Process for the purification of antibodies using affinity resins comprising specific ligands
An antibody purification and affinity technology, applied in the field of antibody purification using affinity resin containing specific ligands, can solve the problems of long process time, increased labor cost, pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0166] Preparation of affinity resin
[0167] Affinity resins can in principle be prepared in two quite different ways: (i) by synthesizing the ligand in free form and then immobilizing the ligand directly or via a linker to the solid phase material (see above), or (ii) by functionalizing the solid phase material followed by sequential synthesis of ligands. For the first approach, immobilization techniques are readily available in the art, eg as described in Hermanson et al. (see above). For the second way, techniques are also available, such as solid-phase peptide synthesis known in the art and its derivatives (Fields, G.B., etc. (1992) Principles and practice of solid-phase peptide synthesis (principle and practice of solid-phase peptide synthesis) Practice). In Synthetic Peptides: A User's Guide (Grant, G.A. Ed.), pp. 77-183, W.H. Freeman; Fields, G.B. Ed. (1997) Solid-phase peptide synthesis (solid-phase peptide synthesis). Methods in Enzymology 289 and Dorwald, F.Z. Org...
Embodiment 1
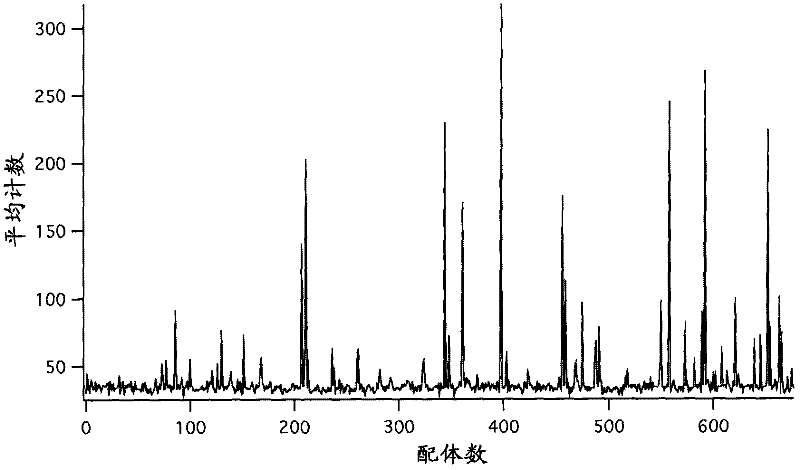
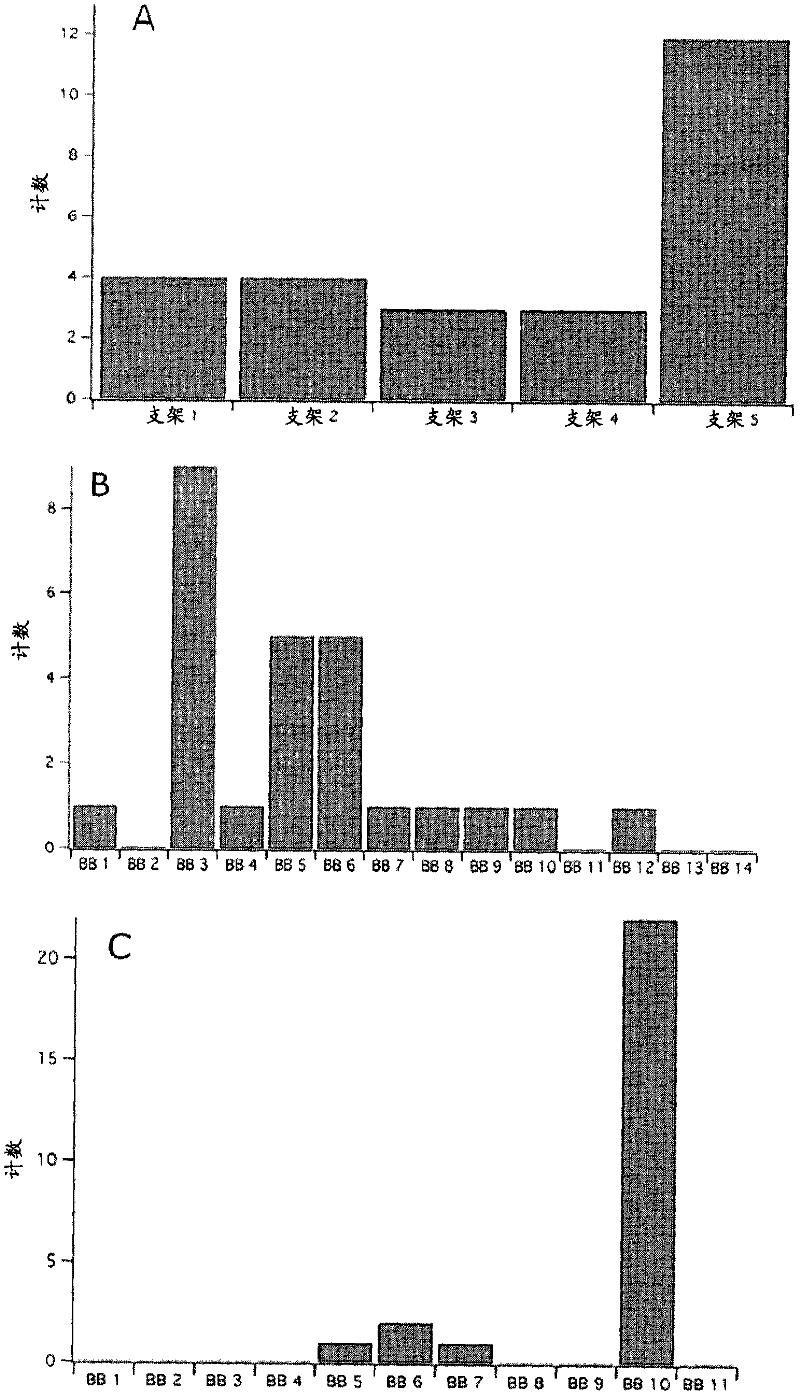
[0264] Example 1. Using PCA to select the structural unit (BUILDING BLOCK) of the combinatorial library
