Patents
Literature
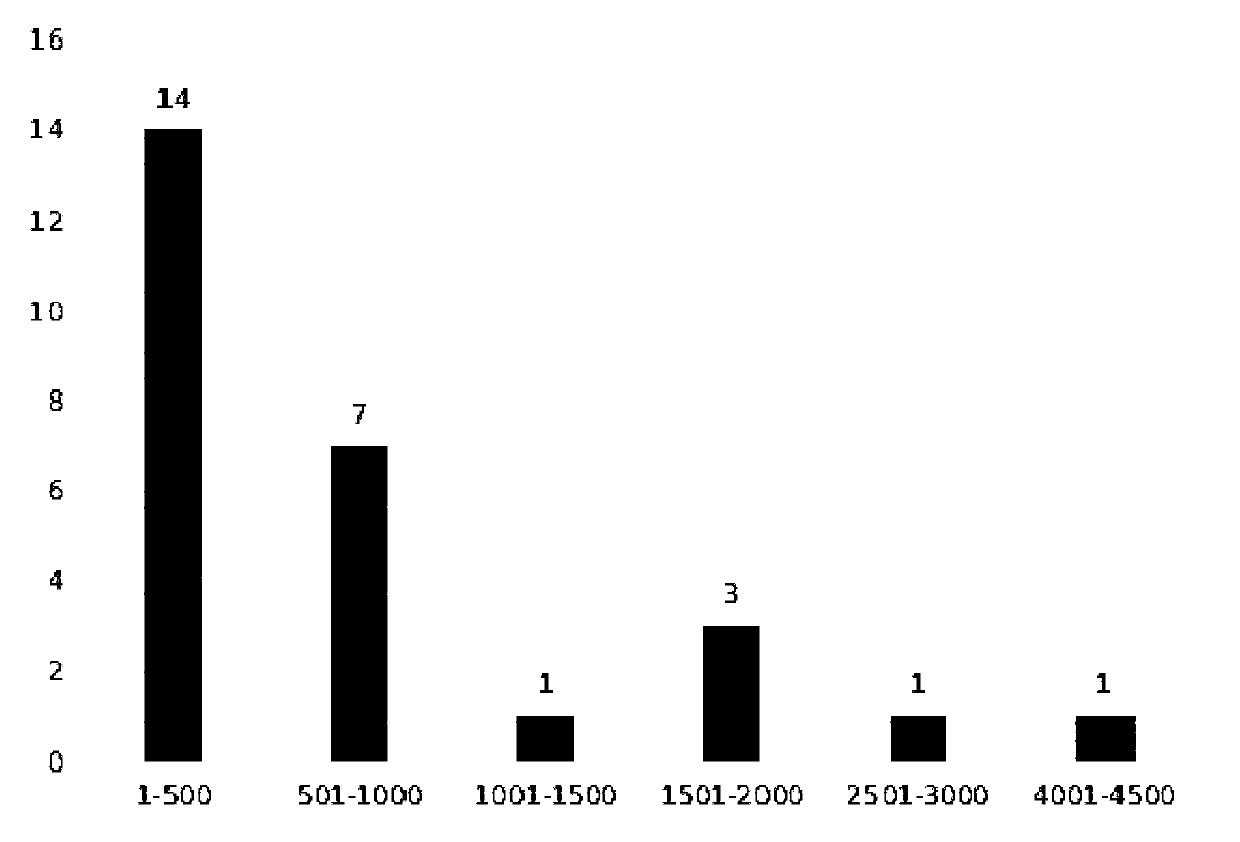
145 results about "Contig" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
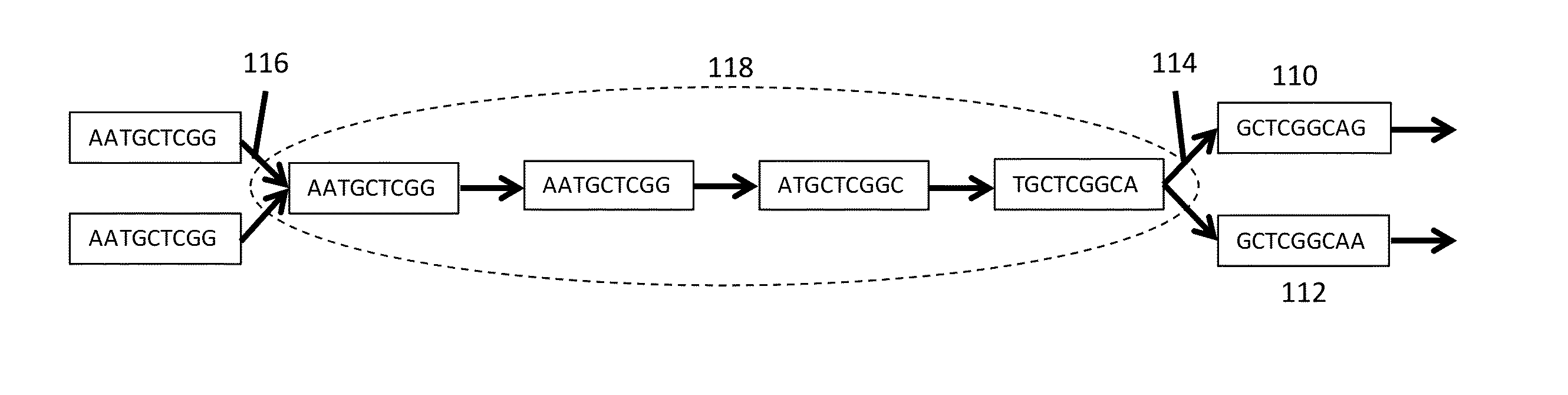
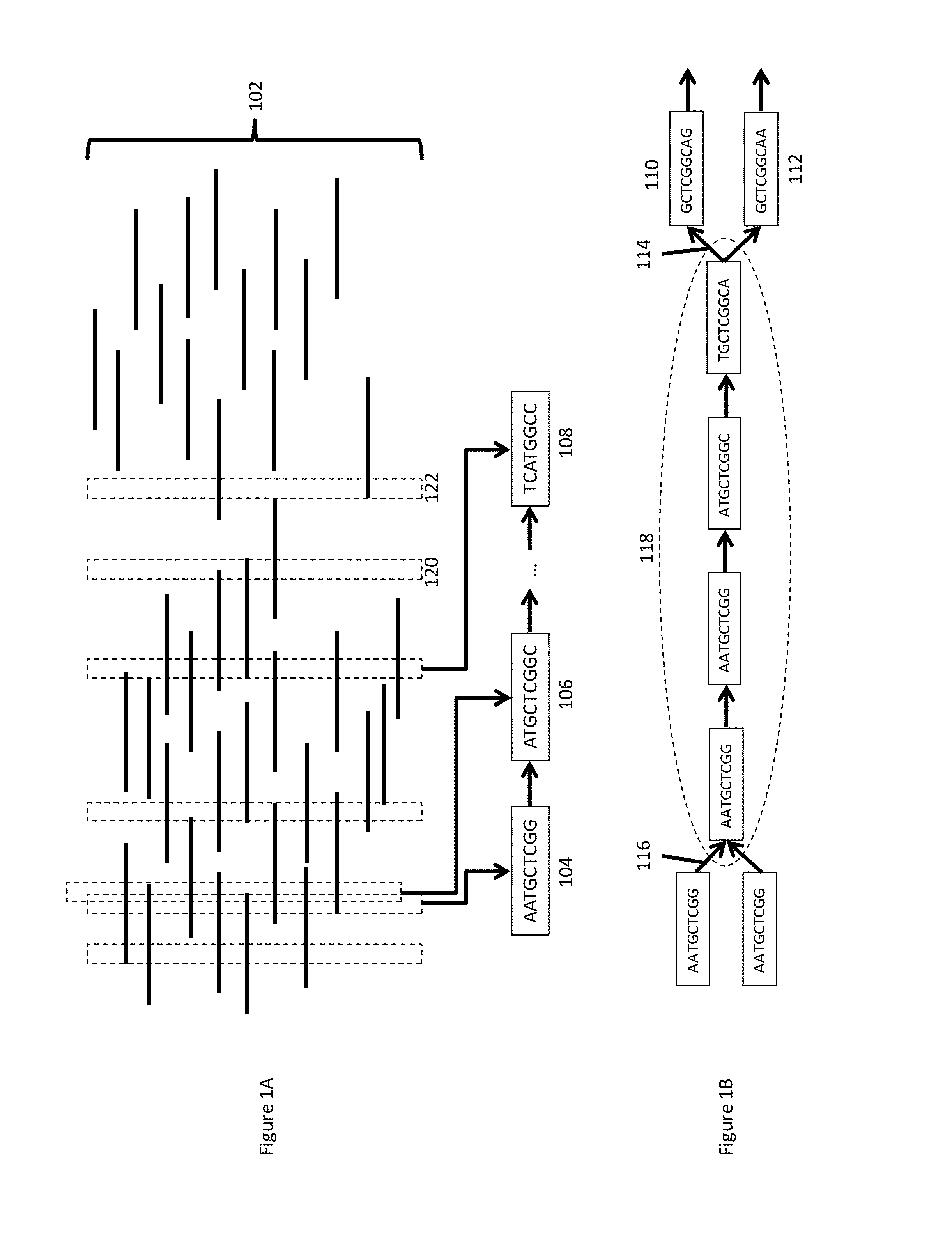
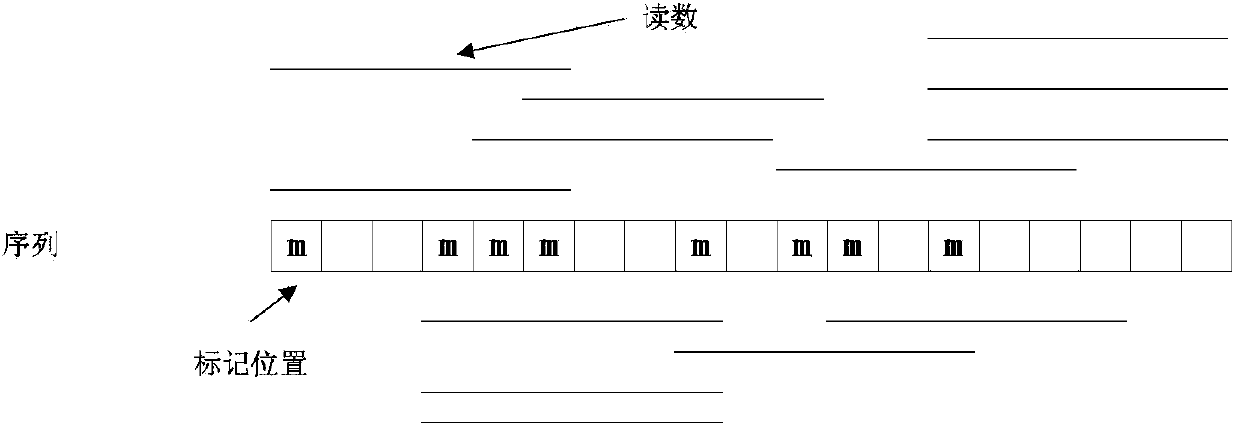
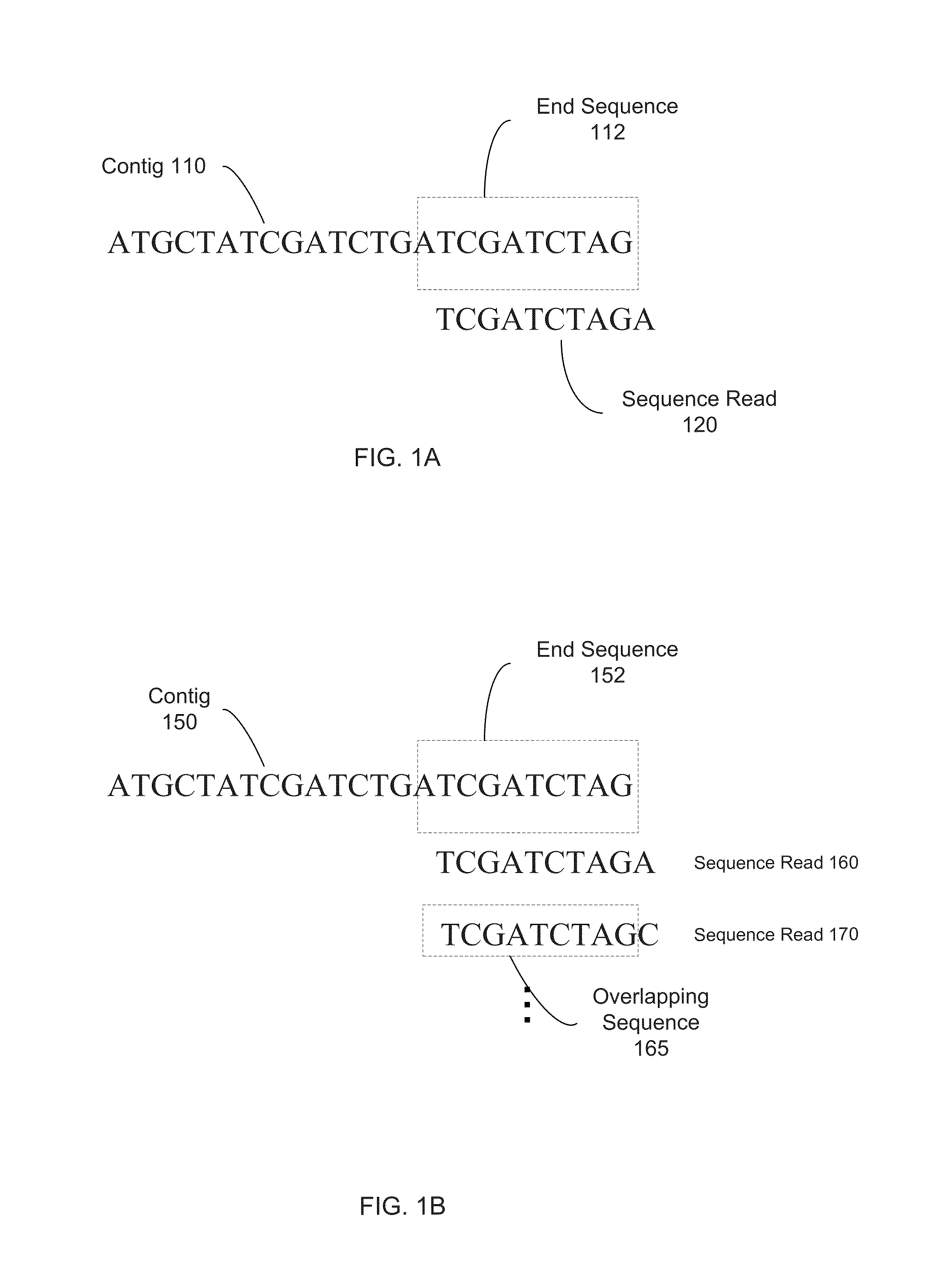
A contig (from contiguous) is a set of overlapping DNA segments that together represent a consensus region of DNA. In bottom-up sequencing projects, a contig refers to overlapping sequence data (reads); in top-down sequencing projects, contig refers to the overlapping clones that form a physical map of the genome that is used to guide sequencing and assembly. Contigs can thus refer both to overlapping DNA sequence and to overlapping physical segments (fragments) contained in clones depending on the context.
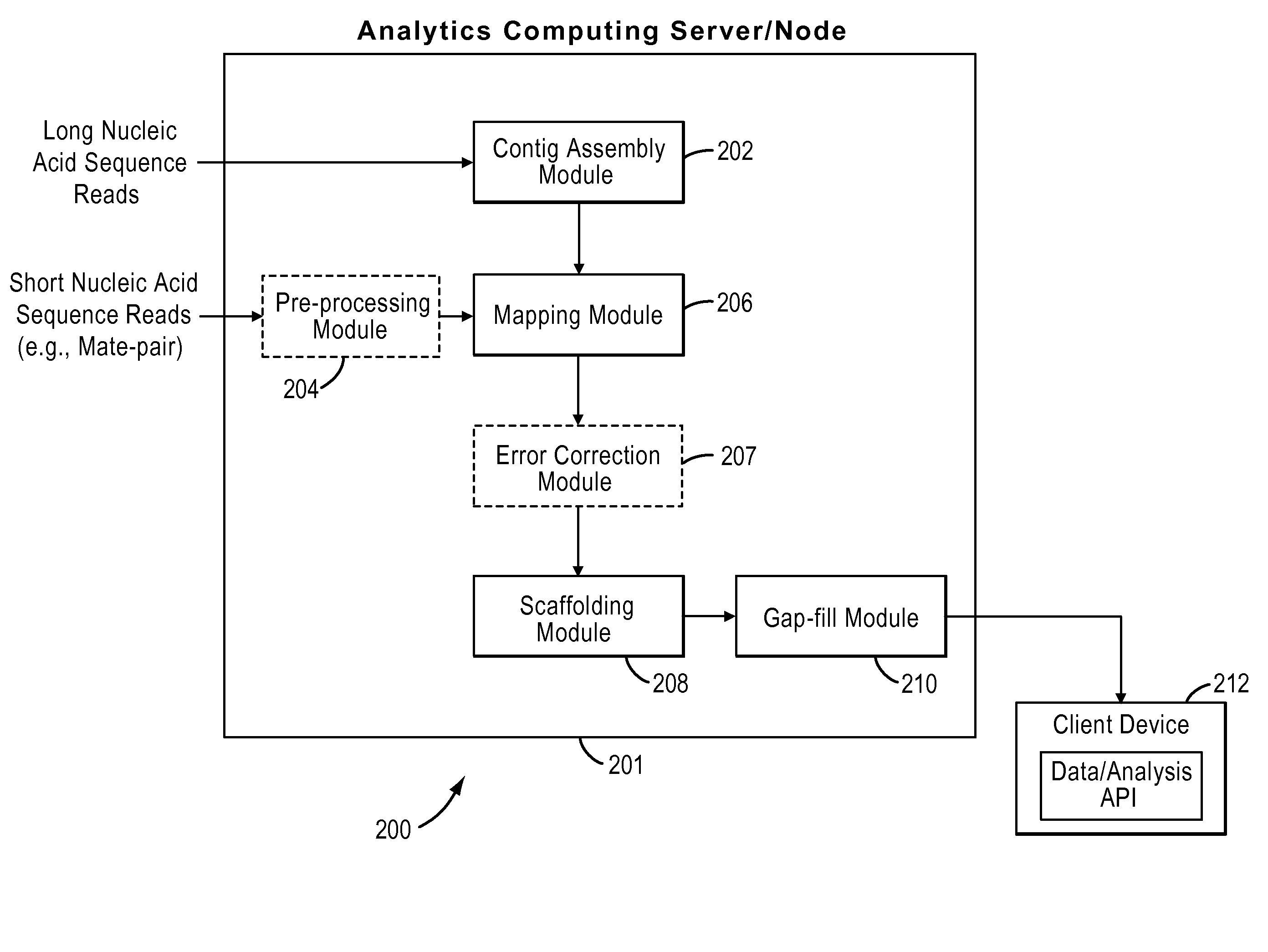
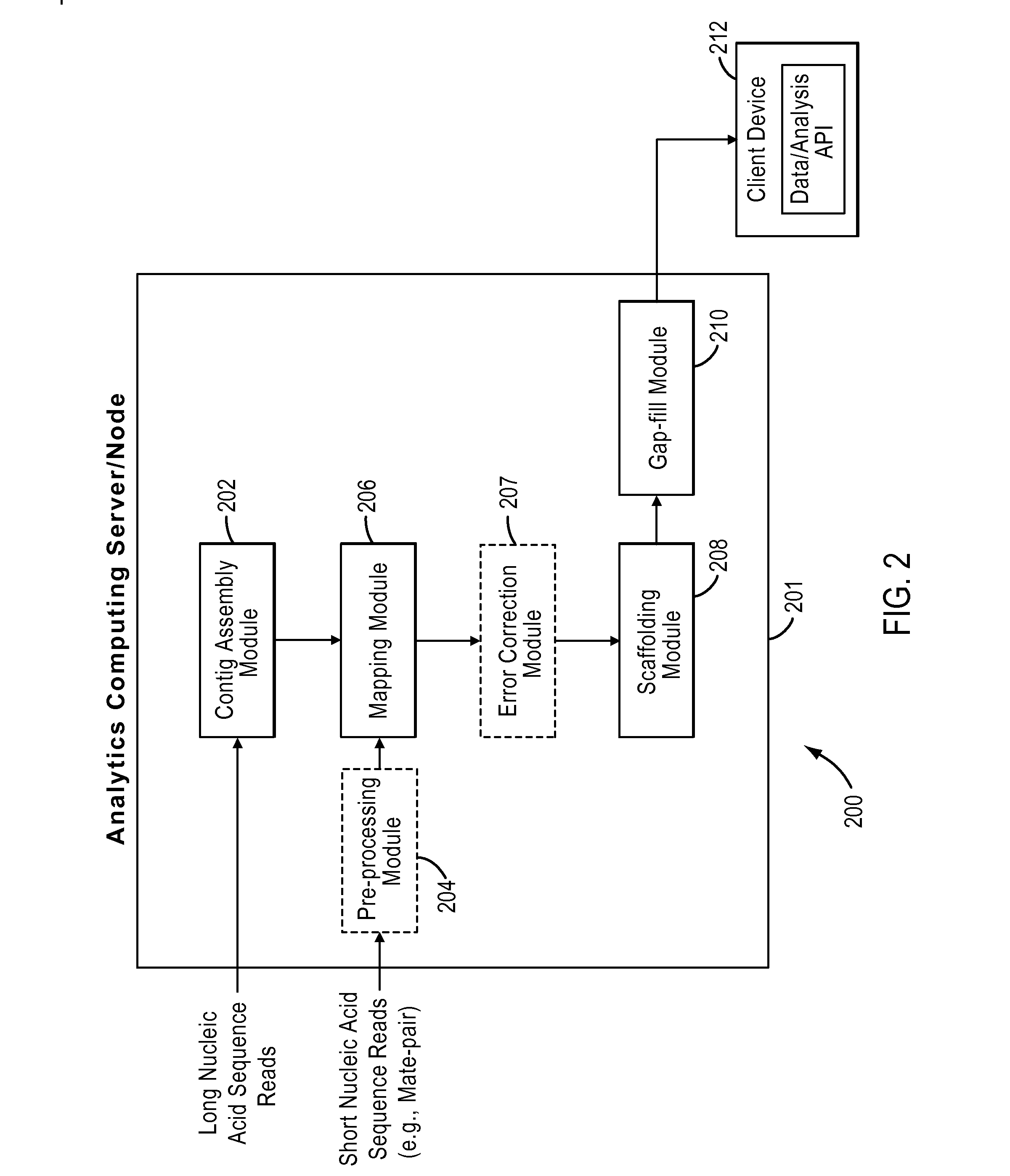
Processes and systems for nucleic acid sequence assembly
Methods, processes, and particularly computer implemented processes and computer program products are provided for use in the analysis of genetic sequence data. The processes and products are employed in the assembly of shorter nucleic acid sequence data into longer linked and preferably contiguous genetic constructs, including large contigs, chromosomes and whole genomes.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Virtual reads for readlength enhancement
InactiveUS20090118129A1Easy to assembleReduce the amount requiredSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementContigGeolocation
Methods arrays and systems that facilitate contig assembly during nucleic acid sequencing are provided. Geographical locations of analyte molecules on an array are correlated with subsequence relationships within larger nucleic acids.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
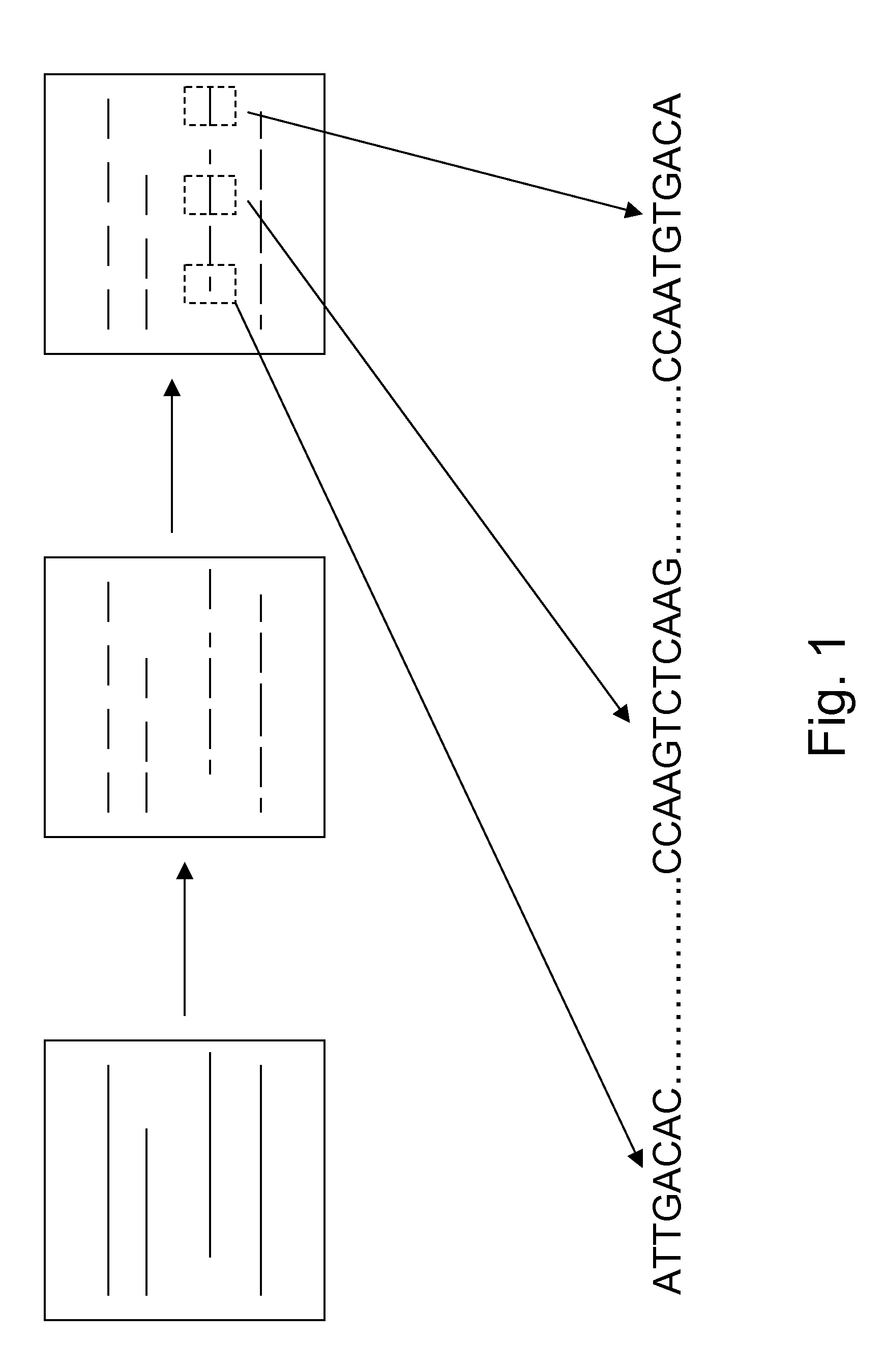
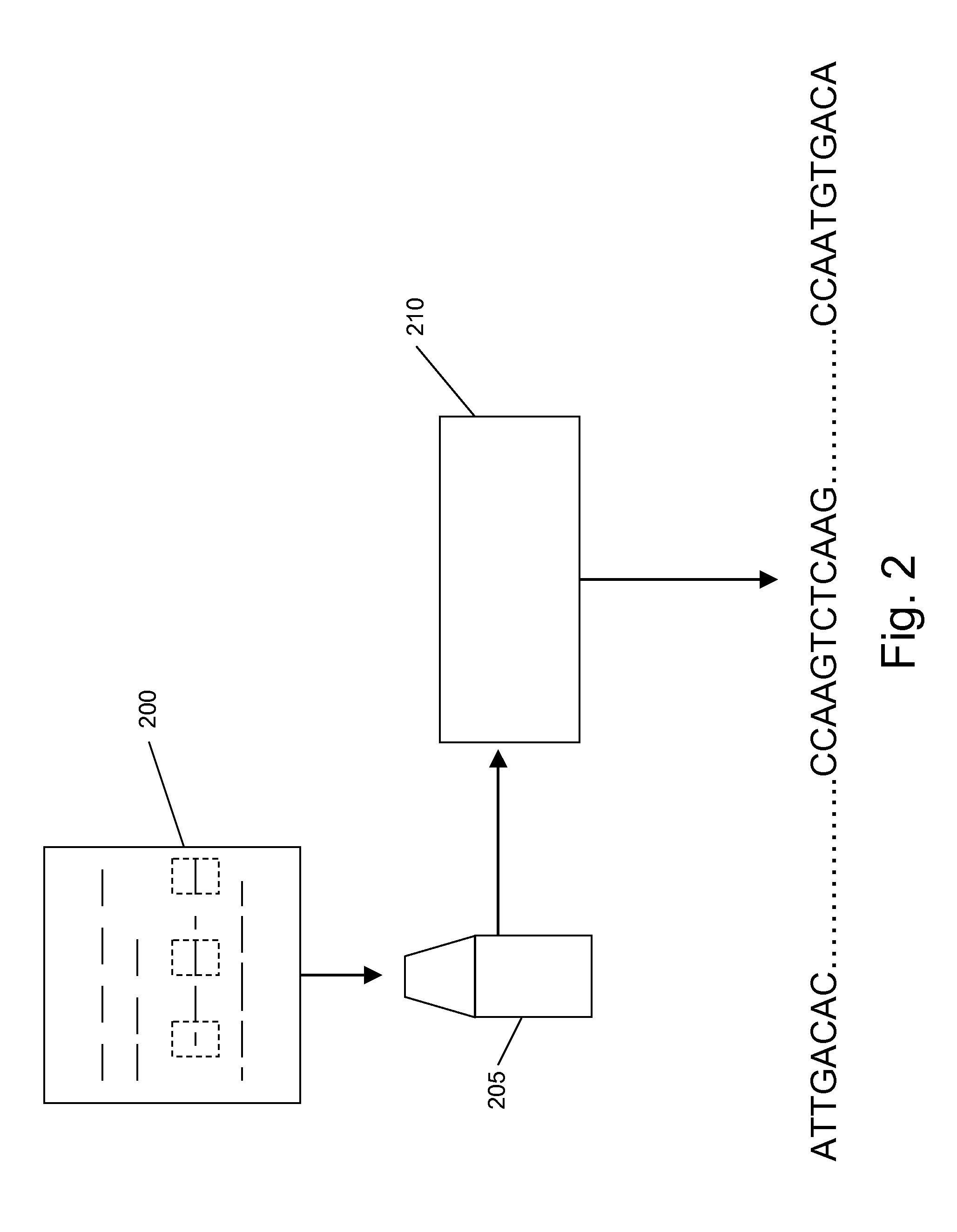
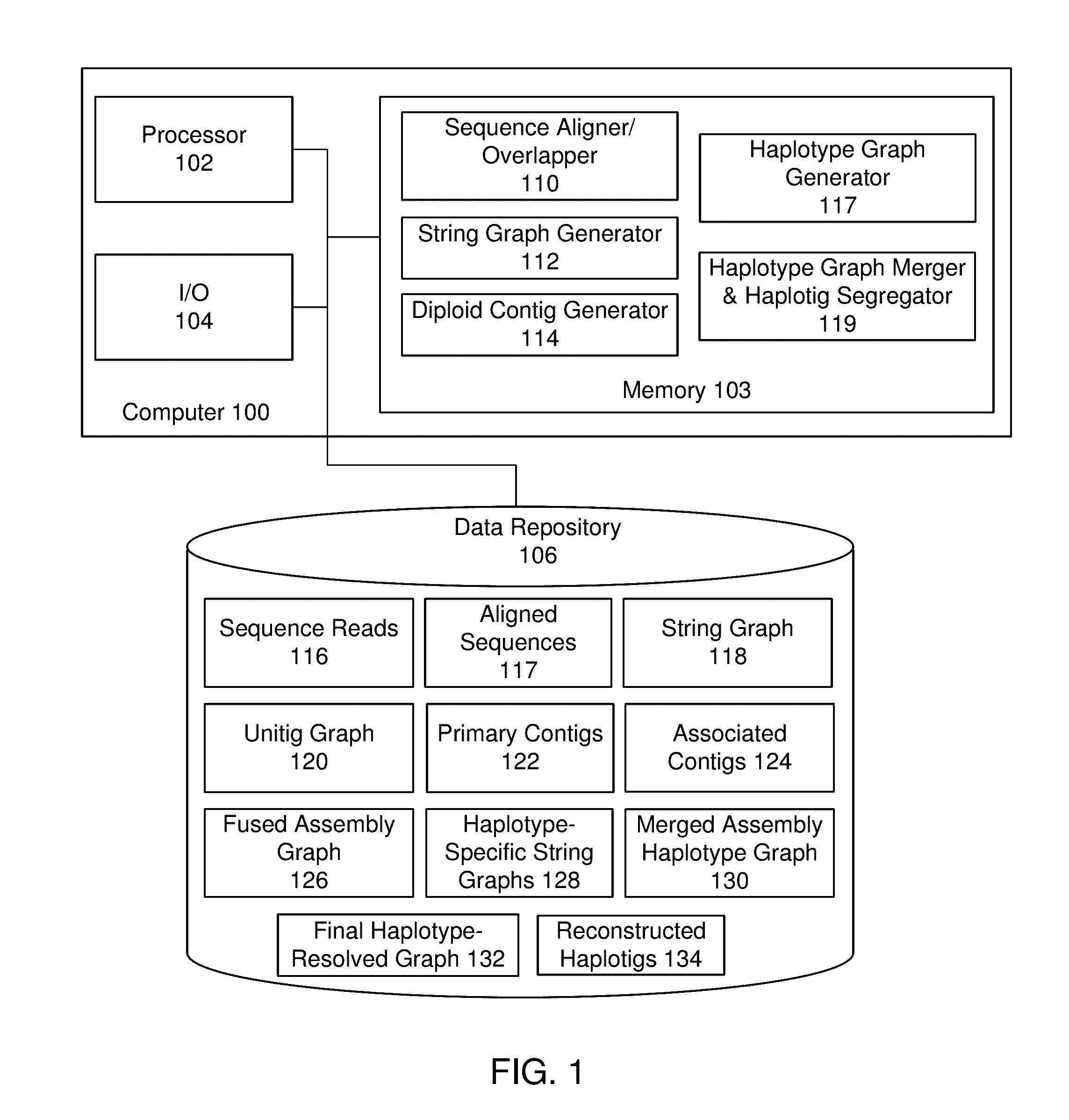
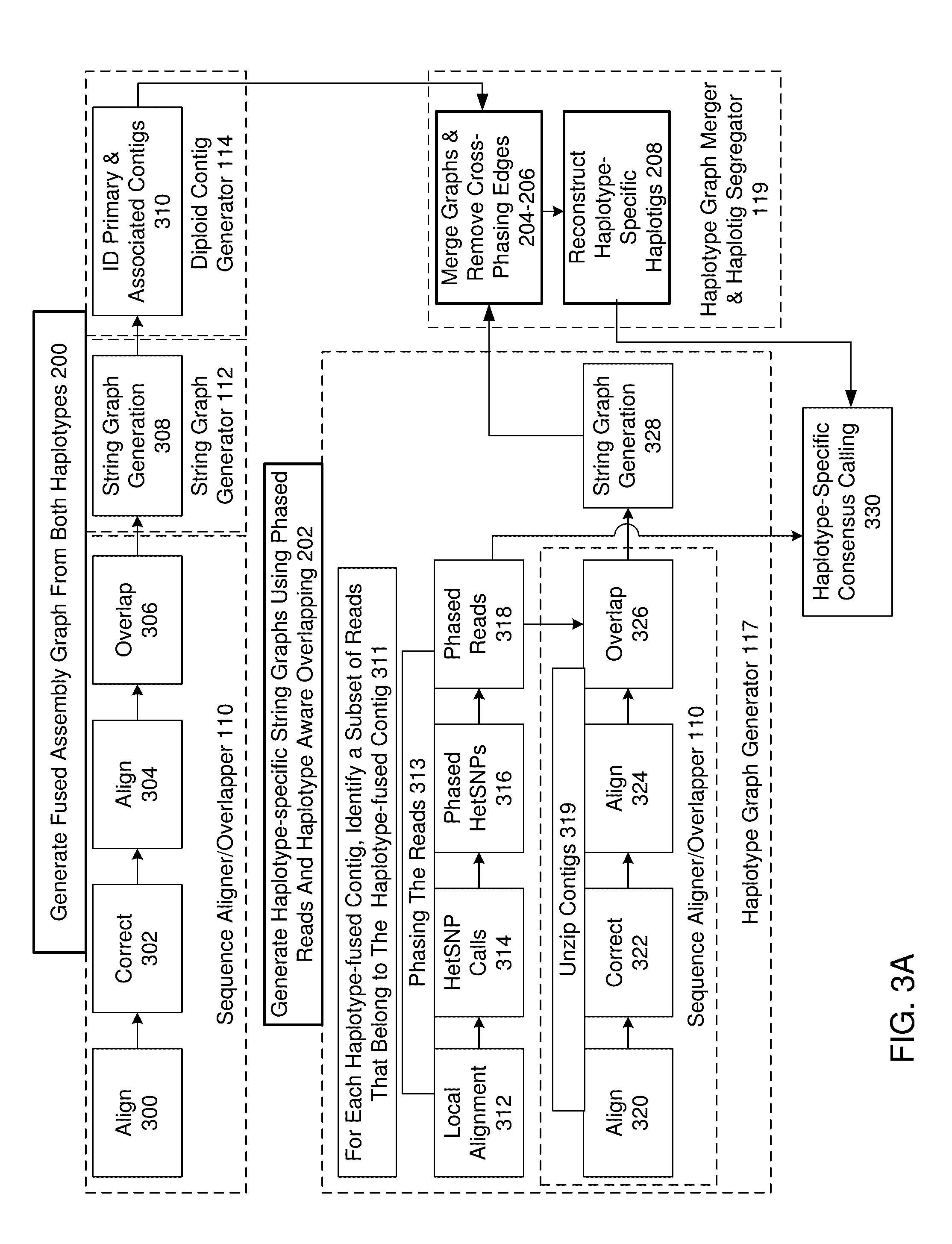
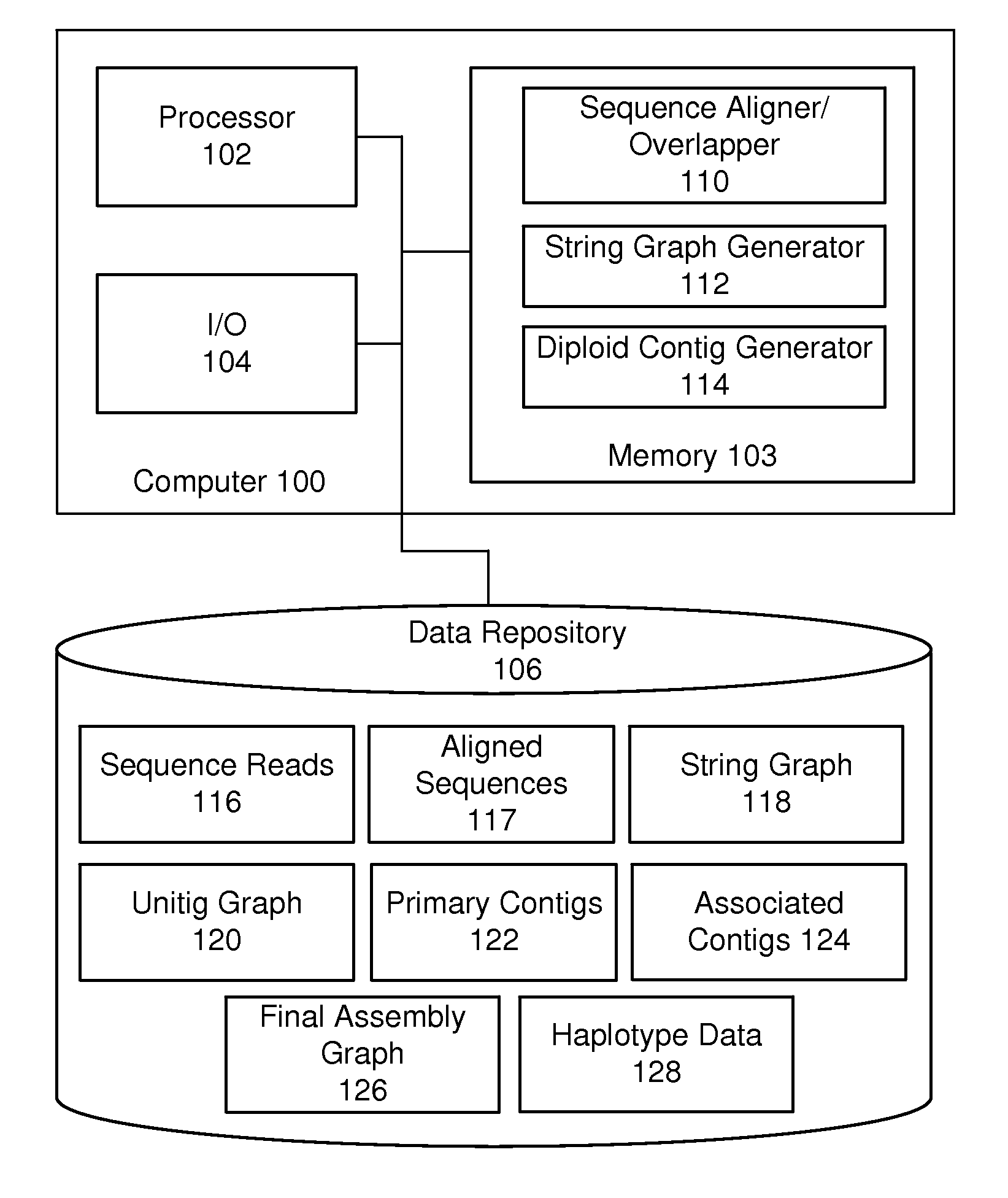
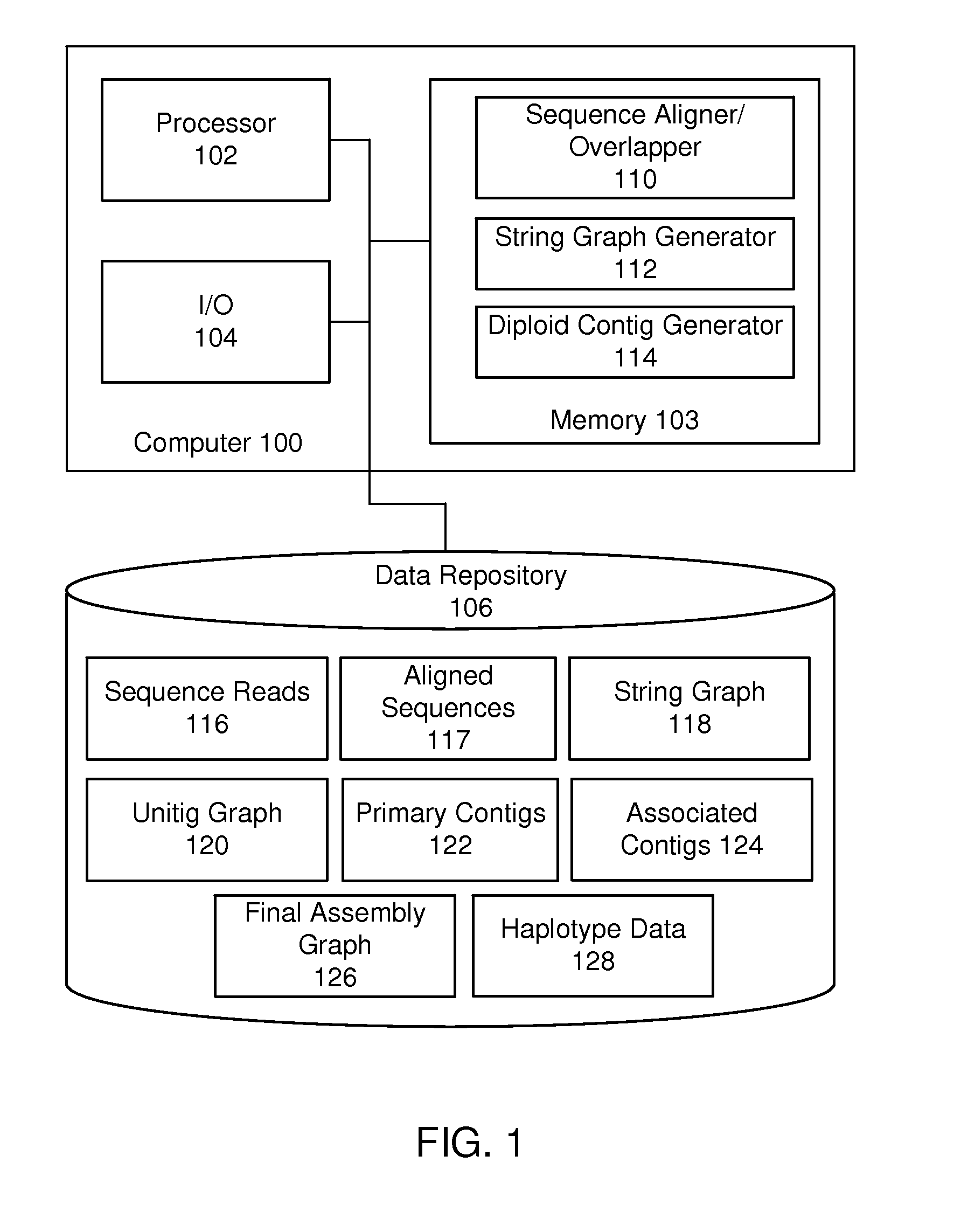
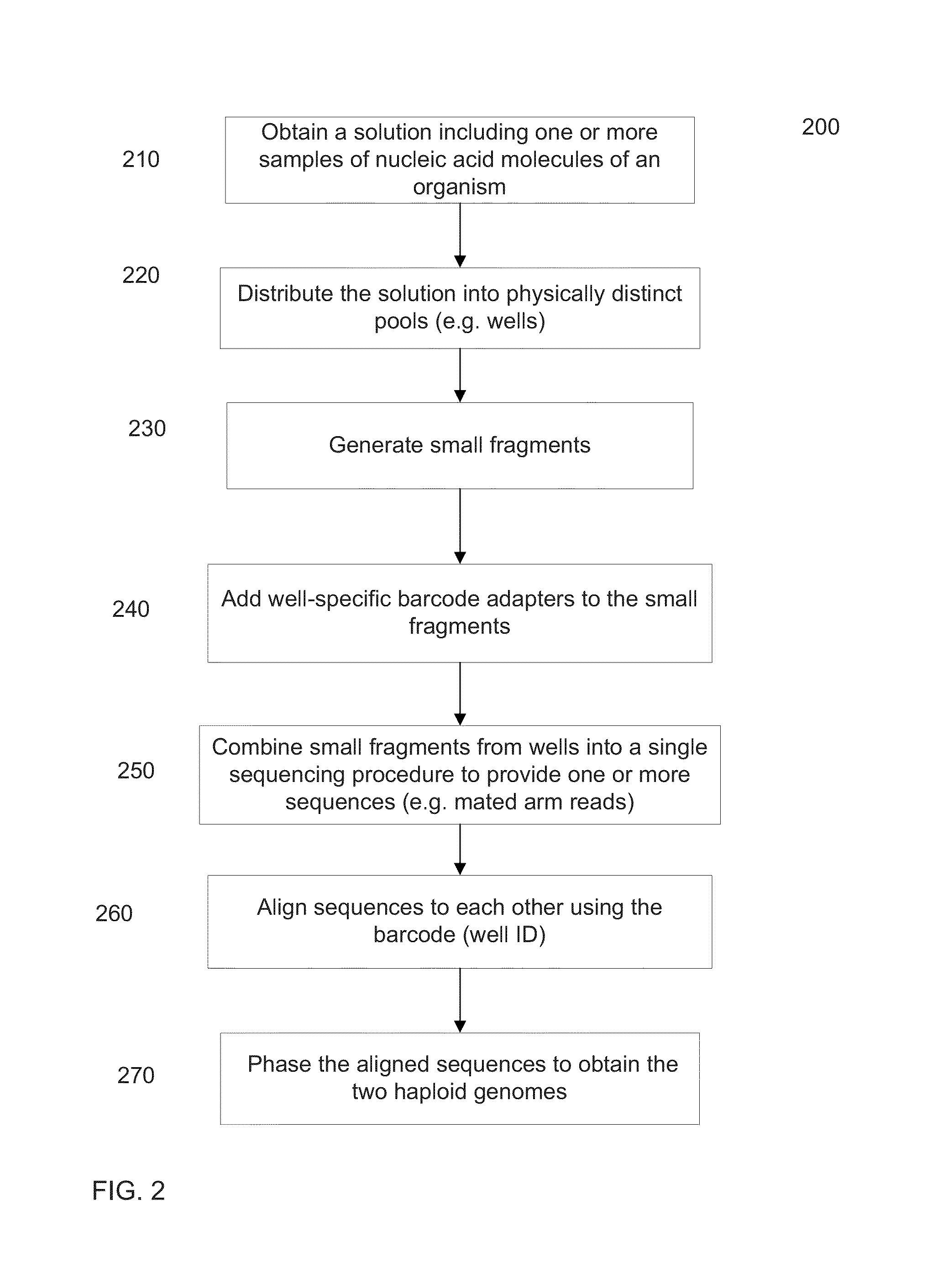
De novo diploid genome assembly and haplotype sequence reconstruction
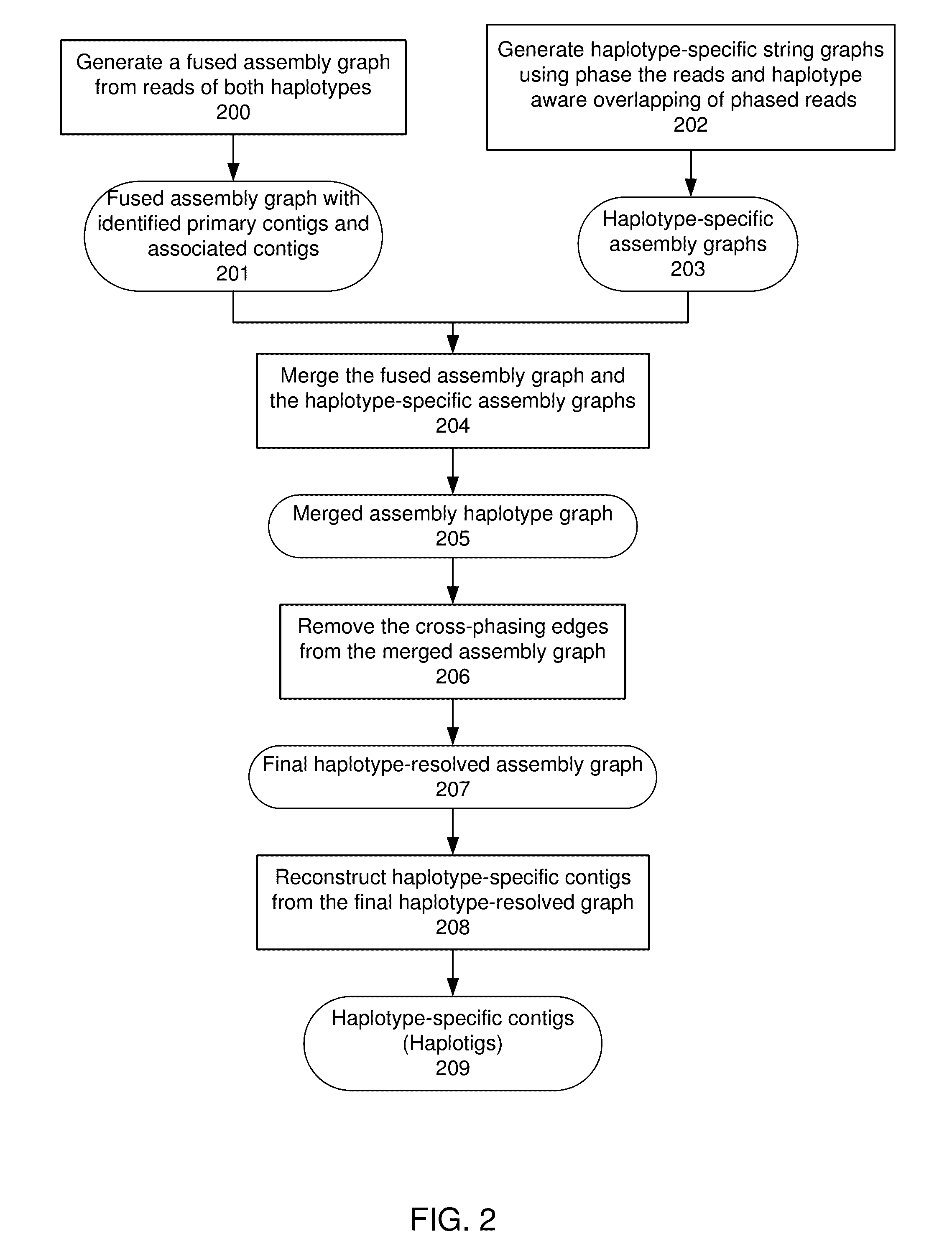
Exemplary embodiments provide methods and systems for diploid genome assembly and haplotype sequence reconstruction. Aspects of the exemplary embodiment include generating a fused assembly graph from reads of both haplotypes, the fused assembly graph including identified primary contigs and associated contigs; generating haplotype-specific assembly graphs using phased reads and haplotype aware overlapping of the phased reads; merging the fused assembly graph and haplotype-specific assembly graphs to generate a merged assembly haplotype graph; removing cross-phasing edges from the merged assembly haplotype graph to generate a final haplotype-resolved assembly graph; and reconstructing haplotype-specific contigs from the final haplotype-resolved assembly graph resulting in haplotype-specific contigs.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Systems and methods for hybrid assembly of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20120330559A1Bulky assemblyBiological testingSequence analysisContigNucleic acid sequencing
Systems and methods for assembling a nucleic acid sequence are disclosed. A plurality of single fragment sequence reads and a plurality of paired fragment sequence reads are received. Each paired fragment sequence read comprises at least two sequence reads separated by an insert. Single fragment sequence reads are assembled into a plurality of contigs, and the paired fragment sequence reads are mapped to the contigs. Further, gap regions comprising a portion of the partially assembled nucleic acid sequence for which the single fragment sequence reads do not map are identified, and hanging pairwise sequence reads of the mapped paired fragment sequence reads are used to fill in the gap region.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Strategies for sequencing complex genomes using high throughput sequencing technologies
