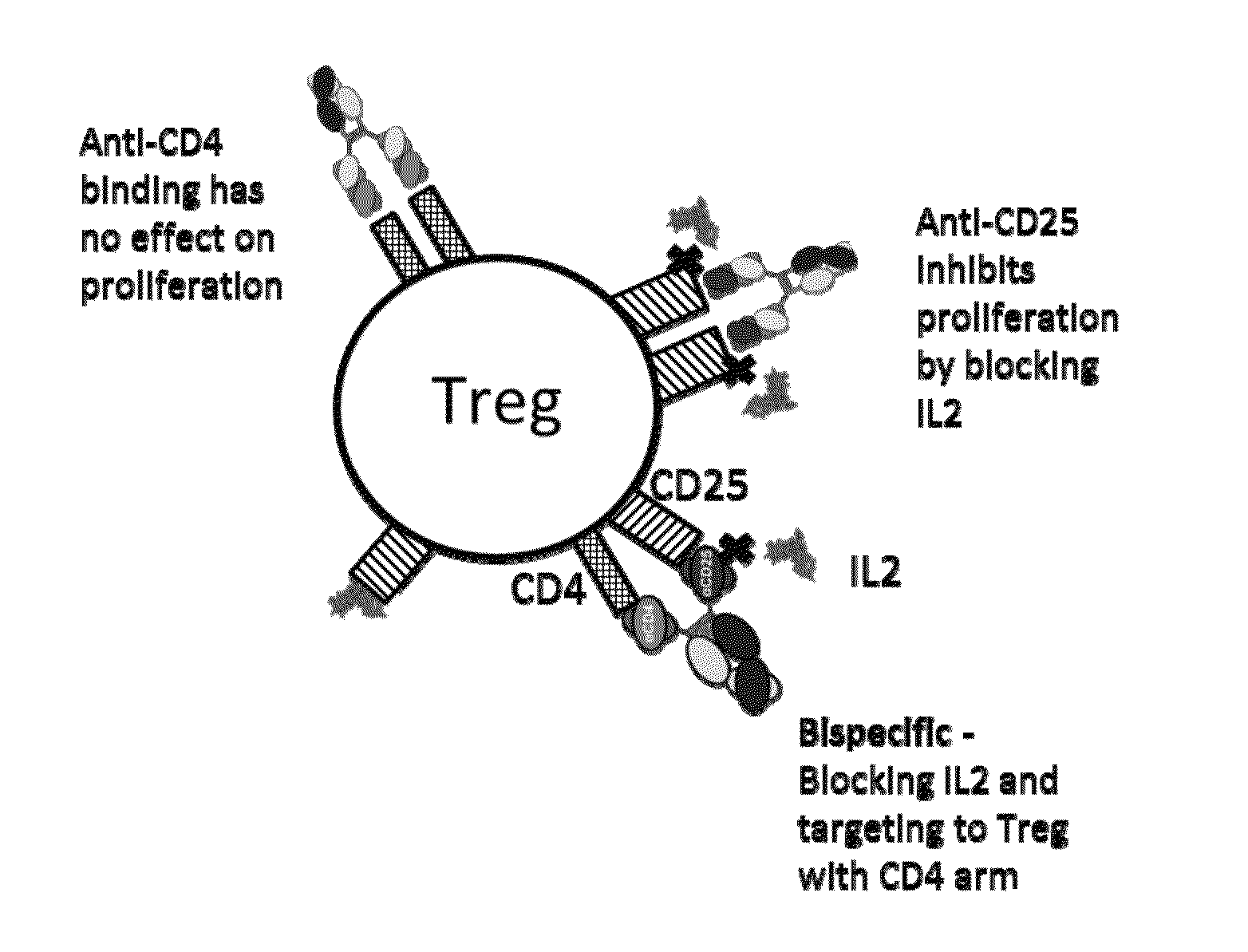
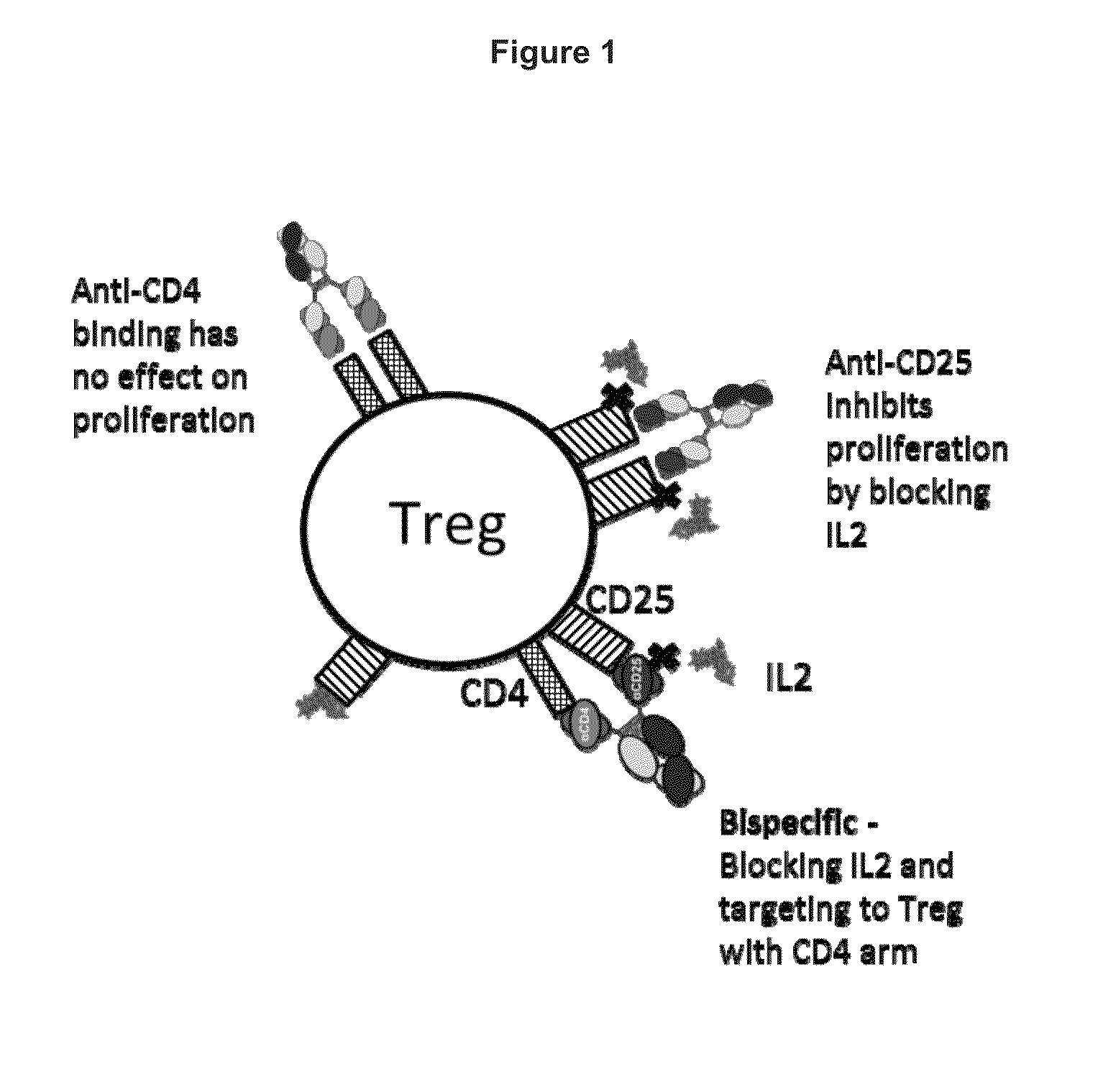
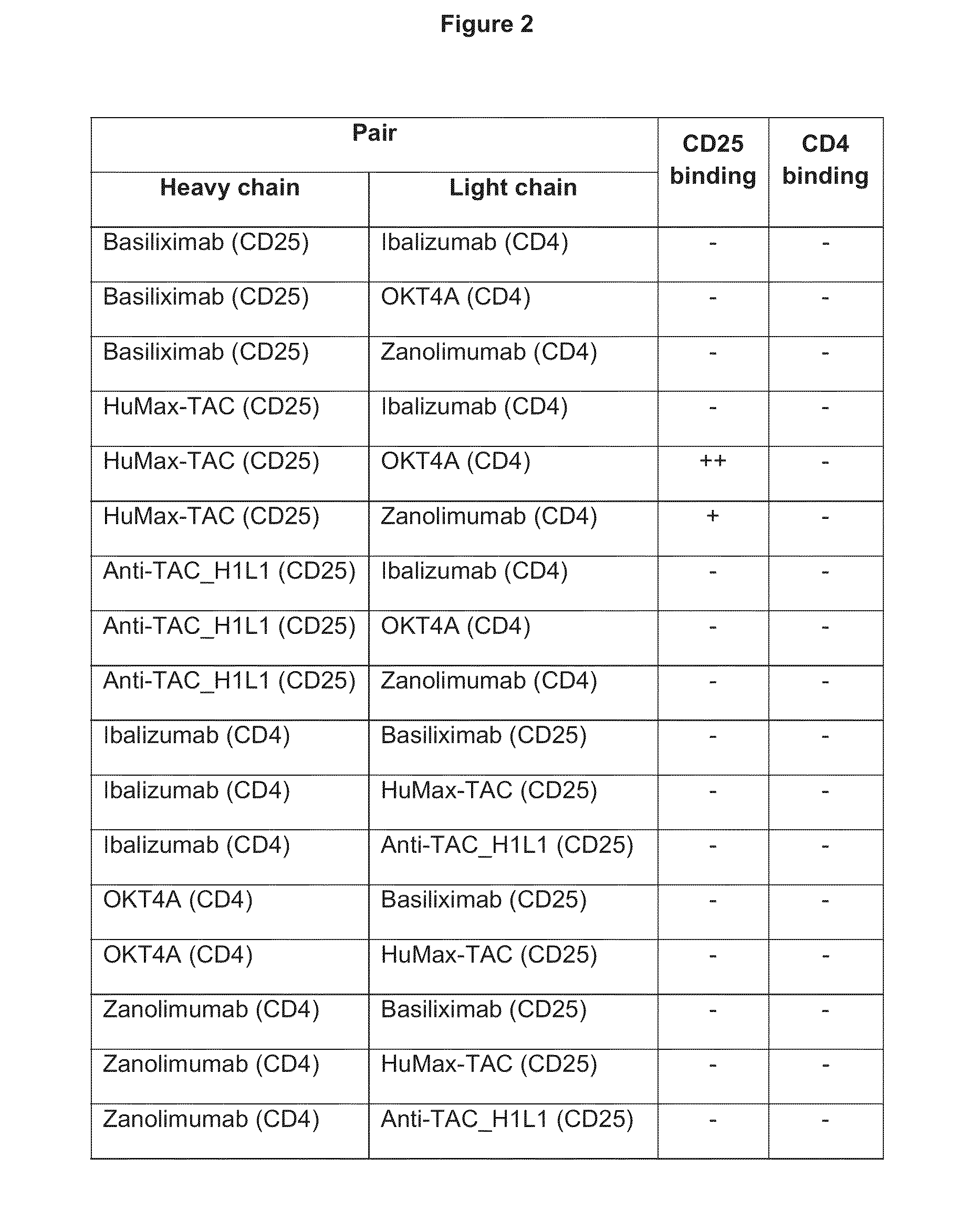
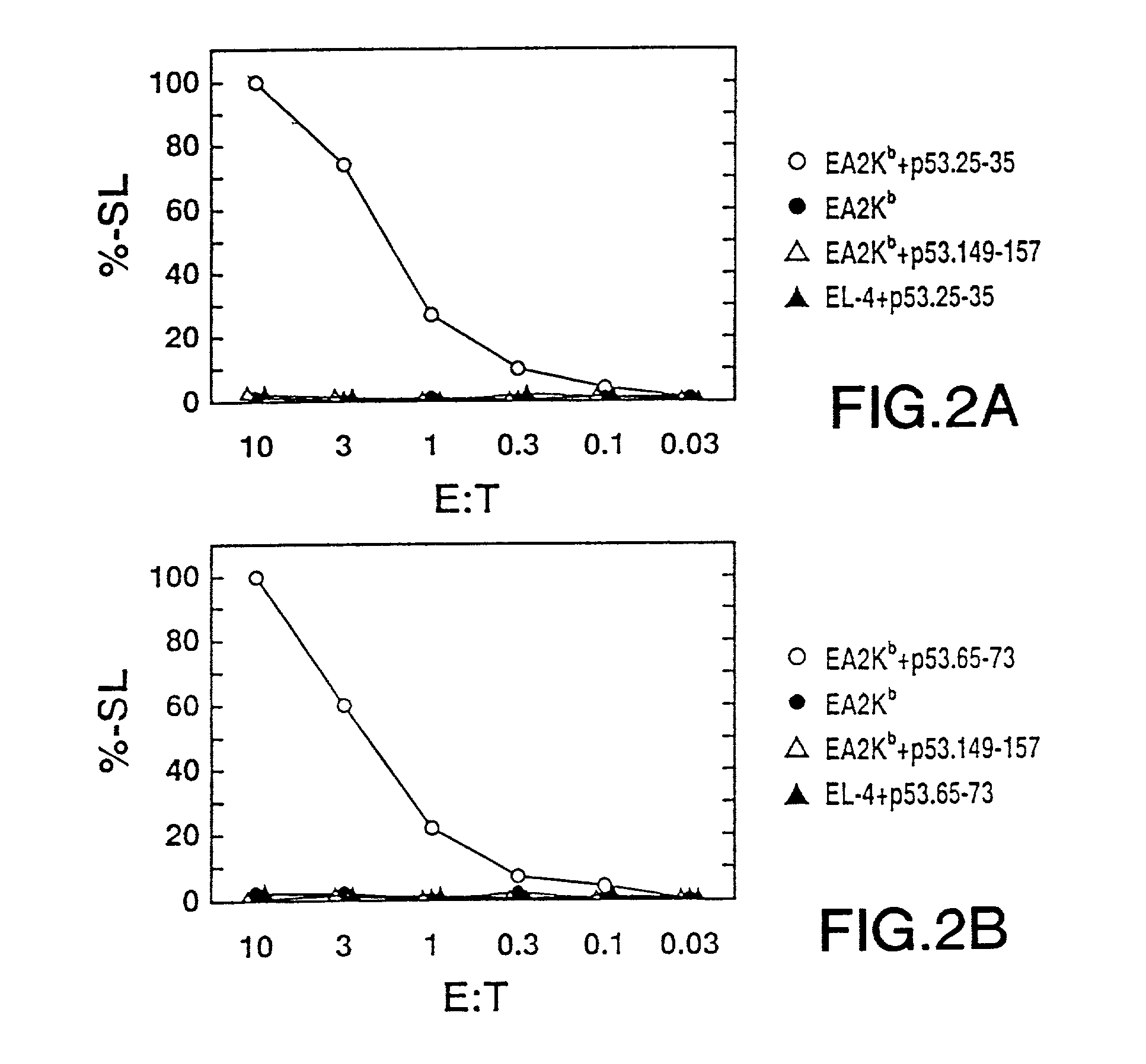
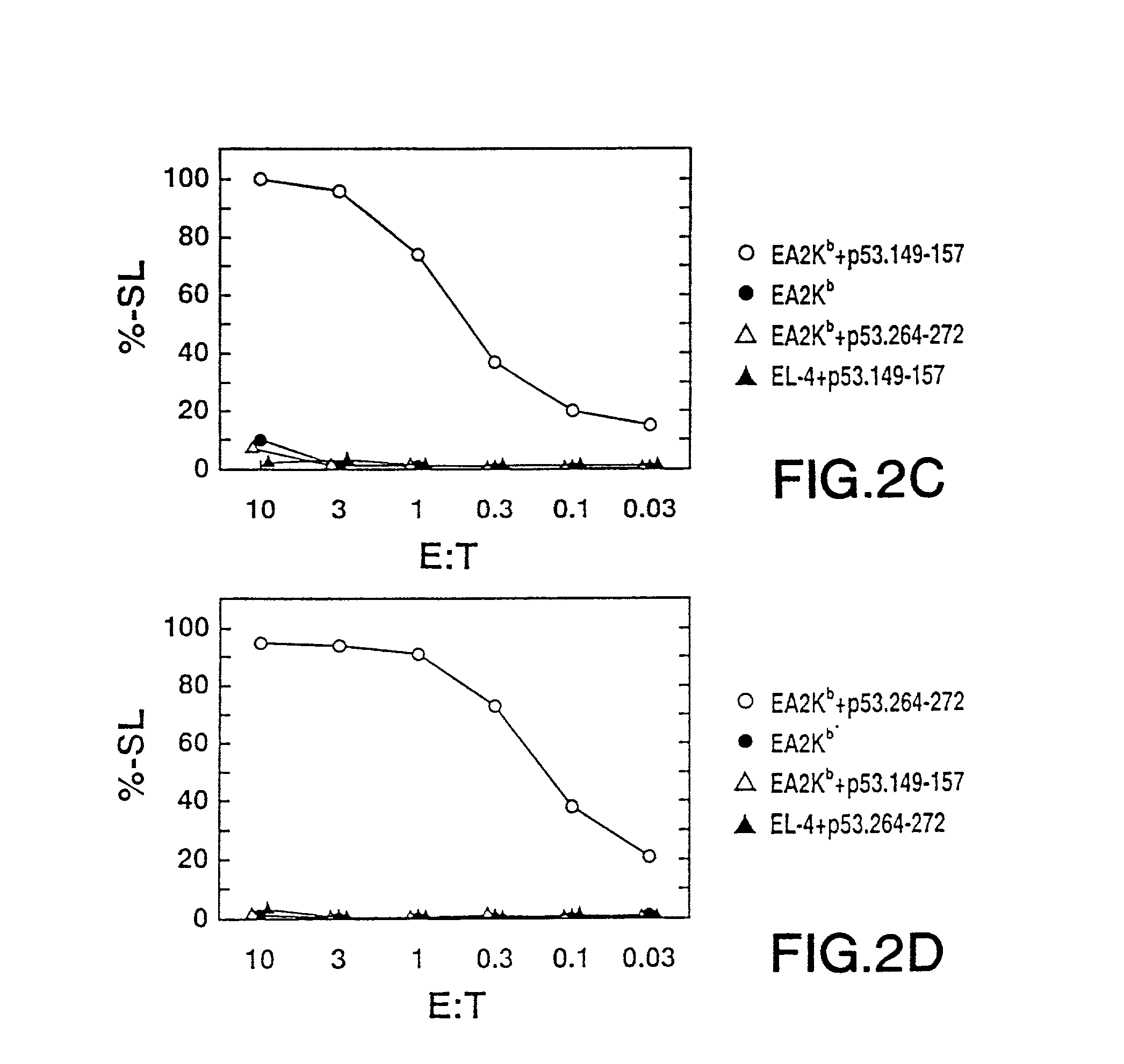
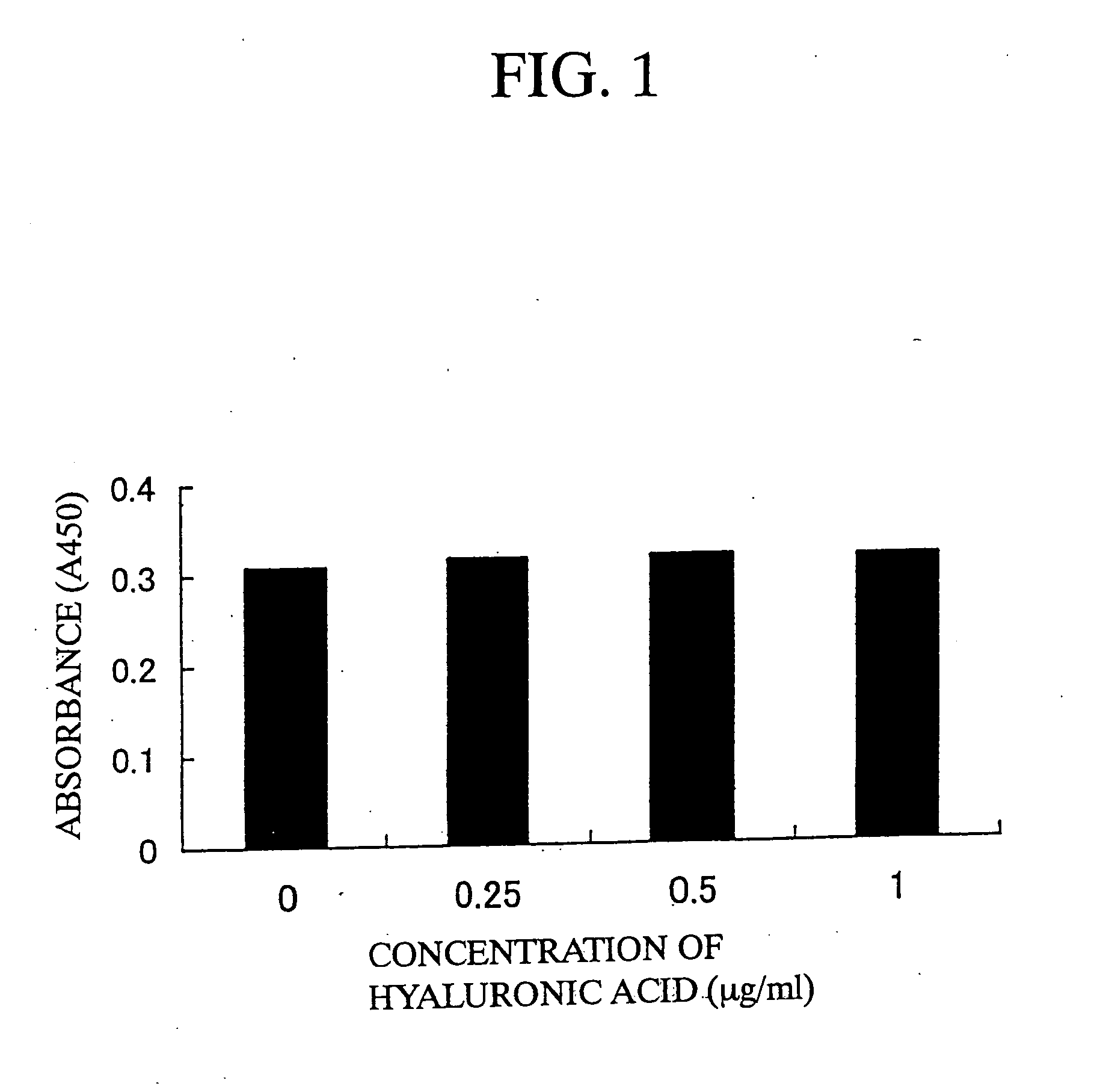
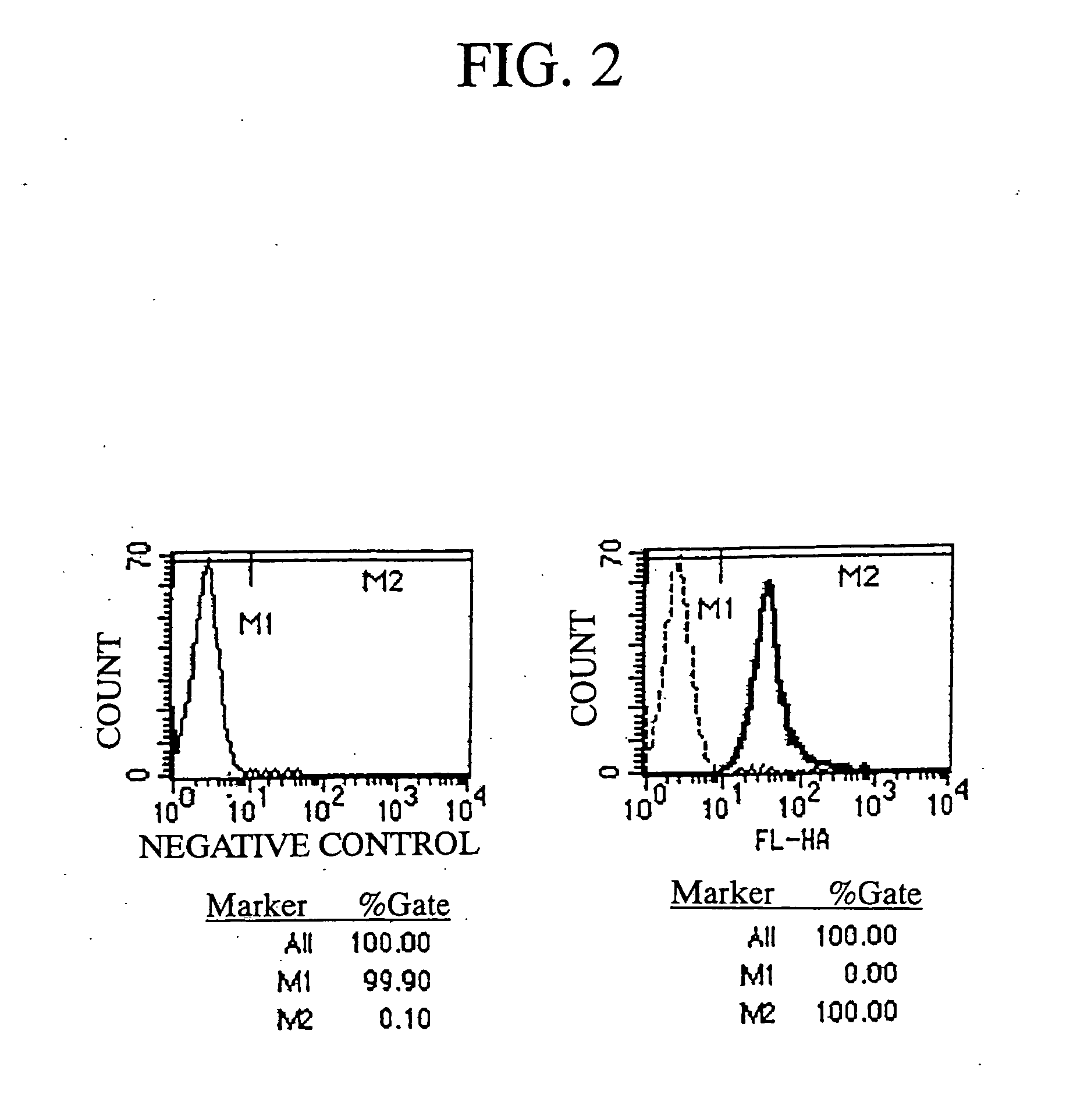
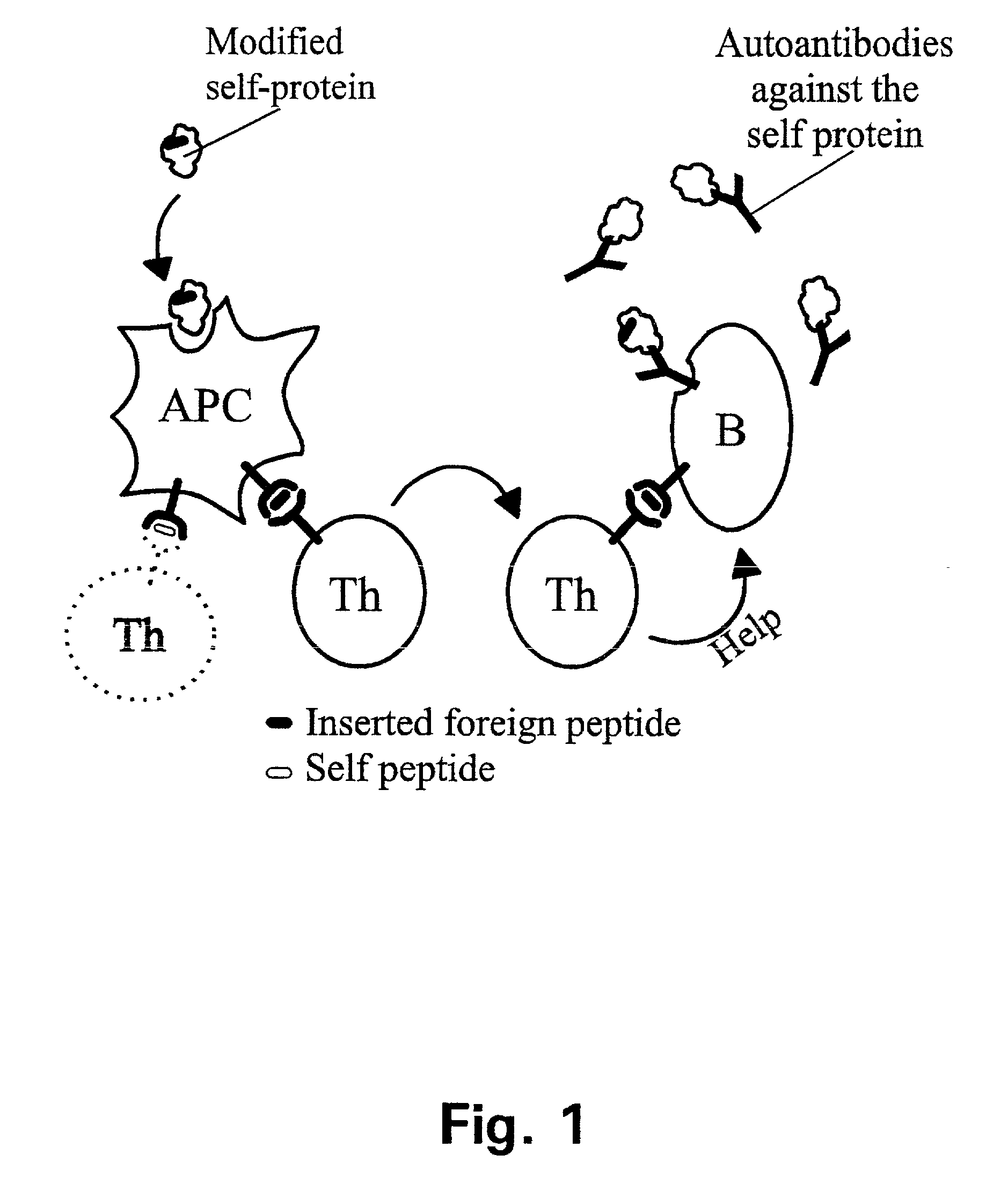
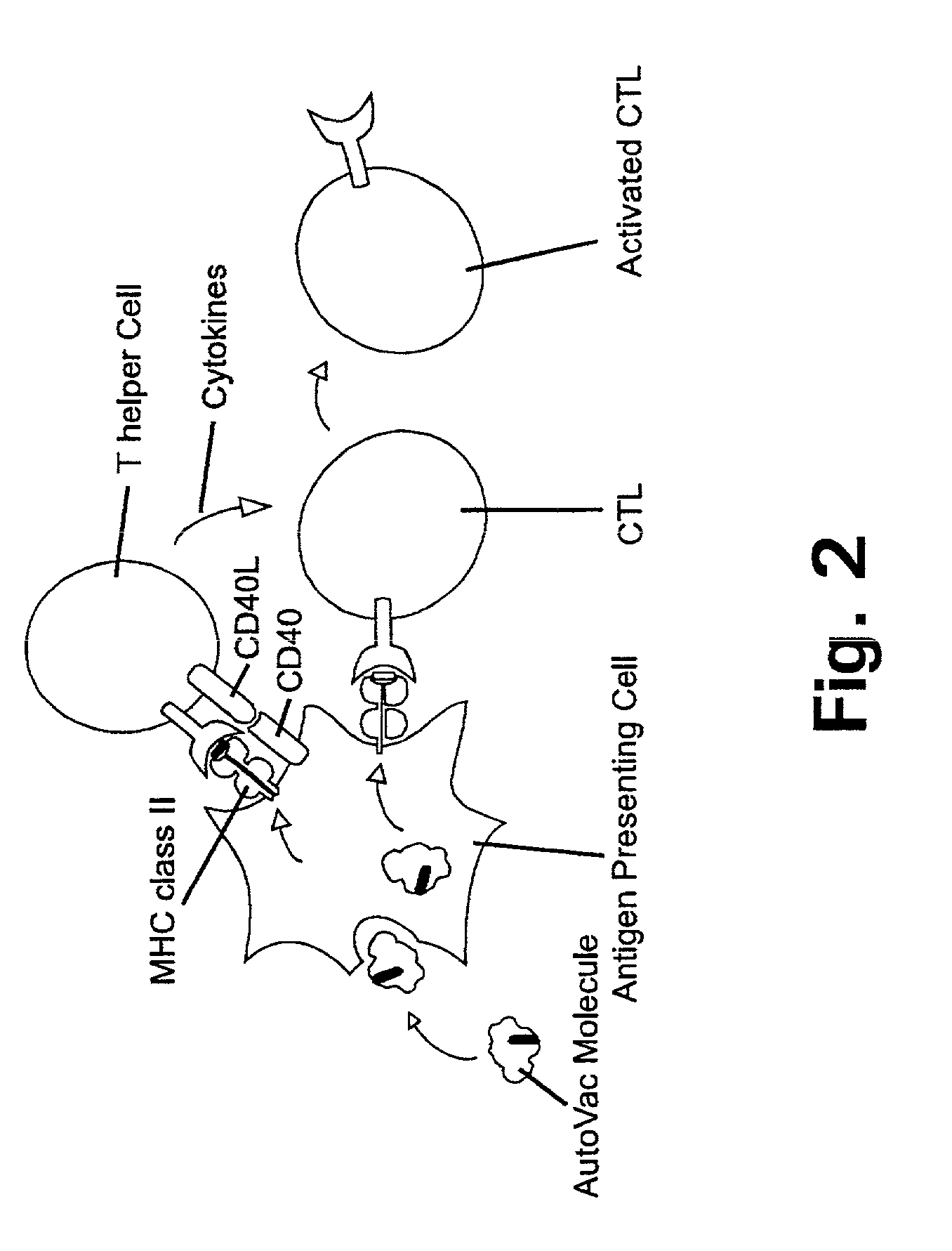
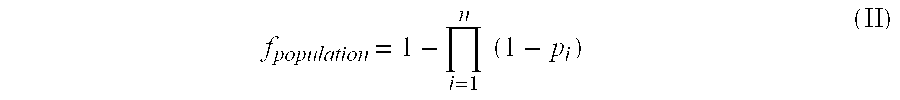Patents
Literature
327 results about "Cytotoxic T cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected (particularly with viruses), or cells that are damaged in other ways.
Constitutive expression of costimulatory ligands on adoptively transferred T lymphocytes
ActiveUS8252592B2Increase self-toleranceIncrease and reduces immune responseFused cellsFermentationRegulatory T cellLymphocyte
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Agents for Suppressing the Induction of Cytotoxic T Cells
ActiveUS20090263384A1Suppressed acute heart transplant rejectionImprove survivalSurgical drugsAntibody ingredientsHistopathology findingTransplanted heart
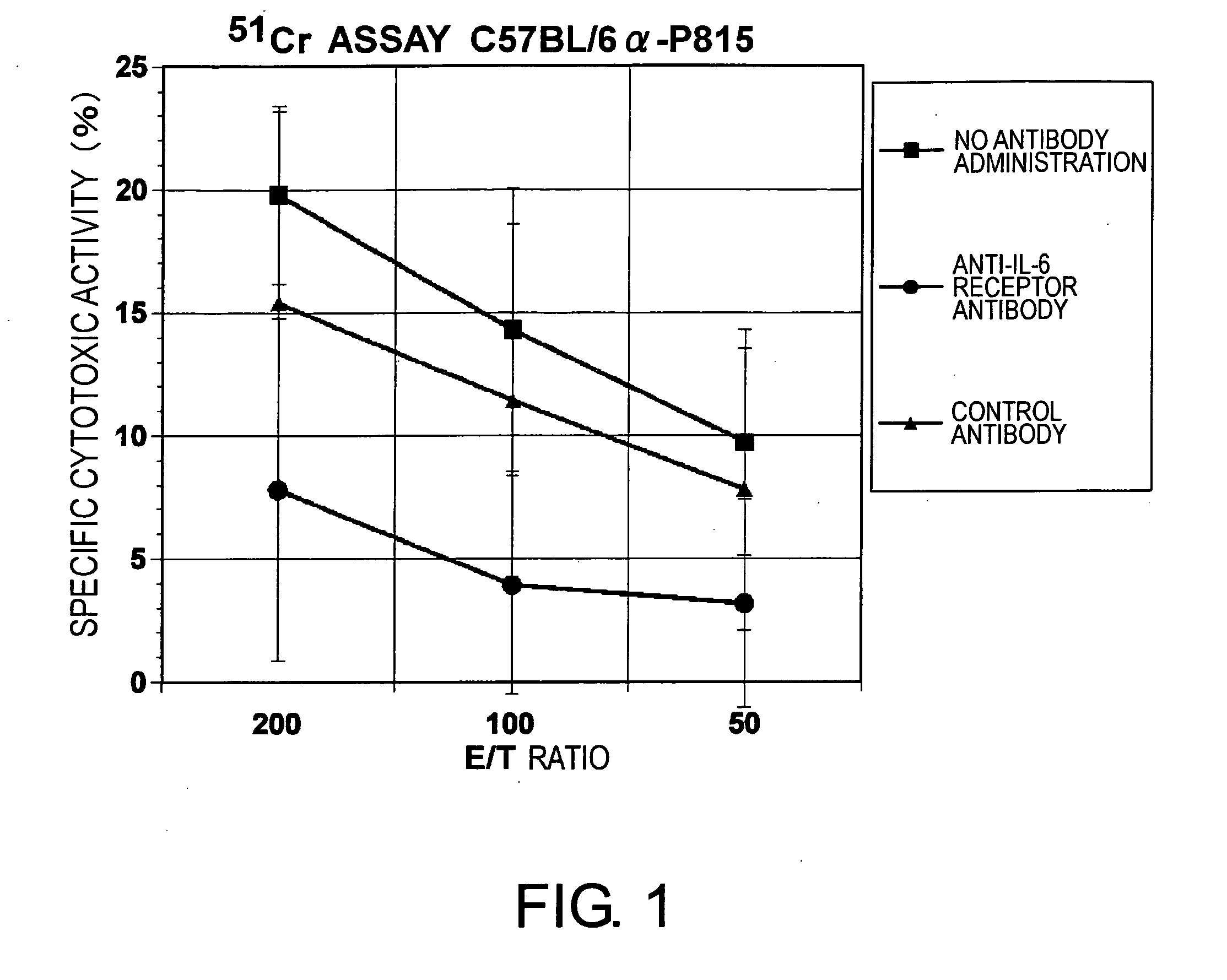
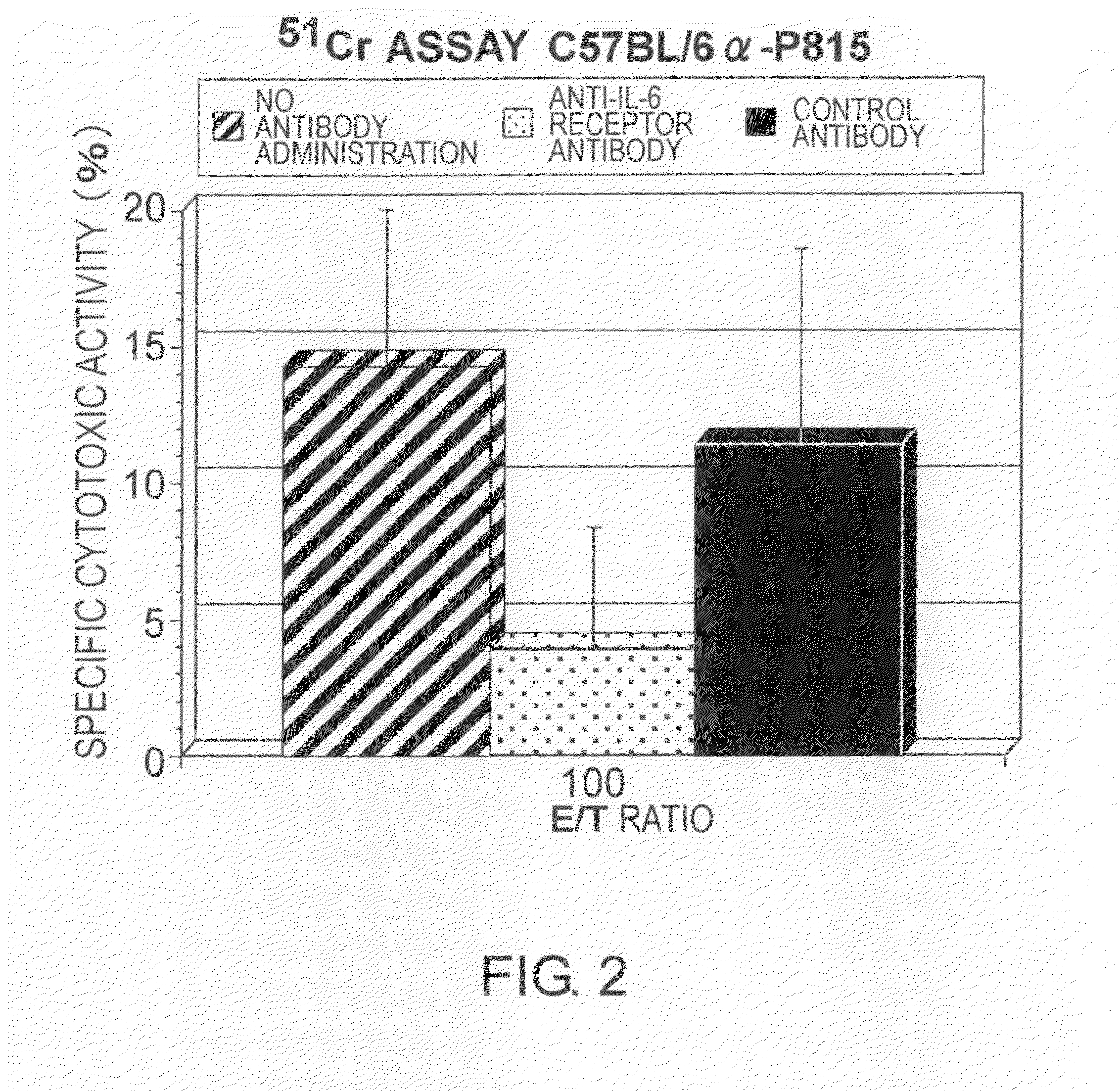
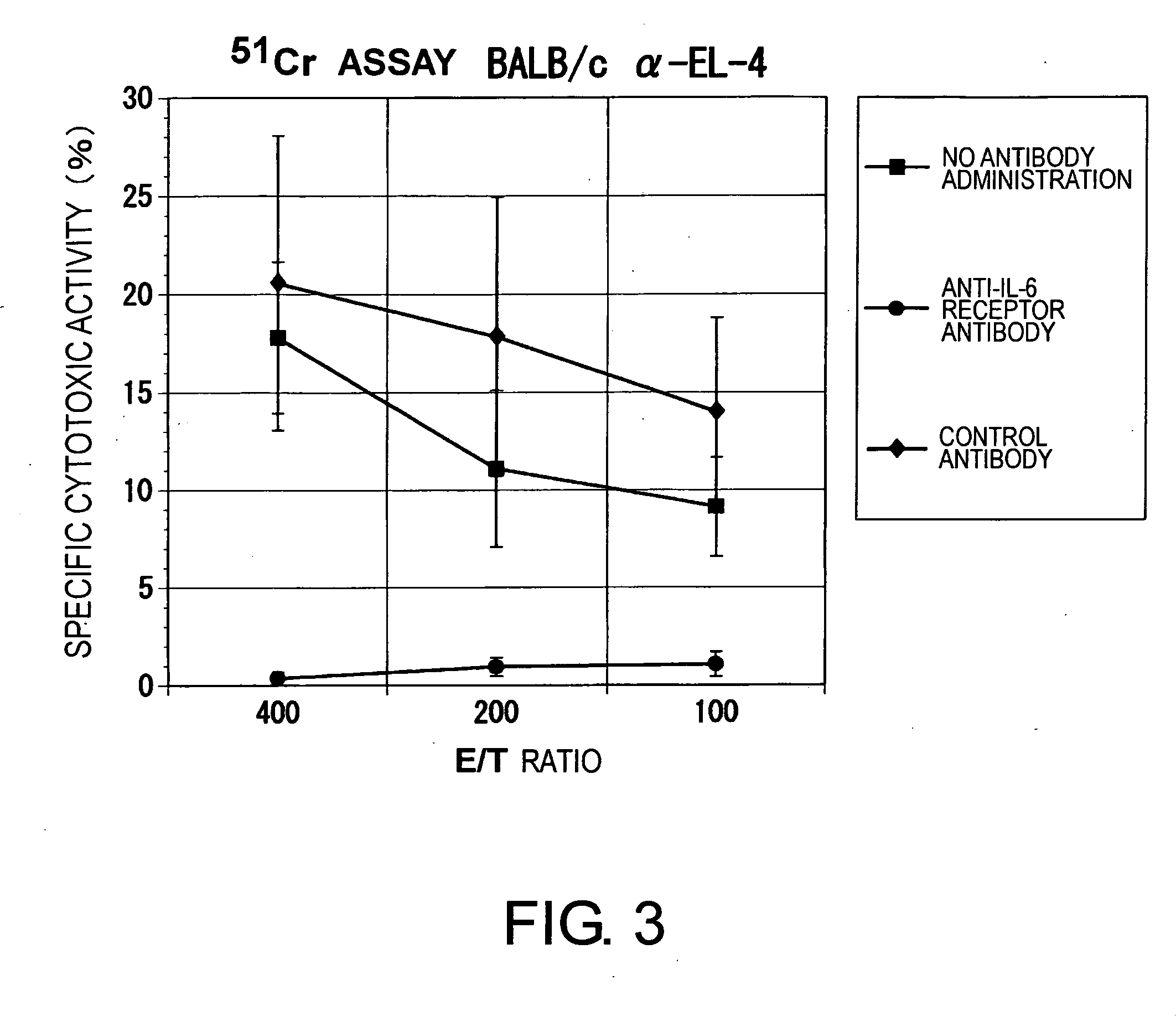
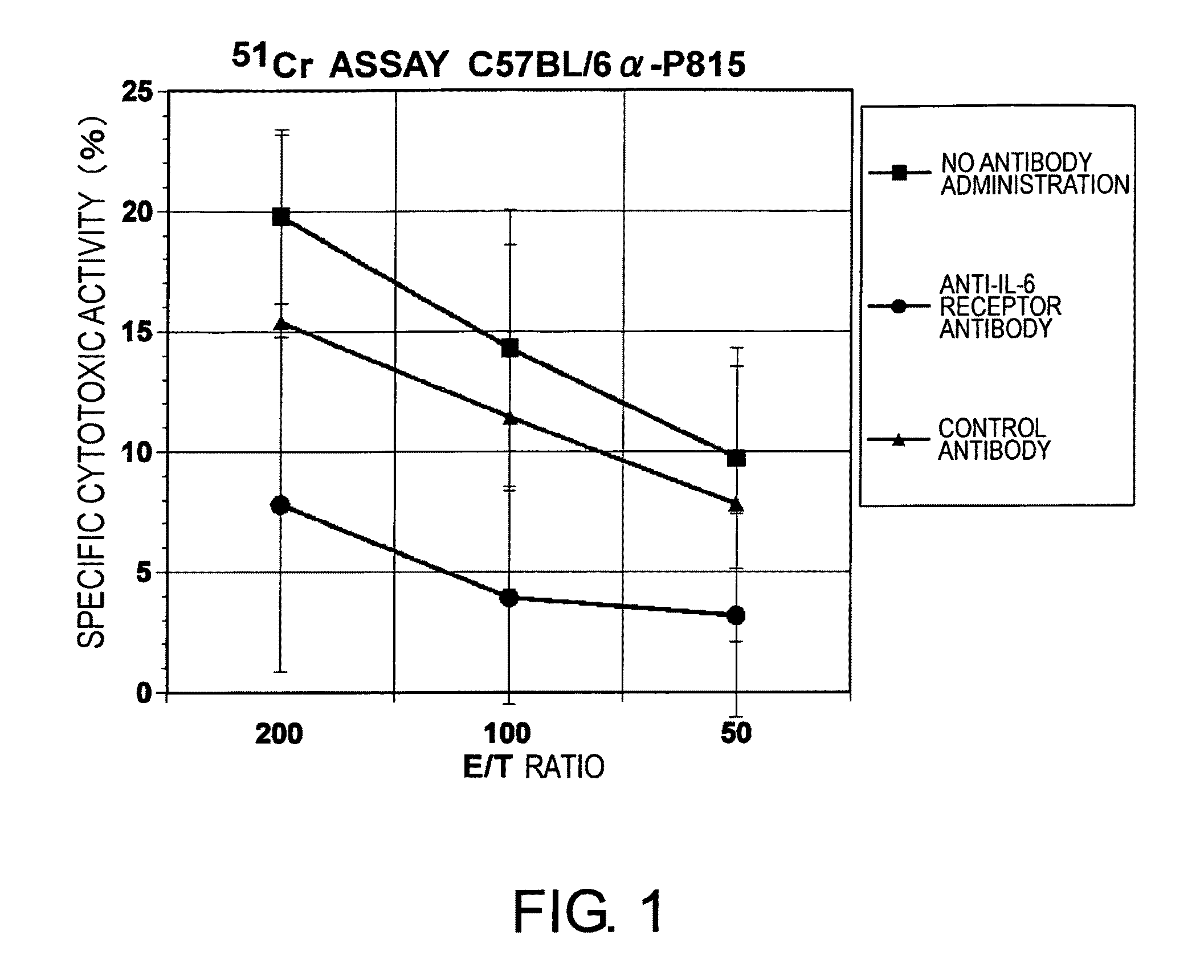
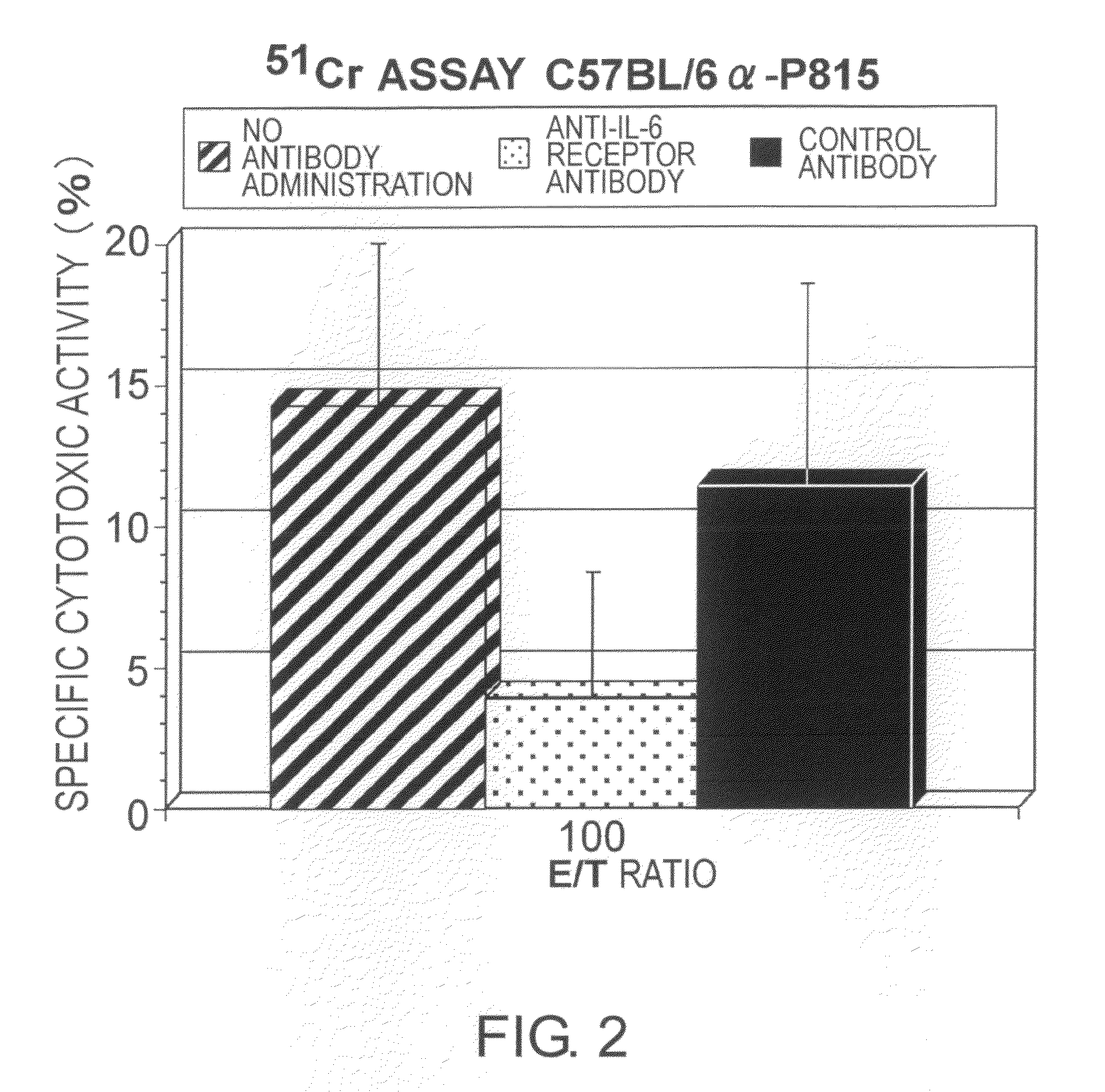
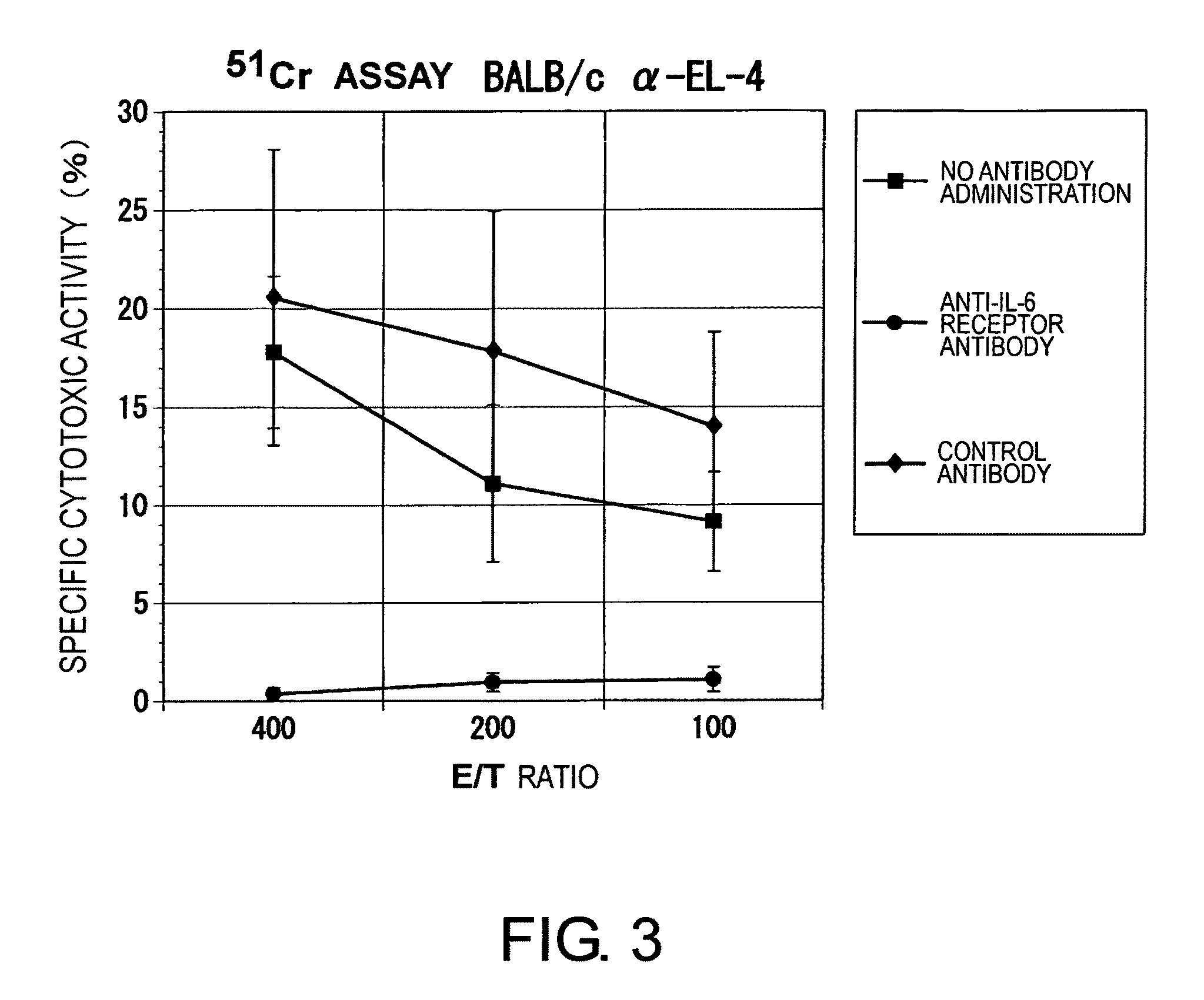
The effect of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies in suppressing cytotoxic T cell induction was examined. The results showed that CTL activity against alloantigens was statistically significantly reduced in mice treated with anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies as compared to mice not treated with antibodies and mice treated with a control antibody. The anti-IL-6 receptor antibody was also administered to recipients of a mouse model for allogenic heart transplantation. As a