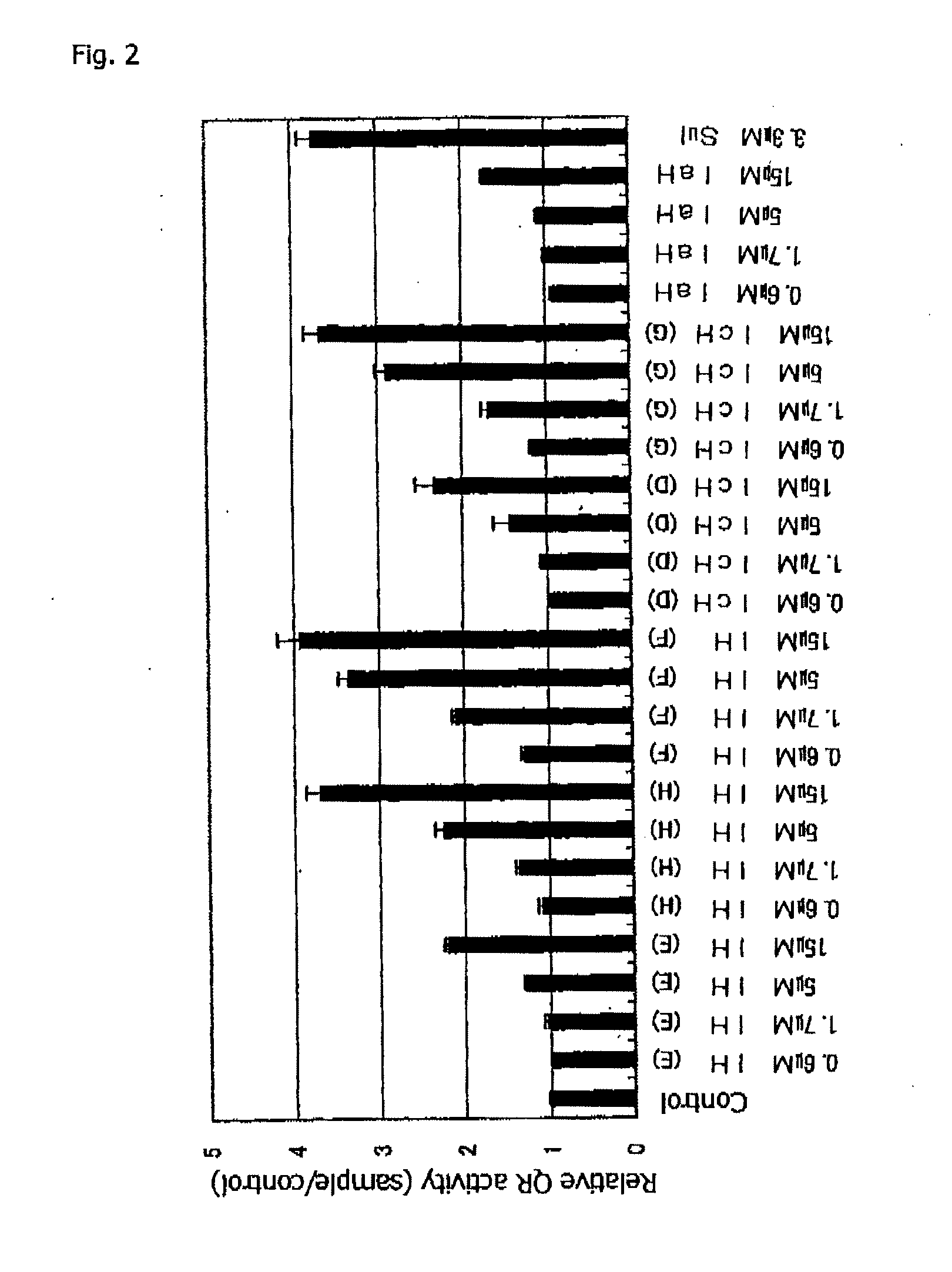
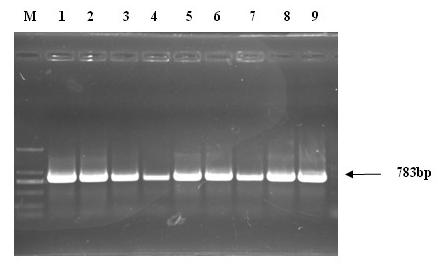
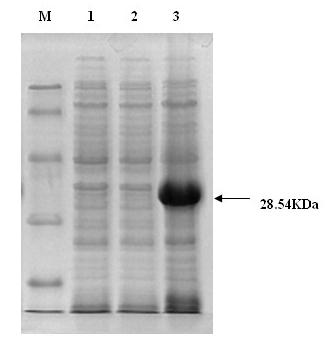
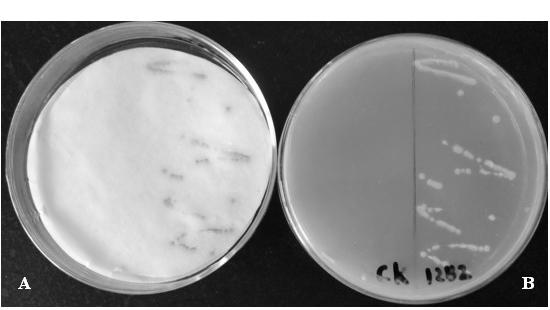
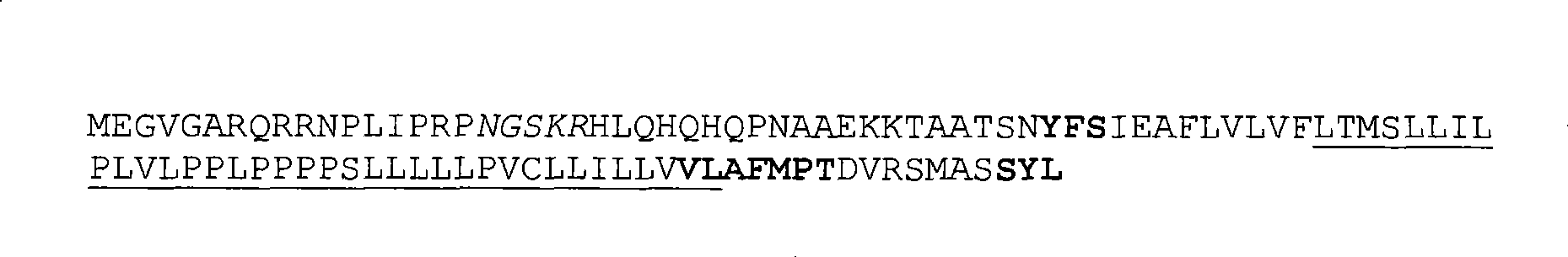Patents
Literature
1291 results about "Transcriptional factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
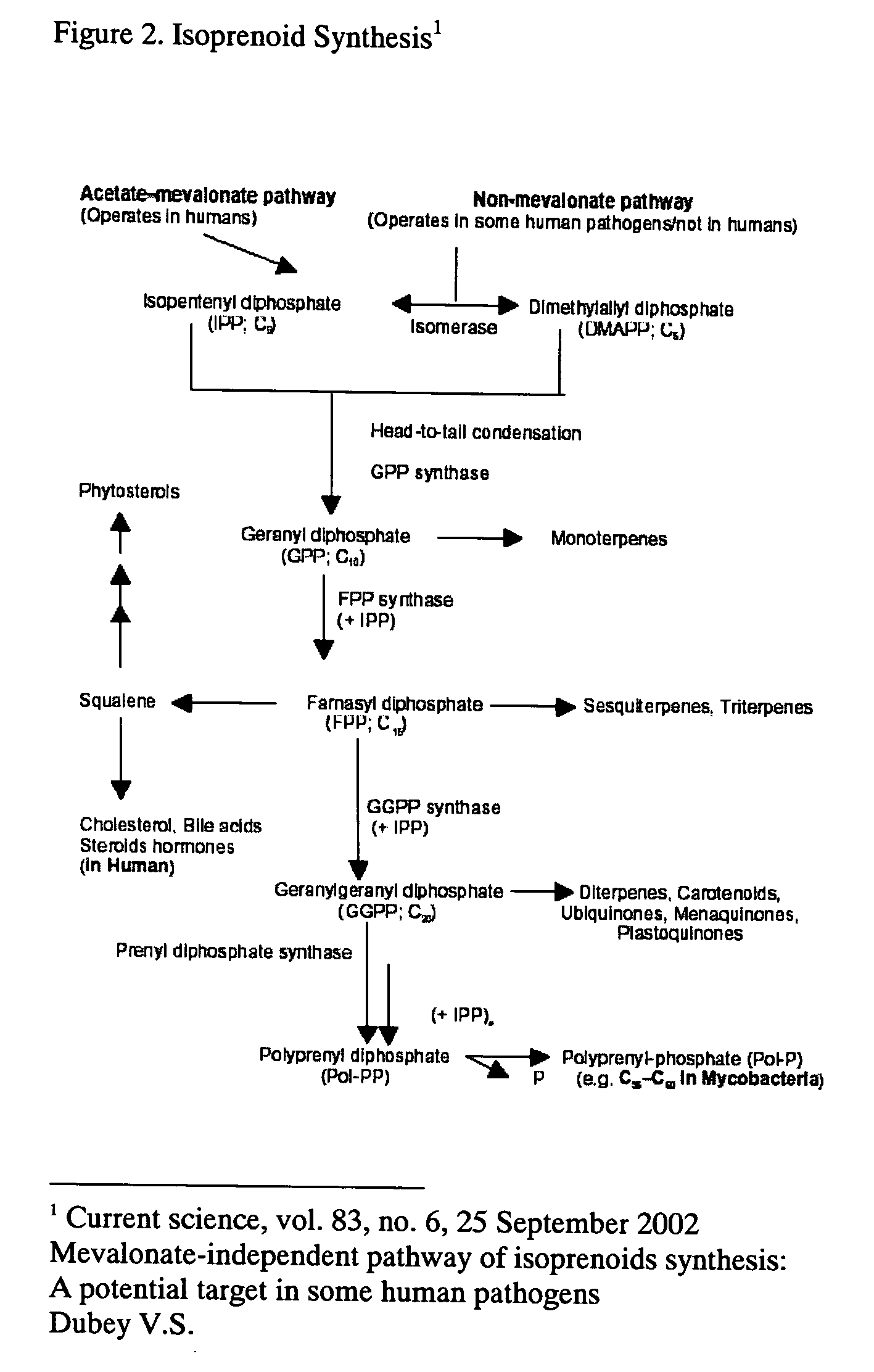
Definition of transcription factor. : any of various proteins that bind to DNA and play a role in the regulation of gene expression by promoting transcription.
Electromagnetic activation of gene expression and cell growth
InactiveUS20050059153A1Accelerating cell cycleReduce inflammationElectrotherapyMutant preparationAngiotensin receptorA-DNA
The invention is directed to a method for accelerating the cell cycle by delivering to a cell an effective amount of electromagnetic energy. The invention also provides a method for activating a cell cycle regulator by delivering to a cell an effective amount of electromagnetic energy. Also provided by the invention is a method for activating a signal transduction protein; a method for activating a transcription factor; a method for activating a DNA synthesis protein; and a method for activating a Receptor. A method for inhibiting an angiotensin receptor as well as a method for reducing inflammation also are provided by the present invention. The invention also is directed to a method for replacing damaged neuronal tissue as well as a method for stimulating growth of administered cells.
Owner:REGENESIS BIOMEDICAL
Method of prevention and treatment of Atherosclerosis, Peripheral vascular disease, Coronary artery disease, aging and age-related disorders including osteoporosis, arthritis, type 2 diabetes, dementia and Alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20060078532A1BiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsInterleukin 6Age related disease
This invention relates to a method for prevention and treatment of Atherosclerosis, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Coronary Artery Disease, and age-related disorders including Osteoporosis, Arthritis, Type II Diabetes, Dementia and Alzheimer's disease in a subject comprising administering to said subject a therapeutically effective dosage of each component or combination of statins, bisphosphonates, cholesterol lowering agents or techniques, interleukin-6 inhibitor / antibody, interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor / antibody, gp130 protein inhibitor / antibody, tyrosine kinases inhibitors / antibodies, STAT transcription factors inhibitors / antibodies, altered IL-6, partial peptides of IL-6 or IL-6 receptor, or SOCS (suppressors of cytokine signaling) protein, or a functional fragment thereof, administered separately, in sequence or simultaneously. Inhibition of the signal transduction pathway for Interleukin 6 mediated inflammation is key to the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, peripheral vascular disease, coronary artery disease, aging and age-related disorders including osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, dementia and some forms of arthritis and tumors. Inhibition of Interleukin 6 mediated inflammation may be achieved indirectly through regulation of endogenous cholesterol synthesis and isoprenoid depletion or by direct inhibition of the signal transduction pathway including interleukin-6 inhibitor / antibody, interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor / antibody, gp130 protein inhibitor / antibody, tyrosine kinases inhibitors / antibodies, STAT transcription factors inhibitors / antibodies, altered IL-6, partial peptides of IL-6 or IL-6 receptor, or SOCS (suppressors of cytokine signaling) protein, or a functional fragment thereof. Said method for prevention and treatment of said disorders is based on inhibition of Interleukin-6 inflammation through regulation of cholesterol metabolism, isoprenoid depletion and inhibition of the signal transduction pathway.
