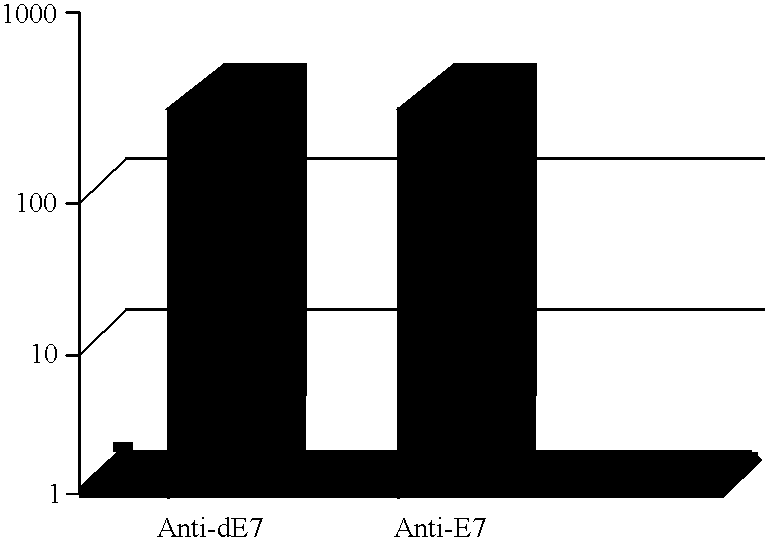Patents
Literature
588 results about "T-Cell Epitopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
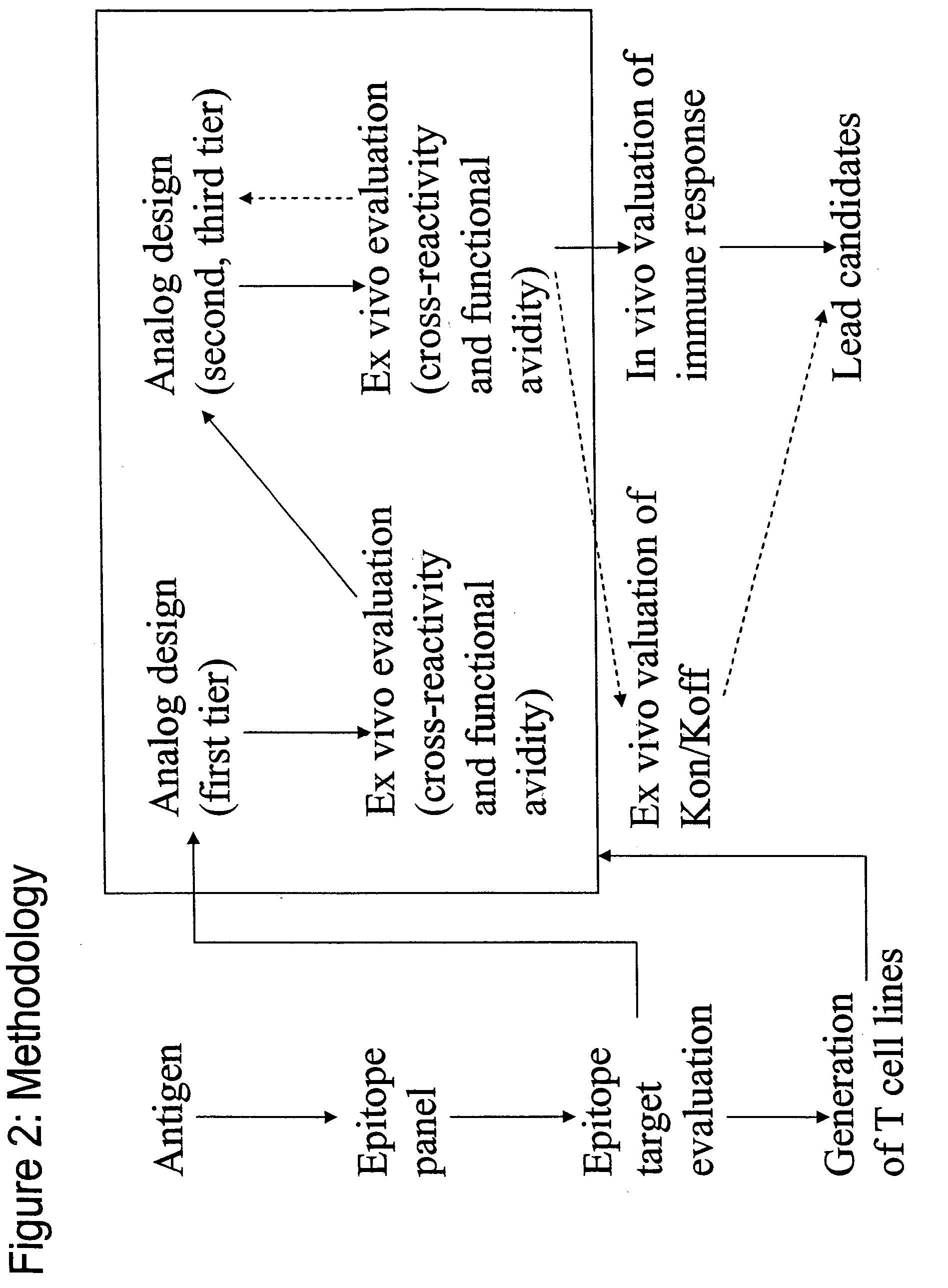
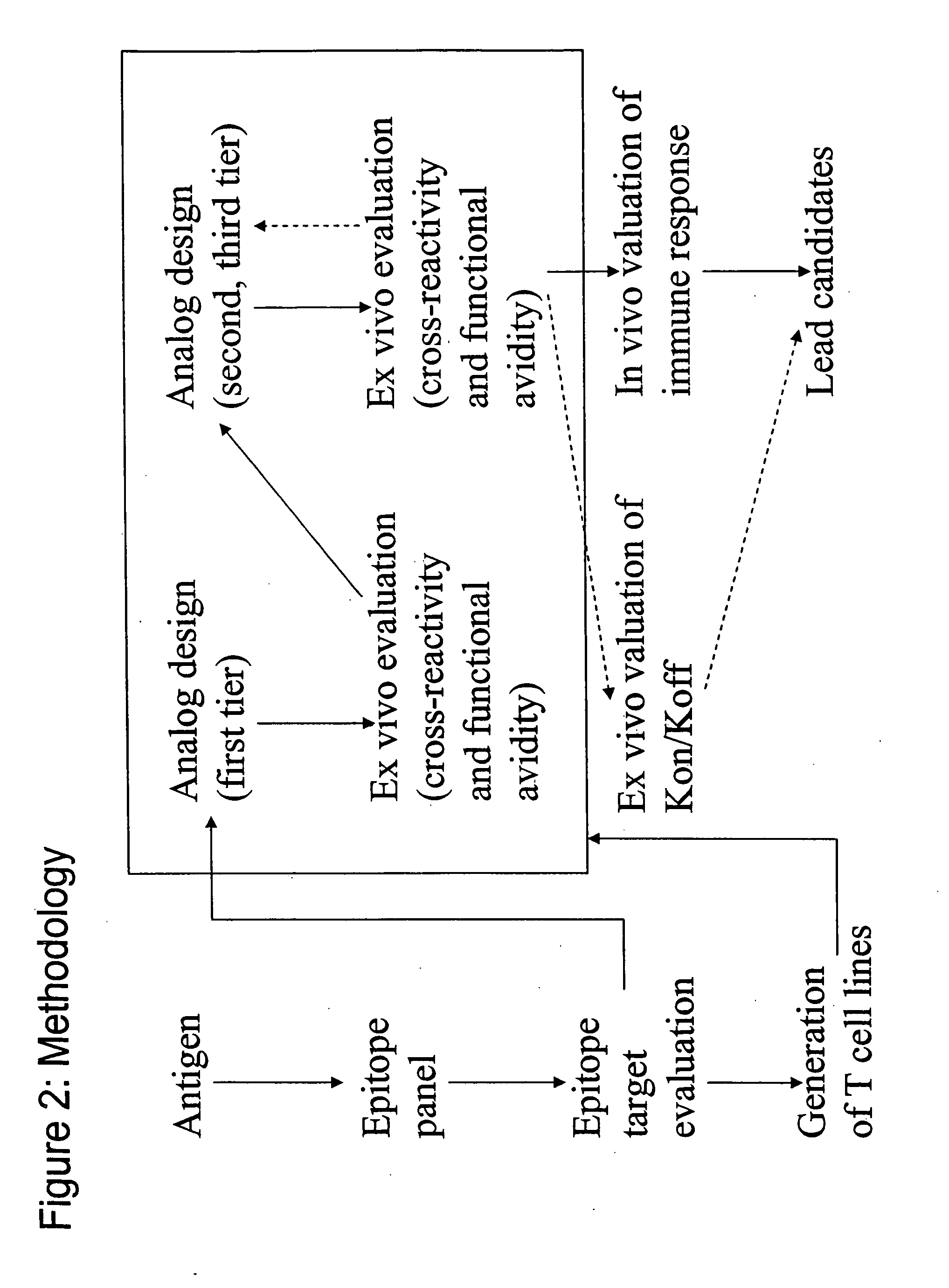
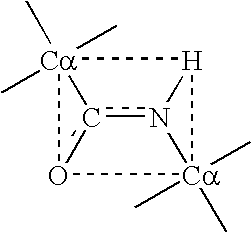
T-cell epitope mapping. T-cell epitopes are defined as peptide sequences which, in association with proteins on antigen-presenting cells (APC), are required for recognition by specific T-cells.
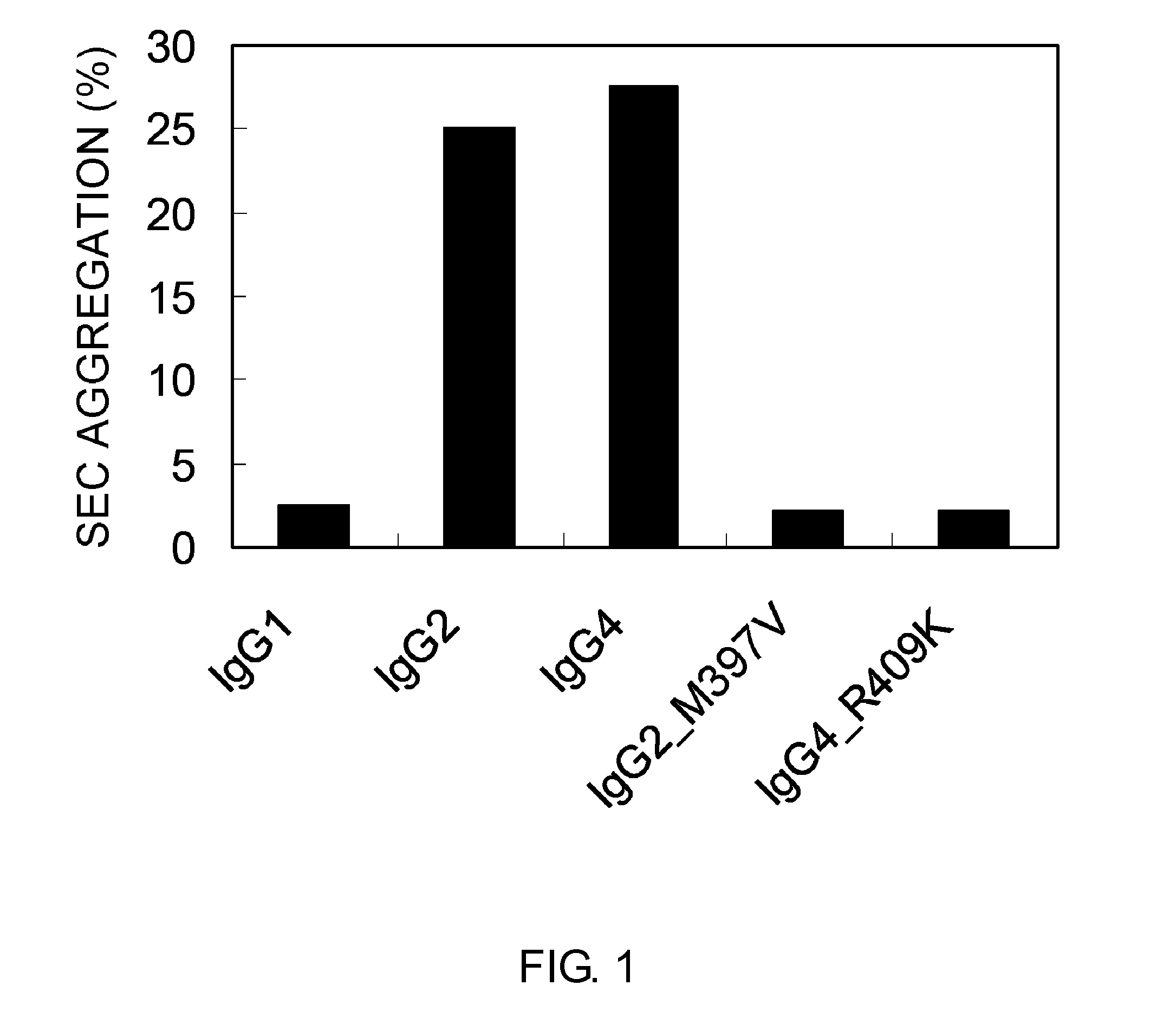
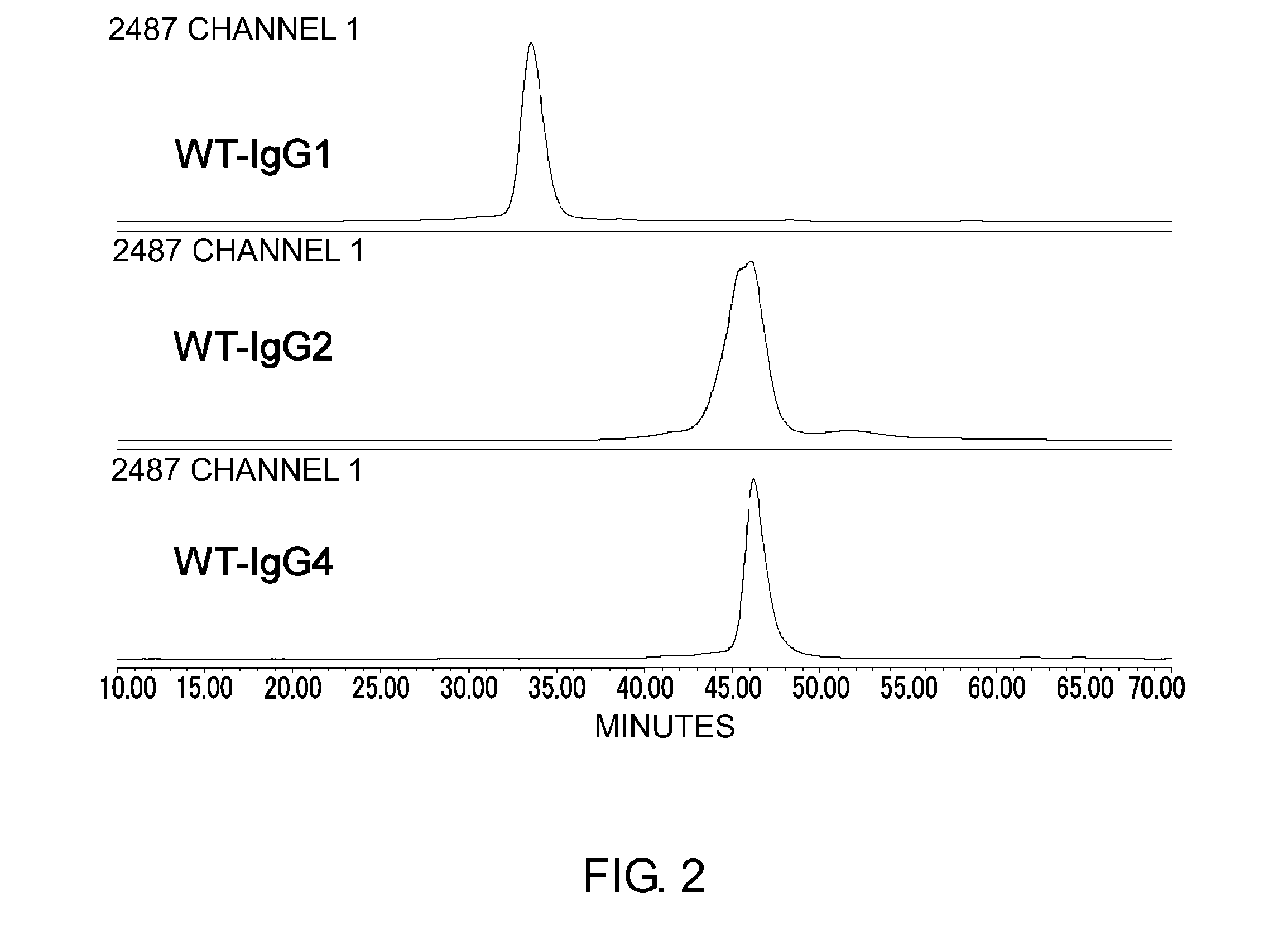
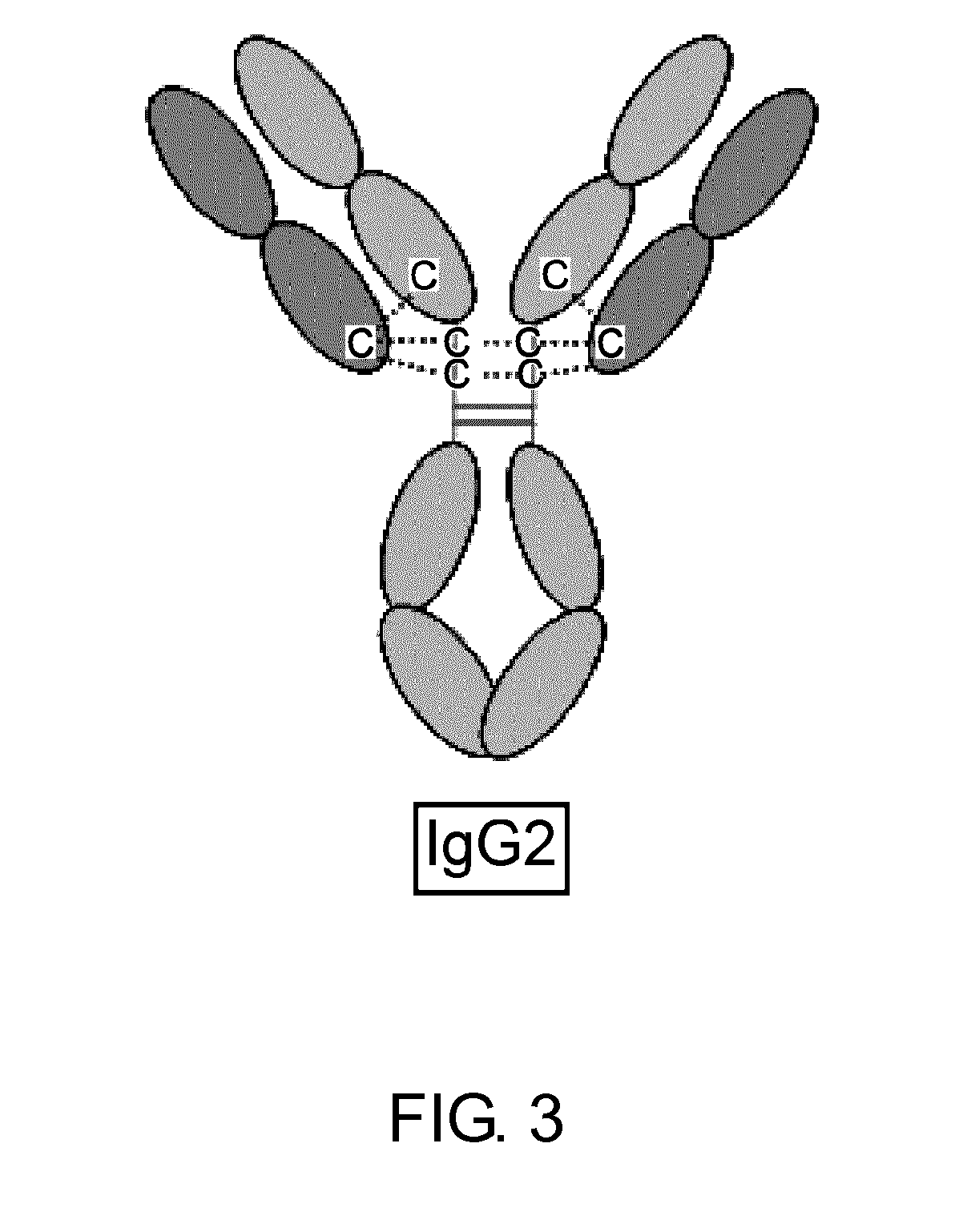
Modified Antibody Constant Region
ActiveUS20100298542A1Improving immunogenicityImprove propertiesAntipyreticAnalgesicsHigh concentrationHinge region
The present inventors succeeded in improving the antibody constant region to have increased stability under acid conditions, reduced heterogeneity originated from disulfide bonds in the hinge region, reduced heterogeneity originated from the H chain C terminus, and increased stability at high concentrations as well as in discovering novel constant region sequences having reduced Fcγ receptor-binding, while minimizing the