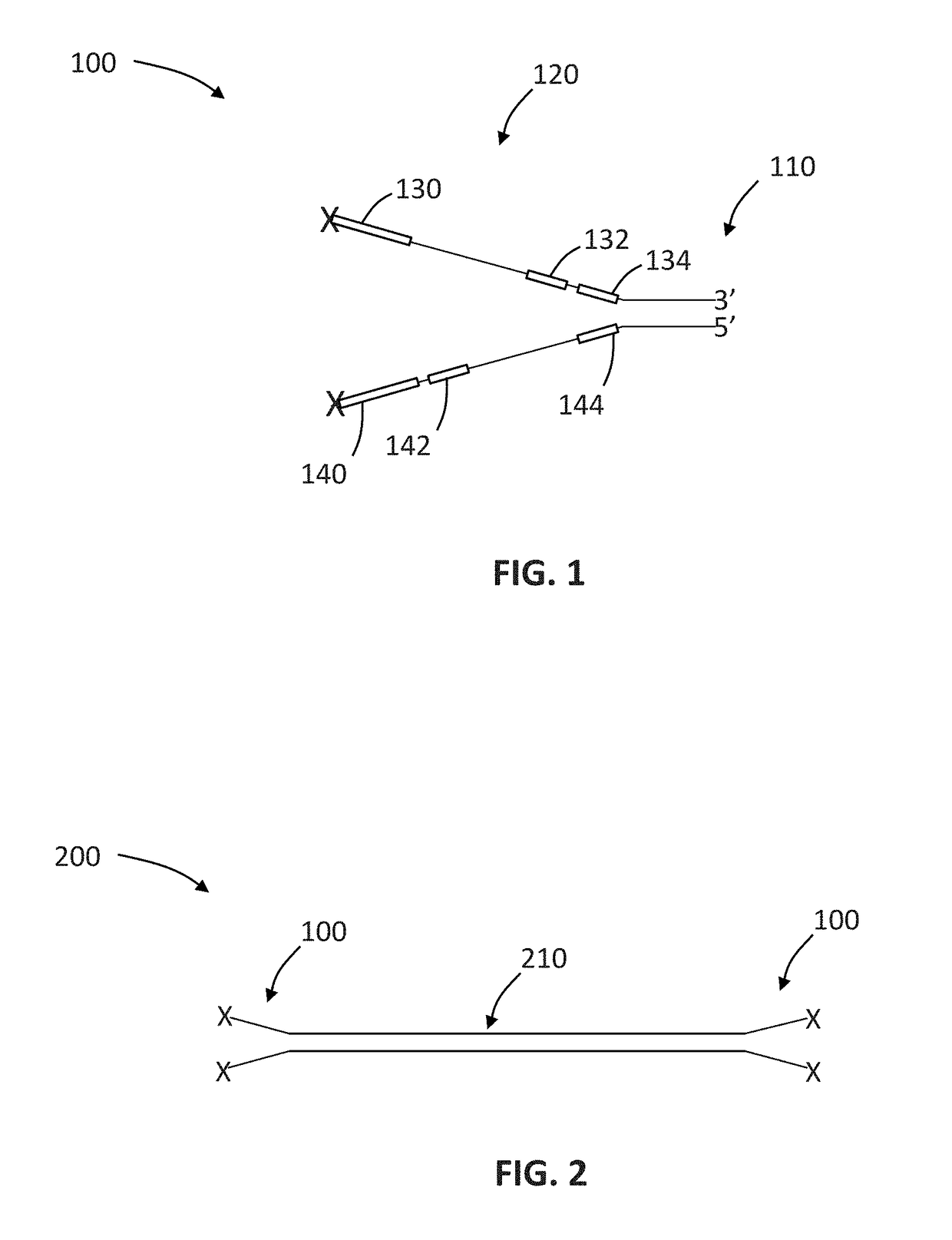
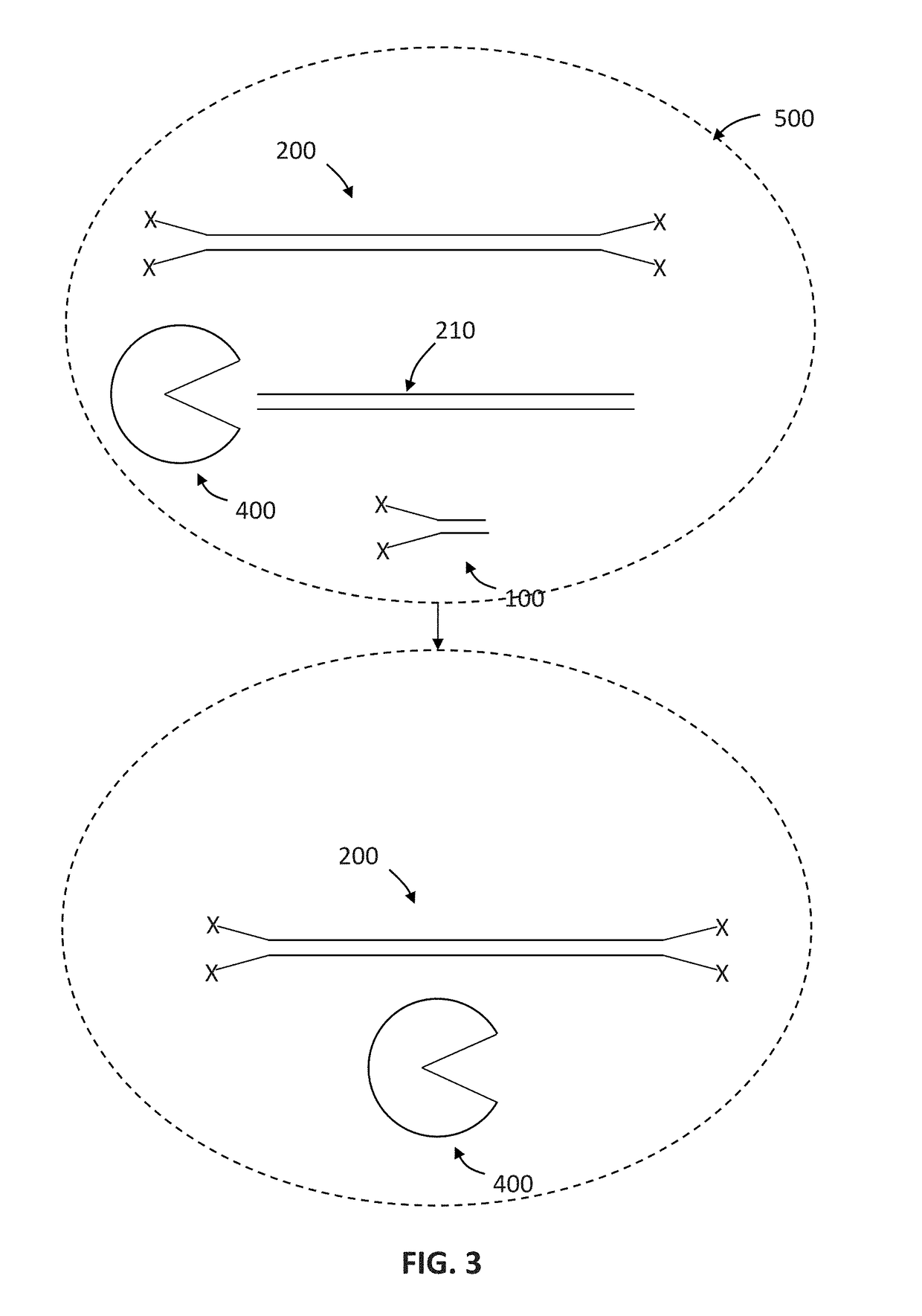
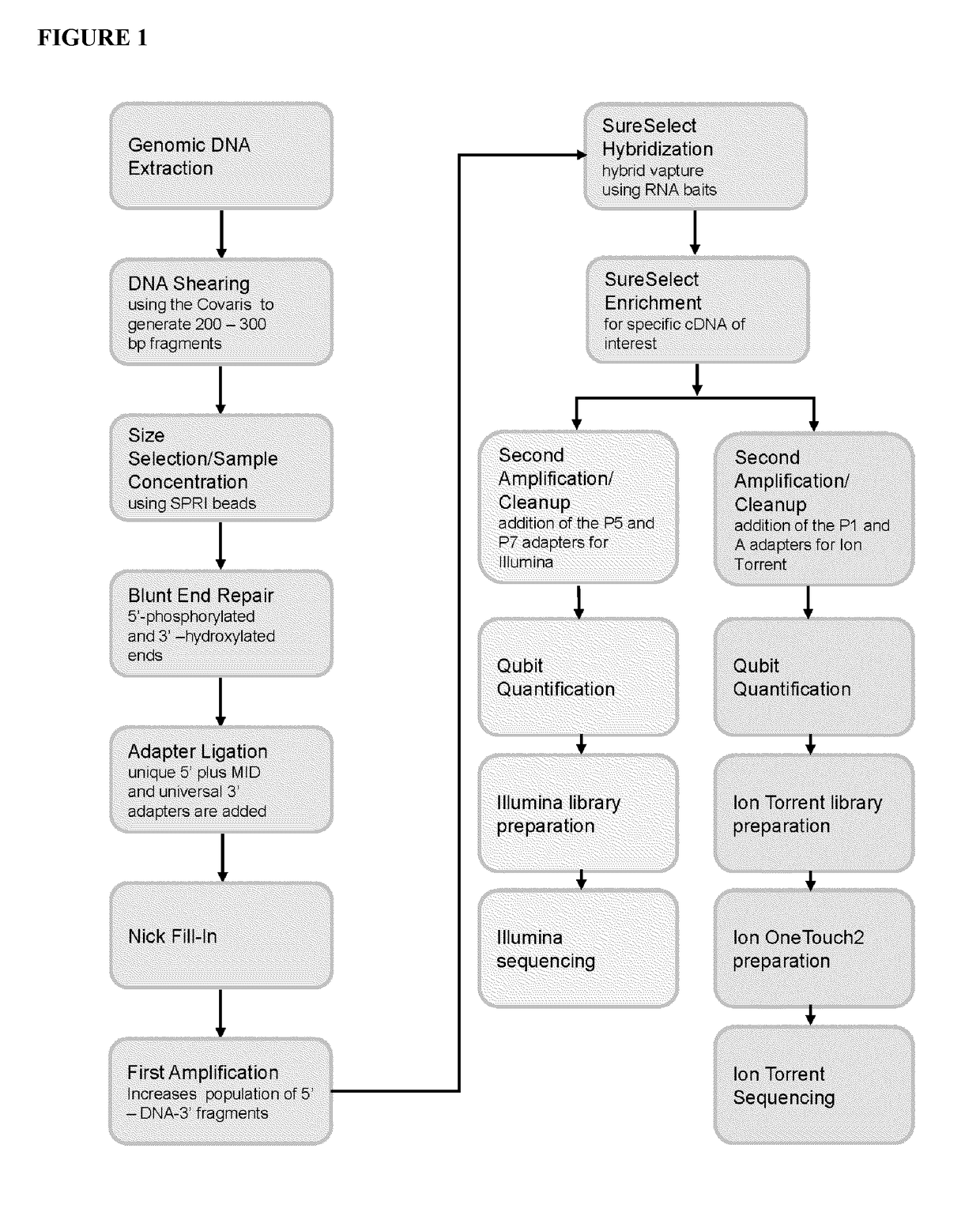
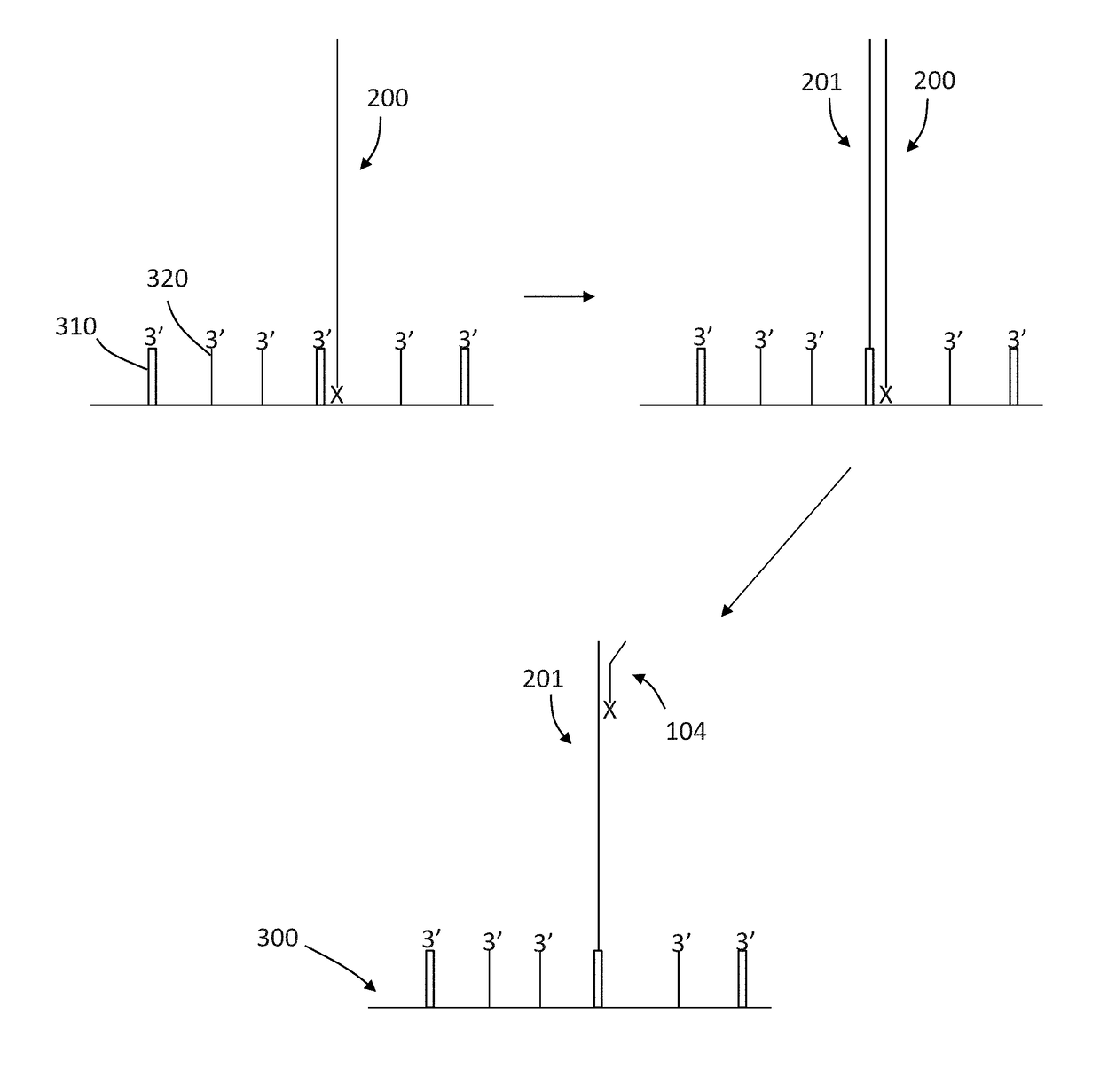
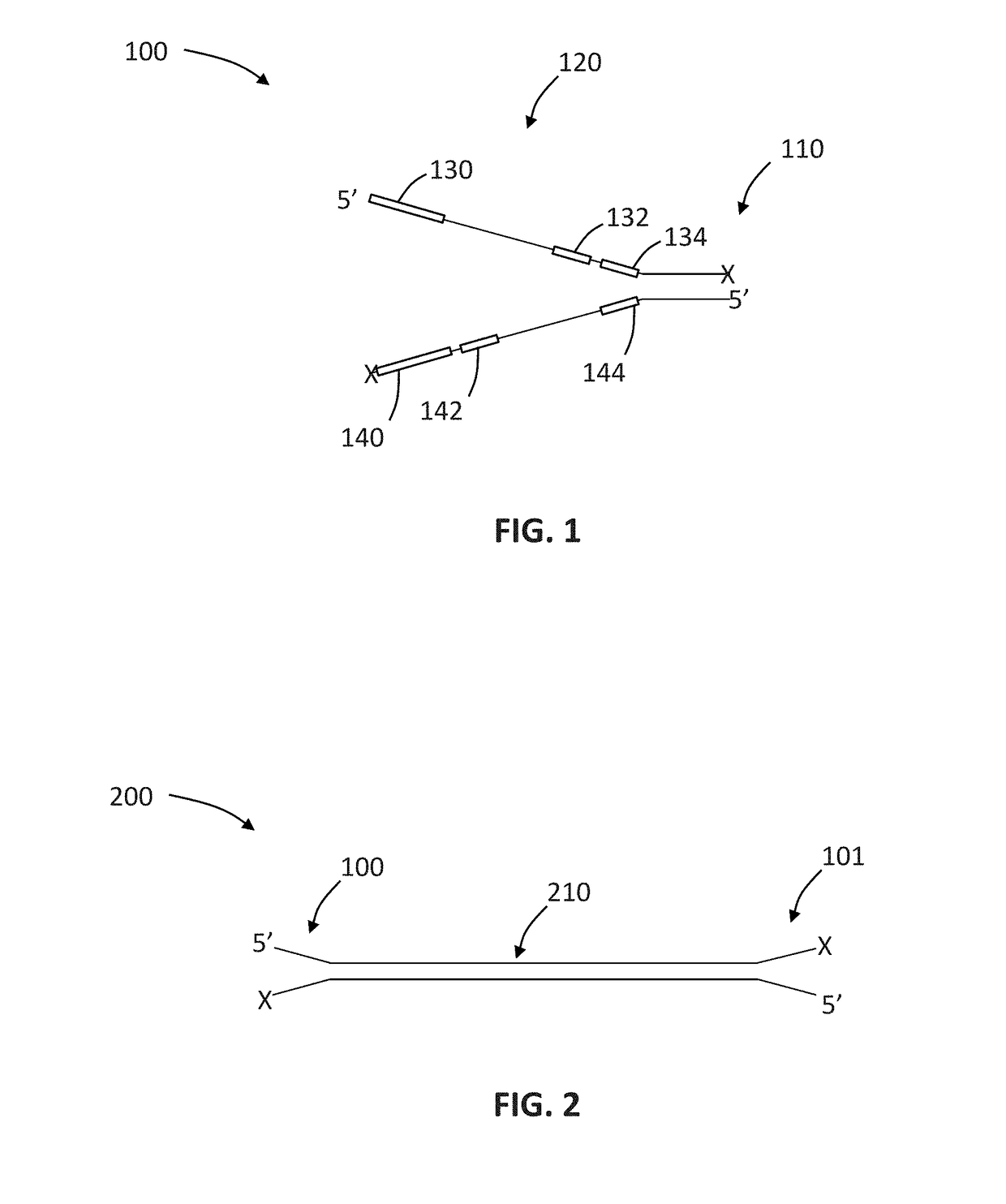
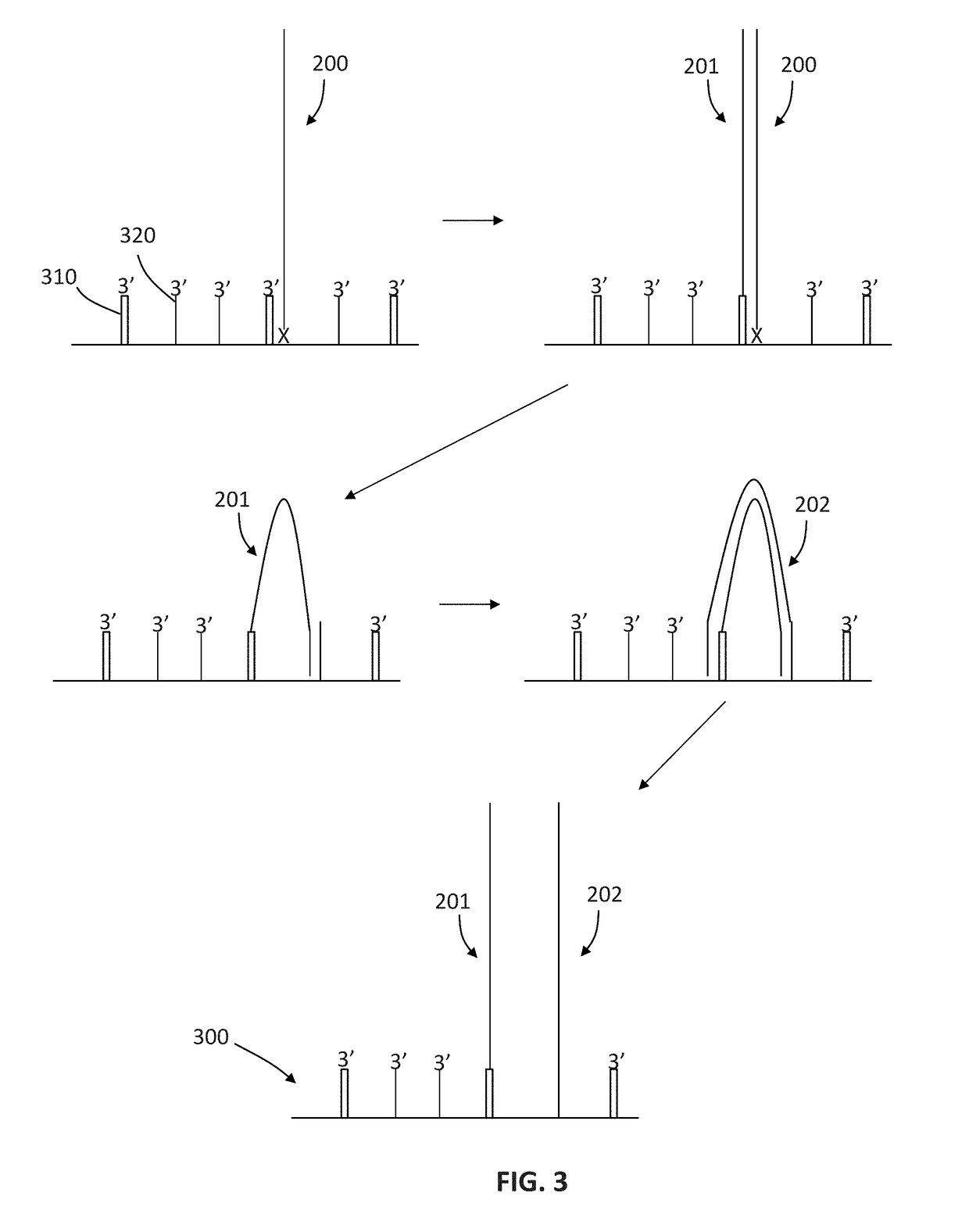
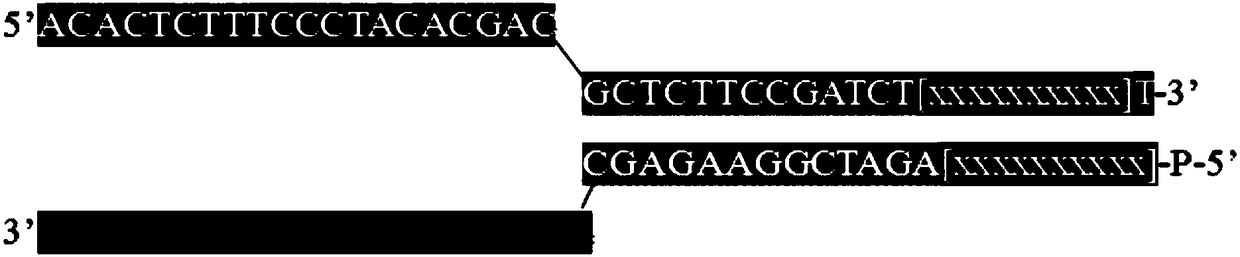
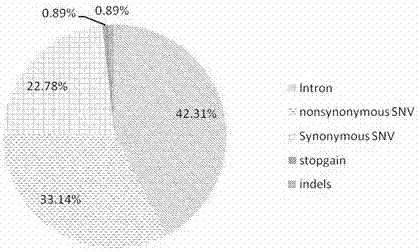
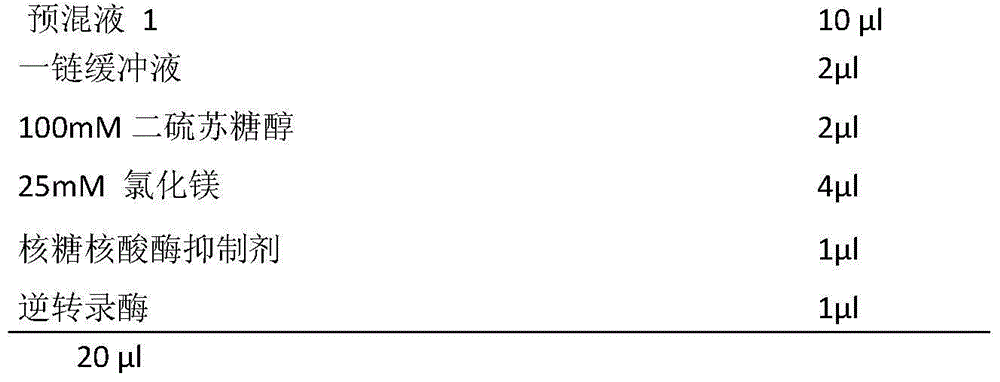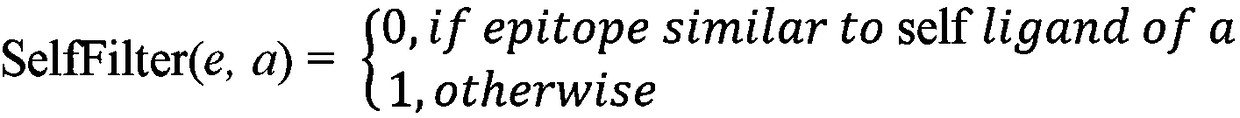Patents
Literature
86 results about "Next generation sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) is a powerful platform that has enabled the sequencing of thousands to millions of DNA molecules simultaneously. Next-generation sequencing (NGS), also known as high-throughput sequencing, is the catch-all term used to describe a number of different modern sequencing technologies.