InactiveUS20090142758A1Easy to useQuick sortingMicrobiological testing/measurementContigNucleotide sequencing
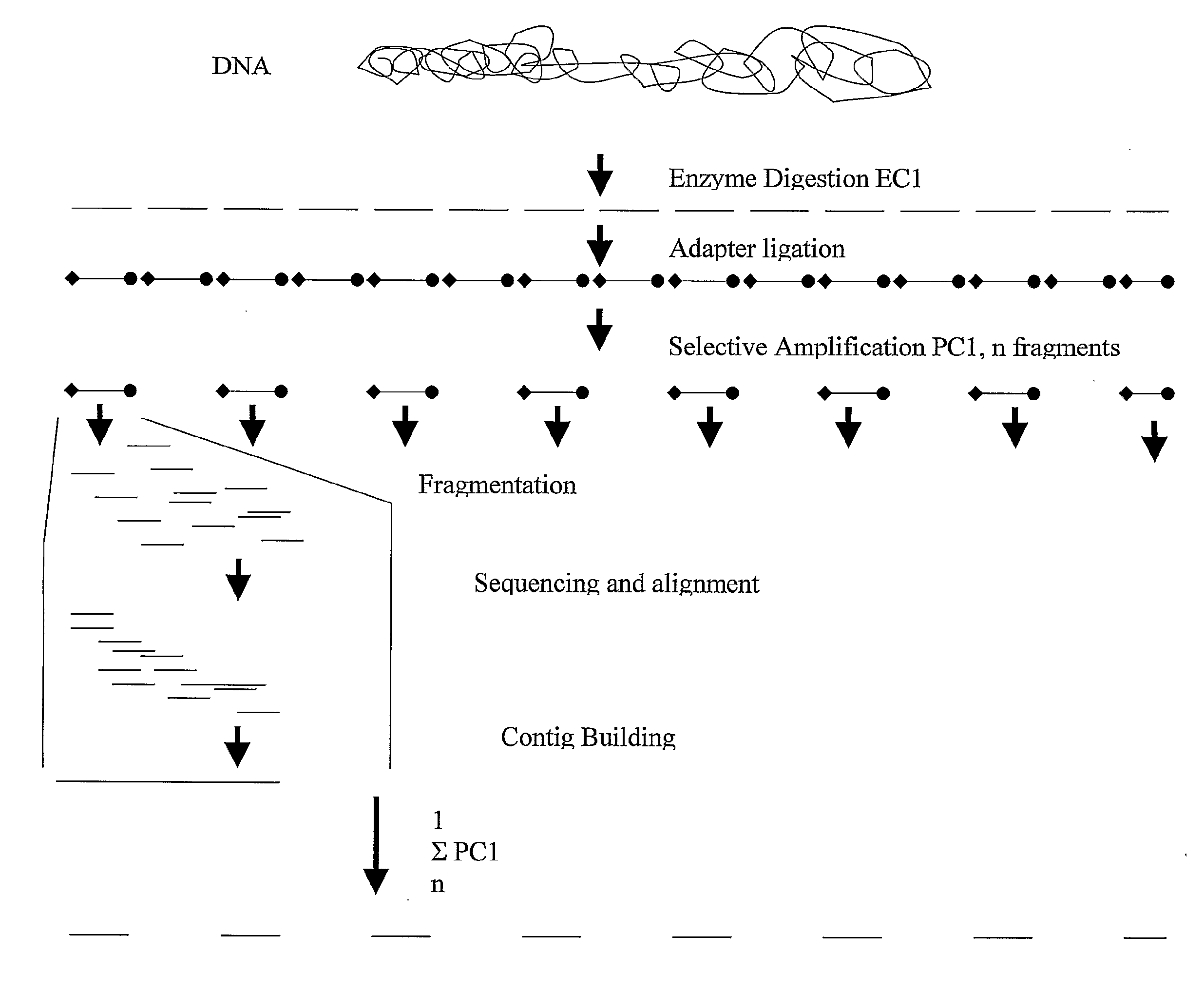
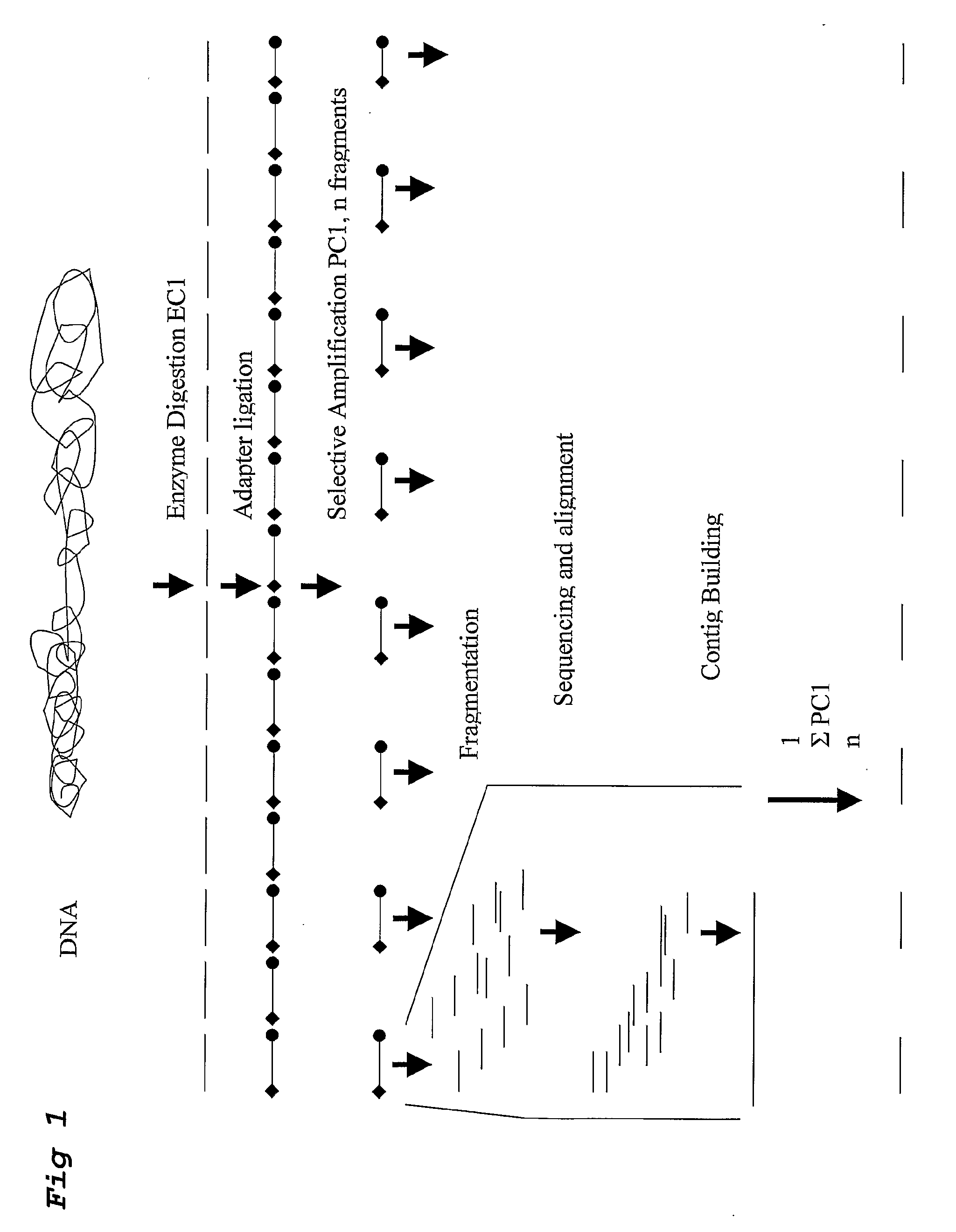
A method for determining a genome sequence comprising the steps of digesting the genome with at least one first restriction endonuclease, ligating at least one adaptor to the restriction fragments of the first subset, selectively amplifying the first set of adaptor-ligated restriction fragments using a first primer combination wherein at least a first primer contains a first selected sequence at the 3′ end of the primer sequence, comprising 1-10 selective nucleotides, repeating these steps with at least a second primer combinations wherein the primer contains a different second selected sequence, fragmenting each of the subsets of amplified adaptor-ligated restriction fragments to generate sequencing libraries, determine the nucleotide sequence of the fragments, aligning the sequence of the fragments in each of the libraries to generate contigs, repeating these steps for one second and / or further restriction endonucleases, aligning the contigs obtained for each of the second and / or further restriction endonucleases to provide for a sequence of the genome.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
High-throughput sequencing data-based genome de novo assembly method
ActiveCN104239750AGuaranteed accuracyReduce the difficulty of assemblySpecial data processing applicationsContigData error
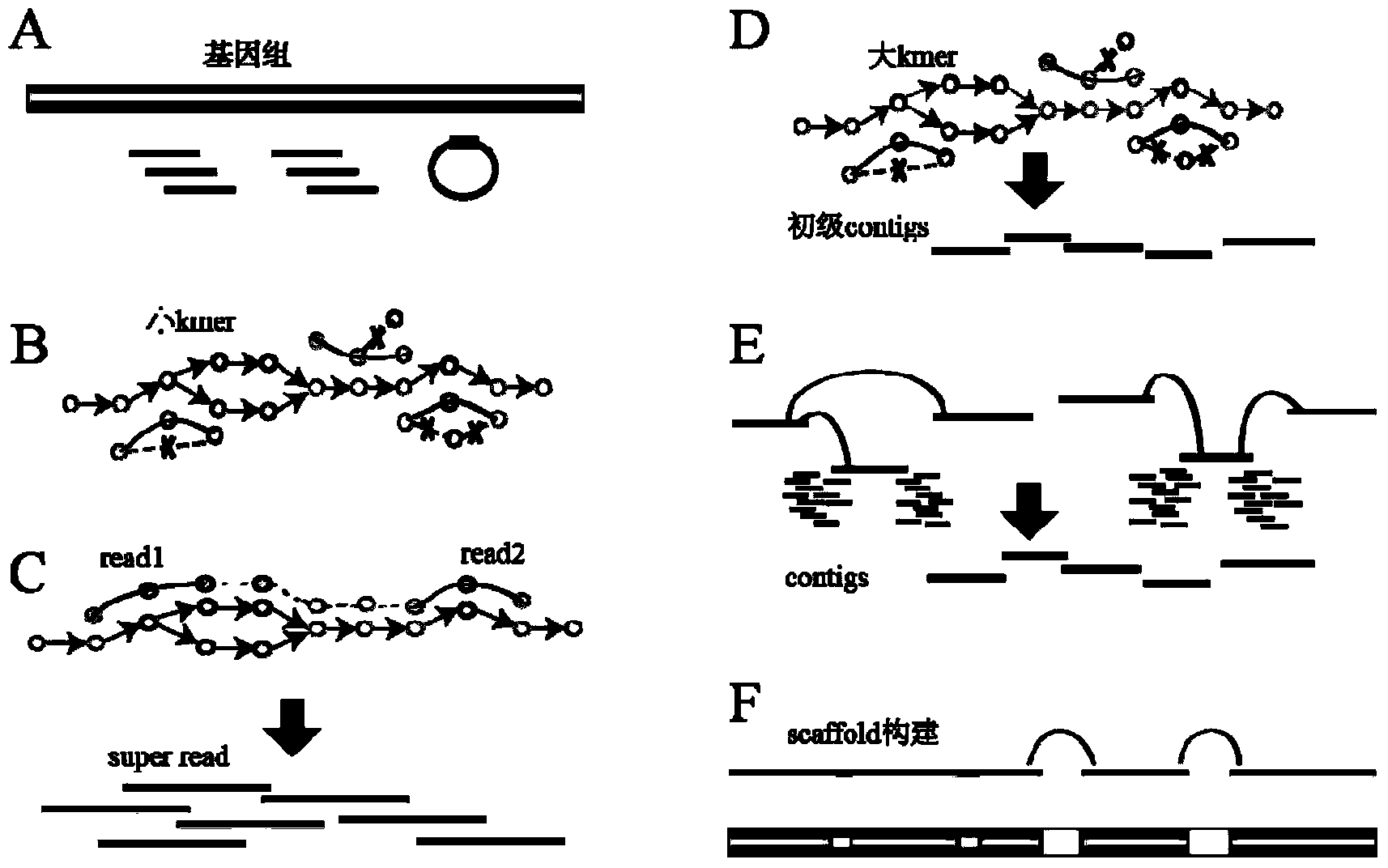
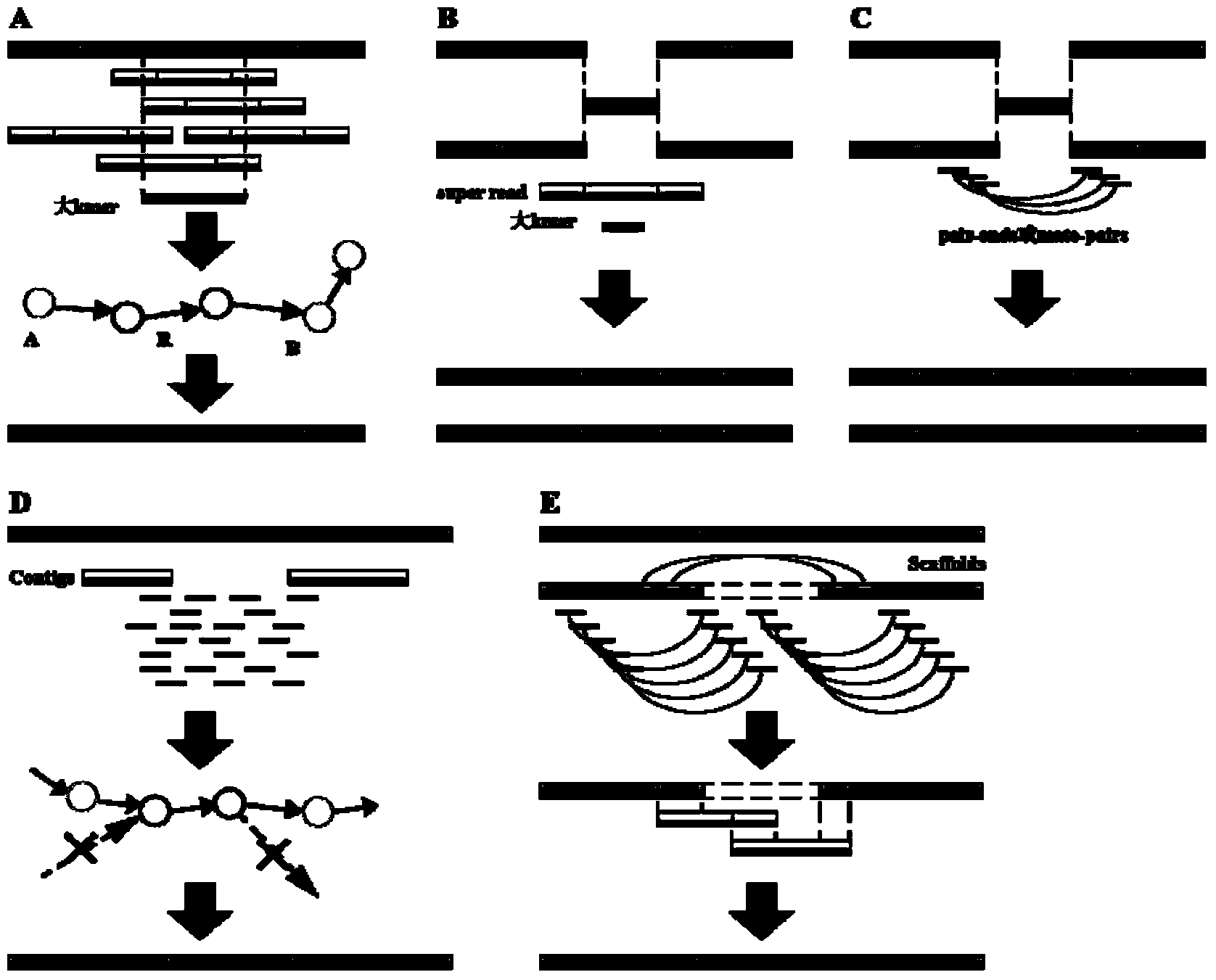
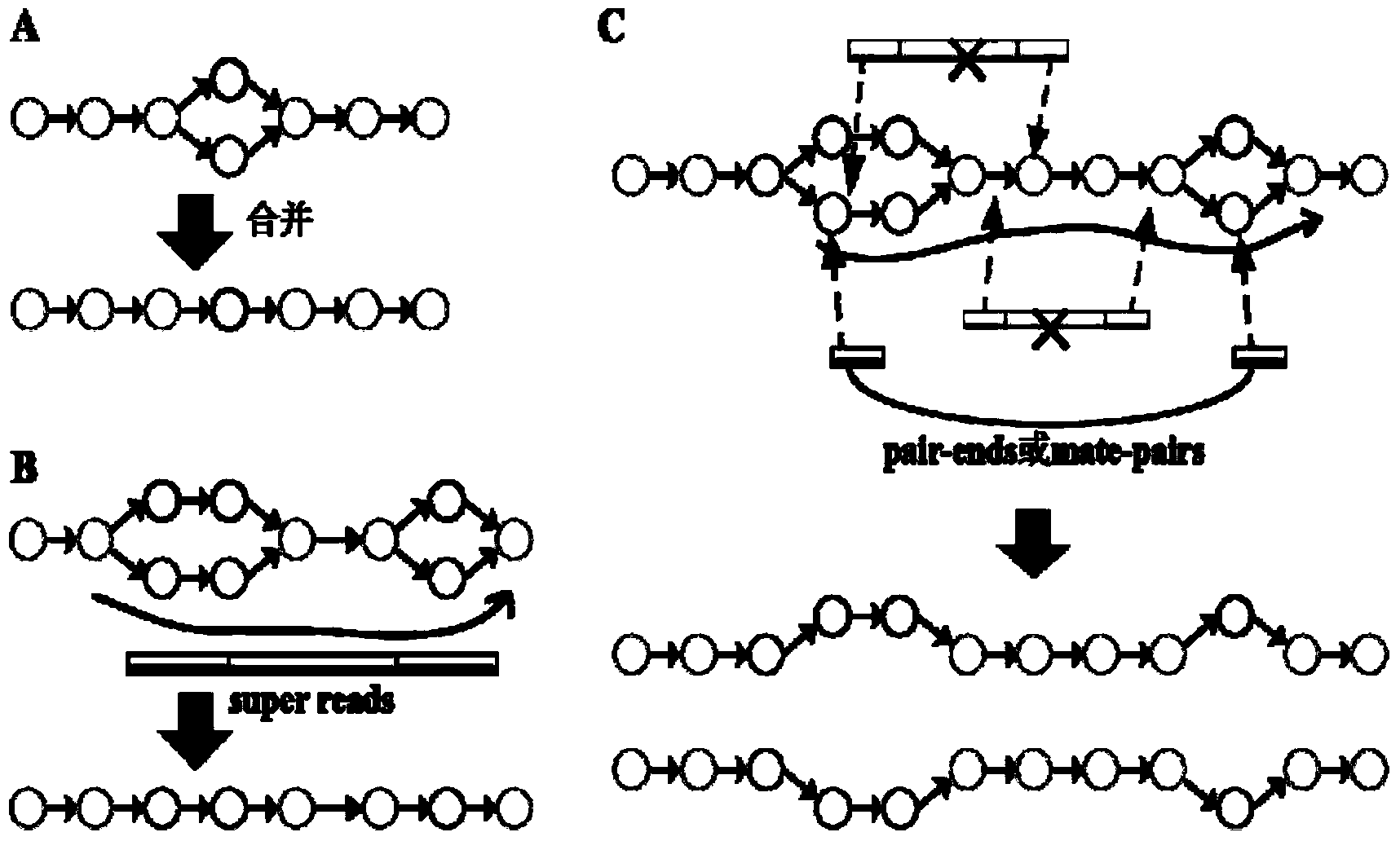
The invention provides a high-throughput sequencing data-based genome de novo assembly method, which comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a de Bruijn graph according to high-throughput sequencing data, and carrying out sequencing data error correction and super read assembly on the basis of the corrected de Bruijn graph; (2) utilizing super read to carry out primary contigs assembly; (3) taking specifically local primary contigs and reads, locally assembling, and combining all local assembly results; (4) sequencing contigs by a sub-graph segmentation algorithm and a simulated annealing algorithm to obtain final scaffolds. The errors brought by high-throughput sequencing are eliminated by de Bruijn graph correction, so that the data accuracy is improved; the sequencing read length is improved by establishing a super read method, and the contigs length is obviously enhanced; the processing capacity of repeated sequences is greatly enhanced by local assembly.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
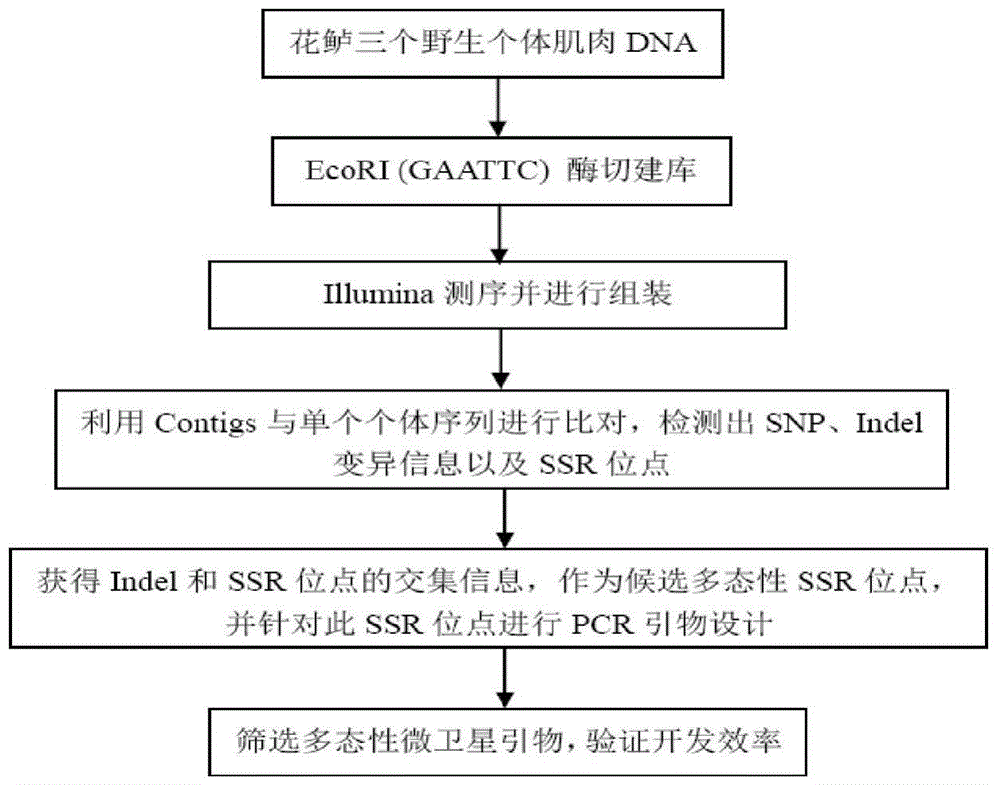
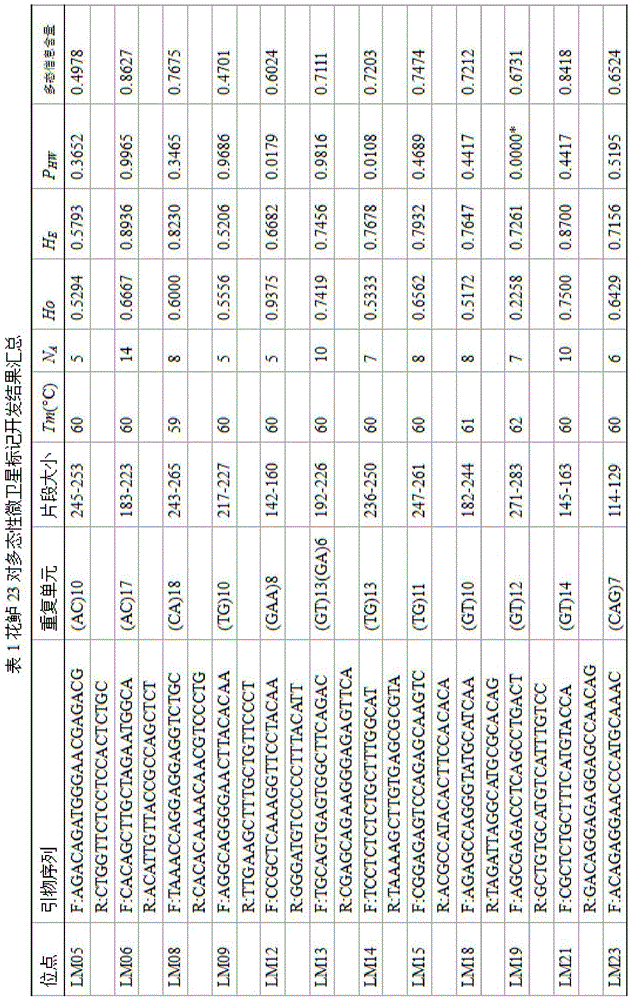
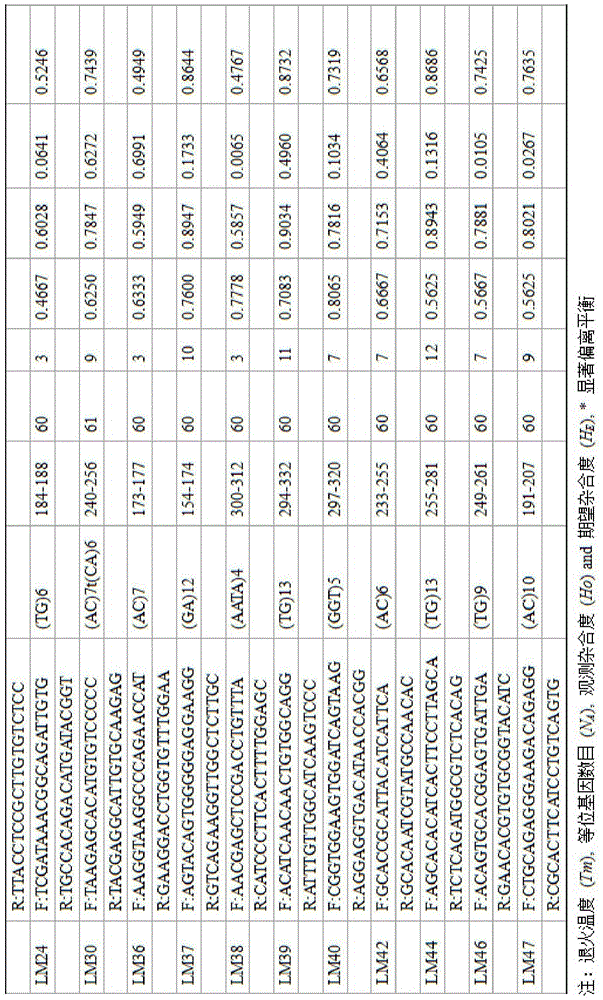
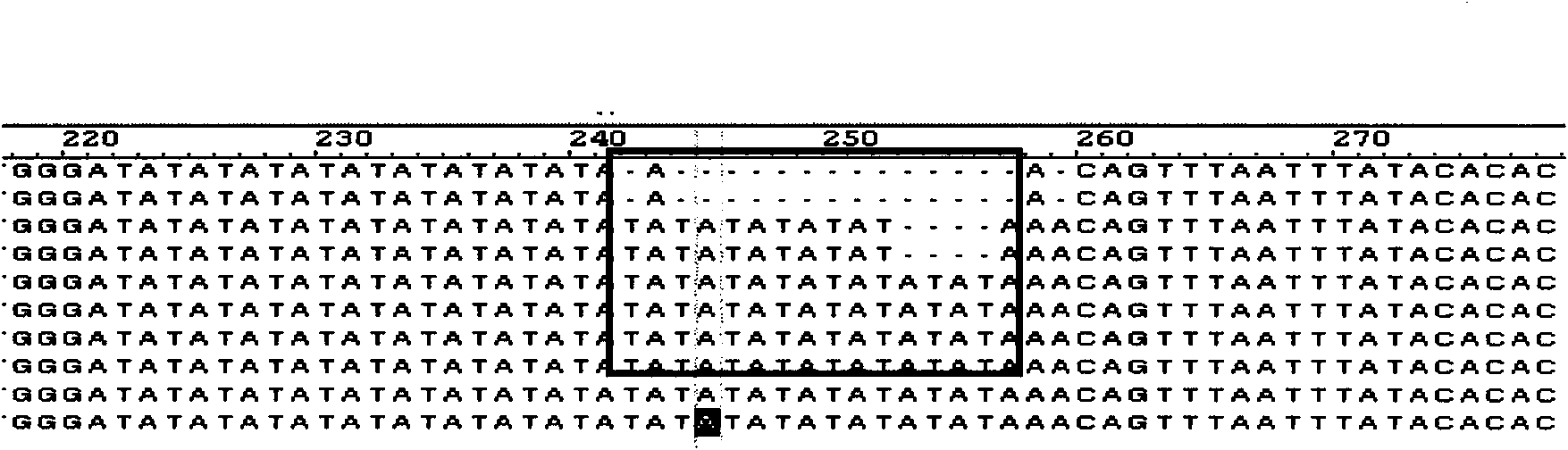
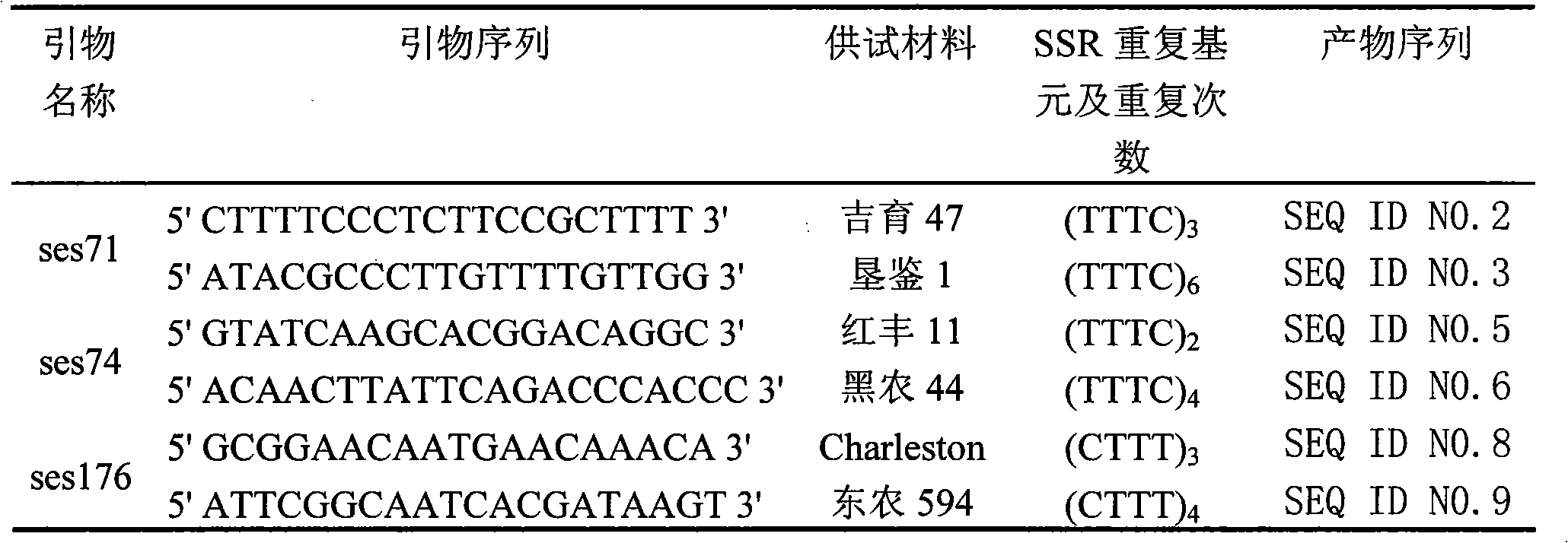
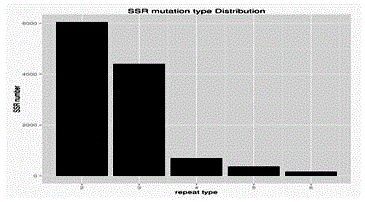
Method for massively and efficiently developing molecular markers on basis of Indel and SSR (simple sequence repeat) site techniques
ActiveCN105695572APromote rapid developmentShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationContigAgricultural science
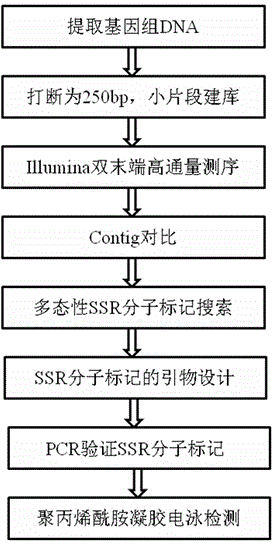
