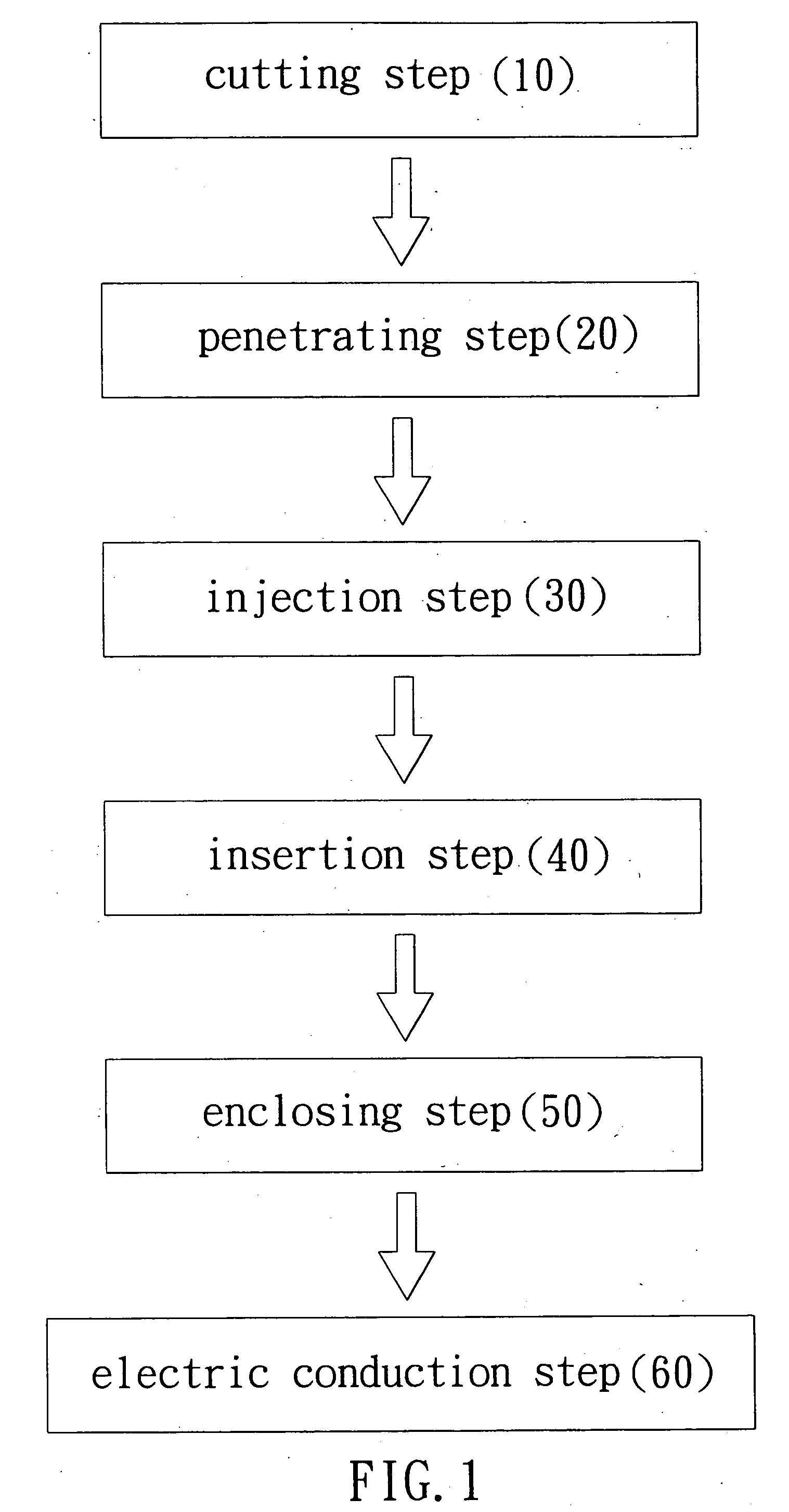
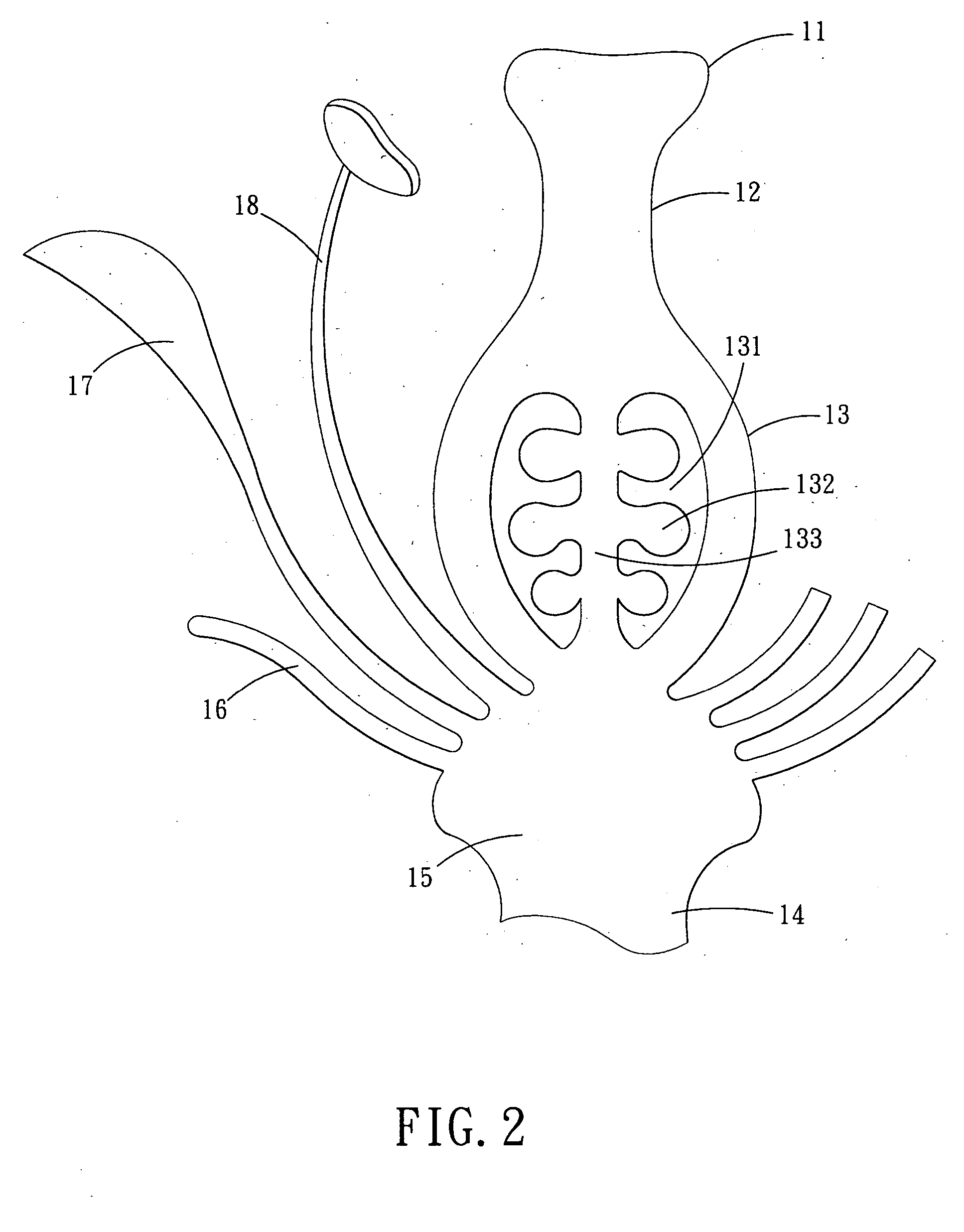
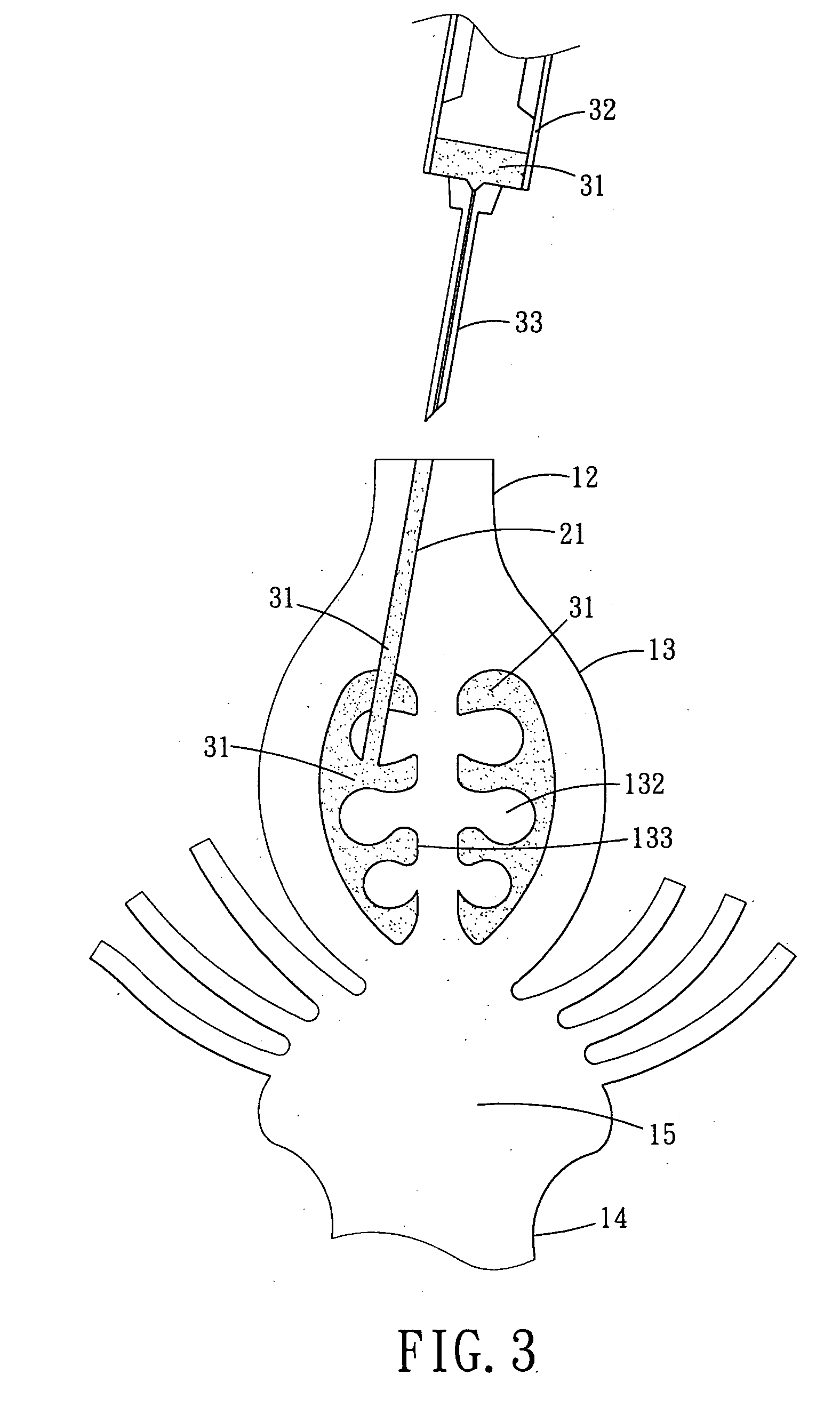
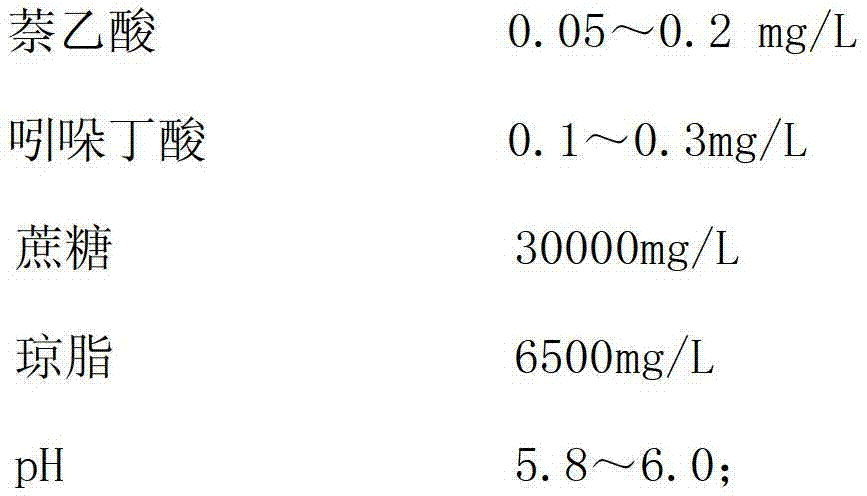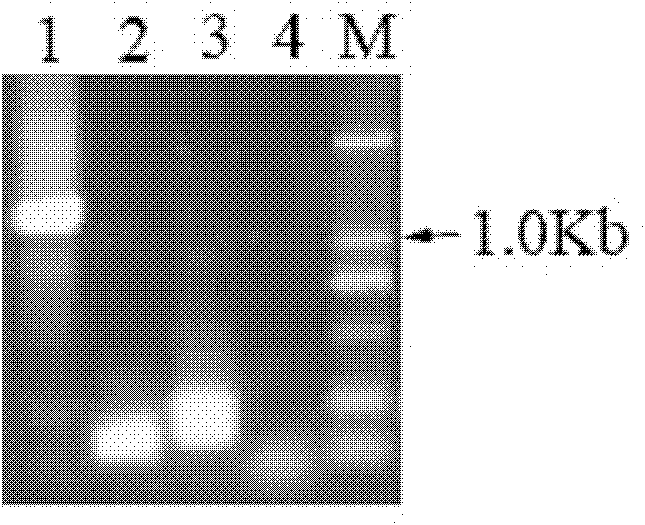Patents
Literature
151 results about "Ovule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
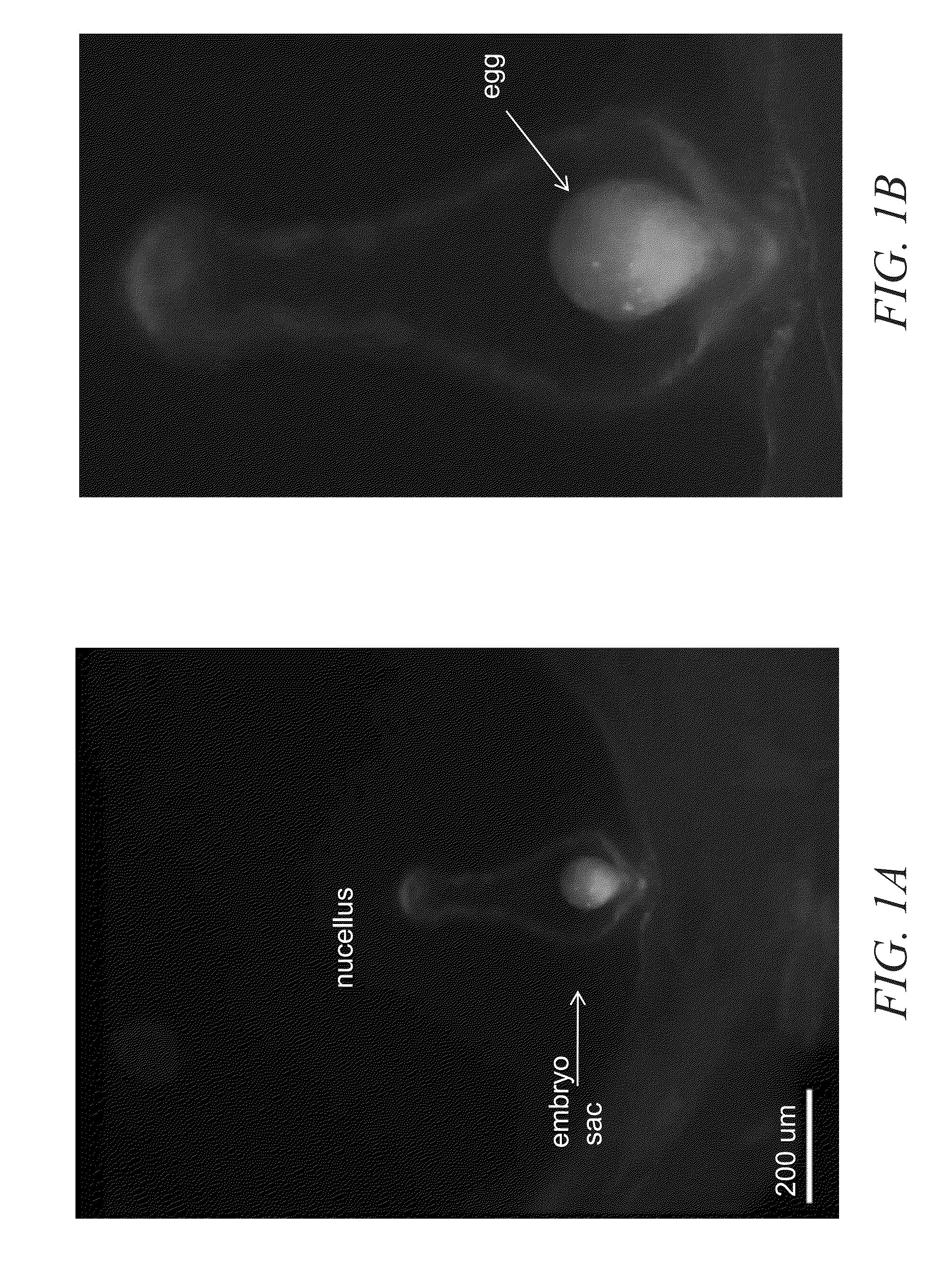
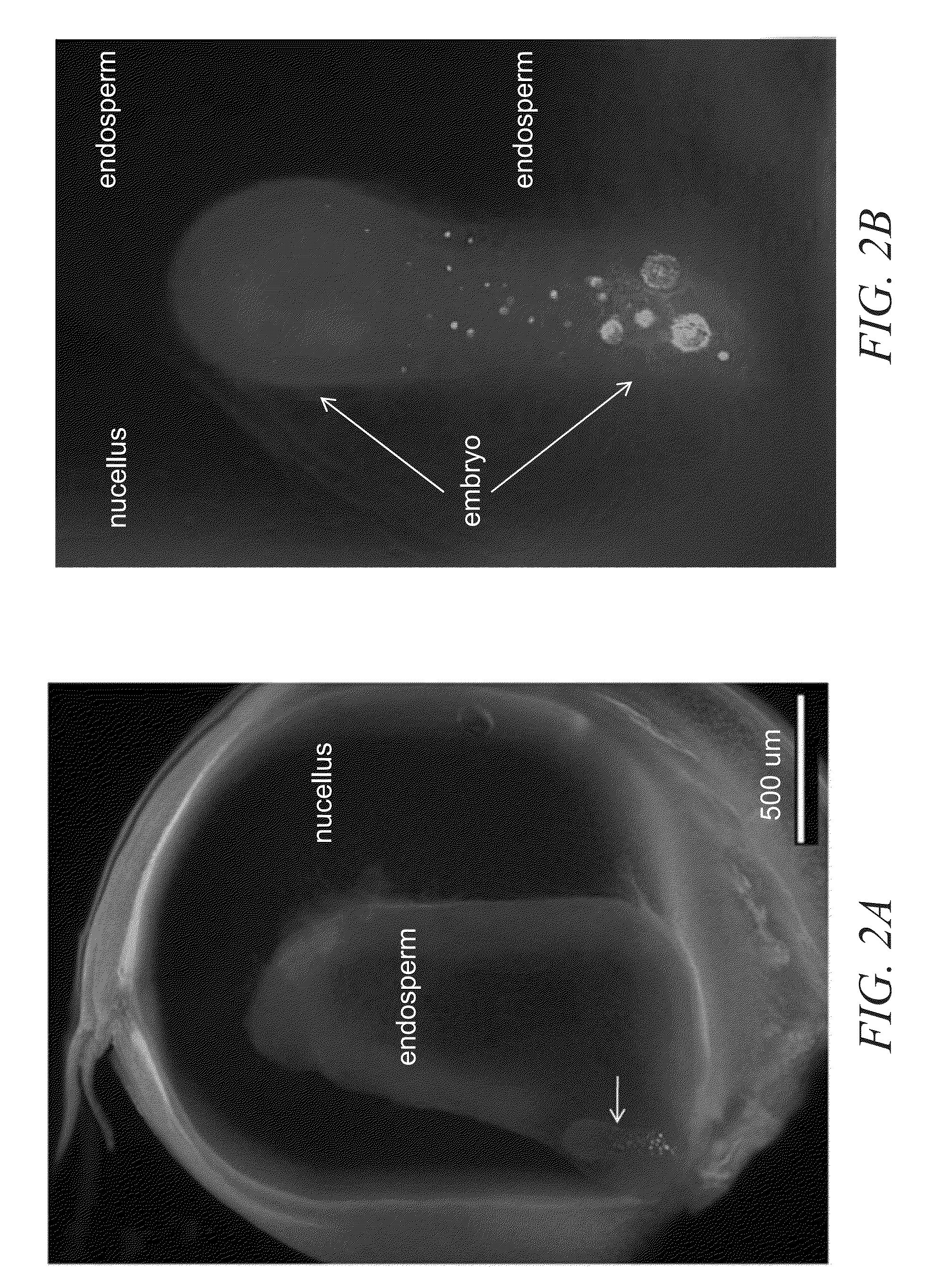
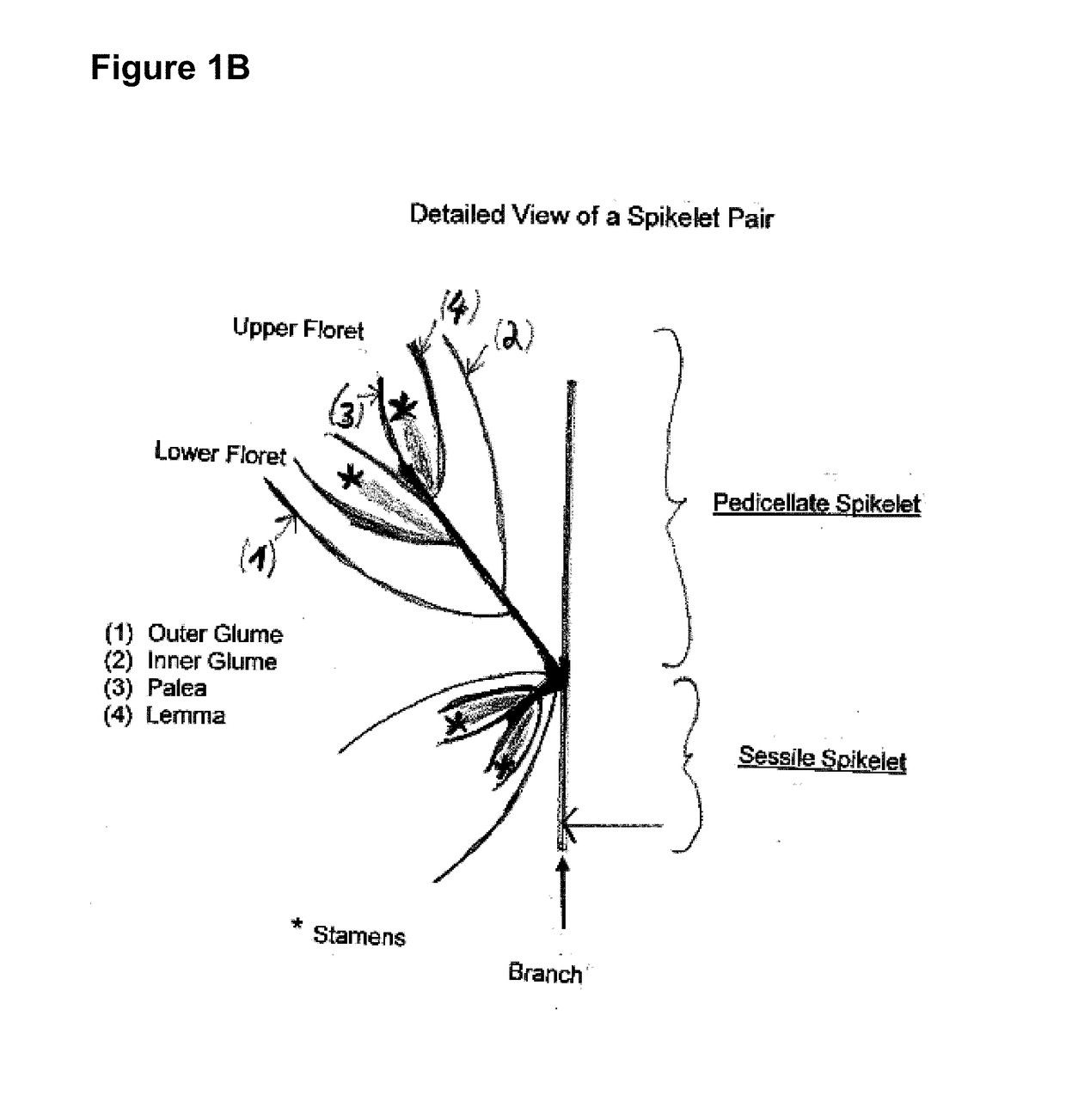
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: The integument, forming its outer layer, the nucellus (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the female gametophyte (formed from a haploid megaspore) in its center. The female gametophyte — specifically termed a megagametophyte— is also called the embryo sac in angiosperms. The megagametophyte produces an egg cell for the purpose of fertilization.
