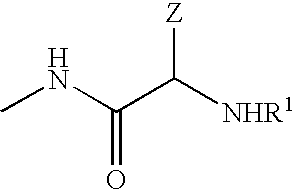
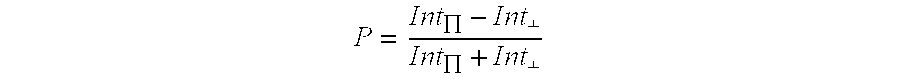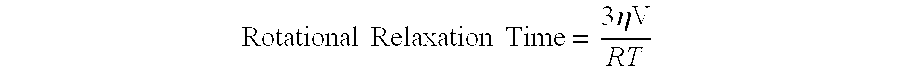Patents
Literature
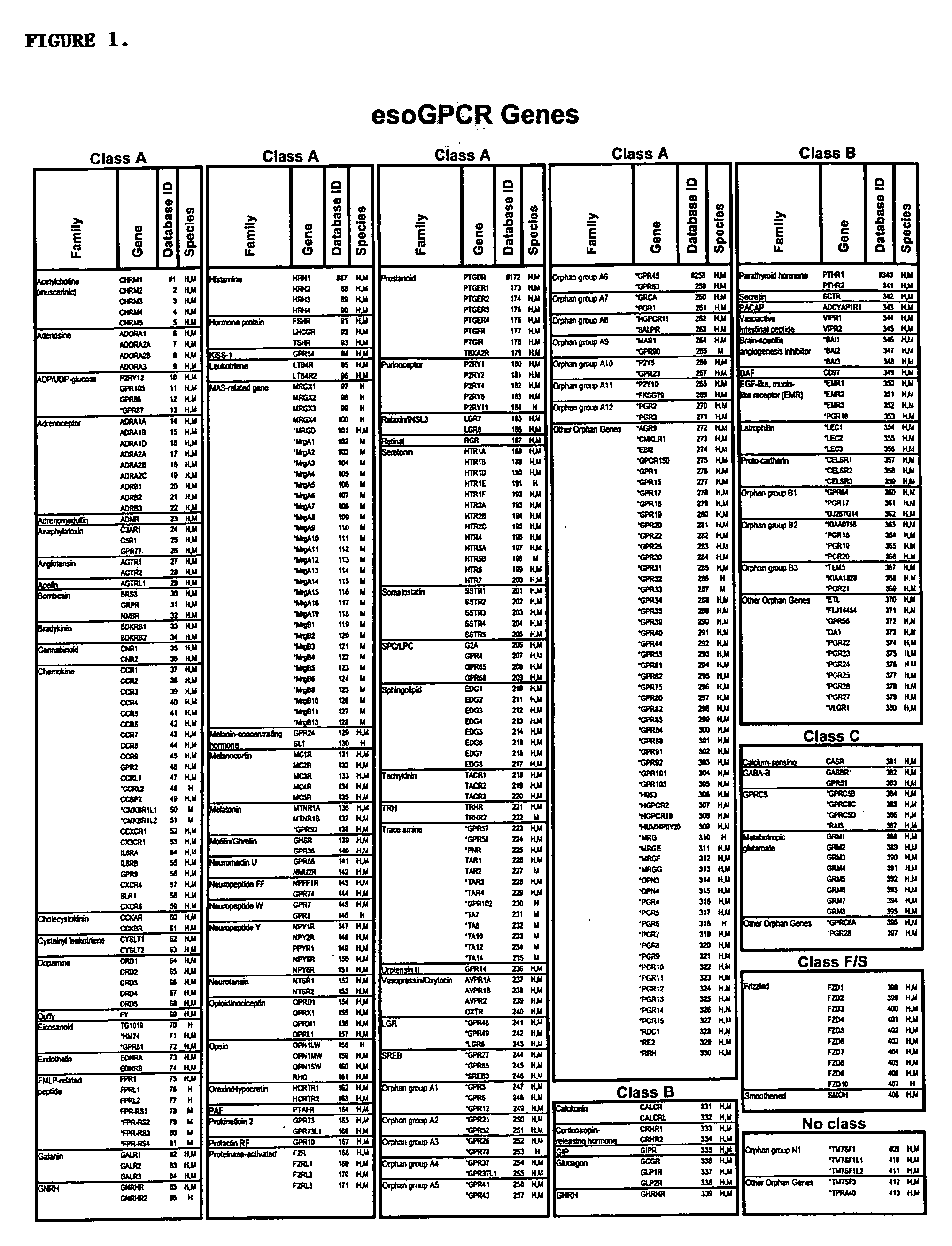
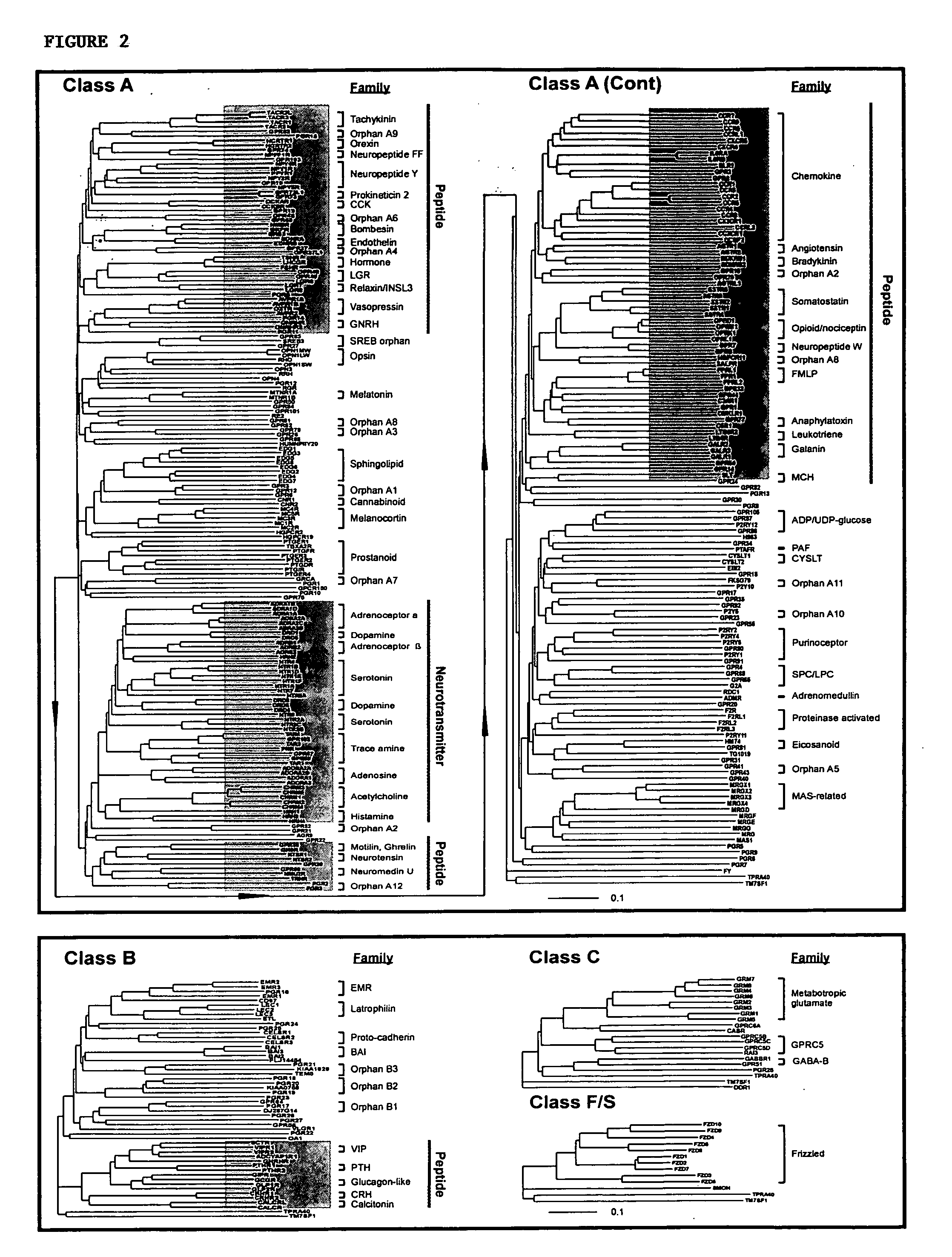
663 results about "G protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases.
