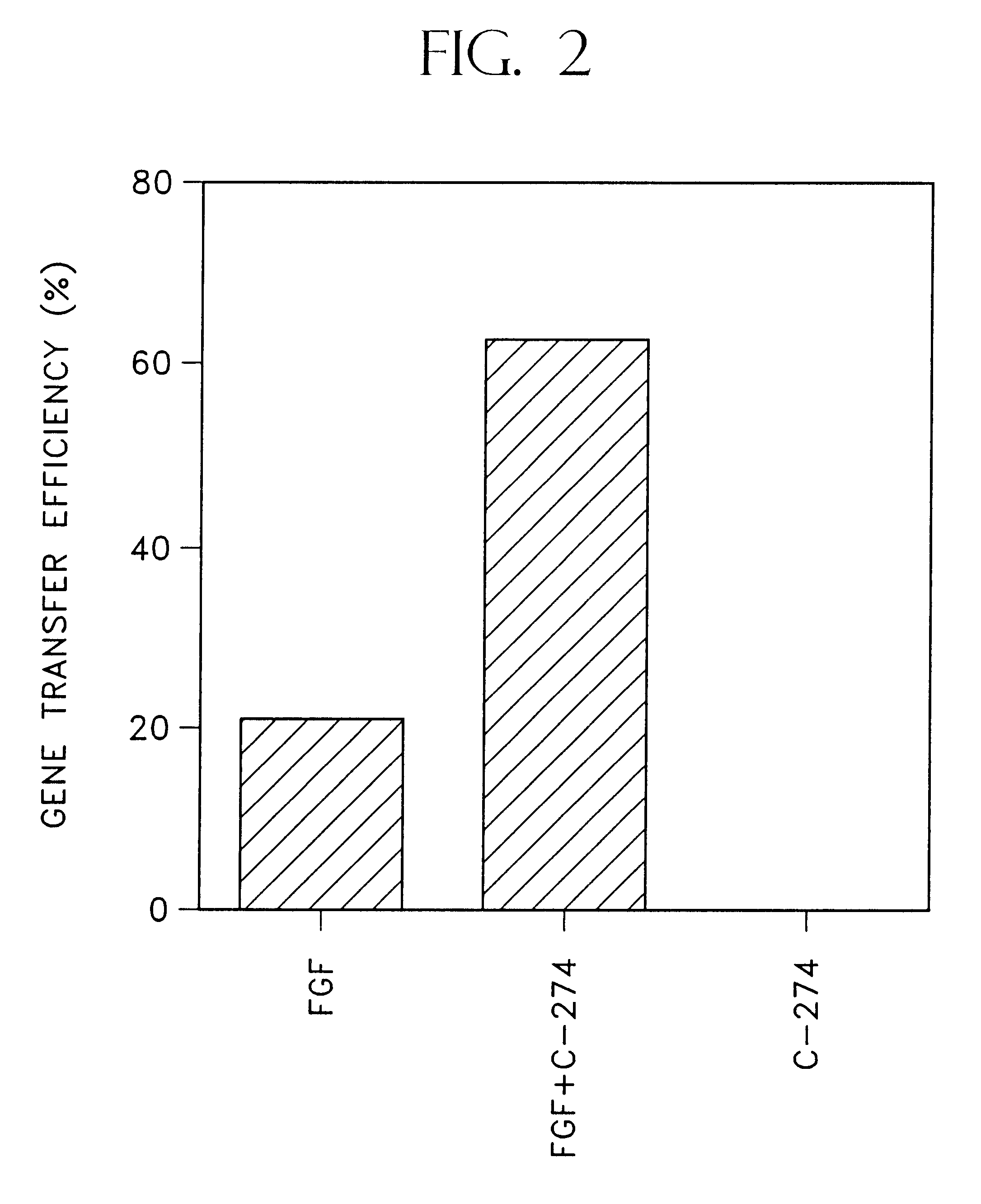
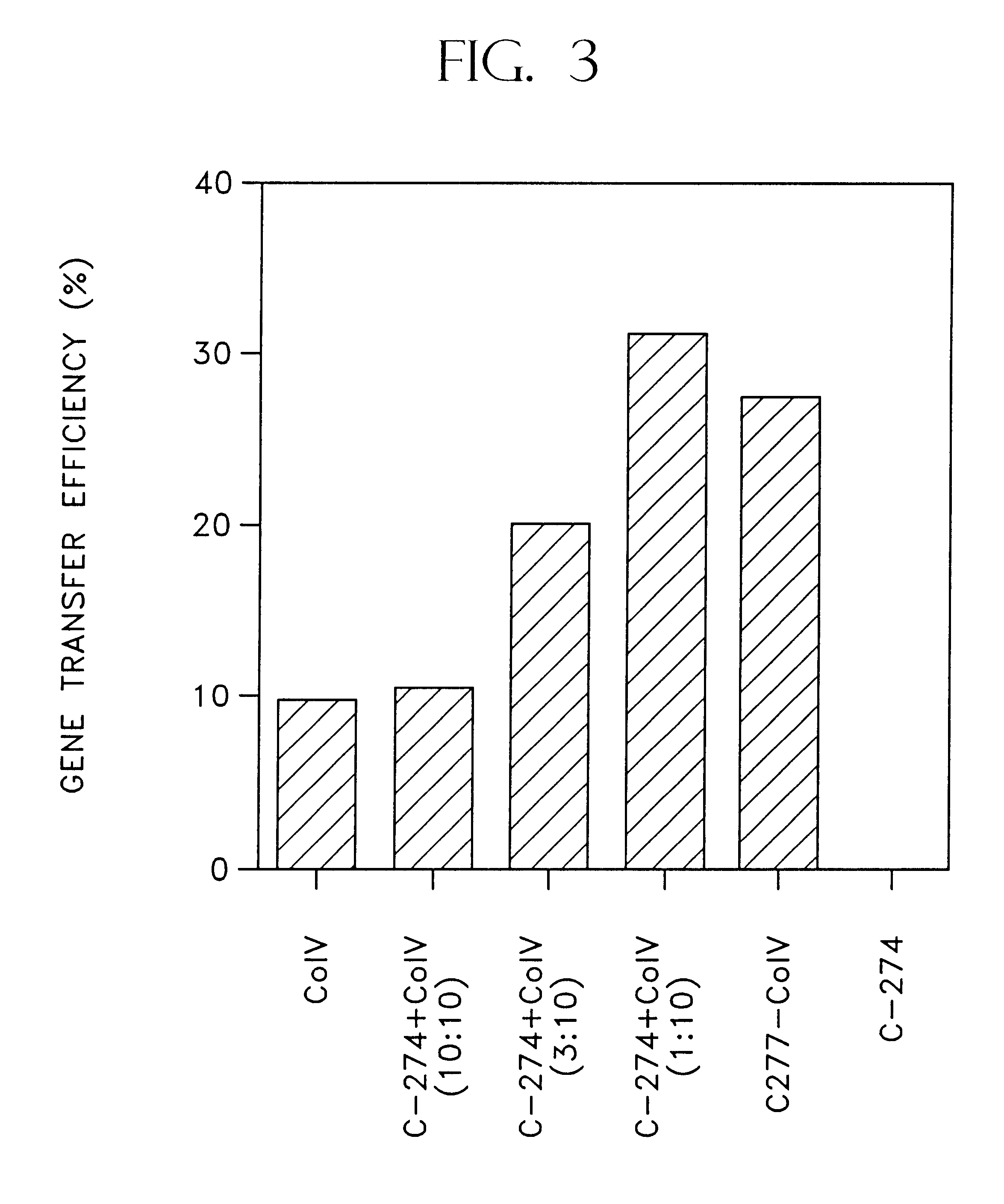
Methods for retroviral mediated gene transfer employing molecules, or mixtures thereof, containing retroviral binding domains and target cell binding domains
InactiveUS6472204B1Efficient and convenient methodGood choiceAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsCell bindingDNA-binding domain
A method is disclosed for increasing the efficiency of retroviral mediated gene transfer into viable target cells, which comprises transducing the target cells by infecting the target cells with a replication defective recombinant retrovirus that infects the target cells in an aqueous medium in the presence of(a) a mixture of an effective amount of a first functional material having a retrovirus binding domain that binds said retrovirus, and an effective amount of a second functional material having a target cell binding domain that binds said target cell, or(b) an effective amount of a bifunctional material having both a retroviral binding domain which does not contain the heparin binding domain derived from human fibronectin, and a target cell binding domain, wherein the bifunctional material has a retrovirus binding domain that binds to said retrovirus and a target cell binding domain that binds to the target cell.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Methods and compositions for modulating transcription factor activity
InactiveUS20050214309A1Increase dissociation rateAvoid problemsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAbnormal tissue growthDNA-binding domain
The present invention relates generally to transcription factor pathways, the modulation of such pathways, agents which modulate the activity of transcription factors, screening molecules to identify transcription factor modulators and cell or animal models for tumor-related transcription factors. More particularly, the present invention relates to the modulation of transcription factors in which the DNA binding domain is distinct from the activation domain by binding an inhibitory agent to a region adjacent to the DNA binding domain.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
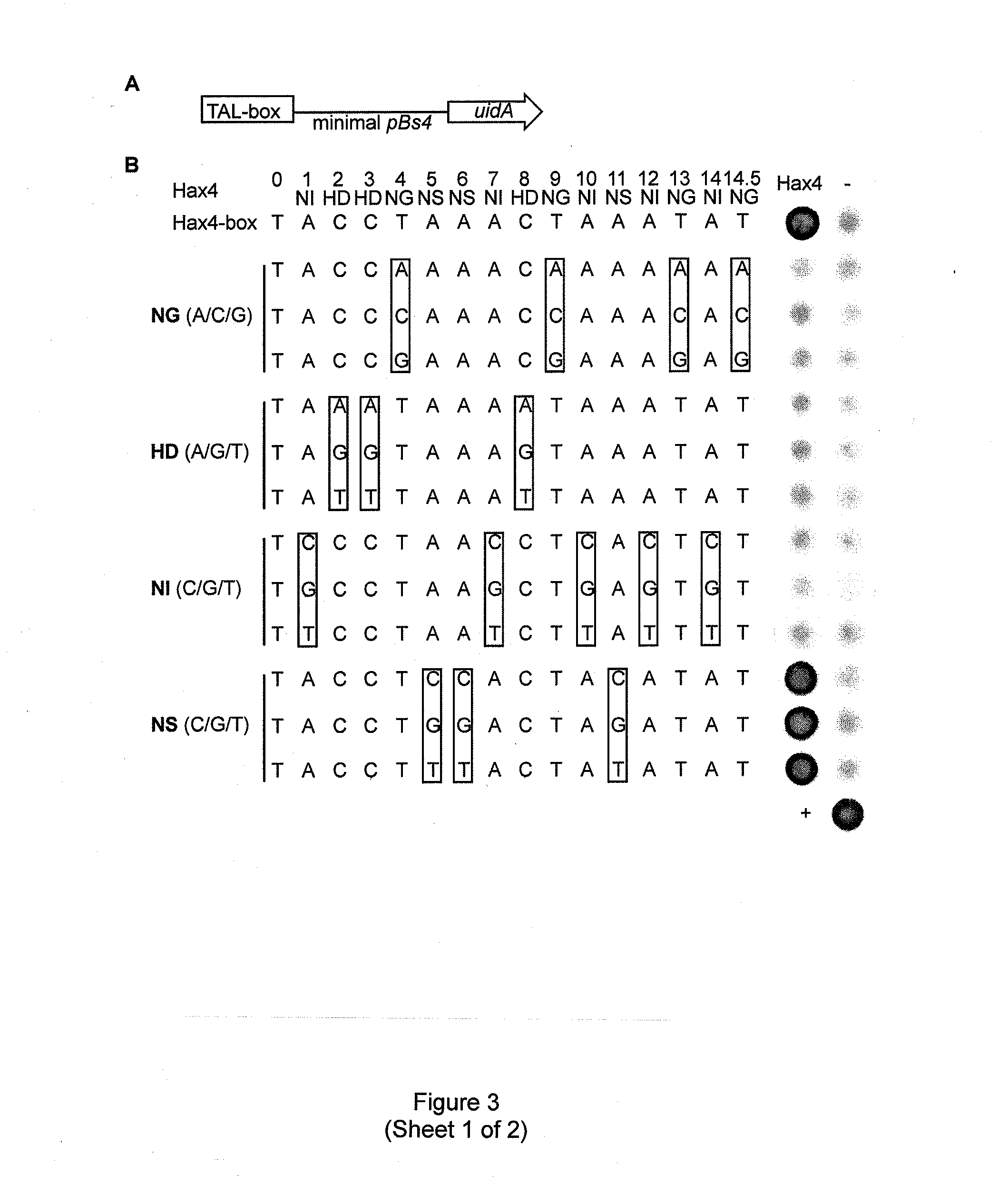
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20180237758A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureDNA-binding domainOff targets