Owner:OMOIGUI OSEMWOTA SOTA
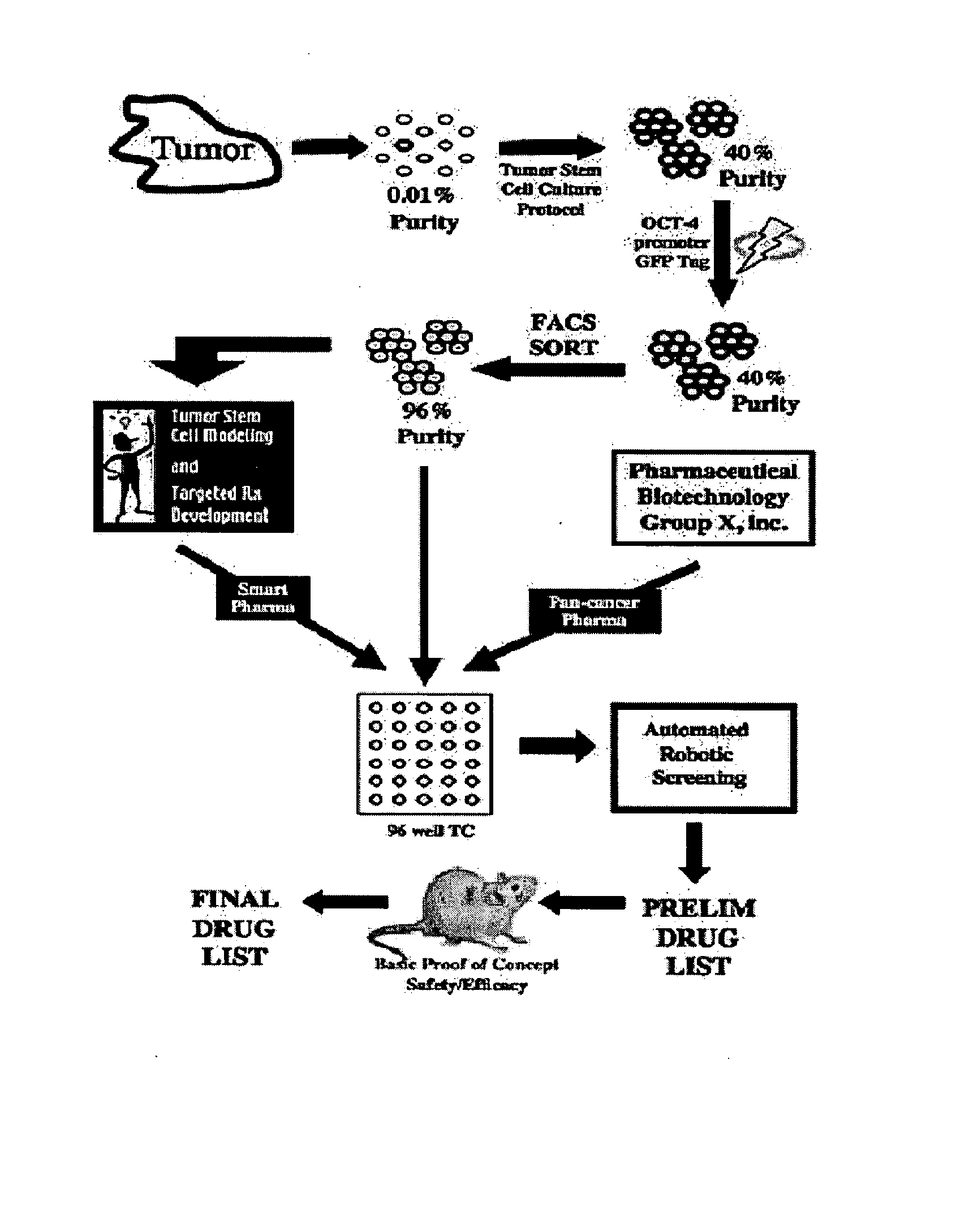
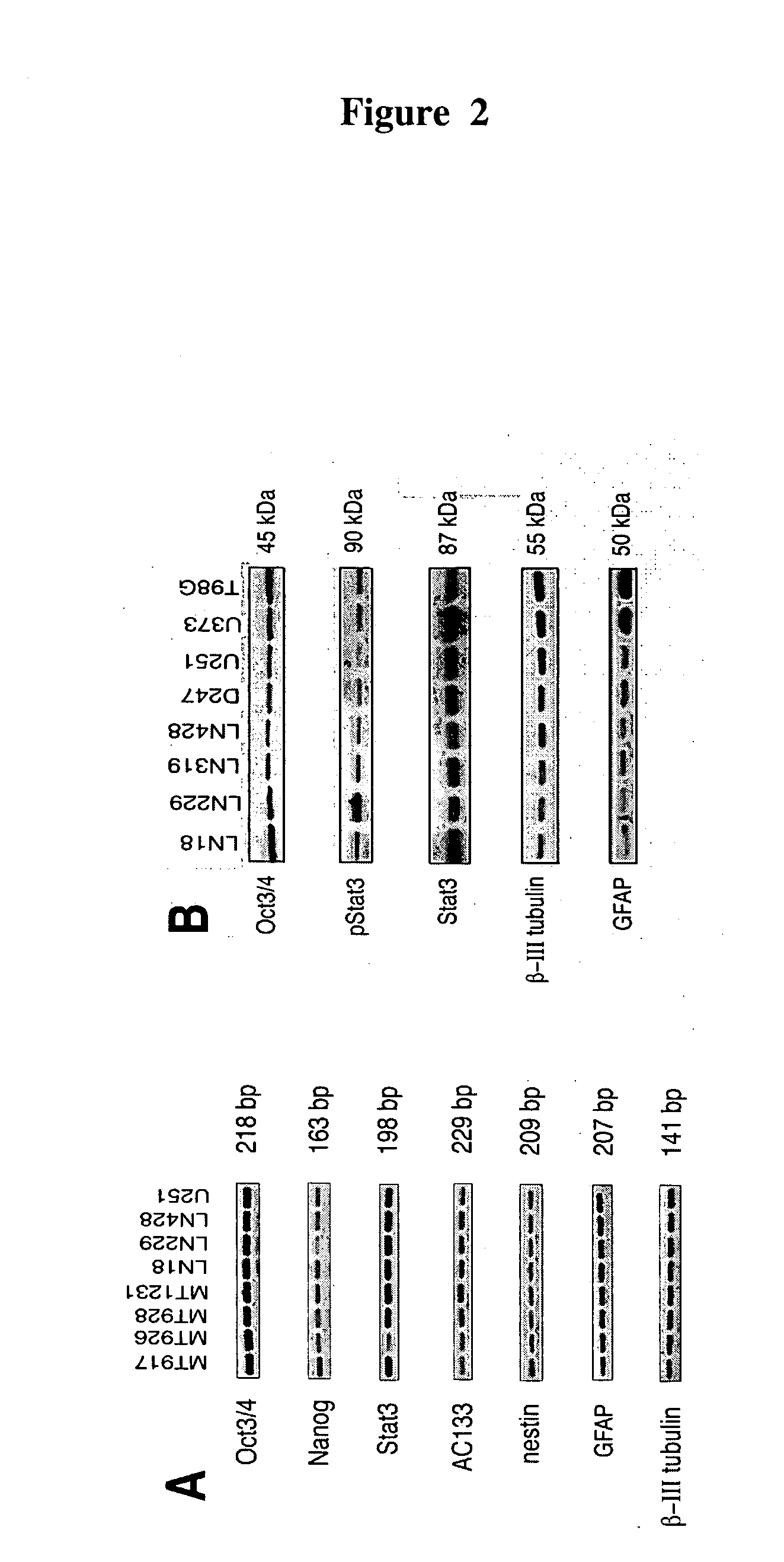
Compositions enriched in neoplastic stem cells and methods comprising same
A neoplastic stem cell population enriched for expression of the OCT4 transcription factor as well as methods for their identification, isolation and enrichment are described. The OCT4-enriched neoplastic stem cell population is further utilized for the induction and analysis of cancer in an animal. In addition, methods of preventing, abrogating, or inhibiting cancer, tumor growth, and metastasis via OCT4 inhibition are further provided.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Biotic and abiotic stress tolerance in plants
InactiveUS20090138981A1Improve the immunityIncreased susceptibilityBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyNucleotide
Transcription factor polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into nucleic acid constructs, including expression vectors, have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these constructs have been shown to be more resistant to disease (in some cases, to more than one pathogen), or more tolerant to an abiotic stress (in some cases, to more than one abiotic stress). The abiotic stress may include, for example, salt, hyperosmotic stress, water deficit, heat, cold, drought, or low nutrient conditions.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
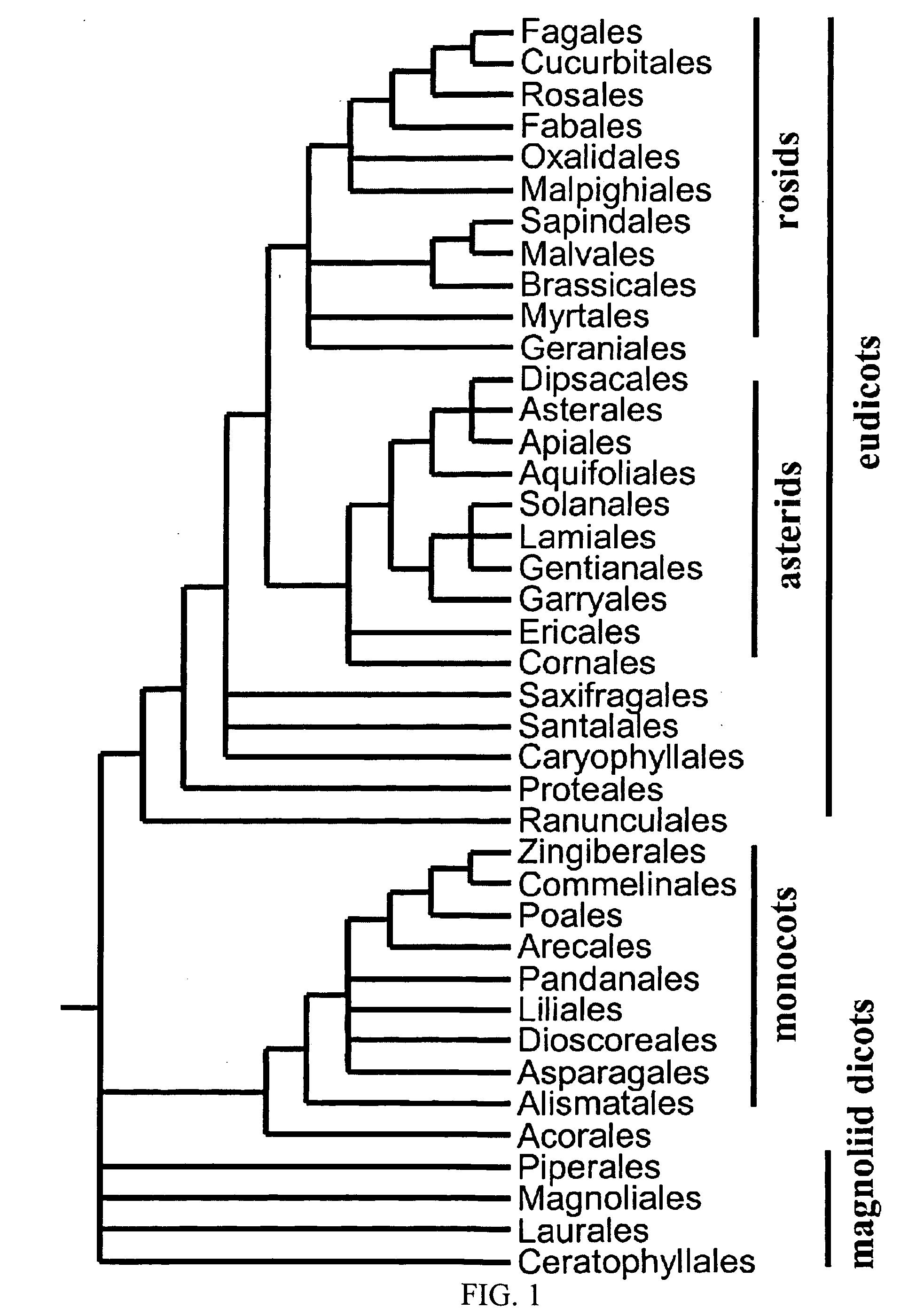
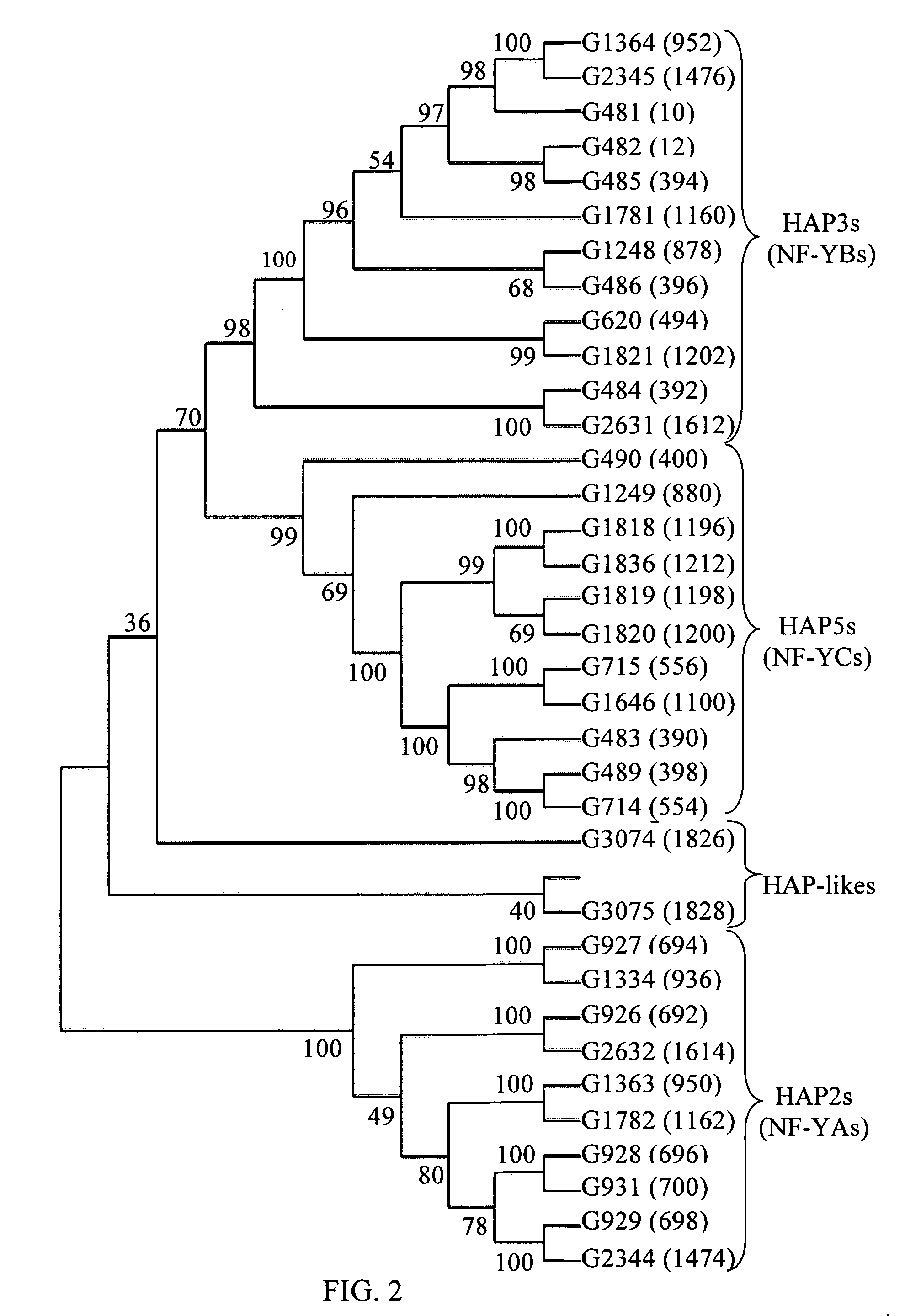
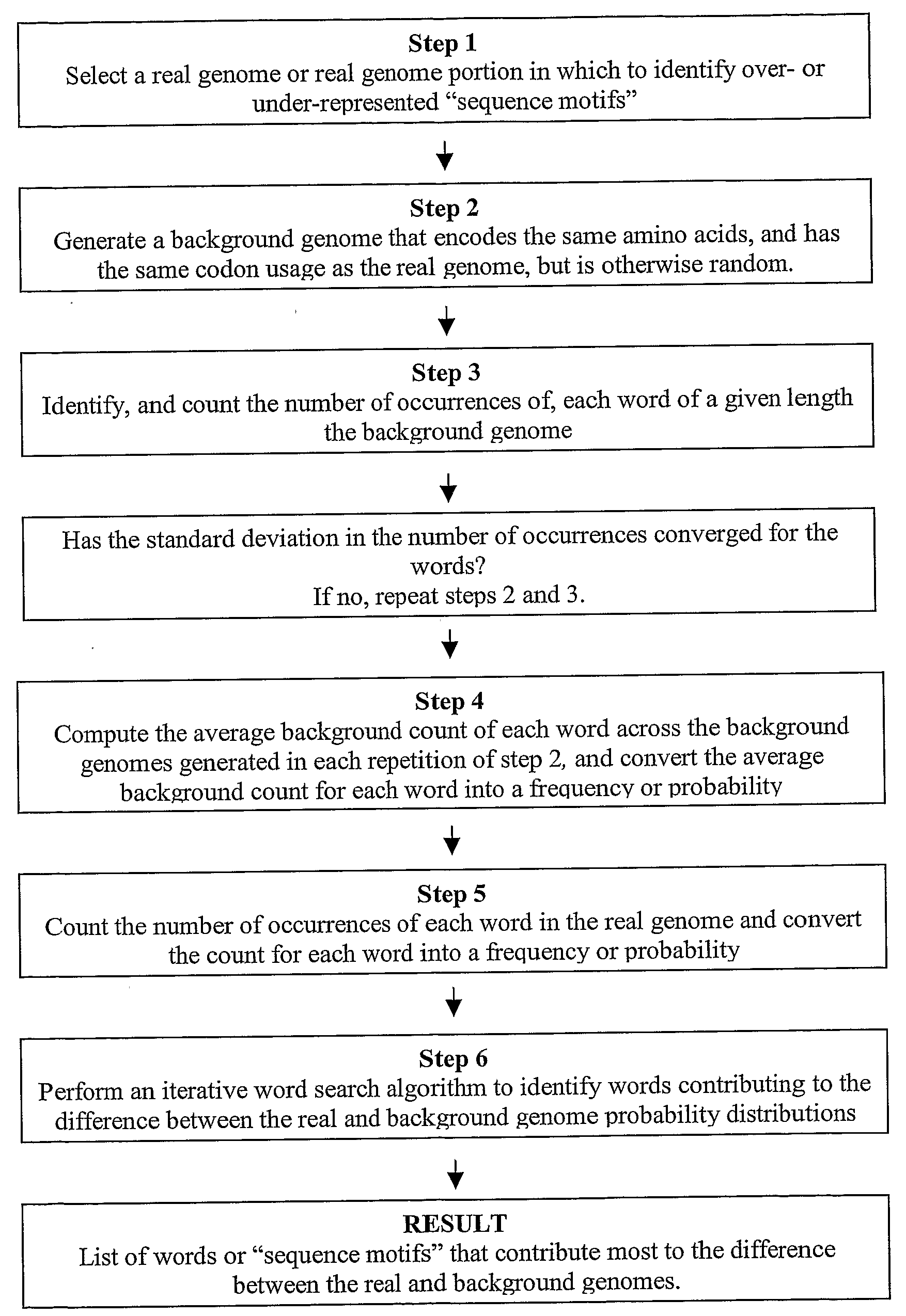
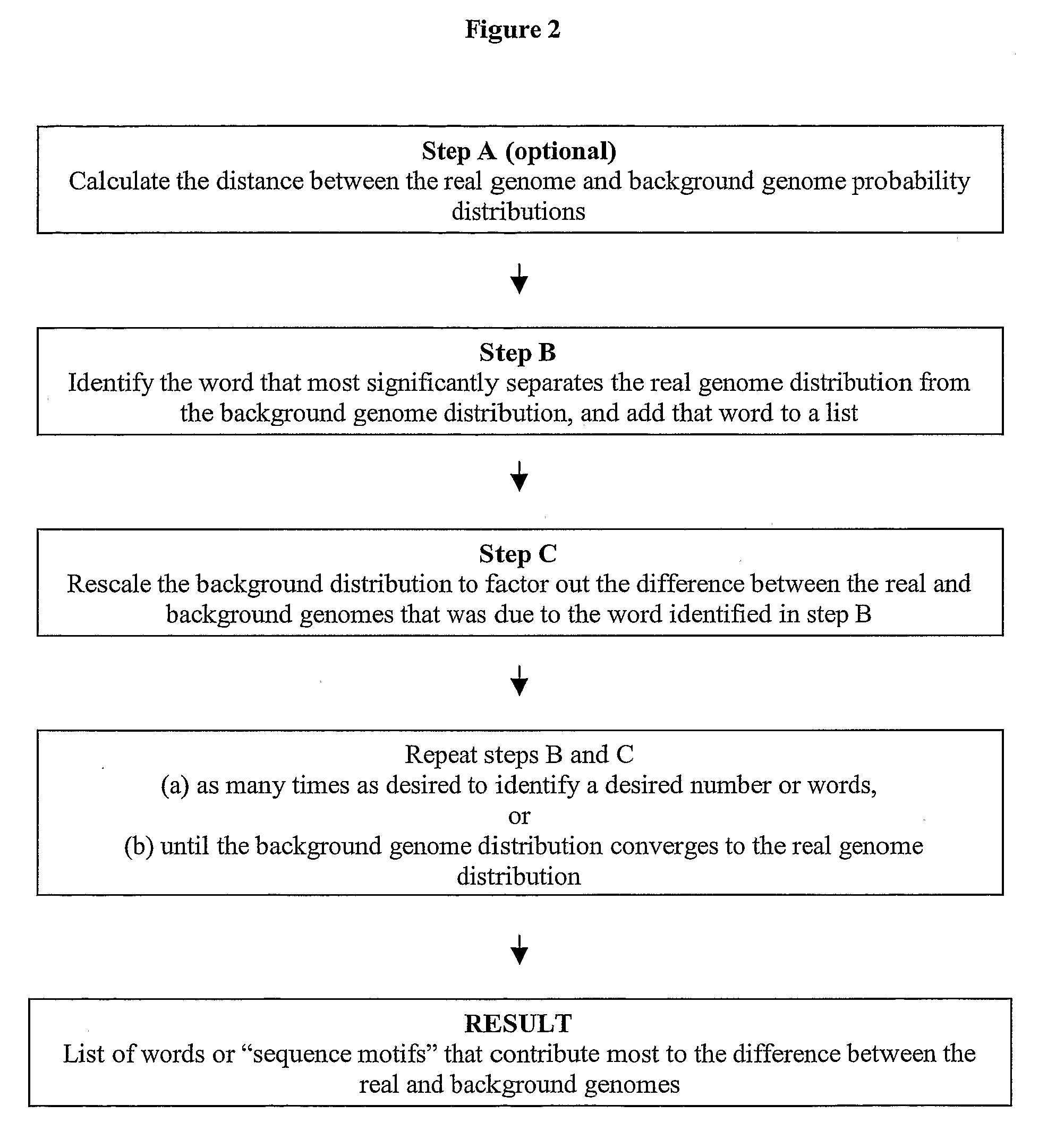
Methods for identifying sequence motifs, and applications thereof
InactiveUS20090208955A1Reduce in quantityIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBinding siteInstability
The present invention relates to methods and algorithms that can be used to identify sequence motifs that are either under- or over-represented in a given nucleotide sequence as compared to the frequency of those sequences that would be expected to occur by chance, or that are either under- or over-represented as compared to the frequency of those sequences that occur in other nucleotide sequences, and to methods of scoring sequences based on the occurrence of these sequence motifs. Such sequence motifs may be biologically significant, for example they may constitute transcription factor binding sites, mRNA stability / instability signals, epigenetic signals, and the like. The methods of the invention can also be used, inter alia, to classify sequences or organisms in terms of their phylogenetic relationships, or to identify the likely host of a pathogenic organism. The methods of the present invention can also be used to optimize expression of proteins.
