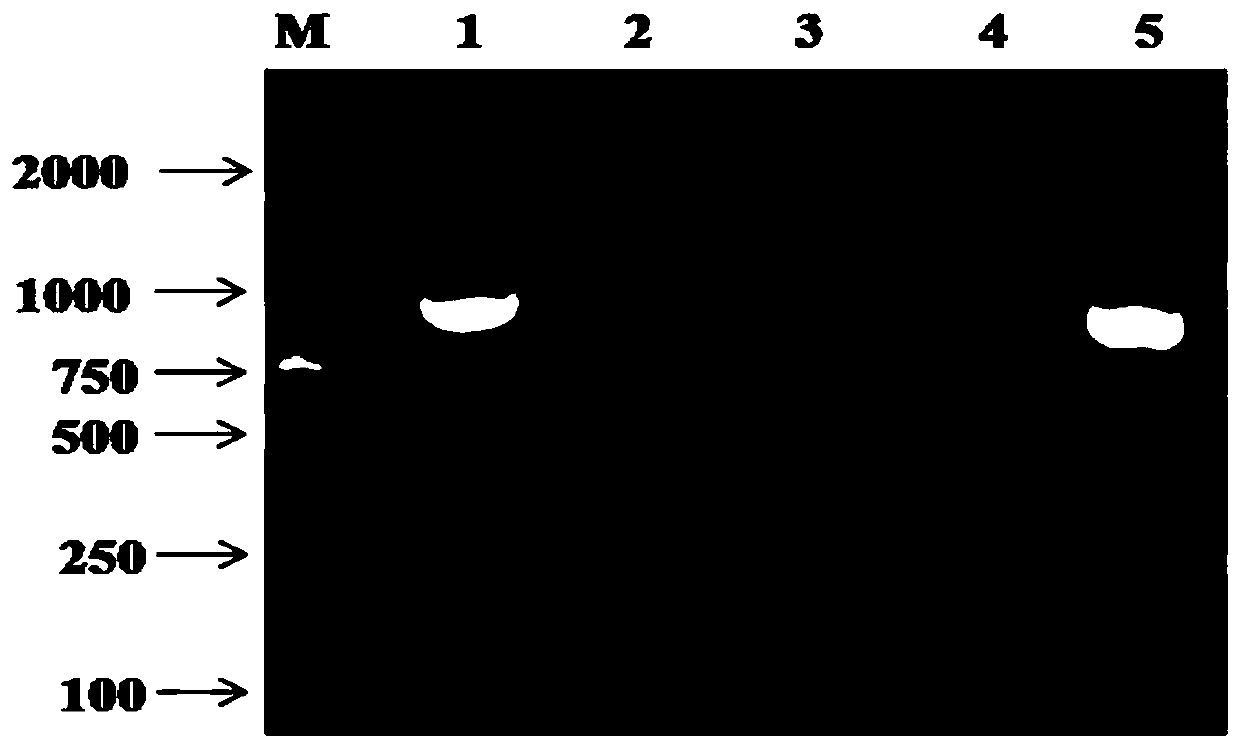
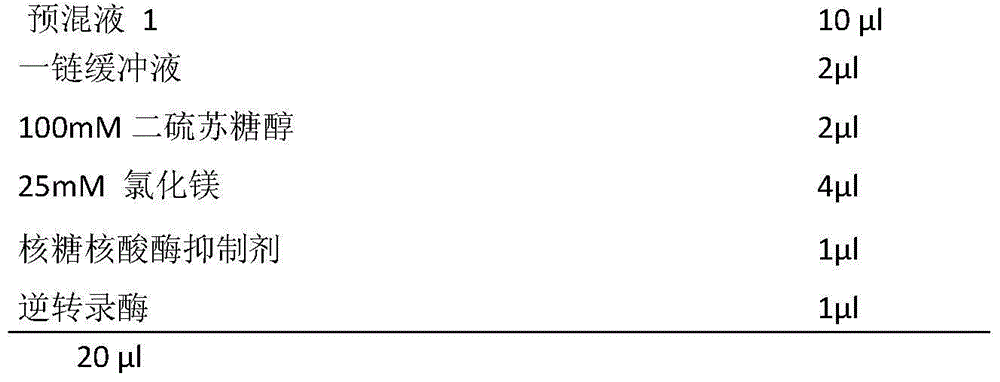Patents
Literature
76 results about "Metagenomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics or community genomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods.
Virus infection detection and identification method based on metagenomics
ActiveCN105112569AHigh detection sensitivityLow initial sample size requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementViral nucleic acidNucleic acid sequence
The invention provides a virus infection detection and identification technology based on metagenomics. The virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics comprises the four portions of sample preparation, high-throughput sequencing, bioinformatic analysis and result re-checking. In the sample preparation portion, viral nucleic acid is effectively extracted or enriched from detection samples according to the requirements of the virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics and characteristics of different types of detection samples, and a nucleic acid library which can be used for a next-generation sequencing instrument is established. In the high-throughput sequencing portion, the nucleic acid library established in the sample preparation step is sequenced so to obtain sufficient high-quality nucleic acid sequence information. In the bioinformatic analysis portion, a large number of high-quality nucleic acid sequences obtained in the high-throughput sequencing step is analyzed to further obtain viral component information prompted by the nucleic acid of the samples. In the result re-checking portion, a bioinformatic analysis result and other information, such as technical contrast, are integrated to perform comprehensive study and judgment, finally alternative infection virus is determined, and other technologies, such as PCR, are utilized to perform re-checking.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Extraction method of soil microbe genome DNA and total RNA
The invention provides a method for effectively extracting crop rhizosphere soil microbe genome DNA and total RNA, which comprises the following steps: firstly, removing humus and other impurities which severely disturb nucleic acid extraction in soil samples by aluminum sulfate; further crushing soil microbe cells by glass beads; adding sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) and LiCl solutions for cracking cells and dissociating nucleic acids; adding the mixture of phenol, chloroform and isoamylol for extracting; and then, depositing the extraction solution by isopropanol and sodium acetate to finally acquire the soil microbe metagenome DNA and total RNA. The method is suitable for extraction of the DNA and total RNA of soil in different regions. The invention establishes an extraction technology which has the advantages of simple and easy operation processes and higher purity of the prepared sample, and can provide an important basis for the research of soil metagenomics.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Metagenomics-based unknown pathogeny rapid identification system and analysis method
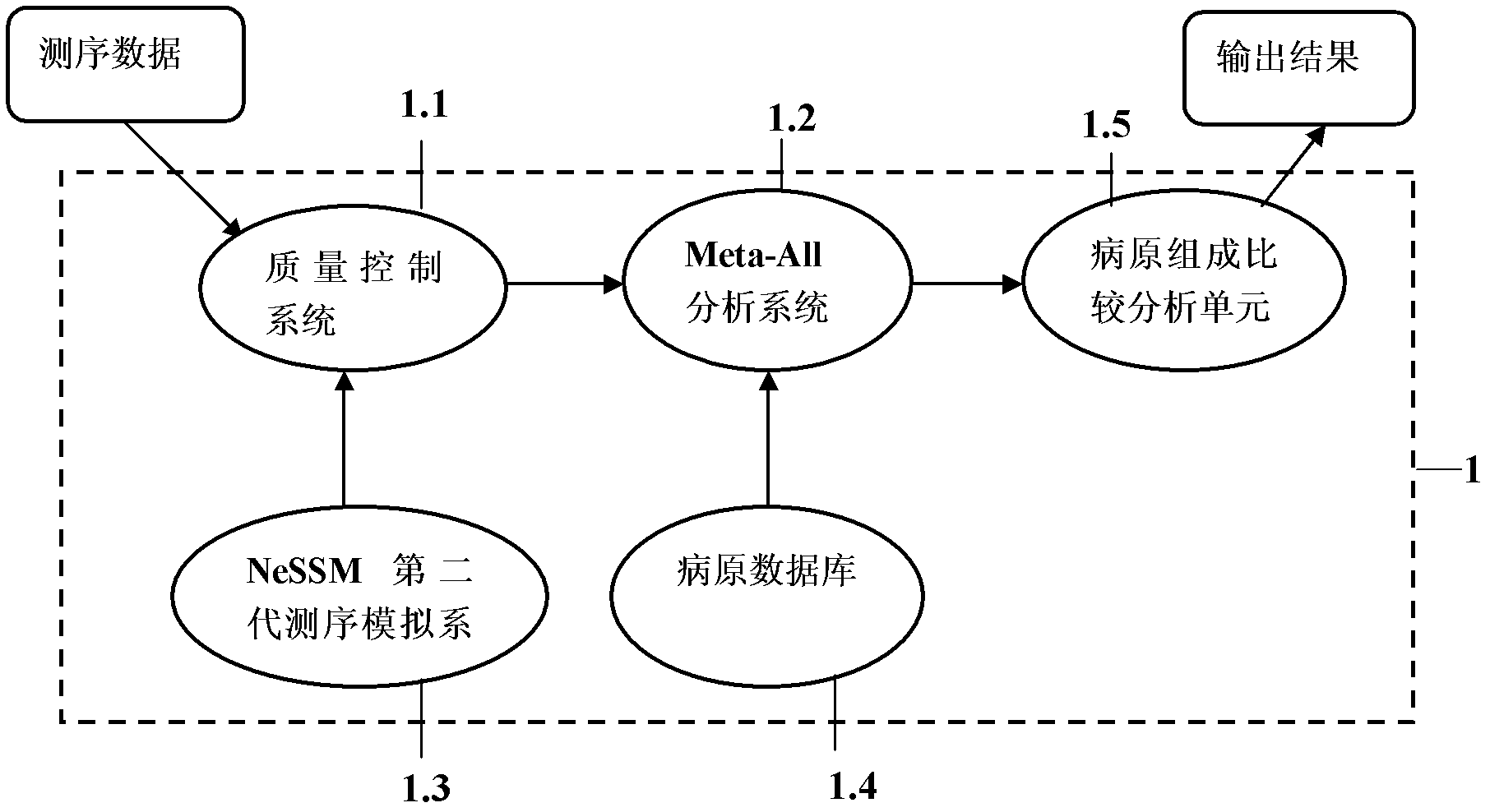
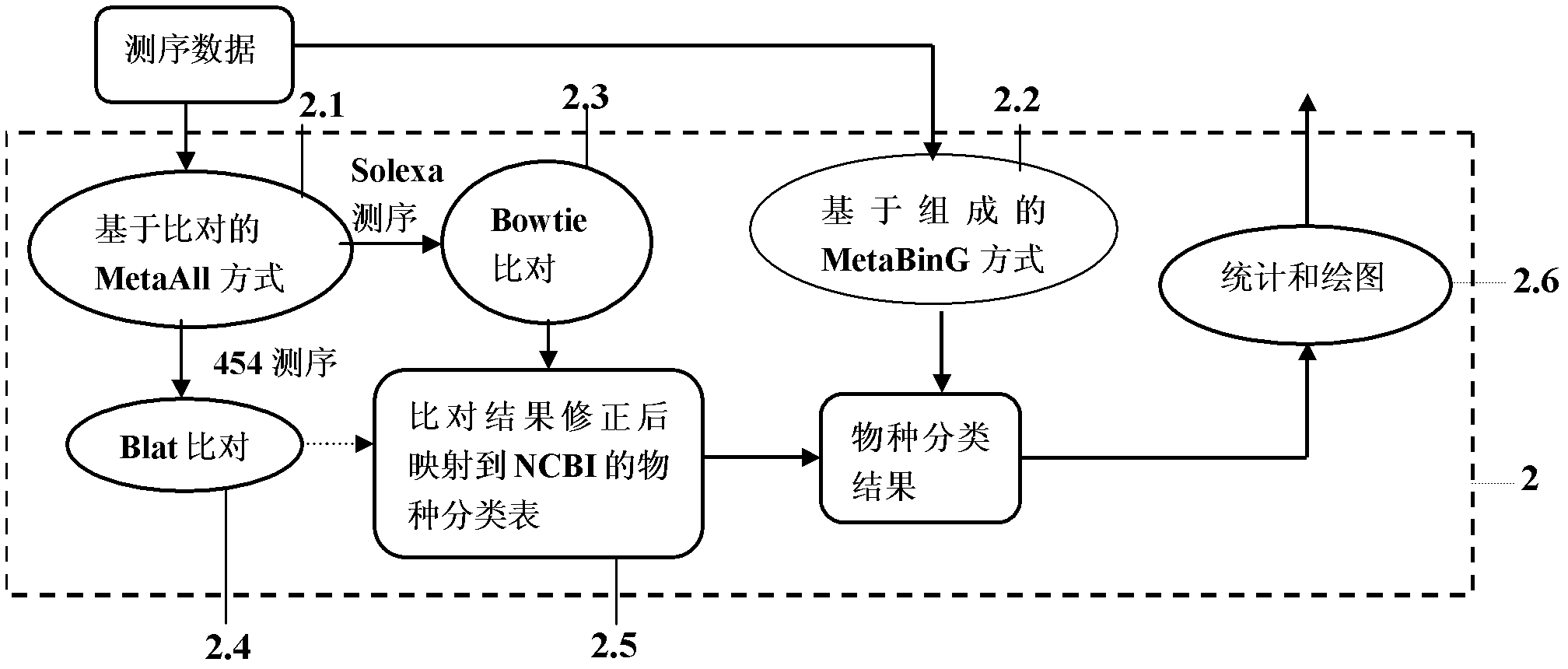
The invention provides a metagenomics-based unknown pathogeny rapid identification system and an analysis method. Unknown pathogeny is identified and analyzed by applying a metagenomics-based method. The metagenomics-based unknown pathogeny rapid identification system comprises a sequencing quality control system, a Meta-All analysis system, an NeSSM second-generation sequencing simulation system, a pathogeny database system and a pathogeny composition comparing and analyzing unit, wherein the sequencing quality control system is used for carrying out quality analysis on sequencing data and removing part the sequencing quality of which does not accord with the requirement; the Meta-All analysis system is used as a main body of the metagenomics-based unknown pathogeny rapid identification system and is used for analyzing the species composition structure in a metagenomic library from the sequencing data; the NeSSM second-generation sequencing simulation system is used as an independent part to be capable of generating simulating sequencing data; the pathogeny database system automatically updates database resources needed to be used by the Meta-All analysis system; and the pathogeny composition comparing and analyzing unit is used for comparing composition structures of pathogenies in metagenomic libraries from different sources according to a species composition table and finding out a pathogeny with high correlation with diseases. The metagenomics-based unknown pathogeny rapid identification system has the advantages that the range of identifying the unknown pathogeny can be rapidly reduced by using the metagenomics-based method, and thus the identification speed is increased; and meanwhile a fully-unknown pathogeny can be analyzed from similar pathogenies.