T-cell epitope identification
ActiveUS20180052176A1Efficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideMembrane bound
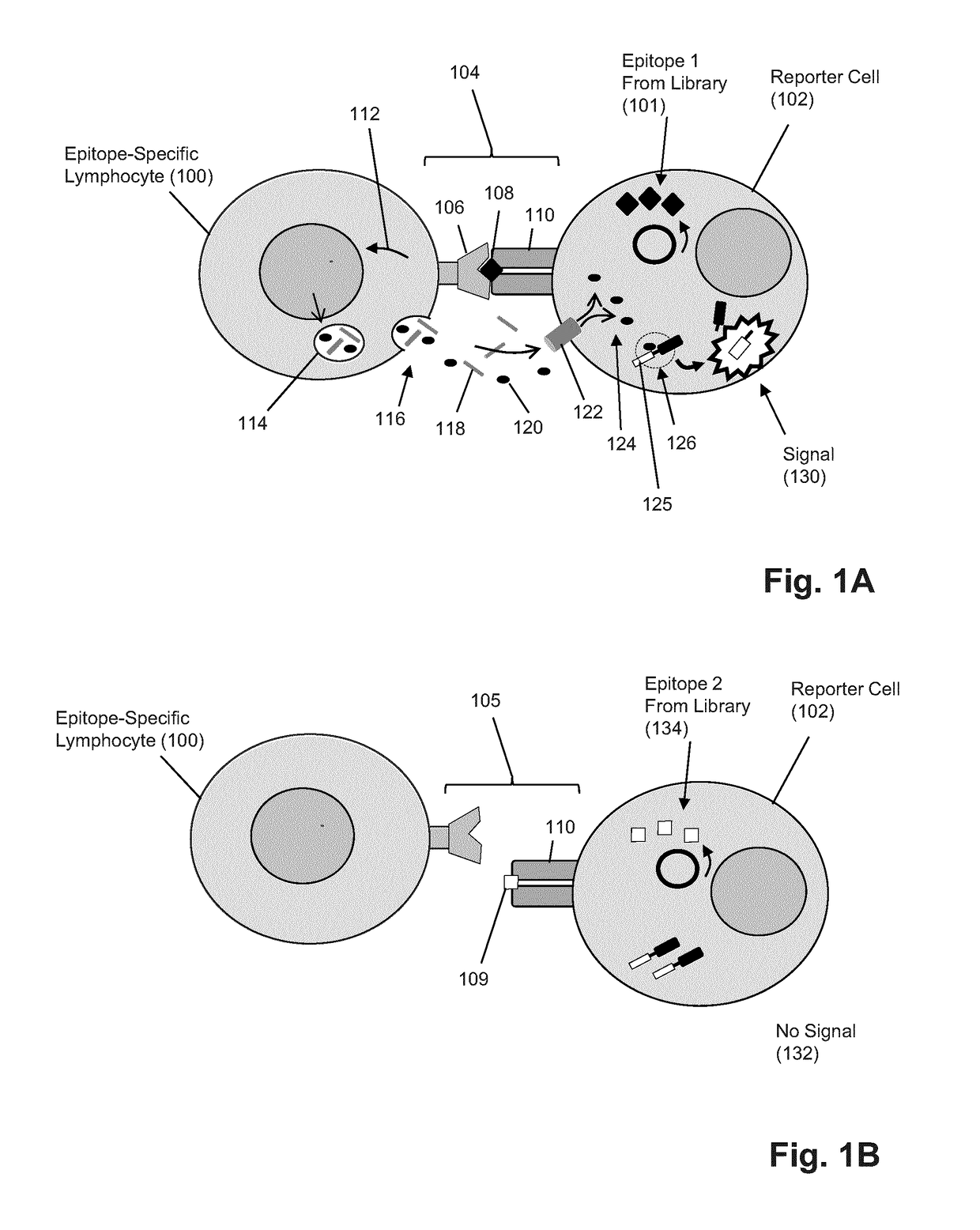
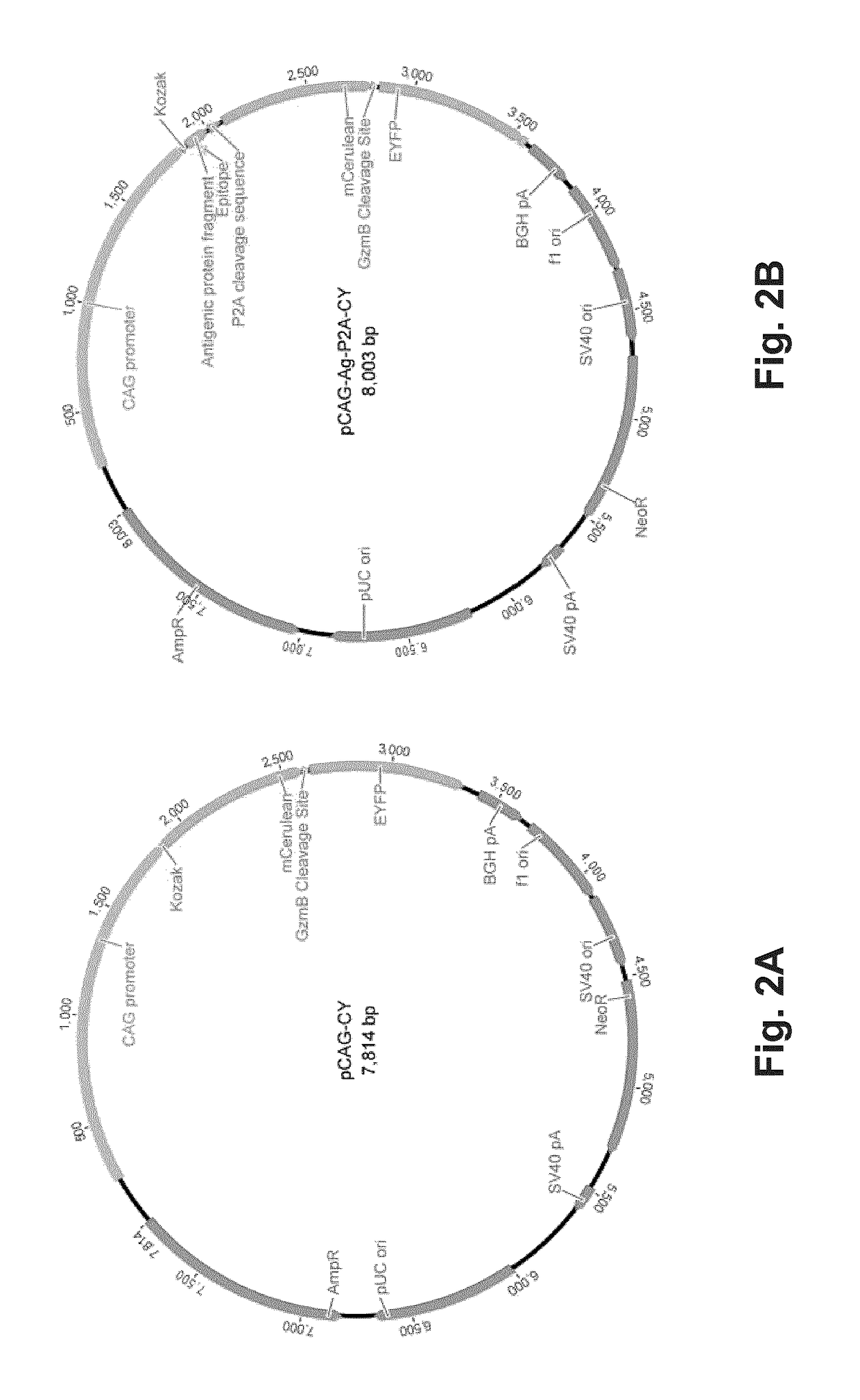
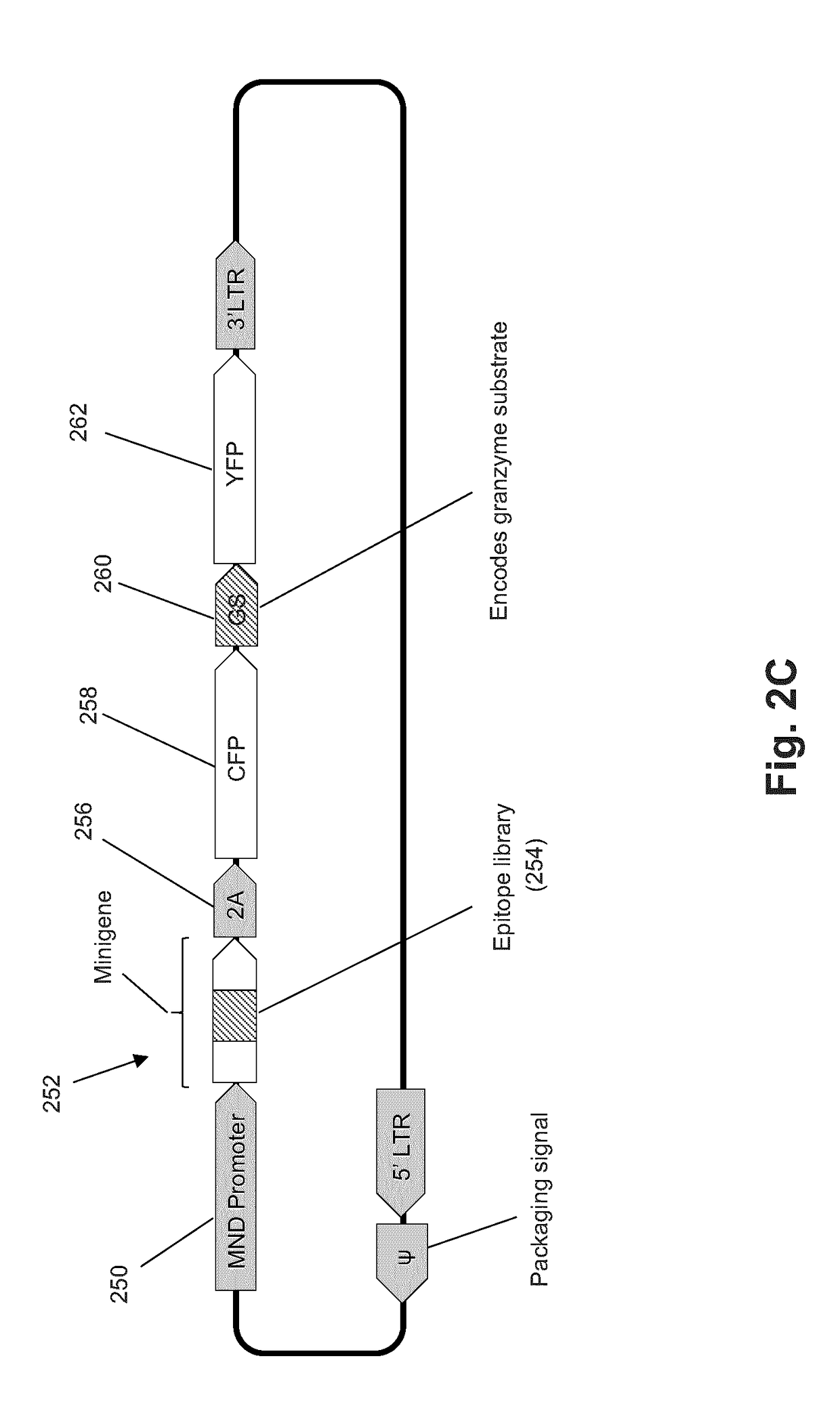
The present invention is a method for determining the identity of the epitopes recognized by T-cells. The method consists of expressing an encoded library of candidate epitope sequences in a recipient reporter cell capable of providing a detectable signal upon cytotoxic attack from a single cognate T-cell followed by contacting the reporter cells with T-cells of interest. The reporter cells with a single indicating cytotoxic attack from a T-cell are isolated and then analyzed by next-generation sequencing in order to identify the epitope sequences. Specifically disclosed is a method in which a library of candidate epitope-encoding nucleic acids are expressed in cells which feature a membrane-bound major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein, said library produced by transfection of plasmids featuring both a nucleotide encoding the candidate epitope and a nucleotide encoding a FRET-based fluorescent protein cleaved by granzyme.
Owner:PROVINCIAL HEALTH SERVICES AUTHORITY
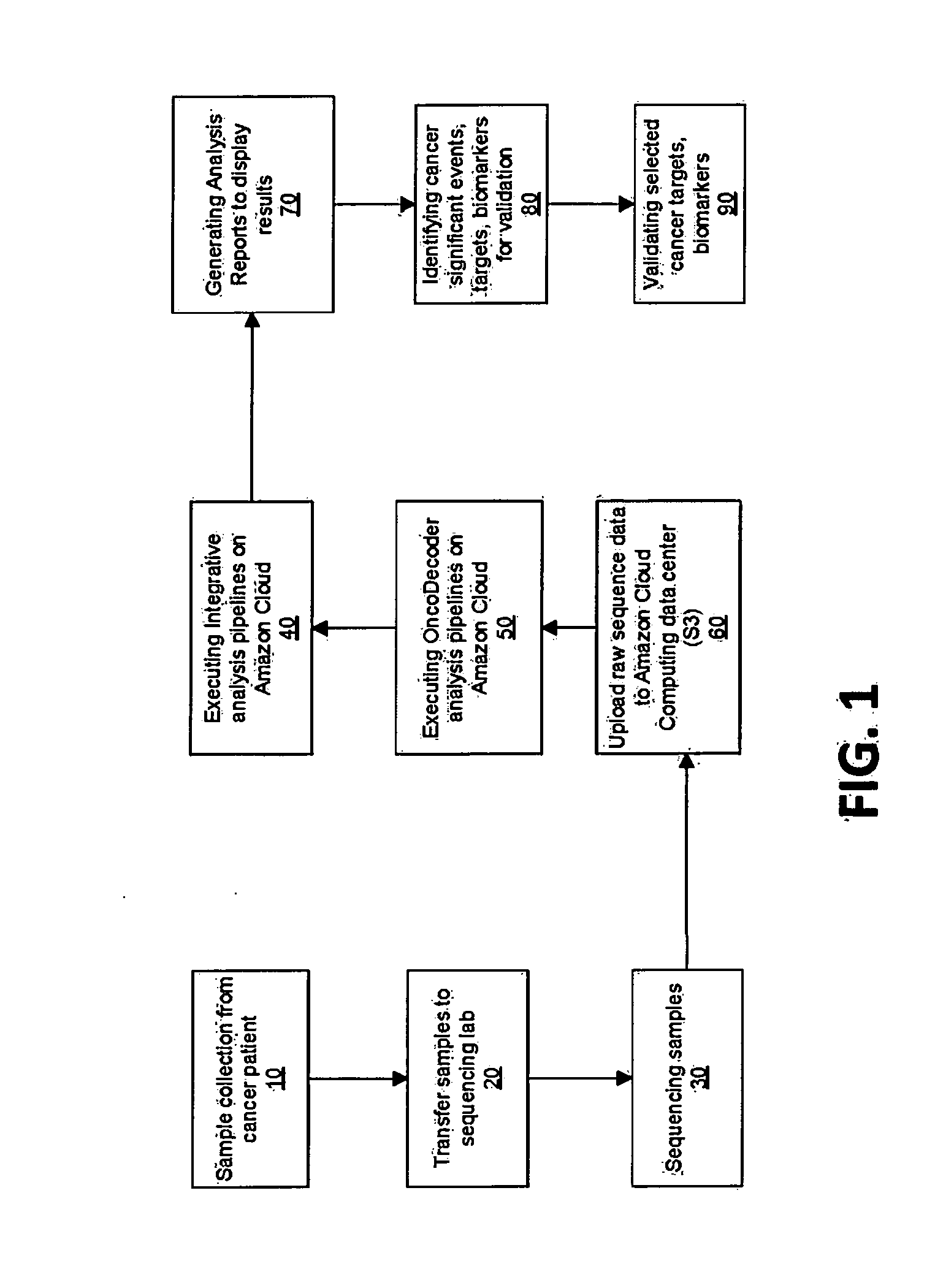
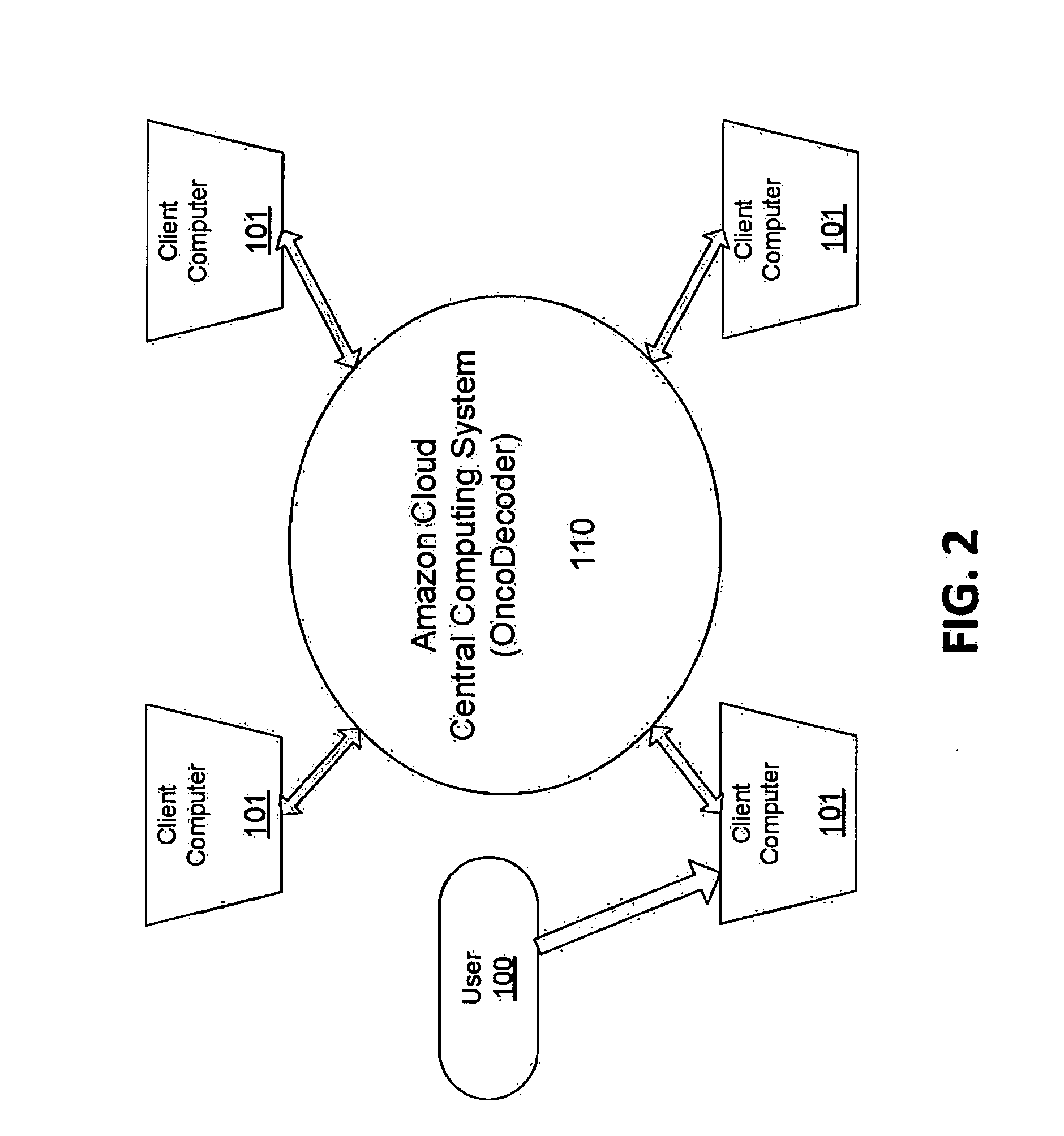
Systems and methods for cancer-specific drug targets and biomarkers discovery
InactiveUS20130184999A1Improve throughputMinimal hardware requirementProteomicsGenomicsHuman cancerBiomarker discovery
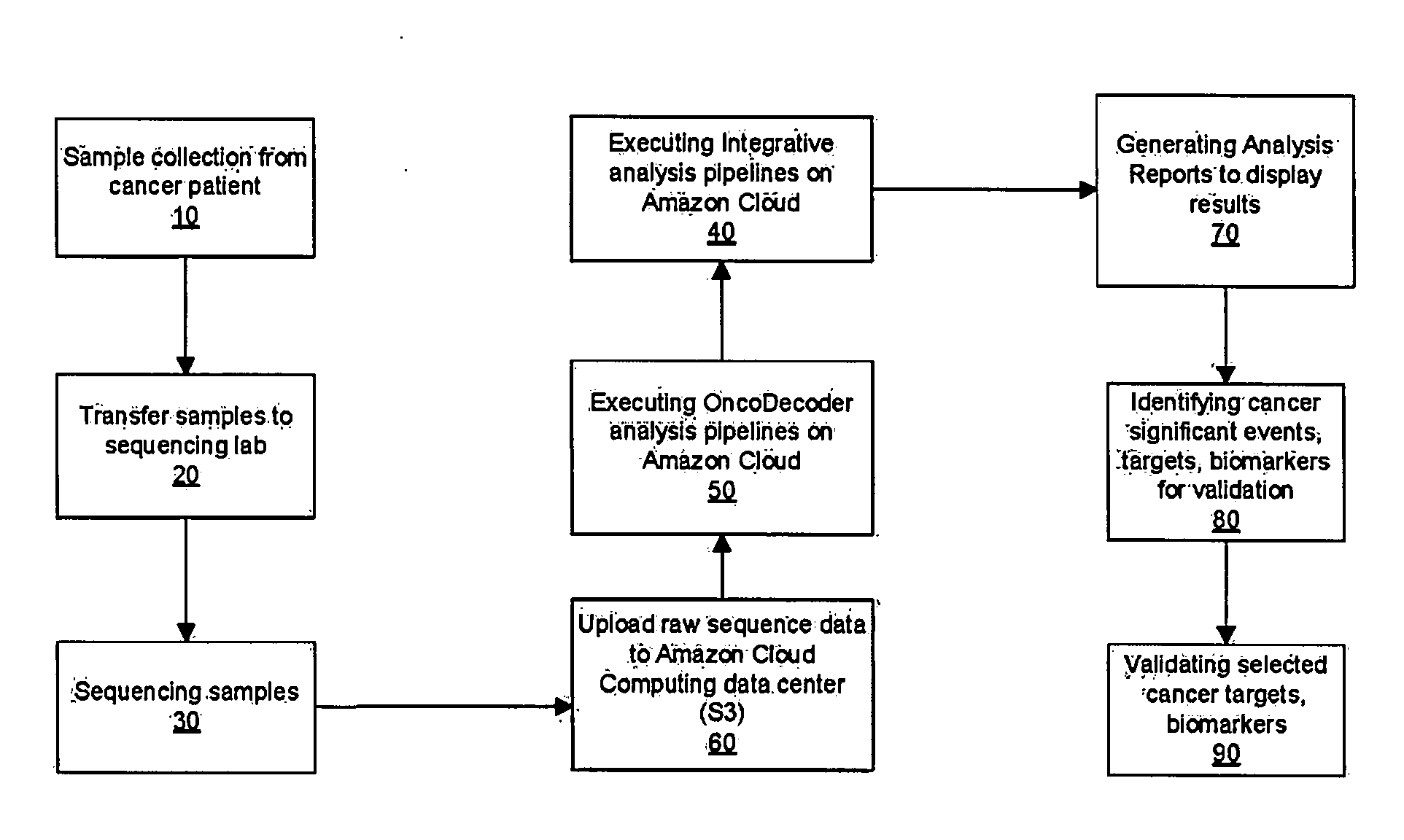
The present invention provides users with cloud-based high throughput computing system for integrative analyses of next generation sequencing genomic data, such that human cancer biomarkers and drug targets can be accurately and quickly identified. Advantageously, the present invention harness a comprehensive systematic analysis pipelines for all types of next generation sequencing genomic data, advanced genomic variants calling algorithms and modeling, variant data correlation and integration, and identification of cancer specific biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Thus, the present invention will aid users so that less of their time and efforts are required in order to obtain precisely the desired information for which they are analyzing.