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Diacylhydrazine ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes in mammalian systems via an ecdysone receptor complex
The present invention relates to methods to use non-steroidal ligands in nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system to modulate exogenous gene expression in which an ecdysone receptor complex comprising: a DNA binding domain; a ligand binding domain; a transactivation domain; and a ligand is contacted with a DNA construct comprising: the exogenous gene and a response element; wherein the exogenous gene is under the control of the response element and binding of the DNA binding domain to the response element in the presence of the ligand results in activation or suppression of the gene.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Circular dumbbell decoy oligodeoxynucleotides (cdodn) containing dna bindings sites of transcription
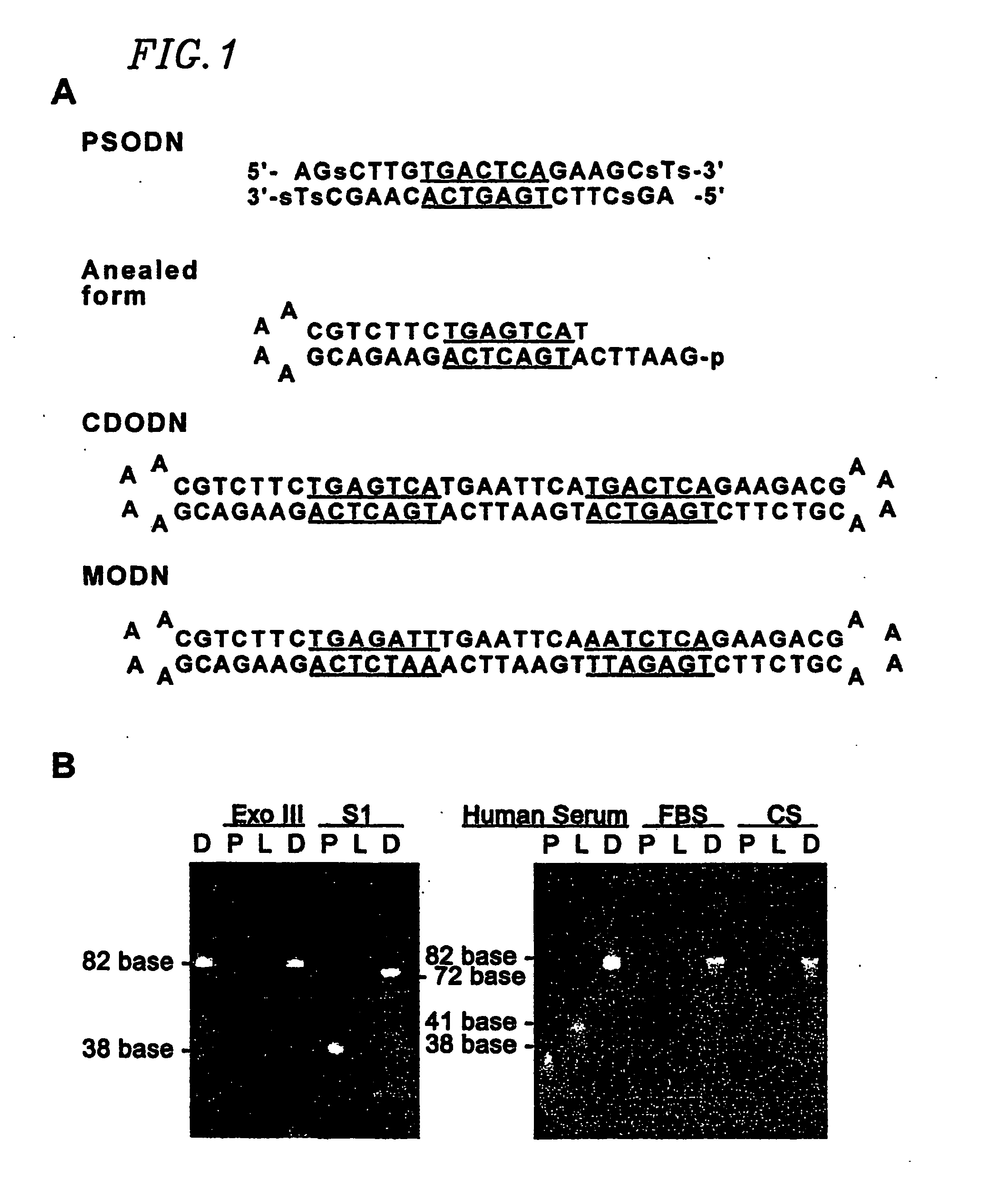
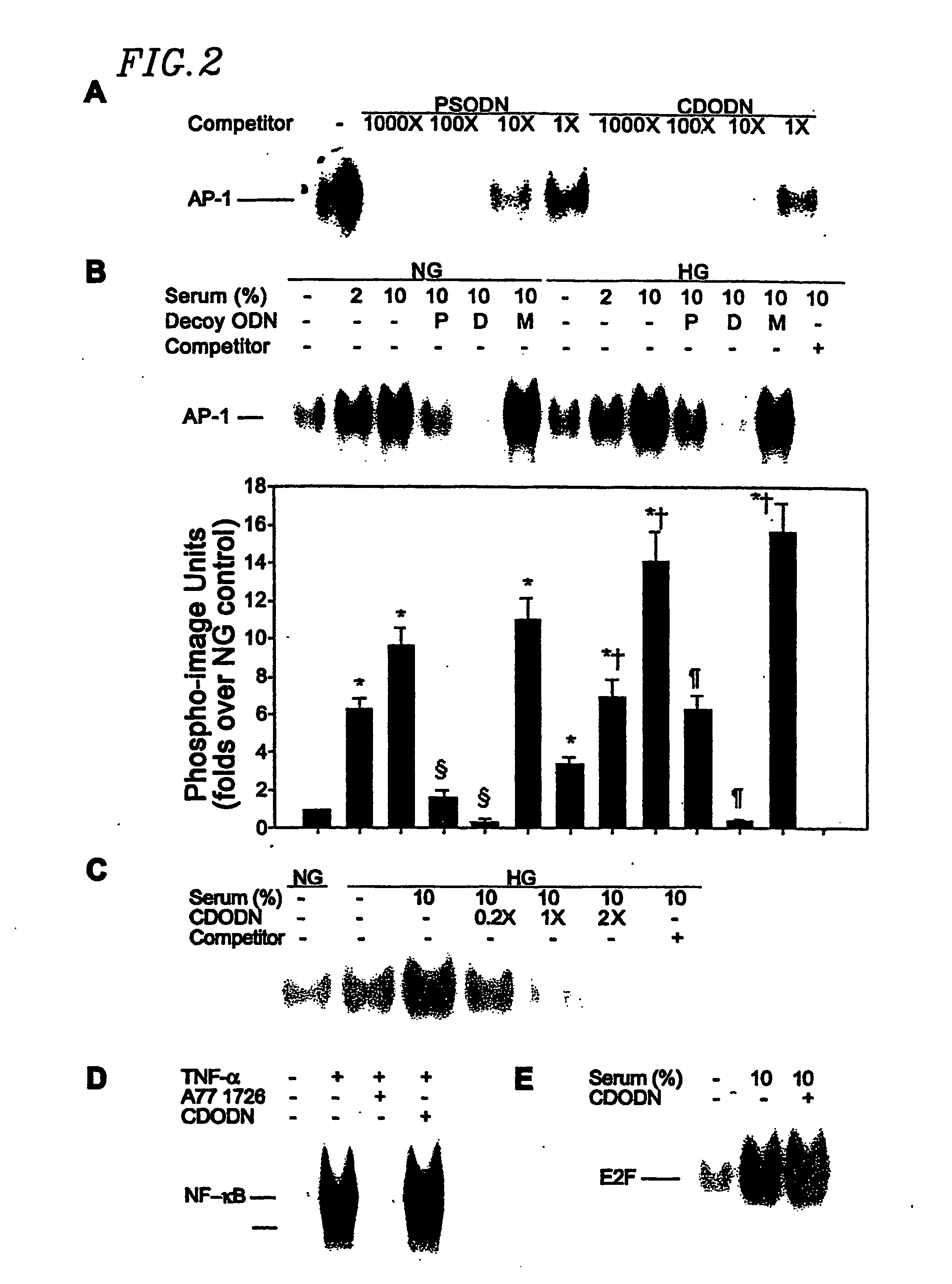
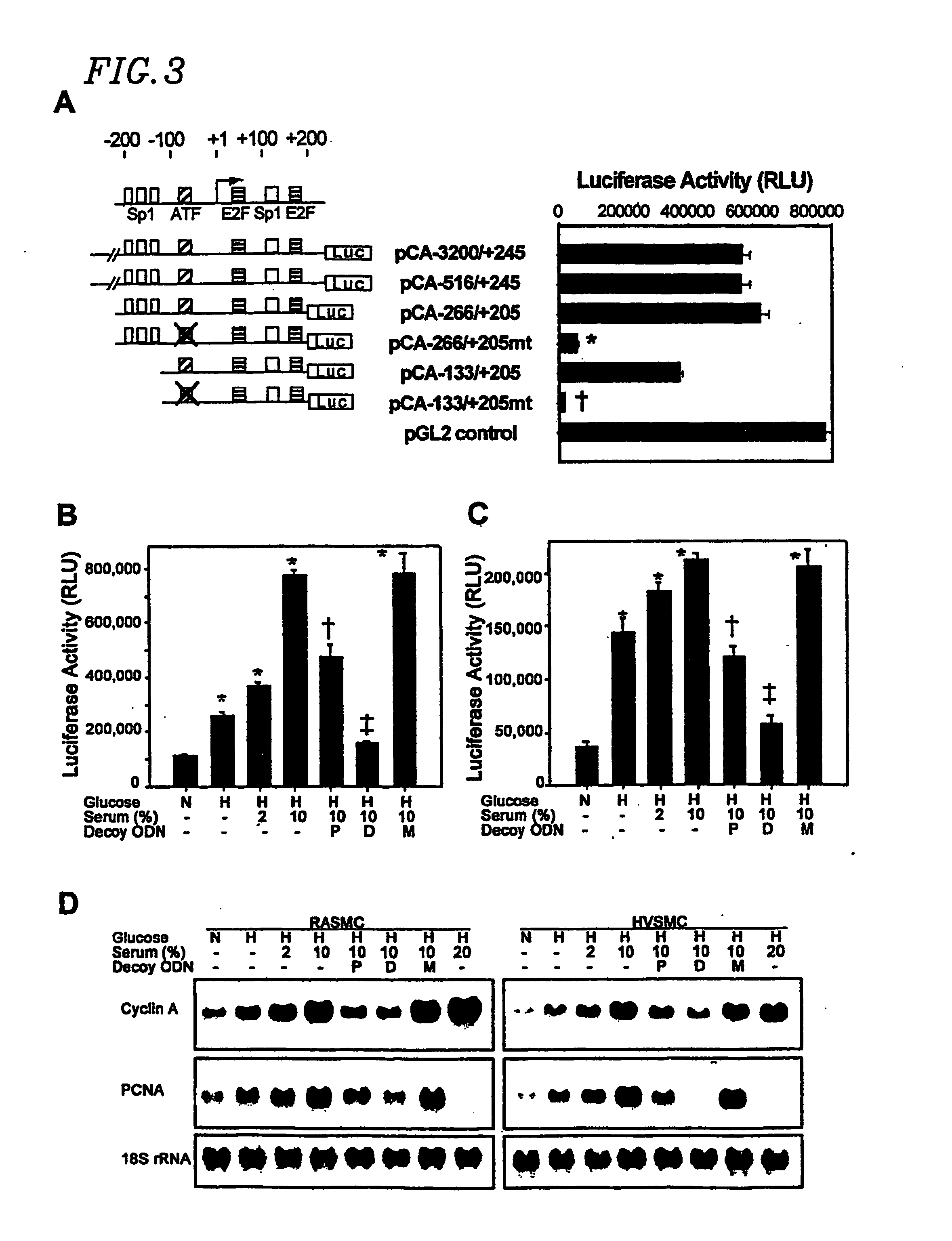
InactiveUS20070014840A1Effectively bind APPrevent trans-activationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA-binding domainDecoy
The present invention provides a circular dumbbell oligodeoxynucleotide (CDODN) comprising two loop structures and a stem structure, wherein the stem structure comprises a nucleotide sequence capable of binding the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional factor. The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising said CDODN. The pharmaceutical composition can be used for treating and / or preventing a disease or disorder related to such a transcriptional factor. The present invention also provides a method for treating and / or preventing a disease or disorder related to such a transcriptional factor, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a CDODN comprising two loop structures and a stem structure, wherein the stem structure comprises a nucleotide sequence capable of binding the DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional factor.
Owner:LEE IN KYU DR +1
Bioavailable diacylhydrazine ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes via an ecdysone receptor complex