[0265]Combinatorial libraries were designed by using two parallel methods. A virtual combinatorial library containing 229,957 members was first generated. For each virtual library member, a set of 118 physicochemical descriptors was calculated according to the method of Cruciani et al. [Ref. Cruciani, C. et al., Molecular fields in quantitative structure-permeation relationships: the VolSurf approach. Journal of Molecular structure- Theochem, 2000.503(1-2): pp. 17-30; Cruciani, G., M.Pastor, and W. Guba, VolSurf: a new tool for the pharmacokinetic optimization of lead compounds. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2000.11: Pages S29-S39]. The resulting models were analyzed using multivariate statistics. To simplify the model, these 118 descriptors are designed as two principal components.
[0266] Then optimize the chemical diversity of the combinatorial libra...
Embodiment 2
[0268] Example 2: Synthesis of combinatorial libraries
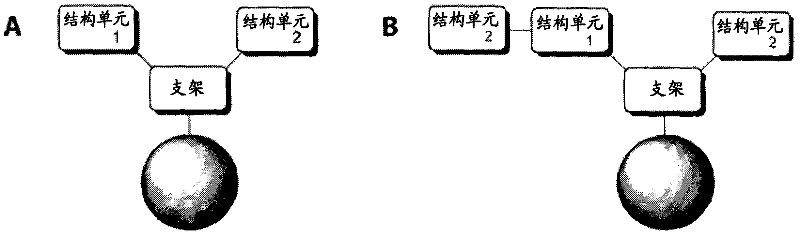
[0269] The general structure of a combinatorial library of affinity ligands designed to bind to Fc fragments is shown in Figure 1. The scaffold is selected from aliphatic di-amino-carboxylic acids, and building blocks 1 and 2 are independently selected from natural amino acids, unnatural amino acids, and carboxylic acids.
[0270]
[0271] Figure 1. Schematic representation of the general structure of a trimeric ligand (A) and a tetrameric ligand (B). picture.
[0272] Combinatorial libraries were synthesized by employing one-bead-one-compound split-and-mix solid-phase synthesis. 770 different ligands were synthesized on approximately 20,000 beads of optically encoded amino-functional polyethylene glycol-acrylamide (PEGA) beads. To maintain access to all compounds throughout the synthesis, encoded bead technology was used to read the optically encoded beads used for the synthesis [WO 2005 / 061094, WO 2005 / 062018. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com