generation of novel T-cell epitope peptides. As a result, the present inventors successfully discovered antibody constant regions with improved physicochemical properties (stability and homogeneity), immunogenicity, safety, and pharmacokinetics.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
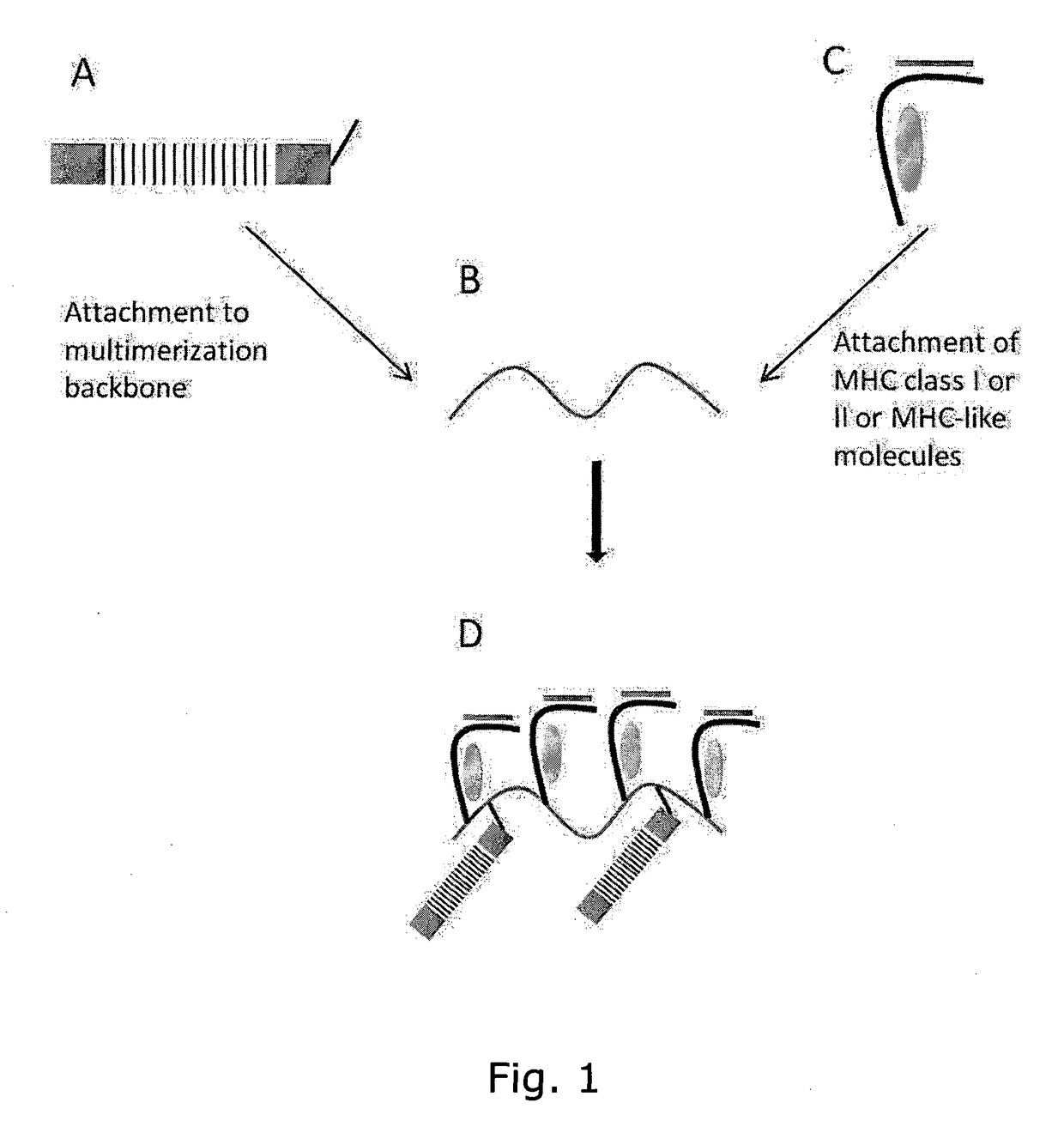
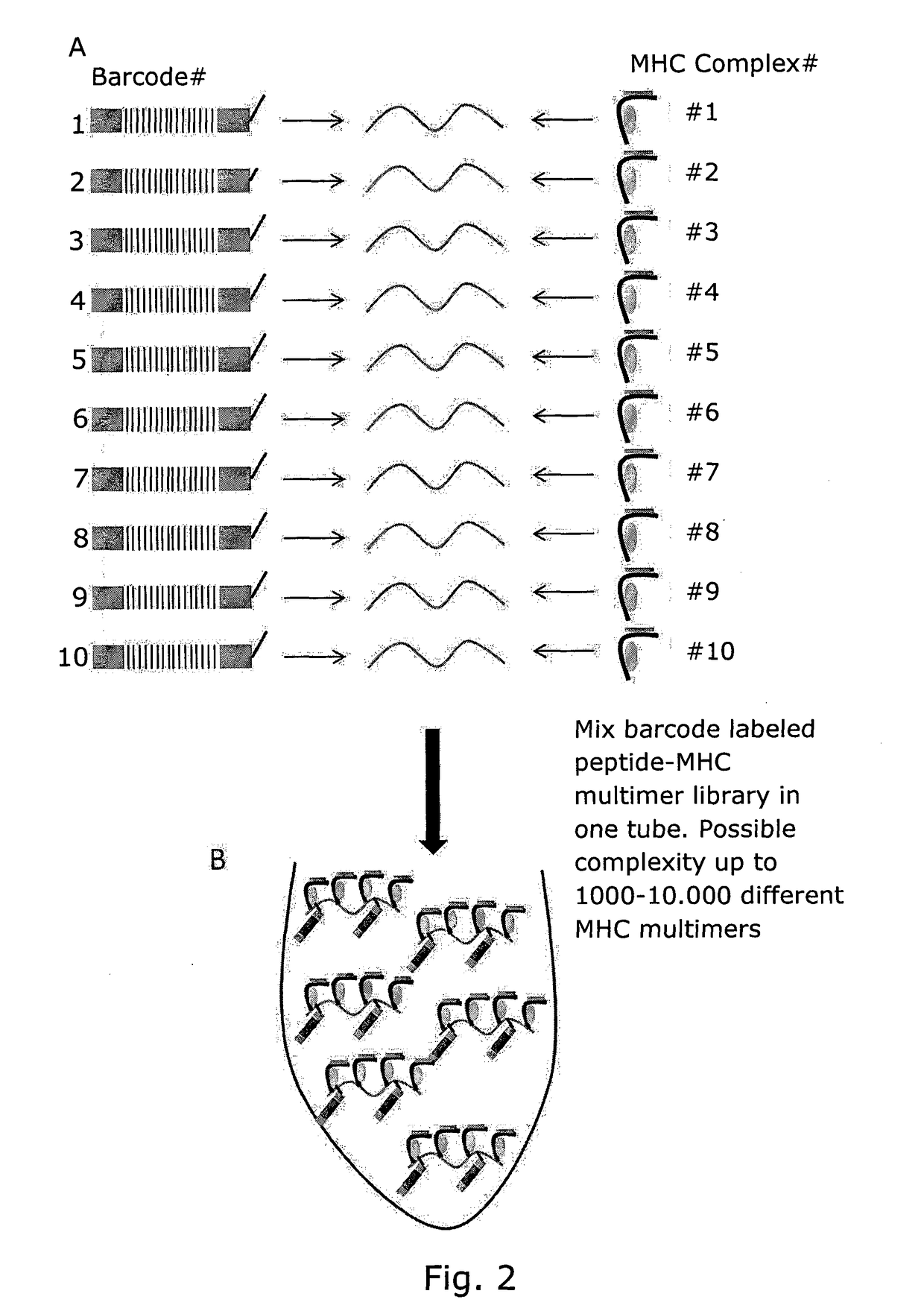
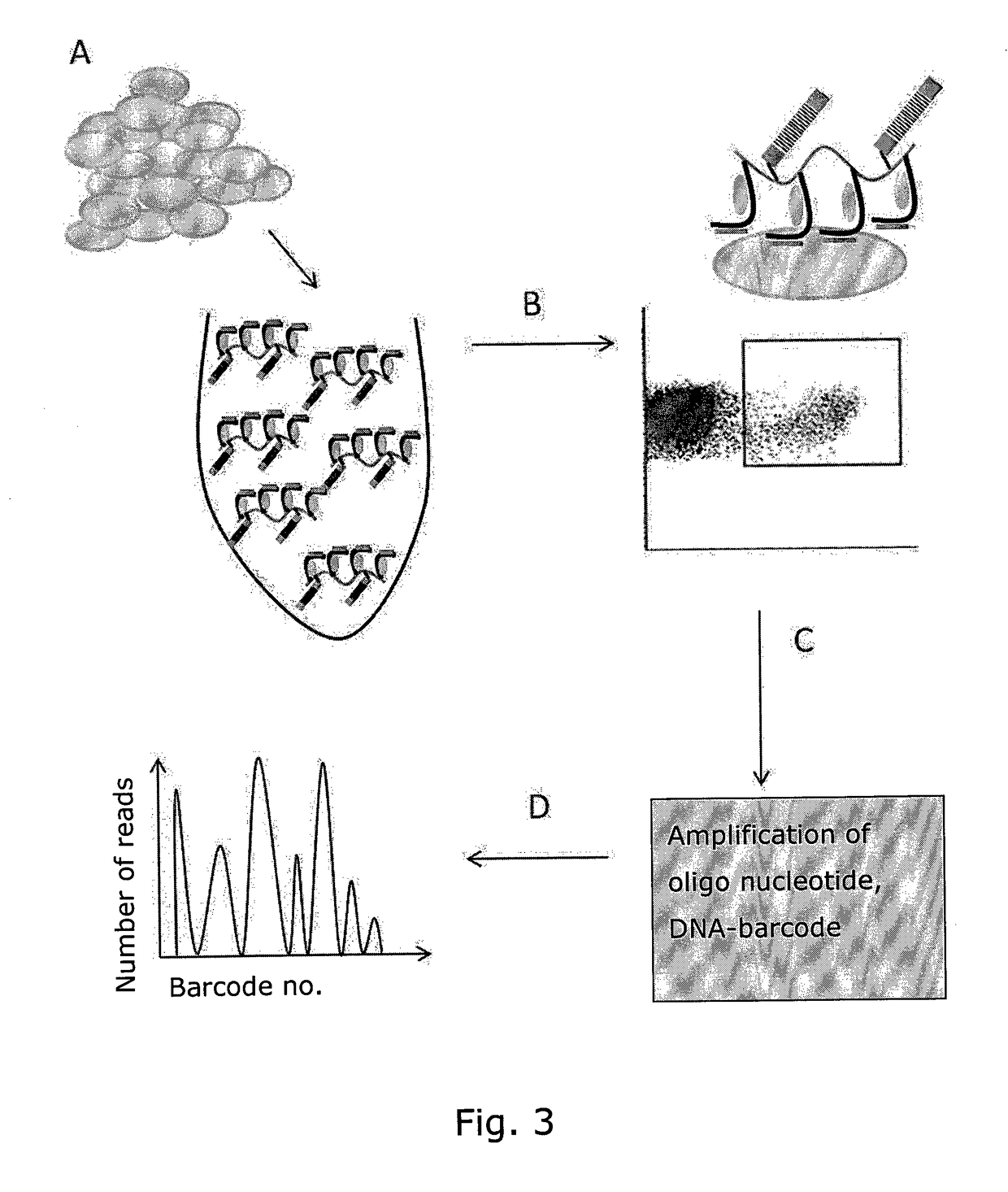
Determining Antigen Recognition through Barcoding of MHC Multimers
PendingUS20170343545A1Improve understandingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSingle sampleVaccination
The present invention describes the use of nucleic acid barcodes as specific labels for MHC multimers to determine the antigen responsiveness in biological samples. After cellular selection the barcode sequence will be revealed by sequencing. This technology allows for detection of multiple (potentially >1000) different antigen-specific cells in a single sample. The technology can be used for T-cell epitope mapping, immune-recognition discovery, diagnostics tests and measuring immune reactivity after vaccination or immune-related therapies.