The invention discloses a method for massively and efficiently developing molecular markers on the basis of Indel and SSR (simple sequence repeat) site techniques. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting at least 3 samples to be developed, and respectively extracting DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) of the samples to be developed; (2) carrying out enzyme digestion on the DNA samples of the samples to be developed, establishing a sequencing library, and carrying out sequencing; (3) mixing the genomes of all the samples to be developed, and assembling to obtain Contigs; (4) comparing the Contigs with the sequences of the sample individuals to be developed, and acquiring SSR sites with Indel inside according to the Indel and SSR site information as a candidate polymorphism SSR site; (5) designing primers according to the obtained candidate polymorphism SSR site, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification and sequencing, and selecting a ribbon-shaped stable clear strip as molecular marker primers to be verified; and (6) carrying out PCR amplification on different samples to be developed by using the obtained molecular marker primers, and selecting the molecular markers with diversity, thereby obtaining the molecular markers. The method enhances the molecular marker development efficiency; and the developed SSR molecular markers can be efficiently applied to research in the aspects of genetics, multiplication release evaluation and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for obtaining EST-SSR mark
InactiveCN101619357AImprove development efficiencyReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationContigConserved sequence
The invention discloses a method for obtaining an EST-SSR mark, comprising the following steps: (1) obtaining an EST sequence containing simple repeat sequence in genome; (2) in the EST sequence which contains the simple repeat sequence and is obtained in the step (1), classifying the EST sequences with the same simple sequence repeat unit into a same type; (3) performing sequence splicing on the EST sequences of the same type obtained in the step (2) to obtain an overlapping group with variable numbers of simple sequence repeat units, an overlapping group without variable numbers of simple sequence repeat units and an EST sequence without overlapping groups; (4) designing primers according to a side-vane conserved sequence of simple repeat sequence in the overlapping group with available numbers of simple sequence repeat units in the step (3), and detecting the polymorphism of the primers to obtain polymorphic primers, i.e. EST-SSR mark. Compared with the conventional method, the invention increases the development efficiency by 2-4 times, and reduces the work capacity and expenditure, thereby shortening the development time, reducing the development cost and simultaneously reducing the possibility of missing the locus of polymorphism SSR.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Read and distance distribution based genome De novo sequence splicing method
ActiveCN104200133ASolution depthSolve the repeatabilitySpecial data processing applicationsContigComputer science
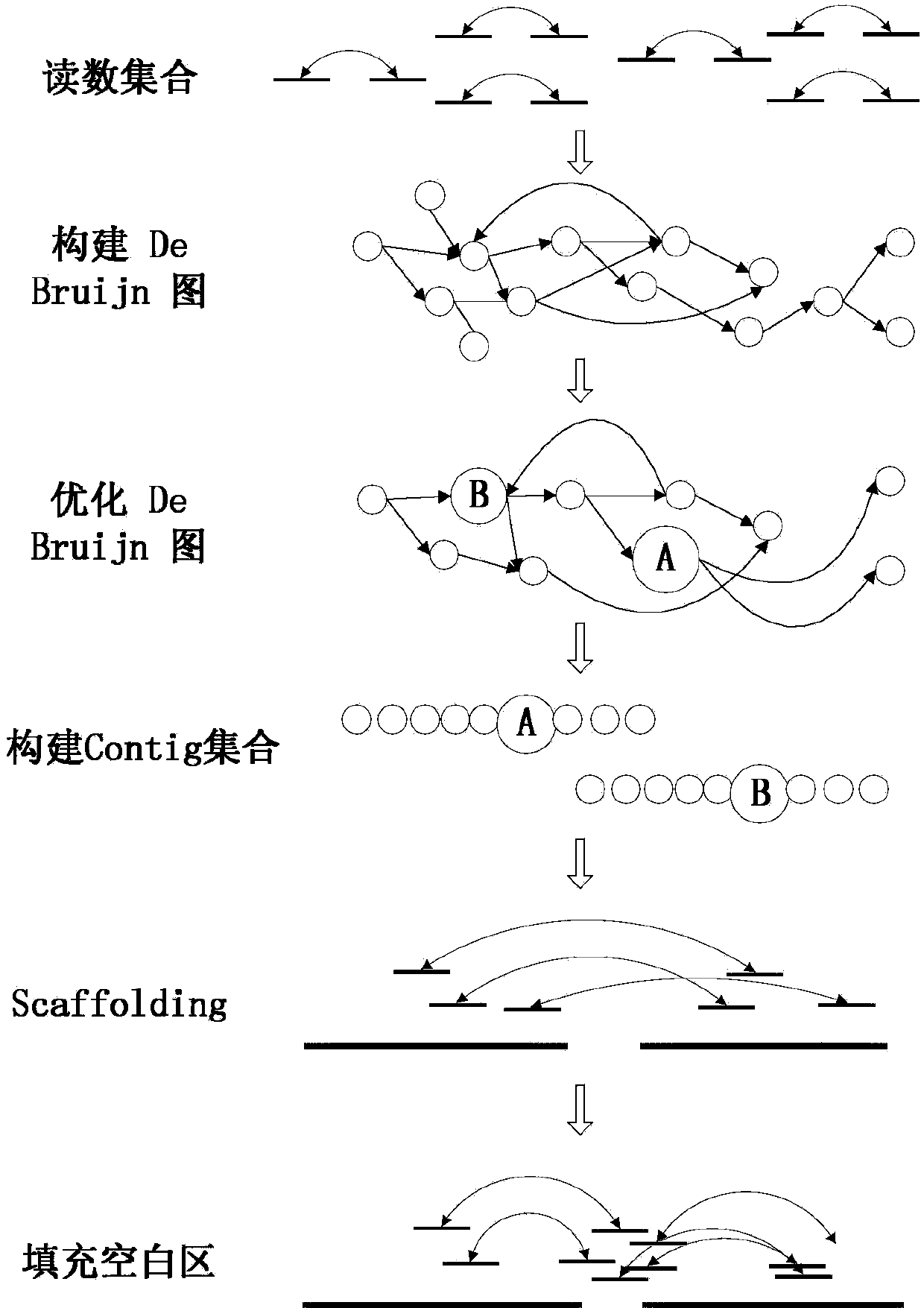
The invention discloses a read and distance distribution based genome De novo sequence splicing method. In the method, overlap relation between reads is stored by means of a De Bruijn diagram, and a new scoring function is provided on the basis of read distribution to apply to processes of contig construction, scaffolding and blank area filling and the like. The scoring function takes full consideration of sequencing depth, k-mer frequency and deviation of insertsize of a complex repeated region. The method is simple and easy to implement, and has good splicing effect in terms of different simulated and real sequencing data, and has high continuity and integrity as compared with the other sequence splicing method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for determining nucleotide sequences using arbitrary primers and low stringency
The invention involves a method for obtaining sequence information from nucleic acid molecules, such as cDNA. The method involves the use of arbitrary primers, and low stringency conditions. Rather than providing information from the termini of nucleic molecules, the method provides information on the more interesting and relevent internal portions of nucleic acid molecules. The method shows how to secure information on ORFs, and how to prepare contig sequences from any source.
