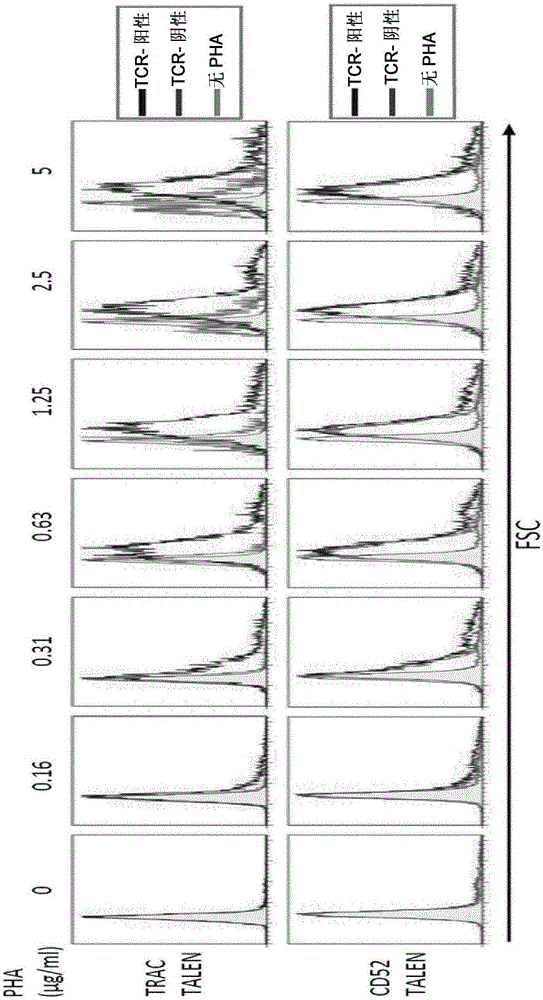
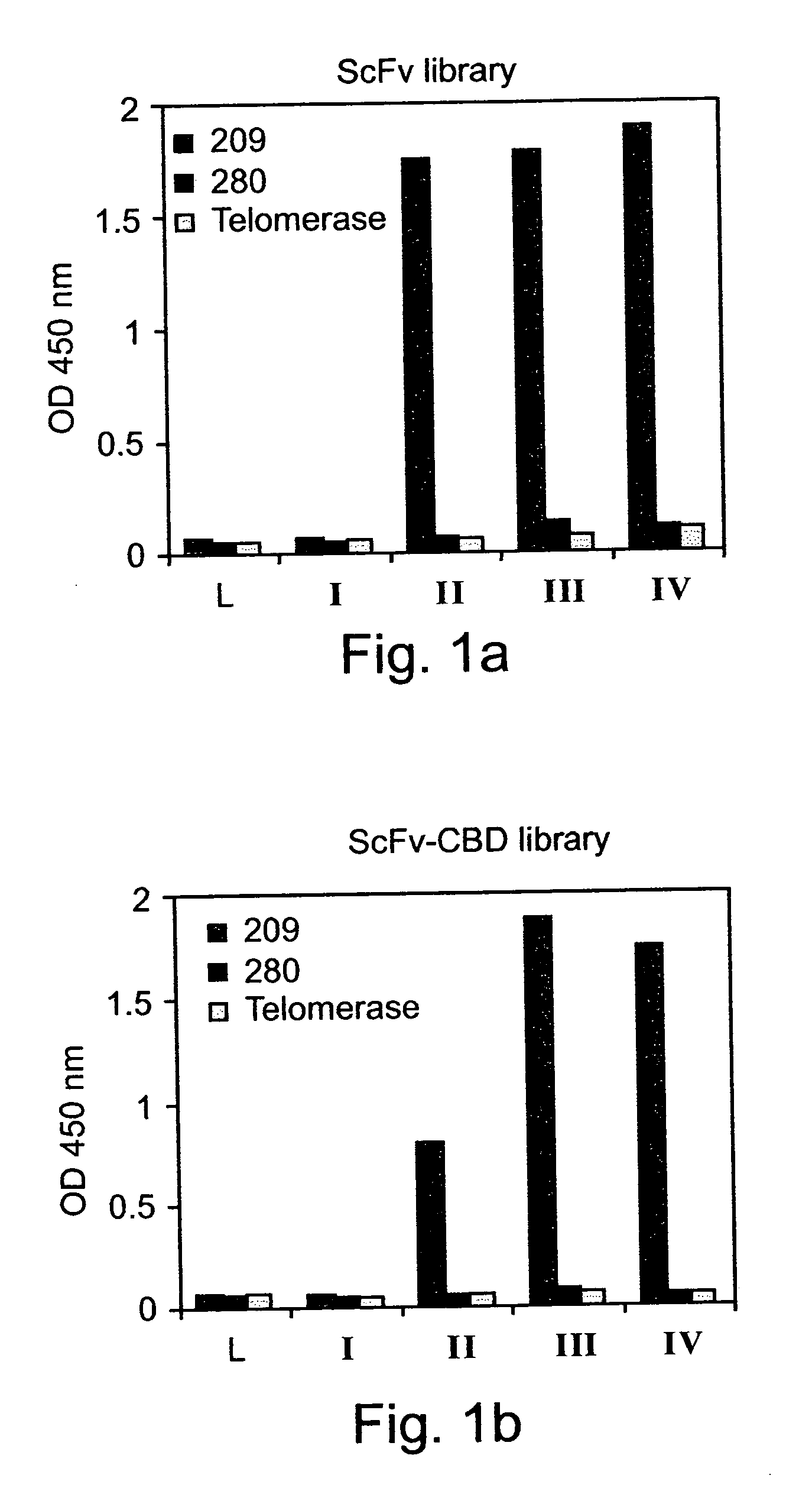
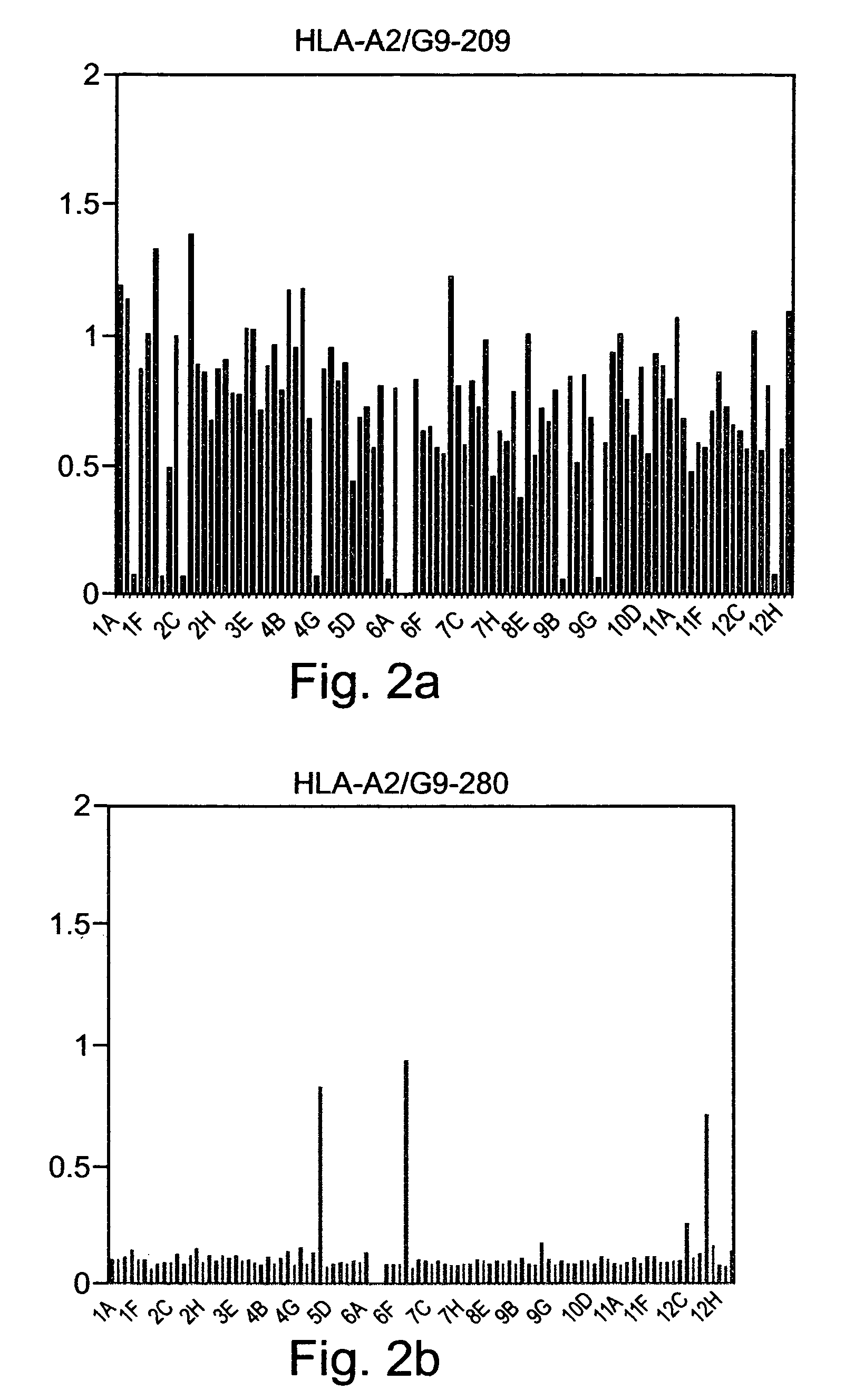
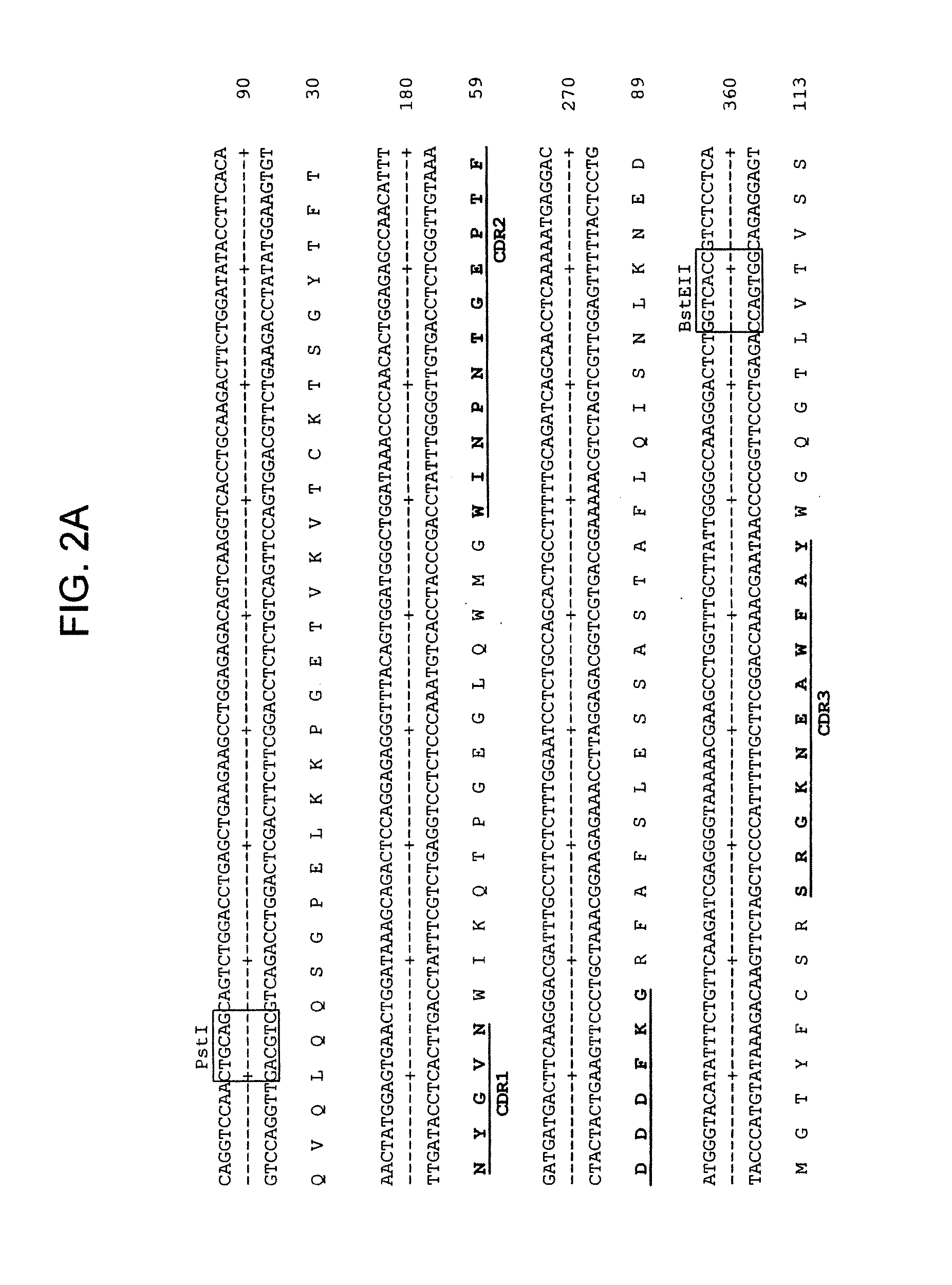
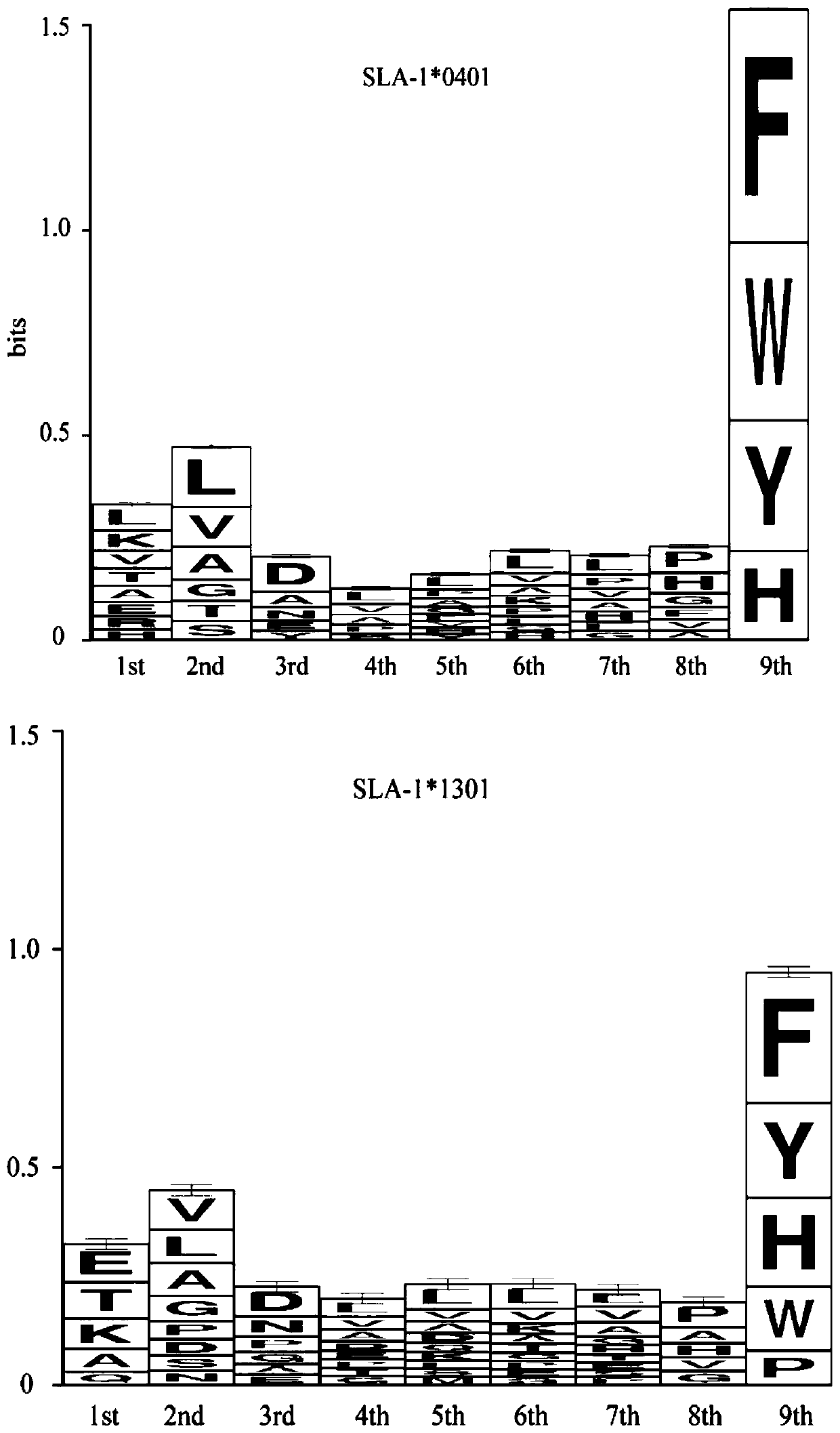
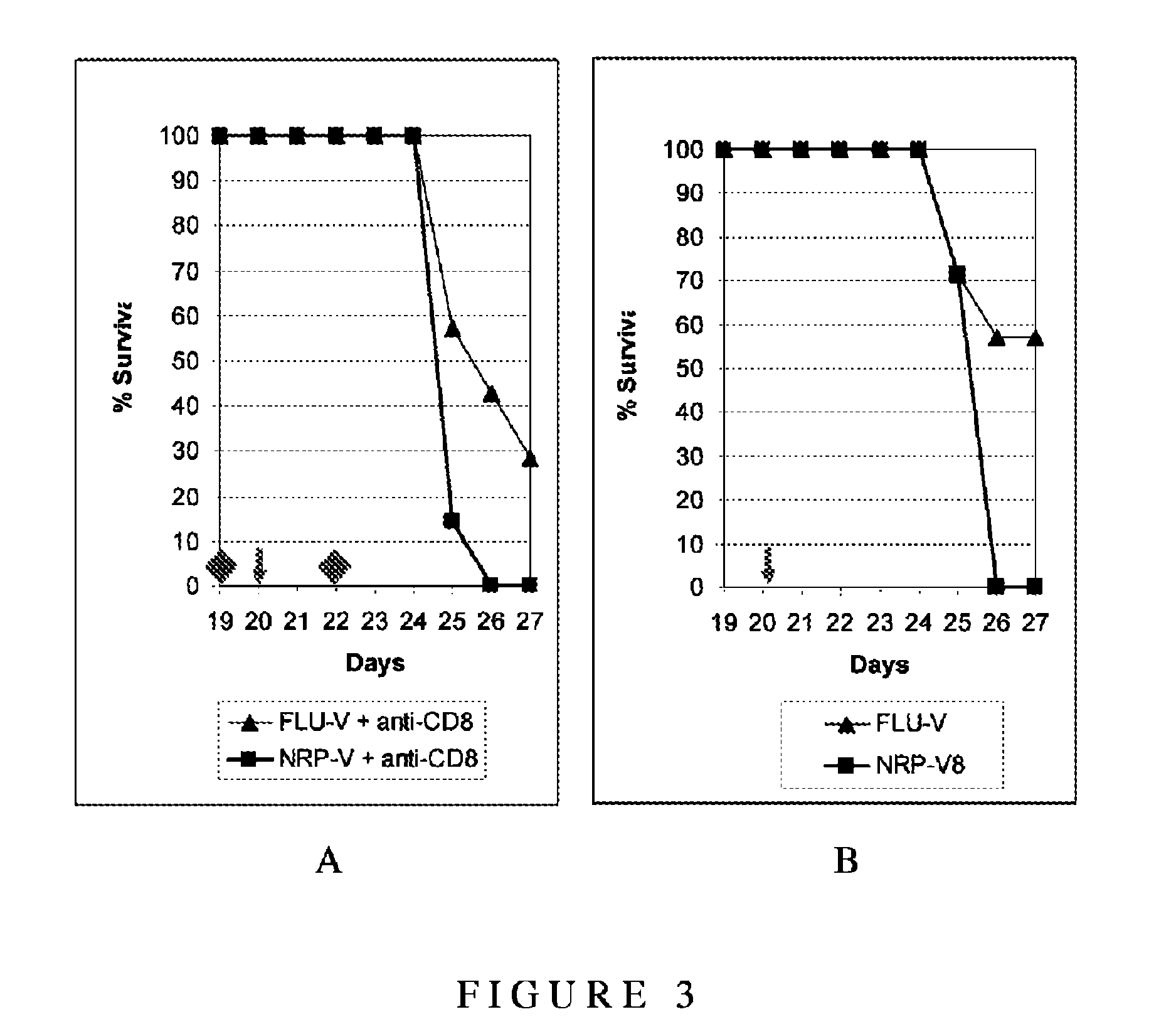
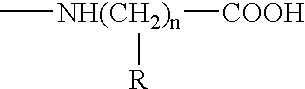Patents
Literature
116 results about "Major histocompatibility complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
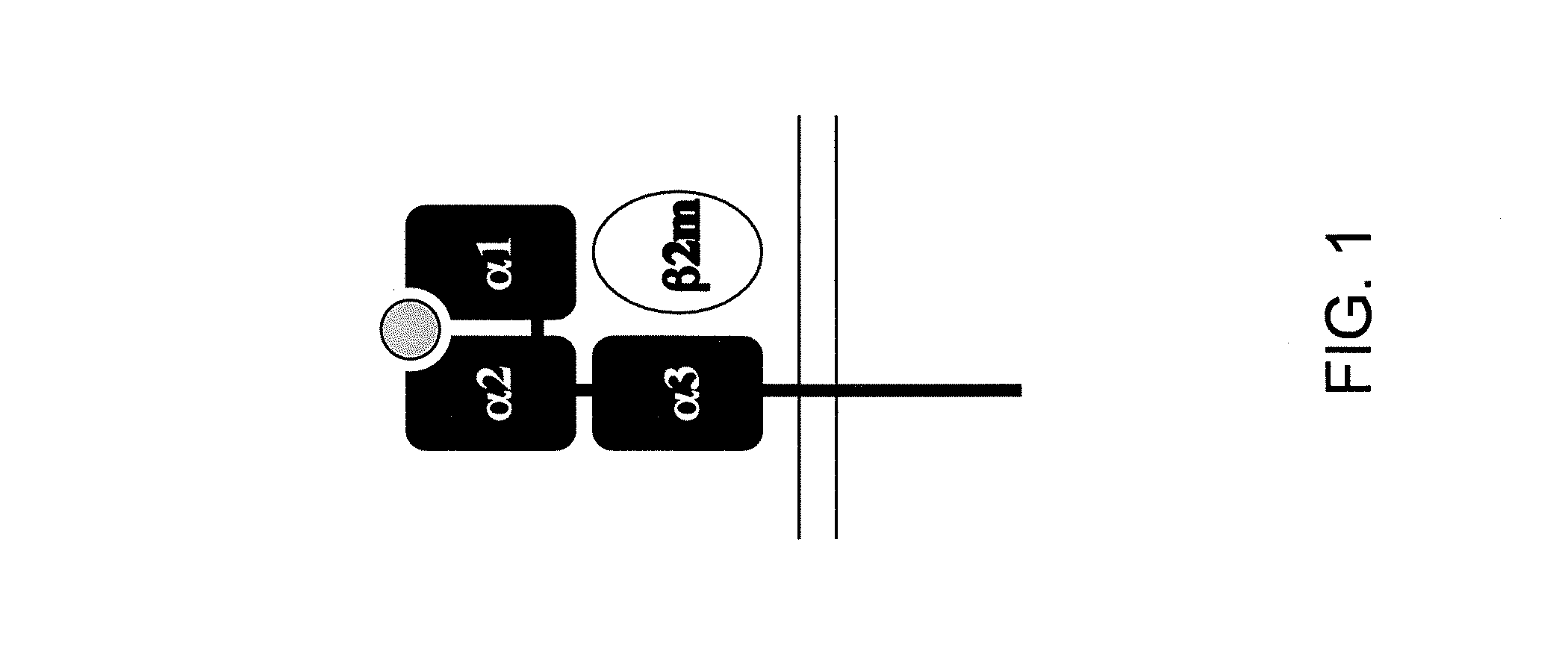
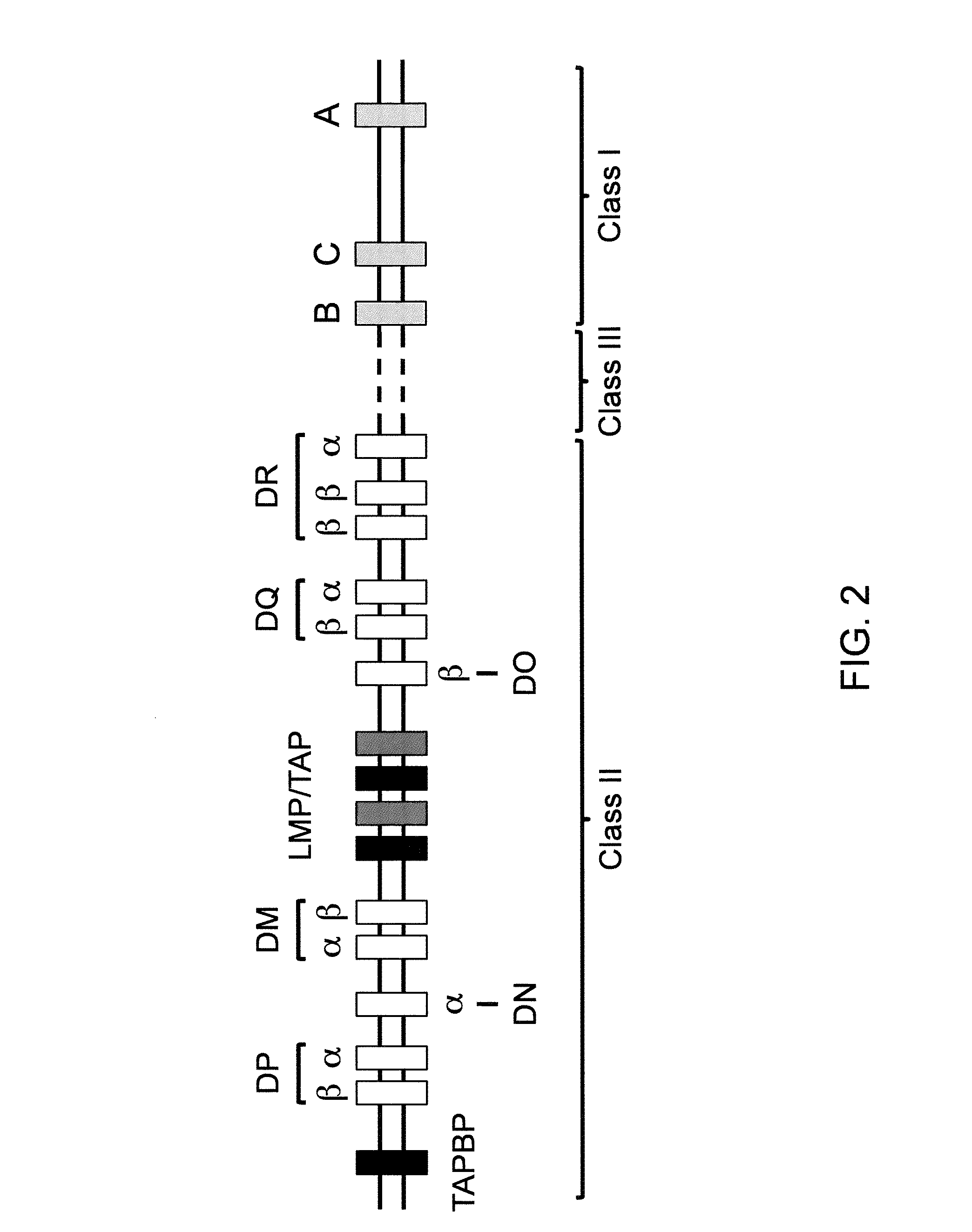
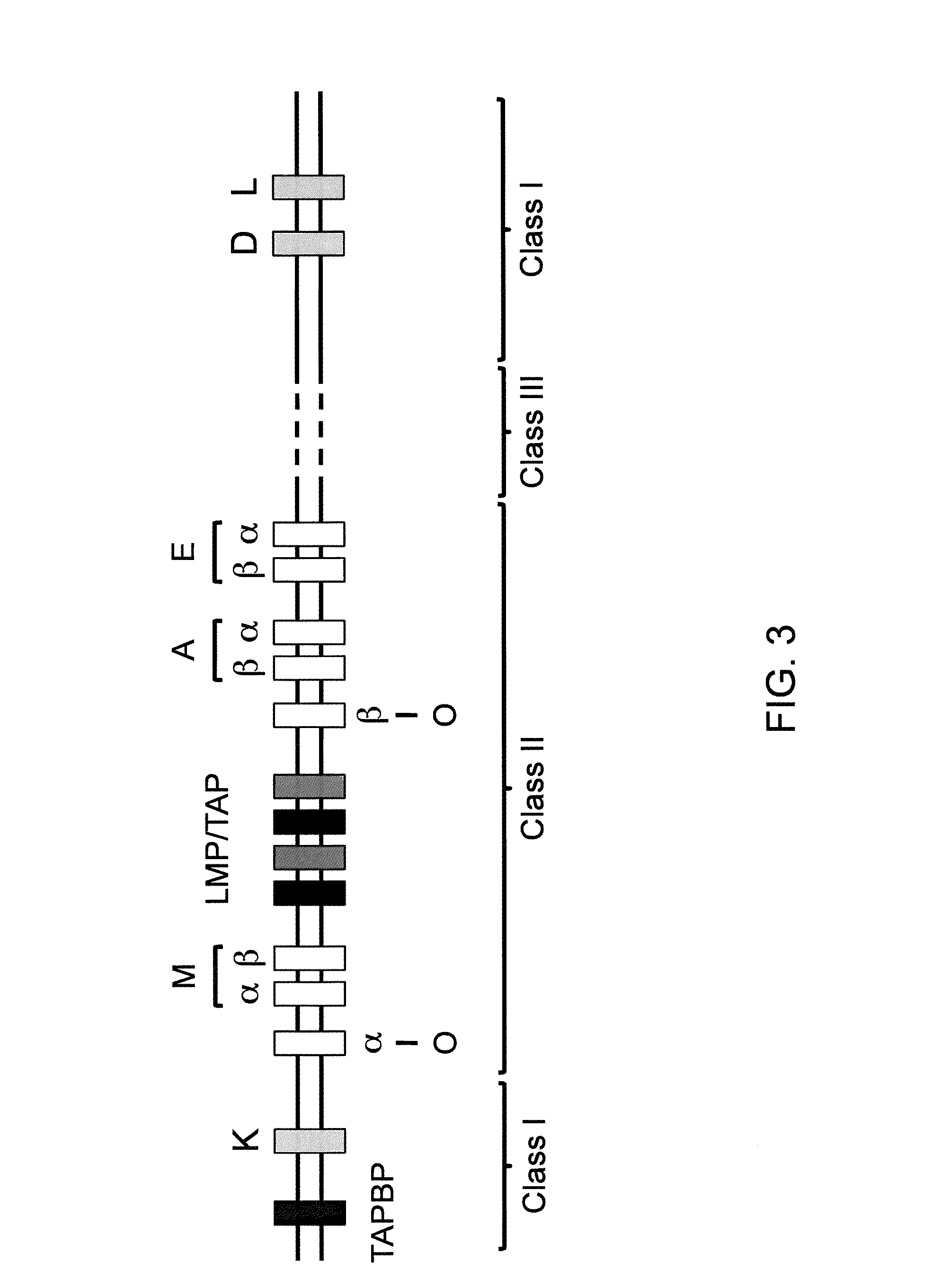