Owner:SHANGHAI CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION TECH
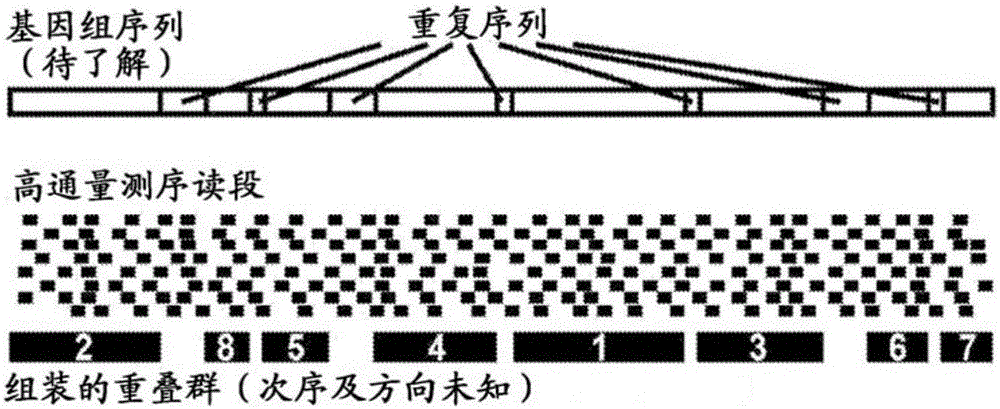
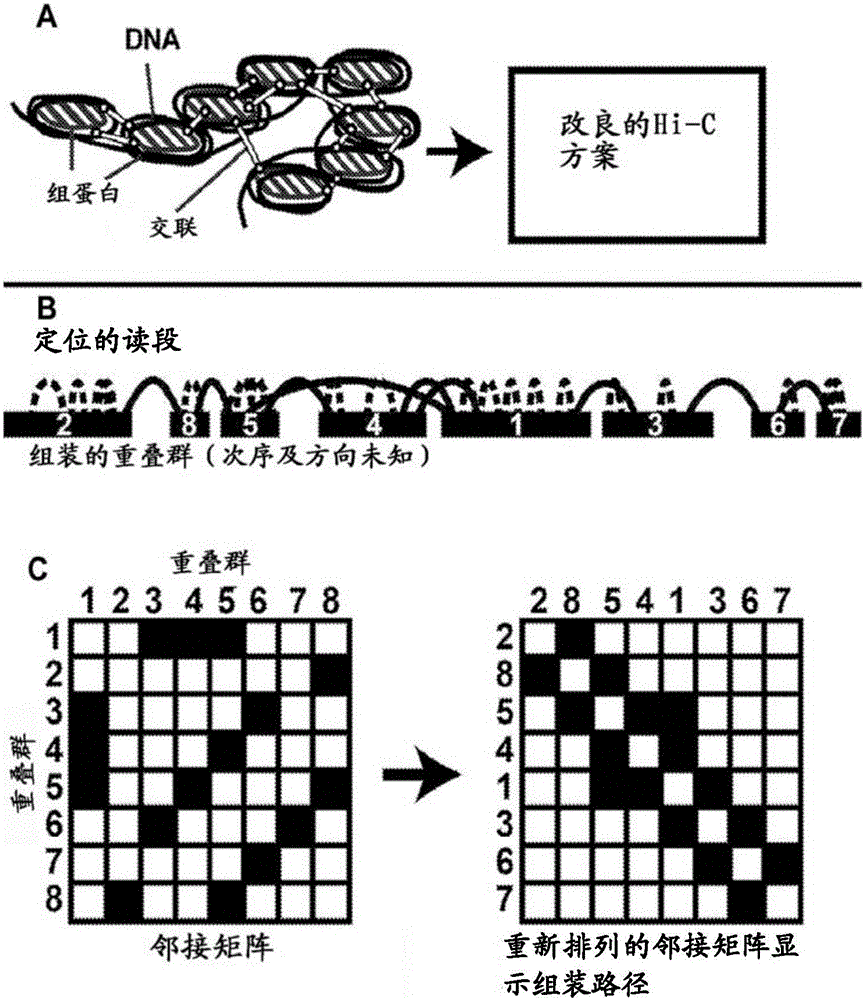
Methods for genome assembly and haplotype phasing
The disclosure provides methods for greatly accelerating and improving de novo genome assembly. The methods disclosed herein utilize methods for data analysis that allow for rapid and inexpensive de novo assembly of genomes from one or more subjects. The disclosure further provides that the methods disclosed herein can be used in a variety of applications, including haplotype phasing, and metagenomics analysis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
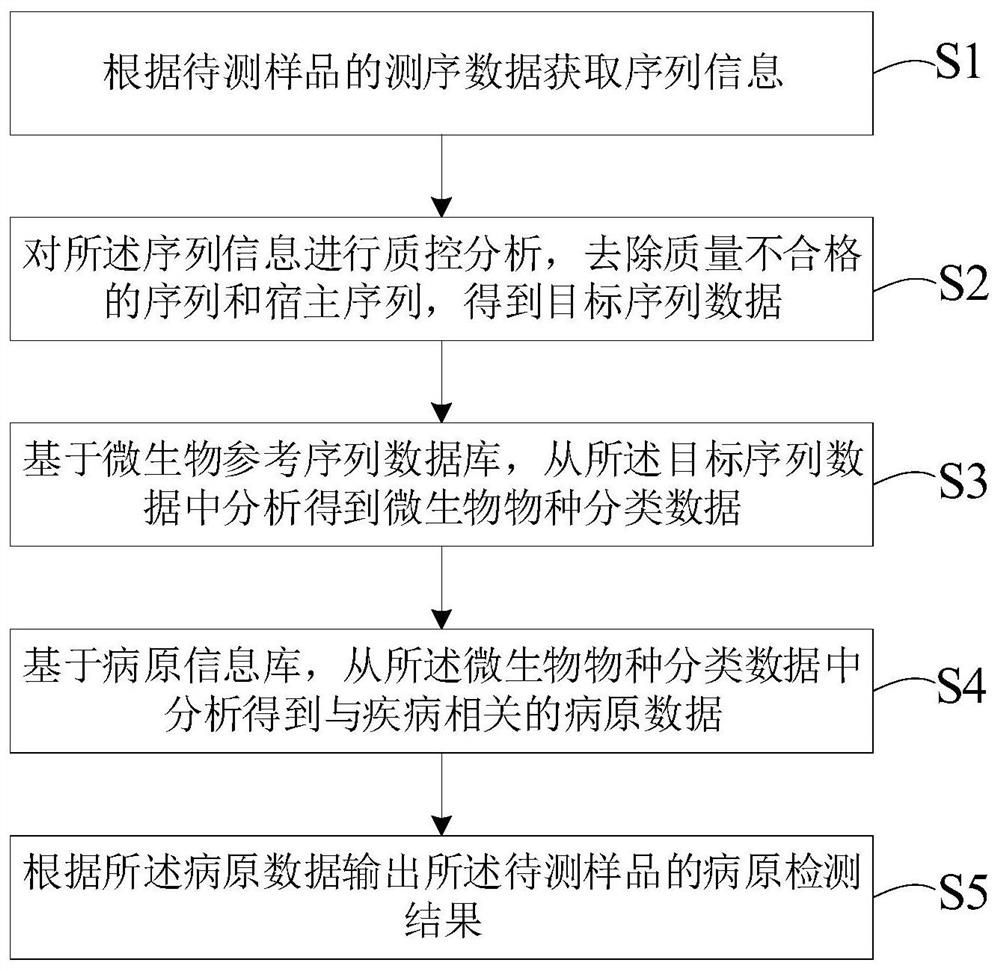
Metagenomics-based pathogen analysis method, analysis device, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN111951895AHigh reference significanceImprove readabilityBiostatisticsSequence analysisGenomicsMicroorganism
The invention relates to a metagenomics-based pathogen analysis method and device, equipment and a storage medium. According to the metagenomics-based automatic pathogen analysis method provided by the invention, on one hand, the flow and tools of a data analysis method are integrated and optimized, and the pathogen identification process is standardized, so that the data analysis time can be greatly shortened, the clinical detection period can be shortened, and rapid detection can be realized; and on the other hand, a platform effectively distinguishes pathogenic bacteria from background bacteria by establishing a microorganism reference sequence database and a pathogen information base and comprehensively evaluating parameters and evidence grades, so that missing detection caused by non-coverage can be effectively prevented, and the reference significance and interpretability of clinical detection results are further improved.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEWORKS TECH CO LTD
Metagenome data analysis method based on next-generation sequencing technology
PendingCN112071366ASolve incomplete problemsThe analysis process is reasonableCharacter and pattern recognitionHybridisationGenomicsContig
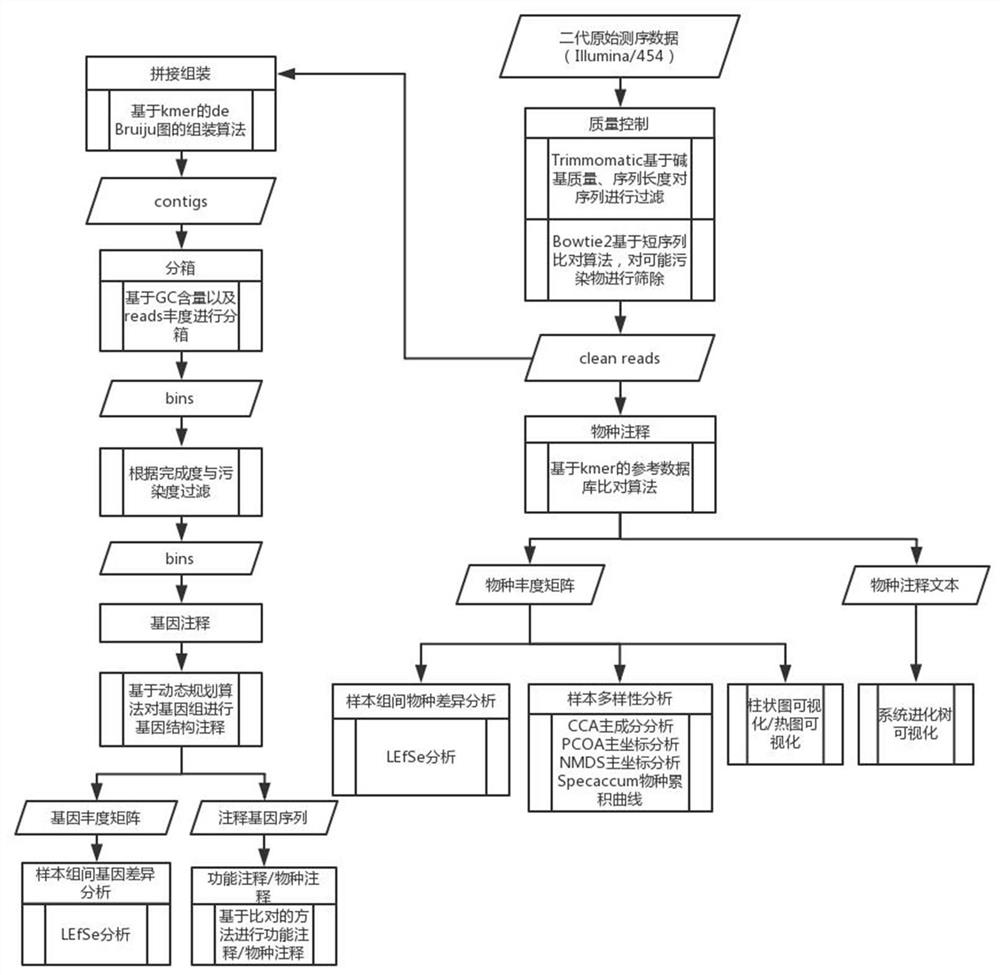
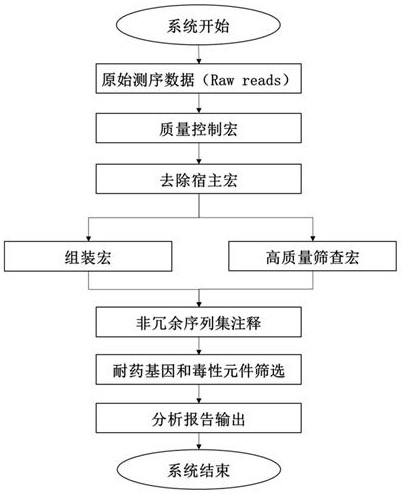
The invention discloses a metagenome data analysis method based on a next-generation sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out quality control on original sequencing data to obtain clean reads; (2) performing species annotation on the clean reads subjected to the quality control; (3) performing statistical analysis on the sample diversity based on a species abundance matrix; (4) performing statistical analysis on species with significant differences among sample groups based on the species abundance matrix; (5) splicing and assembling the clean reads to obtain a contigs sequence; (6) packaging the contigs obtained by splicing and assembling into boxes to obtain bins; (7) carrying out gene annotation on the bins subjected to boxing; (8) performing statistical analysis on the genes with significant differences among the sample groups based on the gene abundance matrix; and (9) based on the gene annotation result, performing function and species annotation on the sequence. A whole process from metagenome next-generation sequencing data processing to species composition analysis, gene composition analysis and function annotation is provided, an accurate analysis result is provided for researchers, and the metagenomics problem is comprehensively analyzed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
A method for extracting total DNA from environmental samples with high efficiency in removing humus
The invention discloses a method for extracting total DNA from an environmental sample with high efficiency for removing humus, comprising the following steps: (1) taking 0.3 g of sieved soil sample in a 2 mL centrifuge tube equipped with three 2.5 mm-3.0 mm sterilized glass beads, Add 1 mL of decomposing buffer, Vortex-Genie2 (Mobio Laboratories Inc) for 1 min, centrifuge at 12000 r / min for 2 min, discard the supernatant; (2) add 1 mL of 0.5 mol / L calcium chloride solution, Vortex-Genie2 (Mobio Laboratories Inc) ) Vortex for 2 min, centrifuge at 12,000 r / min for 1 min, and discard the supernatant; (3) Add 800 μL of DNA extraction buffer, and Vortex-Genie2 (Mobio Laboratories Inc) vortex for 5 s. Rapid and efficient extraction of total soil DNA, providing high-purity genomic DNA for soil metagenomics research.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Detection method for biological community structures of ocean brown tide
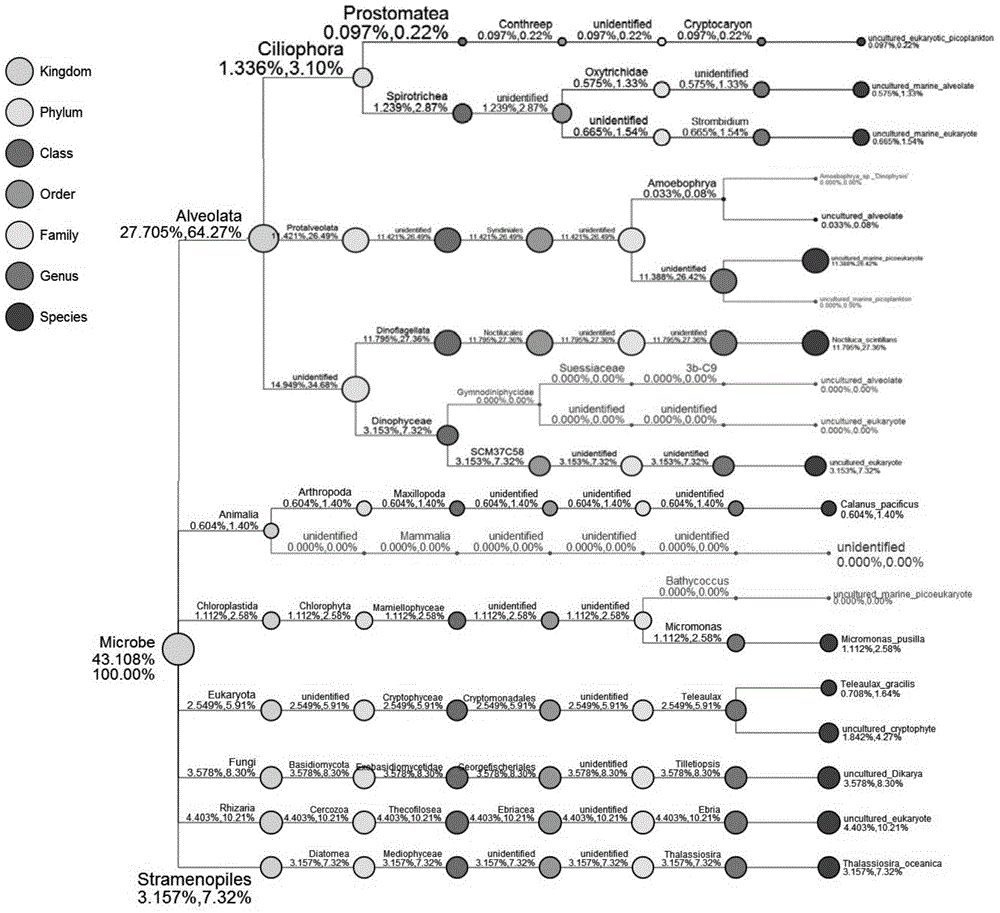
The invention discloses a detection method for the biological community structures of an ocean brown tide. According to the detection method, miniature organism 18S rDNA in a water area environment is detected by virtue of a metagenomics high-throughput sequencing technology, the obtained OUTs and species annotations are combined, and then diversity, uniformity, abundance and dominance index analysis is carried out on the OUTs, thus judging the dominance degrees of organisms in the ocean brown tide; statistics and judgment for the dominance evolvement rules of dominant species in brown tide outbreaks are promoted. The embodiment of the invention designs and verifies primer sequences designed with regard to the organisms in the brown tide, and a verification for the actual brown tide outbreak cases proves that the method disclosed by the invention is capable of authenticating the biological community structures of the ocean brown tide in ocean water, providing a technical support for brown tide monitoring operation, and providing a technical support for avoiding environment risks for healthy mariculture.