result, histopathological findings showed that inflammatory cell infiltration into transplanted hearts was suppressed and the survival period of transplanted hearts was significantly prolonged. Thus, the present inventors for the first time discovered that administration of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies could suppress cytotoxic T cell induction and thereby suppress acute rejection after transplantation.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +2
Detection and measurement of tissue-infiltrating lymphocytes
ActiveUS20130150252A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationDiseaseRegulatory T cell
The present invention is drawn to methods for measuring numbers, levels, and / or ratios of cells, such as lymphocytes, infiltrated into a solid tissue, such as a tumor or a tissue affected by an autoimmune disease, and to methods for making patient prognoses based on such measurements. In one aspect, methods of the invention comprise sorting lymphocytes from an accessible tissue, such as peripheral blood, into functional subsets, such as cytotoxic T cells and regulatory T cells, and generating clonotype profiles of each subset. An inaccessible disease-affected tissue is sampled and one or more clonotype profiles are generated. From the latter clonotype profiles, levels lymphocytes in each of the functional subsets are determined in the disease-affected tissue by their clonotypes, which are identified from lymphocytes sorted into subsets from the accessible tissue.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
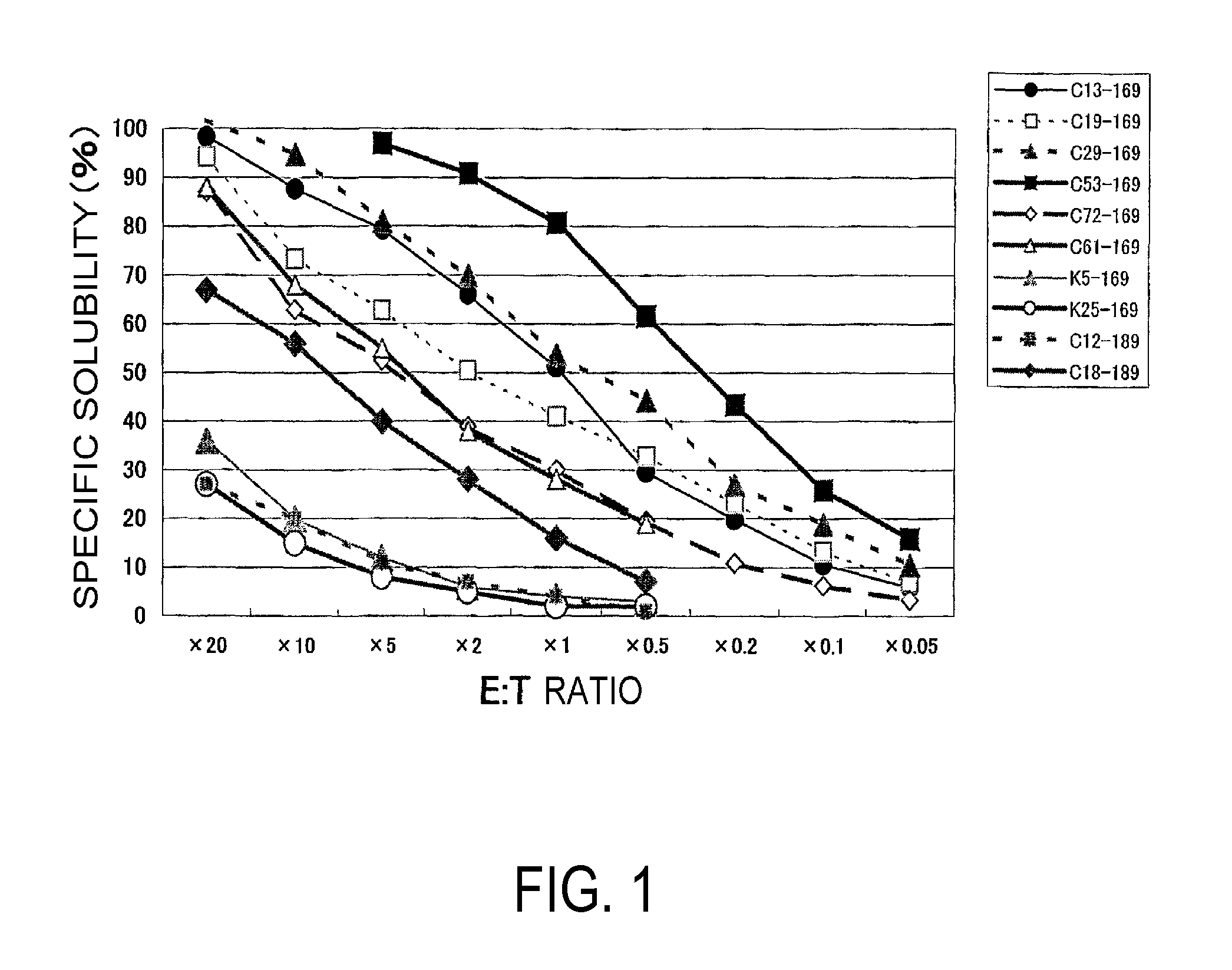
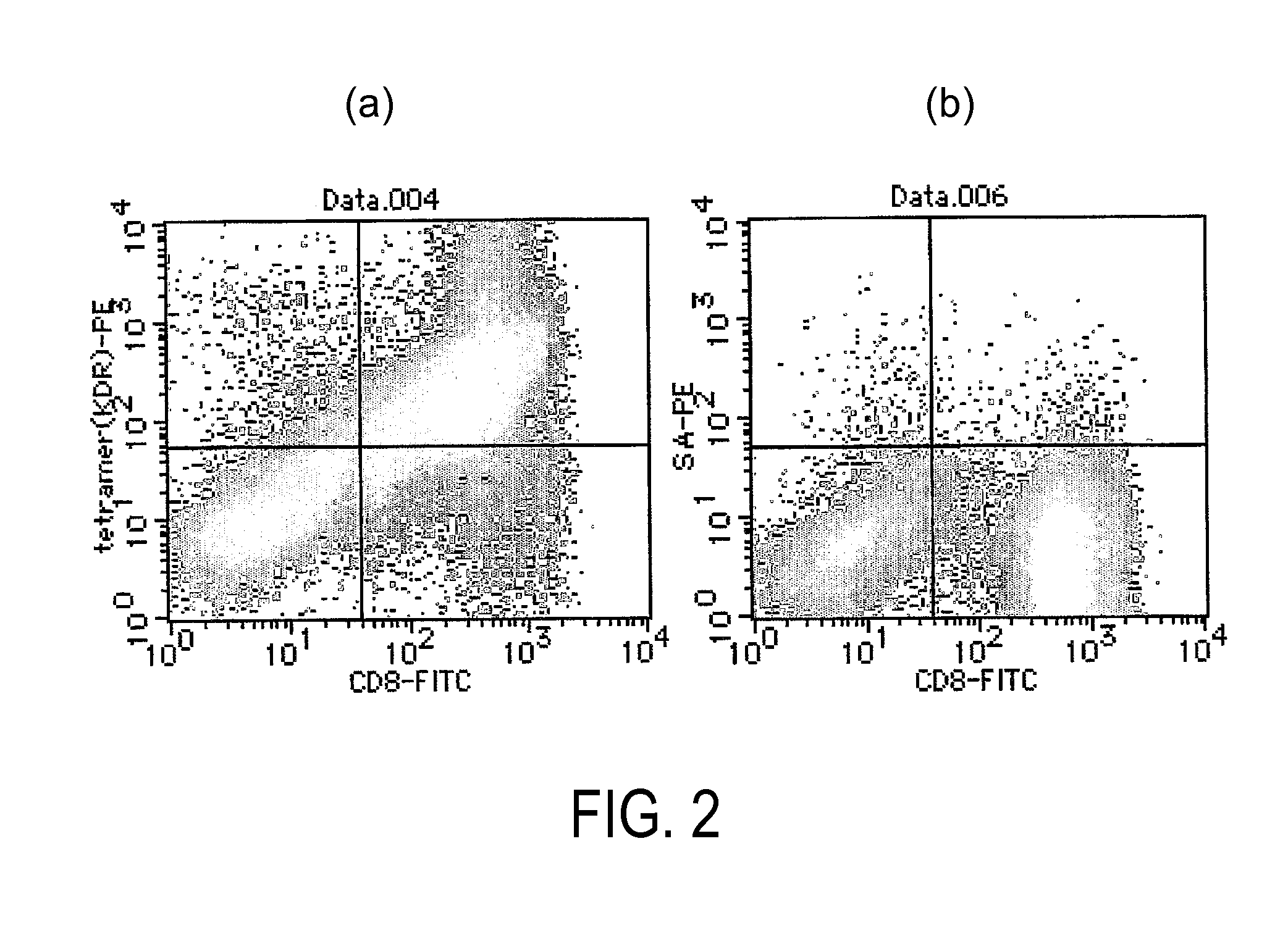
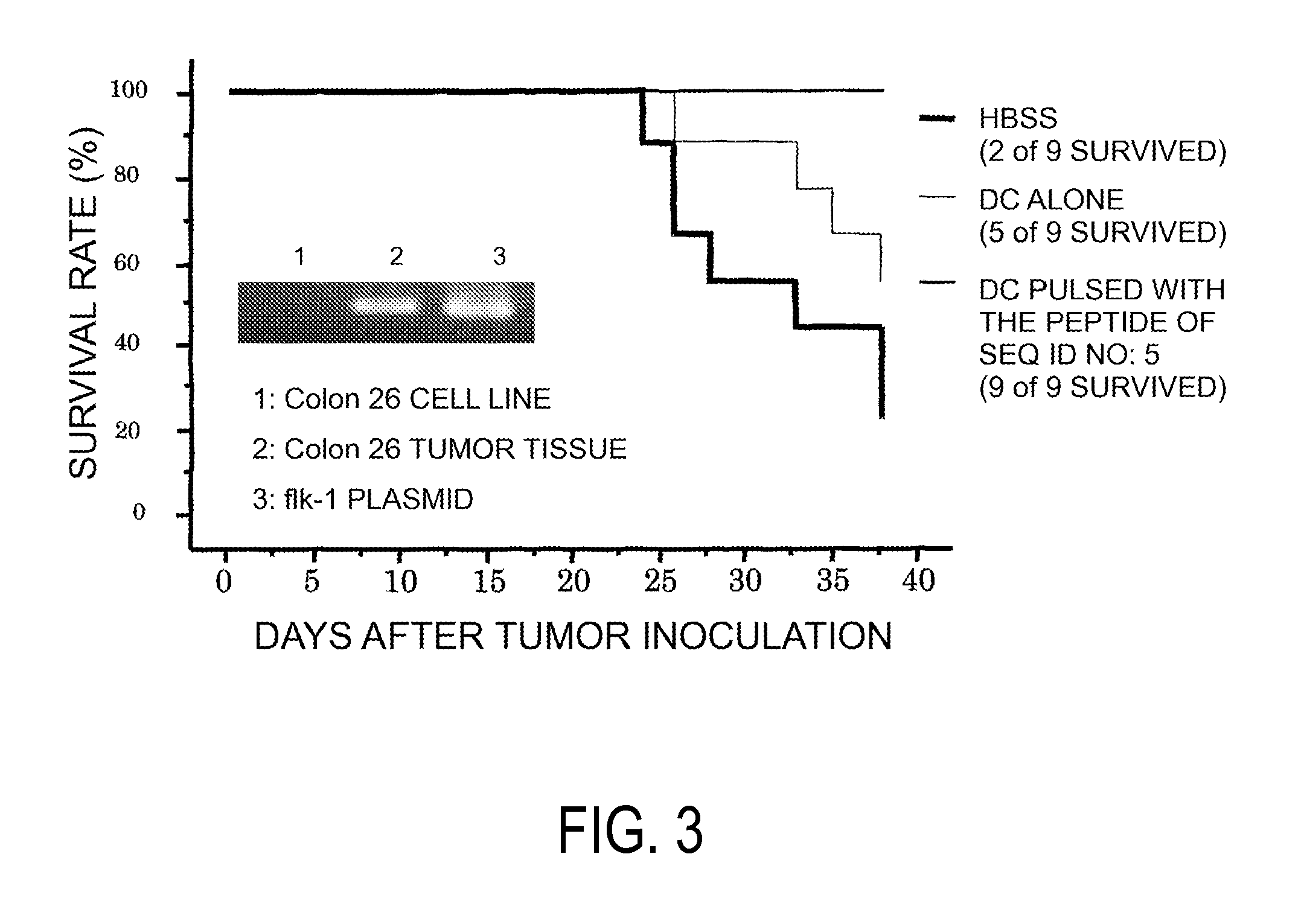
Kdr peptides and vaccines containing the same
InactiveUS20060216301A1Easy to useSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCytotoxicity