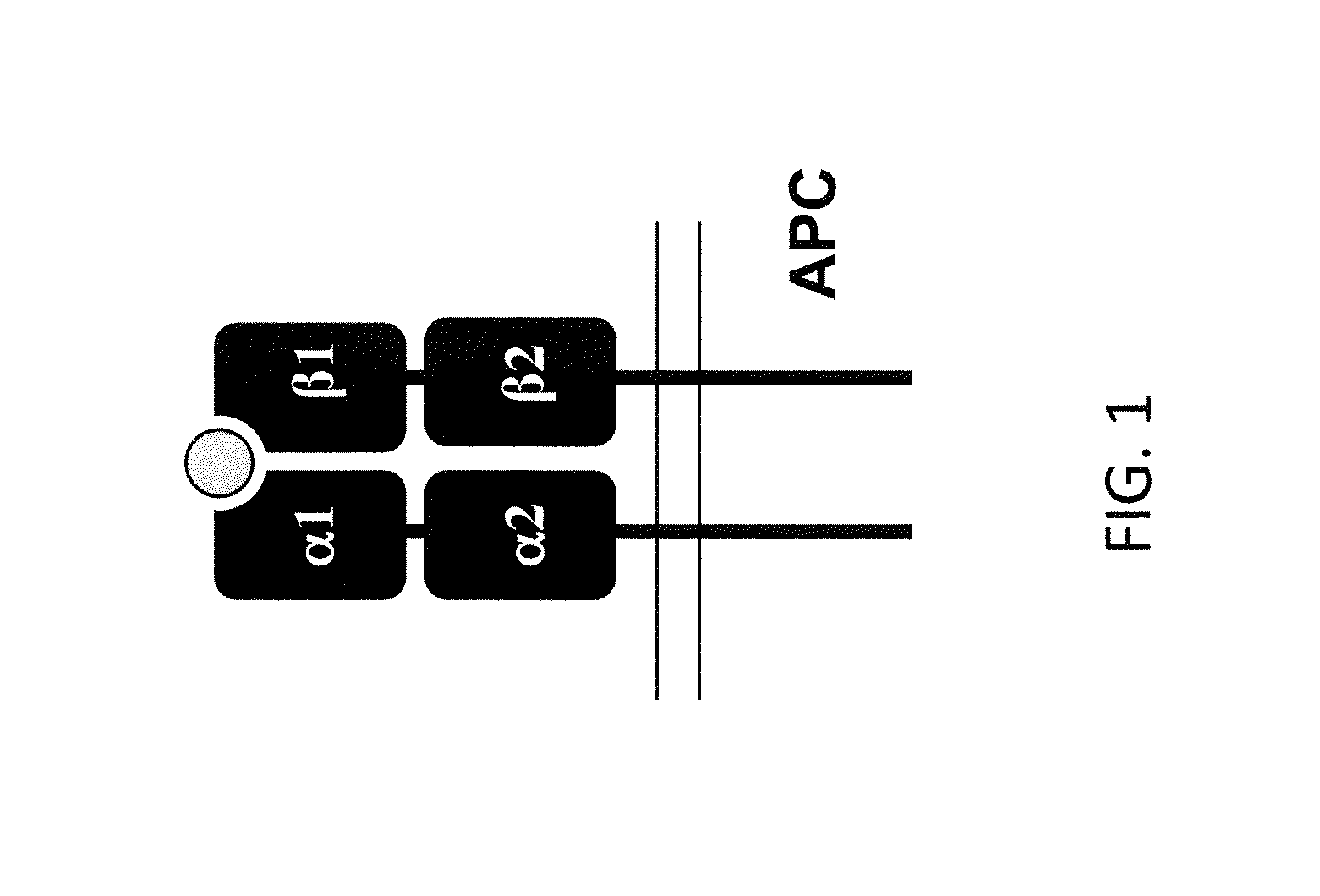
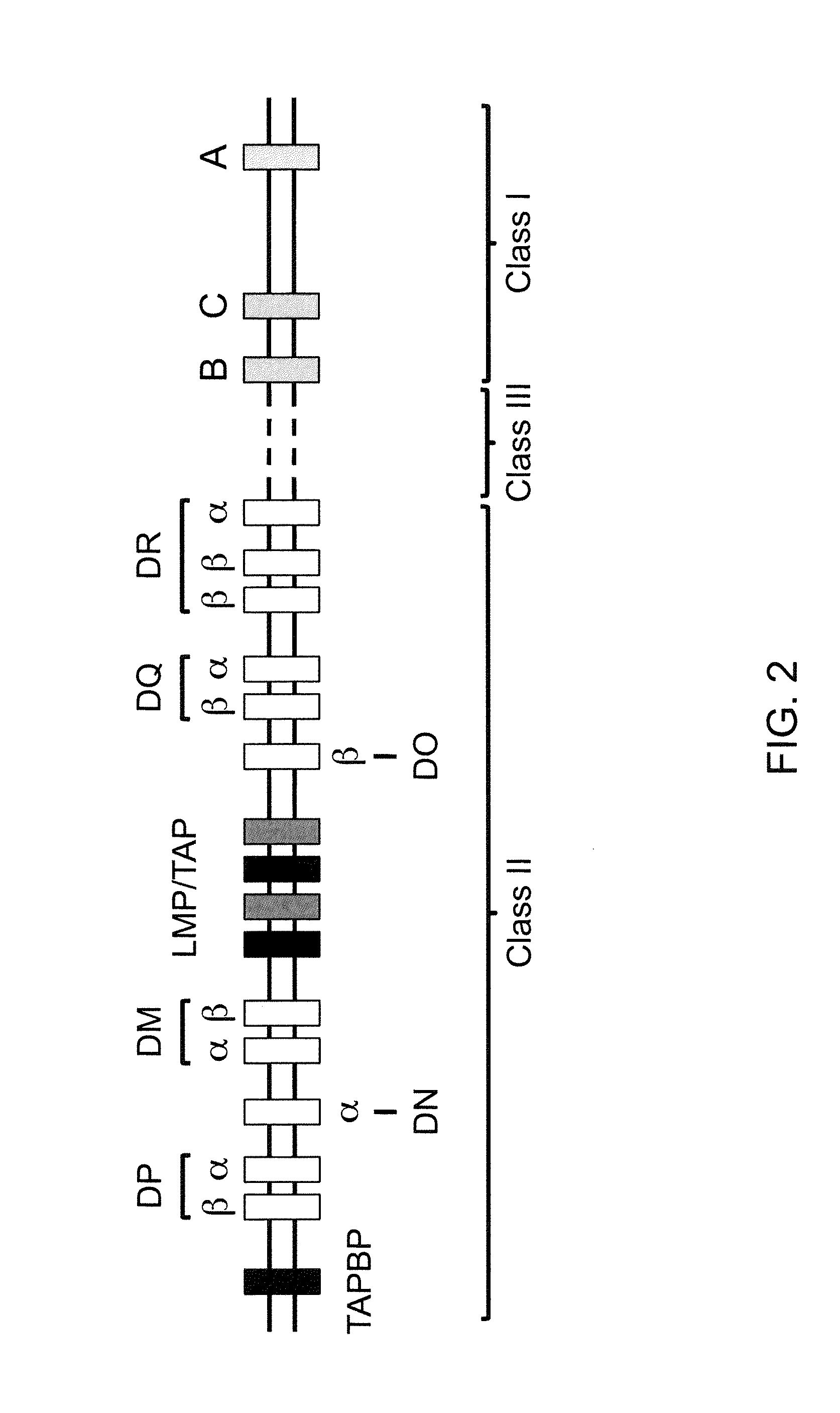
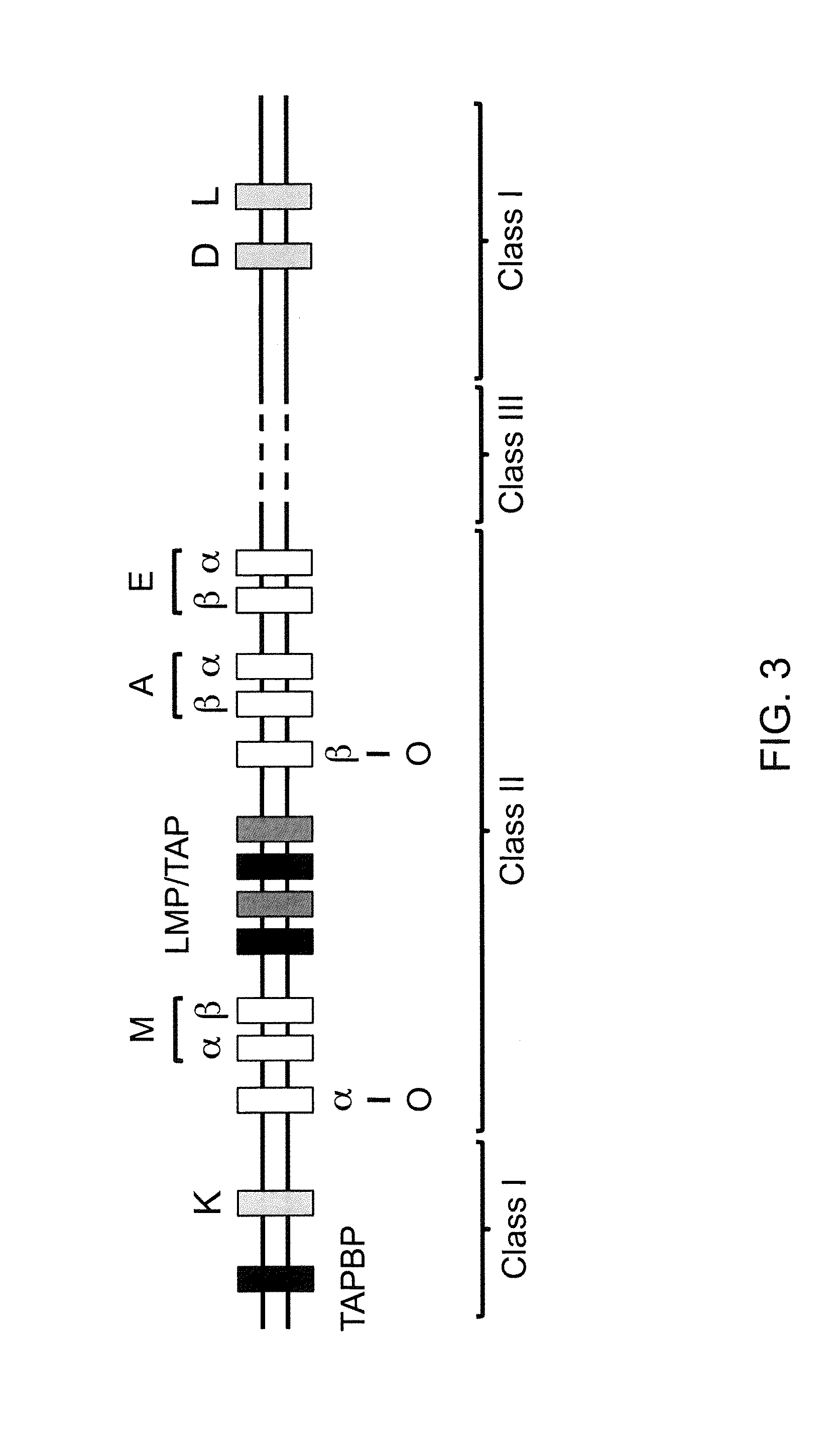
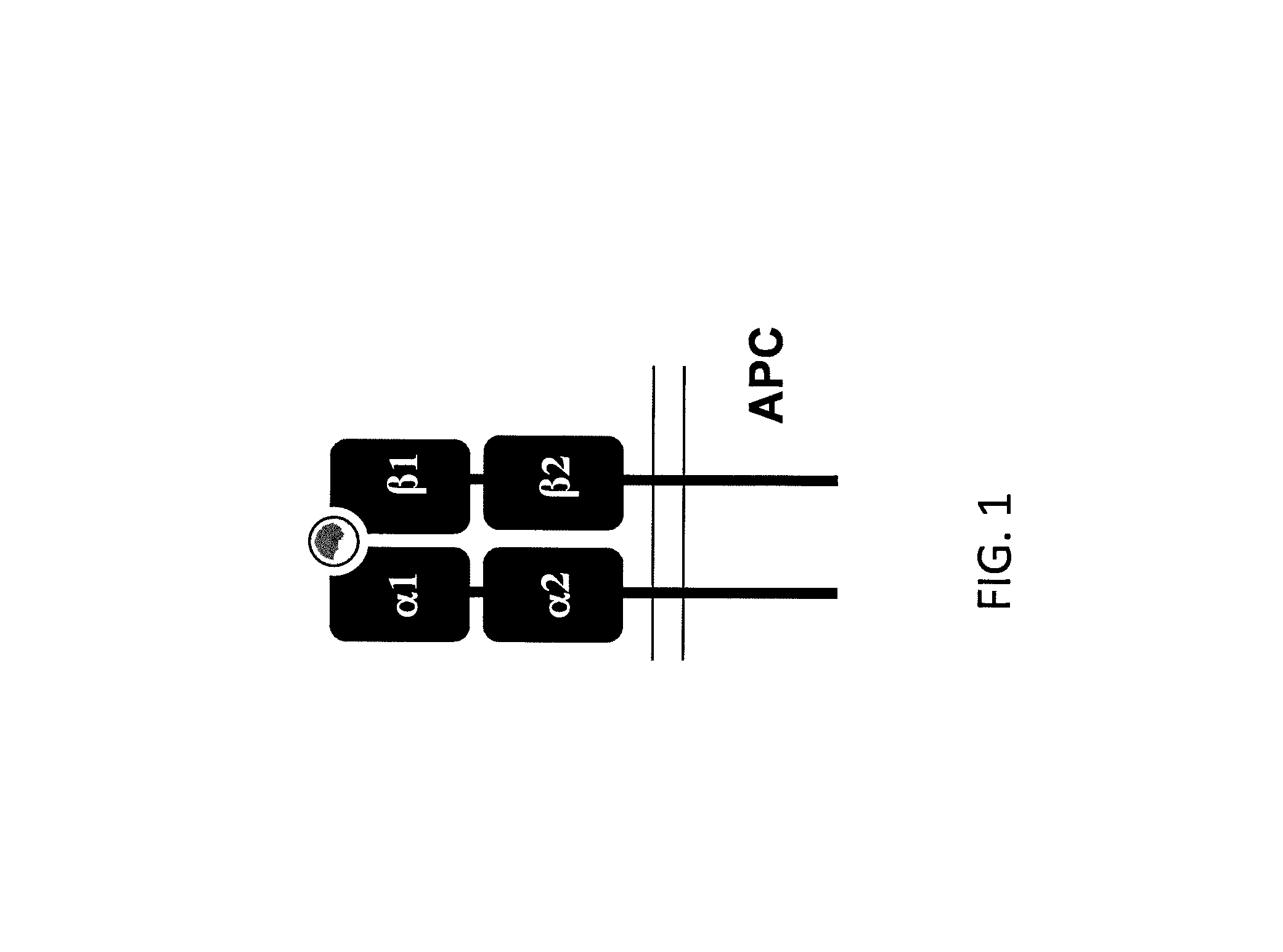
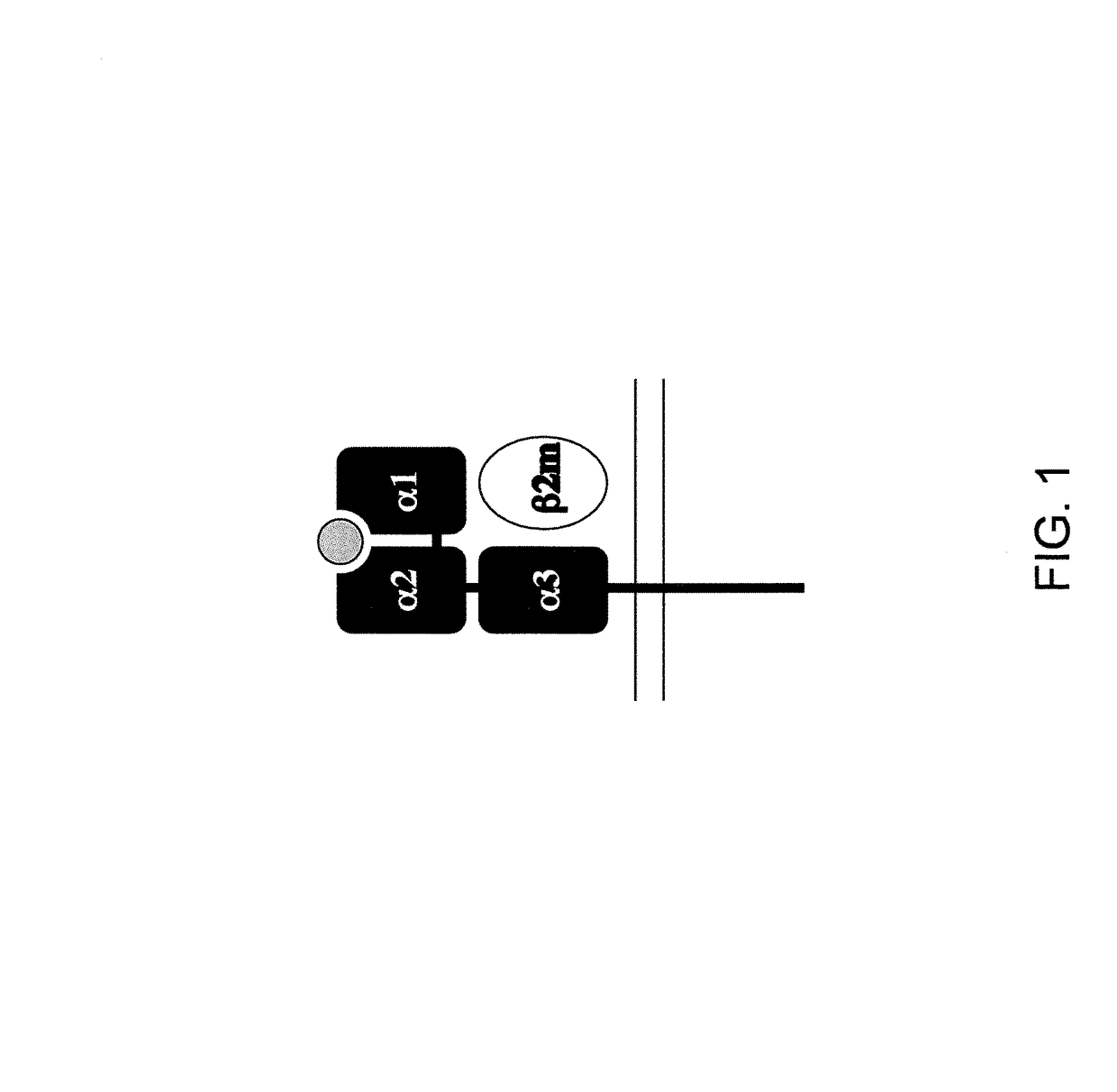
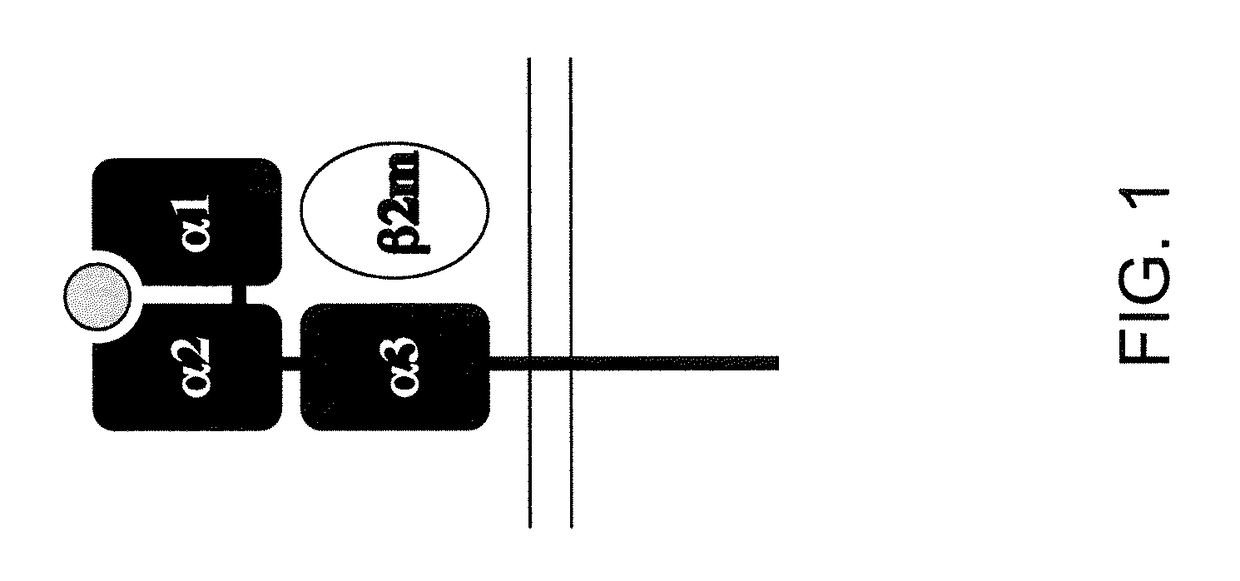
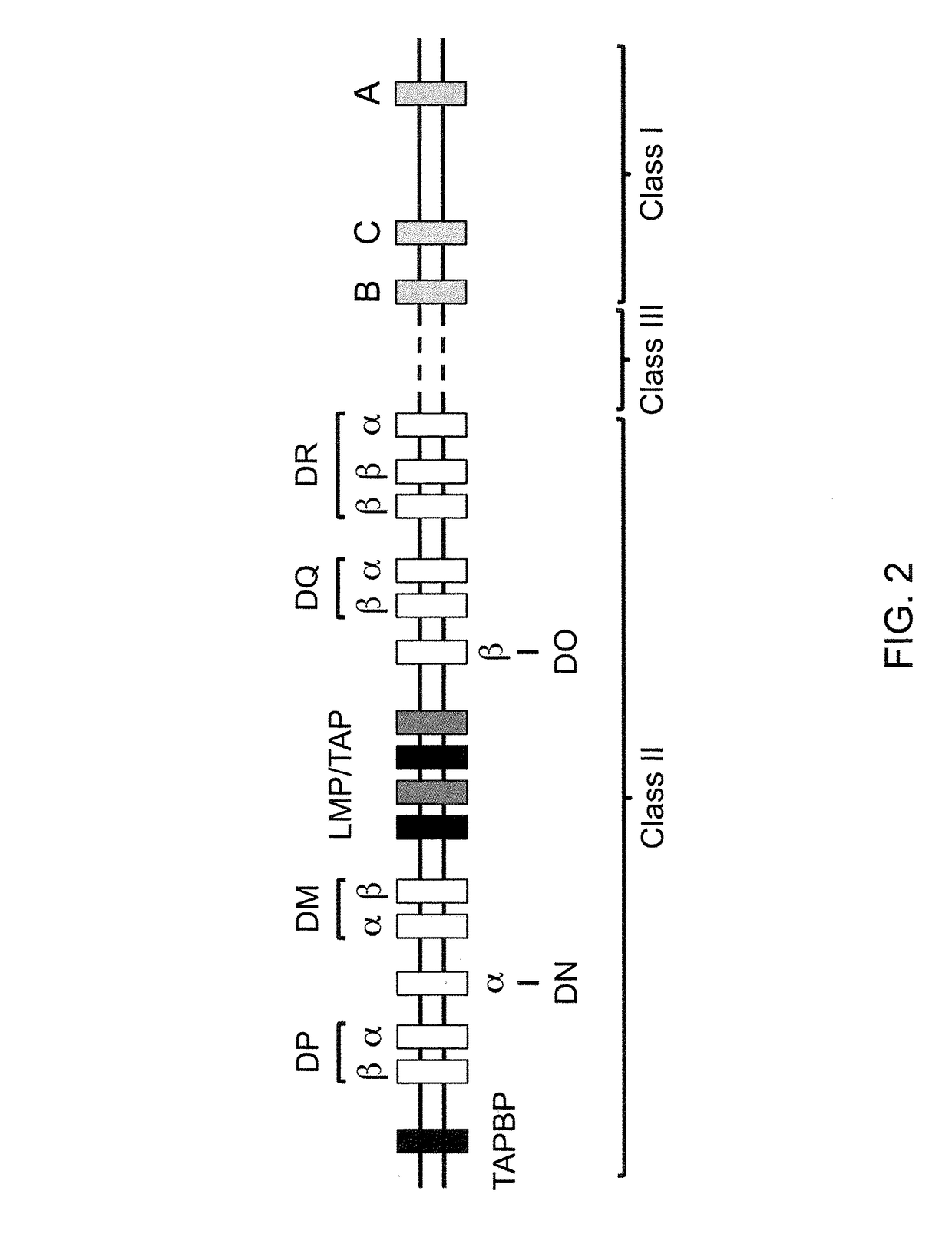
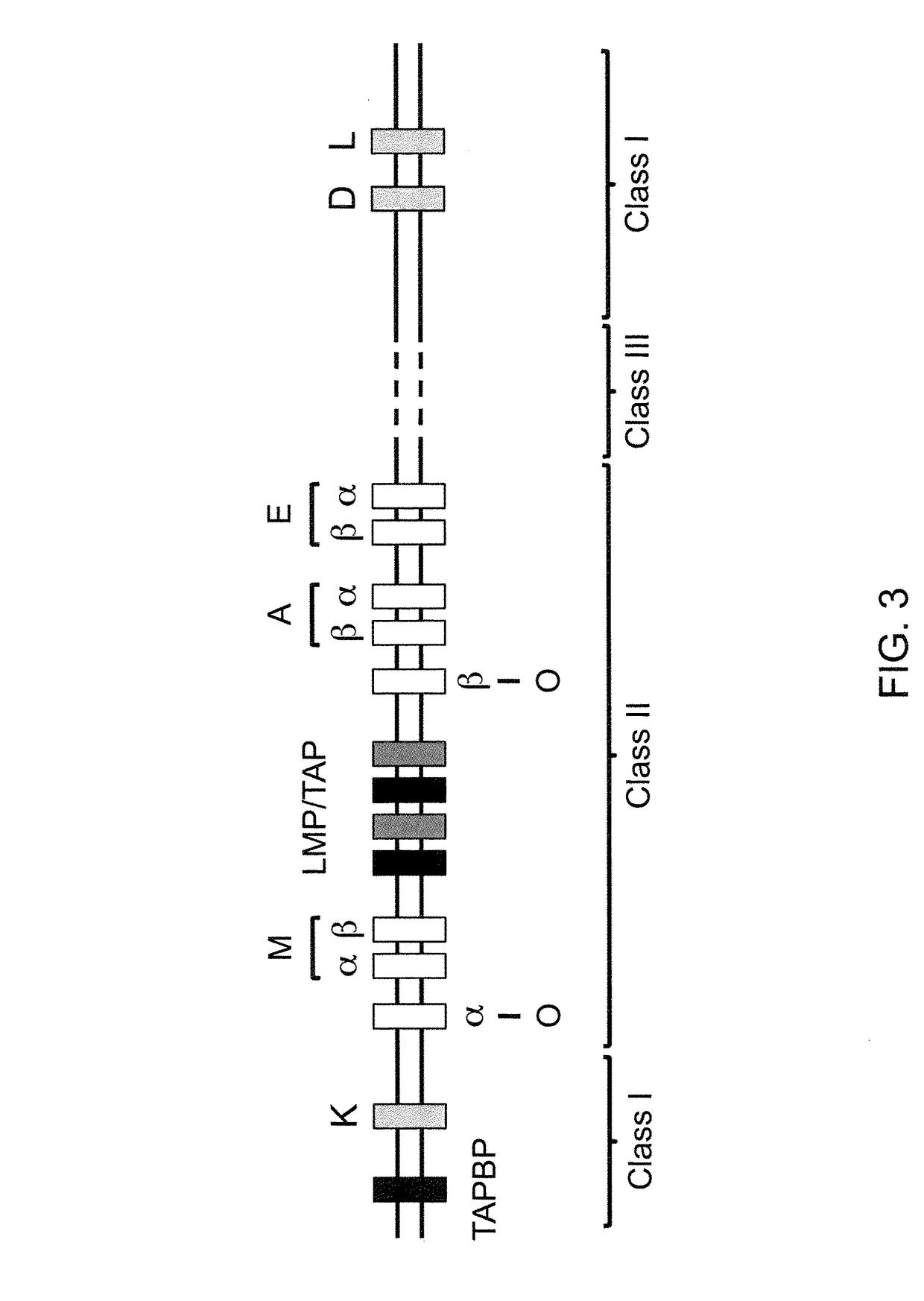
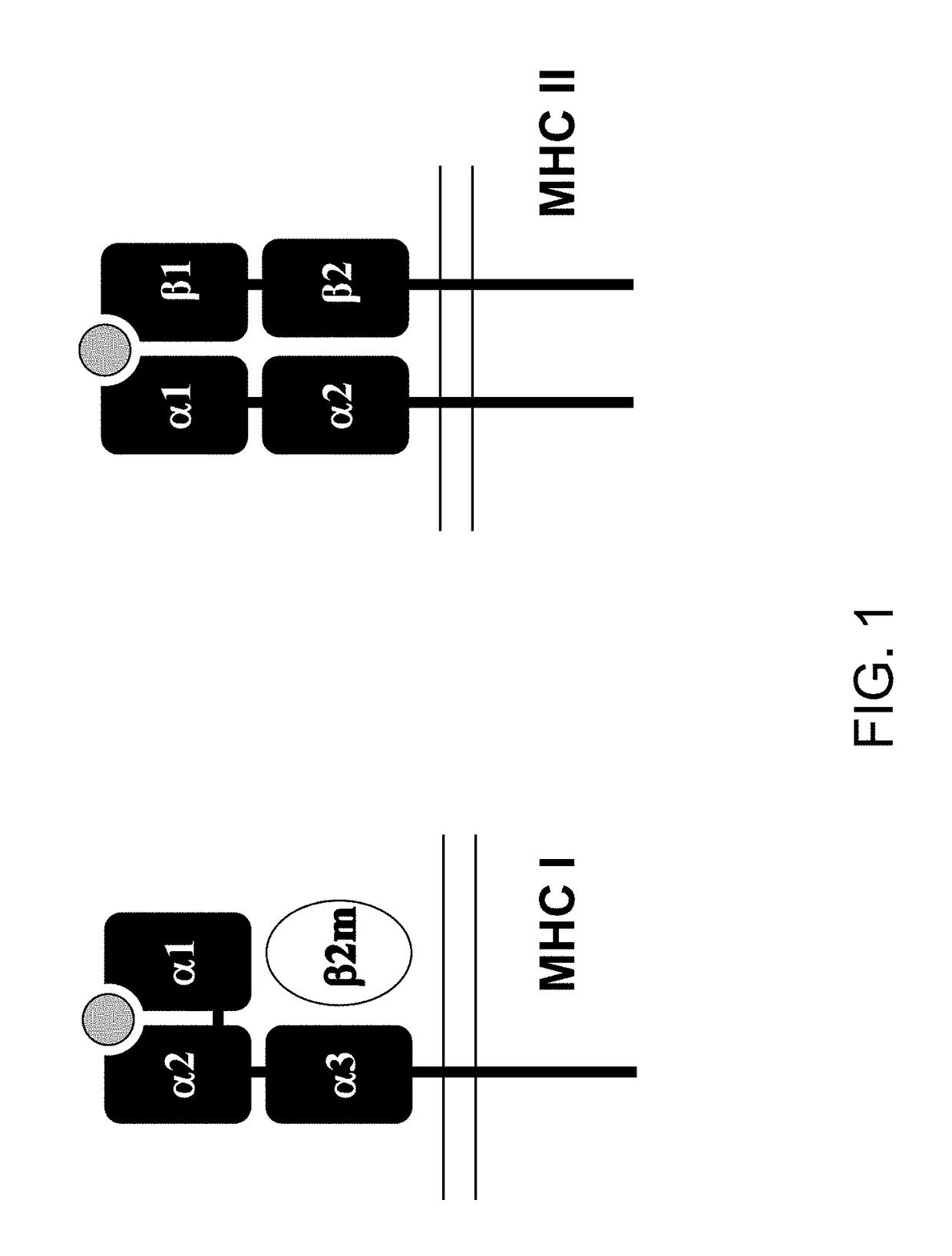
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a set of genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the acquired immune system to recognize foreign molecules in vertebrates, which in turn determines histocompatibility. The main function of MHC molecules is to bind to antigens derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), which are immune cells, with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines compatibility of donors for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to an autoimmune disease via crossreacting immunization. The human MHC is also called the HLA (human leukocyte antigen) complex (often just the HLA). The MHC in mice is called the Histocompatibility system 2 or just the H-2.
