Patents
Literature
229 results about "Genomic library" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
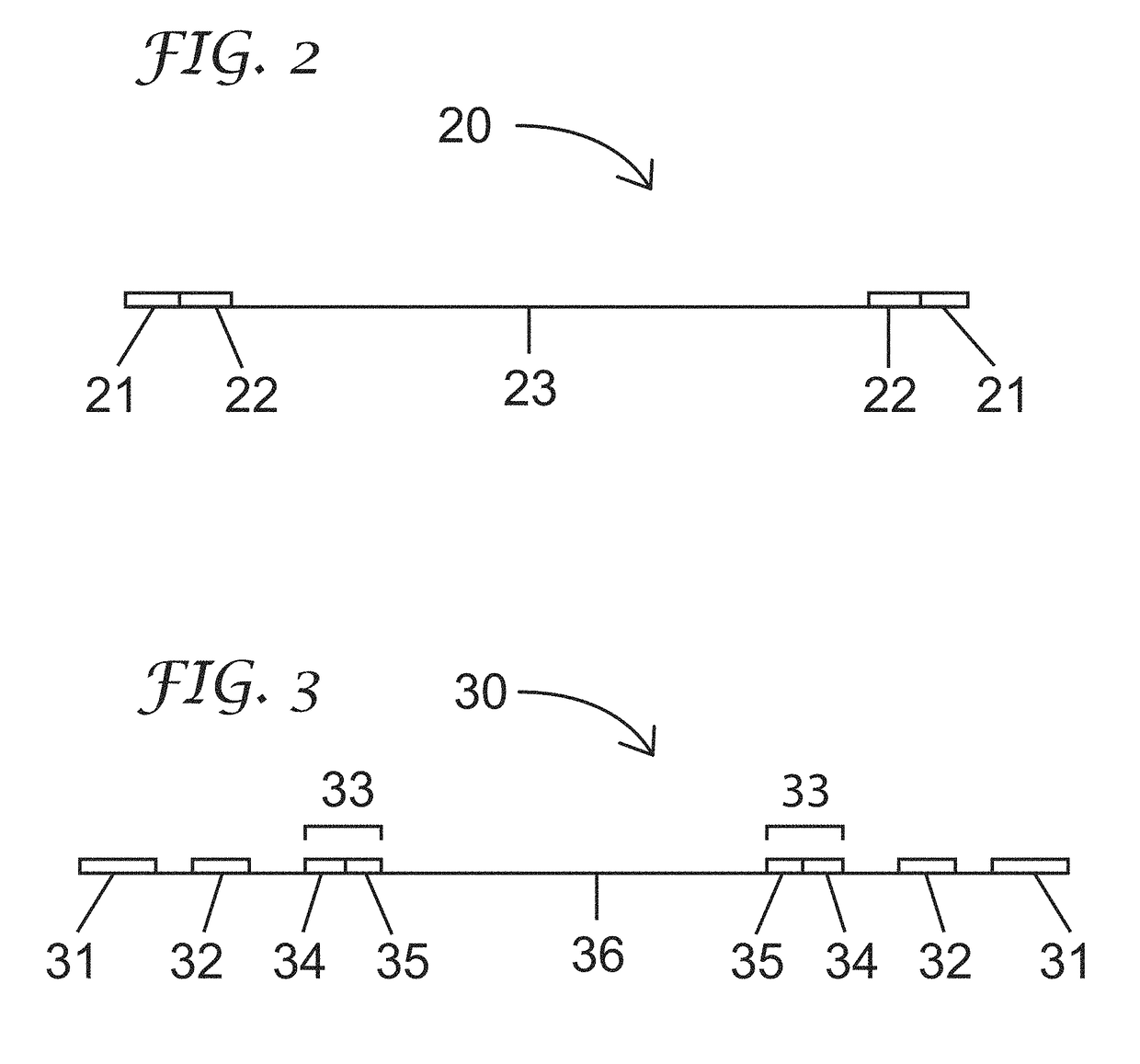
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.
Genomic library construction
InactiveUS7985546B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic libraryNucleic acid sequencing
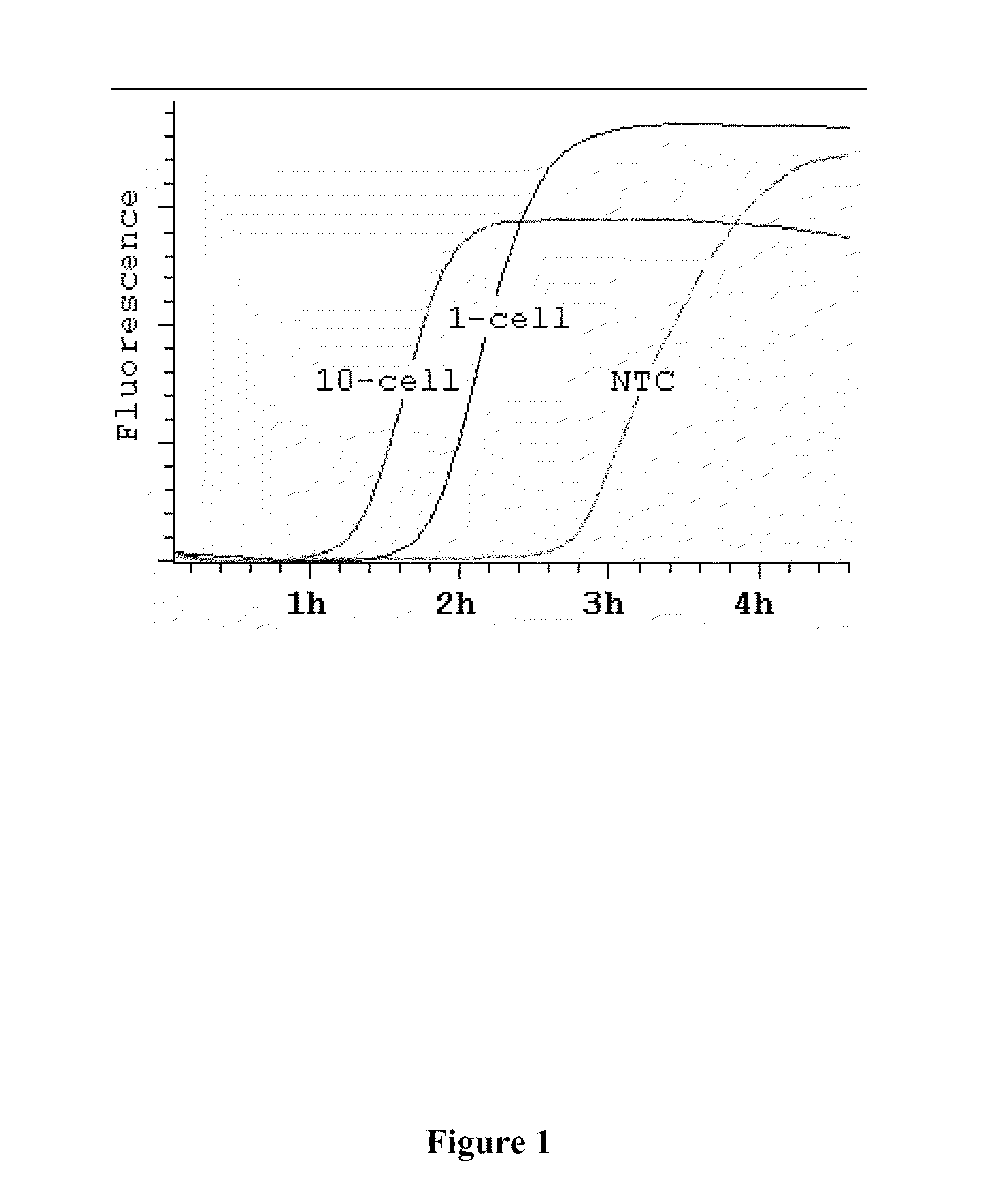
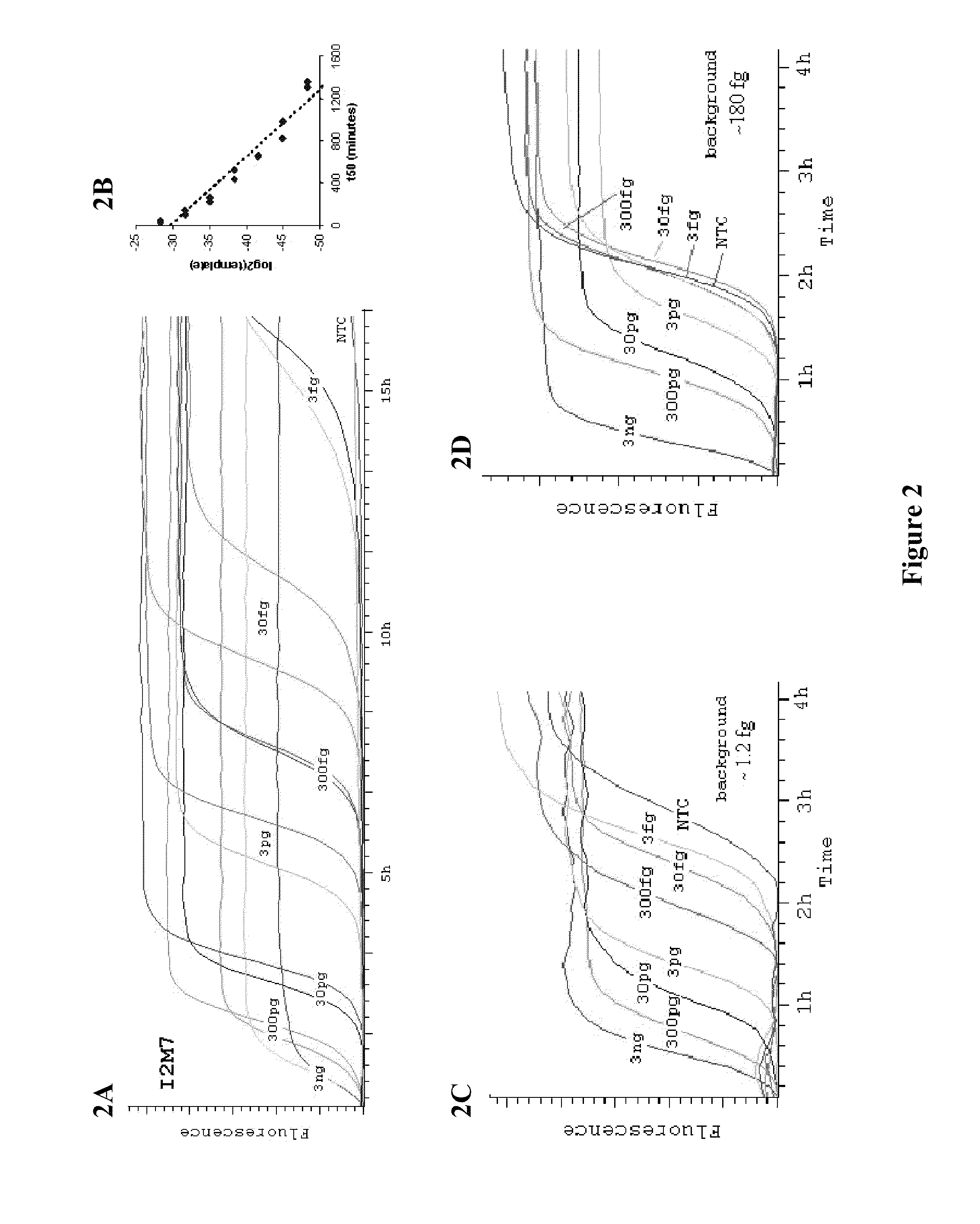
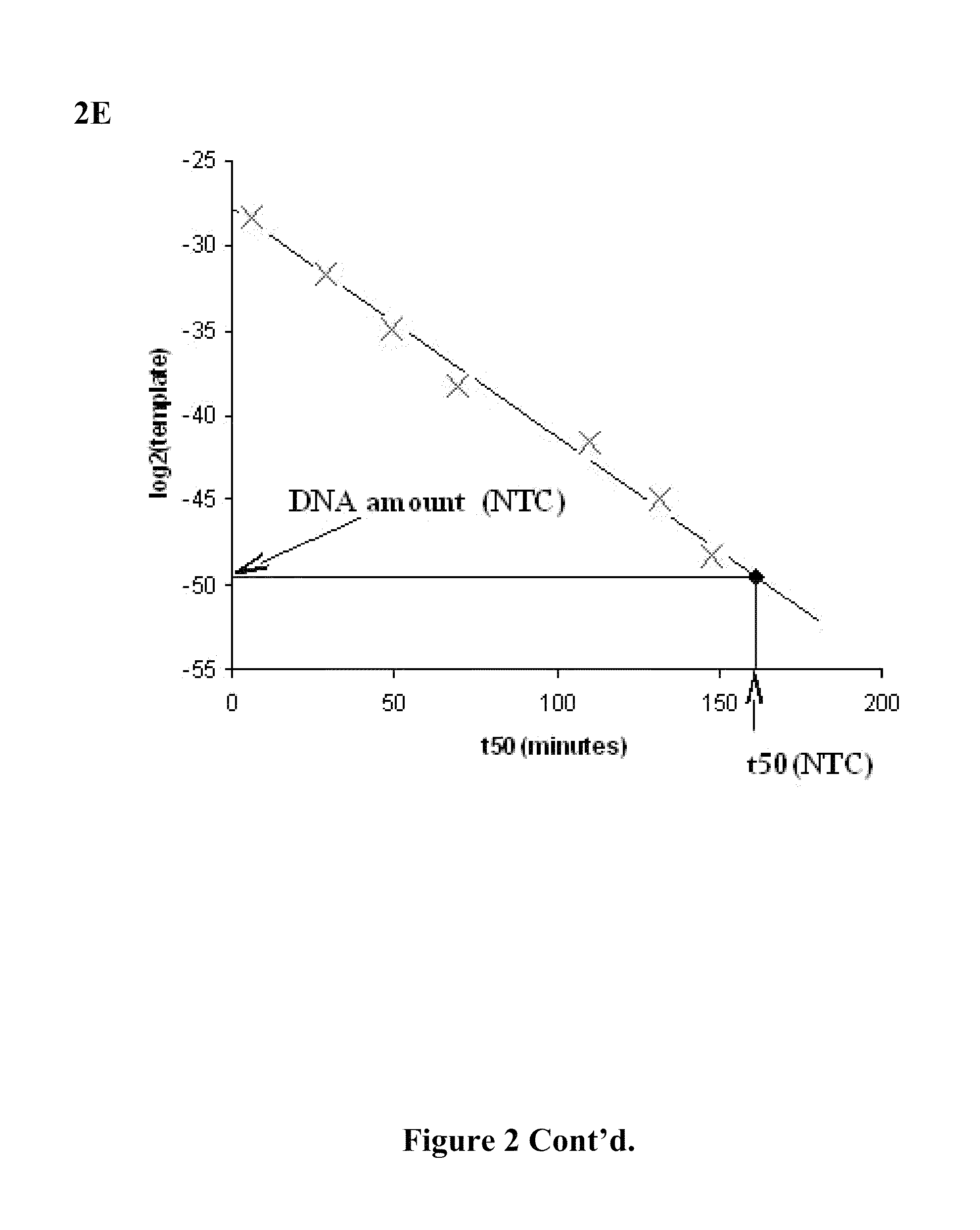
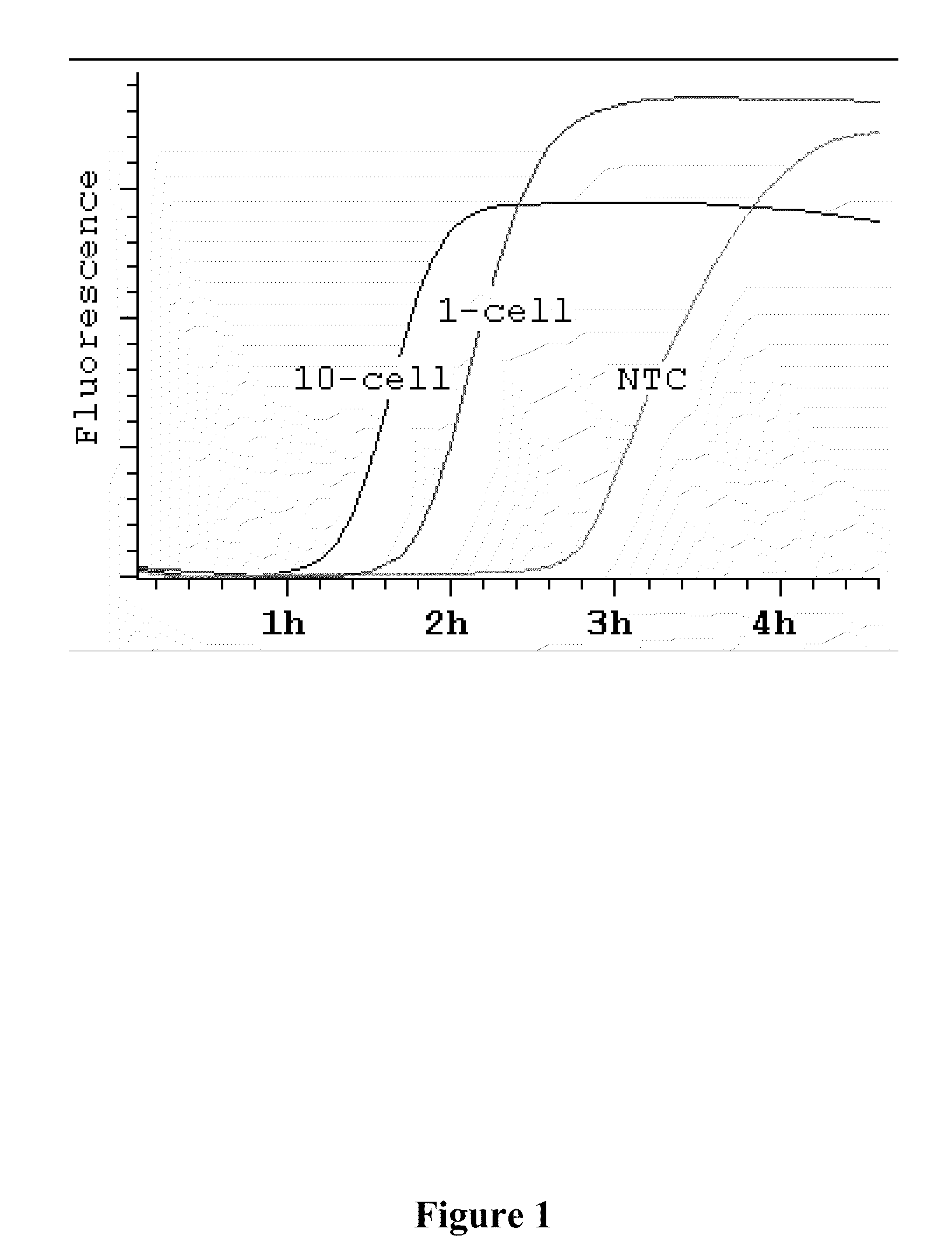
Compositions and methods for amplifying nucleic acid sequences from a single cell are provided. Compositions and methods for constructing a genomic library from a single cell are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Genomic library construction
InactiveUS20090137407A1Eliminate structureReduce presenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingGenomic library
Compositions and methods for amplifying nucleic acid sequences from a single cell are provided. Compositions and methods for constructing a genomic library from a single cell are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
De novo synthesized gene libraries
ActiveUS20160089651A1Less errorHigh surface energySequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic libraryDe novo synthesis
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
Functional genomics using crispr-cas systems, compositions, methods, screens and applications thereof
ActiveUS20160251648A1Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesStable introduction of DNAScreening processGenome scaleGenomics
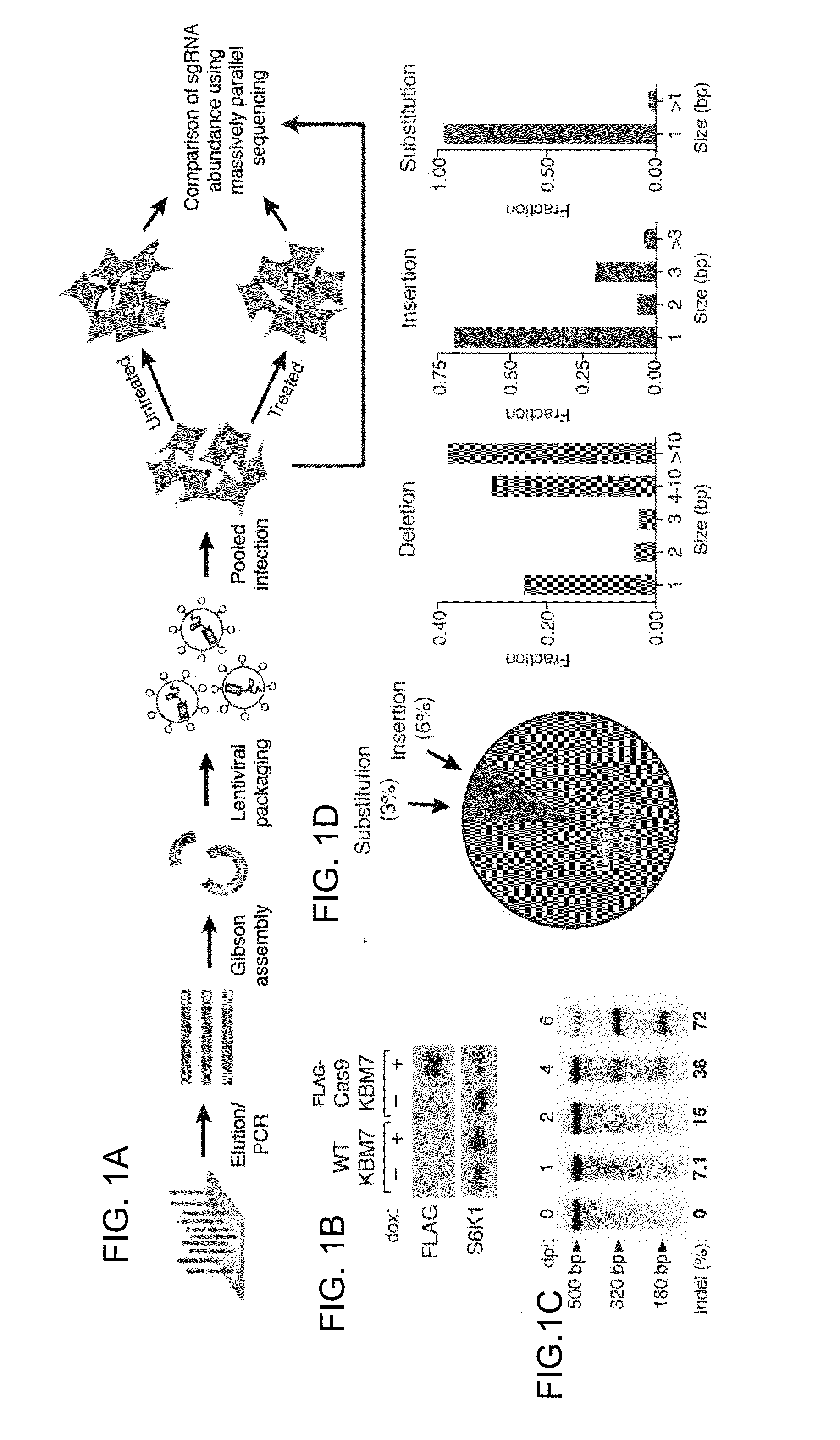
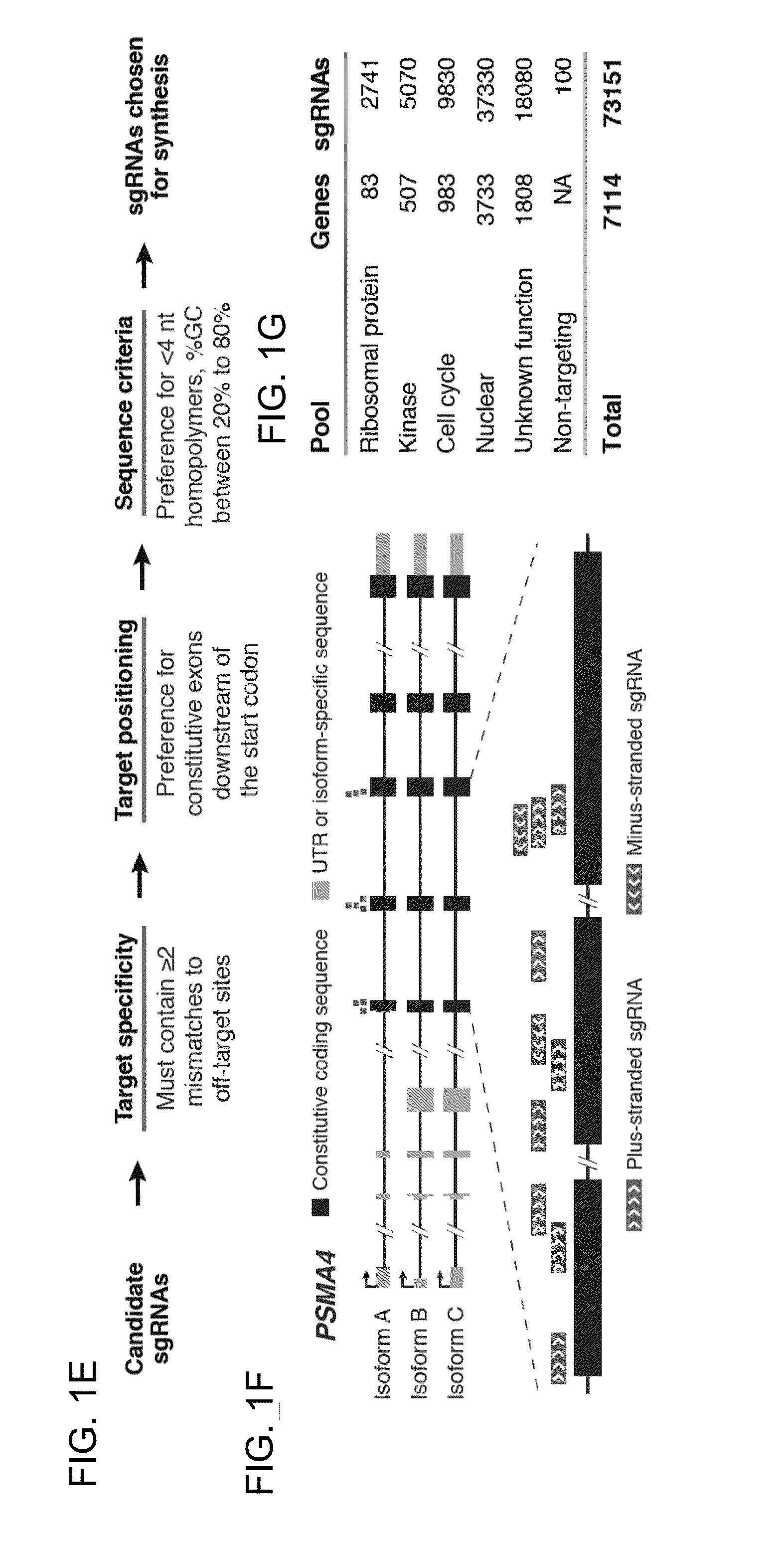
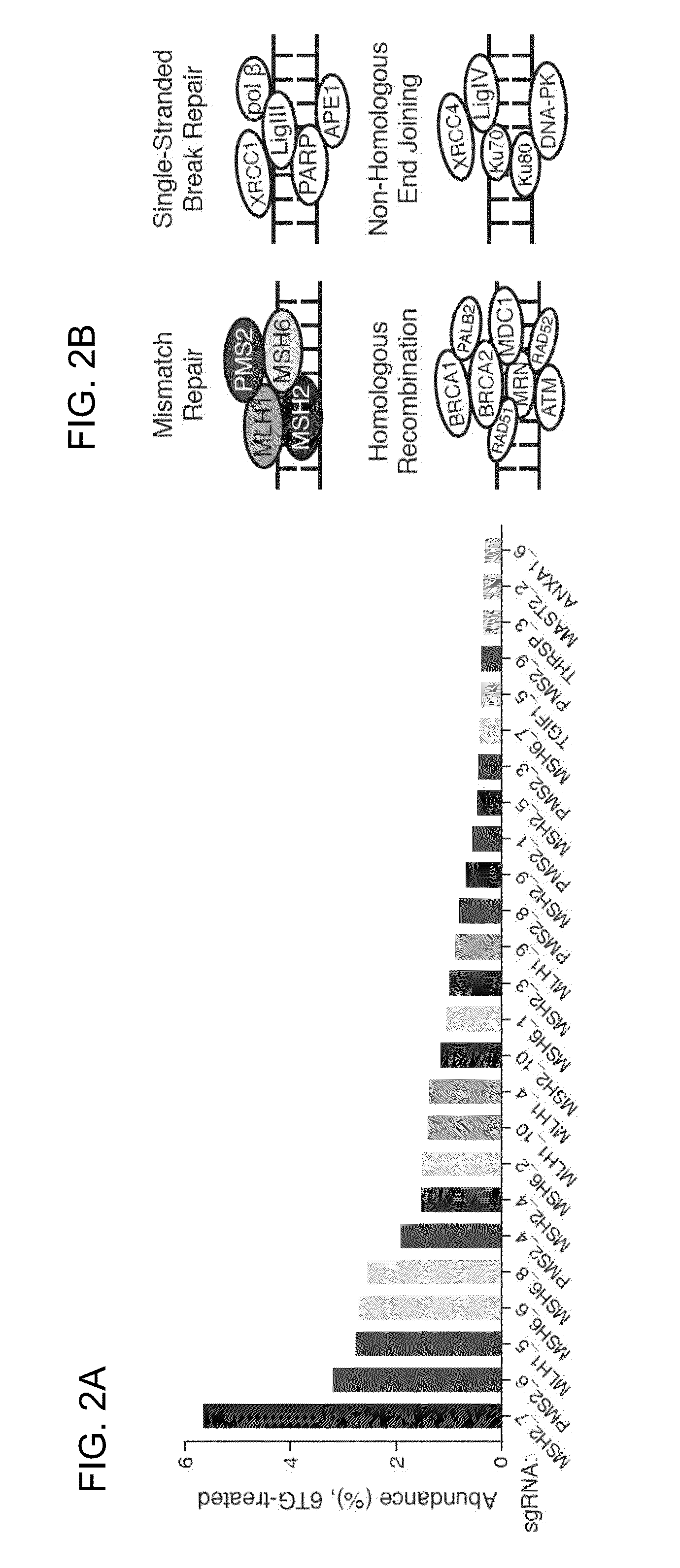