Owner:DING YAN
Virus infection detection and identification method based on metagenomics
ActiveCN105112569AHigh detection sensitivityLow initial sample size requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementViral nucleic acidNucleic acid sequence
The invention provides a virus infection detection and identification technology based on metagenomics. The virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics comprises the four portions of sample preparation, high-throughput sequencing, bioinformatic analysis and result re-checking. In the sample preparation portion, viral nucleic acid is effectively extracted or enriched from detection samples according to the requirements of the virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics and characteristics of different types of detection samples, and a nucleic acid library which can be used for a next-generation sequencing instrument is established. In the high-throughput sequencing portion, the nucleic acid library established in the sample preparation step is sequenced so to obtain sufficient high-quality nucleic acid sequence information. In the bioinformatic analysis portion, a large number of high-quality nucleic acid sequences obtained in the high-throughput sequencing step is analyzed to further obtain viral component information prompted by the nucleic acid of the samples. In the result re-checking portion, a bioinformatic analysis result and other information, such as technical contrast, are integrated to perform comprehensive study and judgment, finally alternative infection virus is determined, and other technologies, such as PCR, are utilized to perform re-checking.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
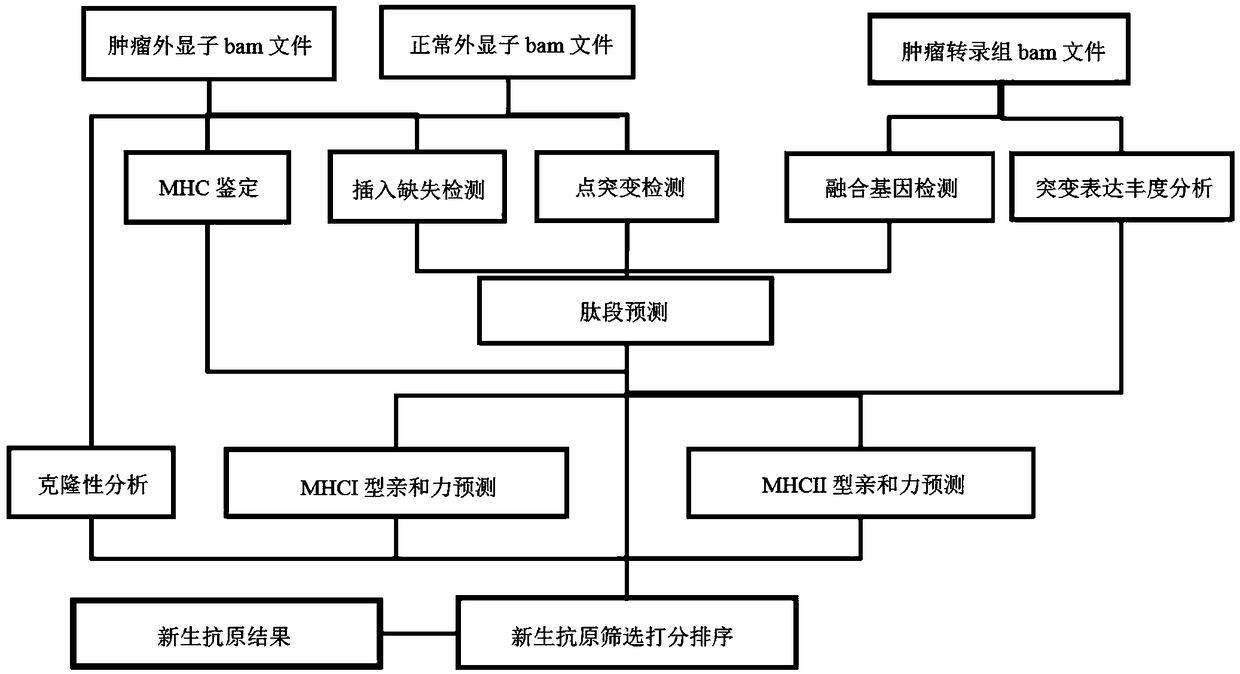
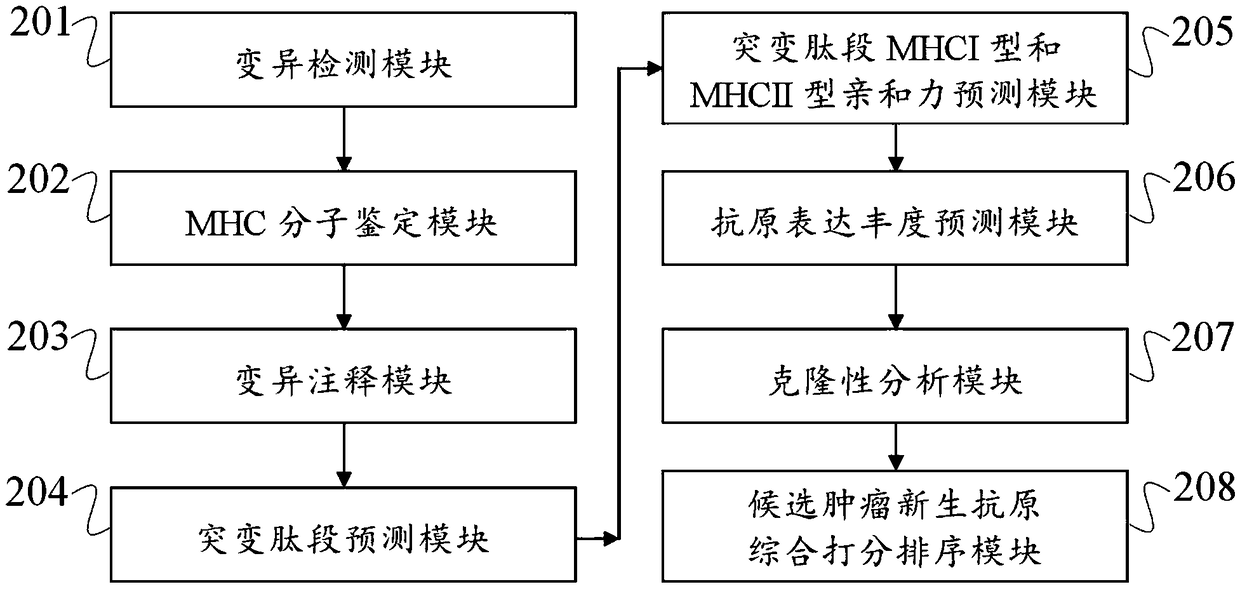
Tumor neoantigen detection method and device based on next-generation sequencing, and storage medium
ActiveCN108796055AQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular identificationClonality Analysis
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
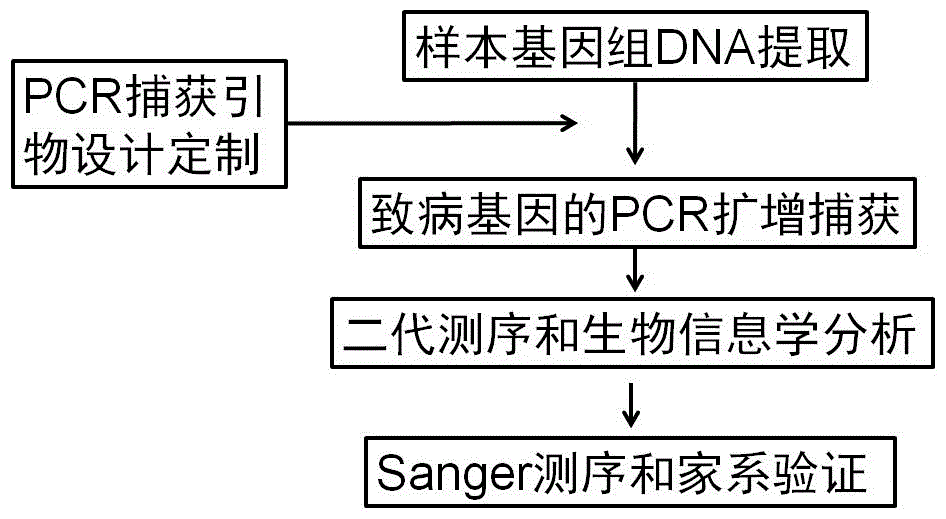
Human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification pathogenic gene and detection method thereof
ActiveCN106834299AEfficient and comprehensive acquisitionAccurate acquisitionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringNervous systemInformation analysis
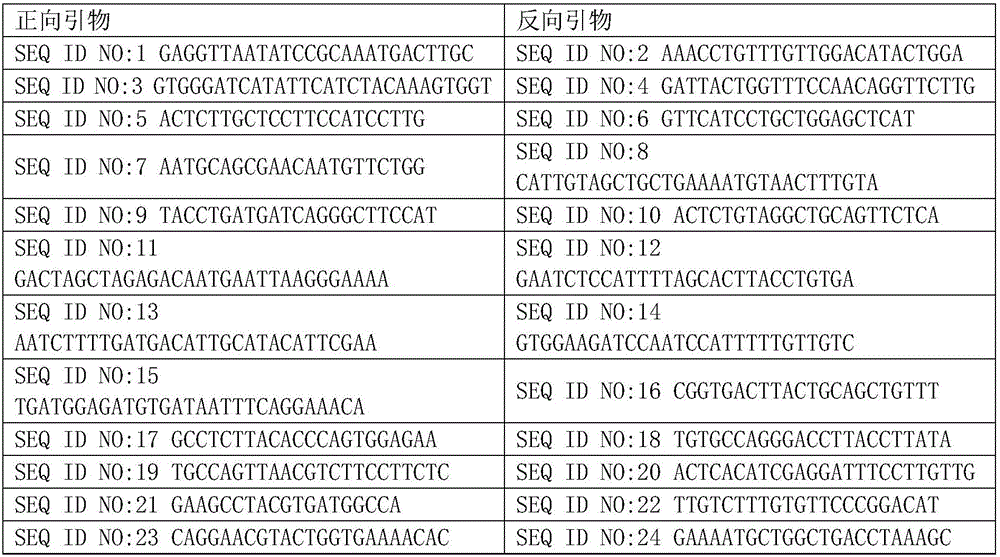
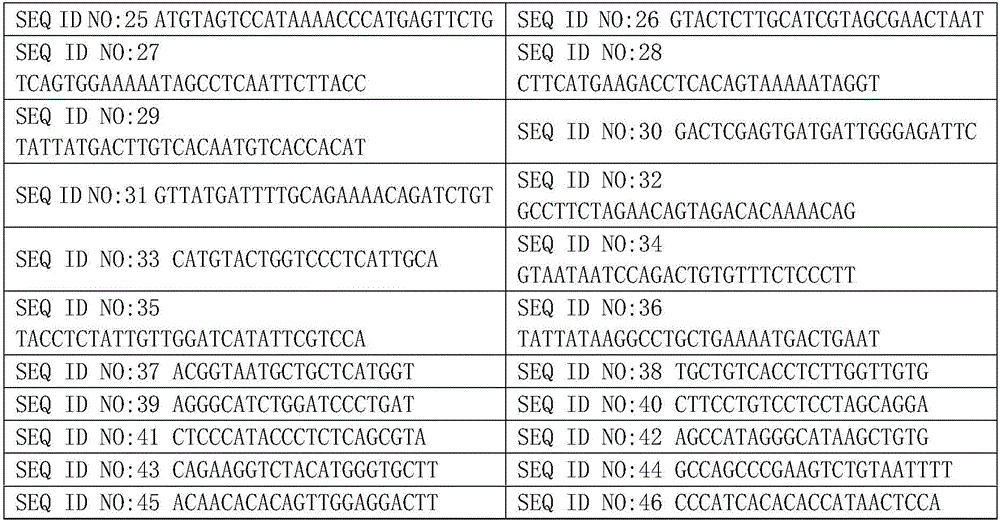
The invention relates to a human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification pathogenic gene and a detection method thereof. Human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification, namely IBGC is a neurodegenerative genetic disease. The invention provides seven mutation forms of four pathogenic genes including SLC20A2 (Sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2), PDGFRB (Platelet-derived Growth Factor Receptor Beta), PDGFB (Platelet-derived Growth Factor Subunit B) and XPR1 (Xenotropic and Polytropic Retrovirus Receptor 1) and sequences of the seven mutation forms are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.7. The form of the pathogenic gene provided by the invention is not reported until now and can provide evidence and lay a foundation for analysis and medicine development of a pathogenic mechanism, pathogenic gene screening and detection, formulation of a therapeutic regimen and the like. Meanwhile, the invention constructs a pathogenic gene detection method; the pathogenic gene detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, capturing a pathogenic gene exon region by utilizing multi-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); carrying out next generation sequencing on the pathogenic gene exon region and carrying out information analysis to find out mutation; finally, identifying the mutation by utilizing Sanger sequencing, wherein a PCR captured primer group comprises amplification primer sequences SEQ ID NO.12 to SEQ ID NO.23, and amplification primer sequences of a Sanger sequencing segment are shown as SEQ ID NO.24 to SEQ ID NO.35. The detection method provided by the invention covers all exons of the four pathogenic genes and can be used for efficiently, comprehensively, rapidly and accurately acquiring mutation information.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Data processing method of next-generation sequencing (NGS) data analysis platform (IMP)
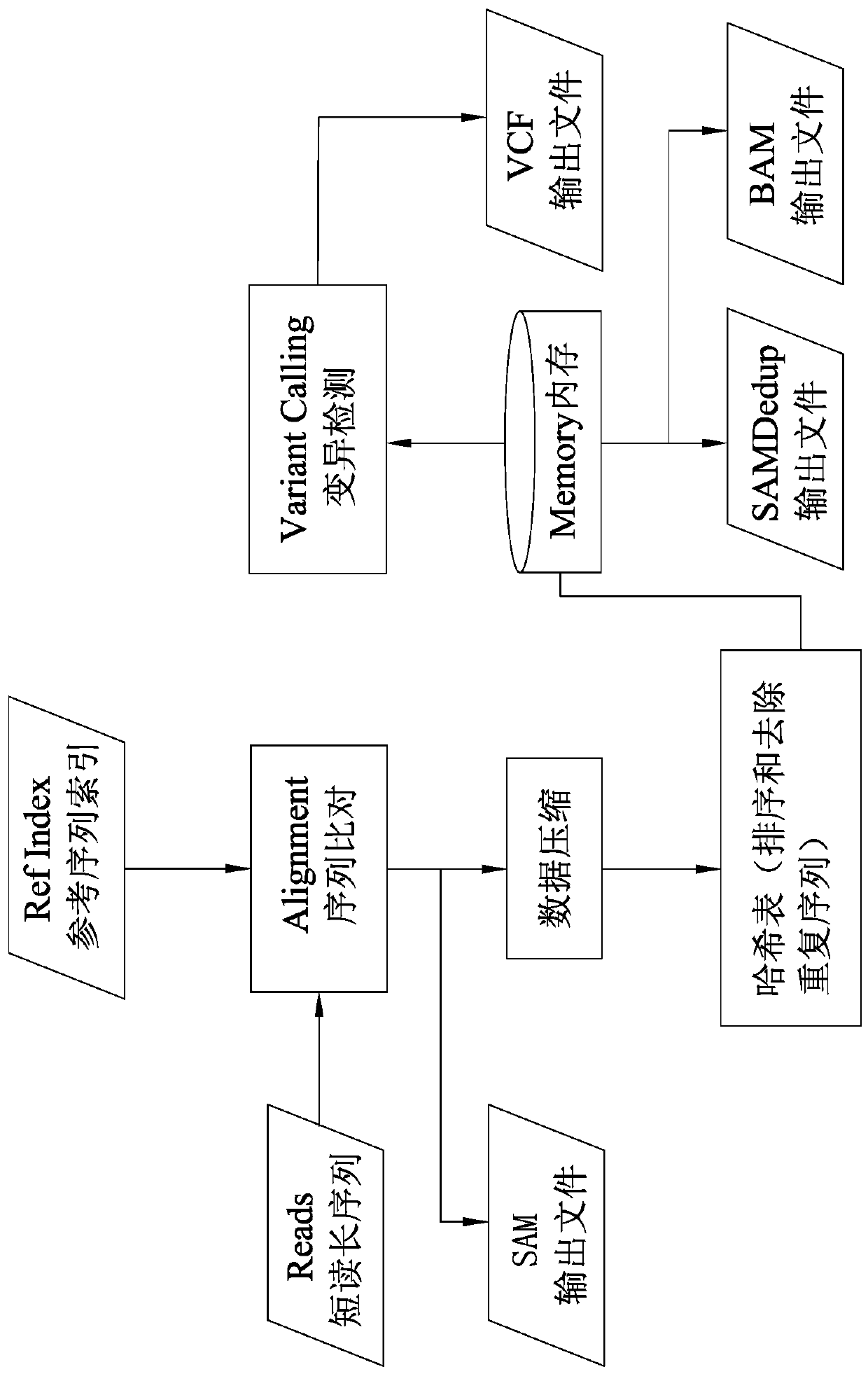
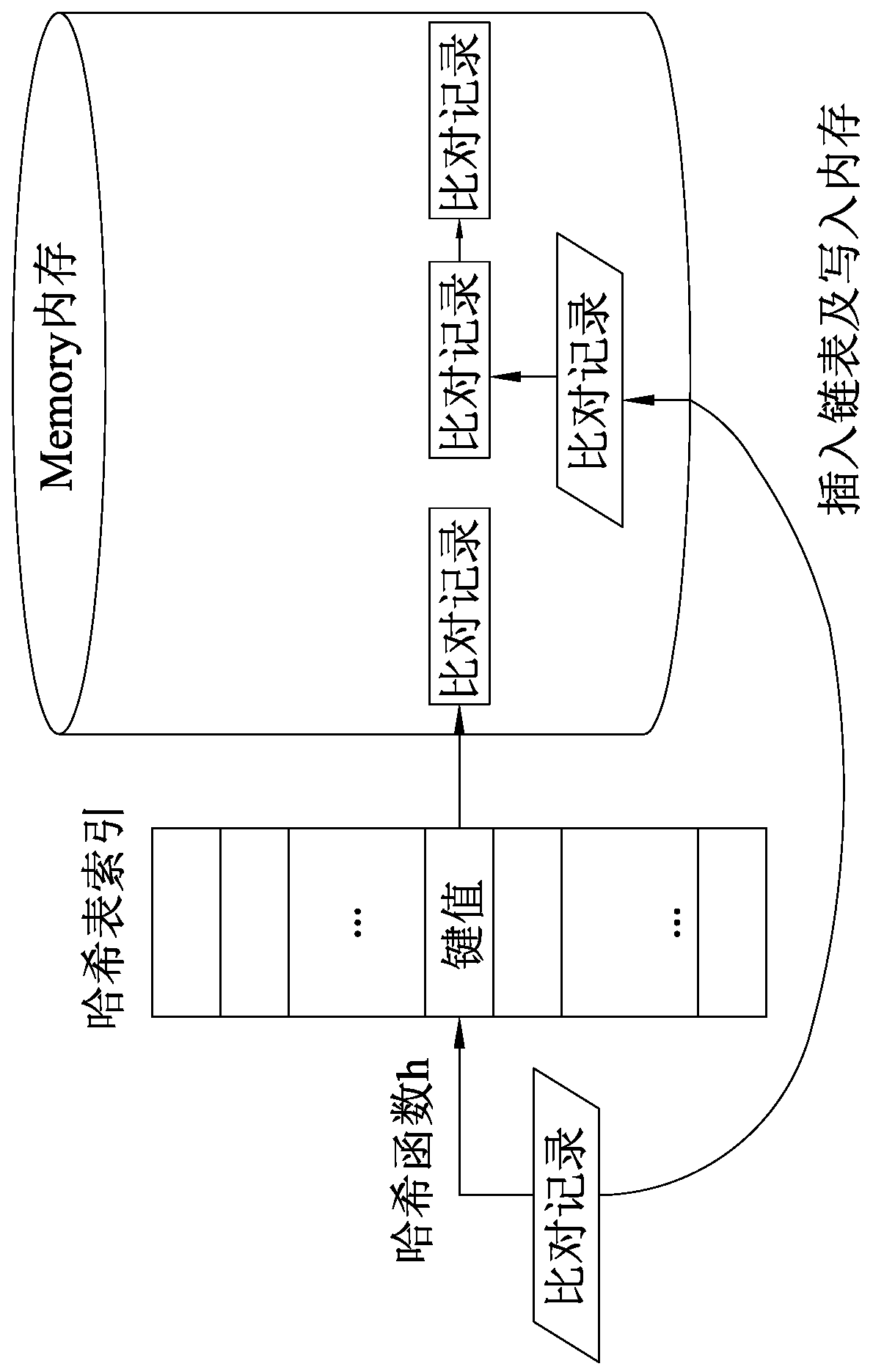
The invention discloses a data processing method of a next-generation sequencing (NGS) data analysis platform (IMP). The next-generation sequencing data analysis platform implements an entire next-generation sequencing processing process as a single step from inputting of short-reading long-sequences of an FASTQ file format to outputting of mutation detection of a standard VCF file format; at thesame time, the method also provides an option of outputting an intermediate result of sequence alignment in a standard SAM or BAM format; longer data searching and loading time required for I / O accessing of hard drives and SSDs can be avoided through massive memory accessing without using slow I / O to exchange data; hash table writing or reading, deletion of duplicated alignment records and mutation detection are all enabled to be faster; quick next-generation sequencing data analysis can be realized on the premise of not impacting analysis quality; and compared with speeds of existing schemes,a speed of the method is increased up to 20 times.