T-cell epitope identification
ActiveUS20180052176A1Efficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideMembrane bound
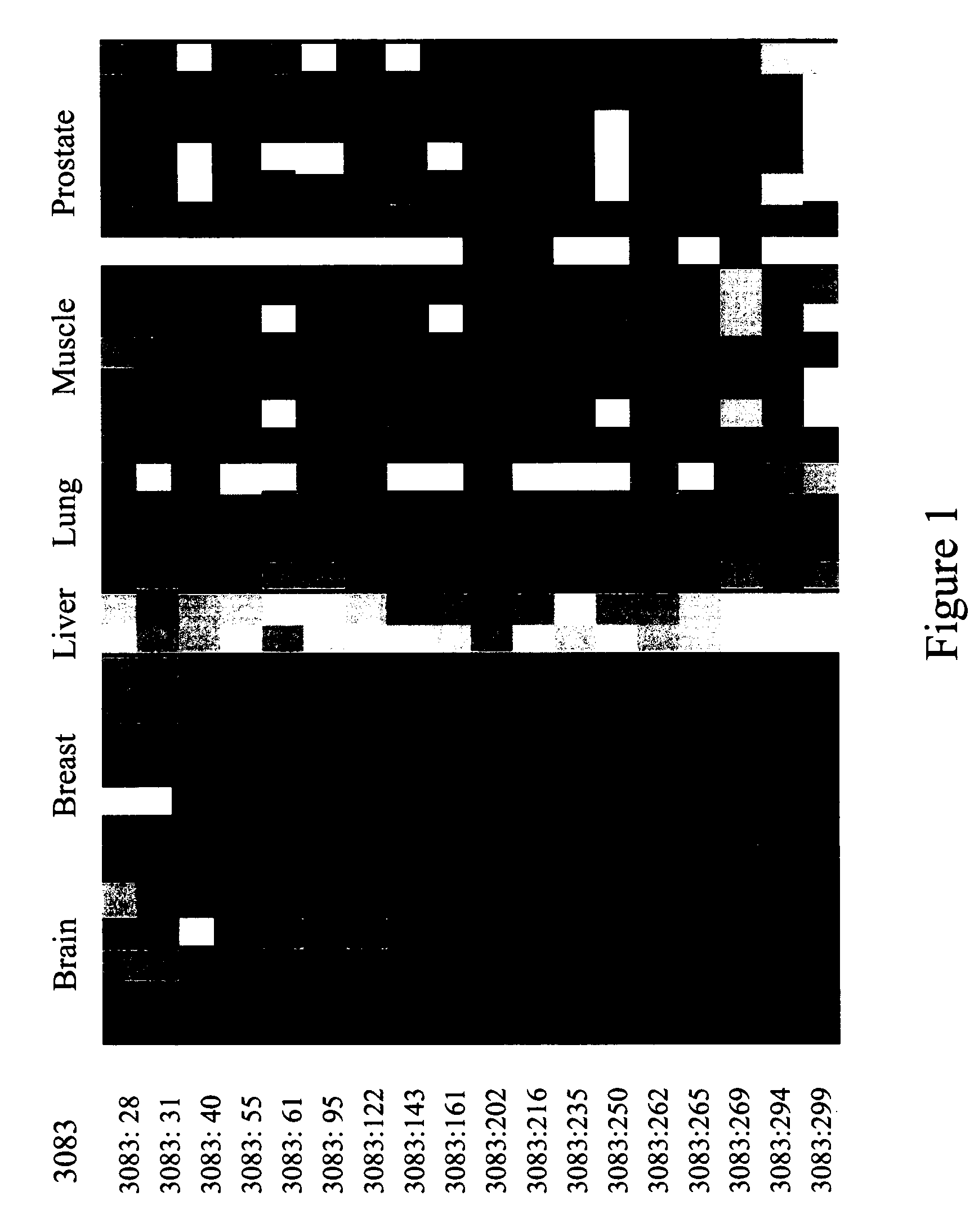
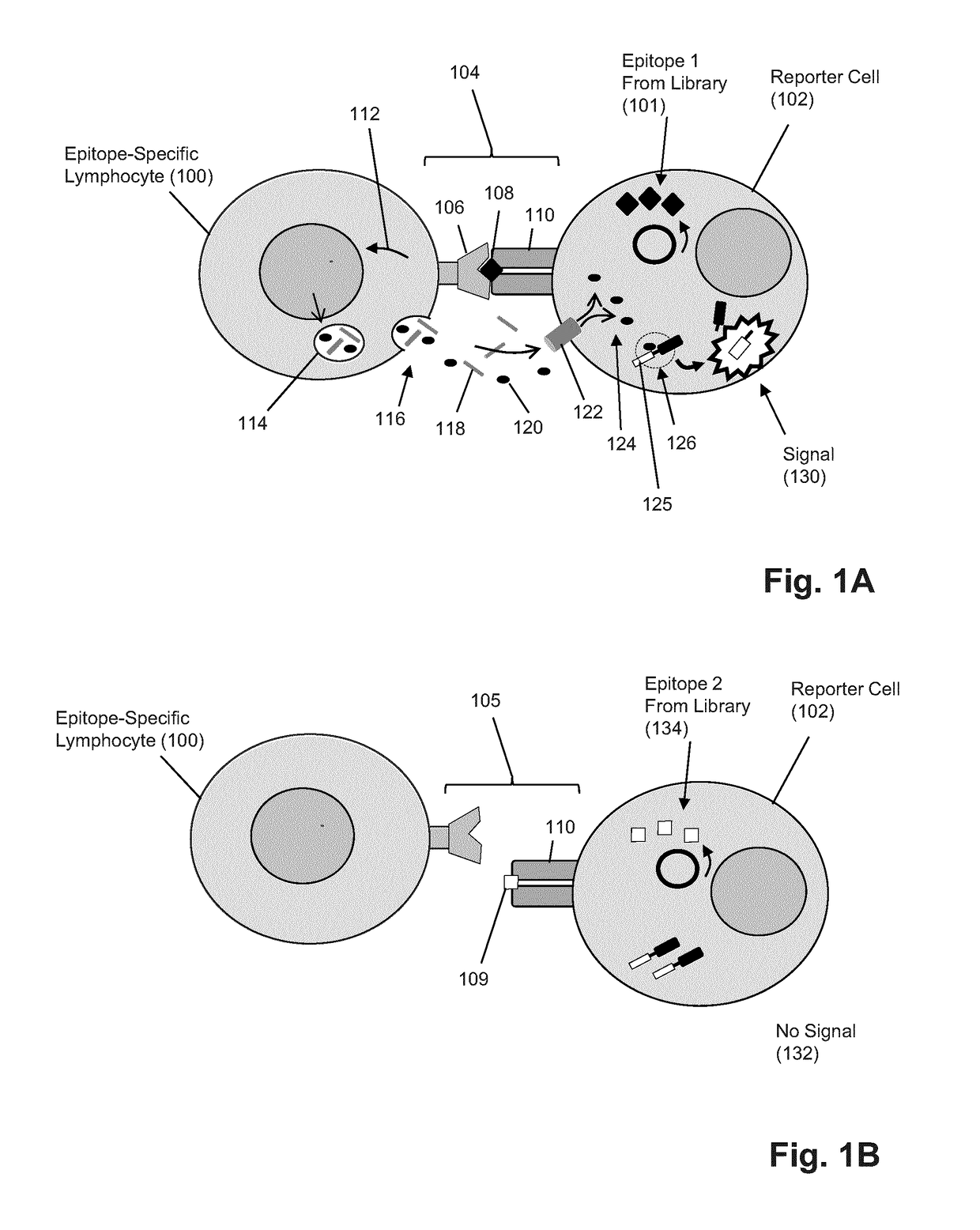
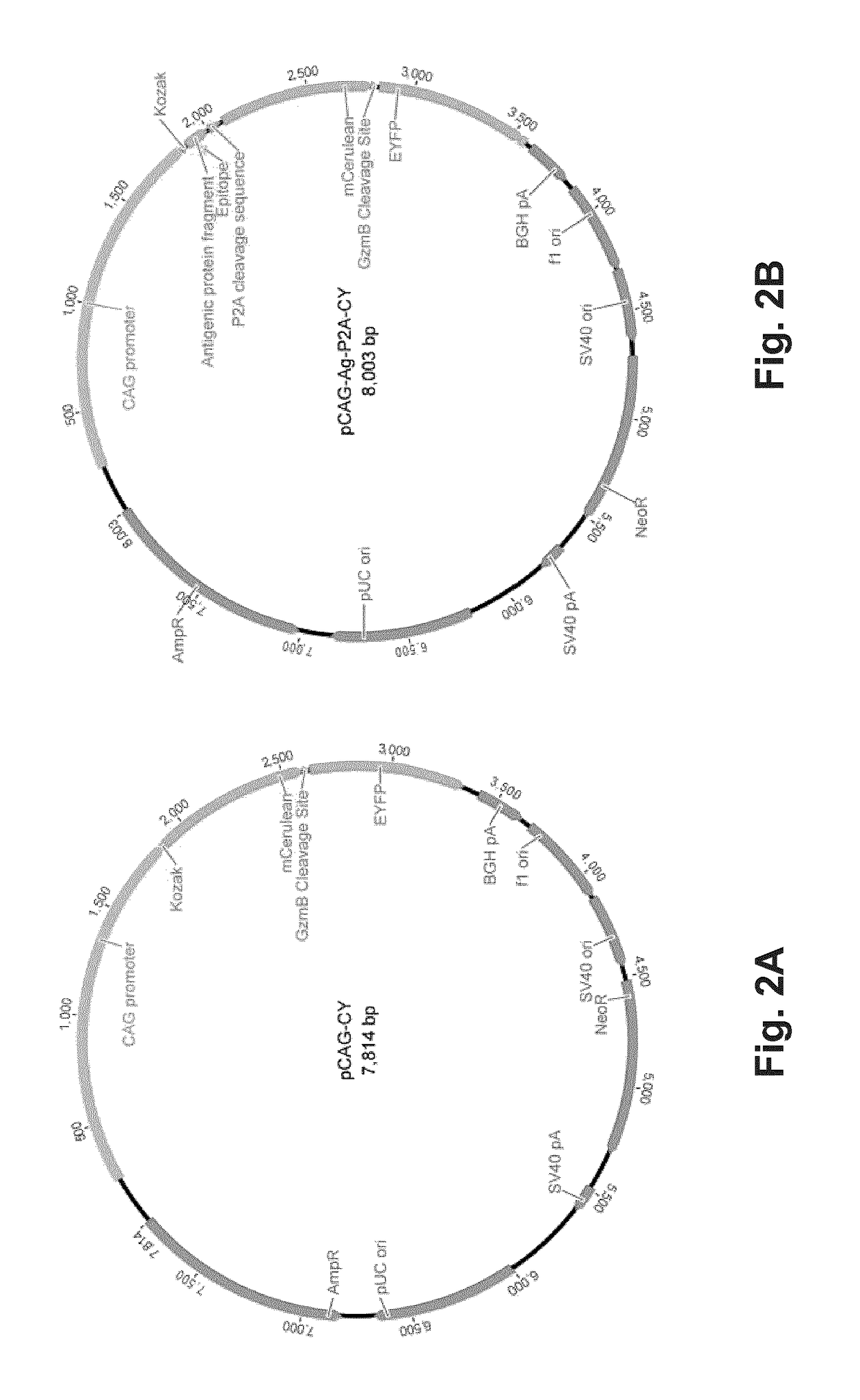
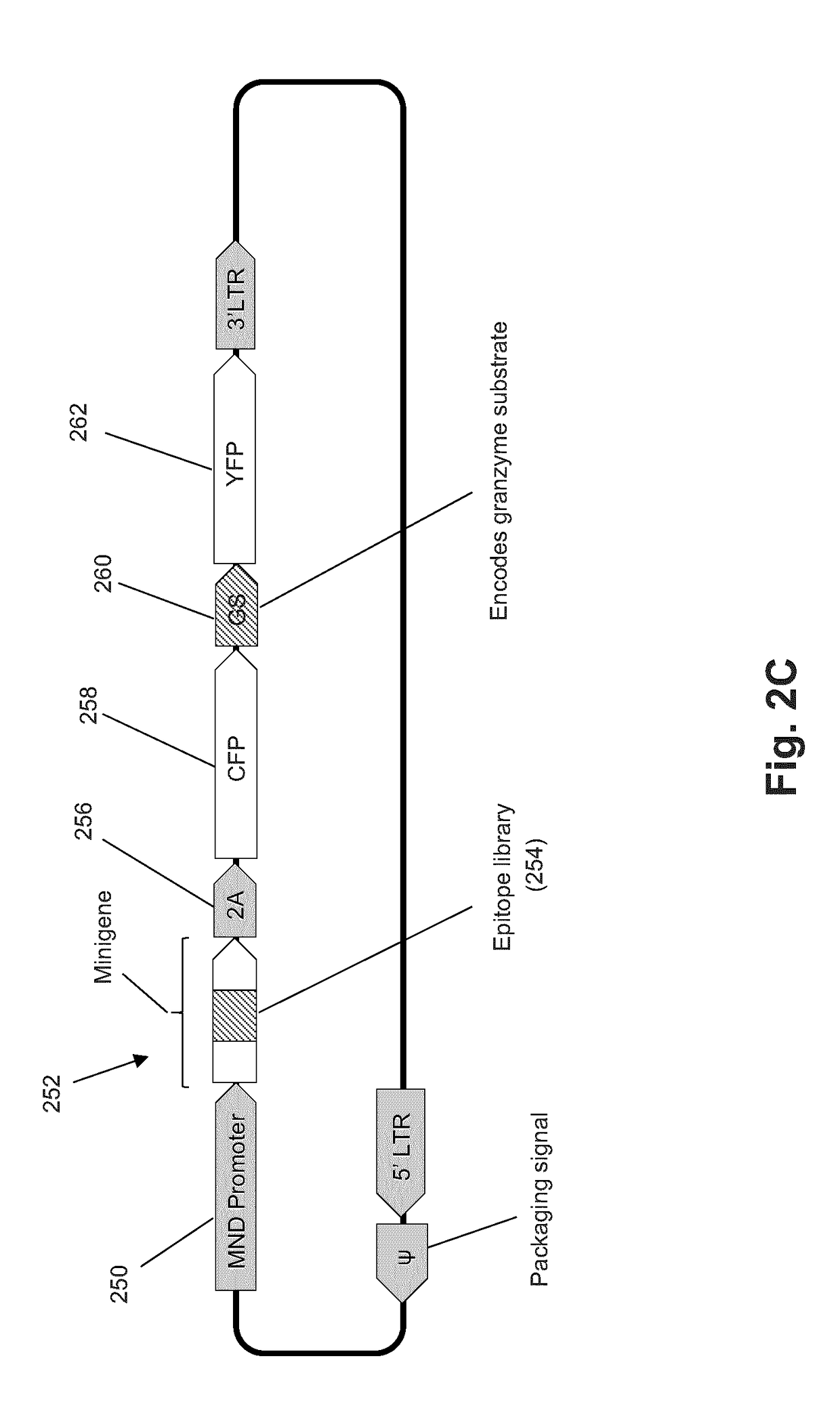
The present invention is a method for determining the identity of the epitopes recognized by T-cells. The method consists of expressing an encoded library of candidate epitope sequences in a recipient reporter cell capable of providing a detectable signal upon cytotoxic attack from a single cognate T-cell followed by contacting the reporter cells with T-cells of interest. The reporter cells with a single indicating cytotoxic attack from a T-cell are isolated and then analyzed by next-generation sequencing in order to identify the epitope sequences. Specifically disclosed is a method in which a library of candidate epitope-encoding nucleic acids are expressed in cells which feature a membrane-bound major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein, said library produced by transfection of plasmids featuring both a nucleotide encoding the candidate epitope and a nucleotide encoding a FRET-based fluorescent protein cleaved by granzyme.
