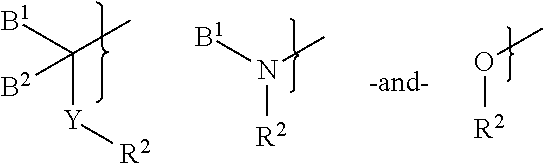
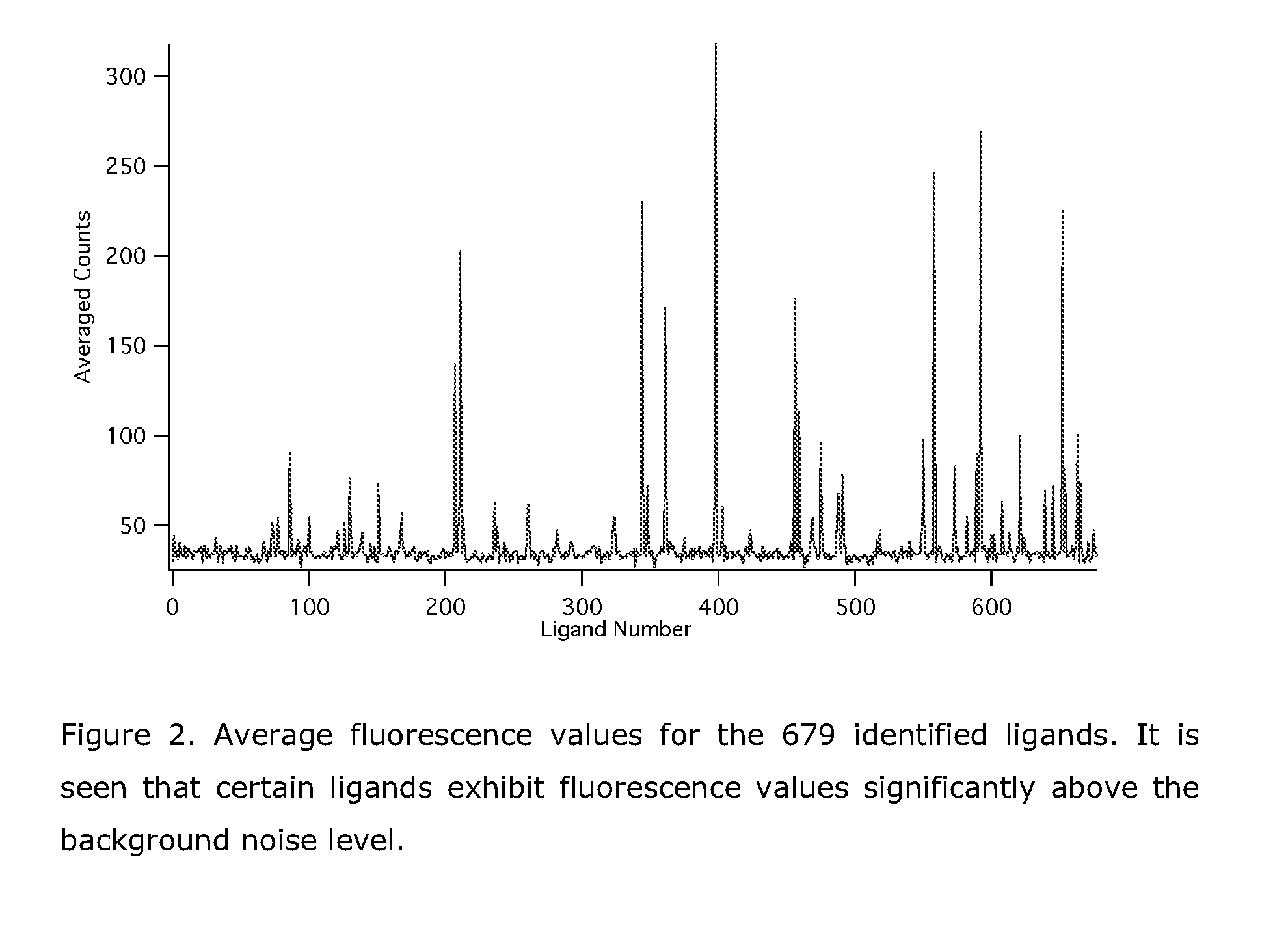
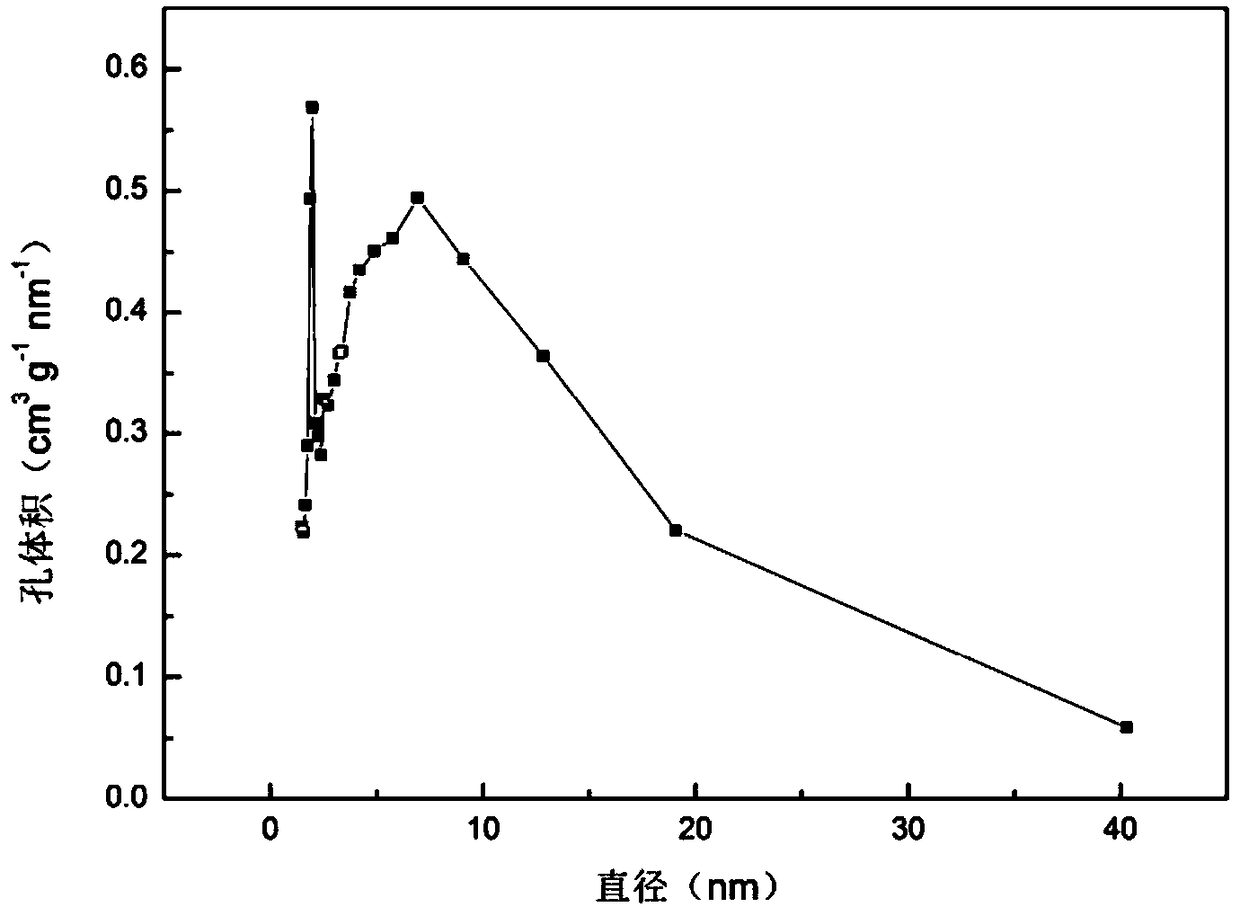
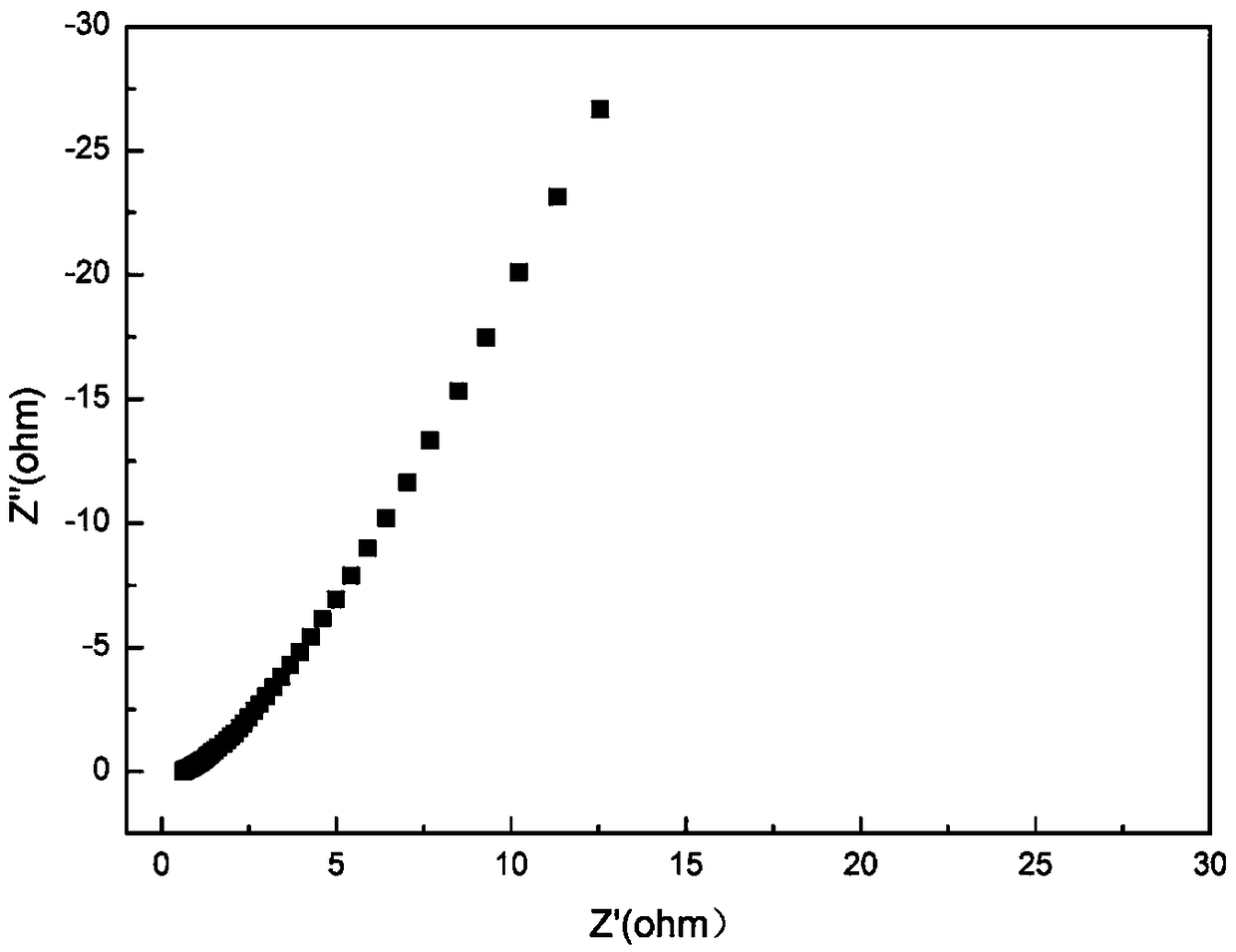
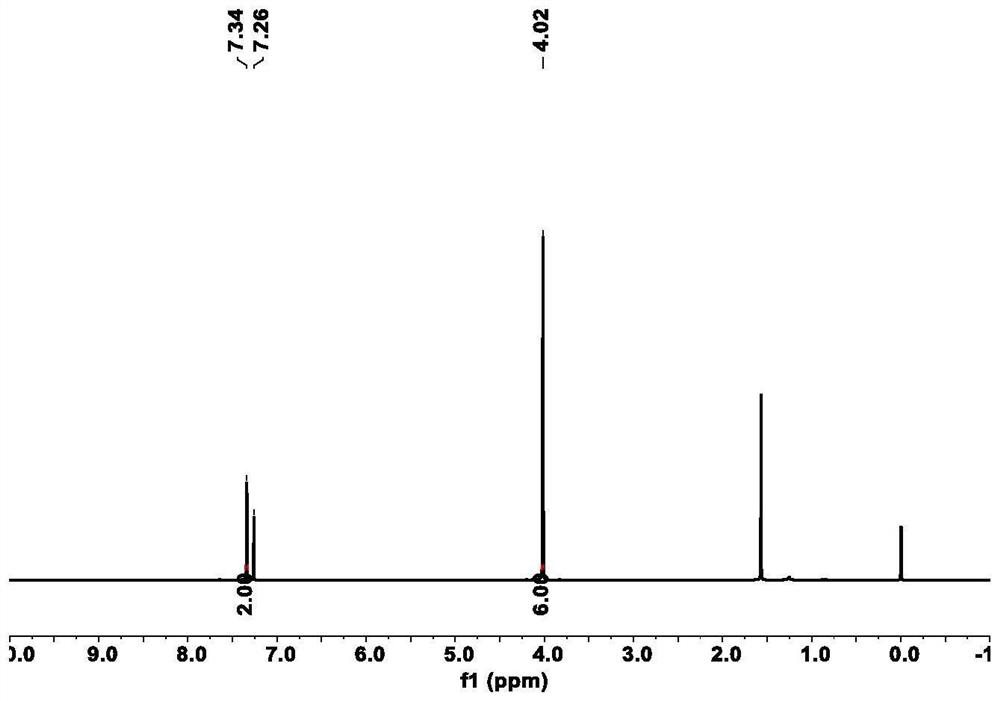
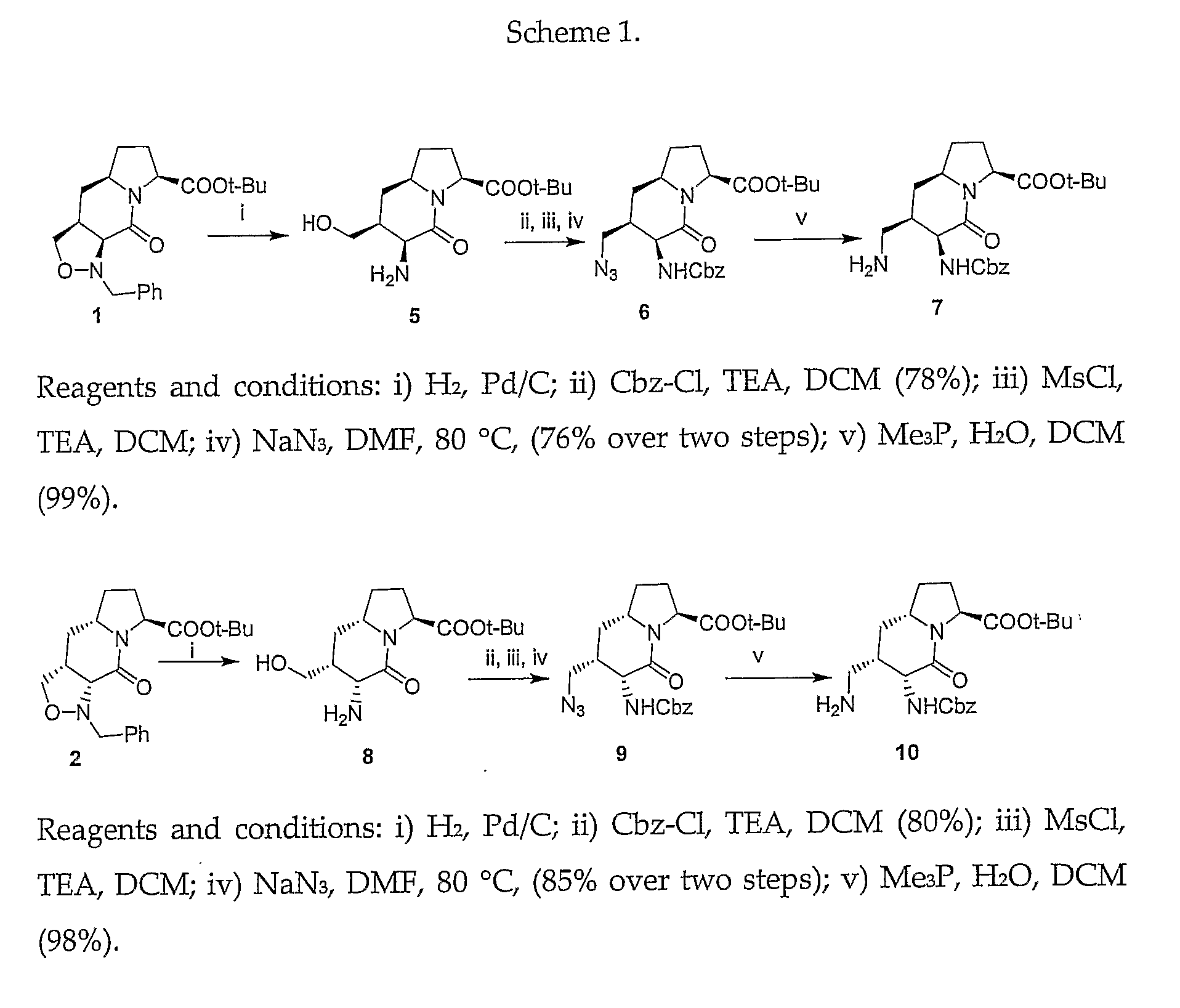
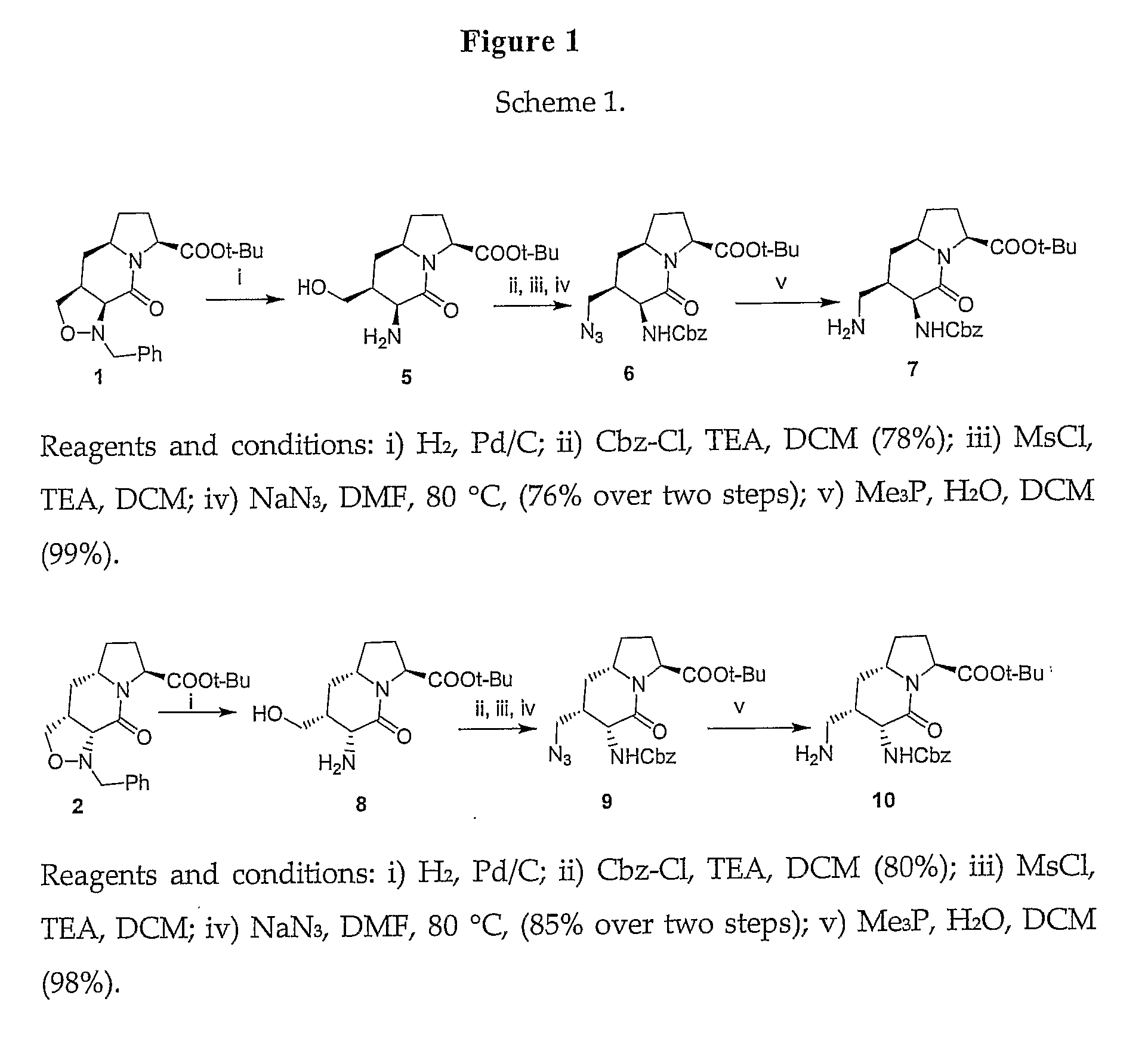
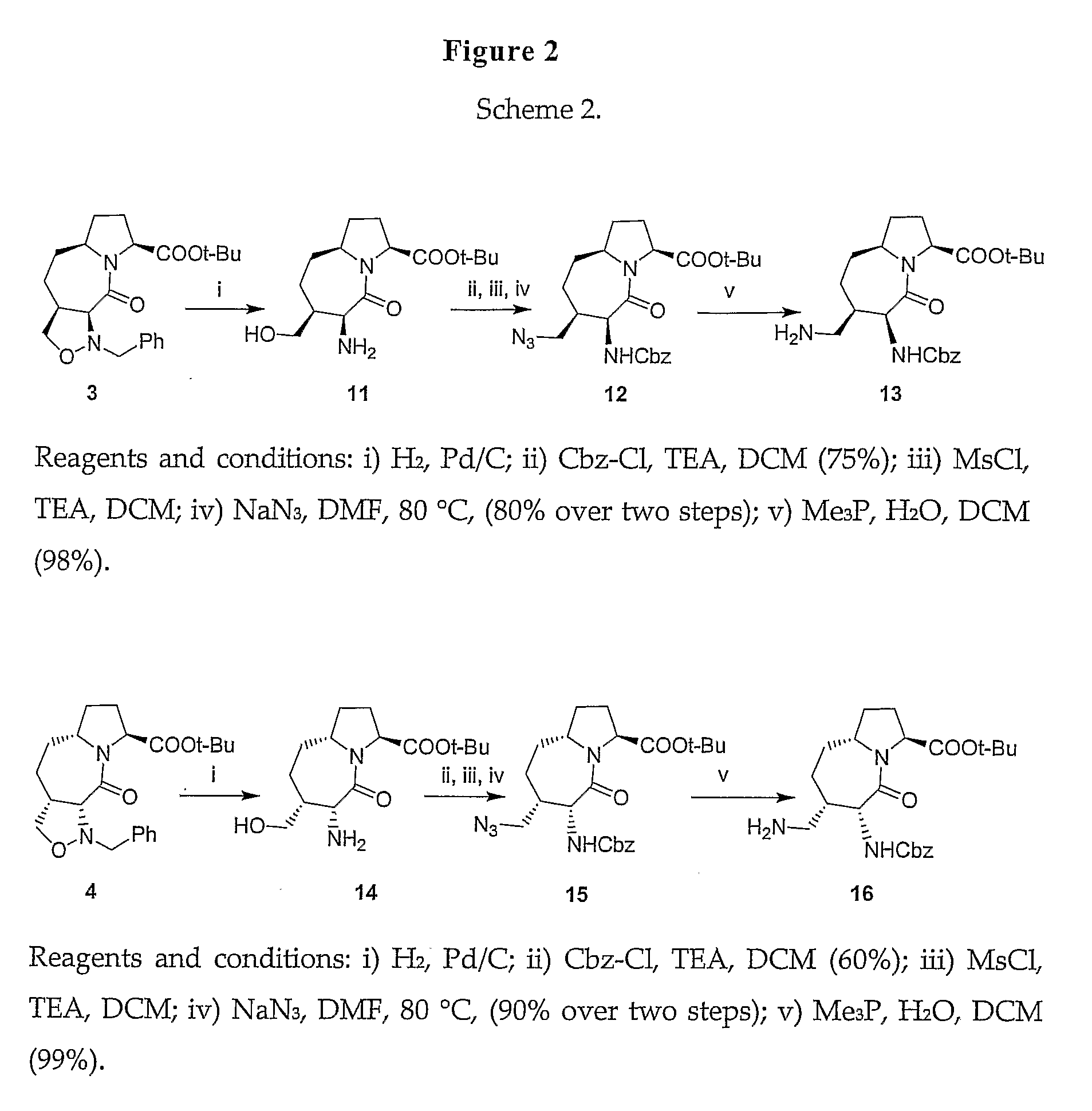
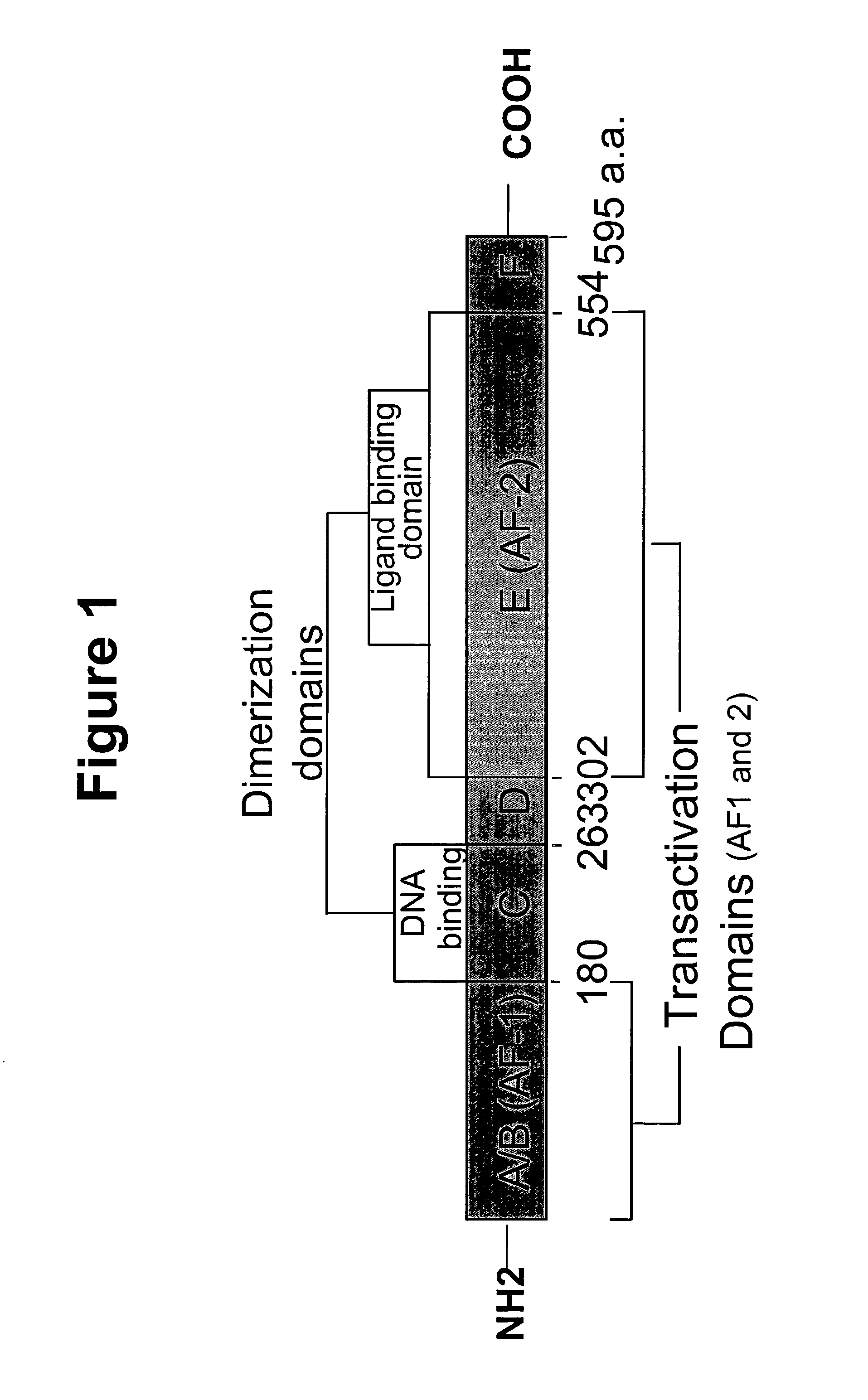
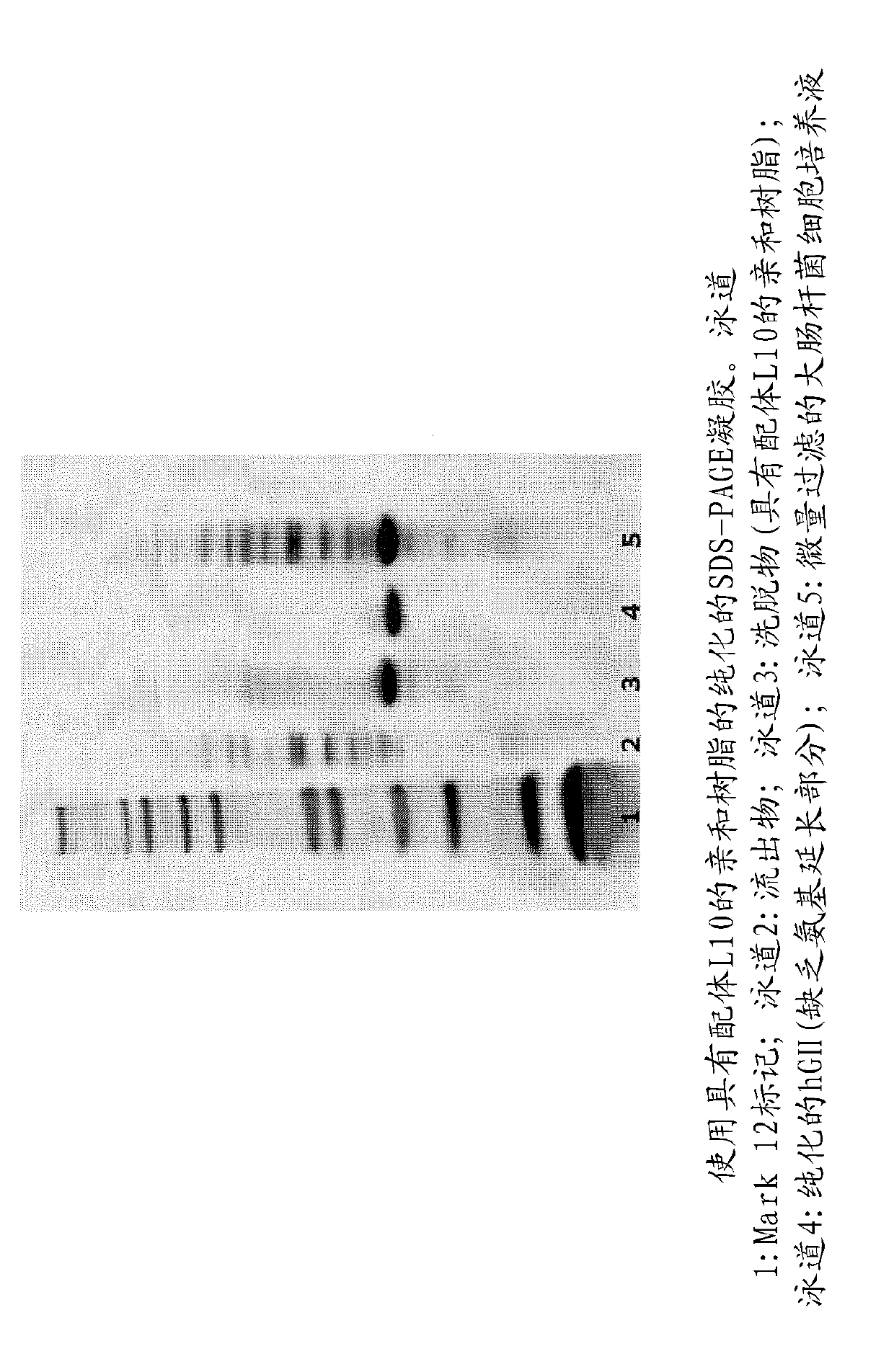
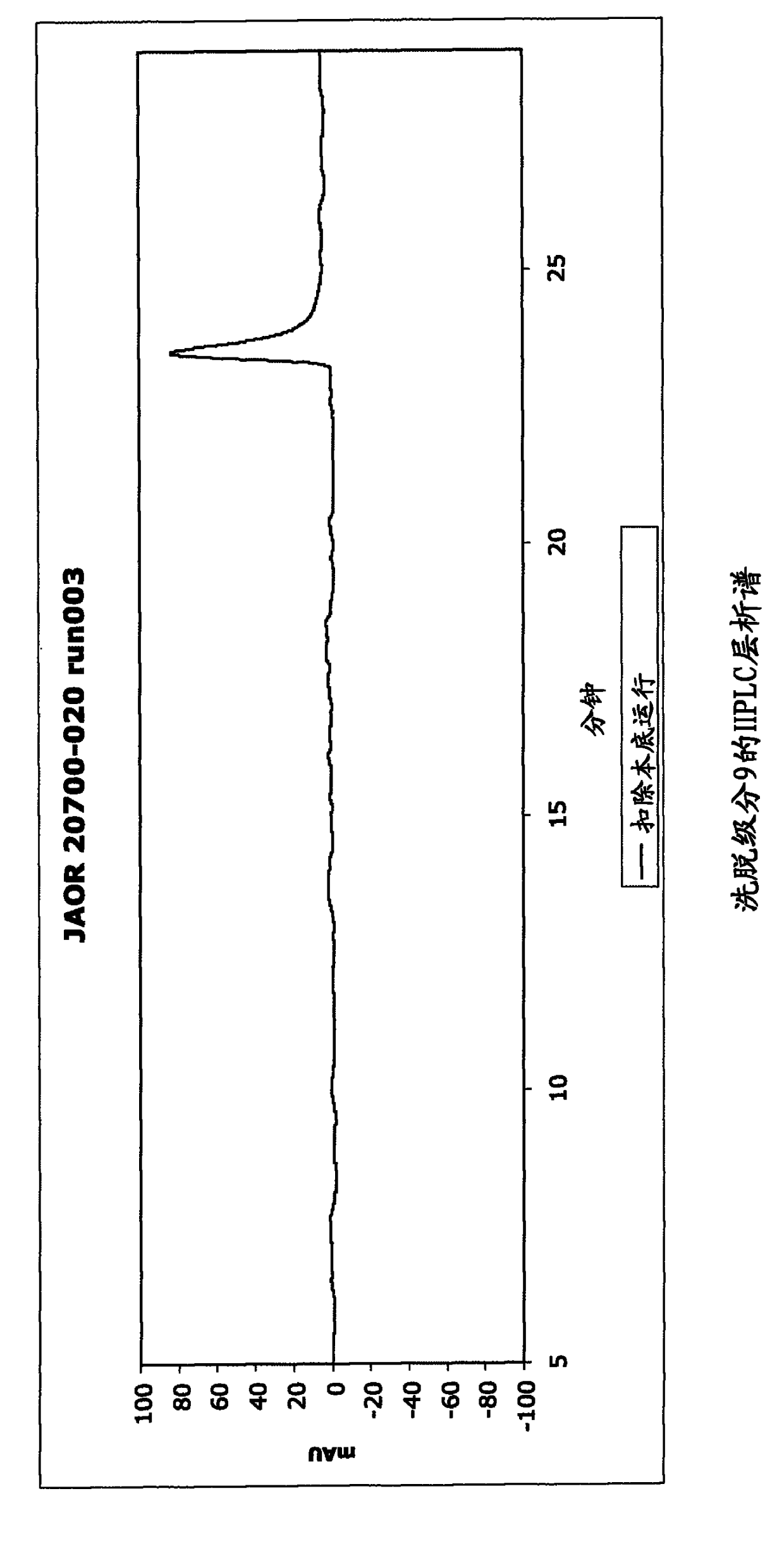
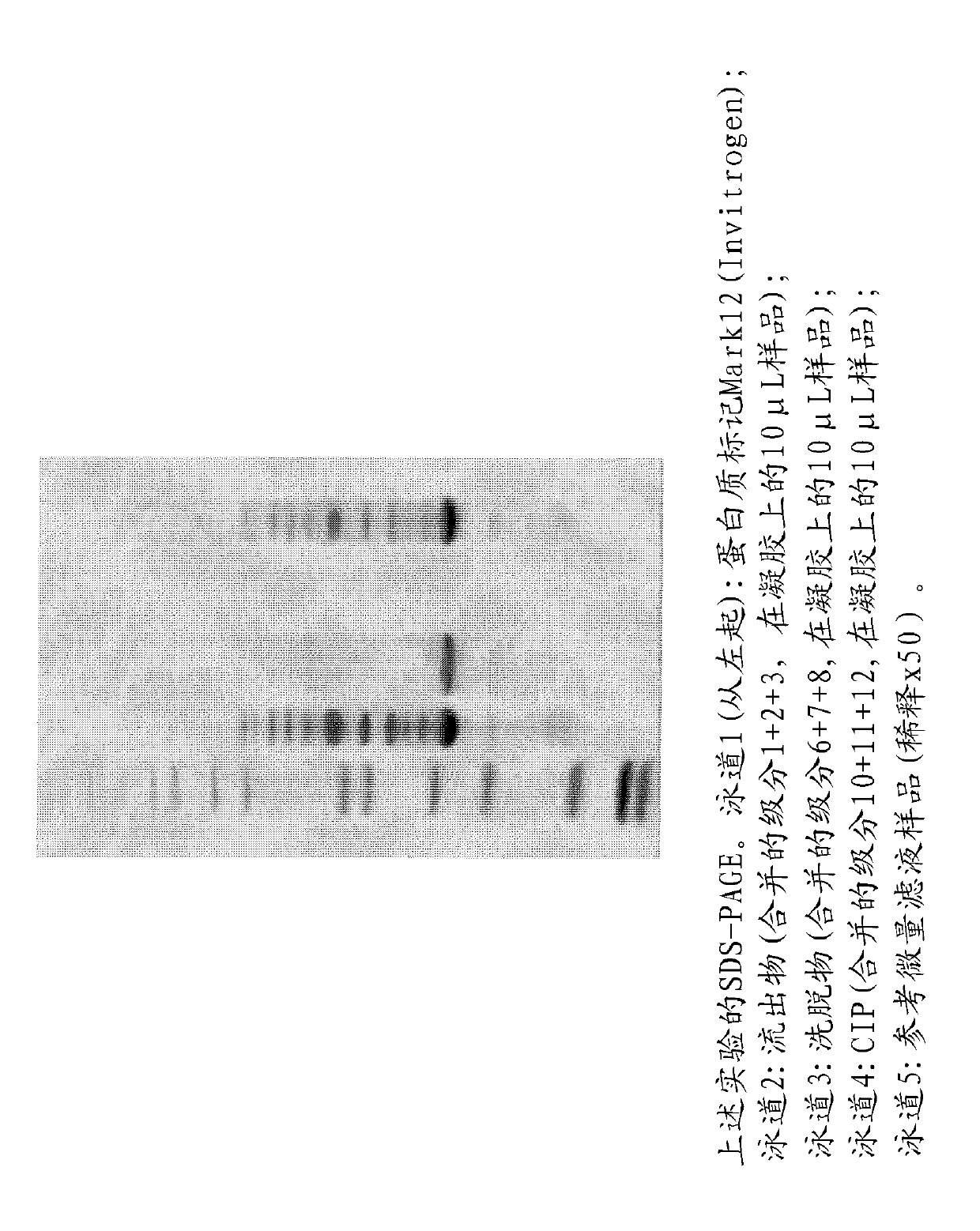
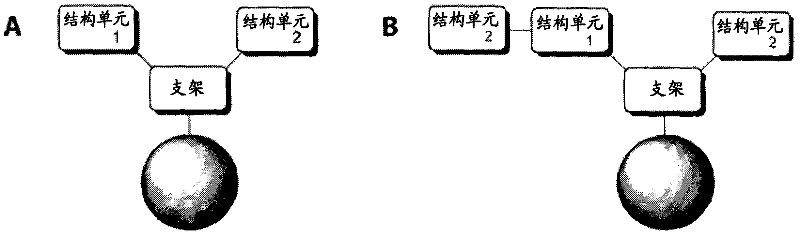
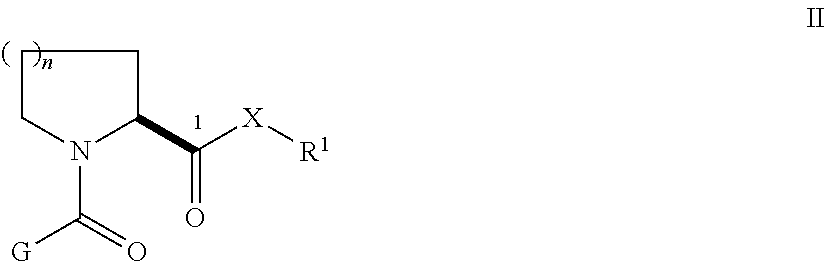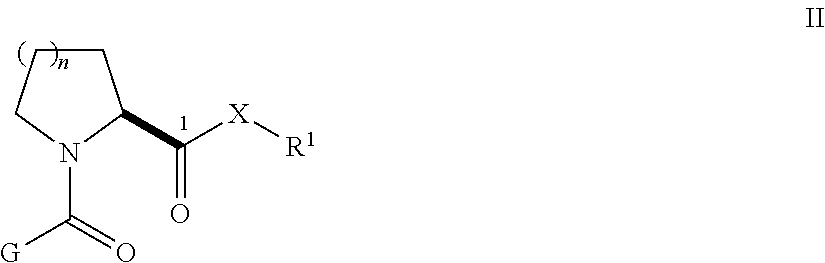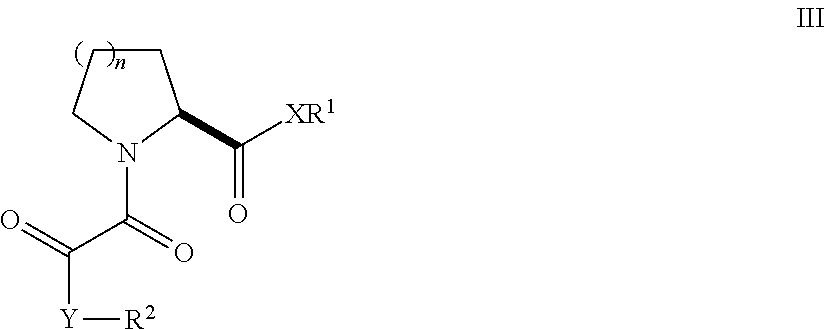Patents
Literature
44 results about "Synthetic ligands" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anti-human T-cell costimulating polypeptide monoclonal antibodies
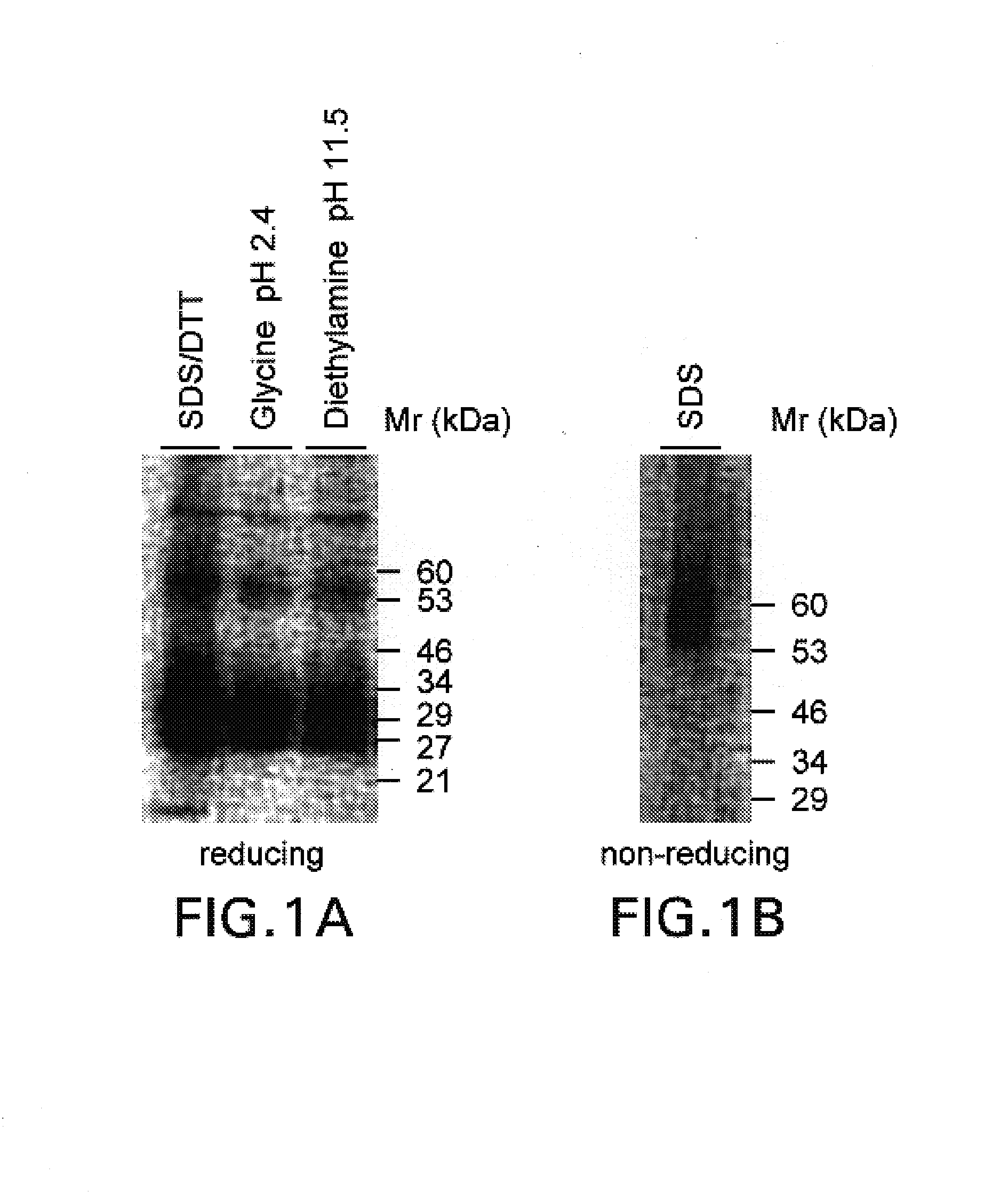
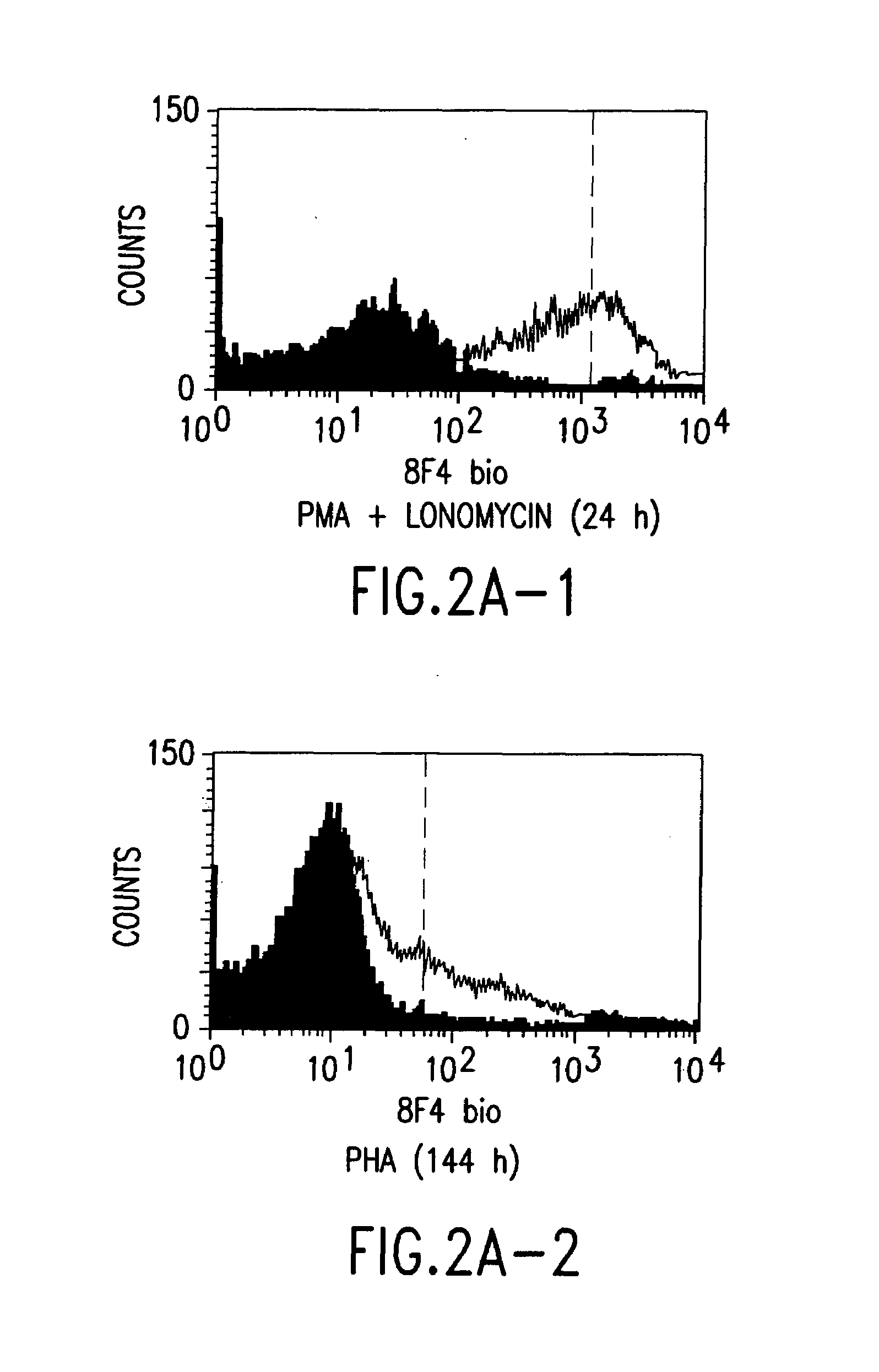
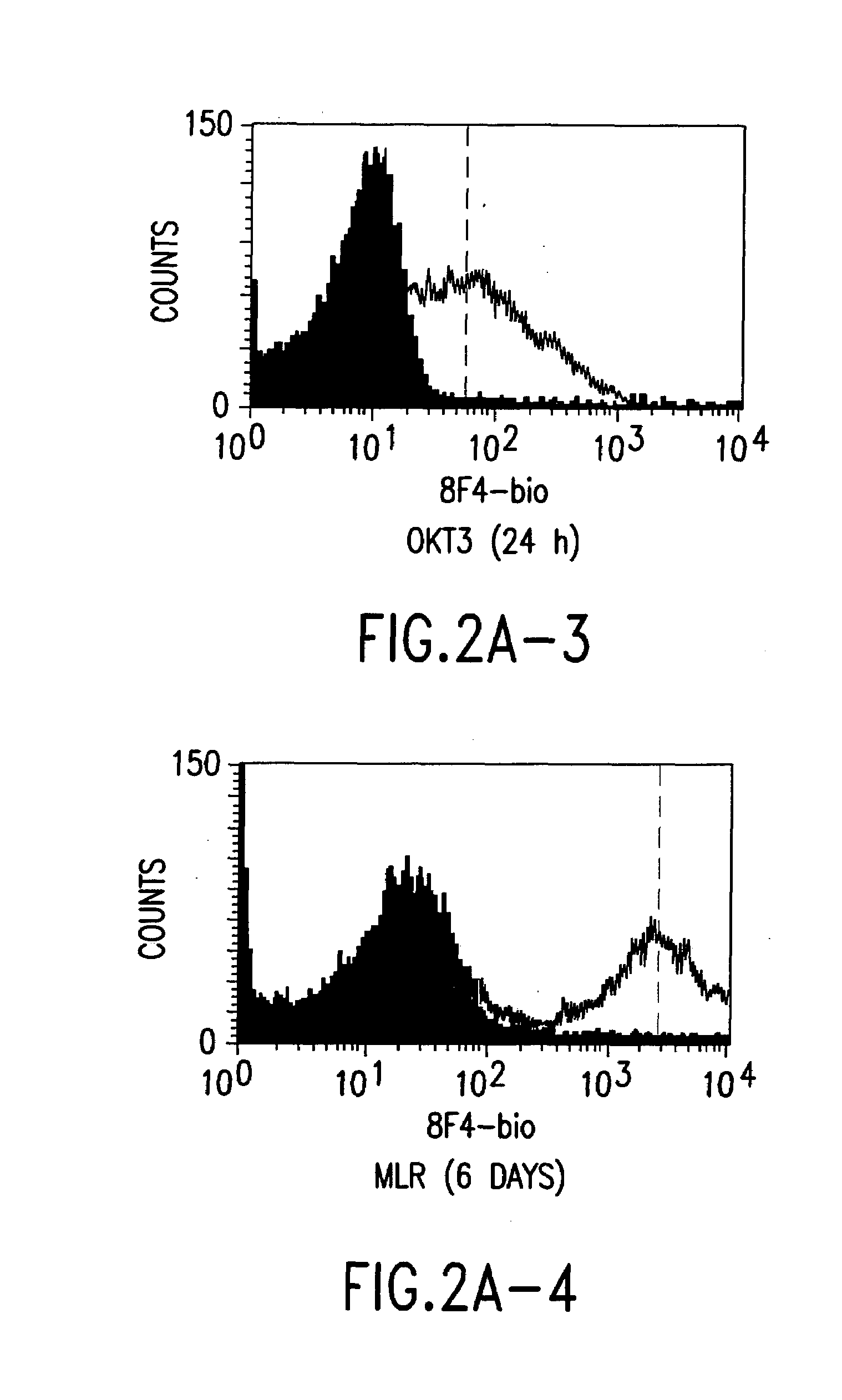