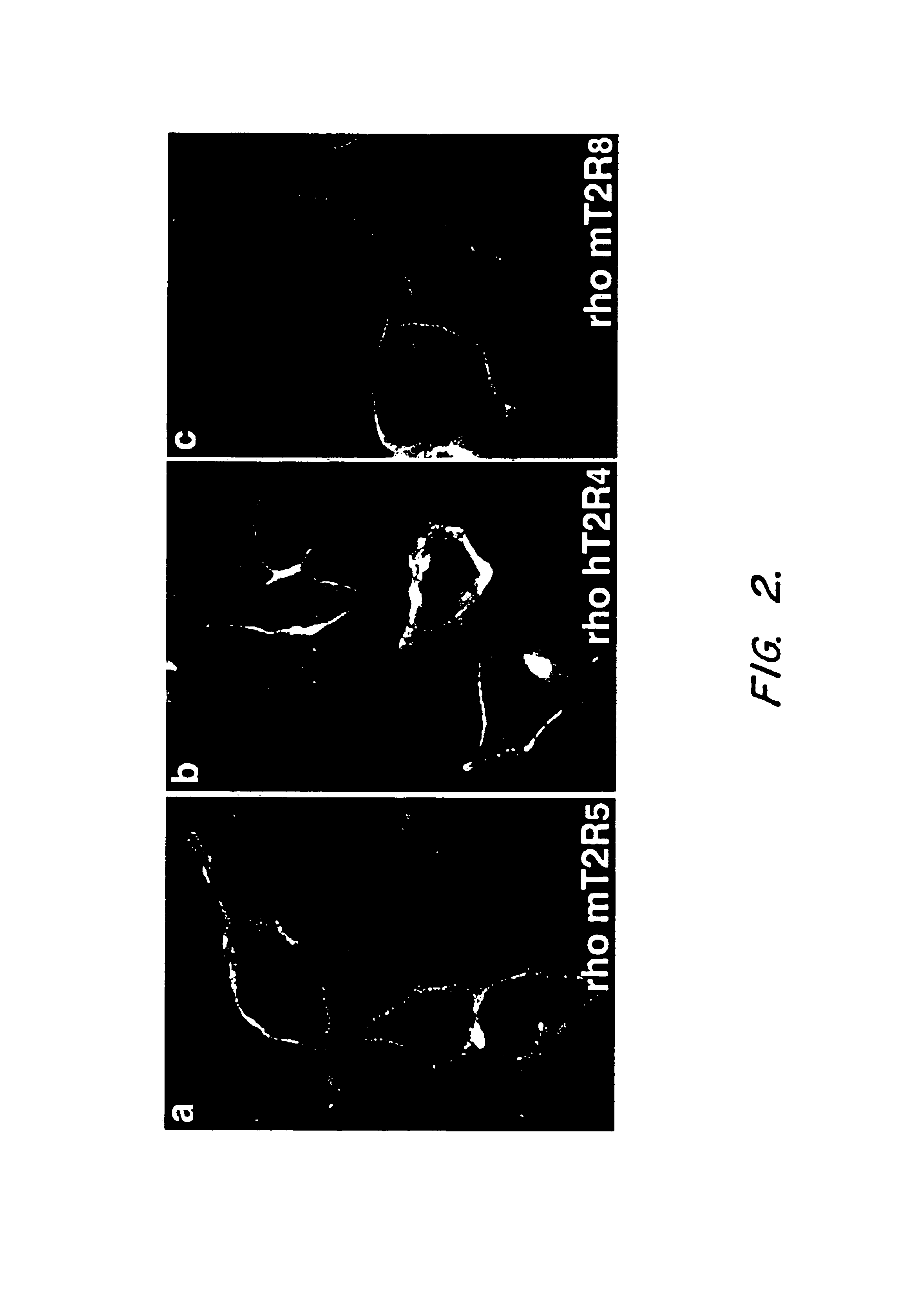
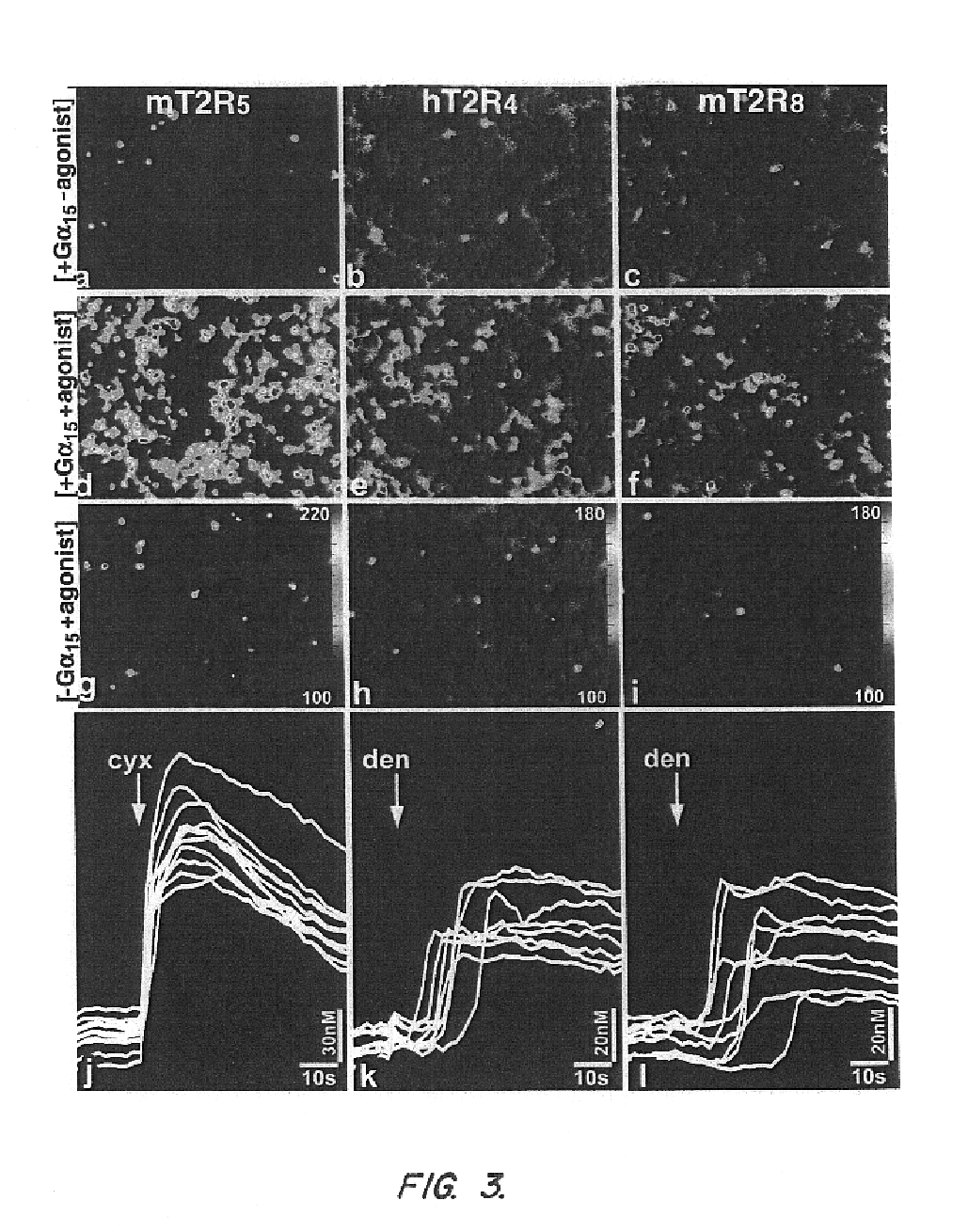
T2R taste receptors and genes ecncoding same
Newly identified mammalian taste-cell-specific G Protein-Coupled Receptors and the genes encoding said receptors are described. Specifically, T2R taste G Protein-Coupled Receptors that are believed to be involved in bitter taste sensation, and the genes encoding the same, are described, along with methods for isolating such genes and for isolating and expressing such receptors. Methods for representing taste perception of a particular tastant in a mammal are also described, as are methods for generating a novel molecules or combinations of molecules that elicit a predetermined taste perception in a mammal, and methods for simulating one or more tastes.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Methods of wound care and treatment
InactiveUS20100021464A1Reduce scarsImprove the level ofBiocideSenses disorderCell membraneWound care
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., gas-enriched electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for use in treating a wound to a surface tissue or a symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Detection of ion channel or receptor activity
InactiveUS20060148104A1Easy accessImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeterologousBiological activation
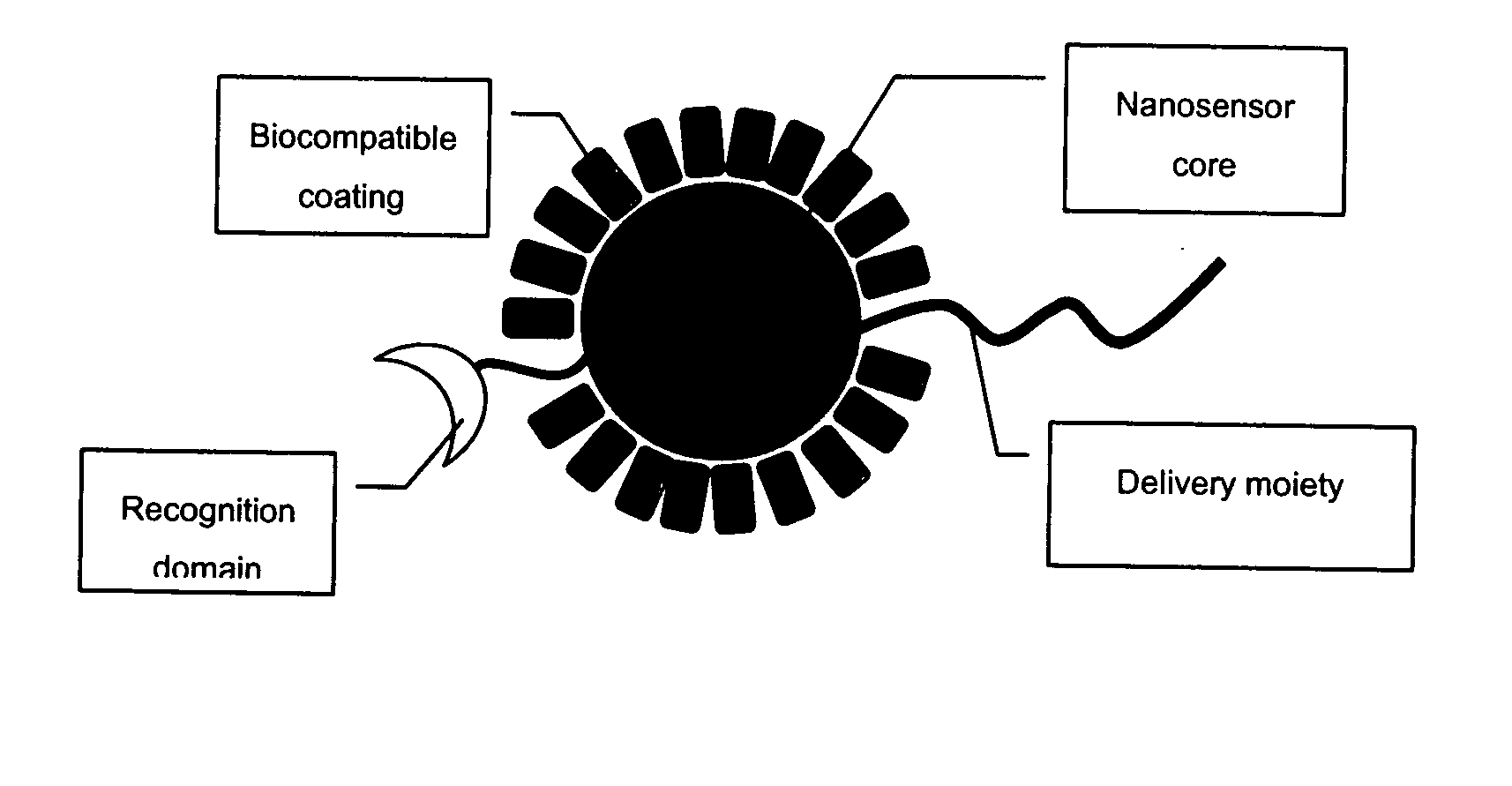
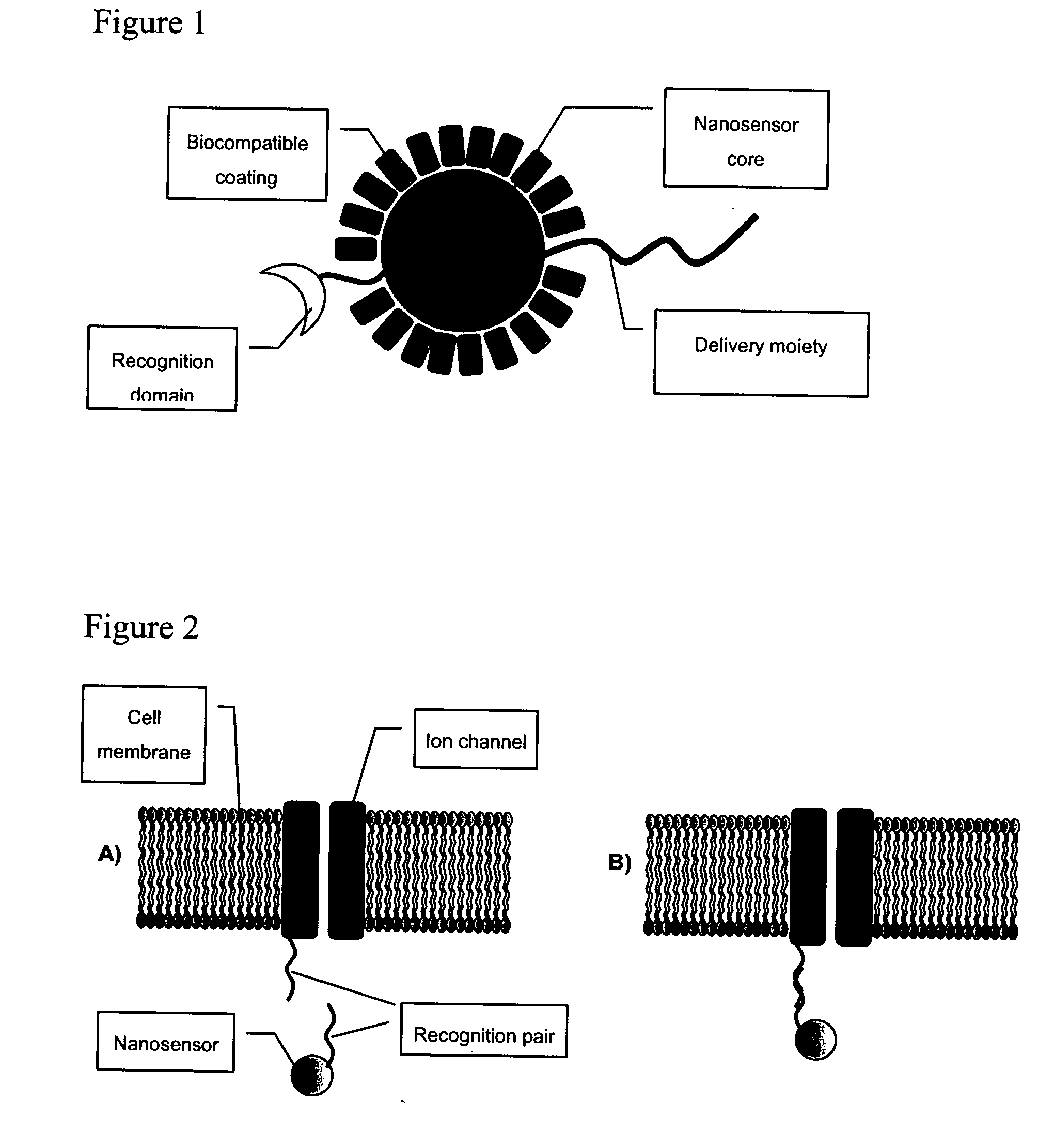
The invention provides nanosensors and nanosensor components for the detection of ion channel activity, receptor activity, or protein protein interactions. Certain of the nanosensor components comprise a nanoparticle and recognition domain. Following contact with cells and, optionally, internalization of the nanosensor component by a cell, the recognition domain binds to a target domain, e.g., a heterologous target domain, of a polypeptide of interest such as an ion channel subunit, G protein coupled receptor (GPCR), or G protein subunit. Ion channel activity, GPCR activity, or altered protein interaction results in a detectable signal. The nanoparticles may be functionalized so that they respond to the presence of an ion by altering their proximity. Certain of the nanosensors utilize the phenomenon of plasmon resonance to produce a signal while others utilize magnetic properties, RET, and / or ion-sensitive moieties. Also provided are polypeptides, e.g., ion channel subunits, comprising a heterologous target domain, and cell lines that express the polypeptides. Further provided are a variety of methods for detecting ion channel activity, receptor activity, or protein interaction and for identifying compounds that modulate one or more of these. In certain embodiments the invention allows the user to detect the activity of specific ion channels even in the presence of other channels that permit passage of the same ion(s) or result in activation of the same downstream targets, thereby achieving improved specificity in high throughput screens while at the same time providing a high signal to noise ratio.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +1
Compositions and methods for treating cystic fibrosis
InactiveUS20100303917A1Increased mucus secretionReduce airflowBiocidePowder deliveryTobramycinCell membrane
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for using same in treating cystic fibrosis or a symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluid compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents (e.g., antibiotics, albuterol, budesonide, etc.). Particular embodiments comprise use and / or synergy with tobramycin for treating bacterial infection, and use and / or synergy with a bronchiodilator. In certain aspects, the methods comprise regulating intracellular signal transduction by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins (like, membrane receptors, including but not limited to G protein coupled receptors, and intercellular junctions).
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
T2R, a novel family of taste receptors
InactiveUS7244584B2Modulated signalCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBacteriaTaste receptor ligandG protein-coupled receptor
The invention provides nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for a novel family of taste transduction G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of taste transduction G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