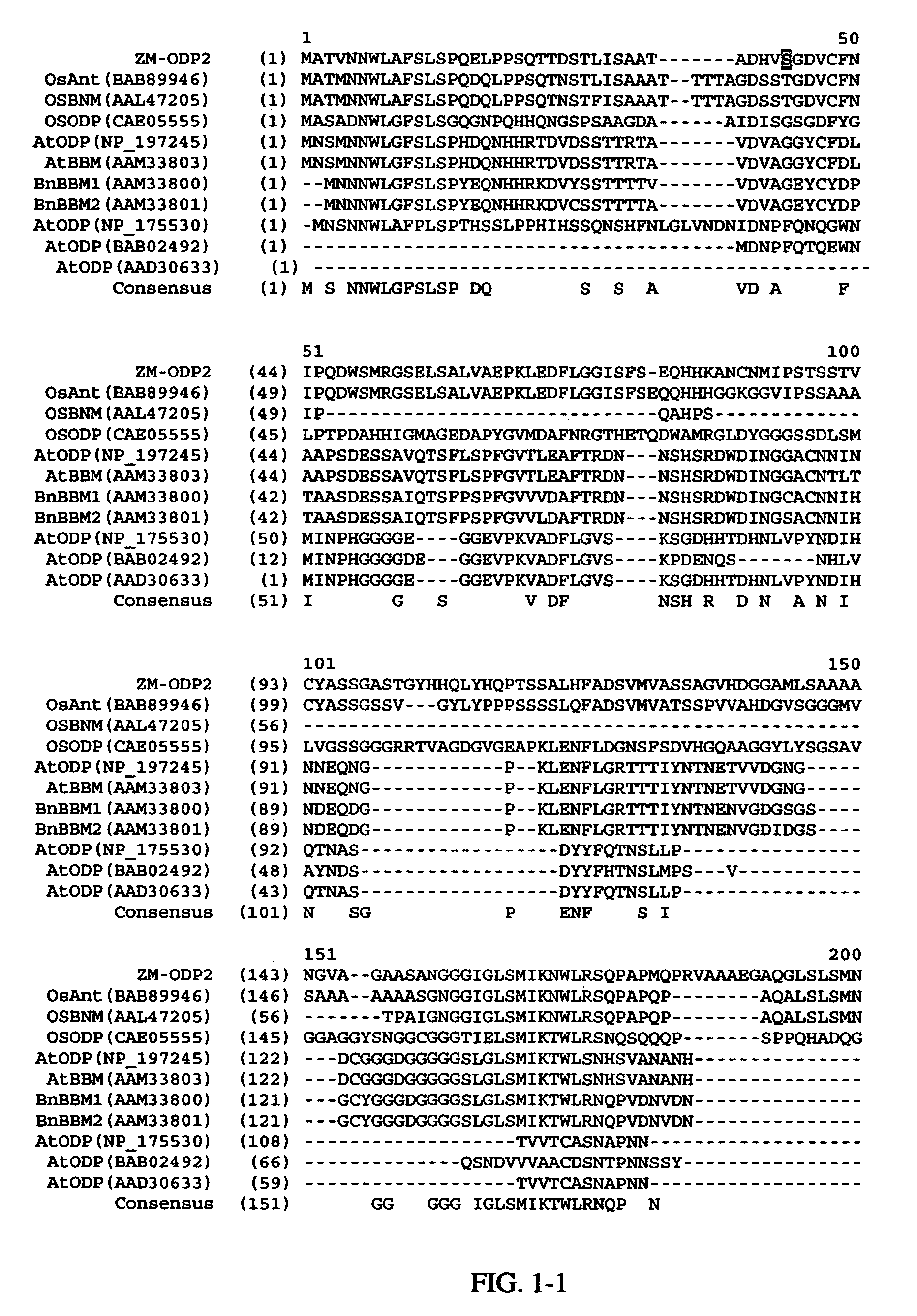
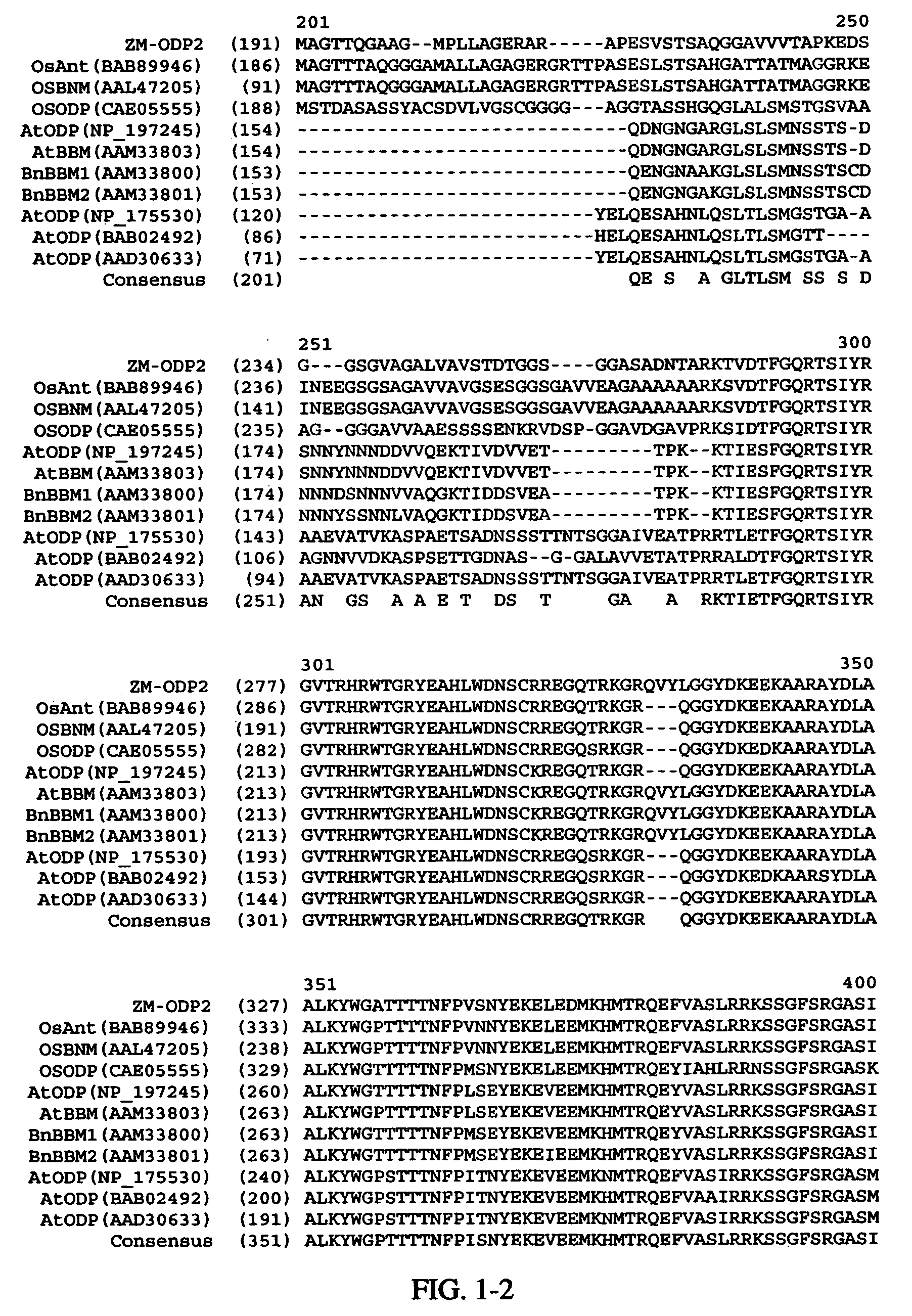
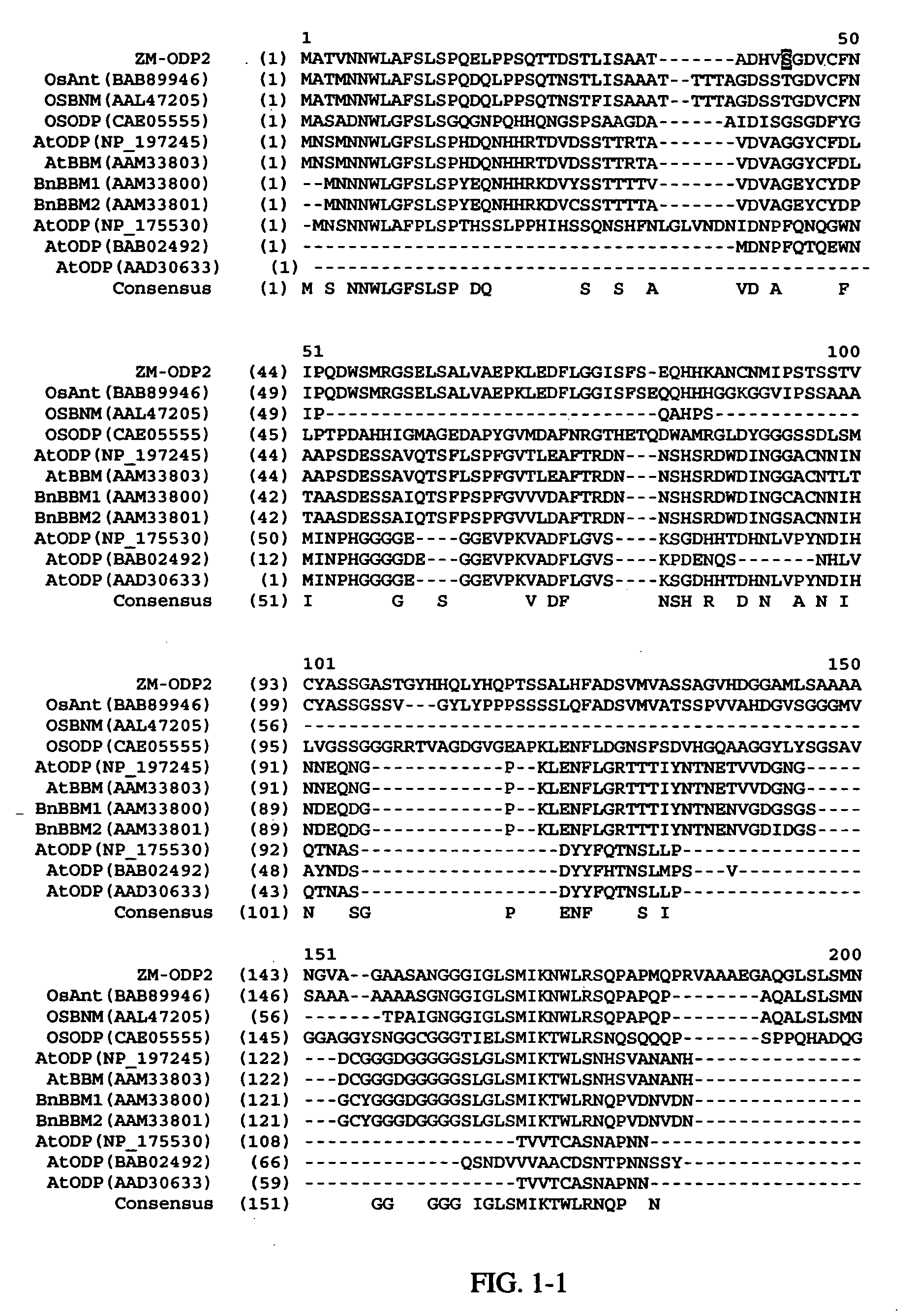
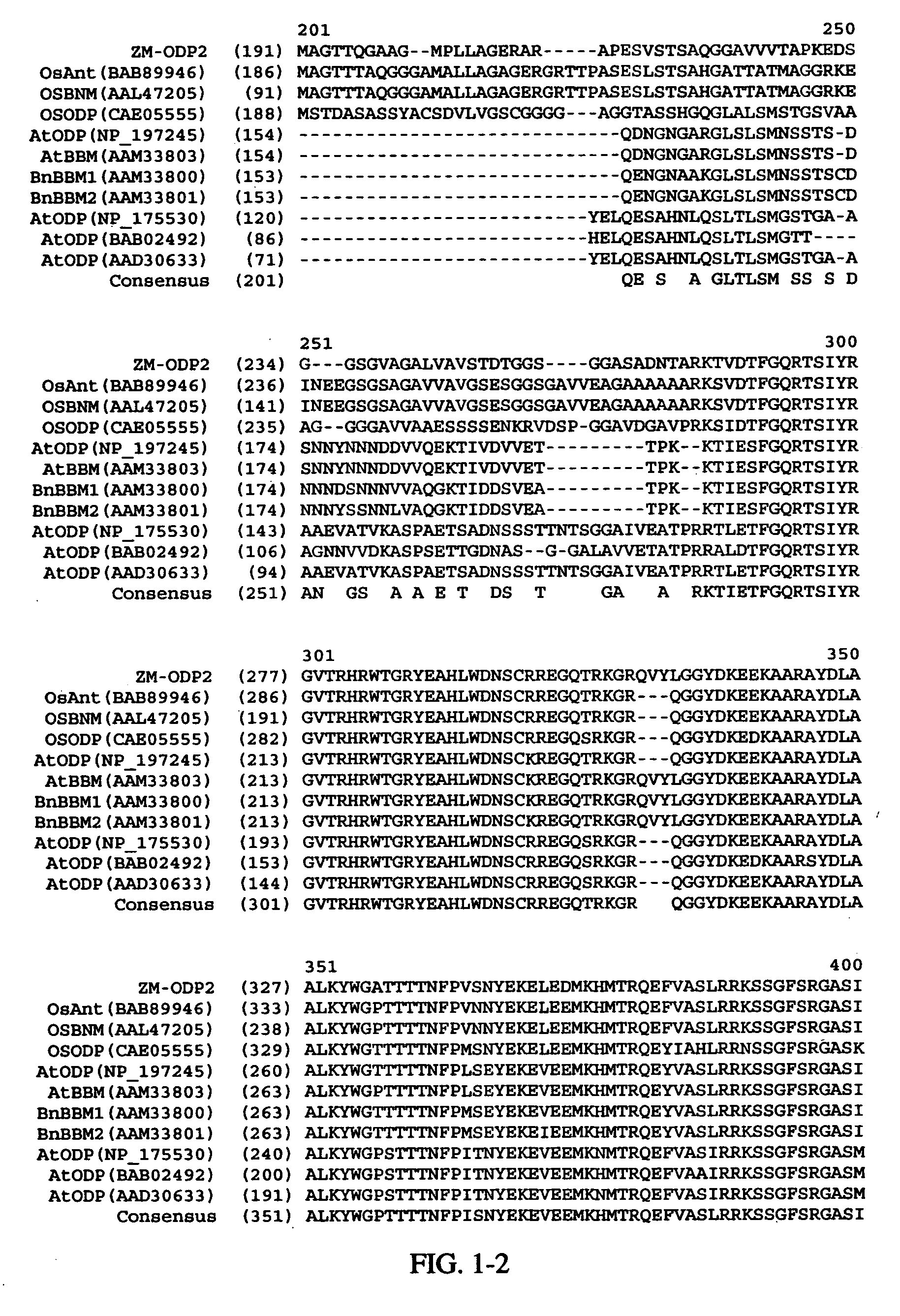
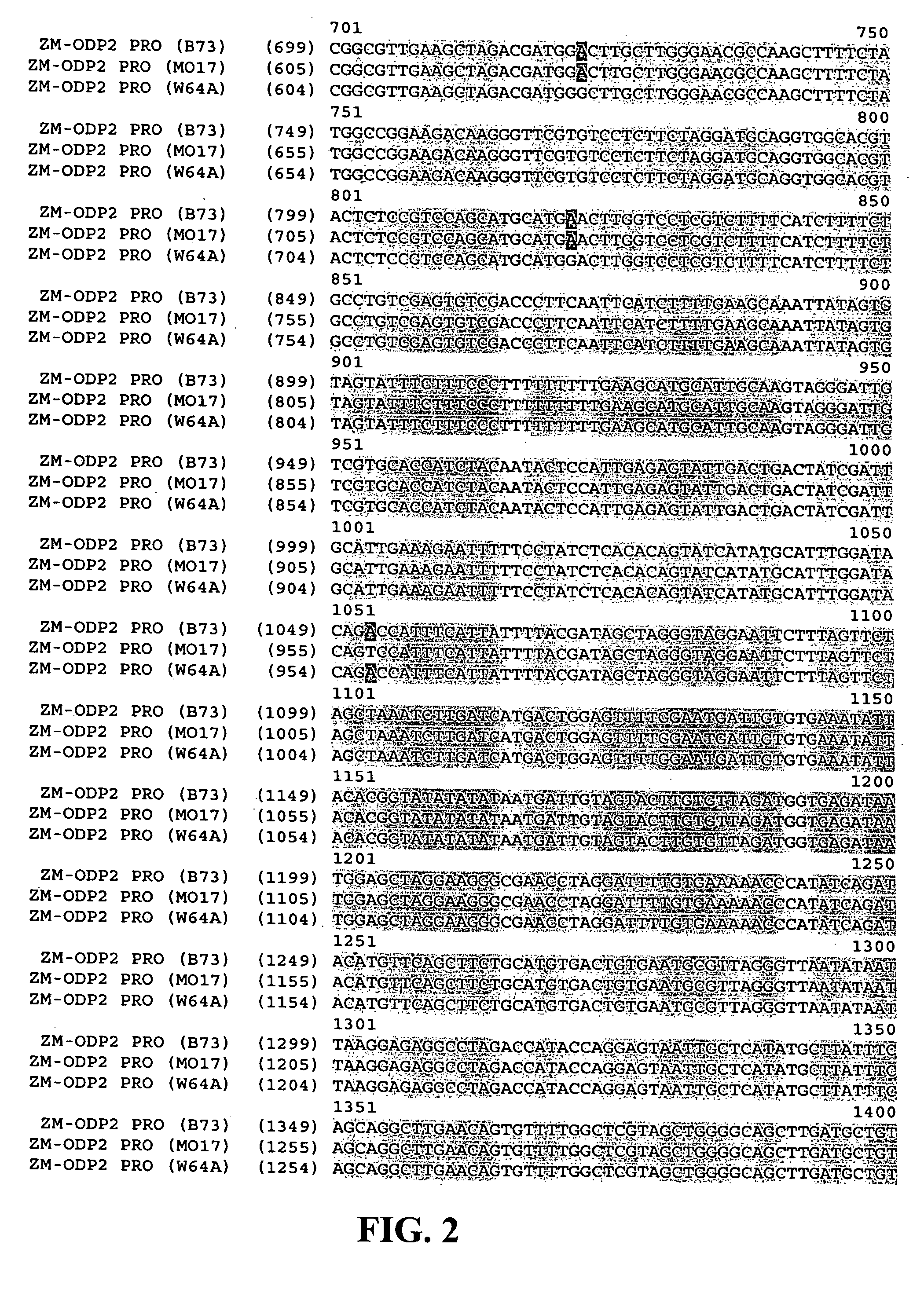
AP2 domain transcription factor ODP2 (ovule development protein 2) and methods of use
ActiveUS7579529B2Altered oil phenotypeReduce oil contentSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationPlant cellTransformation efficiency
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
AP2 domain transcription factor ODP2 (ovule development protein 2) and methods of use
ActiveUS20050257289A1Improve conversion efficiencyImprove planting efficiencySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationNucleotideTransformation efficiency
Methods and compositions for modulating plant development are provided. Nucleotide sequences and amino acid sequences encoding Ovule Development Protein 2 (ODP2) proteins are provided. The sequences can be used in a variety of methods including modulating development, developmental pathways, altering oil content in a plant, increasing transformation efficiencies, modulating stress tolerance, and modulating the regenerative capacity of a plant. Transformed plants, plant cells, tissues, and seed are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Broad-spectrum high-efficiency plant RNA extracting kit
The invention discloses a broad-spectrum and high-efficiency method for extracting RNA from various plant tissues and belongs to the technical field of biochemistry. In the invention, boric acid buffer solution is used as a buffer system, the plant tissue RNA is effectively separated and enriched first, the mixture of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (tris), hydrochloric acid (HCl), ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA-Na2) and sodium chloride (NaCl) is used as extraction buffer solution, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) is used as a detergent, 1 mol / L guanidinium isothiocyanate is used as a strong denaturant for inhibiting the activity of RNase, and thus high-quality RNA is extracted. The method can extract RNA from tissues such as ovules, anthers, blades and fibers of cotton and can extract high-quality RNA from recalcitrant plants such as arabidopsis thaliana, rice, draba matangensis, banana (peel and meat), masson pine and deodar. When the method is used for extracting RNA, the yield is high, the purity is high, and salt pollutant is avoided.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for artificial breeding of farmed sturgeon
A method for artificial breeding of farmed sturgeon is disclosed. The method comprises of growing a plurality of fingerling sturgeon; obtaining a plurality of juvenile sturgeon; identifying at least one male juvenile sturgeon and at least one female juvenile sturgeon; Feeding a predetermined amount of a preselected food material to the male and female sturgeon; Determining maturity based on at least controlling sex hormones and stress hormones of the male and female sturgeon; identifying at least one male matured sturgeon and at least one female matured sturgeon; and Selecting male matured sturgeon and female matured sturgeon, wherein said female matured sturgeon carries a predetermined amount of ovule and wherein said predetermined amount of ovule is processed to obtain a predetermined amount of caviar.
Owner:BAHMANI MAHMOUD
Sweet potato distant hybridization breeding method with high success rate
InactiveCN101715724AEasy to operateIncrease success rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFlowering seasonWild species