Owner:LIAONING OCEAN & FISHERIES SCI RES INST
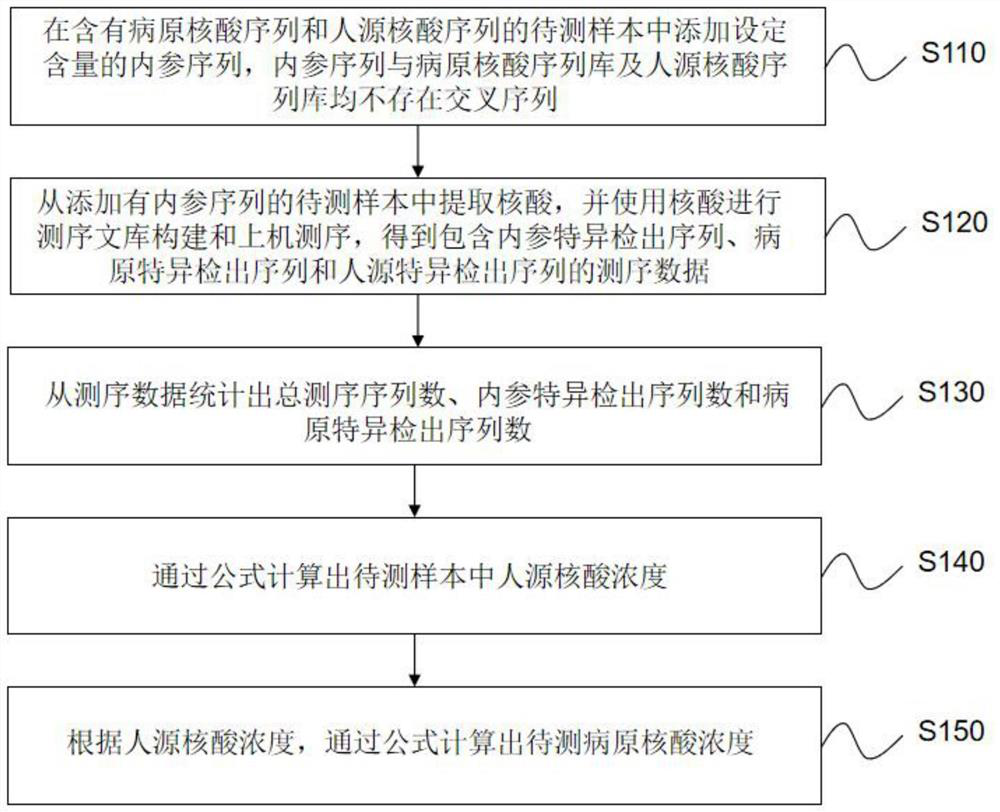
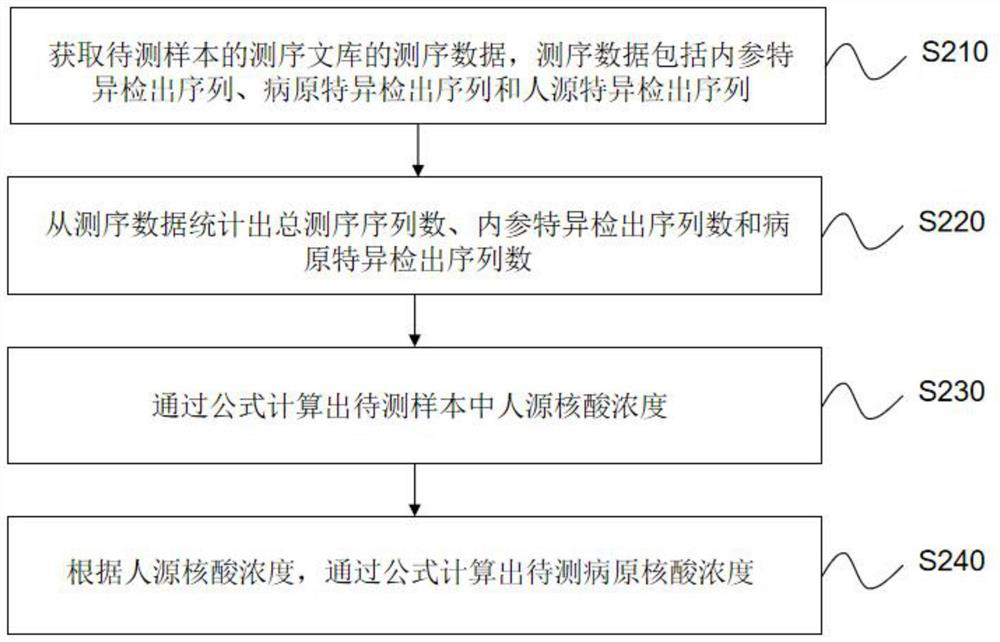
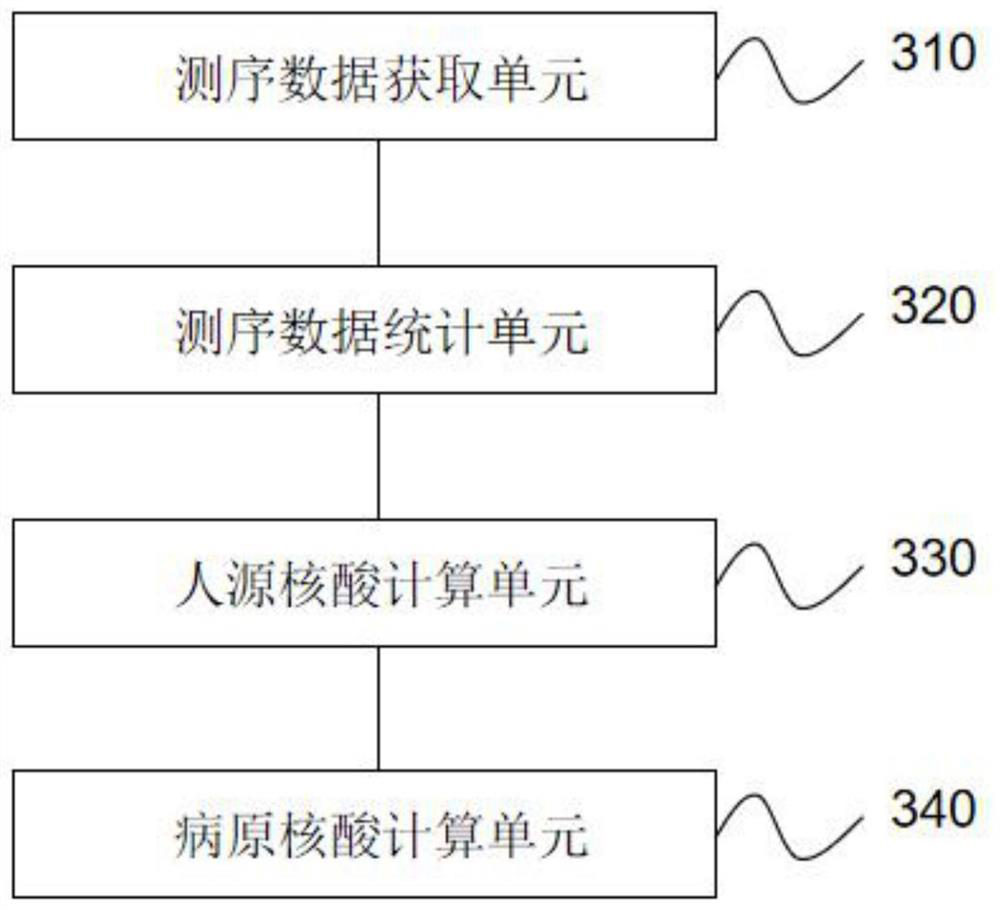
Method and device for quantitatively detecting metagenome pathogens based on internal reference
The invention relates to a method and a device for quantitatively detecting metagenome pathogens based on internal reference. The method comprises the following steps of: adding an internal referencesequence with a set content into a sample to be detected containing a pathogen nucleic acid sequence and a human-derived nucleic acid sequence; extracting nucleic acid from the to-be-detected sample added with the internal reference sequence, and performing sequencing library construction and computer sequencing by using the nucleic acid to obtain sequencing data; counting the total sequencing sequence number, the internal reference specific detection sequence number and the pathogen specific detection sequence number; calculating the concentration of the human-derived nucleic acid in the sample to be detected; and calculating the concentration of the to-be-detected pathogenic nucleic acid according to the concentration of the human-derived nucleic acid. According to the invention, a theoretical calculation model based on a metagenomics pathogen detection technology is established, and the model can carry out auxiliary analysis on abnormal conditions occurring in pathogen metagenome detection.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司 +1
Screening and application of feces gene marker
ActiveCN109658980AEnrich and gain insight into pathological mechanismsEquivalentBiostatisticsProteomicsGenomicsStool dna
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, and particularly to screening and application of a feces gene marker based on high-flux metagenome sequencing analysis. According to the method, through extracting feces DNA for performing macro genome sequencing and ROC curve analysis by means of a shotgun method, the gene marker is screened, and furthermore the gene marker is verified through fluorescent real-time quantified PCR for obtaining consistency. According to the method, metagenome high-flux shotgun sequencing technical measurement is firstly performed in feces of Chinese PD patients, and a screening method for the feces gene marker is established; various different genes in the feces of the PD patient are found; 25 feces gene markers are screened as PD diagnosis markers for auxiliary diagnosis of the PD patient; and the method has important academic meaning and application prospect for enriching and further understanding the pathological mechanism of PD.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pathogenic microorganism detection method and kit based on metagenomics
ActiveCN111020018AImprove build efficiencyReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomicsPathogenic microorganism
The invention provides a pathogenic microorganism detection method and kit based on metagenomics. The method comprises the following steps: extracting nucleic acid; constructing a high-throughput sequencing library; quantifying the sequencing library constructed in the previous step; diluting the quantified sequencing library to 1-4 pM, and carrying out high-throughput sequencing with a sequencer;and analyzing sequencing data obtained in the high-throughput sequencing. The invention further provides a pathogenic microorganism detection kit. The metagenomics-based high-throughput sequencing library construction method and the kit provided by the invention have the advantages that fragmentation enzyme is used for fragmenting DNA, DNA loss is smaller compared with a mechanical method, a fragmentation speed is higher, and the construction efficiency of the whole library is improved.
Owner:天津金匙医学科技有限公司
Method for extracting microorganism total DNA from coal seam water sample
ActiveCN105802957AIncrease concentrationHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationParticulatesPhenol
The invention provides a method for extracting microorganism total DNA from a coal seam water sample, belongs to coal seam water sample microorganism analysis and aims to solve the technical problem by providing the method for extracting microorganism total DNA from a coal seam water sample with complex composition. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating the coal seam water sample, centrifugally removing large particulate impurity, and collecting microorganisms in the water sample by means of membrane filtering; breaking microorganism cells, shredding a filter membrane on which microorganisms are collected, resuspending in a buffer solution, breaking cells by means of a ball mill, inoculating for 2-4 h at 55 DEG C with proteinase K and sodium dodecyl sulfate solution until a solution is clear; purifying and precipitating microorganism total DNA, removing miscellaneous proteins by phenol-chloroform process, and adding isopropanol precipitate to collect total DNA. The total DNA extracting method is suitable for coal seam water sample and related samples with complex composition and is good in cell breaking effect, and extracted genome is high in purity and good in completeness and is directly useful in subsequent metagenomics analysis, DGGE analysis and the like.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV +1