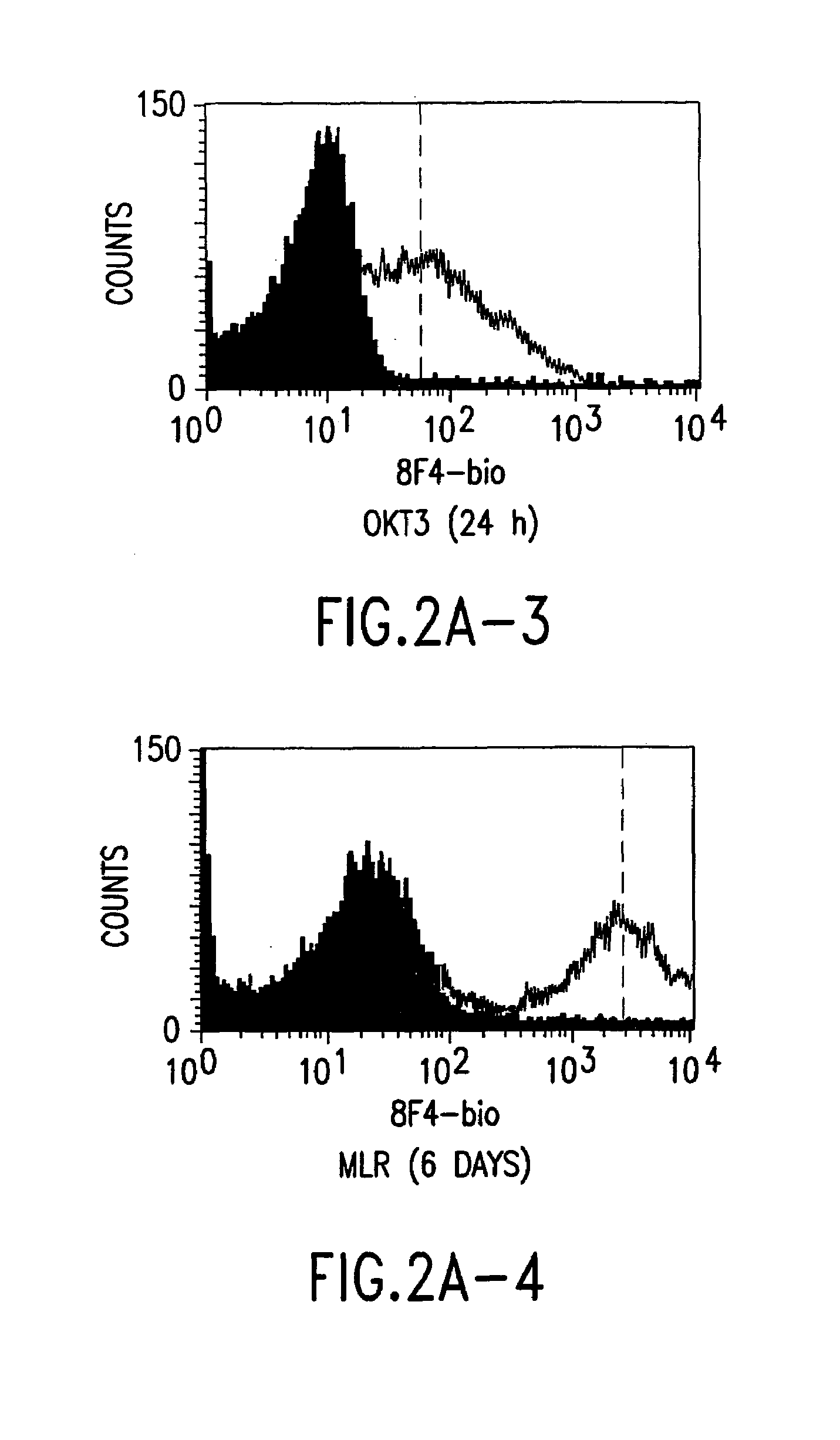
A polypeptide (8F4 molecule) with a T-cell costimulating biological activity is disclosed, as well as monoclonal antibodies against said 8F4 molecule and hybridoma cells which produce the monoclonal antibodies, the use as medicaments of substances which inhibit the biological activity of the disclosed 8F4 polypeptide, in particular monoclonal antibodies, natural or synthetic ligands, agonists or antagonists, in particular for preventing or treating diseases which involve the immune system, the use of said 8F4 molecule or cells containing said 8F4 molecule as medicaments, in particular for preventing or treating diseases which involve the immune system, and the use of substances which specifically recognize the disclosed polypeptide, in particular monoclonal antibodies, natural or synthetic ligands, agonists or antagonists, for diagnosing diseases which involve the immune system.