The present invention generally relates to libraries, kits, methods, applications and screens used in functional genomics that focus on gene function in a cell and that may use vector systems and other aspects related to Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems and components thereof. The present invention also relates to rules for making potent single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for use in CRISPR-Cas systems. Provided are genomic libraries and genome wide libraries, kits, methods of knocking out in parallel every gene in the genome, methods of selecting individual cell knock outs that survive under a selective pressure, methods of identifying the genetic basis of one or more medical symptoms exhibited by a patient, and methods for designing a genome-scale sgRNA library.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Kit for separating genome DNA by using magnetic balls and application thereof
InactiveCN101792757AIncrease productionHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadPhenol
The invention provides a kit for separating genome DNA by using magnetic balls and application thereof. The kit comprises magnetic balls, a magnetic frame, a genome DNA extraction reagent (lysing solution, binding solution, rinsing solution A, rinsing solution B and eluent) and specifications; the main steps of extracting the gene DNA comprise cell lysis, nucleic acid absorption, impurity removing and nucleic acid elution. The application of the kit for extracting the genome DNA does not need to use large-toxicity organic solvents of phenol, chloroform and the like, has good safety, and simple, fast and time-saving operation, and simultaneously can extract a plurality of samples. The kit can extract the genome DNA from materials of animals, plants, bacteria, fungus, blood, virus, animal source feed stuff, samples in the forensic medicine and the like, the DNA has high yield and purity, and the obtained genome DNA can be used for experiments such as PCR amplification, gene cloning, construction of genomic library, sequence measurement, molecular hybridization, molecular marking and the like. The kit can be stored at the temperature of 4 DEG C, also can be placed at room temperature, and is convenient to transport.