Owner:IMMUDEX APS +1
Reducing the immunogenicity of fusion proteins
InactiveUS6992174B2Low immunogenicityHigh expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IIVaccine Immunogenicity
Disclosed are compositions and methods for producing fusion proteins with reduced immunogenicity. Fusion proteins of the invention include a junction region having an amino acid change that reduces the ability of a junctional epitope to bind to MHC Class II, thereby reducing its interaction with a T-cell receptor. Methods of the invention involve analyzing, changing, or modifying one or more amino acids in the junction region of a fusion protein in order to identify a T-cell epitope and reduce its ability to interact with a T cell receptor. Compositions and methods of the invention are useful in therapy.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
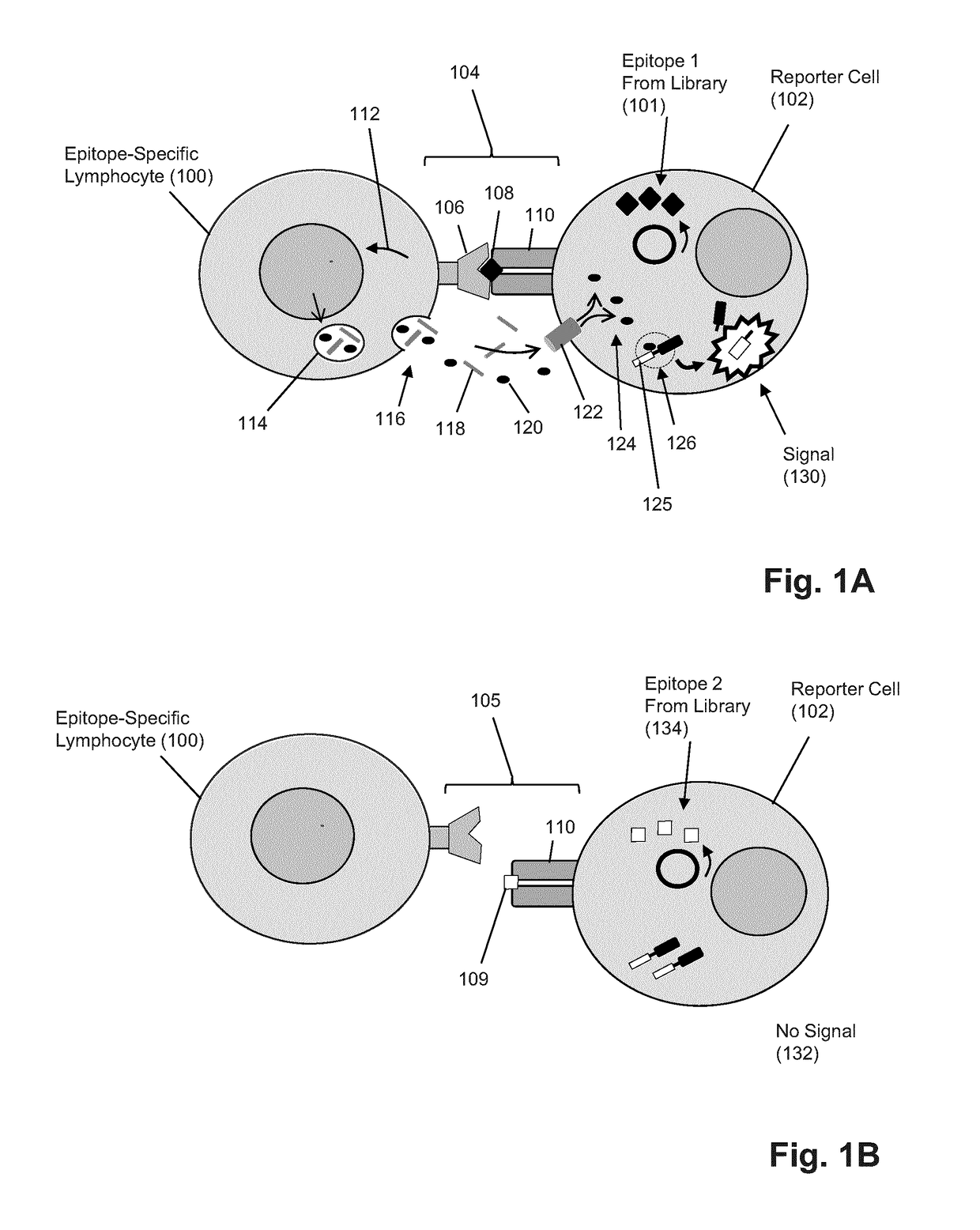
T-cell epitope identification
ActiveUS20180052176A1Efficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideMembrane bound
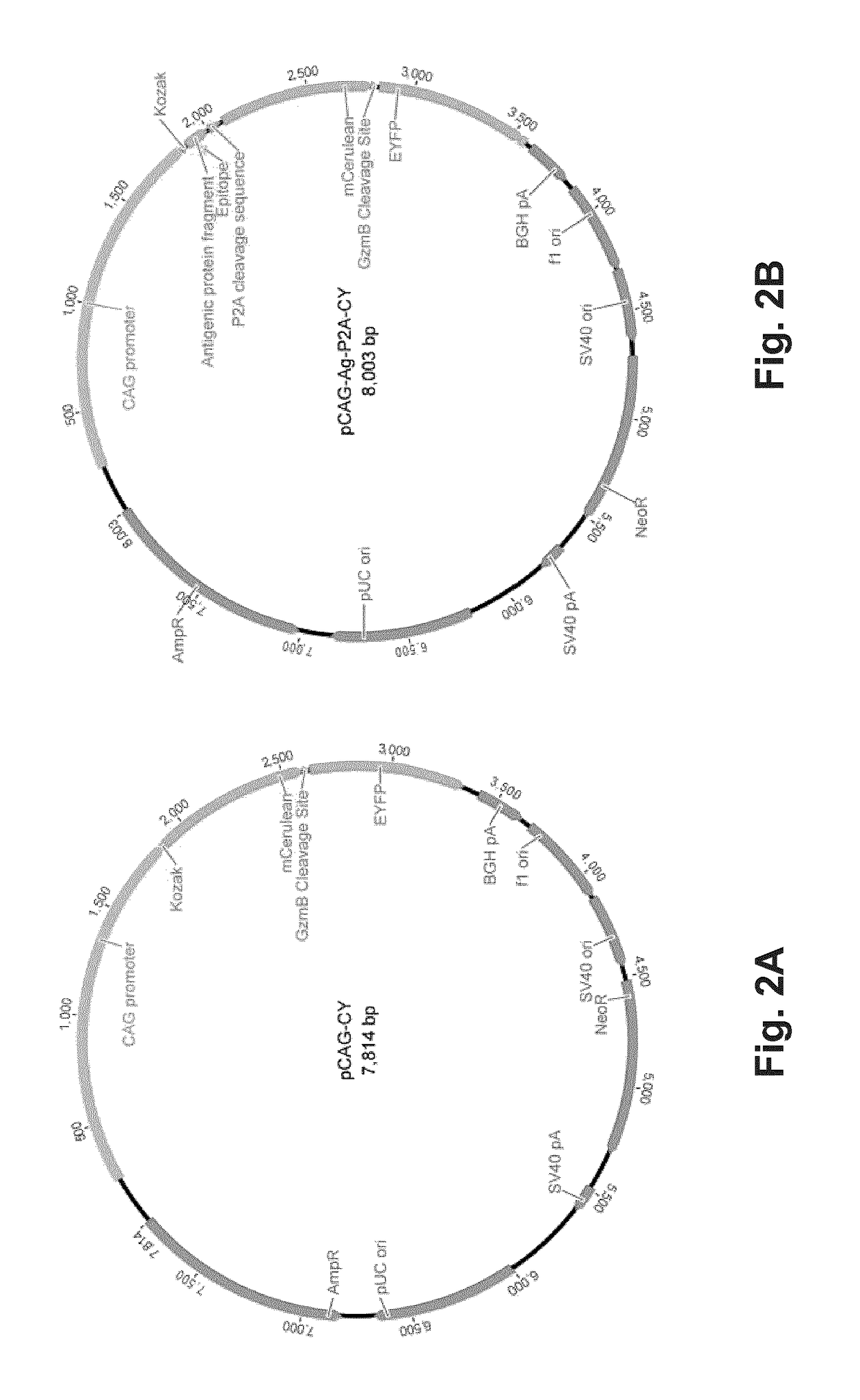
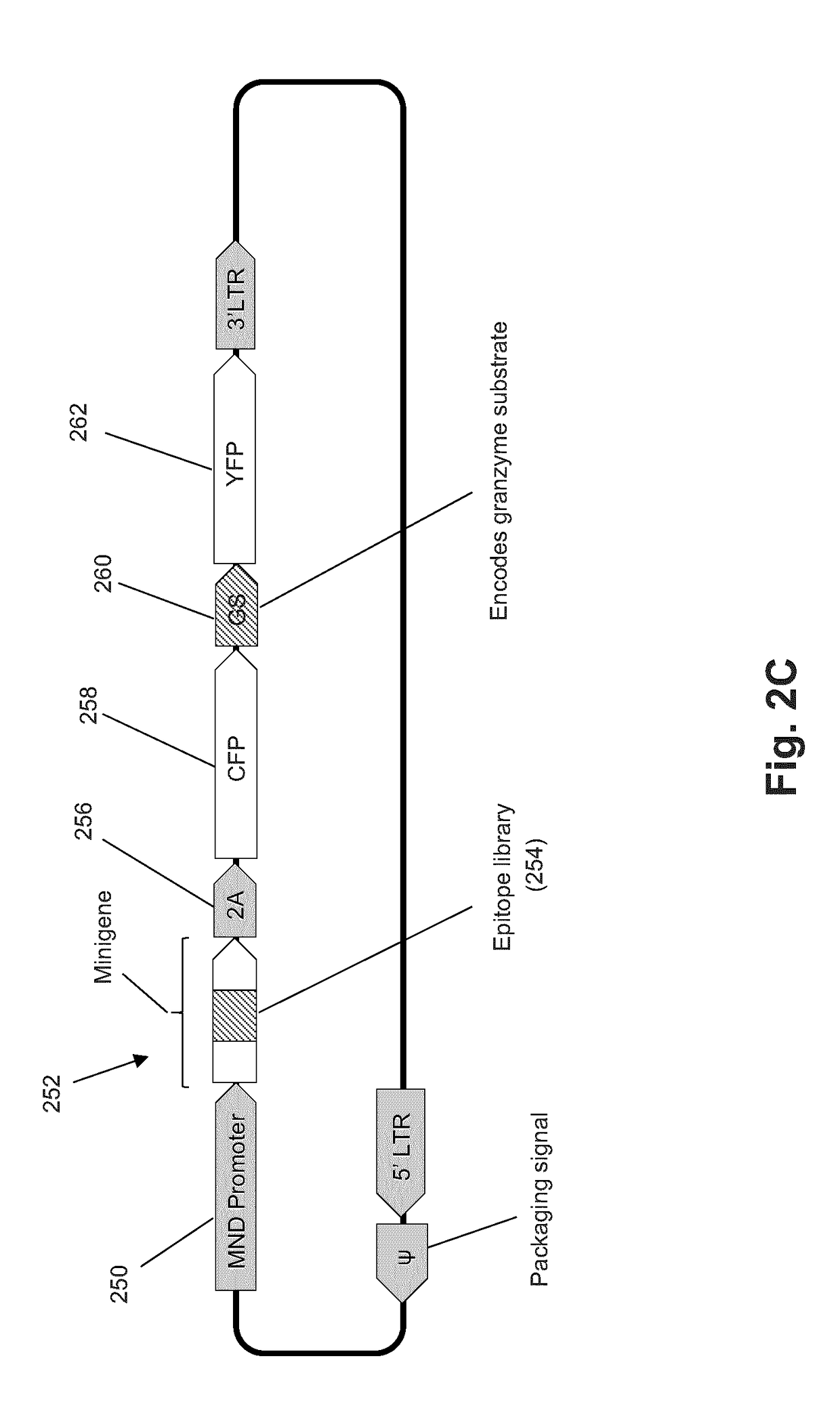
The present invention is a method for determining the identity of the epitopes recognized by T-cells. The method consists of expressing an encoded library of candidate epitope sequences in a recipient reporter cell capable of providing a detectable signal upon cytotoxic attack from a single cognate T-cell followed by contacting the reporter cells with T-cells of interest. The reporter cells with a single indicating cytotoxic attack from a T-cell are isolated and then analyzed by next-generation sequencing in order to identify the epitope sequences. Specifically disclosed is a method in which a library of candidate epitope-encoding nucleic acids are expressed in cells which feature a membrane-bound major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein, said library produced by transfection of plasmids featuring both a nucleotide encoding the candidate epitope and a nucleotide encoding a FRET-based fluorescent protein cleaved by granzyme.