Owner:厦门极元科技有限公司
Harnessing high throughput sequencing for multiplexed specimen analysis
InactiveUS20120185177A1ConfidenceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationChinese remainder theoremUnique identifier
A method of associating a DNA sequence with a specimen pooled among a plurality of specimens, where the specimens may be pooled according to any number of pooling schemes, including the Chinese Remainder Theorem, random pool selection, shifted transversal design, and Chinese Remainder Sieve. A unique identifier is associated with each specimen according to the pooling scheme such that a decoder may associate a DNA sequence with each specimen after next-generation sequencing according to the unique identifier and the chosen pooling scheme.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
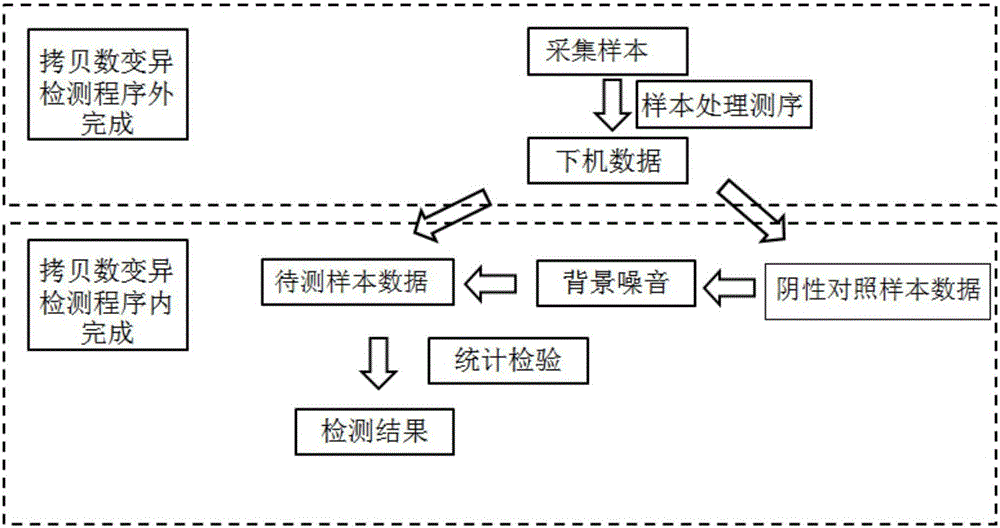
Method and device for detecting copy number variation based on amplicon next generation sequencing
ActiveCN106372459ARaise the thresholdAvoid inspectionHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsData informationBackground noise
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting copy number variation based on amplicon next generation sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a sample to be detected and a negative comparison sample respectively and amplifying a target region with relatively mutated target characters through a plurality of amplicons, wherein the negative comparison sample is a sample with target character related genes which are not mutated; S2, carrying out next generation sequencing to obtain a sequence of the target region; S3, comparing the sequence of the target region and a reference genome, and carrying out data information processing to obtain a coverage degree of each amplicon; and S4, establishing a normal distribution model of the negative comparison sample on the coverage degree of each amplicon respectively and taking the normal distribution model as background noises, carrying out bilateral checking on the coverage degree of each amplicon of the sample to be detected and the normal distribution model, and taking amplicons which do not belong to normal distribution as copy number variation and positively detecting. By adopting the technical scheme provided by the invention, the accuracy of copy number variation detection based on the amplicon next generation sequencing is improved.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
Compositions and methods for improving sample identification in indexed nucleic acid libraries
ActiveUS20180305751A1Lowering indexNucleotide librariesLibrary tagsLibrary preparationPolynucleotide
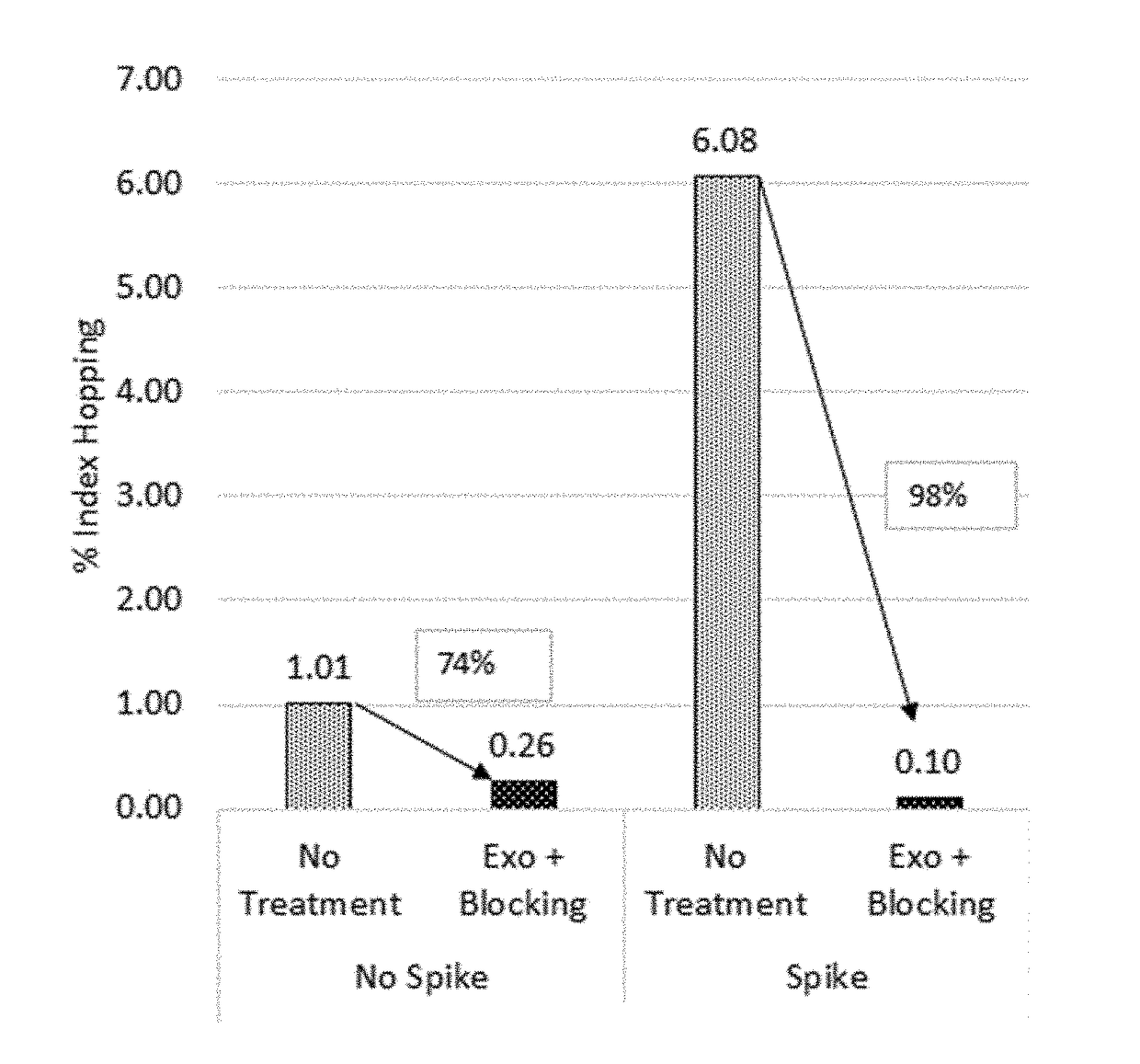
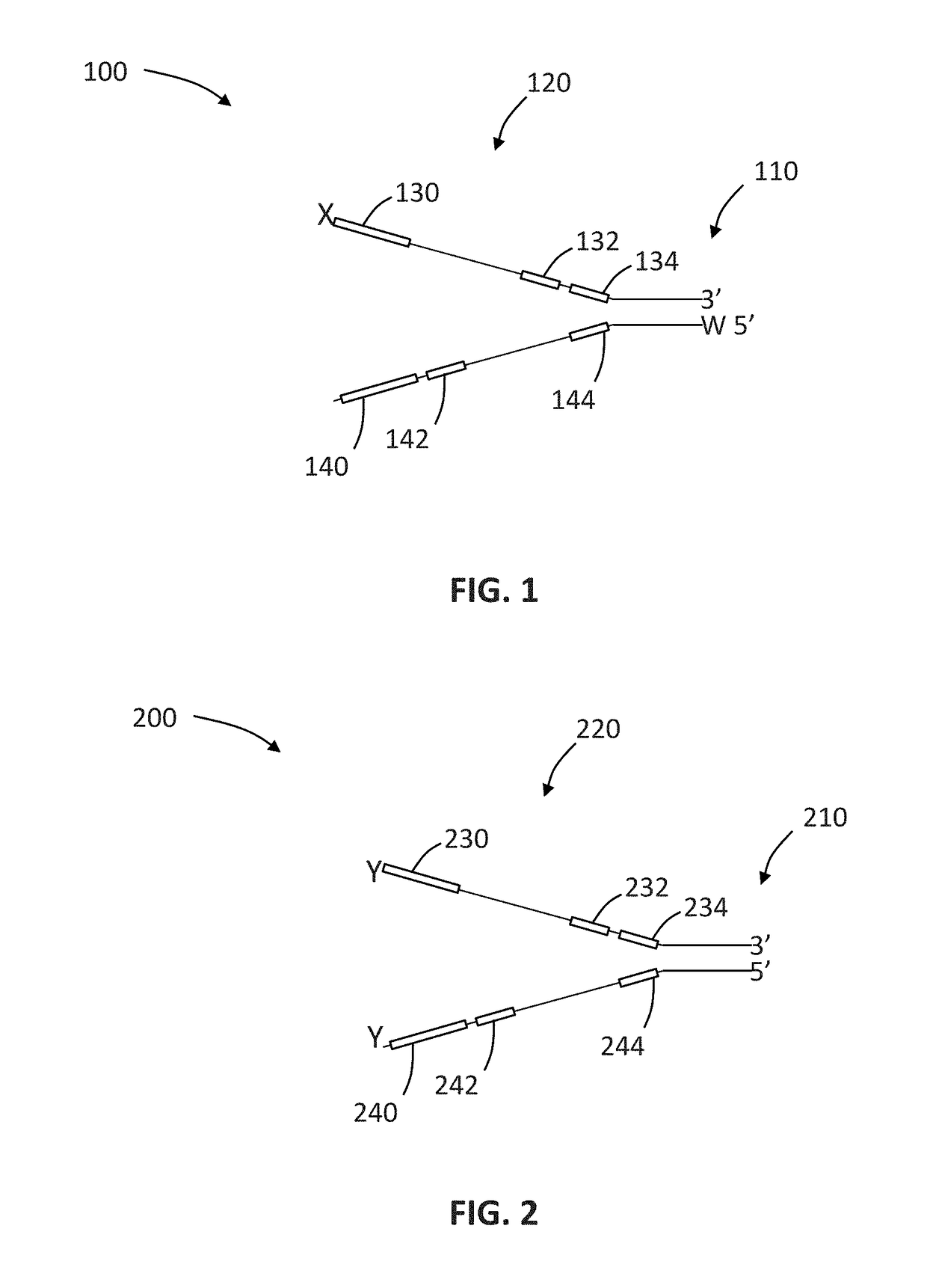
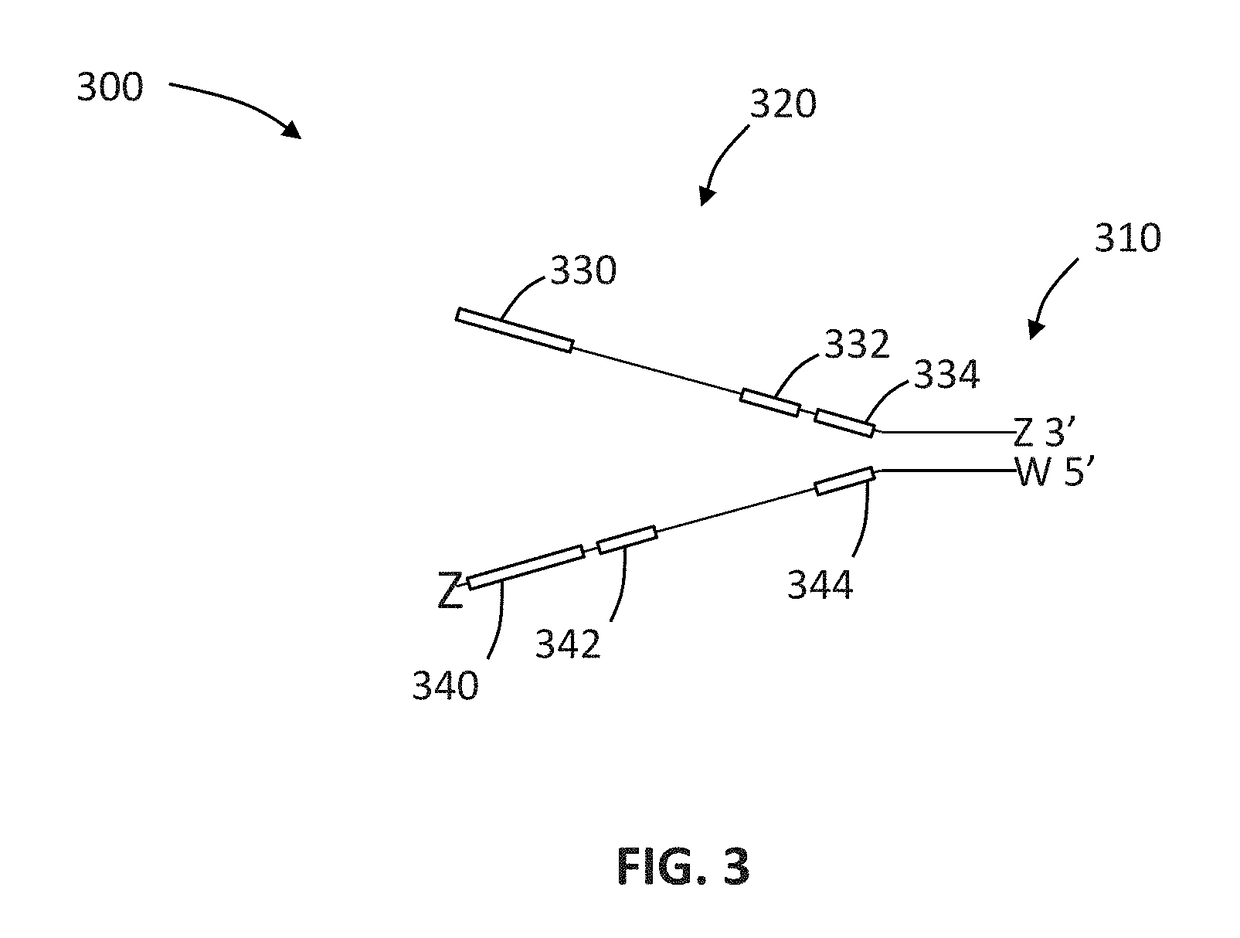
The present invention is concerned with compositions and methods for improving the rate of correct sample identification in indexed nucleic acid library preparations for multiplex next generation sequencing by exonuclease treatment after protective adapters are ligated to target polynucleotides to degrade unincorporated adapters prior to amplification and sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC +1
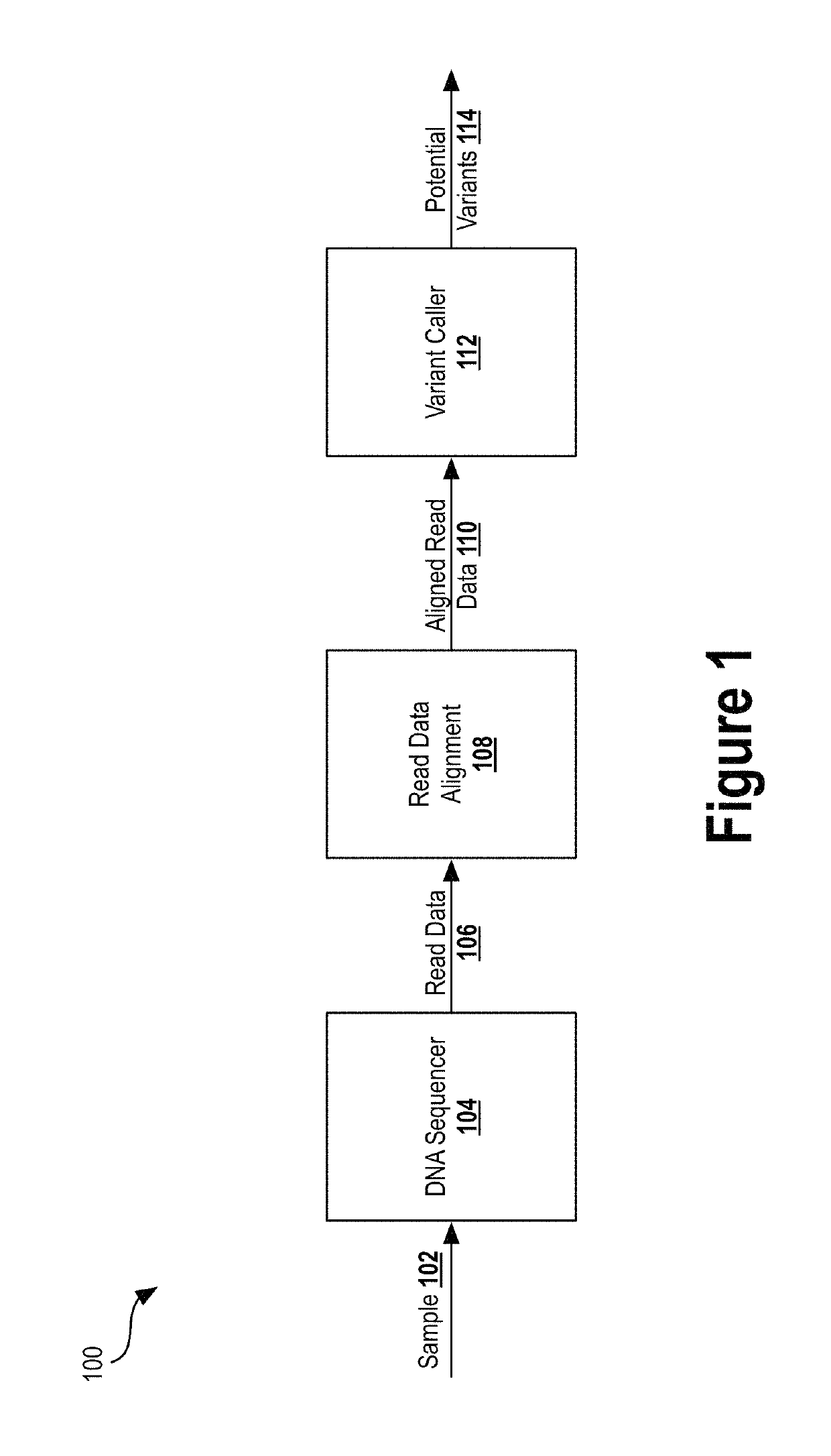
Alignment and variant sequencing analysis pipeline
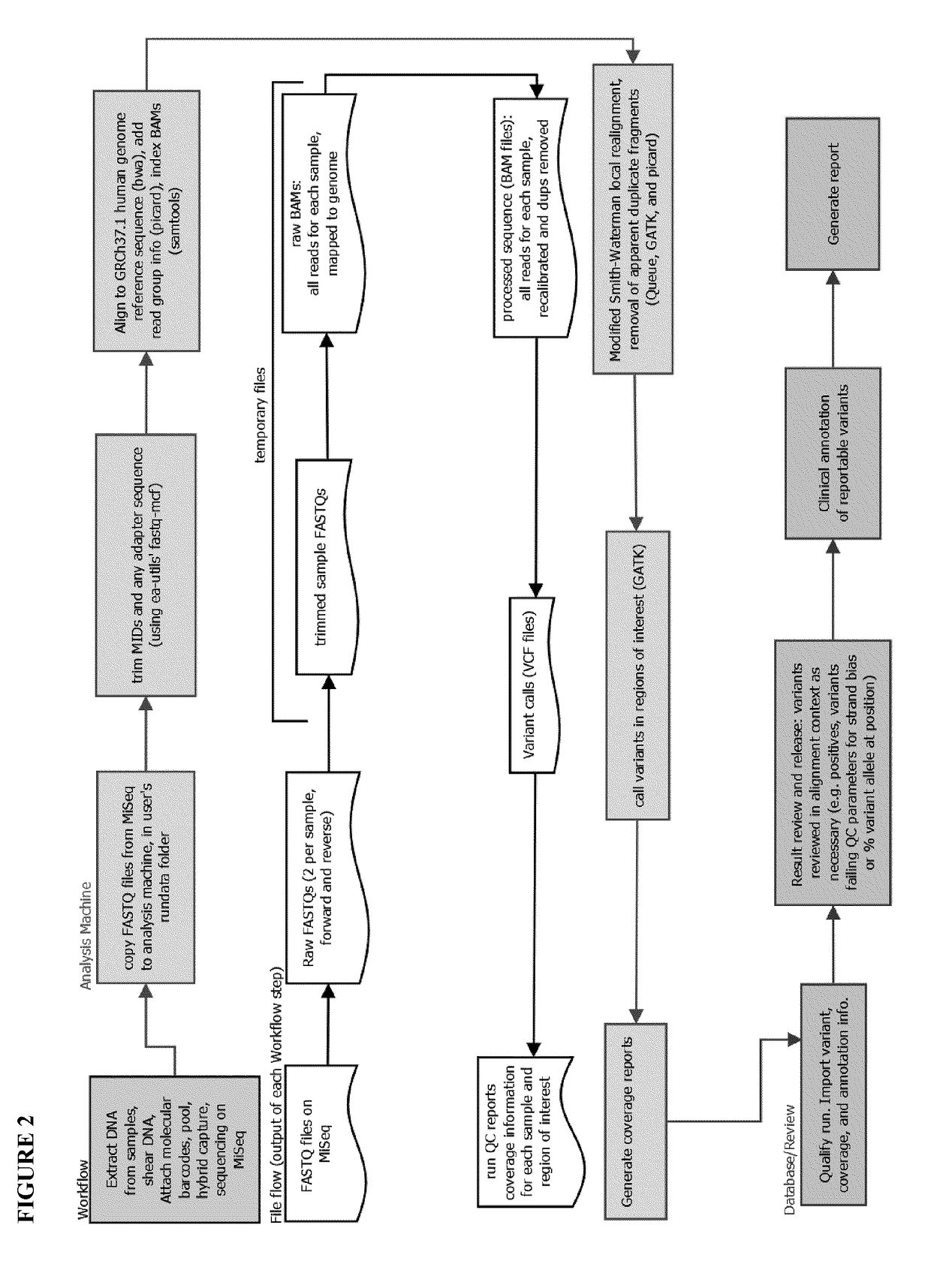
Provided are systems and methods for analyzing genetic sequence data from next generation sequence (NGS) platforms. Also provided are methods for the preparation of samples for nucleic acid sequence analysis by NGS. Variant calling is performed with a modified GATK variant caller. Mapping the reads to a genomic reference sequence is performed with a Burrows Wheeler Aligner (BWA) and does not comprise soft clipping. The genomic reference sequence is GRCh37.1 human genome reference. The sequencing method comprises emulsion PCR (emPCR), rolling circle amplification, or solid-phase amplification. In some embodiments, the solid-phase amplification is clonal bridge amplification.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Compositions and methods for improving sample identification in indexed nucleic acid libraries
ActiveUS20180305753A1Narrowing activity of exonucleaseIndex can be reduced and eliminatedNucleotide librariesLibrary tagsNucleotideLibrary preparation
The present invention is concerned with compositions and methods for improving the rate of correct sample identification in indexed nucleic acid library preparations for multiplex next generation sequencing by exonuclease treatment and optionally blocking the 3′ ends of pooled indexed polynucleotides from multiple samples prior to amplification and sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
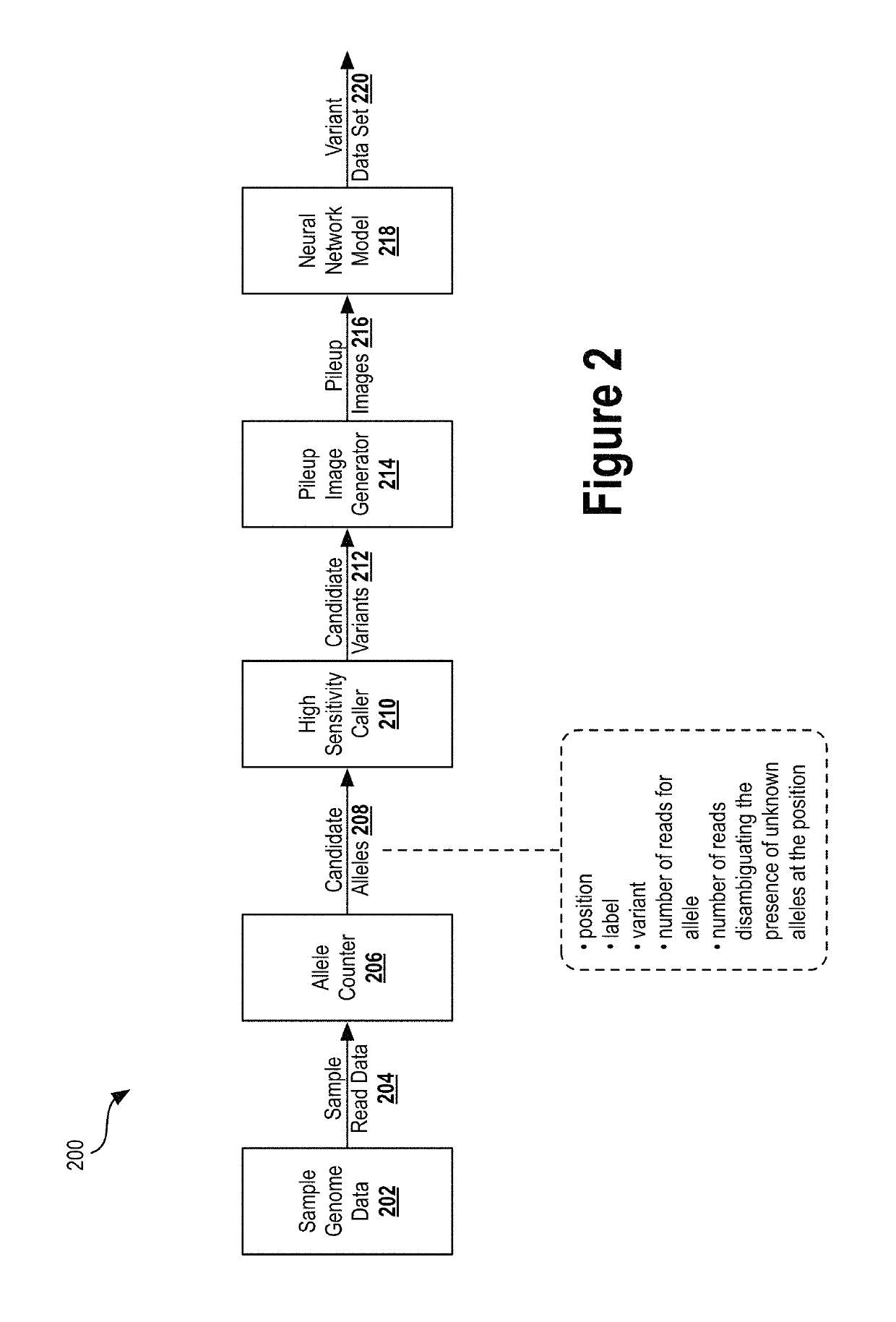
Deep learning analysis pipeline for next generation sequencing