Owner:INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY
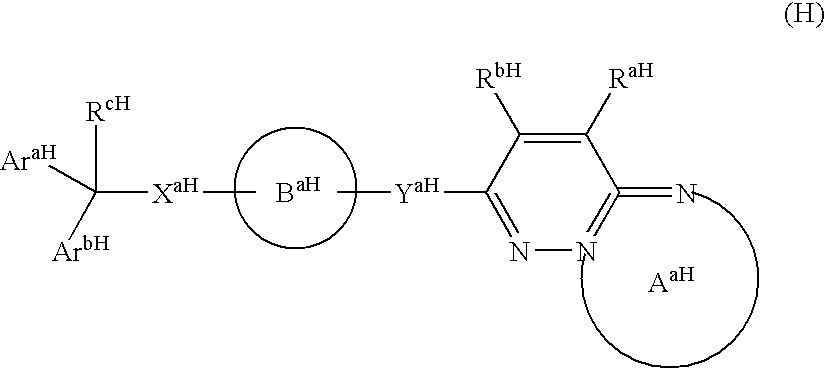
Novel fused heterocyclic compound and use thereof
The compound represented by the general formula (I): wherein, a fused ring AB represents a 5- to 10-membered fused heterocyclic ring; R1 represents (1) a hydrogen atom, (2) a halogen atom, (3) a cyano group, (4) an oxo group, (5) an optionally protected hydroxyl group, (6) an optionally protected carboxyl group, (7) an optionally protected amino group, (8) a cyclic group which may have a substituent (s), (9) an aliphatic hydrocarbon group which may have a substituent (s), or (10) an optionally protected thiol group; n represents 0 or an integer of 1 to 8; provided that n represents an integer of not less than 2, plural R1 are the same or different; a salt thereof, a solvate thereof or a prodrug thereof has a kinase (especially c-Jun N-terminal kinase) inhibitory activity and an inhibitory activity of a function of AP-1 as a transcription factor, it is useful as a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for a for example, a diabetes of metabolic disease, etc., a rheumatoid arthritis of inflammatory, etc.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
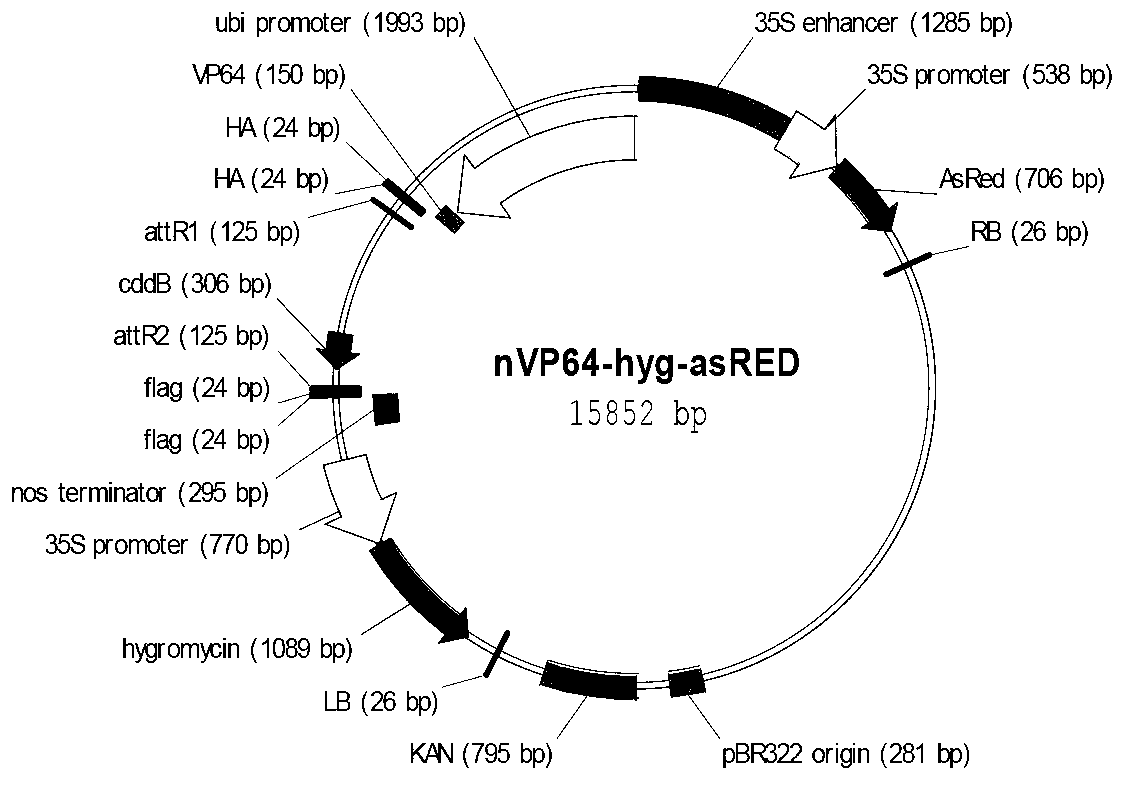
Application of rice transcription factor Os06g08400 genes
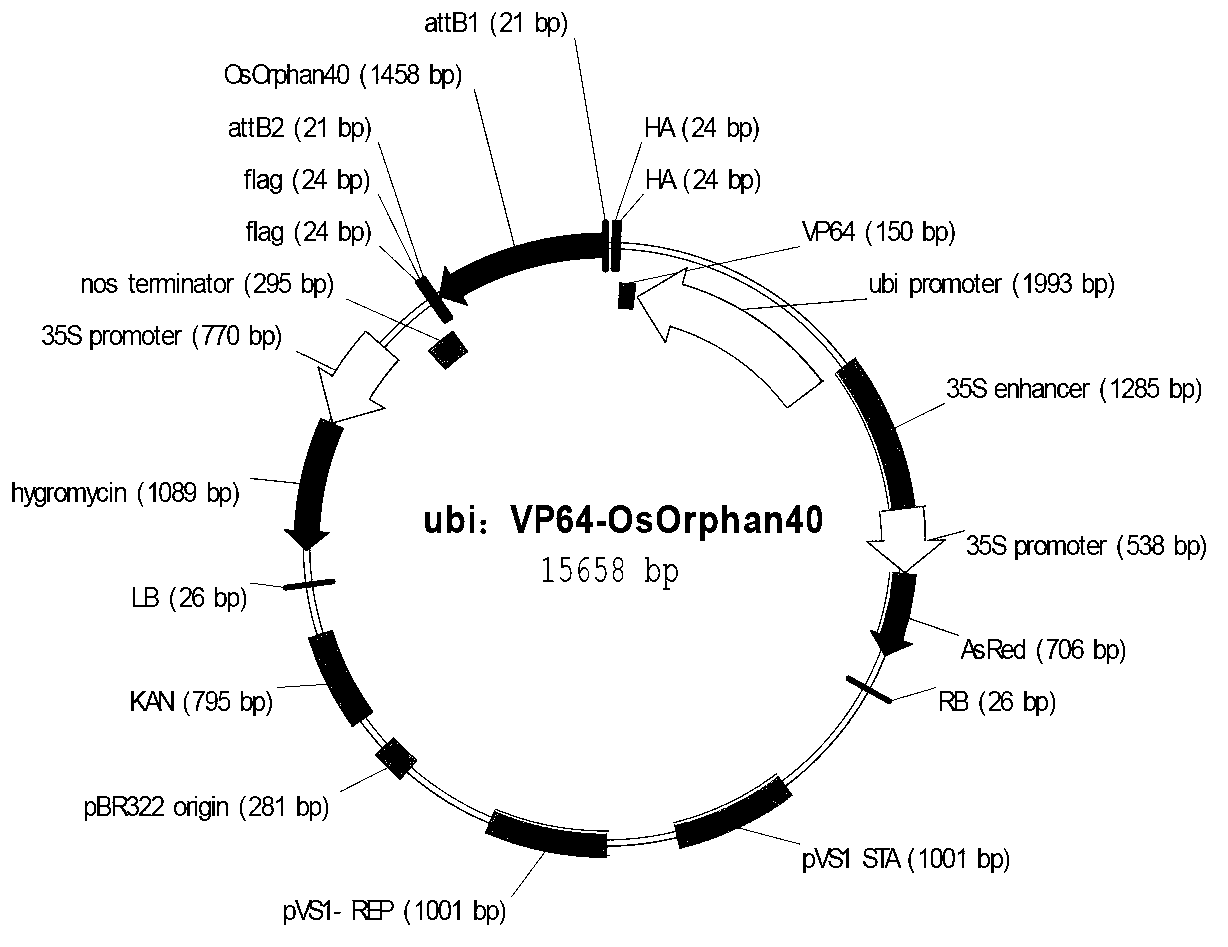
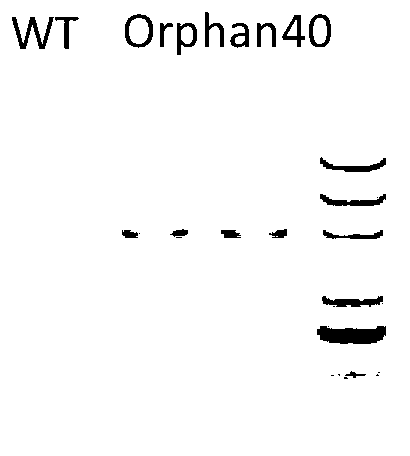
The invention relates to an application of rice transcription factor Os06g08400 genes. A transcription factor activation motif VP64, namely four transcription factor activation motifs VP16, is combined with the rice transcription factor Os06g08400 genes to establish a combined transcription factor, and then the combined transcription factor is converted into crops such as rice so that the characters of rice grains are improved, for example, the rice grains are obviously widened and thickened. The application related by the invention has an important theoretical value for detail definitions of a mechanism for regulating and controlling seed development, and the characters of the rice grains can be improved through a transgene means, so that the application related by the invention is also of importance in production practices.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Environmental stress-responsive promoter and genes encoding transcriptional factor
The present invention provides a stress responsive promoter. The environmental stress responsive promoter of the present invention comprises DNA of the following (a), (b) or (c): (a) DNA consisting of any nucleotide sequence selected from SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 90; (b) DNA consisting of a nucleotide sequence comprising a deletion, substitution or addition of one or more nucleotides relative to any nucleotide sequence selected from SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 90, and functioning as an environmental stress responsive promoter; and (c) DNA hybridizing under stringent conditions to DNA consisting of any nucleotide sequence selected from SEQ ID NOS: 1 to 90, and functioning as an environmental stress responsive promoter.
