Expression Vector
a technology of expression vectors and vectors, applied in the field of expression vectors, can solve the problems of inadequacies in transcription, missing cofactors or chaperones, and incorrect protein folding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
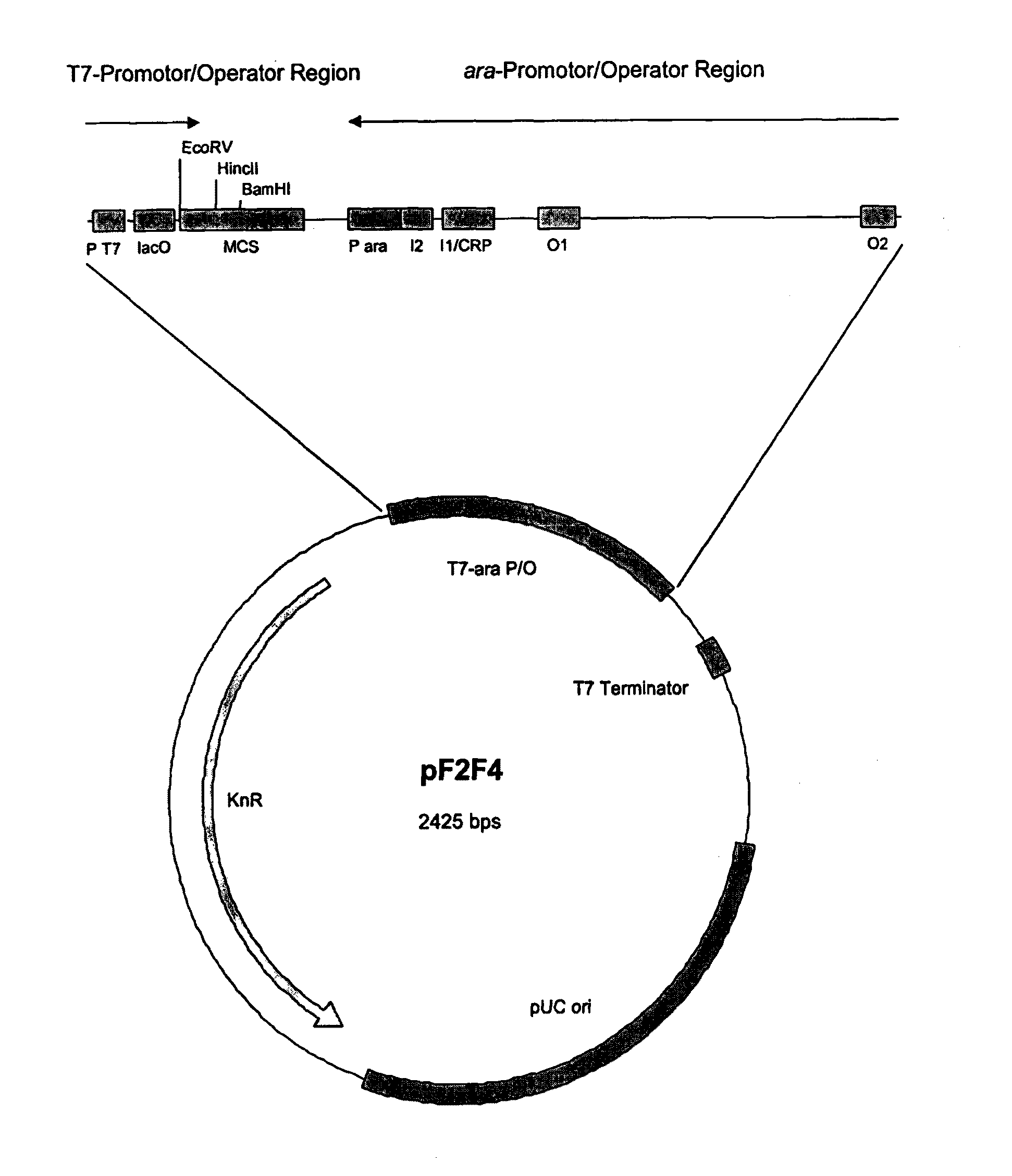
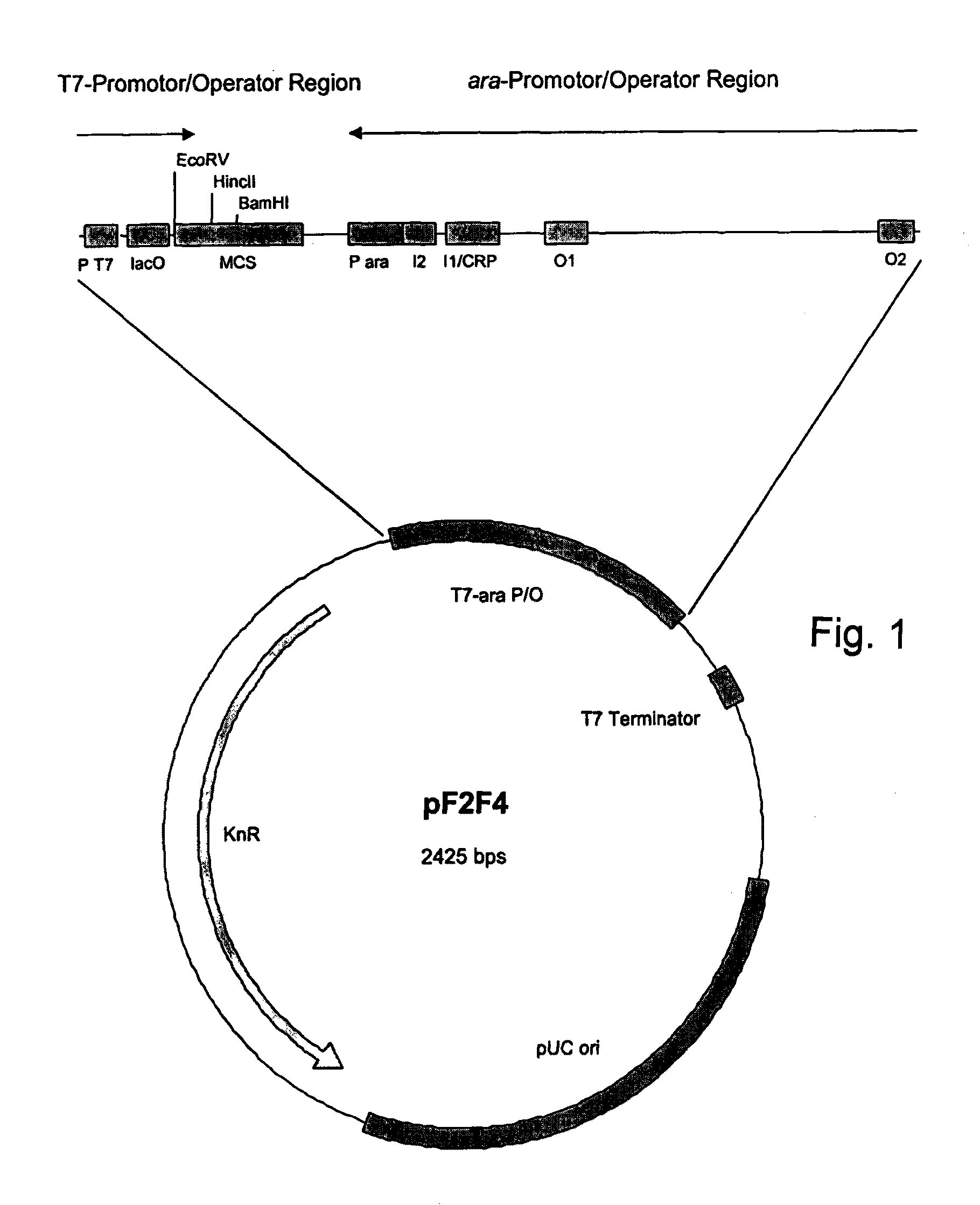
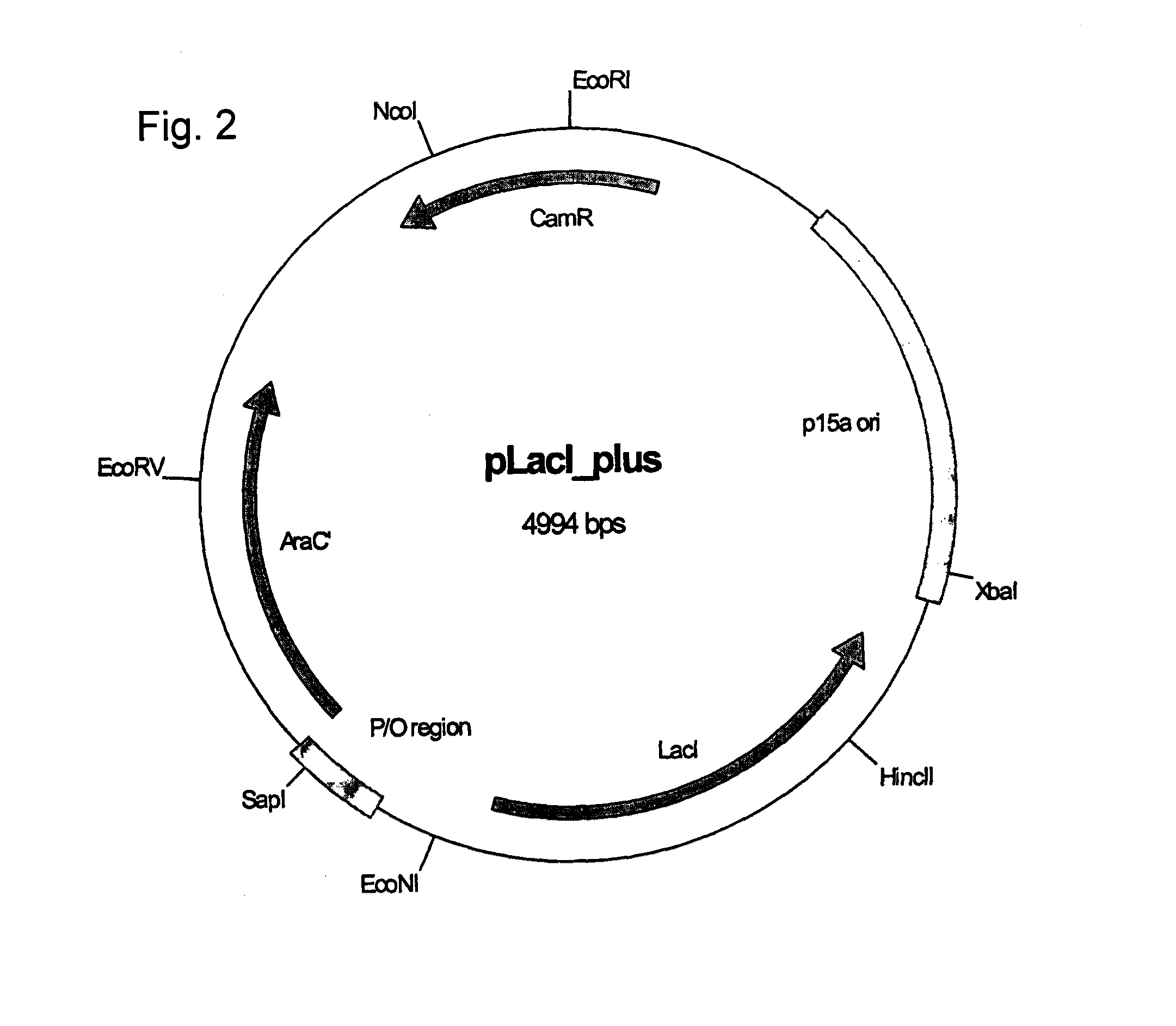
[0194]The promoter strength of the ara or T7 promoter in pF2F4 was investigated in various situations using a reporter gene. The data show that pF2F4, in conjunction with the regulatory plasmid pLacI+(cf. FIG. 2) is optimum for use as the expression plasmid. The reporter gene used was an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), which was inserted in both possible orientations. The gene was under the control of the ara promoter or of the T7 promoter, respectively. Only the