A method for variant calling in a next generation sequencing analysis pipeline involves obtaining a plurality of sequence reads that each include a nucleotide aligned at a nucleotide position within a sample genome. The method also involves obtaining a plurality of alleles associated with the nucleotide position. The method further involves determining that a particular allele of the plurality of alleles matches one or more sequence reads of the plurality of sequence reads, wherein the particular allele is located at the nucleotide position. Additionally, the method involves generating an image based on information associated with the plurality of sequence reads. Further, the method involves determining, by providing the generated image to a trained neural network, a likelihood that the sample genome contains the particular allele. The method may also involves providing an output signal indicative of the determined likelihood.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
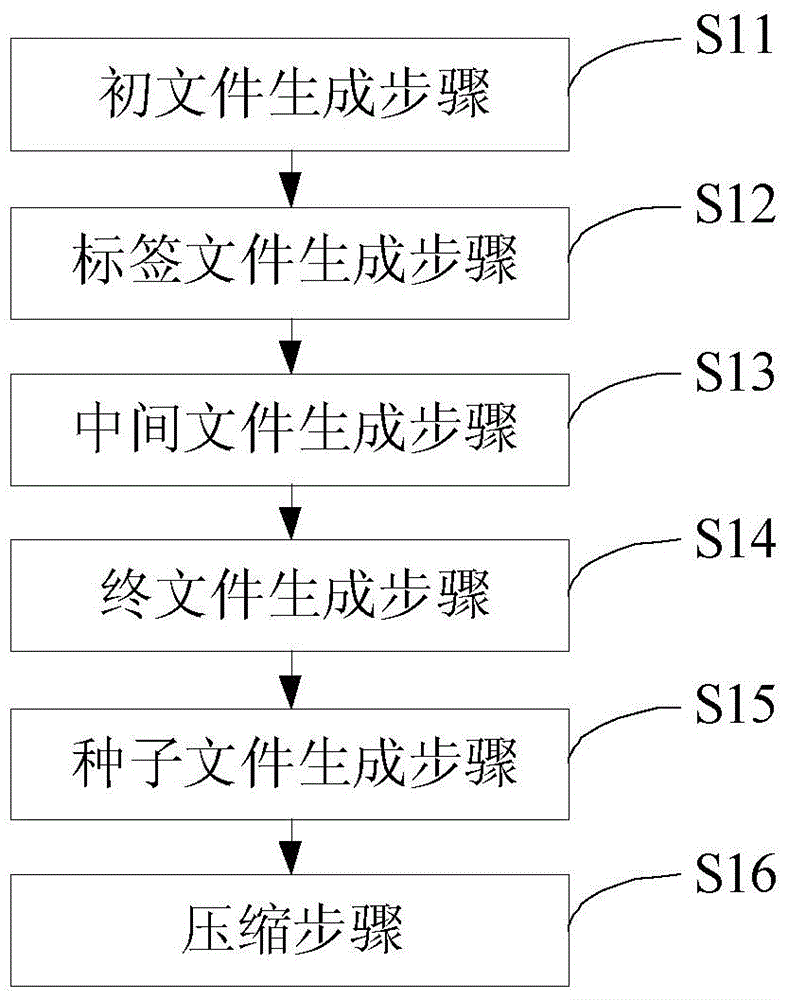
Compression method for next generation sequencing data
ActiveCN105760706ASave storage spaceProcessing speedSpecial data processing applicationsCompression methodParallel processing
The invention discloses a compression method for next generation sequencing data. The method comprises: dividing the next generation sequencing data of each sample according to a first preset length, to generate a BSSL original file; according to a second preset length, establishing a cutting tag file; according to the cutting tag file, processing the BSSL original file, to obtain BSSL intermediate files; combining the BSSL intermediate files to obtain a BSSL final file; counting a frequency distribution result of a seed sequence in the BSSL final file, to obtain a seed file according to the result; combined with the format characteristics of the sequencing data, determining compression rules, and based on the seed file, compressing the next generation sequencing data of each sample. Through dividing the next generation sequencing data and performing parallel processing, processing speed is improved, and combined with seed sequence selection, the seed file is obtained, and the next generation sequencing data is compressed according to the format characteristics of the sequencing data and the seed file, so that storage space of the next generation sequencing data is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
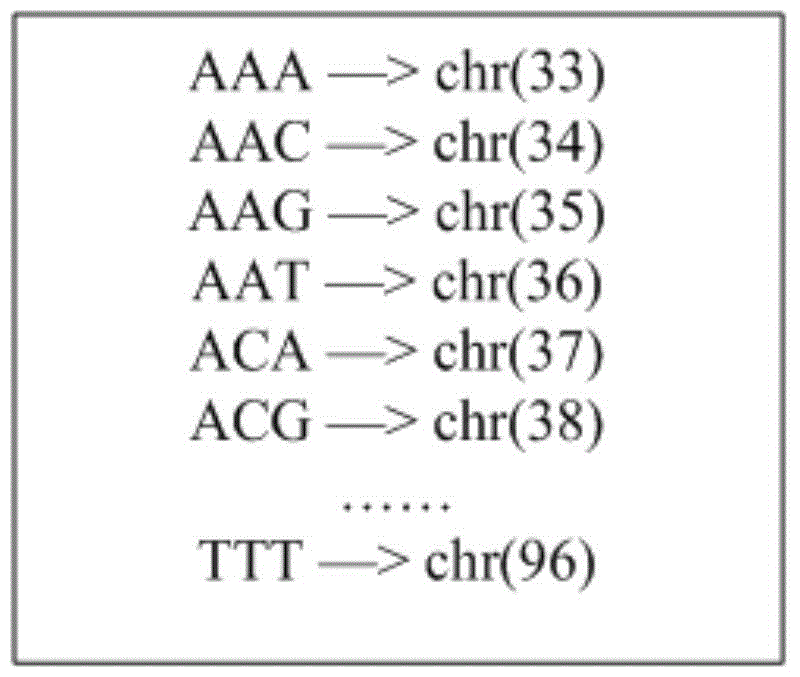
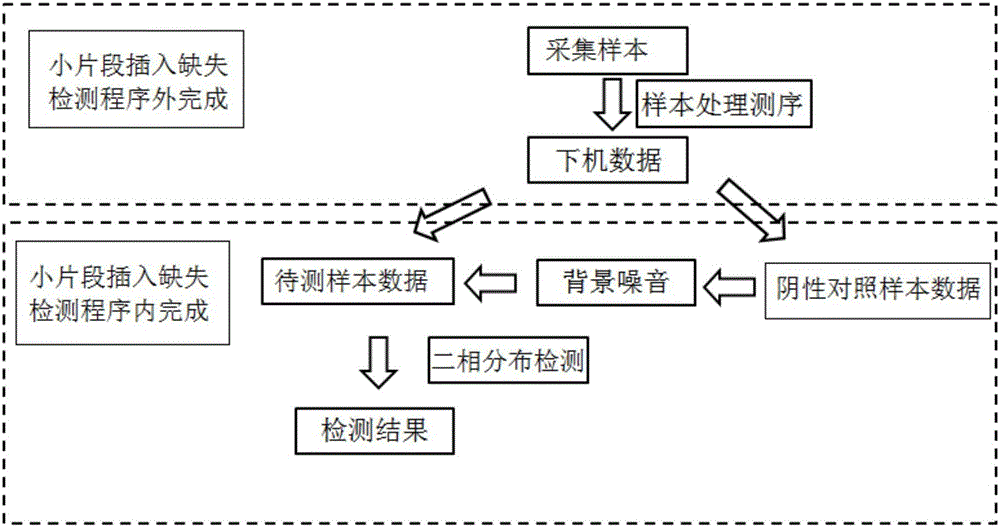
Amplicon next-generation sequencing based small fragment insertion and deletion detection method and device
ActiveCN106355045ANo false positive detectionsHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsReference genesSmall fragment
The invention discloses amplicon next-generation sequencing based small fragment insertion and deletion detection method and device. The amplicon sequencing based small fragment insertion and deletion detection method includes the steps of S1, respectively extracting DNA of a to-be-detected sample and a negative control sample, and amplifying a target region of a mutation related to the target trait by multiple amplicons; S2, carrying out the next-generation sequencing to obtain sequence of the target region; S3, comparing the sequence of the target region with a reference genome, wherein bases which are not matched with the reference genome are subjected to mispairing; S4, processing to obtain background noise of hotspot small fragment insertion and deletion related to the target trait according to the negative control sample, modeling the background noise by means of binomial distribution, distinguishing the hotspot short fragment insertion and deletion and the background noise, on each base, of the to-be-detected sample, and determining the mispairing bases as the small fragment insertion and deletion through positive detection if the proportion of the mispairing bases of the to-be-detected sample to the reference genotype is much different from that of the background noise. By the amplicon next-generation sequencing based small fragment insertion and deletion detection method and device, accuracy of small fragment insertion and deletion detection is improved.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
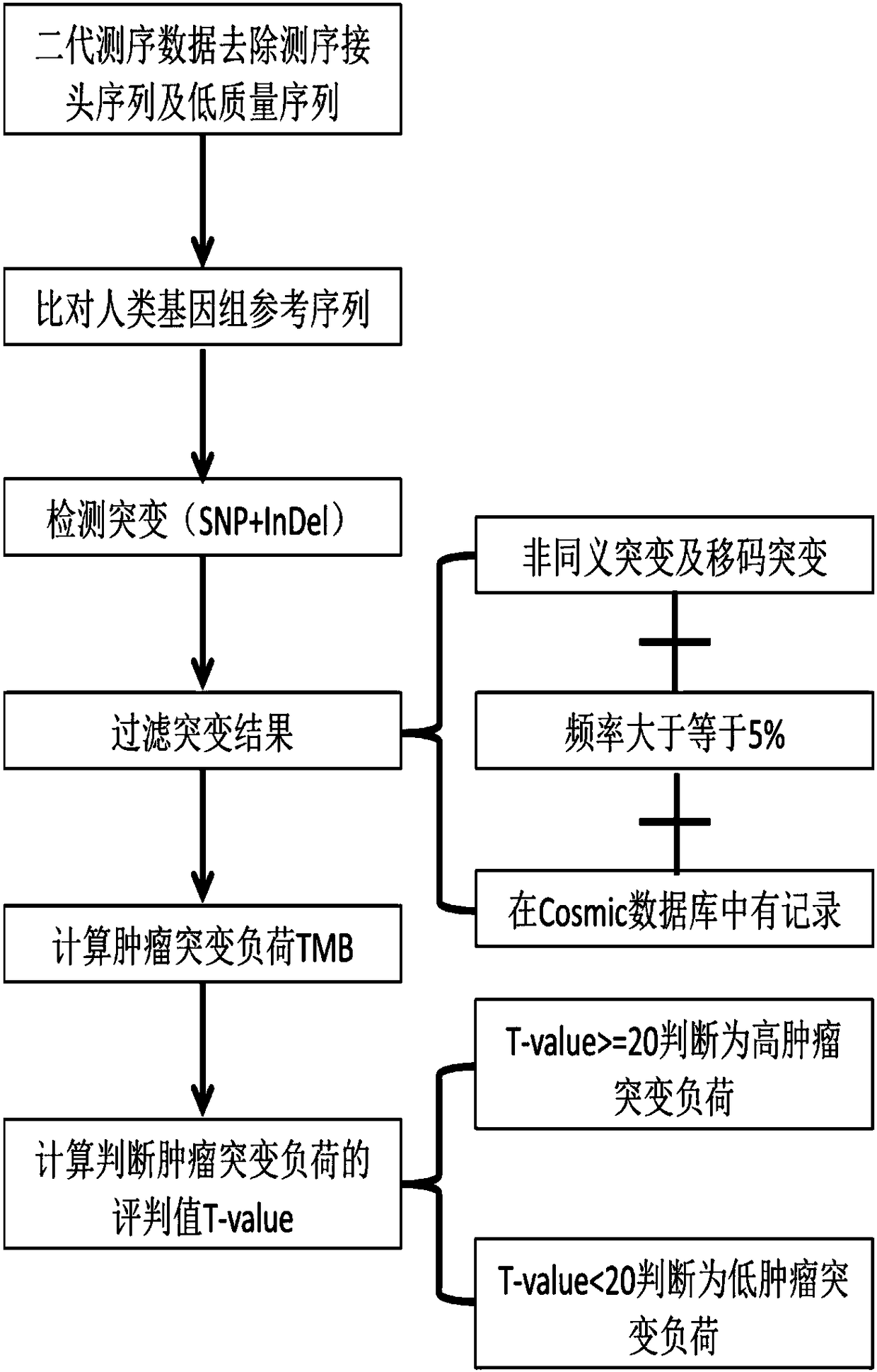
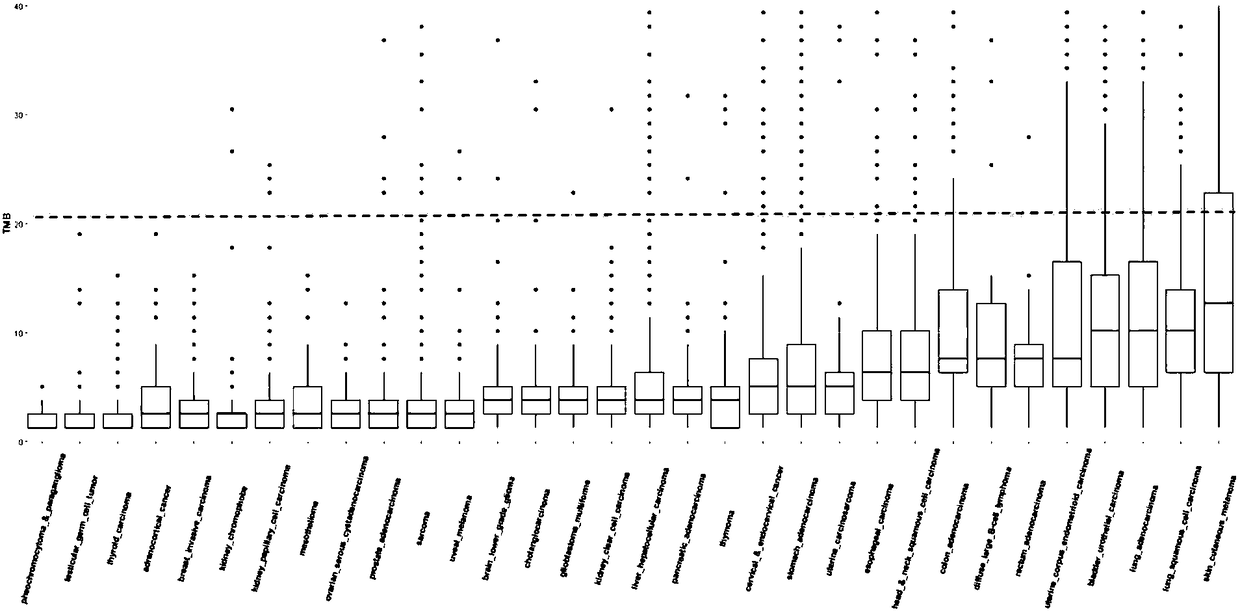
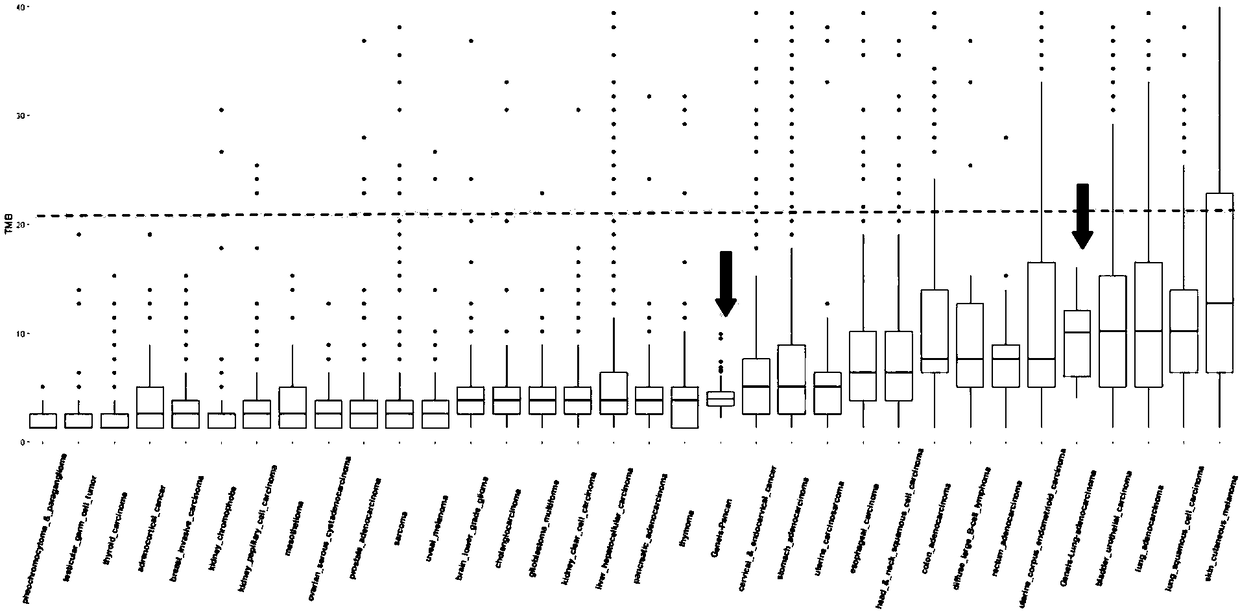
Method for analyzing tumor mutation load on the basis of next-generation sequencing data of single sample
ActiveCN108470114ASave experimentSave sequencingSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSingle sampleSomatic cell
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a tumor mutation load on the basis of the next-generation sequencing data of a single sample. The method disclosed by the invention does not need to detect contrast samples necessary for cell mutation or analyze the cell mutation, the experiment, sequencing and analysis steps of the contrast sample are saved, and therefore, cost and experiment, analysis and unscrambling complexities are greatly lowered.