Owner:PROVINCIAL HEALTH SERVICES AUTHORITY
Influenza immunogen and vaccine
InactiveUS20060115489A1High antibody titerEasy to prepareSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHepatitis B immunizationHepatitis B virus
A chimeric, carboxy-terminal truncated hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid (HBc) protein is disclosed that contains an immunogen for inducing the production of antibodies to the influenza M2 protein. An immunogenic influenza sequence in two to four copies is preferably expressed at or near the N-terminus or in the HBc immunogenic loop sequence. The HBc chimer preferably contains an influenza-specific T cell epitope and is preferably engineered for both enhanced stability of self-assembled particles and enhanced yield of those chimeric particles. Methods of making and using the chimers are also disclosed.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR BIOLOGICS CO +1
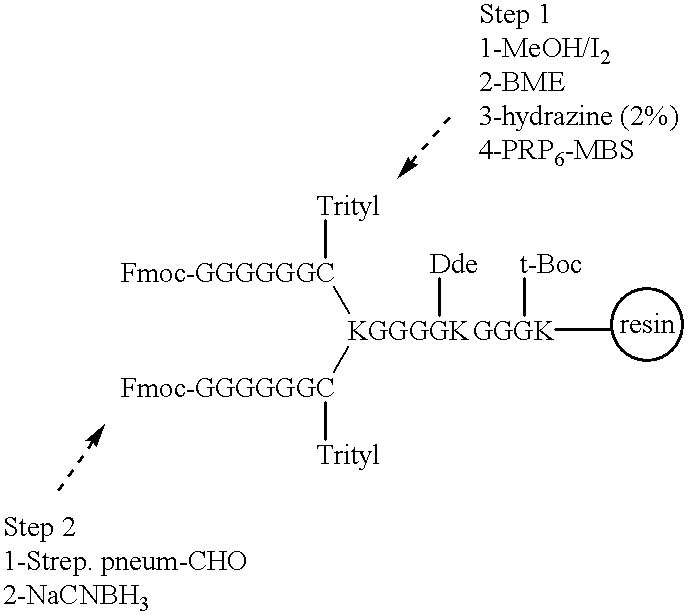
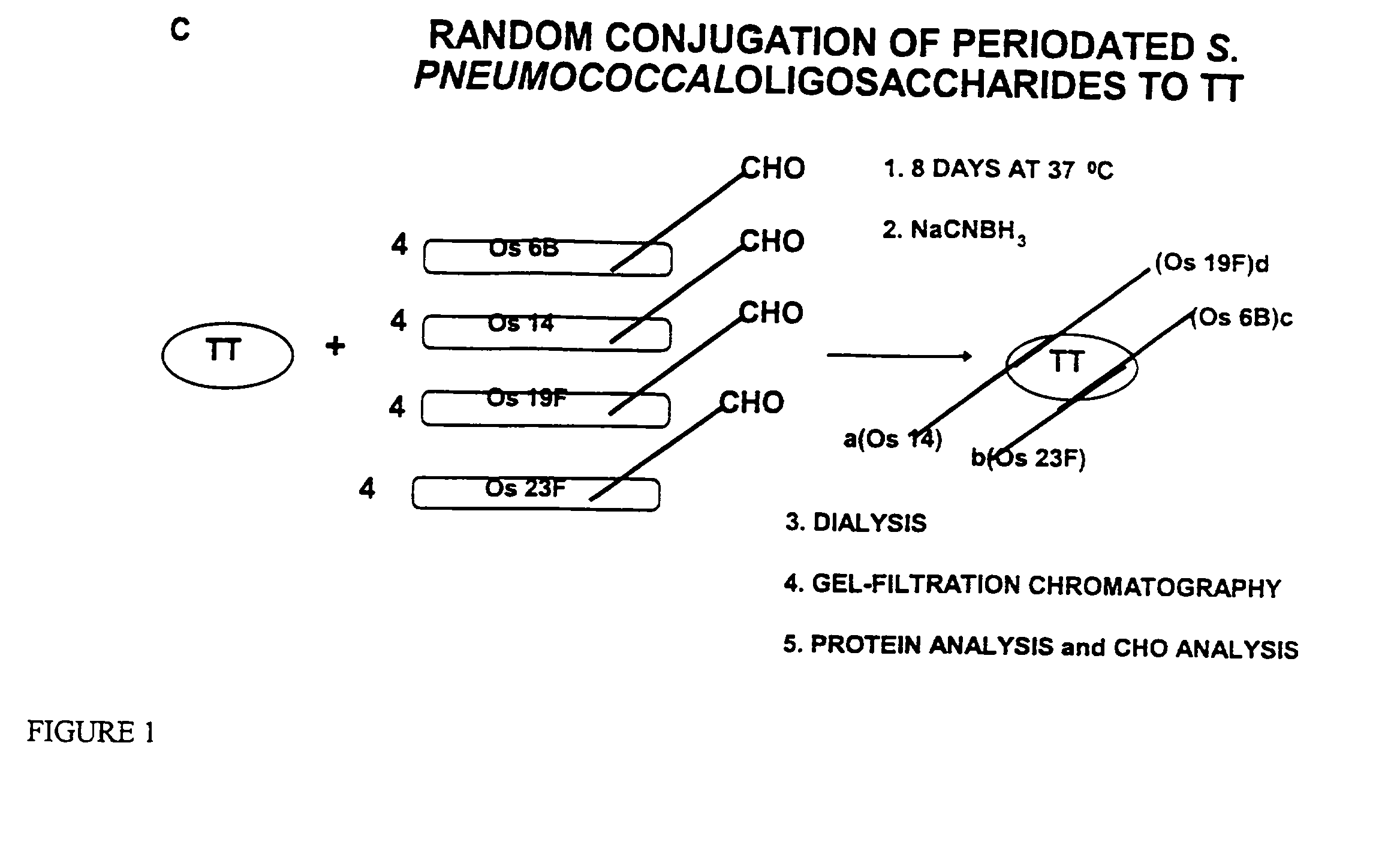
Novel multi-oligosaccharide glycoconjugate bacterial meningitis vaccines
InactiveUS20010048929A1Inhibition effectWeight increaseAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerotypeTumor antigen
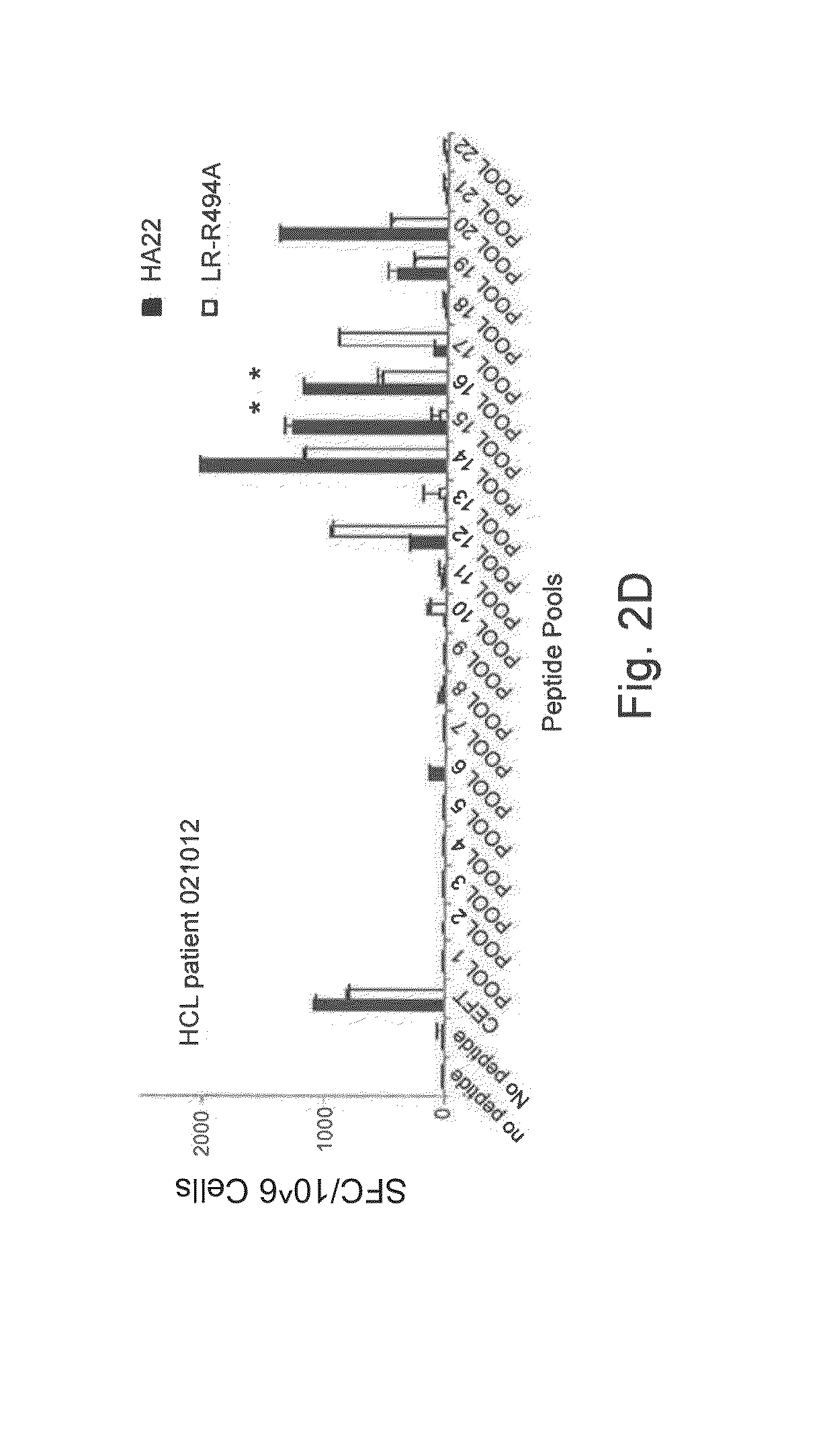
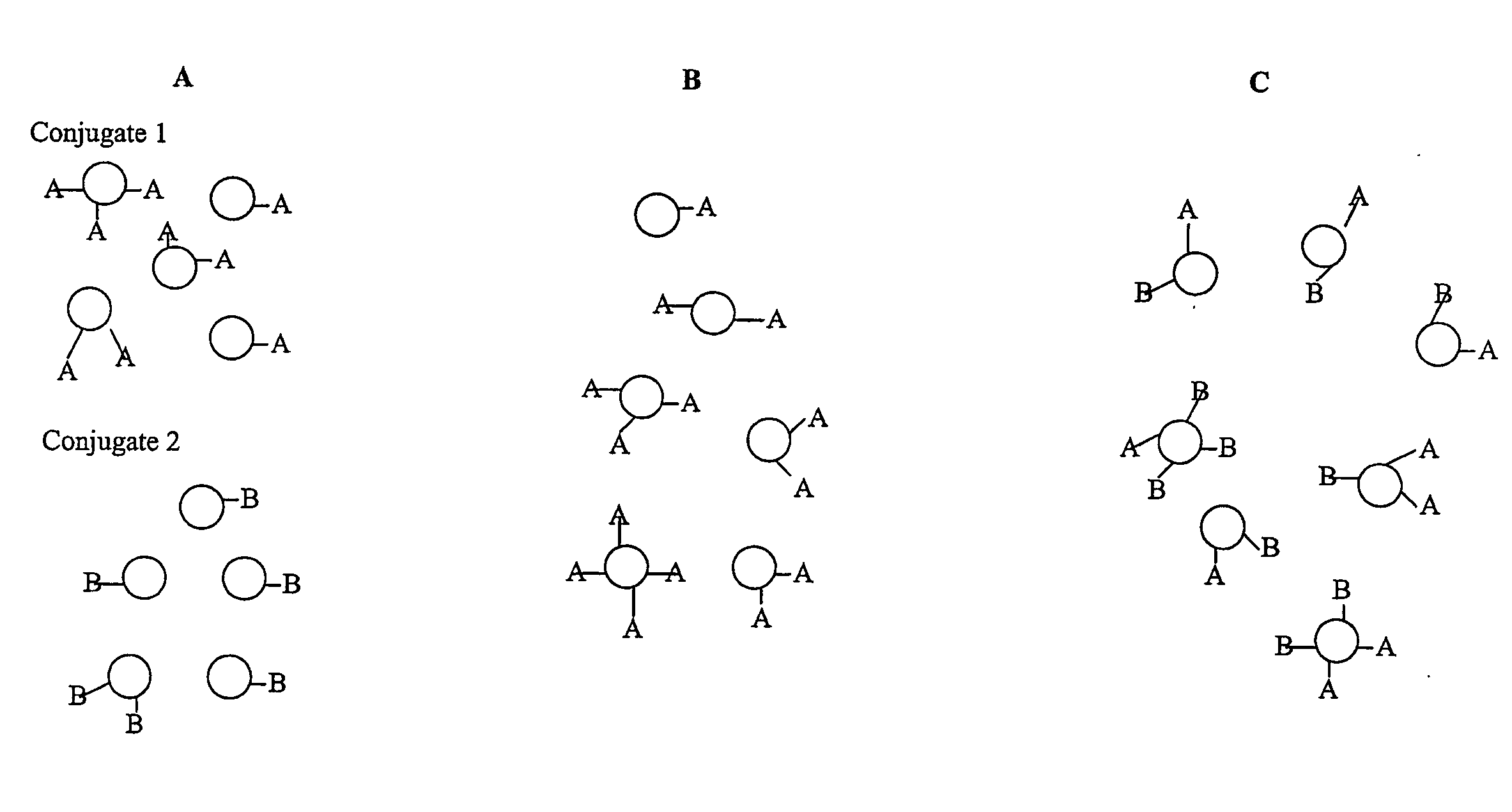
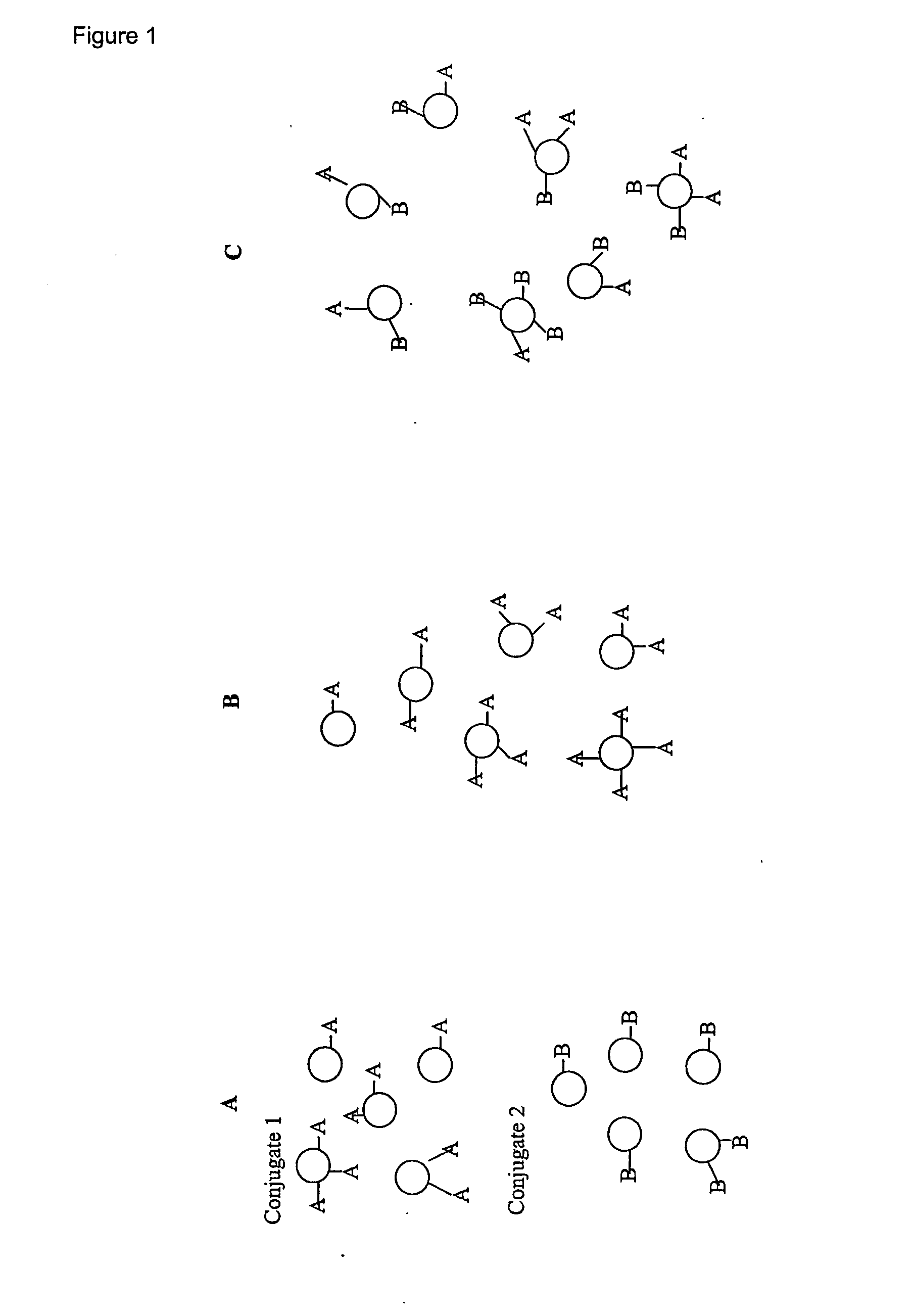
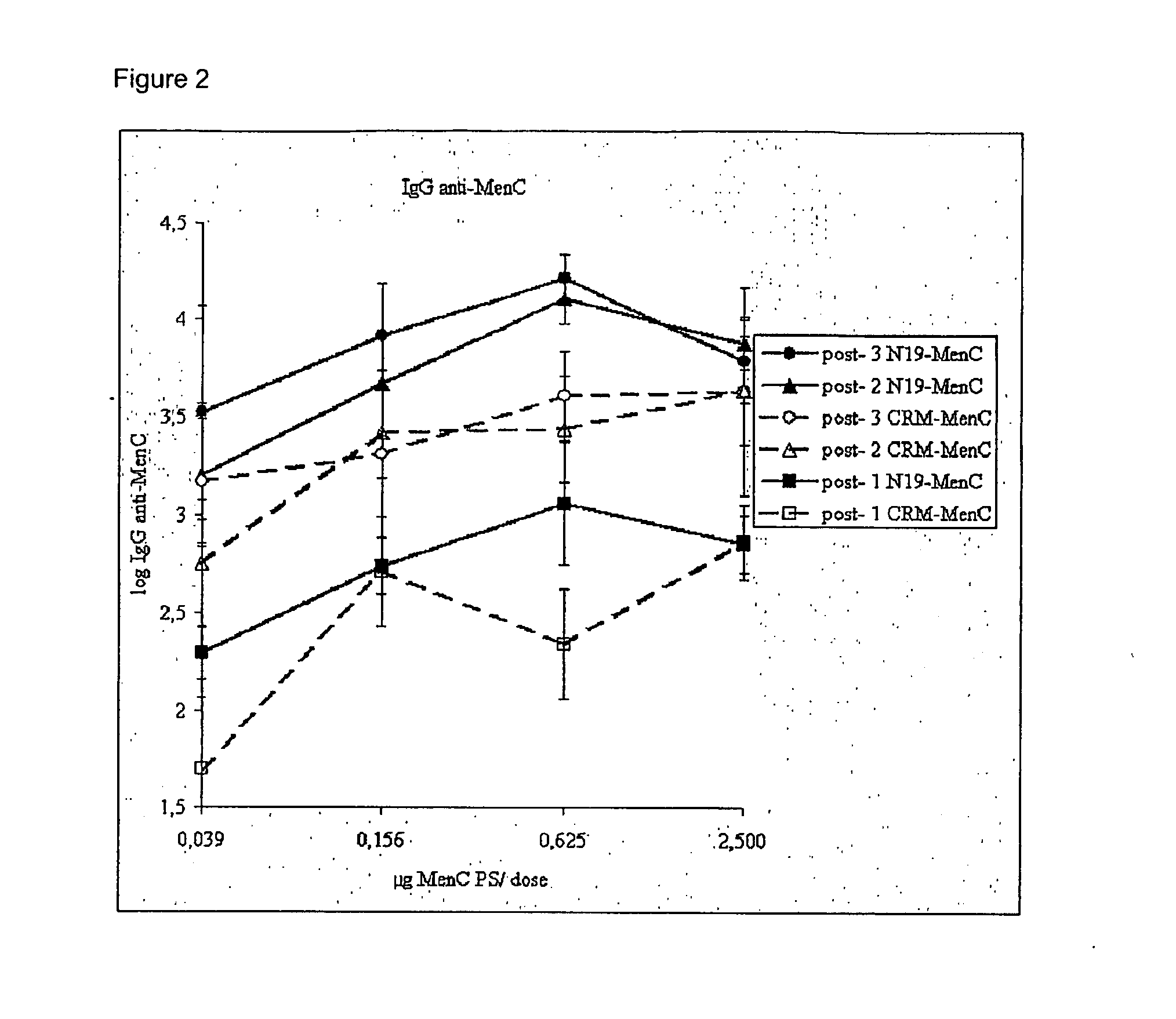
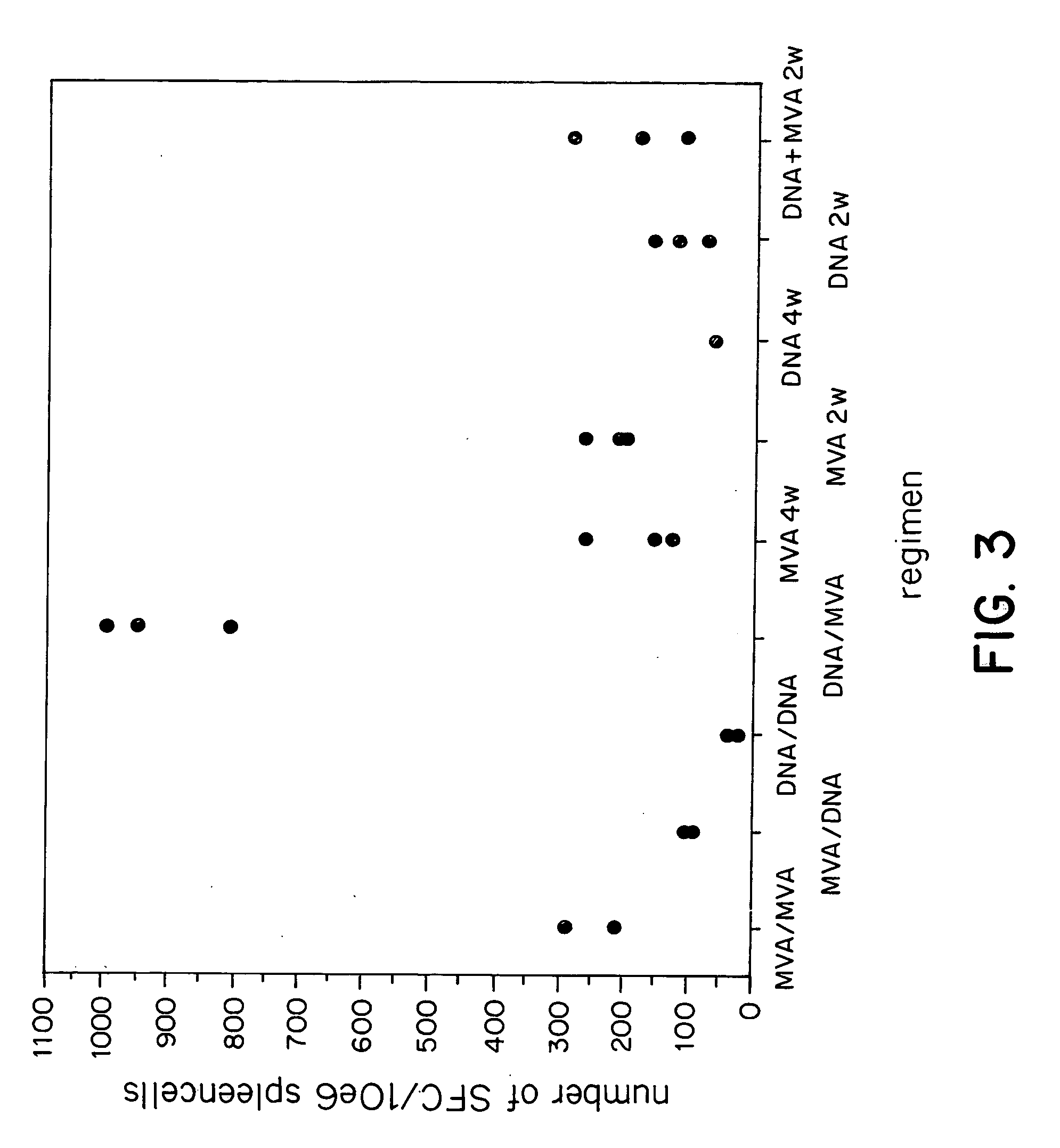
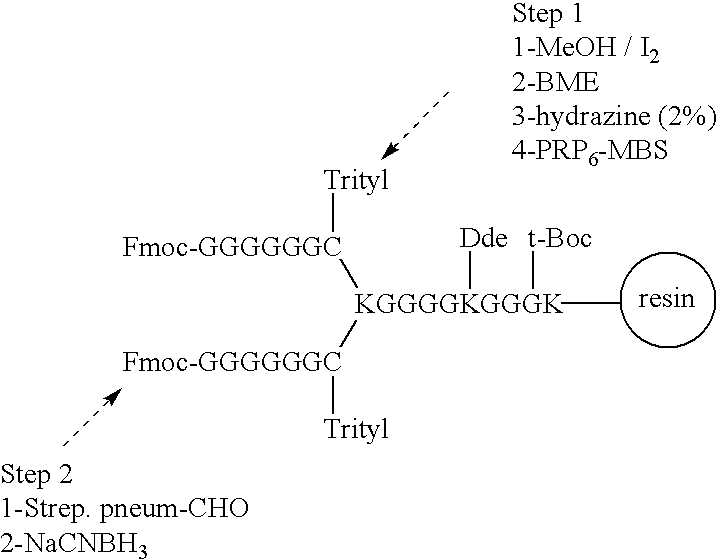
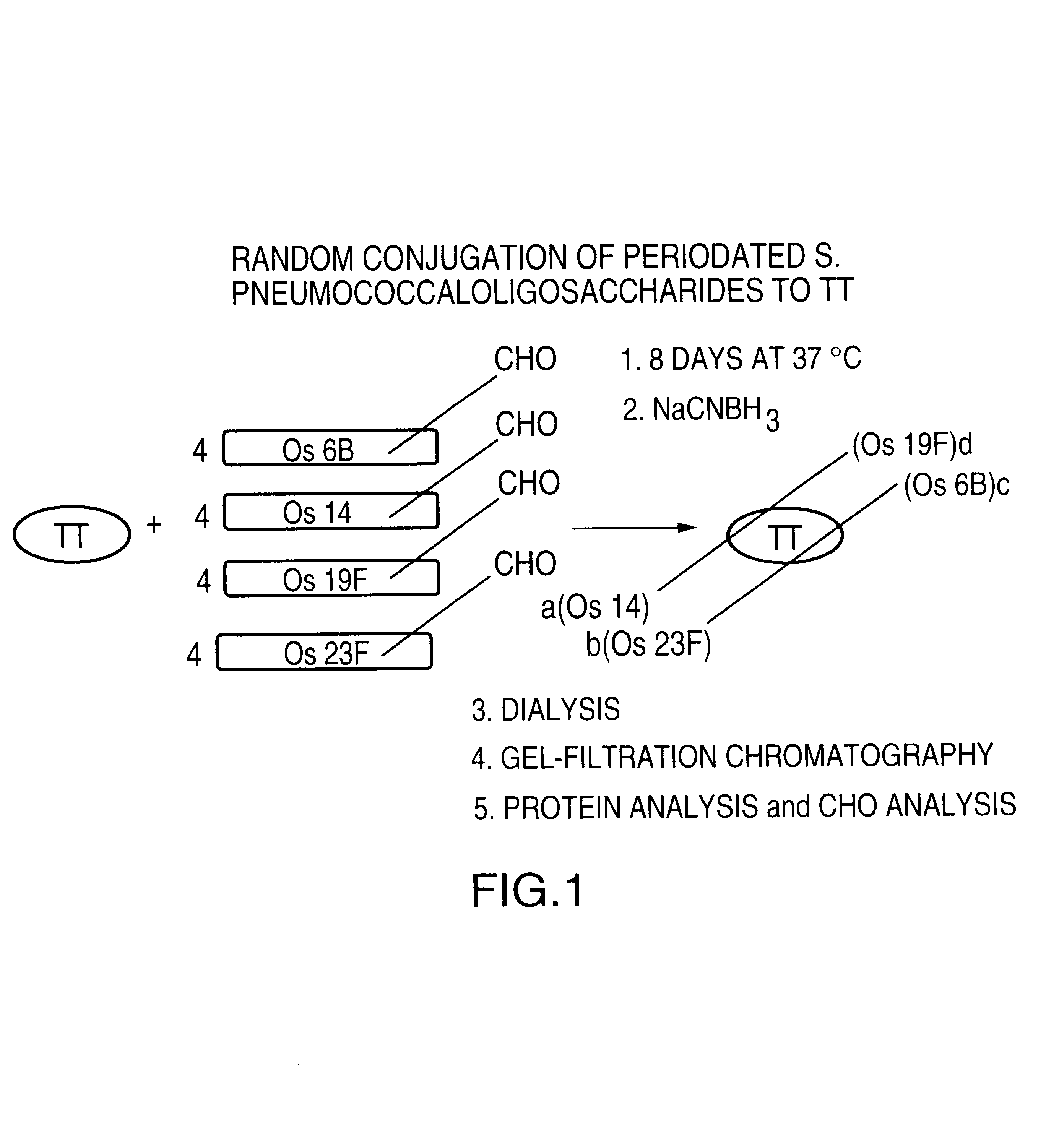
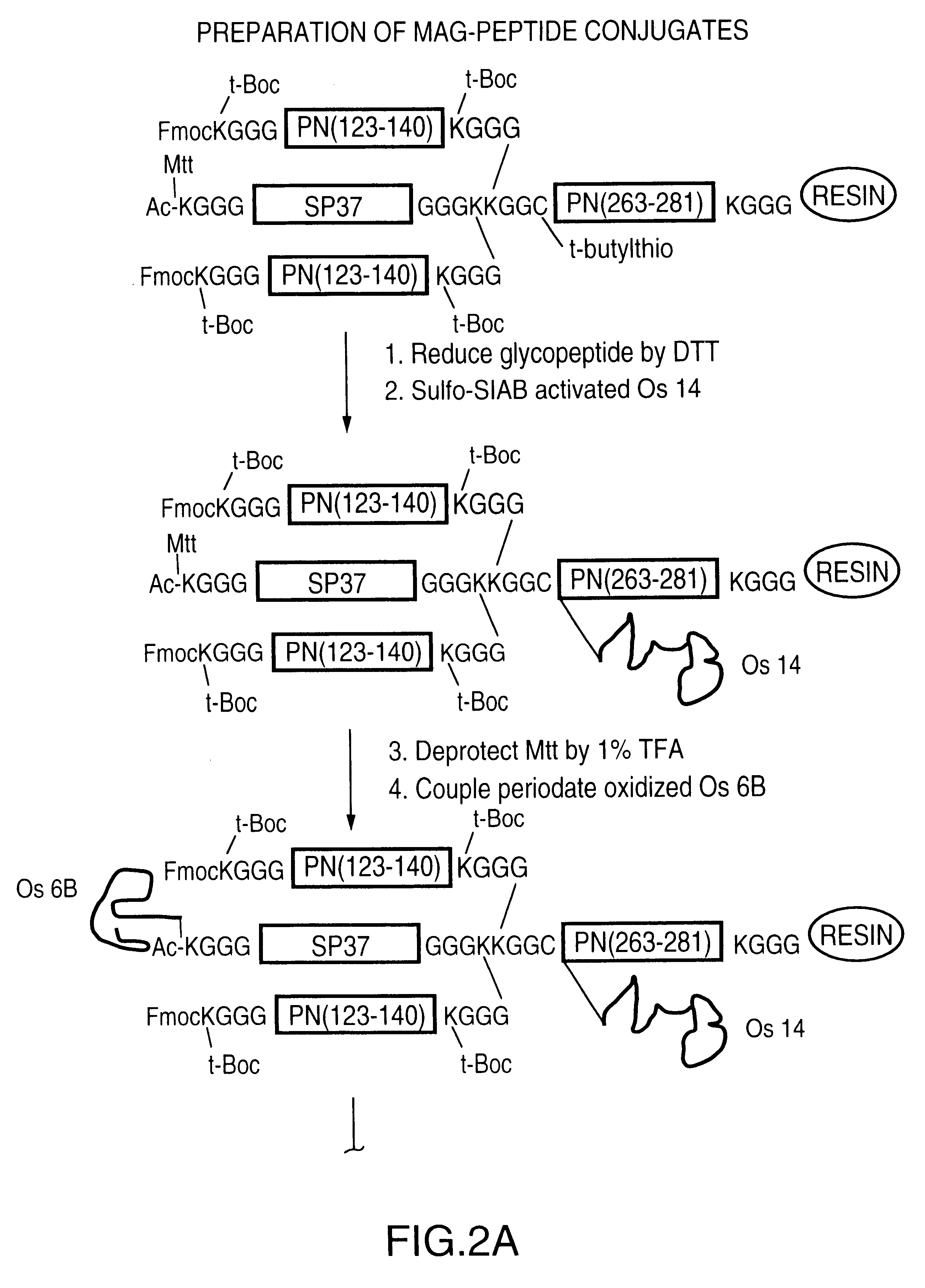
Multivalent immunogenic molecules comprise a carrier molecule containing at least one functional T-cell epitope and multiple different carbohydrate fragments each linker to the carrier molecule and each containing at least one functional B-cell epitope. The carrier molecule inputs enhanced immunogenicity to