Owner:BUNDESREPUBLIK DEUT IETZVERTRETEN DURCH DAS ROBERT KOCH INST VERTRETEN DURCH SEINEN PRASI
Methods of modulating T lymphocyte costimulation with an antibody to an 8F4 polypeptide
A polypeptide (8F4 molecule) with a T-cell costimulating biological activity is disclosed, as well as monoclonal antibodies against said 8F4 molecule and hybridoma cells which produce the monoclonal antibodies, the use as medicaments of substances which inhibit the biological activity of the disclosed 8F4 polypeptide, in particular monoclonal antibodies, natural or synthetic ligands, agonists or antagonists, in particular for preventing or treating diseases which involve the immune system, the use of said 8F4 molecule or cells containing said 8F4 molecule as medicaments, in particular for preventing or treating diseases which involve the immune system, and the use of substances which specifically recognize the disclosed polypeptide, in particular monoclonal antibodies, natural or synthetic ligands, agonists or antagonists, for diagnosing diseases which involve the immune system.
Owner:BUNDESREPUBLIK DEUTSCHLAND
Method for screening combinational bead library; ligands for cancer cells
InactiveUS7262269B2Good adhesionPromote cell growthPeptide librariesLibrary screeningCancer cellCell growth
The invention includes a cell-growth-on-bead assay for screening a one-bead-one-compound combinatorial bead library to identify synthetic ligands for cell attachment and growth or proliferation of epithelial and non-epithelial cells. Cells are incubated with a compound bead library for 24 to 72-hours, allowing them to attach and grow on the beads. Those beads with cells growing are removed, and the ligand on the bead is identified. Also provided are ligands specific for cancer cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nuclear receptor ligands and ligand binding domains
The present invention provides new methods, particularly computational methods, and compositions for the generation of nuclear receptor synthetic ligands based on the three dimensional structure of nuclear receptors, particularly the thyroid receptor (herein referred to as "TR"). Also provided are crystals, nuclear receptor synthetic ligands, and related methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Integrin targeted synthetic ligands for diagnostic and therapeutic applications
ActiveUS8636977B2Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCyclic peptideIntegrin targeting
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Modulation of bacterial quorum sensing with synthetic ligands
ActiveUS7910622B2Diminish and inhibit productionIncrease productionBiocideOrganic chemistryHomoserineBacteria