Owner:GENEIS TECH BEIJING CO LTD
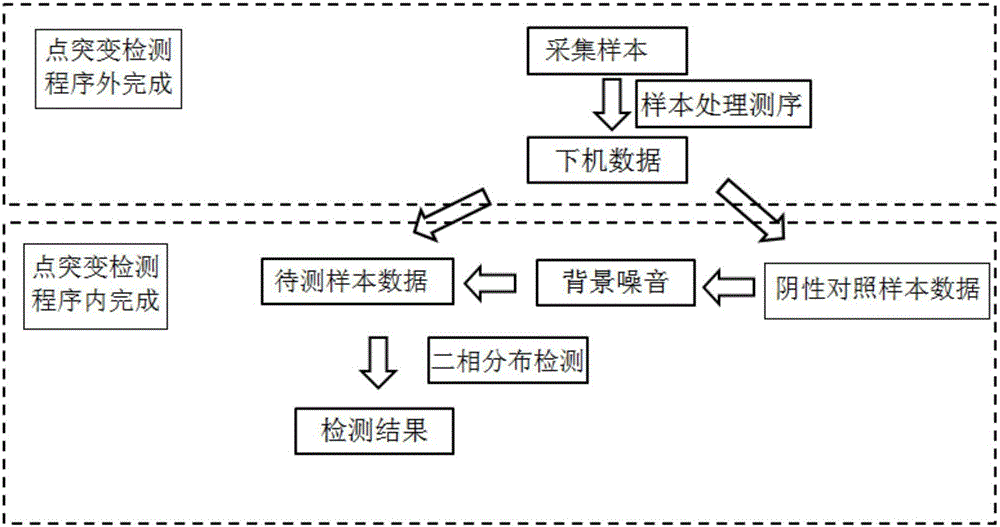
Point mutation detection method and device based on amplicon next-generation sequencing
ActiveCN106282356ANo false positive resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNext generation sequenceReference genome
The invention discloses a point mutation detection method and device based on amplicon next-generation sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: S1. respectively extracting DNAs of a detected sample and a negative control sample, and carrying out multiplex amplicon amplification on the target region related to target characters; S2. carrying out next-generation sequencing to obtain the sequence of the target region; S3. comparing the sequence of the target region with a reference genome, wherein unmatched bases with the reference genome form mismatches; and S4. according to the background noise of the target-character-related hotspot point mutation obtained from the negative control sample, distinguishing hotspot point mutation and background noise in the detected sample on each base by using a binomial distribution model, and if the reference genotype proportion of the mismatches bases of the detected sample is obviously different from the background noise, detecting the mismatched bases as the positive point mutation. The method and device enhance the point mutation detection accuracy based on amplicon next-generation sequencing.
Owner:天津诺禾医学检验所有限公司
Deep sequencing of peripheral blood plasma DNA as a reliable test for confirming the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome
ActiveUS20160130648A1Increase in bone marrow blastsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGackstroemiaHematologic malignancy
Methods are provided for treating, managing, diagnosing and monitoring myelodysplastic syndrome and other hematologic malignancies. These methods comprise the next generation sequencing analysis conducted on cell-free DNA from peripheral blood plasma or serum.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS LAB
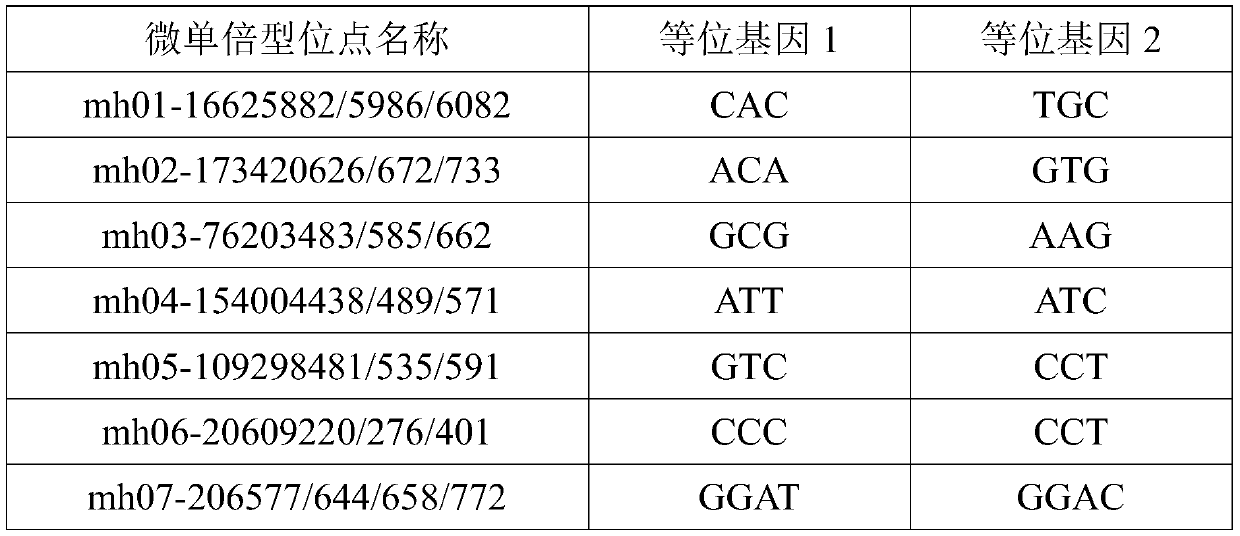
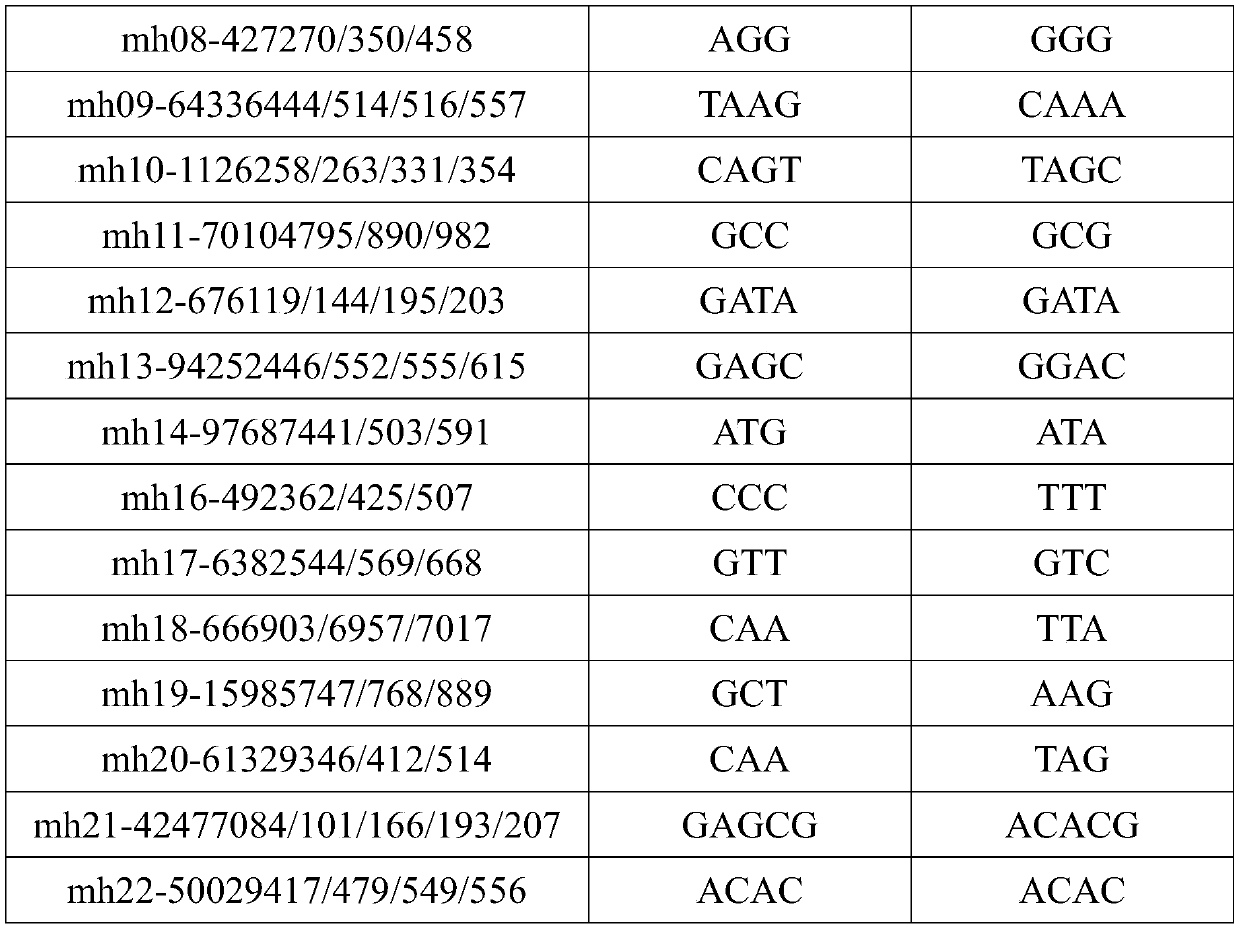
Multiplex amplification system, and next generation sequencing typing kit and typing method for 21 micro-haplotype sites
ActiveCN110218781AShorten the lengthLow mutation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisStr typingAllele frequency
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, and especially relates to a multiplex amplification system, and a next generation sequencing typing kit and typing method for 21 micro-haplotype sites. The 21 micro-haplotype sites in the multiplex amplification system are derived from 21 autosomes, are balanced in allele frequency, are mutually independent between the sites, and have the advantages of polymorphism and low mutation rate. The kit contains 53 PCR-amplified single-end specific primers shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-SEQ ID NO.53, and can detect the 21 microhaplotype sites in a same reaction system. The multiplex amplification system, the kit and the typing method provided by the invention can solve the technical problem that a current STR typing technology cannot obtainan ideal typing result, and allele loss may occur due to excessive number of SNP sites.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
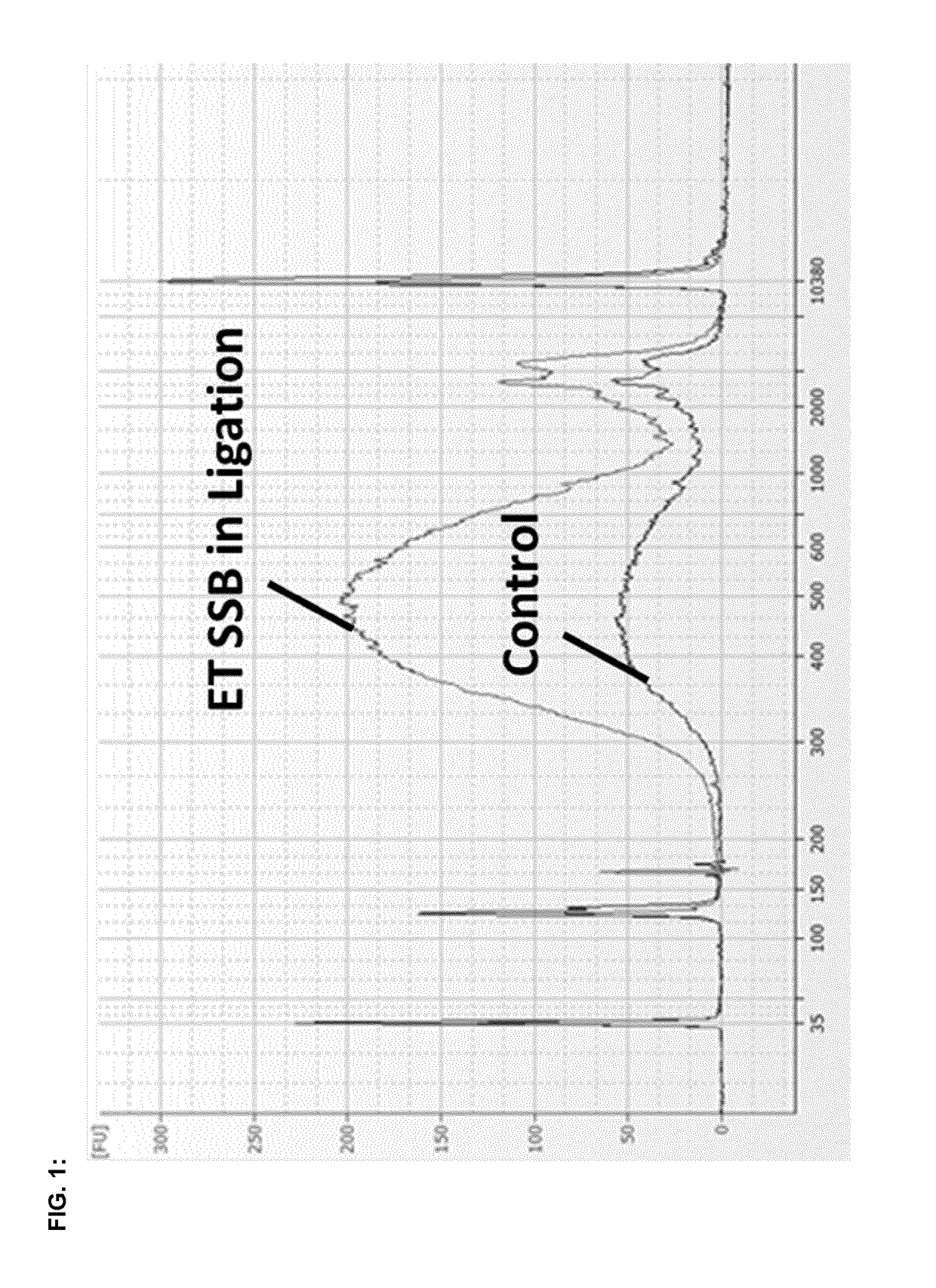
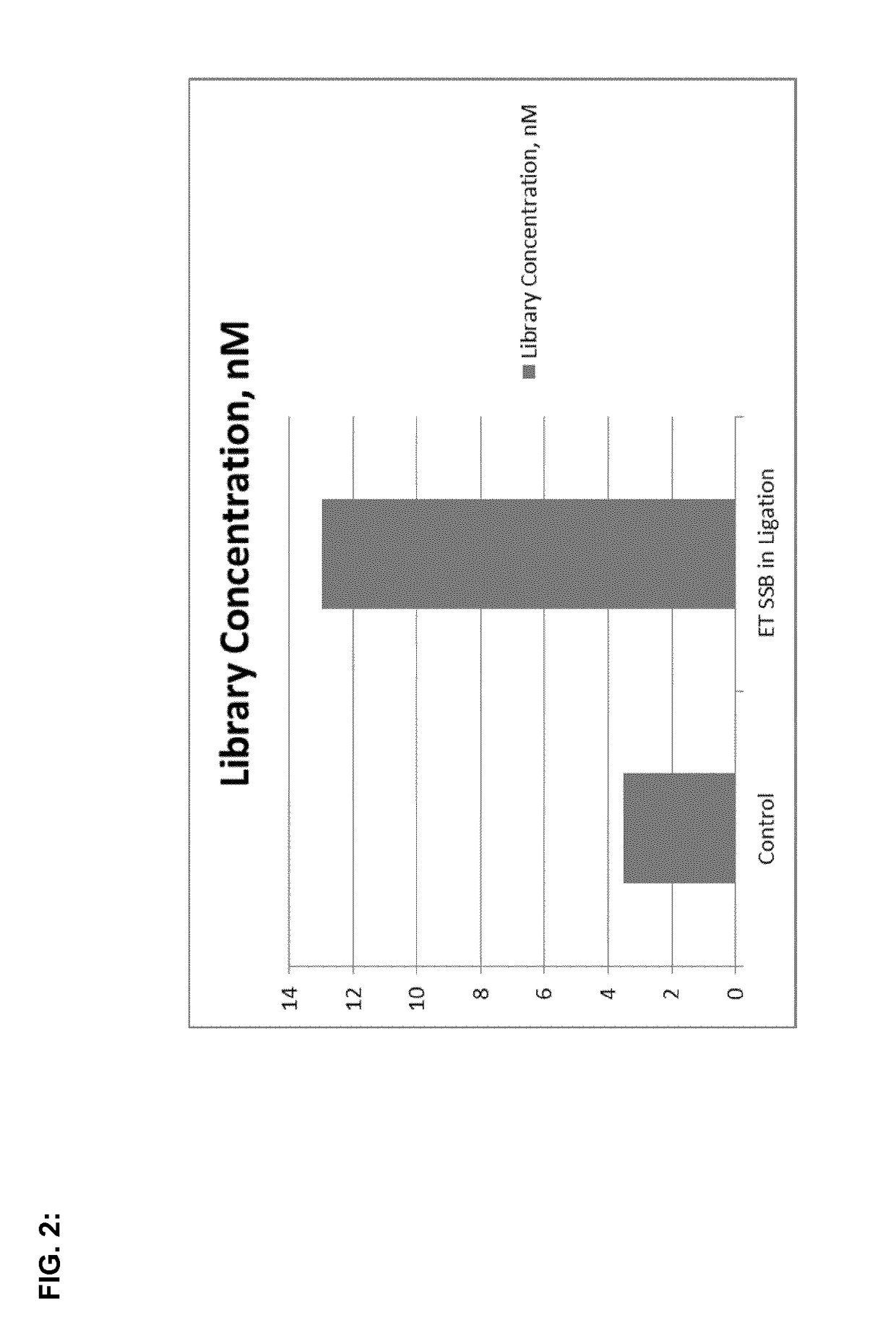
Efficiency improving ligation methods
InactiveUS20180148716A1High stringency conditionImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionDNA fragmentationDouble-stranded DNA binding
The present invention provides new methods and kits to improve the efficiency of ligation reactions, in particular in molecular biology applications, such as the next generation sequencing (NGS) library construction methods. In next-generation sequencing methods, the ligation step is critical in adding sequencing platform-specific adapters to the DNA fragments that are to be sequenced. Said improvement is achieved by the addition of single- or double-stranded DNA-binding proteins in the ligation step.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Compositions and methods for improving sample identification in indexed nucleic acid libraries
The present invention is concerned with compositions and methods for improving the rate of correct sample identification in indexed nucleic acid library preparations for multiplex next generation sequencing by blocking the 3′ ends of pooled indexed polynucleotides from multiple samples prior to amplification and sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
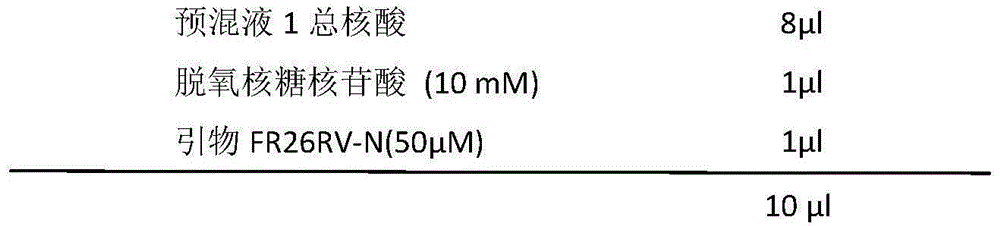
Sequencing method based on molecular tag and next-generation sequencing for reducing sequencing error, kit and application thereof
InactiveCN108148900AEfficient identification of mutationsEfficient identification of amplification errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDouble strandSequence labeling
The invention discloses a sequencing method based on a molecular tag and next-generation sequencing for reducing a sequencing error, a kit and an application thereof. The sequencing method comprises the following steps: S1, synthesizing 4 to 16 normal strands P5 and inverse strands P7 comprising different connectors of fixed specific sequence tags for each sample, annealing the P5 and P7, and forming a Y-shaped connector; S2, filling-in an end of a template DNA, and adding a basic group A on an end 3'; S3, connecting the Y-shaped connector to two ends of the processed template DNA; S4, recovering the template DNA connected with the connector, and gathering and amplifying the template DNA by utilizing a connector primer with the sample tag; S5, recovering a gathered and amplified product; and S6, performing the next-generation sequencing on the gathered and amplified product. By adopting the sequencing method, the mutation, and particularly the asymmetric mutation in a double-strand DNAoriginal template can be effectively identified, so that the amplification error introduced from the first gathering amplification can be effectively identified, and under an Illumina single-end anddual-end sample tag sequencing mode, the drift problem of the sample tag can be effectively solved by virtue of the fixed specific sequence of 4 to 16 unique connectors of a sample.