Total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction method and kit for synchronously removing humic acid and mycoprotein
The invention provides a total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction method and a kit for synchronously removing humic acid and mycoprotein and relates to the field of research of metagenomics in soil microbiology and general microbiology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) suspending samples by utilizing a humic acid combination solution, so as to obtain sediments; (2) adding a buffer solution and proteinase K, and carrying out centrifuging to obtain supernate; (3) adding a coagulant to carry out coagulating sedimentation on the residual humic acid and mycoprotein, and carrying out centrifuging to obtain the supernate; (4) adding isopropanol to precipitate DNA; (5) adding 70% ethanol to wash the sediments, and blowing off the residual ethanol; (6) adding a DNA dissolving solution (TE) to dissolve the sediments, so as to obtain a sample, namely the total DNA. The kit comprises the following components: the humic acid combination solution, a PBS butter liquid, an extraction butter liquid, the proteinase K, a 20% SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfonate) water solution, the coagulant, a DNA washing agent, the 70% ethanol and the DNA dissolving solution. Due to the adoption of the method and the kit, the one-time extraction quantity of the total DNA is enough to carry out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification for dozens of times.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for extracting microbial genome DNA from poplar wood
ActiveCN106754872AReduce degradationAvoid damageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenomic sequencingMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for extracting microbial genome DNA from poplar wood. According to the method, a CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) method and an SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfonate) method are combined, and technical parameters of various steps are optimized, so that the genome DNA extracted by virtue of the method has the advantages of being high in concentration and free from pollution; determined by a spectrophotometer, OD260 / OD230 and OD260 / OD280 values are close to standard values, completely satisfying requirements of 16S rDNA / ITS sequencing and metagenomics sequencing adopted in the later period; therefore, the method can be directly applied to a molecular operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
DNA extracting agent, DNA extracting method and DNA extracting kit
The invention relates to a DNA extracting agent, a DNA extracting method and a DNA extracting kit. The DNA extracting agent includes a lysis solution and a cleaning agent; the lysis solution includesguanidinium isothiocyanate having a final concentration of 1-5 M, Tris-HCl having a final concentration of 0.01-0.2 M, and N-lauroylsarcosine having final mass percent by volume of 1-10%; the cleaningagent includes at least one of crosslinked polyvinyl pyrrolidone and polyvinyl pyrrolidone. The lysis solution and the cleaning agent in the DNA extracting agent can cooperate with each other, degradation of DNA in the extraction process can be decreased, and DNA purity can be improved; DNA prepared with the DNA extracting agent meets the requirements of metagenomics sequencing.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN +1
Method and device for detecting pathogenic microorganisms based on metagenomics
ActiveCN113744807AExpand the scope ofImprove accuracySequence analysisInstrumentsReference genesGenomics
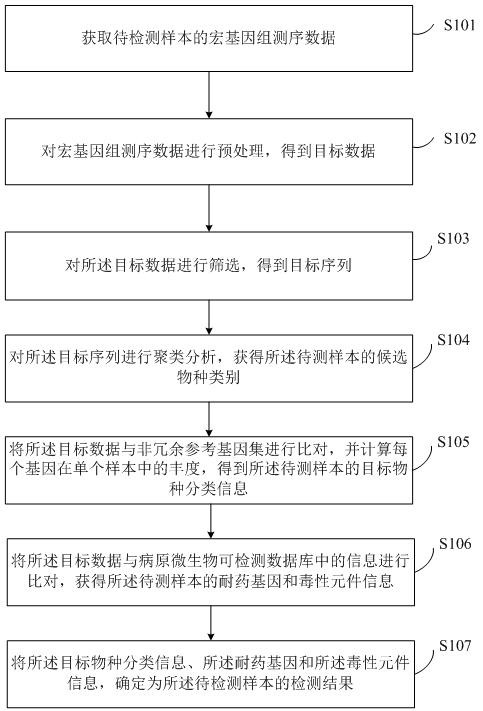
The invention discloses a pathogenic microorganism detection method and device based on metagenomics. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring metagenome sequencing data of a to-be-detected sample; preprocessing the metagenome sequencing data to obtain target data; screening the target data to obtain a target sequence; performing clustering analysis on the target sequence to obtain candidate species categories of the to-be-detected sample; comparing the target data with the non-redundant reference gene set, and calculating abundance of each gene in a single sample to obtain target species classification information of the to-be-detected sample; comparing the target data with information in a pathogenic microorganism detectable database to obtain drug-resistant gene and toxic element information of the to-be-detected sample; and determining the target species classification information, the drug-resistant gene and the toxic element information as a detection result of the to-be-detected sample. According to the invention, the pathogenic microorganism detection applicability range and the pathogenic detection accuracy are improved.