Owner:上海鼎国生物技术有限公司
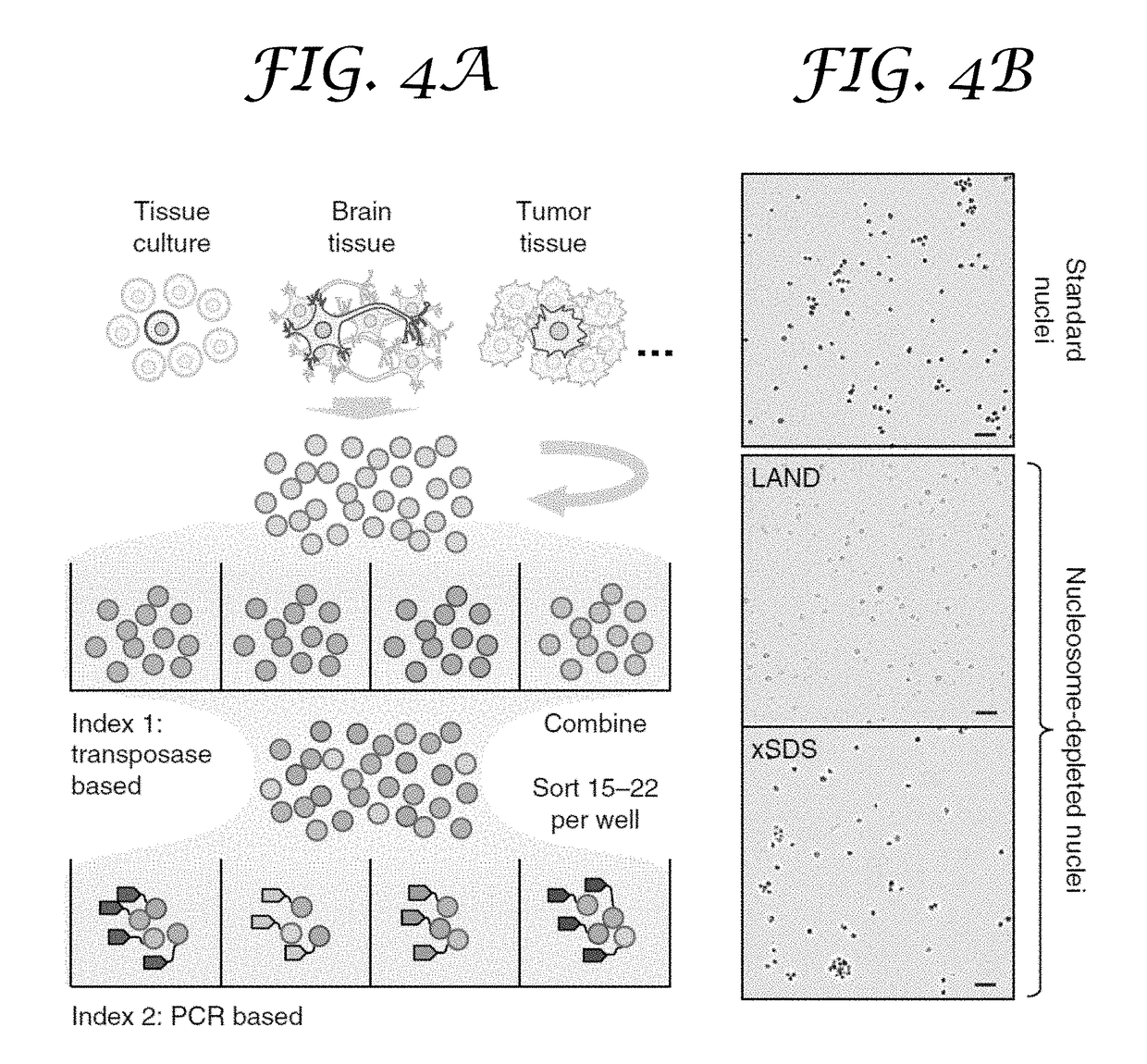
Single cell whole genome libraries and combinatorial indexing methods of making thereof
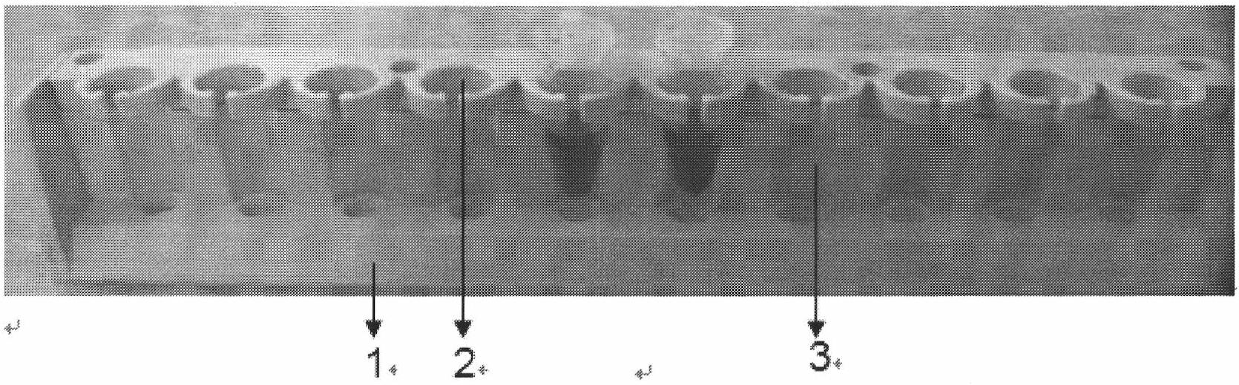
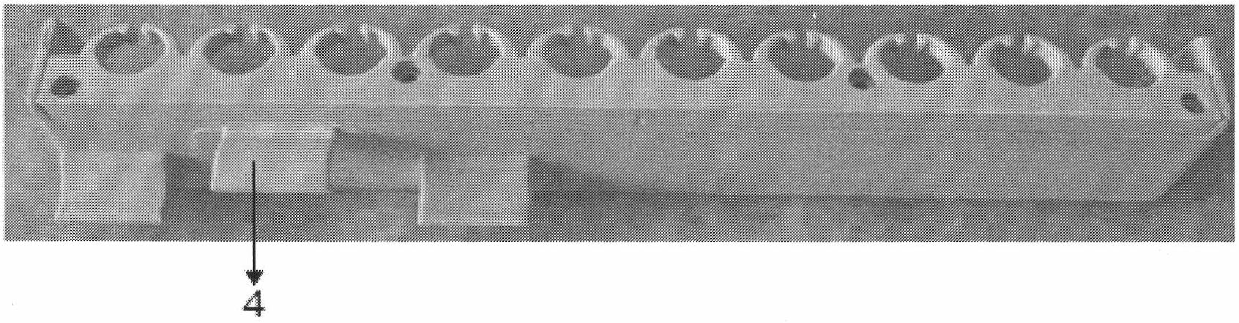
ActiveUS20180023119A1Maintain integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationChemical treatmentGenomic library
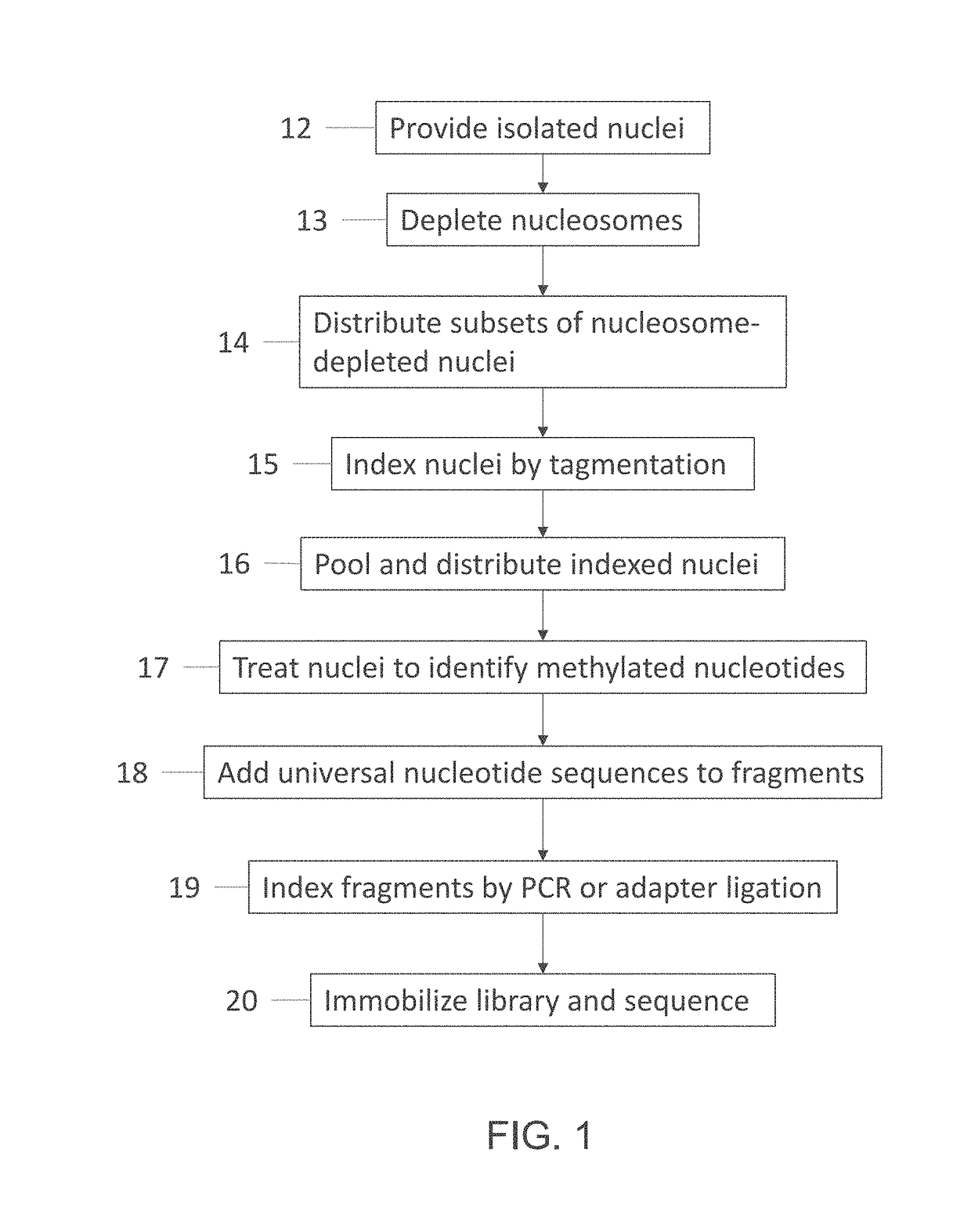
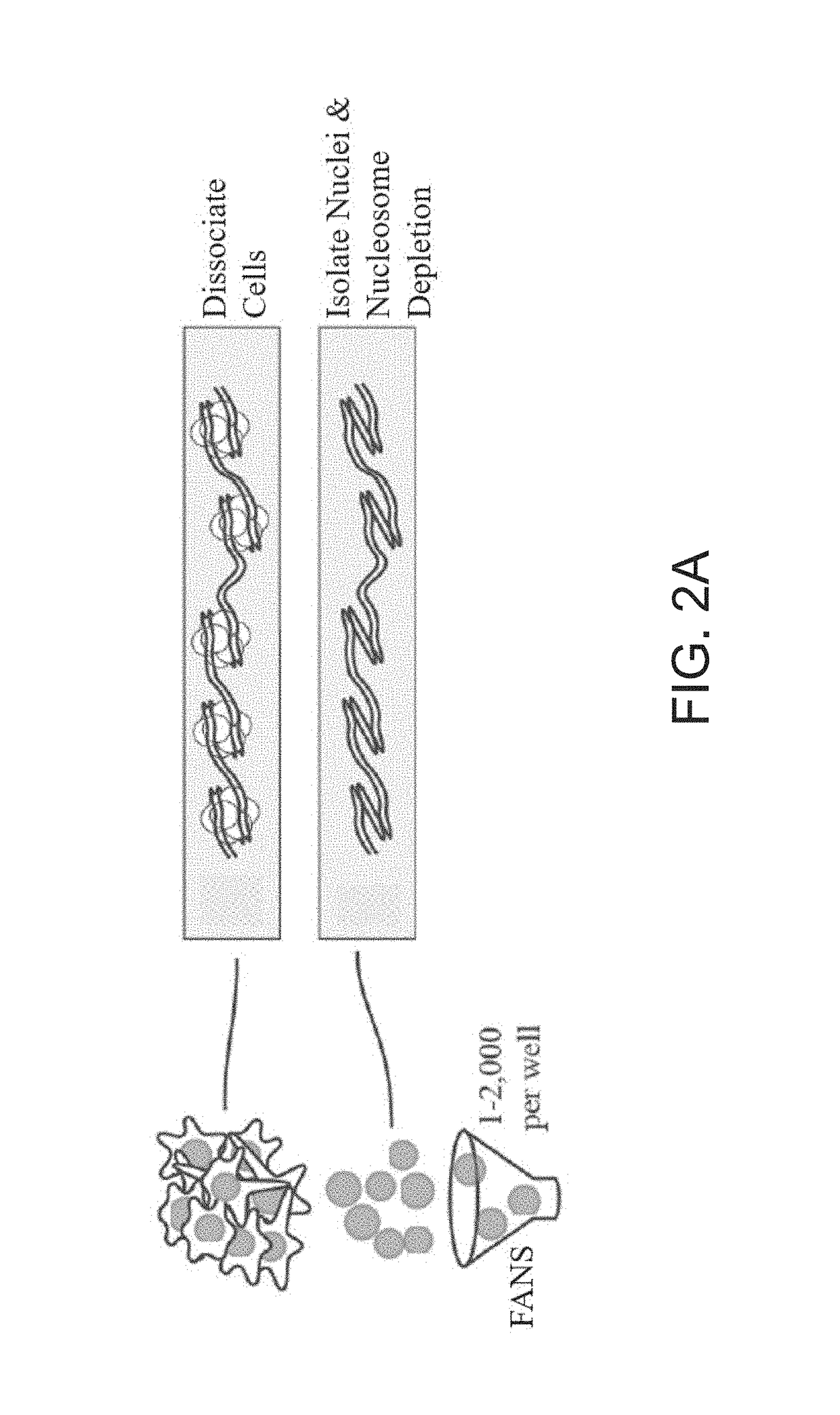
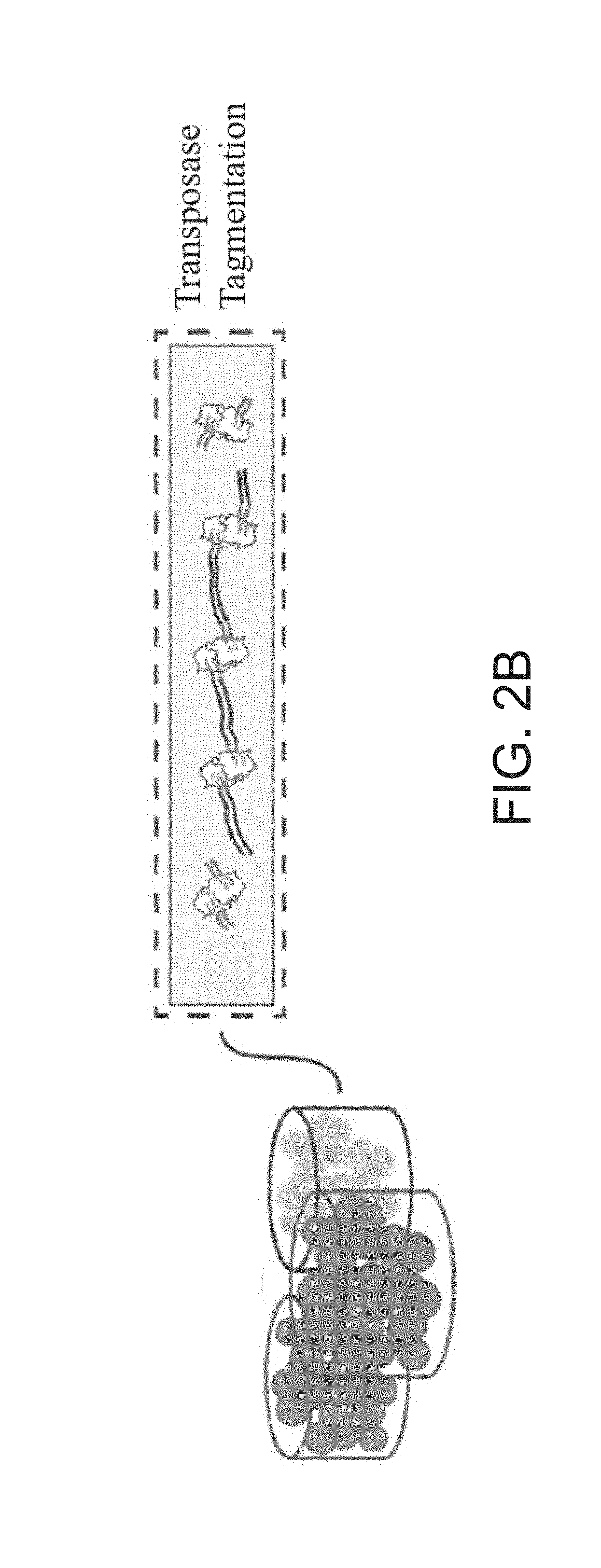
Provided herein are methods for preparing a sequencing library that includes nucleic acids from a plurality of single cells. In one embodiment, the sequencing library includes whole genome nucleic acids from the plurality of single cells. In one embodiment, the method includes generating nucleosome-depleted nuclei by chemical treatment while maintaining integrity of the nuclei. Also provided herein are compositions, such as compositions that include chemically treated nucleosome-depleted isolated nuclei.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +1
Method for isolating a polynucleotide of interest from the genome of a mycobacterium using a BAC-based DNA library application to the detection of mycobacteria
InactiveUS6183957B1Reducing potential for recombinationAvoiding lethal overexpressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenomic DNA
The present invention relates to a method for isolating a polynucleotide of interest that is present in the genome of a first mycobacterium strain and / or is expressed by the first mycobacterium strain, where the polynucleotide of interest is also absent or altered in the genome of a second mycobacterium strain and / or is not expressed in the second mycobacterium. The method comprises: (a) contacting the genomic DNA of the first mycobacterium strain under hybridizing conditions with the DNA of a least one clone that belongs to a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) genomic DNA library of the second mycobacterium strain, and (b) isolating the polynucleotide of interest that does not form a hybrid with the DNA of the second mycobacterium strain. This invention further pertains to a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv genomic DNA library, as well as a Mycobacterium bovis BCG strain Pasteur genomic DNA library, and the recombinant BAC vectors that belong to those genomic DNA libraries. This invention also relates to a method, as well as a kit, for detecting a nucleic acid of a mycobacterium in a biological sample.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Broad host range vectors for shotgun and expression library cloning in Gram negative bacteria
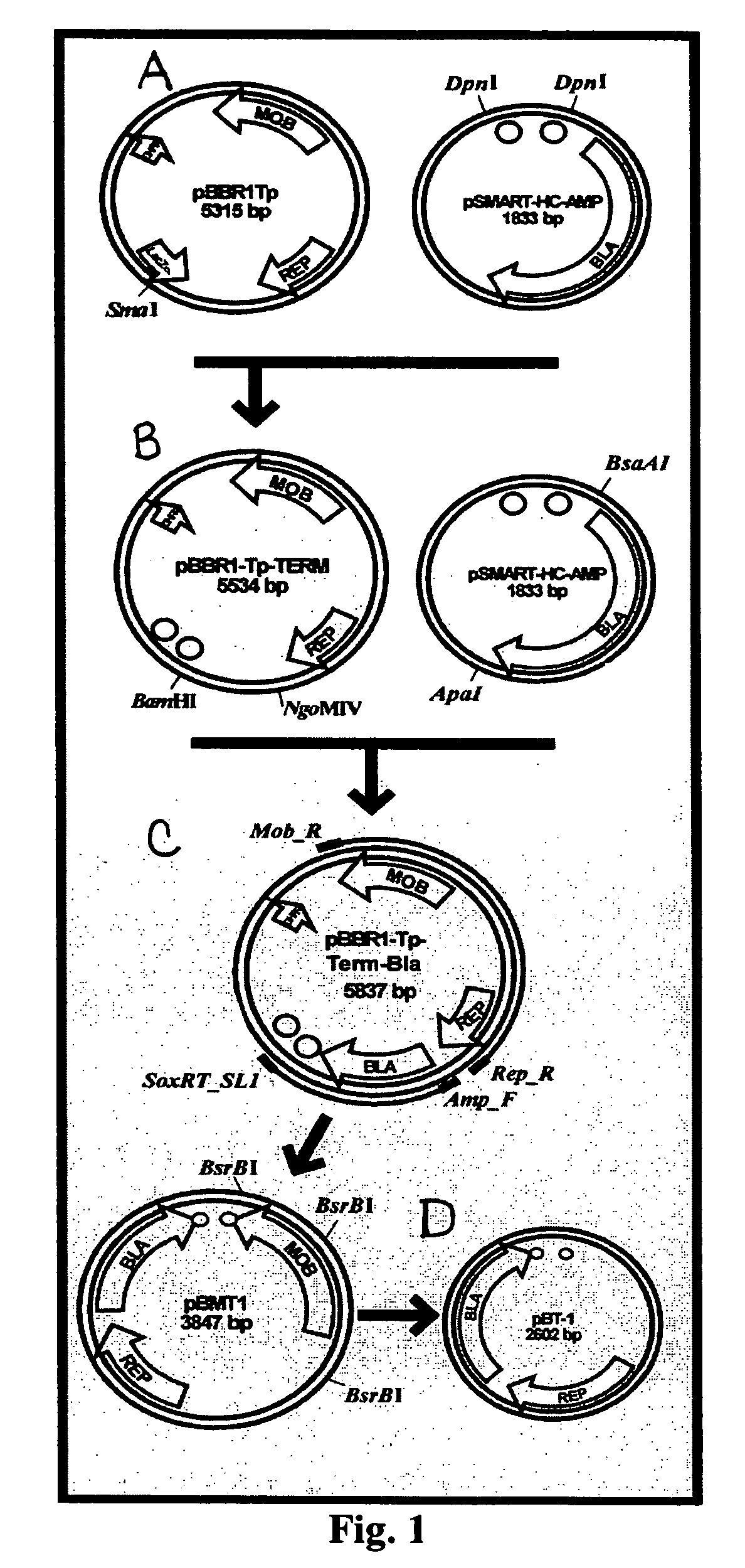
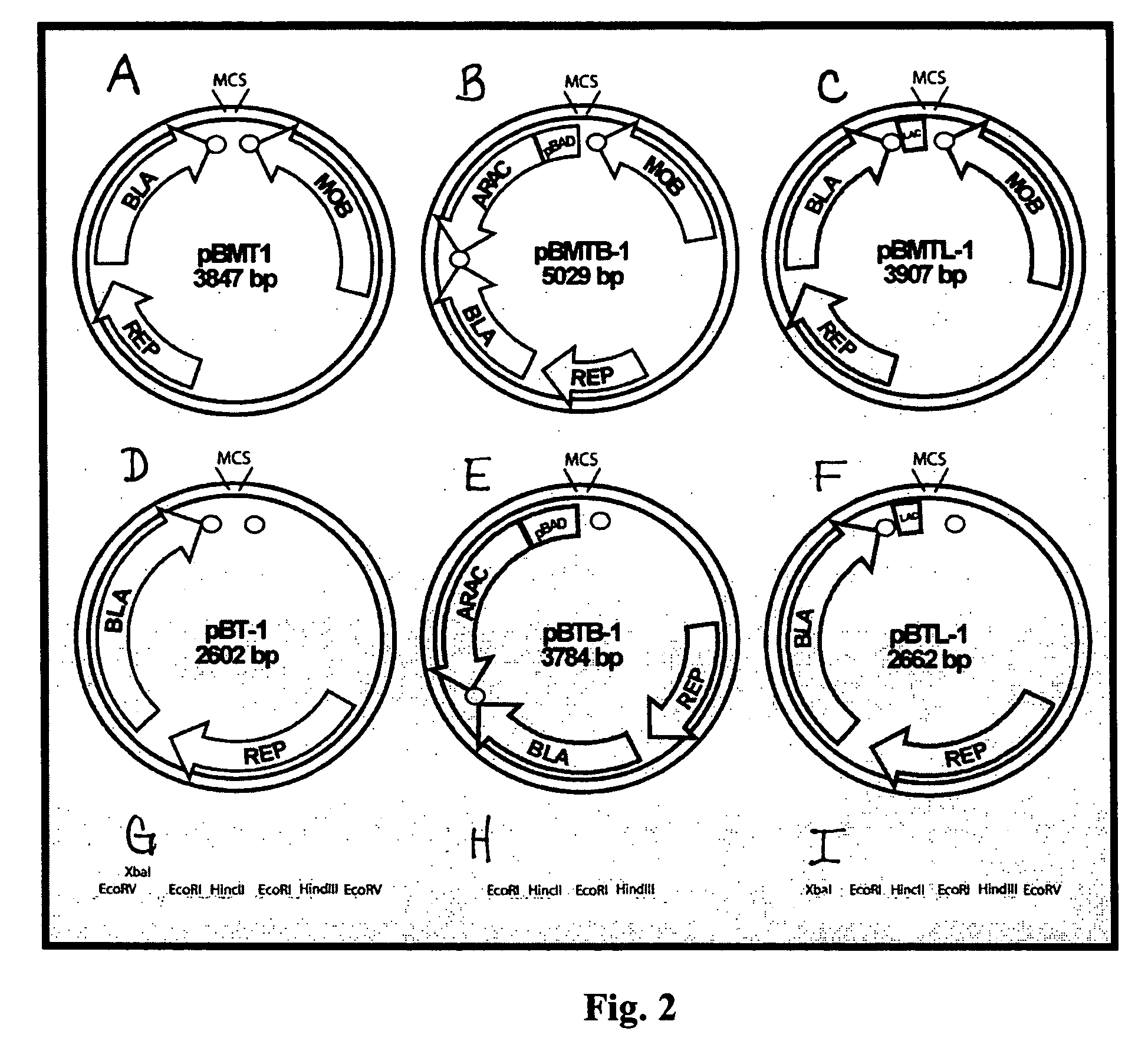
ActiveUS7846688B2Improve stabilityNucleotide librariesMicroorganism librariesExpression LibraryPlasmid Vector
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for the construction of a series of stable vectors for genomic library construction useful in Gram negative species. In certain embodiments, the vectors contain the pBBR1 replicon, capable of to stable replication in a broad range of Gram negative species. In various embodiments, the plasmid vectors may also contain bidirectional, rho-independent transcriptional terminators flanking the multiple cloning site, which allows for greater insert stability, and thus, greater genomic representation. Each vector may vary in its selection marker region, mobilization function, and promoter used to express insert sequences. These vectors are of use in the screening of highly representational genomic libraries in a broad variety of Gram negative species.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20050042606A9Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesGenomic SegmentMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
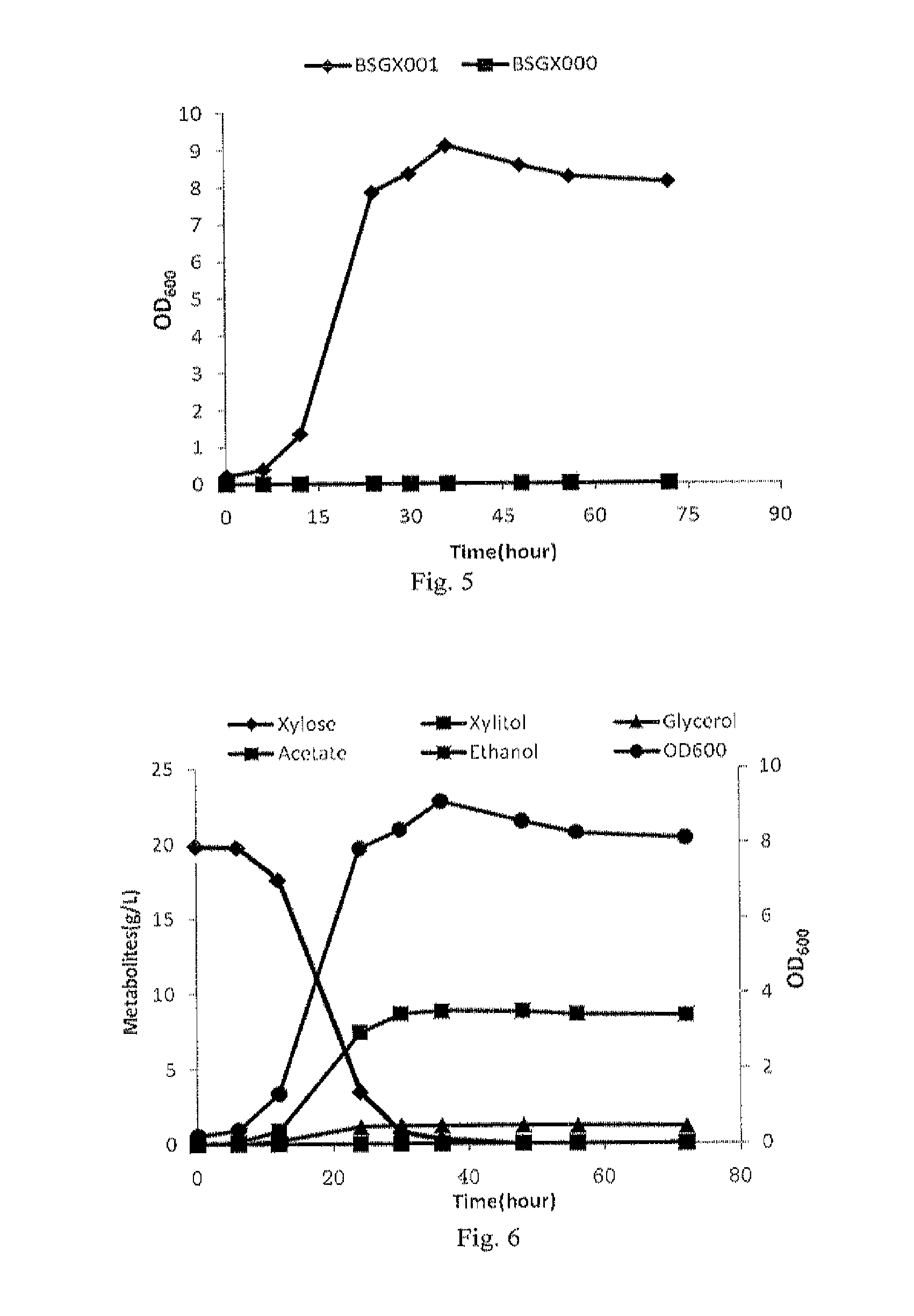
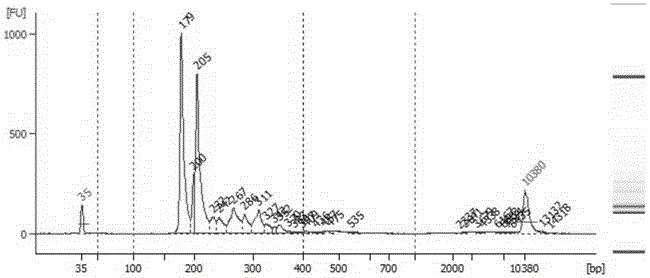
Nucleic acid molecule encoding xylose isomerase and xylose isomerase encoded by the nucleic acid molecule
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Establishment method of gene library of fecal flora based on high-throughput gene sequencing
InactiveCN105937053AFast database buildingImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSequence databaseGenomic library
