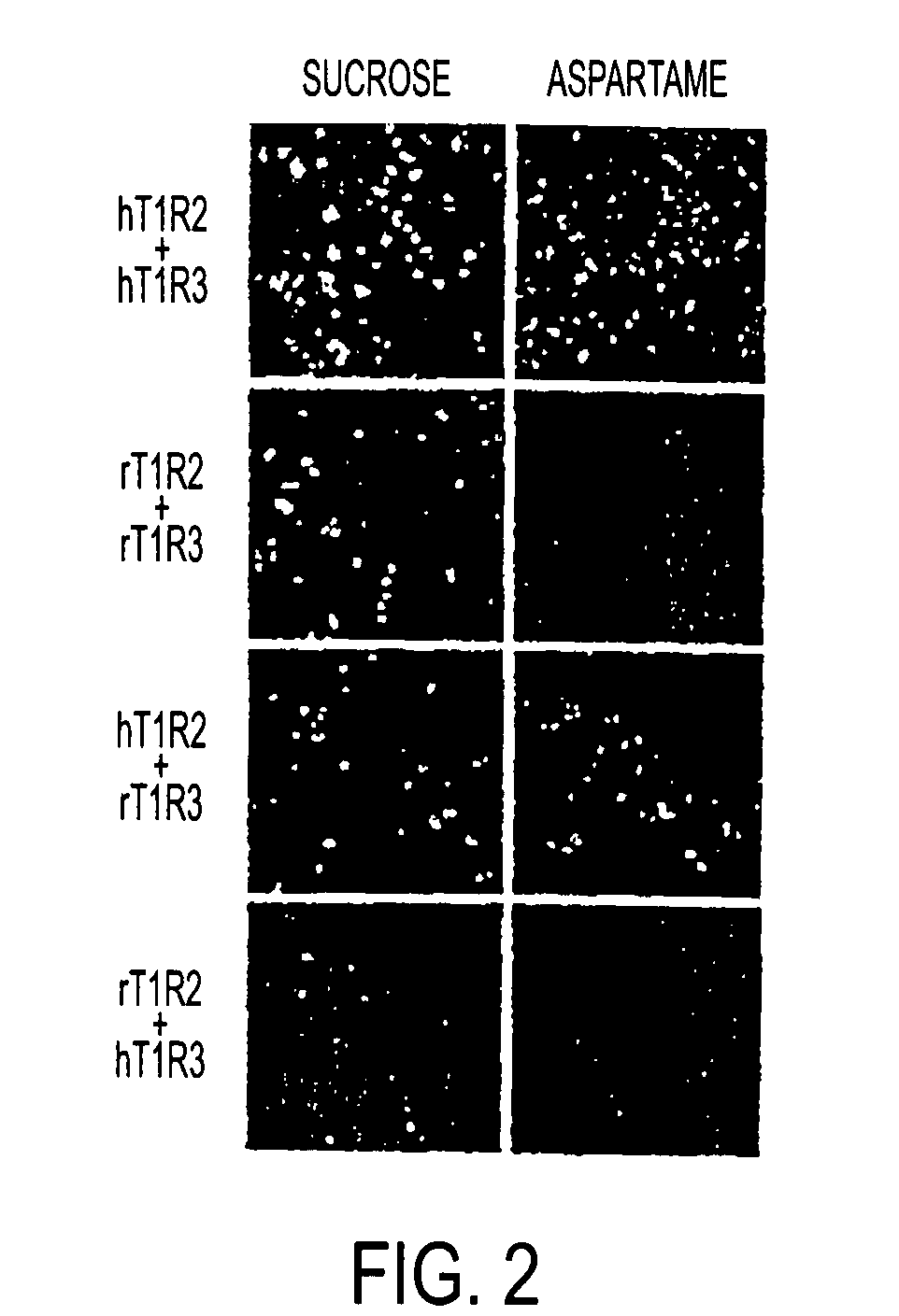
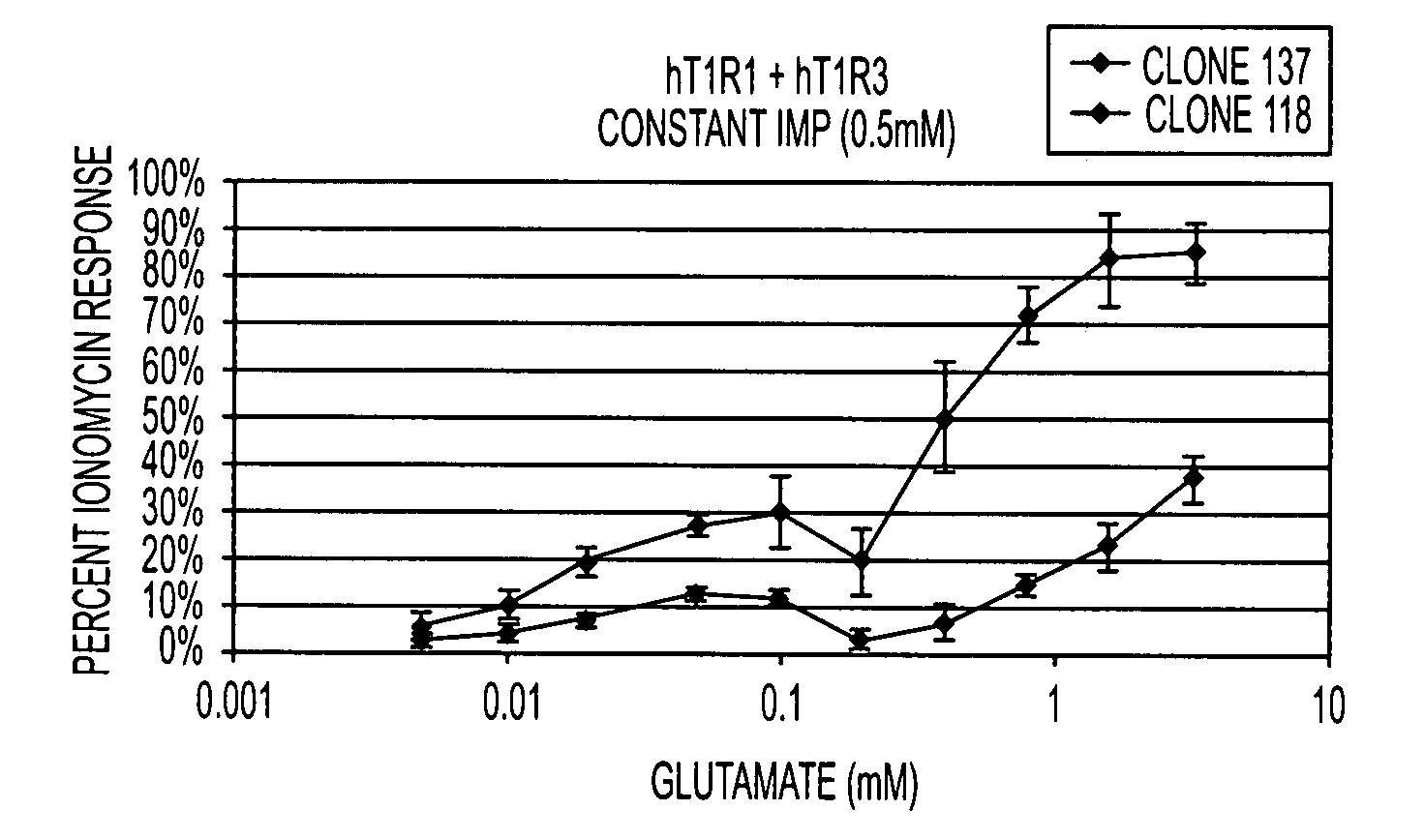
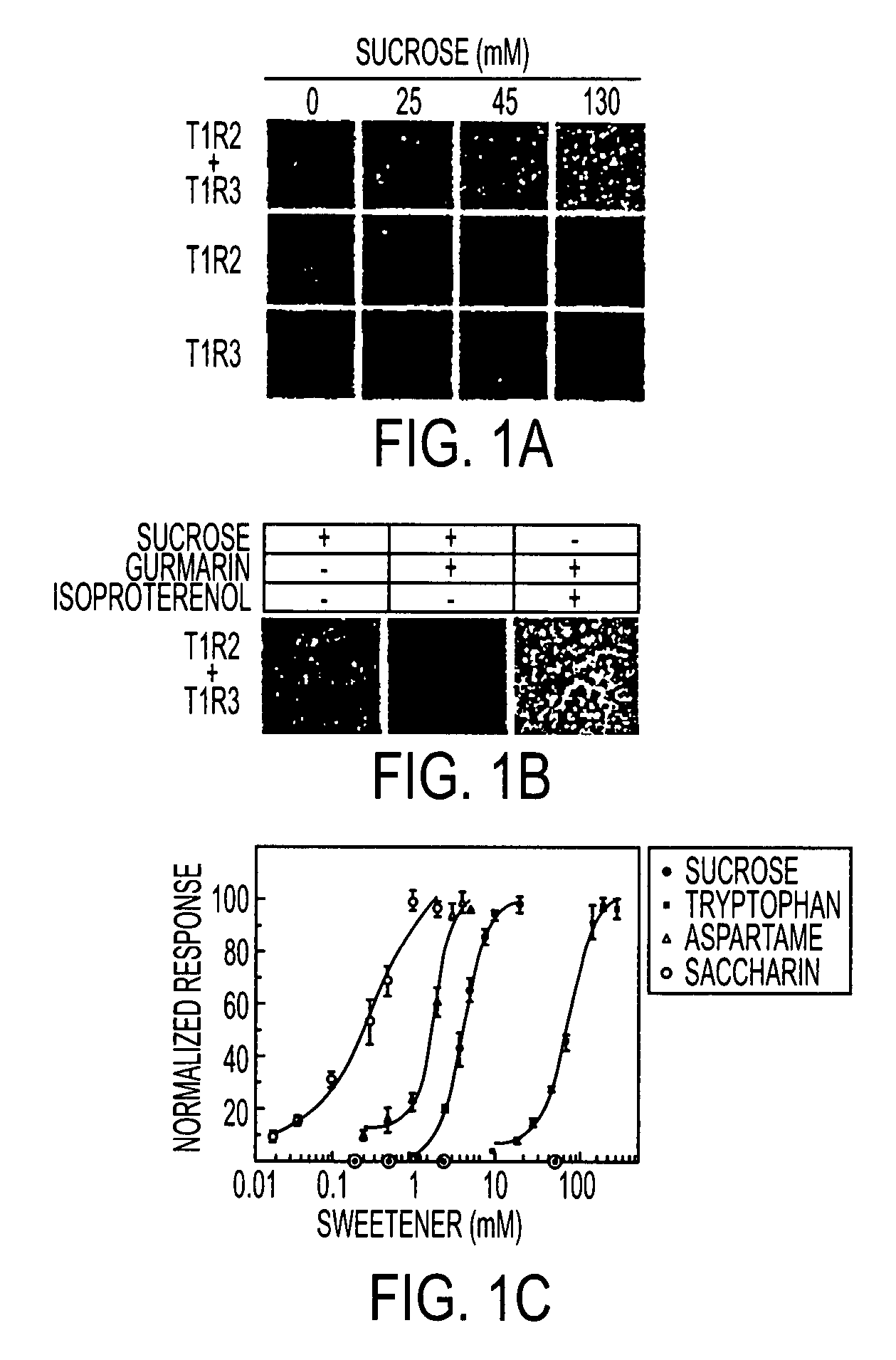
T1R Taste Receptors and Genes Encoding Same
a technology of t1r taste receptor and genes, applied in the field of newly identified mammalian chemosensory g proteincoupled receptors, can solve the problem of lack of information about ligand-receptor recognition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
hT1R3
[0247] The hT1R3 genomic DNA is provided below as SEQ ID NO 1 and SEQ ID NO 2 with predicted coding sequences (cds) shown in boldface. The break between the 5′ and 3′ contigs is shown as elipses (‘ . . . ’). The hT1R3 predicted cds are described in SEQ ID NO 3. Finally, a preferred, predicted hT1R3 amino acid sequence is provided as SEQ ID NO 4, using the one-letter code for the amino acids.