Owner:微岩医学科技(北京)有限公司 +1
Method for extracting microorganism total DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in pu'er tea piling fermentation process
The invention discloses a method for extracting microorganism total DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in a pu'er tea piling fermentation process at high quality. The method comprises the following steps of: separating microorganisms on the surface of pu'er tea by using ultrasonic wave and vortex oscillation; washing the microorganisms by using washing buffer solution; performing rough extraction on the microorganism total DNA by using DNA extract; and purifying the roughly extracted DNA. The method provided by the invention is low in cost and high in DNA extraction rate; the extracted DNA has high completeness and high purity and can meet the requirements of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) without purification or dilution; the purified DNA can meet the requirements of molecular biology research; and meanwhile, the extracted DNA covers bacteria and fungi and the requirements of subsequent researches in microorganism diversity, functional genes, metagenomics and the like can be met.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
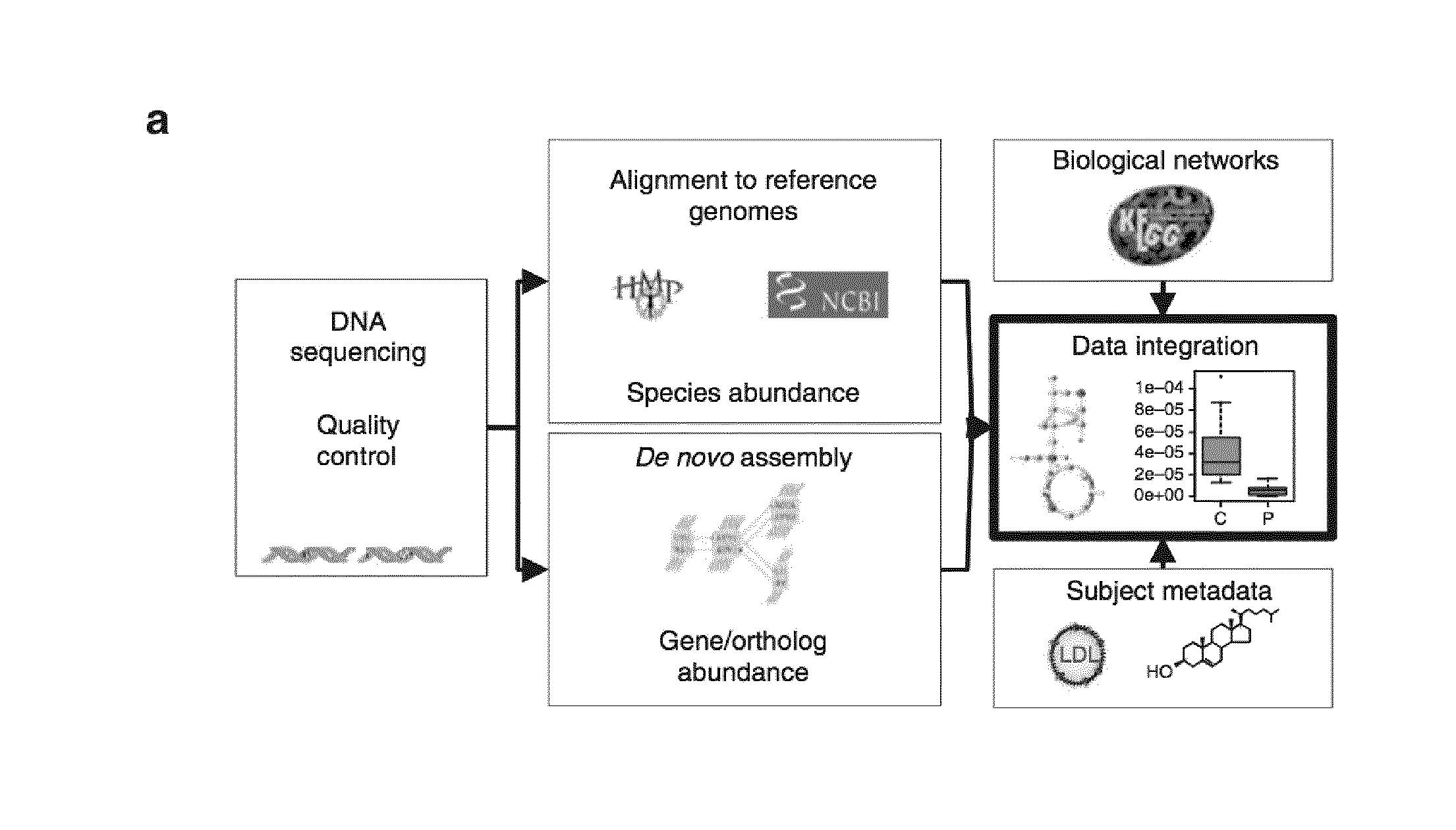
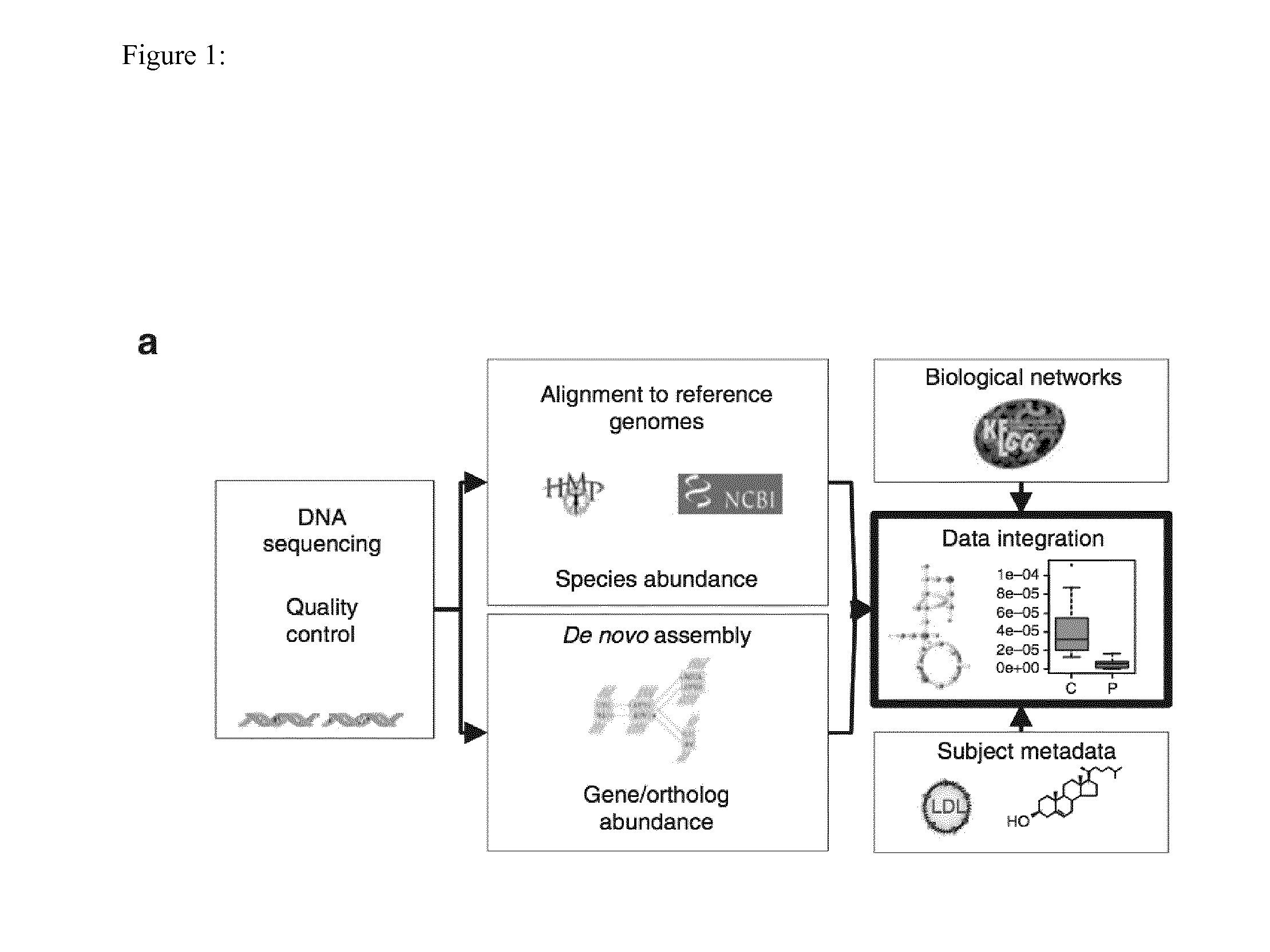
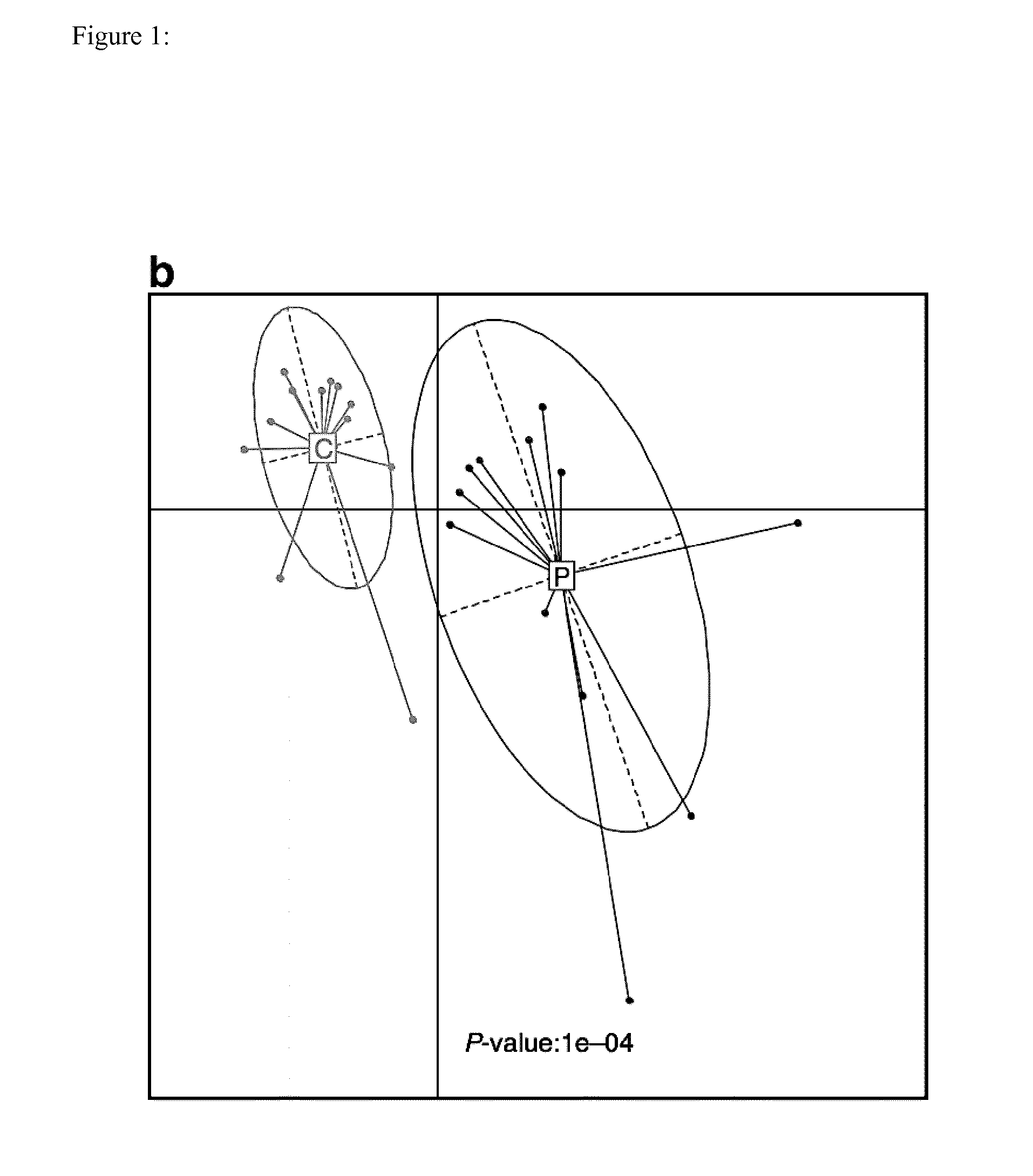
Identification of a Person having Risk for Atherosclerosis and Associated Disease by the Person's Gut Microbiome and the Prevention of such Diseases
InactiveUS20150299776A1Lower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideIntestinal microorganismsTreatment strategy
The present invention provides the use of metagenomics to identify a compositional or functional alteration of the gut metagenome related to atherosclerosis or atherosclerotic associated disease. Also provided are methods to identify a person having risk for atherosclerosis and associated diseases by determining the presence of specific bacterial groups or species and also metabolic functions in the person's gut microbiota and to use such information to develop a prevention or treatment strategy.