Owner:深圳因和生物科技有限公司
Construction method of T cell antigen receptor diversity sequencing library and kit
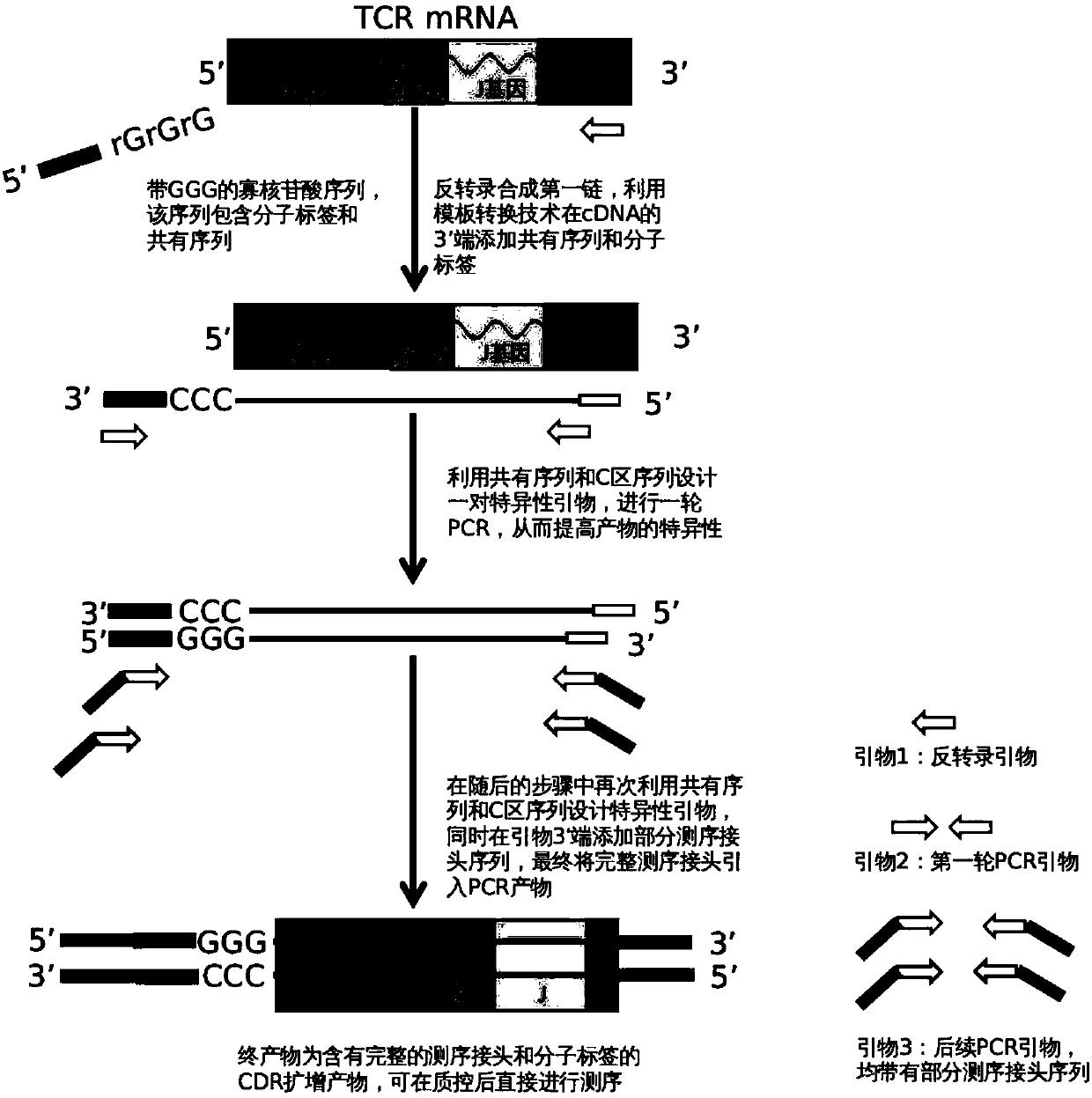
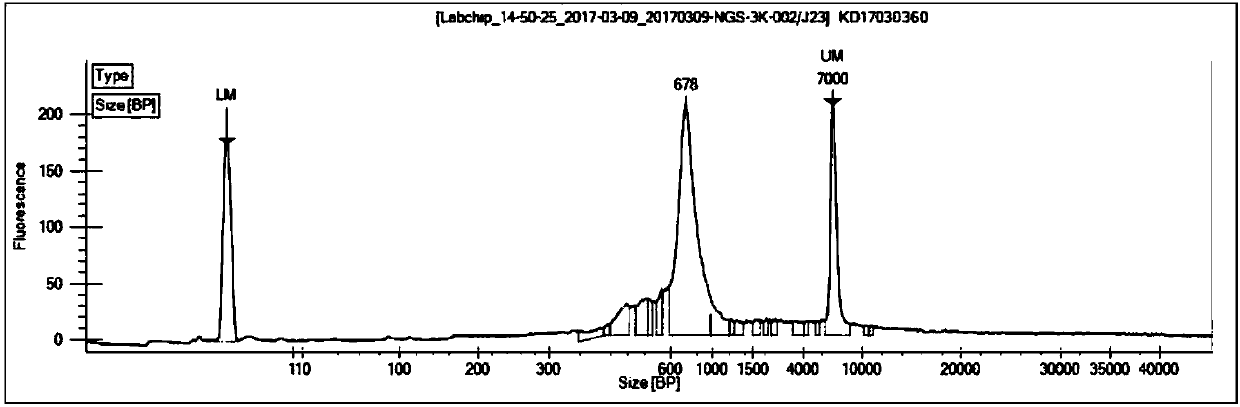
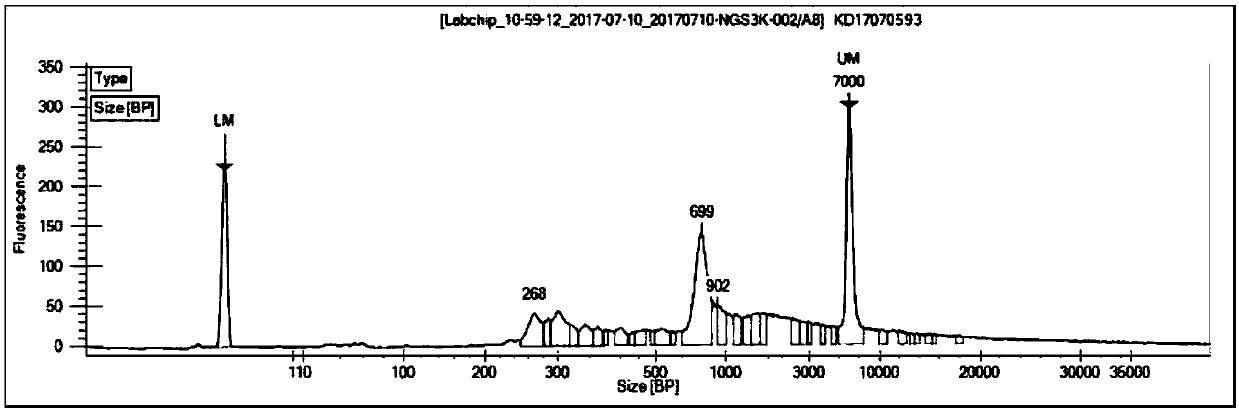
ActiveCN107779495AImplement the buildCorrect mistakesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSequence designT-Cell Antigen Receptors
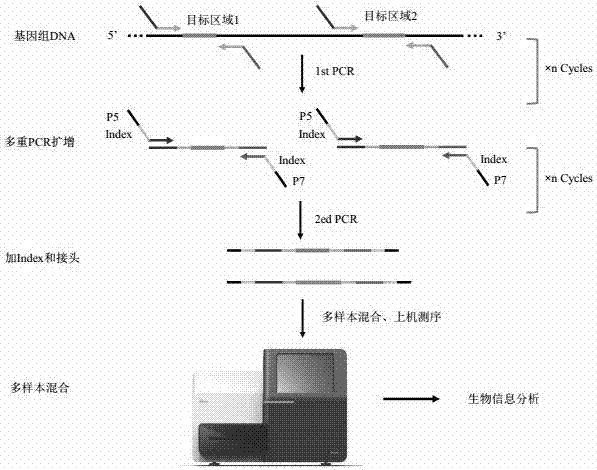
The invention relates to a construction method of a T cell antigen receptor diversity sequencing library and a kit. The construction method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: amplifying regions V, D and J of a TRB gene expressed by a human or mouse T lymphocyte by utilizing a designed specific primer specific to a consensus sequence of a region C of the human or mouse TRB gene, synchronously introducing a next generation sequencing joint sequence into an amplified product, and directly sequencing the regions V, D and J of the TRB gene.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
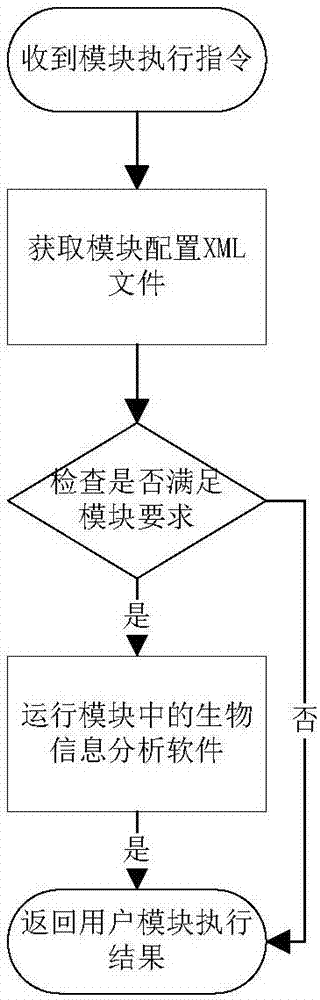
Bioinformatics analysis method and system for next-generation sequencing DNA mutation detection
InactiveCN107122626AImprove maintainabilityImprove stabilitySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsInformation analysisAnalysis data
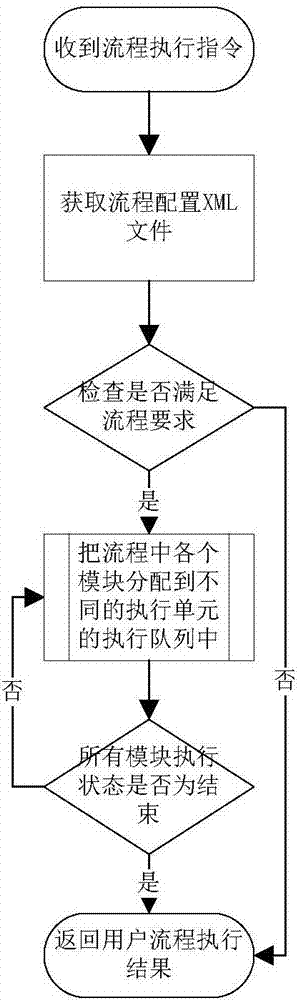
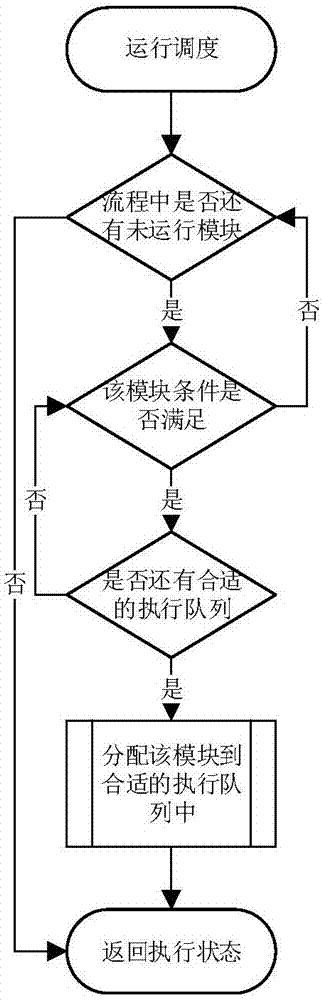
The invention provides a bioinformatics analysis method and system for next-generation sequencing DNA mutation detection. The system comprises a bio-information analysis module used for providing basic component units of a biological analysis process and finishing basic functions of bio-information analysis, an intermediate data conversion module used for performing format conversion on data generated by the bio-information analysis module and providing biological analysis data sources and results meeting the requirements, and a running environment configuration module used for configuring relative paths or absolute paths of all input files, output files, configuration files, data files, temporary files, log records, scripts and applications during running of different biological analysis processes and running related environment variables. According to the method and the system, the design is performed only for the DNA mutation detection, namely, a specific bio-information analysis process, so that unnecessary functions are prevented from being introduced, the maintainability and stability of the system are improved, and the flexibility maximization of process establishment is ensured.
Owner:上海海云生物科技有限公司
Next generation sequencing primer probe set and detection method of microsatellite instability state
PendingCN109082470AInstructiveIncrease profitMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationTissue sample
The invention relates to a next generation sequencing detection method of a microsatellite instability state. The method includes: performing DNA fragmentation on the cancer tissue sample and normal tissue reference substance of a tumor patient, polishing and adding tail A to tail ends, and performing joint connection; designing primers and probes for target area capturing and primers for amplification, the probes are one-way DNA extension probes aiming at five microsatellite loci, and using the probes and the primers to perform target area capturing and then performing amplification to obtaina library; sequencing to obtain the repeated sequence length distribution data of the five microsatellite loci of the cancer tissue sample and the normal tissue reference substance, and comparing thedata of the five microsatellite loci of the cancer tissue sample and the normal tissue reference substance to judge the stability of the microsatellite loci. The invention further relates to a next generation sequencing primer probe set of the microsatellite instability state. The next generation sequencing detection method can reduce influence of sequencing depth on result judgement and is simple, practicable, high in accuracy, high in sensitivity and low in cost.
Owner:上海赛安生物医药科技股份有限公司
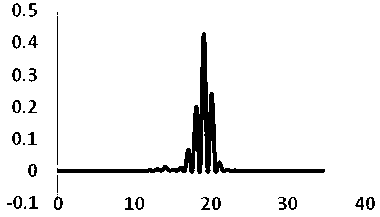
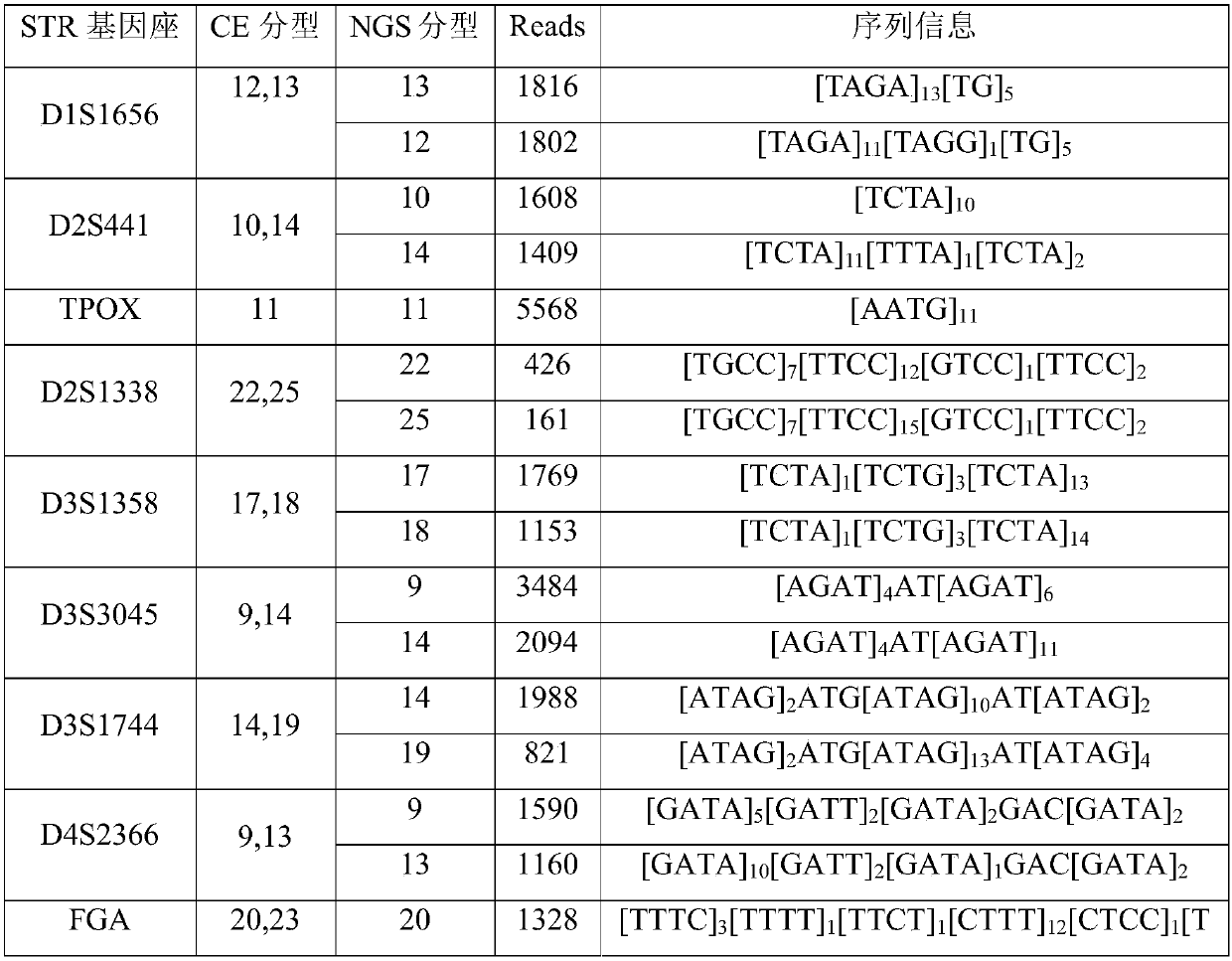
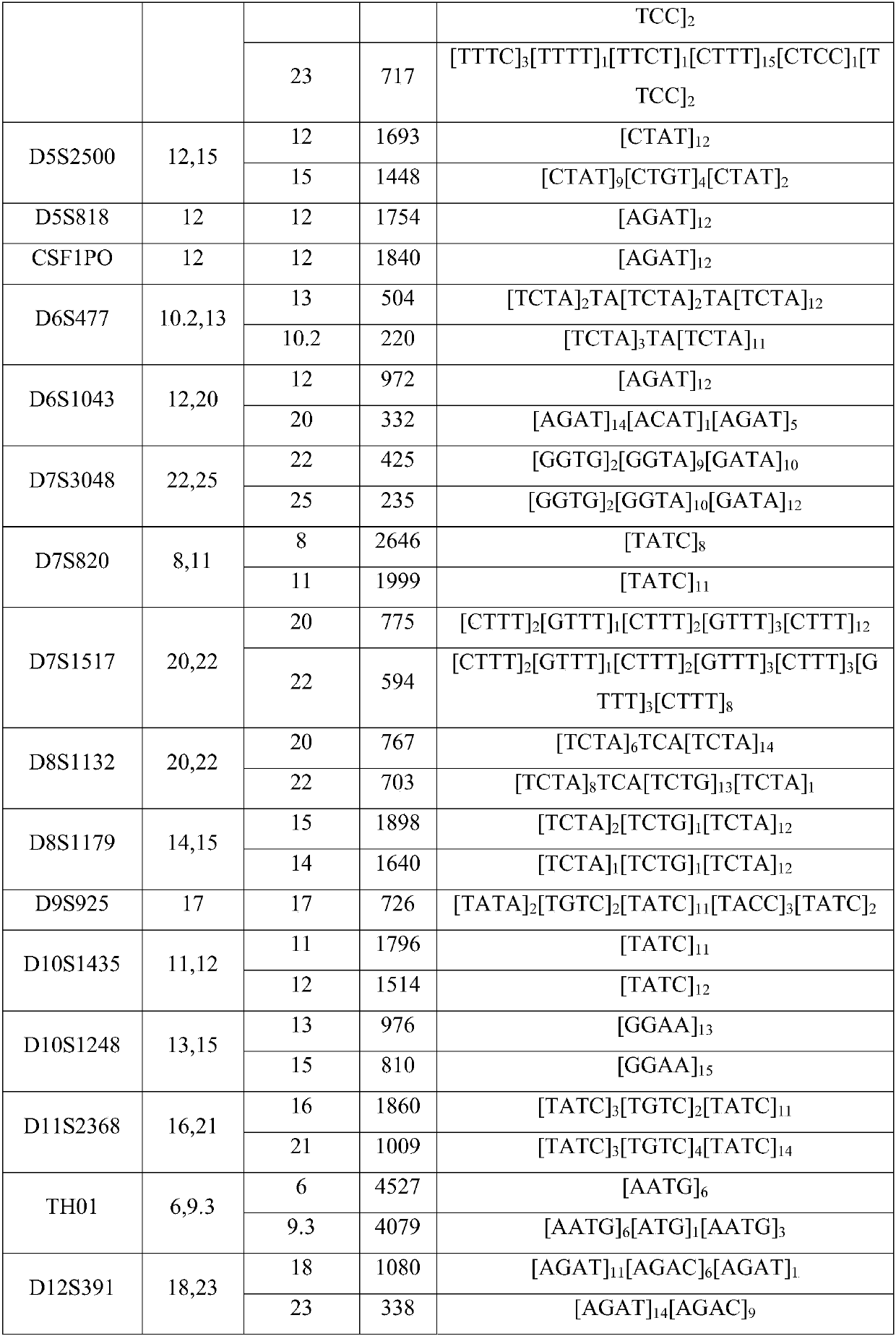
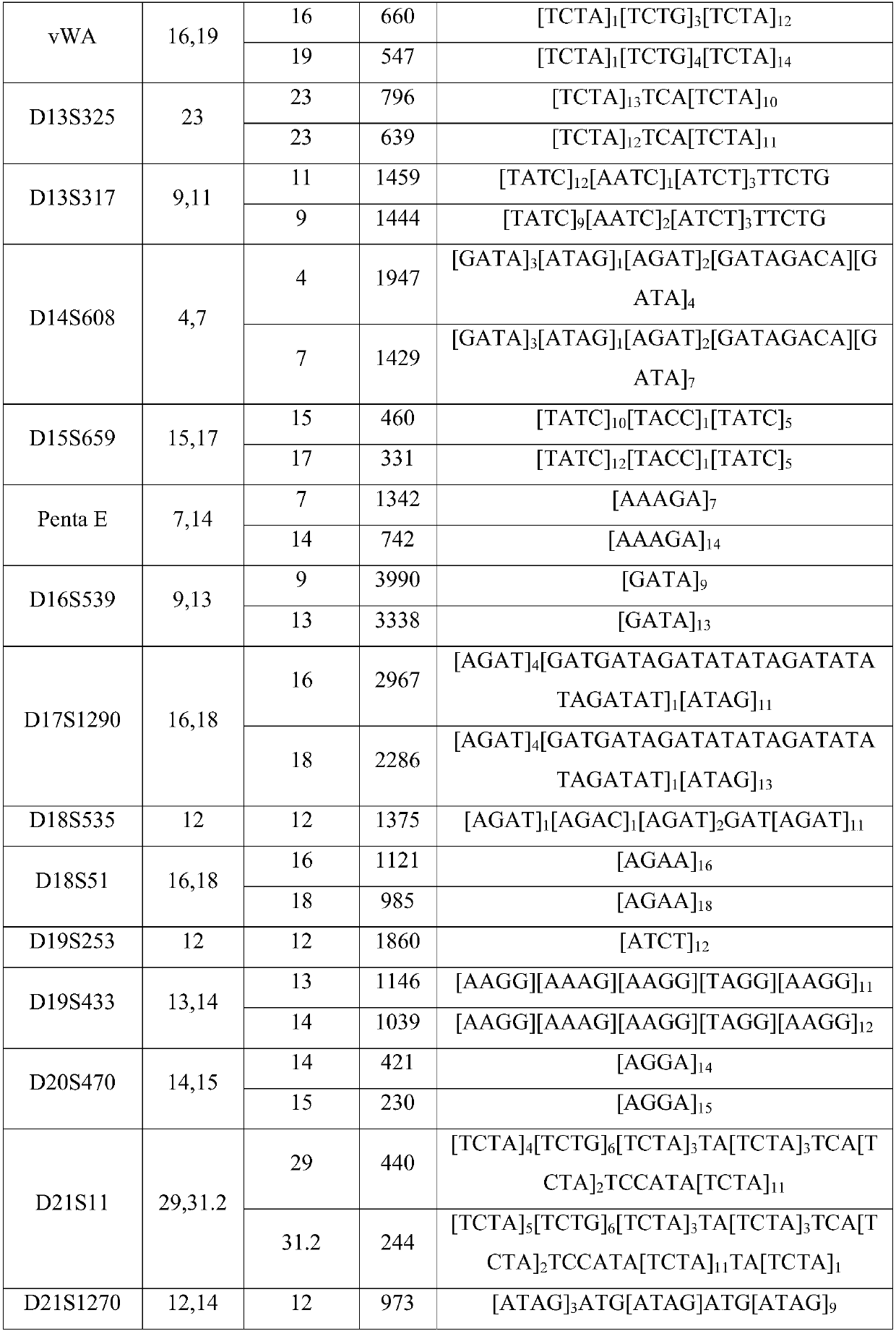
Next generation sequencing typing reagent kit of 43 STR sites and method
The invention relates to a next generation sequencing typing reagent kit of 43 STR sites and a method. The reagent kit comprises a PCR amplification reagent kit, wherein the PCR amplification reagentkit comprises 79 PCR amplification single-end specific primers of the 43 STR sites, and the nucleotide sequence of the PCR amplification single-end specific primers is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.79. The primers in the reagent kit can enable the polymorphism of each gene locus to be increased, so that probability of exclusion and system effectiveness can be improved, and the testing result is accurate and reliable; and testing results can provide new data for development of a NGS-STR typing technique, and a new detection scheme is provided for cases of target missing person survey, complex genetic relationship identification and the like through united application of a plurality of STR sites of the reagent kits in the prior art.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Adapter for next-generation sequencing
ActiveCN106939344AReduce false positive mutationsImprove Sequencing AccuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideSingle strand dna
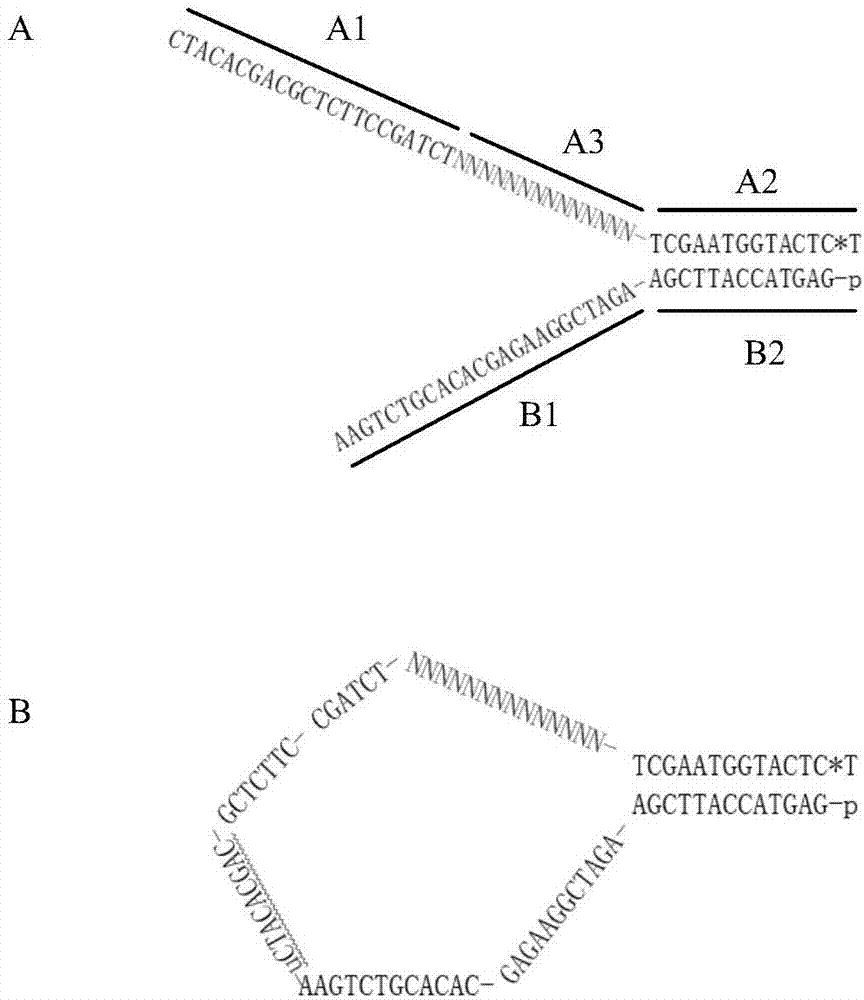
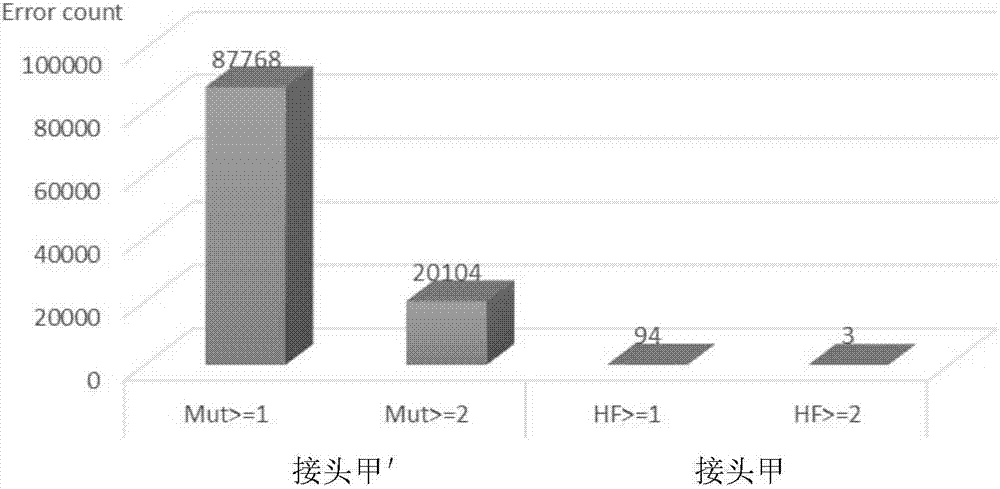