The present invention provides nonapeptides selected from peptides comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2, 3, 5, 8, 11, or 12; nonapeptides or decapeptides selected from peptides comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 29, 30, 33, 34, 40, or 46; and peptides with cytotoxic T cell inducibility, in which one, two, or several amino acids are substituted or added to the above-mentioned amino acid sequences, as well as pharmaceuticals for treating or preventing tumors, where the pharmaceuticals comprise these peptides. The peptides of this invention can be used as vaccines.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Methods of gene therapy using herpes viral vectors expressing GM-CSF
A genetically disabled mutant virus has a genome which is defective in respect of a selected gene that is essential for the production of infectious new virus particles, and which carries heterologous genetic material encoding an immunomodulatory protein such as GM-CSF, IL-2, or others, such that the mutant virus can infect normal host cells and cause expression of immunomodulatory protein, but the mutant virus cannot cause production of infectious new virus particles except when the virus infects recombinant complementing host cells expressing a gene that provides the function of the essential viral gene; the site of insertion of the heterologous genetic material encoding the immunomodulatory protein preferably being at the site of the defect in the selected essential viral gene. Uses include prophylactic and therapeutic use in generating an immune response in a subject treated therewith; use in the preparation of an immunogen such as a vaccine for use in tumor therapy; use in the in-vitro expansion of (e.g. virus-specific) cytotoxic T cells; and therapeutic or prophylactic use in corrective gene therapy.