Owner:RIKEN
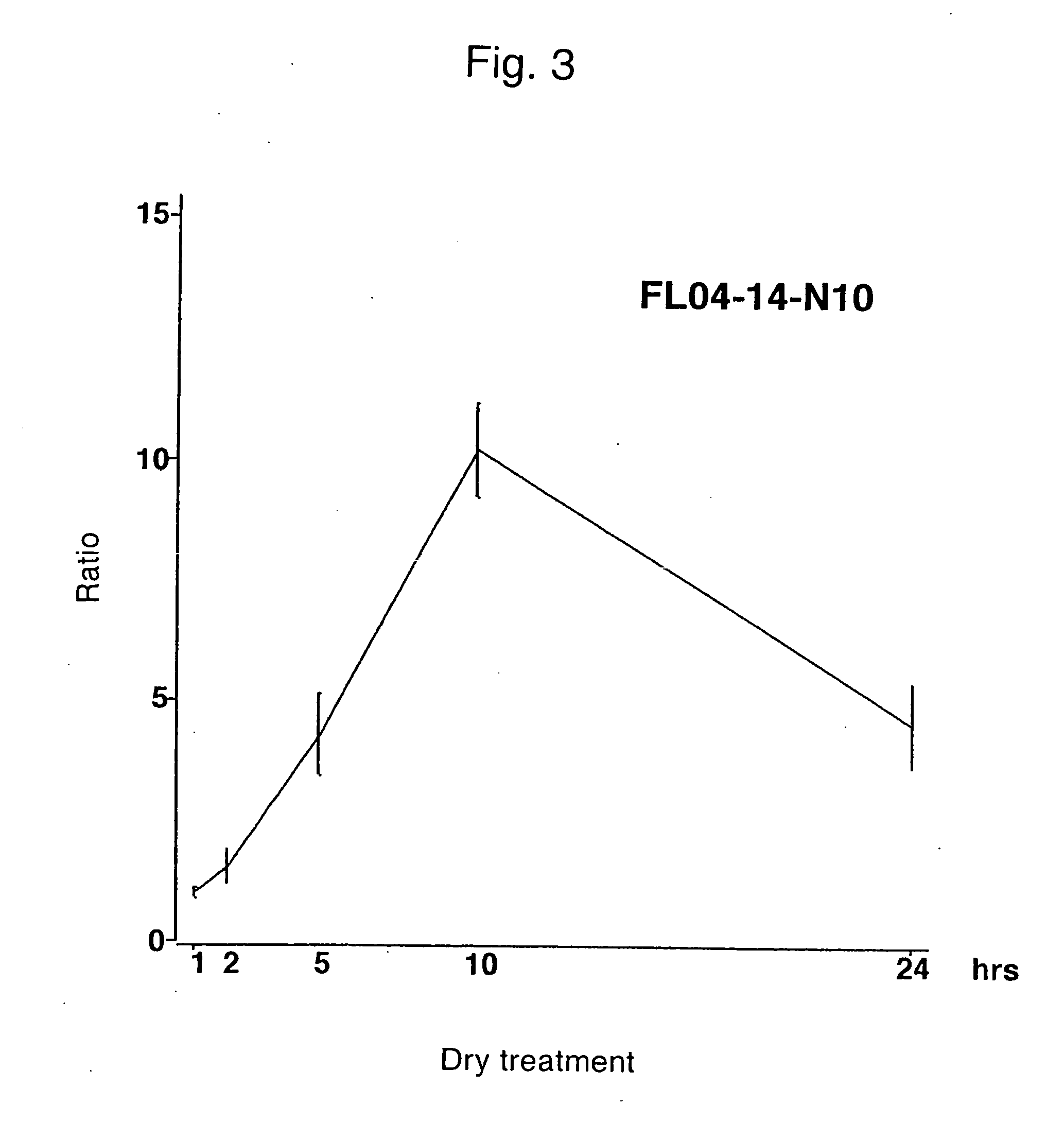
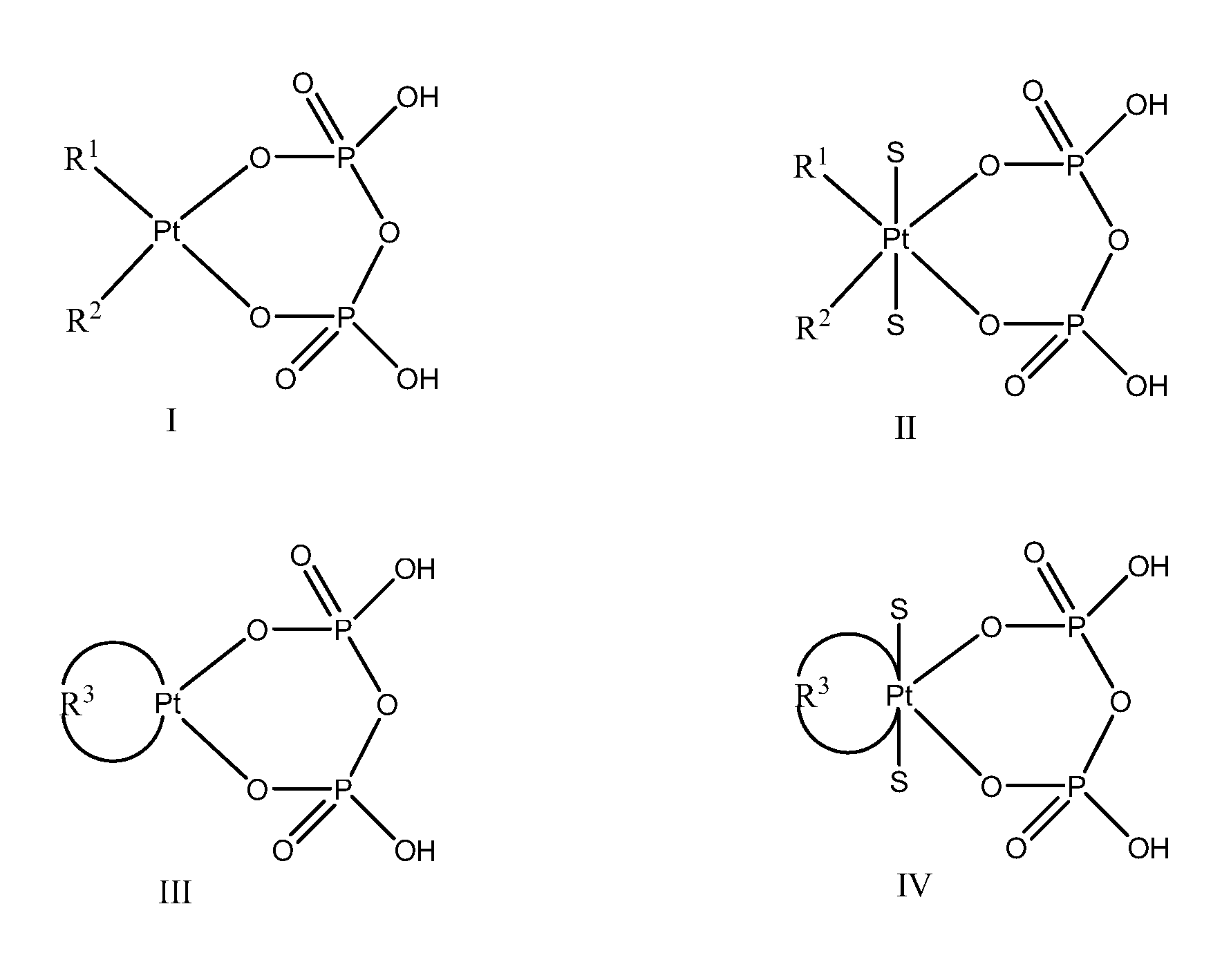
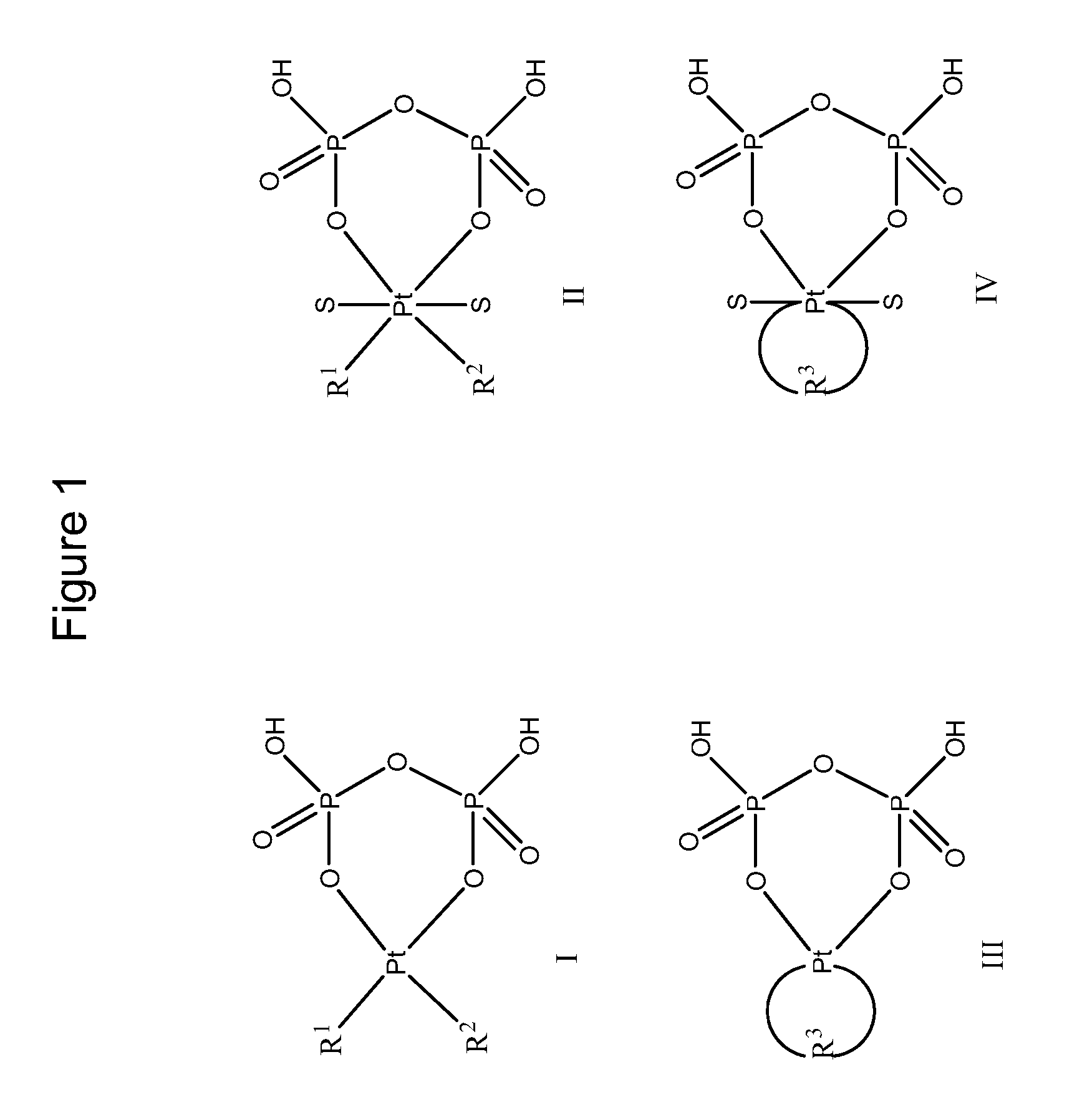
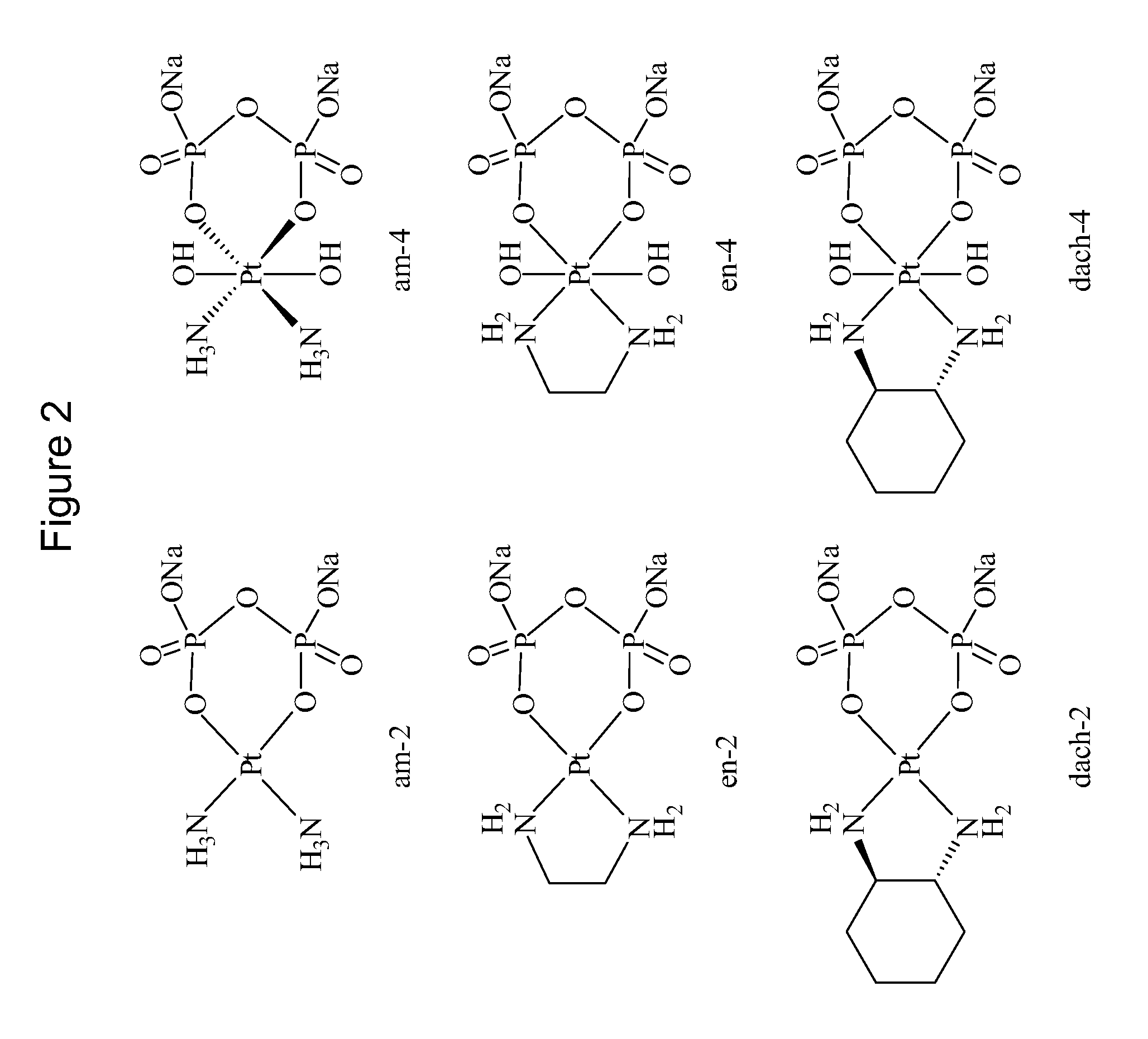
Phosphaplatins and their use in the treatment of cancers resistant to cisplatin and carboplatin
The present invention provides phosphaplatins, stable isolated monomeric phosphate complexes of platinum (II) and (IV), and methods of use thereof for treating cancers, including cisplatin- and carboplatin-resistant cancers. Unlike cisplatin, these complexes do not readily undergo hydrolysis and are quite soluble and stable in aqueous solutions. Moreover, these complexes—unlike cisplatin, carboplatin, and related platinum-based anti-cancer agents—do not bind DNA. Rather, data suggests that phosphaplatins trigger overexpression of fas and fas-related transcription factors and some proapoptotic genes such as Bak and Bax. Nevertheless, the complexes exhibit tremendous cytotoxicity towards cancer cells. Thus, the present invention provides novel platinum anticancer agents that have a different molecular target than those in the art.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Stress tolerance in plants
Transcription factor polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into nucleic acid constructs, including expression vectors, have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these constructs have been shown to be more resistant to disease (in some cases, to more than one pathogen), or more tolerant to an abiotic stress (in some cases, to more than one abiotic stress). The abiotic stress may include, for example, salt, hyperosmotic stress, water deficit, heat, cold, drought, or low nutrient conditions.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Cotton fiber transcriptional factors
Novel DNA constructs are provided which may be used as molecular probes or inserted into a plant host to provide for modification of transcription of a DNA sequence of interest in cotton fiber, particularly in very early fiber development. The DNA constructs comprise a cotton fiber transcriptional initiation regulatory region associated with a gene which is expressed in cotton fiber.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Conferring biotic and abiotic stress tolerance in plants
The invention relates to plant transcription factor polypeptides, polynucleotides that encode them, homologs from a variety of plant species, and methods of using the polynucleotides and polypeptides to produce transgenic plants having advantageous properties, tolerance low nitrogen, cold and water deficit conditions, and resistance to disease, as compared to wild-type or other control plants.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Transcription regulatory gene and peptide
ActiveUS20050183169A1Simple structurePotent capacity for repressing transcription of genePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsTranscription Regulation GeneMetabolic enzymes
This invention relates to a peptide or protein capable of converting a transcription factor into a transcriptional repressor, a gene encoding such peptide or protein, a chimeric protein in which the aforementioned peptide or protein is fused to a transcription factor, a chimeric gene in which the gene encoding a peptide or protein is fused to a gene encoding a transcription factor, a recombinant vector having such chimeric gene, and a transformant comprising such recombinant vector. The peptide of the invention that is capable of converting a transcription factor into a transcriptional repressor is very short. Thus, it can be very easily synthesized, and it can effectively and selectively repress the transcription of a specific gene. Accordingly, such gene is applicable to and useful in a wide variety of fields, such as repression of the expression of cancerous genes and regulation of the expression of genes encoding pigment-metabolic enzymes.