the multiple carbohydrate fragments. The carbohydrate fragments may be capsular oligosaccharide fragments from Streptococcus pneumoniae, which may be serotypes 1, 4, 5, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F or 23F, or Neisseria meningitidis, which may be serotype A, B, C, W-135 or Y. Such oligosaccharide fragments may be sized from 2 to 5 kDa. Alternatively, the carbohydrate fragments may be fragments of carbohydrate-based tumor antigens, such as Globo H, LeY or STn. The multivalent molecules may be produced by random conjugation or site-directed conjugation of the carbohydrate fragments to the carrier molecule. The multivalent molecules may be employed in vaccines or in the generation of antibodies for diagnostic application.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
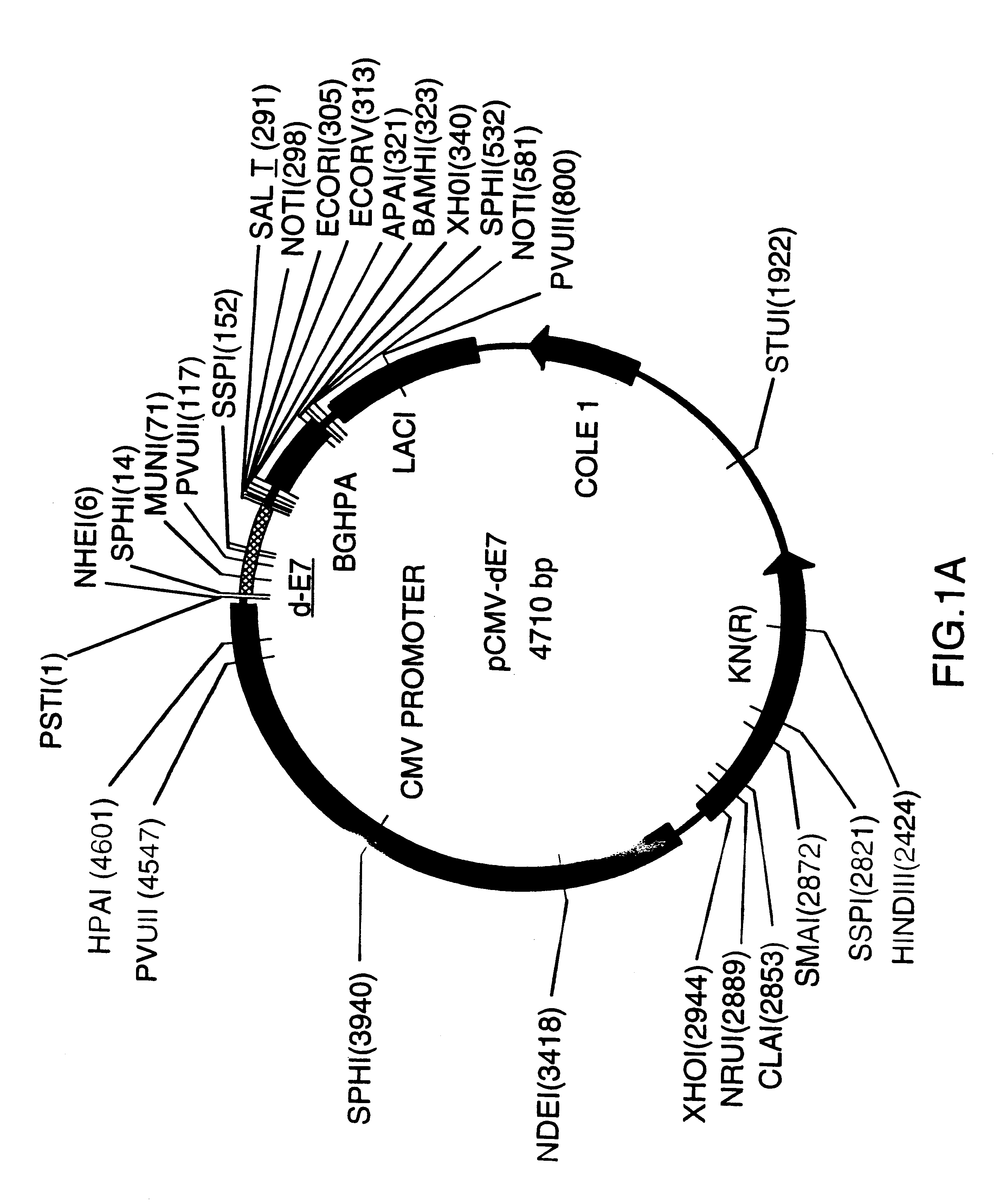
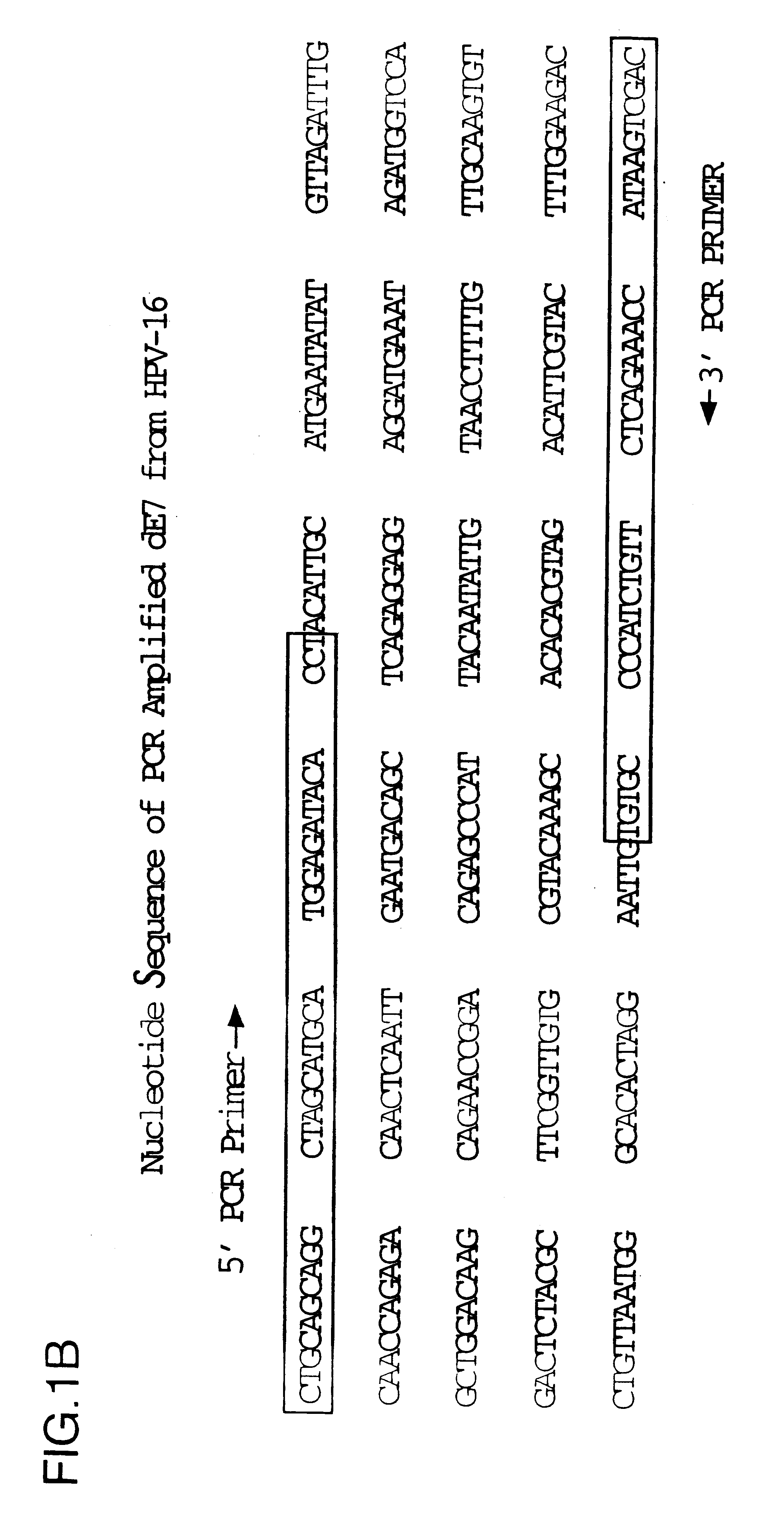
Vectors for DNA immunization against cervical cancer
InactiveUS6235523B1Improving immunogenicitySlow and sustained releaseOrganic active ingredientsVirusesAntigenDna immunization
Vectors for DNA immunization against cervical cancer comprise a nucleic acid molecule encoding at least one non-toxic T-cell epitope of the E6 and / or E7 antigens of a strain of human papilloma virus (HPV) associated with cervical cancer, such as HPV-16, and a promoter operatively coupled to the nucleic acid molecule for expression of the nucleic acid molecule in a host to which the vector is administered.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
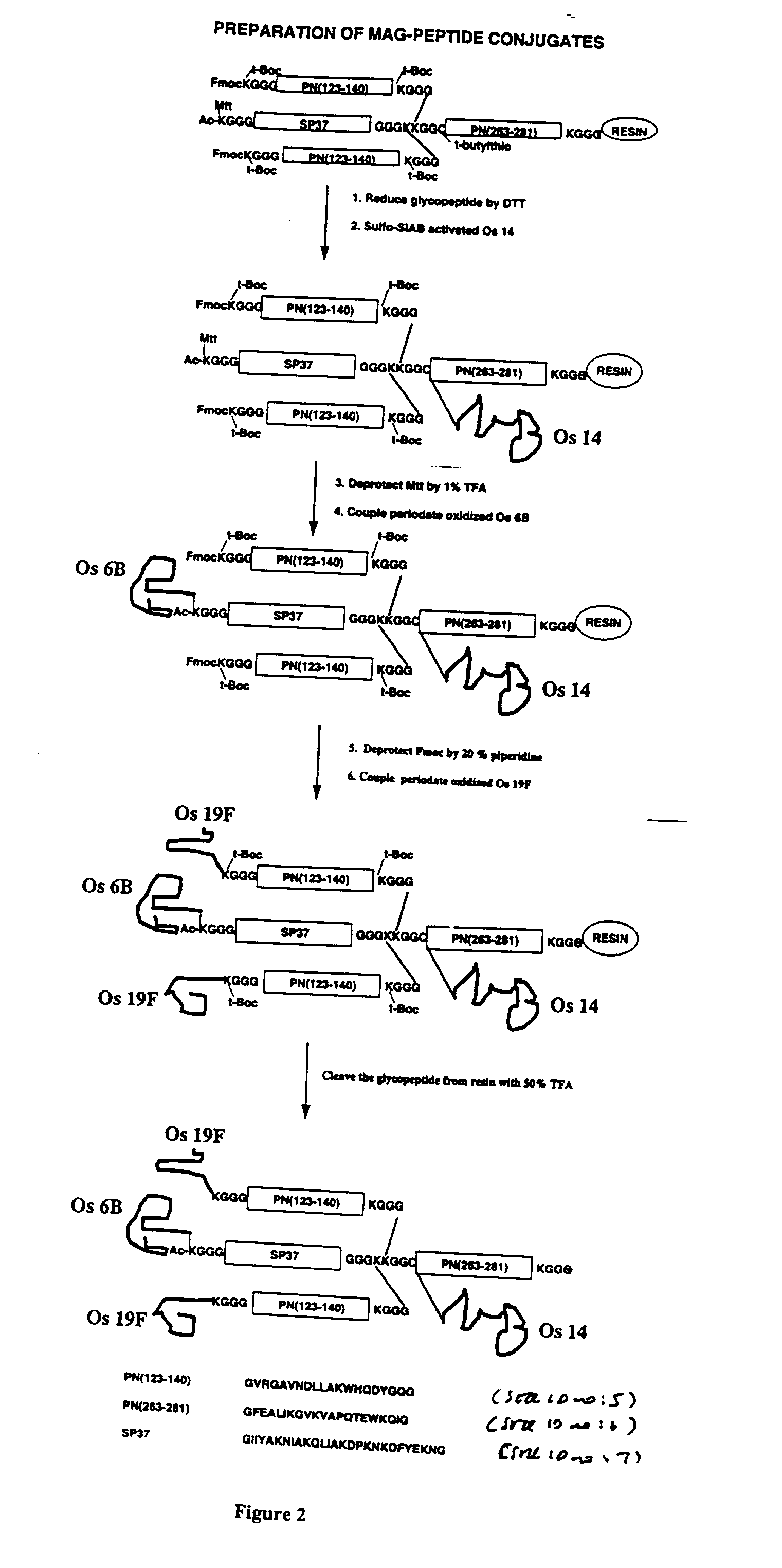
Polyepitope carrier protein
InactiveUS6855321B1Facilitate subsequent purificationAccurate supervisionAntibacterial agentsVirusesCarrier proteinCD4 antigen