Owner:PROVINCIAL HEALTH SERVICES AUTHORITY
Genetically Modified Major Histocompatibility Complex Mice
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods and compositions for differentiating tissues for cell types using epigenetic markers
InactiveUS20060183128A1Accurate and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomic DNAEpigenetic Profile
The present invention provides, inter alia, a method for generating a genome-wide epigenomic map, comprising a correlation between methylation variable CpG positions (MVP) and genomic DNA sample types. MVP are those CpG positions that show a variable quantitative level of methylation between sample types. Particular genomic regions of interest (ROI) provide preferred marker sequences that comprise multiple, and preferably proximate MVP, and that have novel utility for distinguishing sample types. The epigenic maps have broad utility, for example, in identifying sample types, or for distinguishing between and among sample types. In a preferred embodiment the epigenomic map is based on methylation variable regions (MVP) within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), and has utility, for example, in identifying the cell or tissue source of a genomic DNA sample, or for distinguishing one or more particular cell or tissue types among other cell or tissue types. Analysis of epigenetic characteristics of one, or of a set of nucleic acid sequences, in the context of an inventive epigenomic map, allows for the determination of an origin of the nucleic acids.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method for generating t-cells compatible for allogenic transplantation
InactiveUS20170016025A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCIITAAuto immune disease
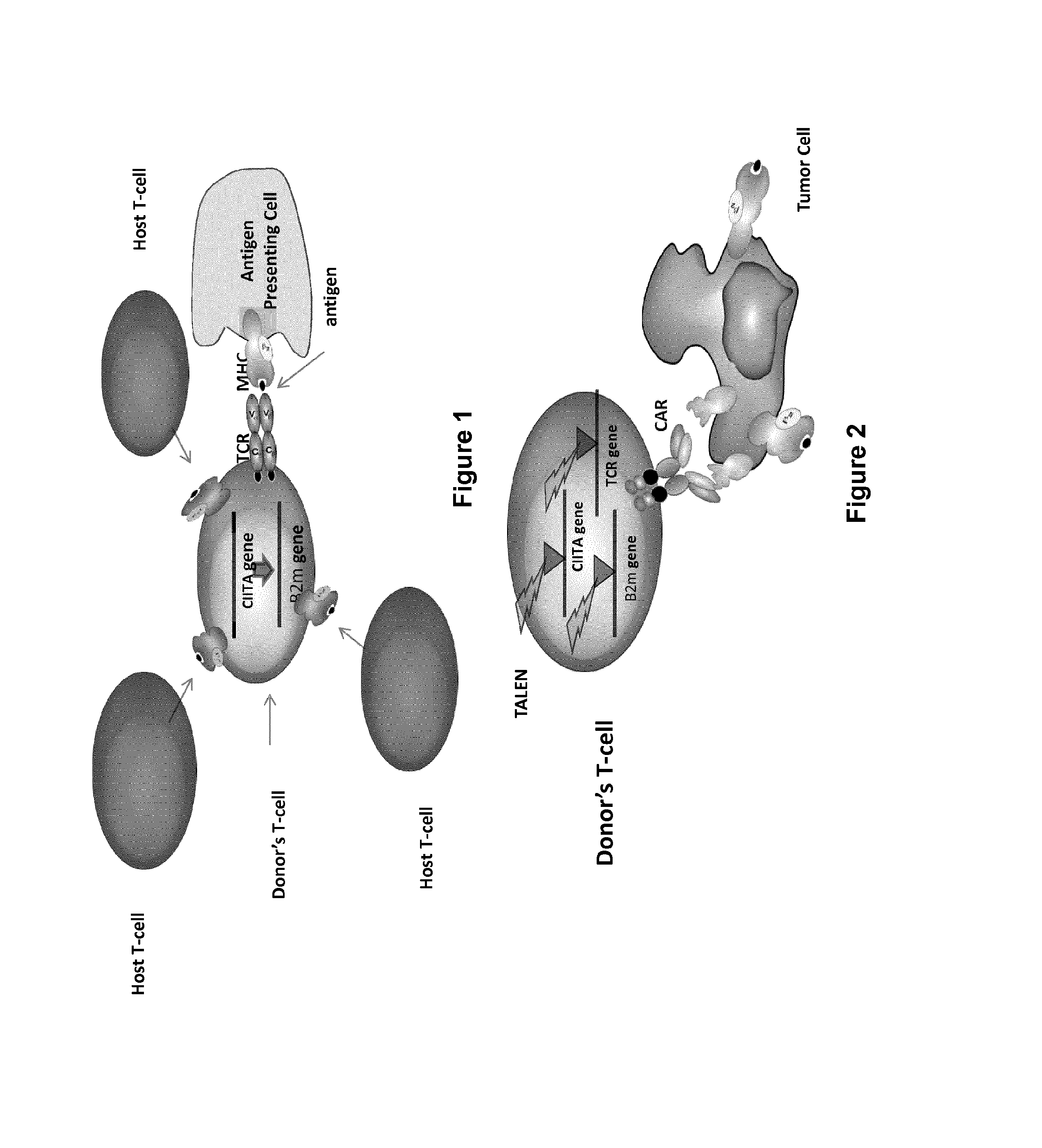
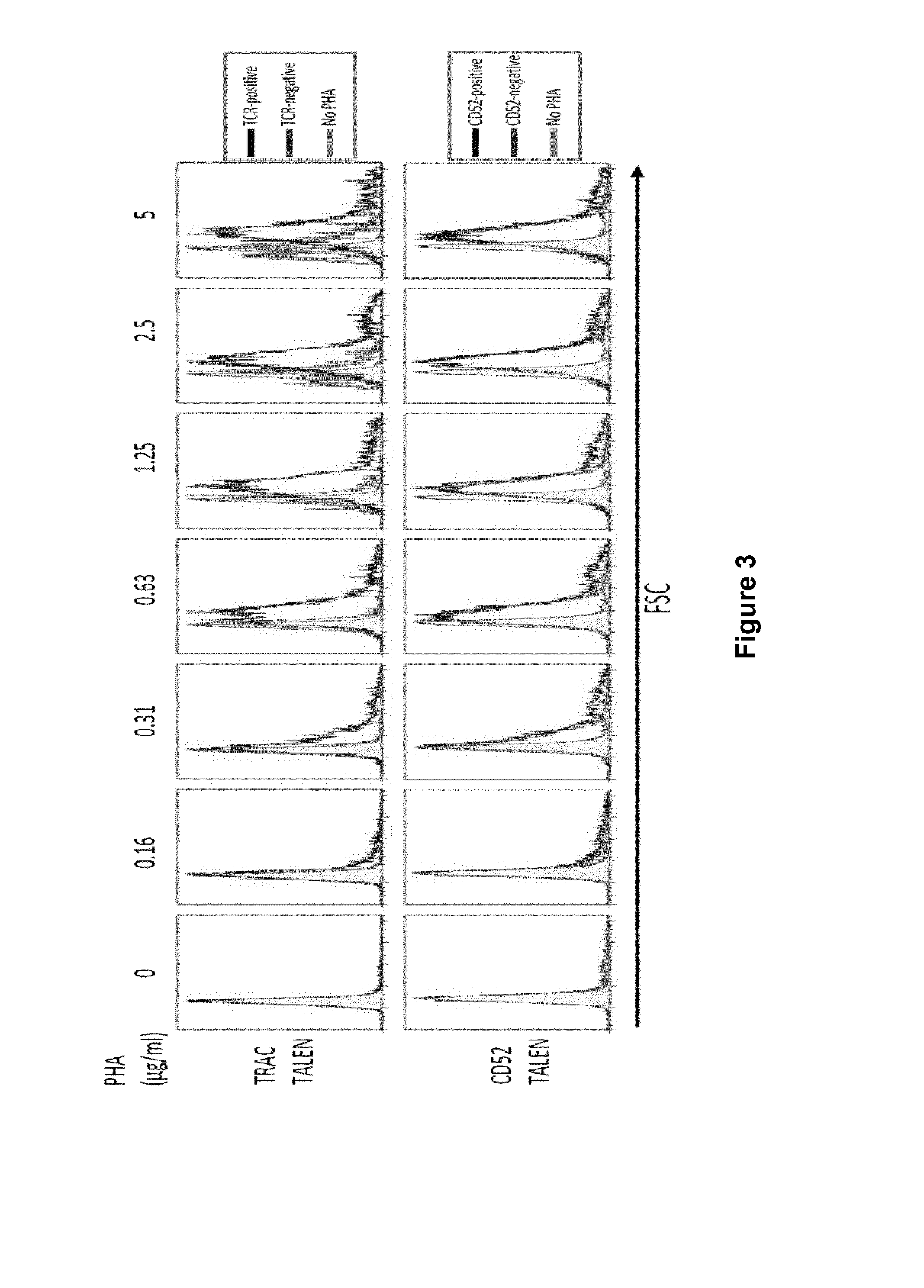
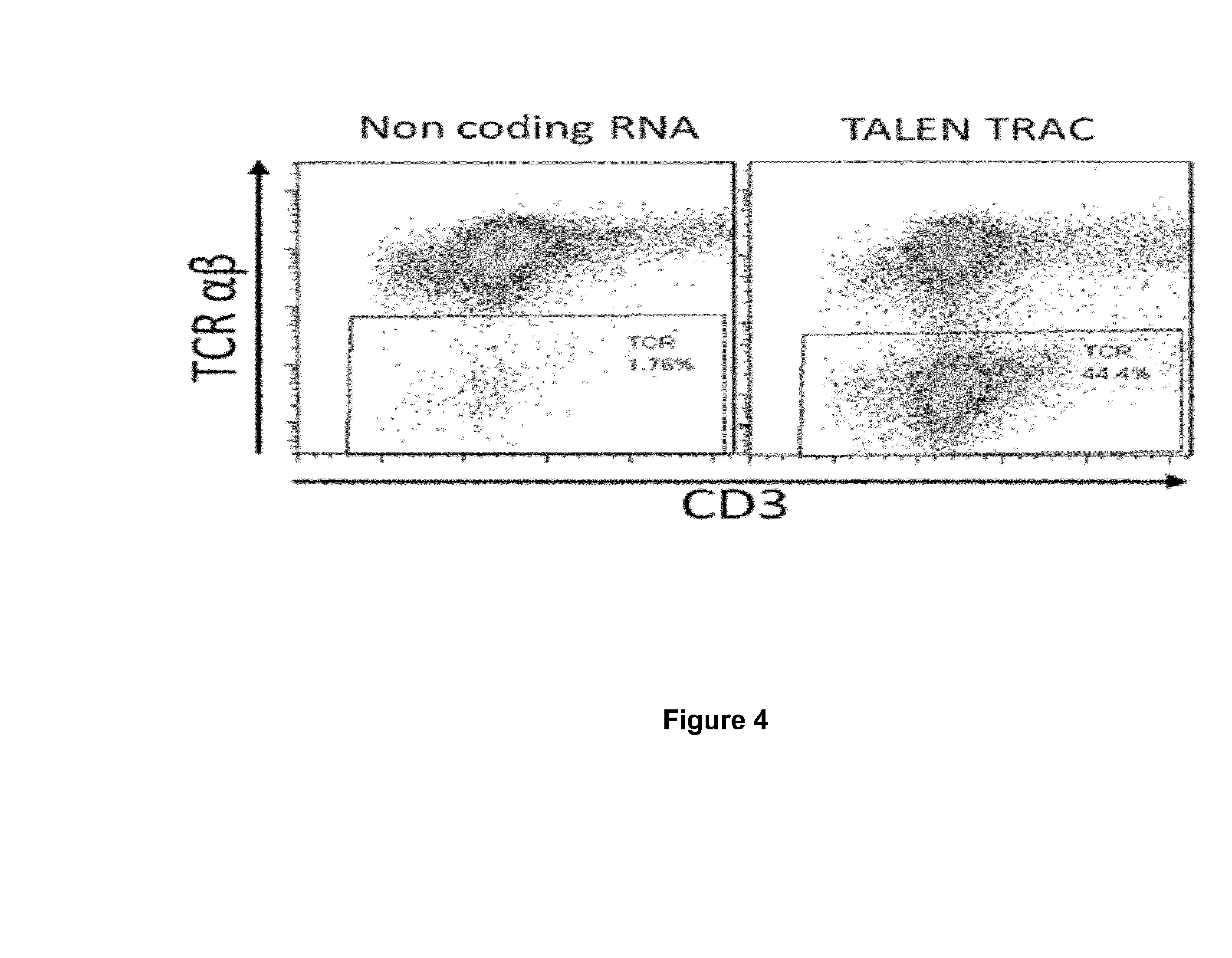
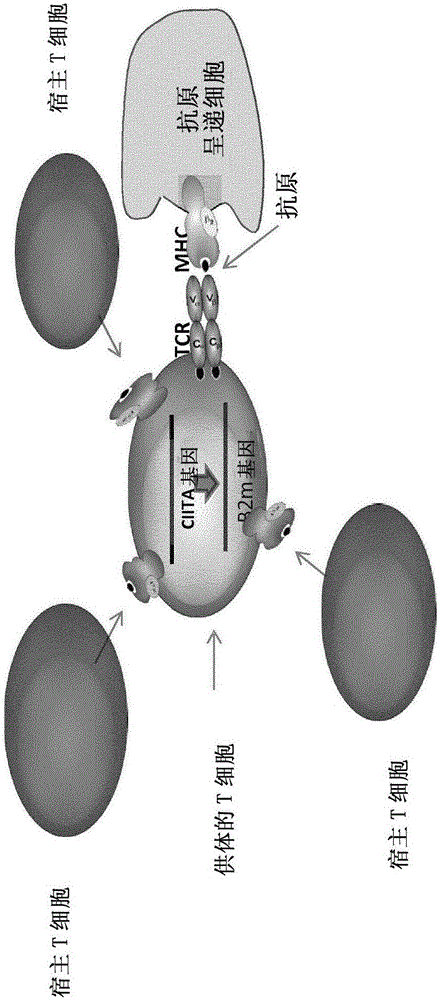
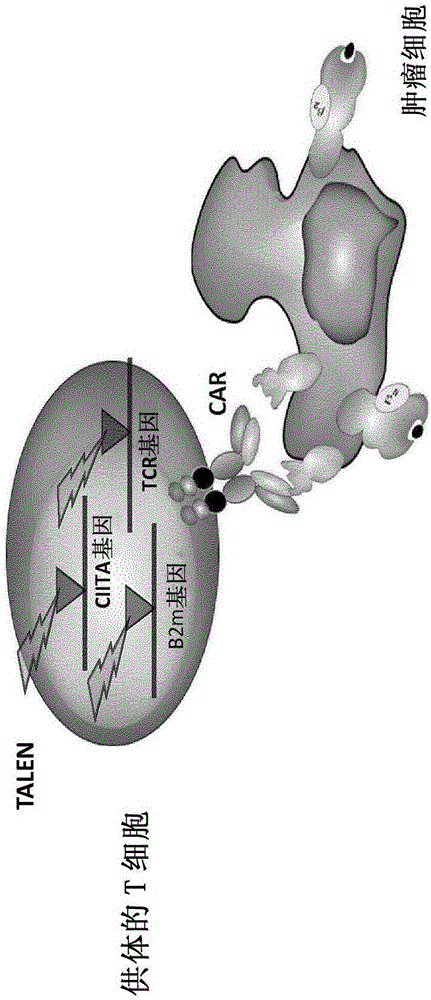
The present invention pertains to engineered T-cells, method for their preparation and their use as medicament, particularly for immunotherapy. The engineered T-cells of the invention are characterized in that the expression of beta 2-microglobulin (B2M) and / or class II major histocompatibility complex transactivator (CIITA) is inhibited, e.g., by using rare-cutting endonucleases able to selectively inactivating by DNA cleavage the gene encoding B2M and / or CIITA, or by using nucleic acid molecules which inhibit the expression of B2M and / or CIITA. In order to further render the T-cell non-alloreactive, at least one gene encoding a component of the T-cell receptor is inactivated, e.g., by using a rare-cutting endonucleases able to selectively inactivating by DNA cleavage the gene encoding said TCR component. In addition, expression of immunosuppressive polypeptide can be performed on those modified T-cells in order to prolong the survival of these modified T cells in host organism. Such modified T-cell is particularly suitable for allogeneic transplantations, especially because it reduces both the risk of rejection by the host's immune system and the risk of developing graft versus host disease. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer, infections and auto-immune diseases.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Methods for using dendritic cells to activate gamma/delta-T cell receptor-positive T cells
InactiveUS6821778B1Control progressIncrease the number ofArtificial cell constructsBlood/immune system cellsAdoptive cellular immunotherapyDendritic cell
This invention relates to methods of using human dendritic cells to present antigens for the induction of antigen-specific T cell-mediated immune responses. In particular, it relates to the isolation of dendritic cells from human blood, exposing the cells to antigens, co-culturing the antigen-pulsed dendritic cells with gammadelta-T cell receptor-positive-T cells (gammadelta-TCR<+> T cells) obtained from unprimed or weakly primed individuals for the stimulation of antigen-specific T cell proliferative and cytotoxic activities. The dendritic cell antigen presentation system described herein has a wide range of applications, including but not limited to, activation and expansion of large numbers of antigen-specific major histocompatibility complex-unrestricted T cells for use in adoptive cellular immunotherapy against infectious diseases and cancer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for generating T-cells compatible for allogenic transplantation
ActiveCN106103475APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCIITAAutoimmune disease
The present invention pertains to engineered T-cells, method for their preparation and their use as medicament, particularly for immunotherapy. The engineered T-cells of the invention are characterized in that the expression of beta 2-microglobulin (B2M) and / or class I I major histocompatibility complex transactivator (CIITA) is inhibited, e.g., by using rare-cutting endonucleases able to selectively inactivating by DNA cleavage the gene encoding B2M and / or CIITA, or by using nucleic acid molecules which inhibit the expression of B2M and / or CIITA. In order to further render the T-cell non-alloreactive, at least one gene encoding a component of the T-cell receptor is inactivated, e.g., by using a rare-cutting endonucleases able to selectively inactivating by DNA cleavage the gene encoding said TCR component. In addition, expression of immunosuppressive polypeptide can be performed on those modified T-cells in order to prolong the survival of these modified T cells in host organism. Such modified T-cell is particularly suitable for allogeneic transplantations, especially because it reduces both the risk of rejection by the host's immune system and the risk of developing graft versus host disease. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer, infections and auto-immune diseases.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Antibody having a T-cell receptor-like specificity, yet higher affinity, and the use of same in the detection and treatment of cancer, viral infection and autoimmune disease