Owner:CANTAB PHARMA RES
Antigen specific T cell therapy
Provided are methods for generating immune cells of the desired type and specificity in a host. The methods may be used to treat a disease or disorder, such as a tumor in a patient. Target cells, preferably hematopoietic stem cells such as primary bone marrow cells are transfected with a polynucleotide encoding a T cell receptor with the desired specificity. The transfected cells are then transferred to the host where they develop into mature, functional immune cells. The source of the T cell receptor can determine the stem cell's fate. Thus transfecting stem cells with TCRs from cytotoxic cells will lead to the generation of cytotoxic T cells in the host, while TCRs from helper cells will produce helper cells. Both arms of T cell immunity can be generated simultaneously in a host. Additionally, the immune response to the desired antigen can be further stimulated by immunizing the host with the antigen.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide
The invention is a prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide which comprises more than one PSA epitope peptide, which conforms to one or more human HLA class I motifs. The prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide in combination with various HLA-class I molecules or interactions with various T-cell receptors elicits PSA specific cellular immune responses. The prostate specific antigen oligo-epitope peptide is useful as an immunogen in the prevention or treatment of prostatic cancer, in the inhibition of prostatic cancer cells and in the establishment and characterization of PSA-specific cytotoxic T-cell lines.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
Compositions and methods for immunotherapy
ActiveUS20150376296A1Decrease in immune activityReduces and eliminates immune activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMuscular disorderRegulatory T cellChimeric antigen receptor
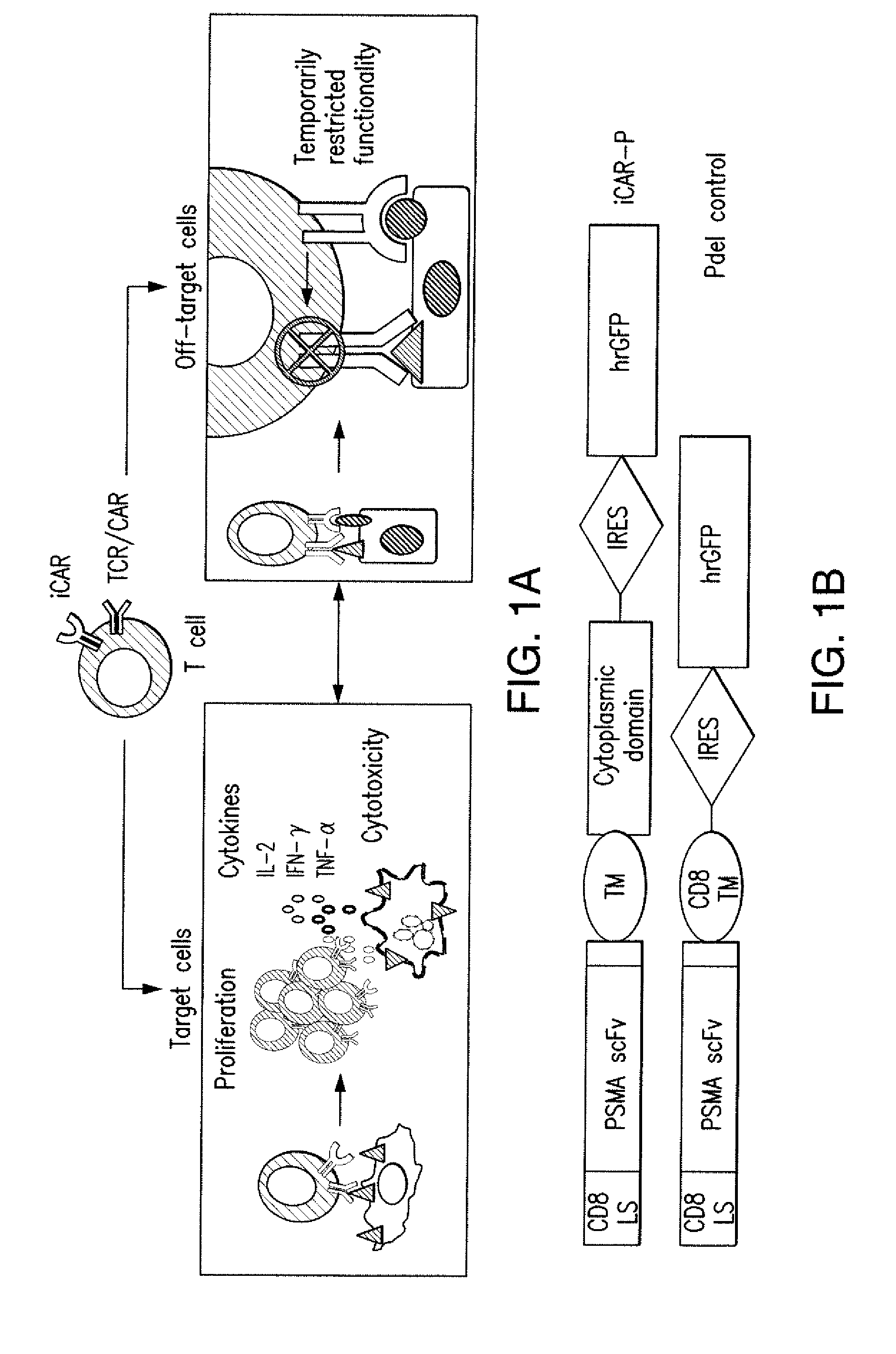
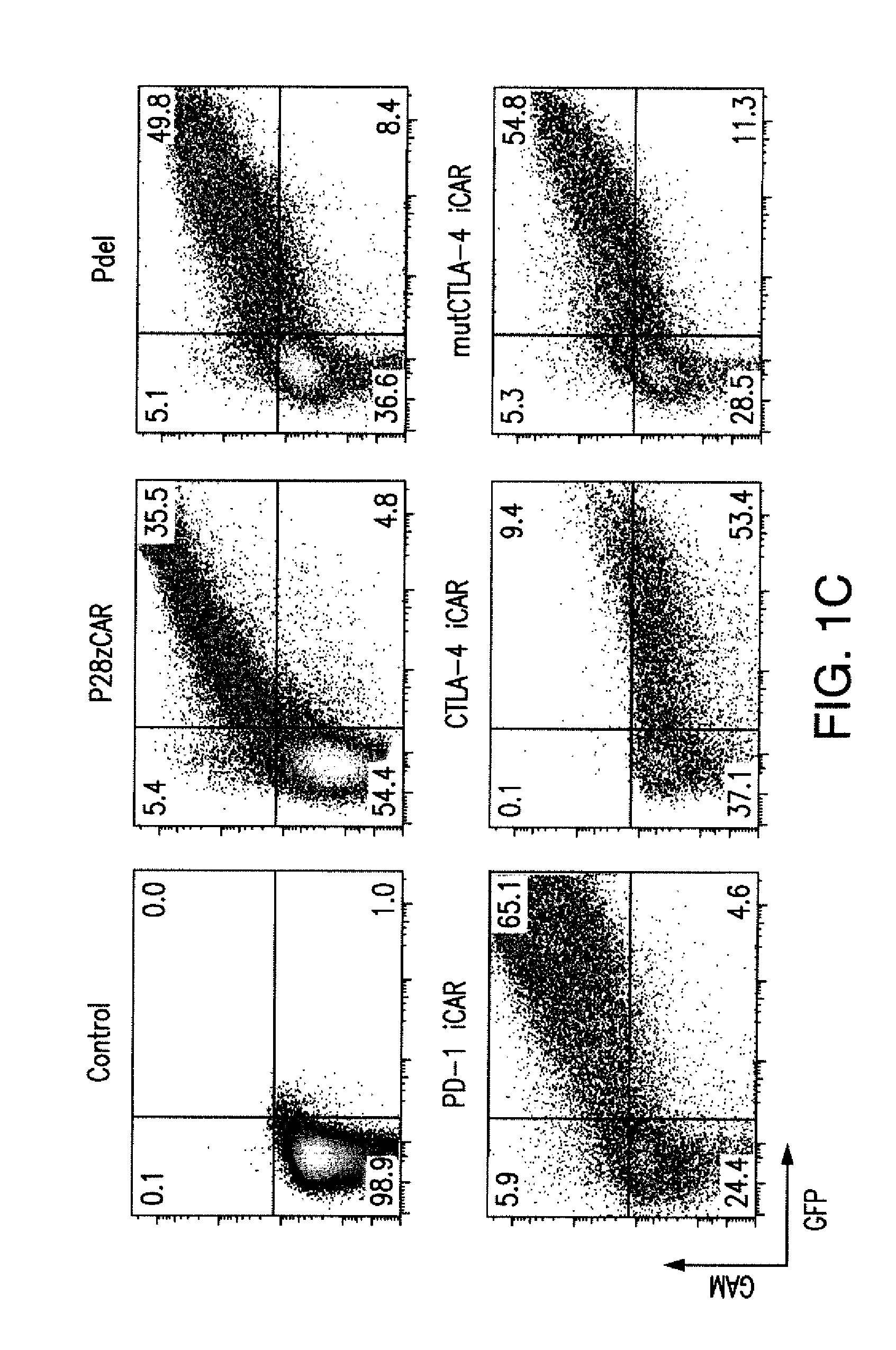
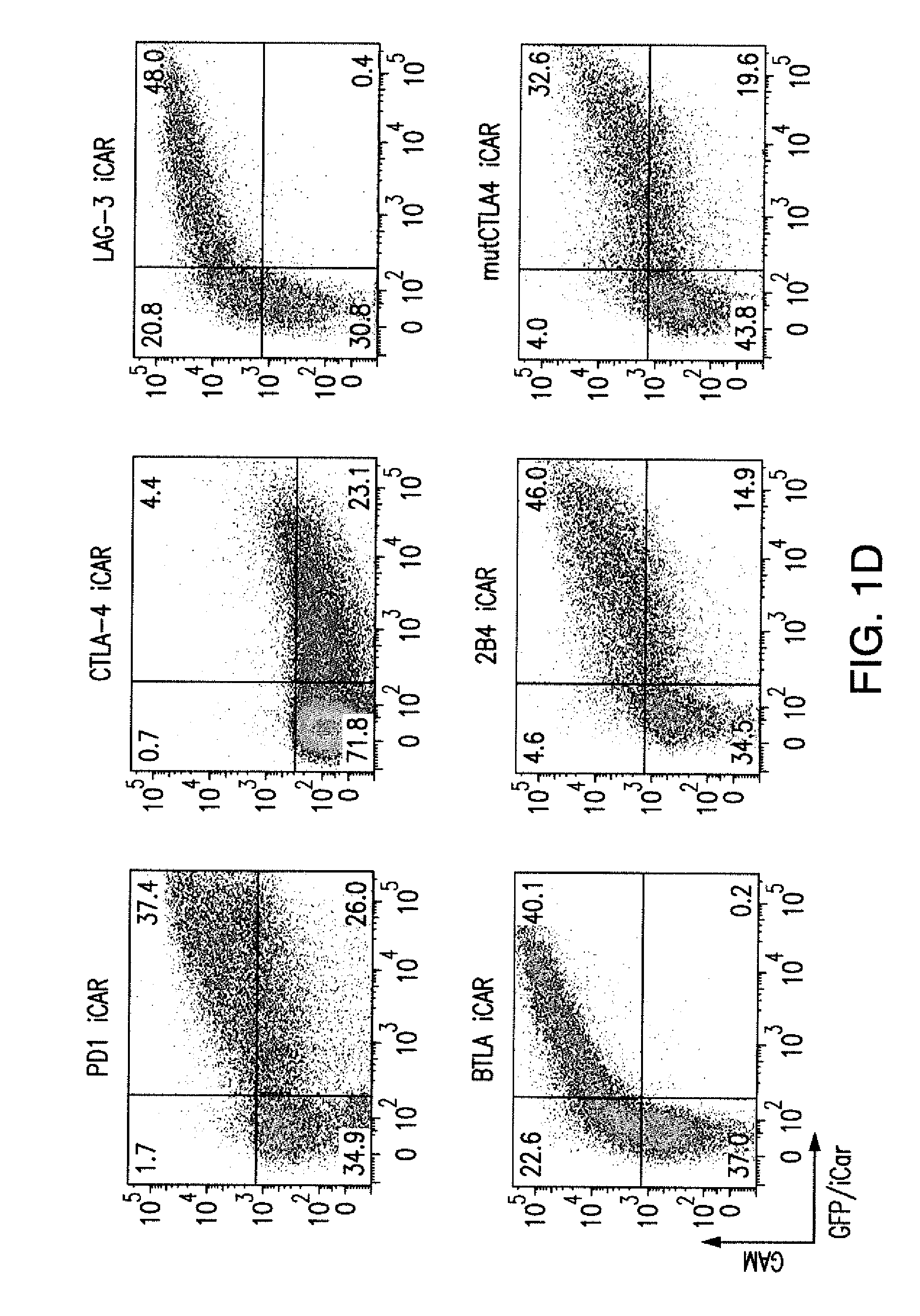
The present invention provides immunoresponsive cells, including T cells, cytotoxic T cells, regulatory T cells, and Natural Killer (NK) cells, expressing an antigen recognizing receptor and an inhibitory chimeric antigen receptor (iCAR). Methods of using the immunoresponsive cell include those for the treatment of neoplasia and other pathologies where an increase in an antigen-specific immune response is desired.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Compositions and methods for immunotherapy
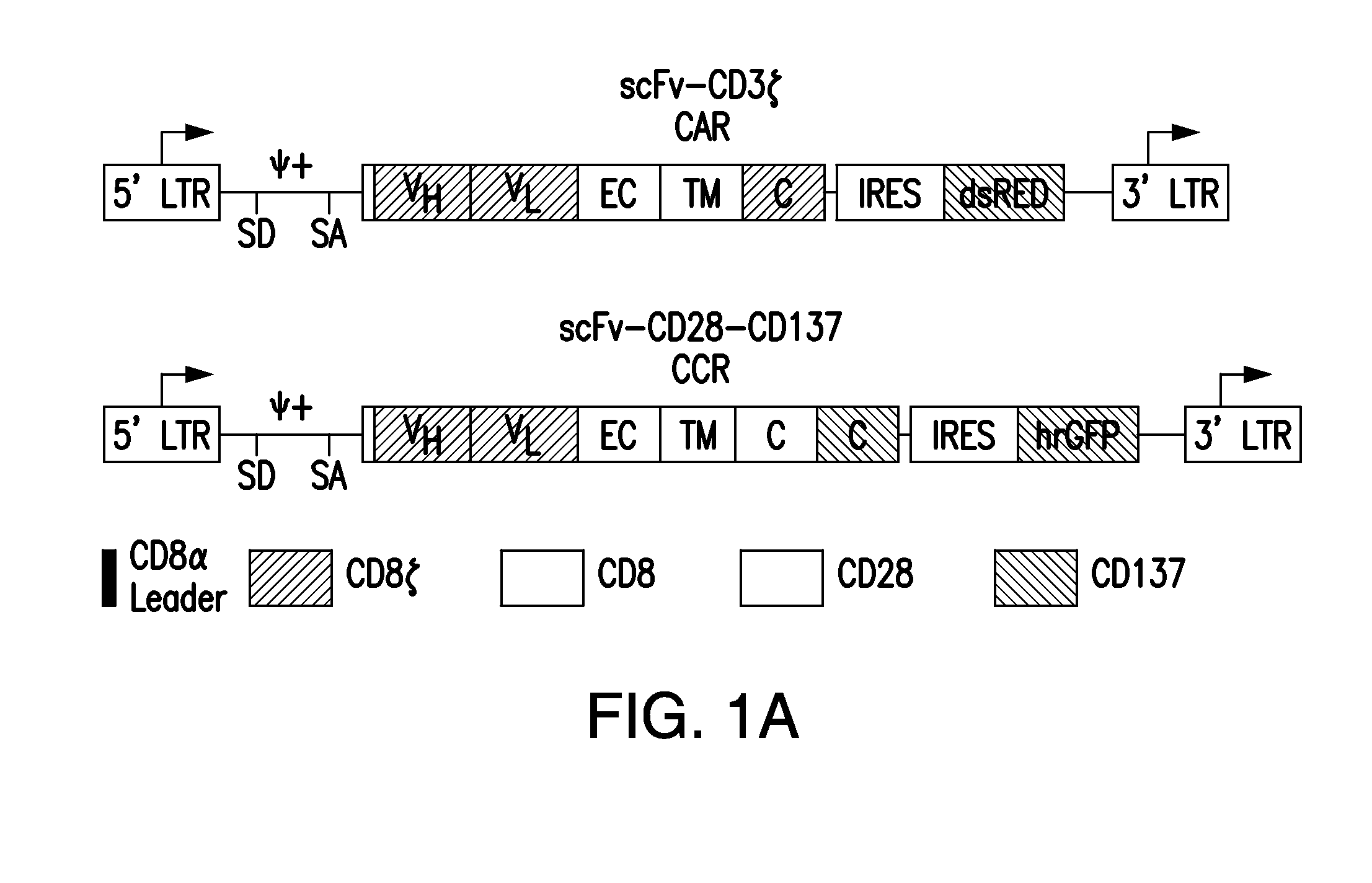
ActiveUS20150342993A1Decrease number of tumorShrink tumorAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRegulatory T cellT cell
The present invention provides immunoresponsive cells, including T cells, cytotoxic T cells, regulatory T cells, and Natural Killer (NK) cells, expressing at least one of an antigen recognizing receptor and one of a chimeric costimulatory receptor. Methods of using the immunoresponsive cell include those for the treatment of neoplasia and other pathologies where an increase in an antigen-specific immune response is desired.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Novel human cytomegalovirus (hcmv) cytotoxic t cell epitopes, polyepitopes compositions comprising same and diagnostic and prophylactic and therapeutic uses therefor
InactiveUS20050019344A1Minimizing formulation difficultyReduce in quantityViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCtl epitopeVaccination
The present invention provides CTL epitope peptides and polyepitope peptides from 14 distinct antigens of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) that are restricted through HLA the most commonly prevalent class I alleles in different ethnic populations of the world. These epitopes provide an important platform for CTL epitope-based vaccines against HCMV. The present invention further provides vaccine composiitons comprising the subject epitope and polyepitope peptides and methods for vaccination of humans and for the adoptive transfer of HCMV-specific T cells to human subjects. The present invention further provides reagents and methods for determining the HCMV status or level of HCMV-specific immunity of a subject.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
Novel immunotherapy against several tumors of the blood, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
The present invention relates to peptides, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated cytotoxic T cell (CTL) peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses. The present invention relates to several novel peptide sequences and their variants derived from HLA class I and HLA class II molecules of human tumor cells that can be used in vaccine compositions for eliciting anti-tumor immune responses.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Methods for enhancing anti-tumor antibody therapy
InactiveUS9005619B2Improve anti-tumor effectEnhances target cell killingBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCell Surface AntigensAgonist