Compositions and methods for treating asthma and other lung disorders
InactiveUS20100008997A1Powder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesOxygen
Provided are compositions and methods for treating lung or respiratory disorders or conditions characterized by airflow obstruction or limitation, or a symptom thereof (e.g., asthma, rhinitis, allergic rhinitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and COPD-associated conditions (e.g., bronchitis, emphysema, asthma), emphysema, pneumonia, bronchitis, influenza, SARS, tuberculosis, and whooping cough (pertussis), and the like) in a subject in need thereof by administering a therapeutic composition comprising at least one electrokinetically altered fluid (gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures as disclosed herein. In certain aspects, the methods comprise regulating intracellular signal transduction by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins (e.g., membrane receptors, (e.g., to G protein coupled receptors, and intercellular junctions)). Additional aspects include therapeutic compositions, and combination treatment methods comprising administration of electrokinetically generated fluid in combination with at least one additional therapeutic agent.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Methods for screening for binding partners of G-protein coupled receptors
ActiveUS9260505B2Improve stabilityImprove thermal stabilityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionG protein-coupled receptorMolecular biology
A method of producing a conformational specific binding partner of a GPCR, the method comprising: a) providing a mutant GPCR of a parent GPCR, wherein the mutant GPCR has increased stability in a particular conformation relative to the parent GPCR; b) providing a test compound; c) determining whether the test compound binds to the mutant GPCR when residing in a particular conformation; and d) isolating a test compound that binds to the mutant GPCR when residing in the particular formation. Methods of producing GPCRs with increased stability relative to a parent GPCR are also disclosed.
Owner:HEPTARES THERAPEUTICS
Compositions and methods for treating digestive disorders
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for using same in treating digestive disorders or at least one symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluid compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ioinic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said digestive disorders by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Compositions and methods for treating cystic fibrosis
Particular aspects provide electrokinetically-generated fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-generated gas-enriched fluids and solutions), and therapeutic compositions and methods comprising use thereof in treating at least one symptom of cystic fibrosis. In particular embodiments, at least one symptom of cystic fibrosis treated by the present invention include inhibition of Pseudomonas infection, synergy with tobramycin (including TOBI) for use against bacterial infection, and synergy with a bronchiodilator. In particular embodiments, the electrokinetically-generated fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods comprise combination with other therapeutic agents (e.g., antibiotics, albuterol, budesonide, etc.). In certain aspects, the methods comprise regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G protein coupled receptors, and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes).
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Compositions and methods for treating cystic fibrosis
InactiveUS20100004189A1Increased mucus secretionReduce airflowBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsTobramycinCell membrane
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for using same in treating cystic fibrosis or a symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluid compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents (e.g., antibiotics, albuterol, budesonide, etc.). Particular embodiments comprise use and / or synergy with tobramycin for treating bacterial infection, and use and / or synergy with a bronchiodilator. In certain aspects, the methods comprise regulating intracellular signal transduction by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins (like, membrane receptors, including but not limited to G protein coupled receptors, and intercellular junctions).