Owner:GREENSOGNA +1
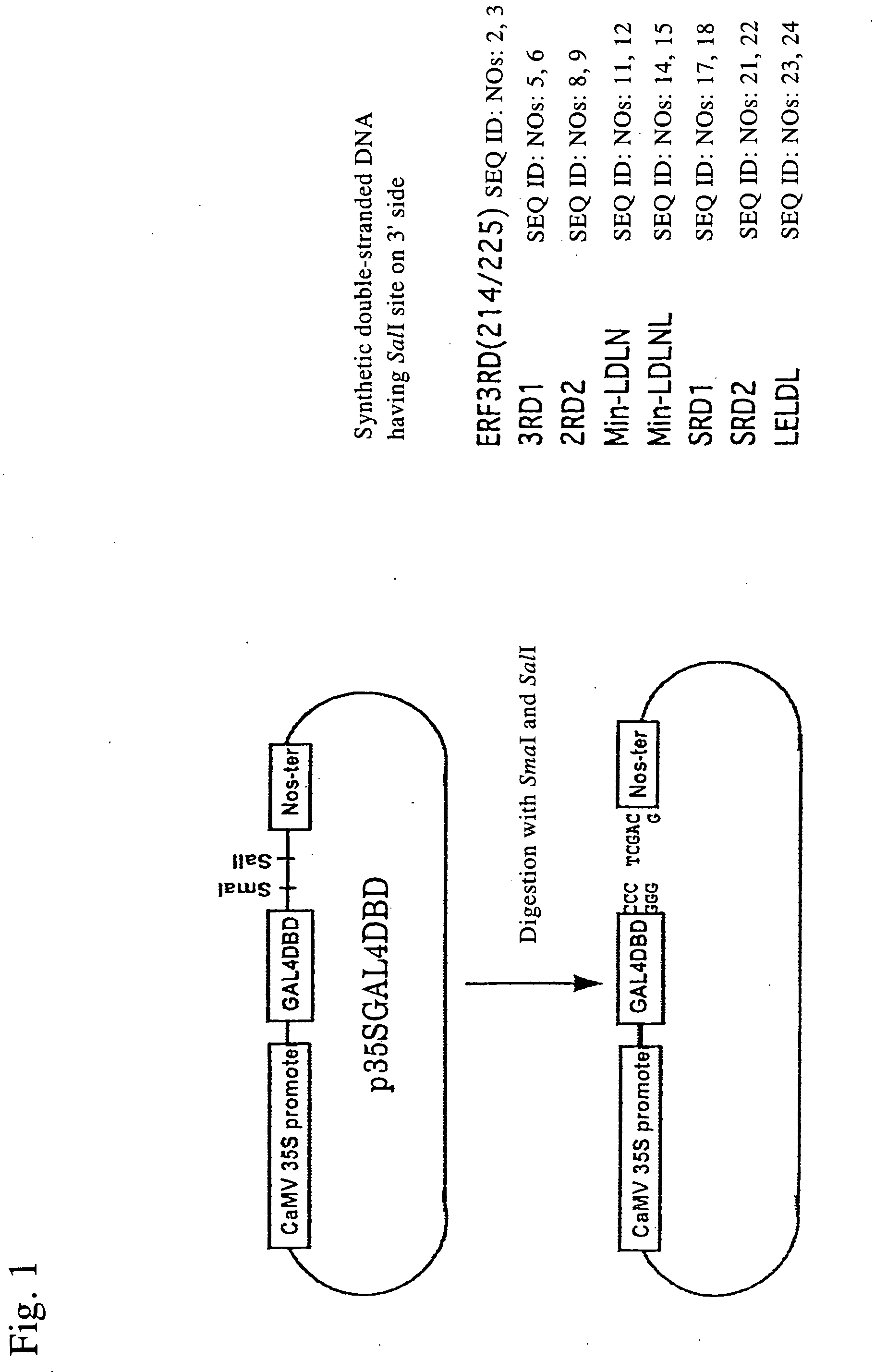
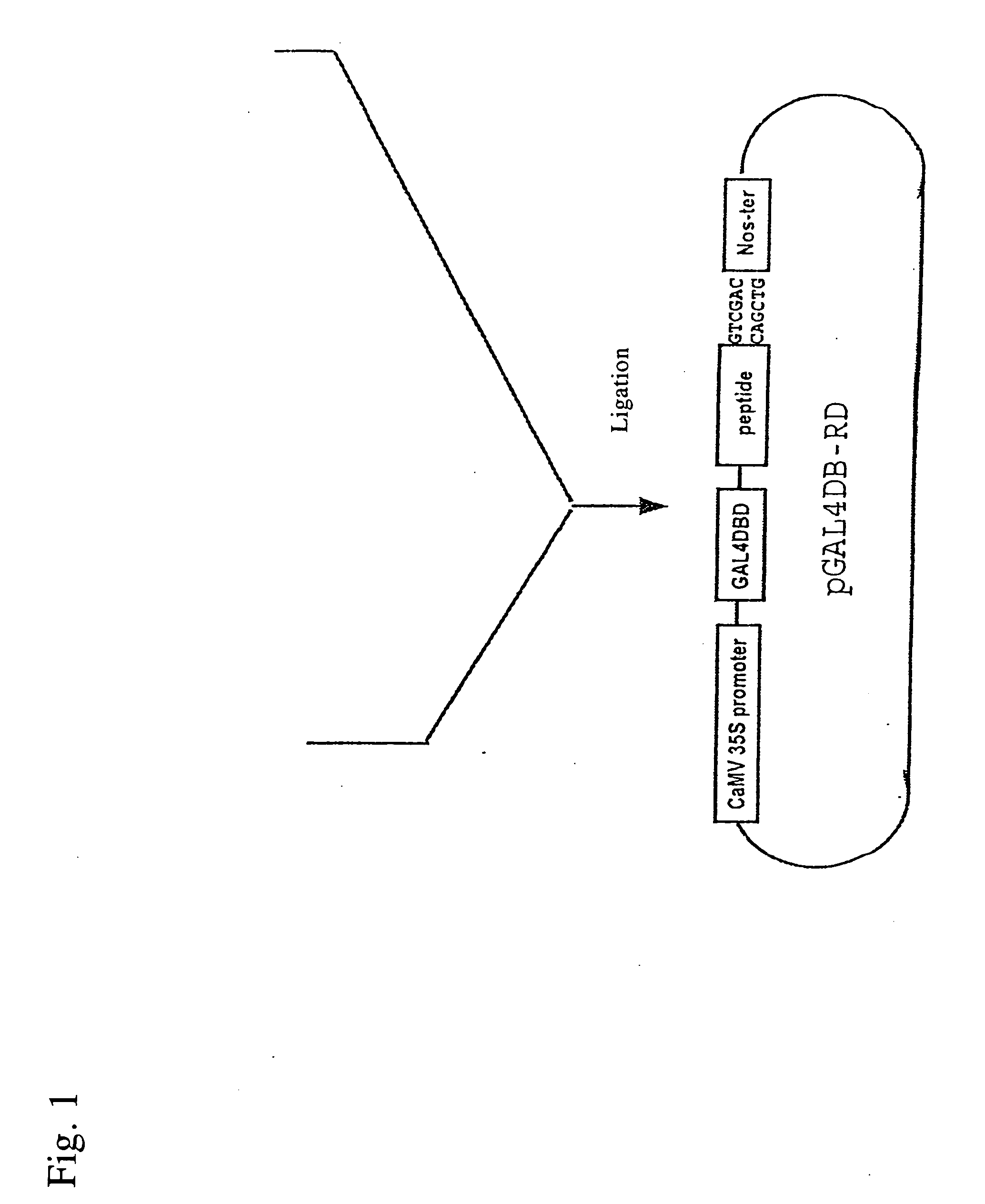
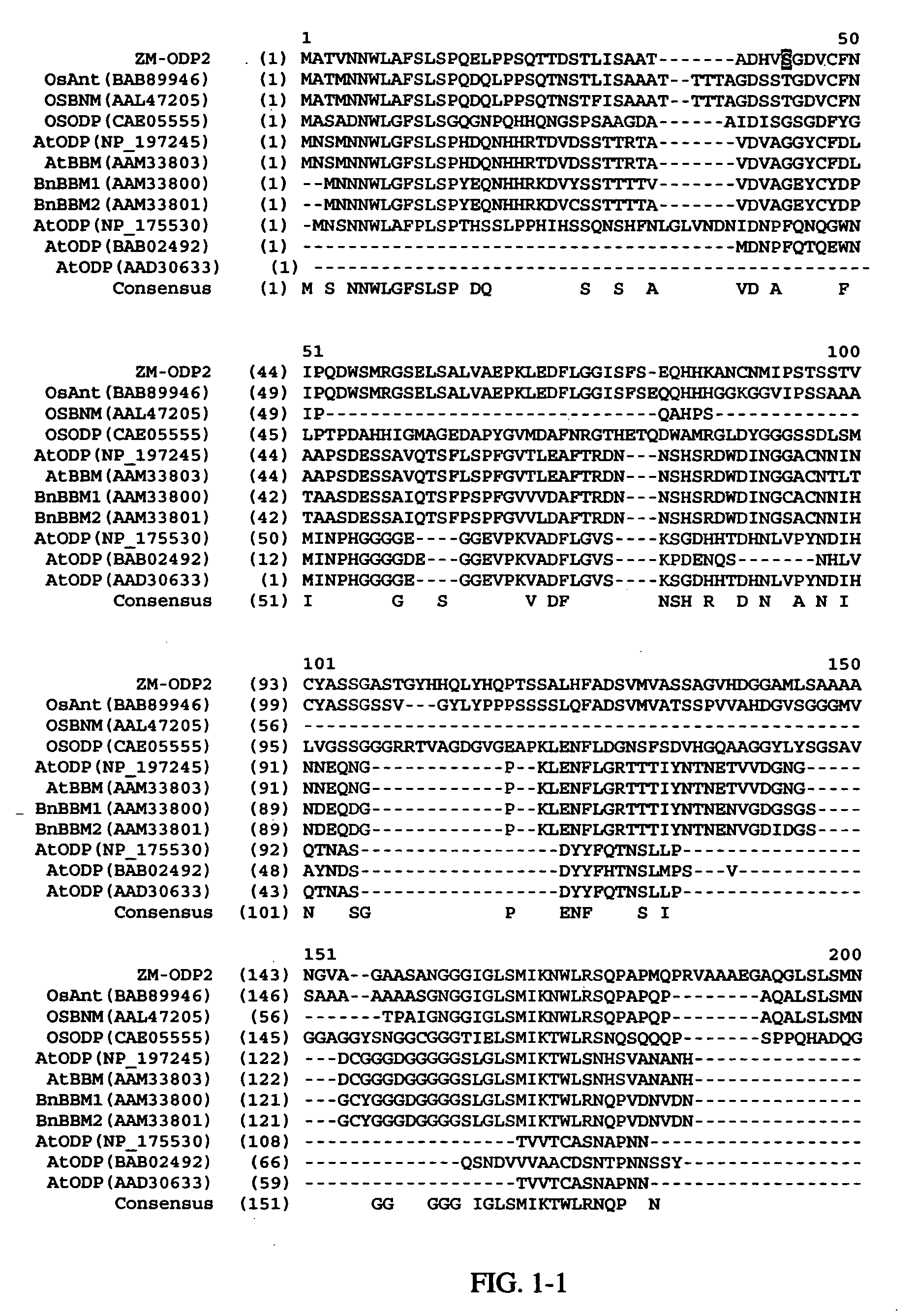
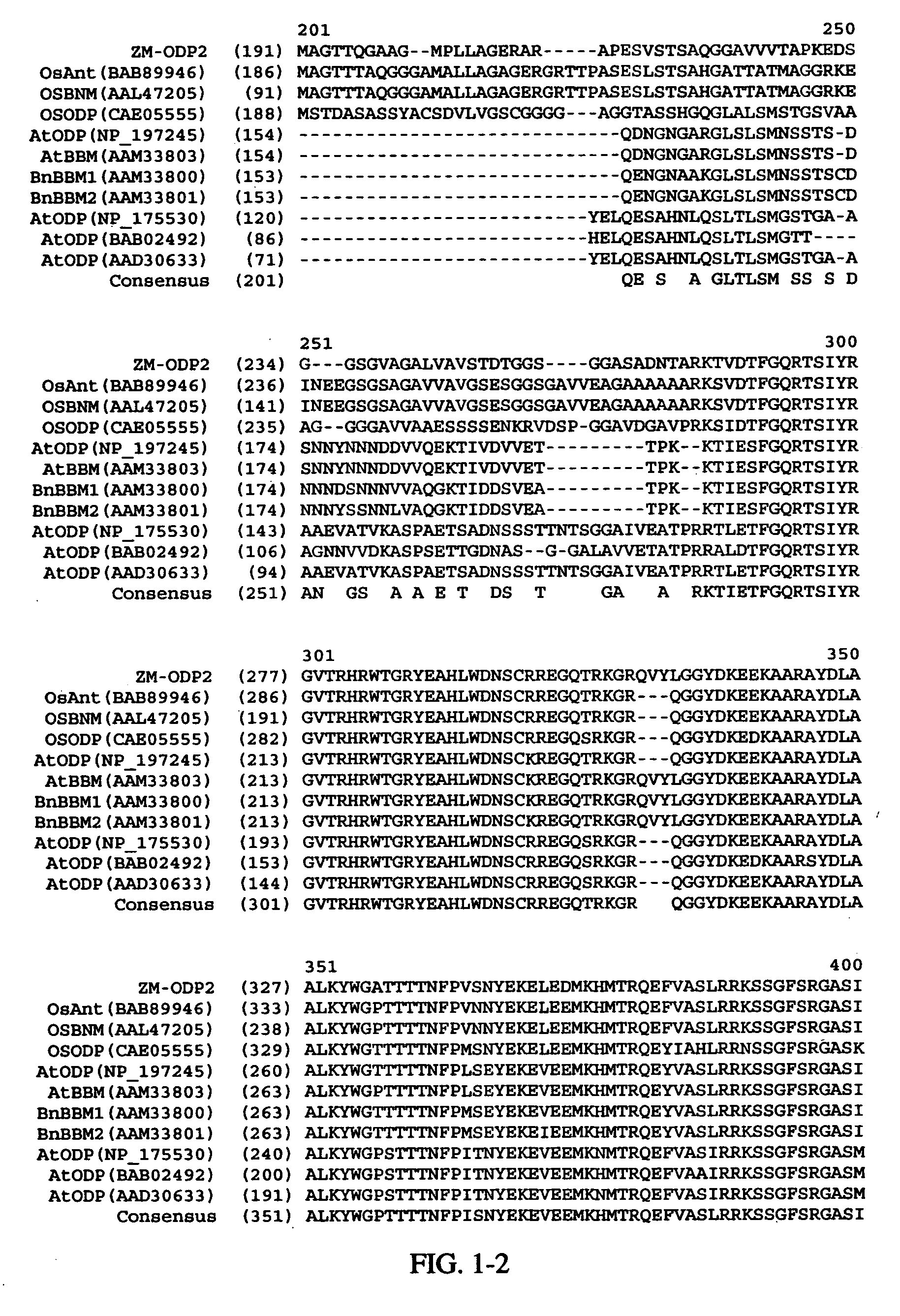
AP2 domain transcription factor ODP2 (ovule development protein 2) and methods of use
ActiveUS20050257289A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove planting efficiencySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationNucleotideTransformation efficiency
Methods and compositions for modulating plant development are provided. Nucleotide sequences and amino acid sequences encoding Ovule Development Protein 2 (ODP2) proteins are provided. The sequences can be used in a variety of methods including modulating development, developmental pathways, altering oil content in a plant, increasing transformation efficiencies, modulating stress tolerance, and modulating the regenerative capacity of a plant. Transformed plants, plant cells, tissues, and seed are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Decoy composition for treating and preventing inflammatory disease
It is intended to efficiently treat an inflammatory disease without causing side effects. This object can be achieved by providing a medicinal composition for treating and preventing an inflammatory disease and disorders, and disorders caused by the disease and disorders which contains at least one decoy of NF-κB or an analogous transcriptional factor and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier; and a method of treating and preventing an inflammatory disease and disorders, and disorders caused by the disease and disorders which comprises the step of administering to a patient a composition containing at least one decoy of NF-κB or an analogous transcriptional factor and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
Transcriptional factor relevant to resistant adversity from Arabidopsis thaliana, coded gene, and application
This invention discloses stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor, its coding gene and application. The stress-tolerant R2R3 MYB transcription factor is derived from Arabidoesis thaliana, and can be applied in culturing stress-tolerant plants that can resist abscisic acid, high salt and draught. The transcription factor is one of the following amino acid residue sequences: (1) SEQ ID NO.1; (2) protein by substituting, deleting or adding 1-10 amino acid residues of SEQ ID NO.1, which can regulate the stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have important meaning to research on plant stress-tolerant mechanism, and method for improving draught, salt and stress tolerance of plants. The protein and its coding gene have potential application in stress-tolerant genetic engineering of plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
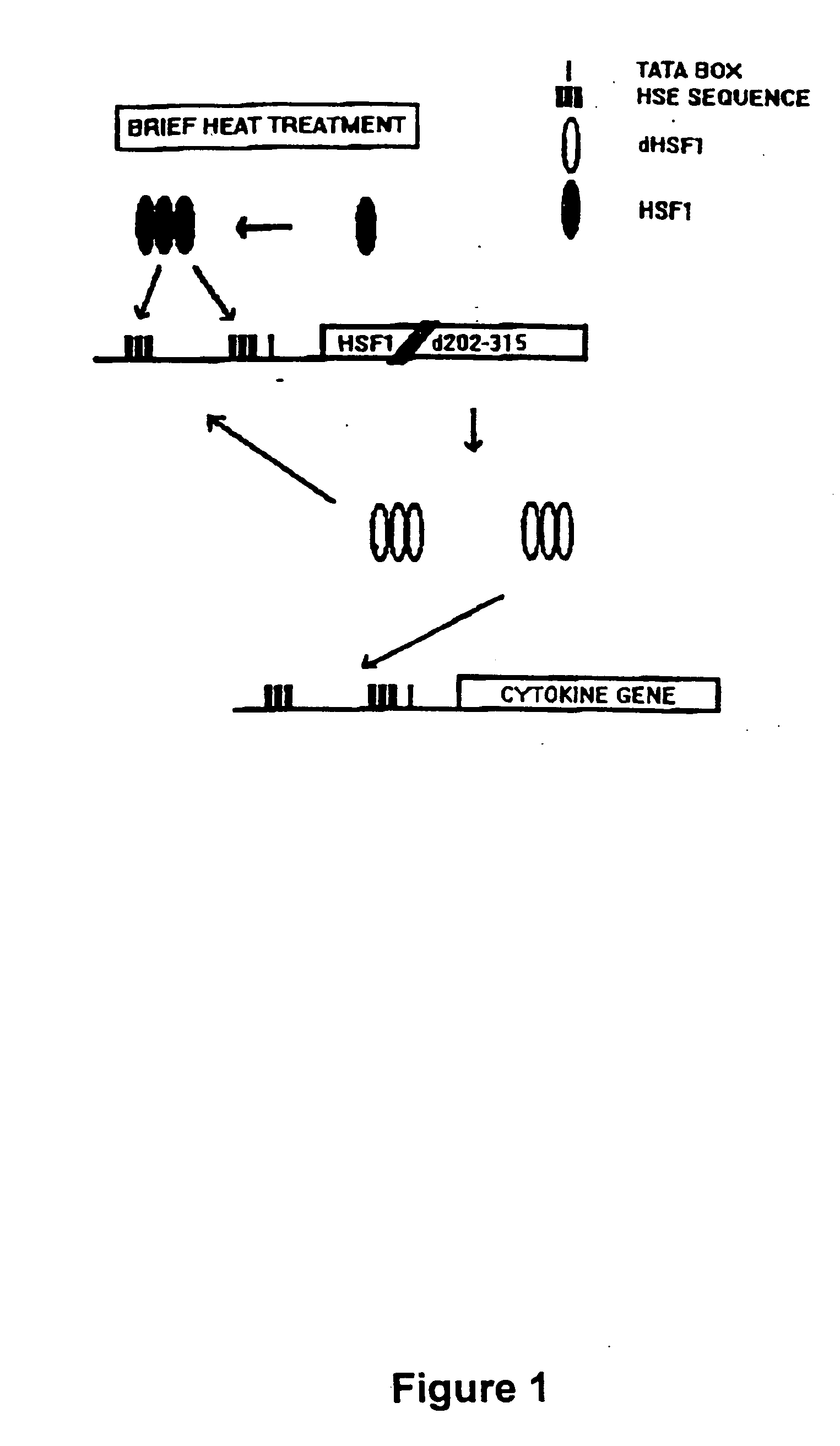