The invention relates to polyepitope carrier proteins that comprise at least five CD4+ T cell epitopes, for conjugation to capsular polysaccharides. The carrier proteins are use useful as components of vaccines that can elicit a T-cell dependent immune response. These vaccines arm particularly useful to confer protection against infection from encapsulated bacteria in infants between the ages of 3 months and about 2 years.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
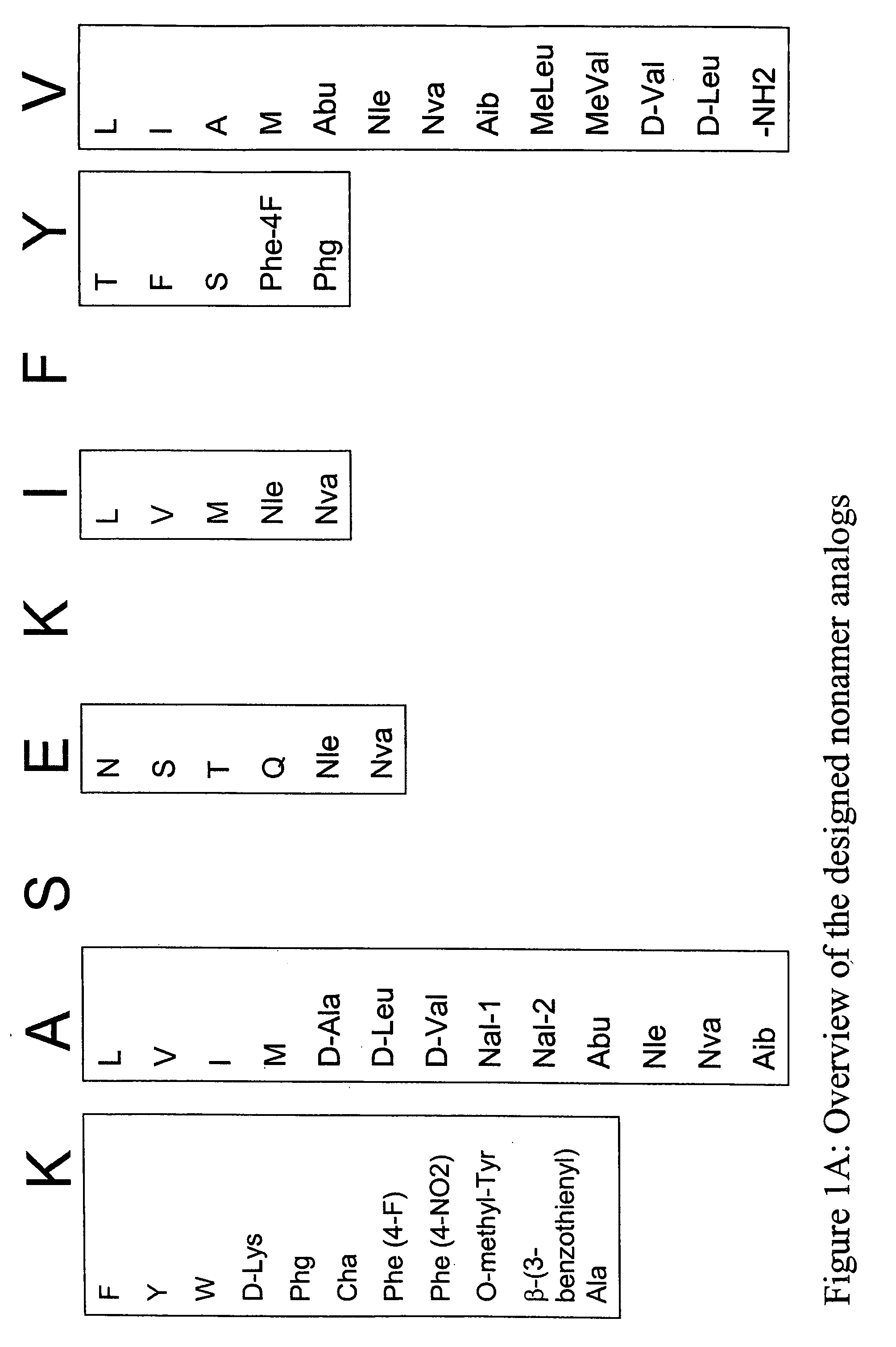
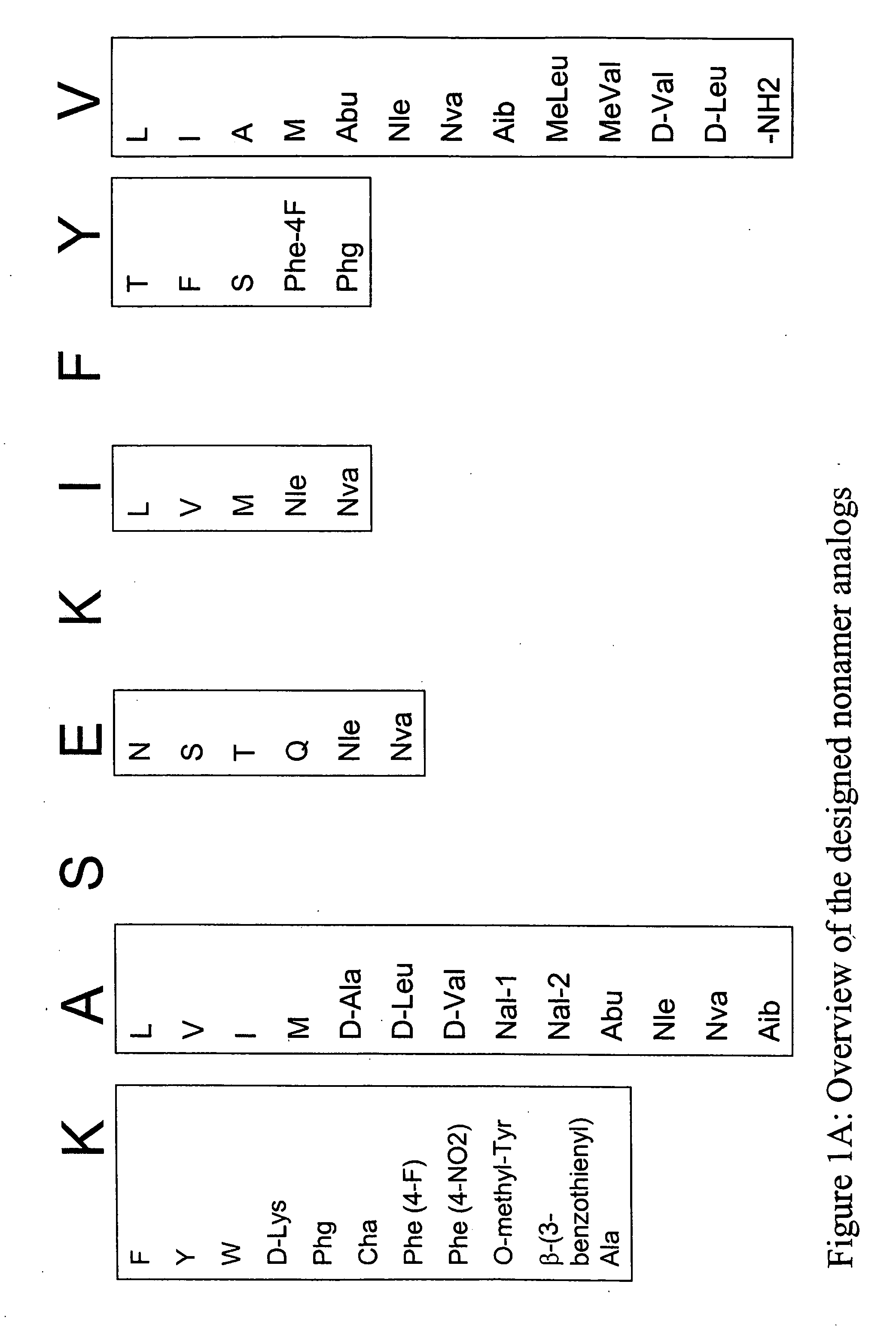
Epitope analogs
InactiveUS20060057673A1Similar and improved immunological propertyTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionAmino acid
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
SSX-2 peptide analogs
InactiveUS20060063913A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid substitutionAmino acid
Some embodiments relate to analogs of peptides corresponding to class I MHC-restricted T cell epitopes and methods for their generation. These analogs can contain amino acid substitutions at residues that directly interact with MHC molecules, and can confer improved, modified or useful immunologic properties. Additionally classes of analogs, in which the various substitutions comprise the non-standard residues norleucine and / or norvaline, are disclosed.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Antigenic composition
InactiveUS7148191B2Exceeds contributionEffective T cell responseBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesAntigenPeptide
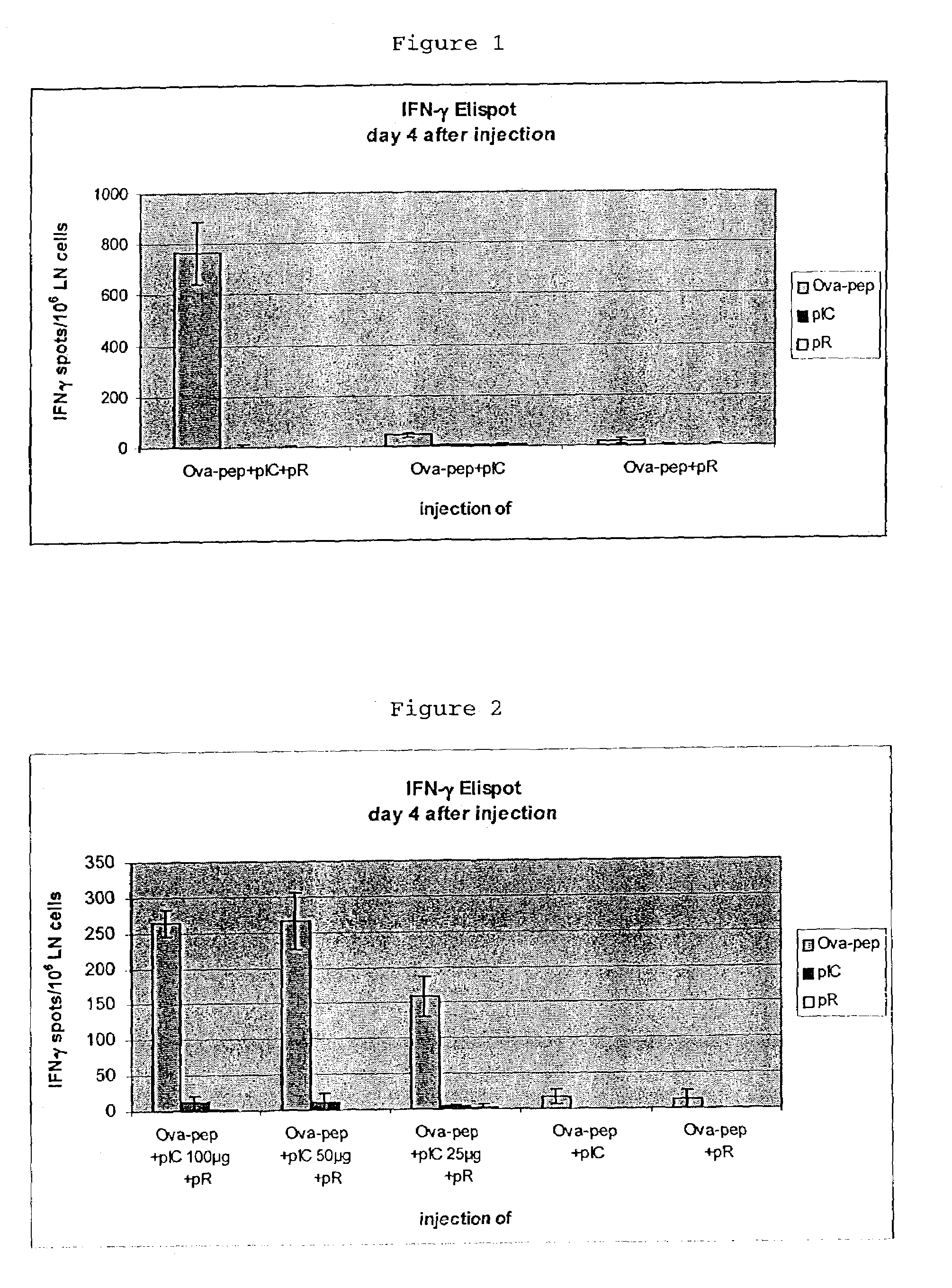
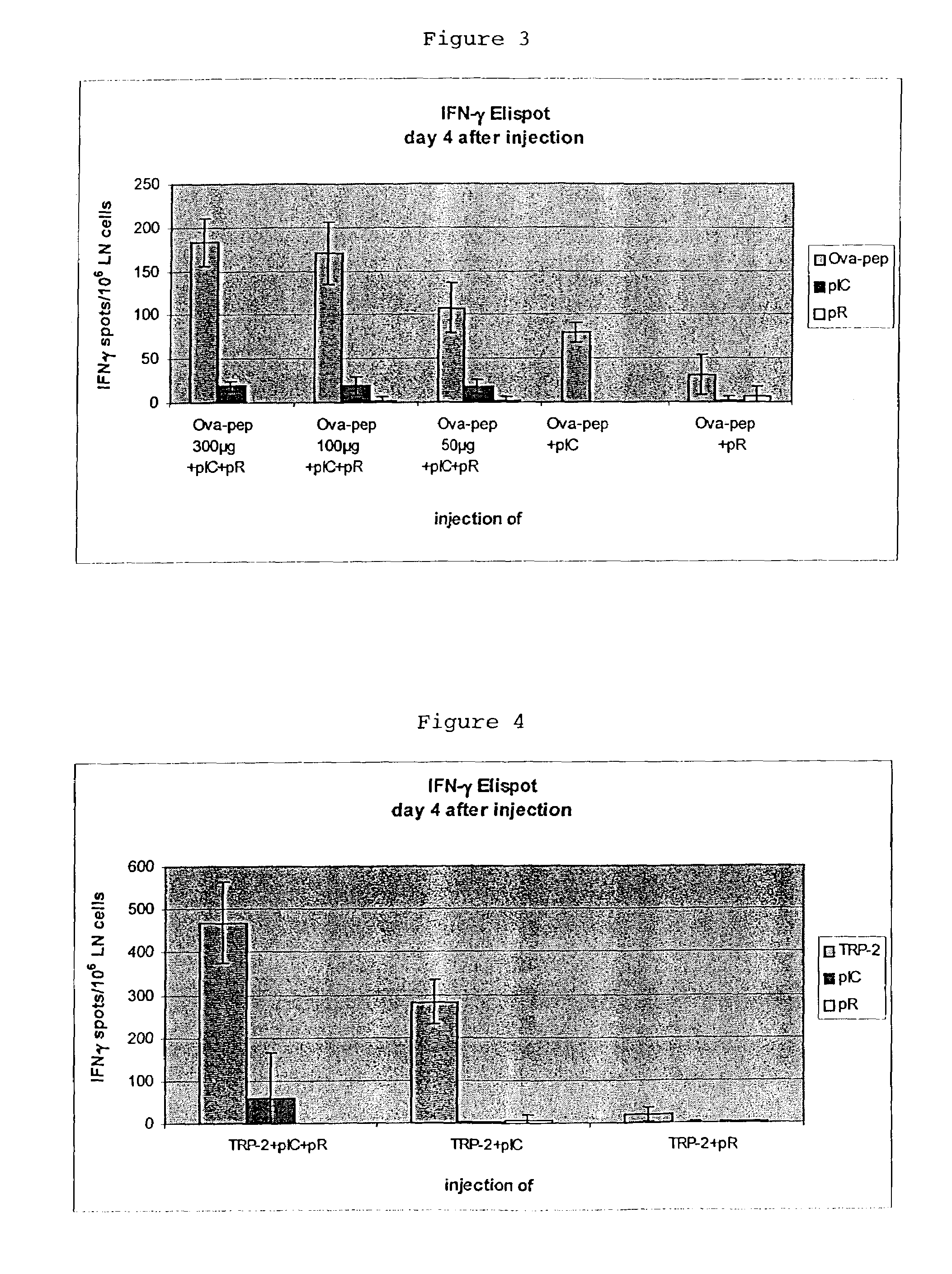
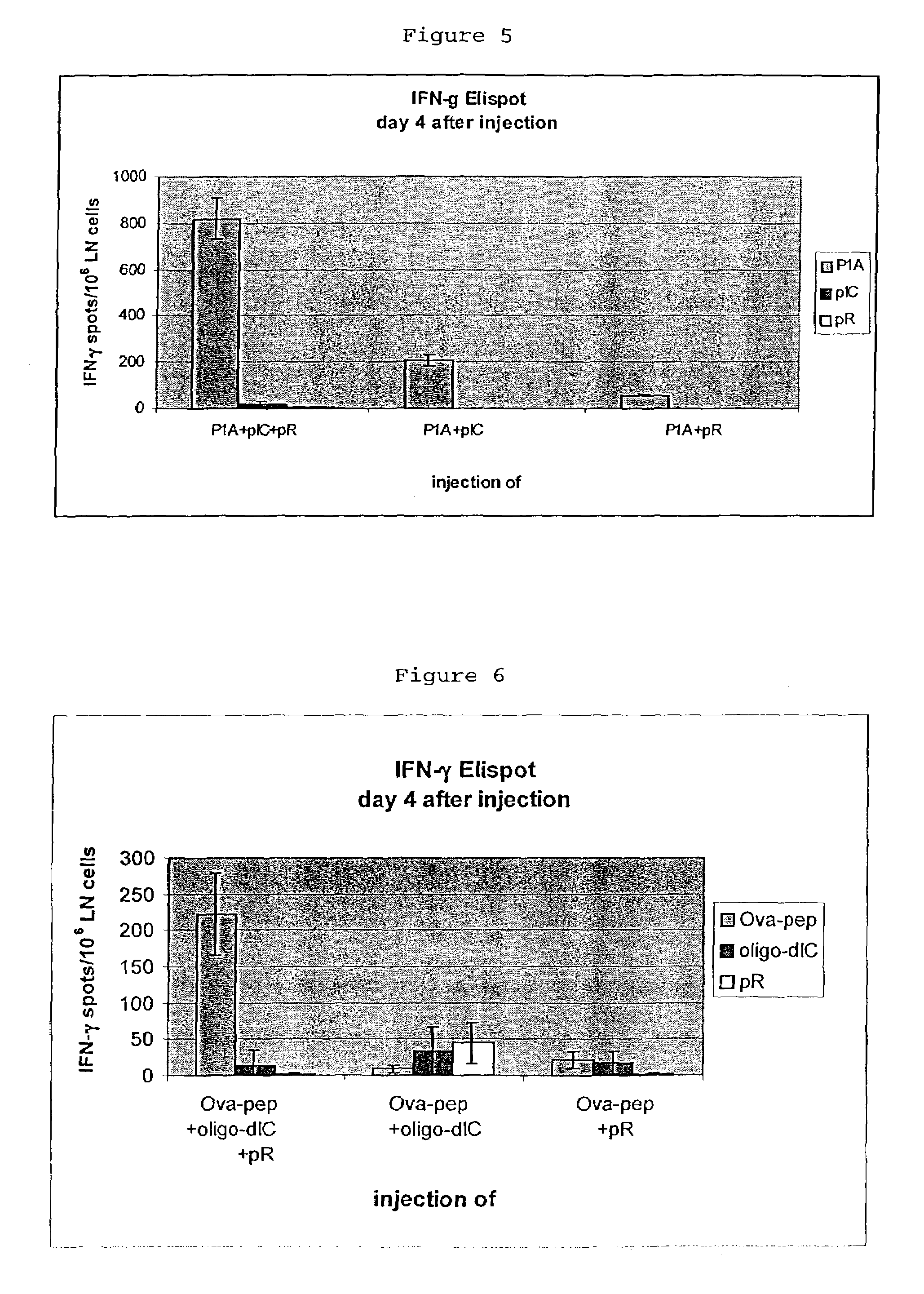
The invention relates to a composition comprisinga T cell epitope or a mixture of T cell epitopesa polycationic peptide anda nucleic acid based on inosin and cytosin and its use as a vaccine.
Owner:INTERCELL BIOMEDIZINISCHE FORSCHNUNGS & ENTWICKLUNG AG
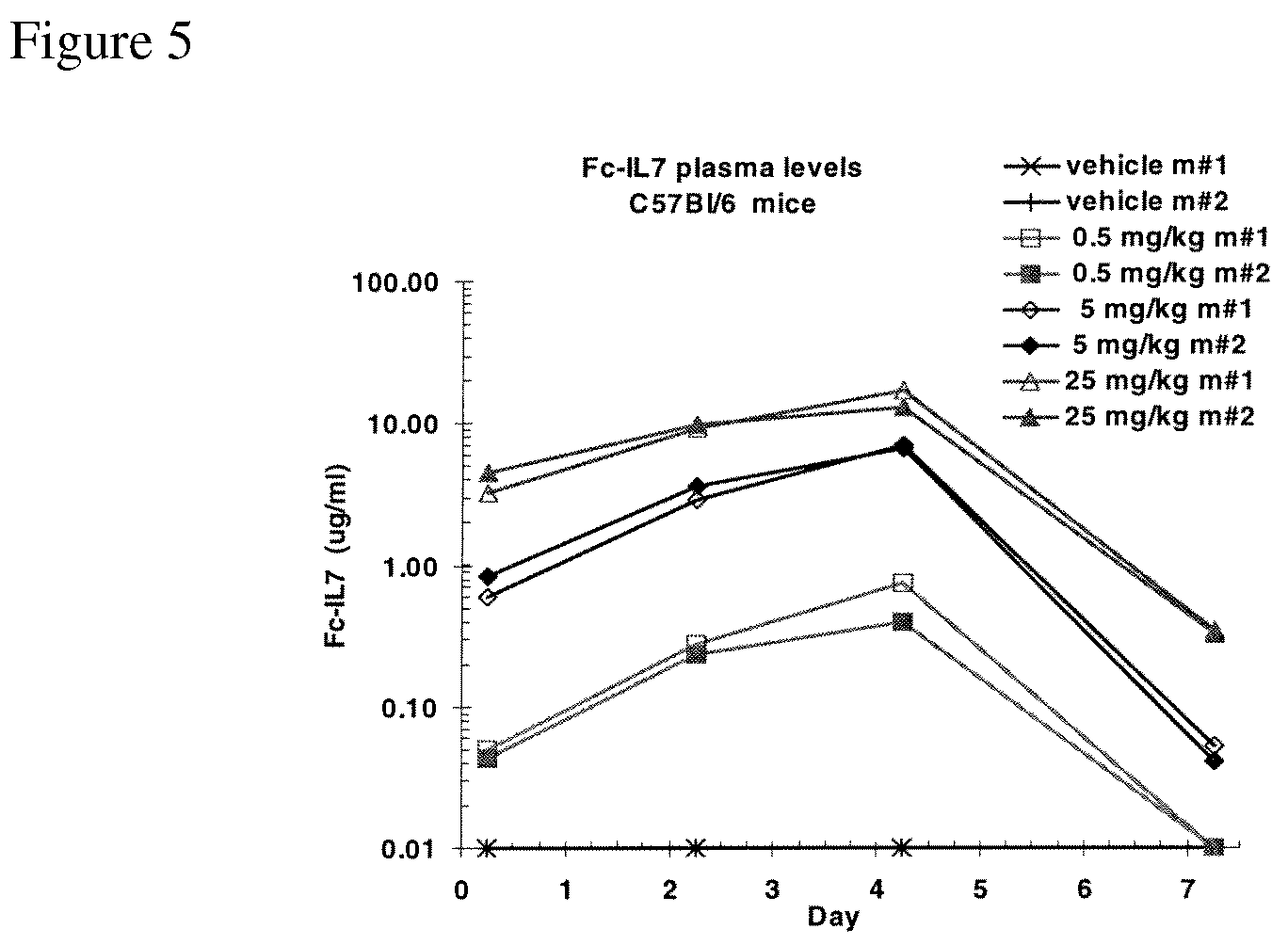
IL-7 variants with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS20060141581A1Low immunogenicityGood biological propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsWhite blood cellVaccine Immunogenicity