Methods of enhancing the efficacy of antibody-directed cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) for therapy directed to killing of tumor cells are disclosed. Cancer specific cell surface antigens are bound by monoclonal antibodies, thereby stimulating a cytotoxic T cell response characterized by an upregulation of cell surface expression of costimulatory molecules on the T cell. The ADCC response is augmented by the subsequent administration of a second antibody that is an agonist of the costimulatory molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for suppressing acute rejection of a heart transplant
ActiveUS8623355B2Improve survivalSuppression of rejectionSurgical drugsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHistopathology findingT cell
The effect of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies in suppressing cytotoxic T cell induction was examined. The results showed that CTL activity against alloantigens was statistically significantly reduced in mice treated with anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies as compared to mice not treated with antibodies and mice treated with a control antibody. The anti-IL-6 receptor antibody was also administered to recipients of a mouse model for allogenic heart transplantation. As a result, histopathological findings showed that inflammatory cell infiltration into transplanted hearts was suppressed and the survival period of transplanted hearts was significantly prolonged. Thus, the present inventors for the first time discovered that administration of anti-IL-6 receptor antibodies could suppress cytotoxic T cell induction and thereby suppress acute rejection after transplantation.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +2
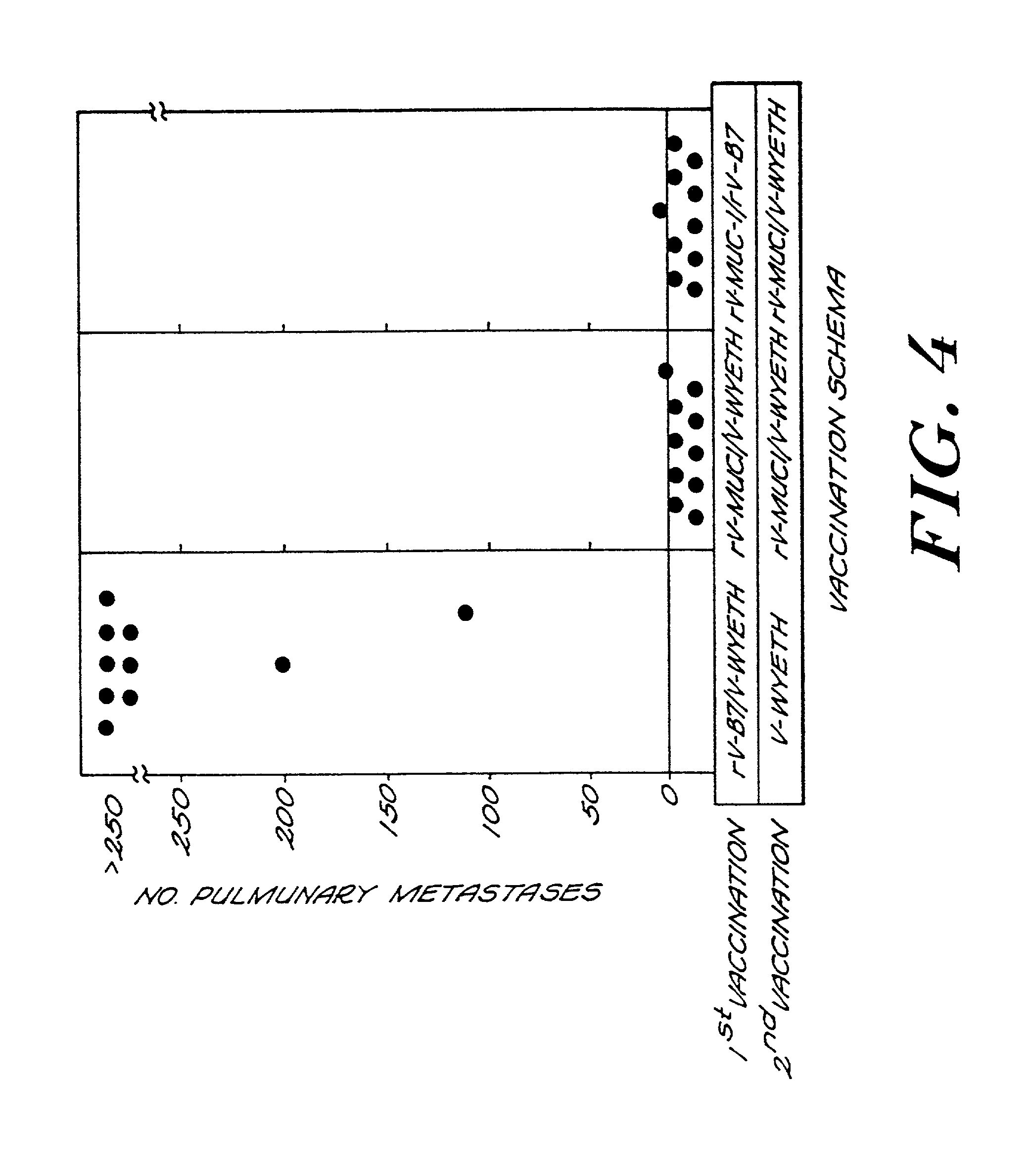
Recombinant pox virus for immunization against MUC1 tumor-associated antigen
Recombinant pox viruses capable of expressing an immunogenic fragment of the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen are disclosed. The recombinant viruses can be used as vaccines to prevent the establishment of or treat tumors or pre-tumorous cells expressing the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen. The vaccines can be provided as an admixture comprising: (1) a recombinant pox virus encoding the immunogenic fragment of the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen, and (2) a recombinant pox virus encoding a T-cell co-stimulatory factor. The vaccine admixture can be used, e.g., to prevent establishment of tumors or pre-tumorous cells expressing the MUC1 tumor-associated antigen. The MUC1 specific cytotoxic T-cells can be isolated and expanded and used in a method for treating a host having a tumor expressing MCU1 positive tumor cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
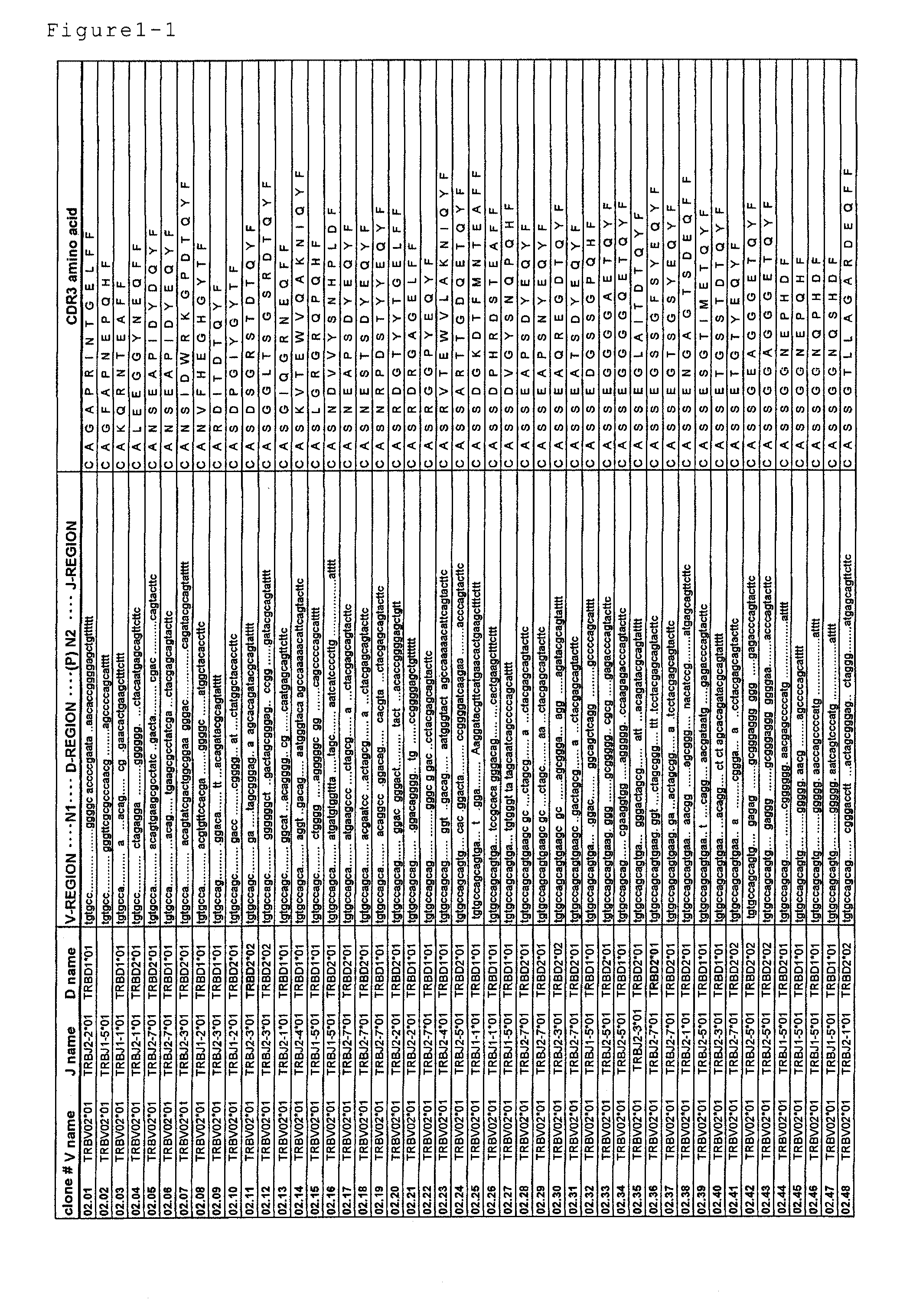
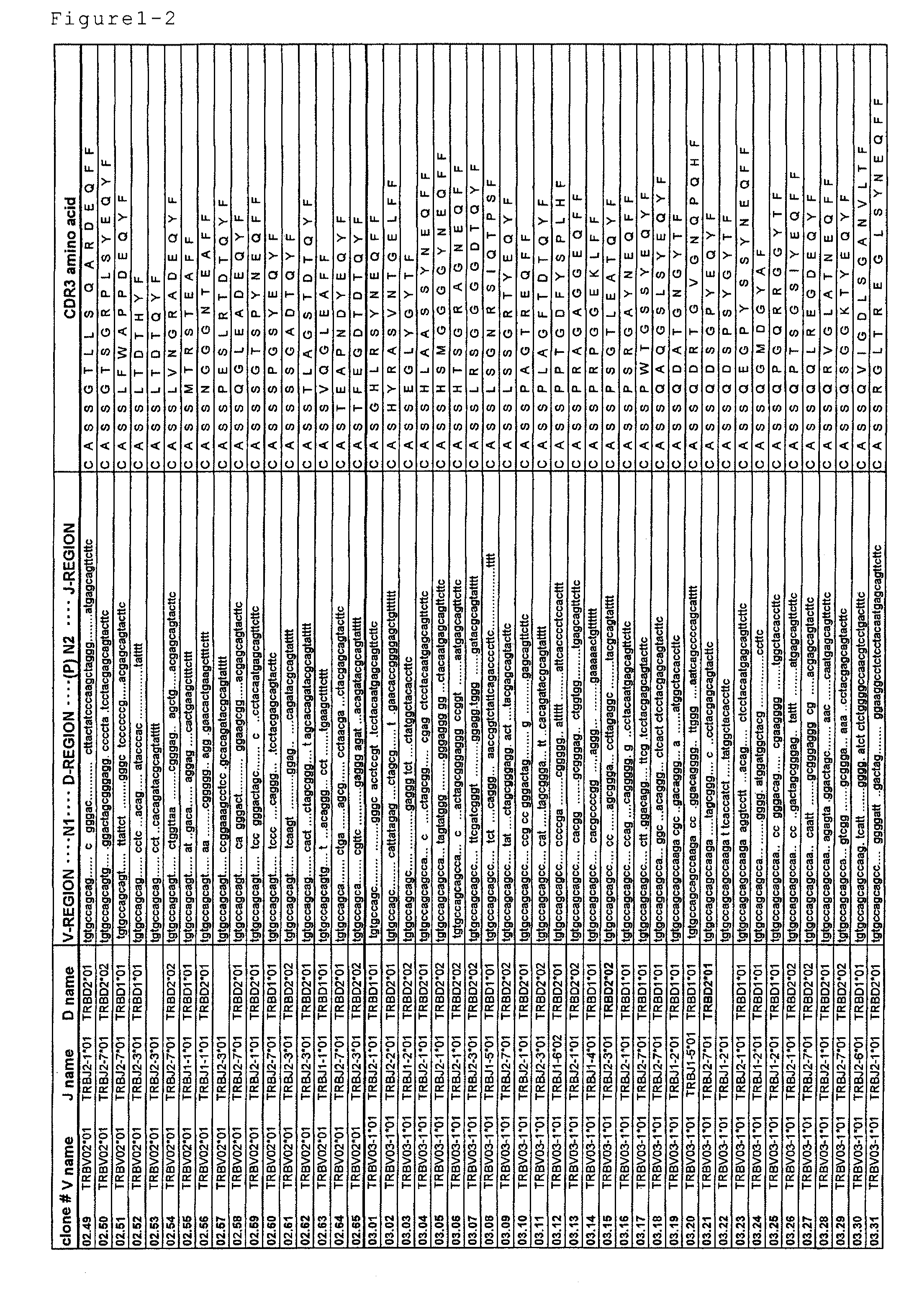
Cancer antigen-specific t-cell receptor gene, peptide encoded by the gene, and use of them
InactiveUS20100190163A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenNucleotide
Disclosed are: a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence for CDR3 region of T-cell receptor (TCR) gene of WT1-specific cytotoxic T-cell (CTL) for WT1 protein; a method for the detection or treatment of cancer using the nucleotide sequence or the amino acid sequence; and a chip, a primer set, a kit, an apparatus and the like for use in the detection of cancer, each of which comprises the nucleotide sequence or the amino acid sequence.
Owner:INT INST OF CANCER IMMUNOLOGY INC
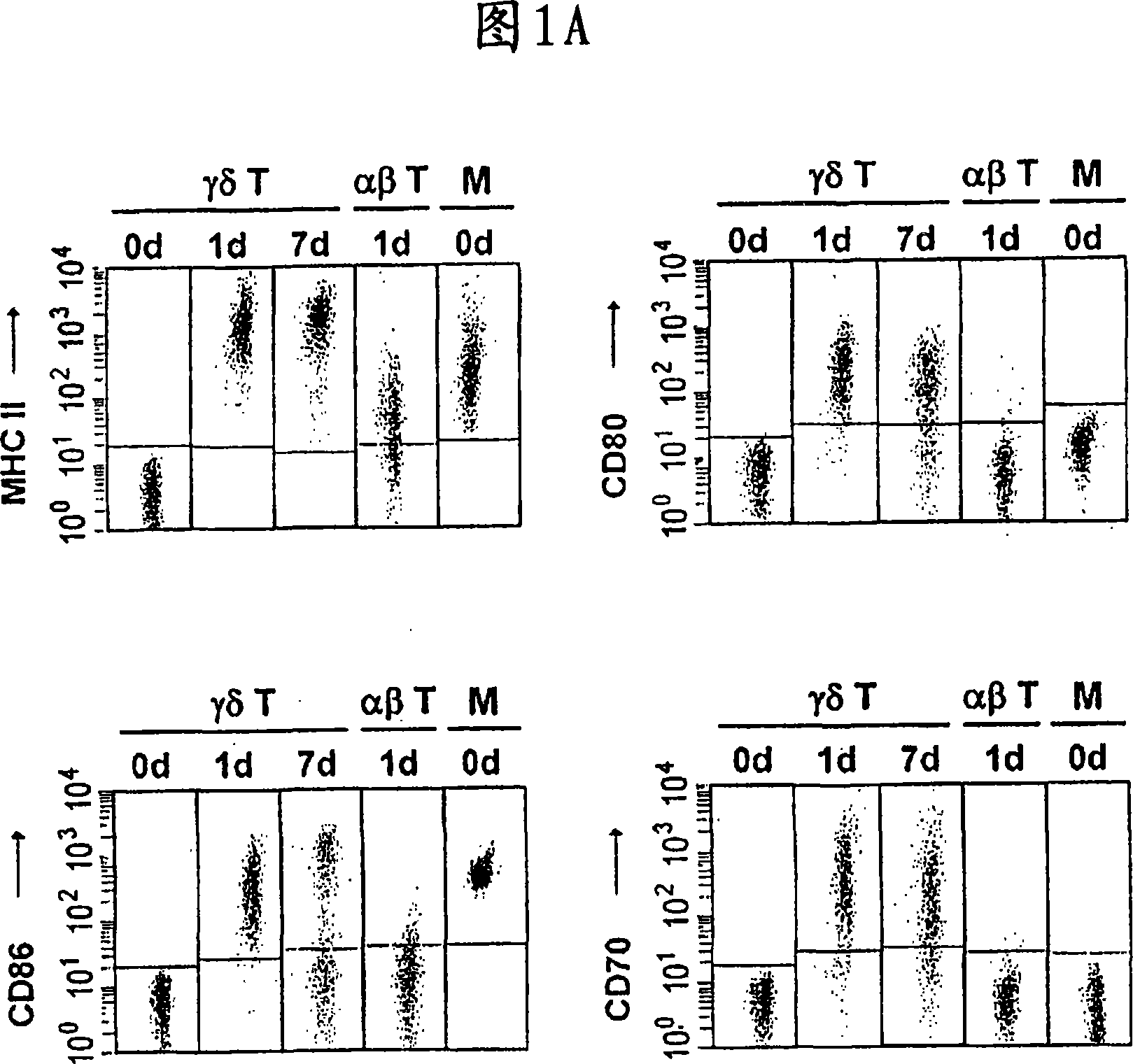
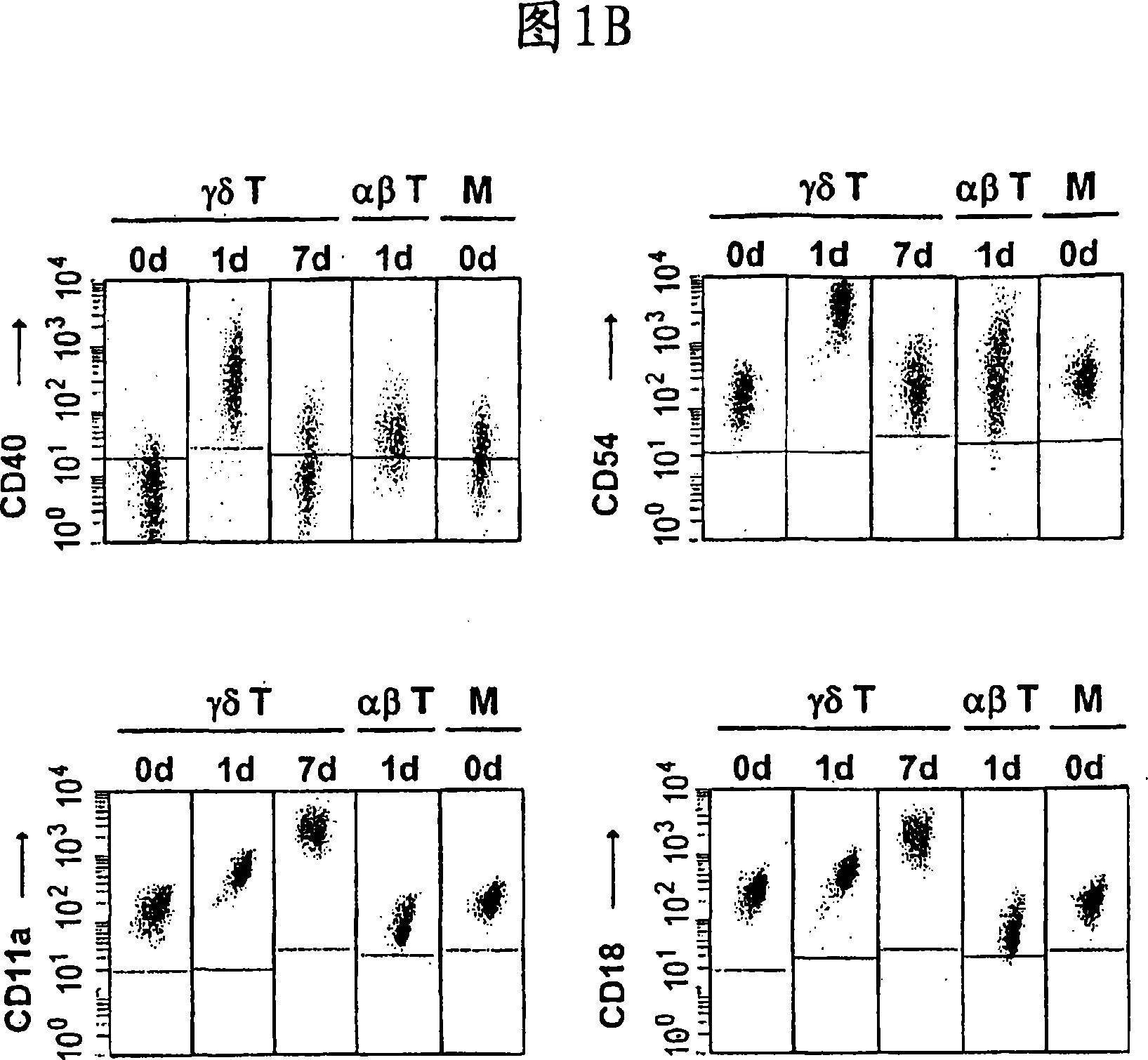
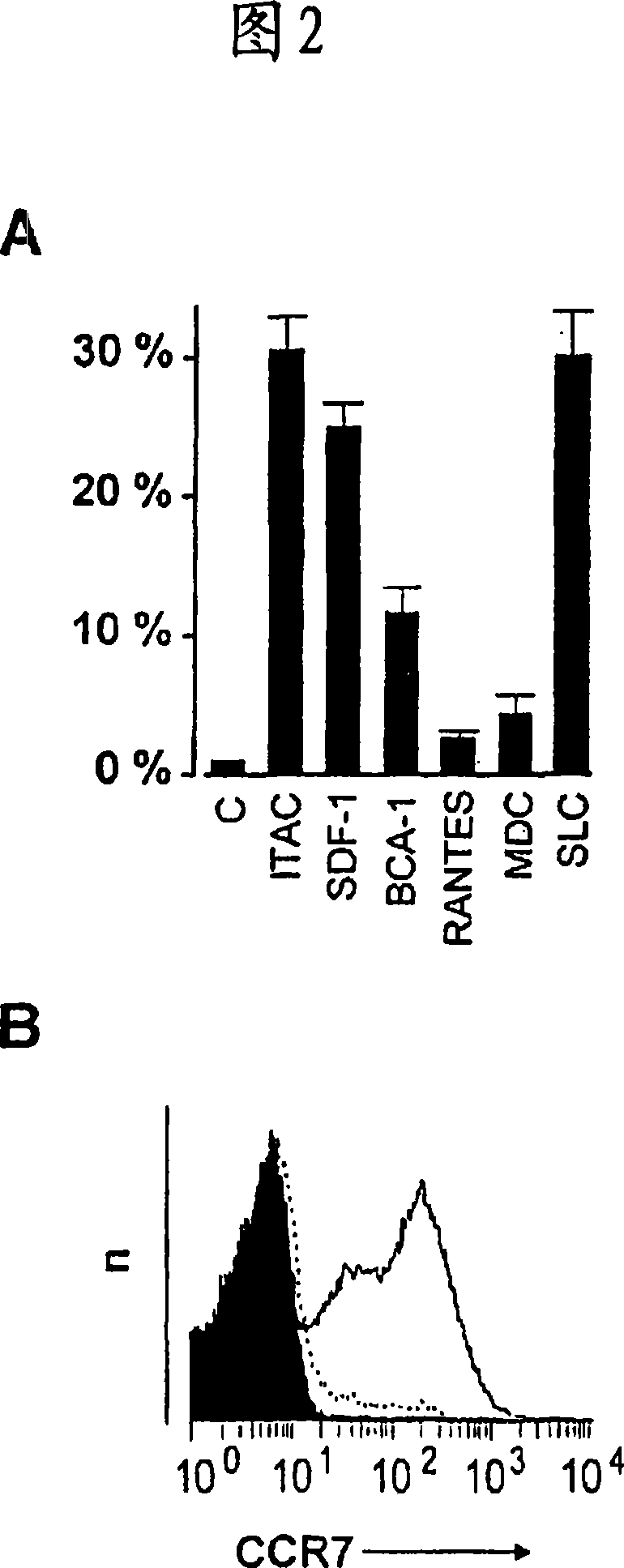
Preparation of antigen-presenting human gamma delta t cells and use in immunotherapy
InactiveCN101031641AGood effectEffective antigen uptakeTissue cultureVaccinationEpidermal Dendritic Cells
The invention relates to a method for the preparation of efficient antigen-presenting human Gamma Delta T cells, to the Gamma Delta T cells prepared by such a method, and to their use in immunotherapy, vaccination, vaccine development and diagnostics. Similar to dendritic cells (DCs) in potency and efficacy, these human Gamma Delta T cells process antigens and present antigenic peptides to Alpha Beta T cells and induce antigen-specific responses (proliferation and differentiation) in nave Alpha Beta T cells. Gamma Delta T cells are easily purified from peripheral blood, acquire''maturation'' status (expression of essential adhesion, co-stimulatory and major histocompatibility complex molecules) within 1 day of in vitro culture under stimulation and induce strong primary and secondary T helper cell and cytotoxic T cell responses. The Gamma Delta T cells may be used in a method of treatment of tumors or chronic or recurrent infectious diseases, in identification of novel tumor or pathogen-derived antigens, and in the diagnosis of the immune competence of a patient.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CARDIFF CONSULTANTS LTD
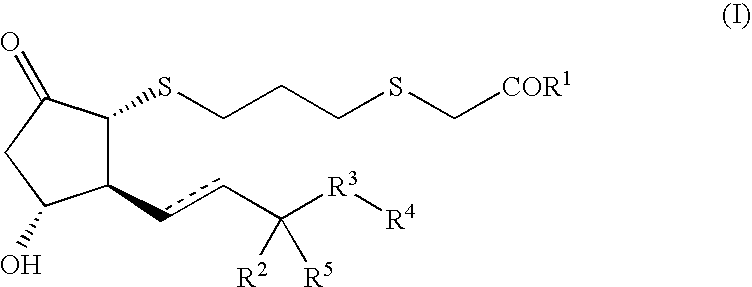
Cytotoxic t cell activator comprising ep4 agonist
InactiveUS20100216689A1Reduce usageUseful in treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseInfection disease
Disclosed is a substance which has a low molecular weight, can be applied in a simpler manner, and has an immunopotentiating activity against cancer and / or a microorganism-mediated infectious disease.An EP4 agonist exhibits an immunopotentiating activity through the activation of a cytotoxic T cell, and is therefore useful for the prevention and / or treatment of cancer or a microorganism-mediated infection disease.