InactiveUS6992176B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseAutoimmune disease
An isolated molecule which comprises an antibody specifically bindable with a binding affinity below 20 nanomolar, preferably below 10 nanomolar, to a human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I being complexed with a HLA-restricted antigen and optionally further comprises an identifiable or therapeutic moiety conjugated to the antibody.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Genetically Modified Major Histocompatibility Complex Animals
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express a humanized MHC II protein (humanized MHC II α and β polypeptides), as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same. Methods of using the genetically modified animals to study various aspects of human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express a humanized MHC II protein (humanized MHC II α and β polypeptides), as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the humanized MHC II protein. Also provided are constructs for and methods of making the genetically modified non-human animals. Methods of using the genetically modified non-human animals to study various aspects of the human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
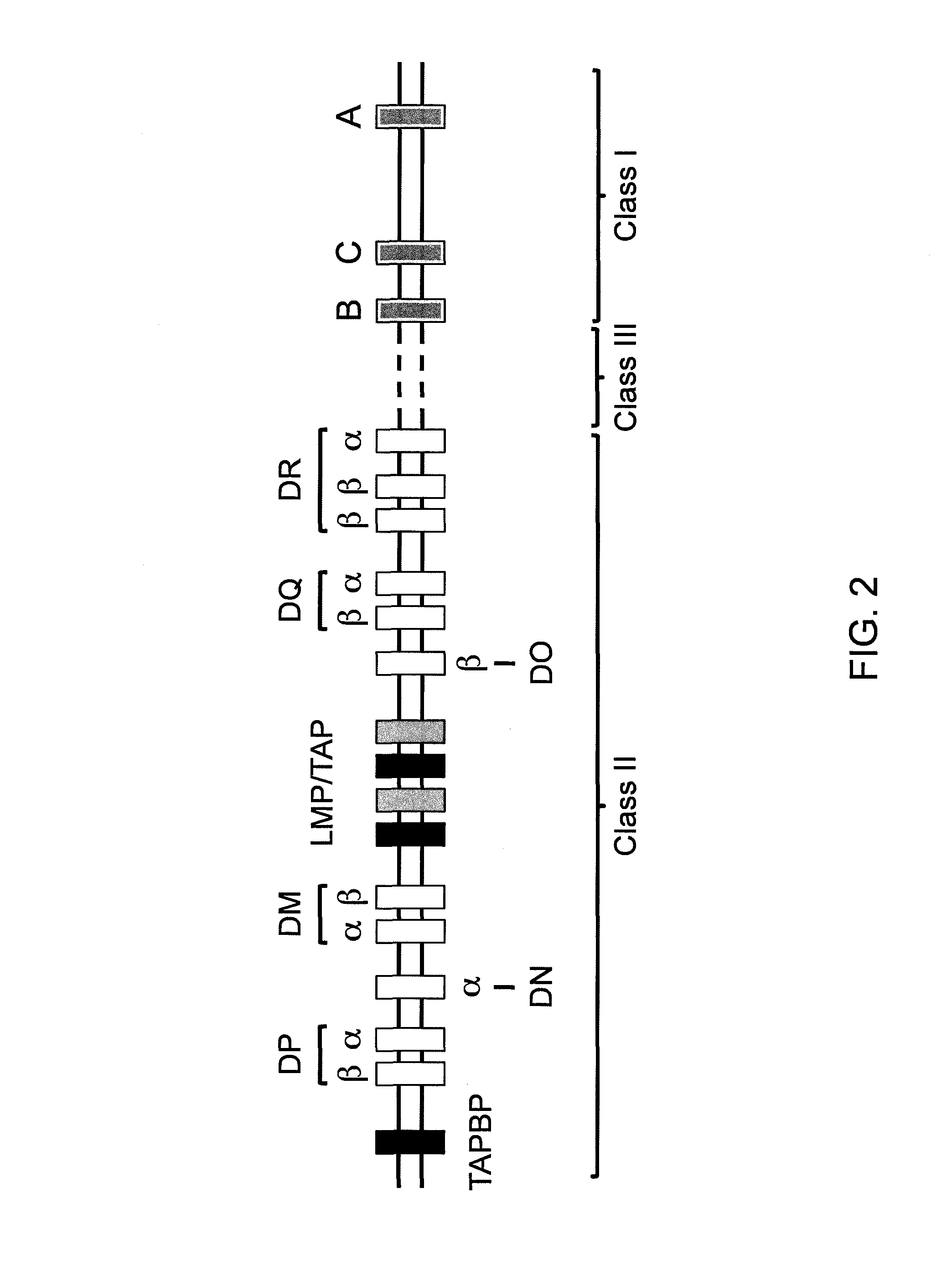
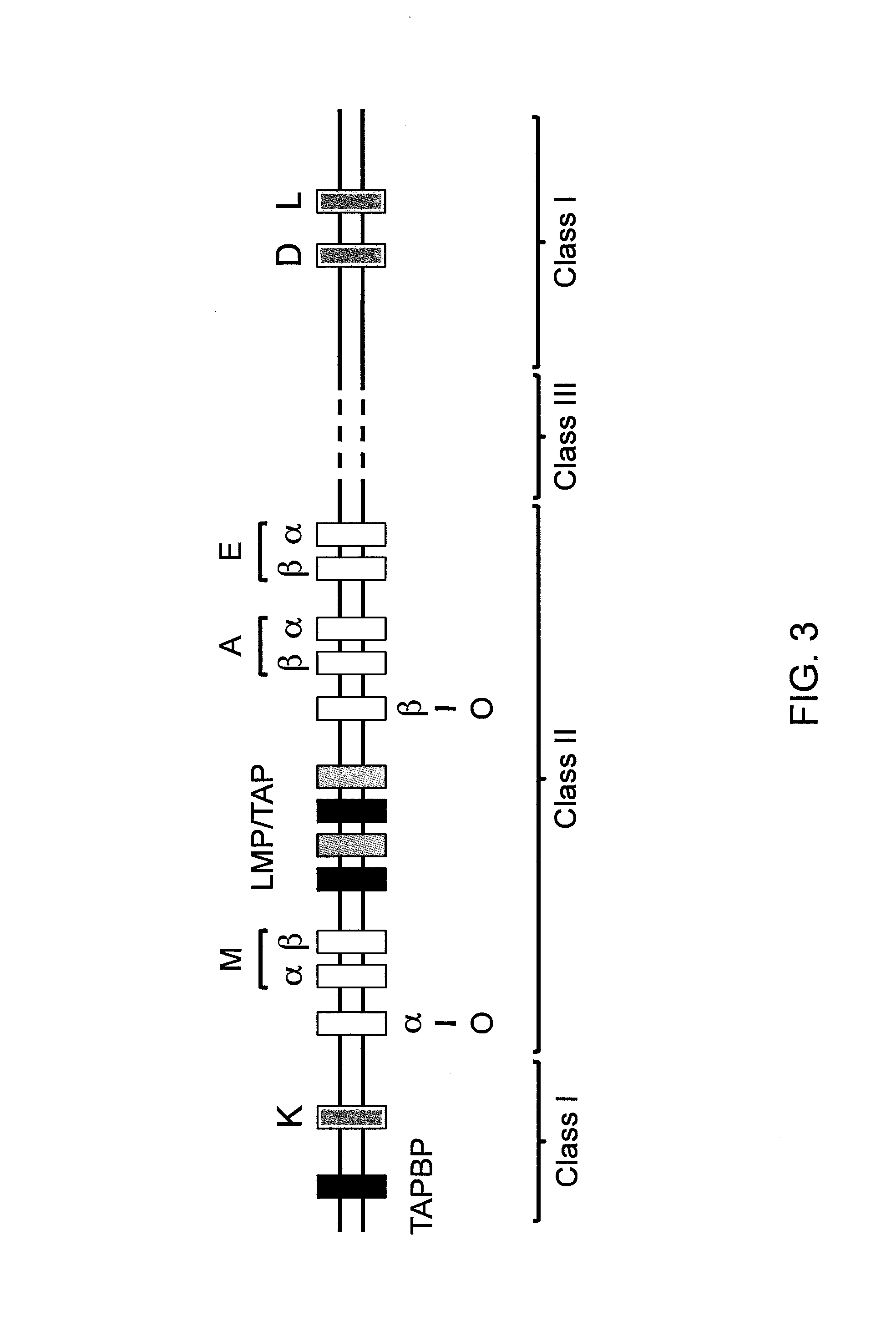
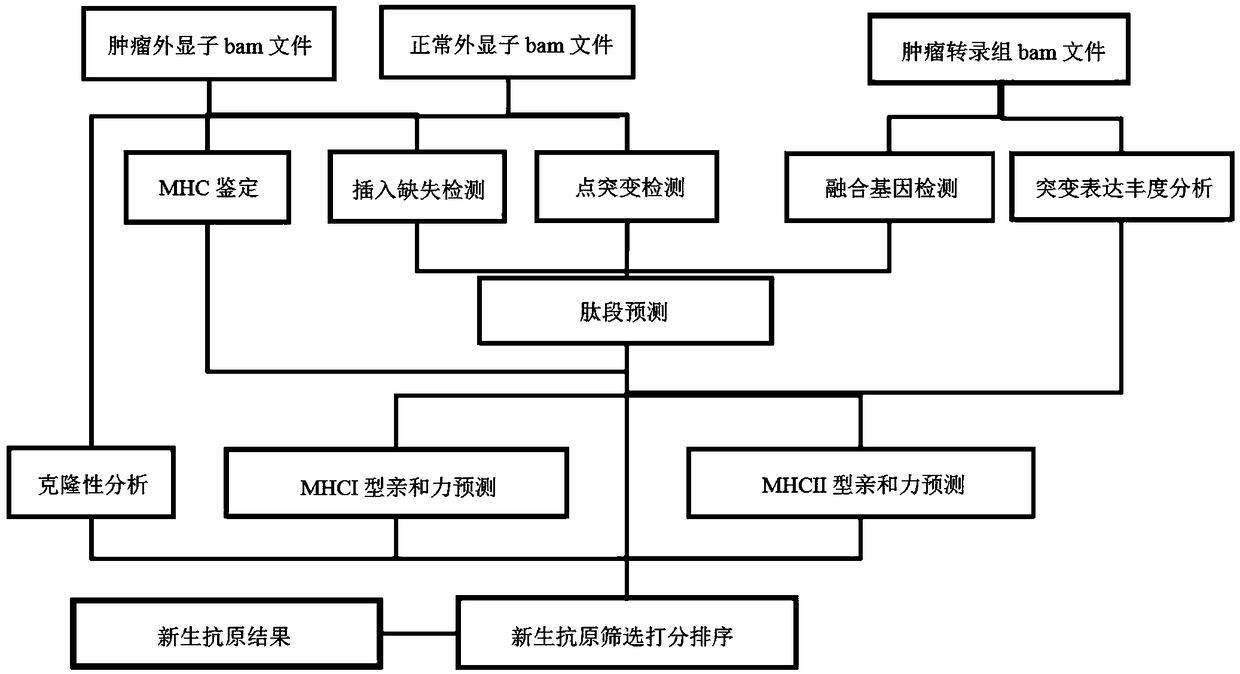
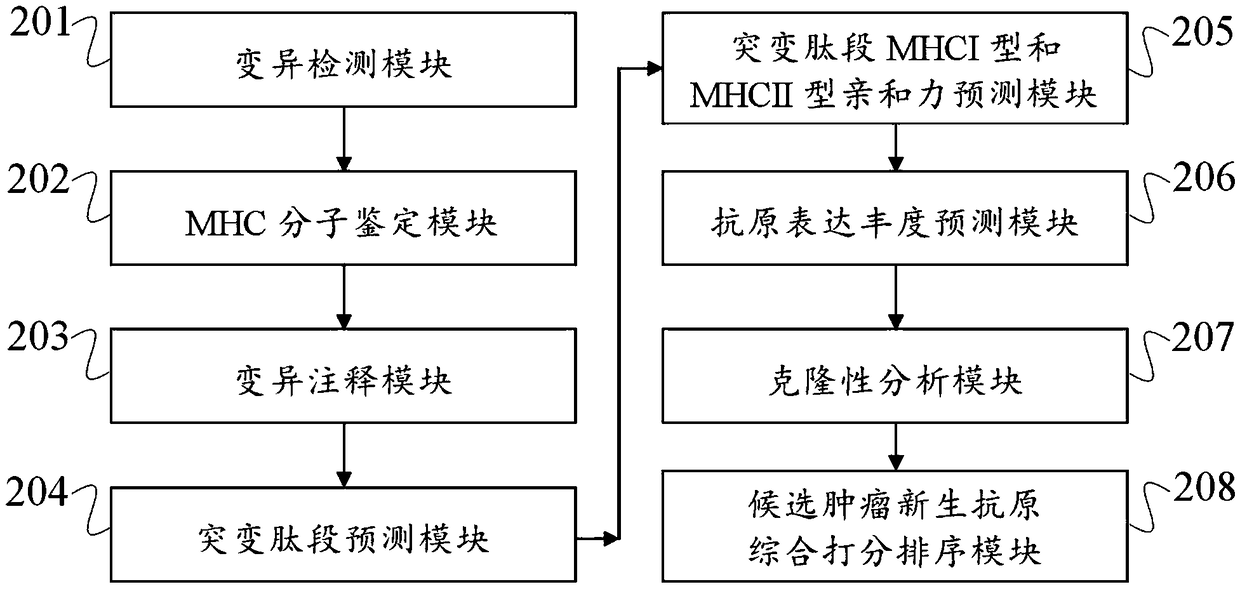
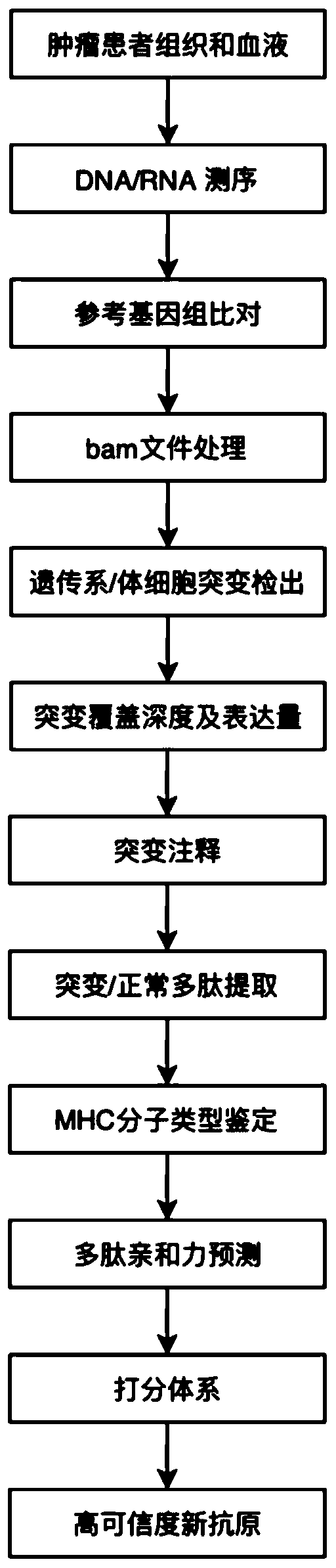
Tumor neoantigen detection method and device based on next-generation sequencing, and storage medium
ActiveCN108796055AQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular identificationClonality Analysis
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
Preparation of antigen-presenting human gamma delta t cells and use in immunotherapy
InactiveCN101031641AGood effectEffective antigen uptakeTissue cultureVaccinationEpidermal Dendritic Cells
The invention relates to a method for the preparation of efficient antigen-presenting human Gamma Delta T cells, to the Gamma Delta T cells prepared by such a method, and to their use in immunotherapy, vaccination, vaccine development and diagnostics. Similar to dendritic cells (DCs) in potency and efficacy, these human Gamma Delta T cells process antigens and present antigenic peptides to Alpha Beta T cells and induce antigen-specific responses (proliferation and differentiation) in nave Alpha Beta T cells. Gamma Delta T cells are easily purified from peripheral blood, acquire''maturation'' status (expression of essential adhesion, co-stimulatory and major histocompatibility complex molecules) within 1 day of in vitro culture under stimulation and induce strong primary and secondary T helper cell and cytotoxic T cell responses. The Gamma Delta T cells may be used in a method of treatment of tumors or chronic or recurrent infectious diseases, in identification of novel tumor or pathogen-derived antigens, and in the diagnosis of the immune competence of a patient.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CARDIFF CONSULTANTS LTD
Internalizing Anti-CD74 Antibodies and Methods of Use
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
African swine fever cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitope polypeptide and application thereof
ActiveCN110862435AImprove securityVerify securityVirus peptidesAntiviralsAfrican swine feverT lymphocyte
The invention provides an African swine fever cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitope polypeptide and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of polypeptide vaccines. According to the invention, polypeptides which are derived from African swine fever virus (ASFV) and can be stably bound by major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) are screened through a bioinformatic method and a method for identifying binding motifs of MHC I, and the screened polypeptide has the capability of starting CD8+T cells to generate immune response and stimulating organisms to specifically generate CTL, wherein an amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is shown in any one of from SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.18. The polypeptide provided by the invention can be used for preparingAfrican swine fever specific epitope vaccines or polypeptide vaccines, has high safety and good specificity, and has a potential application value in prevention and control work of African swine fever.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Automatic protection method for computer virus
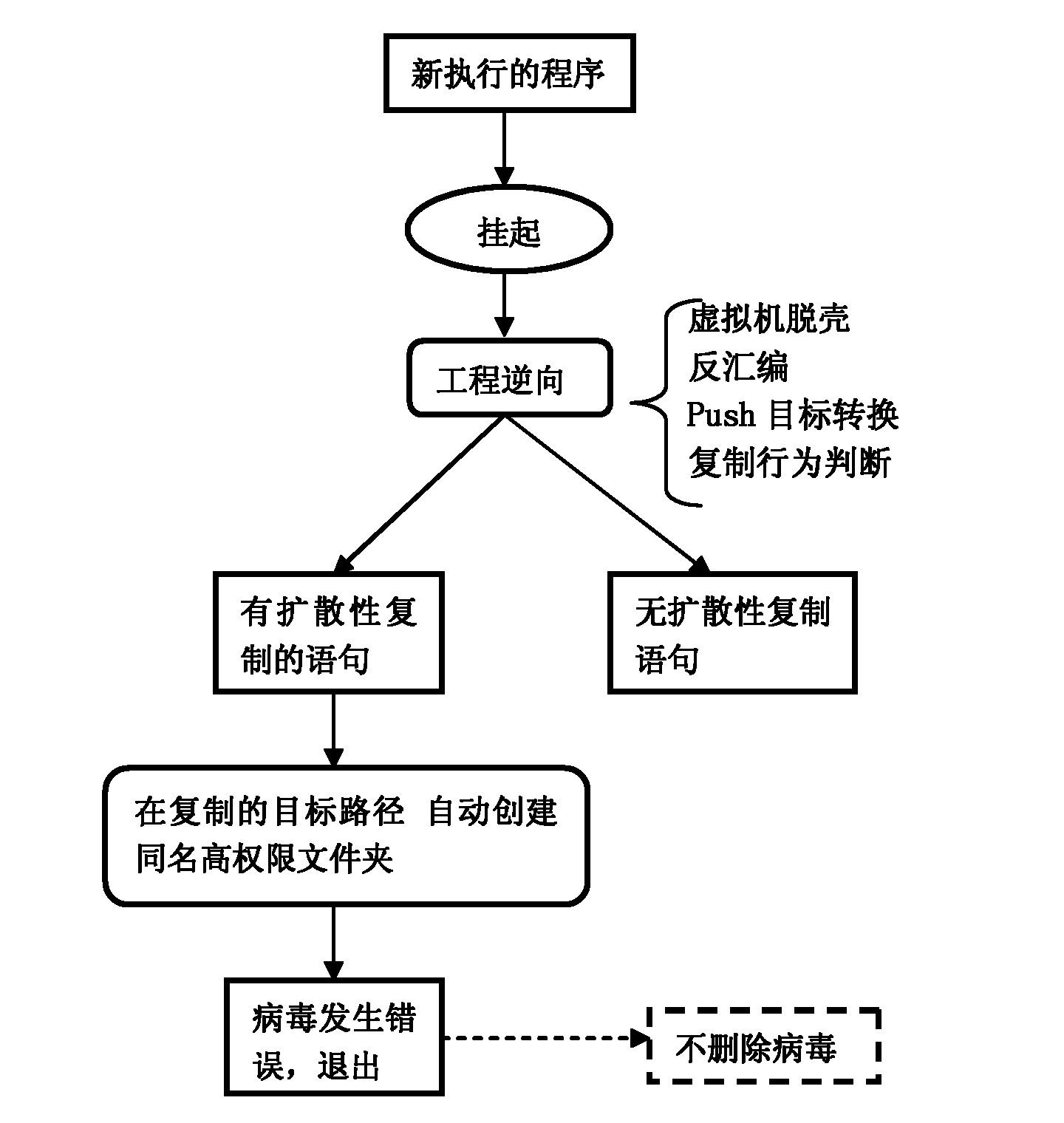
ActiveCN102034047ASelf-immunityEffective interceptionPlatform integrity maintainanceInterconnectionByte