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Compositions and methods for treating inflammation
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for using same in treating inflammation or at least one symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluid compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-generated fluids (electrokinetically-generated gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
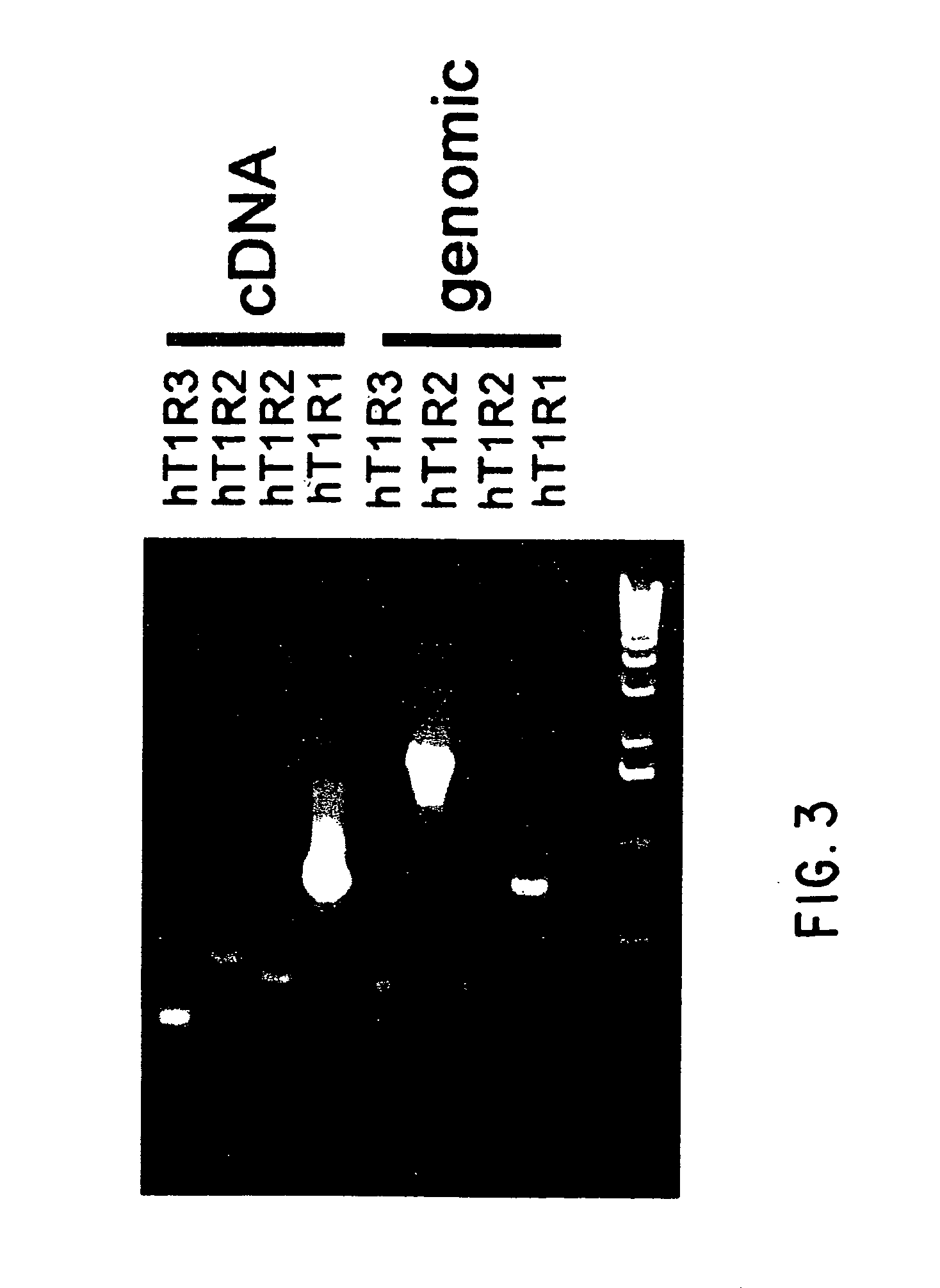
T1R taste receptors and genes encoding same
Newly identified mammalian taste-cell-specific G protein-coupled receptors, and the genes and cDNA encoding said receptors are described. Specifically, T1R G protein-coupled receptors active in taste signaling, and the genes and cDNA encoding the same, are described, along with methods for isolating such genes and for isolating and expressing such receptors. Methods for representing taste perception of a particular tastant in a mammal are also described, as are methods for generating novel molecules or combinations of molecules that elicit a predetermined taste perception in a mammal, and methods for simulating one or more tastes. Further, methods for stimulating or blocking taste perception in a mammal are also disclosed.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
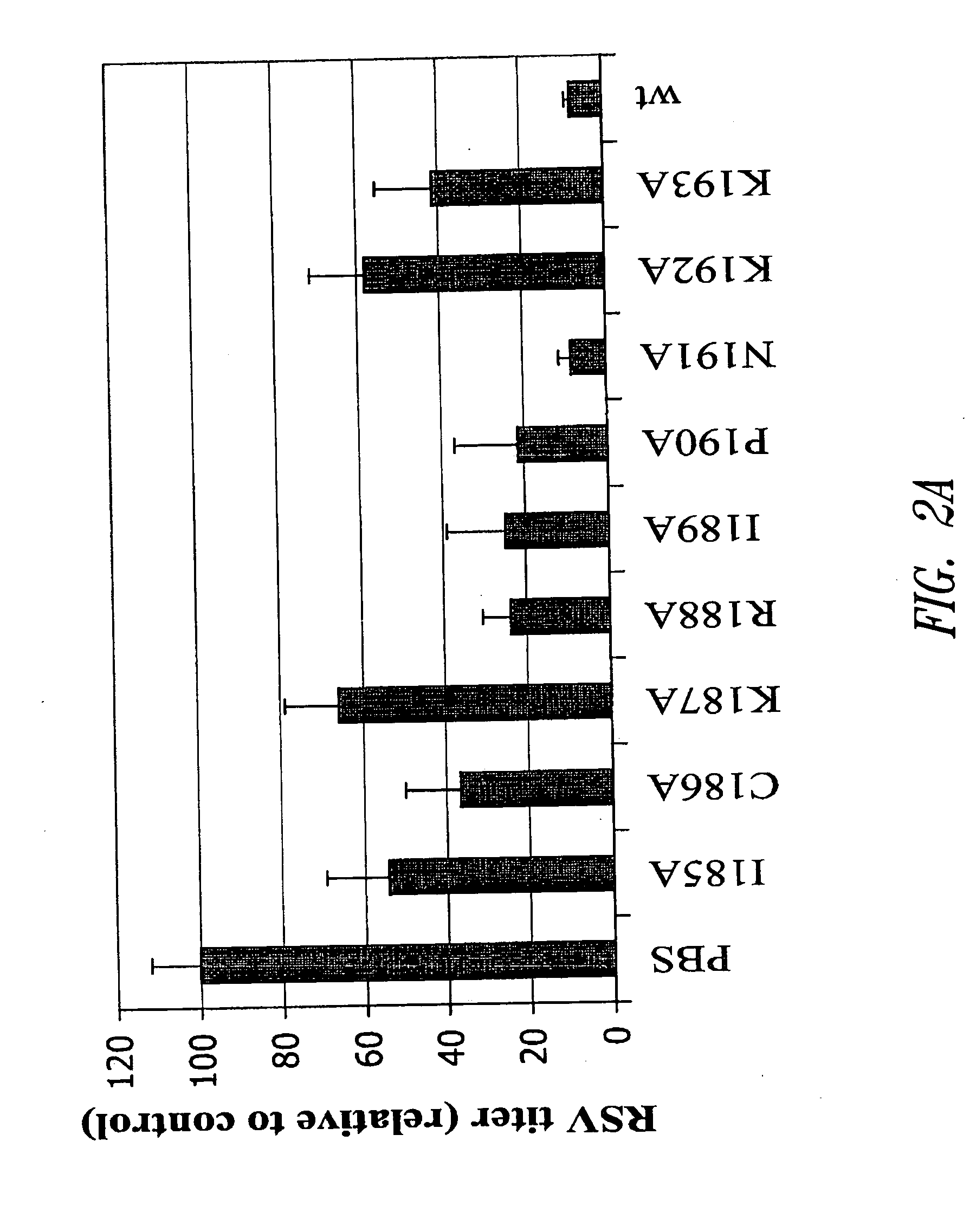
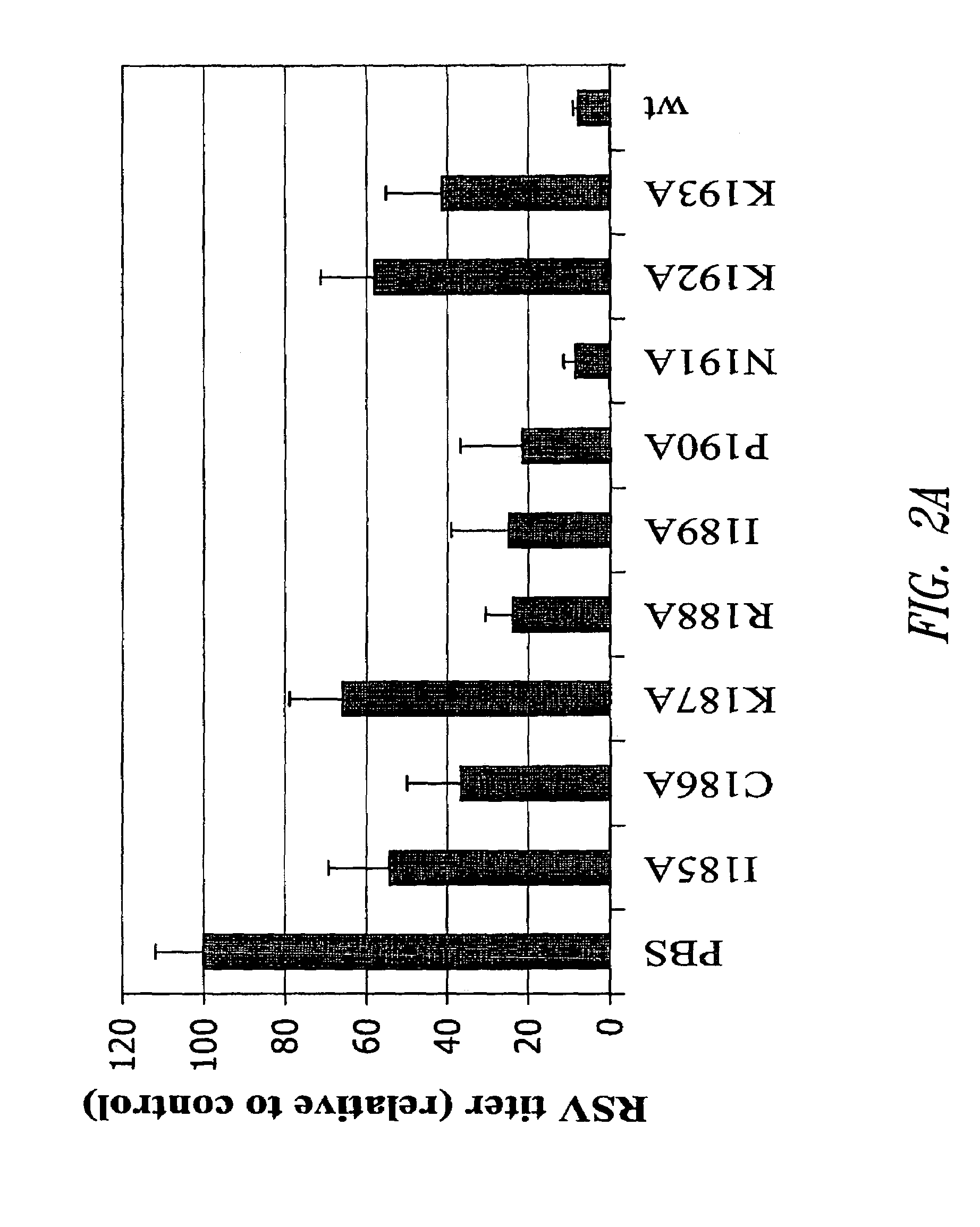
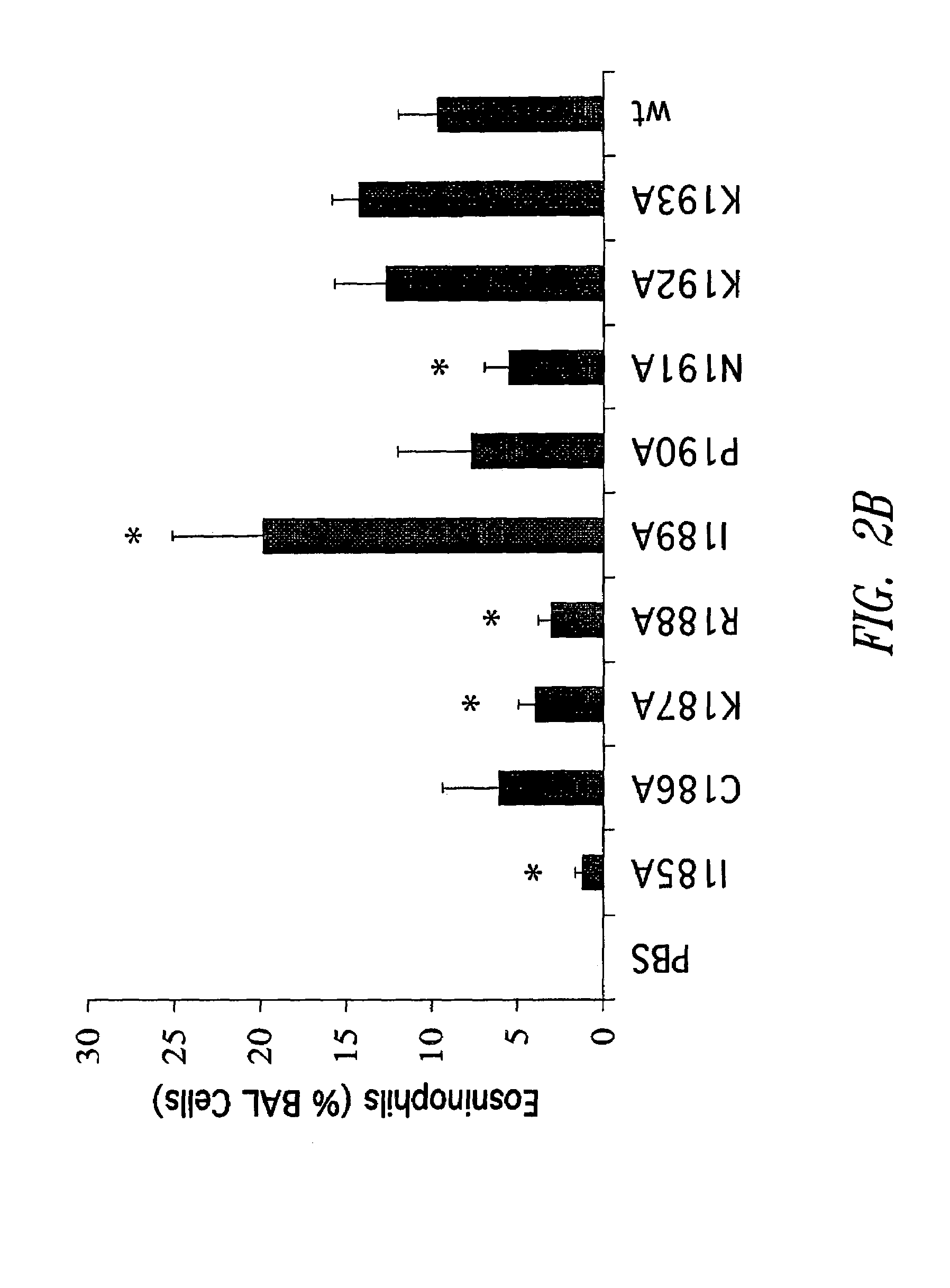
Subunit vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus infection
InactiveUS20050042230A1Reduced responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesPrevention infectionProtection sex
The present invention relates generally to methods of treating or preventing RSV infections, and more specifically, to compositions, and the use thereof, comprising one or more RSV G protein immunogen or fragment thereof capable of eliciting protective immunity without eliciting an immunopathological response or eliciting a reduced immunopathological response.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL CORP LAVAL
Methods of wound care and treatment
InactiveUS20110081384A1Reduce scarsImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryCell membraneWound care
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., gas-enriched electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for use in treating a wound to a surface tissue or a symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
G protein coupled receptors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060134109A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderAgonistGenetically modified mouse
Owner:OMEROS CORP
Compositions and methods for treating asthma and other lung disorders