The present invention relates to non-steroidal ligands for use in nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system, and a method to modulate exogenous gene expression in which an ecdysone receptor complex comprising: a DNA binding domain; a ligand binding domain; a transactivation domain; and a ligand is contacted with a DNA construct comprising: the exogenous gene and a response element; wherein the exogenous gene is under the control of the response element and binding of the DNA binding domain to the response element in the presence of the ligand results in activation or suppression of the gene.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Fusion polypeptide comprising two ligand binding domains
InactiveUS7011972B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsReceptors for hormonesDNA-binding domainBinding domain
Single chain, monomeric polypeptide gene switches are provided. The gene switches include ligand binding domains and at least one functional domain. Preferred functional domains are DNA binding domains and transcriptional regulating domains. Methods of regulating gene function using the switches are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Methods and kits for improving retroviral-mediated gene transfer utilizing molecules, or mixture thereof, containing retroviral binding domains and target cell binding domains
InactiveUS6426042B1Efficient executionEasy to carryVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCell bindingDNA-binding domain
The present invention provides a kit to carry out retrovirus-mediated gene transfer into target cells. The kit contains a functional material bearing a retrovirus binding domain, another functional material bearing a target cell binding domain, an artificial substrate for incubating the retrovirus contacted with the target cells, and a target cell growth factor for pre-stimulating target cells to spur them along the cell cycle. The kit of the invention may further comprise a recombinant retroviral vector, necessary buffers, and the like.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Fusion polypeptides and uses thereof
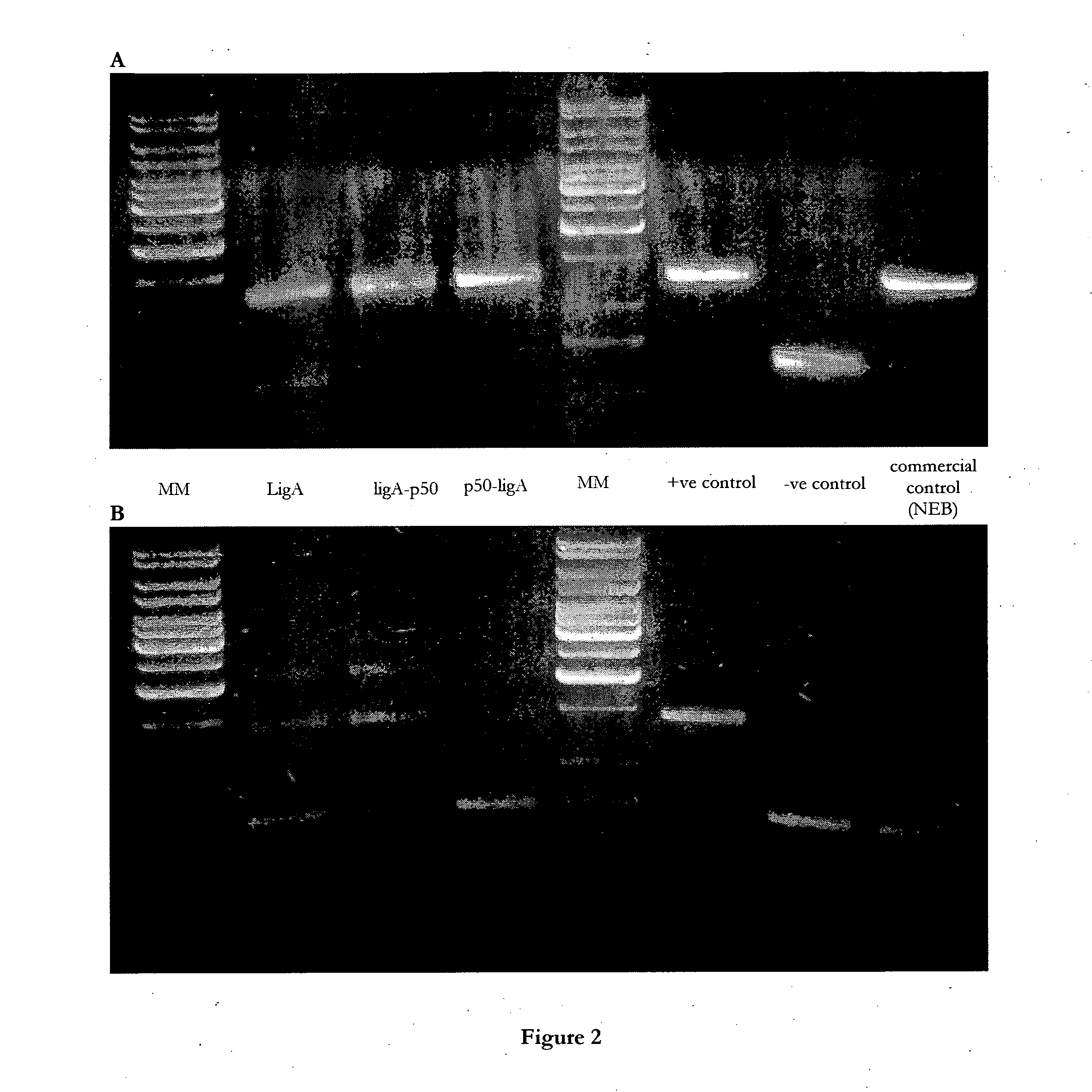
The invention relates to fusion polypeptides comprising a polynucleotide-binding domain, such as a DNA-binding domain, and a ligase domain, such as a DNA ligase domain, methods for the production of such fusion polypeptides, and uses of the fusion polypeptides, for example in a range of molecular biological techniques as well as applications in the diagnostics, protein production, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical and medical fields.