An establishment method of a gene library of fecal flora based on high-throughput gene sequencing employs a ''nested PCR'' method for enrichment amplification on 16S rDNA, so as to reduce the host and food residue genome pollution by the maximum; and V3 and V6 are combined for specific amplification and massive parallel sequencing, so as to obtain the a target gene sequence database of the flora. The library can increase the identification of the bacterial flora from Genus level to Species level. The method can maximally avoid the interference of host cell nucleic acid, and completely and efficiently detect 16SrDNA tag sequence of all bacteria varieties, so as to accurately determine the ecological structure of the intestinal flora.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SAGENE BIOTECH
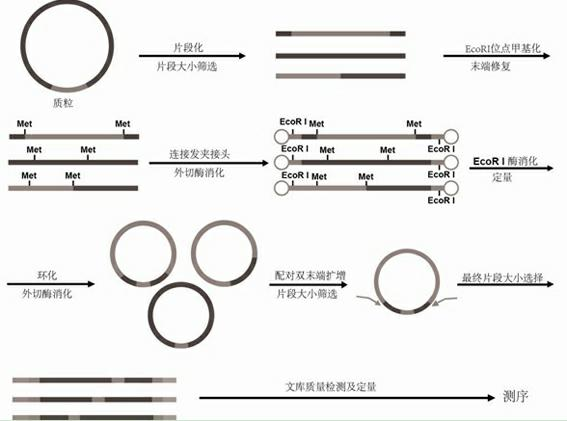
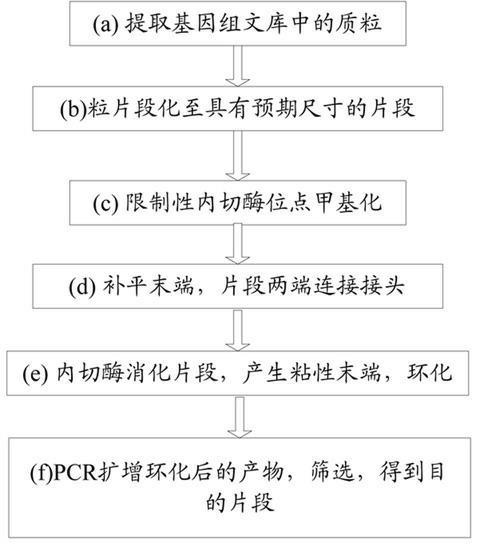
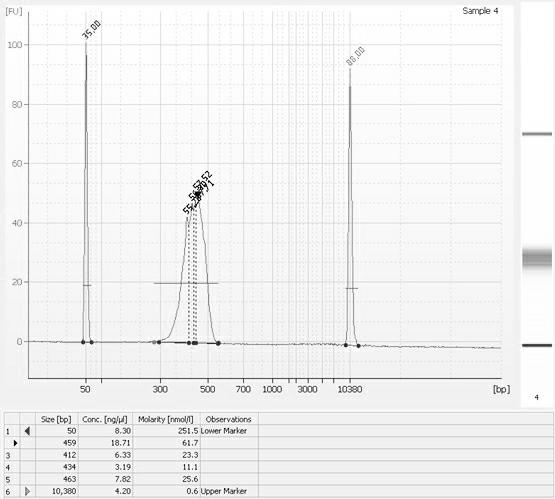
Paired-end library construction method and method for sequencing genome by using library
InactiveCN102181943AReduce workloadLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenomic sequencingDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a paired-end library construction method and a method for sequencing a genome by using the library. The paired-end library construction method comprises the following steps of: performing plasmid extraction on clone in a constructed genome DNA library, fragmenting the extracted plasmid DNA, performing methyl protection on the restriction endonuclease site on the fragmented DNA, adding a hairclip type joint, performing enzyme cutting and cyclization to obtain circular DNA, then amplifying the genome library paired-end fragment in the circular DNA through a pair of composite primers to obtain a paired-end sequence of ultra-long span, and finally performing high flux sequencing. The paired-end sequence obtained by using the method can be applied to splicing of a new species genome sequence so as to further improve the splicing quality.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
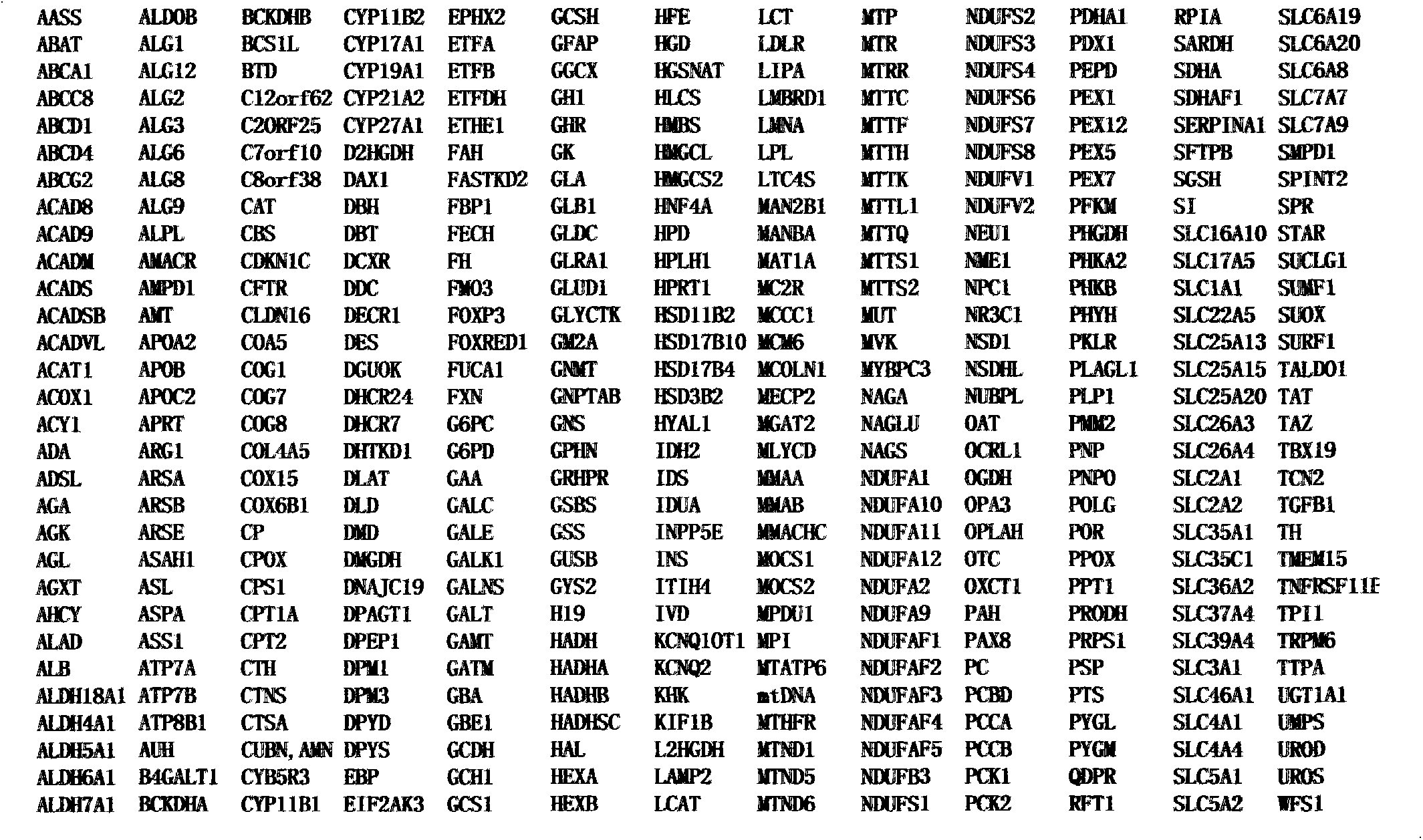
Screening method of inherited metabolic disorder gene
InactiveCN103305618AAccurate diagnosisReduce harmMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodGenomic library
The invention provides a screening method of all inherited metabolic disorder genes for genetic diagnosis within an exon area, which is fast and accurate and can cover the newest inherited metabolic disorder genes. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: drawing 3-5ml of blood from an individual, extracting 3-5 microgrammes of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) from the blood, interrupting and amplifying the DNA to construct a whole genome library for the patient, capturing the virulence genes by using an inherited metabolic disorder gene scanning kit provided by the invention, carrying out high-throughput sequencing by using a sequencing machine, and analyzing and finding mutation information relevant to the genes so as to obtain the mutation conditions of the inherited metabolic disorder genes of the individual to reach the purpose of accurate genetic diagnosis. Dozens of to thousands of genes and millions of loci can be captured and detected once by taking advantage of the high-throughput sequencing, and the screening method covers known 700 inherited metabolic disorders.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
Single cell whole genome libraries for methylation sequencing
PendingUS20180355348A1Dramatic cost reductionImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationPresent methodGenomic library
Provided herein are methods for preparing sequencing libraries for determining the methylation status of nucleic acids from a plurality of single cells. The present methods combine split-and-pool combinatorial indexing and bisulfite treatment techniques to characterize the methylation profiles of large numbers of single cells quickly, accurately and inexpensively.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC +1
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
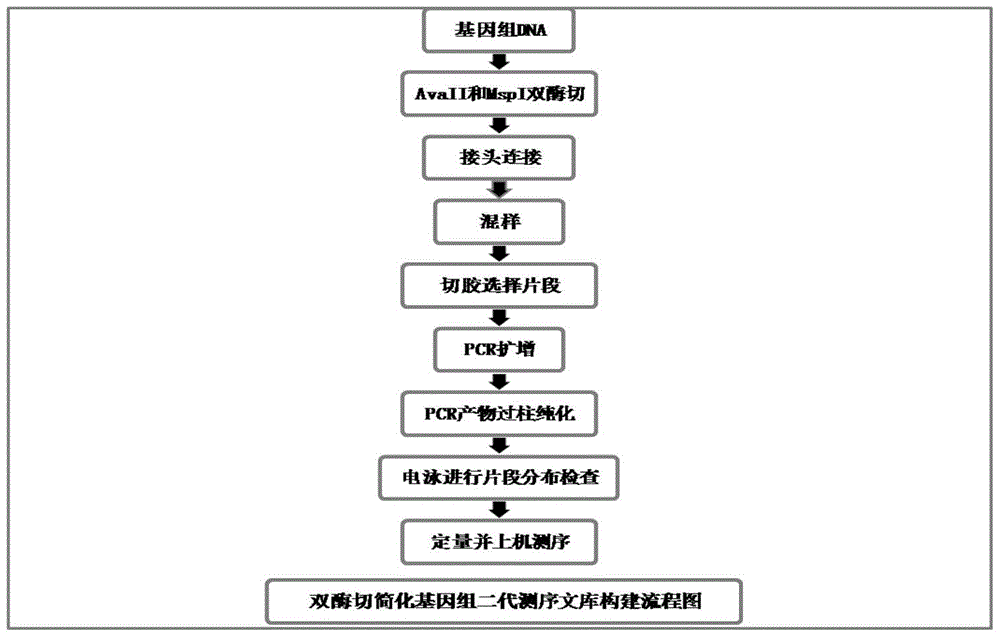
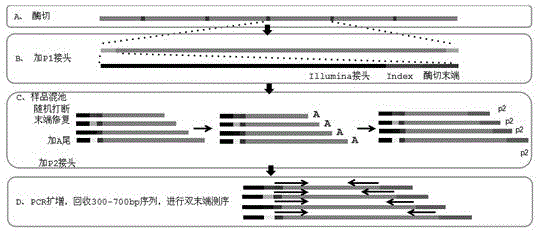
Construction method for double enzyme digestion simplified genome next generation sequencing library and matched kit
InactiveCN105696088AGet rid of dependenceSimplify the library building processMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomic sequencingEnzyme digestion