Owner:METABOGEN
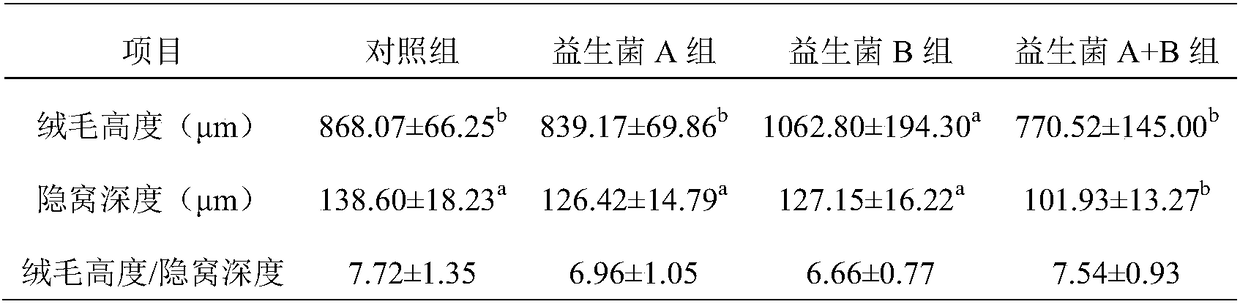
Screening method of feed probiotics capable of preventing chicken's infection caused by clostridium perfringens
InactiveCN108165619AAvoid discomfortAvoid blindnessMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesIntestinal microorganismsScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method of feed probiotics capable of preventing chicken's infection caused by clostridium perfringens. The method comprises following steps: screening chickens infected by clostridium perfringens in clinic and disease resistant chickens; collecting the intestinal chyme samples; carrying out high throughput sequencing on microbial floras in the intestinal tractsof infected chickens and disease resistant chickens; comparing and analyzing the microbes in the intestinal tracts of infected chickens and disease resistant chickens through a metagenomics method; and screening and identifying probiotics capable of preventing infection caused by clostridium perfringens. According to the method, the metagenomics big data of floras in the intestinal tracts of infected chickens and disease resistant chickens is analyzed; probiotics capable of preventing infection caused by clostridium perfringens are selected from massive microbial floras in the intestinal tracts of disease resistant chickens, the screened probiotics are from same animals, the rejection between probiotics and a host is avoided, moreover, the screening is targeted, aimless screening is avoided, and a large amount of labor, resources, and time is saved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
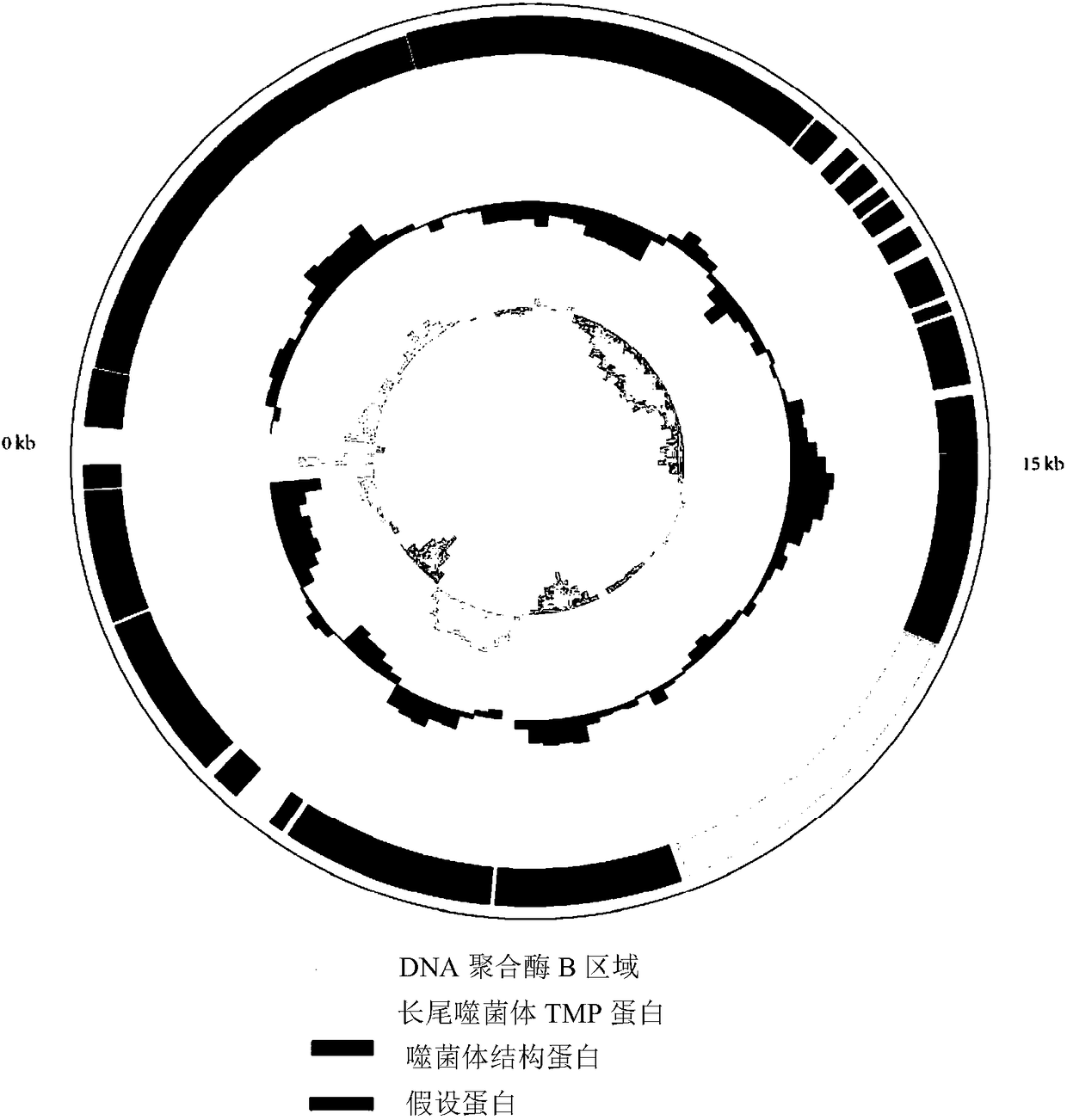
Siphoviridae as well as obtaining method and application thereof
InactiveCN108220249AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesOral diseaseEtiology
The invention discloses a siphoviridae. The siphoviridae contains nucleotide sequence for enclosing an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also discloses an obtaining method and application of the siphoviridae. The siphoviridae disclosed by the invention is a novel virus obtained by being separated from an oral cavity of a periodontitis patient by adopting a viral metagenomicsmethod and provides a new basis for an etiology, treatment and prevention strategy of oral diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
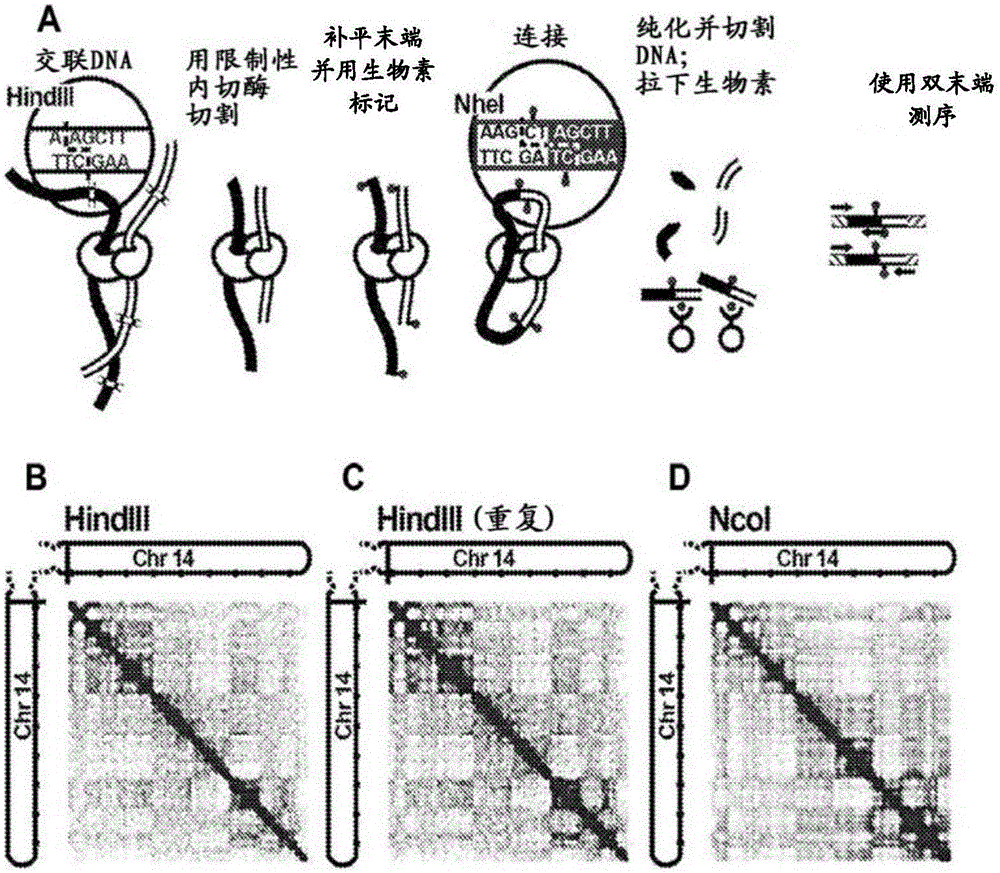
Hi-C high-throughput sequencing library building method suitable for microbial metagenomics and application
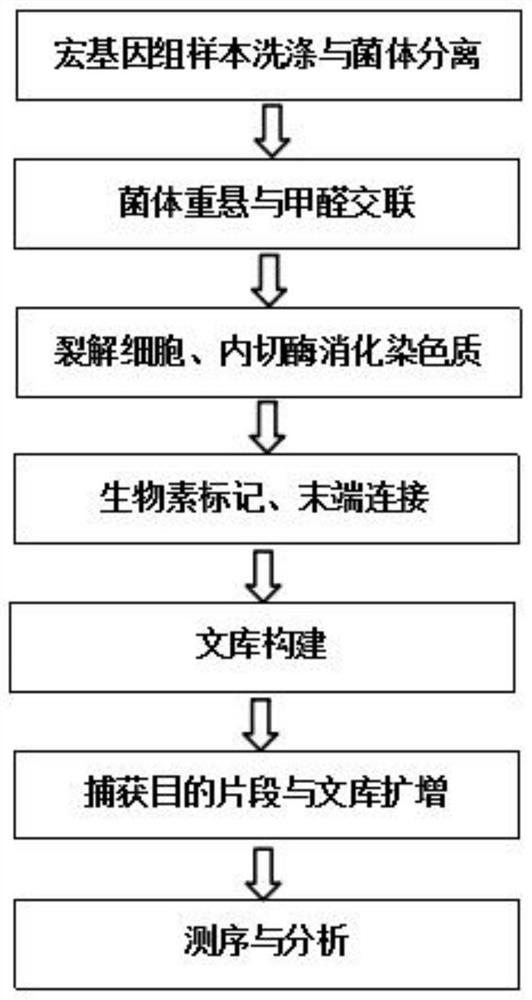
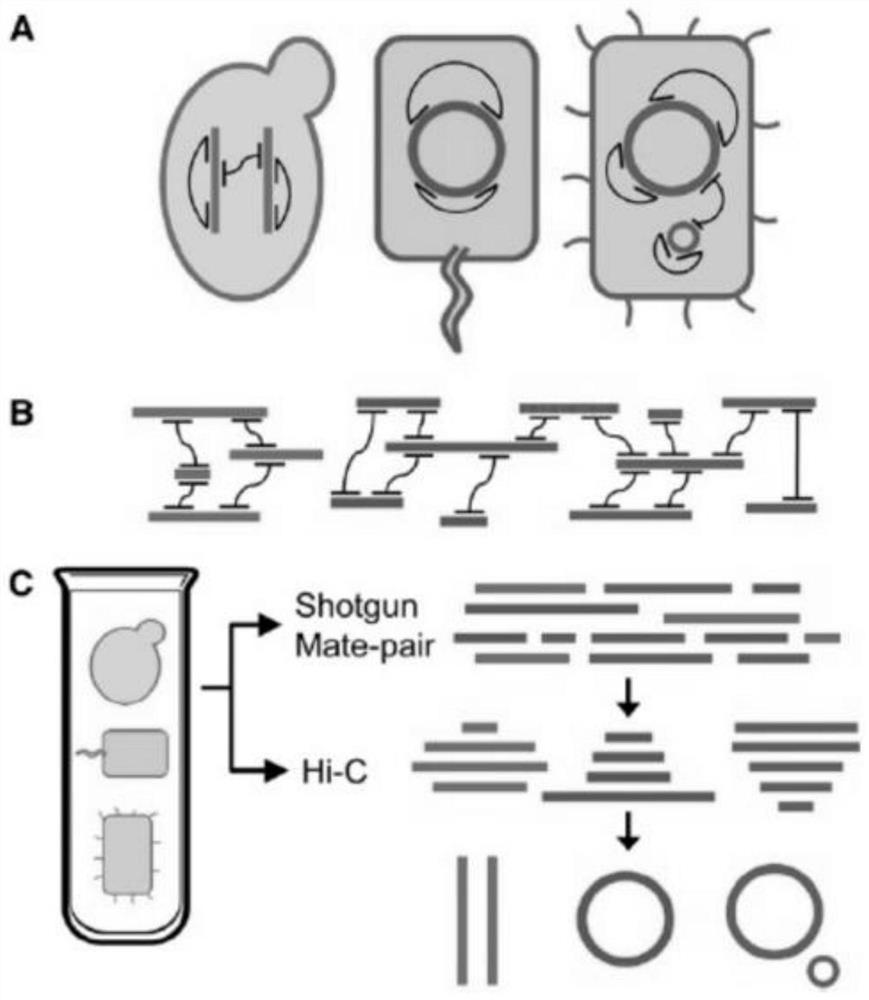
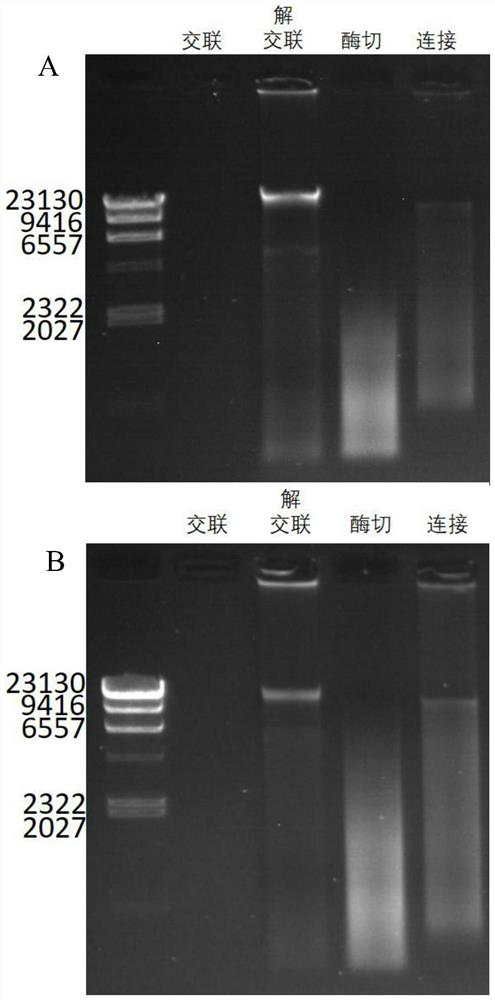
PendingCN111909983ARealize high-throughput sequencing library constructionIncrease effective data rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention relates to a Hi-C high-throughput sequencing library building method suitable for microbial metagenomics and application. The sequencing library building method comprises the following steps that 1), a metagenome sample is taken to be subjected to microbial and impurity separation, and formaldehyde cross-linking is carried out; 2), endonuclease digestion disruption is carried out oncell chromatin to obtain a material after endonuclease digestion; 3), end filling is carried out on the material after endonuclease digestion; 4), DNA cell nucleus intramolecular connection is carriedout; 5), unconnected end biotin is removed to obtain purified DNA, and the purified DNA is subjected to fragmenting, end repairing and A-tailing, and ligation adaptor; 6), DNA target fragments are sorted; and 7), the target fragments are captured by biotin, and library amplification and sequencing are carried out. According to the Hi-C high-throughput sequencing library building method suitable for microbial metagenomics and the application, microorganisms in a complex environment are enriched through separation of the microorganisms and environmental impurities, metagenome data analysis is not limited to a single species any more, and various microorganisms in the complex environment can be subjected to clustering analysis, so that Hi-C high-throughput sequencing library building of microbial metagenomics is achieved, and the application range of the Hi-C technology is expanded.
Owner:WUHAN FRASERGEN CO LTD
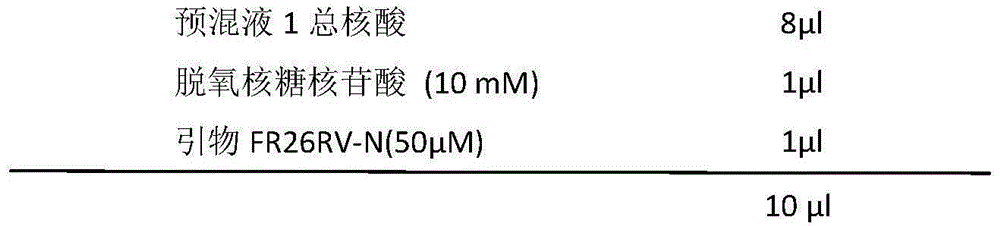
Metagenomics-based respiratory tract throat swab sample library building method and pathogen detection method
ActiveCN112646859AIncrease concentrationImprove utilization efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsA-DNA
The invention provides a metagenomics-based respiratory tract throat swab sample library building method and a pathogen detection method, and relates to the technical field of microbiological detection. The library building method comprises the following steps: (a) pretreatment of a to-be-detected sample solution: adding lysozyme for digestion; (b) extraction of total nucleic acid of the sample: not adding carrier RNA in an extraction process; (c) cDNA synthesis: carrying out reverse transcription by adopting a random primer; (d) purifying a product synthesized in step (c) by using magnetic beads; and (e) construction of a sample DNA library. Based on a DNA-RNA co-sequencing principle, the invention provides the metagenomics-based method suitable for throat swab sample library building and detection and pathogen detection of a throat swab sample metagenome can be realized through a single reaction.