The invention discloses an adapter for next-generation sequencing. The adapter disclosed in the invention is composed of a single-stranded DNA A and a single-stranded DNA B or composed of a single-stranded DNA C and a single-stranded DNA D. The single-stranded DNA A, from terminal 5' to terminal 3', is as shown in a formula (I), i.e., A1-A3-A2, wherein each nucleotide of A3 is A, T, C or G; the single-stranded DNA B, from terminal 3' to terminal 5', is as shown in a formula (II), i.e., B1-B2, wherein A2 and B2 are complementary, A1 and B1 are not complementary, A3, B1 and A1 are not complementary, the sequences of A1 and A2 are different, and the sequences of B1 and B2 are different; the single-stranded DNA C is composed of A1 and A2; and the single-stranded DNA D is composed of B1, B2 and A3. Experimental results show that the adapter provided by the invention can easily and efficiently reduce false positive mutation in next-generation sequencing so as to realize more sensitive detection of low-frequency mutation in heterogeneous mixed samples like heterogeneous samples and chimera samples of tumors.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
Detection kit for Thrombophilia-related gene mutation
ActiveCN107012238AWide detection rangeImplement point mutation detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementGene defectBiological studies
The invention discloses a detection kit for Thrombophilia-related gene mutation. The detection kit comprises ddH2O, 10*buffer (Takara), 2*GC buffer I, dNTP, MgCl2, HSTaq, multiplex PCR primer mixed liquid, Illumina I5 / I7 primer series reagents. The detection kit has the advantages that the detection kit uses the multiplex PCR enriching next generation sequencing technology to comprehensively and systematically detect the point mutation of all exons and control regions of 18 genes which include PROC, PROS1, THBD, PROCR, F5, AT3, HCF2, F2, F7, F8, F9, F10, F11, F12, PLG, ADAMTSl3, HRG and TFPI and performs detection aiming at the specific polymorphic sites of three genes which include PLAT, FGG and HABP2; the detection kit is used for biological researches and molecularly diagnosing the Thrombophilia caused by the defects of the genes above; the detection kit is wide in detection range, high in throughput, fast and accurate in detection method, high in detection accuracy, low in cost, and the like.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
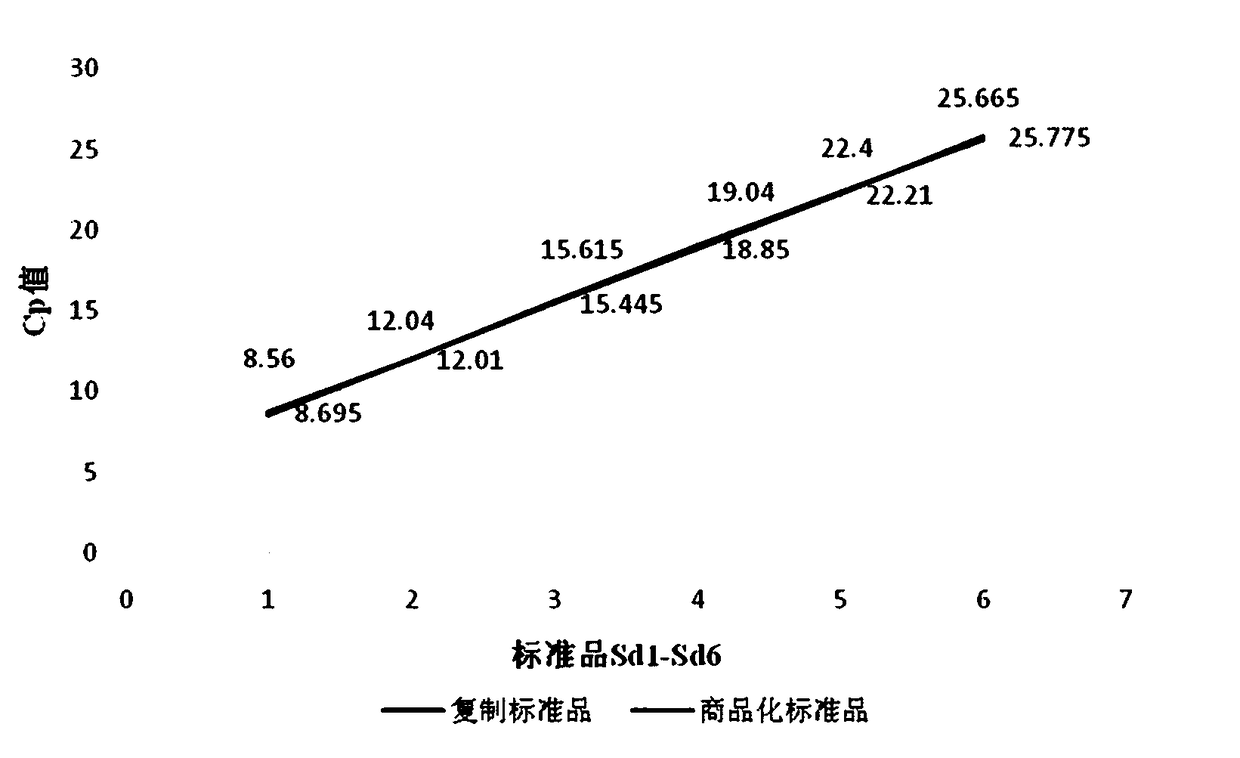
Quantitative standard substance applied to qPCR (quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) accurate quantification of Illumina platform next generation sequencing sample and duplication method thereof
InactiveCN108103174AQuantitatively accurateEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingBiology
The invention discloses a quantitative standard substance applied to qPCR (quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) accurate quantification of an Illumina platform next generation sequencing sample anda duplication method thereof. The duplication method comprises the following steps: (1) performing PCR amplification by using a linker primer P1 and a linker primer P2 and taking a standard substancein a commercialized kit as a template, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the linker primer P1 is 5'-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGA-3', and the nucleotide sequence of the linker primer P2 is 5'-CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAG-3'; (2) purifying with AMPure XP bead at the end of a reaction, performing Qubit quantification at the end of purification, initially diluting step by step by 10 times after Qubit concentration measurement, performing a quantitative experiment on the diluted sample, picking up a sample which is closest to the commercialized standard substance in concentration to serve as a duplicated standard substance 1, and diluting the duplicated standard substance with enzyme-free water step by step by 10 times to obtain second to sixth duplicated standard substances; (3) preserving the duplicated standard substances in a solution containing a buffering system and a stabilizer. The quantitative standard substance is accurate in quantification, and is convenient to use; compared with the commercialized kit, the quantitative standard substance has the advantage that the experiment cost is lowered greatly.
Owner:北京中源维康基因科技有限公司
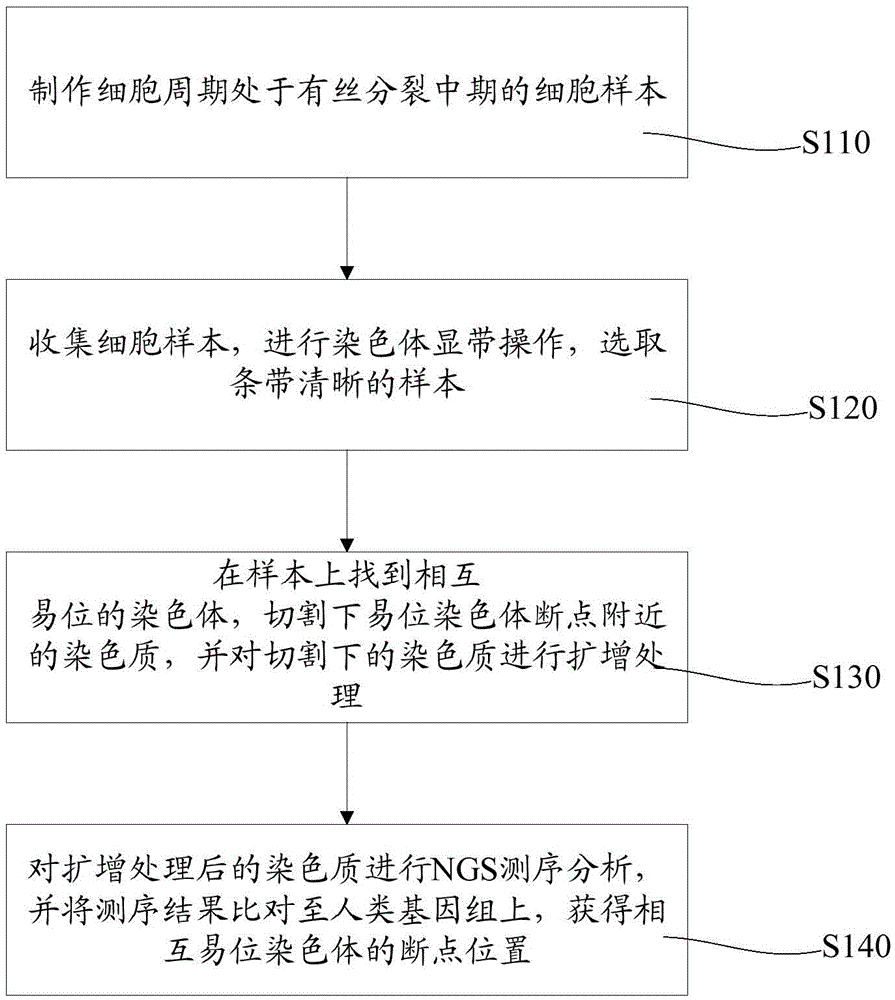
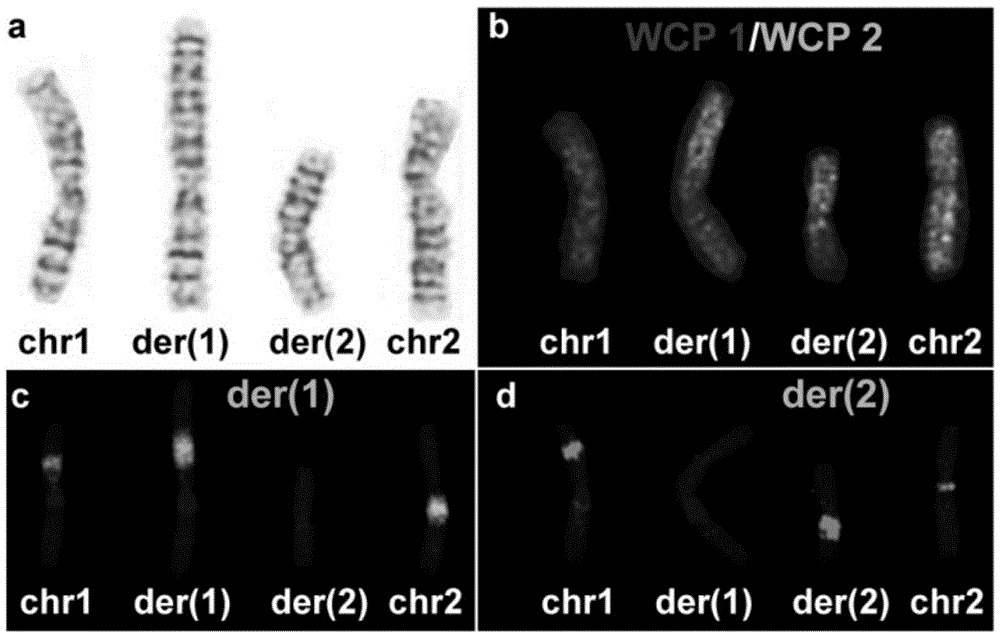
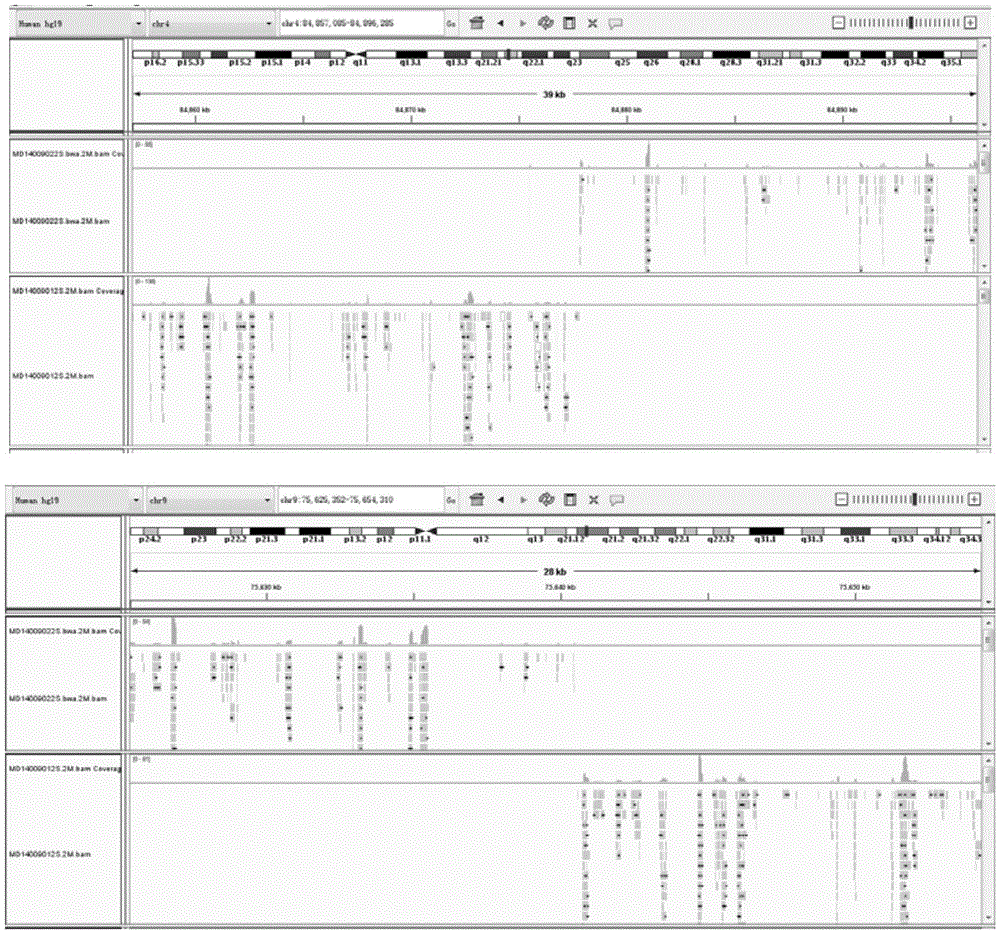
Method for analyzing breakpoints of reciprocal translocation chromosomes
ActiveCN105039569AEasy accessReduce the difficulty of analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisChromosome microdissection
The invention relates to a method for analyzing breakpoints of reciprocal translocation chromosomes. The method has the beneficial effects that chromatins near the breakpoints of translocation chromosomes are obtained by utilizing the chromosome microdissection technology and then the breakpoints can be rapidly and accurately positioned at a relatively low price by utilizing the NGS (next generation sequencing) technology for sequencing analysis, thus being beneficial to subsequent analysis of the reciprocal translocation chromosomes, for example, primers can be designed by utilizing the information to diagnose the PGD (preimplantation genetic diagnosis) embryos of reciprocal translocation chromosome carriers to distinguish completely normal embryos from embryos carrying the reciprocal translocation chromosomes; transmission of the reciprocal translocation chromosomes in families is blocked by only transplanting the completely normal embryos.
Owner:GUANGXIU-GAOXIN LIFE SCI CO LTD HUNAN +1
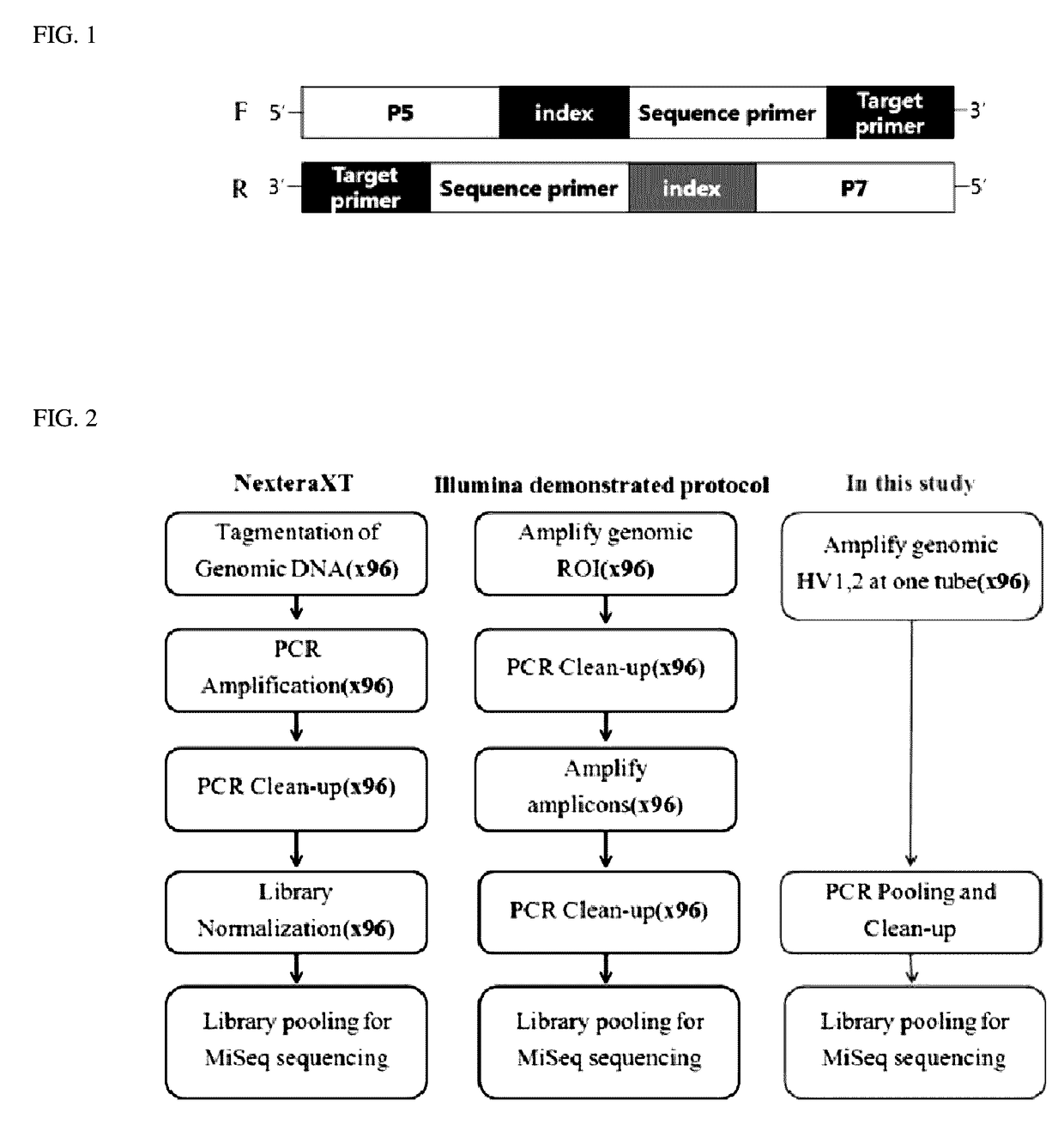
Primer set for preparation of ngs library and method and kit for making ngs library using the same
The present disclosure relates to a primer set for preparation of a library used for next generation sequencing (NGS), and a method and a kit for making an NGS library using the same. The method for making the next generation sequencing (NGS) library using the primer set according to the present disclosure is able to simply analyze large amounts of samples as compared to the existing method for making a library, which is effectively usable for analysis of target DNA sequences or for database construction, in large amounts of samples.
Owner:REPUBLIC OF KOREA (NTL FORENSIC SERVICE DIRECTOR MINIST OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION & SECURITY)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com