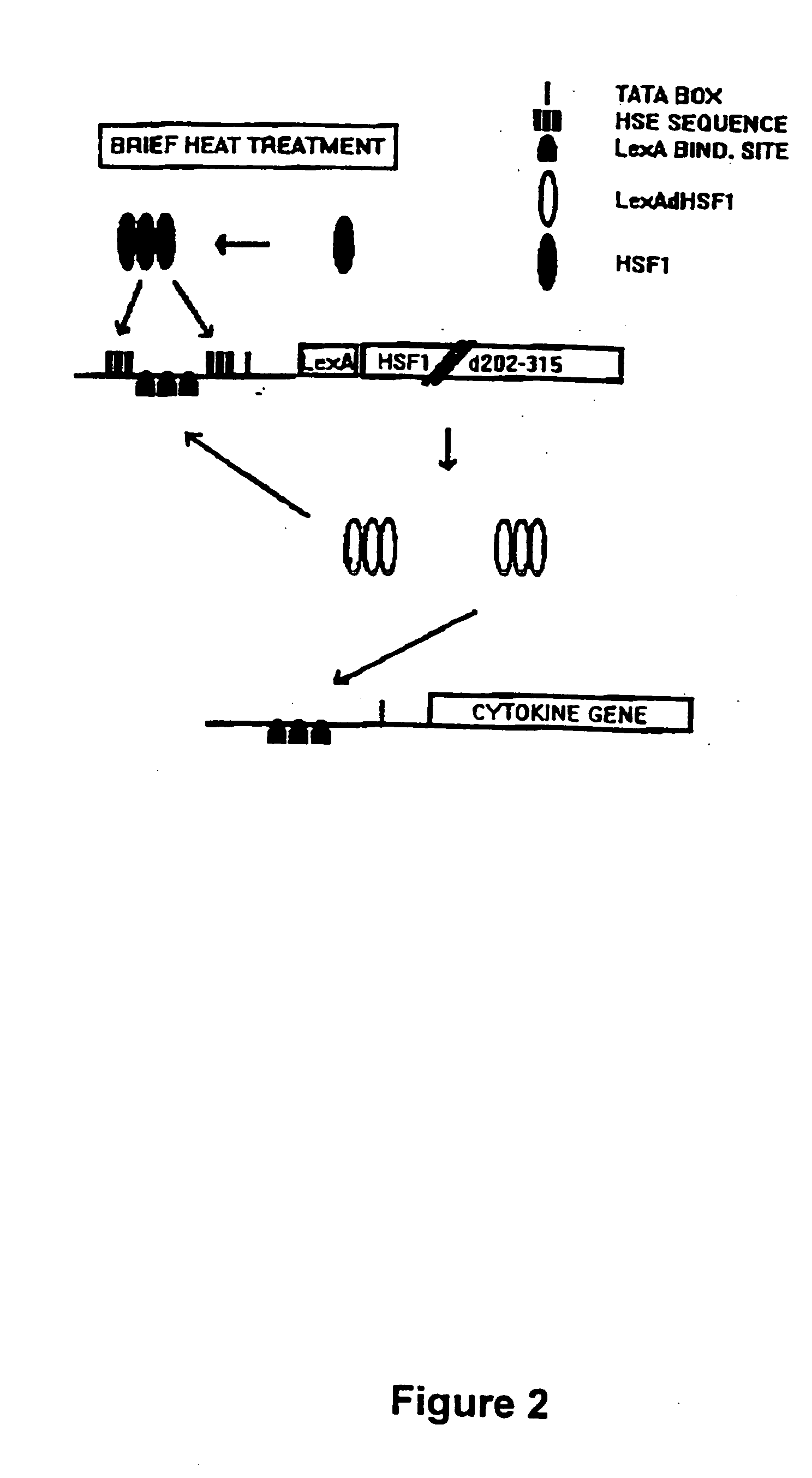
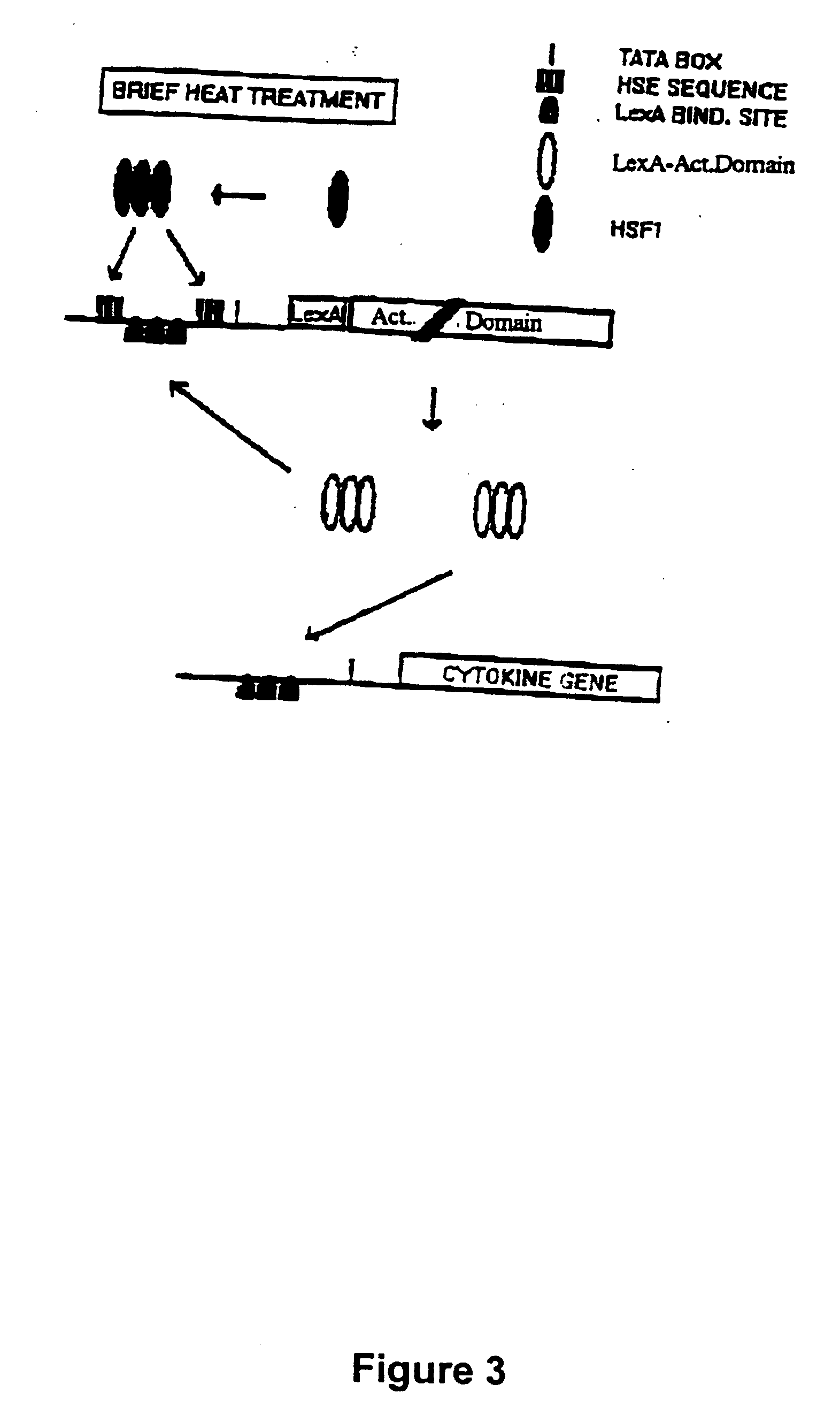
Molecular regulatory circuits to achieve sustained activation of genes of interest by a single stress
The exposure of cells, tissues and organs to “stress,” such as elevated temperature, stimulates production of active heat stress transcription factors (HSF), which in turn, induce expression of genes regulated by stress promoters. Normally, the activity of stress promoters declines after cells, tissues and organs are returned to a normal condition. The present invention relates to molecular circuits that provide for sustained expression of a gene of interest subsequent to a single application of stress. Generally, the molecular circuits of the invention comprise (a) a first nucleic acid molecule that comprises a gene encoding a transcription factor and a first promoter or a combination promoter activatable by stress and by the transcription factor, wherein the first promoter or the combination promoter and the transcription factor gene are operably linked, and (b) a second nucleic acid molecule that comprises a gene of interest and a second promoter activatable by the transcription factor, wherein the second promoter and the gene of interest are operably linked.
Owner:VOELLMY RICHARD
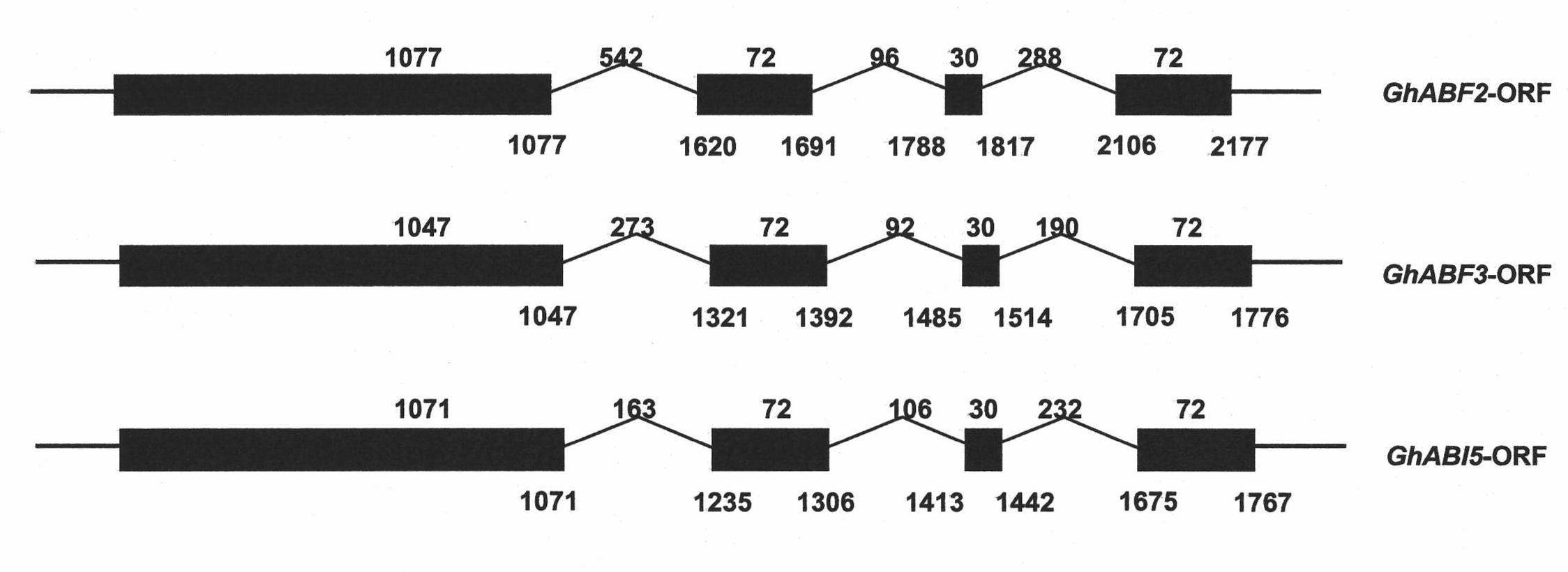
Three cotton ABF/AREB/ABI5/DPBF type transcription factors and coding genes and application thereof
InactiveCN102060919AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
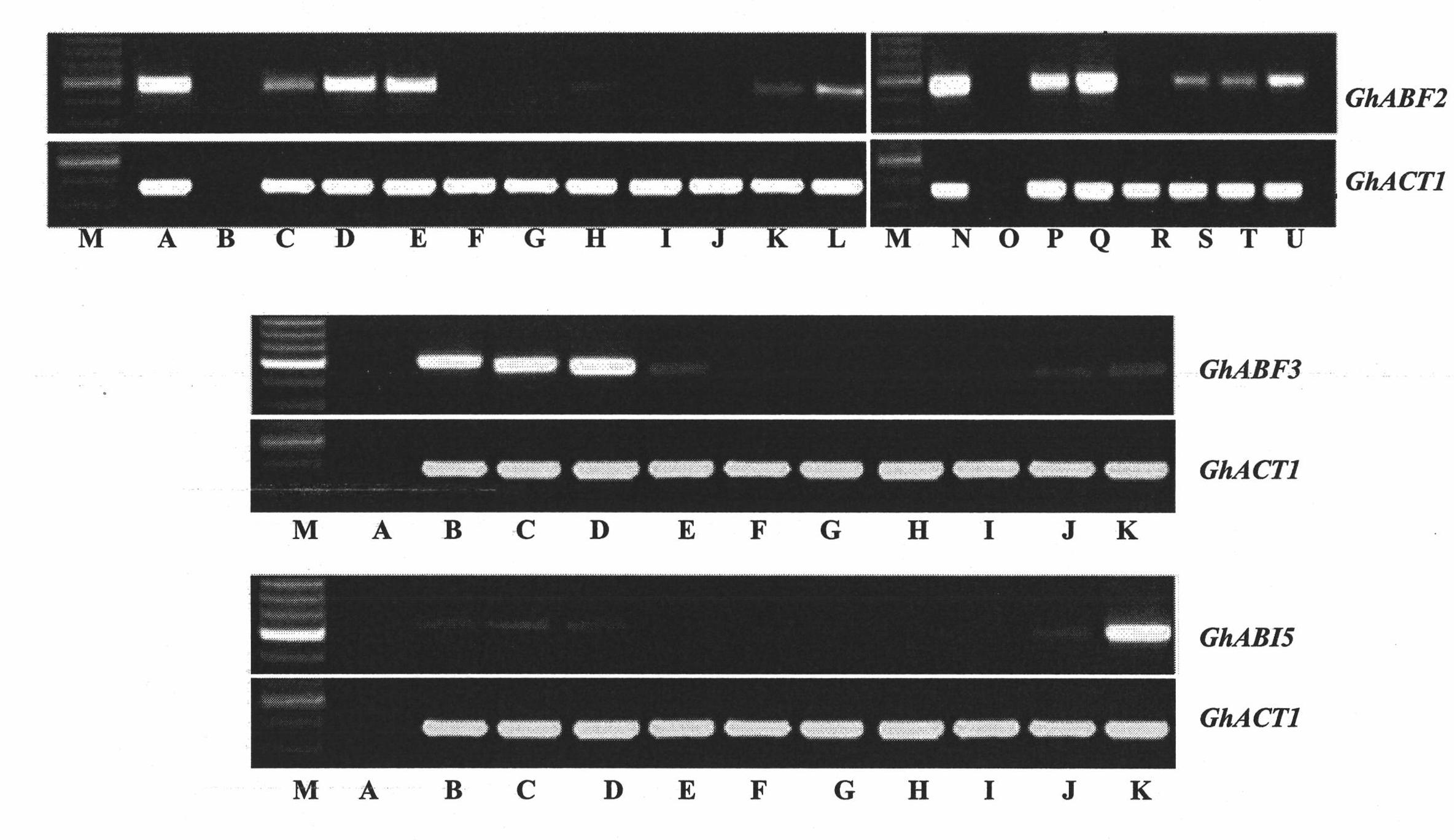
The invention discloses three novel cotton ABF / AREB / ABI5 / DPBF type transcription factors GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5, and coding genes and application thereof. Amino acid sequences of the GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5 are shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, 5 and 8 respectively. Nucleotide sequences of the coding genes GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5 are shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, 4 and 7 respectively. The invention also discloses the structural characteristics on genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and a ribonucleic acid (RNA) editing law of reading frame regions of the coding genes GhABF2, GhABF3 and GhABI5. The invention also discloses the cotton expression characteristics and yeast expression characteristics of the three genes and the characteristic that the three genes can improve the drought resistance of arabidopsis thaliana. The genes provide gene resources for culturing a plant variety resistant to abiotic stress, and have great significance for improving the abiotic stress resistance of plants.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Compositions and methods for improved plant feedstock