Owner:中国人民解放军疾病预防控制中心
16S and metagenome sequencing data association analysis method and system, and equipment
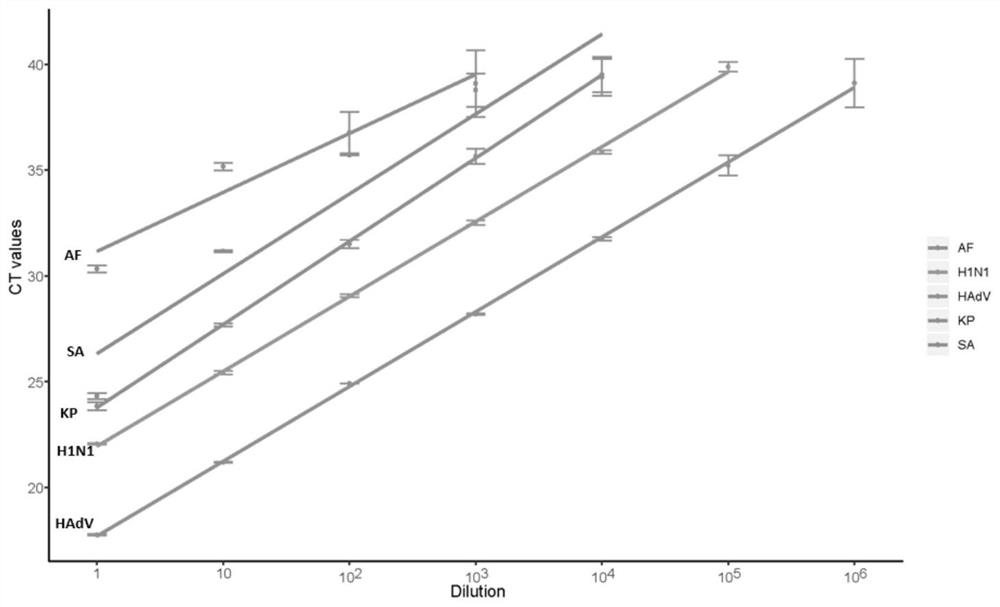
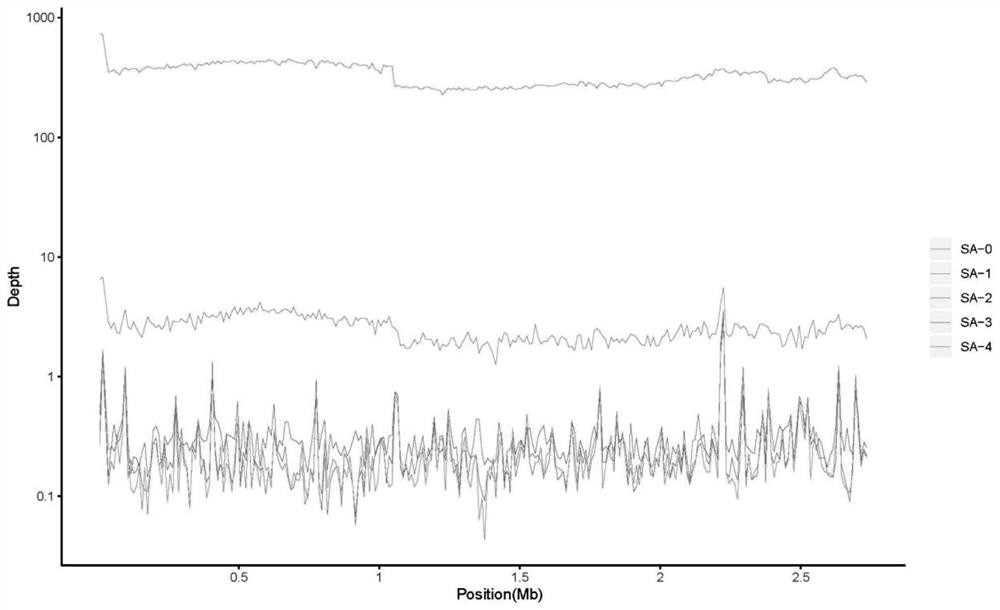
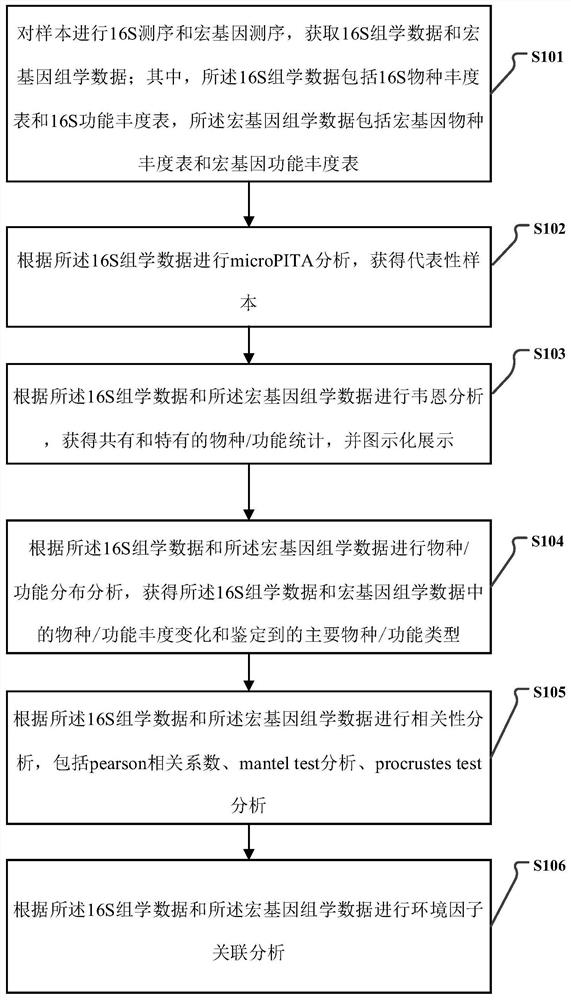
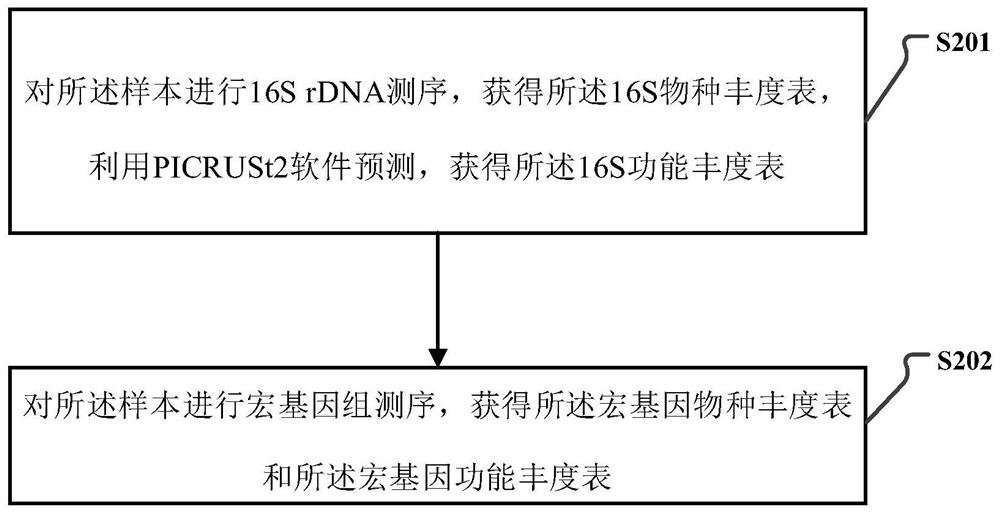
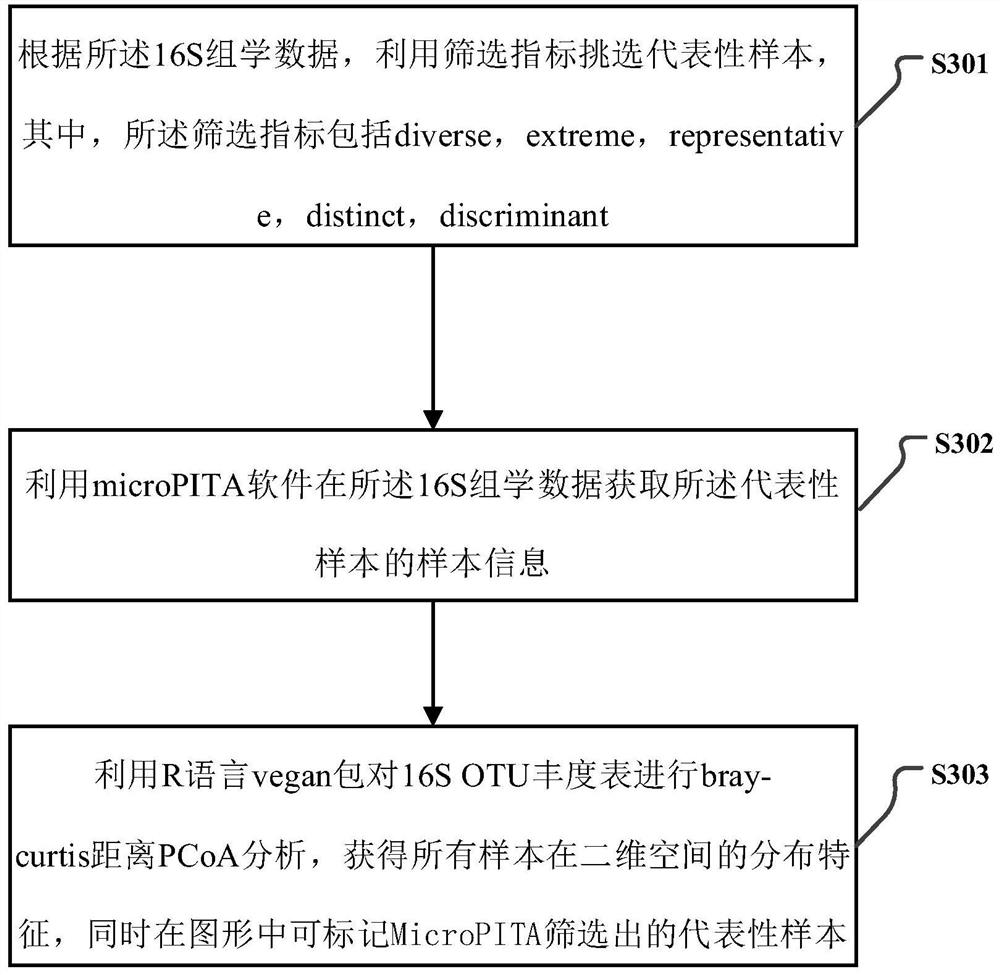
ActiveCN112669899AComplement each otherSupport each otherData visualisationSequence analysisGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a 16S and metagenome sequencing data association analysis method and system, and equipment. According to the scheme, the method comprises the following steps: performing 16S sequencing and metagenomics sequencing on a sample to obtain 16S omics data and metagenomics data; carrying out microPITA analysis according to the 16S omics data to obtain a representative sample; performing Ween analysis according to the 16S omics data and the metagenomics data to obtain common and specific statistical species / function statistics, and performing graphical display; carrying out species / function distribution analysis to obtain species / function abundance changes and main species / function types in all the samples of the two omics; and performing correlation analysis and environmental factor correlation analysis according to the 16S omics data and the metagenomics data. According to the scheme, the 16S and metagenome sequencing data correlation analysis method is provided, the metagenome extension data is used for researching the depth, 16S is used for verifying the analysis accuracy of metagenome data, and mutual complementation and verification of two omics data are achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENE DENOVO BIOTECH
dna extraction reagent, dna extraction method and dna extraction kit
The invention relates to a DNA extracting agent, a DNA extracting method and a DNA extracting kit. The DNA extracting agent includes a lysis solution and a cleaning agent; the lysis solution includesguanidinium isothiocyanate having a final concentration of 1-5 M, Tris-HCl having a final concentration of 0.01-0.2 M, and N-lauroylsarcosine having final mass percent by volume of 1-10%; the cleaningagent includes at least one of crosslinked polyvinyl pyrrolidone and polyvinyl pyrrolidone. The lysis solution and the cleaning agent in the DNA extracting agent can cooperate with each other, degradation of DNA in the extraction process can be decreased, and DNA purity can be improved; DNA prepared with the DNA extracting agent meets the requirements of metagenomics sequencing.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN +1
Bat-derived adeno-associated virus genome, amplification primers and their application, and amplification method
The invention discloses a bat-derived adeno-associated virus genome, amplification primers and their application, and an amplification method. to the amplification primers, five pairs of primers are used herein as upstream primers and downstream primers; an adeno-associated virus RNA template extracted from a bat sample is subjected to RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) amplification to obtain the amplification primers; the amplification primers are subjected to nucleotide sequencing; a complete sequence of the bat-derived adeno-associated virus genome is acquired by splicing and comparing. In allusion to characteristics of the bat-derived adeno-associated virus genome, short sequence fragments of the bat-derived adeno-associated virus genome are acquired by sequencing in reference to metagenomics in the lab; a fragmented amplification strategy is designed according to an open reading box included in the genome; the corresponding primers are designed according tothe conserved region; five pairs of primers are acquired by screening and are effective in amplifying genome sequencing of the bat-derived adeno-associated virus. The bat-derived adeno-associated virus genome amplification primers are widely applicable to the demand for detecting bat-derived adeno-associated viruses and to the corresponding field of scientific research.
Owner:中国人民解放军东部战区疾病预防控制中心
Biosensor and construction method of gene trapping system
The invention discloses a biosensor and a construction method of a gene trapping system, and belongs to the technical field of biotechnologies. The biosensor is a transformant or a recombinant constructed by using Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1 as a chassis organism. The construction method of the gene trapping system comprises the steps that gene fragments are trapped; and the trapped gene fragments are sequenced to obtain the sequence of the trapped gene fragments. By adopting the biosensor and the construction method of the gene trapping system, a technology developed on the basis of related technologies of the prior micro genomics, based on the whole-cell biosensor and used for trapping functional genes from environmental samples is provided.