Provided are compositions and methods for treating lung or respiratory disorders or conditions characterized by airflow obstruction or limitation, or a symptom thereof (e.g., asthma, rhinitis, allergic rhinitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and COPD-associated conditions (e.g., bronchitis, emphysema, asthma), emphysema, pneumonia, bronchitis, influenza, SARS, tuberculosis, and whooping cough (pertussis), and the like) in a subject in need thereof by administering a therapeutic composition comprising at least one electrokinetically altered fluid (gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures as disclosed herein. In certain aspects, the methods comprise regulating intracellular signal transduction by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential and / or conductance, membrane proteins (e.g., membrane receptors, (e.g., to G protein coupled receptors, and intercellular junctions)). Additional aspects include therapeutic compositions, and combination therapies comprising administration of the electrokinetically generated fluids with at least one additional therapeutic agent.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Compositions and methods for treating inflammation
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for using same in treating inflammation or at least one symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluid compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-generated fluids (electrokinetically-generated gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
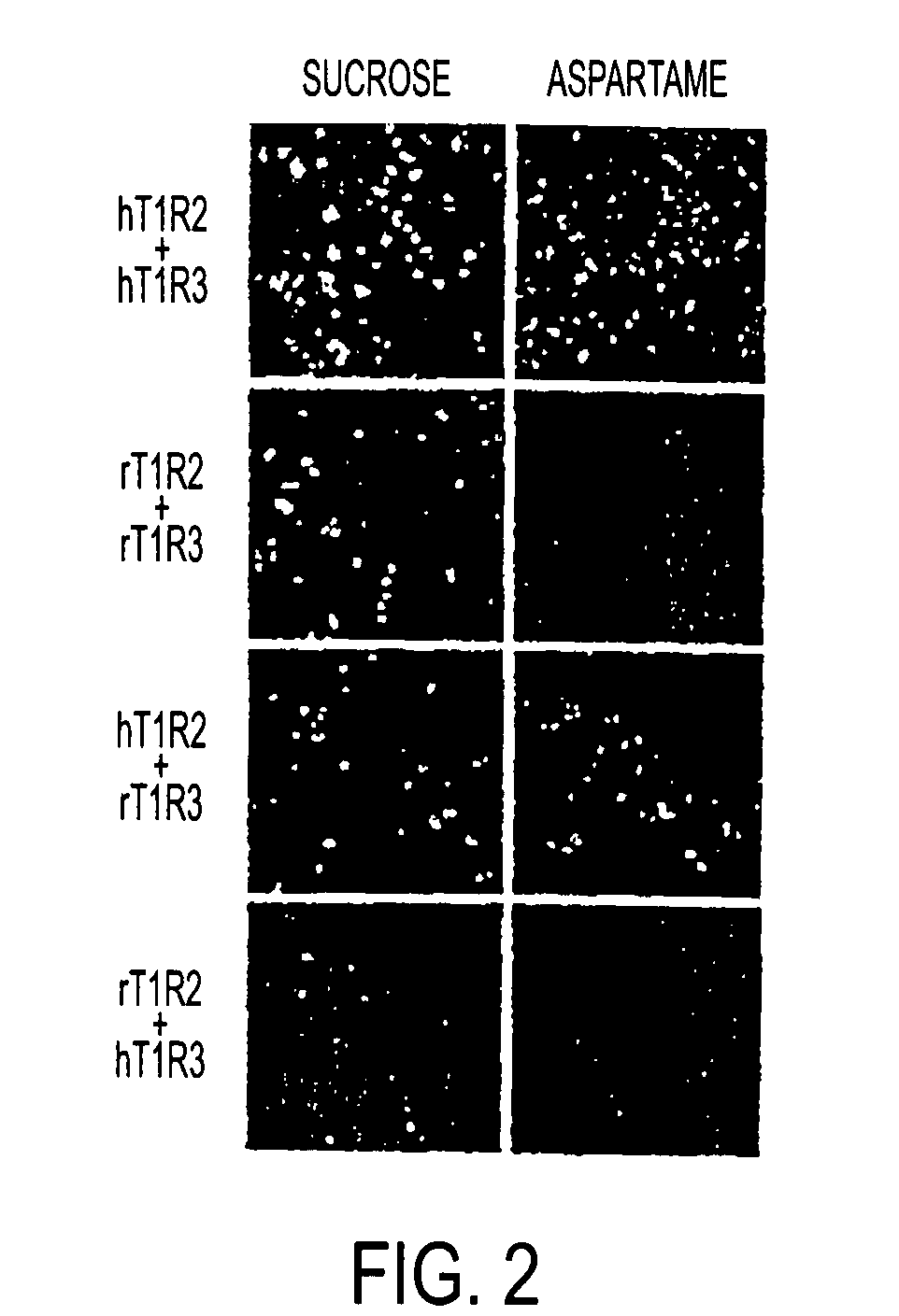
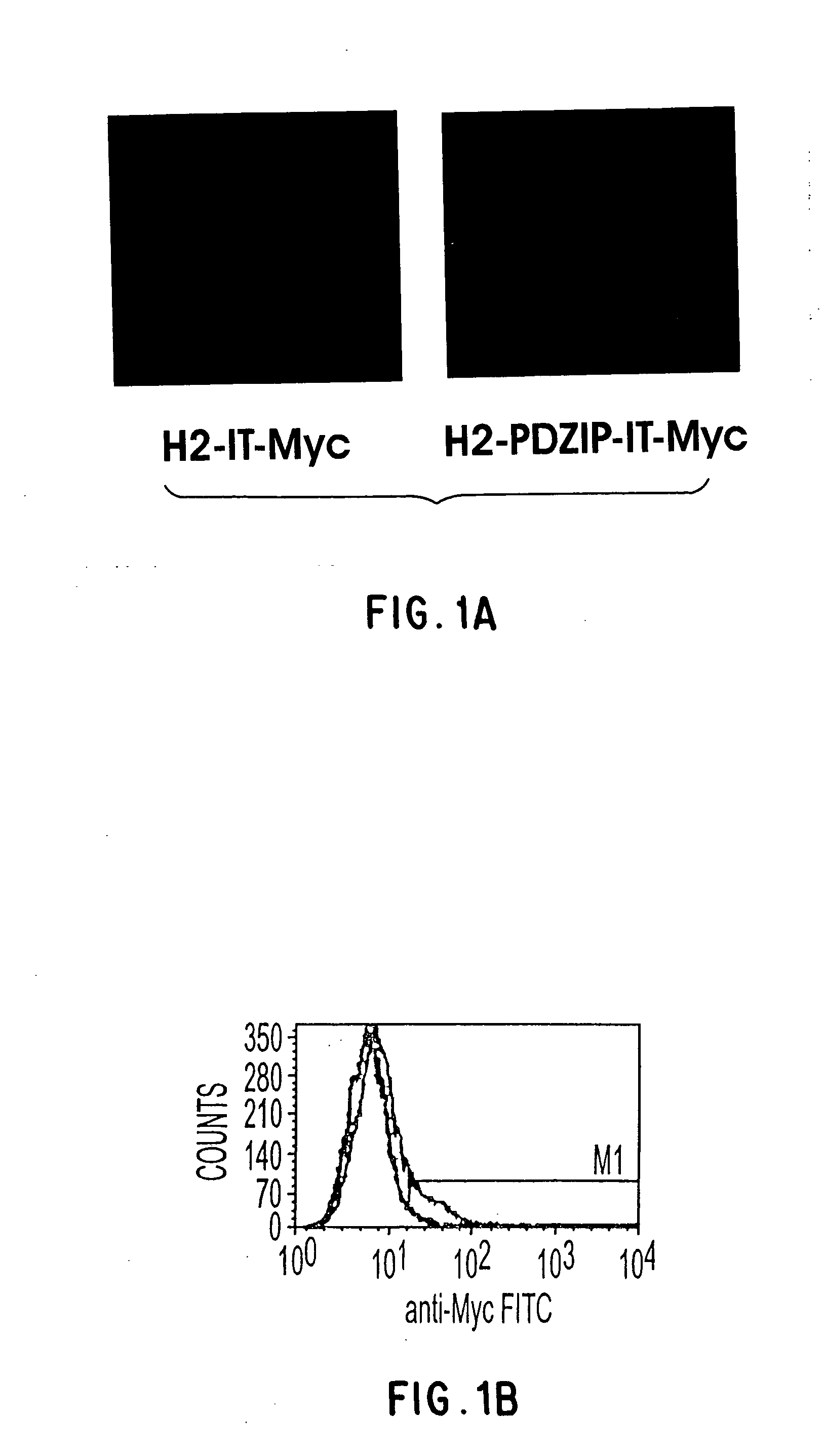
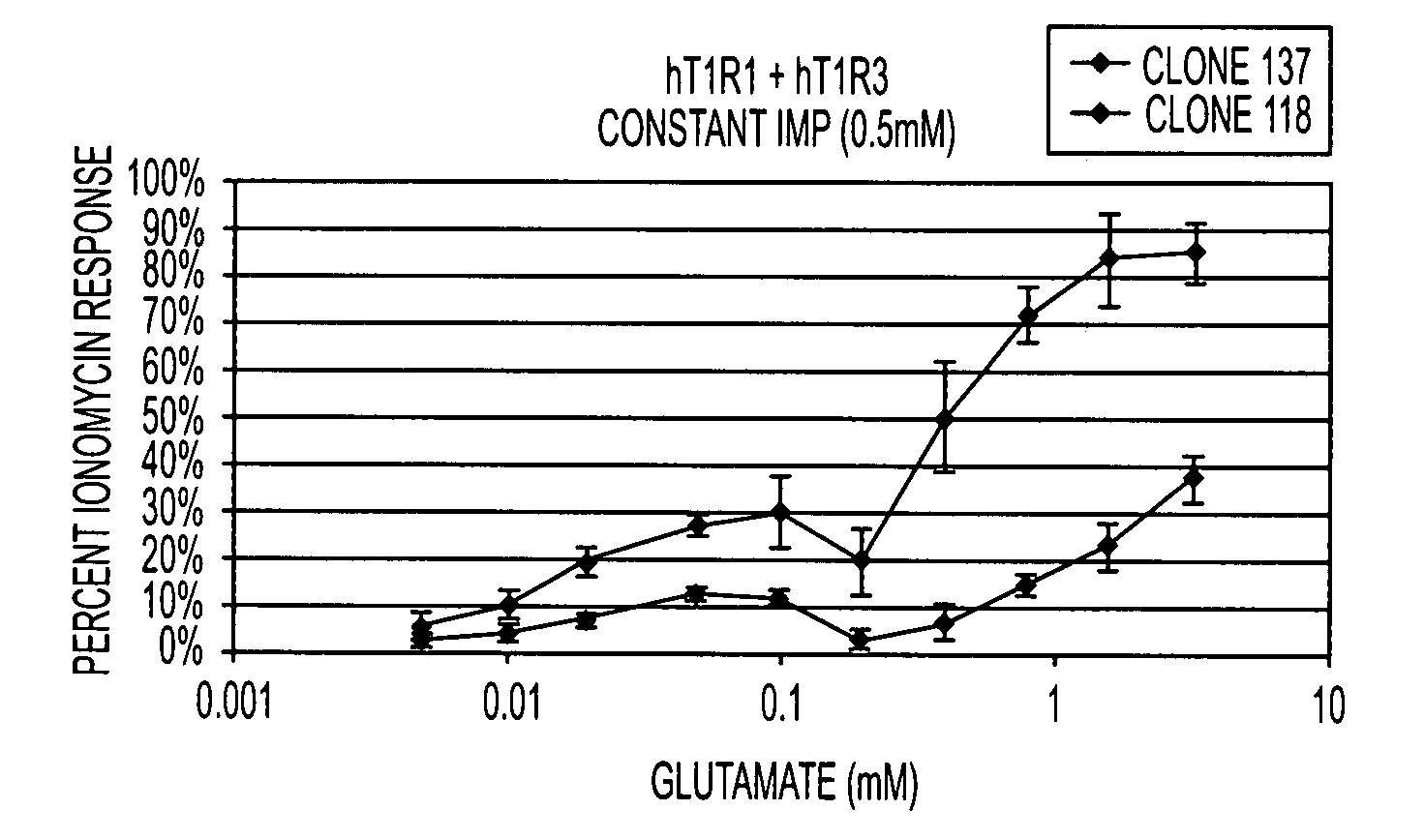
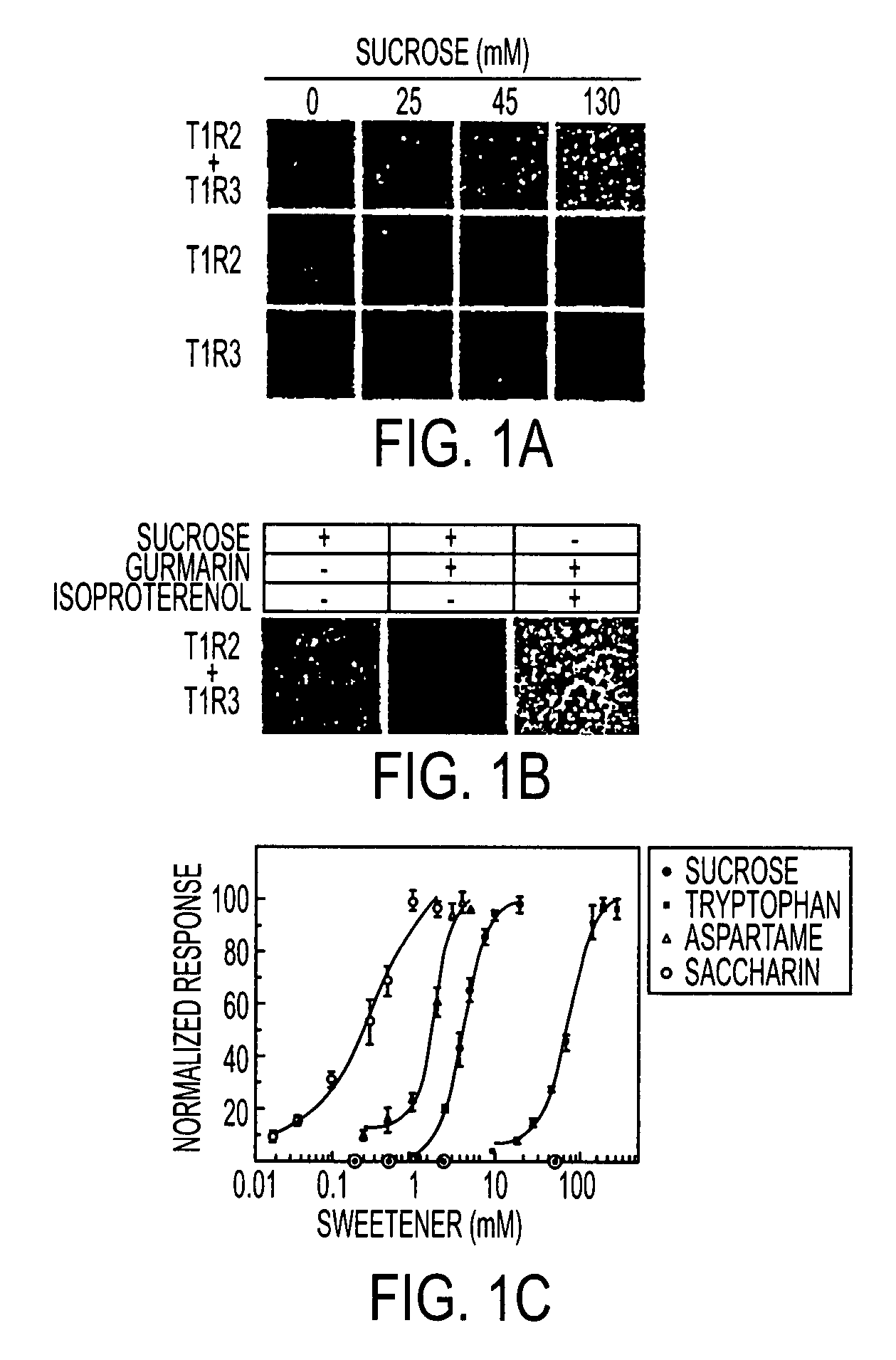
T1R hetero-oligomeric taste receptor
Newly identified mammalian taste-cell-specific G protein-coupled receptors which function as hetero-oligomeric complexes in the sweet taste transduction pathway, and the genes and cDNA encoding said receptors are described. Specifically, T1R G protein-coupled receptors active in sweet taste signaling as hetero-oligomeric complexes, and the genes and cDNA encoding the same, are described, along with methods for isolating such genes and for isolating and expressing such receptors. Methods for identifying putative taste modulating compounds using such hetero-oligomeric complexes also described, as is a novel surface expression facilitating peptide useful for targeting integral plasma membrane proteins to the surface of a cell.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Compositions and methods for treating multiple sclerosis