The invention provides a construction method for a simplified genome next generation sequencing library based on double enzyme digestion and a kit. Aiming at defects of an existing construction method for the double enzyme digestion simplified genome next generation sequencing library, the double enzyme digestion combined range is expanded, and excessive dependence on expensive instruments of constructing the simplified genome library is reduced, the library construction flow path is simplified, library construction cost is reduced, the sequencing efficiency is improved, and meanwhile the technology is easy and flexible to operate and easier for researchers to master and can be realized in a common molecule lab. The construction method is particularly suitable for miniature or medium-scale labs needing to conduct SNP molecular marker development, genetic map construction, population genetics research, phylogeny biological research and the like on a great number of species with incomplete reference genomes. The construction method has good practical application value and application prospects in the fields of molecular breeding of agriculture, conservation biology and evolutionary biology.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting high-molecular-weight genome from animal feces
InactiveCN102586234AHigh molecular weightSimple methodDNA preparationSodium acetateMolecular identification
The invention relates to a method for extracting high-molecular-weight genome from animal feces. The method comprises the steps of sample treatment, bacterial cell lysis and extraction of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). Specifically, the method comprises the steps of: dissolving an animal feces sample with aseptic PBS (Phosphate Buffered Saline) buffer, carrying out low-speed centrifuging and filtering to remove food residues in the feces, collecting bacterial cells, performing wall breaking on the bacteria by adopting lysozyme, decolorizing peptidase, protease and SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate), extracting with a mixture of phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol as well as a mixture of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol, precipitating with isopropanol and sodium acetate, washing and drying, dissolving, and digesting RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) with RNAse (Ribonuclease). According to the invention, the method is simple in operation; and the DNA molecular weight of the extracted genome achieves more than 40kb, so that the researches on microorganism molecule ecological diversity, molecular identification, target gene amplification, macro genome library construction and the like are met.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Screening method of infantile autism gene
InactiveCN103290135AGuaranteed catchLower quality requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementInfantile autism3-deoxyribose
The invention provides a screening method of an infantile autism gene. The screening method is quick and accurate and can cover all exon areas of the latest infantile autism gene. According to the basic scheme, the screening method comprises the following steps of: drawing 3 to 5ml of blood from an individual; extracting 3-5ug of DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) from the flood; breaking and amplifying the DNA to construct a whole-genome library for a patient; trapping relevant virulence genes through an infantile autism gene scanning kit; performing high-throughput sequencing through a new generation sequenator; and analyzing and finding out the gene-related mutant information to obtain the mutation conditions of the gene related to the infantile autism of the individual so as to realize the purpose of accurate genetic diagnosis.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
Chinese prawn B683 microsatellite label detecting technique
The present invention relates to a detection technique of Chinese prawn B683 microsatellite marker, which includes the following steps: firstly, extracting Chinese prawn genomic DNA; utilizing microsatellite sequence contained in Chinese prawn genomic library to design specific primer at two ends of its sequence; and making PCR amplification of genomic DNA of Chinese prawn; and making the PCR product undergo the process of denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis separation, and analyzing band produced by said product and obtaining the genetic polymorphism map of Chinese prawn.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Gene encoding beta-glucosidase
InactiveCN101363026AAvoid pollutionSolve the world energy crisisEnzymesGenetic engineeringBeta-glucosidaseNucleotide