hT1R3 genomic DNA - 5′ contig (SEQ ID NO: 1)(SEQ ID NO: 1)AGCCTGGCAGTGGCCTCAGGCAGAGTCTGACGCGCACAAACTTTCAGGCCCAGGAAGCGAGGACACCACTGGGGCCCCAGGGTGTGGCAAGTGAGGATGGCAAGGGTTTTGCTAAACAAATCCTCTGCCCGCTCCCCGCCCCGGGCTCACTCCATGTGAGGCCCCAGTCGGGGCAGCCACCTGCCGTGCCTGTTGGAAGTTGCCTCTGCCATGCTGGGCCCTGCTGTCCTGGGCCTCAGCCTCTGGGCTCGGTACAGAGGTGGGACGGCCTGGGTCGGGGTCAGGGTGACCAGGTCTGGGGTGCTCCTGAGCTGGGGCCGAGGTGGCCATCTGCGGTTCTGTGTGGCCCCAGGTTCTCCTCAAACGGCCTGCTCTGGGCACTGGCCATGAAAATGGCCGTCAGTGGGGCGCCCCCCACCATCACCCACCCCCAACCAACCCCTGCCCCGTGGGAGCCCCTTGTGTCAGGAGAATGChT1R3 genomic DNA - 3′ contig (SEQ ID NO 2)(SEQ ID NO 2). . ....
example 2
rT1R3 and mT1R3
[0248] Segments of the rat and mouse T1R3 genes were isolated by PCR amplification from genomic DNA using degenerate primers based on the human T1R3 sequence. The degenerate primers SAP077 (5′-CGNTTYYTNGCNTGGGGNGARCC-3′; SEQ ID NO 5) and SAP079 (5′-CGNGCNCGRTTRTARCANCCNGG-3′; SEQ ID NO 6) are complementary to human T1R3 residues RFLAWGEPA (corresponding to SEQ ID NO 7) and PGCYNRAR (corresponding to SEQ ID NO 8), respectively. The PCR products were cloned and sequenced. Plasmid SAV115 carries a cloned segment of the mouse T1R3 gene, and SAV118 carries a segment of the rat gene. These sequences, shown below, clearly represent the rodent counterparts of human T1R3, since the mouse segment is 74% identical to the corresponding segment of human T1R3, and the rat segment is 80% identical to the corresponding segment of human T1R3. The mouse and rat segments are 88% identical. No other database sequences are more than 40% identical to these T1R3 segments.
SAV115 mouse T1R...
example 3
Cloning of rT1R3
[0249] The mT1R3 and rT1R3 fragments identified above as SEQ ID NOs 9 and 11 were used to screen a rat taste tissue-derived cDNA library. One positive clone was sequenced and found to contain the full-length rT1R3 sequence presented below as SEQ ID NO 13. Sequence comparison to the mT1R3 and rT1R3 partial sequences and to the full-length hT1R3 sequence established that this cDNA represents the rat counterpart to hT1R3. For example, the pairwise amino acid identity between rT1R3 and hT1R3 is approximately 72%, whereas the most related annotated sequence in public DNA sequence data banks is only approximately 33% identical to rT1R3.
rT1R3 predicted cds (SEQ. ID NO. 13)(SEQ ID NO 13)ATGCCGGGTTTGGCTATCTTGGGCCTCAGTCTGGCTGCTTTCCTGGAGCTTGGGATGGGGTCCTCTTTGTGTCTGTCACAGCAATTCAAGGCACAAGGGGACTATATATTGGGTGGACTATTCCCCTGGGCACAACTGAGGAGGCCACTCTCAACCAGAGAACACAGCCCAACGGCATCCTATGTACCAGGTTCTCGCCCCTTGGTTTGTTCCTGGCCATGGCTATGAAGATGGCTGTAGAGGAGATCAACAATGGATCTGCCTTGCTCCCTGGGCTGCGACTGGGCTAT...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com