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for use in treating inflammatory neurodegenerative condition or disease or at least one symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ioinic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Compositions and methods for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient for treating an inflammatory neurodegenerative condition or disease (e.g., multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson's disease (PD), Alzheimer's disease (AD)) or at least one symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential and / or conductance, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Compositions and methods for treating multiple sclerosis
InactiveUS20100015235A1Sufficient amountPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCell membrane
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (gas-enriched electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity, and therapeutic compositions and methods for use in treating inflammatory neurodegenerative condition or disease or at least one symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membranes, membrane potential, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
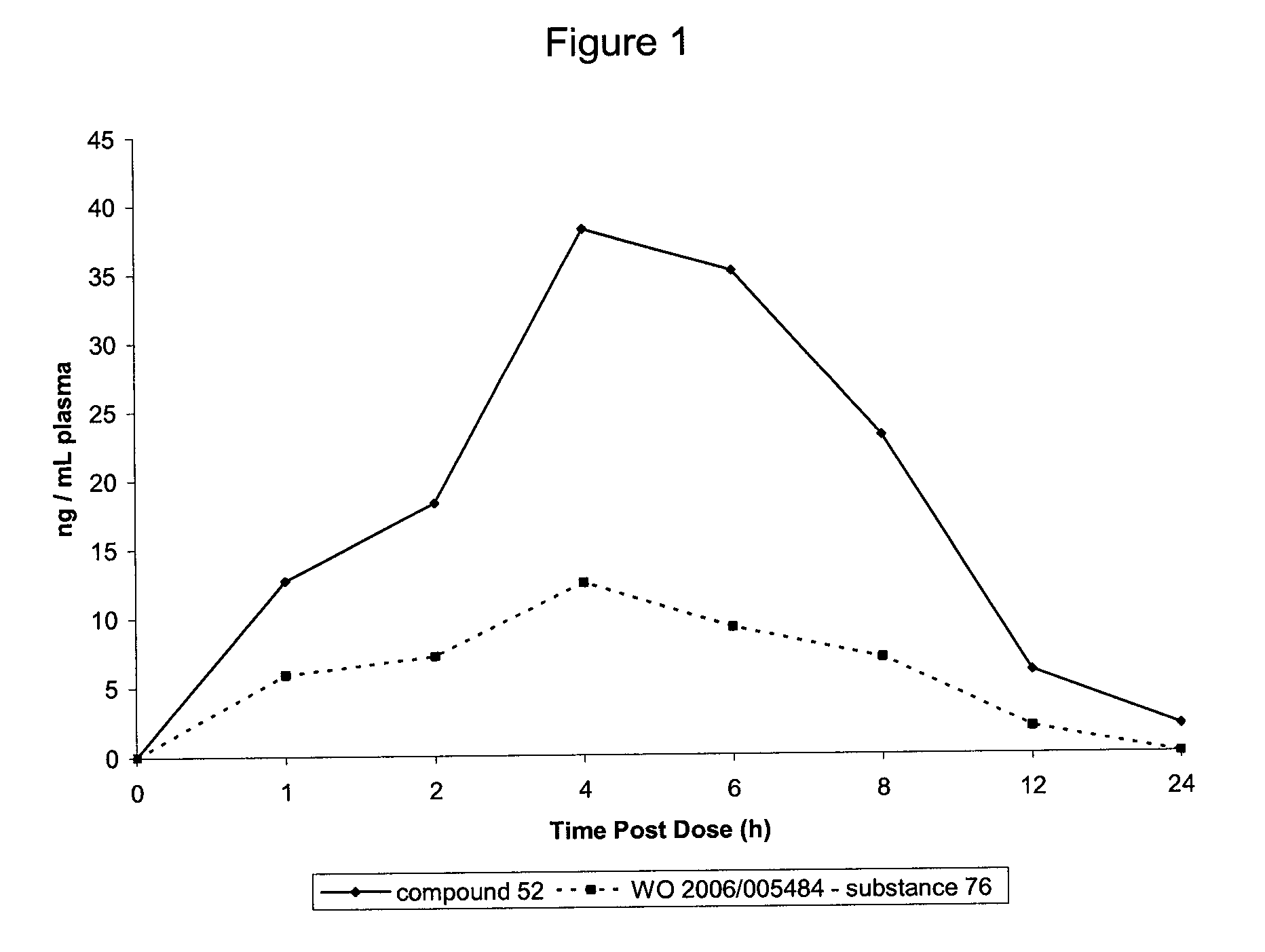
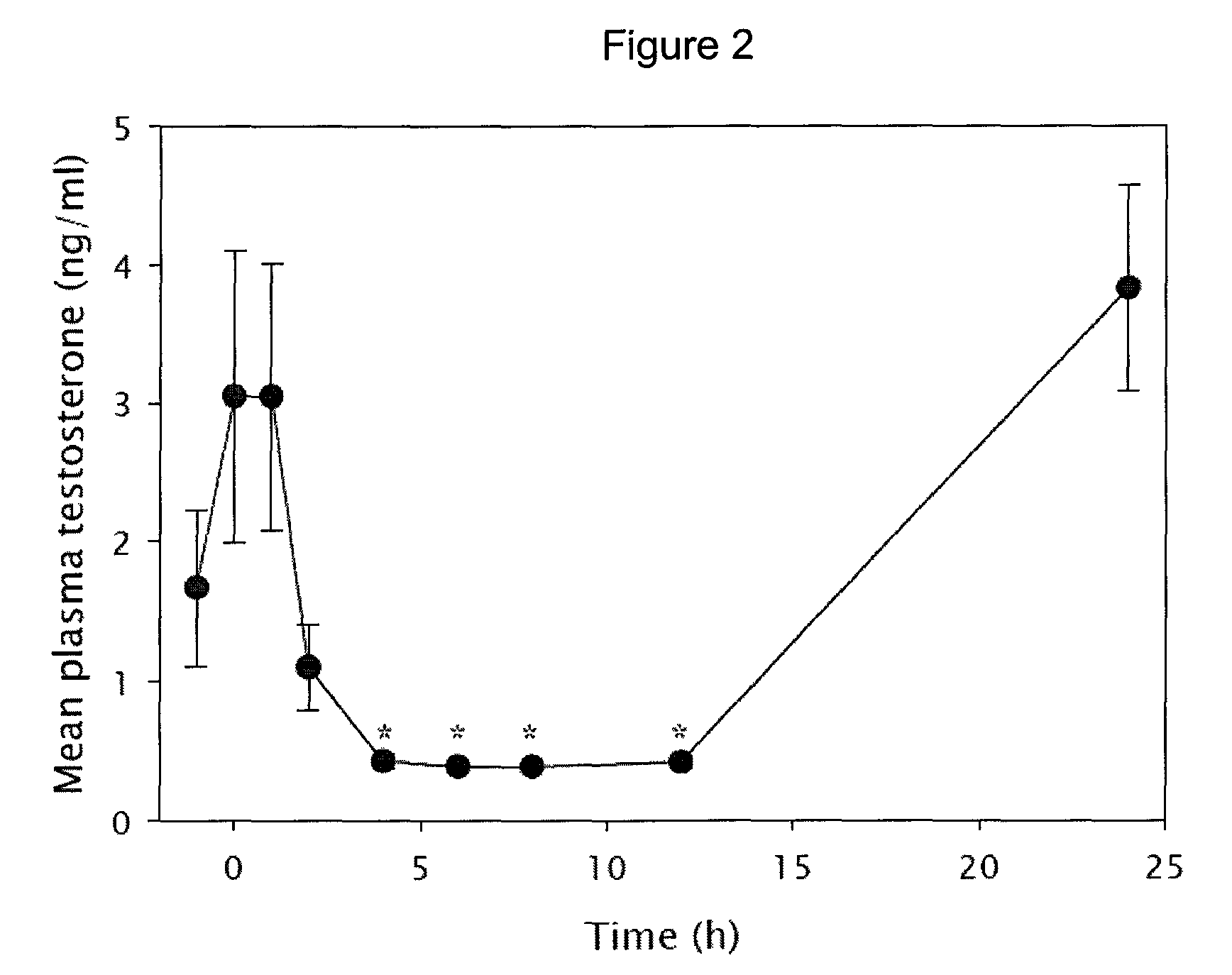
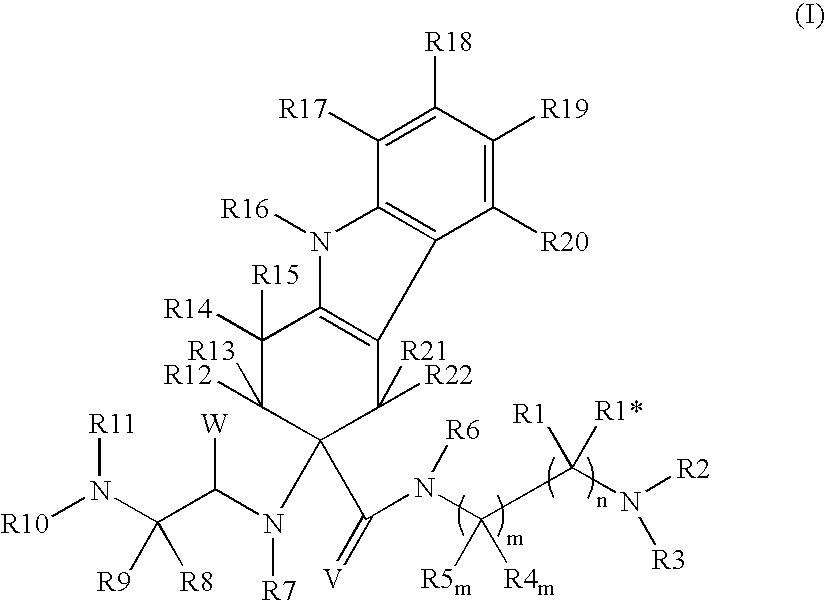
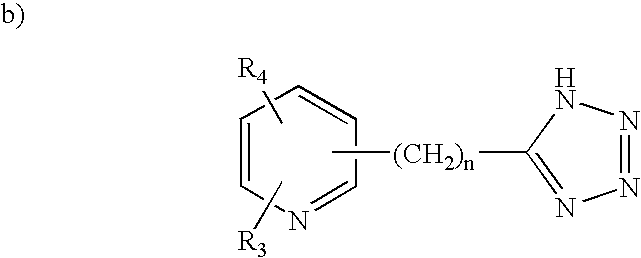
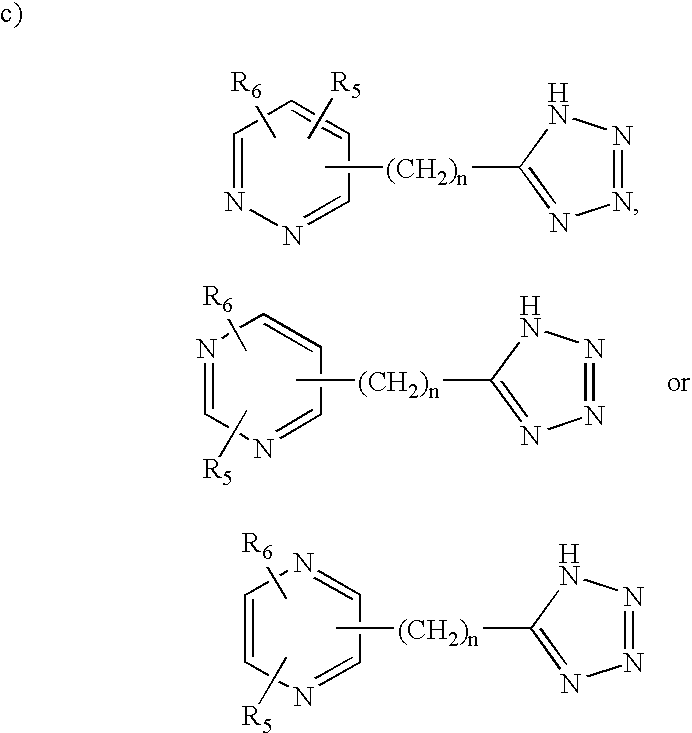
Tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives as ligands of G-protein coupled receptors
InactiveUS8148546B2Good metabolic stabilityImprove solubilityBiocideSenses disorderCarbazoleG protein-coupled receptor
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
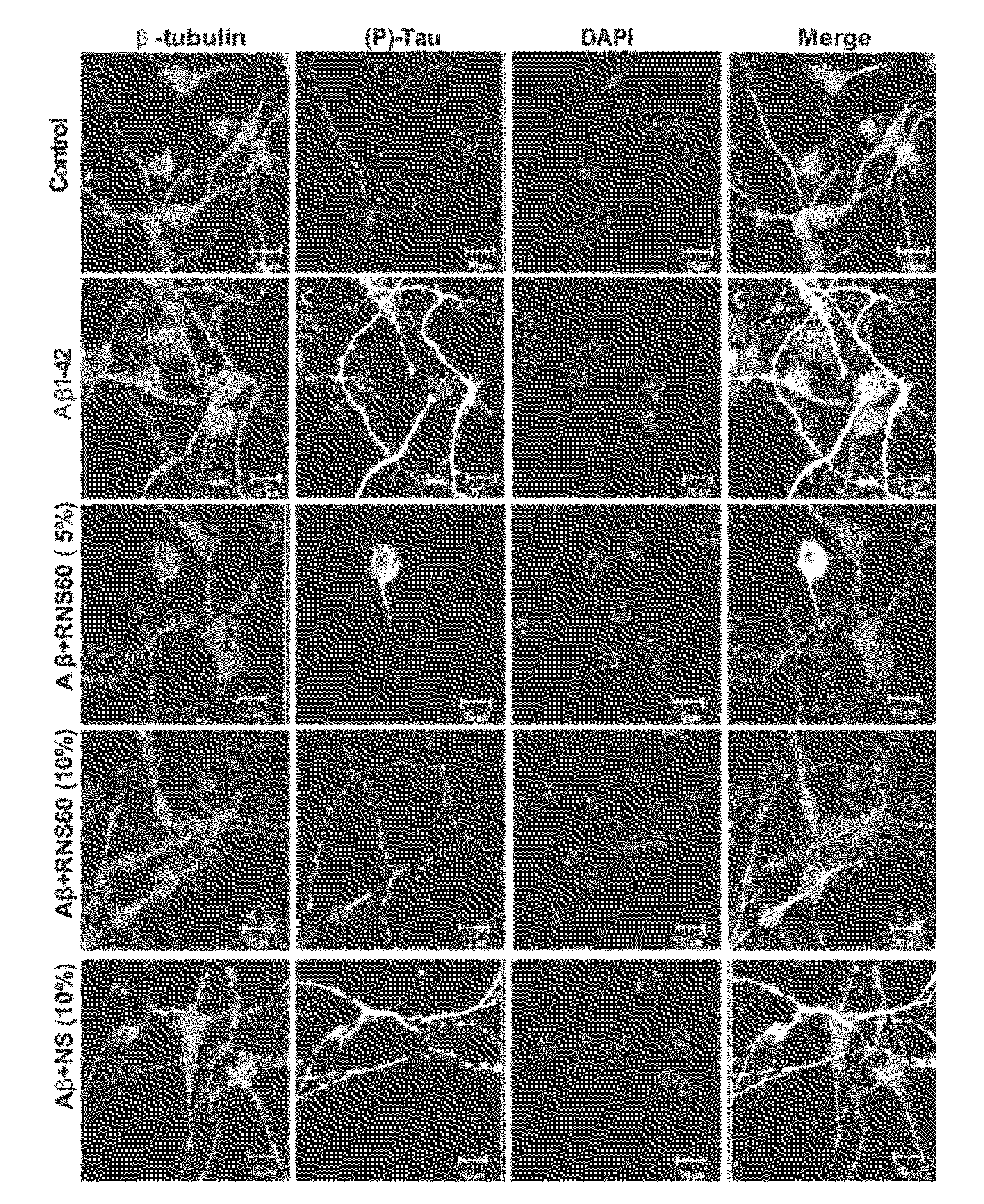
Compositions and methods for treatment of taupathy
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-altered gas-enriched fluids and solutions) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient for treating an inflammatory neurodegenerative condition or disease (e.g., a taupathy) or at least one symptom thereof. The electrokinetically-altered fluids or therapeutic compositions and methods include electrokinetically-altered ionic aqueous fluids optionally in combination with other therapeutic agents. Particular aspects provide for modulating phosphorylation of tau protein. Particular aspects provide for regulating or modulating intracellular signal transduction associated with said inflammatory responses by modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and / or conductance, membrane proteins such as membrane receptors, including but not limited to G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and intercellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes). Other embodiments include particular routes of administration or formulations for the electrokinetically-altered fluids and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Cyclic agonists and antagonists of C5a receptors and G protein-coupled receptors