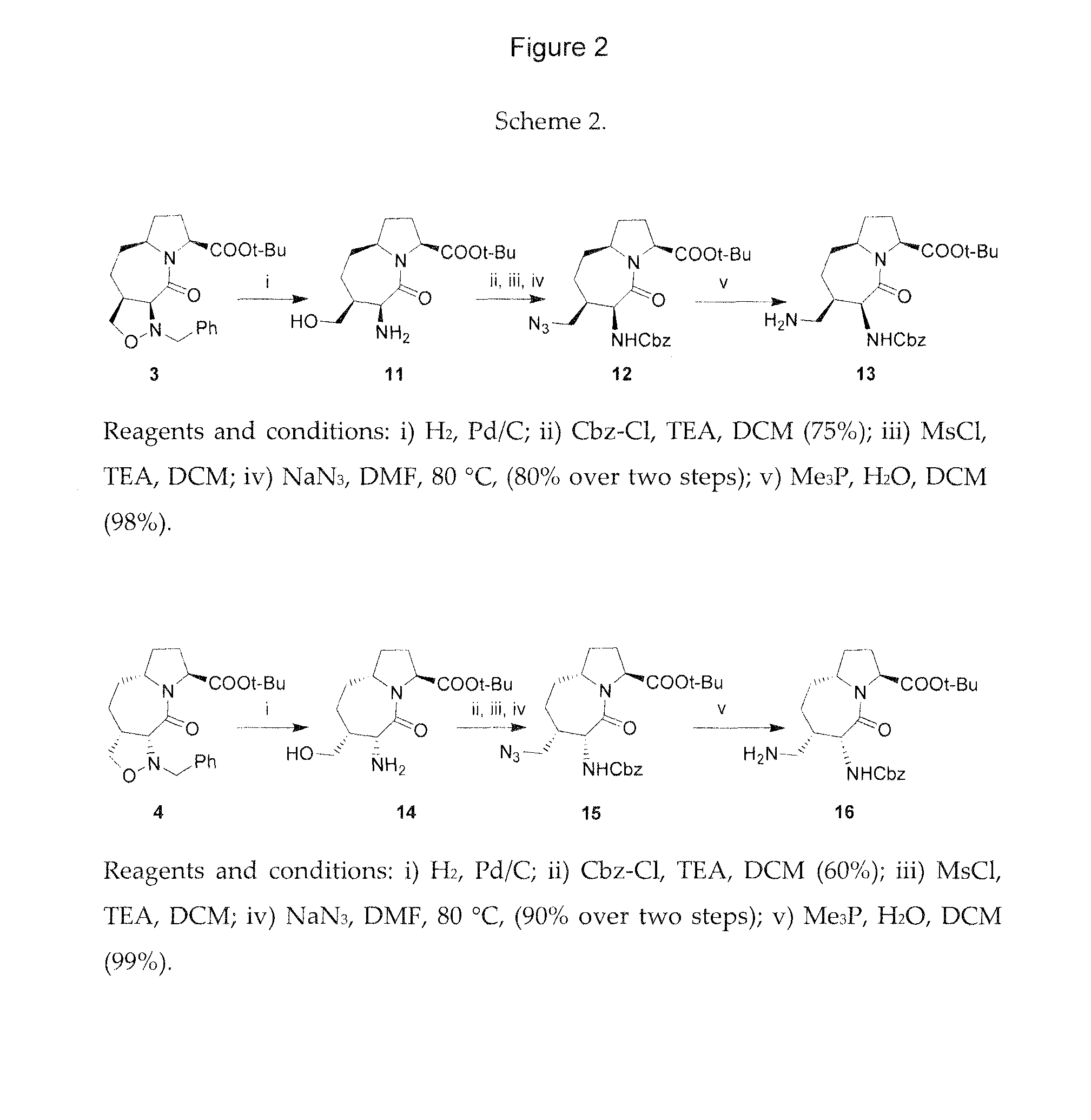
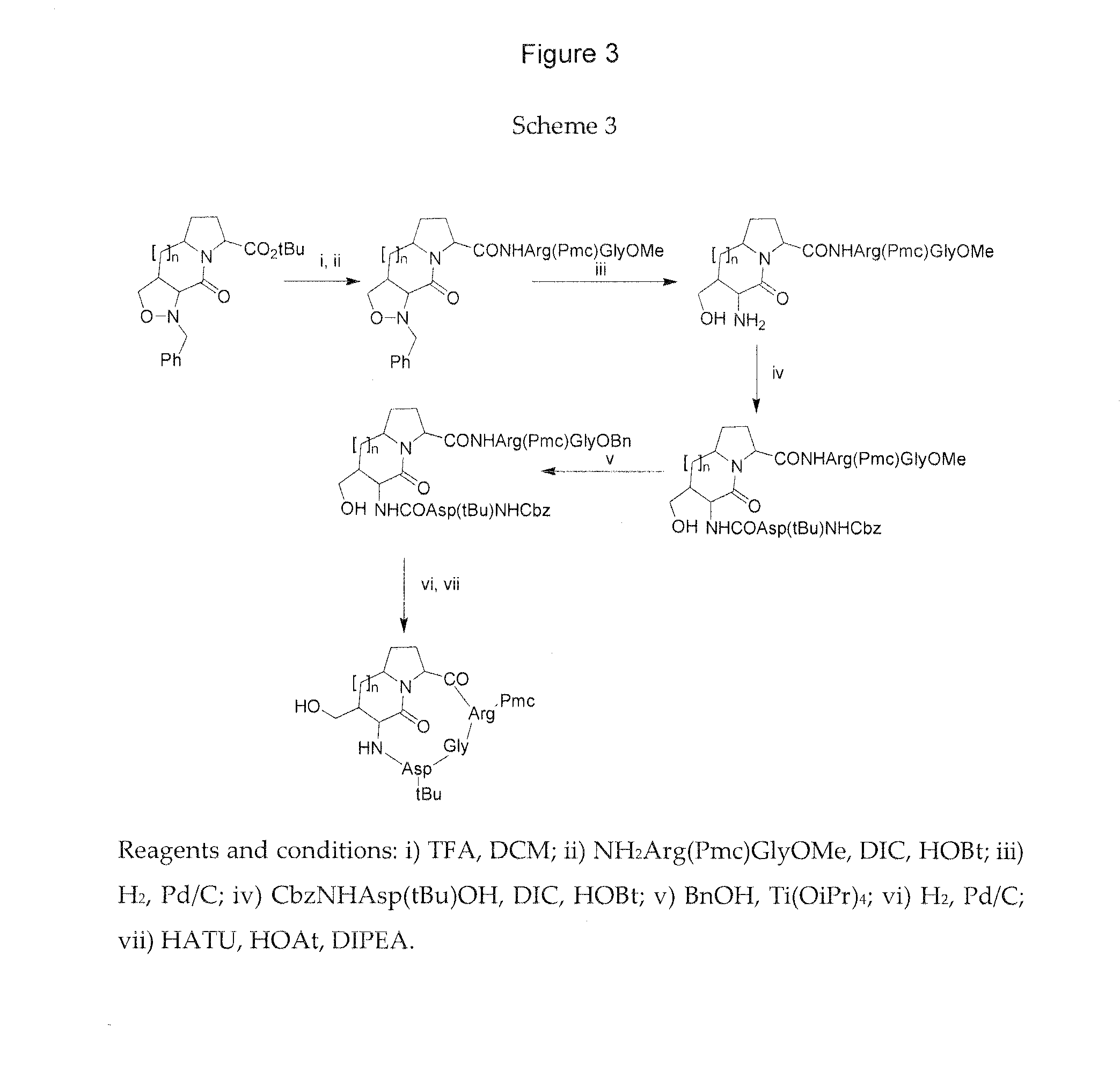
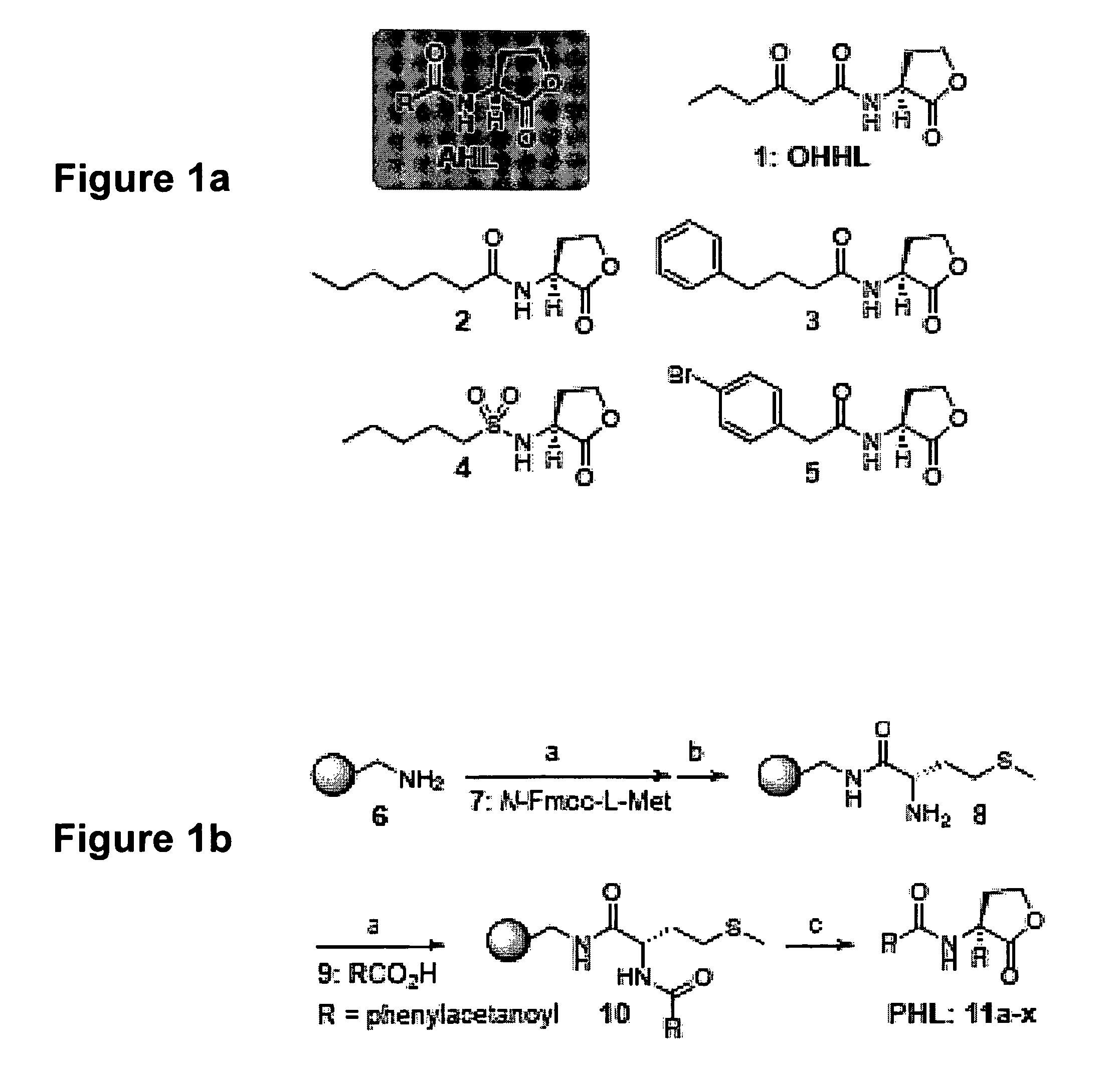
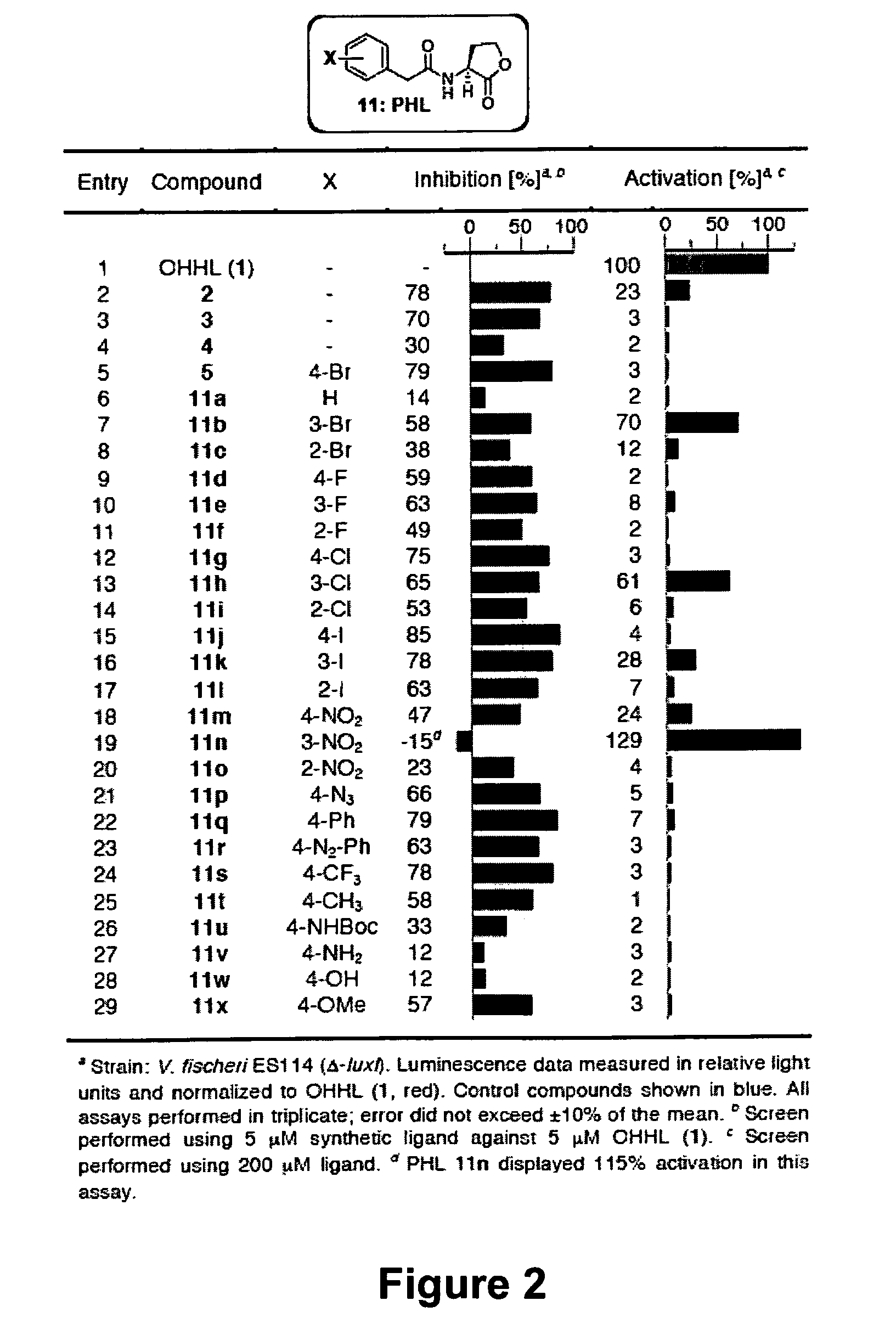
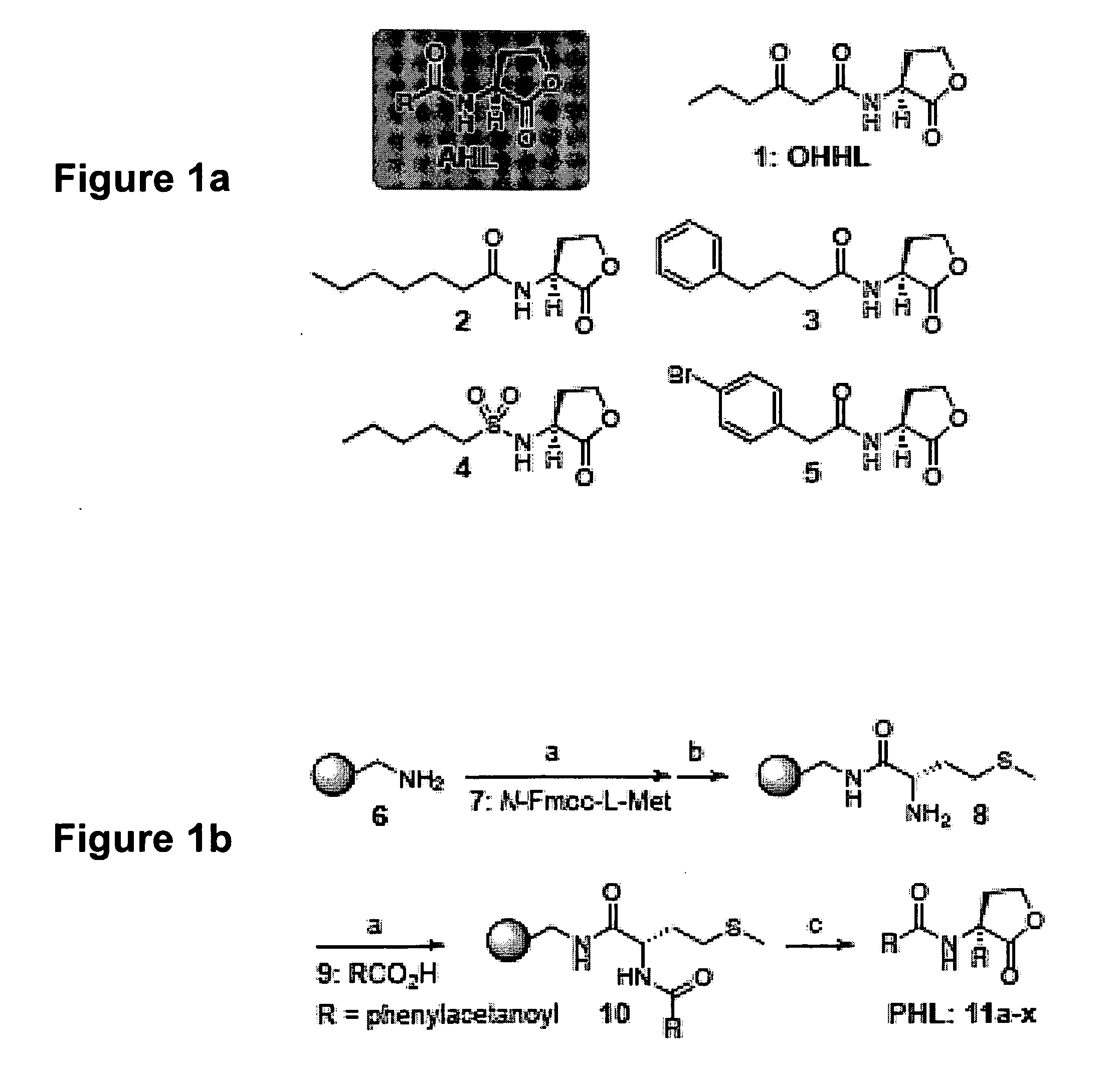
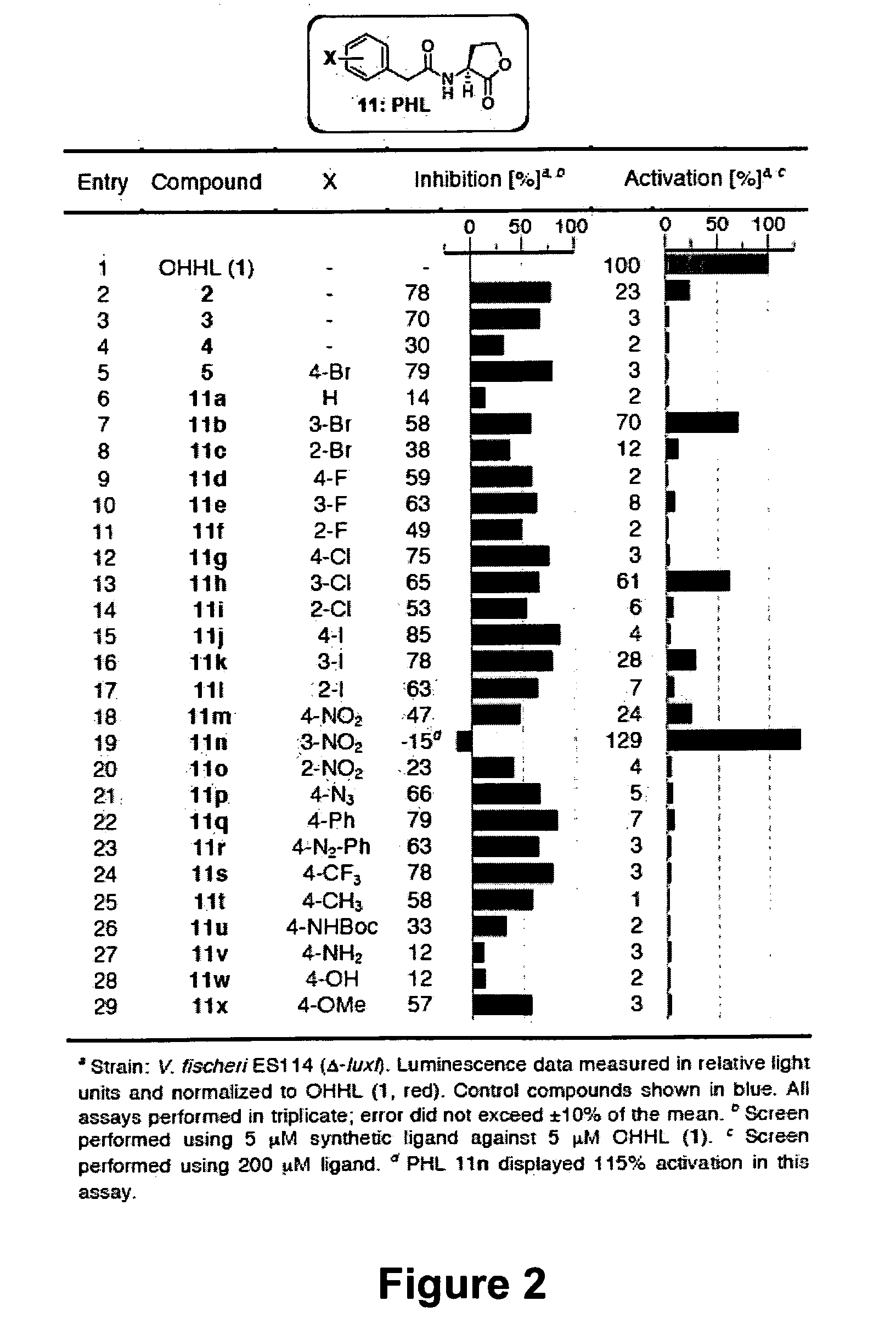
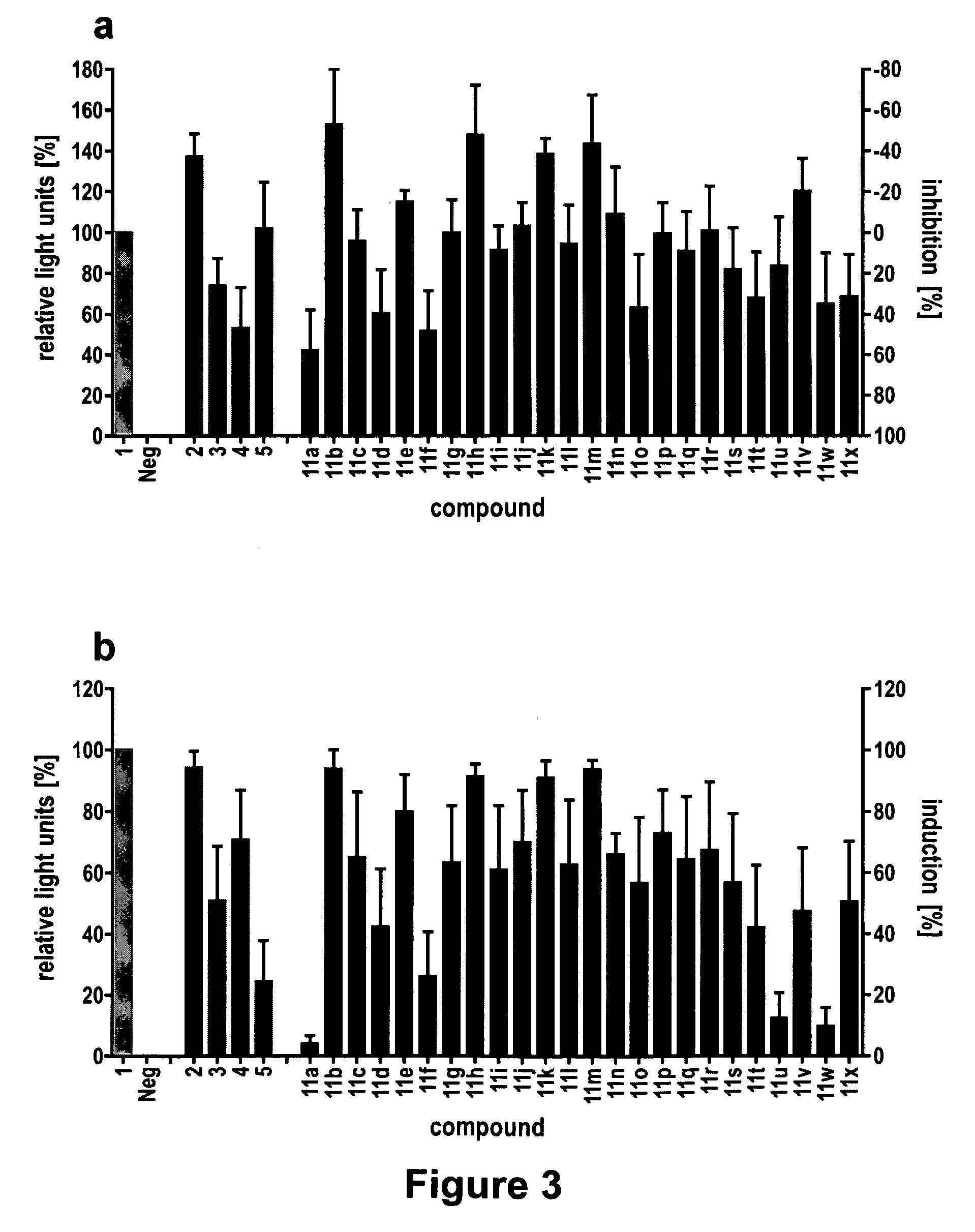
The present invention provides compounds and methods for modulation of the quorum sensing of bacteria. In an embodiment, the compounds of the present invention are able to act as replacements for naturally occurring bacterial quorum sensing ligands in a ligand-protein binding system; that is, they imitate the effect of natural ligands and produce an agonistic effect. In another embodiment, the compounds of the present invention are able to act in a manner which disturbs or inhibits the naturally occurring ligand-protein binding system in quorum sensing bacteria; that is, they produce an antagonistic effect. The compounds of the present invention comprise N-acylated-homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprised of a wide range of acyl groups.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for treating neurological disorders
InactiveUS20180193414A1Reduce cell viabilityReduced activityNervous disorderVectorsDiseasePain controlling
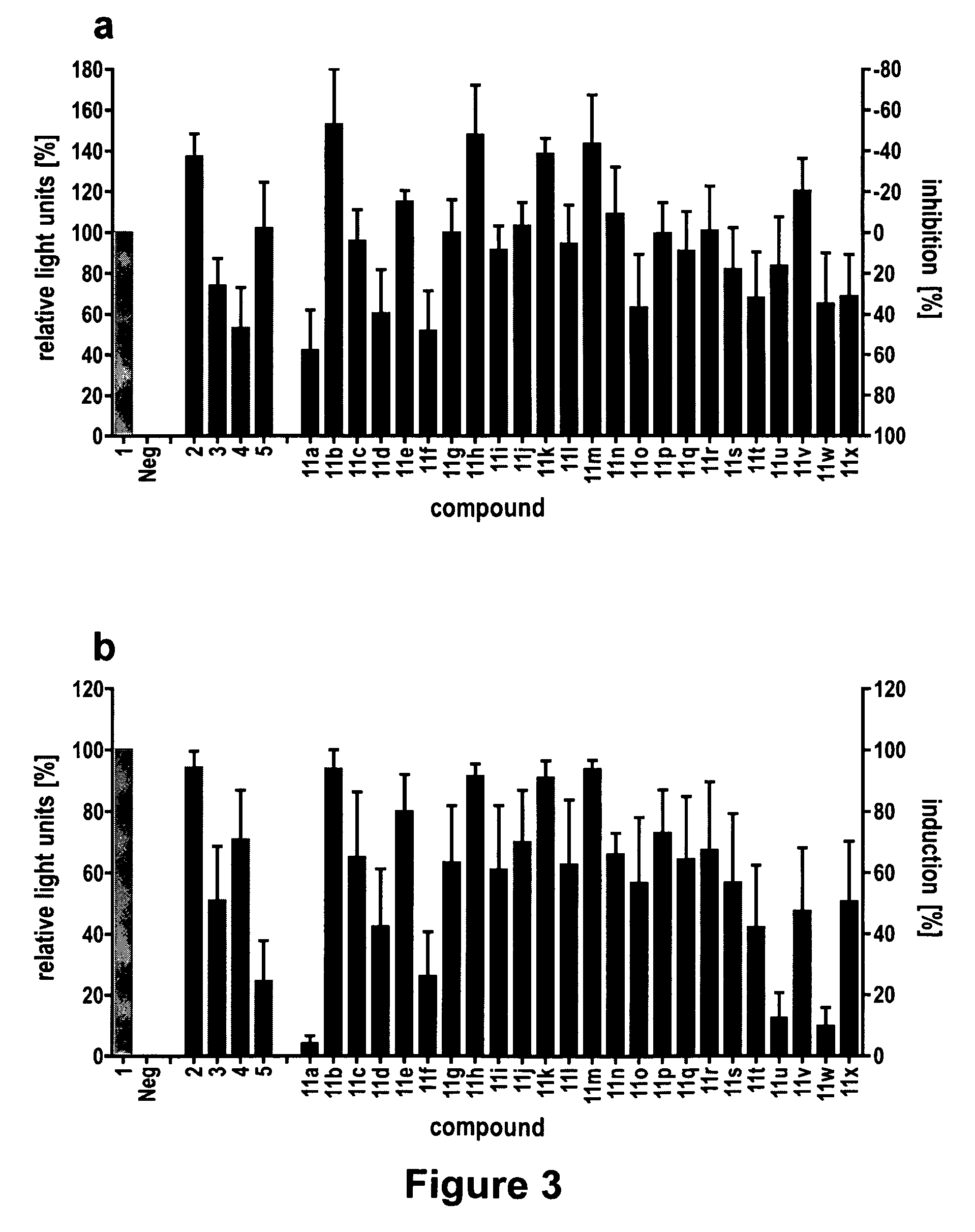
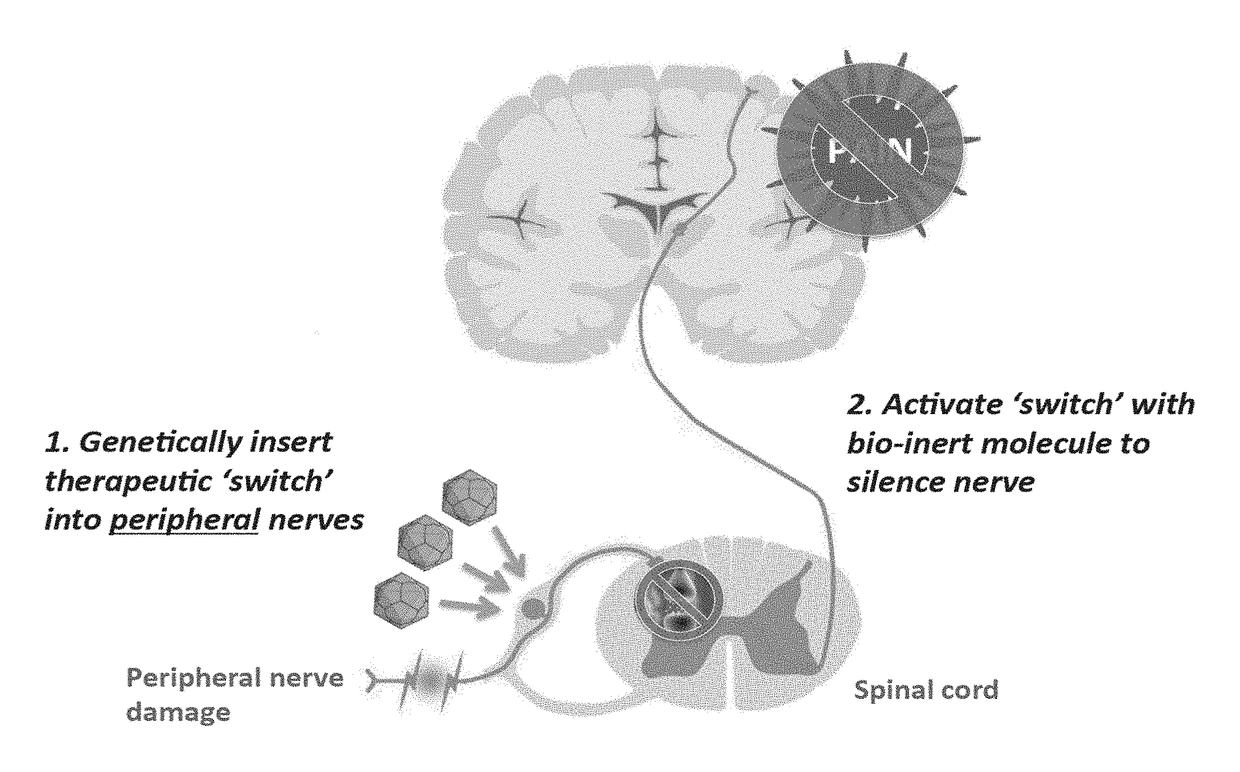
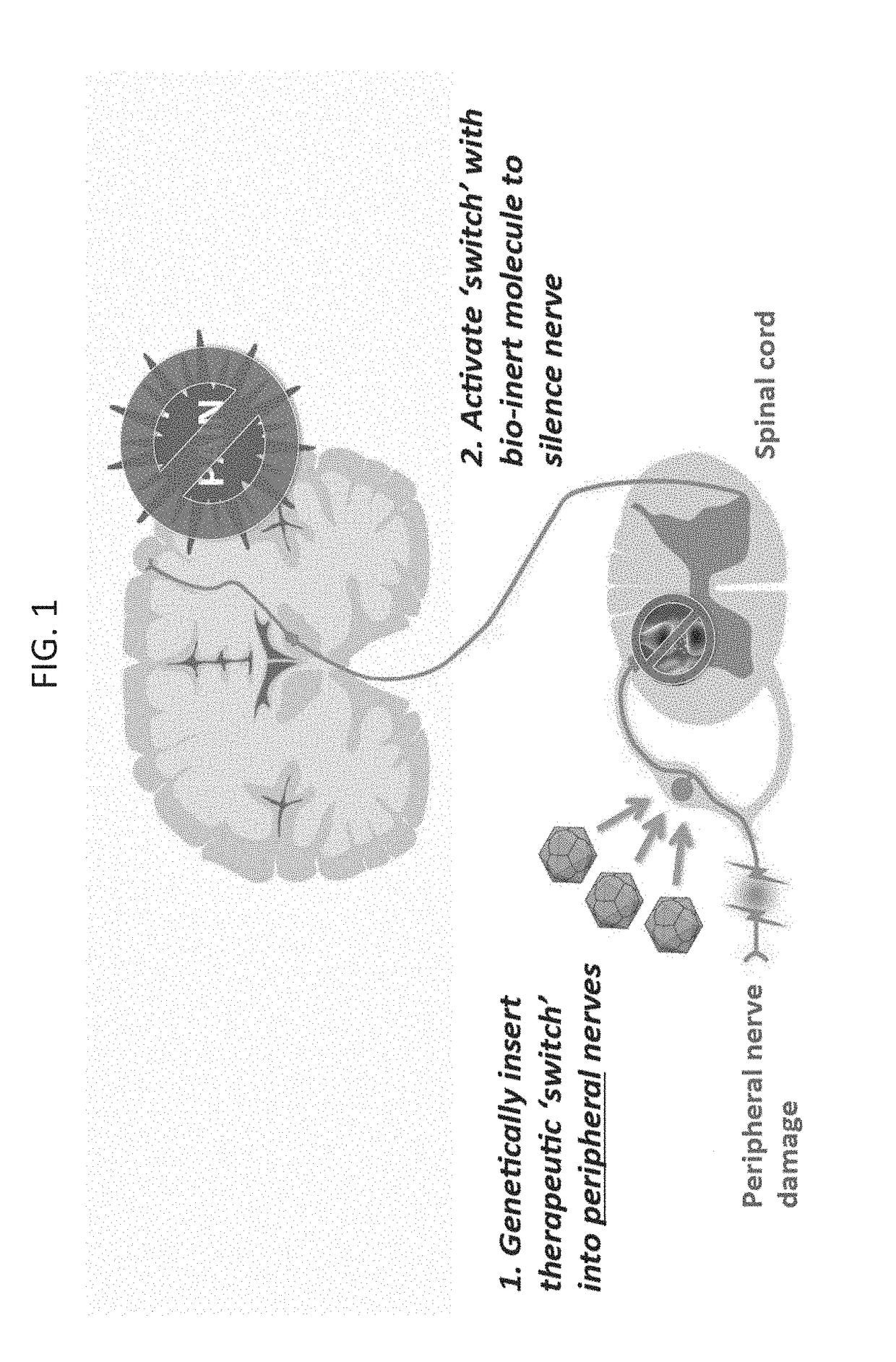
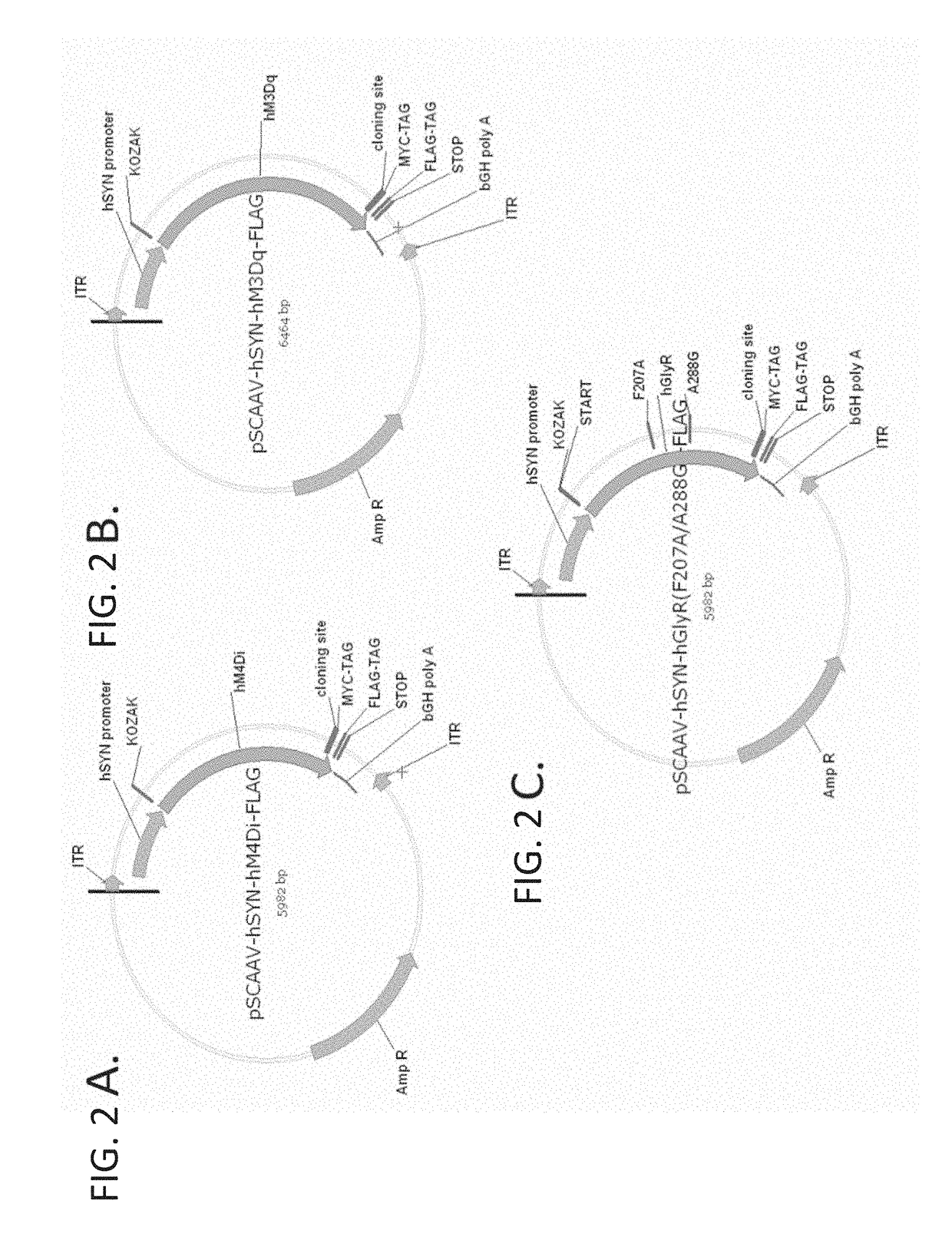
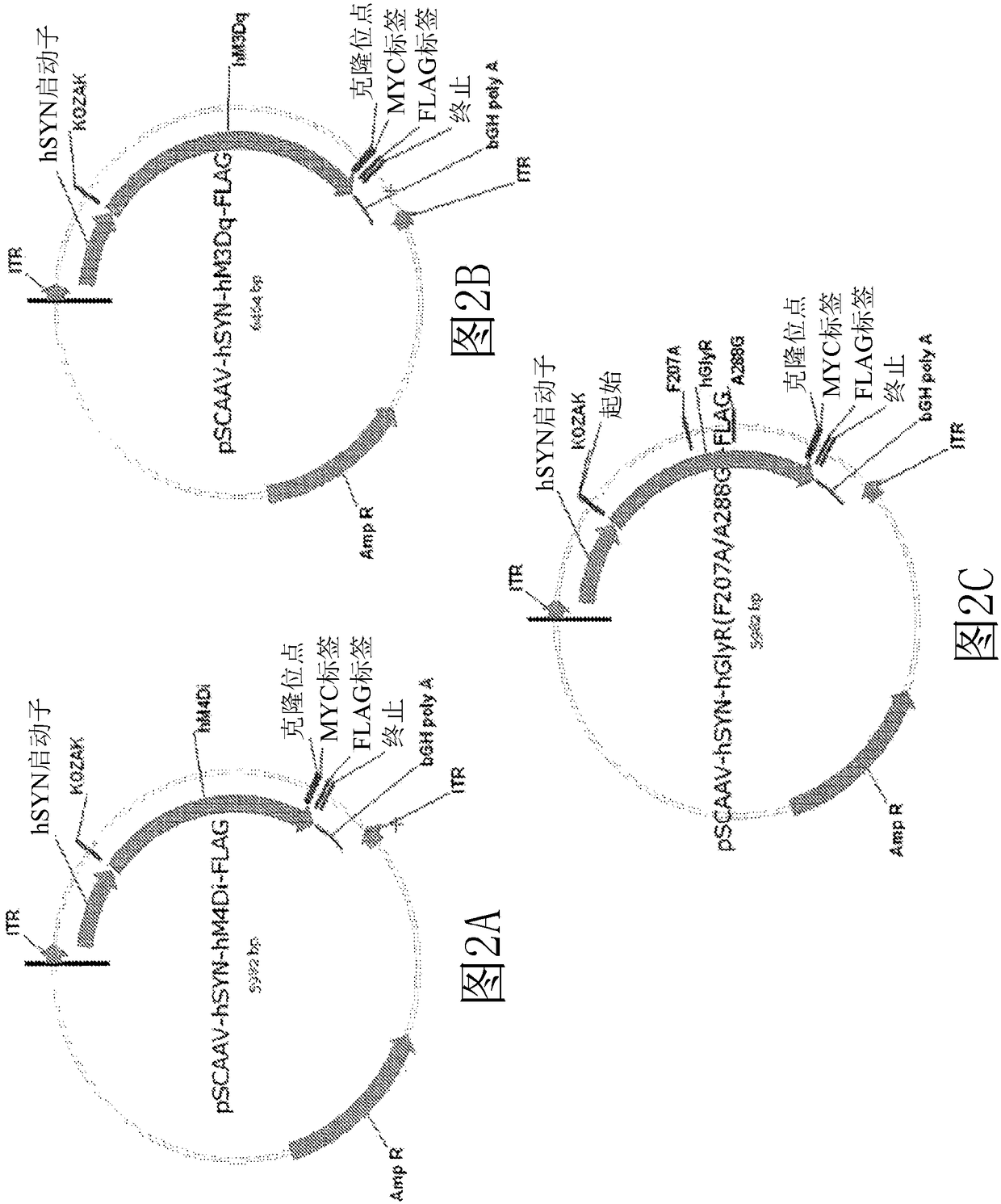
The present invention generally provides vectors, compositions, and methods of using the same for treating neurological disorders, including managing pain. The compositions and methods include the use of G protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels to treat neurological indications including pain, epilepsy and satiety disorders. The compositions and methods further include the use of synthetic ligands to activate the G protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels in the treatment of neurological disease.
Owner:CODA BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and methods for treating neurological disorders
The present invention generally provides vectors, compositions, and methods of using the same for treating neurological disorders, including managing pain. The compositions and methods include the useof G protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels to treat neurological indications including pain, epilepsy and satiety disorders. The compositions and methods further include the use ofsynthetic ligands to activate the G protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels in the treatment of neurological disease.