The invention provides a gene of coded beta-glucosaccharase, which is called Unbgl1B and is obtained by constructing Metagenome DNA library of uncultured microorganisms of alkality contaminated soil and by the detecting and screening method of the activity of the beta-glucosaccharase of clone library, so as to be one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences and partial sequence thereof in sequence 1 of a sequence table; 2) DNA sequences having more than 80% of homoeology compared with the DNA sequences defined by the sequence 1 of the sequence table. The DNA in the sequence 1 of a sequence table is DNA sequences of a pGEM-3Zf(+) part of a cloning vector and DNA of exogenetic uncultured microorganisms cloned on the vector, and the exogenetic DNA segment consists of 838 basic groups; the GC content of the gene is 54.3%. The gene is used for producing the beta-glucosaccharase, so as to dissociate cellobiose into single glucose molecule.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Extraction of duck enteritis virus genom DNA and sequence thereof
InactiveCN101182526AHigh homologyShort copy cycleFermentationGenetic engineeringPUC19Escherichia coli
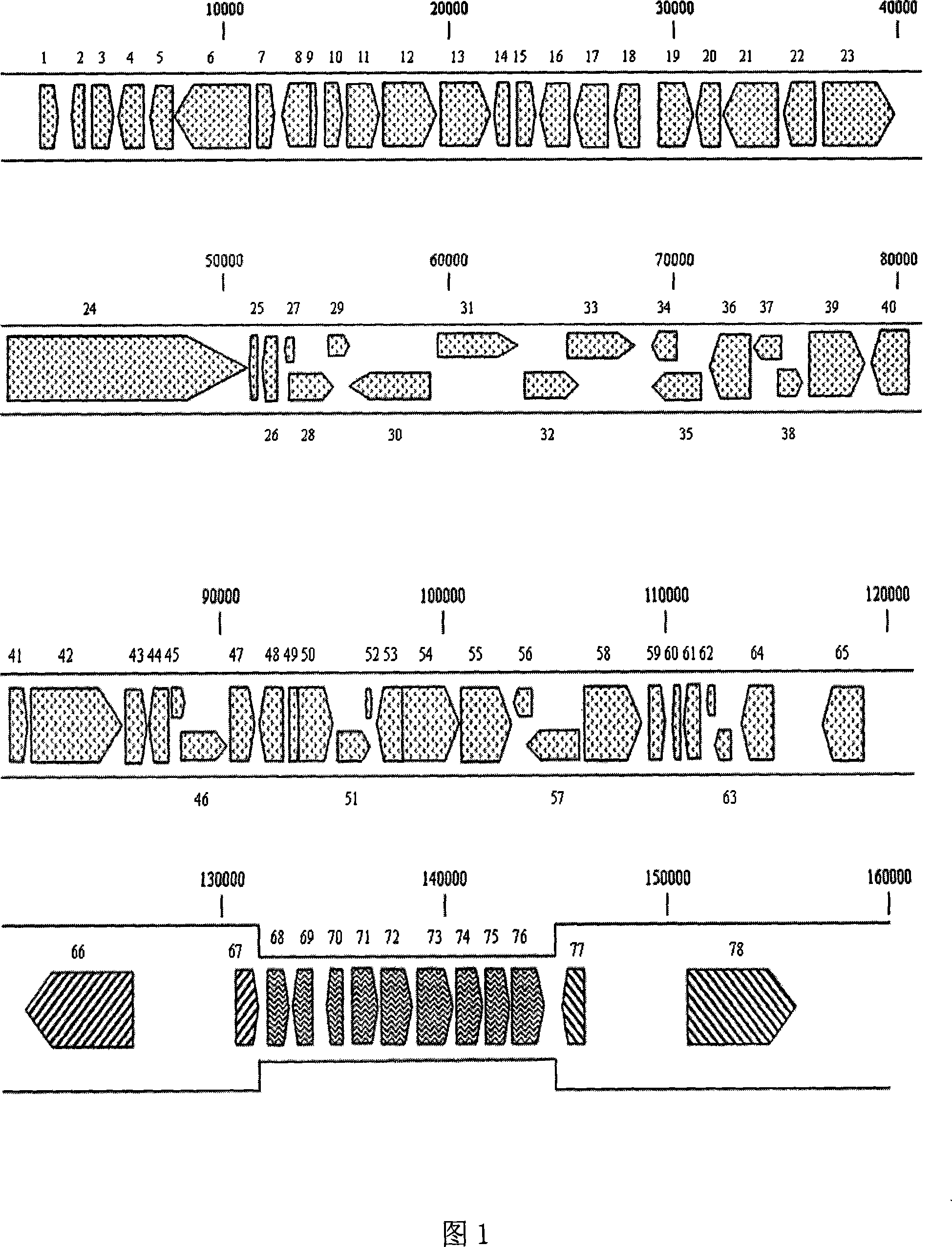
The invention discloses a DNA extraction method of Duck Enteritis Virus genome and the genome sequence. Firstly, the pyrolysis of chicken embryo fibroblast which is infected with DEV is processed by hypertonic buffer; then the nuclease is added for the digestion of cell DNA; and the virus genome DNA is obtained through phenol chloroform extracting method. The obtained sample is broken randomly into 2kb to 2.5kb fragments; the pUC19 vector is linked to transform host E. coli and construct genomic library. The positive clones in the library are randomly sequenced; the total sequence length has 6 times coverage rate for the virus genome. The sequence result is assembled and clustered to obtain the whole DEV genome sequence with the length of156512bp. The analysis shows that the genome structure is the same with that of the members of Varicella virus in Alpha- herpesus subfamily, which provides theoretical basis for the classification of DEV.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for screening beta-glucosaccharase gene from mildewed sugarcane leaves based on metagenomic technology
PendingCN105462999AHighly solubleEfficient soluble expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesBiotechnologyBeta-glucosidase
The invention discloses a beta-glucosaccharase gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the beta-glucosaccharase gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses recombinant beta-glucosaccharase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is shown as the SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also discloses a screening method of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase. The screening method comprises the following steps: extraction of microbial metagenomic DNA from the mildewed sugarcane leaves; establishment of a metagenomic library; screening of the beta-glucosaccharase gene from the metagenomic library, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the beta-glucosaccharase gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1; and cloning and expression for the obtained beta-glucosaccharase gene, thus the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is obtained, wherein the amino acid sequence of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is shown as the SEQ ID NO.2. The recombinant beta-glucosaccharase has extremely high activity and is not sensitive to hydrolysis products under the alkaline condition.
Owner:江西省农业科学院农业应用微生物研究所
Process of cloning new resistance gene of wild rice
InactiveCN101045928AQuick searchOvercome the cumbersome processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOryzaAgricultural science
The present invention discloses process of cloning new resistance gene of wild rice. The process includes the first constructing library of convertible genomes of donor wild rice, the subsequent designing primer according to the conservation sequences of the cloned rice blast resisting gene and bacterial leaf spot resisting gene to obtain amplified product as the probe, performing bead enrichment on the library with the marked probe to establish candidate resistance gene enriching library, and the final spot hybridization analysis and PCR identification on the cloning of the enriching library, the cloning sequencing analysis and function verification of the amplified product. The present invention integrates candidate resistance gene cloning technology and bead enriching library constructing technology, and is suitable for cloning of wild rice resistance gene and other beneficial plant gene.