Owner:SIMPSON ANDREW JOHN GEORGE +2
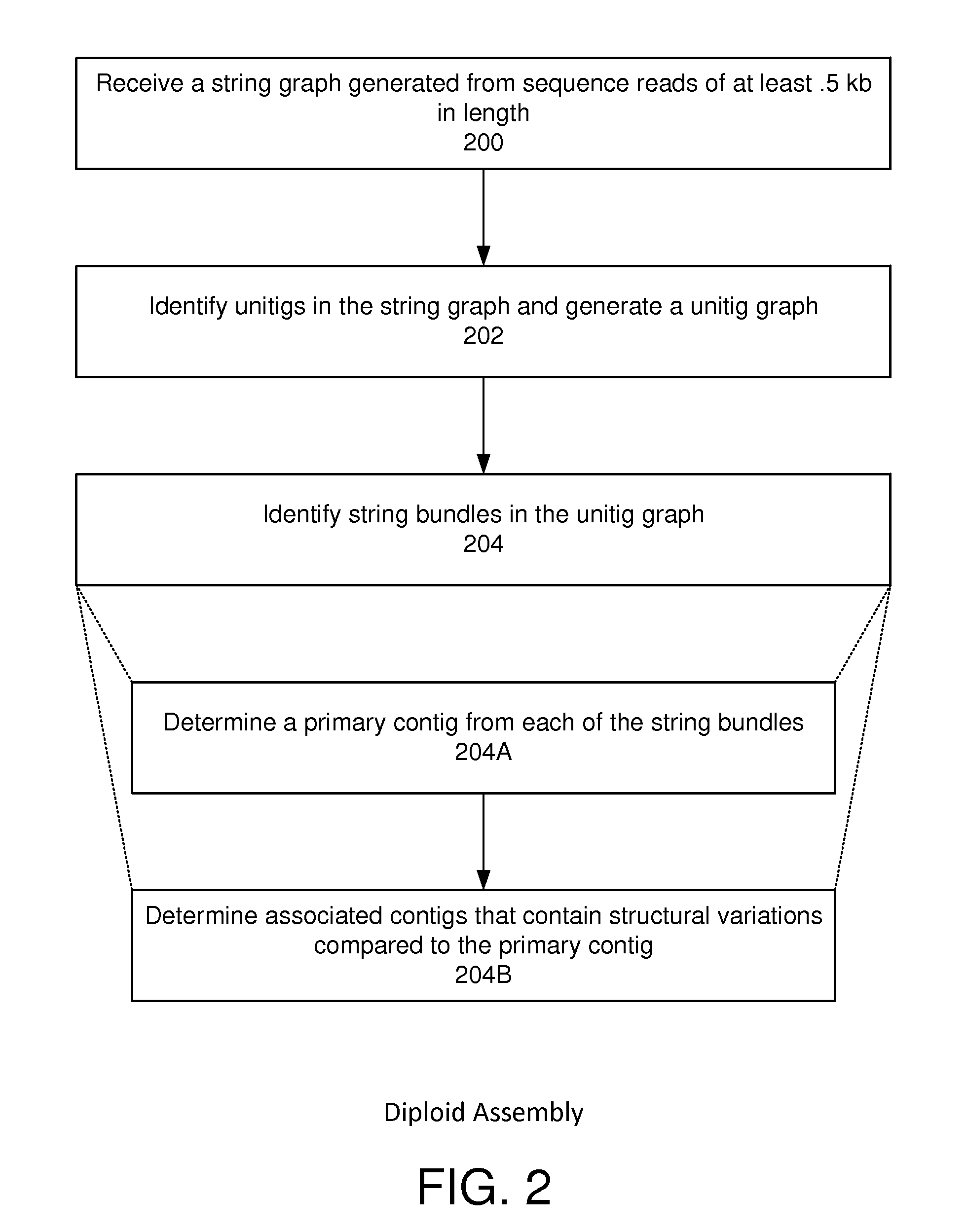
String graph assembly for polyploid genomes
InactiveUS20150169823A1Avoid excessive errorIncrease chanceBiological testingSequence analysisContigTheoretical computer science
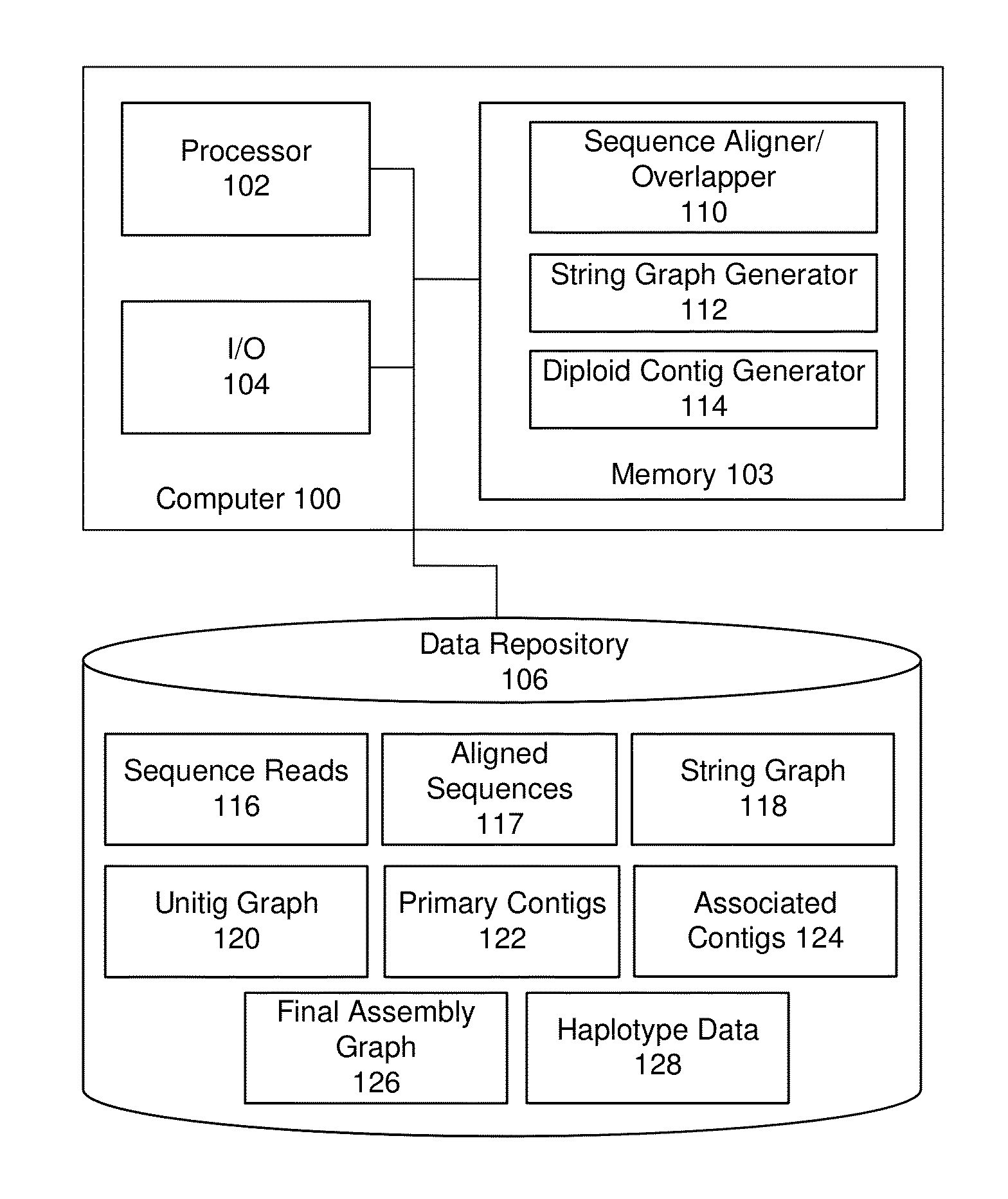
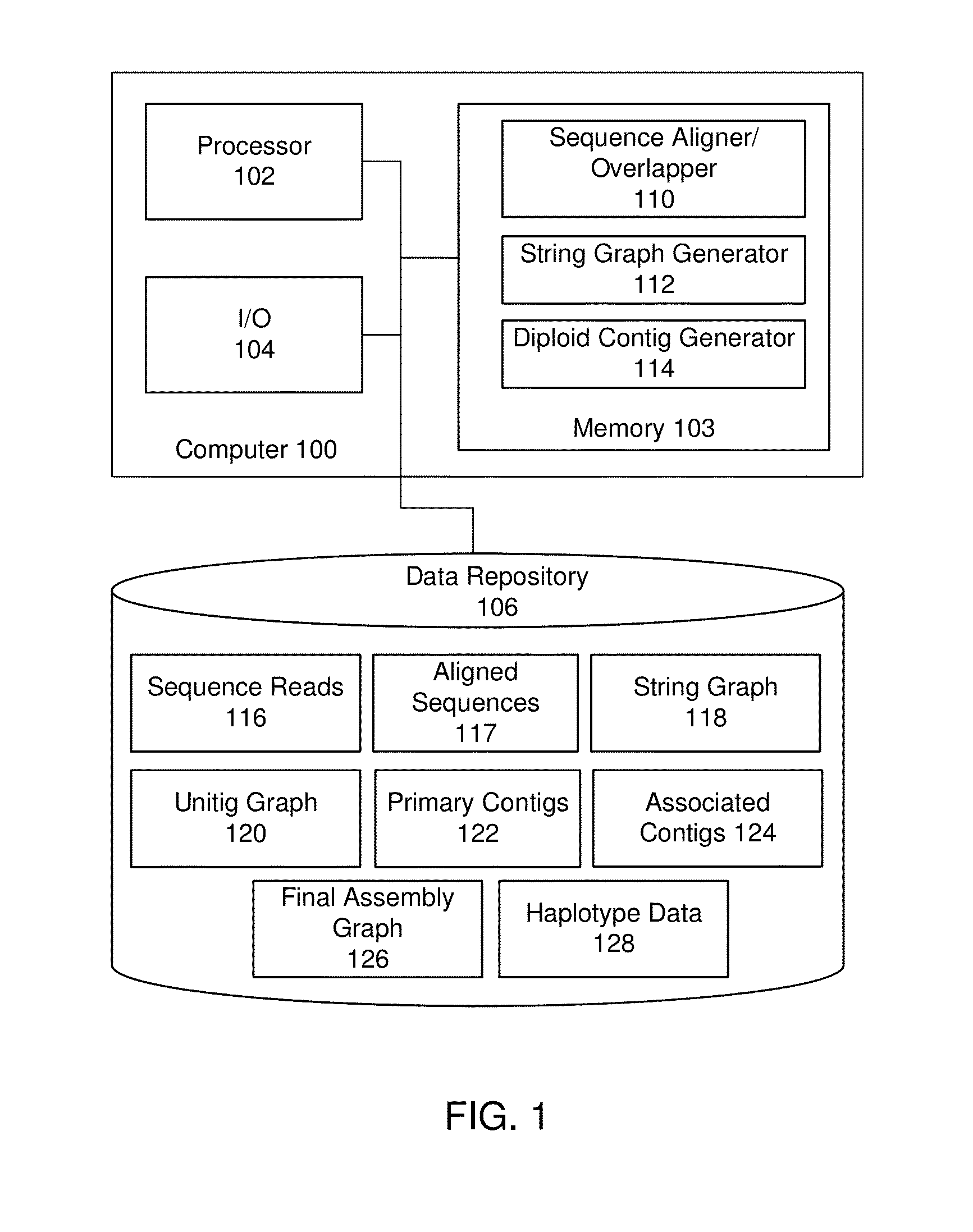
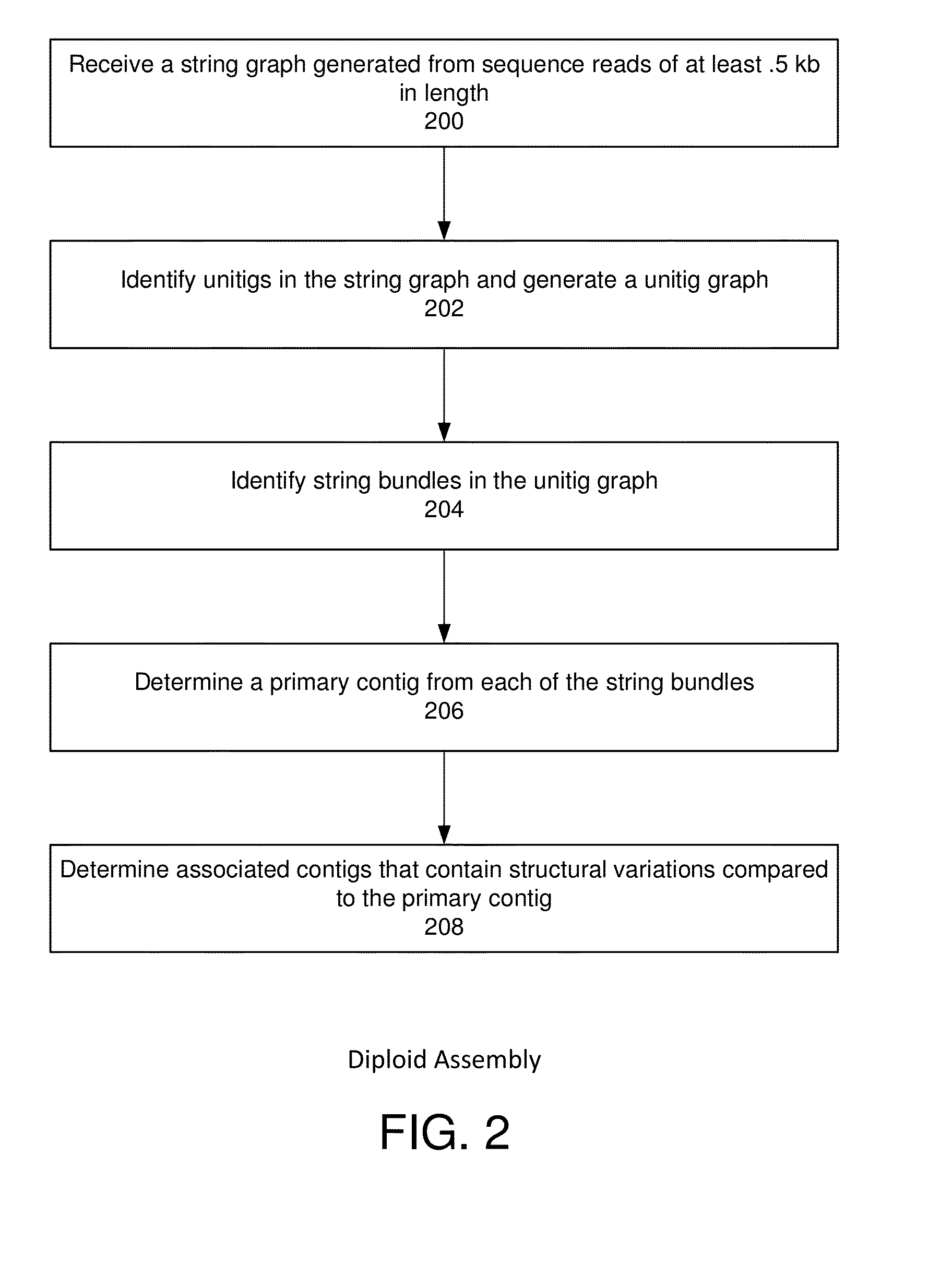
Exemplary embodiments provide methods and systems for string graph assembly of polyploid genomes. Aspects of the exemplary embodiment include receiving a string graph generated from sequence reads of at least 0.5 kb in length; identifying unitigs in the string graph and generating a unitig graph; identifying string bundles in the unitig graph; determining a primary contig from each of the string bundles; and determining associated contigs that contain structural variations compared to the primary contig.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
High throughput DNA sequencing vector
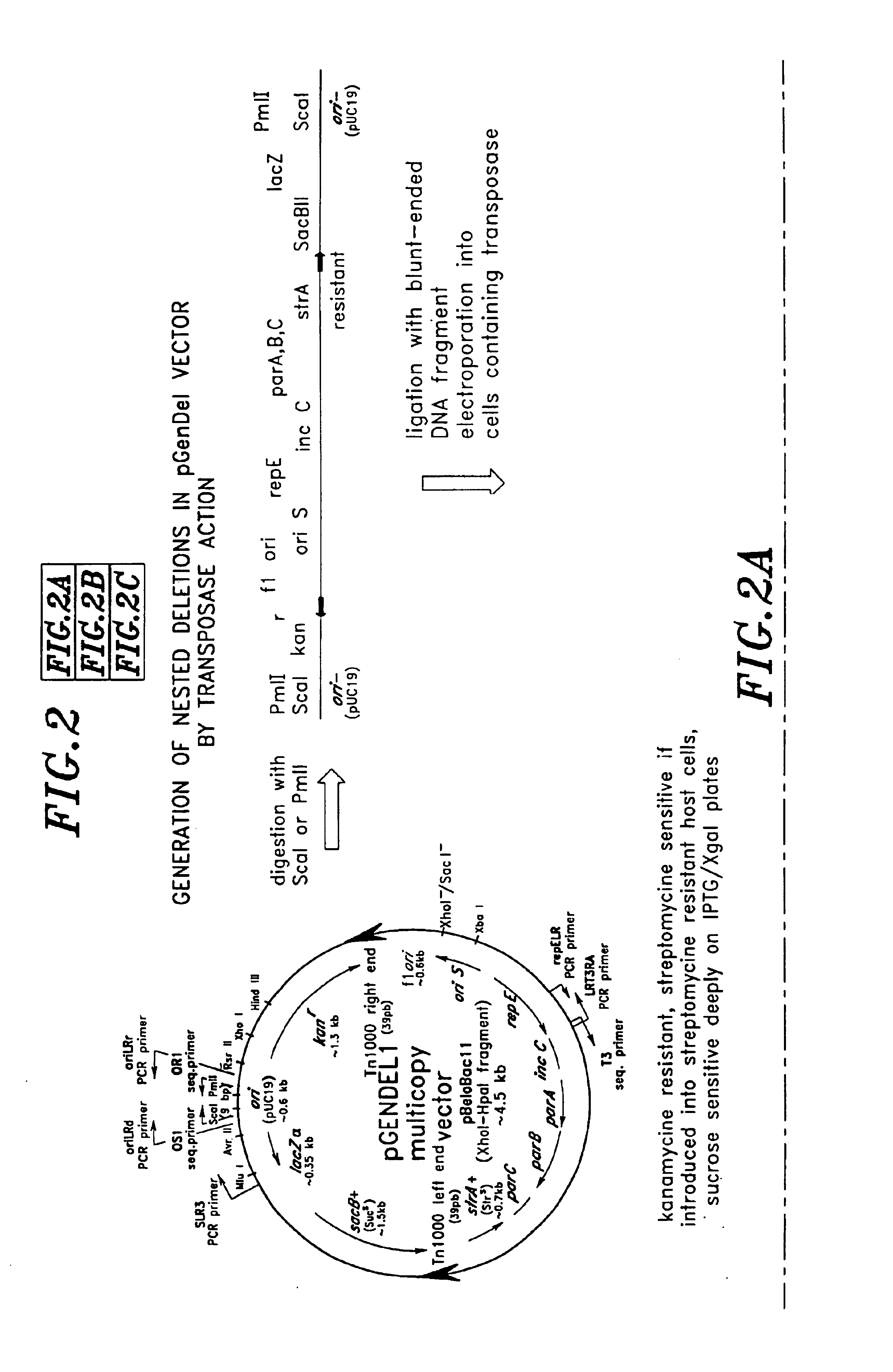
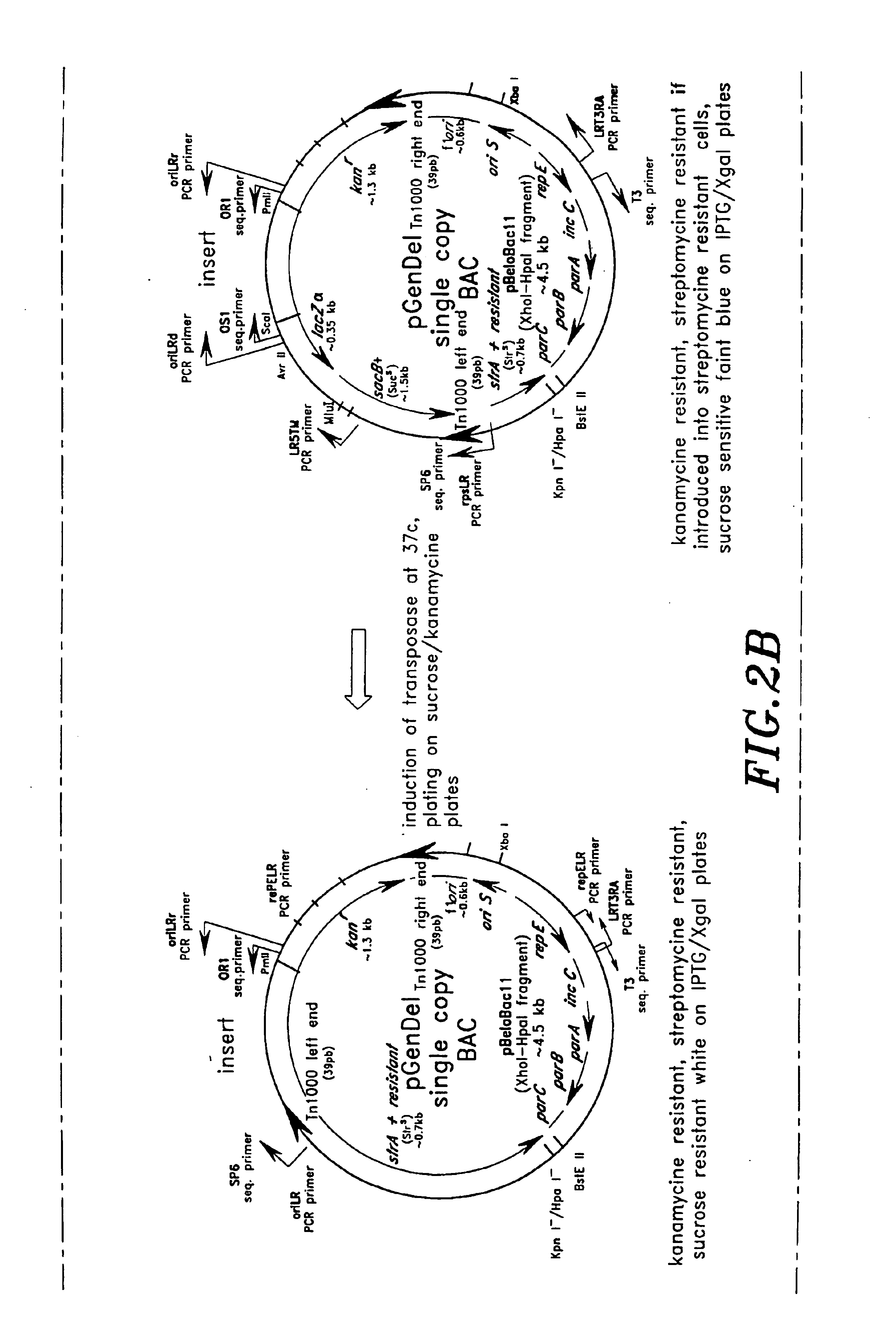
InactiveUS6955902B2Reduce the number of copiesHigh copy numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementContigHigh-Throughput DNA Sequencing
High throughput DNA sequencing vectors for generating nested deletions using enzymatic techniques and / or transposition-based techniques are disclosed. Methods of constructing contigs of long DNA sequences and methods of generating nested deletions are also disclosed. A truncated lacZ derivative useful in measuring the copy number of the lacZ derivative in a host cell is also disclosed.
Owner:SERONO GENETICS INST SA
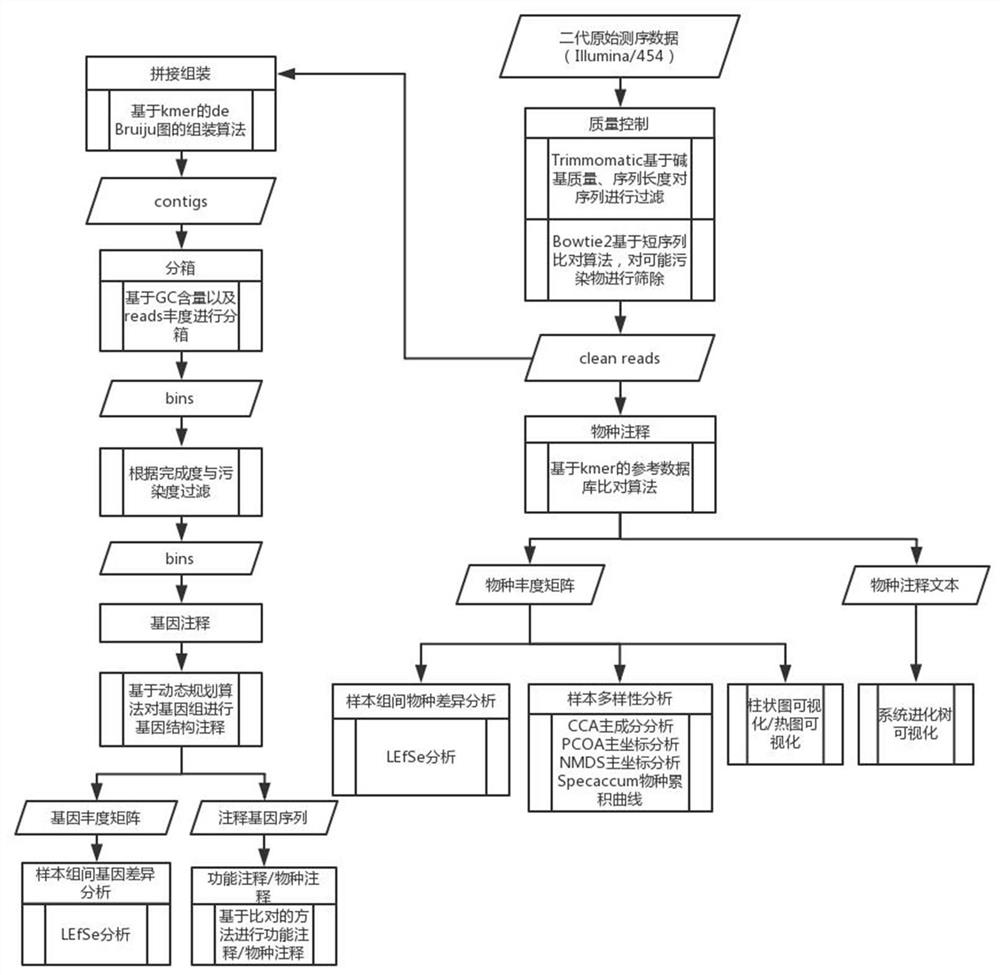
Metagenome data analysis method based on next-generation sequencing technology
PendingCN112071366ASolve incomplete problemsThe analysis process is reasonableCharacter and pattern recognitionHybridisationGenomicsContig
The invention discloses a metagenome data analysis method based on a next-generation sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out quality control on original sequencing data to obtain clean reads; (2) performing species annotation on the clean reads subjected to the quality control; (3) performing statistical analysis on the sample diversity based on a species abundance matrix; (4) performing statistical analysis on species with significant differences among sample groups based on the species abundance matrix; (5) splicing and assembling the clean reads to obtain a contigs sequence; (6) packaging the contigs obtained by splicing and assembling into boxes to obtain bins; (7) carrying out gene annotation on the bins subjected to boxing; (8) performing statistical analysis on the genes with significant differences among the sample groups based on the gene abundance matrix; and (9) based on the gene annotation result, performing function and species annotation on the sequence. A whole process from metagenome next-generation sequencing data processing to species composition analysis, gene composition analysis and function annotation is provided, an accurate analysis result is provided for researchers, and the metagenomics problem is comprehensively analyzed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
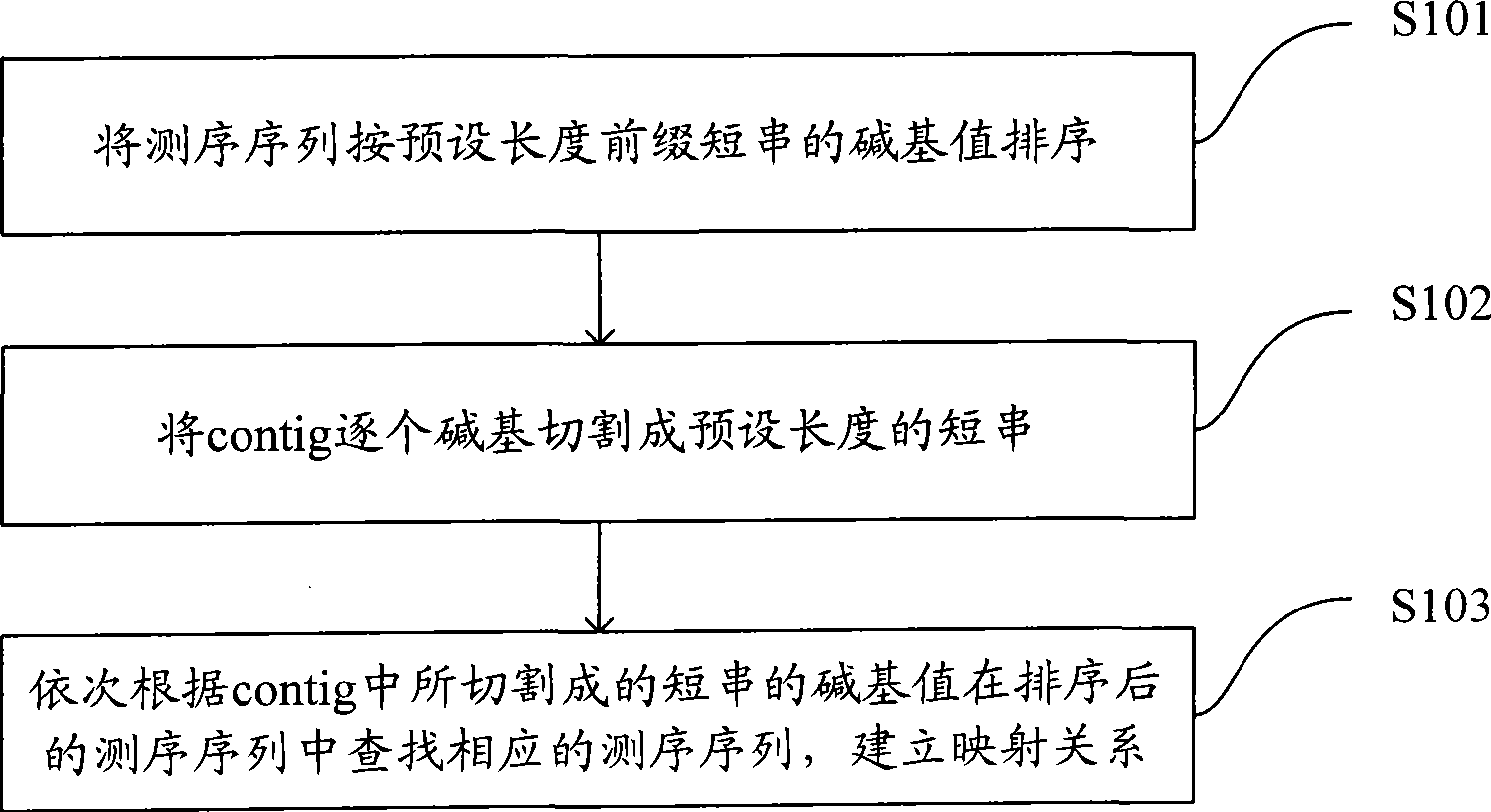
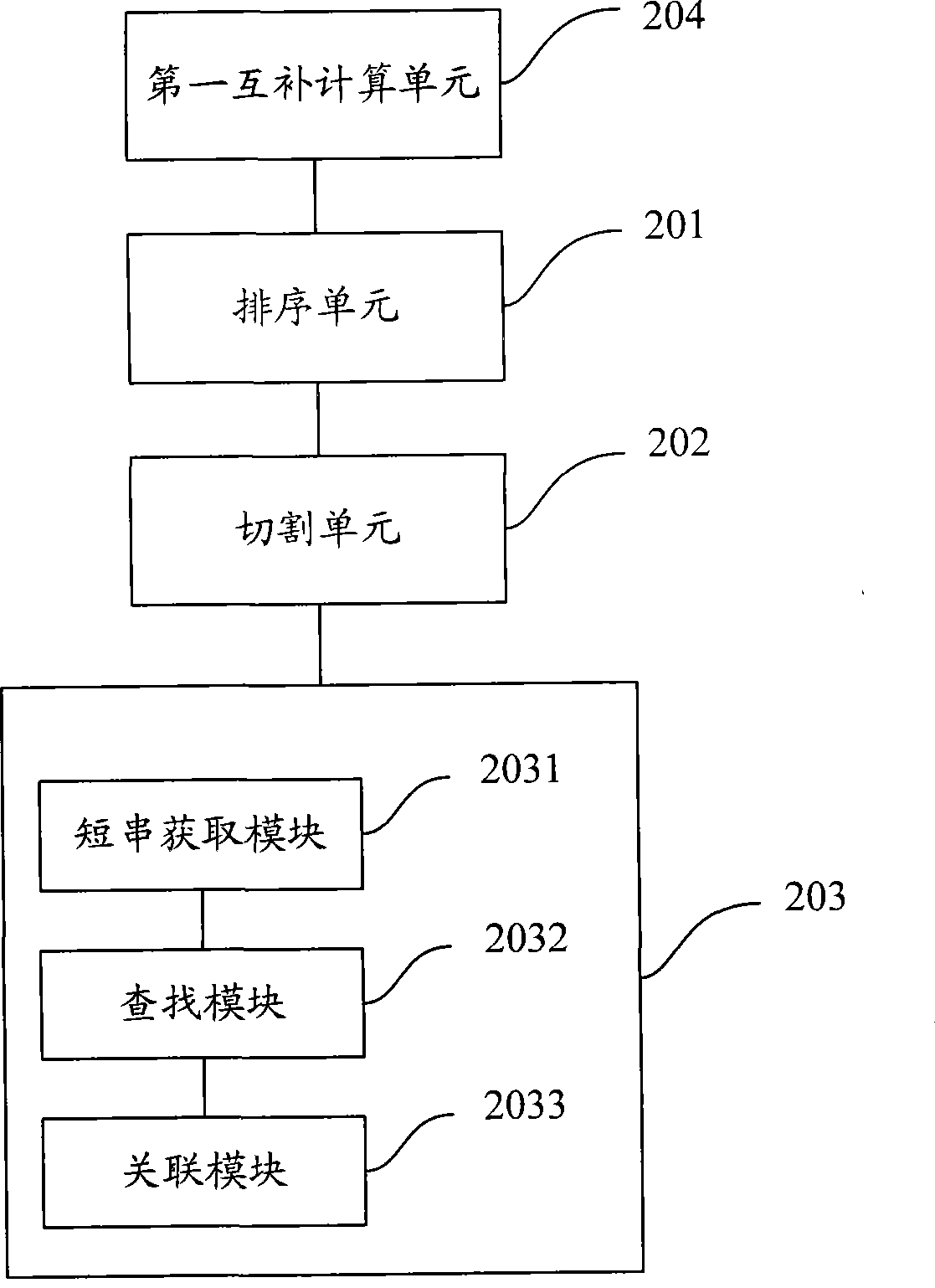
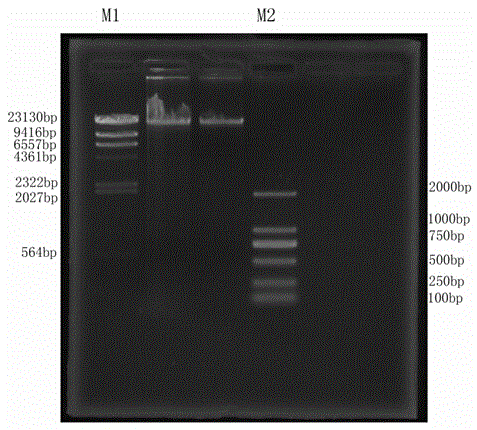
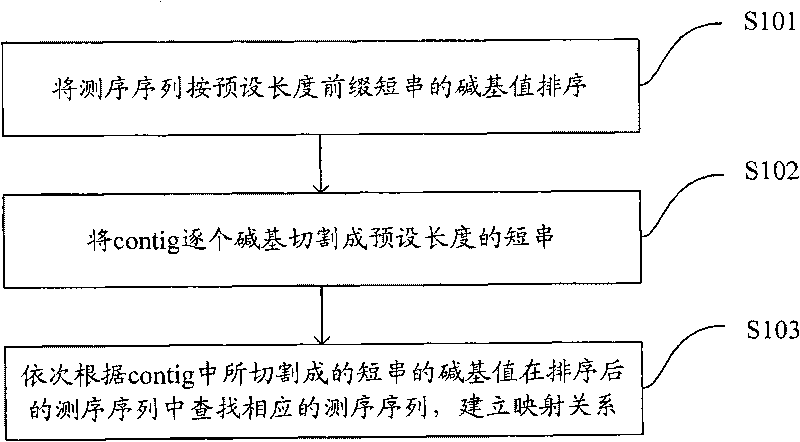
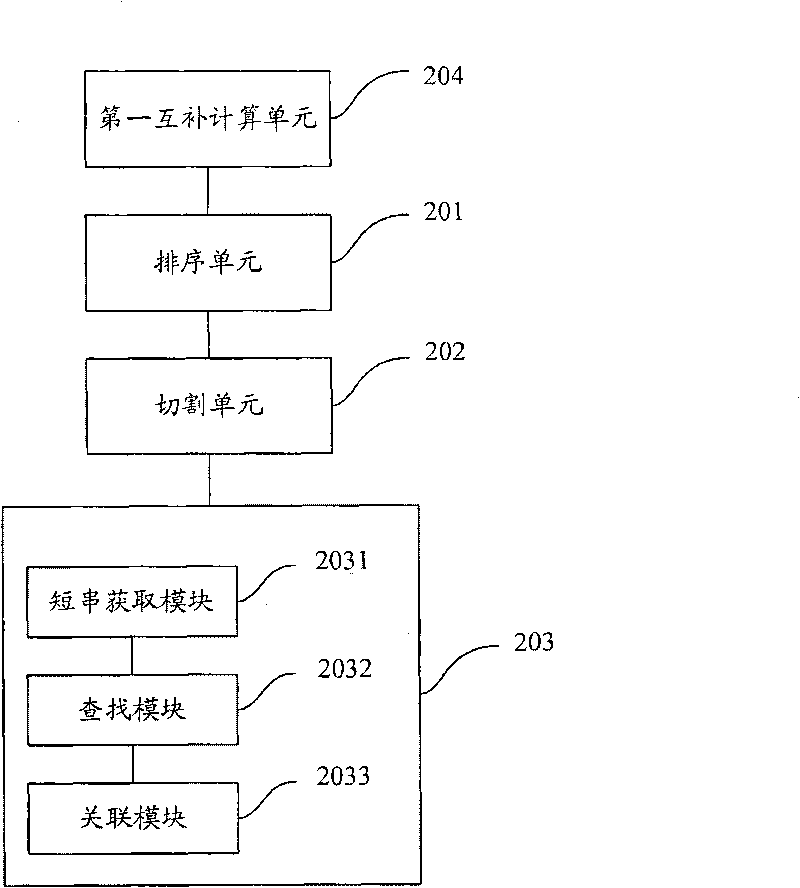
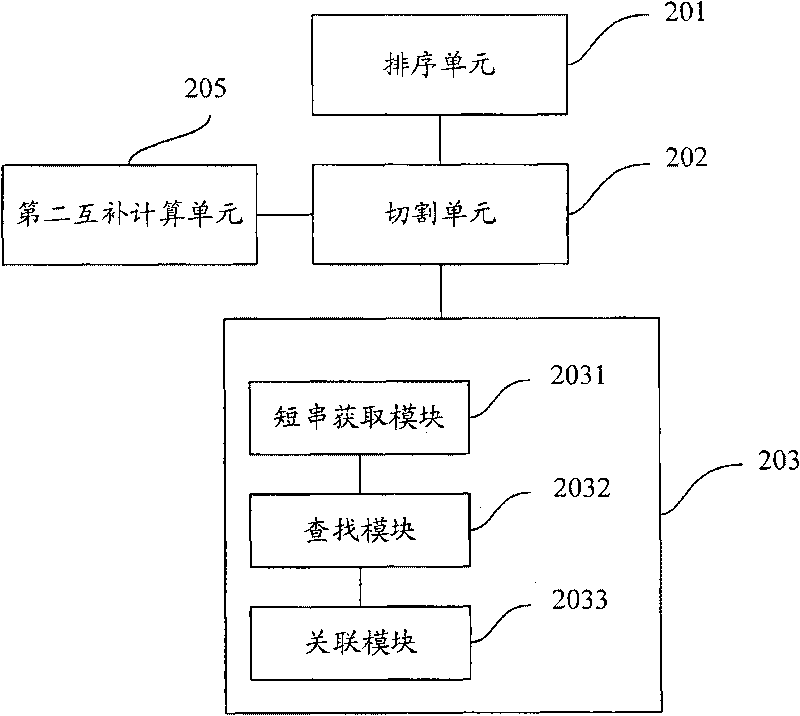
Short sequence mapping method and system
InactiveCN101430741AExtended processing timeLength prefix short processing timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsContigShort string