Owner:HAMAMATSU UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
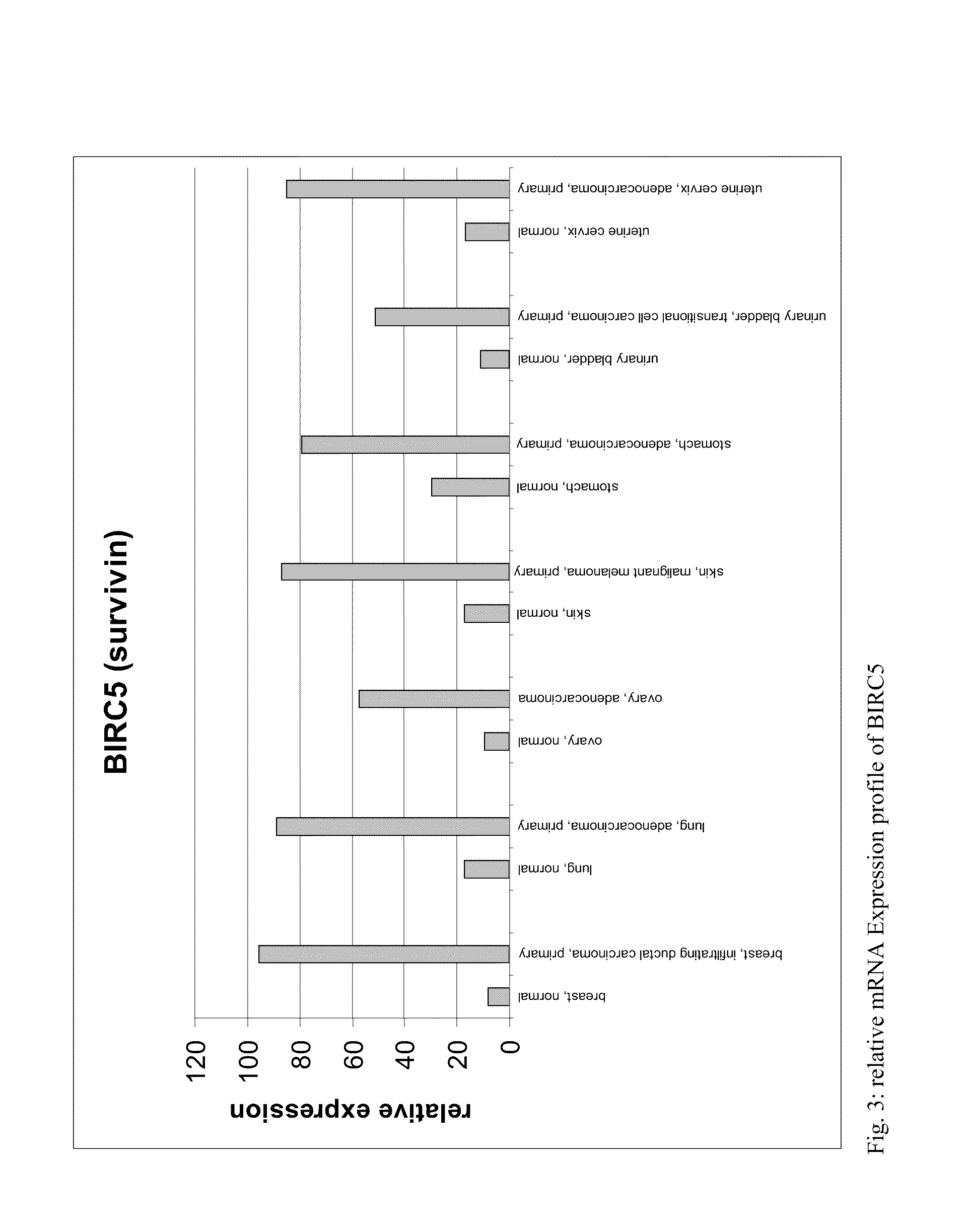
Survivin-derived peptides and use thereof
InactiveUS20040210035A1Easy to filterWeak affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesMHC class IWilms' tumor
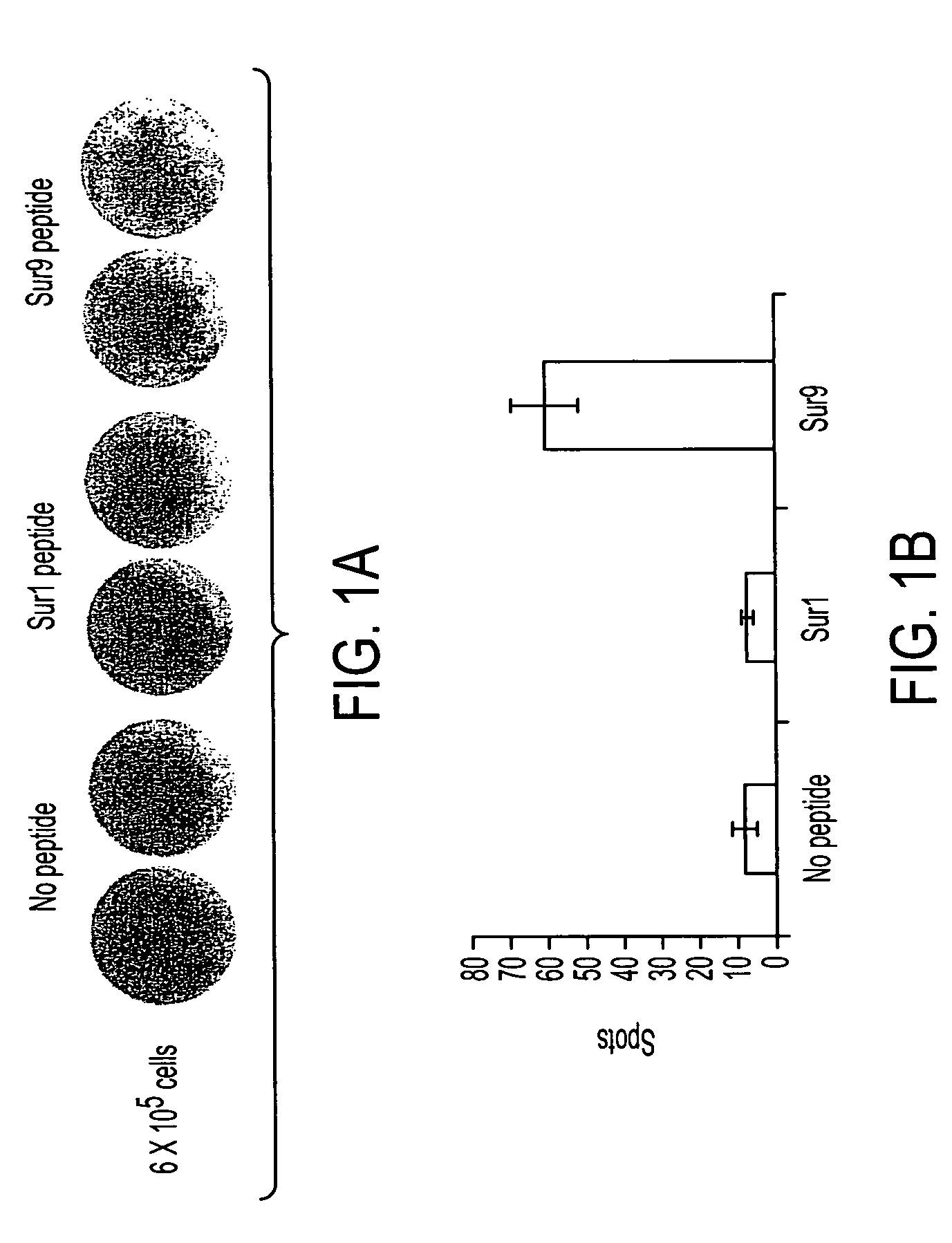
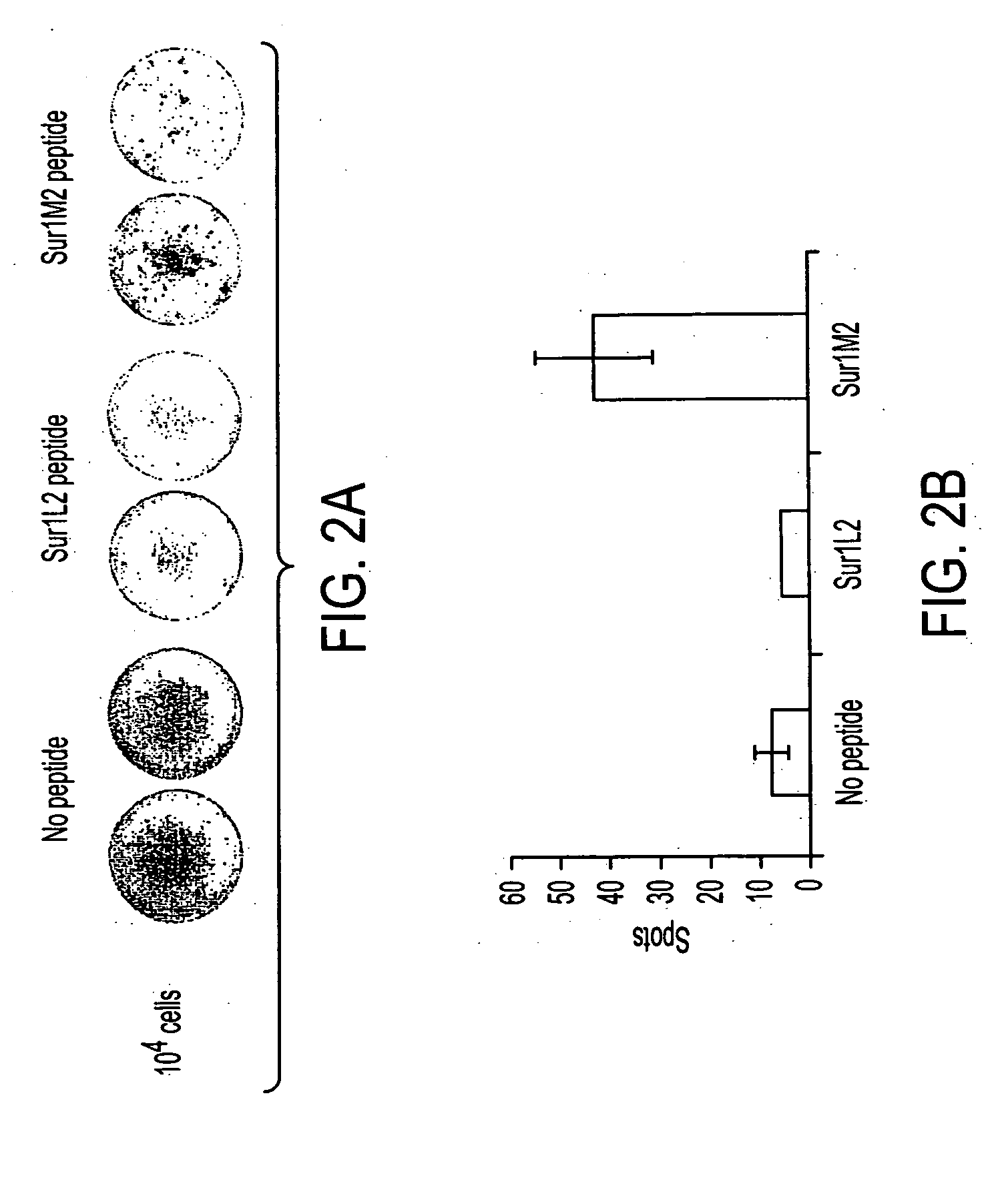
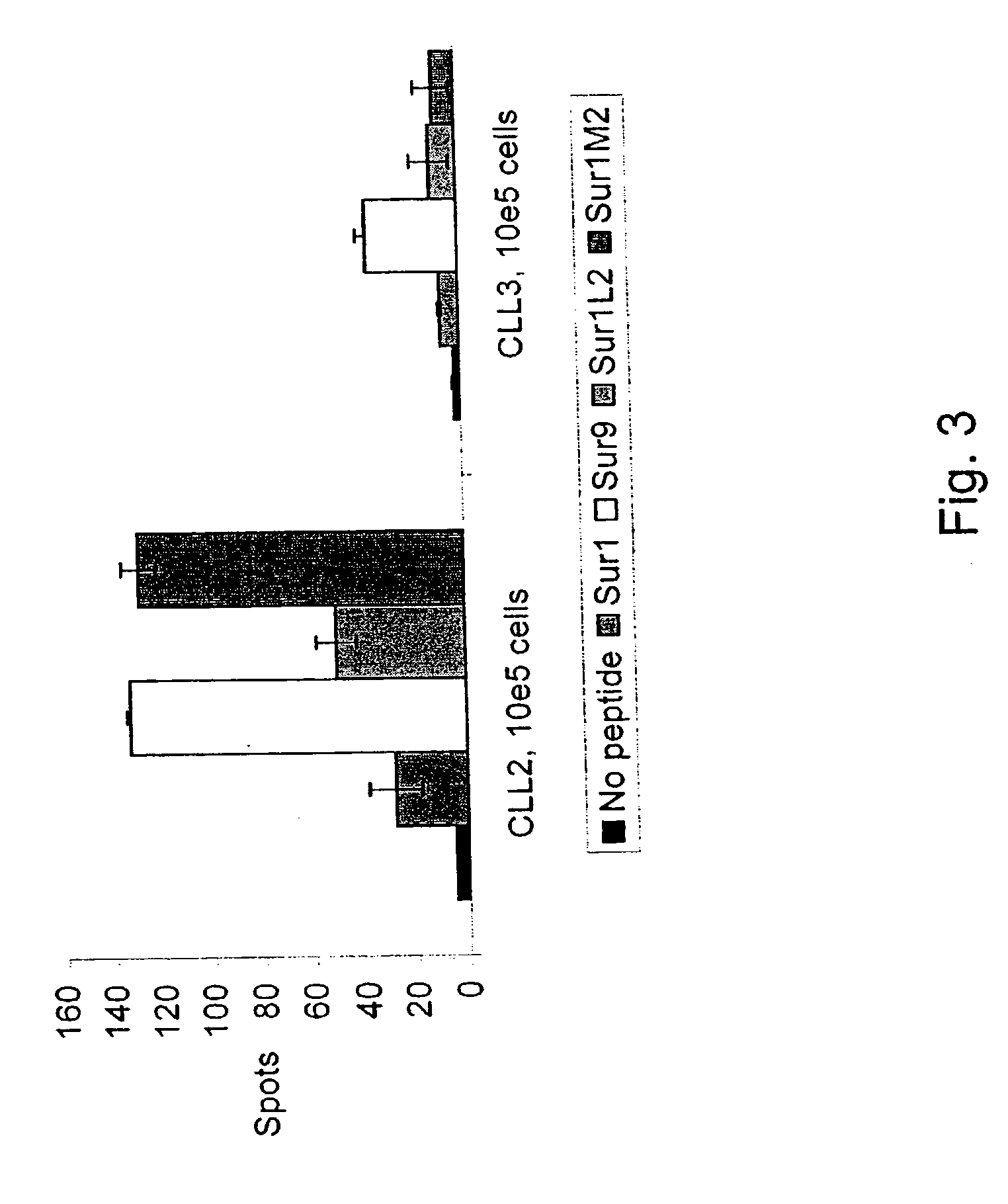
MHC Class I-restricted peptides derived from the tumor associated antigen, survivin, which peptides are capable of binding to Class I HLA molecules at a high affinity, capable of eliciting INF-gamma-producing cells in a PBL population of a cancer patient and capable of in situ detection of cytotoxic T cells in a tumor tissue, therapeutic and diagnostic composition comprising the peptide and uses hereof.
Owner:SURVAC
Method for producing cytotoxic T-cells
InactiveUS7521197B2Low efficacyReduce usageBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsT lymphocytePeripheral blood lymphocyte
The invention relates to the method for producing antipeptide cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) by attaching a complex of a class I HLA and a peptide to antigen presenting cell(s) (APCs) present in a sample of peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs), optionally removing excess class I HLA / peptide complex, and incubating with proliferative cytokine. The invention further relates to a CTL obtainable by these methods and to a method of treating a subject by administering such a CTL to the subject.
Owner:ALEXIS BIOTECH
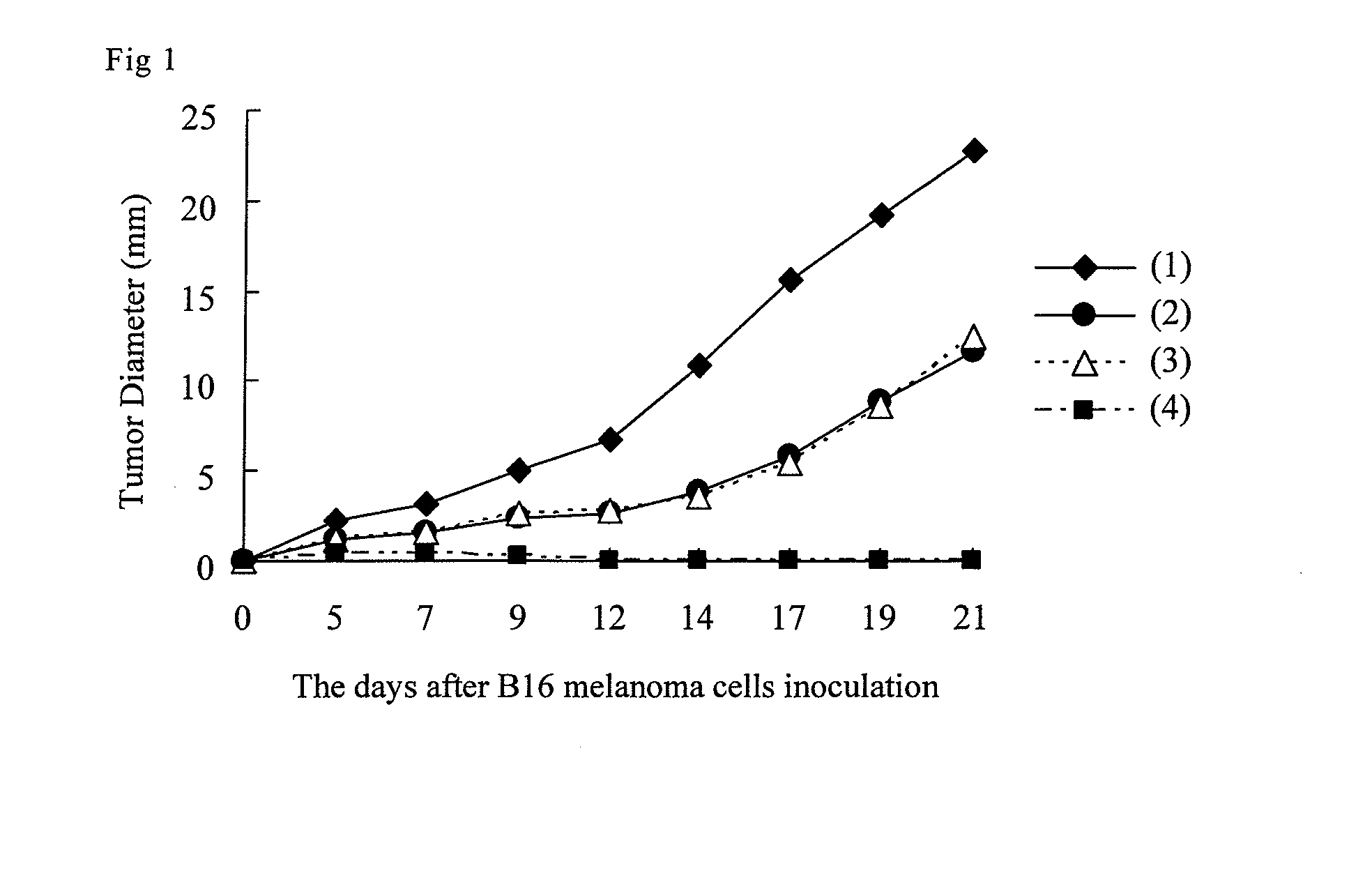
In vivo activation of tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells
The present invention relates to methods and compositions of activating cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in vivo with specificity for particular antigenic peptides, and to methods and compositions of using activated CTLs in vivo for the treatment of a variety of disease conditions. In some preferred embodiments, the invention provides methods of employing a polypeptide of the amino acid sequence VMAGVGSPYV to specifically activating CTLs in subjects having a breast cancer overexpressing a Her-2 / Neu protein, and methods of using the polypeptide to treat such subjects.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method of extended culture for antigen-specific cytotoxic lumphocytes
The present invention is a method for inducing cytotoxic T cell having an antigen-specific cytotoxic activity, a method for maintaining the cell, a method for continuously culturing the cell or a method for expanding the cell, comprising the step of culturing a cytotoxic T cell in the presence of at least one substance selected from the group consisting of (A) a substance having a binding activity to CD44; (B) a substance capable of regulating a signal emitted by binding a CD44 ligand to CD44; (C) a substance capable of inhibiting binding of a growth factor to a growth factor receptor; (D) a substance capable of regulating a signal emitted by binding of a growth factor to a growth factor receptor; and (E) fibronectin, a fragment thereof or a mixture thereof.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
KDR peptides and vaccines comprising the same
The present invention provides nonapeptides selected from peptides comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2, 3, 5, 8, 11, or 12; nonapeptides or decapeptides selected from peptides comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 29, 30, 33, 34, 40, or 46; and peptides with cytotoxic T cell inducibility, in which one, two, or several amino acids are substituted or added to the above-mentioned amino acid sequences, as well as pharmaceuticals for treating or preventing tumors, where the pharmaceuticals comprise these peptides. The peptides of this invention can be used as vaccines.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Novel therapeutic vaccine formulations
The present invention relates to a novel method and formulation for the induction of immune responses against polypeptide antigens. In particular, the invention provides a method and formulation for induction of cytotoxic T cell responses against a polypeptide antigen of choice. The formulations are characterized by containing chitosan in admixture with the polypeptide antigen, preferably in the form of microparticles that may be cross-linked.