InactiveUS20060160726A1Easy to assembleImprove inflammatory responseNervous disorderAntipyreticG protein-coupled receptorAgonist
Owner:PROMICS
Novel screening method
InactiveUS20050089866A1Improve the level ofSuppressed cAMP productionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFatty acidAmino acid
By using (1) a G protein-coupled receptor protein having the same or substantially the same amino acid sequence as the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or its salt and (2) a fatty acid or an eicosanoid, a compound or its salt that can change the binding properties of the receptor protein or its salt to the fatty acid or the eicosanoid can be screened efficiently.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Compositions and methods for modulating cellular membrane-mediated intracellular signal transduction
Provided are electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., gas-enriched (e.g., oxygen-enriched) electrokinetic fluids) comprising an ionic aqueous solution of charge-stabilized oxygen-containing nanostructures in an amount sufficient to provide, upon contact with a cell, modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity. Particular aspects of the present invention provide compositions and methods suitable for modulation of at least one of cellular membrane potential and cellular membrane conductivity. Additional aspects provide compositions and methods suitable for modulating intracellular signal transduction, including modulation of at least one of membrane structure, membrane potential or membrane conductivity, membrane proteins or receptors, ion channels, and calcium dependant cellular messaging systems, comprising use of the inventive electrokinetically altered solutions to impart electrochemical and / or conformational changes in membranous structures (e.g., membrane proteins, receptors and / or other components) including G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), G-proteins, and / or intracellular junctions (e.g., tight junctions, gap junctions, zona adherins and desmasomes).
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Human G protein-coupled receptors and modulators thereof for the treatment of metabolic-related disorders
InactiveUS6902902B2Lower Level RequirementsBiocideCompound screeningDyslipidemiaCoronary heart disease