The invention discloses a sweet potato distant hybridization breeding method with a high success rate, and relates to the technical field of plant innovation and new variety breeding of crops. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a wide-compatibility parental sweet potato Xushu 18 as a female parent, and regulating the flower season of the Xushu 18 to be synchronous with that of a wild specie sweet potato by a grafting and dark treatment method; performing water culture on a male parent and the female parent indoor to naturally take root and blossom; after the male parent and the female parent blossom, performing hybrid pollination; after pollinating, coating a hybridization treating fluid (40mg / L 6-benzyladenine, 45mg / L 2,4-dichlorphenoxyacetic acid and 40mg / L naphthylacetic acid) on the stem base of an ovary and the whole flower stalk, and continuously treating for 7 days; and for a combined hybridized ovule which stops early development, adopting immature embryo rescue technology. The hybridization method and a hybridization system of the invention have the advantages of high operability and high success rate. The method is also suitable for indoor directed hybridization of a field naturally blossoming sweet potato material and a conventional sexual hybridization breeding of the sweet potato.
Owner:XUZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-efficient breeding technique of Eurasian raisin grape
ActiveCN101564011AAvoid difficultiesEfficient Breeding TechnologyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGrowth plantIndoleacetic Acids
The present invention relates to a high-efficient breeding technique of Eurasian raisin grape. After the raisin grape has flowered for 30-50d, the young fruit of the grape is picked. The ovule is taken out in a sterilized state. The embryo is inoculated to an MS culture medium containing different levels of plant growth regulators of gibberellic acid (GA3), indoleacetic acid (IAA) and 6-benzylaminopurine (6-BA) for executing embryo rescue. The average embryo development rate using the breeding technique of the invention is increased from 8.3-11.9% of a patient disclosed in the background art to 84%. The germination rate obtains 75.33% and the seedling rate obtains 74.17%. Furthermore the embryo rescue technique of the raisin grape obtained through the technique of the invention has the advantages of increased seedling rate of offspring, easier obtainment of more filial generation, increased parent selection range of raisin grape cross breeding, accelerated breeding process of new species of the raisin grape and increased breeding efficiency of the raisin grape through increasing the embryo development rate and the germination rate of the raisin grape.
Owner:HANGZHOU BLUE SKY LANDSCAPE CONSTR GROUP
Methods for the in planta transformation of plants and manufacturing processes and products based and obtainable thereform
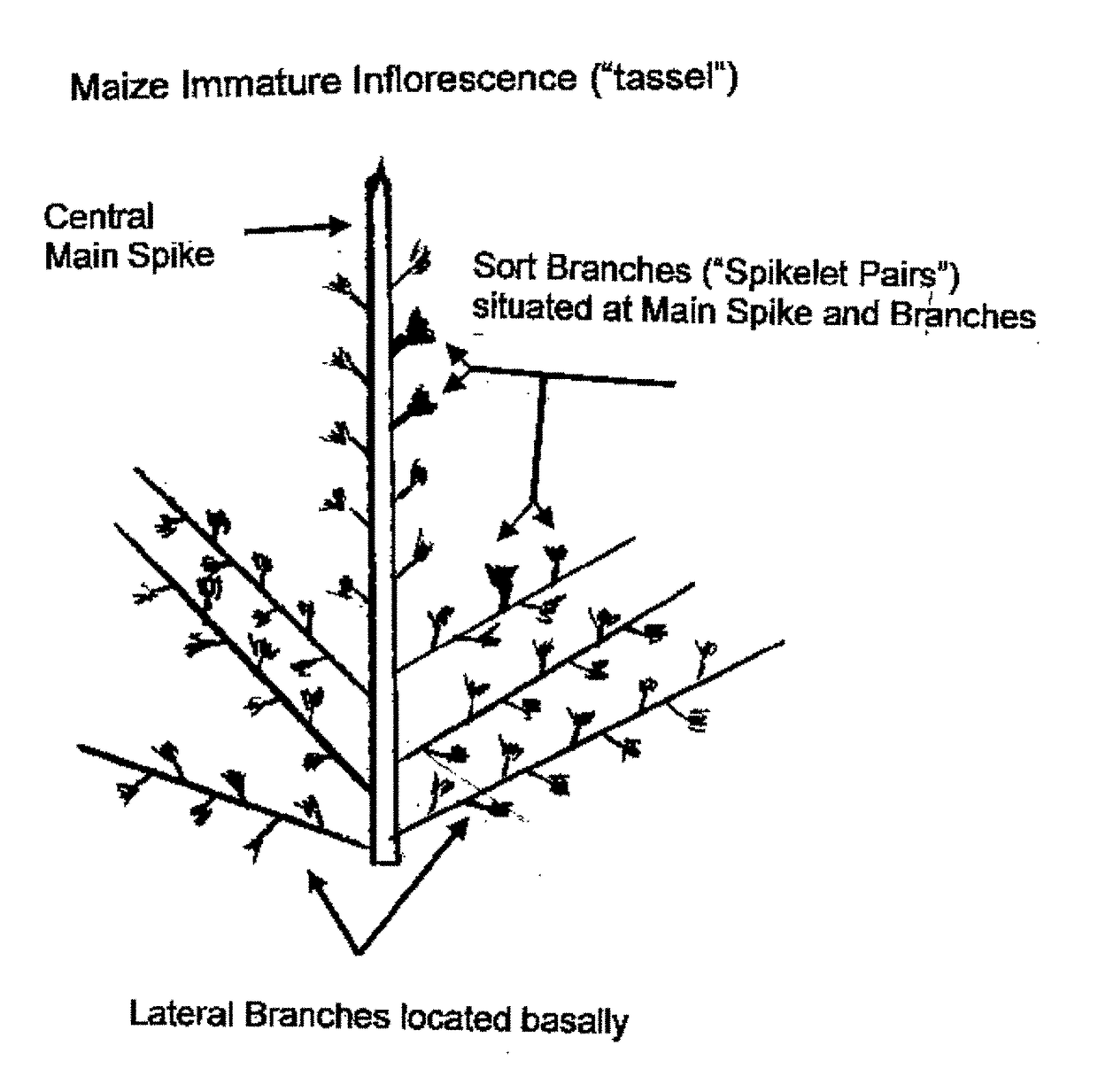
InactiveUS20180142248A1Stable introduction/integrationEliminate needVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyInflorescence
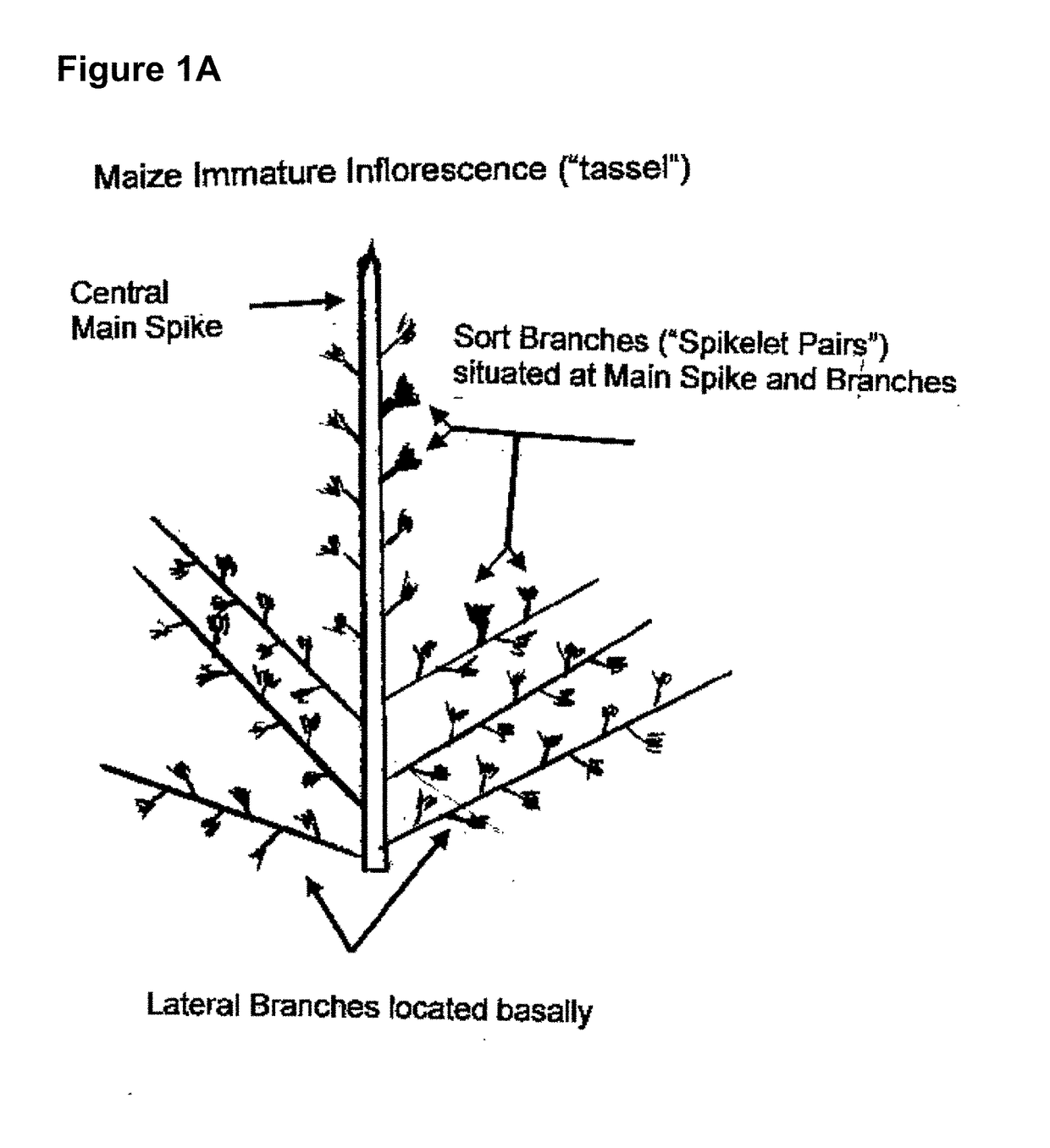
The present invention relates to in planta transformation methods for plants or plant materials with a genetic construct, wherein at least one meristematic cell of a meristematic tissue of an immature inflorescence able to differentiate into a gamete of a pollen or of an ovule is exposed and then transformed, wherein the transformation can be performed to yield a stable integration or to yield a transient introduction of a genetic construct of interest. Further provided are methods for manufacturing a transgenic plant, or methods for manufacturing a genetically manipulated plant based on the in planta transformation methods according to the present invention. In addition, there is provided a plant or a progeny thereof manufactured according to the transformation and / or manufacturing methods according to the present invention.