The invention is applicable to the technical field of gene engineering, and provides a method for mapping a short sequence and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: ordering an order-checking sequence according to base values of prefixed short strings with predetermined length; cutting each base of a contig to a short string with the predetermined length; searching a corresponding order-checking sequence in an ordered order-checking sequence in sequence according to the base value of the cut short string in the contig so as to establish a mapping relation. In the invention, the method for mapping the short sequence used in a short sequence assembly is realized by ordering the order-checking sequence according to the base values of the prefixed short strings with the predetermined length, cutting each base of the contig to the short string with the predetermined length and searching the corresponding order-checking sequence in the ordered order-checking sequence in sequence according to the base value of the cut short string in the contig so as to establish the mapping relation. Therefore, the method has short treatment time and high efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
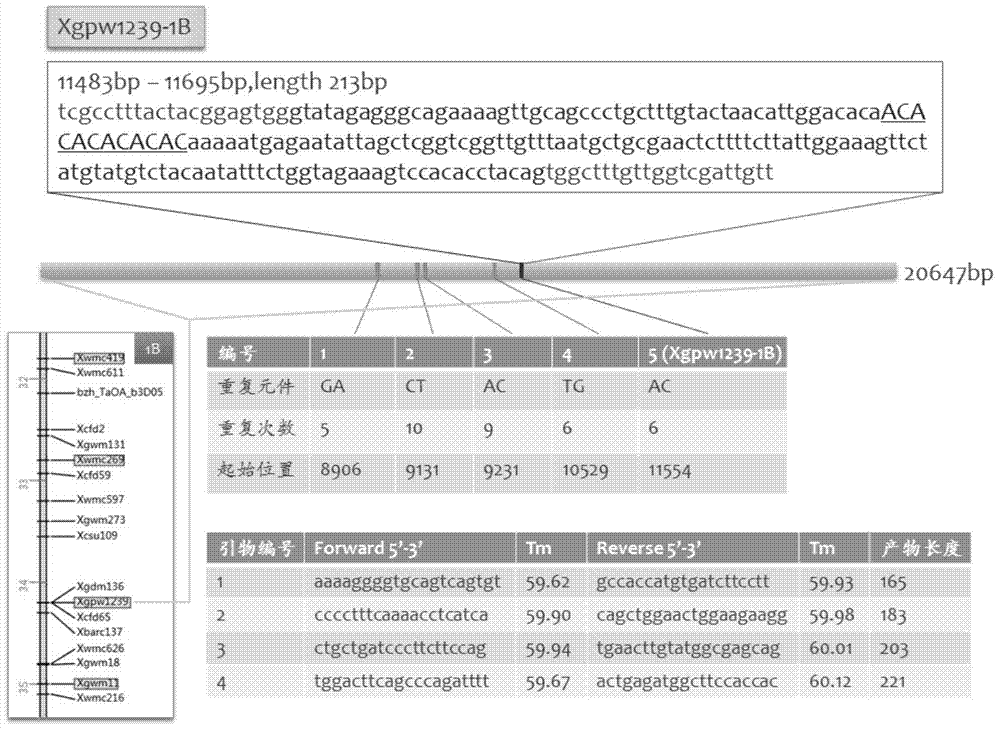
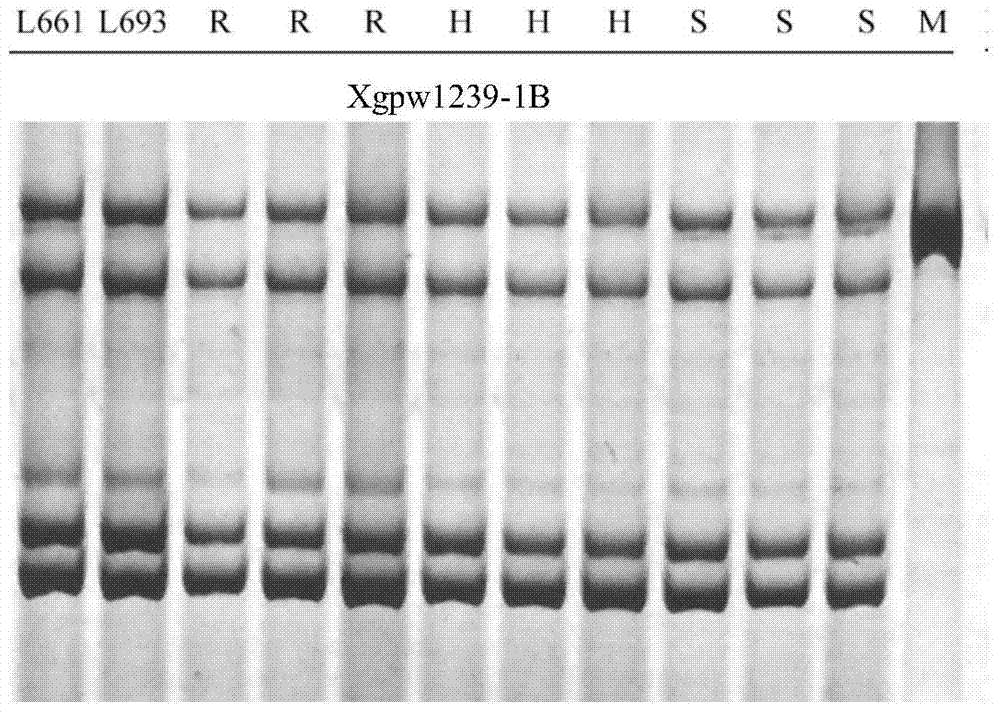
Design method of SSR label primer and wheat SSR label primers
InactiveCN103571833AIncrease the number ofFast encryptionMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsContigTest group
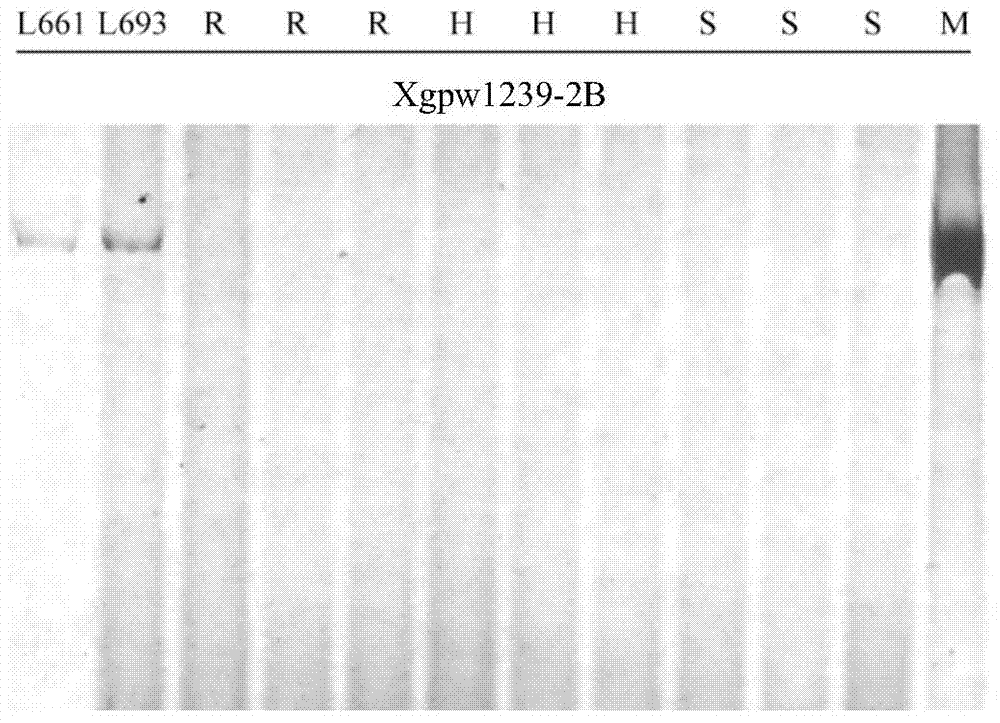
The invention discloses a design method of an SSR label primer. In order to overcome the defect of insufficient polymorphism of the conventional SSR label primer, the invention provides a method for designing a novel SSR label primer based on a draft sequence of a genome. The design method comprises the following steps: firstly selecting an SSR label primer with a known site as a starting SSR label primer; secondly, comparing the starting SSR label primer with the draft sequence of a chromosome to which the starting SSR label primer belongs, and finding a contig in a comparison result; thirdly, searching an SSR sequence in the contig as a finishing SSR sequence; finally, designing the SSR label primer based on the finishing SSR sequence. The invention provides 14 pairs of novel SSR label primers related to wheat stripe rust resistance, and a method for establishing a wheat genetic map with L693*L661 and L661*L693F2 single plants as a mapping population, wherein five pairs of the SSR label primers generate genetic polymorphism in a genetic test group. According to the design method, the number of the SSR label primers with known sites can be quickly increased and the polymorphism of the SSR label is increased; the genetic map can be quickly encrypted through combination with initial gene localization.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Improved strategies for sequencing complex genomes using high throughput sequencing technologies
A method for determining a genome sequence comprising the steps of digesting the genome with at least one first restriction endonuclease, ligating at least one adaptor to the restriction fragments of the first subset, selectively amplifying the first set of adaptor-ligated restriction fragments using a first primer combination wherein at least a first primer contains a first selected sequence at the 3' end of the primer sequence, comprising 1-10 selective nucleotides, repeating these steps with at least a second primer combinations wherein the primer contains a different second selected sequence, fragmenting each of the subsets of amplified adaptor-ligated restriction fragments to generate sequencing libraries, determine the nucleotide sequence of the fragments, aligning the sequence of the fragments in each of the libraries to generate contigs, repeating these steps for one second and / or further restriction endonucleases, aligning the contigs obtained for each of the second and / or further restriction endonucleases to provide for a sequence of the genome.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Method for developing genome simple sequence repeats (SSR) molecular marker