Owner:PHARMEXA
Tolerance-induced targeted antibody production
InactiveUS20070036809A1Growth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAbnormal tissue growthTolerance induction
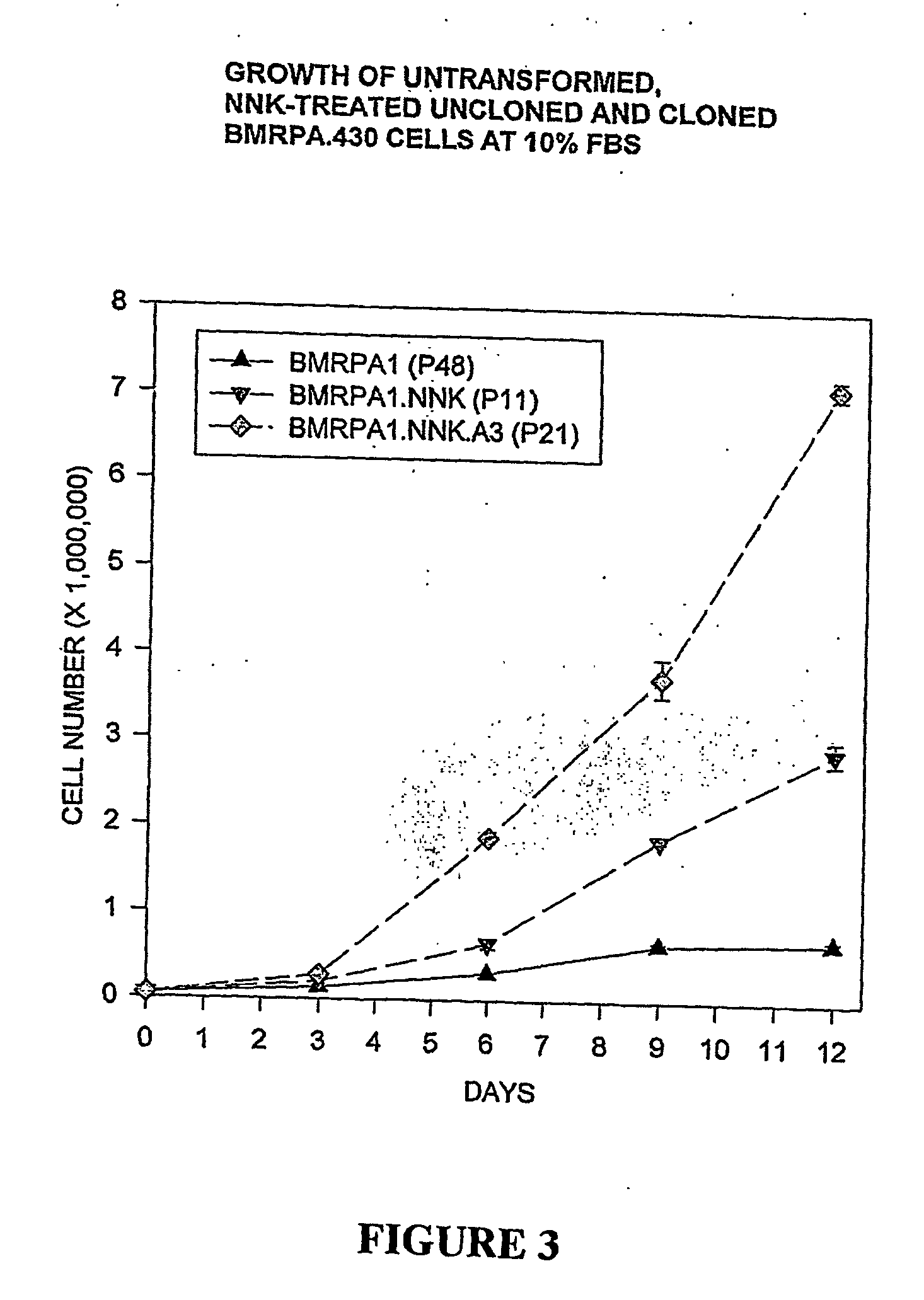
The present invention provides methods for directing the immune response of an animal towards immunologically weak or rare antigens such as tumor antigens. The methods combine subtractive immunization with hyperimmunization and result in the controlled or directed production of target-specific antibodies, helper T cells (CD4+-T lymphocytes) and cytotoxic T cells (CD8+-T lymphocytes). Also provided by the present invention are untransformed and transformed cell lines, and growth media necessary to grow the untransformed cell line in a differentiated state. Monoclonal antibodies which react with different neoplastic cell lines and hybridomas producing such antibodies are also provided.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Cytotoxic t-cell epitope peptides that specifically attack epstein-barr virus-infected cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090305324A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsEpitopeNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
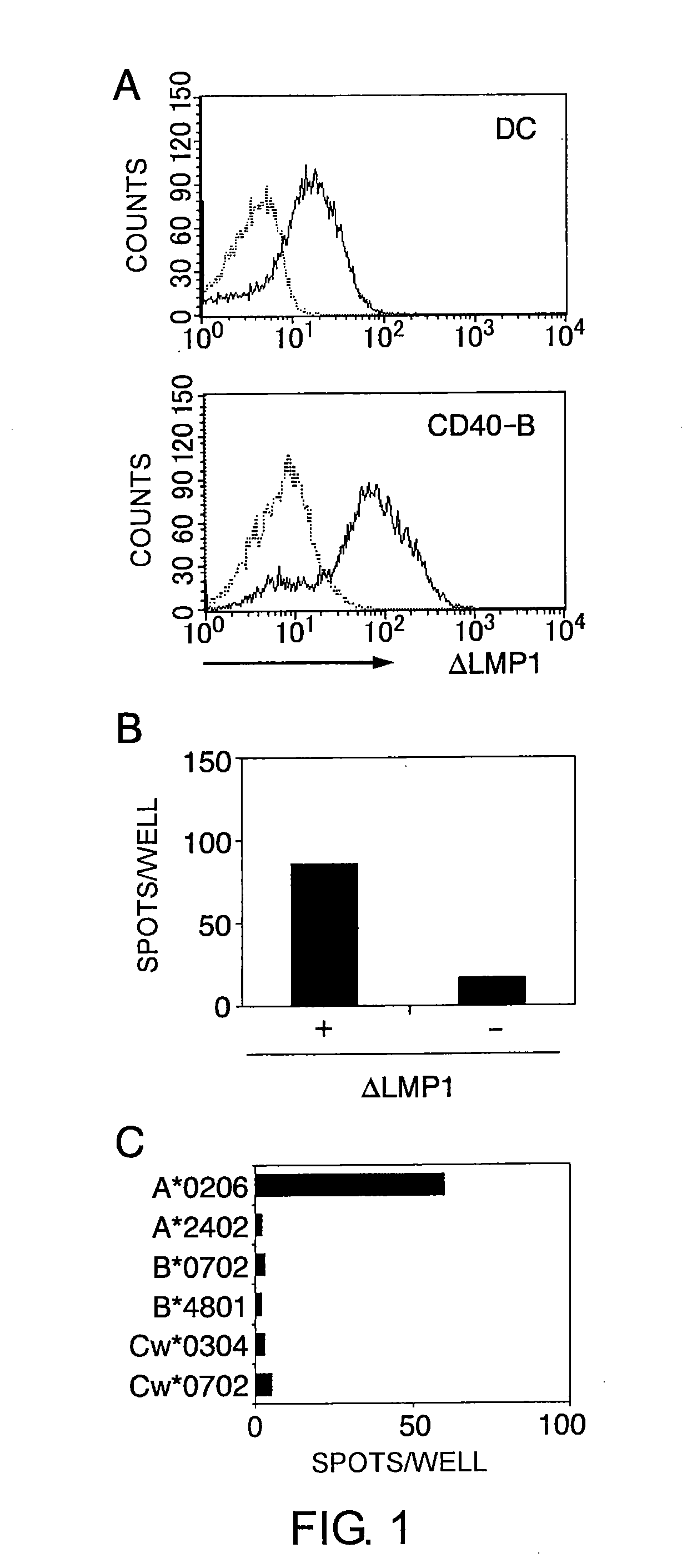
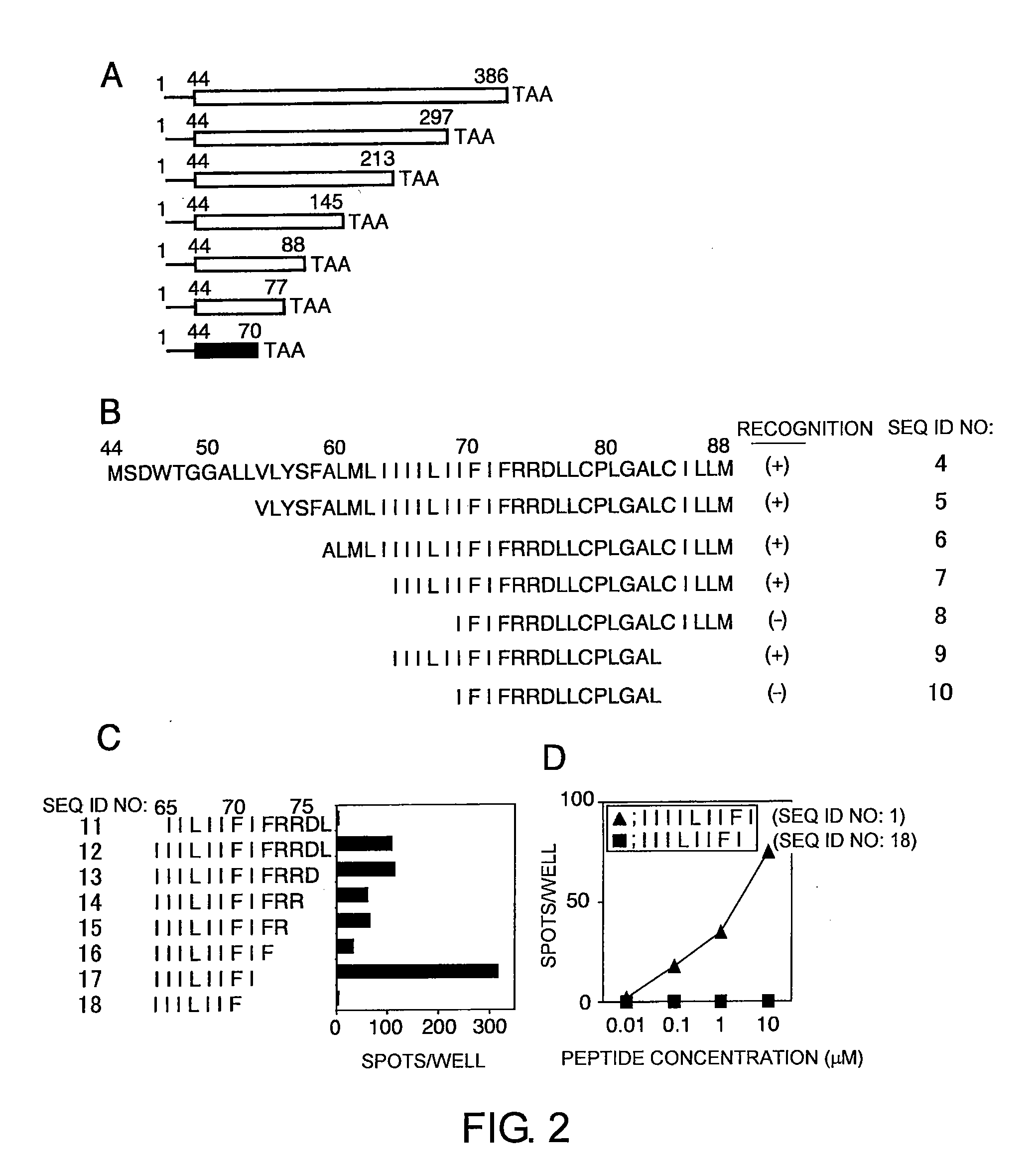
The present inventors introduced mRNAs for the Epstein-Barr virus proteins LMP1 and EBNA1 into antigen-presenting cells, and as a result, demonstrated that the cells induced Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T cells. The present inventors also demonstrated that the cytotoxic T cells recognized epitope peptides presented via HLA-A*0206, HLA-Cw*0303, or HLA-Cw*0304, inhibited the outgrowth of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells, and lysed Epstein-Barr virus-infected NK lymphomas and NK cells.
Owner:AICHI PREFECTURE +1
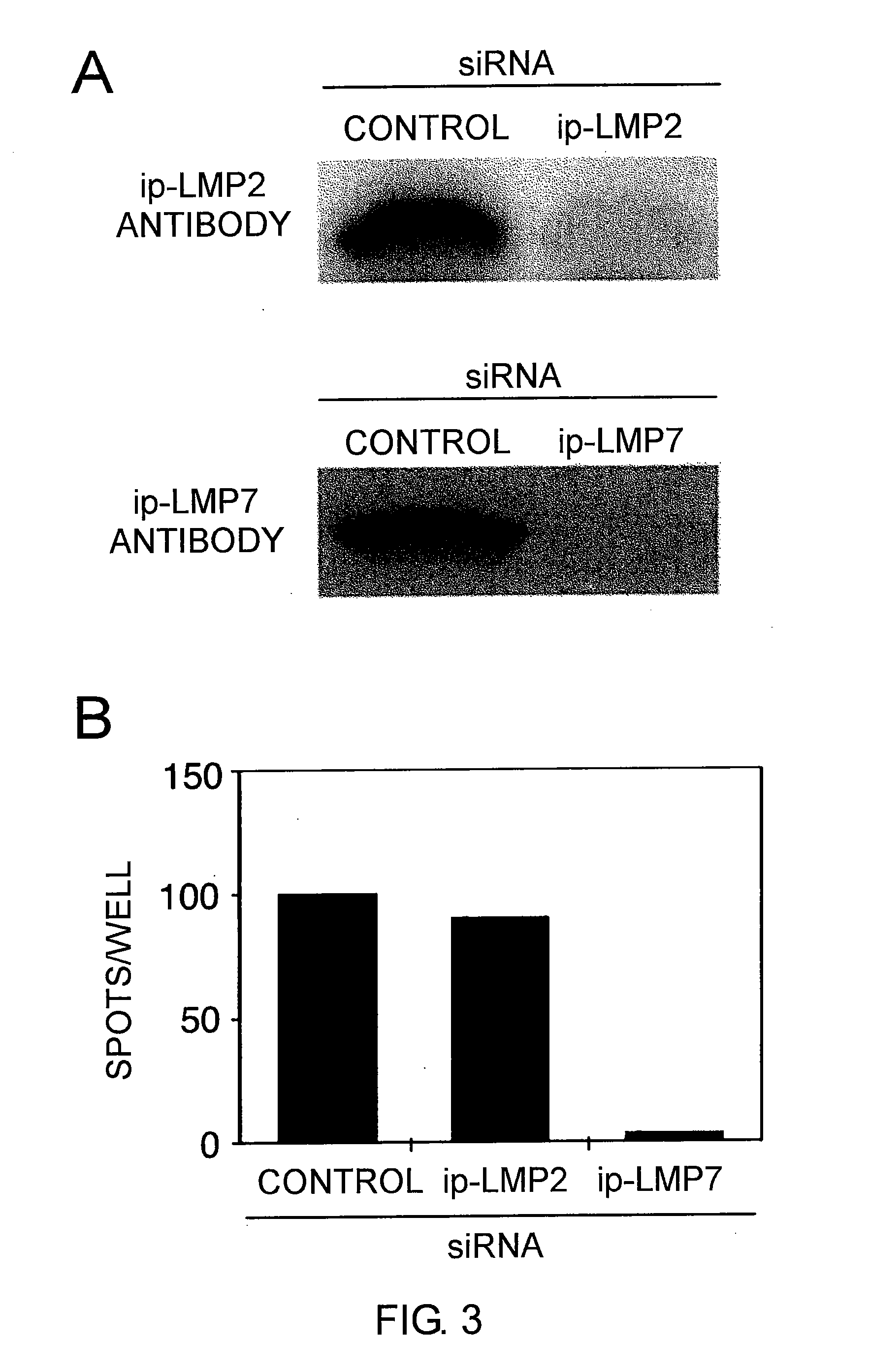
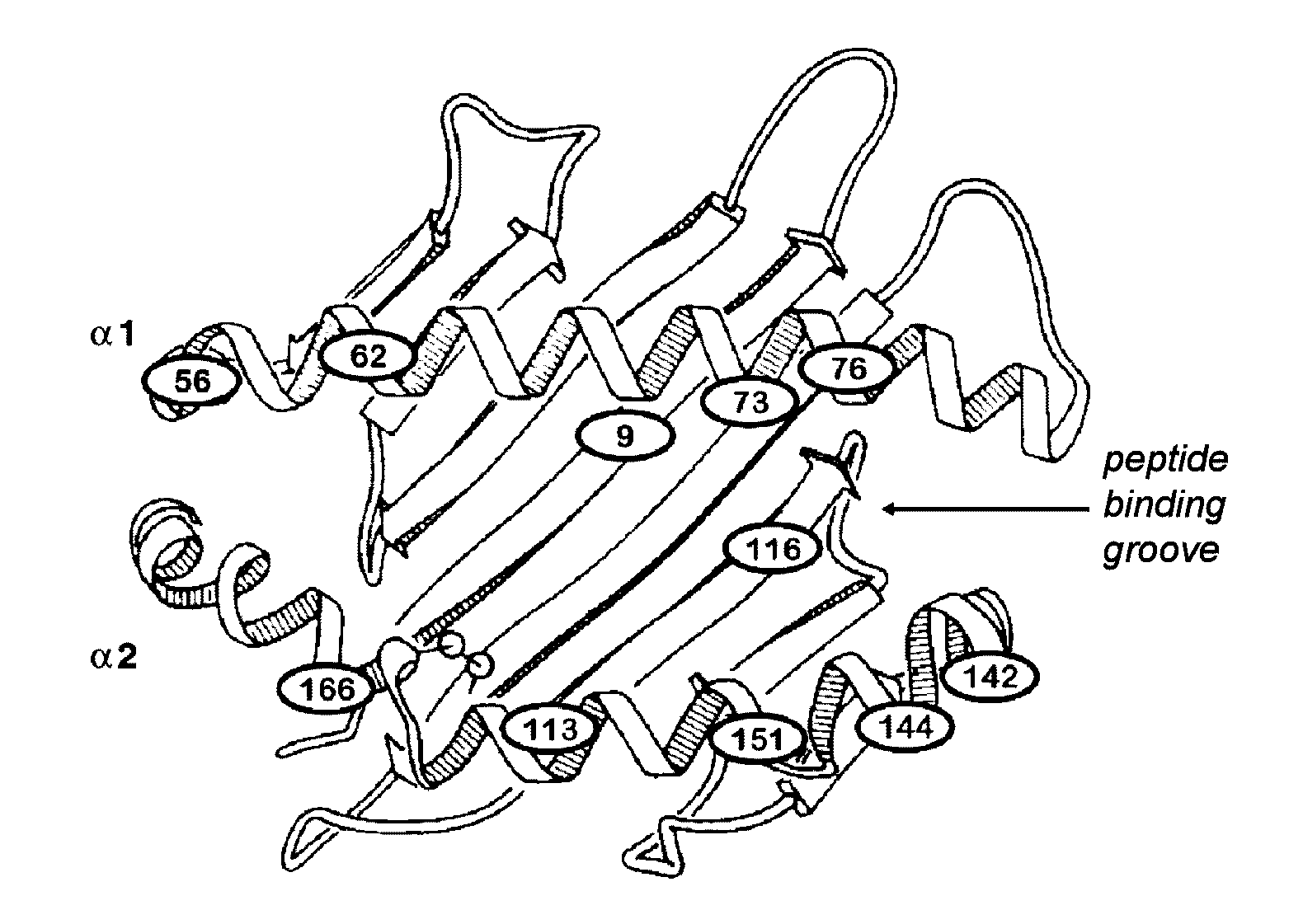
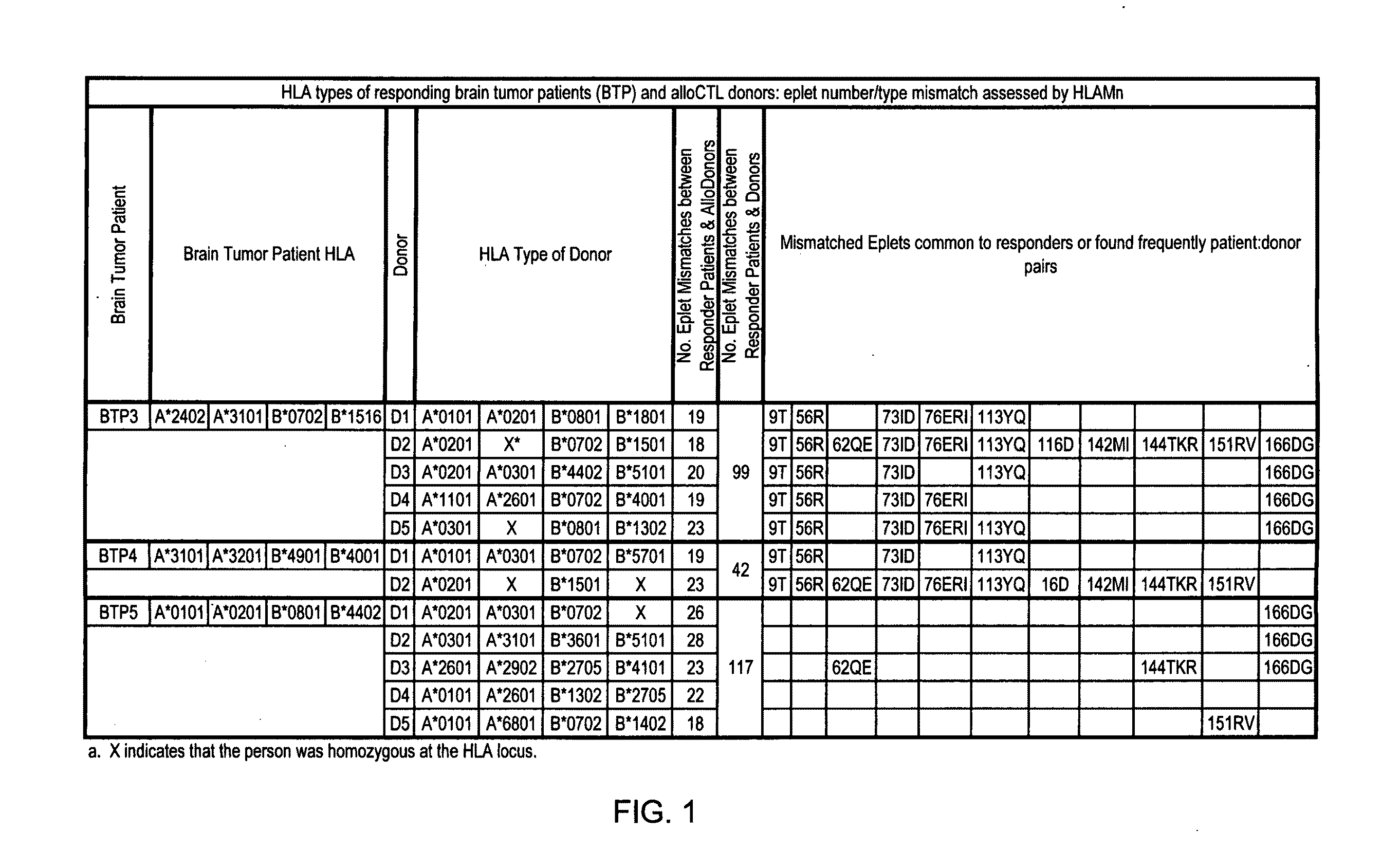
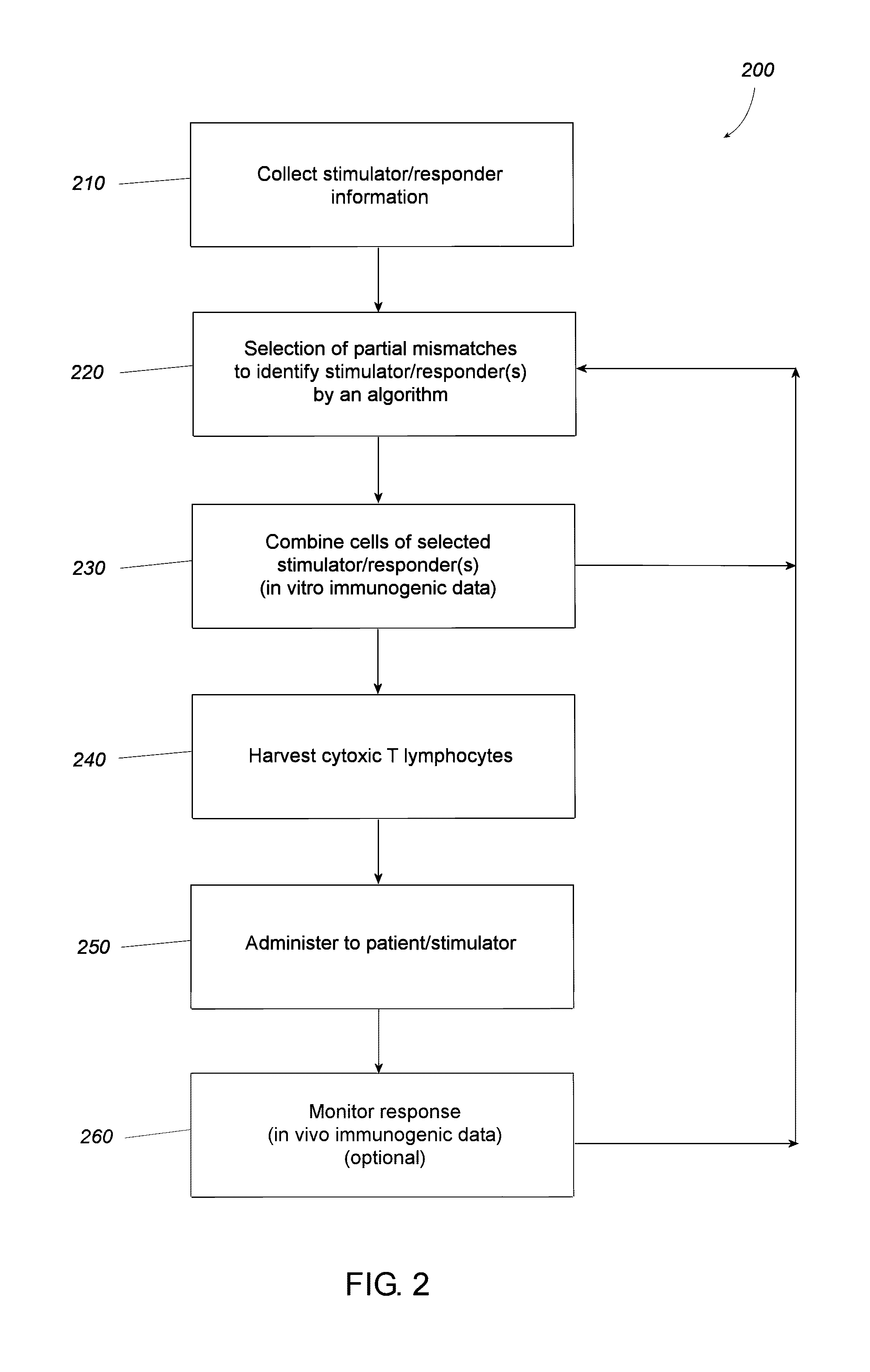
Pairing processes for preparing reactive cytotoxic T cells
InactiveUS20110135617A1Simple compositionImprove methodBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseIn vivo
Provided in certain embodiments are methods for pairing patient cells and donor cells to prepare cytotoxic T cells, either in vitro or, when their formation is induced in a subject, in vivo. Such cytotoxic T cells could be administered to the patient for treating certain disorders, such as a cancer (for example, brain cancer).