Owner:KWS SAAT SE & CO KGAA
Production method for fluorescent microscopic slices of ovule of pollinated azalea
The invention provides a production method for fluorescent microscopic slices of ovule of pollinated azalea. The production method comprises the following steps: sampling pistil of pollinated azalea; and fixing, softening, dyeing, stripping ovary walls and tabletting. In the steps of sampling and fixing, pollinated azalea flowers are picked, flower petals are stripped, only pistil parts comprising stigmas and ovaries are remained and are put into an FAA fixing solution to be fixed, and after 24 hours, the pistil parts are converted into a 70% ethanol solution to be stored; in the softening process, the fixed materials are put into a drying oven to be heated and softened; in the dyeing process, the softened materials are dyed with a 0.1% water-soluble aniline blue dyeing solution without light for one night; in the ovary wall stripping process, the dyed materials are subjected to ovary wall stripping treatment; and in the tabletting process, tabletting is performed on the stripped materials to obtain the slices. According to the method, the slices of ovule of pollinated azalea, which are clearly dyed and have complete tissue structure, can be obtained; and comprehensive fertilization information can be observed.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Colored cotton ovule in vitro culture method
InactiveCN103931494AGuaranteed nutrition supplyKeep aliveHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFiberContamination rate
The invention discloses a colored cotton ovule in vitro culture method, which comprises the steps of: collecting 0-2 days old young bolls of green cotton or brown cotton of the day, pulling off the corolla, stripping calyxes, and retaining flower stalks; washing the young bolls with distilled water twice, conducting disinfection with 75% alcohol for 5-15min under a sterile condition, then performing soaking with 0.1% mercury chloride for 5-15min, and conducting washing with sterile water 5-8 times, and stripping ovules; inoculating the ovules under a sterile condition into a BT medium containing hormone ZR, GA3 and IAA, inoculating 15-25 ovules of one ovary into each bottle, and carrying out dark culture for 30-40d at 30-32DEG C. Preferably, during inoculation of green cotton ovules, the hormone ratio wais GA31.0micromol / L+IAA5.0micromol / L+ZR2.5micromol / L, and during inoculation of brown cotton ovules, the hormone ratio is GA31.0micromol / L+IAA1.0micromol / L+ZR1.0micromol / L. The method provided by the invention can reduce the contamination rate, improve the survival rate, and promote cotton fiber growth and pigment synthesis.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Micropropagation method for rubber tree good variety somatic embryo plant
InactiveCN103125382AHigh quality glue materialHigh speedPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsPlantletSeedling
Owner:YUNNAN INST OF TROPICAL CROPS
Field culture european large cherry budbreaking chemicals and budbreaking method in regions south of the Changjiang river
The invention relates to a dormancy-breaking agent of an European large cherry cultivated out-door in the region at the south of the Changjiang River, and a dormancy-breaking method thereof, which are used for carrying out dormancy-breaking to the European large cherry and promoting the growth of an ovule and a megaspore. The dormancy-breaking agent is prepared by diluting a cyanamide solution of 50 percent to 1-2 percent and then being added with osmotic agent fatty alcohol polyethenoxy ether of 0.05 percent. The European large cherry is treated for two times. The first treatment is carried out about 30 days before the sprouting of the European large cherry and the whole branch of the European large cherry is sprayed up by using the dormancy-breaking agent; the second treatment is carried out after one week of the first treatment, and the same dormancy-breaking method is treated repeatly for consolidating the effects. The method is applicable to the large cherry varieties of 'early-red precious stone', 'red light', 'early-mahapphala', 'pioneer', 'Lapins' and the like. The dormancy-breaking agent has easy preparation and safe use, and can lead the European large cherry to sprout in advance for more than one week, with neat sprout and blossom, the flower quantity is increased, the percentage of fertile fruit is improved, the growth of the young sprout is promoted, the leaf area is increased and the fruit quality is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for obtaining poinsettia filial generation through utilizing young embryo rescue
InactiveCN102845312AOvercoming difficultiesOvercome difficult phenomenaCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue culturePoinsettiaPollination
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a poinsettia filial generation through utilizing young embryo rescue. The method is characterized in that 15-22d of ovules which are subjected to artificial cross pollination are subjected to young embryo rescue through adopting in-vitro culture; and the method comprises the following specific steps of: (1) ovule stripping, (2) induction culturing, (3) subculturing, multiplying and rooting, and (4) transplanting. By utilizing the method, poinsettia hybrid ovules are effectively prevented from premature failure, the hybrid survival rate of the poinsettia filial generation is improved, the culture period of the poinsettia filial generation is shortened, and the method can be applied to poinsettia hybridization breeding.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Ethylene response factor gene of cotton transcription factor
ActiveCN103305528AHigh speedEasy to operateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionFiberResponse factor
The invention belongs to the field of application of biotechnology and relates to an ethylene response factor gene of a cotton transcription factor. The ethylene response factor gene is Gh ERF7, a sequence of the ethylene response factor gene in upland cotton vitex 8891 and tetraploid upland cotton (G.hirsutum) TM-1 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the sequence of the ethylene response factor gene in a tetraploid sea island cotton (G.barbadense) H7124 is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and a sequence of the ethylene response factor gene in Africa cotton (G.herbaceum) and Asian cotton (G.arboreum) genome is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. An ethylene response factor family gene (Gh ERF7) has no obvious response on adversity but is related to growth of cotton ovule and early fiber and yield of cotton, and the yield of cotton is obviously increased as the ethylene response factor gene exists in a genome. The ethylene response factor gene can regulate expression of some genes related to control on cotton yield factors, so that great contribution is done to increase of the yield of cotton, and the yield of cotton is hopefully greatly increased when the ethylene response factor gene is excessively expressed.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
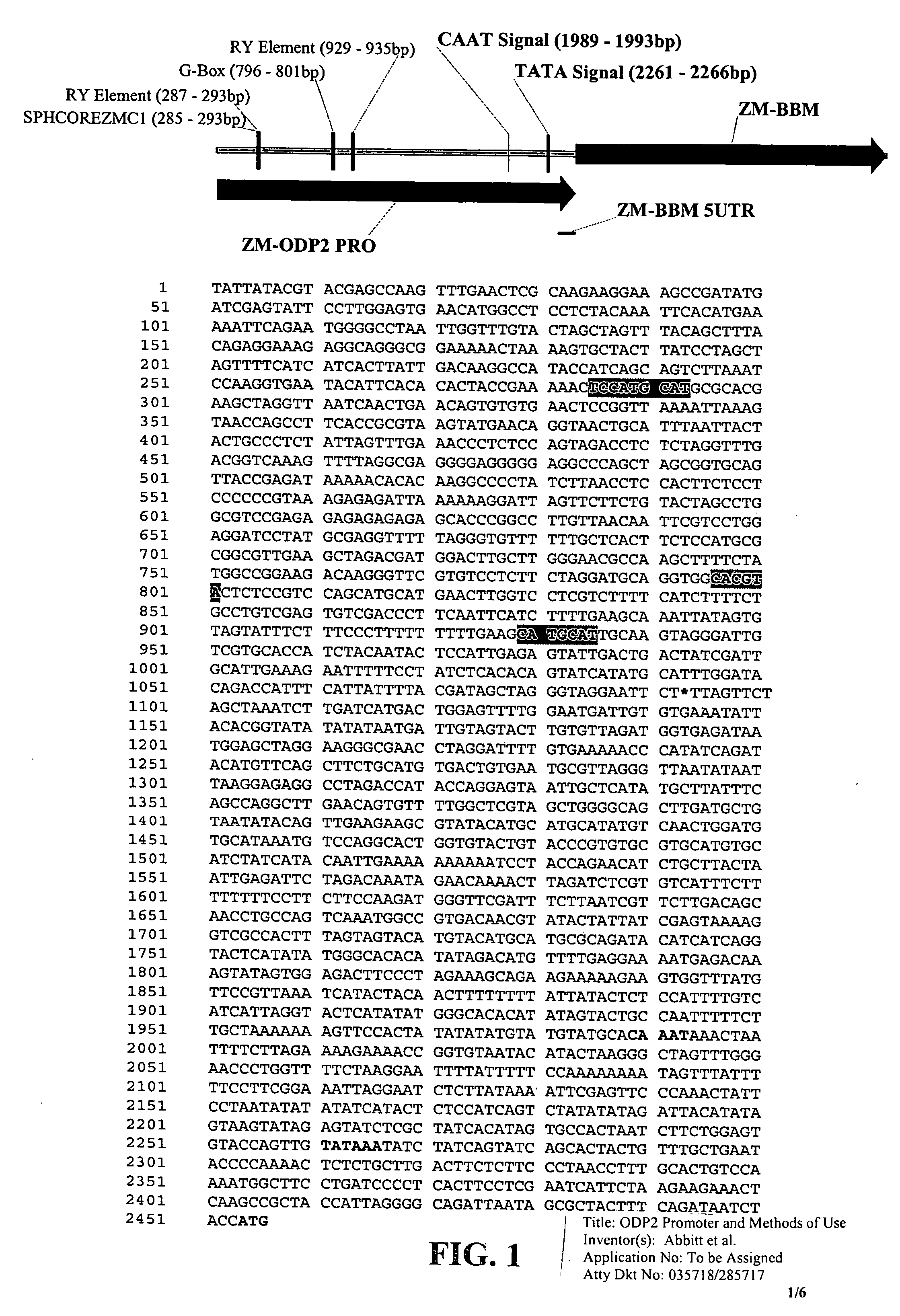
ODP2 promoter and methods of use
InactiveUS20050223432A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotidePlant cell
Compositions and methods for regulating expression of nucleotide sequences of interest in a plant are provided. Compositions include novel nucleic acid molecules, and variants and fragments thereof, for promoter sequences isolated from the maize Ovule Development Protein 2 (ODP2) gene. A method for expressing a nucleotide sequence of interest in a plant using the promoter sequences disclosed herein is further provided. The method comprises introducing into a plant or plant cell an expression cassette comprising an ODP2 promoter of the present invention operably linked to a nucleotide sequence of interest. In particular, the compositions and methods find use in regulating expression of nucleotide sequences of interest in a seed-preferred manner. Transformed plants, plant cells, and seeds comprising the ODP2 promoter sequence or variants and fragments thereof are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for obtaining haploid of cultivated dendranthema morifolium
ActiveCN102124950ABroaden your mindBroaden the fieldPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGermplasmInflorescence
