Tumor neoantigen detection method and device based on next-generation sequencing, and storage medium
An antigen detection and tumor technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, special data processing applications, etc. The effect of predicting the outcome
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] This example utilizes the published data in Yadav, Mahesh, et al. "Predicting immunogenic tumor mutations by combining mass spectrometry and exome sequencing." Nature 515.7528 (2014): 572. (hereinafter referred to as Document 1): mouse model MC-38 The exome data and transcriptome data of tumor samples and normal samples; the tumor neoantigen detection method based on next-generation sequencing was used to detect tumor neoantigens, as follows:
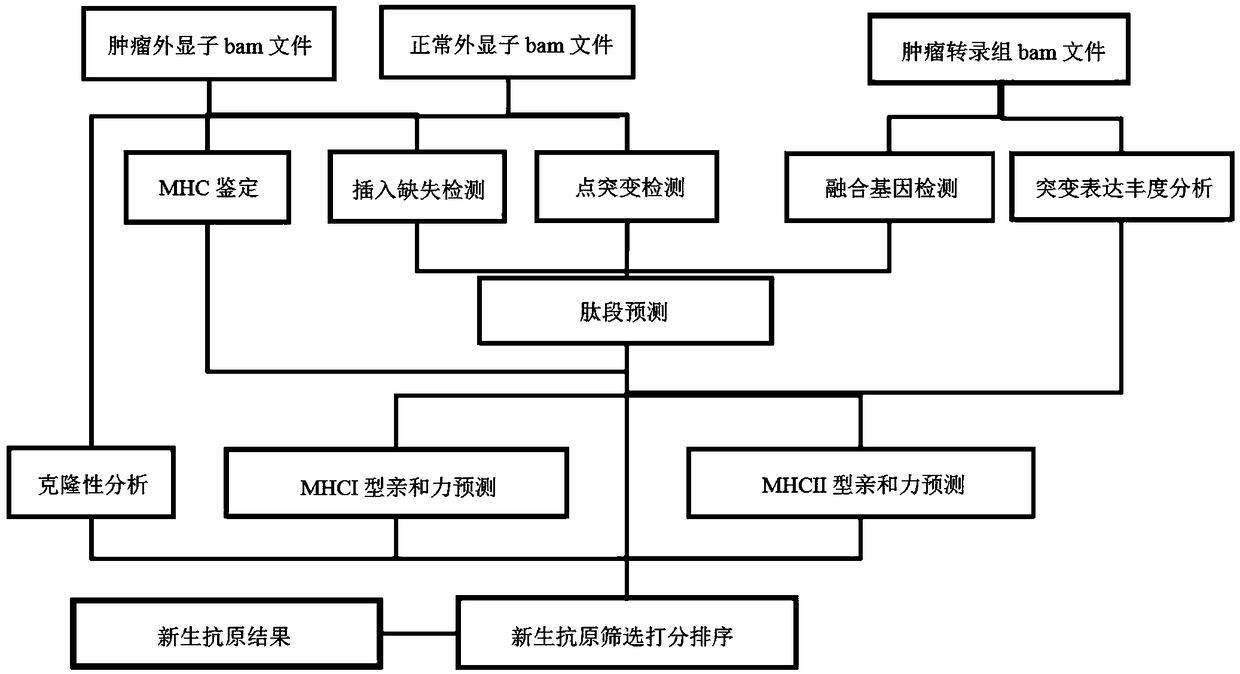
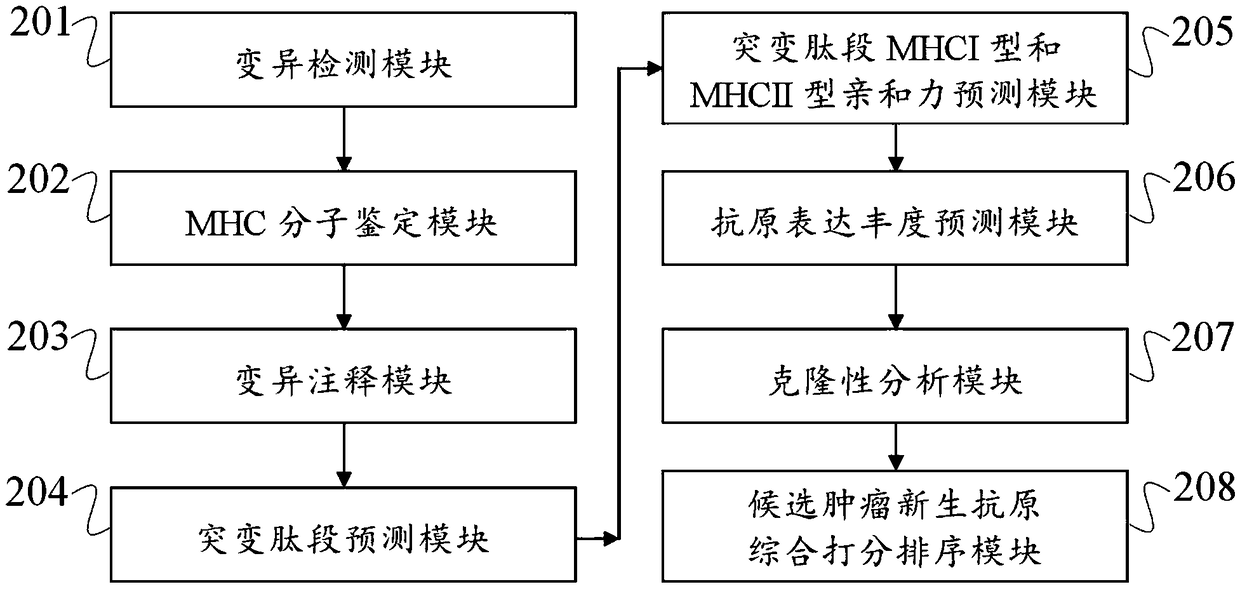
[0096] (1) Variation detection
[0097] By comparing the bam files obtained by DNA sequencing of tumor samples and normal samples, VarScan and mutect software were used to detect tumor somatic point mutations (single nucleotide variant, SNV) and insertion and deletion (insertion and deletion, InDel). In order to obtain high-quality mutations, use the intersection of the two software as high-quality candidate mutations. For the detection of fusion genes, STAR-Fusion was used to detect the aligned RNA bam format files.
[0098] (...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Using published data ICC24 (Sia D, Losic B, Moeini A, et al.Massive parallelsequencing uncovers actionable FGFR2-PPHLN1fusion and ARAF mutations in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.