Owner:PROMISING FUTURE
Multicomponent conjugates which bind to target molecules and stimulate T cell lysis
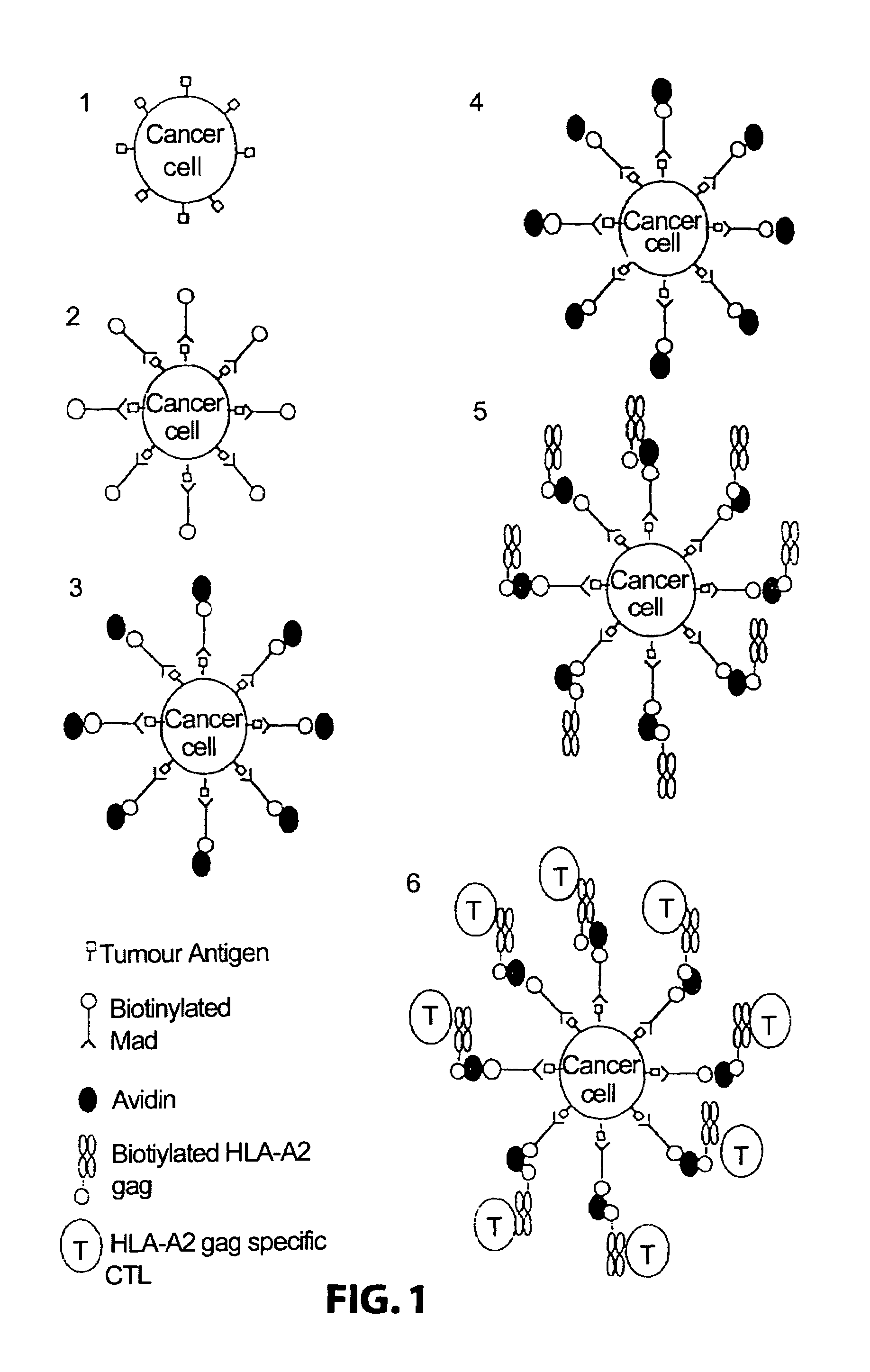
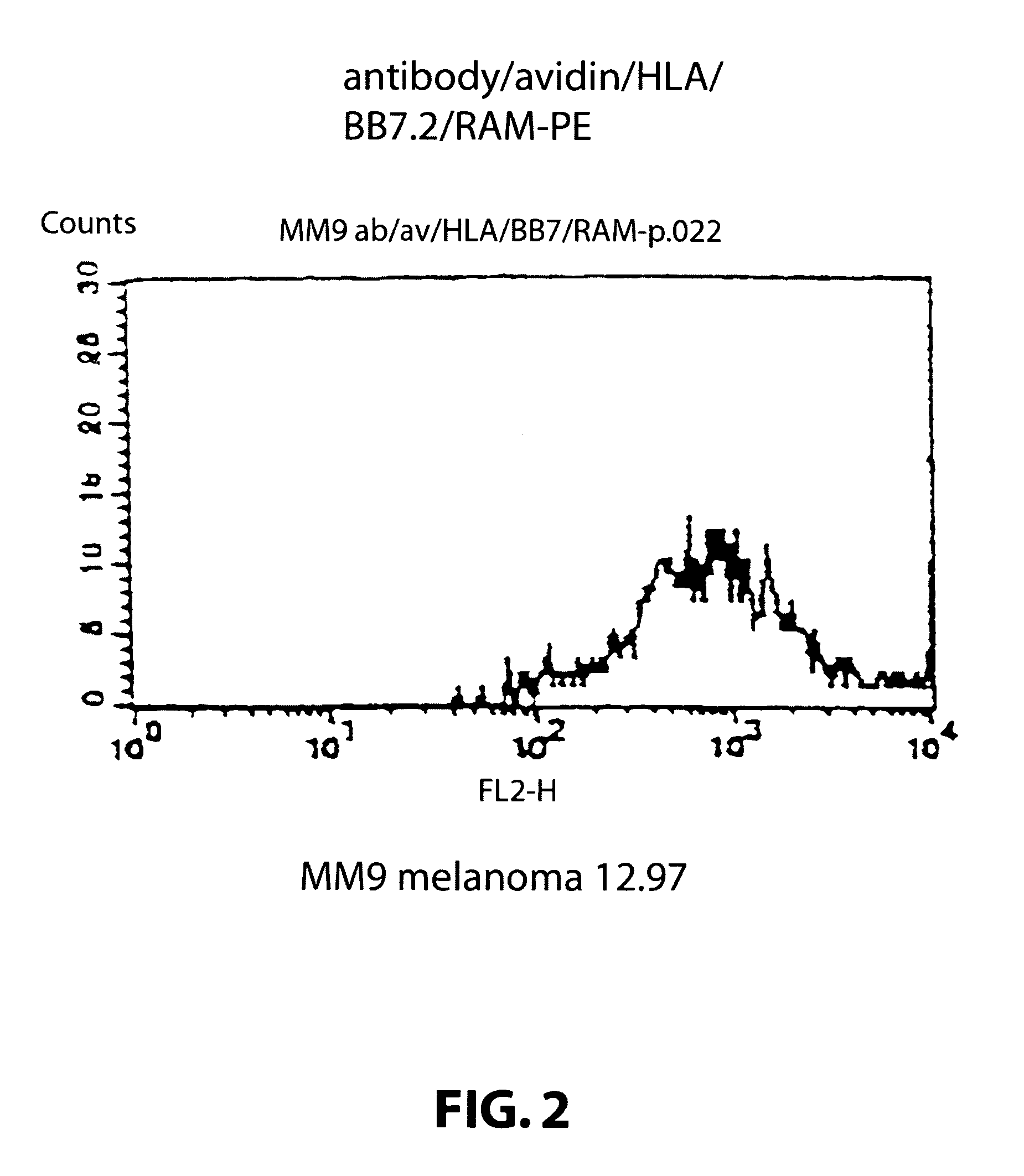
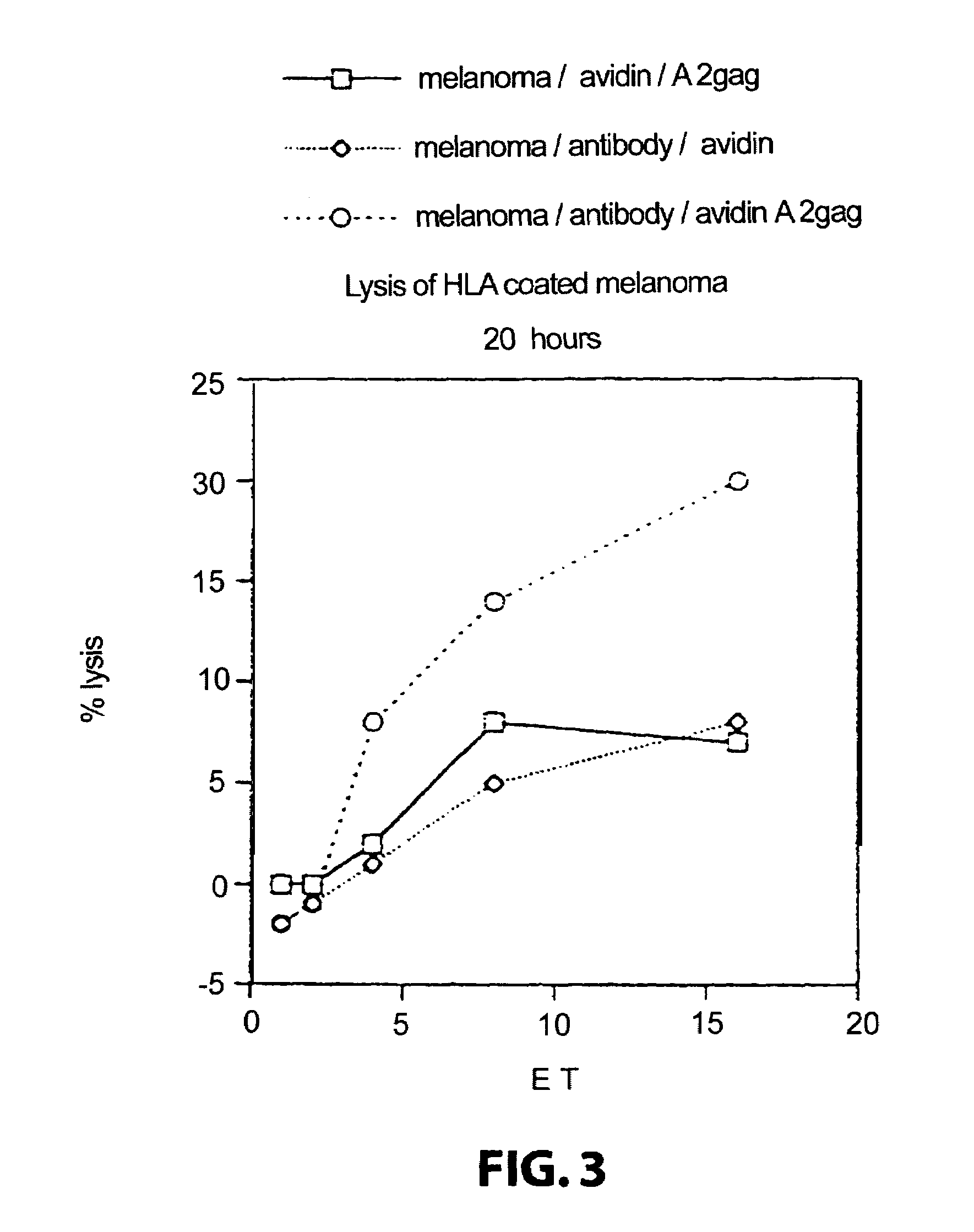
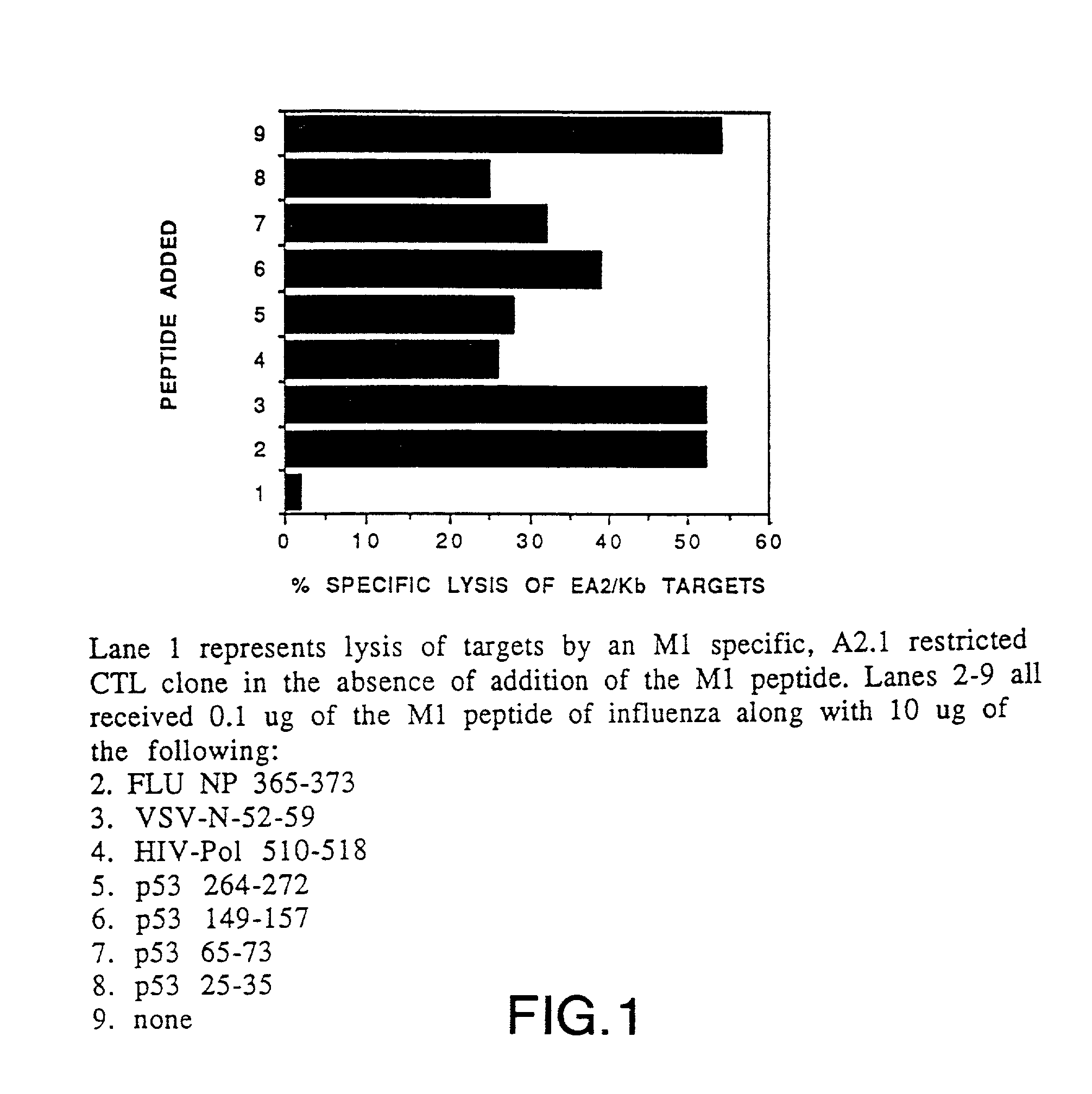
The invention relates to immunoconjugates of formula: A-B-(C)n where B may be present or absent, A is a specific binding protein such as an antibody or an antibody binding fragment, or a ligand binding to a receptor present on target cells B comprises at least one molecule to which "A" and "C" bind, such as an avidin / streptavidin complex, "C" is an MHC molecule, and "n" is a whole number ranging from 1 to 10. The conjugates provide the exquisite binding specificity of antibodies, combined with an ability to stimulate cytotoxic T cells to identify and to destroy cells on which the conjugate is bound and oligomerized. The conjugates are useful both therapeutically and diagnostically.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES +1
Novel and powerful mhc-class ii peptides derived from survivin
ActiveUS20100029571A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to peptides, nucleic acids, and cells for use in the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to survivin-derived tumor-associated cytotoxic T cell (CTL) peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses. The present invention specifically relates to three novel peptide sequences and variants thereof derived from HLA class I and class II molecules of human tumor cells that can be used in vaccine compositions for eliciting anti-tumor immune responses.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Kdr peptides and vaccines comprising the same
InactiveUS20090252752A1Senses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTGE VACCINEPharmaceutical Substances
The present invention provides nonapeptides selected from peptides comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2, 3, 5, 8, 11, or 12; nonapeptides or decapeptides selected from peptides comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:29, 30, 33, 34, 40, or 46; and peptides with cytotoxic T cell inducibility, in which one, two, or several amino acids are substituted or added to the above-mentioned amino acid sequences, as well as pharmaceuticals for treating or preventing tumors, where the pharmaceuticals comprise these peptides. The peptides of this invention can be used as vaccines.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com