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology breeding, and discloses a method for obtaining a haploid of cultivated dendranthema morifolium. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a cultivated dendranthema morifolium variety as a 'female parent', pollinating and hybridizing by utilizing inactivated pollen of a mentor male parent, and culturing ovules in vitro in a tissue culture way to overcome the barrier of the production and identification of the haploid of the cultivated dendranthema morifolium, Dendranthema. The morphological identification and cytological identification are performed on obtained haploid materials; the haploid materials that morphological features such as stems, leaves, inflorescences, pores and the like are different from those of the 'female parent' or specific characters appear are selected for the cytological identification; and the haploid is obtained if chromosomes are one half of that of the 'female parent'. By the method, haploids of multiple cultivated species are successfully produced, and novel materials are provided for germplasm innovation as well as origin and evolution research of Dendranthema plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
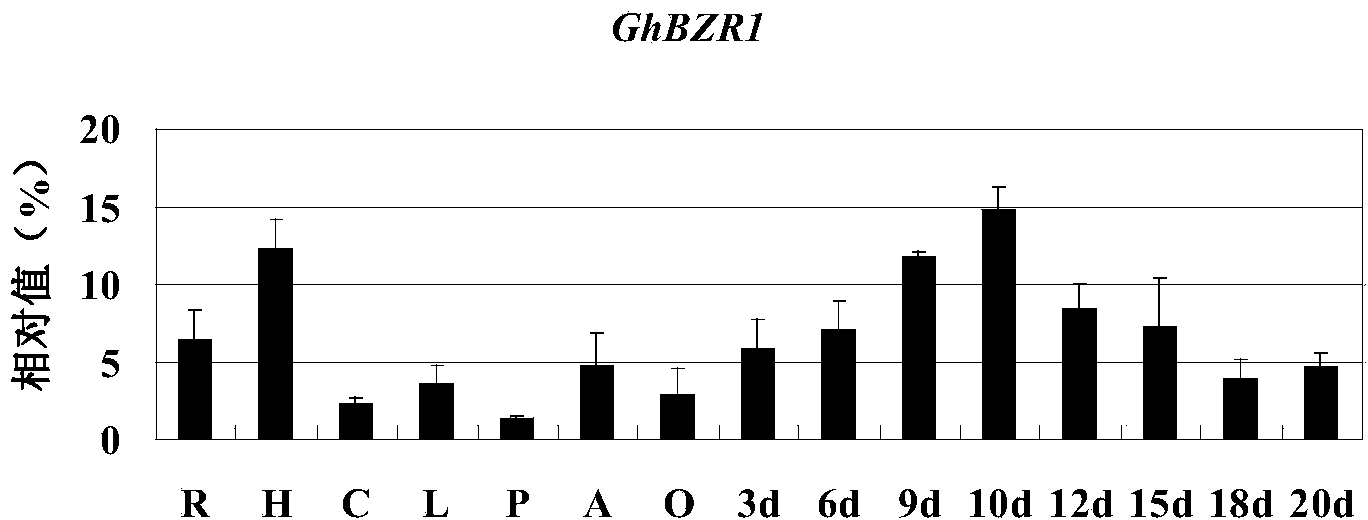
Identification and application of cotton gene BZR1
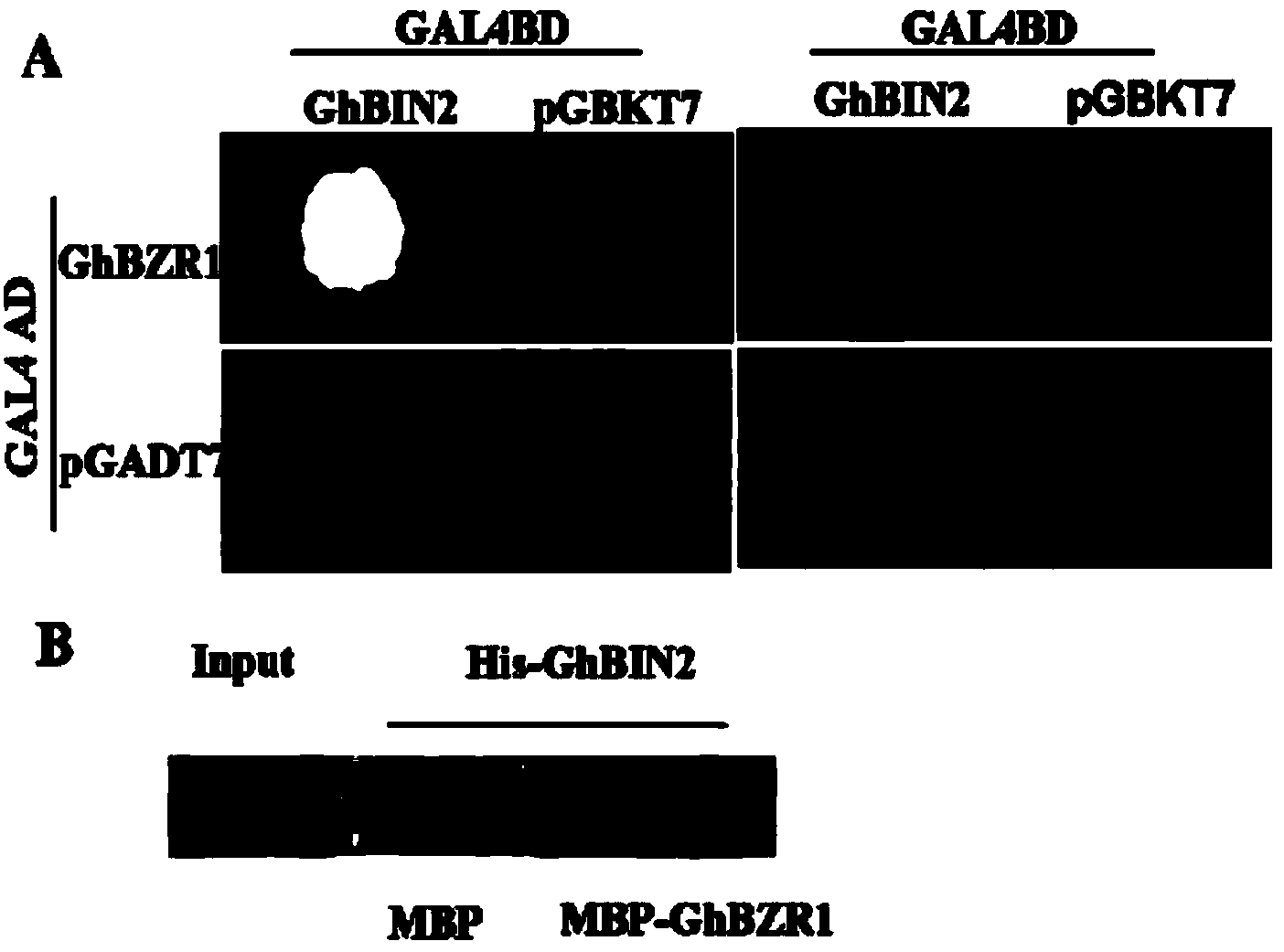
InactiveCN103981193AEnhanced interactionReduce protrusionPlant peptidesFermentationFunctional identificationADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to cloning and functional identification of a gene GhBZR1 for preferential expression of cotton fibers. The gene GhBZR1 is 1410bp in overall length and is coded with a protein containing amino acid 313. If a large amount of mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) of the gene GhBZR1 is accumulated in cotton fiber cells during a stretching development stage, the gene GhBZR1 is considered as a fiber preferential expression gene. The protein GhBZR1 is positioned in a cytoplasm and a cell nucleus, and is accumulatively increased in the cell nucleus after being induced by BL (Butyrolactone). The protein GhBZR1 can interact with a protein GhBIN2 and can be phosphorylated by the protein GhBIN2, thereby promoting the interaction carried out between the protein GhBZR1 and a protein 14-3-3. Thus, if the over-expression of the GhBZR1 is carried out in a mutant bri1 of arabidopsis BR, the scrubby phenotype of the arabidopsis BR can be restored. If the expression of the gene GhBZR1 in the cotton is inhibited by utilizing an RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid interfere) technique, the development of ovules and fibers of a transgenic cotton plant is apparently affected. Thus, the result speculates that the cotton fiber development and the fiber quality character are regulated by the gene GhBZR1 possibly in a manner of influencing a BR signal.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Breeding method of gerbera jamesonii homozygote plant
ActiveCN103109736AHigh induction rateImprove accuracyPlant genotype modificationDirect evaluationPloidy
The invention provides a breeding method of a gerbera jamesonii homozygote plant, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The breeding method comprises the steps of: through flower bud selection, low-temperature treatment and disinfection, picking off ovules and introducing into a same culture medium for synchronously carrying out callus induction, bud differentiation and subculture, carrying out chromosome reduplication on a primarily selected haplobiont, primarily selecting a reduplicated strain for expanding propagation and rooting culture, hybridizing in field strains, and selecting again to obtain an excellent homozygote plant. According to the invention, the callus induction, bud differentiation and subculture of ovules are carried out by using one culture medium, and thus a tissue culture flow is simplified; and by adopting a method of combining indoor indirect evaluation and field direct evaluation, the step of evaluating the ploidy of chromosome is omitted, the difficulty that a genotype is not homozygous due to a chimera existing in an obtaining and reduplication process of the haplobiont is avoided, the gerbera jamesonii homozygote plant can be simply and rapidly bred and propagated, and a selfing life with excellent and stable characters is provided for the breeding of new variety.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for embryo rescue at different developmental stages of early phase of lilium formolongi distant hybridization
ActiveCN105123528AOvercome obstaclesVariety of colorsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureDevelopmental stageLilium formolongi
The invention belongs to the field of tissue culture of plants and particularly provides a method for embryo rescue at different developmental stages of the early phase of lilium formolongi distant hybridization. The method comprises steps as follows: 1), after lilium formolongi distant hybridization, ovaries are taken to be sterilized and disinfected; 2), embryo rescue at different developmental stages is performed in 5-25 days after pollination as follows: the ovaries are sliced and cultured, ovules are obtained and subjected to tissue culture, and hybridized tissue culture seedlings are obtained; embryo rescue at different developmental stages is performed in 35-40 days after pollination as follows: in vitro culture of ovules or in vitro culture of embryos is performed, and the hybridized tissue culture seedlings are obtained. The invention further provides an application of the method for embryo rescue at different developmental stages of the early phase of lilium formolongi distant hybridization in lily breeding. According to the method for embryo rescue at different developmental stages of the early phase of lilium formolongi distant hybridization, the barrier of incompatibility after distant hybridization fertilization of lilium formolongi and lilium oriental hybrid lines can be overcome, and the ovules with the embryos and hybrid seedlings are obtained.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining distant hybridization offspring of common head cabbage and cabbage type rape
InactiveCN108308020ARestore fertilityShorten the rescue induction timeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGermplasmBud
The invention provides a method for obtaining a distant hybridization offspring of a common head cabbage and a cabbage type rape, and belongs to the field of biotechnological breeding. The method comprises the steps that (1) a common head cabbage cytoplasmic male sterility is selected to serve as a female parent, a cabbage type rape restorer serves as a male parent, and the female parent and the male parent are isolated after hand pollination is conducted; (2) an ovary after being pollinated for 18-25 days is cut and disinfected; (3) in-vitro culture is conducted for 18-25 days; (4) an ovule in the ovary which is subjected to in-vitro culture is peeled off, and then subjected to induction culture to germinate; (5) differentiation culture is conducted, and a F1 generation seedling is obtained; and (6) a lateral bud of the F1 generation seedling is separated and transplanted onto a rooting medium, and a complete hybridization seedling is obtained. The method utilizes an embryo rescue technique to overcome the problem that the hybridization seedling cannot be obtained due to abortion of a young embryo is prone to occurring in the distant hybridization process of the common head cabbage and the cabbage type rape, an excellent recovery gene of the rape is transferred into a common head cabbage cytoplasmic male sterile cultivated species, the fertility of cabbage is recovered, and the technical evidences are provided for innovation and application of germplasm resources of cabbage.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for simplifying saving of seedless grape embryo
InactiveCN101982065ASimple test stepsSimplify the cultivation stepsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureRadicleAbortion
The invention relates to a method for simplifying saving of a seedless grape embryo, which is achieved by saving an in vitro embryo of the seedless grape embryo and comprises the following steps: preparing a synthetic medium, selecting and sterilizing young fruit, carrying out isolated culturing on the ovule, embryo stripping and embryo culture; selecting seed abortion seedless grape young fruit 72 days after flower blooming, washing the young fruit and sterilizing the young fruit at a clean bench respectively by corrosive sublimate and alcohol and stripping the ovule under aseptic conditions; then, inoculating the young fruit on the synthetic medium for carrying out dark culture, wherein the pH value of culture medium is 5.8-6.2 and culture temperature is 25-30 DEG C; carrying out embryo stripping treatment on the ovule after the ovule is cultured for 40-60 days; and continuing to inoculate the ovule to the synthetic medium and carrying out illumination culture on the ovule for 2000-4000LX. When the illumination culture is carried out on the ovule for 20-30 days, then embryo begins to germinate, a radicle gradually grows at the lower part of the embryo and two cotyledons gradually grown at the upper part of the embryo and finally the seedling is obtained. According to the method in the invention, a growth culture medium, a germination culture medium and a seedling formation culture medium are integrated into a whole and the saving of the seedless grape embryo is simplified and accelerated.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