InactiveCN104313146ALower Sequencing CostsMeet the requirements of finding a large number of SSR molecular markersMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosome localisationContig
The invention discloses a method for developing genome simple sequence repeats (SSR) molecular marker. The method comprises the steps of taking two plant samples, respectively establishing banks for DNA of the samples, thereby obtaining two corresponding libraries; respectively sequencing the libraries by an Illumina sequencing technology, then carrying out micropackaging, seeking in Contigs obtained through micropackage so as to obtain the SSR of the samples, and screening the common SSR in the two samples, wherein the common SSR has the same chromosomal location and the same repetitive unit; and carrying out polymorphism screening on the two samples according to the common SSR, and judging whether the two samples are in porlymorphism according to the difference of times of the repetition of the SSR of the two samples. The method not only meets the requirement of seeking a lot of SSR molecular markers, but also has low cost; due to the advantages of high polymorphism, dominant heredity, wide distribution and few template DNA, the SSR molecular markers can be widely used in genetic diversity analysis, genetic mapping, quantitative trait loci (QTL) location, molecular marker assisted breeding and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
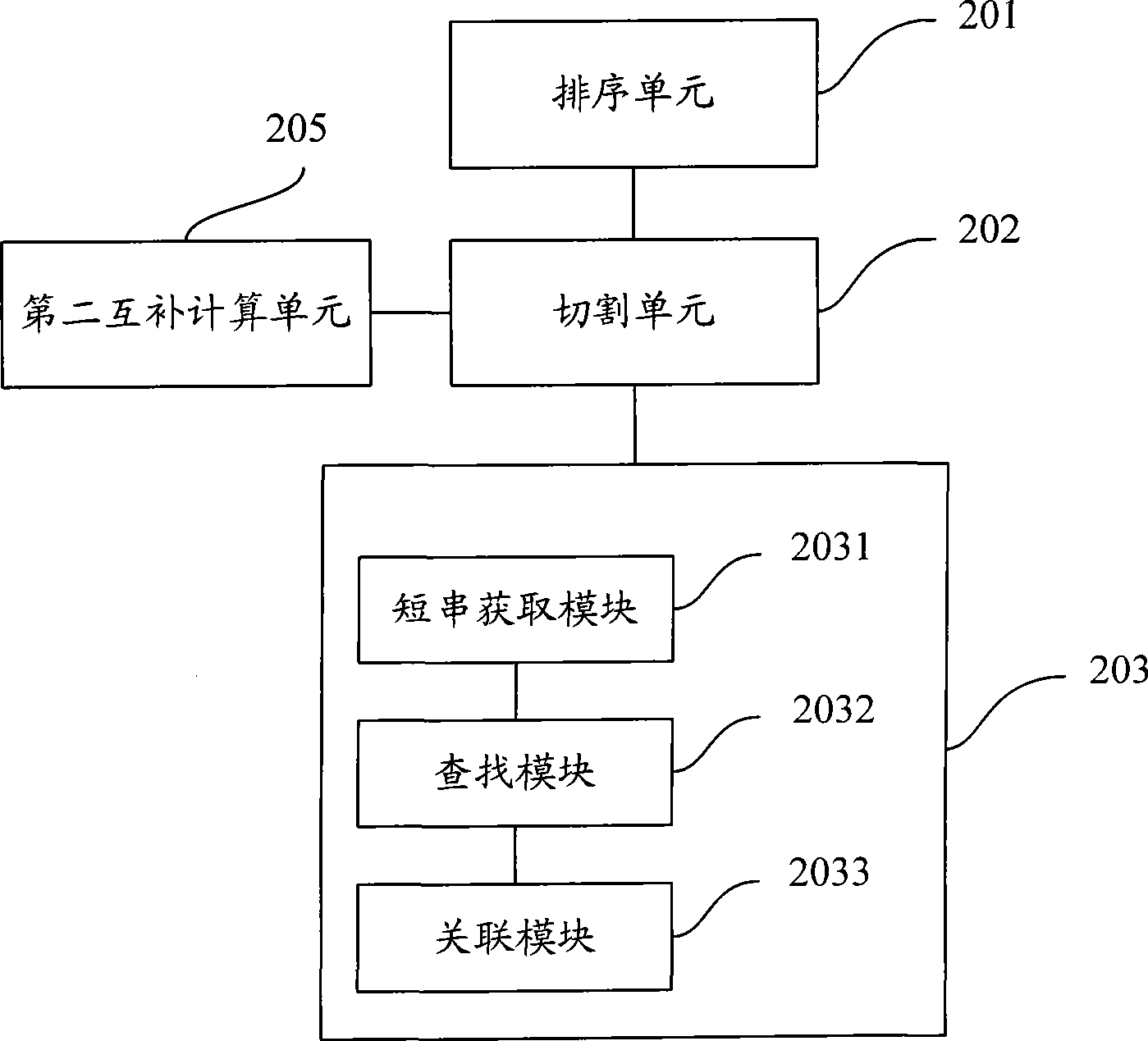
Method and system for fast processing genome short sequence mapping
ActiveCN101751517AReduce processing timeImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsContigShort string
Being applicable to the technical field of genetic engineering, the invention provides a method and a system for fast processing genome short sequence mapping, comprising the following steps: ranking sequencing sequence according to base number of short strings of preset length; cutting basic groups of sequence contig into short strings of preset length; searching corresponding sequencing sequence in ranked sequencing sequence according to base number of short strings cut from the sequence contig; then establishing mapping relation. In the invention, the sequencing sequence is ranked according to base number of short strings of preset strings and basic groups of sequence contig are cut into short strings of preset length; in addition, the corresponding sequencing sequence in ranked sequencing sequence is searched according to base number of short strings cut from the sequence contig; finally mapping relation is established; so that short sequence mapping applied to short sequence assembling is realized, processing time is short and processing efficiency is high.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Microbial data processing method for high-throughput sequencing
The invention discloses a microbial data processing method for high-throughput sequencing. According to the method, contig assembling and binning are performed on microbial 16s RNA read segments of high-throughput sequencing; microbial contigs are marked with q-PCR, so that the microbial contigs comprise marker genes; biological contigs containing the marker gene are removed, so that high-qualitymicrobial metagenomic sequencing data are obtained. Sequence clustering and other methods are adopted to identify and remove sequences from pollutants, so that the microbial metagenomic sequencing data with higher purity can be obtained, and therefore, gene expression results based on the microbial metatranscriptomic sequencing data are more accurate. The method of the invention, with the microbial metagenomic sequencing data as a research object, can improve the quality of the microbial metagenomic sequencing data based on bioinformatics ideas.