Owner:MASSEY UNIVERISTY
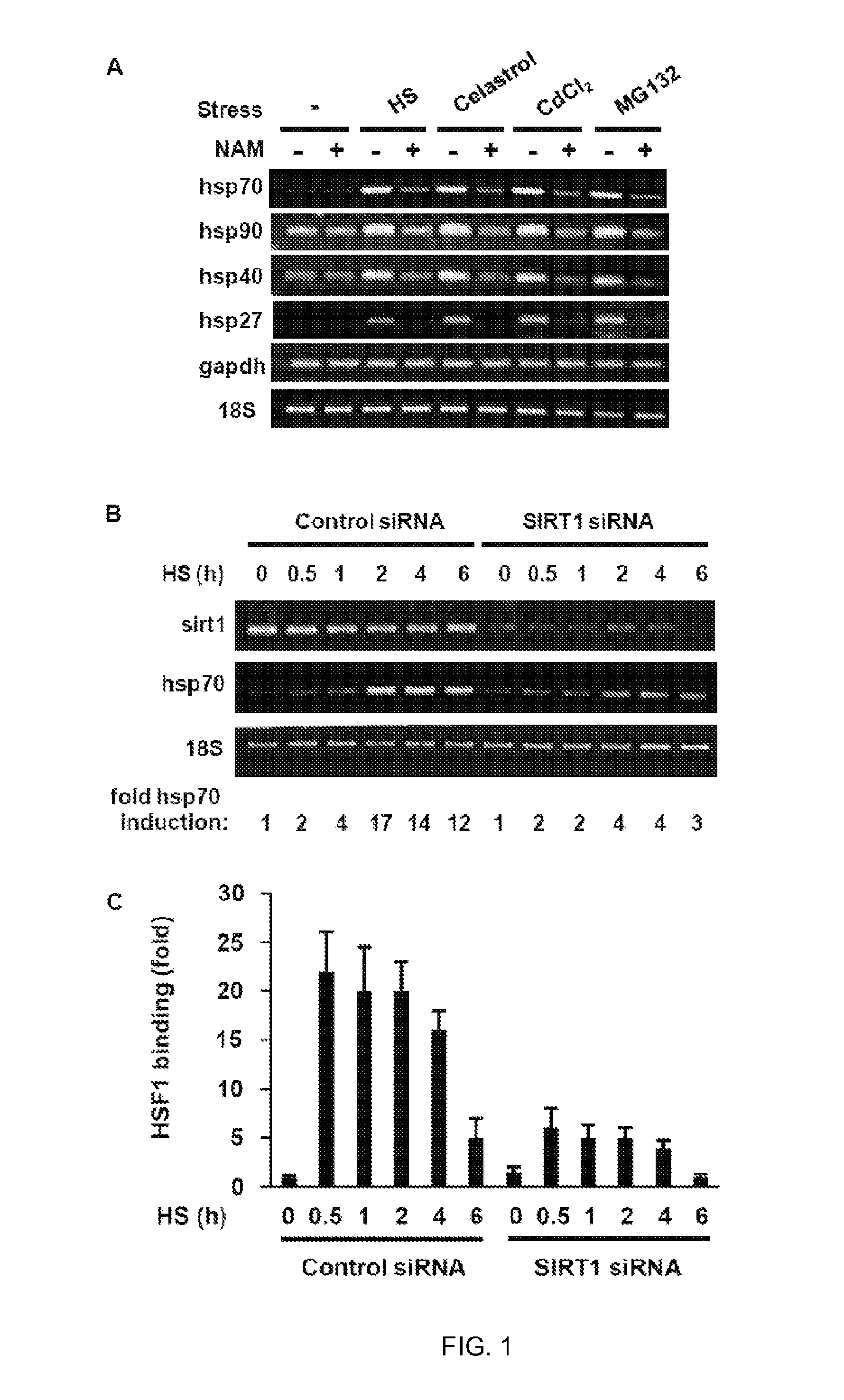
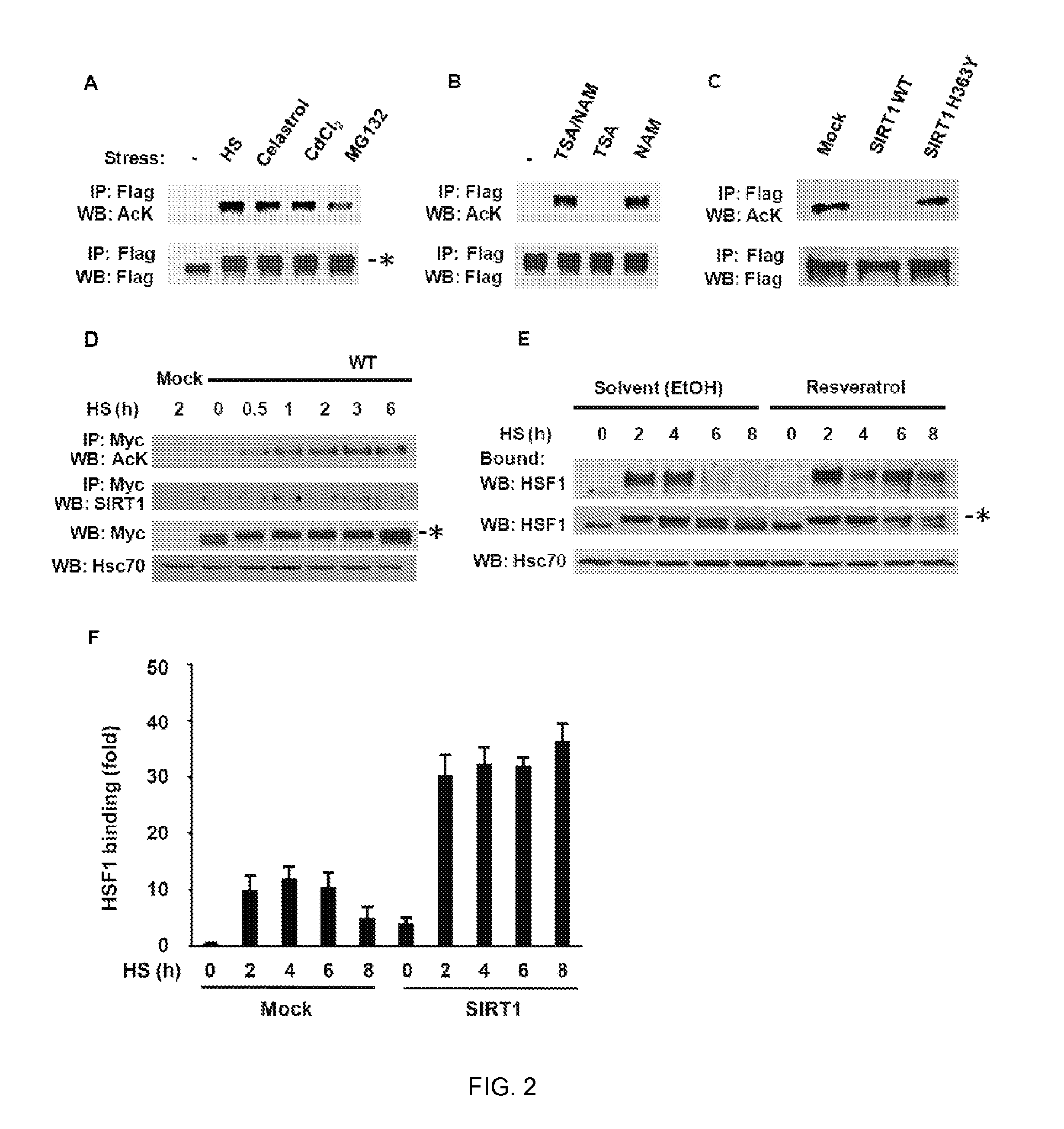
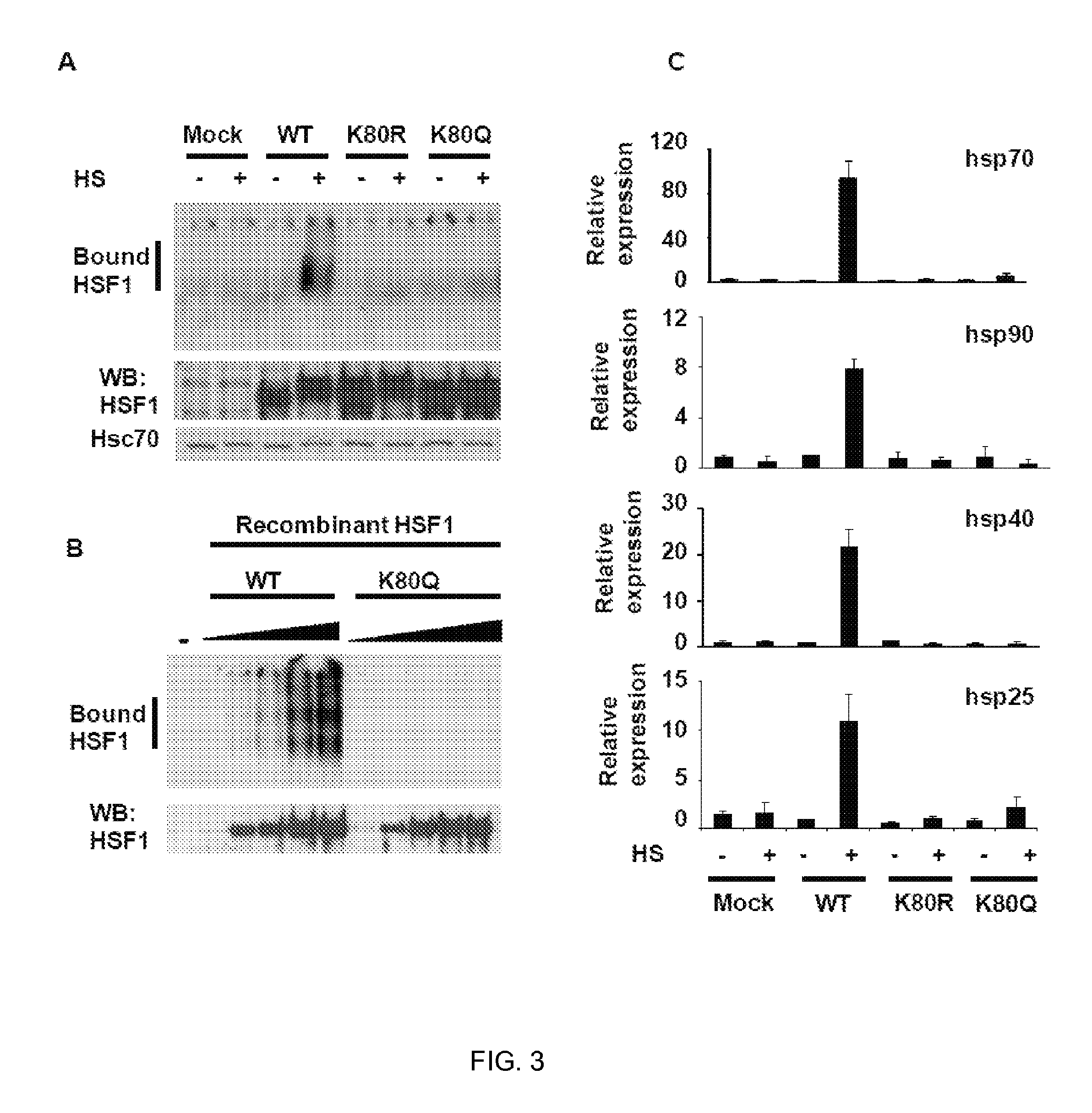
Method of modulating hsf-1
ActiveUS20110311508A1Prolongs HSF DNA bindingPromote lowerBiocideCompound screeningDNA-binding domainAcetylation
The present invention is directed to methods of modulating HSF1 activity comprising modifying the acetylation of the DNA binding domain of the HSF1.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