Owner:CODA BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
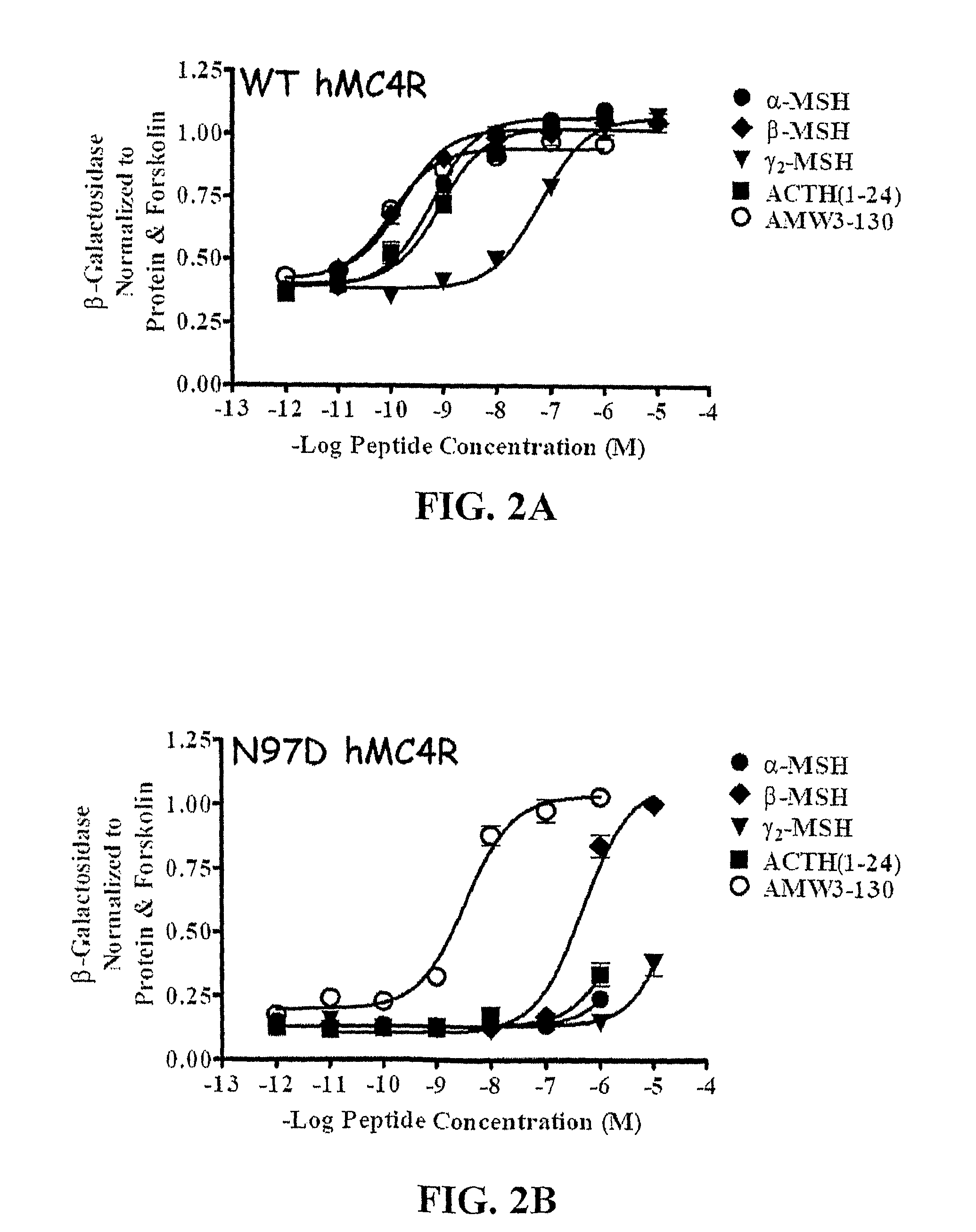
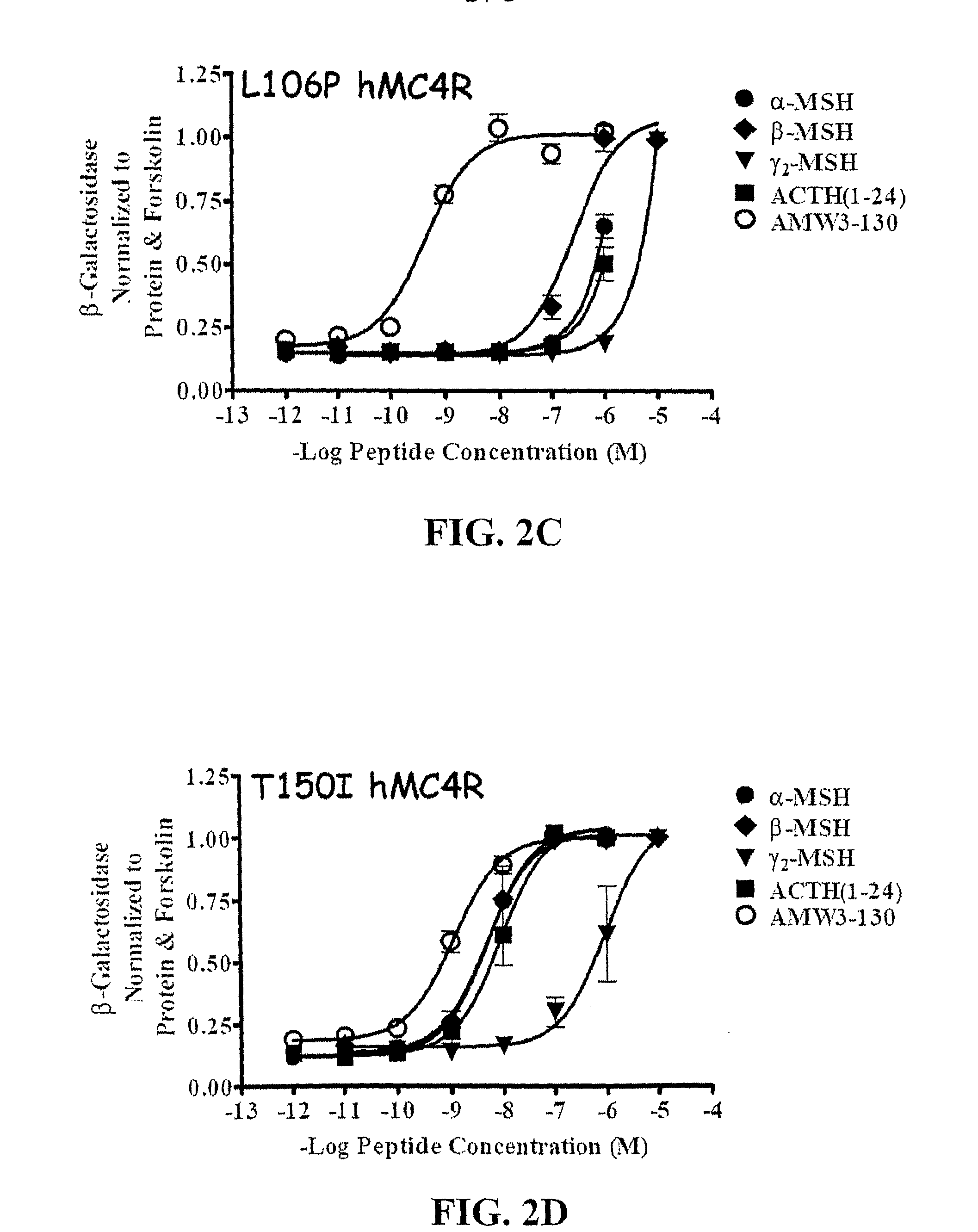
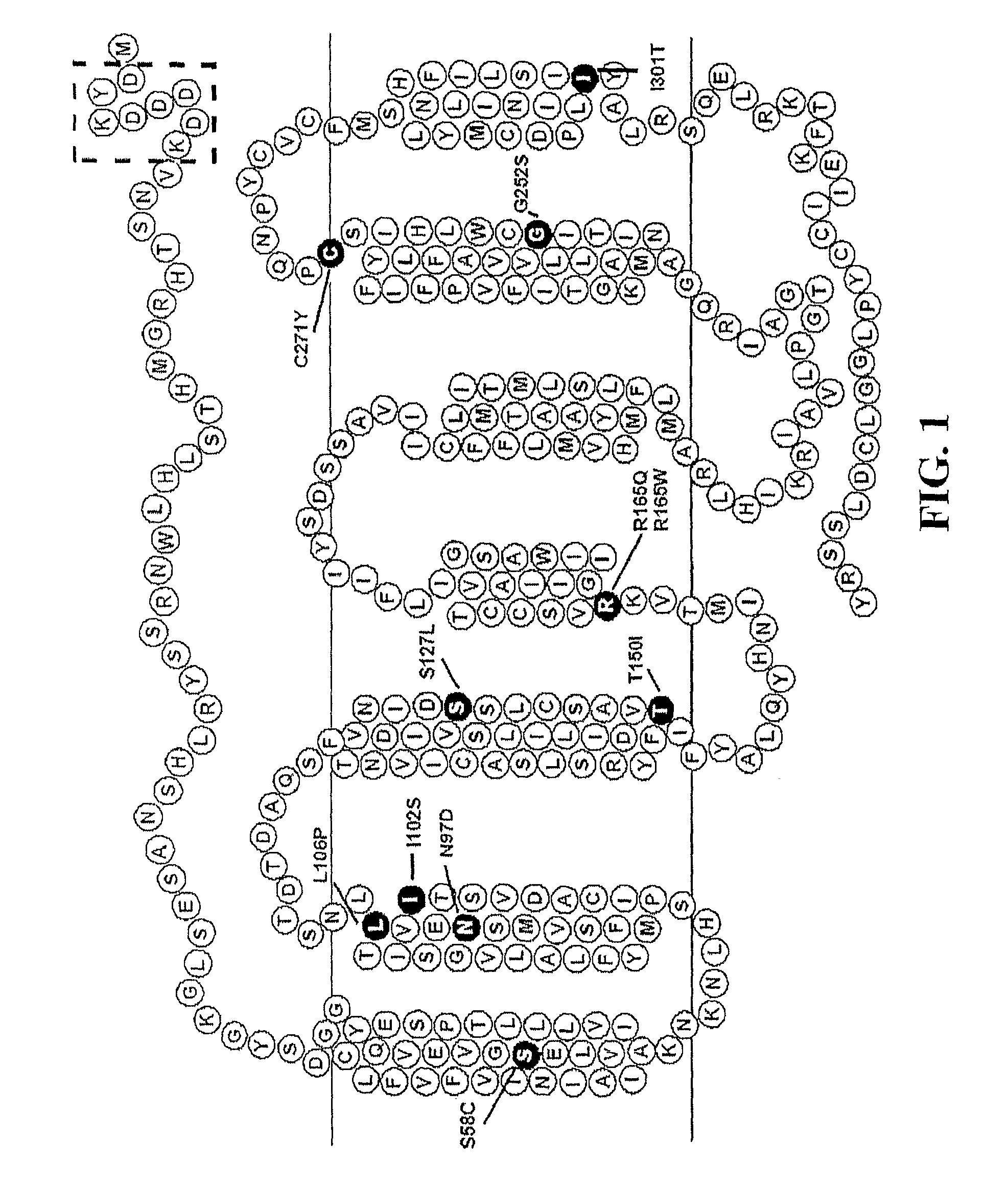
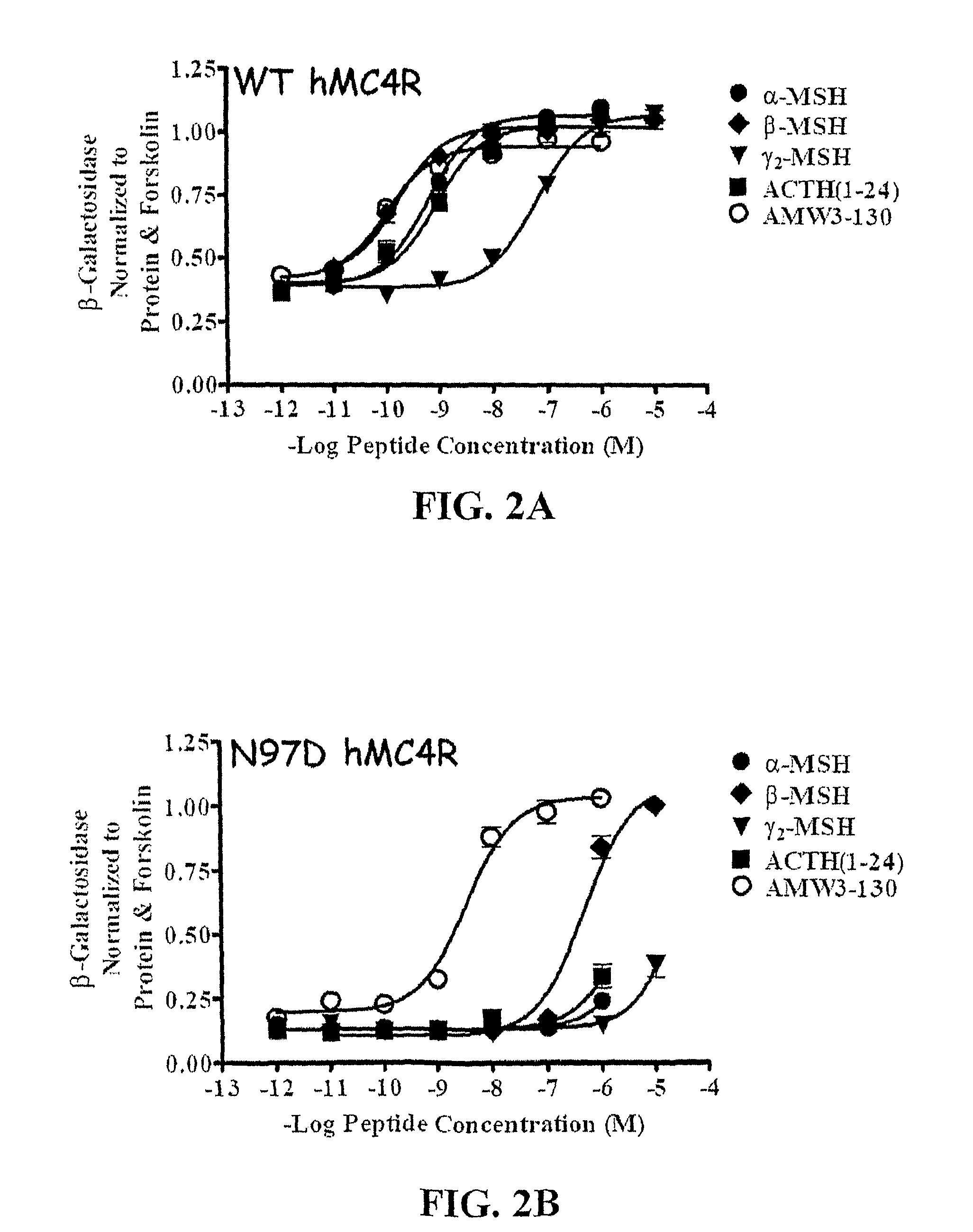
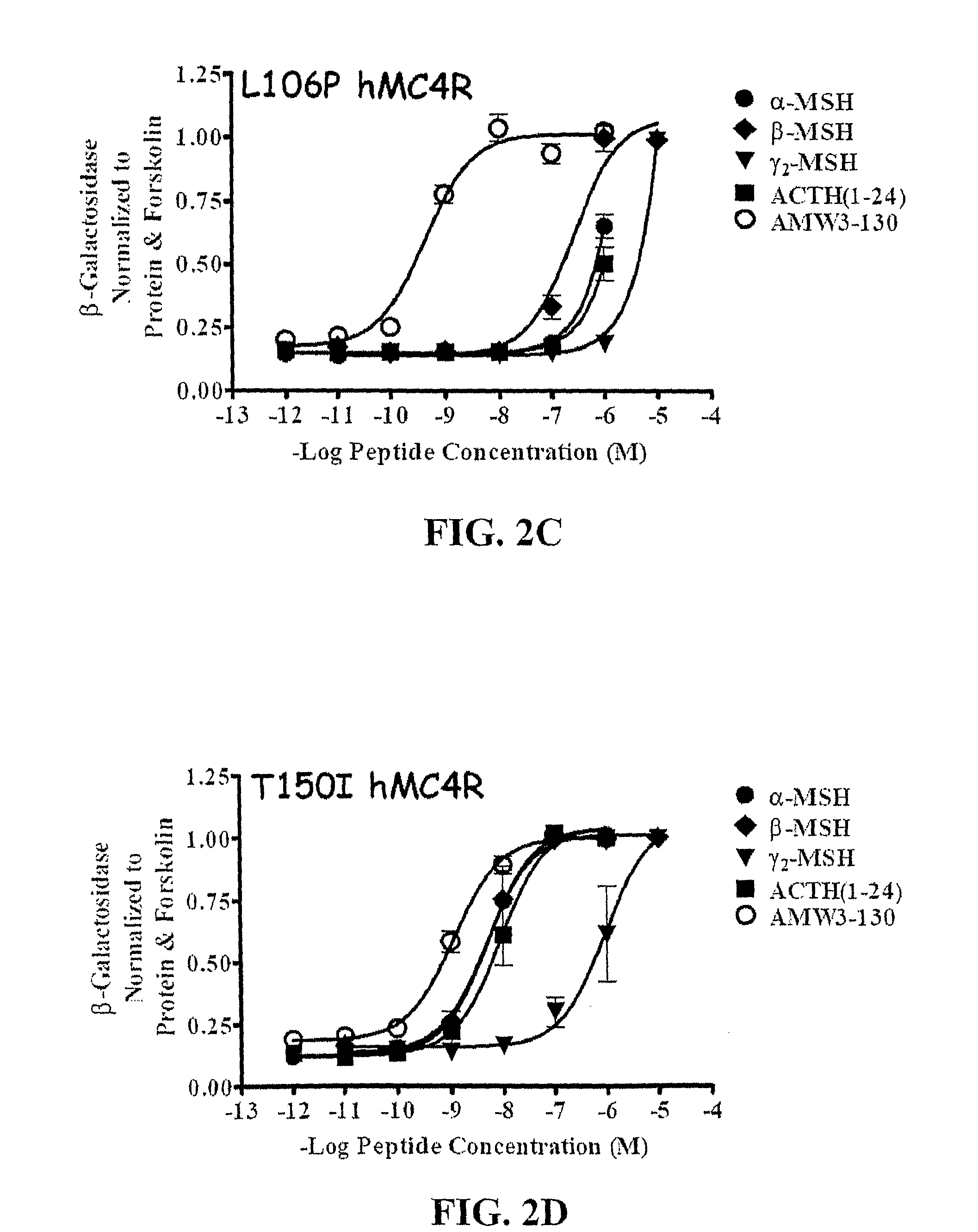
Peptides with Efficacy in Rescuing Melanocortin-4 Receptor Polymorphic Agonist Signaling
InactiveUS20090176712A1Improved melanocortin receptor stimulationImprove the quality of lifeAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMetabolism disorderMelanocortin agonistAgonist
Disclosed are novel ligands based on an AGRP template that can rescue endogenous melanocortin agonist and / or antagonist dysfunction at MCR polymorphisms. In particular, the present invention provides novel synthetic ligands based on AGRP templates that can rescue endogenous melanocortin agonist dysfunction at MC4R polymorphisms to treat children and adults with these mutations and increase their quality of life.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
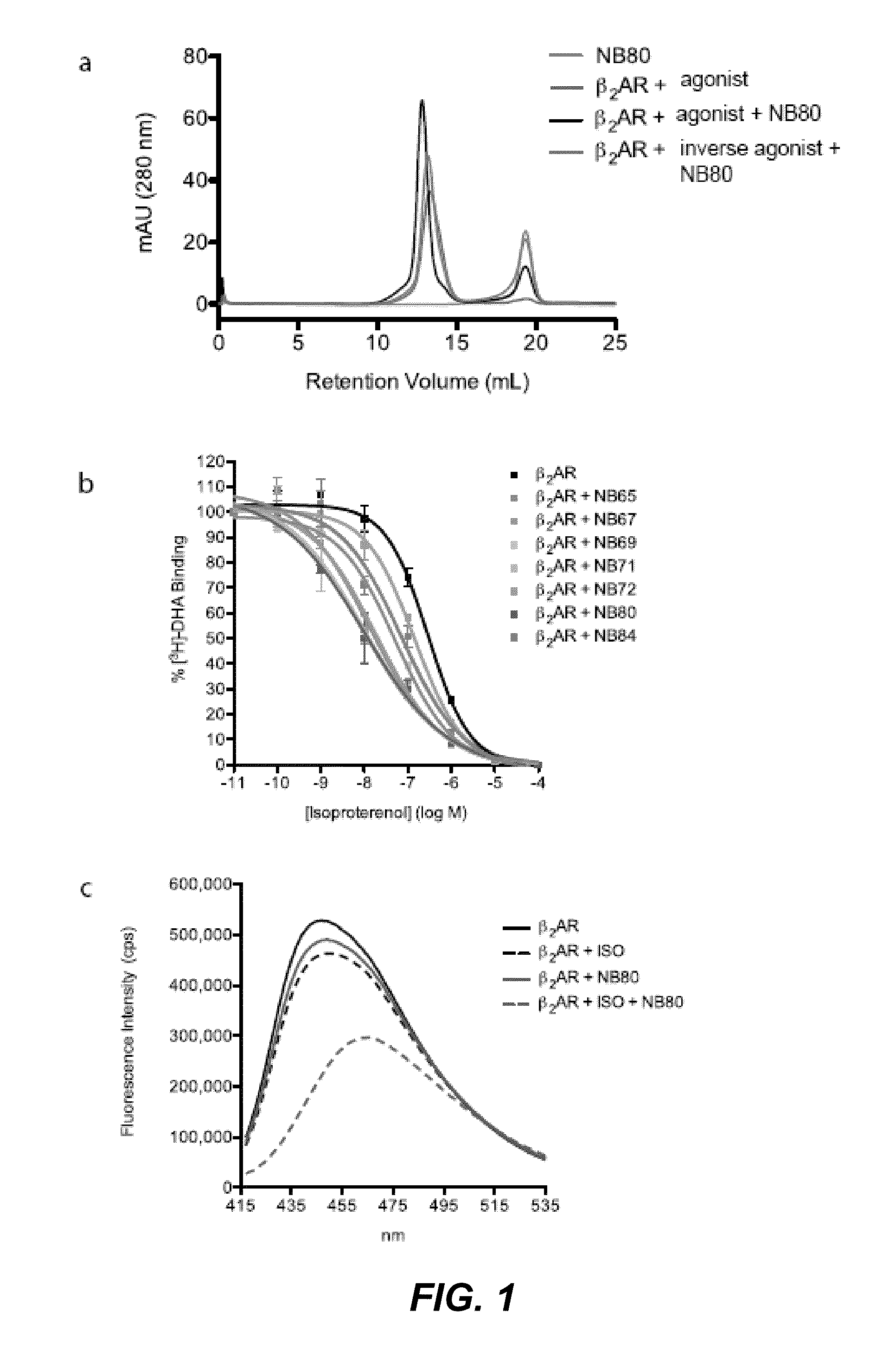
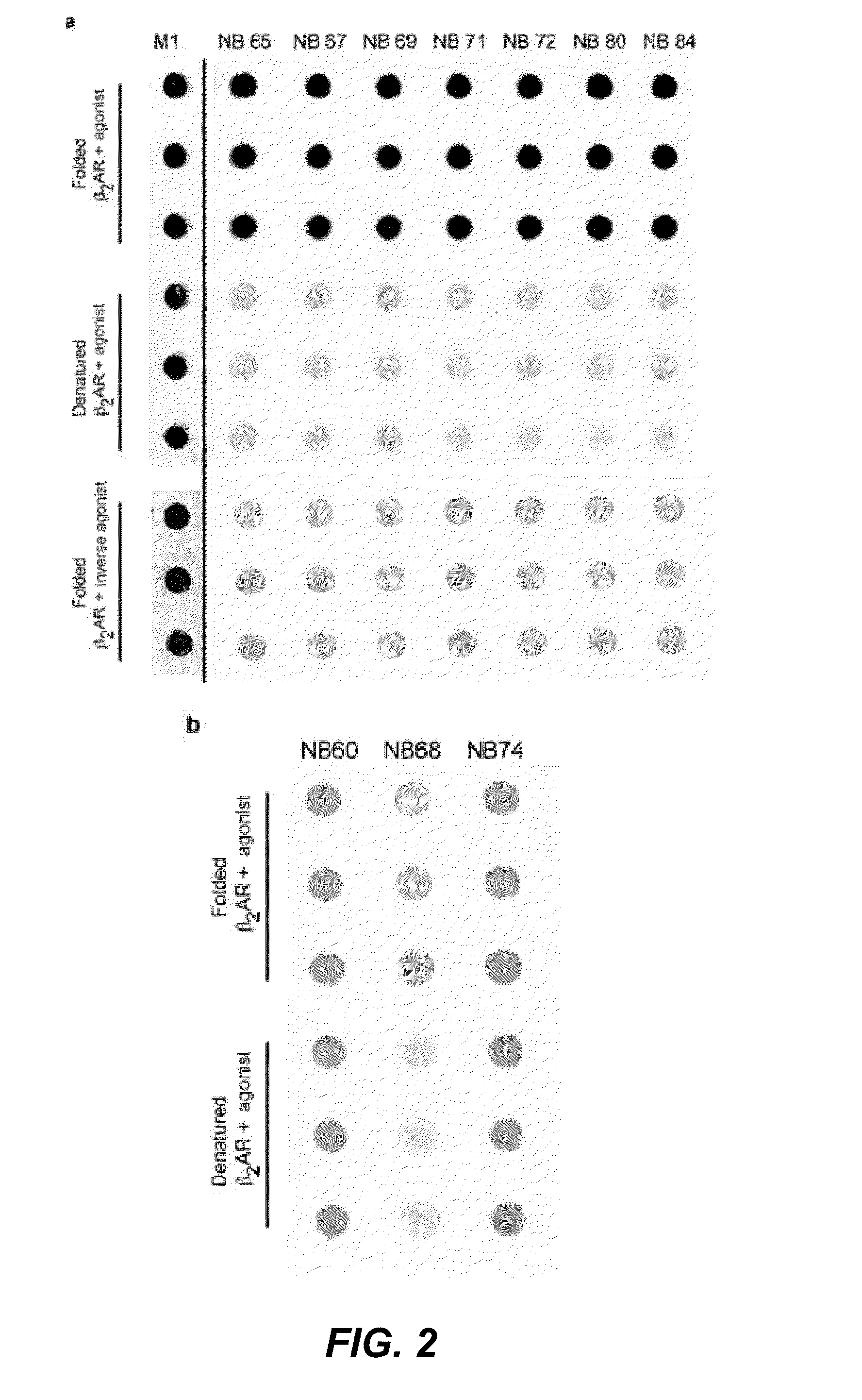
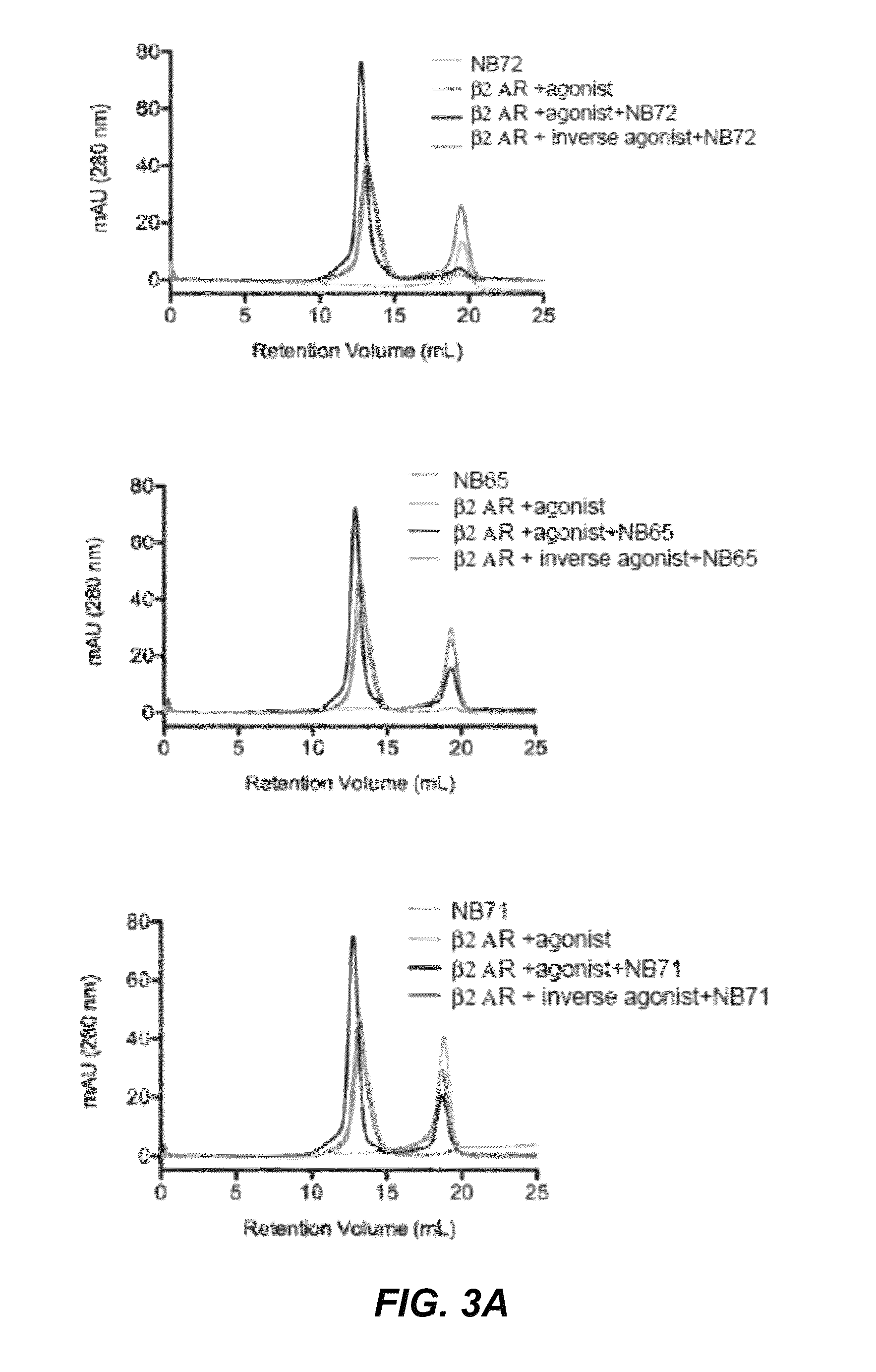
Protein binding domains stabilizing functional conformational states of GPCRs and uses thereof
ActiveUS9453065B2Improve thermal stabilityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderG protein-coupled receptorBinding domain
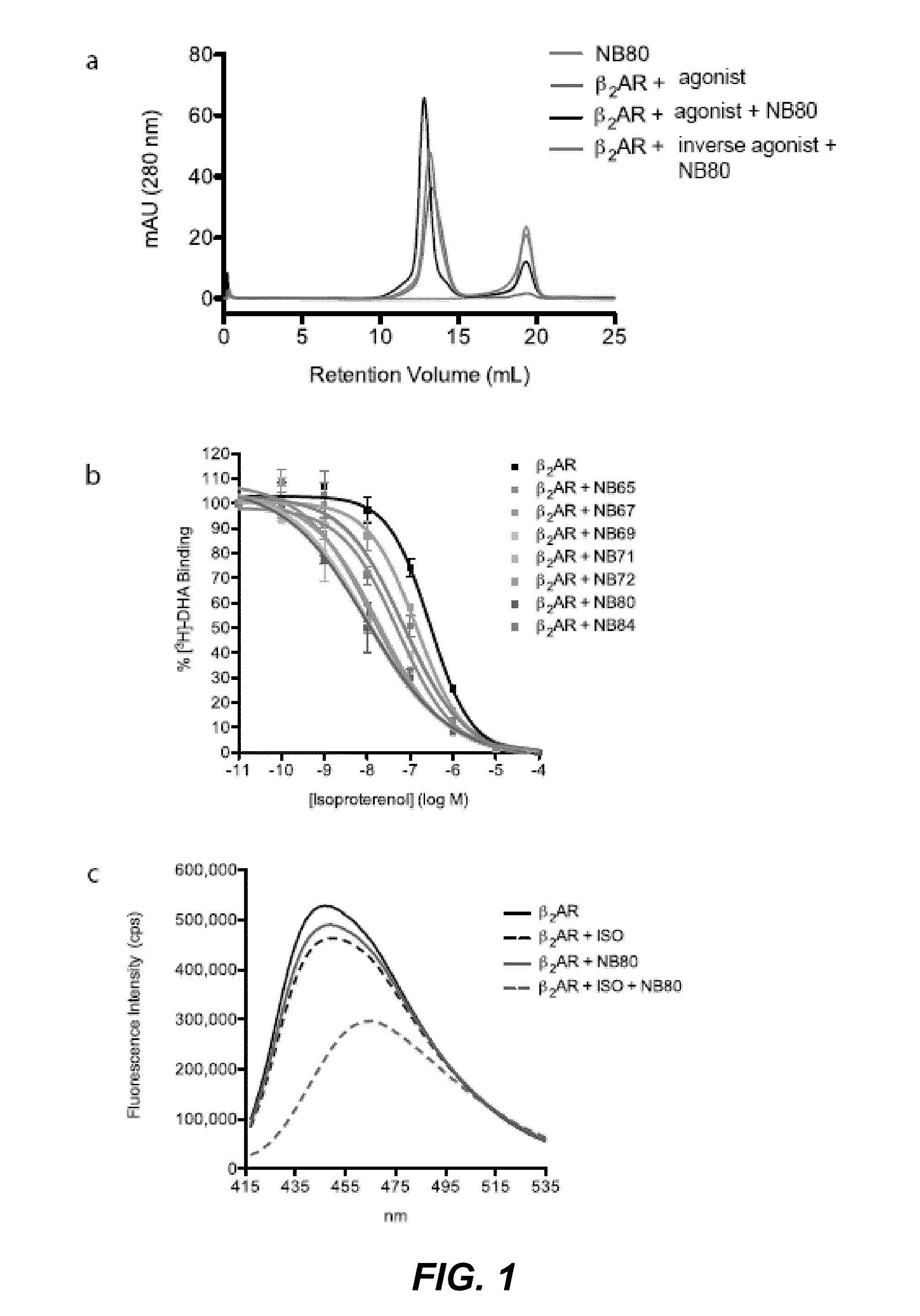
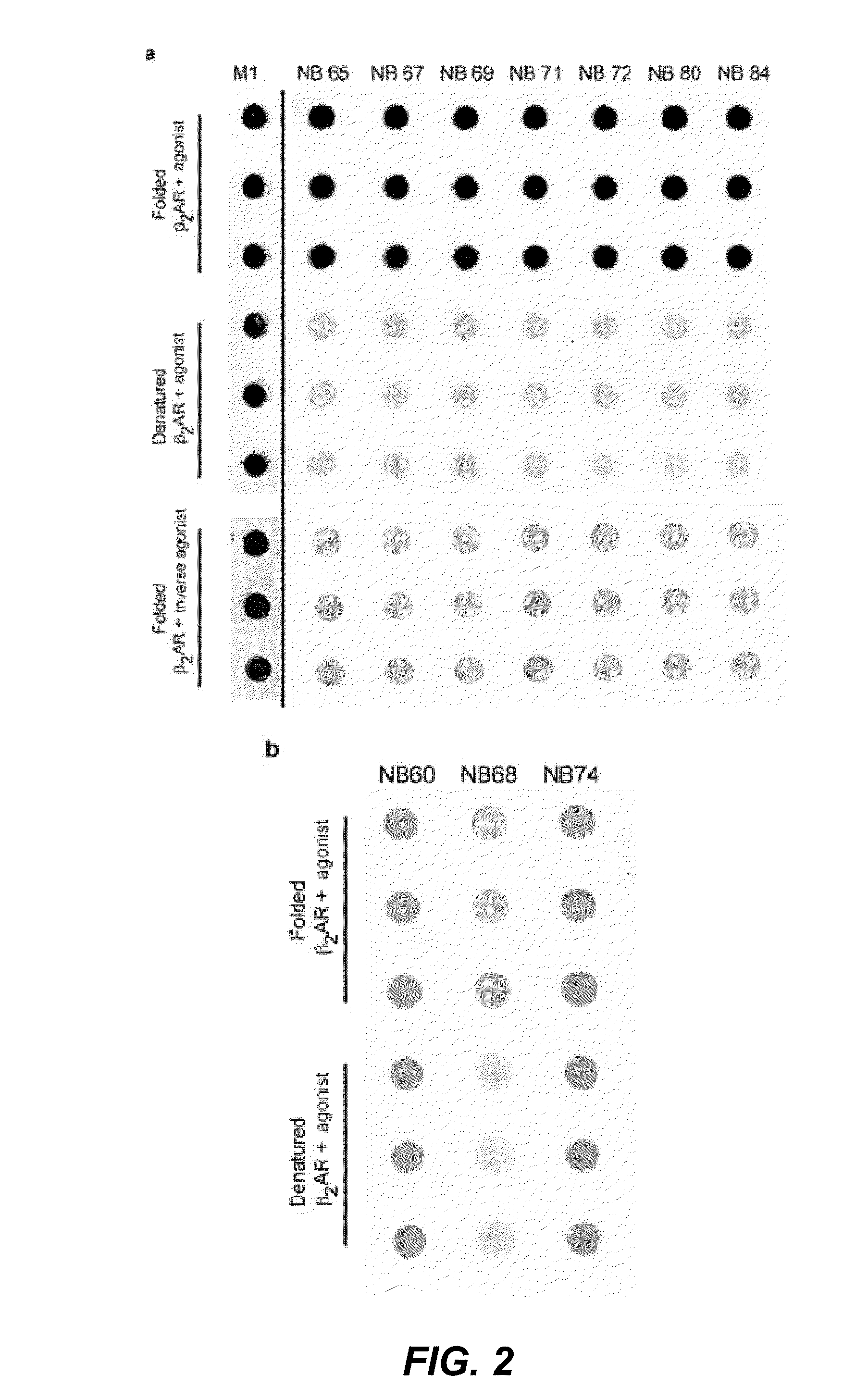
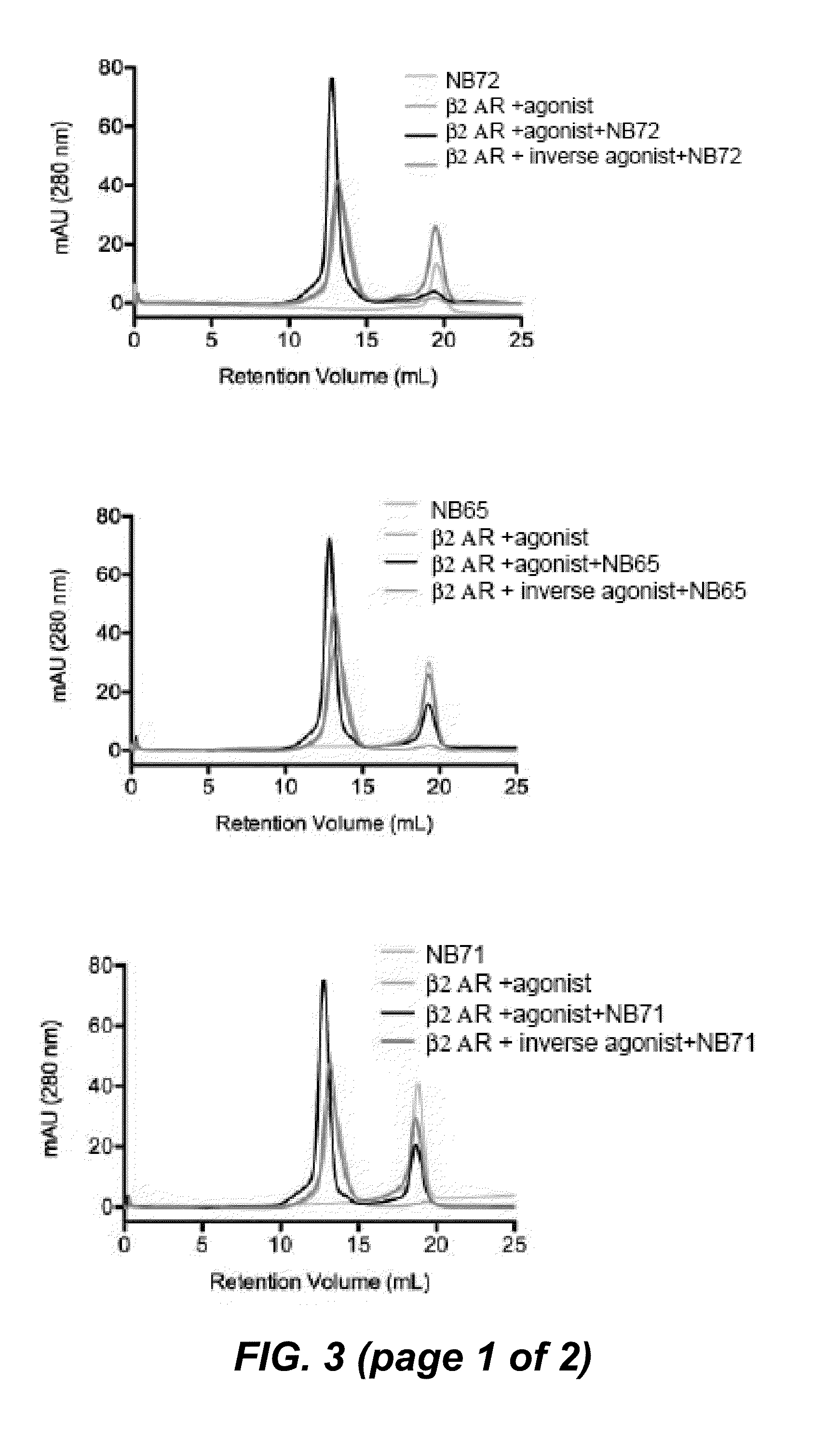
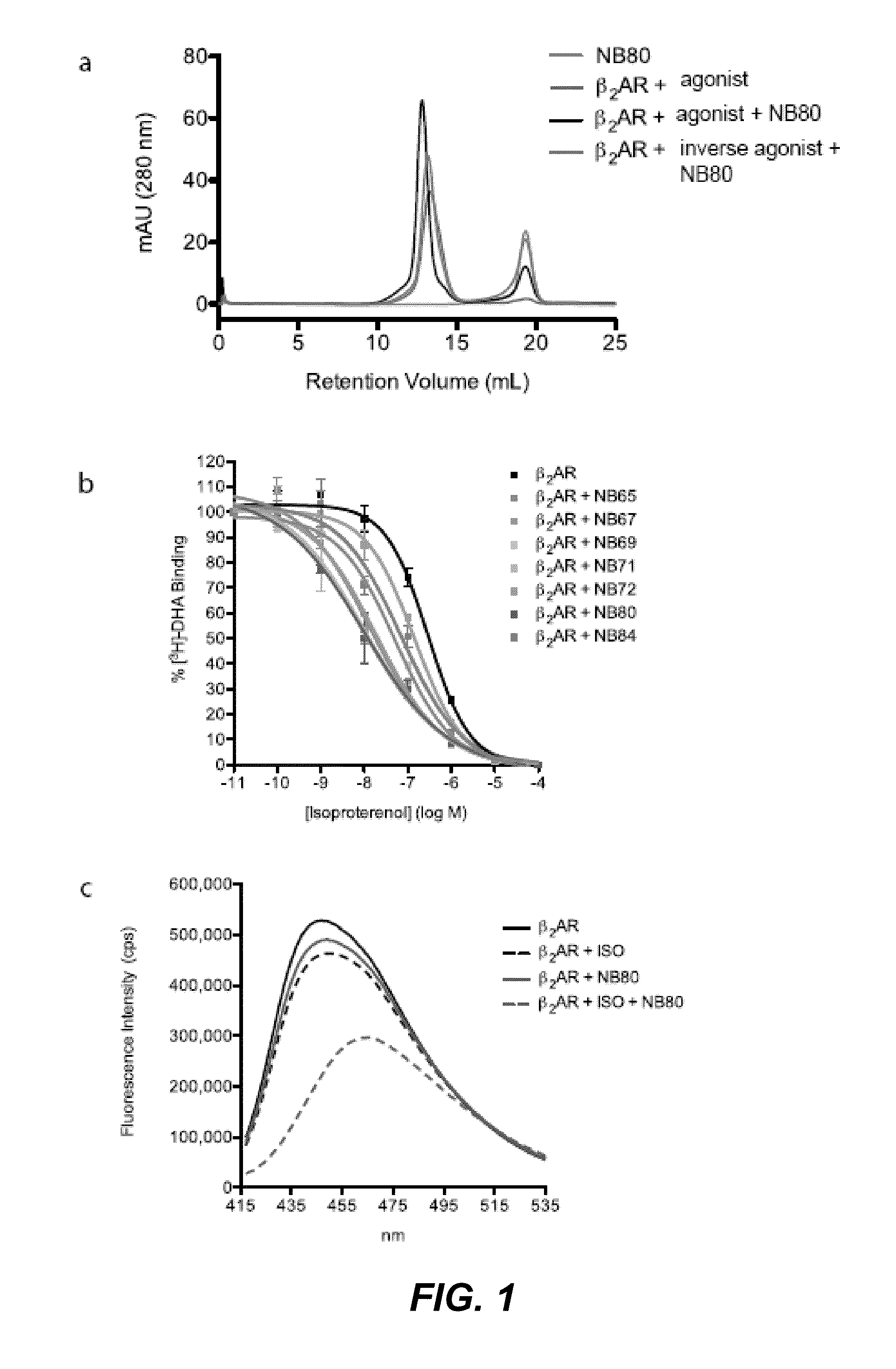
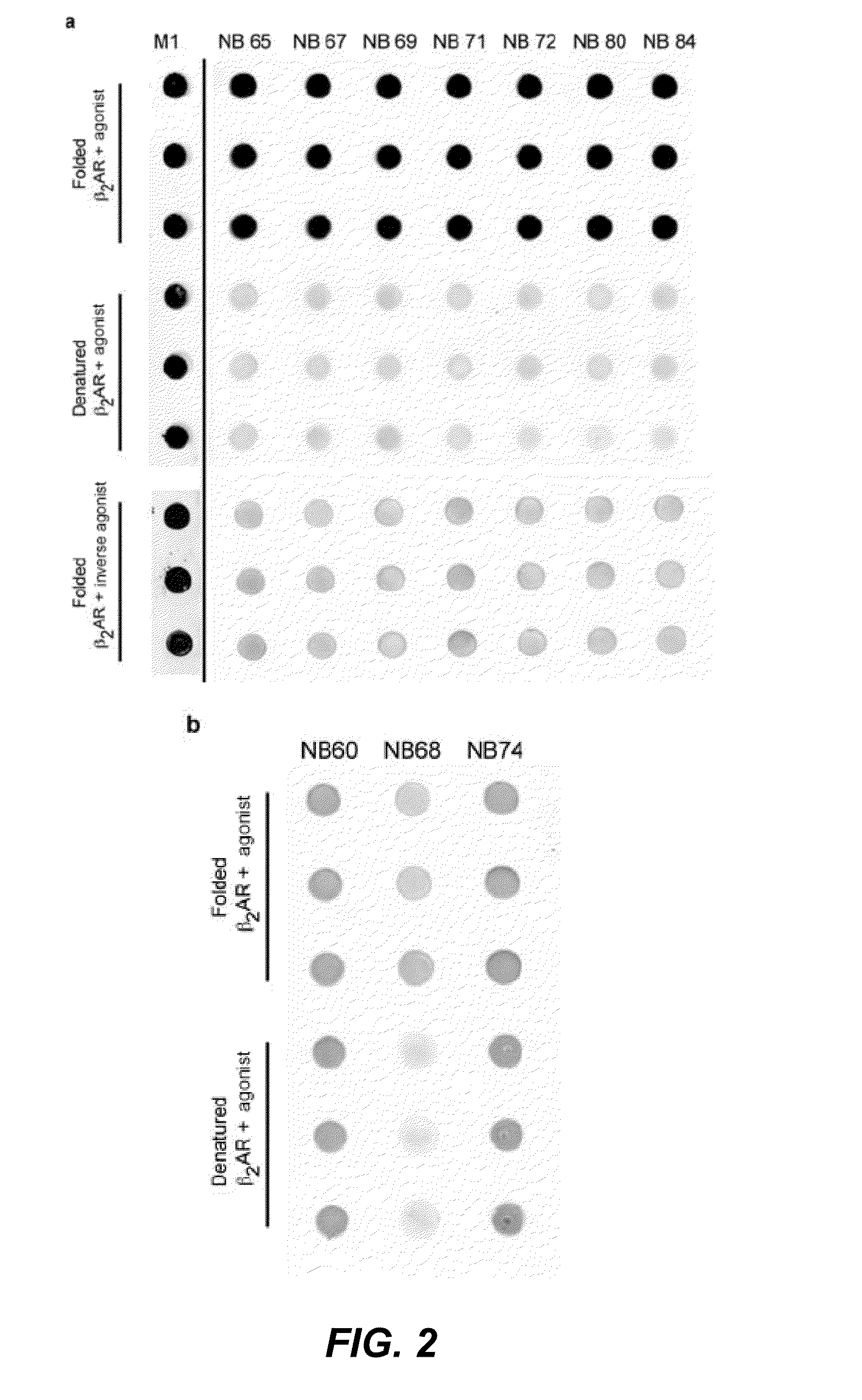
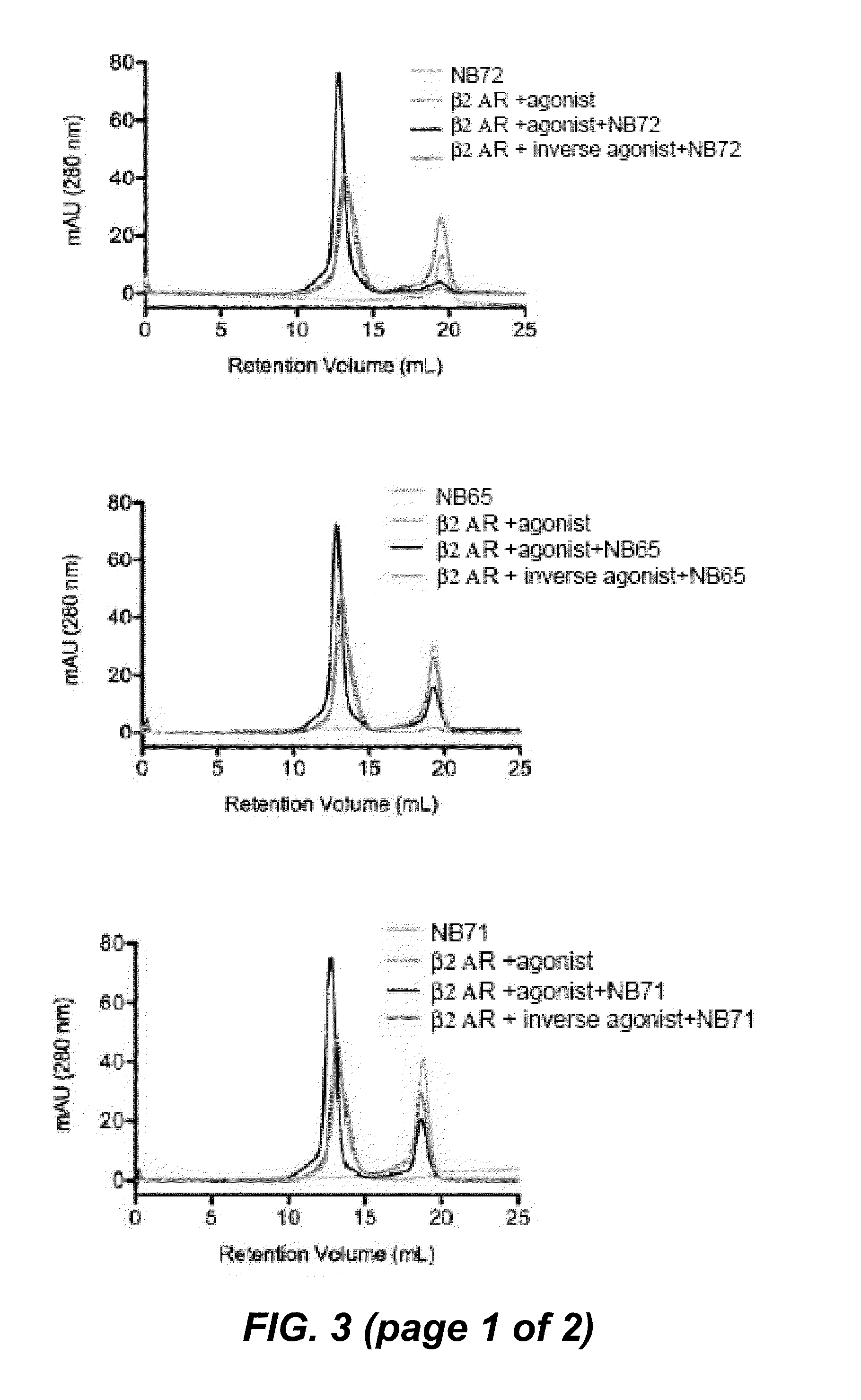
The disclosure relates to the field of GPCR structure biology and signaling. In particular, it relates to protein binding domains directed against or capable of specifically binding to a functional conformational state of a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). More specifically, it provides protein binding domains that are capable of increasing the stability of a functional conformational state of a GPCR, in particular, increasing the stability of a GPCR in its active conformational state. The protein binding domains hereof can be used as a tool for the structural and functional characterization of G-protein-coupled receptors bound to various natural and synthetic ligands, as well as for screening and drug discovery efforts targeting GPCRs. Moreover, also encompassed are the diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic usefulness of these protein binding domains for GPCR-related diseases.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Modulation of Bacterial Quorum Sensing with Synthetic Ligands
ActiveUS20080312319A1Diminish and inhibit productionIncrease productionBiocideOrganic chemistryHomoserineLactone formation
The present invention provides compounds and methods for modulation of the quorum sensing of bacteria. In an embodiment, the compounds of the present invention are able to act as replacements for naturally occurring bacterial quorum sensing ligands in a ligand-protein binding system; that is, they imitate the effect of natural ligands and produce an agonistic effect. In another embodiment, the compounds of the present invention are able to act in a manner which disturbs or inhibits the naturally occurring ligand-protein binding system in quorum sensing bacteria; that is, they produce an antagonistic effect. The compounds of the present invention comprise N-acylated-homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprised of a wide range of acyl groups.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Protein binding domains stabilizing functional conformational states of gpcrs and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130137856A1Improve thermal stabilityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderStructural biologyDisease
The present invention relates to the field of GPCR structure biology and signaling. In particular, the present invention relates to protein binding domains directed against or capable of specifically binding to a functional conformational state of a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). More specifically, the present invention provides protein binding domains that are capable of increasing the stability of a functional conformational state of a GPCR, in particular, increasing the stability of a GPCR in its active conformational state. The protein binding domains of the present invention can be used as a tool for the structural and functional characterization of G-protein-coupled receptors bound to various natural and synthetic ligands, as well as for screening and drug discovery efforts targeting GPCRs. Moreover, the invention also encompasses the diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic usefulness of these protein binding domains for GPCR-related diseases.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Binding domains directed against gpcr:g protein complexes and uses derived thereof
ActiveUS20140275487A1Easy to identifyStable captureVirusesUnicellular algaeHeterologousStructural biology
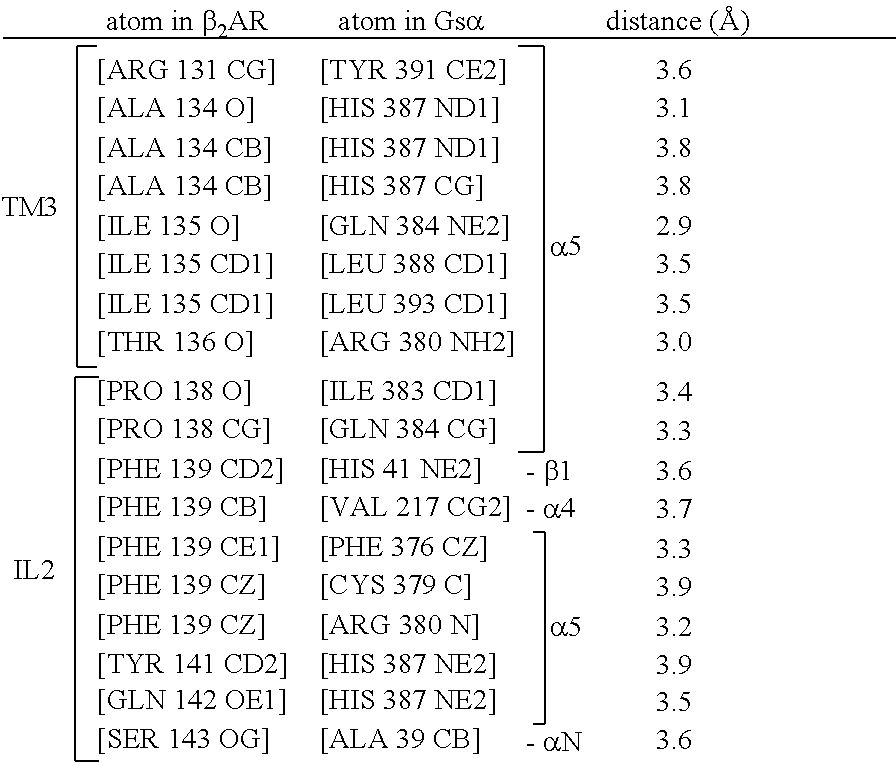
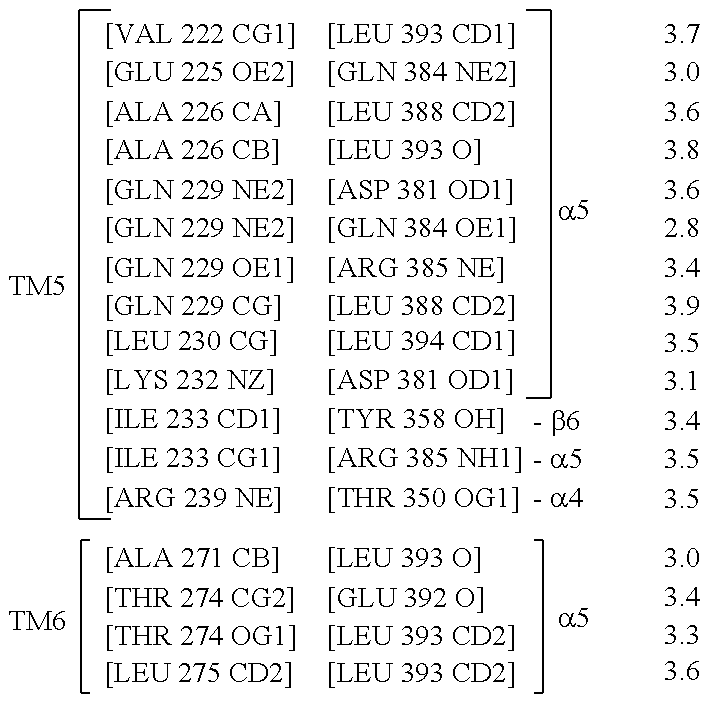