Owner:EZHOU INST OF IND TECH HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Analysis and integration method and device for sequencing of medium-short gene segment
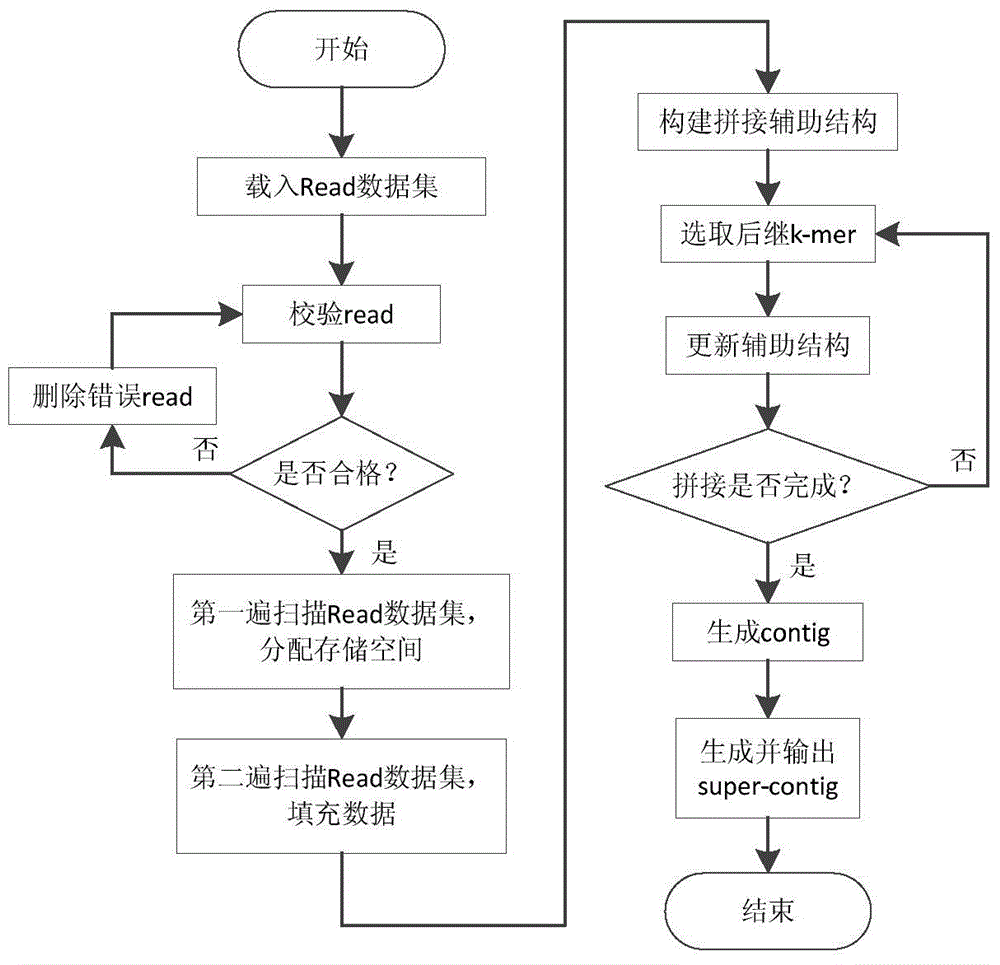
InactiveCN104965999AReduce memory consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsLongest common subsequence problemContig
The present invention provides an analysis and integration method and device for sequencing of a medium-short gene segment. The method comprises: checking a read sequence and removing gene sequences comprising errors and unreliable information; reading processed read data, analyzing the data and constructing a k-mer structure and a quad-tree structure; constructing an integration storage table and recording the progress condition of the integration process and read information which currently participates in integration; after selecting initial k-mer to start to carry out integration, continuously selecting subsequent k-mer according to an integration scoring formula, and updating the information in the integration storage table structure in real time so as to obtain contig sequences; and combining the contig sequences on the basis of a longest common subsequence method by utilizing read-pair information and generating and outputting super-contig. Aiming at the special requirements of the integration method for performance, the device provided by the present invention is of an embedded handheld structure; and by utilizing the method and the device which are provided by the present invention, analysis and integration on sequencing of the medium-short gene segment can be rapidly and accurately implemented.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
String graph assembly for polyploid genomes
PendingUS20150286775A1Avoid excessive errorIncrease chanceBiological testingSequence analysisContigTheoretical computer science
Exemplary embodiments provide methods and systems for string graph assembly of polyploid genomes. Aspects of the exemplary embodiment include receiving a string graph generated from sequence reads of at least 0.5 kb in length; identifying unitigs in the string graph and generating a unitig graph; and identifying string bundles in the unitig graph by: determining a primary contig from each of the string bundles; and determining associated contigs that contain structural variations compared to the primary contig.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Genome information assisted breeding method-breeding parent selection based on SNP clustering information and PAV variation information
InactiveCN106169034AAccurately and effectively obtainReduce workloadBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a genome information assisted breeding method for parent selection by means of SNP clustering and PAV variation. The essence of the genome information assisted breeding method is to obtain genome sequencing information of candidate parents with the help of genomic and bioinformatics methods; on one hand, a high-quality SNP data set is obtained through sequence alignment, a genetic distance matrix of the candidate parents is calculated, and the affinity between the candidate parents is judged with the help of a clustering tree; on the other hand, a Denovo assembled candidate parent contig is positioned to a reference genome, and the PAV variation of candidate parent target trait related genes is obtained according to the physical location. By combining the PAV variation and affinity information based on SNP, a parent subset is screened out from a large number of candidate parents for phenotype identification; finally, a selected breeding parent is determined by combining the phenotype identification result of the parent subset. The genome information assisted breeding method belongs to the field of rice molecular breeding, the range of the materials for phenotype identification can be effectively narrowed from the large number of the candidate parents, the workload of phenotype identification is reduced, and the breeding work efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
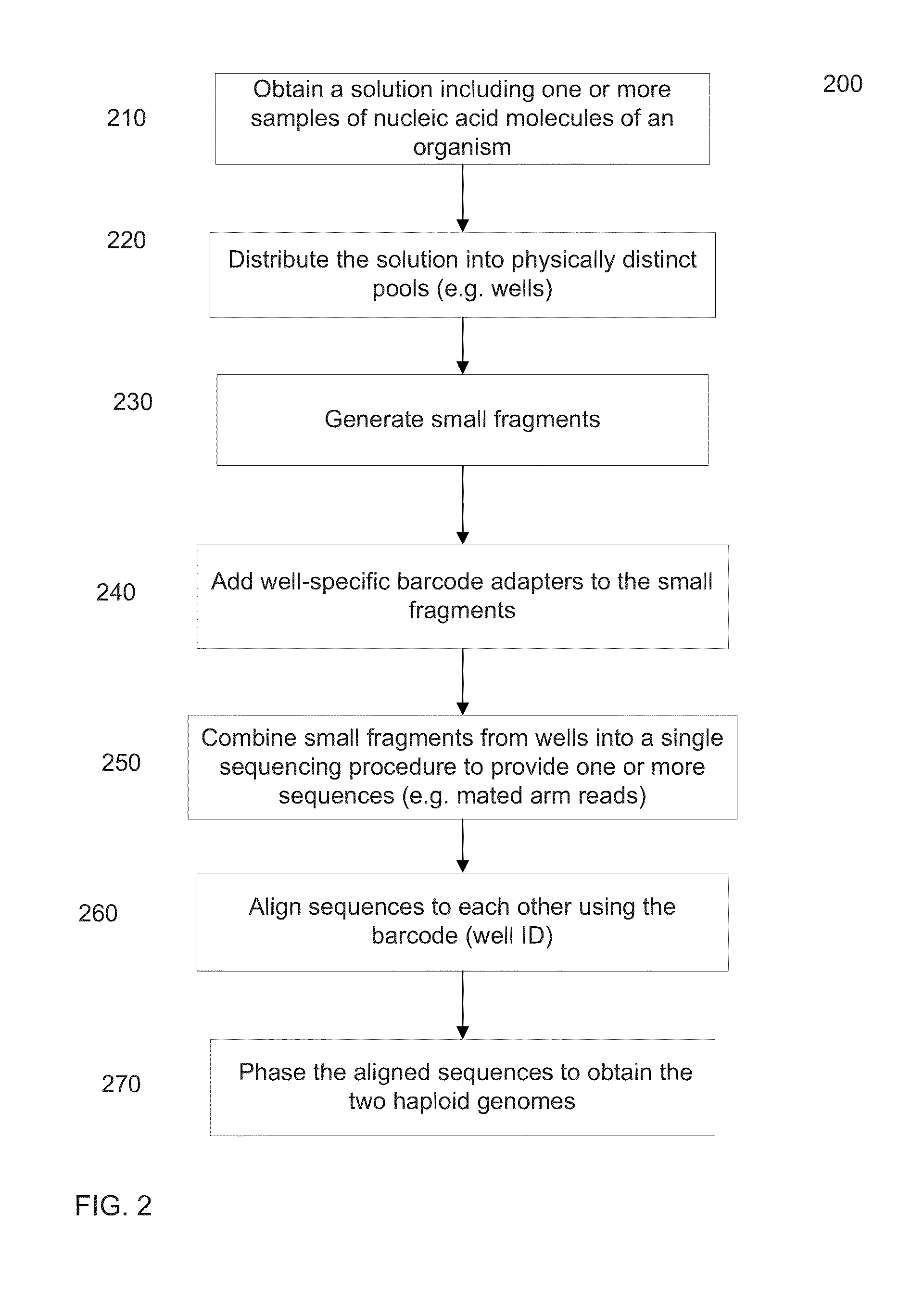
Long fragment de novo assembly using short reads
Techniques perform de novo assembly. The assembly can use labels that indicate origins of the nucleic acid molecules. For example, a representative set of labels identified from initial reads that overlap with a seed can be used. Mate pair information can be used. A sequence read that aligns to an end of a contig can lead to using the other sequence read of a mate pair, and the other sequence read can be used to determine which branch to use to extend, e.g., in an external cloud or helper contig. A kmer index can include labels indicating an origin of each of the nucleic acid molecules that include each kmer, memory addresses of the reads that correspond to each kmer in the index, and a position in each of the mate pairs that includes the kmer. Haploid seeds can also be determined using polymorphic loci identified in a population.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Method for assembling chloroplast genome sequence
InactiveCN104450682AEfficient assemblyValid verificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationContigClosed loop
The invention discloses a method for assembling a chloroplast genome sequence. According to the method, the chloroplast does not need to be separated specially; a sample is sequenced by use of a new generation sequencing technique; Reads available in mapping into a reference genome are selected according to a reference chloroplast genome sequence; the Reads obtained by screening are assembled with a plurality of kmers to construct Contigs; the sequence of the Contigs and the reference chloroplast genome sequence are compared and ranked; the assembly and ranking result of one kmer is selected as the principal result, the extension of the sequence is realized according to the ranking result; the overlay regions of the polymerous sequences at the head and the tail are combined to obtain the complete sequence of the reference assembled chloroplast genome. The method for assembling the chloroplast genome sequence has the advantages that DeNovo assembly is performed by directly utilizing NGS genome sequencing data to obtain the complete chloroplast genome sequence, effective self-assembly and verified closed loop are realized, and the quality of the assembled sequence can be evaluated and determined.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for developing endangered rhododendron molle SSR primer on basis of RAD-seq
ActiveCN104598773AEfficient methodAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsContigGenomic library
The invention provides a method for developing an endangered rhododendron molle SSR primer on the basis of RAD-seq. The method comprises the steps: establishing a rhododendron molle genomic library, acquiring 7.653G of Raw Data and 7.513G of filtered Clean data after the paired-end sequencing and subsequent treatment; clustering reads containing enzyme recognition sites by utilizing cd-hit-est clustering software, and gathering areas which are consistent in Reads2 capture when in RAD sequencing; at most mispairing three basic groups between Reads2, gathering the reads with similar RAD-tag by virtue of the sequence similarity of the Reads2, locally assembling each type of screened sequencing data by utilizing VelvetOptimiser assembling software, and selecting a best congtig to search SSR; collectively obtaining 11961 SSR fragments for designing the SSR primer after the contig is filtered; designing the SSR primer by utilizing Primer3, wherein 11687 pairs of SSR primers can be successfully designed by utilizing the method; randomly selecting 60 pairs of primers to carry out polymorphic detection for 6 parts of rhododendron molle DNAs in different geographical distribution. By adopting the method, a novel concept is provided for developing the rhododendron molle SSR primer.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