[J].Nature Communications,2015,6:6087-6087.), using the example 1 tumor neoantigen detection method for neoantigen detection. The results showed that by using the method of Example 1, 5 antigenic peptides that could be recognized by HLA were detected, including a fusion gene with high frequency in ICC that could be recognized by HLA-01, which was derived from the fusion gene FGFR2-PPHLN1 of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. It can be seen that by using the method for detecting neoplastic antigens in Example 1, new neoplastic antigens in cholangiocarcinoma have been discovered. There is no good treatment for advanced cholangiocarcinoma, and the survival rate is low; the neoantigen was detected by the method of Example 1, and a new treatment method for cholangiocarcinoma was discovered, which pro...
Embodiment 3
[0136] This method was used to detect neoantigens in 288 samples of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), and the 288 samples of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma came from the following 4 literatures:
[0137] Hiromi Nakamura, Yasuhito Arai1, Yasushi Totoki, et al.Genomic spectrum of biliary tract cancer.[J].Nature Genetics,2015,47(9):1003.
[0138] Shanshan Zou, Jiarui Li, Huabang Zhou, et al. Mutational landscape of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5:5696.
[0139] Yuchen Jiao, Timothy M Pawlik, Robert A Anders, et al. Exome sequencing identifies frequent inactivating mutations in BAP1, ARID1A and PBRM1 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas.[J].Nature Genetics,2013,45(12):1470-U93.
[0140] Sia D, Losic B, Moeini A, et al.Massive parallel sequencing uncoversactionable FGFR2–PPHLN1 fusion and ARAF mutations in intrahepaticcholangiocarcinoma.[J].Nature Communications,2015,6:6087-6087.
[0141] The analysis results of 18813 non-synonymous mutati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com