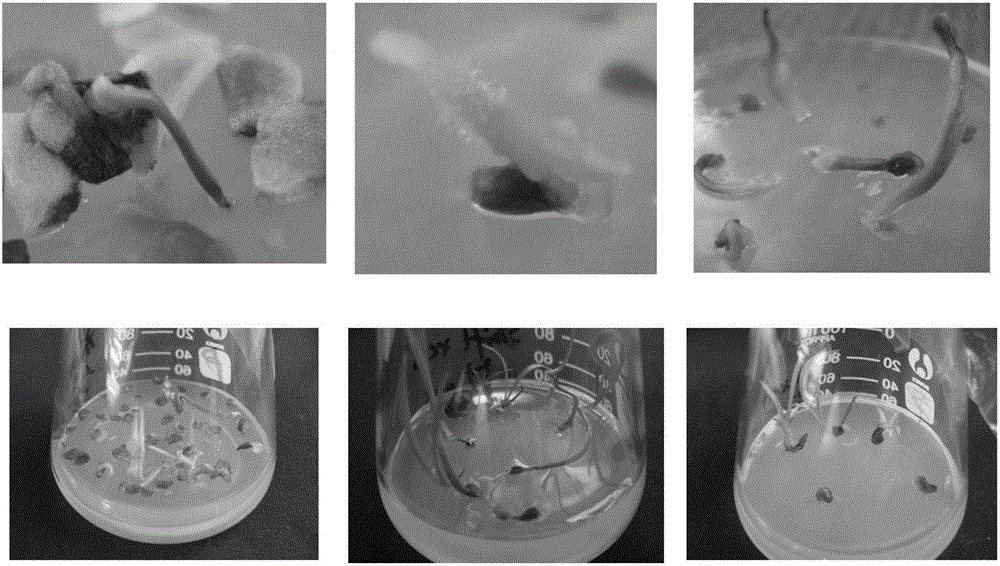
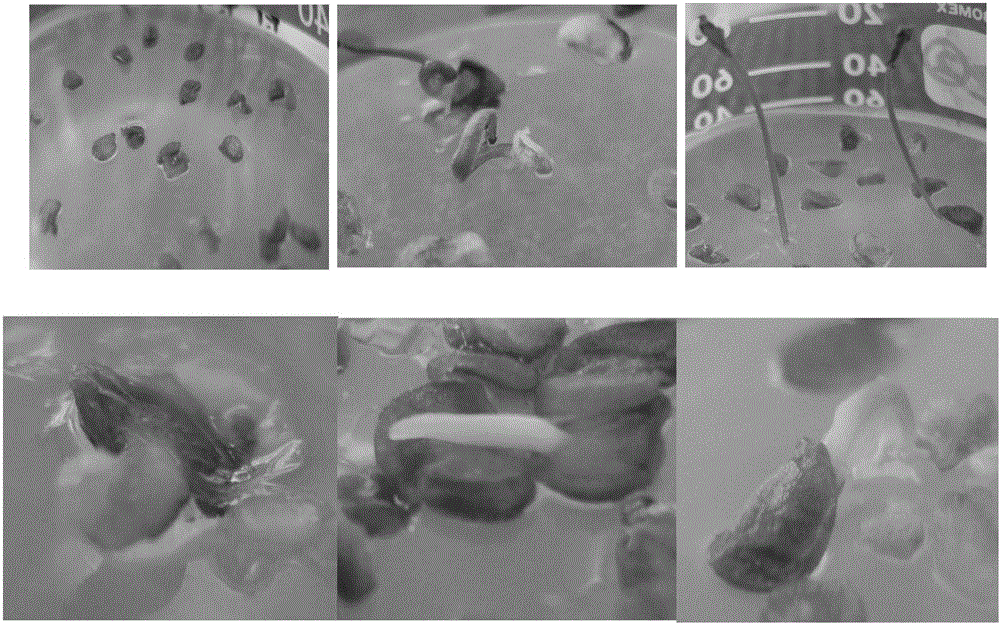
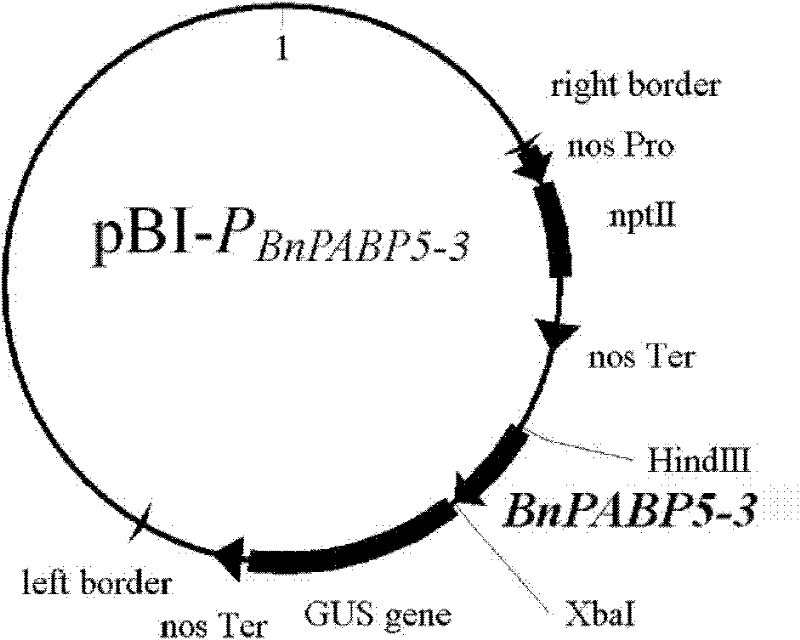
Preparation method and application of brassica napus BnPABP5-3 promoter
InactiveCN102226180ATissue-specific expression functionHigh biosecurityFermentationPlant genotype modificationBrassicaGermplasm
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a brassica napus BnPABP5-3 promoter (PBnPABP5-3). A genome walking method is utilized to clone a PBnPABP5-3 sequence: an SDS (sodium dodecyl sulphate) cracking process is applied to extract genome DNA; in different systems, endonucleases DraI, EcoRV, PvuII and StuI are used to digest DNA, and the digested DNA is respectively connected with joint segments, then primary PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification is carried out by taking the DNA connected with the joint segments as templates, and secondary PCR amplification is carried out by taking 50-time diluted solution of products of the primary PCR as a template, thus the PBnPABP5-3 is obtained. The PBnPABP5-3 can be applied to the anther, pollen grain, root tip and ovule of a plant. The promoter has the function of driving expression of a foreign gene, the expression part is in the anther, pollen grain, root tip and ovule of the plant, and the promoter has application potential in the improvement of the safety of rape edible oil, the improvement of the stress resistance and lodging resistance, improvement of the quality of crops, artificial sterile line creation, germ plasma resource enrichment and the like.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Double-phase culture-medium for improving antiviral and nuclease-free grape-embryo crash breeding efficiency and its production
A two-phase culture medium for improving anucleate antiviral glucose embryo crash breeding efficiency and its production are disclosed. The procedure is carried out by preparing liquid-phase culture medium and solid-phase culture medium proportionally, using liquid to kill bacterium at high-pressure, pouring it into solid-phase culturing medium supernatant and preparing solid-phase culture medium. It has better anucleate antiviral glucose embryo development rate and breeding rate.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for cultivating Lilium oriental hybrid embryos
InactiveCN102599053APrevent premature agingAddressing Post Fertilization BarriersPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGermplasmPollination
The invention relates to a method for cultivating Lilium oriental hybrid embryos, which is effective in breeding effect and short in breeding period. The method includes: pollinating a Lilium oriental hybrid line; sectioning and peeling small embryos, ovules or ovaries; and performing isolated culture. By cross pollination of the ovaries and young embryos and isolated culture, the embryos can be taken out for culturing before abortion to avoid premature senility of distant hybrid embryos, and accordingly Lilium post-fertilization barrier can be overcome effectively, a great amount of distant hybrid embryos are allowed to continue growing into normal seeds, a breeding procedure is drawn close as soon as possible, and the breeding cycle is shortened. In addition, a great amount of distant hybrids are obtained, Lilium interspecific distant hybridization is achieved, and a batch of novel germplasm is created. The embryo rescue technology and the technology of within-bottle Lilium bulbing are combined, so that culture cycle of Lilium hybrids is shortened effectively, and hybrid survival rate is increased.
Owner:赵兴华
Cultivation method of polyploid pomegranate
InactiveCN103392606AReduce incubation timeOvercome time-consuming disadvantagesHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHybrid seedNormal female
The invention relates to a cultivation method of polyploid pomegranate. The cultivation method comprises following steps: selecting branched flower buds and branches which grow on the top of a diploid plant, inducing the flower to generate polyploid pollen by dropwise adding chemical materials into the flower buds, carrying out hybridizations between induced male flowers and normal female flowers or between induced female flowers and normal male flowers so as to obtain polyploid hybrid fruits, culturing the hybrid seeds in the hybrid fruits so as to obtain polyploid plants, and culturing the polyploid plants in a tissue cultivation mode so as to obtain polyploid pomegranate plants. The cultivation method overcomes the shortage that a large amount of time is consumed by the conventional chromosome reduplication methods. The cultivation method utilizes the fact that the pollen and ovule cells in the reproductive organs are haploids, namely 1n chromosome, during the pomegranate blossom period, uses chemical materials to process the pollen and ovule cells to induce chromosome doubling, thus largely reduces the time of chromosome doubling process, and has the advantages of available materials, simple operation, and high success rate.
Owner:南京大渊美容保健有限公司
Engineering male sterility or non-transgenic pollen
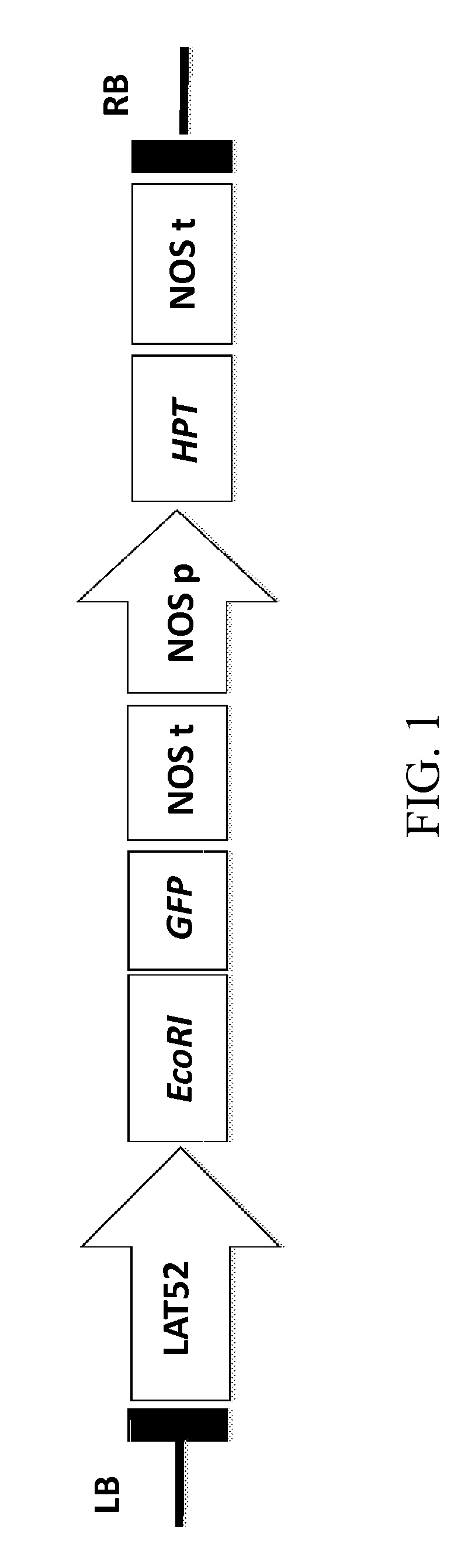
InactiveUS20130007911A1MicroorganismsOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotideTransgene
The present invention relates to methods of blocking or reducing genetically modified plant (GMO) pollen flow using a “non-lethal” approach. In this aspect, at least one transgenic polynucleotide of interest is linked to a pollen-ablation construct as described herein. The pollen-ablation construct contains a polynucleotide encoding a restriction enzyme that renders the transgenic pollen unable to fertilize a sexually compatible ovule.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Isolated culture method for peony ovules
InactiveCN102511395ASolve the problem of hybrid abortionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsOvaryCulture mediums
The invention relates to an isolated culture method for peony ovules. After peony ovaries which are fertilized for 15 to 90 days are disinfected by mercuric chloride, the ovules are taken out and divided into a 15-to-48-day ovule group and a 49-to-90-day ovule group; the 15-to-48-day ovule group is inoculated into MS culture medium, cultured in the dark for 3 to 15 days, then inoculated into MS culture medium II, cultured in the dark for 10 days and then cultured in light for 7 to 27 days; afterwards, the 15-to-48-day ovule group is inoculated into the MS culture medium II again and cultured in light for 8 to 28 days, so that mature peony seeds I are obtained; and after being first cultured in the dark for 10 days, the 49-to-90-day ovule group is cultured in light for 7 to 27 days, then inoculated in the MS culture medium II again and cultured in light for 8 to 28 days, so that mature peony seeds II are obtained. The isolated culture method for peony ovules can be used in the isolatedresearch on peony embryo development, and solves the problems of the early abortion of the embryos of good-looking peony varieties and the abortion of distant somatic hybrid peonies, and by way of ovule culture, the improved research on peony varieties can be carried out as well.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for plant gene transfering by electrical shock and ovary injection
InactiveUS20050160502A1Improve pollination rateIncrease opportunitiesOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiologyOvary
A method for plant gene transfer by electrical shock and ovary injection, comprises: cutting a stigma off a style after pollination when the pollen tube reaches ovule, creating a passage between the style and ovary; injecting an exotic DNA into the ovary via the passage; inserting a conductive piece into a locule via the passage as a negative electrode; covering the ovary with a conductive layer and the conductive layer serves as a positive electrode; creating an electric field by connecting the conductive piece and the conductive layer to an electric device.