ActiveUS20120322122A1Improving biofuel feedstockReducing lignin productionSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationBiologyTranscription factor
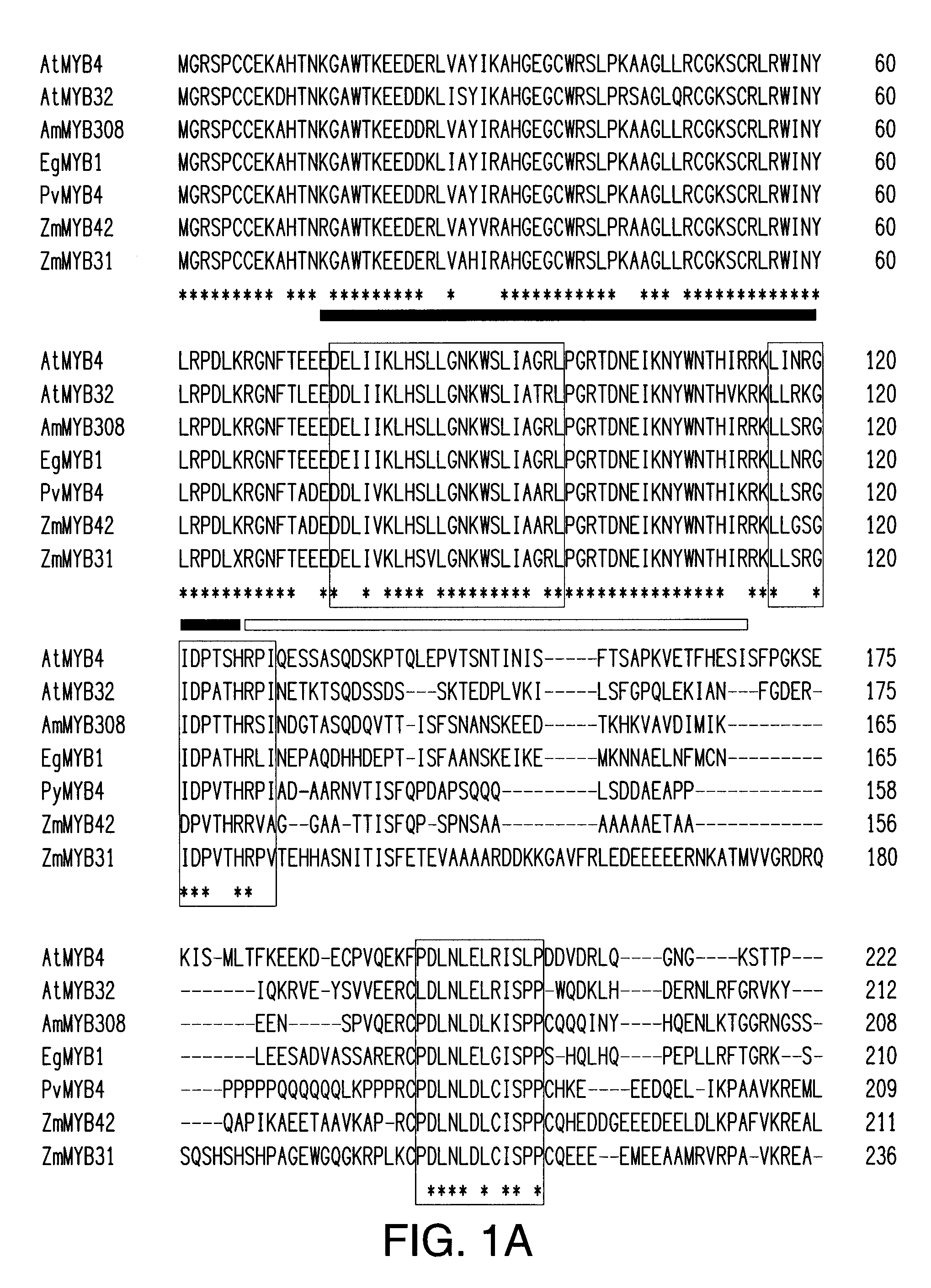
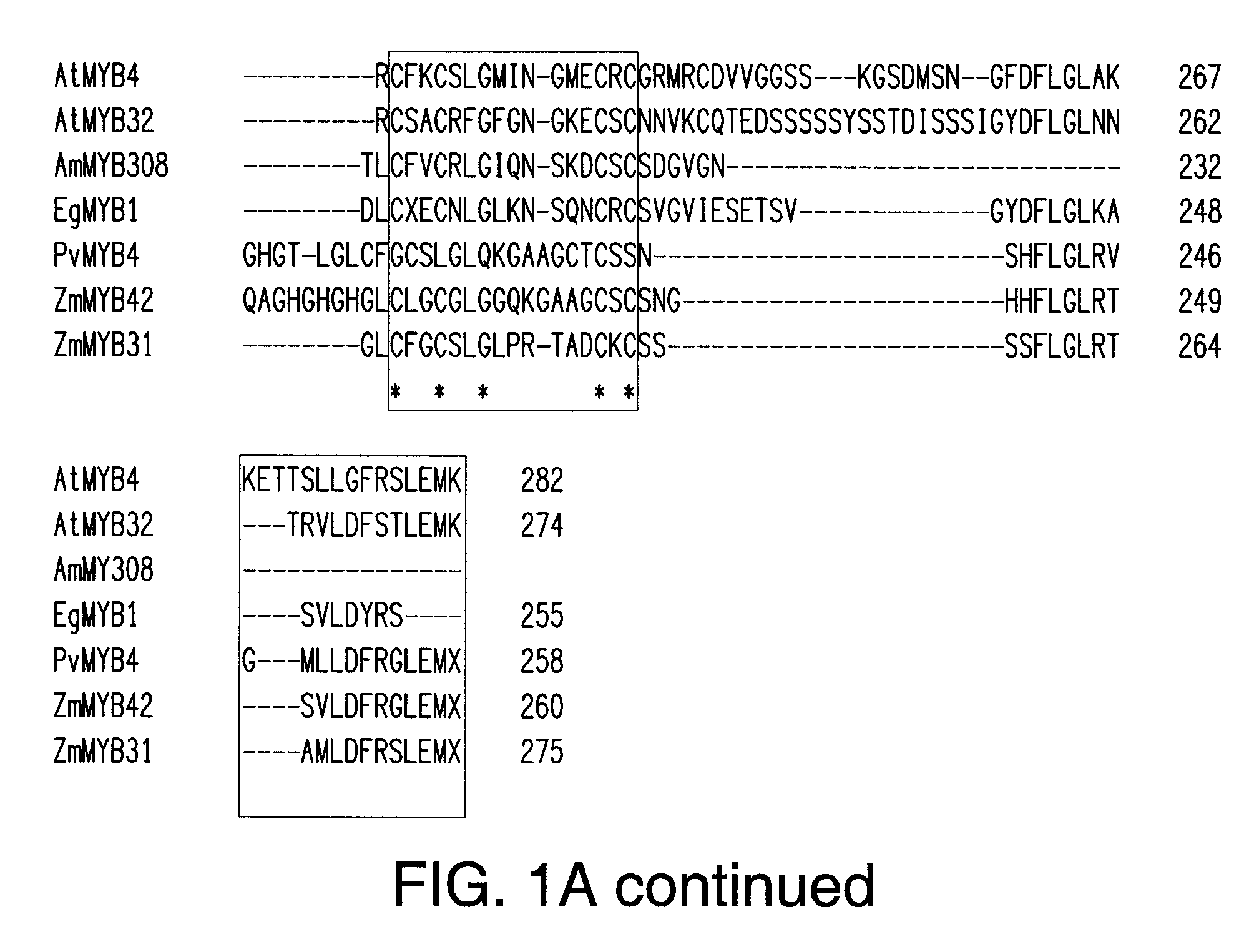
The invention provides methods for modifying lignin content and composition in plants and achieving associated benefits therefrom involving altered expression of newly discovered MYB4 transcription factors. Nucleic acid constructs for modifying MYB4 transcription factor expression are described. By over-expressing the identified MYB4 transcription factors, for example, an accompanying decrease in lignin content may be achieved. Plants are provided by the invention comprising such modifications, as are methods for their preparation and use.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Plants having improved growth characteristics and methods for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GRP (Growth-Related Protein). The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GRP, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. The GRP may be one of the following: Seed Yield Regulator (SYR), FG-GAP1 CYP90B, CDC27, AT-hook transcription factors, DOF transcription factors and Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitors (CKIs).
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
A method, kit and application for preparing induced pluripotent stem cells
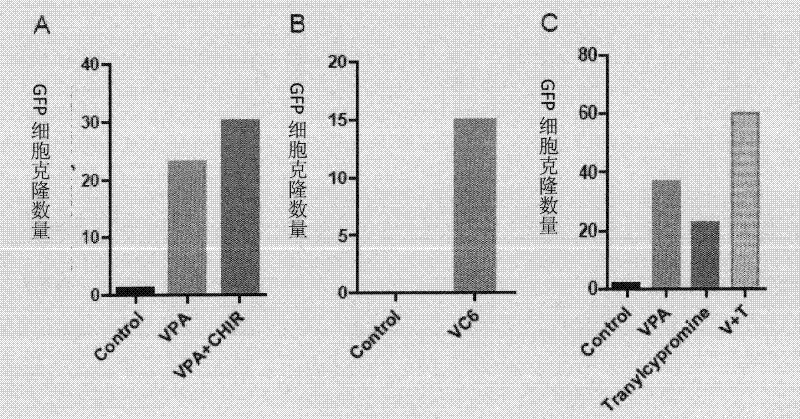
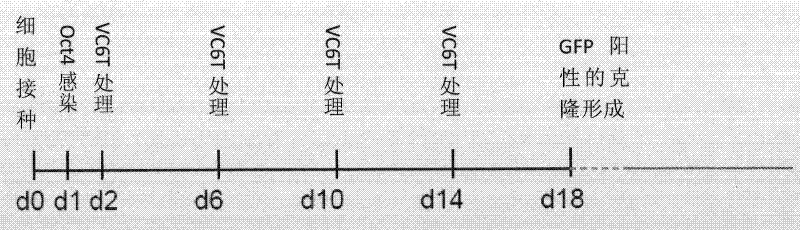
The invention provides a method for preparing induced pluripotent stem cells. A combination of 4 small molecule compounds (HDAC inhibitor, GSK3-beta inhibitor, TGF-beta inhibitor and H3K4 demethylation inhibitor) or at least two of them (such as GSK3 -beta inhibitor and TGF-beta inhibitor), can induce induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) under the condition of introducing only one transcription factor (Oct4).
Owner:BEIJING RUIPU CHENCHUANG TECH +1
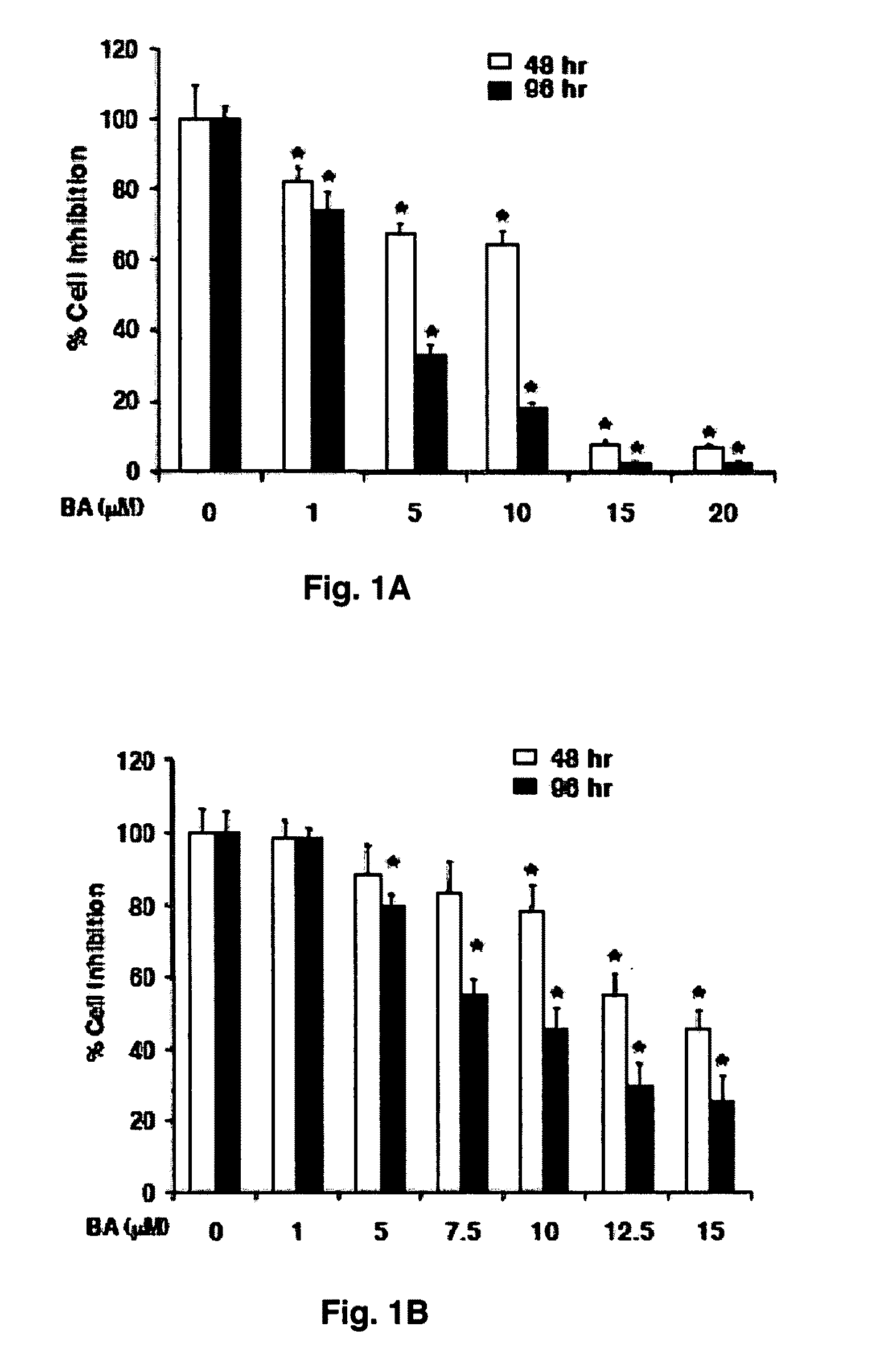
Betulinic acid, derivatives and analogs thereof and uses therefor
Provided herein provided herein are novel analogs and derivatives of betulinic acid. Also provided is a method for inhibiting an activity of one or more specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors cells associated with a neoplastic disease using betulinic acid, betulinic acid analog(s) and / or derivative(s) effective to decrease expression of a microRNA with concomitant increase in Sp suppressor gene expression. The betulinic acid analogs and derivatives also are effective in methods provided herein for inhibiting proliferation of cells associated with a neoplastic disease for treating a cancer or for reducing toxicity of a cancer therapy in a subject via administration of an analog or derivative of betulinic acid and, optionally, another anticancer drug.