Owner:HUNAN WEST CITY HYBRID RICE GENE TECH +1
Expression Vector
InactiveUS20120021950A1Improve efficiencyLibrary screeningNucleic acid vectorSystems researchGenomic library
An expression vector including two separately inducible converging promoters P1 and P2, and expression system including such an expression vector and an additional regulator vector, a method of protein expression using such an expression system, and a method of investigating (meta)genome libraries using such an expression system.
Owner:C LECTA GMBH
Blue crab ptssr17 microsatellite DNA marker testing technique
ActiveCN101294217AEasy to detectSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatelliteGenotype
The invention relates to a detection technology by ptssr17 microsatellite DNA markers in a blue crab. The technology is characterized in that: first, genome DNA of the blue crab is extracted and diluted to reserve; second, by utilizing a ptssr17 microsatellite core sequence in a genomic library of the blue crab, specificity primers are designed at the two ends of the sequence thereof; third, the genome DNA of different geographic groups of the blue crab or individuals in a blue crab group is processed through the PCR amplification by using the primers, and PCR products are processed through the modified polyacrylamide gel detection; finally, bands which are generated in the products are utilized for analyzing so as to determine the genotype of each individual, thereby obtaining a polymorphic map on the enormous genetic variation of the blue crab in the a ptssr17 core sequence area. The polymorphic map that the ptssr17 genetic mark gene locus of the blue crab shows the enormous genetic variation can be obtained rapidly; the method is simple and convenient; the each individual genotype of the blue crab at the locus can be detected intuitively from the obtained results. The detection technology is mainly used in the genetic marks among the blue crab groups, the genealogical identification, the genetic map construction, etc.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for separation and purification of large-fragment DNA from soil
InactiveCN103103180AEasy to operateOperation steps are adjustableDNA preparationMicrobe DNABiological studies
The invention belongs to the fields of soil microorganisms, biochemistry and molecular biology and relates to a method for separation and purification of a large-fragment DNA from soil. The method is used for indirect separation and purification of a large-fragment DNA having molecular weight more than 30kb from various types of soil, wherein the large-fragment DNA is used for construction of a metagenomic library, or is used for separation of soil microbial gene clusters. The method solves the problem that separation of microbial cells from soil and preparation of large-fragment soil DNA having high purity and satisfying various biological study demands are realized difficultly by the existing indirect method, and is an efficient method for extraction of soil microorganism DNA having a large fragment and high purity.
Owner:XINJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
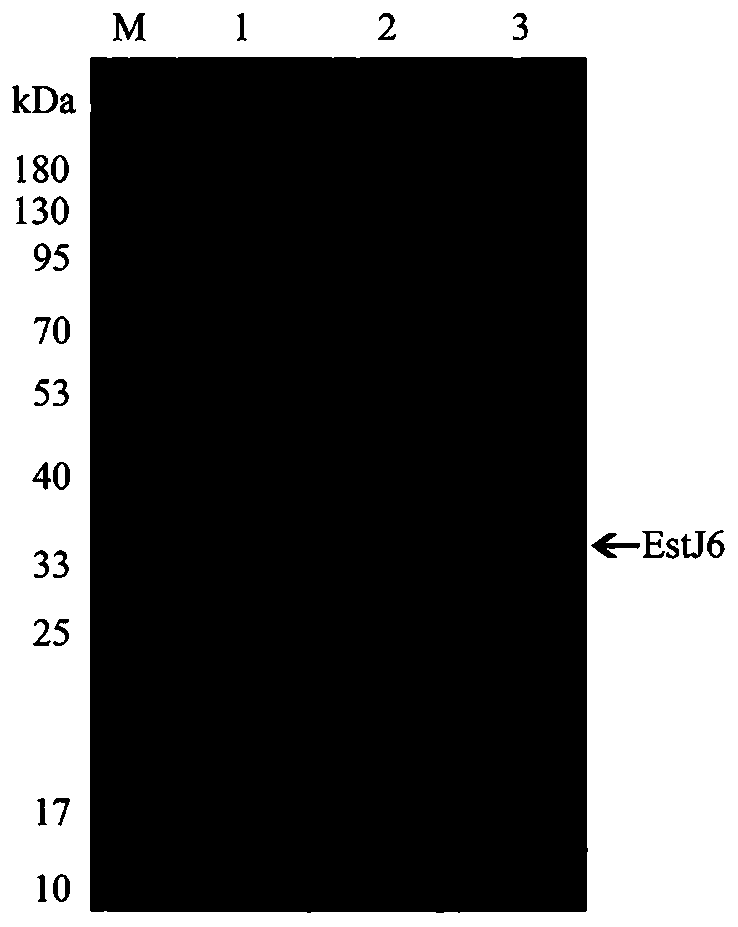
Novel phthalate hydrolase EstJ6 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110982803AImprove space utilizationBroad substrate specificityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention provides a novel phthalate hydrolase gene derived from a soil metagenome library. The nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of the novel phthalate hydrolase gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. After the esterase gene is connected to an expression vector pET28a (+), the esterase gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to realize heterologous expression. The molecular weight of the purified recombinase (EstJ6) is 33.31 kDa. The EstJ6 has wide substrate specificity on phthalate, and the EstJ6 not only can hydrolyze phthalate with a simple side chain,but also can hydrolyze diethyl hexyl phthalate and monoethyl hexyl phthalate with complex and longer side chains. In addition, site-specific mutagenesis experiments show that the catalytic triad residue of EstJ6 is S146-E240-H270, and mutation of any amino acid in the three causes the EstJ6 to lose the catalytic ability. The novel phthalate hydrolase disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fields of food industry, agriculture, biotechnology and the like due to the specific activity and enzymatic characteristics of the novel phthalate hydrolase.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for separating short interspersed repeated segments based on magnetic bead probe complexes