Modified interleukin-7 (IL-7) polypeptides are disclosed. The modified IL-7 polypeptides have alterations to one or more potential T-cell epitopes, thereby to reduce a T-cell response.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Novel method for down-regulation of amyloid
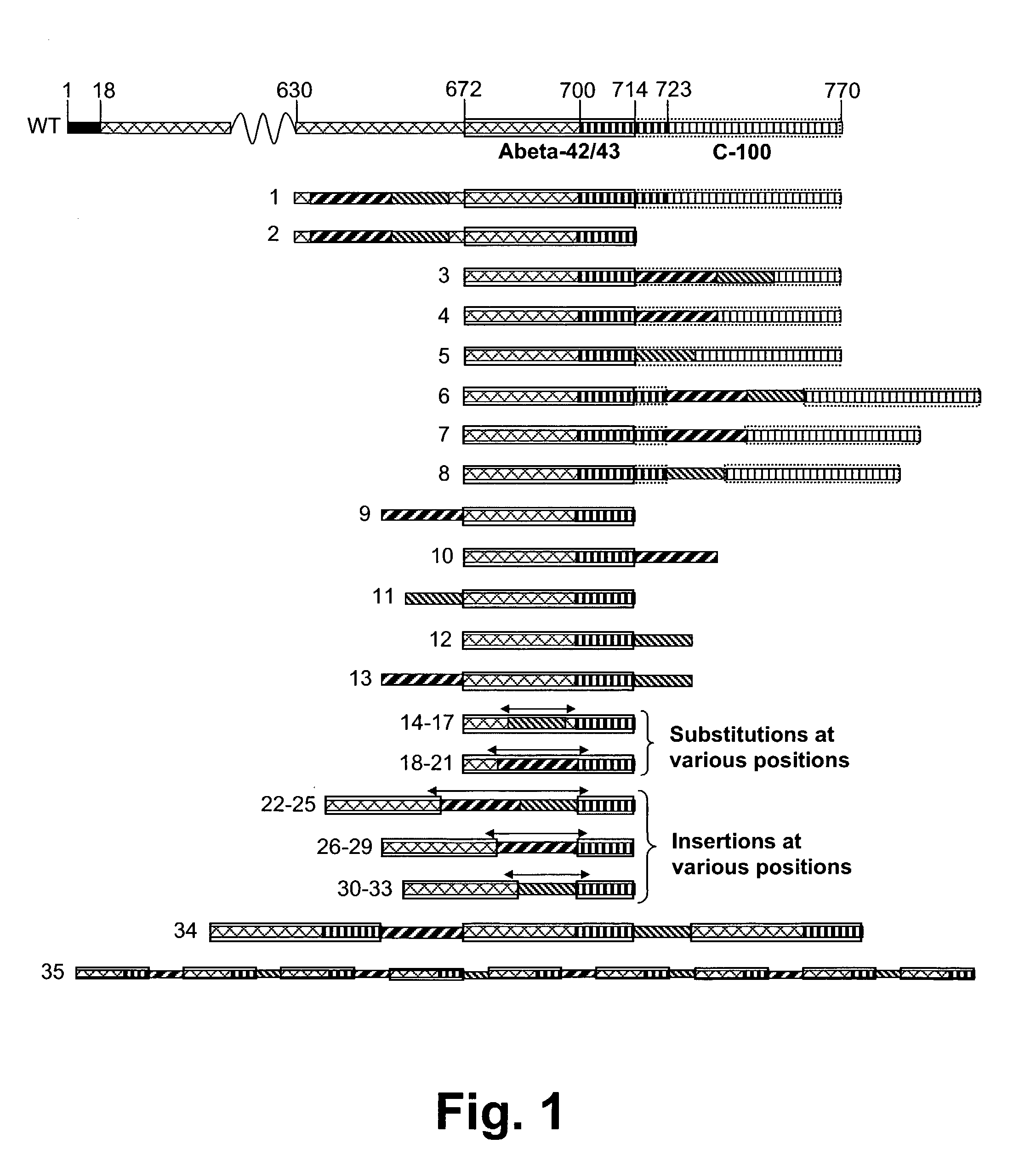
Disclosed are novel methods for combatting diseases characterized by deposition of amyloid. The methods generally rely on immunization against amyloid precursor protien (APP) or beta amyloid (Abeta). Immunization is preferably effected by administration of analogues of autologous APP or Abeta, said analogues being capable of inducing antibody production against the autologous amyloidogenic polypeptides. Especially preferred as an immunogen is autologous Abeta which has been modified by introduction of one single or a few foreign, immunodominant and promiscuous T-cell epitopes. Also disclosed are nucleic acid vaccination against APP or Abeta and vaccination using live vaccines as well as methods and means useful for the vaccination. Such methods and means include methods for the preparation of analogues and pharmaceutical formulations, as well as nucleic acid fragments, vectors, transformed cells, polypeptides and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
Methods and reagents for vaccination which generate a CD8 T cell immune response
InactiveUS6663871B1Increase boost effectGood effectVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenVaccination
New methods and reagents for vaccination are described which generate a CD8 T cell immune response against malarial and other antigens such as viral and tumour antigens. Novel vaccination regimes are described which employ a priming composition and a boosting composition, the boosting composition comprising a non-replicating or replication-impaired pox virus vector carrying at least one CD8 T cell epitope which is also present in the priming composition.