The present invention relates to the field of G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) structural biology and signaling. In particular, the present invention relates to binding domains directed against and / or specifically binding to GPCR:G protein complexes. Also provided are nucleic acid sequences encoding such binding domains and cells expressing or capable of expressing such binding domains. The binding domains of the present invention can be used as universal tools for the structural and functional characterization of G-protein coupled receptors in complex with downstream heterotrimeric G proteins and bound to various natural or synthetic ligands, for investigating the dynamic features of G protein activation, as well as for screening and drug discovery efforts that make use of GPCR:G protein complexes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +3
Protein binding domains stabilizing functional conformational states of gpcrs and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130183287A1Improve thermal stabilityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugBinding domain
The disclosure relates to the field of GPCR structure biology and signaling. In particular, it relates to protein binding domains directed against or capable of specifically binding to a functional conformational state of a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). More specifically, it provides protein binding domains that are capable of increasing the stability of a functional conformational state of a GPCR, in particular, increasing the stability of a GPCR in its active conformational state. The protein binding domains hereof can be used as a tool for the structural and functional characterization of G-protein-coupled receptors bound to various natural and synthetic ligands, as well as for screening and drug discovery efforts targeting GPCRs. Moreover, also encompassed are the diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic usefulness of these protein binding domains for GPCR-related diseases.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Process for the Purification of Antibodies Using Affinity Resins Comprising Specific Ligands
InactiveUS20110319592A1Stable baseCheap stableTripeptide ingredientsSaccharide peptide ingredientsMonoclonal antibodyOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to a novel process for the purification of antibodies, e.g. monoclonal antibodies. The process utilizes an affinity resin comprising a solid phase material having immobilized thereto one or more low-molecular weight synthetic ligands. The affinity resins enable the separation of antibodies from even closely related proteins.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Nitrogen-doped super-stable porous polymer composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109369870ASimple methodLow costHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCOBALTOUS NITRATEDimethyl formamide
The invention relates to a nitrogen-doped super-stable porous polymer composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method adopts the following steps: (1) synthesizing a ligandfrom melamine and p-formylbenzoic acid in an o-xylene solvent, and performing purification treatment; and (2) adding the ligand and cobalt nitrate hexahydrate into DMF (Dimethyl Formamide) and an ethanol solvent for reacting, washing after reaction completion, and drying at a temperature of 75-85 DEG C, thereby obtaining the nitrogen-doped super-stable porous polymer composite material. Compared with the prior art, the electrode material prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of double electric layer capacitors and pseudocapacitors, has good capacitive performance and excellent cycling stability, and is an ideal supercapacitor electrode material.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Polyhydroxy compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113549082AHigh crystallinityImprove stabilityOrganic chemistryCell electrodesPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to the technical field of metal organic framework materials, in particular to a polyhydroxy compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The polyhydroxy compound is a 2D[pi]-containing conjugated nitrogen-doped polyhydroxy ligand. By introducing nitrogen atoms and changing the electron density of the ligand, the deprotonation process is relatively easy in the ligand synthesis process, a single crystal can be obtained, and after MOF is synthesized, the MOF is used as a post-modification site and is coordinated with other metals, so that the conductivity is enhanced by increasing the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon size of the ligand and enhancing pi-pi conjugation.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
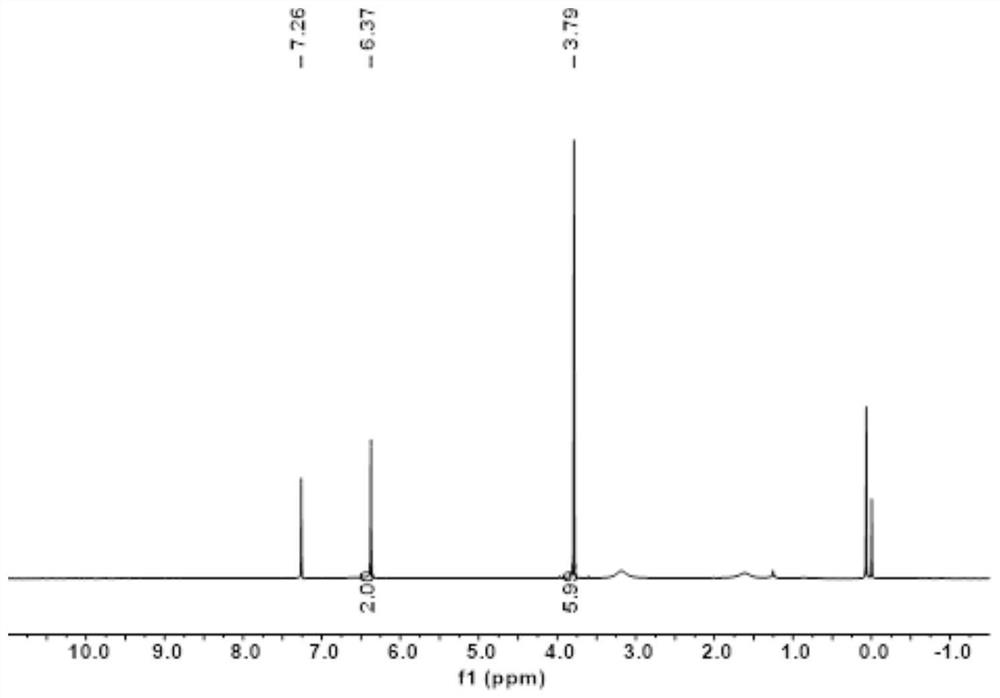
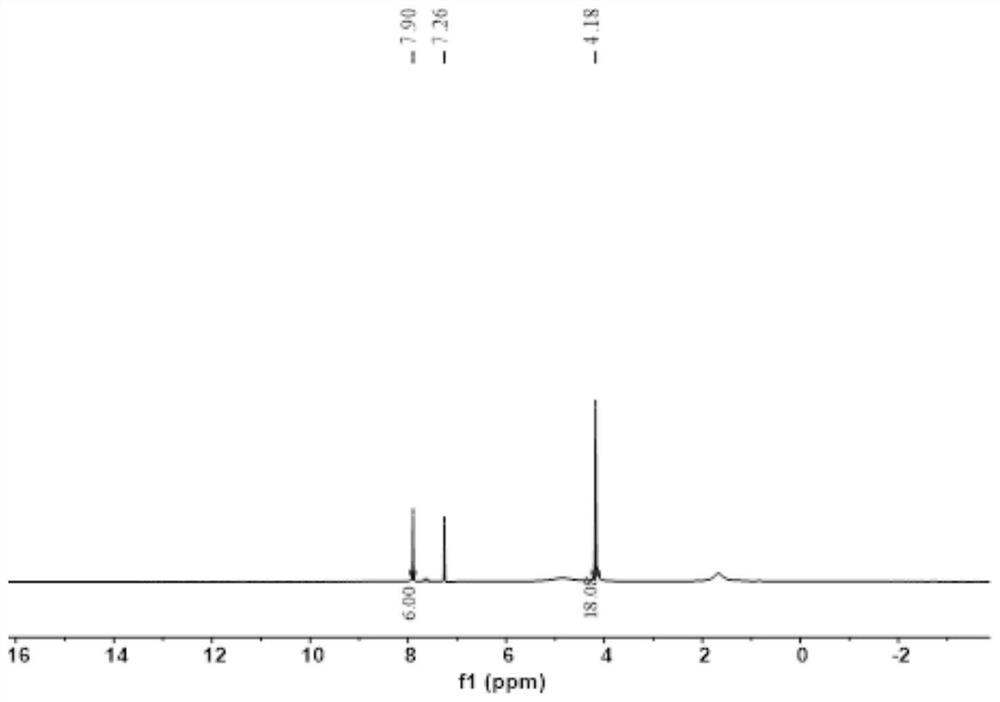
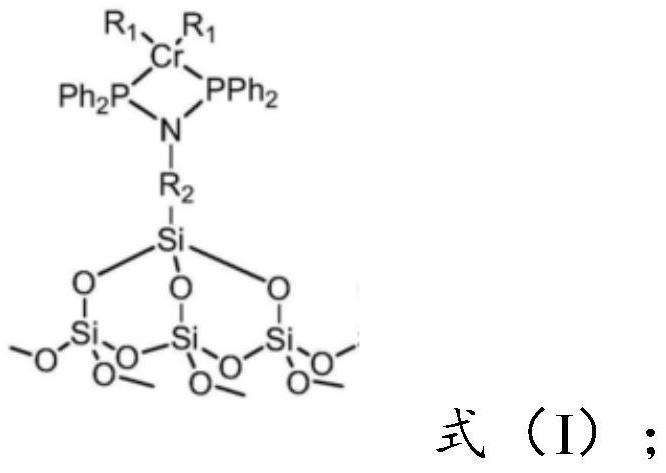
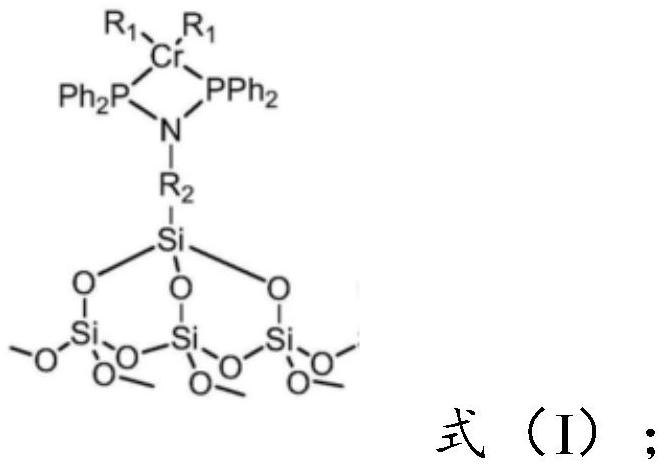
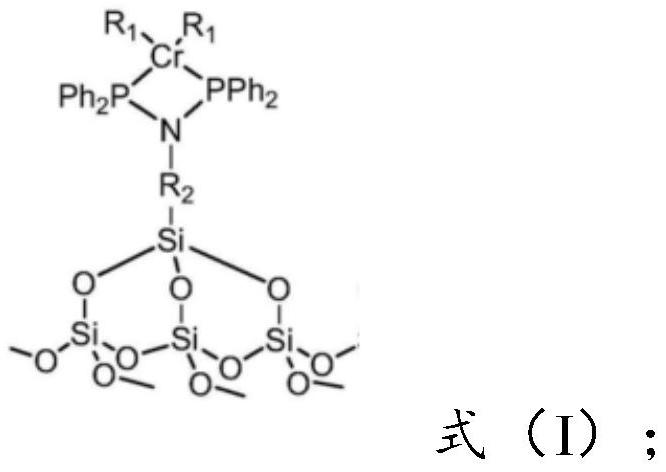
Preparation method of catalyst for synthesizing 1-octylene through selective oligomerization of ethylene