The present invention relates to methods of identifying whether a candidate compound is a modulator of a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). In preferred embodiments, the GPCR is human. In other preferred embodiments, the GPCR is coupled to Gi and lowers the level of intracellular cAMP. In other preferred embodiments, the GPCR is expressed endogenously by adipocytes. In further preferred embodiments, the GPCR inhibits intracellular lipolysis. In other further preferred embodiments, the GPCR is a nicotinic acid receptor. The present invention also relates to methods of using a modulator of said GPCR. Preferred modulator is agonist. Agonists of the invention are useful as therapeutic agents for the prevention or treatment of metabolic-related disorders, including dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, stroke, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
T1R Taste Receptors and Genes Encoding Same
Newly identified mammalian taste-cell-specific G protein-coupled receptors, and the genes and cDNA encoding said receptors are described. Specifically, T1R G protein-coupled receptors active in taste signaling, and the genes and cDNA encoding the same, are described, along with methods for isolating such genes and for isolating and expressing such receptors. Methods for representing taste perception of a particular taste stimulus in a mammal are also described, as are methods for generating novel molecules or combinations of molecules that elicit a predetermined taste perception in a mammal, and methods for simulating one or more tastes. Further, methods for stimulating or blocking taste perception in a mammal are also disclosed.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Heterocyclic analgesic compounds and methods of use thereof
One aspect of the present invention relates to novel heterocyclic compounds. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of the novel heterocyclic compounds as ligands for various cellular receptors, including opiate receptors, other G-protein-coupled receptors, and ion channels. An additional aspect of the present invention relates to the use of the novel heterocyclic compounds as analgesics.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Subunit vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus infection
The present invention relates generally to methods of treating or preventing RSV infections, and more specifically, to compositions, and the use thereof, comprising one or more RSV G protein immunogen or fragment thereof capable of eliciting protective immunity without eliciting an immunopathological response or eliciting a reduced immunopathological response.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL CORP LAVAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com