Owner:TAIWAN AGRI RES INST COUNCIL OF AGRI
Method for obtaining plant graft chimaera progeny by embryo rescue
InactiveCN101828525AEasy to operateThe effect of embryo rescue is remarkableCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsNutrient solutionFilter paper
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a plant graft chimaera progeny by embryo rescue, which comprises the following steps of: (1) picking an ovary in 1 day before the immature embryo of a crucifer graft chimaera is aborted; (2) sterilizing and flushing the ovary; (3) placing the ovary on a culture dish paved with filter paper which is fully soaked in nutrient solution, dissecting one end of the ovary and then tearing the ovary along a ventral suture, selecting and cutting light green and glossy ovule, suspensor and ovary wall tissue connected with the suspensor and inoculating the three to a development culture medium, culturing the three under a dark condition at the temperature of 25 + / - 2 DEG C, and then culturing the three under light; (4) picking mature seeds, inoculating the seeds to a sprouting culture medium, and culturing the seeds under the dark condition at the temperature of 25 + / - 2 DEG C; (5) after the seeds are sprouted and grow main leaves, transferring the seedlings to a sub-cultured medium to perform culture, and then transferring the seedlings to a rooting culture medium to perform rooting; and (6) taking the routed seedlings out, transplanting the seedlings to a nutrition pot filled with matrix, hardening the seedlings for 6 to 12 days, and then transferring the seedlings to a field so as to obtain the plant graft chimaera progeny.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compositions and methods for the expression of a sequence in a reproductive tissue of a plant
InactiveUS20150152430A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesEgg cellHeterologous
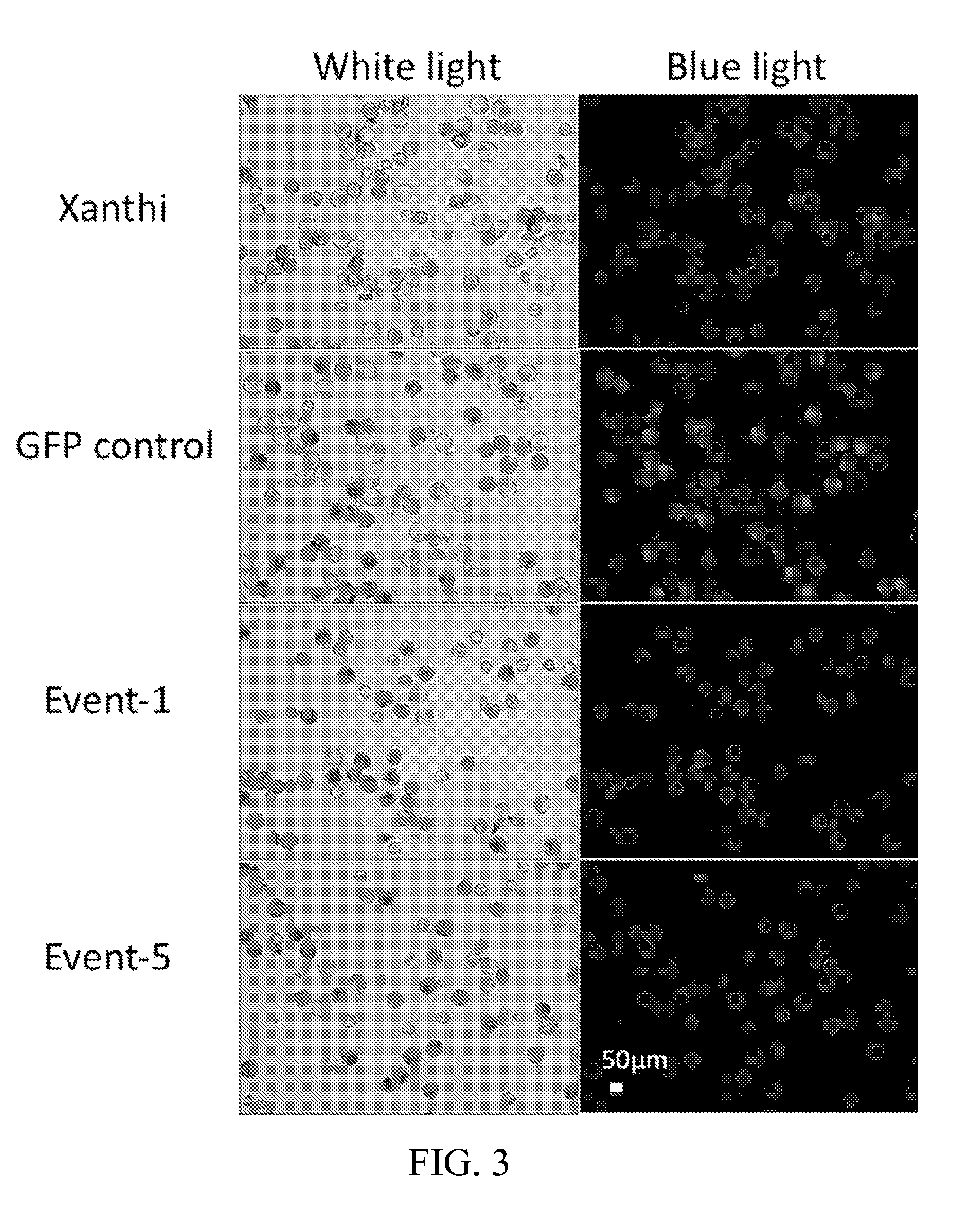
Compositions and methods for regulating expression of heterologous nucleotide sequences in a plant are provided. Compositions include promoter sequences with direct expression in an egg cell or embryonic cell-preferred manner. Such compositions find use in, for example, a method for expressing a heterologous nucleotide sequence in a plant; detection of specific cell types in the ovule and targeted ablation of specific cell types.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
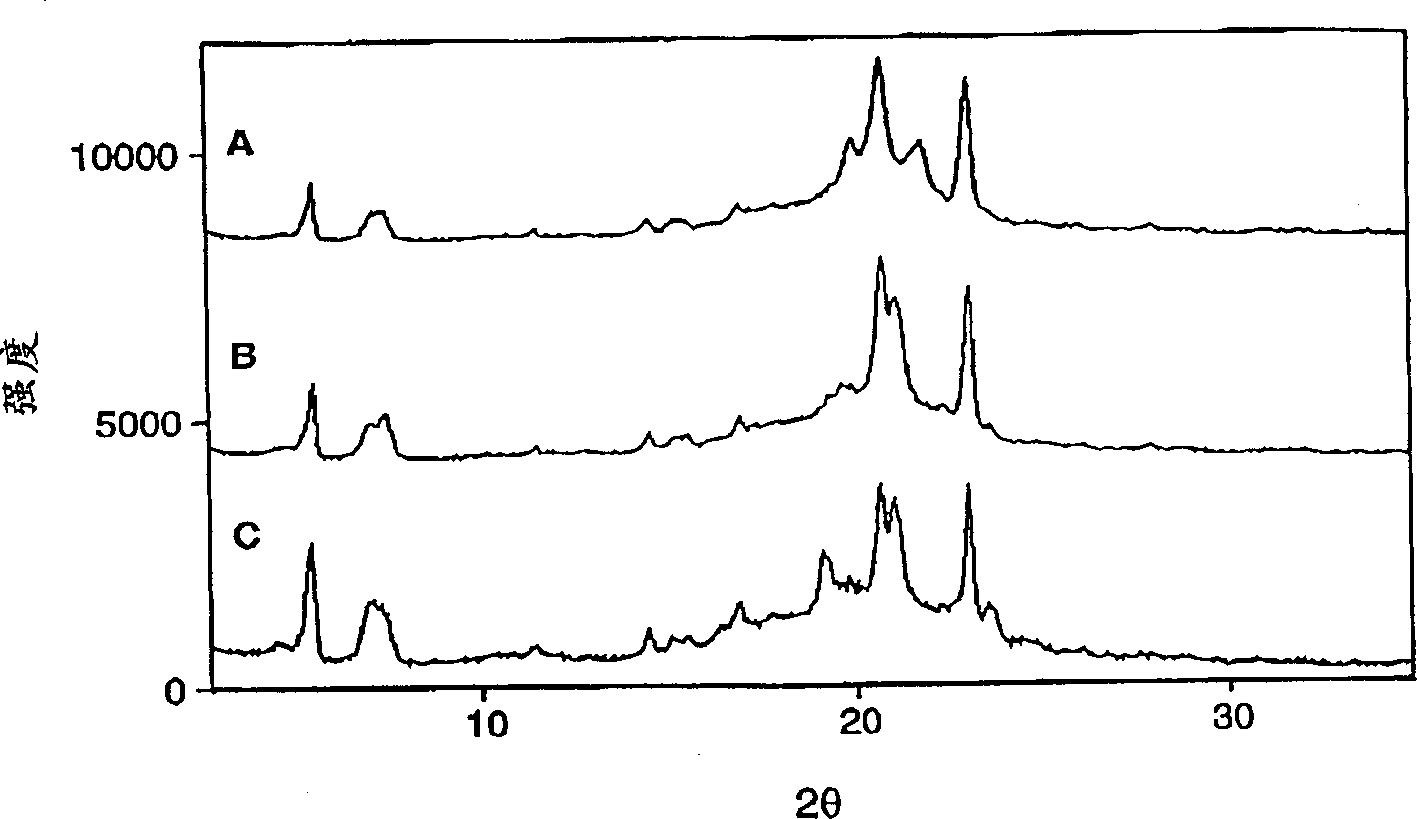
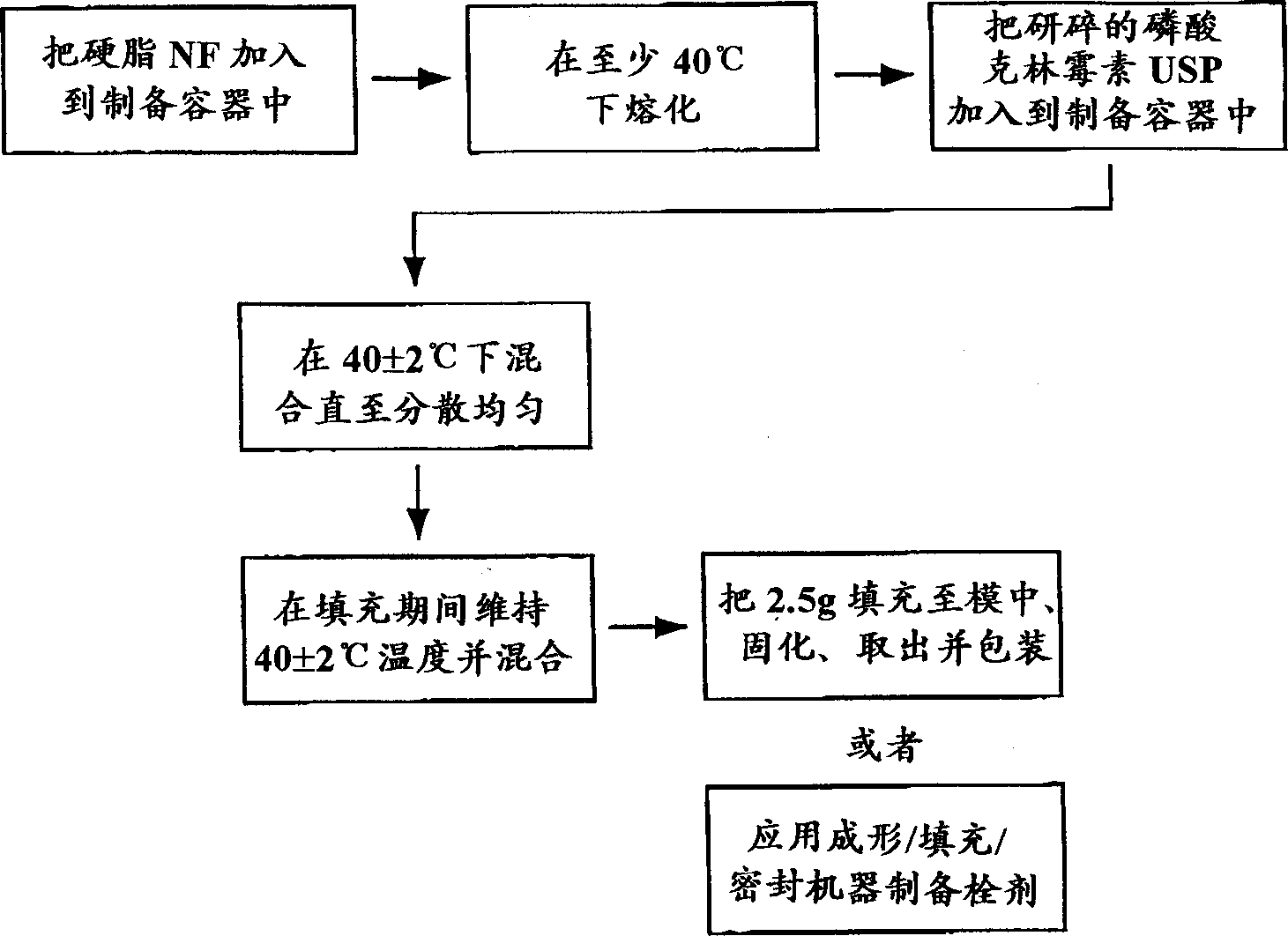
Intravaginal clindamycin ovule composition
InactiveCN1360495AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsVaginal SuppositoryBacterial vaginosis
A highly storage-stable composition for vaginal administration of clindamycin is disclosed which is useful for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. The composition is a vaginal suppository containing an antimicrobially effective amount of clindamycin dispersed in a Hard Fat NF suppository base. Hard Fat NF suppository bases provide a clindamycin product having long term storage stability while providing efficacy against bacterial vaginosis which is equivalent to clindamycin vaginal creams.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com