The invention discloses an automatic protection method for a computer virus. A protection program is constructed and installed in a computer by taking a human immune system as a model; and the protection program realizes immunity of the computer from a virus program by monitoring a new program, performing engineering reversing, judging a diffusive replication statement, acquiring a replication target path, automatically creating a high-authority antibody folder, simulating byte count register (BCR) homologous judgment in the human immune system, presenting a peptide section by using a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) II and releasing an antibody by using a cell B. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that: a virus database and manual scanning are not needed, network interconnection is not needed to update the virus database, the antibody is automatically produced aiming at a computer malicious program, and the computer malicious program is effectively intercepted, so the computer has active defense capacity to the virus. Tests show that the interception rate of the tested virus can reach over 99.7 percent.
Owner:JIANGSU GUORUI XINAN TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human MHC I polypeptide and / or human or humanized β2 microglobulin polypeptide, as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same. Methods of using the genetically modified animals to study various aspects of human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
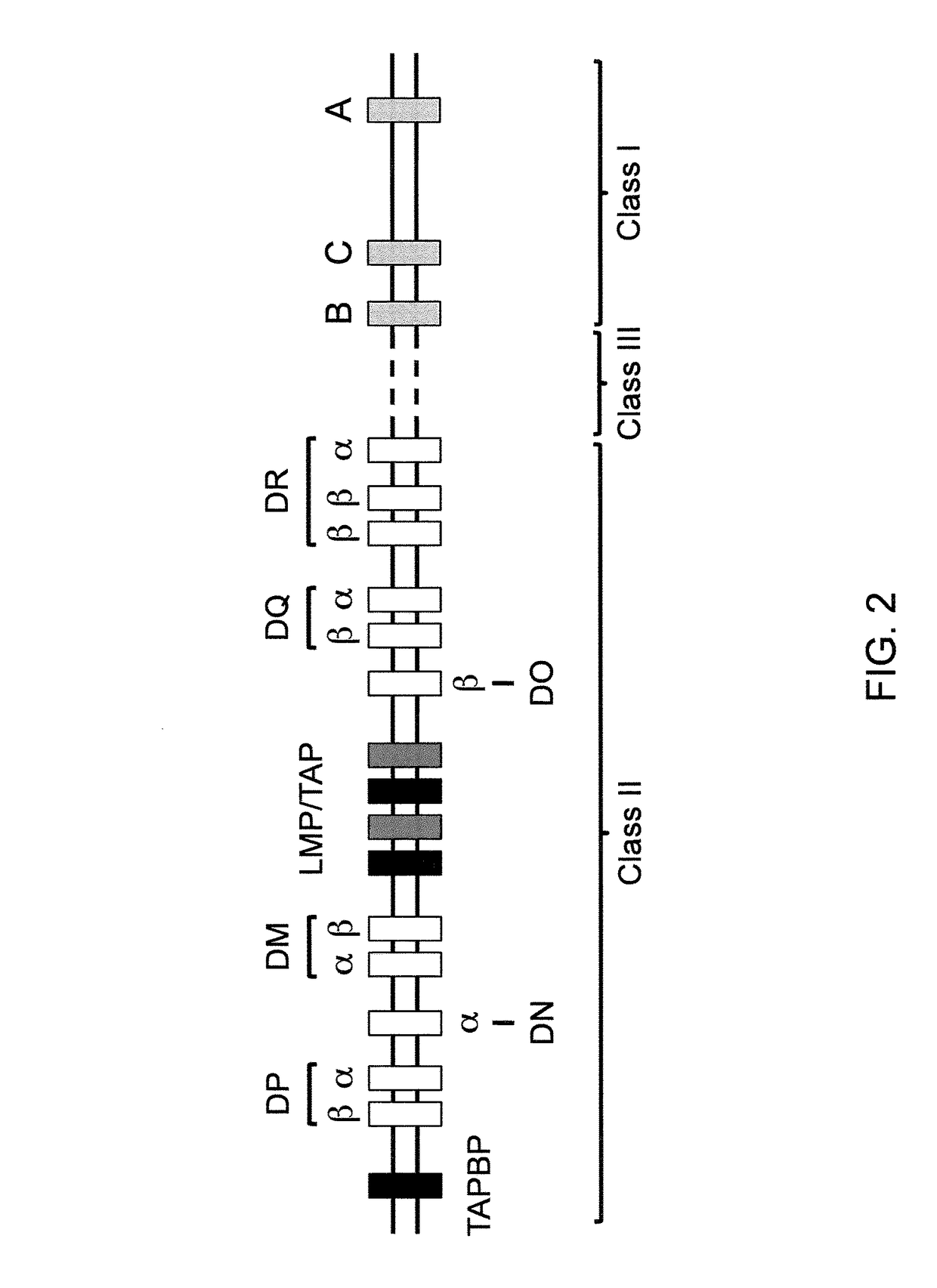
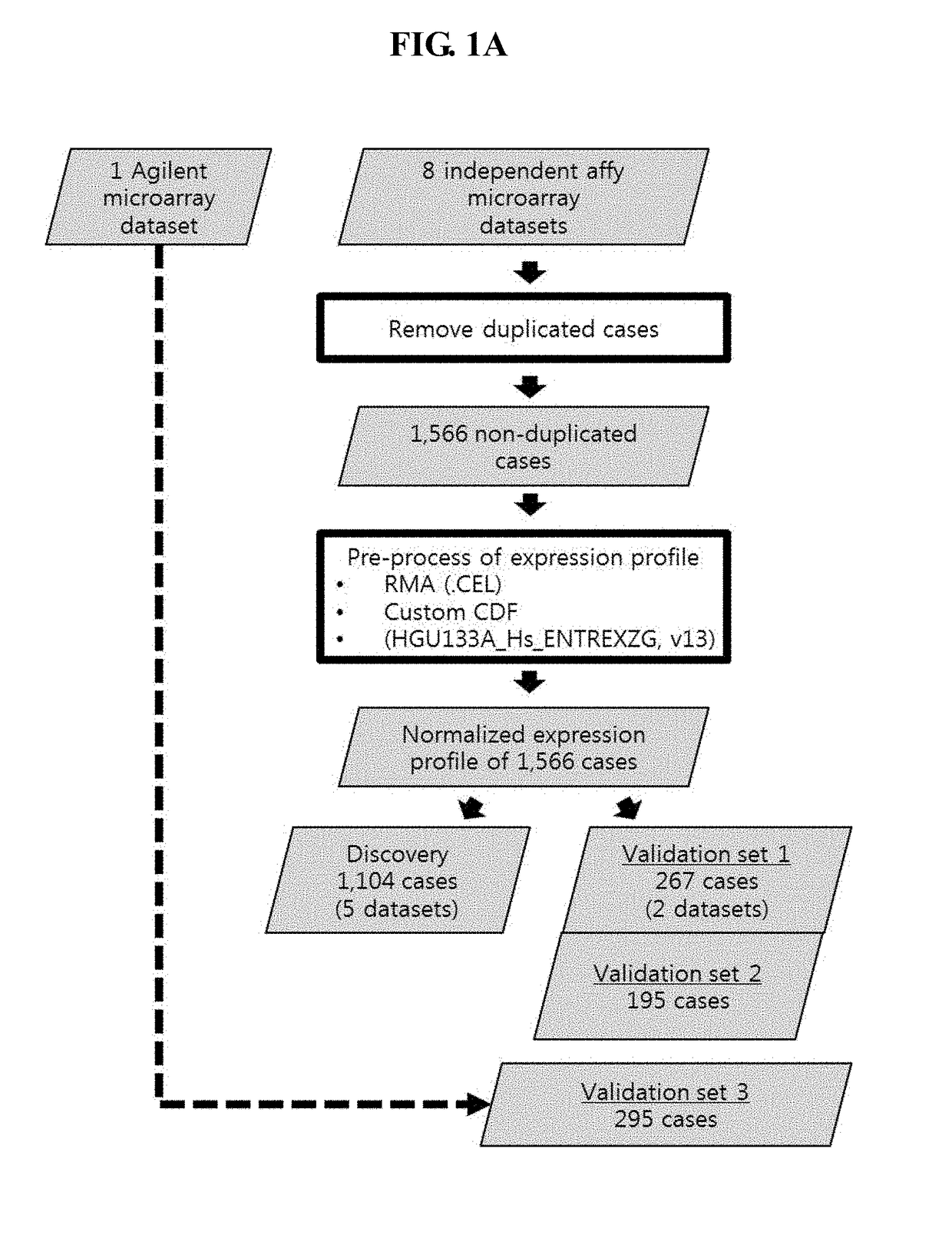
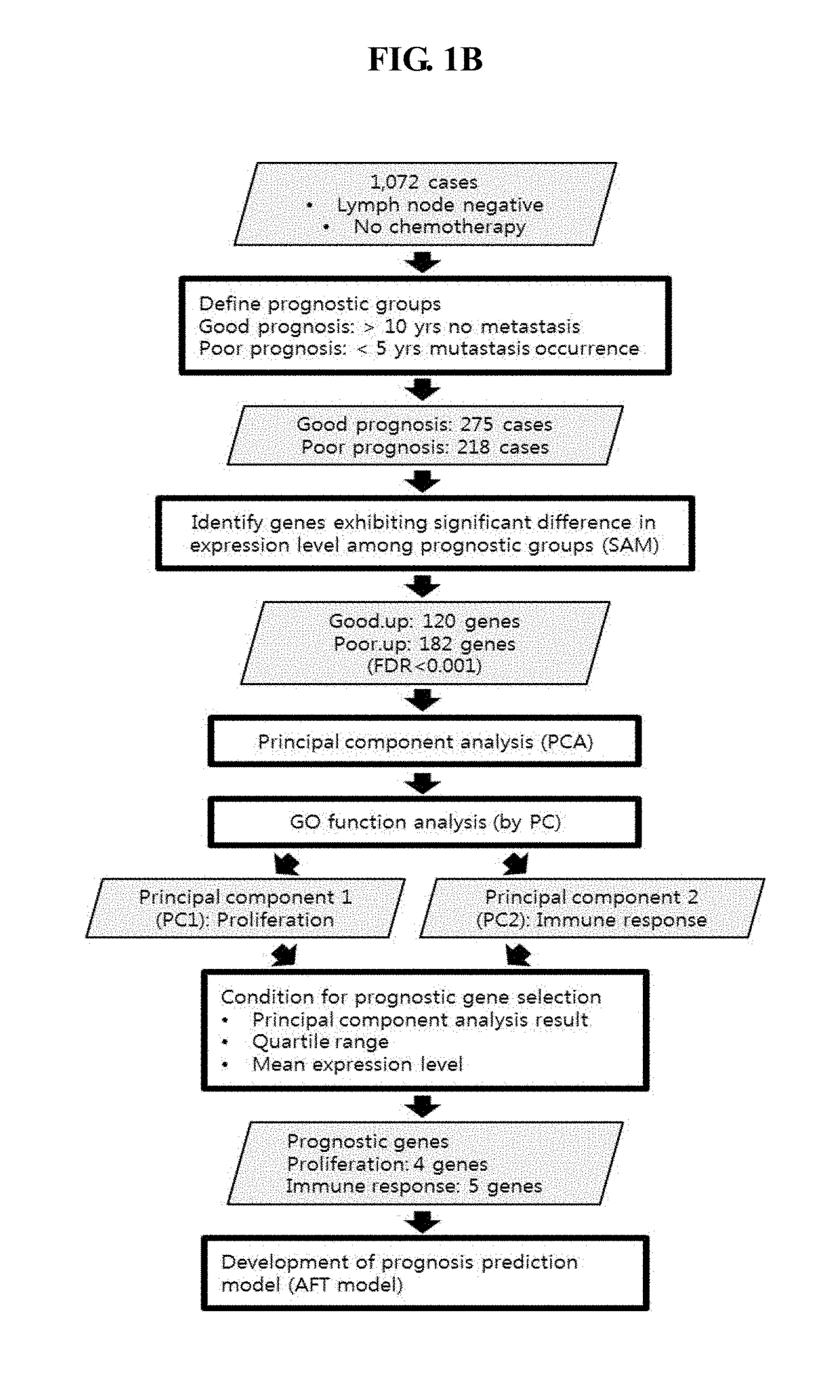
Genetic marker for early breast cancer prognosis prediction and diagnosis, and use thereof
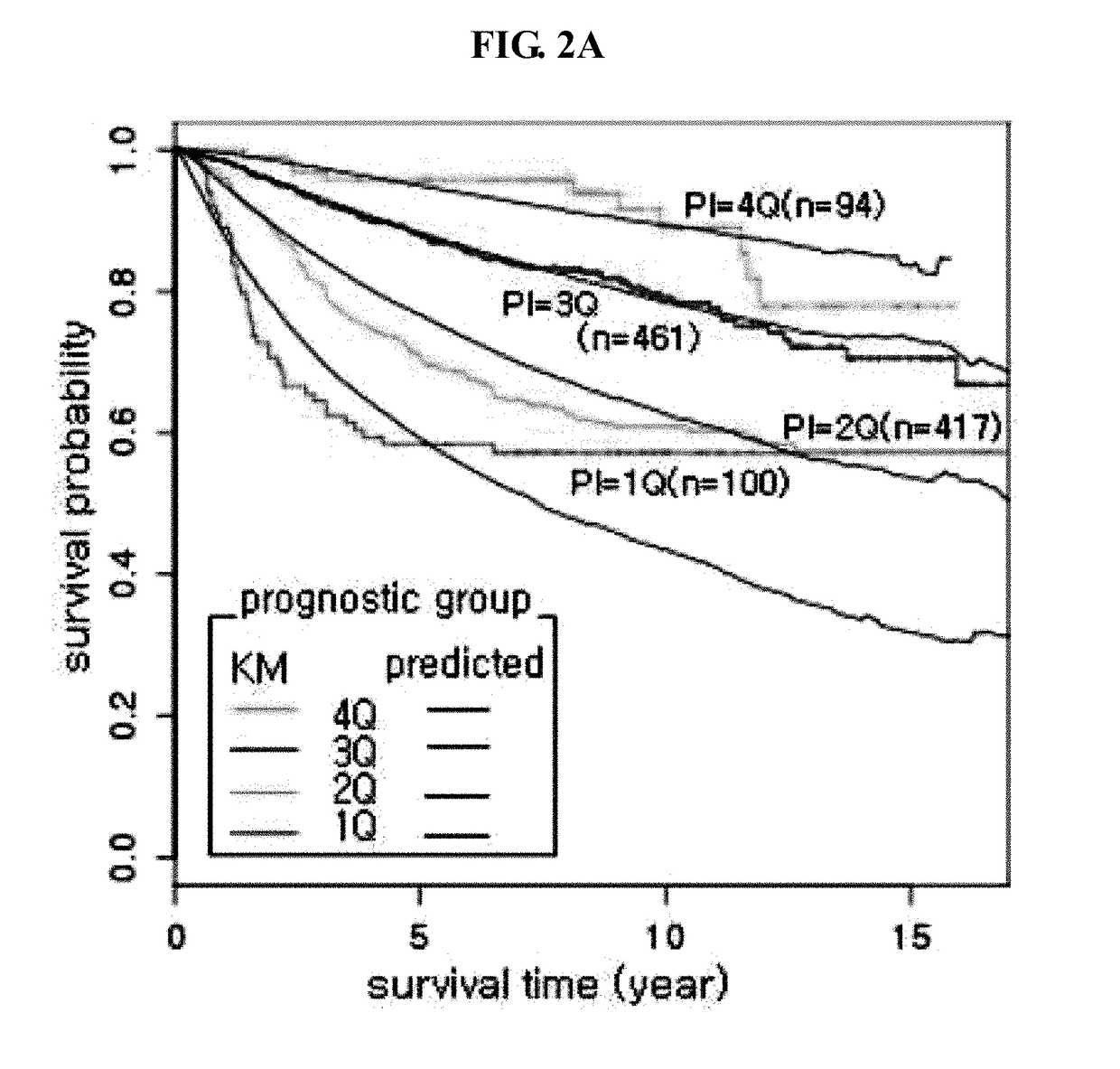
ActiveUS20190040473A1Predict prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementT-Cell Receptor BetaEarly breast cancer
The present invention relates to a gene for predicting or diagnosing the prognosis of early-stage breast cancer and to a use thereof, and more specifically relates to a genetic marker for predicting or diagnosing the prognosis of breast cancer, including TRBC1 (T cell receptor beta constant 1), BTN3A2 (butyrophilin, subfamily 3, member A2) or HLA-DPA1 (major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1) for providing information necessary for predicting or diagnosing the prognosis of a breast cancer patient. The genetic marker of the present invention allows the prediction or diagnosis of the prognosis of a breast cancer patient, and can therefore advantageously be used for the purpose of providing a direction as to the future course of breast cancer treatment, including a decision on whether anticancer therapy is necessary.
Owner:GENCURIX
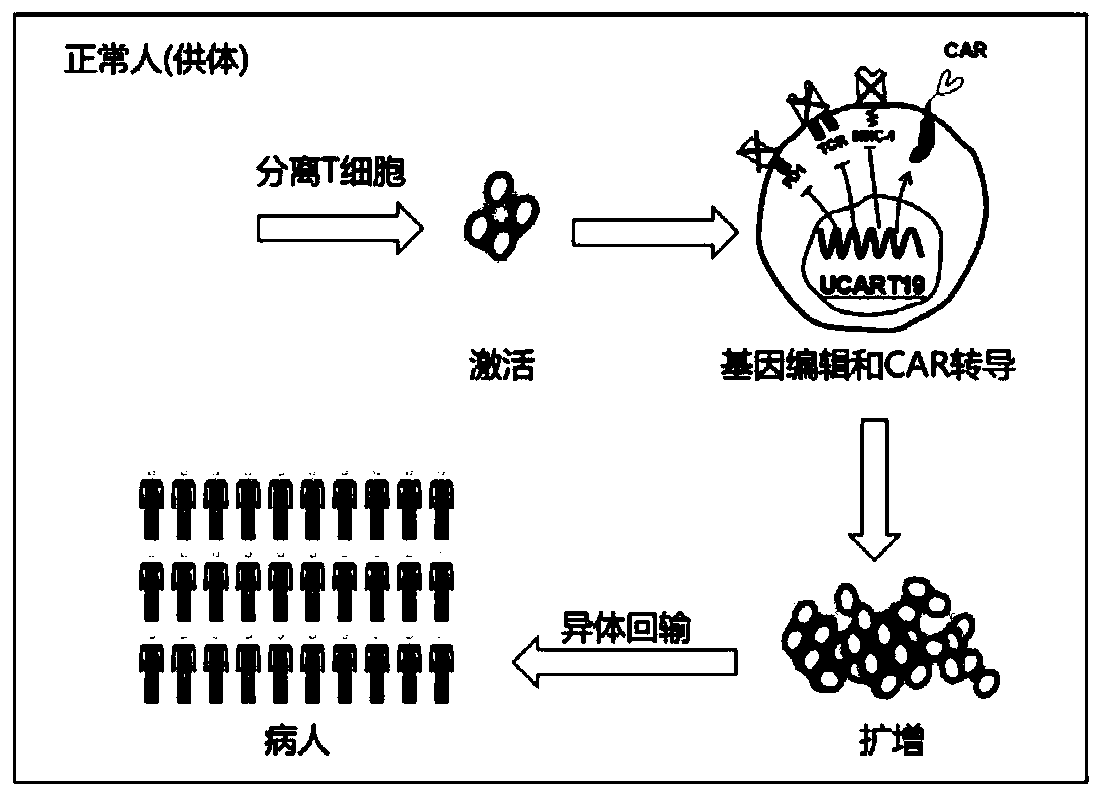
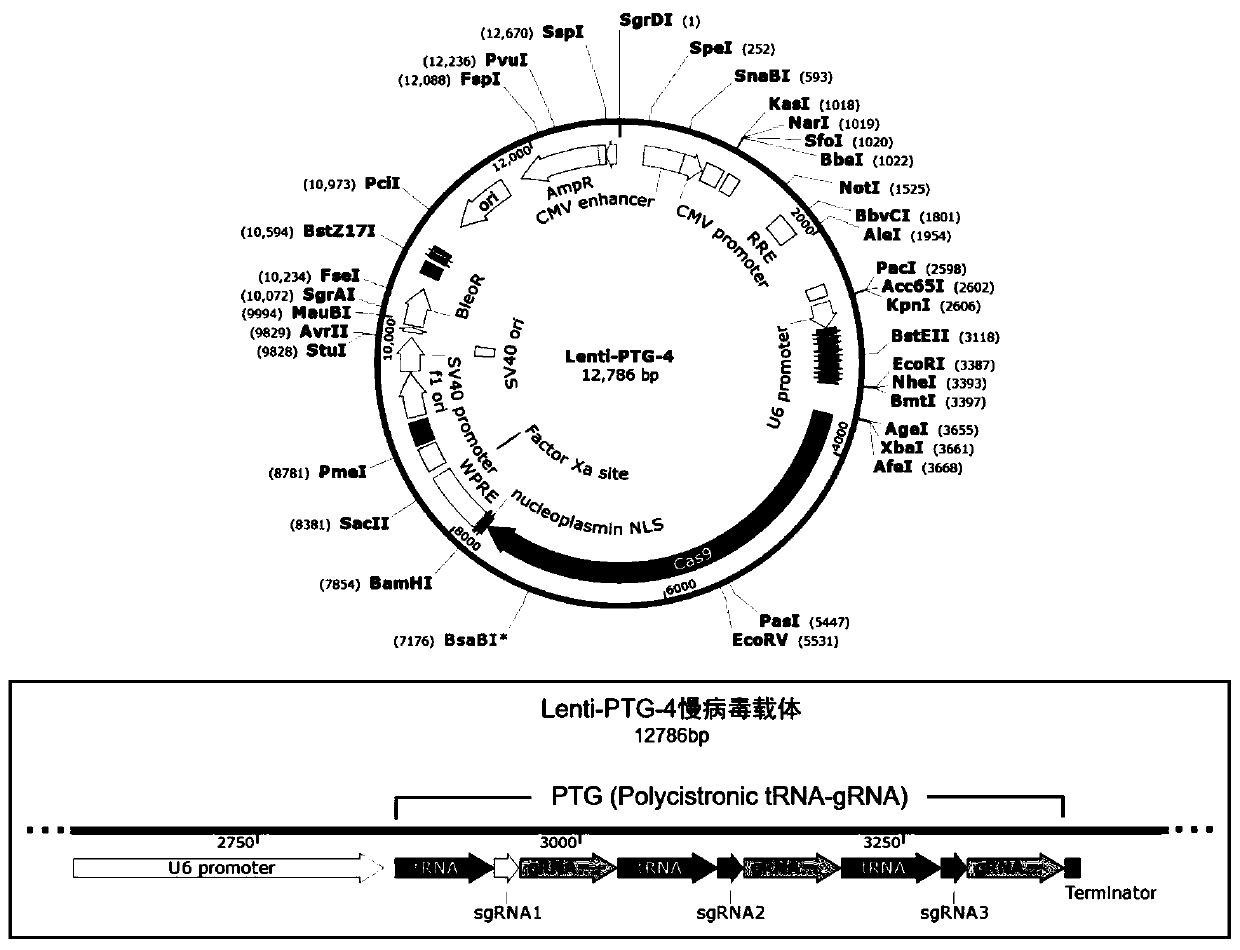
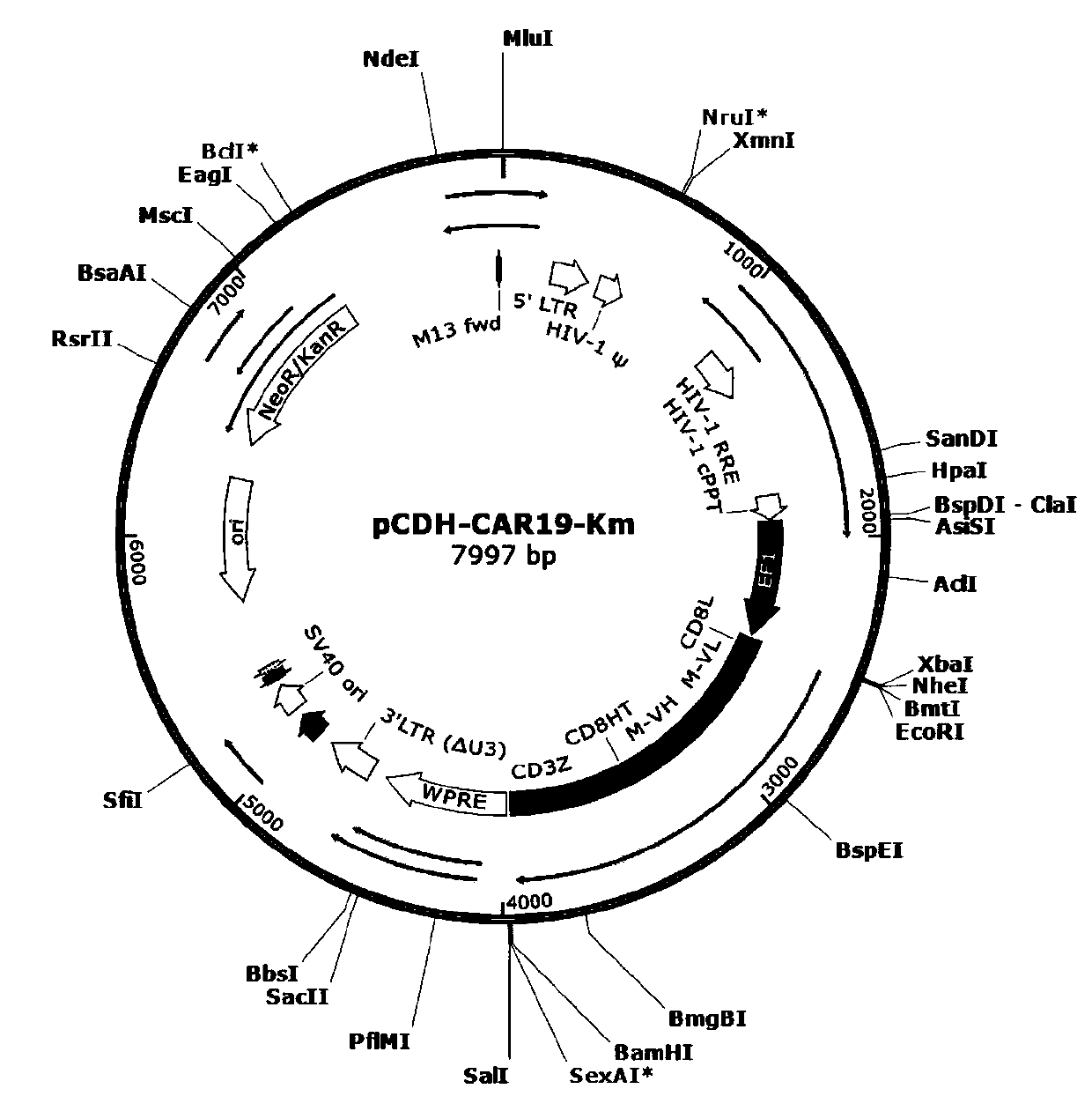
General type CAR-T cell and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN109722437AEfficient knockoutDoes not affect expressionStable introduction of DNAMammal material medical ingredientsT-Cell Antigen ReceptorsMicrobiology
The invention provides sgRNA or PTG (Polycistronic tRNA-gRNA), through combination with a CRISPR-Cas9 technique, a T cell antigen receptor (TCR) can be knocked out, or one or more of genes relevant tomajor histocompatibility complex (MHCI) and immunosuppression molecules can be knocked out. The invention also provides a general type CAR-T cell which can express chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) butcannot express TCR, and a preparation method of the general type CAR-T cell. The general type CAR-T cell prepared by the preparation method is suitable for heterogeneity antigen, has generality and has higher killability at the same time.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO GENE TECH CO LTD
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex animals
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human MHC I polypeptide and / or human or humanized β2 microglobulin polypeptide, as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same. Methods of using the genetically modified animals to study various aspects of human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
High-throughput prediction method for neoantigens of pan-cancer tumor and application thereof
ActiveCN110706742AIncrease credibilityEfficient and accurate screeningProteomicsGenomicsParanasal Sinus CarcinomaOriginal data
The invention discloses a high-throughput prediction method for neoantigens of pan-cancer tumor and application thereof. According to the prediction method disclosed by the invention, mutation and MHC(Major Histocompatibility Complex) detection are carried out on the basis of a next-generation sequencing original data file, and candidate tumor neoantigens are scored from multiple dimensions, so that the false positive of neoantigen screening can be reduced, and the neoantigens with high credibility can be screened out through scoring sorting. The method disclosed by the invention can be suitable for multiple cancer species, can predict the tumor neoantigen without distinguishing the cancer species, and lays a foundation for immunotherapy based on the tumor neoantigen.
Owner:中生康元生物科技(北京)有限公司
Peptide sequences and compositions
ActiveUS8475802B2Great opportunitySsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeVirus Protein
Provided is a polypeptide having no more than 100 amino acids, which polypeptide has one or more sequences having at least 60% homology with any of SEQ ID 1-6, or has two or more epitopes having 7 amino acids or more, each epitope having at least 60% homology with a sub-sequence of any of SEQ ID 1-6 that has the same length as the epitope:SEQ ID 1DLEALMEWLKTRPILSPLTKGILGFVFTLTVPSEQ ID 2LLYCLMVMYLNPGNYSMQVKLGTLCALCEKQASHSSEQ ID 3DLIFLARSALILRGSVAHKSCSEQ ID 4PGIADIEDLTLLARSMVVVRPSEQ ID 5LLIDGTASLSPGMMMGMFNMLSTVLGVSILNLGQSEQ ID 6IIGILHLILWILDRLFFKCIYRLFwherein, the polypeptide is immunogenic in a vertebrate expressing a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) allele, and wherein the polypeptide is not a complete influenza virus protein.