Owner:BEIJING WELLSENS BIOTECH
Facial skin surface microorganism sampling method based on metagenomics and application
PendingCN111996233AWon't hurtAvoid stimulationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyFacial skin
The invention relates to a facial skin surface microorganism sampling method based on metagenomics. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dipping a disposable medical disinfection cotton swabinto sterile normal saline, and performing sampling in an area specified by a disposable sterilization specification plate; (2) in a sterile room, collecting samples according to the sequence of leftcheek, right cheek and forehead of a subject, and circling the cotton swabs obtained in the step (1) for 50 times in each area; and (3) putting the sampled cotton swab obtained in the step (2) into asterile Pbw solution, and performing storing at 4 DEG C for later use. The skin surface of the subject is not damaged in the sampling process, skin irritation caused by invasive sampling is avoided, safety is higher, and the method is suitable for facial skin sampling. Subsequent microbial community sequencing verifies that compared with other skin microbial sampling methods, the method provided by the invention can better restore the real micro-ecology of the skin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for activity quantification and host identification of antibiotic resistance gene in environment based on metatranscriptomics and metagenomics
The invention relates to a method for activity quantification of a novel antibiotic resistance gene in an environment based on metatranscriptomics and metagenomics. The method specifically comprises the following steps: 1) extracting total DNA and RNA from an environmental microorganism sample; 2) performing metagenome sequencing on a DNA sample, and performing macro transcriptome sequencing on a RNA sample; and (3) analyzing metagenome sequencing and metatranscriptome sequencing results, identifying the novel antibiotic resistance gene and the host thereof, and quantifying the activity of the novel antibiotic resistance gene. The method disclosed by the invention does not depend on strain isolated culture, and activity quantification and host identification of the antibiotic resistance gene in environmental microorganism samples can be realized by combining metagenome and metatranscriptome methods.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Extraction reagent and extraction method for fermented bean curd microorganism flora DNA
The present invention discloses an extraction reagent and an extraction method for fermented bean curd microorganism flora DNA. The extraction reagent comprises a cell separation solution, a cell rinsing solution, a cell lysing solution, a PCR inhibitory substance precipitation solution and a washing solution. Based on characteristics of high content of soybean residues and richness of organic acids and amino acids in fermented bean curd samples, processes of fermented bean curd microorganism recovery, cell lysis, PCR reaction substance removal and highly-efficient DNA recovery are designed. For the PCR reaction substance removal, a combination method of ammonium sulfate, guanidine hydrochloride and CTAB is applied, and at the same time, polysaccharides, polyphenols and interfering proteins are removed. Therefore, high-quality DNA is acquired for subsequent molecular biology experiments. The method can simultaneously extract DNA of fermented bean curd bacteria and fungi, and the extracted DNA is successfully used for PCR reaction and high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA and ITS genes and is also successfully applied to sequencing and analysis of metagenomics.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA ZHONGSHAN INST
Screening method of feed probiotics capable of preventing porcine salmonella infection
InactiveCN107893110AAvoid discomfortAvoid blindnessMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicroorganismScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method of feed probiotics capable of preventing porcine salmonella infection. The screening method comprises the following steps: screening piglets infected by salmonella and disease resistant piglets, collecting intestinal content samples of piglets infected by salmonella and disease resistant piglets; carrying out high-throughput sequencing on intestinal microbial floras of piglets infected by salmonella and disease resistant piglets; performing meta-genomic comparison and analysis on intestinal microbes of piglets infected by salmonella and disease resistant piglets; and screening and identifying probiotics capable of preventing salmonella infection. The provided screening method screens out probiotics capable of preventing salmonella infection from agreat amount of microbial floras of disease resistant piglets, and is strongly targeted, the blindness of screening is avoided, the screening efficiency is improved, and a large amount of labor, materials, and time is saved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com