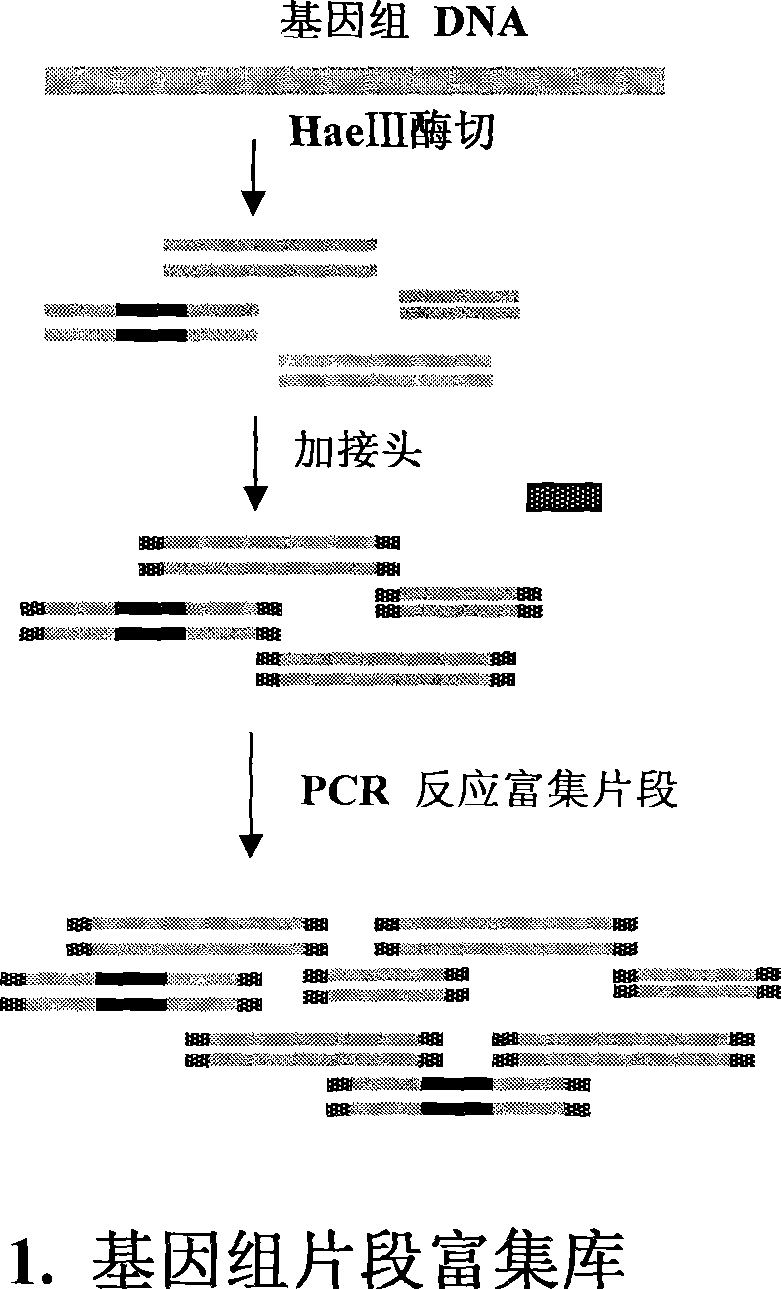
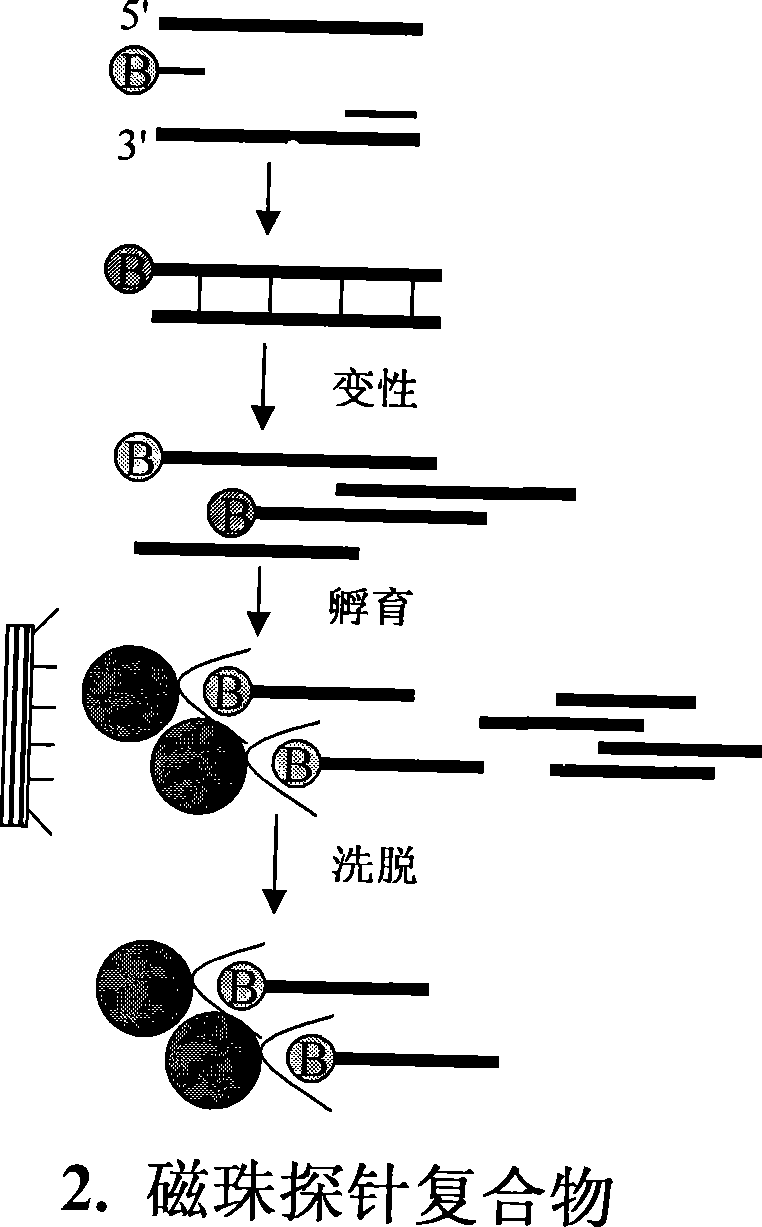
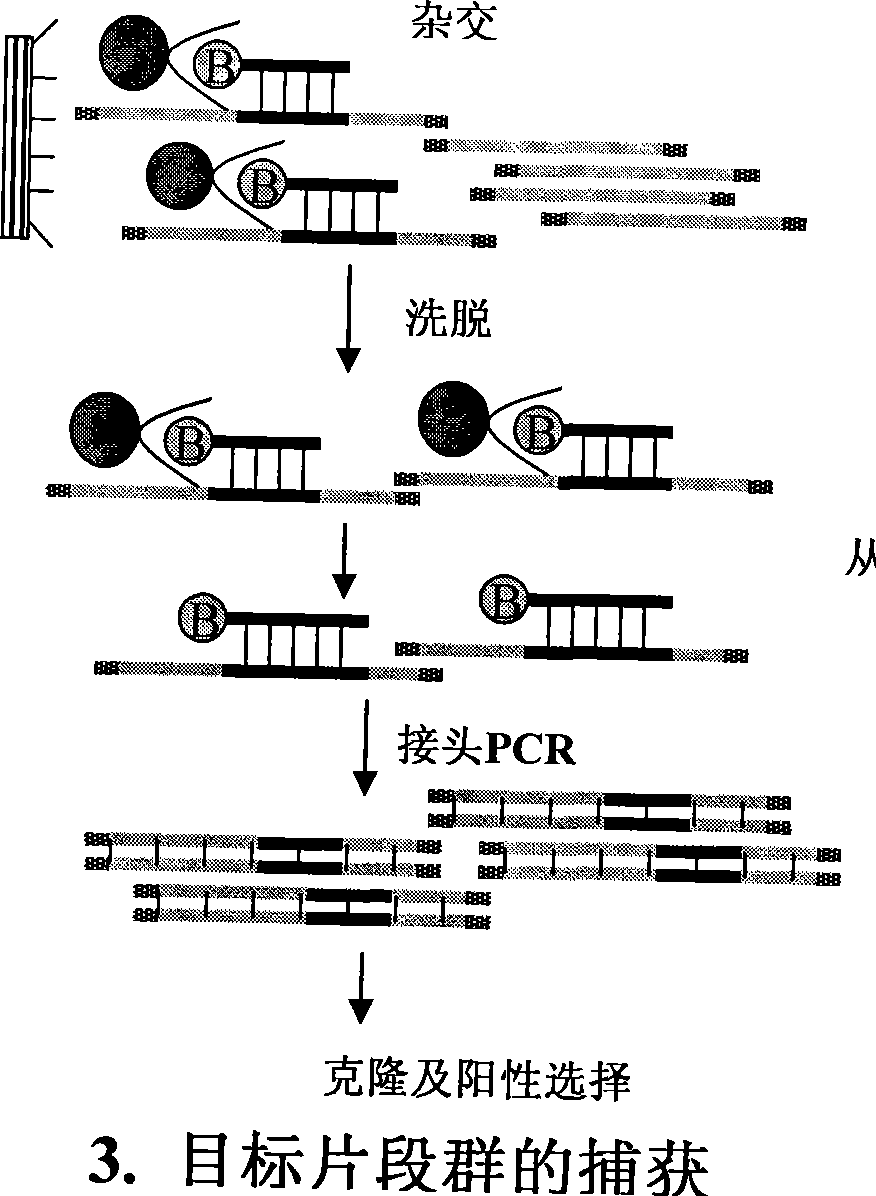
InactiveCN101381724AShort experiment cycleReduce consumption costDNA preparationPositive selectionGenomic Segment
The invention discloses a method for separation, dispersion and sequence repetition of a bead-probe complex. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the preparation of a genome fragment enriched library, which is to perform restriction enzyme digestion on a genome, to recover fragments with adequate dimensions, to add linkers on T4 ligase, and to perform cyclic amplification of the genome fragment library after restriction enzyme digestion through PCR of a small number of linkers; secondly, the preparation of the bead-probe complex, which is to realize biotin labeled DNA probes by the primer amplification method, and to bind biotin labeled single-chain probes on beads; and thirdly, acquisition of a target fragment group, which is to perform crossover on the bead-probe complex and the genome library, to acquire a target fragment, to separate and clone the target fragment, and to perform positive selection on the target fragment. The method is simple, high-efficiency and quick, shortens the experimental period, reduces the cost consumption, greatly improves the efficiency, and does not require special experimental equipment.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Method for developing endangered rhododendron molle SSR primer on basis of RAD-seq
ActiveCN104598773AEfficient methodAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsContigGenomic library
The invention provides a method for developing an endangered rhododendron molle SSR primer on the basis of RAD-seq. The method comprises the steps: establishing a rhododendron molle genomic library, acquiring 7.653G of Raw Data and 7.513G of filtered Clean data after the paired-end sequencing and subsequent treatment; clustering reads containing enzyme recognition sites by utilizing cd-hit-est clustering software, and gathering areas which are consistent in Reads2 capture when in RAD sequencing; at most mispairing three basic groups between Reads2, gathering the reads with similar RAD-tag by virtue of the sequence similarity of the Reads2, locally assembling each type of screened sequencing data by utilizing VelvetOptimiser assembling software, and selecting a best congtig to search SSR; collectively obtaining 11961 SSR fragments for designing the SSR primer after the contig is filtered; designing the SSR primer by utilizing Primer3, wherein 11687 pairs of SSR primers can be successfully designed by utilizing the method; randomly selecting 60 pairs of primers to carry out polymorphic detection for 6 parts of rhododendron molle DNAs in different geographical distribution. By adopting the method, a novel concept is provided for developing the rhododendron molle SSR primer.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Chitosanase gene derived from soil metagenome library and obtaining method and application of chitosanase gene
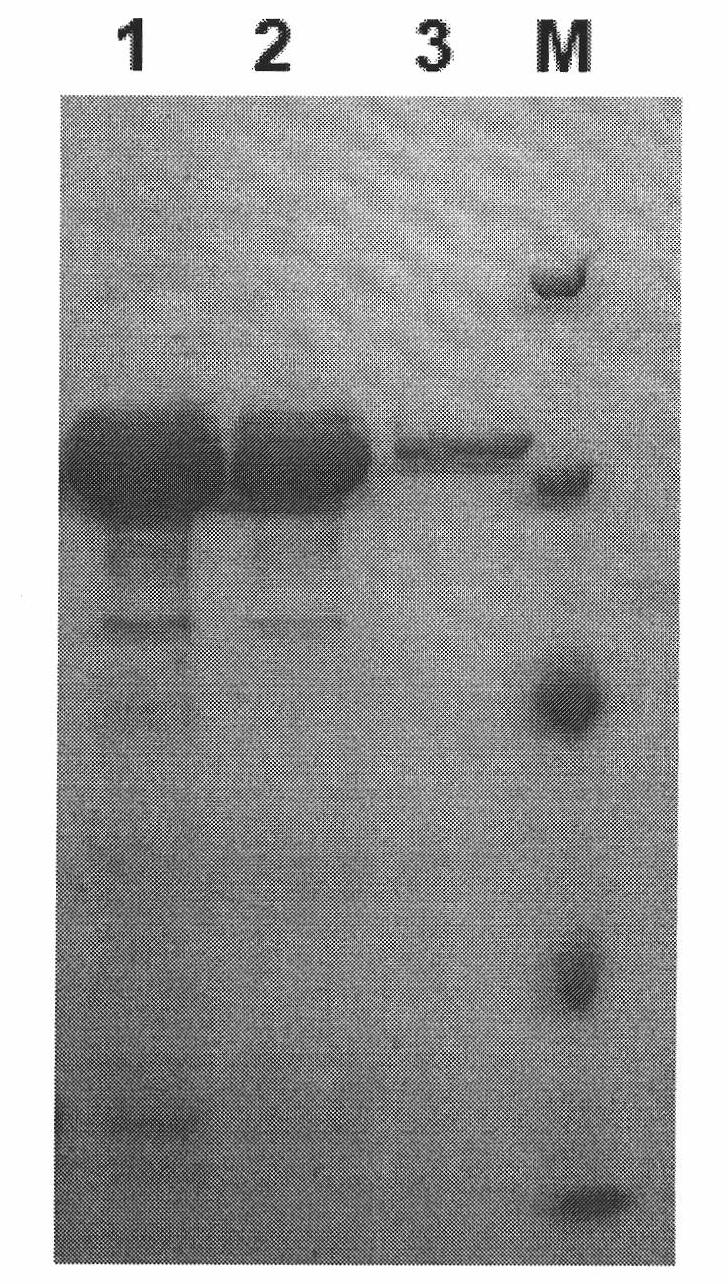
InactiveCN103361374AHigh catalytic activityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaEnzymesEscherichia coliGenomic library
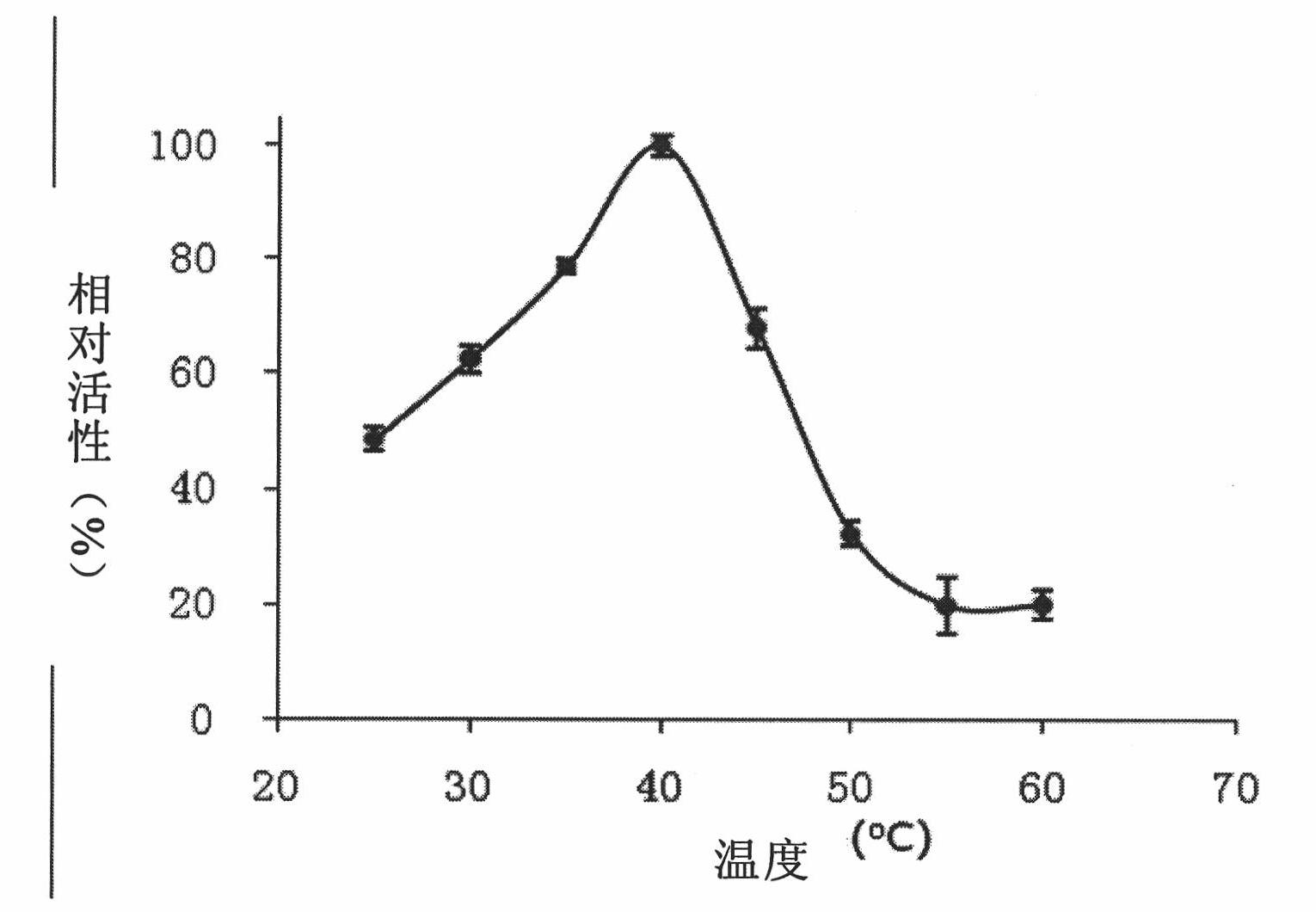
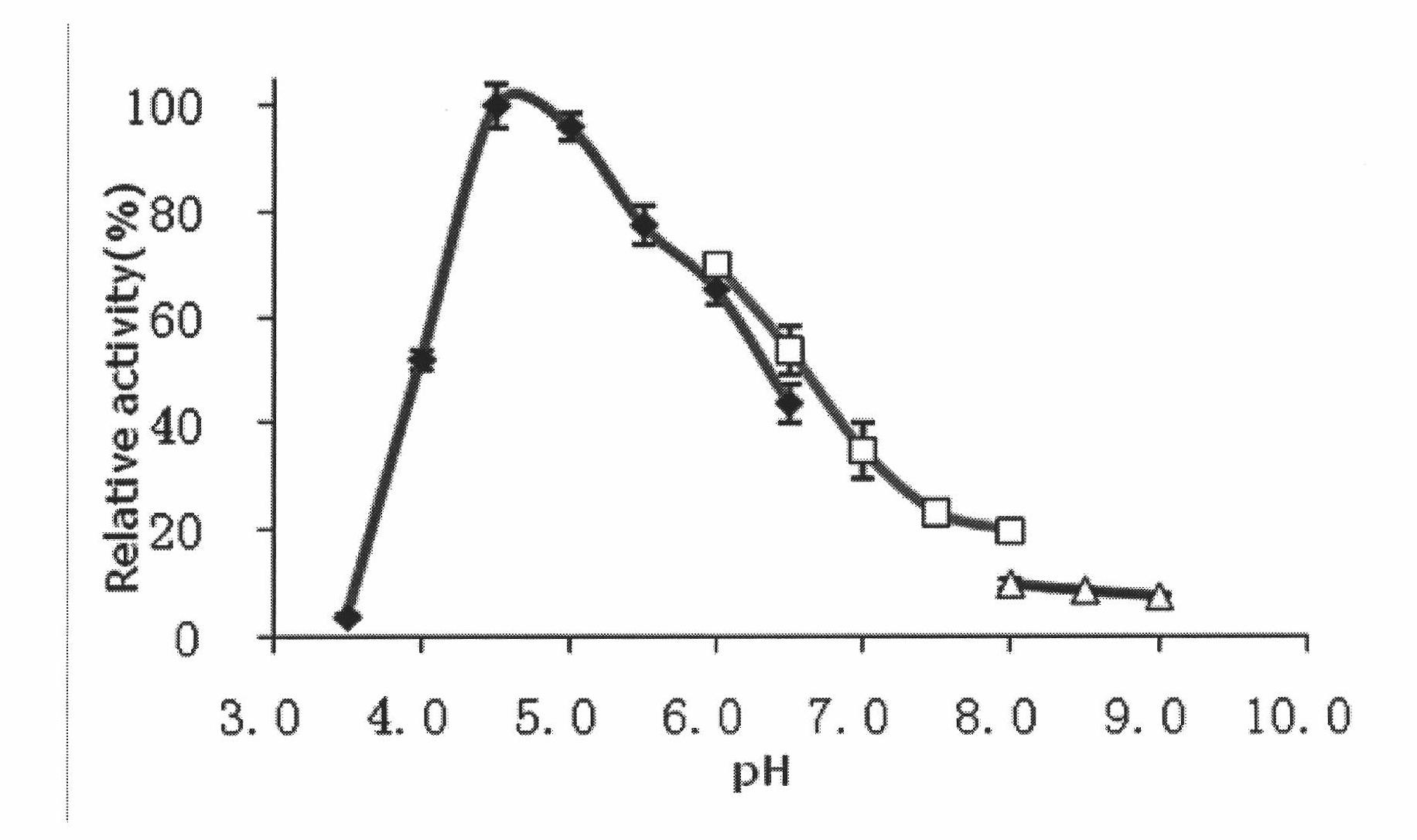
The invention provides chitosanase gene derived from soil metagenome library, and the DNA sequence of the chitosanase gene is shown in SEQID NO:1. The invention also provides chitosanase obtained by encoding of the chitosanase gene and recombinant plasmid including the chitosanase gene, and further provides escherichia coli engineering bacteria containing the chitosanase gene and an obtaining method thereof. The obtaining method of the chitosanase gene is simple, and the escherichia coli engineering bacteria containing the chitosanase gene is provided. The chitosanase can be obtained through high-efficiency expressionof the escherichia coli engineering bacteria. The bioinformatics analysis shows that the obtained chitosanase gene belongs to the forty-sixth family of glycoside hydrolase. The chitosanase gene has high catalytic activity and good thermal stability, with optimal action temperature being 55 DEG C and pH being 6.0, and has great industrial value and economic value.
Owner:YANGZHOU RIXING BIO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com