ActiveCN112742480AEvenly distributedEvenly dispersedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation method of a catalyst for synthesizing 1-octylene through selective oligomerization of ethylene. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a amino-containing molecular sieve; mixing the amino-containing molecular sieve, a solvent, an acid-binding agent and diphenylphosphine chloride, stirring for reaction, filtering, and recrystallizing to obtain a PNP ligand; and mixing the PNP ligand with a chromium source and a solvent, heating for reaction, filtering, washing and drying to obtain the supported heterogeneous catalyst with a structure shown in the formula (I). The synthesis of the amino-containing molecular sieve can make amino functional groups uniformly distributed on the carrier, then the PNP ligand is synthesized in situ through a reaction method of the amino-containing molecular sieve and the diphenylphosphine chloride, and the structure is more stable. The supported heterogeneous catalyst prepared by the method has the advantages that the active center of the catalyst is uniformly dispersed; and when the catalyst is applied to the ethylene selective oligomerization reaction, the catalytic activity is higher and can reach 10<6> g / (molCr.h), and the 1-octene selectivity is higher.
Owner:SHANDONG JINGBO PETROCHEM
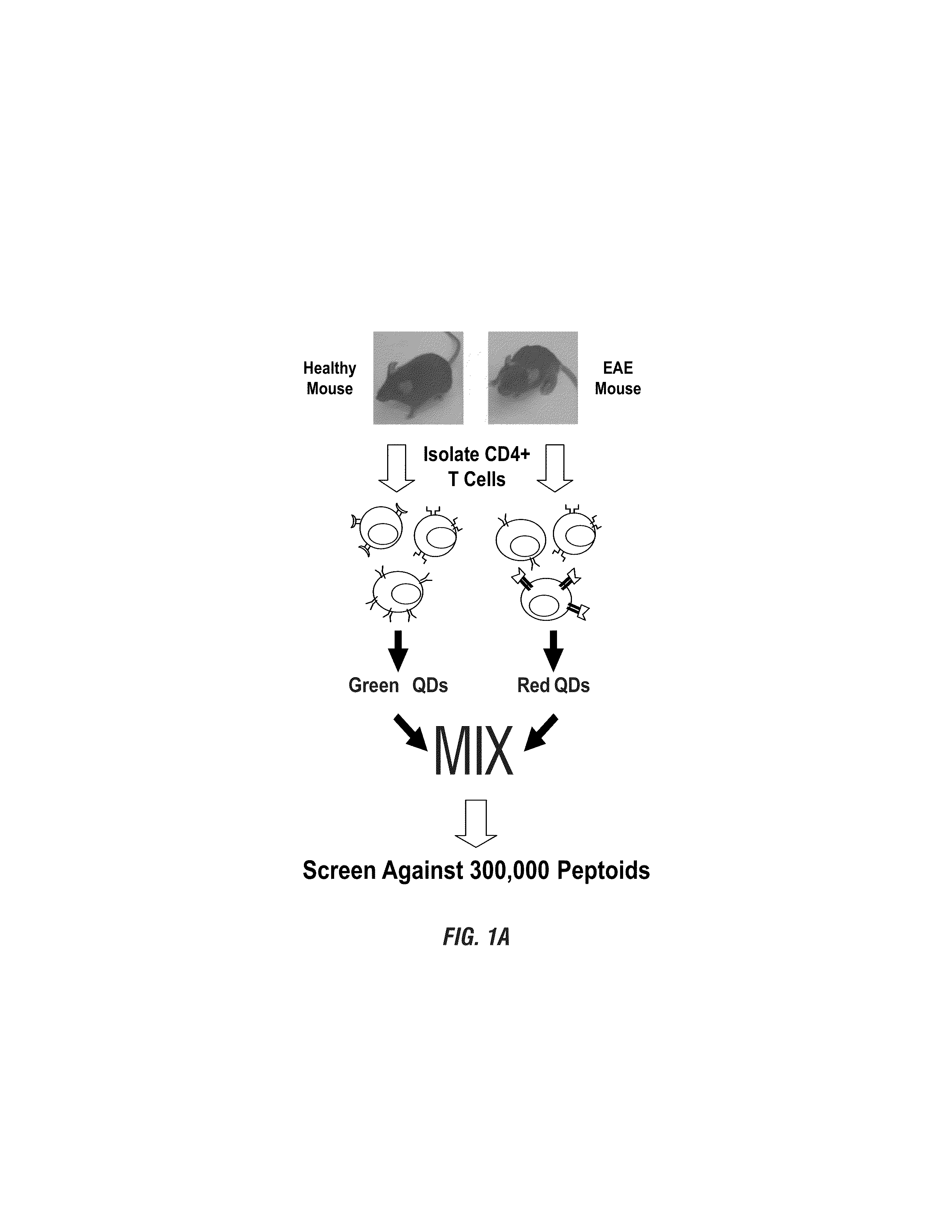
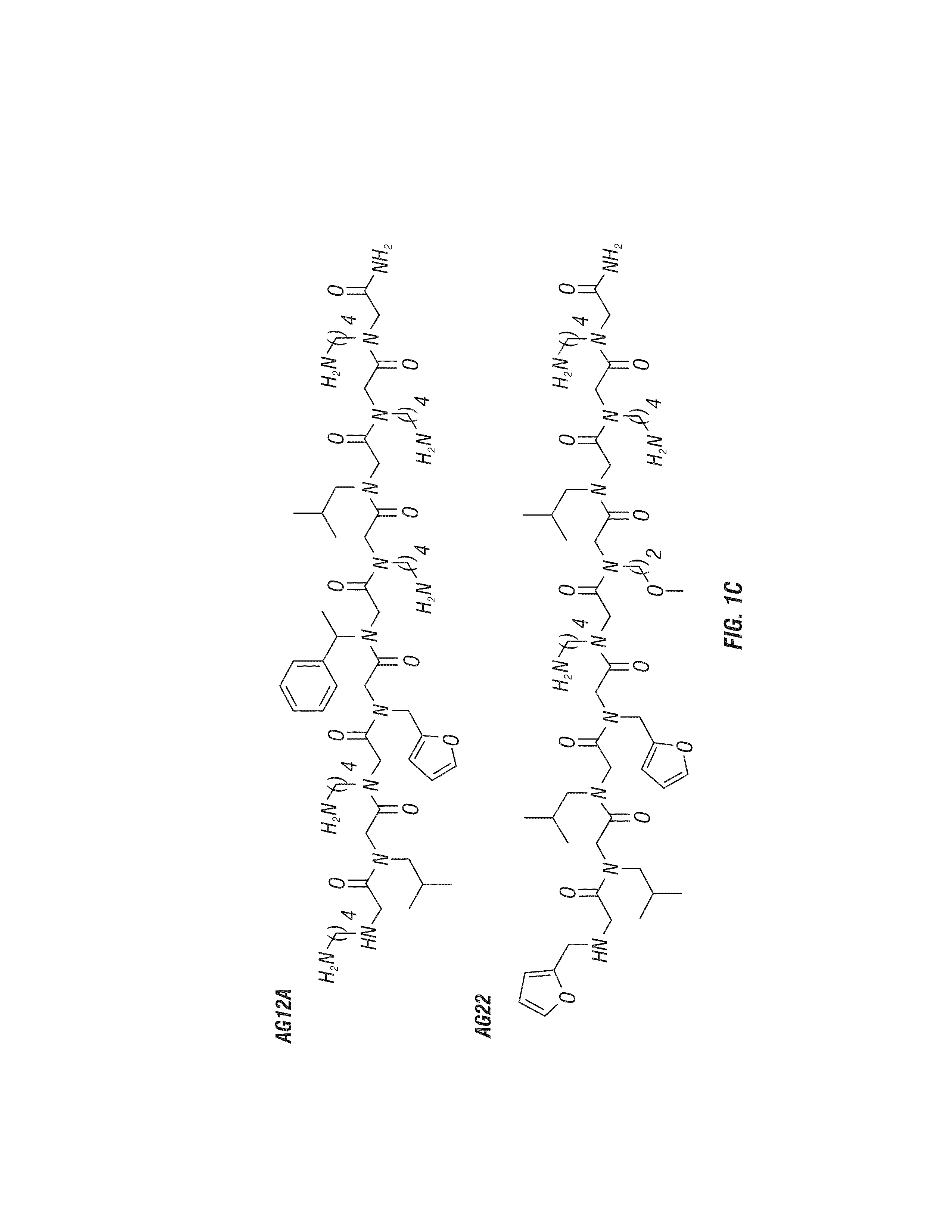
Identifying synthetic ligands that bind t-cells from patients having an autoimmune disease
The present invention provides for the identification of autoreactive T cell populations from individuals having autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and EAE. Peptoids recognized by autoreactive T cells can be used to identify various types of autoimmune disease, and can also be used to target therapies against such populations.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Integrin Targeted Synthetic Ligands for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Method of identifying production using gene expression
InactiveCN1350062AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDNA-binding domainResponse element
A method for identifying a product involves the steps of: (1) associating with the product a marker ligand; and (2) detecting the marker ligand in the product at a later point in time as a means of identifying the product by contacting the product with a detector composition. The detector composition comprises one or more first nucleotide sequences encoding one or more natural or synthetic ligand-dependent transcription factors, wherein said factors comprise at least one ligand binding domain, at least one DNA binding domain and at least one transactivation domain; and a second nucleotide sequence encoding a reporter gene under the regulatory control of a receptor response element or a modified or synthetic response element. The detector composition, a cell line containing the first and second nucleotide sequences, kits using them and products marked with specific marker ligands are useful in this method.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
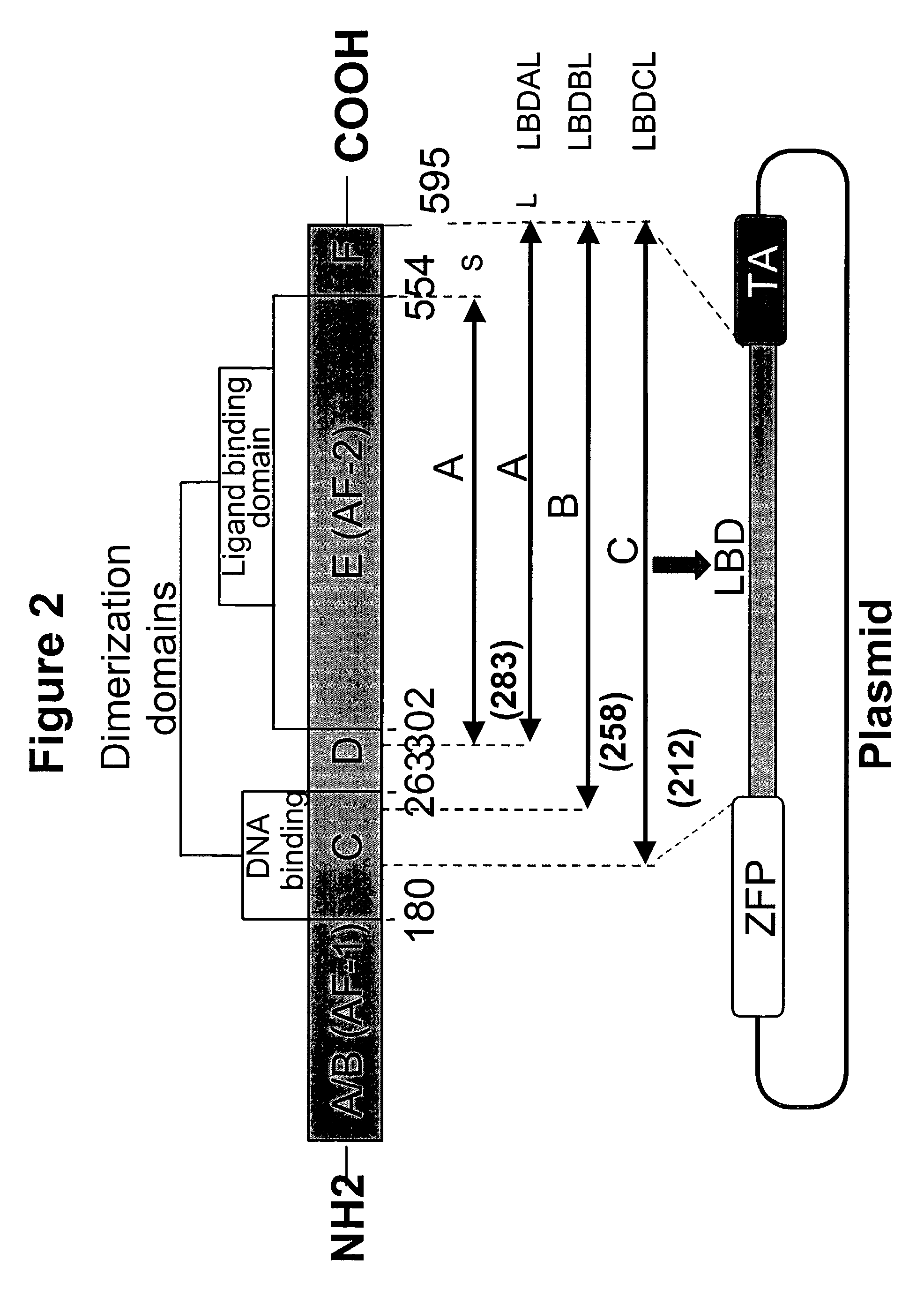
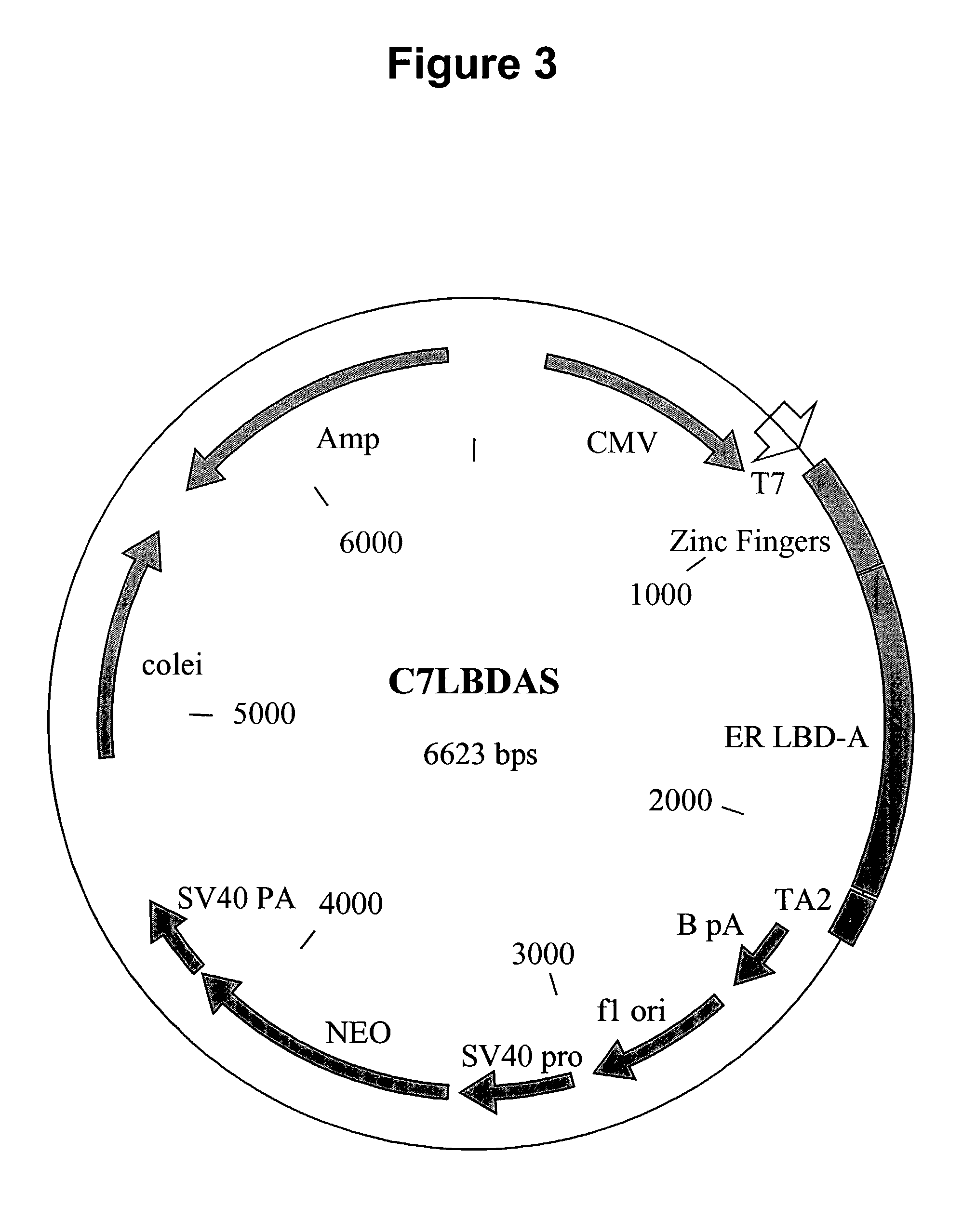
Nucleic acids encoding estrogen receptor ligand binding domain variants
Mutants of steroid receptor ligand binding domains and synthetic ligands which have specific binding affinities for these receptors are provided. The use of these LBD-ligand combinations for construction of selective “molecular gene switches” is disclosed. Methods of regulating gene function using these switches are provided.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
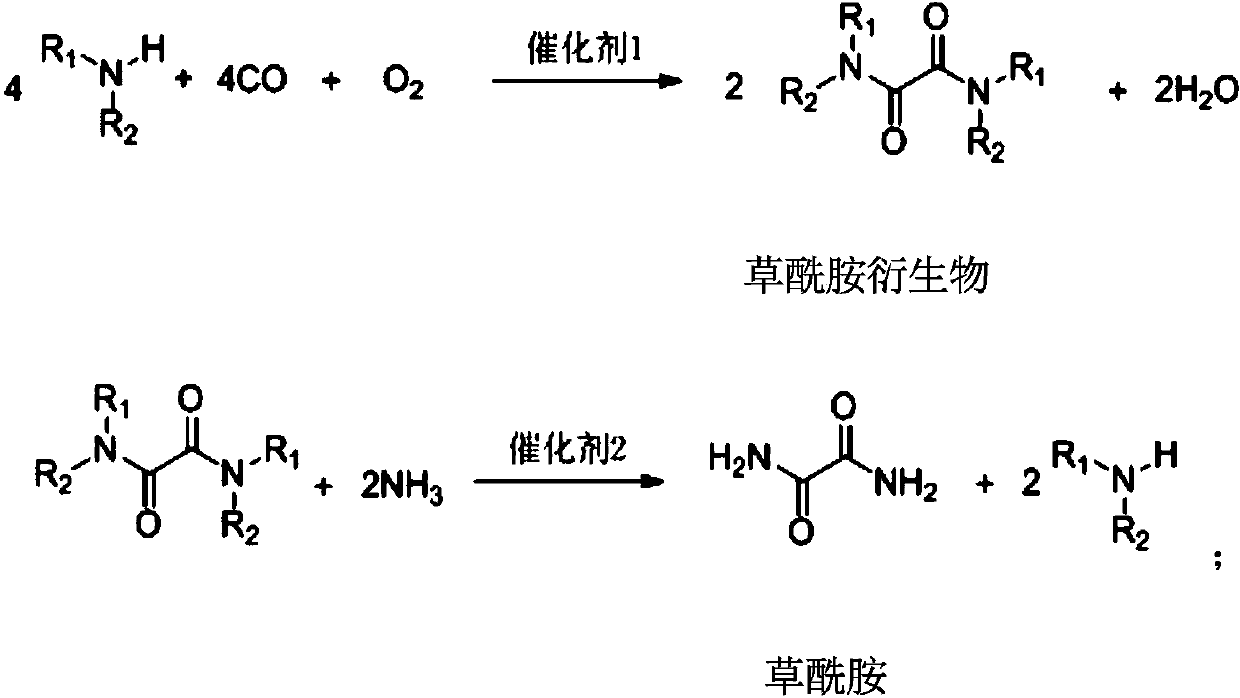
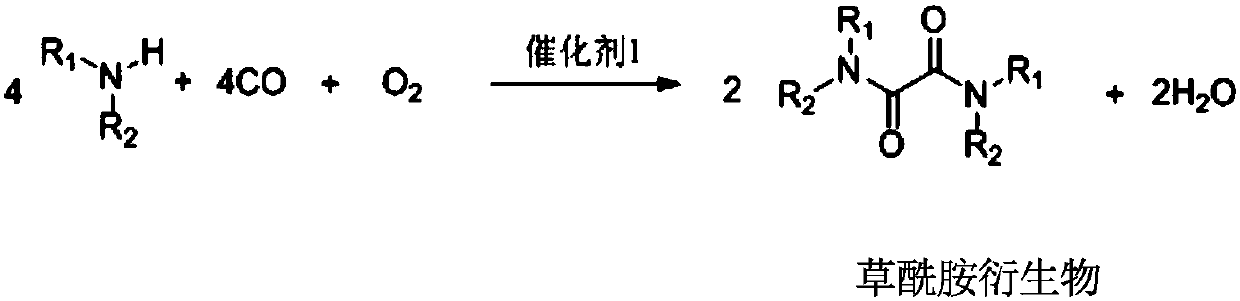
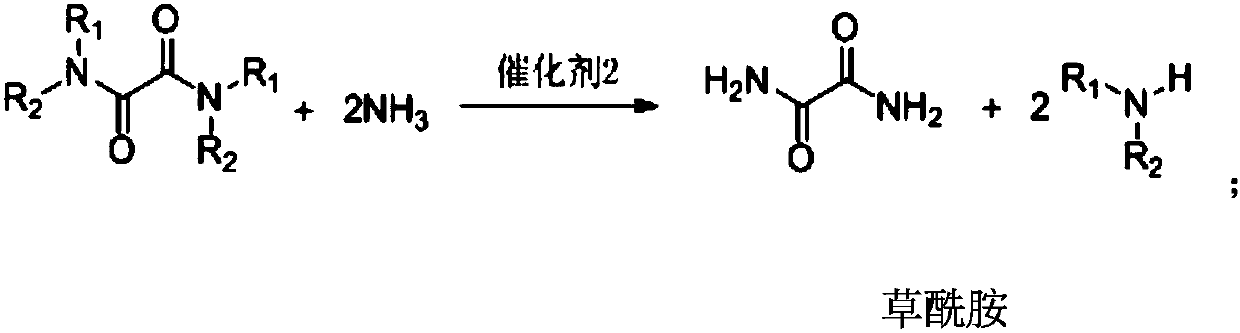
Preparation method of oxamide
ActiveCN110041218ASimple preparation processEasy to recycleOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationFood additiveAminolysis
The invention provides a preparation method of oxamide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: an intermediate oxamide derivative is prepared from CO, O2 and amine compounds as raw materials by oxidation and carbonylation under the action of a catalyst 1, and then, oxamide is prepared through aminolysis of the oxamide derivative under the action of a catalyst 2. A novel method is used for coproducing oxamide and the oxamide derivative, and the problems that oxalate synthesis materials are poisonous, catalyst efficiency is low and the like in the original technology for synthesizing oxamide through aminolysis of oxalate are solved. Besides, the technologically synthesized oxamide derivative has good substrate applicability and can be applied to fields of medicine, pesticides,synthetic ligands, food additives and the like.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
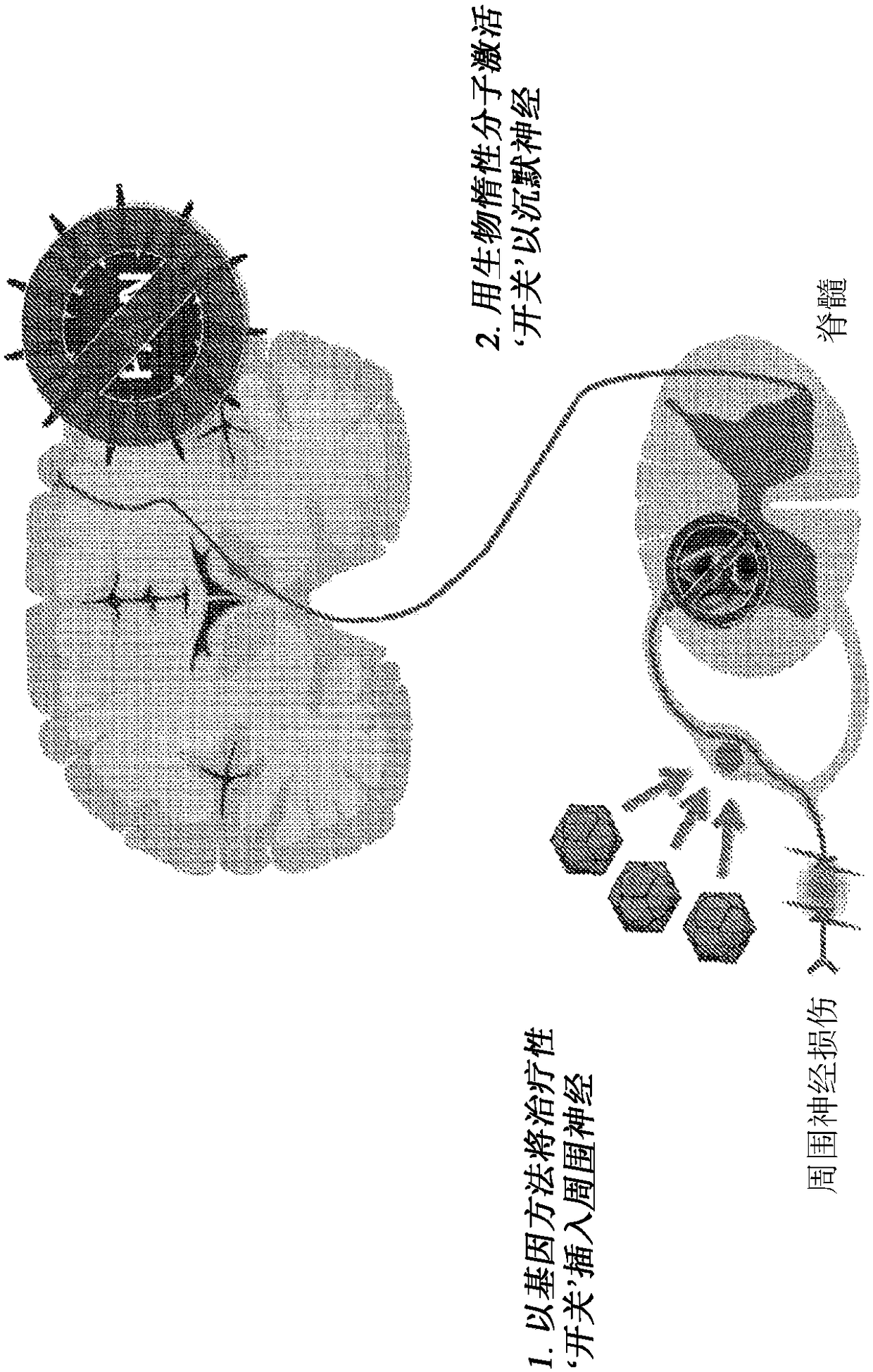
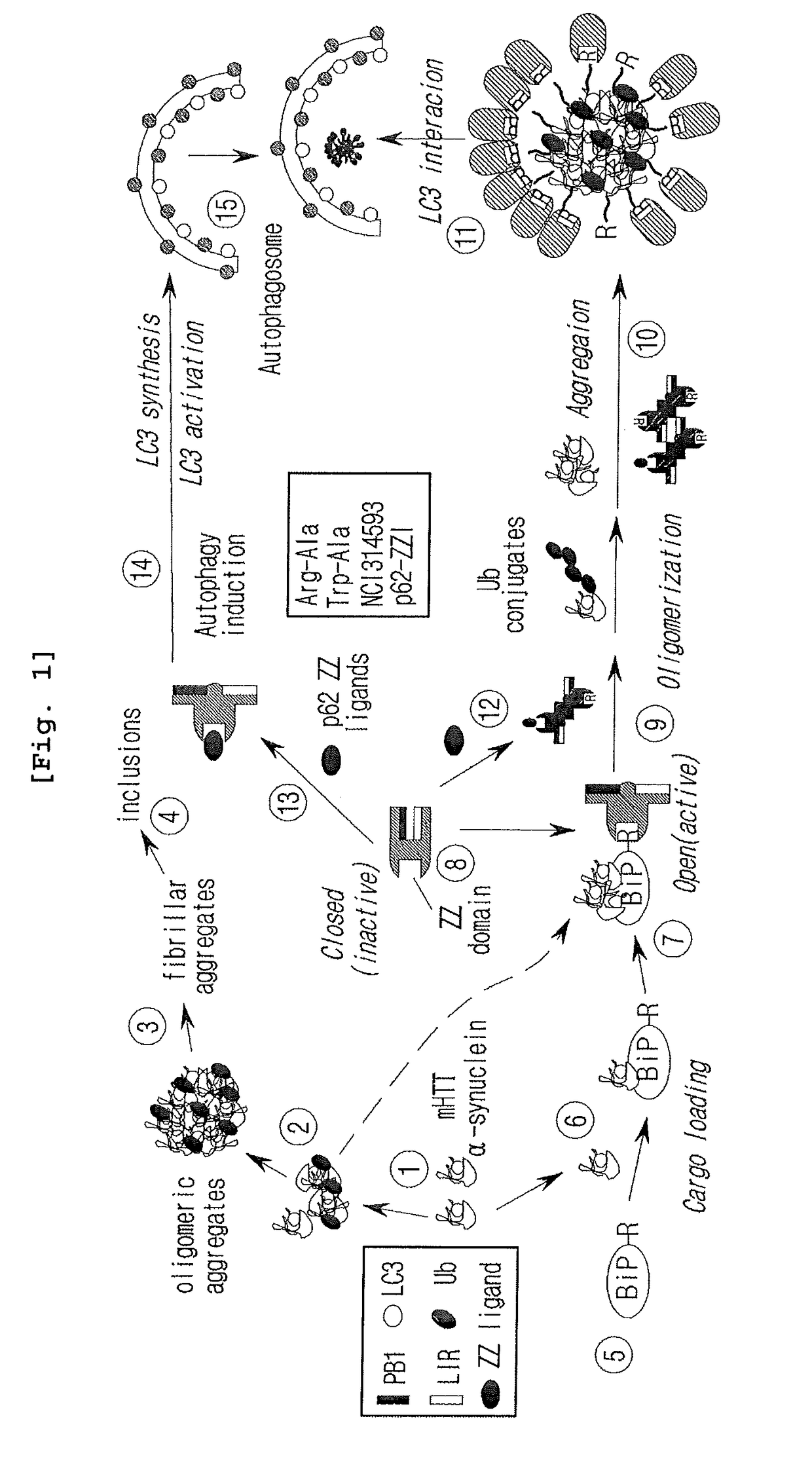
Prevention and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Autophagy Activity Mediated by A Synthetic Ligand or Arginylated BIP Binding to the P62 ZZ Domain
ActiveUS20180243244A1Easy to useNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsLysosomal proteolysisInclusion bodies
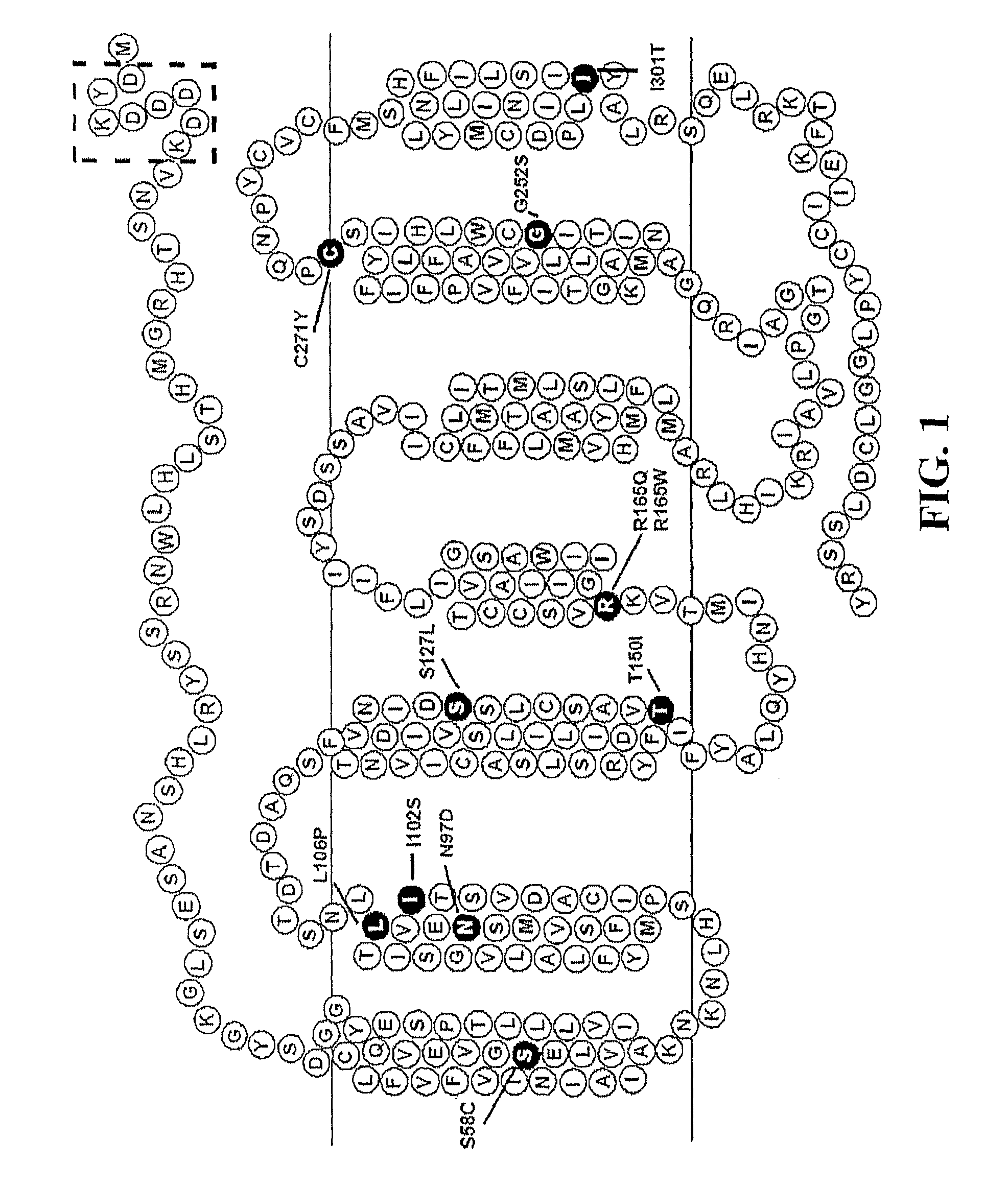
