Identification and antibiotic characterization of pathogens in metagenomic sample
A metagenomics, pathogen technology, applied in the field of metagenomics, which can solve problems such as misleading clinicians and failing to characterize pathogen antibiotic susceptibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
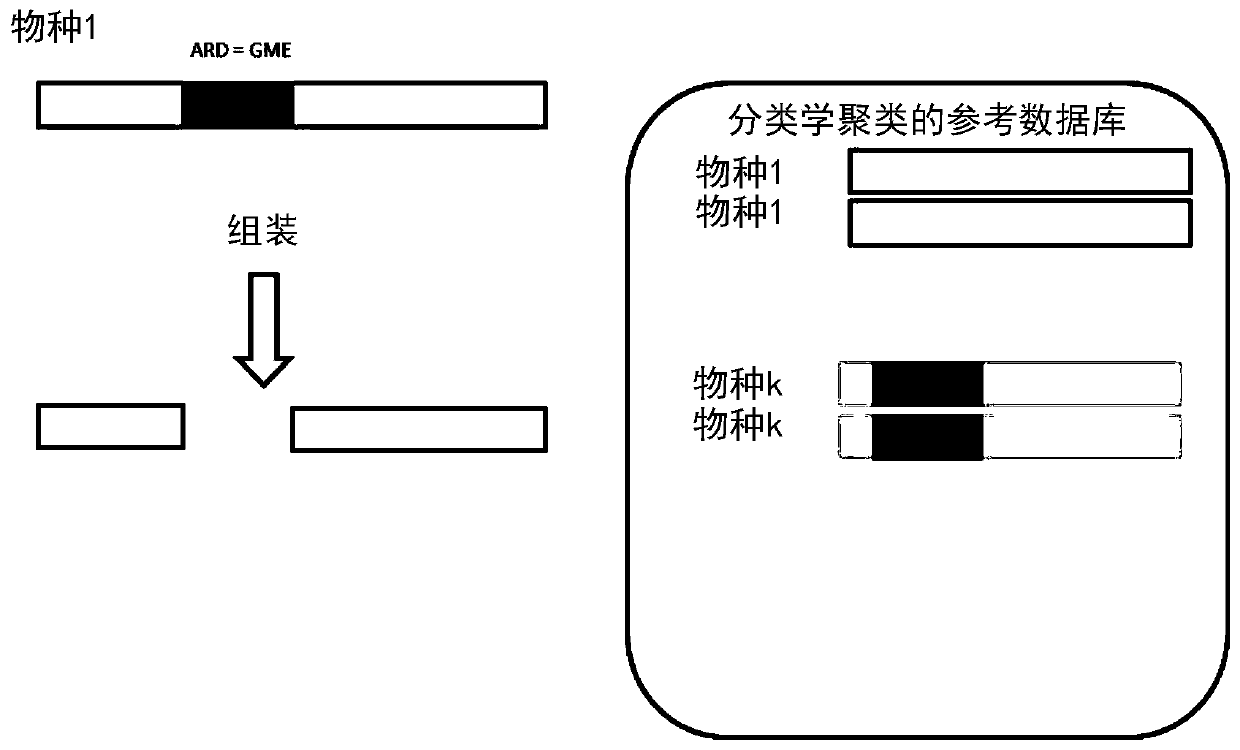
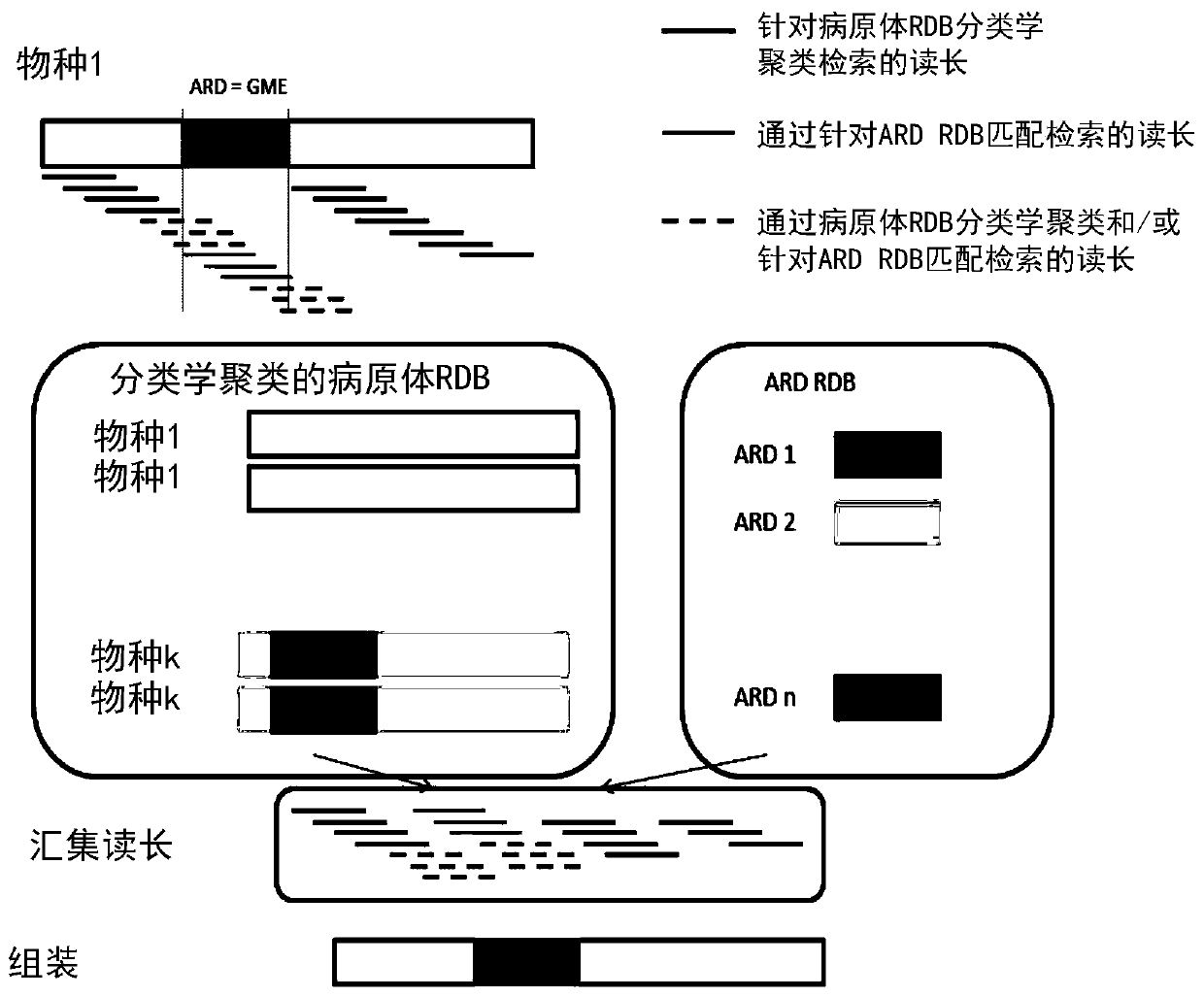
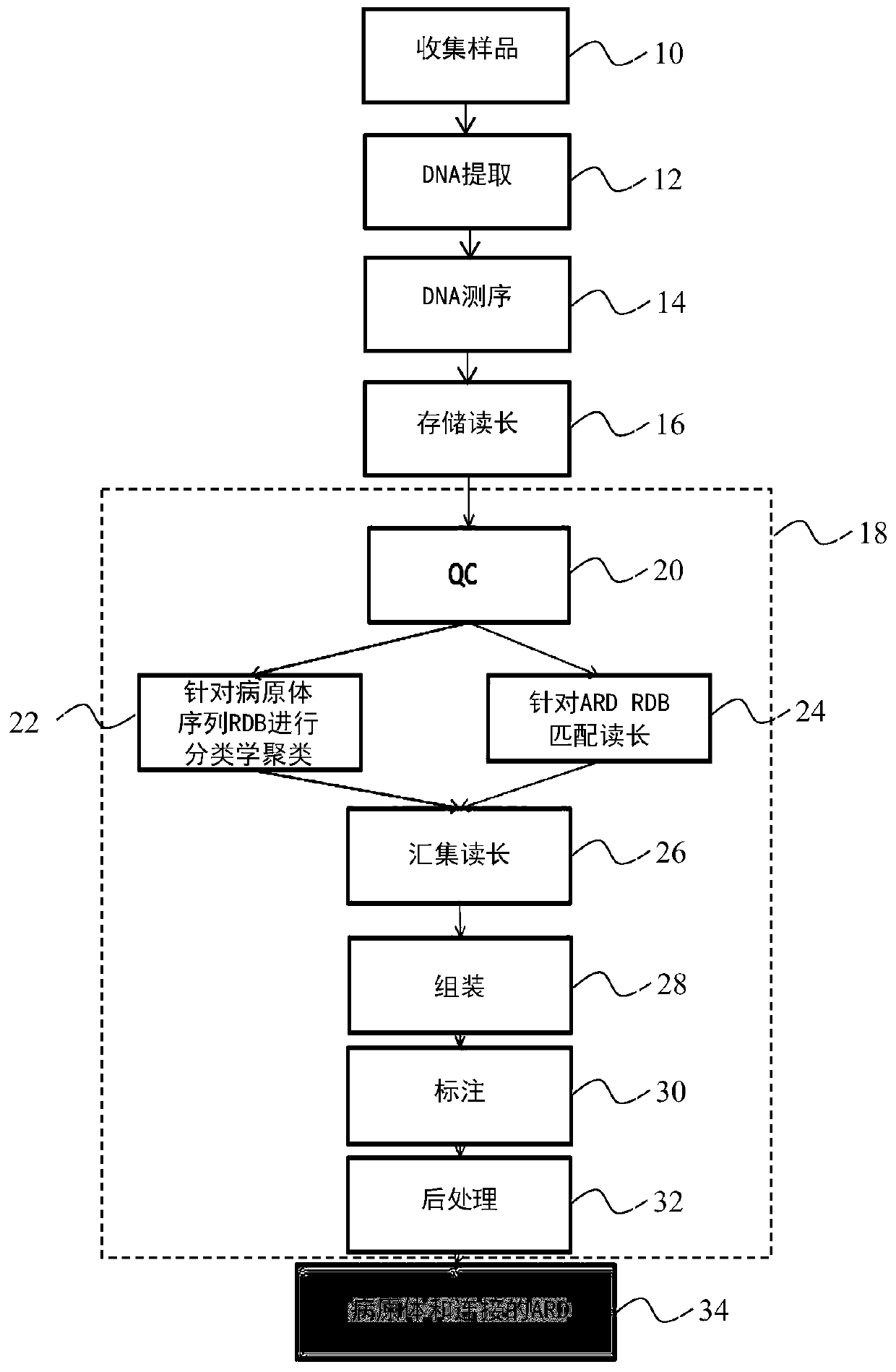
[0065] Embodiments of the invention are now described in connection with the characterization of pathogens contained in (small) bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) of intensive care unit (ICU) patients, in particular respiratory acquired pneumonia (VAP). The goal is to list all pathogens present in the sample, along with antibiotic resistance determinants and, if possible, associate ARDs with pathogens.
[0066] refer to image 3 , a BAL sample is collected from a patient at 10 and then processed at 12 to extract nucleic acid from pathogens contained in the sample. This preparation in turn includes, for example, the following:
[0067] - a host cell removal step by means of a saponin preparation, as described in document US 2015 / 0337362;
[0068] - a lysis step, such as mechanical, enzymatic or osmotic lysis, which disrupts the membranes of the cells in the sample, thereby releasing their acidic nucleic acid content, destroys proteins by adding proteases and destroys RNA by adding ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com