combination of regulatory plasmid encoded Lad and AraC with the pF2F4 plasmid leads to maximum possible expression starting from the Ara promoter and from the T7 promoter (FIG. 3).
[0195]The ara promoter activity is lowered in the BL21 strain with simultaneous T7 induction to approx. 10% of the initial activity (FIG. 4A). The possibility of this effect being based on competitive inhibition of the regulator AraC by IPTG can be ruled out, as the inhibition is only observed in E. coli BL21(DE3). No significant decline in ara promo...
example 2
Example of Application of pF2F4: Screening for Esterase / Lipase Activity in a Metagenome Bank
[0196]A metagenome library set up in pF2F4 was screened for esterase / lipase-activity, using the cluster screening method (Greiner-Stoeffele, T., Struhalla, M., 2005, WO 2004 / 002386). The hit rate was compared with that of a metagenome bank cloned into the conventional pUC-vector. The target activity was an activity that is readily detectable with an established enzyme assay, and whose occurrence in metagenome banks has been described sufficiently in the literature.
1. Preparation of the Metagenome Bank
[0197]For the metagenome banks used, metagenomic DNA (mgDNA) was isolated from the contents of a sheep's rumen by direct lysis (Zhou. J.; Bruns, M. A.; Tiedje, J. M. (1996): DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol; 62(2): 316-22). For preparing the metagenome bank in pF2F4, the mgDNA was then partially digested with the restriction enzyme AluI and ligated by stand...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| incubation time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| OD | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| catalytic activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com