Owner:PEPTCELL
CD8+T cell epitope polypeptide of S1 protein of chicken IBV (Infectious Bronchitis Virus) S1 protein
ActiveCN103387604AGood immune protectionAvoid immunosuppressionAntiviralsPeptidesADAMTS ProteinsProtein engineering
The invention provides universal CD8+T cell epitope polypeptide of a chicken IBV (Infectious Bronchitis Virus) S1 protein, and belongs to the field of gene and protein engineering. The epitope polypeptides are prepared by the following steps: screening 21 epitope polypeptides in accordance with binding motif sequences in amino acid sequences of the S1 genes of the IBV virus according to the binding motif sequences of haplotype chicken major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I-type molecules; then, taking lymphocytes of three constructed SPF (Specific Pathogen Free) chicken immunized by DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) recombinant plasmids of the S1 genes containing different subtype IBVs, determining the capacity of the 21 polypeptides which induce chicken splenic lymphocytes to secrete interferon-gamma by using an ELIspot (Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay) method, and finally, screening to obtain four universal functional T cell epitope polypeptides of IBV, wherein the sequences are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-4. The four epitope polypeptides provided by the invention are combined in use to prepare a universal vaccine for IBV. The invention further provides a method for screening the epitope of the functional T cell of the S1 protein of the IBV.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex mice
ActiveUS10154658B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDepsipeptidesPhysiologyTransgenesis
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human MHC I and MHC II polypeptides and / or human or humanized β2 microglobulin polypeptide, as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same. Methods of using the genetically modified animals to study various aspects of human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
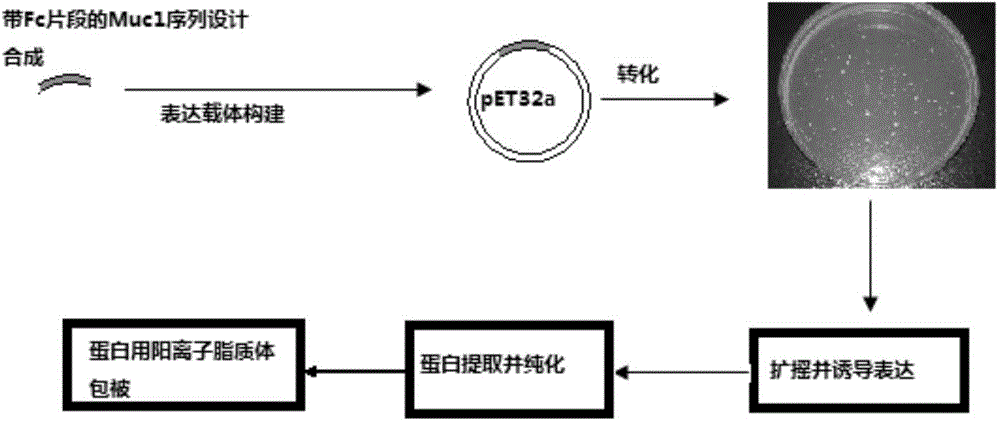
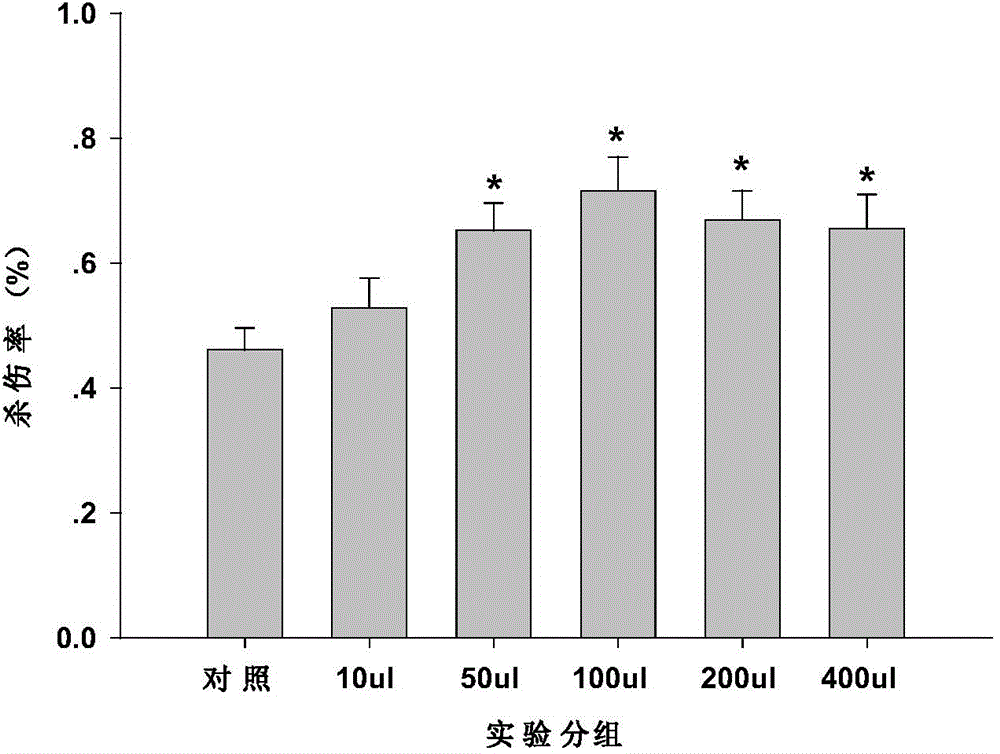
MUC1-Fc polypeptide vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104800838AEasy to solveGood treatment effectAntibody ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsEscherichia coliTreatment effect
The invention relates to an MUC1-Fc polypeptide vaccine as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The polypeptide vaccine comprises MUC1 antigen peptide containing immune globulin Fc segments, and the sequence of the peptide is represented by SEQ ID NO:1; with the adoption of the genetic engineering technology, the sequence of the MUC1 antigen peptide containing the immune globulin Fc segments is built to a carrier, and the MUC1 antigen peptide is expressed and purified in escherichia coli and coated with carriers such as lipidosome and the like so as to obtain the MUC1-Fc polypeptide vaccine. The MUC1-Fc polypeptide vaccine contains MHC (major histocompatibility complex) I and MHC II binding epitopes simultaneously, thereby being capable of breaking through MHC restrictive factors, effectively activating cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) reaction, having higher killing effect on tumor cells and achieving better preventing and treating effects.
Owner:BENHEALTH BIOPHARMACEUTIC SHENZHEN CO LTD
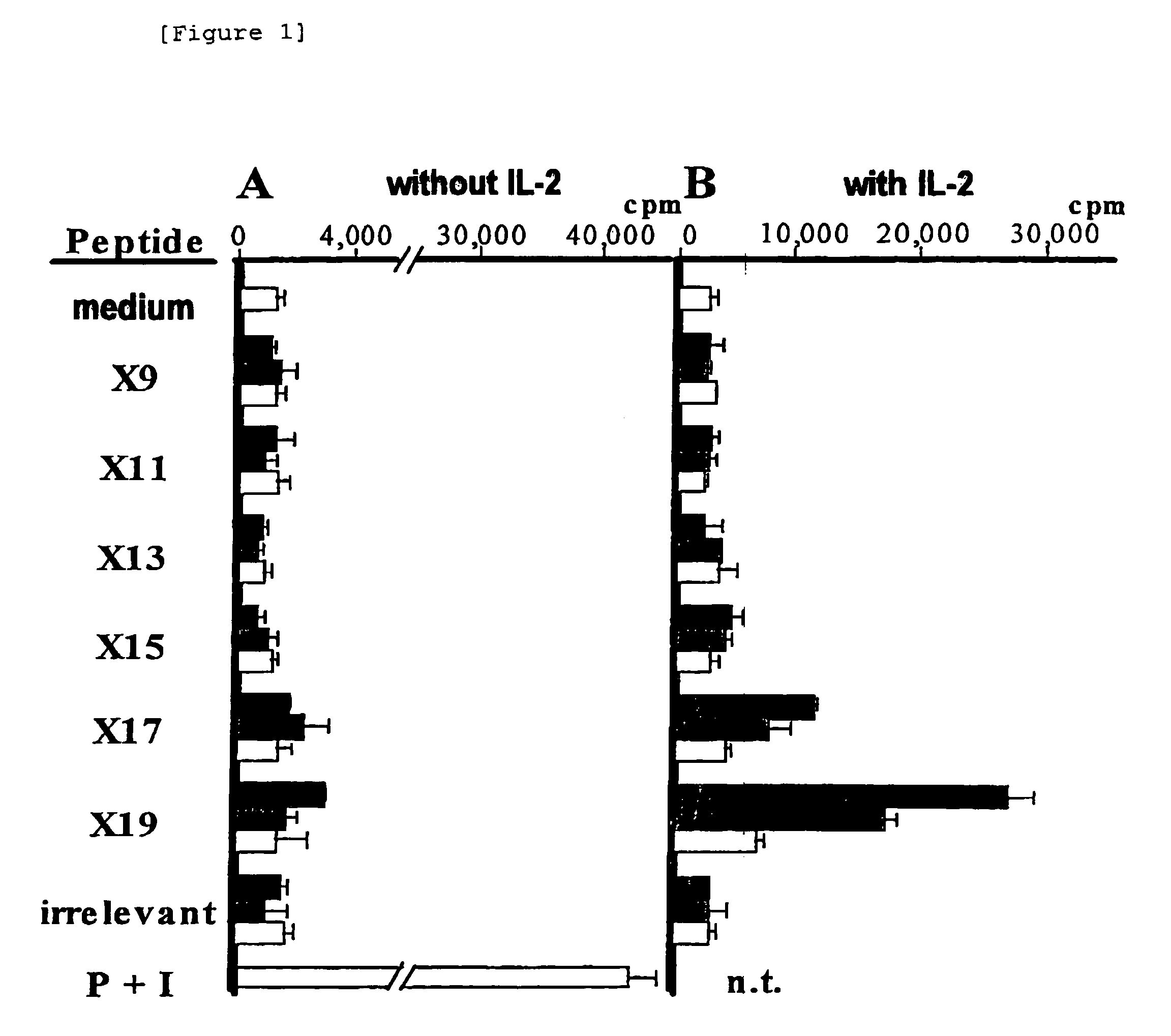
Clonal expansion of T cells of unknown specificity and identification of ligand recognized by the clonally expanded T cells
A process for clonally expanding T cells of unknown specificity and a process for identifying a peptide ligand recognized by said T cells are provided.A process for clonally expanding T cells of unknown specificity which comprises co-culturing said T cells of unknown specificity with combinatorial randomized peptide library (Xn peptide library wherein n is a number of amino acids) consisted of peptides having a randomized amino acid sequence consisted of amino acid residues selected from nineteen kinds of naturally occurring amino acid other than cysteine, an interleukin, and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II antigen-expressing cells with DNA synthesis being suspended, said cells being derived from the individual where said T cells are obtained; and a process for identifying a peptide ligand recognized by the T cell clone of unknown specificity obtained by said process, which comprises determining proliferating activity of said T cell clone with Xn peptide library, in the presence of an interleukin and MHC class II antigen-expressing cells with DNA synthesis being suspended, said cells being derived from the individual where said T cells are obtained, to thereby determine a peptide sequence that can activate proliferation of T cells.
Owner:JURIDICAL FOUND THE CHEMO SERO THERAPEUTIC RES INST
Method for detecting early diagnosis of uterus cancer related to HPV16/18 early protein antibody utilizing polypeptide
This invention discloses a method for early stage diagnosis of uterine neck cancer related to HPV16, 18 early and late stage protein antibody by using specific polypeptide. It utilizes that the expression of MHC major histocompatibility complex I, II antigen and the existence of tumour and the defection before cancerization of uterine cervix are intimately involved, especially the HLA which is associated with the cancerization of uterine cervix esoderma cell, (CIN) immersed cancer, and cervical carcinoma is human leukocyte antigen molecule, and all immunity decomposing in the body with a series of complex cell-conducting changes into little polypeptide molecule combining break and is connected with MHC. The HLA-DR antigen in the high uterine cervix defecting time CIN III markedly increases expression and regulate and control. The cellular immunity medium (CMI) is immune to HVS, E2, E4, E6 and E7 polypeptide and is connected with antibody of HPV16 early protein by screening polypeptide sequence which is associated with height and antibody.
Owner:BEIJING SHUWEIKANG BIOCHEM TECH
Controlling distribution of epitopes in polypeptide sequences
The present invention describes a novel method for the design of polypeptides with controlled distribution of immunogentic epitopes. The method allows for the controlled elimination or introductionof epitopes in consideration of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule binding motifs.
Owner:PHARMACIA CORP
Biological agent for effectively killing and wounding tumor cells
ActiveCN105106237AFast growthGood antitumor activityMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsLymphocyteBiochemistry
The invention provides a biological agent for effectively killing and wounding tumor cells. Human NK (natural killer) cells, mature B lymphocyte cells and CIK (cytokine-induced killer) cells are amplified through induction in vitro, and are combined according to a certain proportion, and the biological agent for effectively killing and wounding the tumor cells is provided. The biological agent with a combined tumor killing effect has the advantages of high tumor killing activity, wide tumor killing spectra and zero MHC (major histocompatibility complex) limitation.
Owner:BEIJING BIOHEALTHCARE BIOTECH
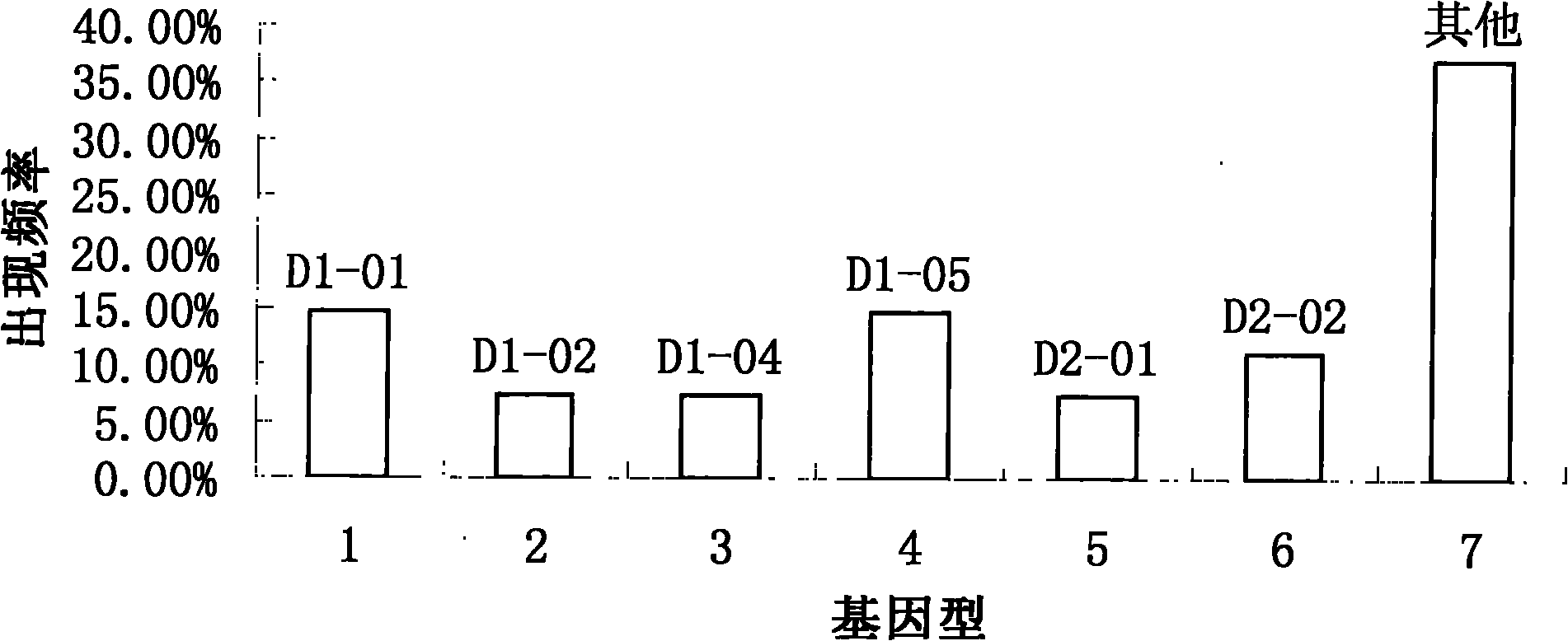
Garrupa MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) IIB gene as well as cloning method and application thereof
InactiveCN102010868AEasy to operateImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesDiseaseNucleotide
The invention discloses a garrupa MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) IIB gene as well as a cloning method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the garrupa MHC IIB gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and the amino acid sequence of protein encoded by the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. In the invention, by using a homologous cloning method, the MHC IIB gene is separated from garrupa, 12 different MHC IIB gene types are identified, the correlation between the polymorphism and the disease resistance of the MHC IIB gene are analyzed, and 6 molecular marks of the MHC IIB gene relevant to the disease resistance of the garrupa are screened; and the cloning method is suitable for screening the marks relevant to the disease resistance of the garrupa and breeding disease-resistant species.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Use of allogenic or syngenic major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules as universal adjuvants for vaccines against neoplastic disease, infection and autoimmune disease
InactiveUS20060240033A1Enhance antigen-specific immune responseImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsAdjuvantAutoimmune condition
The present invention is directed to the discovery that allogenic or syngenic adjuvant stimulation can cause local inflammation which increases the antigen presentation capability of cells in the vicinity of adjuvant stimulation. By discovering this phenomenon, the present invention provides a novel method for augmenting the immunogencity of an antigen by conjointly administering an allogenic or syngenic MHC molecule (as a universal adjuvant) to trigger a local inflammatory reaction to enhance antigen presentation at the site of delivery.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for screening tumor specific T cell from TIL (tumor infiltrating lymphocyte)
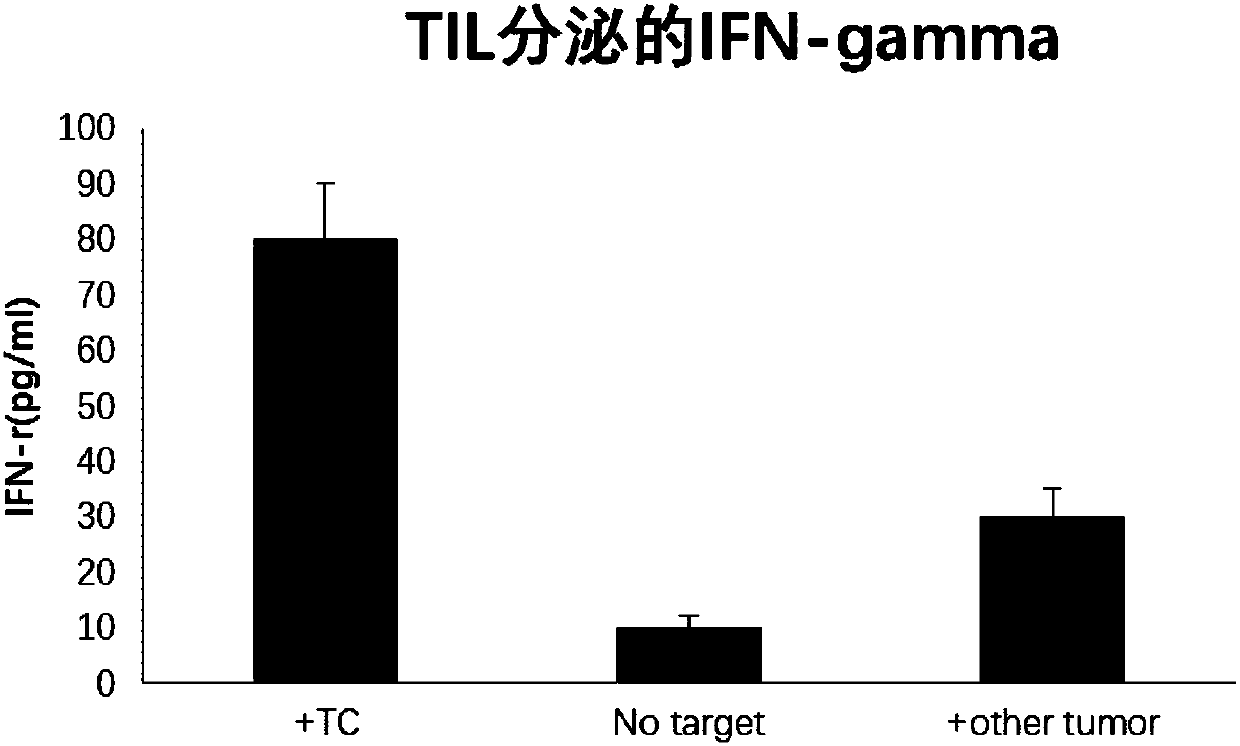
PendingCN109988748AGrowth inhibitionEfficient screeningCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsLymphocyteTumor-specific antigen
The invention discloses a method for screening a tumor specific T cell from a TIL (tumor infiltrating lymphocyte). The method includes the steps of screening a tumor specific antigen peptide of a to-be-tested tumor patient; constructing a composite of an MHC (major histocompatibility complex) and the tumor specific antigen peptide, wherein the MHC and antigen peptide composite can be combined witha TCR (T cell receptor) of a T cell of a tumor specific antigen; adding an IFN-r positive TIL of the to-be-tested tumor patient to the MHC and antigen peptide composite, performing incubation, and screening the tumor specific T cell. The invention also provides a tumor specific polypeptide screened by the method, and application of the screened tumor specific T cell and the polypeptide in products related to cancer therapy. By the method, the tumor specific T cell and the tumor specific polypeptide can be efficiently screened out, and accordingly, an effective choice for tumor immunotherapy is provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com