The pharmacokinetics and key technologies of the present invention are summarized in FIG. 1. Particularly, malignant misfolded proteins such as mutant huntingtin and alpha-synuclein are coagulated and grow into oligomeric coagulum (①, ②, fibrillar coagulum (③) and eventually inclusion body (④). Young neurons produce a large amount of Nt-Arg through N-terminal arginylation (⑤) of vesicle chaperones such as BiP secreted into the cytoplasm, and then arginylated BiP (R-BiP) is secreted binds to the misfolded proteins (⑥). As a ligand, the Nt-Arg of R-BiP binds to the p62 ZZ domain (⑦), and the normally inactivated closed form of p62 is changed to an open form, leading to structural activation (⑧). As a result, PB1 and LC3-binding domains are exposed. The PB1 domain induces oligomerization (⑨), leading to the concentration as a p62 body (⑩) that is a coagulum capable of being degraded by autophagy. Then, p62 binds to LC3, which is protruding from the autopagosomal membranes, leading to the completion of autophagy targeting (⑪) and lysosomal proteolysis. Since autophagy proteolysis including steps (⑤)-(⑪) is strong in young neurons, cytotoxic protein coagulums (①-⑤) do not accumulate. However in aged neurons, autophagy proteolysis including steps ⑤-⑪ is weakened, and protein coagulums (①-⑤) accumulate and become cytotoxic. In this invention, p62 is intentionally activated (⑫, ⑬) by using low mass ligands of the p62 ZZ domain to effectively remove huntingtin and alpha-synuclein protein coagulums. Particularly, in step ⑫, p62 ligated with a ligand accelerates the oligomerization of p62-R-BiP-misfolded protein (⑨) and the formation of autophagy coagulum (⑩). In step (⑬), the ligand-p62 conjugate acts as an autophagy activator (⑭) to induce the synthesis of LC3 and the conversion of LC3-I into LC3-II in order to accelerate the formation of autophagosomes (⑮).
Owner:AUTOTAC BIO
Process for the purification of human growth hormone polypeptides using affinity resins comprising specific ligands
InactiveCN102216325AGrowth hormonesPeptides with abnormal peptide linkSomatotropic hormoneHuman growth hormone
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Process for the purification of antibodies using affinity resins comprising specific ligands
InactiveCN102216319APeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsPurification methodsMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to a novel process for the purification of antibodies, e.g. monoclonal antibodies. The process utilizes an affinity resin comprising a solid phase material having immobilized thereto one or more low-molecular weight synthetic ligands. The affinity resins enable the separation of antibodies from even closely related proteins.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Biological active ligands of melanocortin receptors
InactiveUS8058240B2Increase stimulationImprove the quality of lifeMetabolism disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMelanocortin agonistMelanocortin 1 receptor
Disclosed are novel ligands based on an AGRP template that can rescue endogenous melanocortin agonist and / or antagonist dysfunction at MCR polymorphisms. In particular, the present invention provides novel synthetic ligands based on AGRP templates that can rescue endogenous melanocortin agonist dysfunction at MC4R polymorphisms to treat children and adults with these mutations and increase their quality of life.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
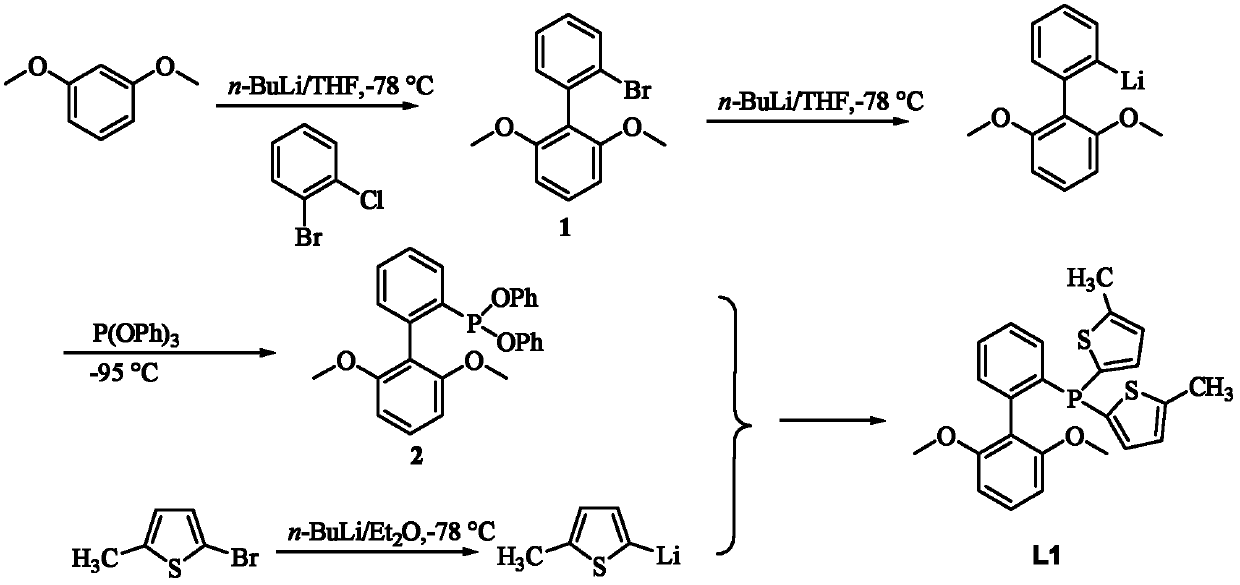
A large-volume electron-rich phosphine ligand catalyst and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102268041AHigh activityExtend your lifeGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlkaneLone electron pair
The invention discloses a bulky electron-rich phosphine ligand compound and a preparation method thereof. The structural formula of the phosphine ligand is shown in formula I; wherein, R represents an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, an alkynyl group, an alkoxy group or an aryl group substituted by an alkane. The method for preparing the compound of formula I comprises the following steps: reacting the compound shown in formula II with the compound shown in formula III at -90°C to -60°C for 2-5h, and then reacting at room temperature for 5-15 hours, namely have to. The lone electron pair on the methoxyl oxygen in the large-volume thiophene-containing ligand synthesized by the present invention can increase the electron cloud density of the molecule, which is beneficial to stabilizing the Pd intermediate in the reaction process, preventing cyclization, and increasing steric hindrance. Improve catalyst life. In addition, the thiophene ring is a group with a stronger electron supply than aryl or alkyl, which is beneficial to increase the electron cloud density on the phosphine and improve the activity of the ligand. The ligand of the present invention is coordinated with the palladium catalyst and then applied to Suzuki coupling or polymerization reaction to synthesize photoelectric polymer materials with high molecular weight and high yield.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com