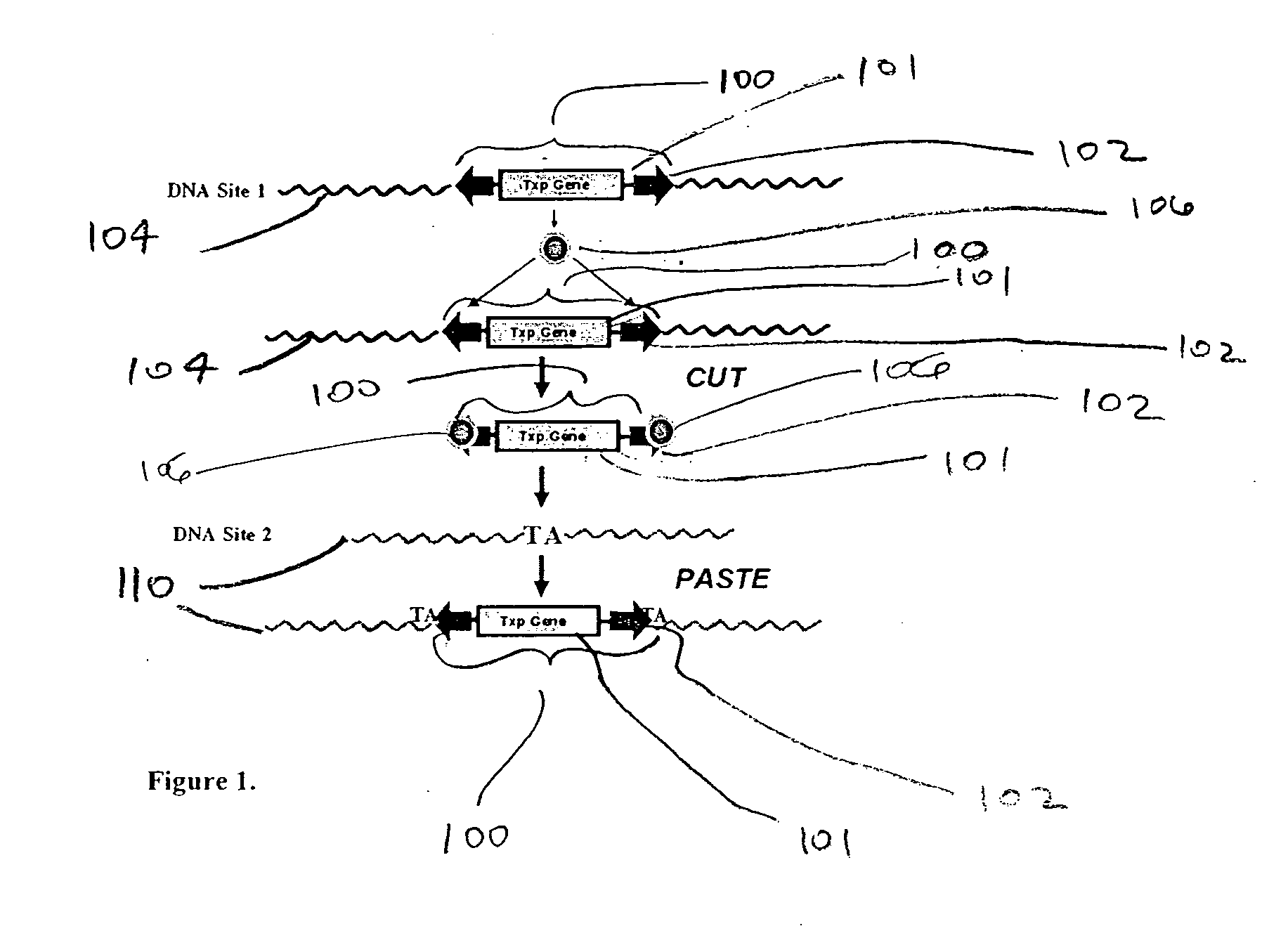
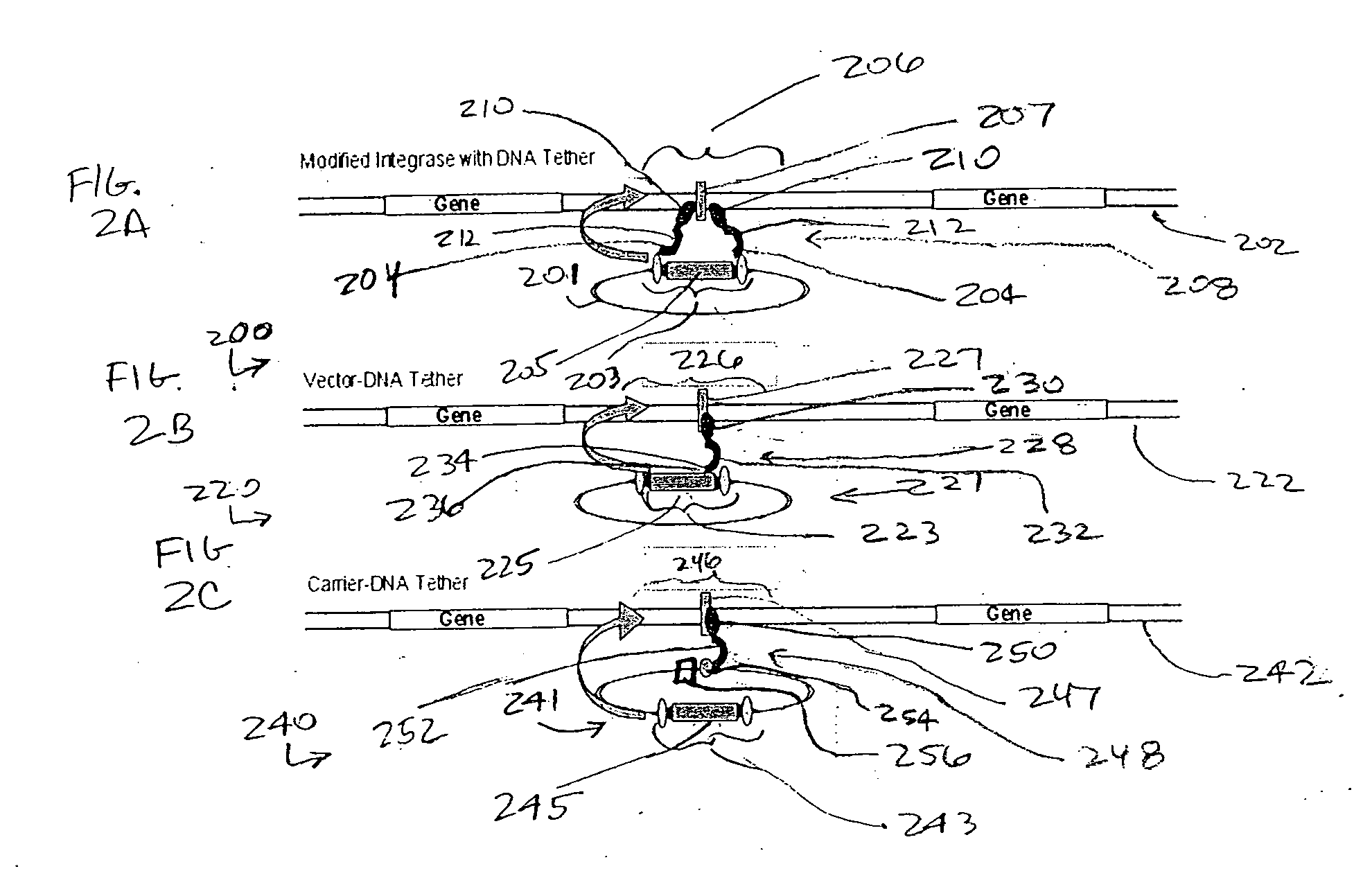
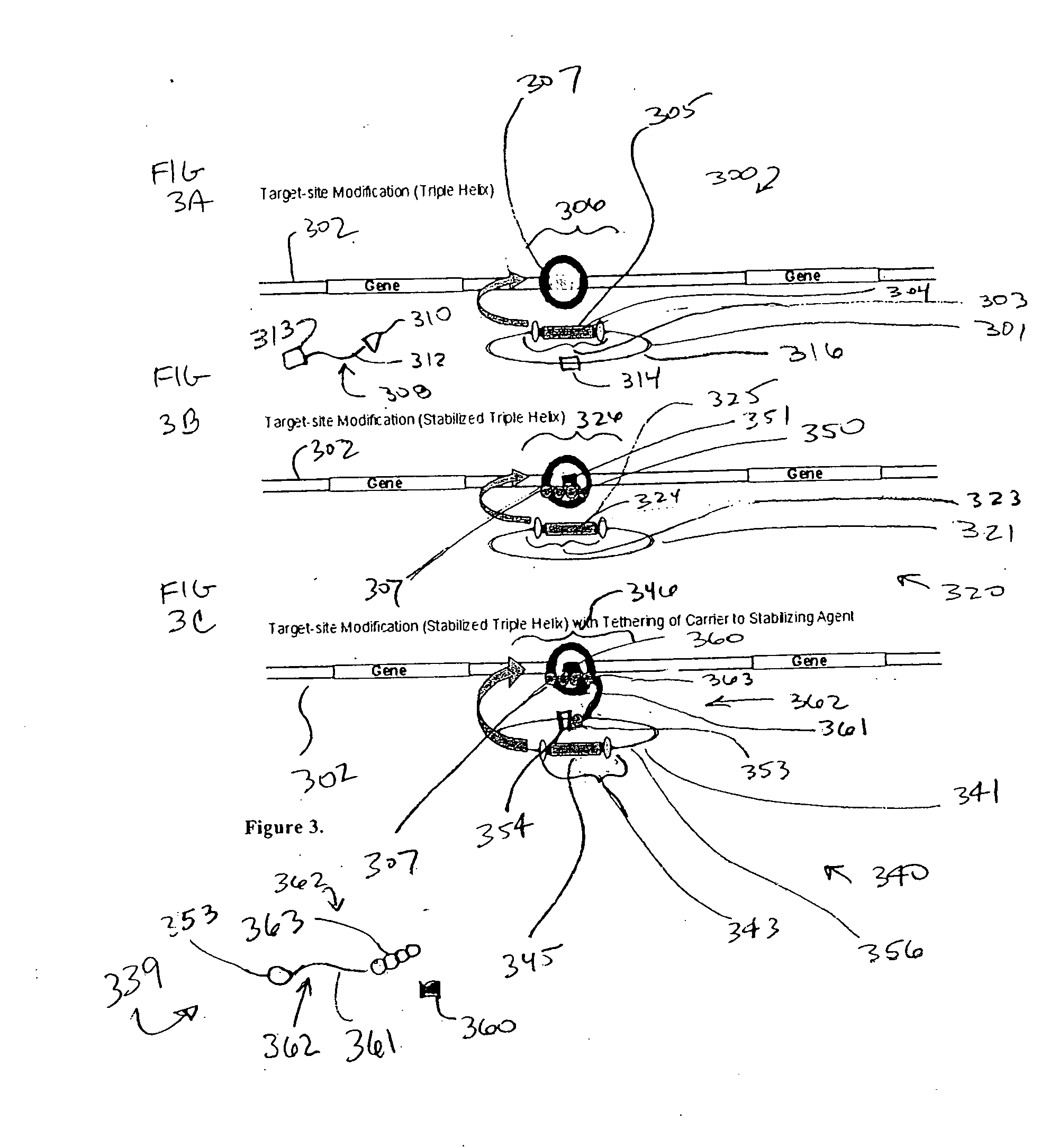
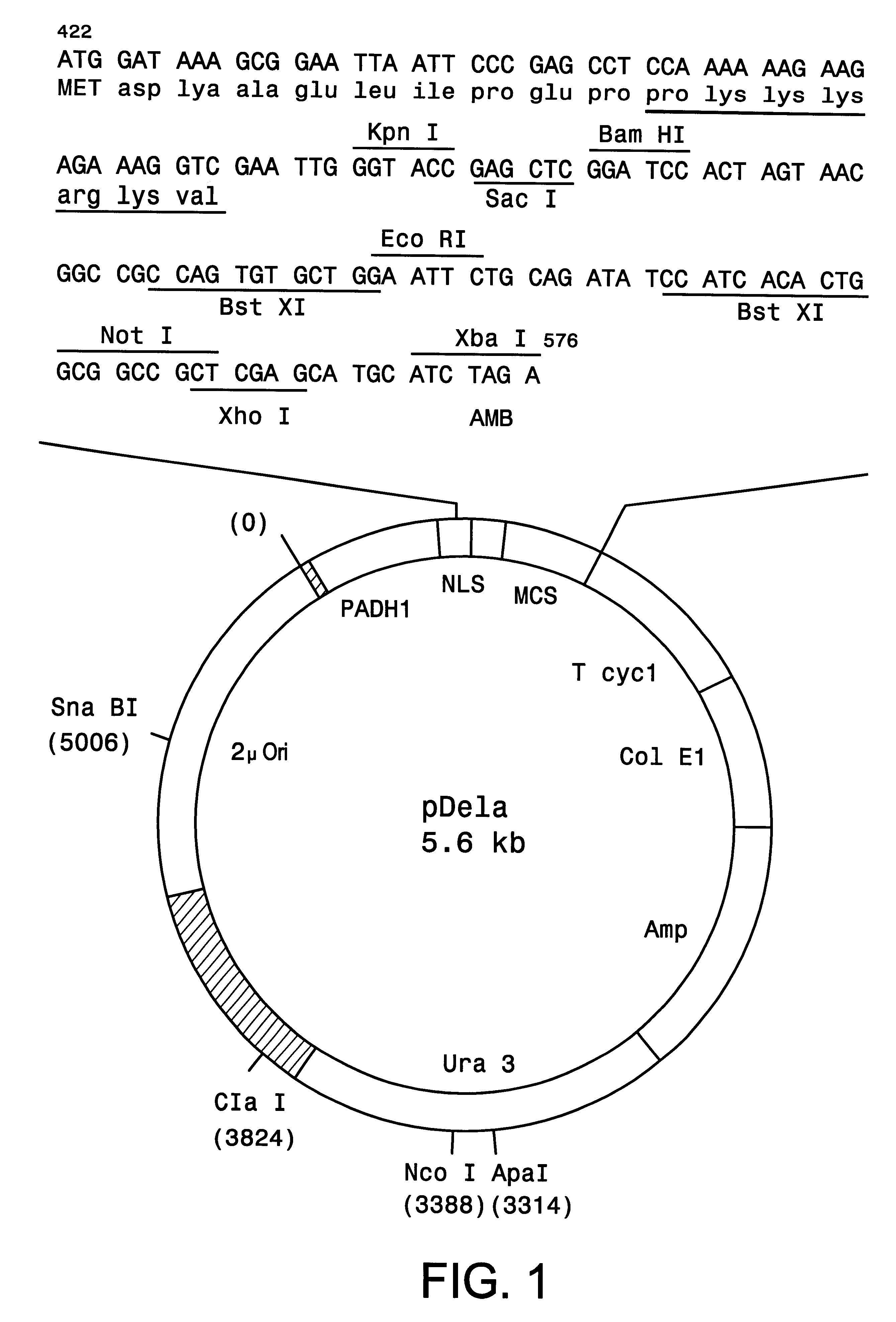
Integration-site directed vector systems
ActiveUS20070031380A1Without compromising performanceReduce and eliminate effectBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDNA-binding domainVector system
Some aspects of the application describe materials and methods for making a molecular tether. A molecular tether, in certain embodiments, includes a target-DNA-binding domain having a specific binding affinity for a target-DNA segment in a host chromosome, a carrier-binding domain that specifically binds to a DNA segment on a carrier, and a spacer covalently bonded to the target DNA-binding domain and the carrier-binding domain.