Owner:SAFE STEPHEN H +1
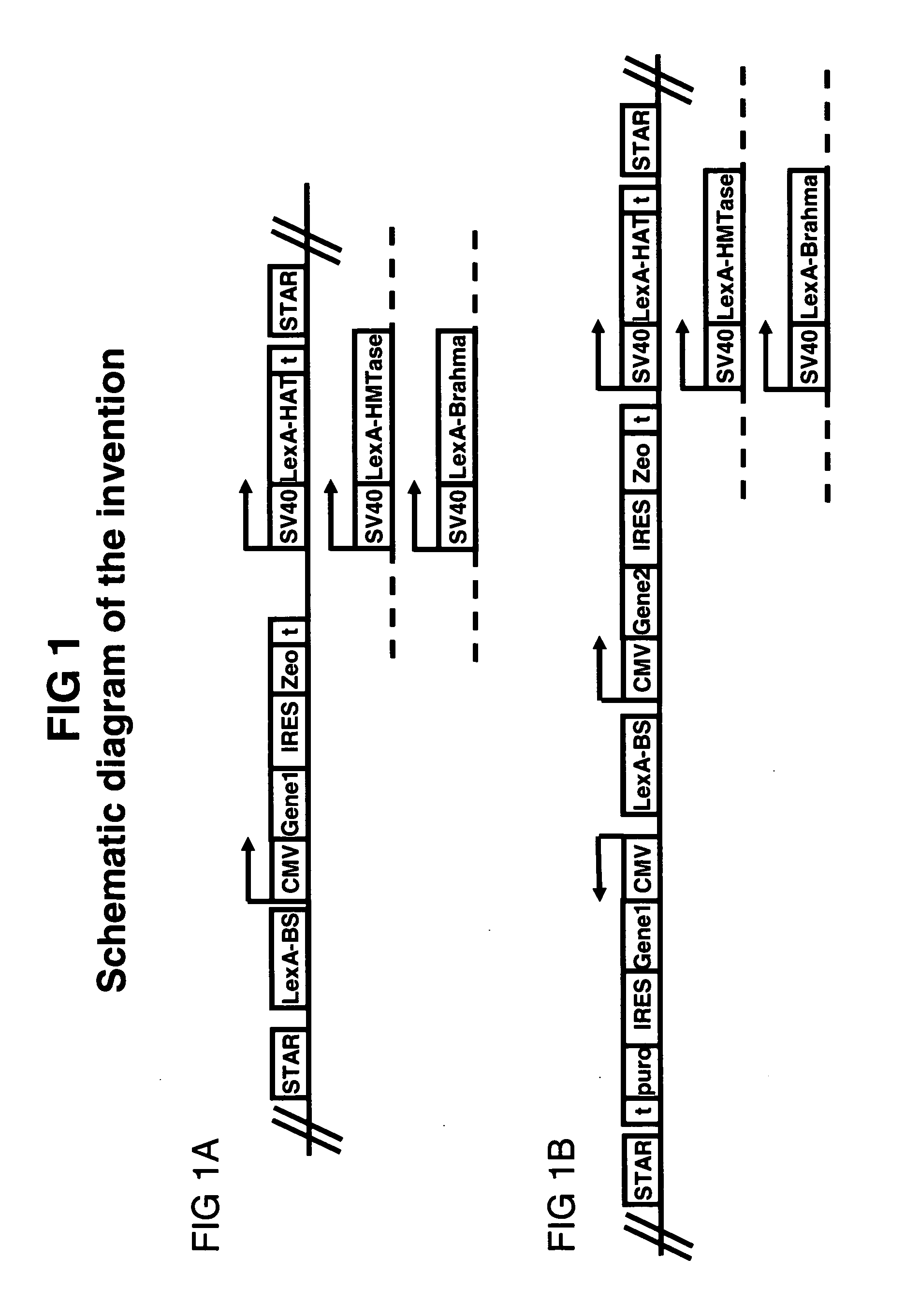
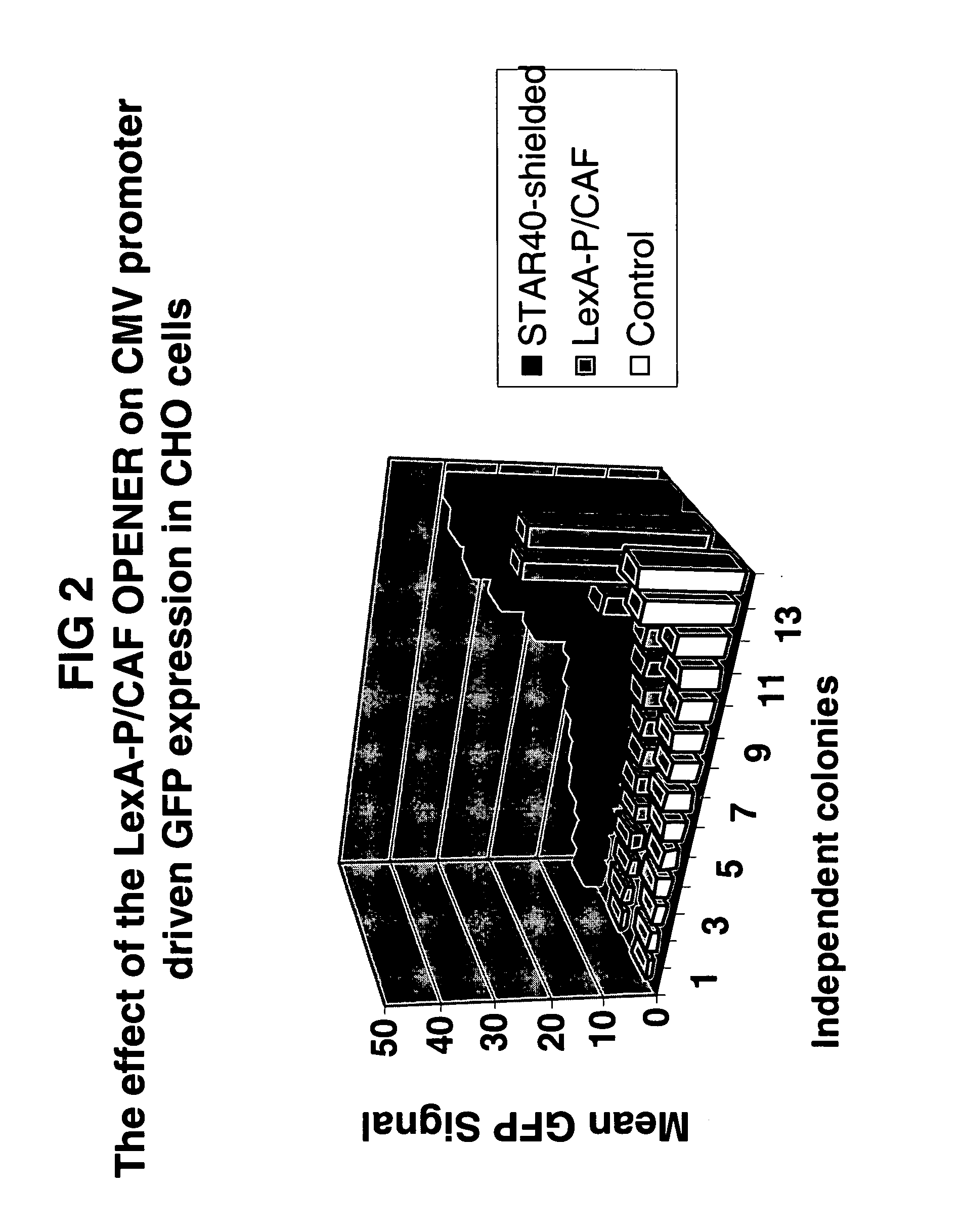
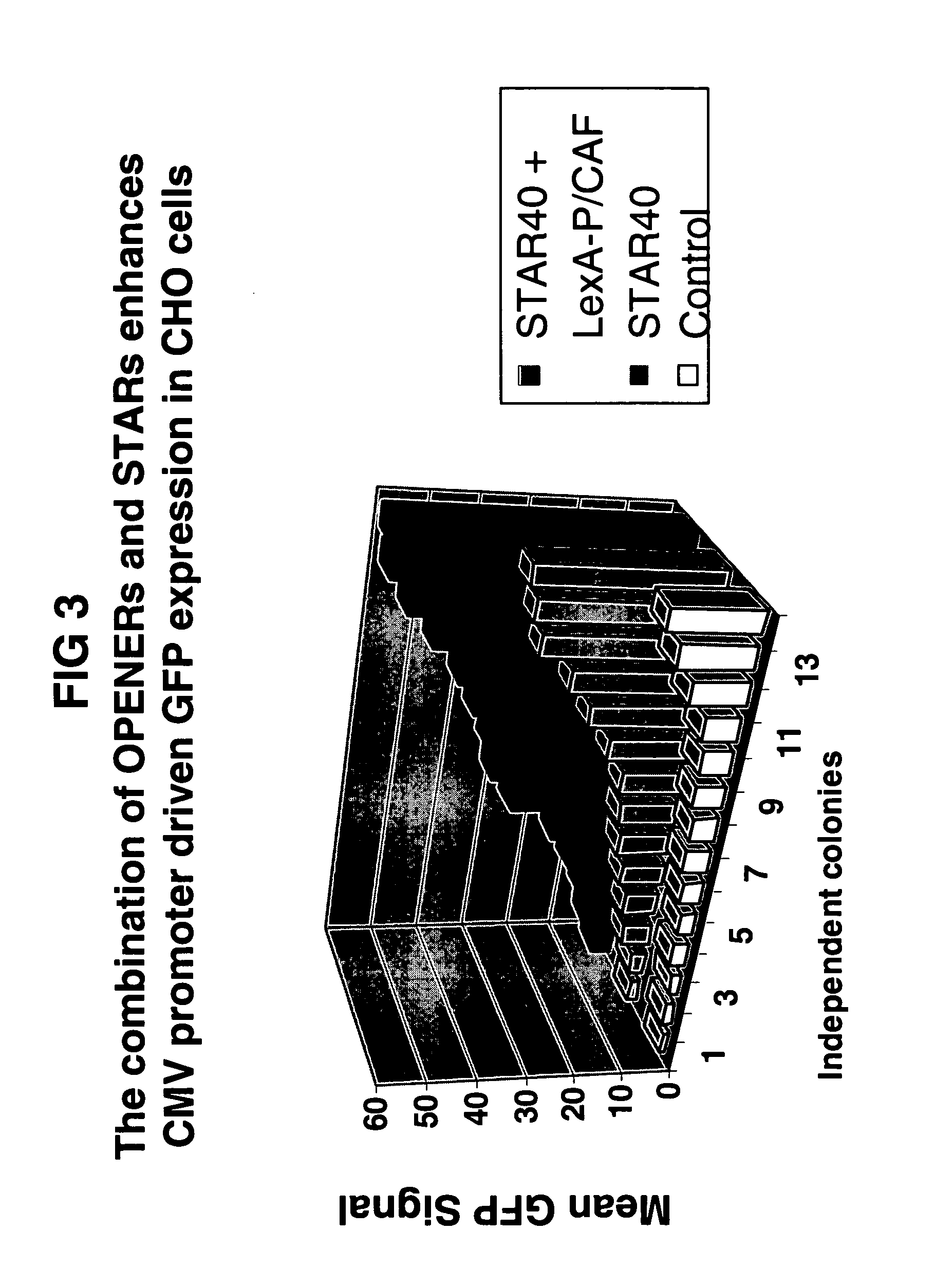
Means and methods for producing a protein through chromatin openers that are capable of rendering chromatin more accessible to transcription factors
ActiveUS20060003416A1Improved characteristicPronounced effect characteristicVectorsSugar derivativesTRAP SequenceChromatin modification
Described are means and methods for providing a cell with a protein expression unit, the method comprising providing a nucleic acid sequence comprising the unit with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a binding site for a member of a chromatin modification system for rendering chromatin more accessible for transcription (opener), wherein the opener is present in the cell. Preferred openers comprise histone modification proteins, chromatin remodeling proteins and trithorax group proteins or equivalents. The cells thus generated and nucleic acid sequences encoding such openers are provided. Openers are preferred in the context of STAR and TRAP sequences.
Owner:CHROMAGENICS BV
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1
ActiveCN105087601AIncrease contentHigh expressionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjWRKY1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and WRKY transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Agents for Activating the Transcription Factor Nrf2 and Foods Having Such Function
InactiveUS20070248705A1High activityReduce the amount of solutionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFactor iiBiological activation
A composition, an Nrf2 activating agent, and a food according to the present invention comprise isohumulones or isomerized hop extract as an active ingredient. They are useful in treating, preventing, or ameliorating a disease of condition which is treatable, preventable, or ameliorable by the activation of transcription factor Nrf2. More specifically, the composition, the Nrf2 activating agent and the food according to the present invention are useful in treating, preventing, ameliorating, or alleviating chronic diseases which are believed to be caused or exacerbated by cellular damages due to oxidative stress in the body or environmental substances (for example, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes, cerebral nerve degenerative diseases, skin diseases, eye diseases, asthma, and cancer) or delaying progress of these diseases, or in detoxificating xenobiotic substances.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Soybean MYB (v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog) transcription factor as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102161698ATo promote metabolismIncreased synthetic contentPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a soybean MYB (v-myb avian myeloblastosis viral oncogene homolog) transcription factor as well as a coding gene and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of the gene engineering. The MYB provided by the invention has the name of GmMYB12B2, and the amino acid residue sequence of the MYB is disclosed by SEQ ID No.2; and the nucleotide sequence of the coding gene of the soybean MYB transcription factor is disclosed by SEQ ID No.1. The gene disclosed by the invention has an important meaning on the flavonoid metabolism of improved plants, and especially has an important meaning on culturing high-isoflavone soybean varieties.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT (Asparatate AminoTransferase) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides hitherto unknown ASPAT-encoding nucleic acids and constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for increasing various plant yield-related traits by increasing expression in a plant of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a MYB91 like transcription factor (MYB91 ) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having increased expression of a nucleic acid sequence encoding an MYB91 polypeptide, which plants have increased yield- related traits relative to control plants. The invention additionally relates to nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and plants containing said nucleic acid sequences. Even furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA (Gibberellic Acid-Stimulated Arabidopsis). The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. Yet furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an AUX / IAA (auxin / indoleacetic acid) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding IAA polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising AUX / IAA-encoding nucleic acids, useful in performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Method for improving plant tolerance to environmental stress
Provided are DNA sequences encoding a novel type of AP2 domain-containing transcription factor as well as methods for obtaining similar sequences. Also described are methods for obtaining plants with improved growth and enhanced stress tolerance, particularly tolerance to osmotic and dehydration stress, such methods comprising expression of such DNA sequences in a plant or parts thereof. Further described are diagnostic compositions comprising the aforementioned DNA sequences and the use of such sequences in plant breeding and / or agriculture.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Application of Arabidopsis transcription factor in breeding drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice
The invention relates to application of Arabidopsis transcription factor in breeding drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice. Nucleotide sequences of the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB44 are shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Encoded protein sequences of the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB44 are shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Conditions that are met for the nucleotide sequences and the encoded protein sequences include: first, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.1, or the sequences highly homologous to the DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1; second, other encodable sequencecs with the same protein as the DNA sequences shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO.2; third, the sequences the same functional as the DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1, or sub-segments contained in the highly homologous DNA sequences shown on the 88th site to the 1005th site in the SEQ ID NO.1. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is applied to breeding of the drought-resistant salt-tolerant rice. An expression vector of the MYB44 gene can be introduced into plant cells by biotechnology. Transforming hosts, available to use the expression vector containing the MYB44 gene, can be monocotyledons such as rice, corn and wheat. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is also applicable to dicotyledons such as tobacco and soybean. The Arabidopsis transcription factor is used to breed drought-resistant salt-tolerant plant varieties.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation
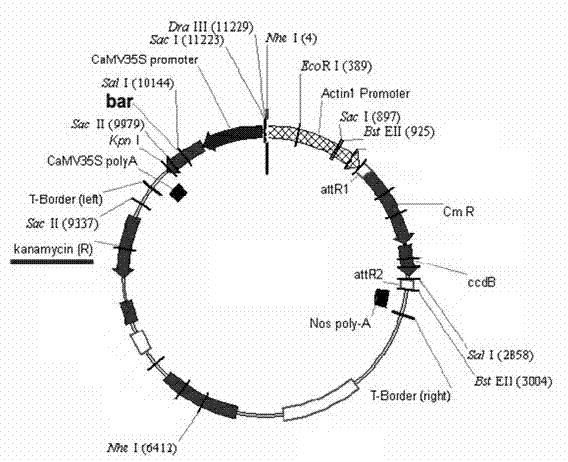
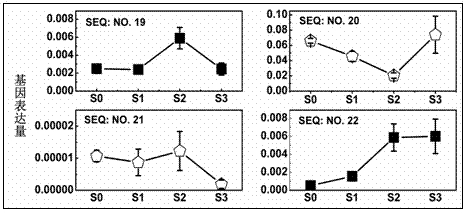
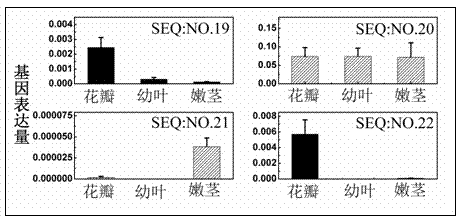
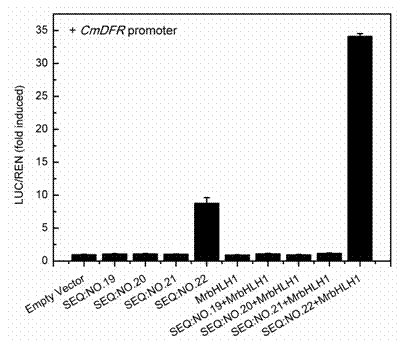
The invention provides an MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 implicated in chrysanthemum petal anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The coding region sequence of the MYB transcription factor CmMYB6 contains 765 nucleotides. A CmMYB6 amino acid sequence contains a conserved R2R3 MYB domain, a [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif and an ANDV motif exist in the R3 domain, the [D / E]Lx2[R / K]x3Lx6Lx3R motif can interact with bHLH, and the ANDV motif is the characteristic motif of the MYB transcription factor implicated in anthocyanin biosynthesis regulation. The gene expression of CmMYB6 rises in the petal growth process and is significantly and positively correlated with anthocyanin synthesis the CmMYB6 can induce the activity of synthesis of a key gene CmDFR promoter from anthocyanin, and the CmMYB6 has substantially enhanced induction usefulness and can strongly induce accumulation of tobacco leaf anthocyanin during cooperative expression of the CmMYB6 and MrbHLH1. The MYB transcription factor can be used in transcription regulation of plant anthocyanin biosynthesis and plant color modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com