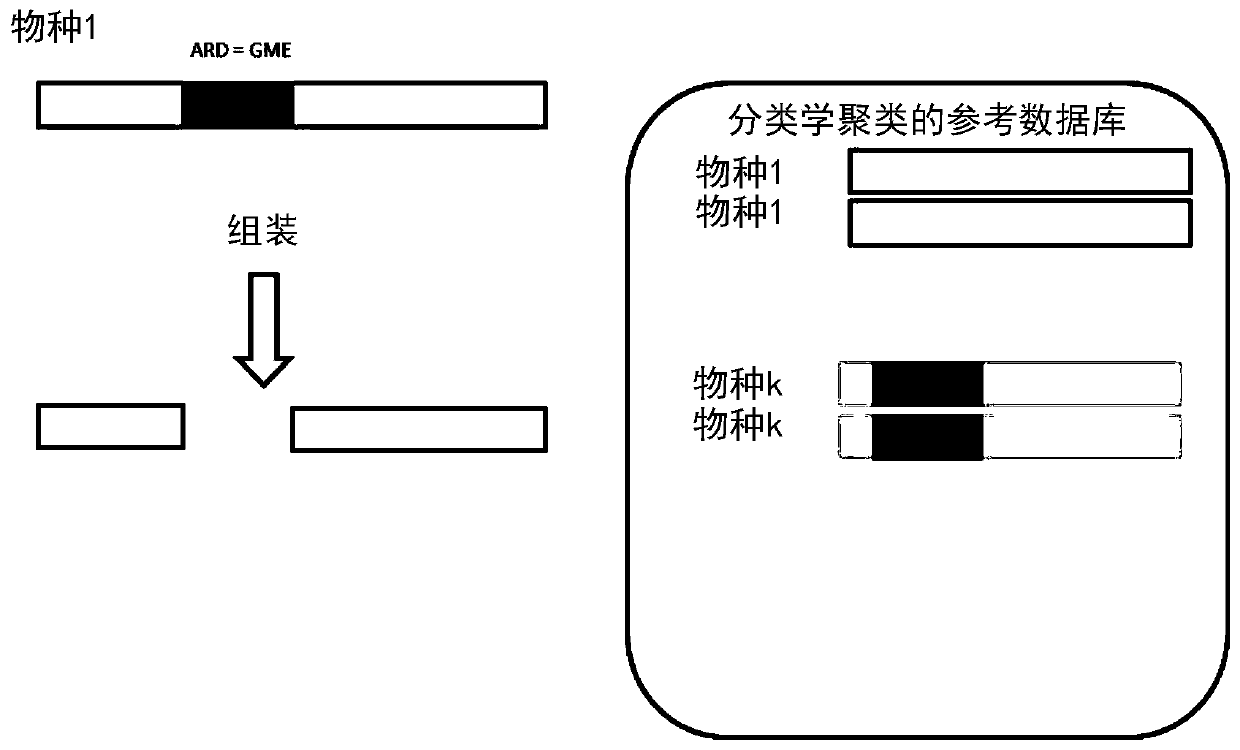
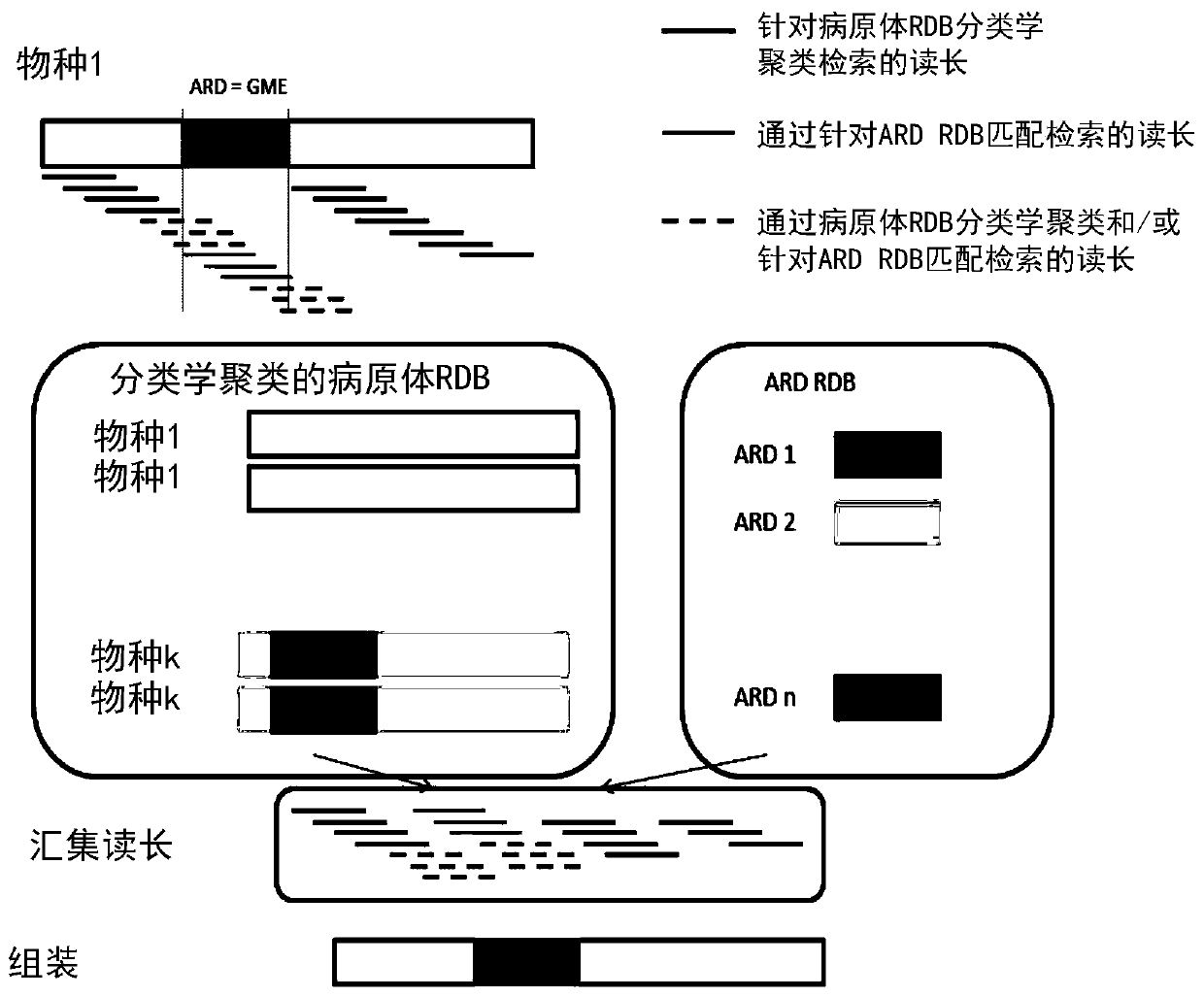
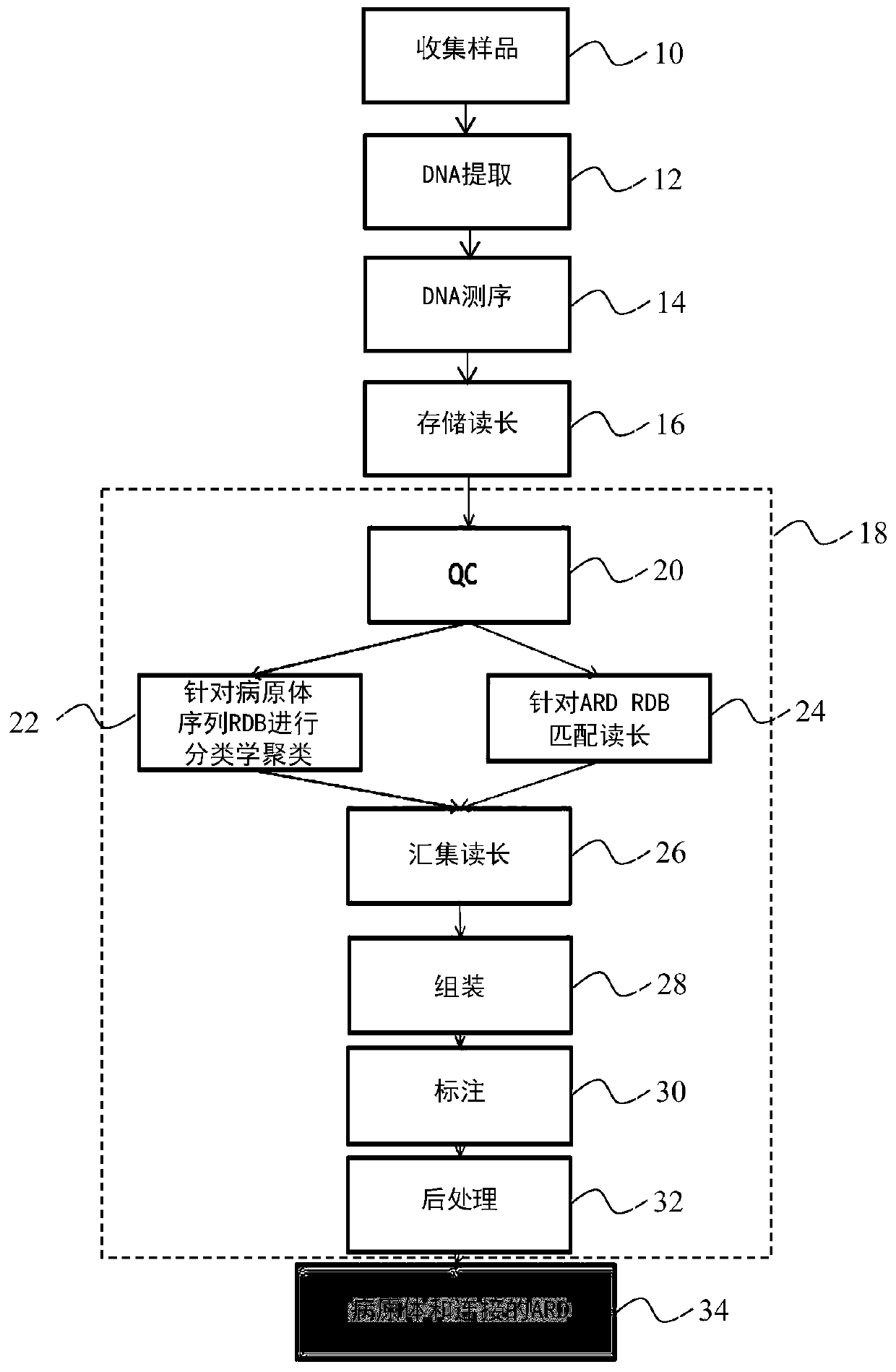
Identification and antibiotic characterization of pathogens in metagenomic sample
A method for identifying a pathogen contained in a metagenomic sample and for identifying pathogenic markers in the genome of said pathogen comprises: processing (12) the sample to extract DNA from pathogens, sequencing (14) the extracted DNA, thereby producing a set of reads, comparing (22) the set of reads to a database of genomes of known pathogens in order to assign reads to said pathogens; producing (26) a pool of reads comprising the reads assigned to a pathogen and assembling (28) the pooled reads to produce contigs, comparing (30) the contigs to a second database of markers to check whether the produced contigs contain a marker, The method further comprise the step of comparing (24) the reads to the second database to assign reads to the markers, a read being assigned to a marker if it falls entirely into said marker or if it is astride said marker, and the pool also comprises the reads assigned to the markers, the contigs being thereby being assembled from reads assigned to apathogen and reads assigned to the markers.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
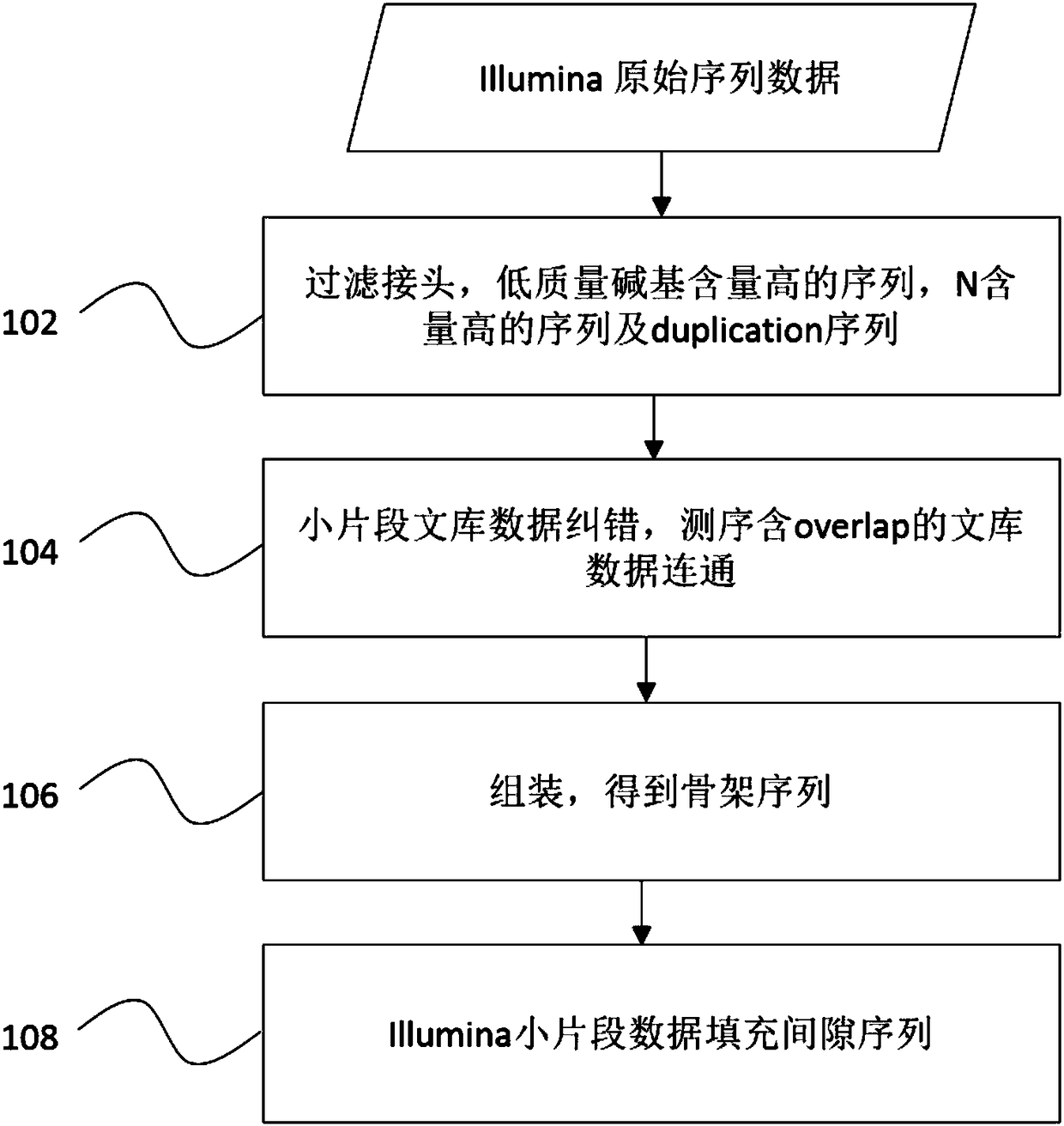
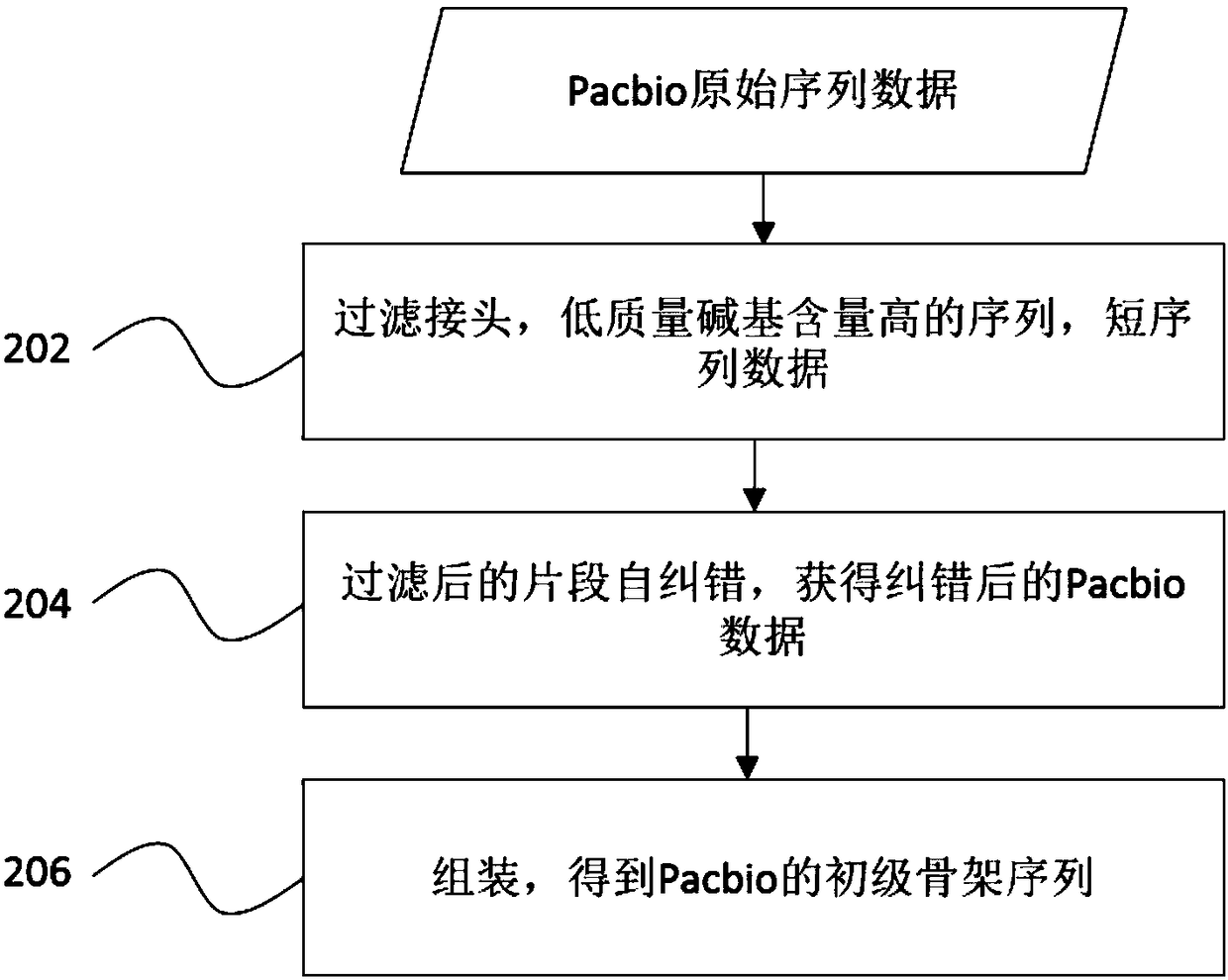
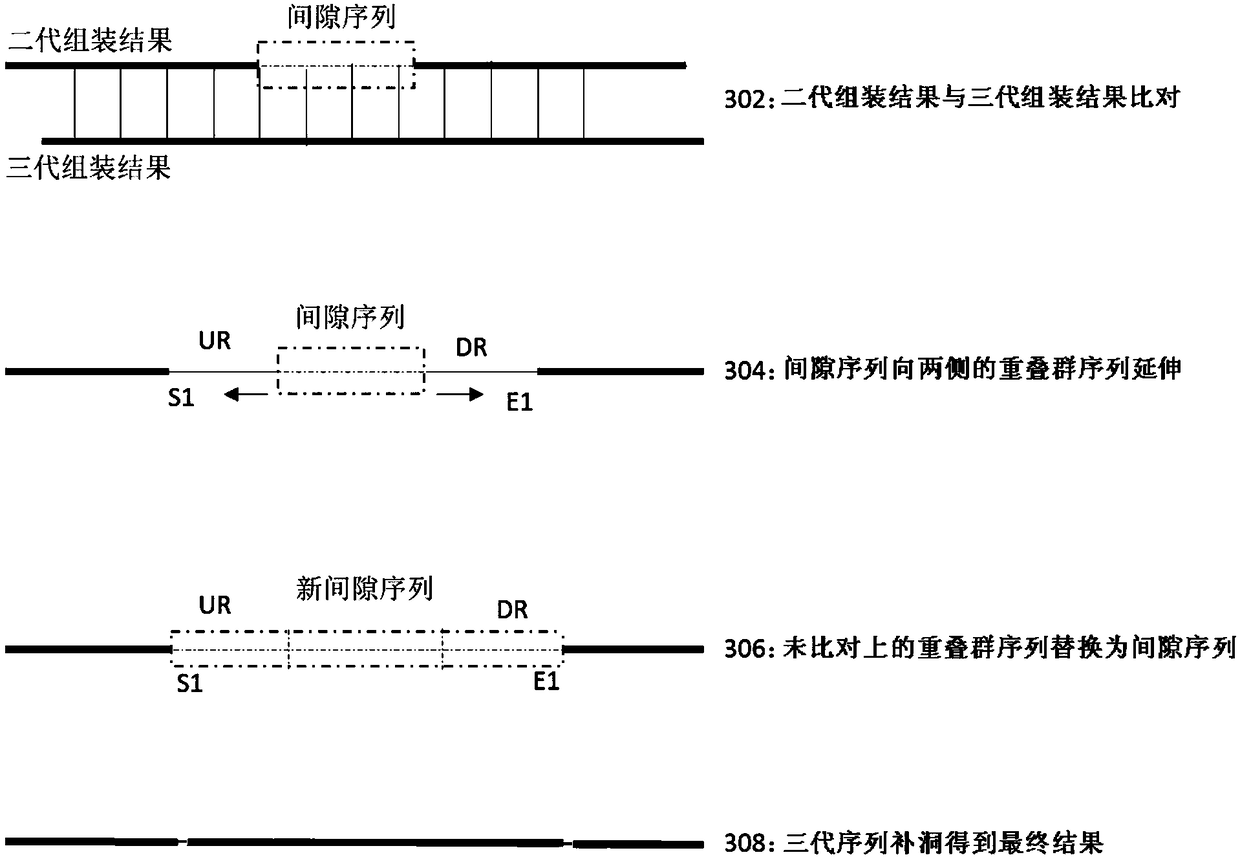
Method and devices of using third-generation sequence to optimize second-generation assembly result
ActiveCN108460245AImprove accuracyImprove integrityHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsContigComputer science
The invention discloses a method and devices of using a third-generation sequence to optimize a second-generation assembly result. The method includes: obtaining the second-generation assembly resultand a third-generation assembly result; using the third-generation assembly result as a reference sequence, and aligning the second-generation assembly result to the reference sequence; obtaining sequences which are in contig sequences of both sides of gap sequences of the second-generation assembly result and are aligned or not aligned to the reference sequence; substituting for gap sequences bysequences, which are not aligned to the reference sequence, to obtain the new gap sequences; and using third-generation data to carry out hole filling on the new gap sequences to obtain an optimized second-generation assembly result. The method can improve accuracy of genome assembly indicators and splicing.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
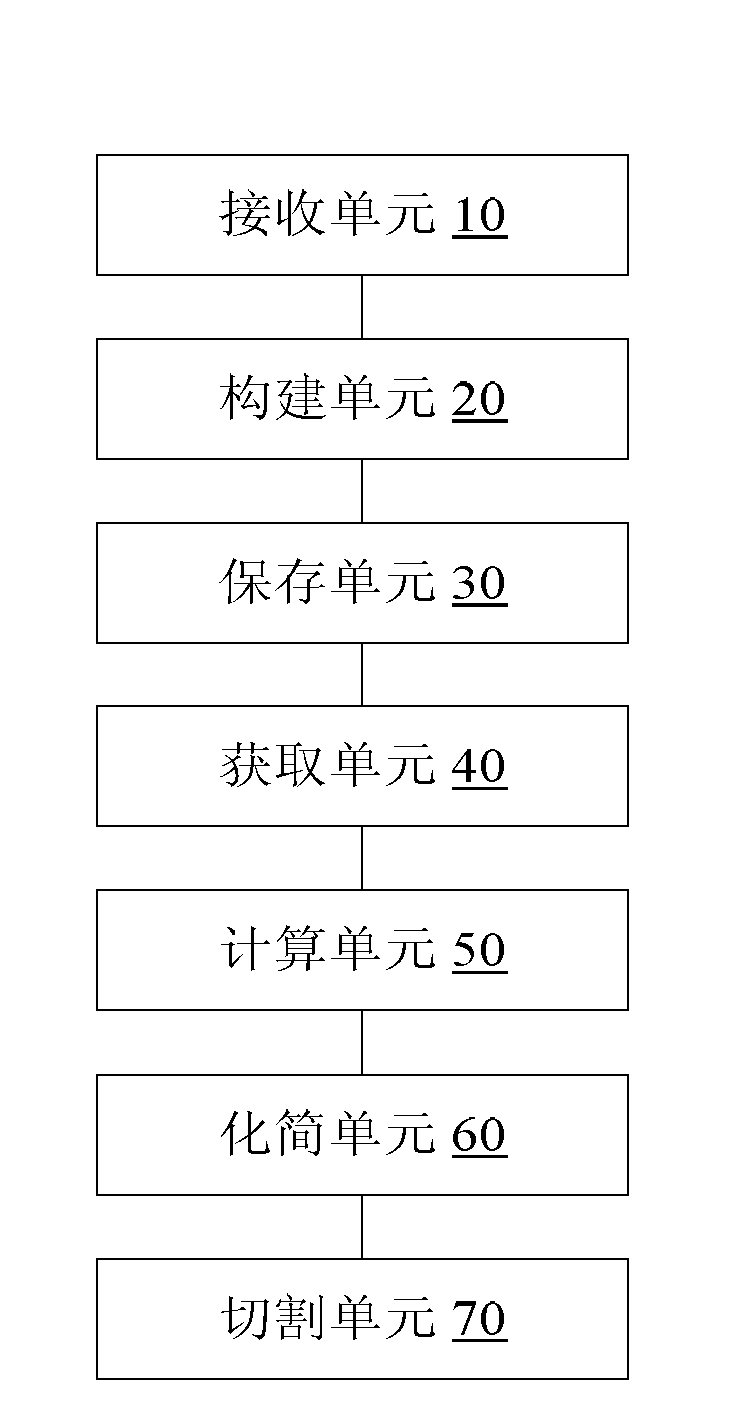
Method and device for processing gene sequence data
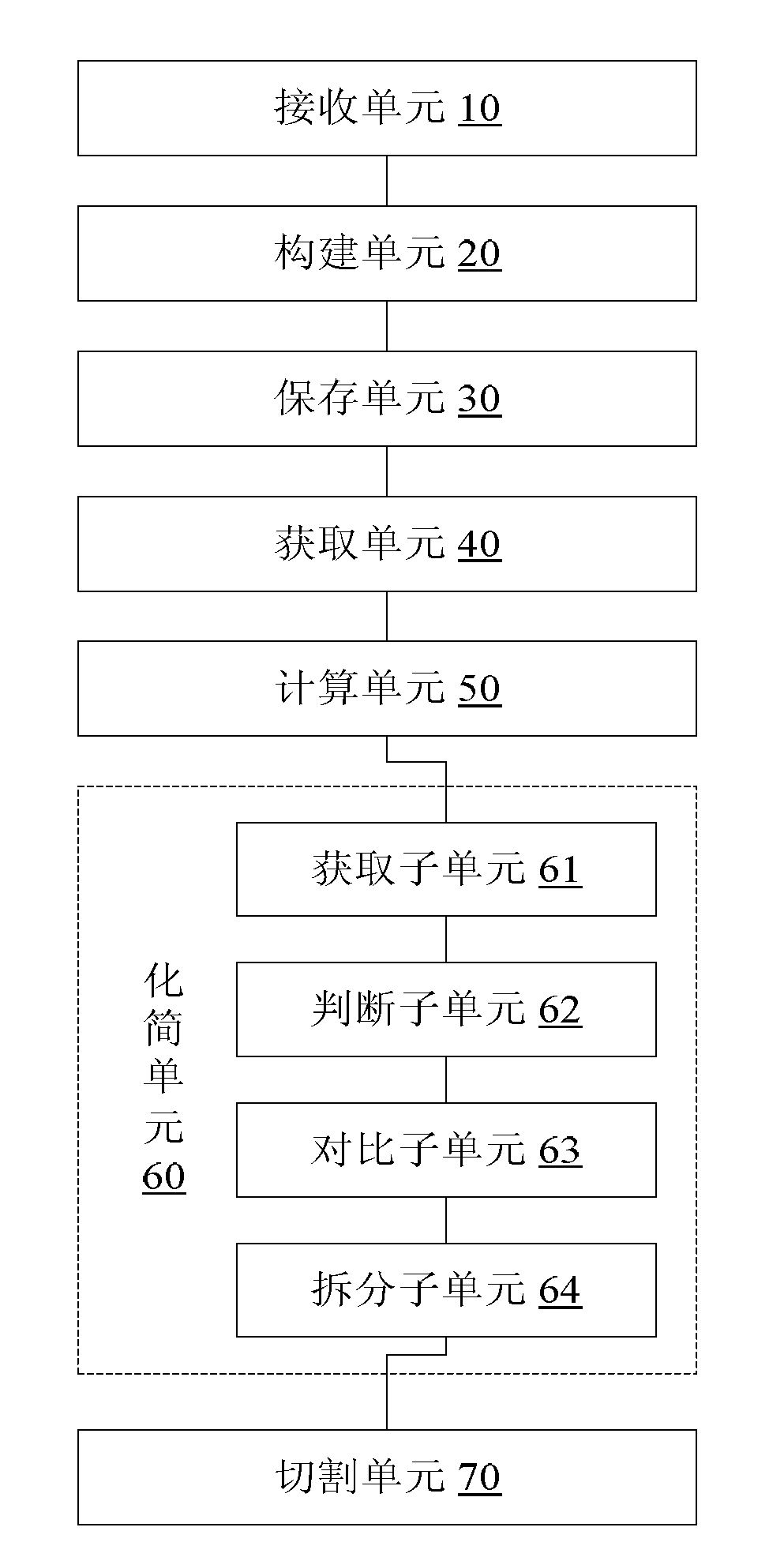
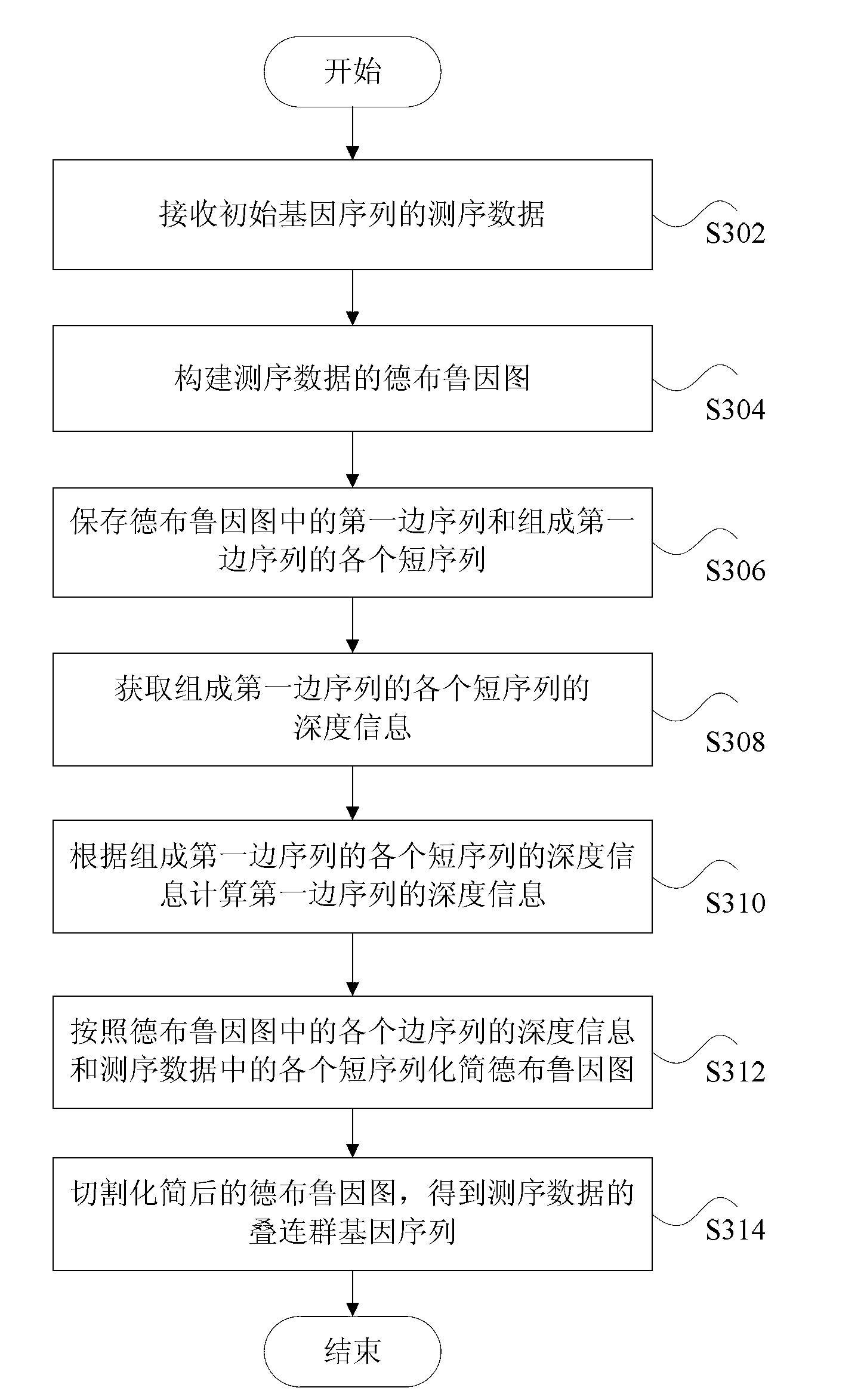
ActiveCN102841987AReduce the degree of deviation from the genetic sequence of the organism itselfAvoid lostSpecial data processing applicationsProcessed GenesContig
The invention discloses a method and a device for processing gene sequence data. The method for processing the gene sequence data comprises the steps of: receiving a sequencing data of an initial gene sequence; building a de Brujin graph of the sequencing data; storing a first edge sequence in the de Brujin graph and each short sequence for forming the first edge sequence; obtaining depth information of each short sequence for forming the first edge sequence; calculating the depth information of the first edge sequence according to the depth information of each short sequence for forming the first edge sequence; and simplifying the de Brujin graph according to the depth information of each edge sequence in the de Brujin graph and each short sequence in the sequencing data, and cutting the simplified de Brujin graph to obtain a contig gene sequence of the sequencing data. By the method and device, the problem of biological information loss easily caused by the method for processing the gene sequence data in the prior art is solved, so as to achieve the effect of improving the assembling availability of the gene sequence.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
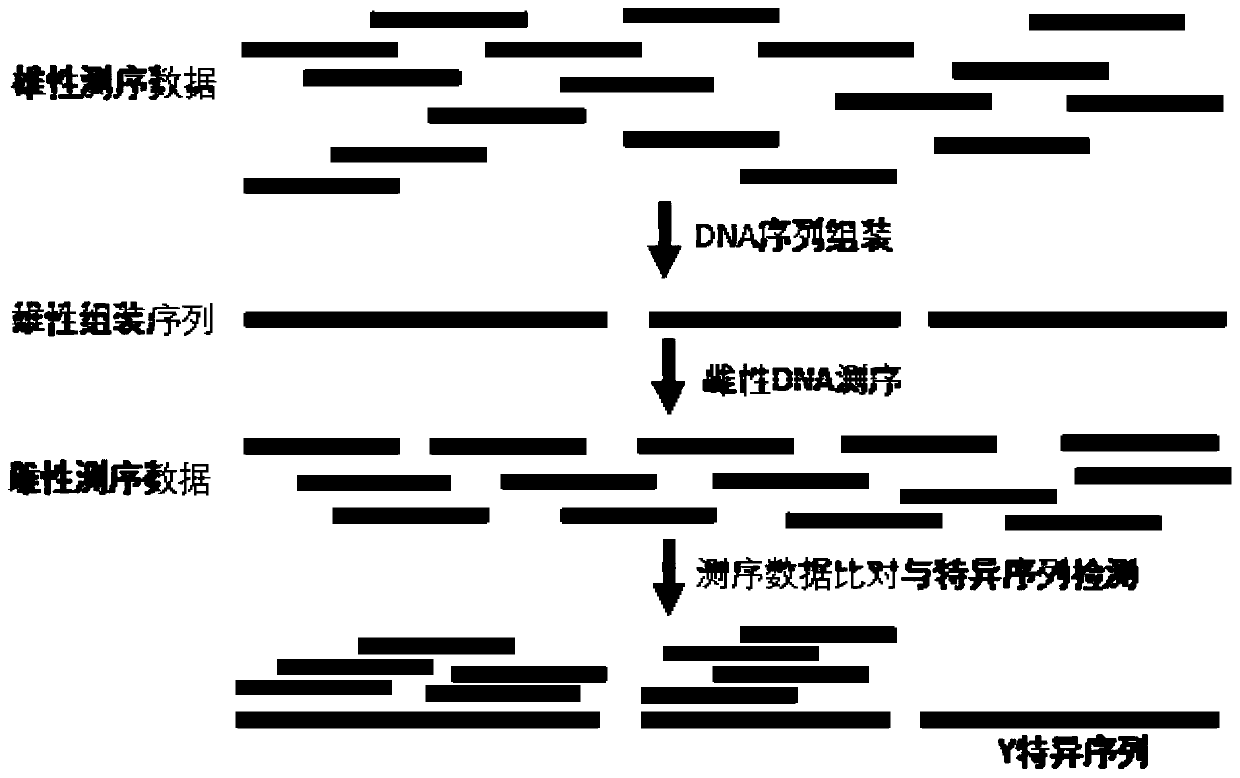
Siniperca chuatsi male molecular marker primers and application thereof
ActiveCN110777210AQuick filterRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyContig
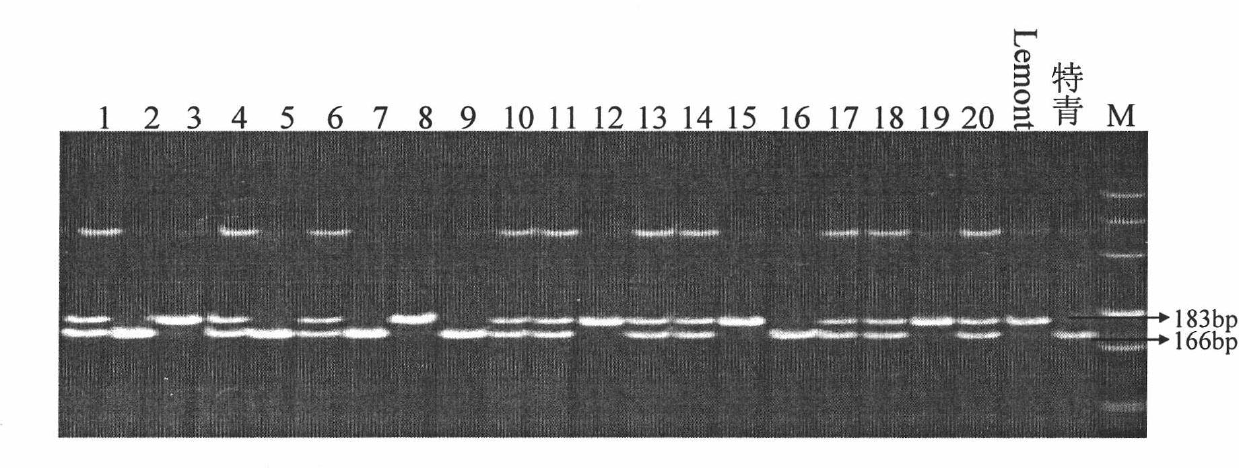
The invention provides siniperca chuatsi male molecular marker primers. The primers at least comprise one of a primer pair 1 and a primer pair 2, wherein the primer pair 1 comprises a Contig-1 upstream primer and a Contig-1 downstream primer, and the primer pair 2 comprises a Contig-2 upstream primer and a Contig-2 downstream primer; the nucleotide sequence of the Contig-1 upstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the nucleotide sequence of the Contig-1 downstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, the nucleotide sequence of the Contig-2 upstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, and thenucleotide sequence of the Contig-2 downstream primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. The primers can be used for quickly and accurately identifying the sex of siniperca chuatsi. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a method for identifying the sex of the siniperca chuatsi, and the method is short in consumed time and high in efficiency.
Owner:广东梁氏水产种业有限公司
Closely linked molecular marker for novel gene (SS2) of rice sink source
InactiveCN102433334AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEarly generationAgricultural science
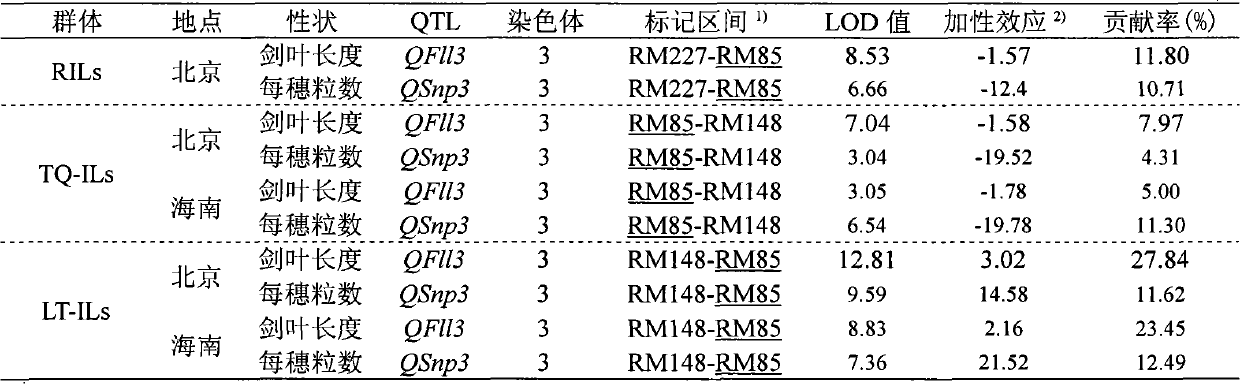
The invention relates to a closely linked molecular marker for a novel gene (SS2) of a rice sink source and belongs to the fields of super-high-yield breeding of rice and molecular genetics. The invention aims at constructing a set of contig system of a target segment by using an F2 secondary separation group constructed by selfing a near-isogenic line carrying an SS2 heterozygous segment as a testing piece according to the linked separation rule; high-precision linked analysis for a target gene is carried out by combining with a phenotype; after two-point repeated identification for two years, the SS2 is finally and finely positioned in an interval of 104Kb on the 3rd chromosome, and a molecular marker SL14 based on a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) closely linked with the SS2 is obtained. The closely linked molecular marker disclosed by the invention is applied to super-high-yield breeding of the rice, so that a genotype individium for simultaneously influencing the sink (the numberof grain per ear) and source (the length of sword leaves) characters can be quickly and accurately identified; the early generation selection of a breeding material is carried out; and the progress of the super-high-yield breeding of the rice is accelerated.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com