Owner:IMMUSOFT CORP
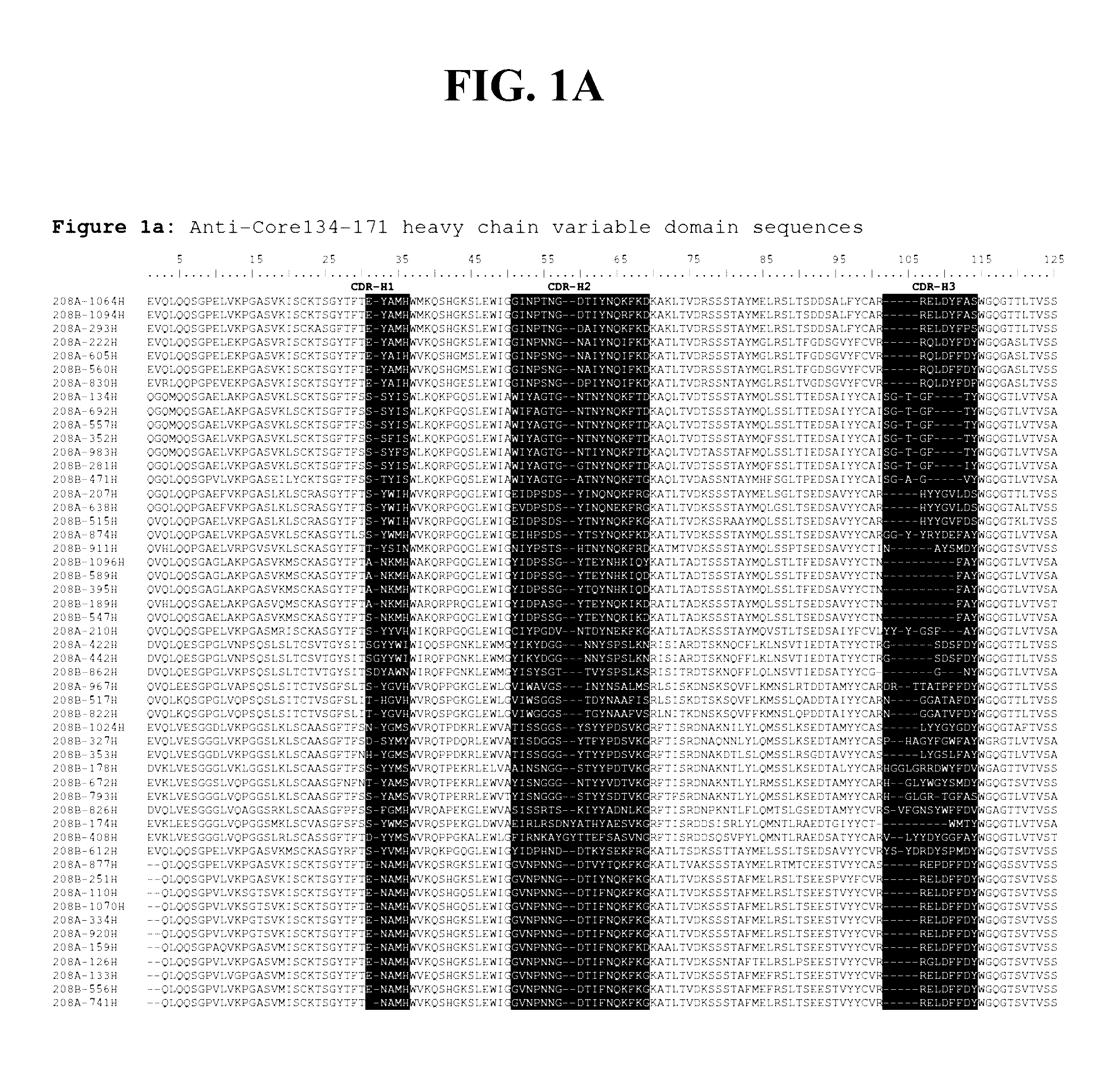
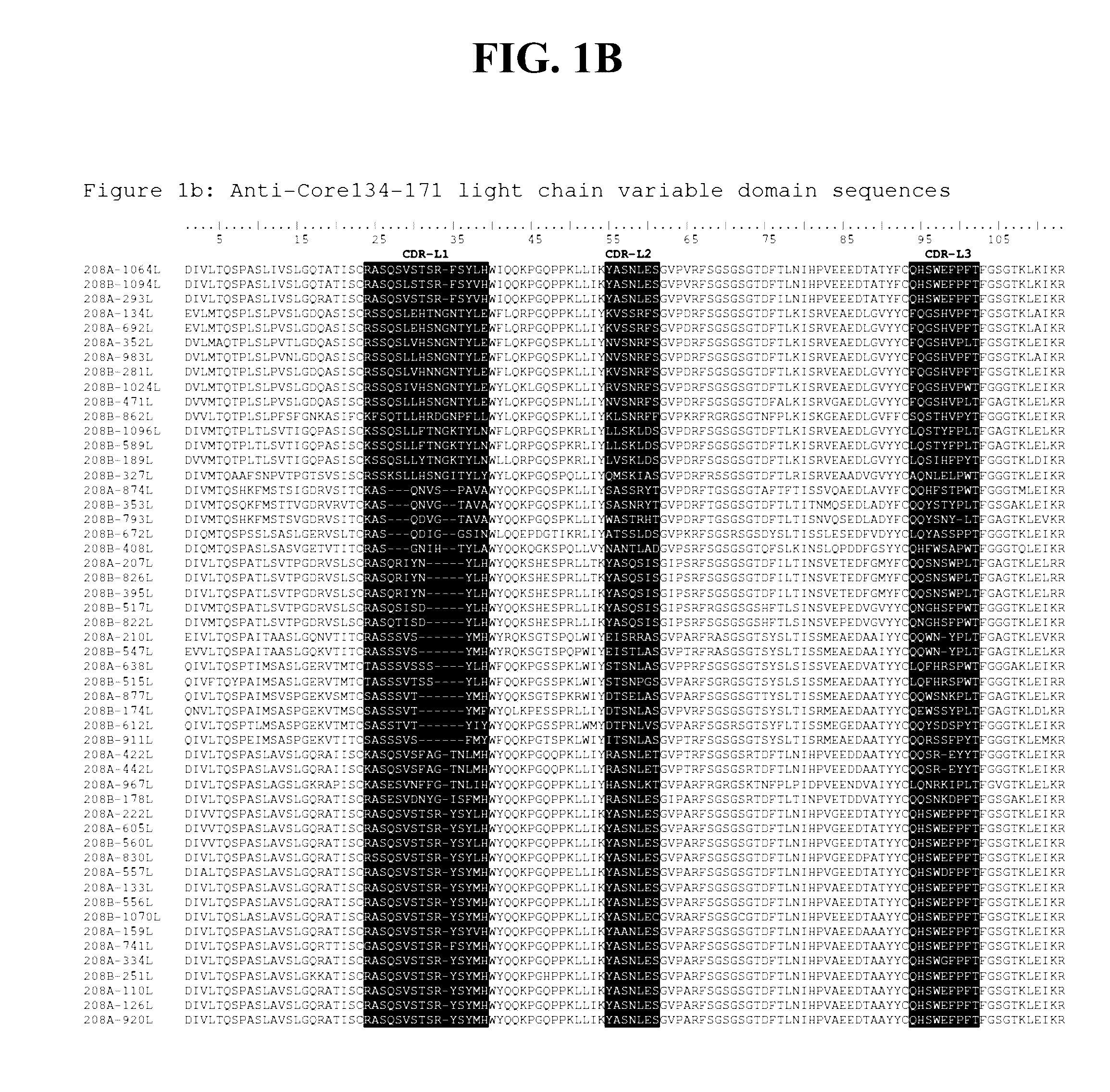
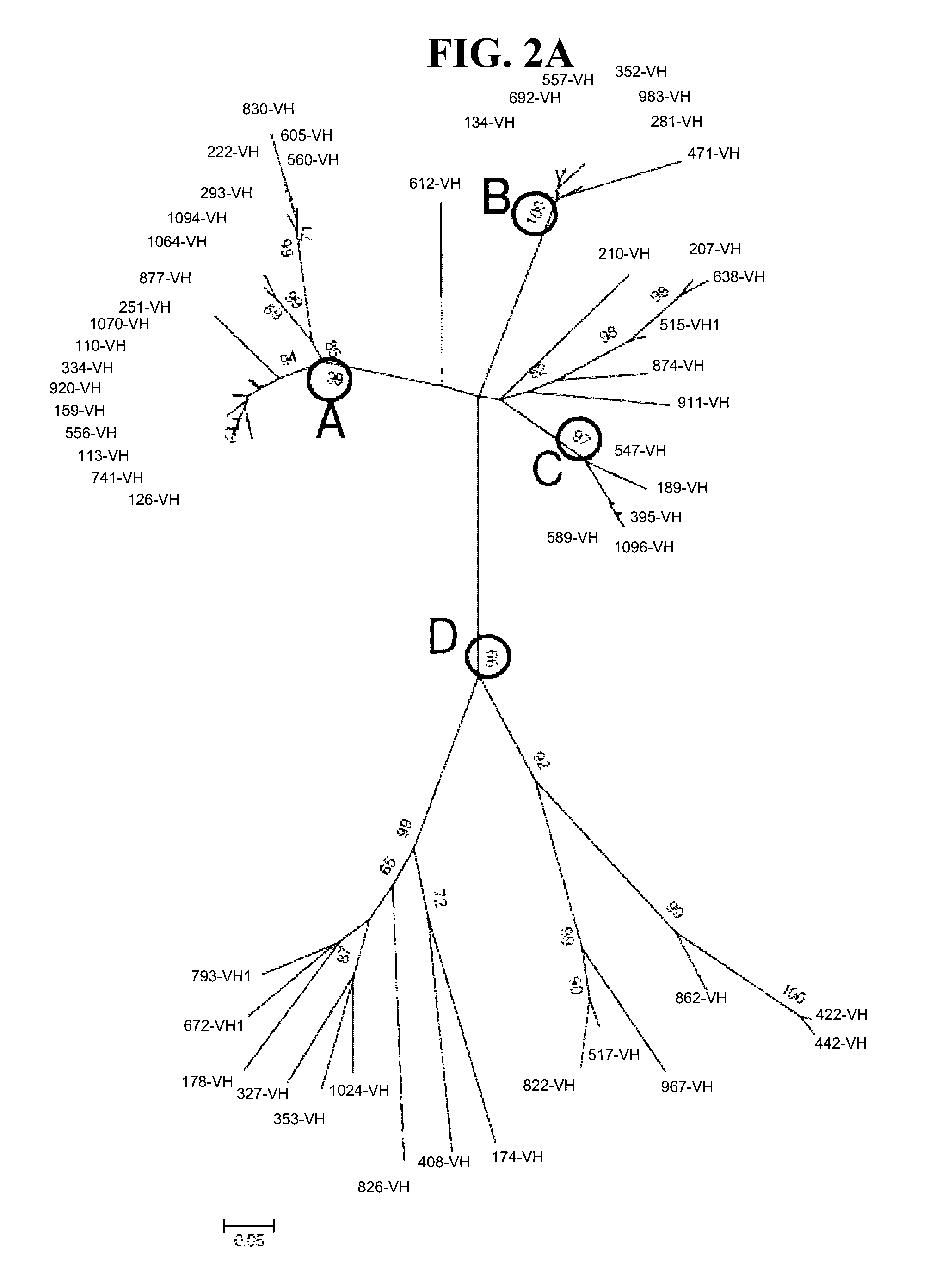
Detection methods employing hcv core lipid and DNA binding domain monoclonal antibodies
ActiveUS20170052184A1Easy to adaptImmunoglobulins against virusesDisease diagnosisEpitopeDNA-binding domain
The present disclosure provides detection methods employing HCV core lipid binding domain and DNA binding domain monoclonal antibodies or antibody fragments. In certain embodiments, the lipid binding domain monoclonal antibody or antibody fragment recognizes an epitope in amino acids 141 to 161 of HCV core protein and the DNA binding domain antibody or antibody fragment recognizes an epitope in amino acids 95-123 (e.g., in amino acids 99-117) of HCV core protein.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC +1
Method and kit for detection of multiple protein interactions
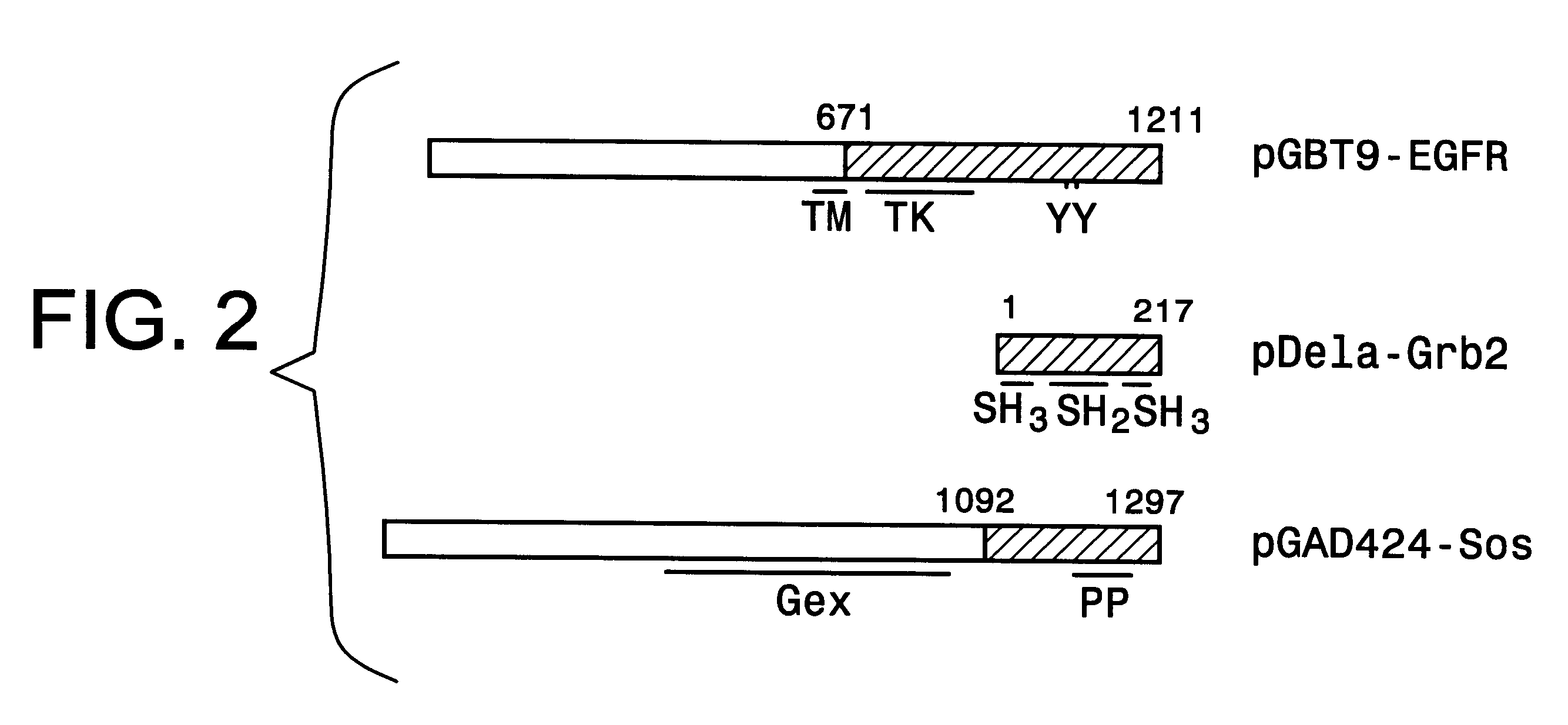
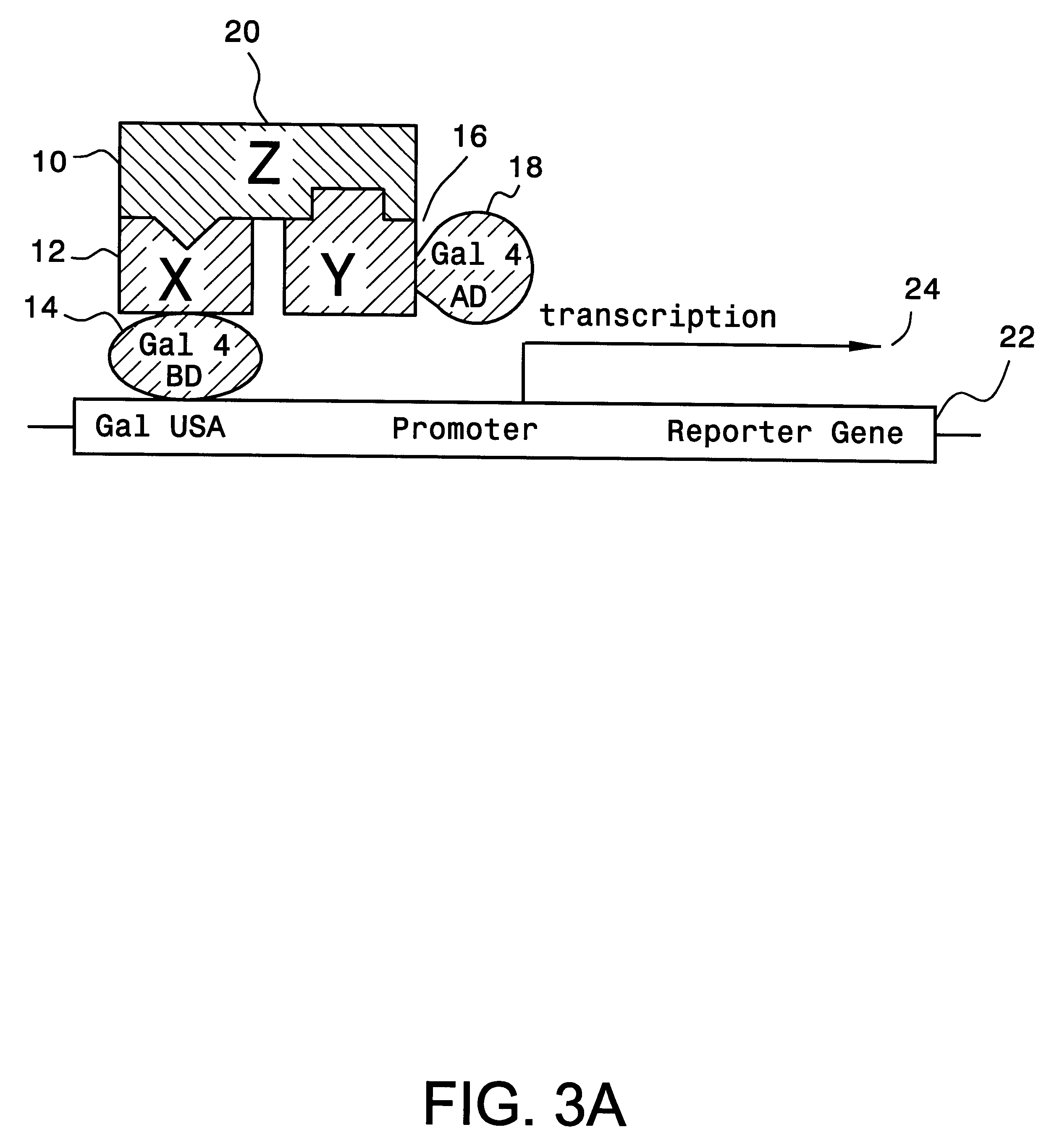
A method and a kit for detecting interactions between three or more proteins, in vivo, using reconstitution of the activity of a transcriptional activator is provided. Reconstitution of the transcriptional activator makes use of chimeric genes which express hybrid proteins. In one embodiment, three types of hybrid proteins are prepared. The first hybrid contains the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator fused to the first test protein. The second hybrid protein contains a transcriptional activation domain fused to the second test protein. The third hybrid protein contains a nuclear localization peptide fused to a third test protein and mediates assembly of the three-protein complex involving the three hybrids. If the three test proteins are able to interact, they bring into close proximity the two domains of the transcriptional activator. This proximity is sufficient to cause transcription, which can be detected by the activity of a marker gene that contains a binding site for the DNA-binding domain.
Owner:GUILFORD PHARMACEUTICALS INC
PCR reaction mixtures with decreased non-specific activity
ActiveUS8916352B2Strong specificityFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainArginine
The present invention provides methods for improving the specificity of nucleic acid amplification comprising incubating a nucleic acid molecule with a polymerase-Sso7 DNA binding domain conjugate and arginine, spermidine, or spermine. The present invention also provides reaction mixtures and kits for improving the specificity of nucleic acid amplification.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Ketone ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes via an ecdysone receptor complex
This invention relates to a method to modulate exogenous gene expression in which an ecdysone receptor complex comprising: a DNA binding domain; a ligand binding domain; a transactivation domain; and a ligand is contacted with a DNA construct comprising: the exogenous gene and a response element; wherein the exogenous gene is under the control of the response element and binding of the DNA binding domain to the response element in the presence of the ligand results in activation or suppression of the gene. The ligands comprise a class of ketones.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com