Owner:OXXON THERAPEUTICS LTD
Modified pseudomonas exotoxin a
ActiveUS20150099707A1Increased serum half-lifeOptimize treatment planOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
The invention provides a Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising an amino acid sequence having a substitution of one or more B-cell and / or T-cell epitopes. The invention further provides related chimeric molecules, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions. Methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal, methods of inhibiting the growth of a target cell, methods of producing the PE, and methods of producing the chimeric molecule are further provided by the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Saccharide Conjugate Vaccines
InactiveUS20080260773A1Improve bioavailabilityImprove efficacyAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsConjugate vaccineCarrier protein
The invention provides compositions comprising a combination of two or more monovalent conjugates, each of said two or more monovalent conjugates comprising a carrier protein comprising T cell epitopes from two or more pathogens conjugated to saccharide antigen. The invention also provides a multivalent conjugate comprising two or more antigenically distinct saccharide antigens conjugated to the same carrier protein molecule, wherein the carrier protein comprises T cell epitopes from two or more pathogens. Further compositions comprise one or more of said monovalent conjugates and one or more of said multivalent conjugates. The invention further provides methods for making said compositions and uses for said compositions.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Reducing the immunogenicity of fusion proteins
InactiveUS20060025573A1Improve clinical efficacyExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IICellular receptor
Disclosed are compositions and methods for producing fusion proteins with reduced immunogenicity. Fusion proteins of the invention include a junction region having an amino acid change that reduces the ability of a junctional epitope to bind to MHC Class II, thereby reducing its interaction with a T-cell receptor. Methods of the invention involve analyzing, changing, or modifying one or more amino acids in the junction region of a fusion protein in order to identify a T-cell epitope and reduce its ability to interact with a T cell receptor. Compositions and methods of the invention are useful in therapy.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
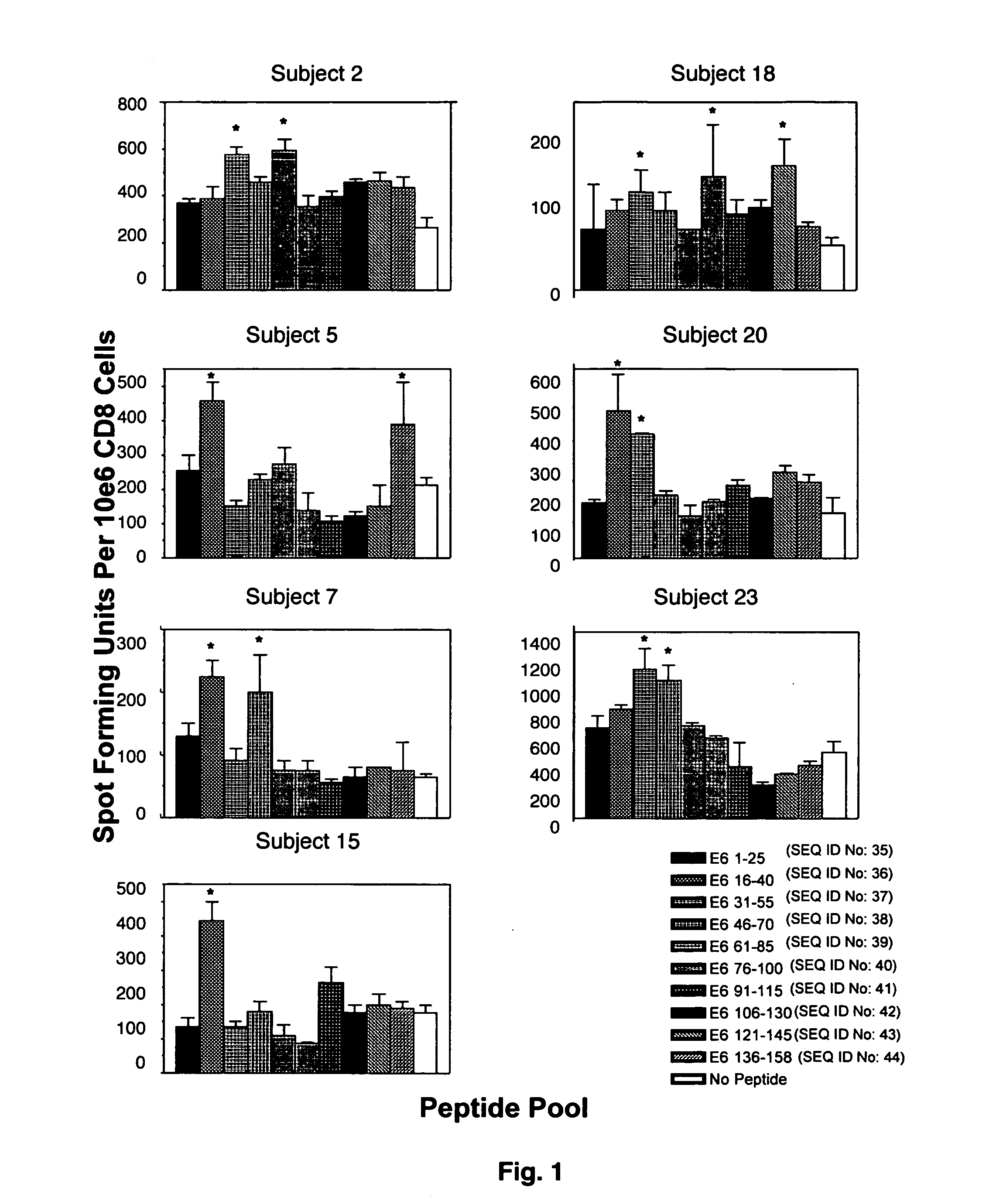
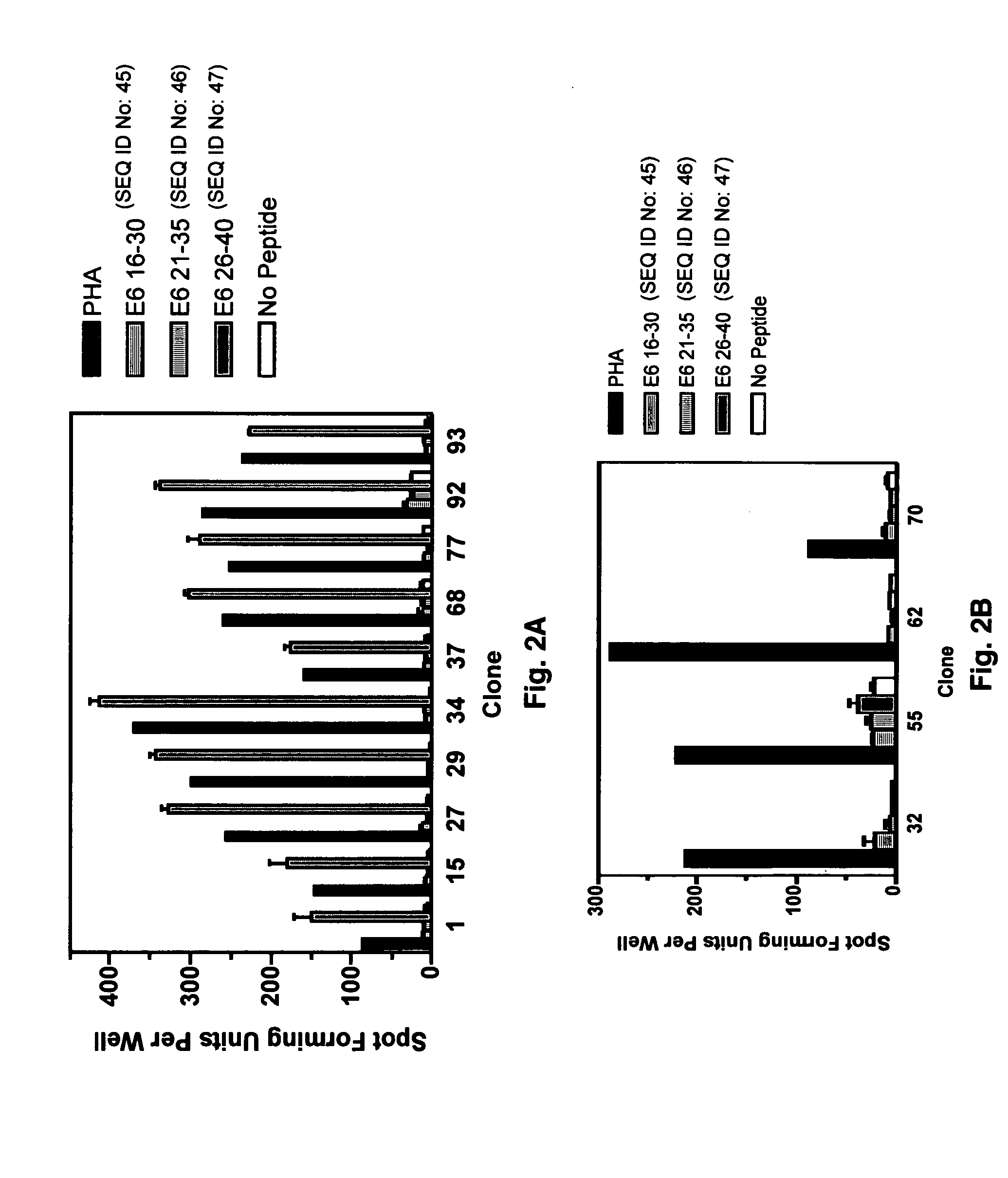
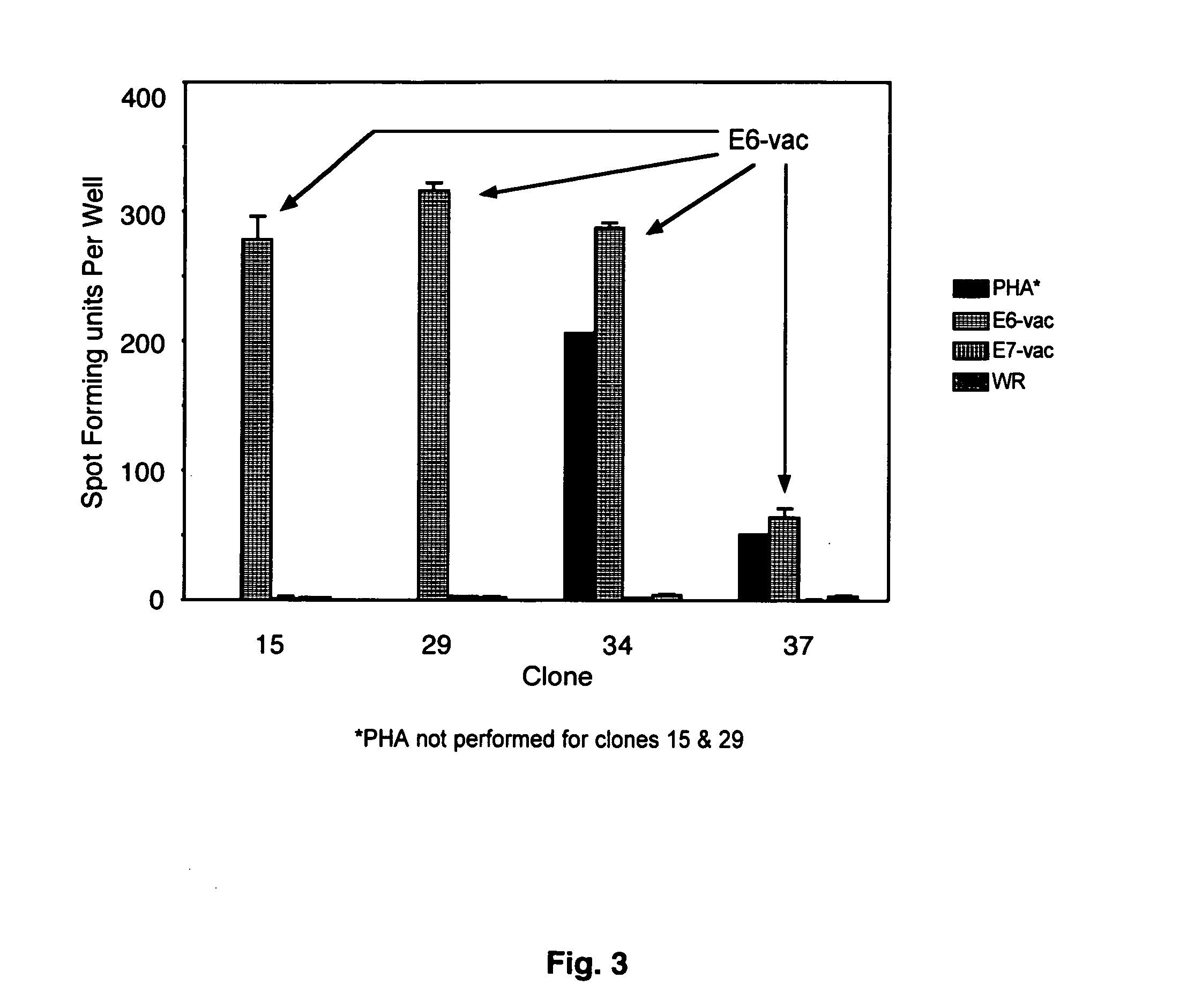
CD8 T cell epitopes in HPV 16 E6 and E7 proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060182763A1Peptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsHuman papillomavirusDendritic cell
The present invention is directed to the examination of the pattern of immunodominant CD8 T cell epitopes in the E6 and E7 protein of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its further characterization in terms of its amino acid sequence and HLA restriction. These epitopes are identified based on their ability to induce strong CD8 T cell response and therefore, are important as sources of antigens for dendritic cell immunotherapy to treat cervical cancer. The present invention contemplates identifying a number of similar epitopes restricted by a wide variety of HLA types so that they can be used in concert to develop a preventative vaccine, which can be used for general population.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
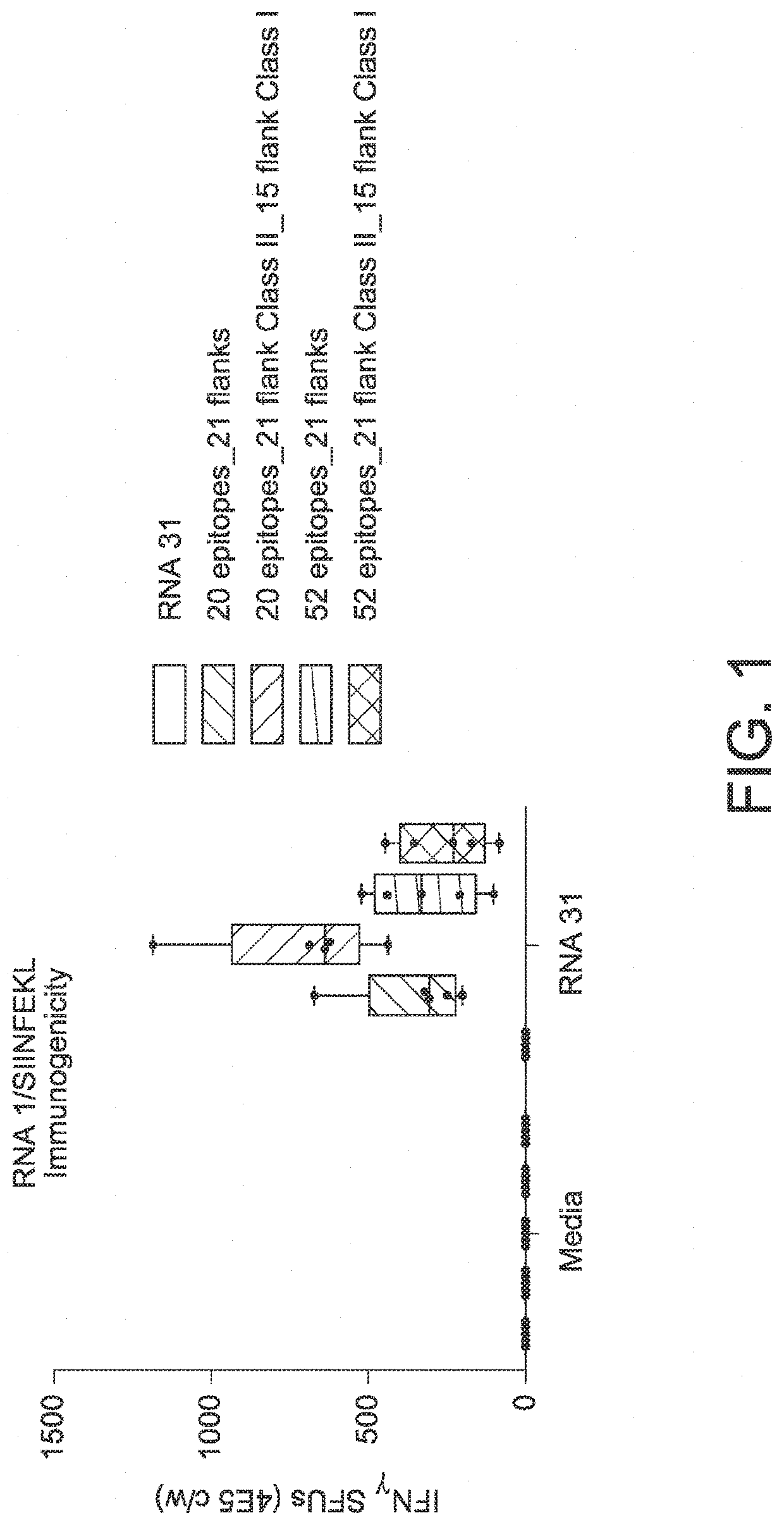
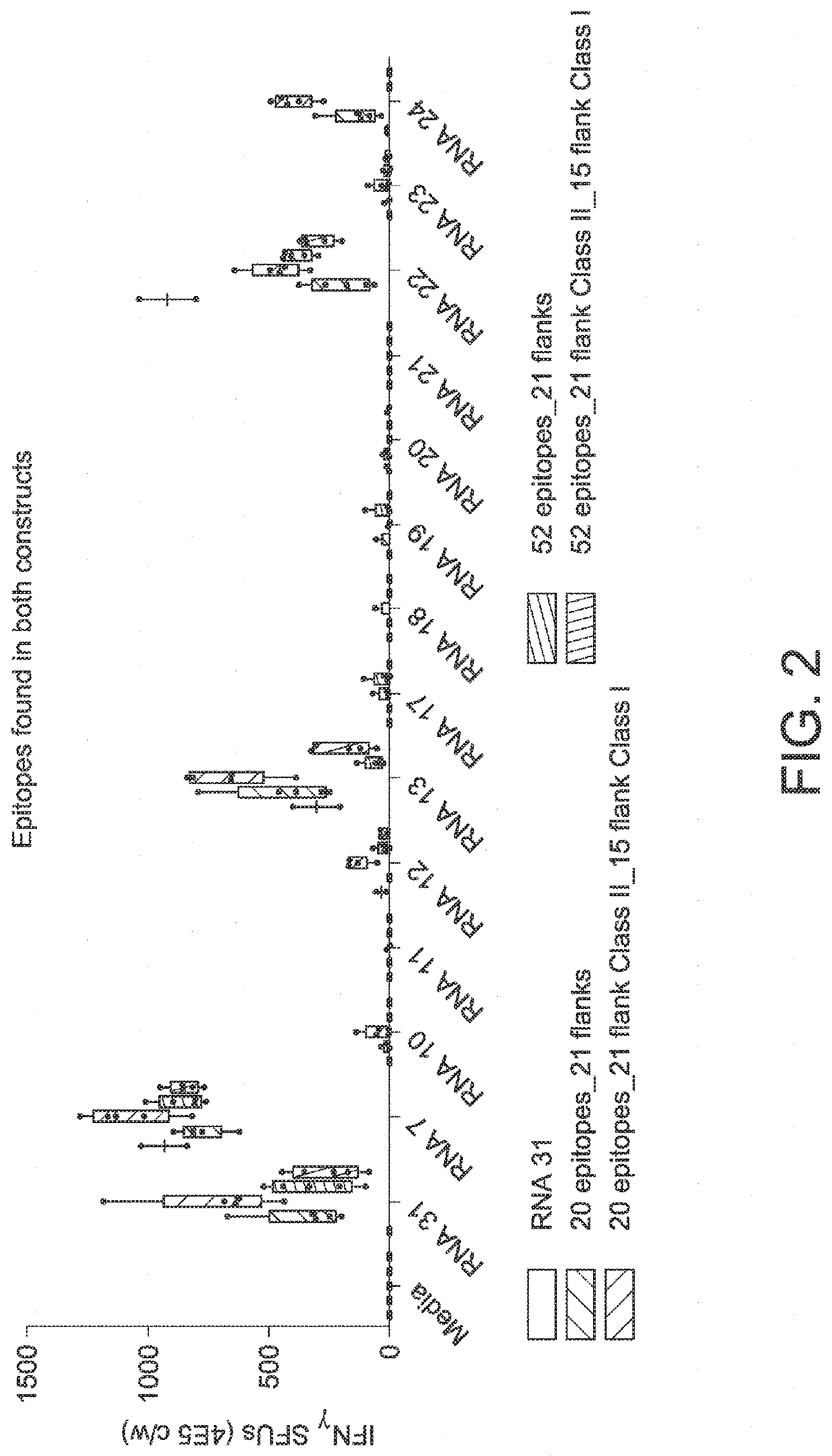
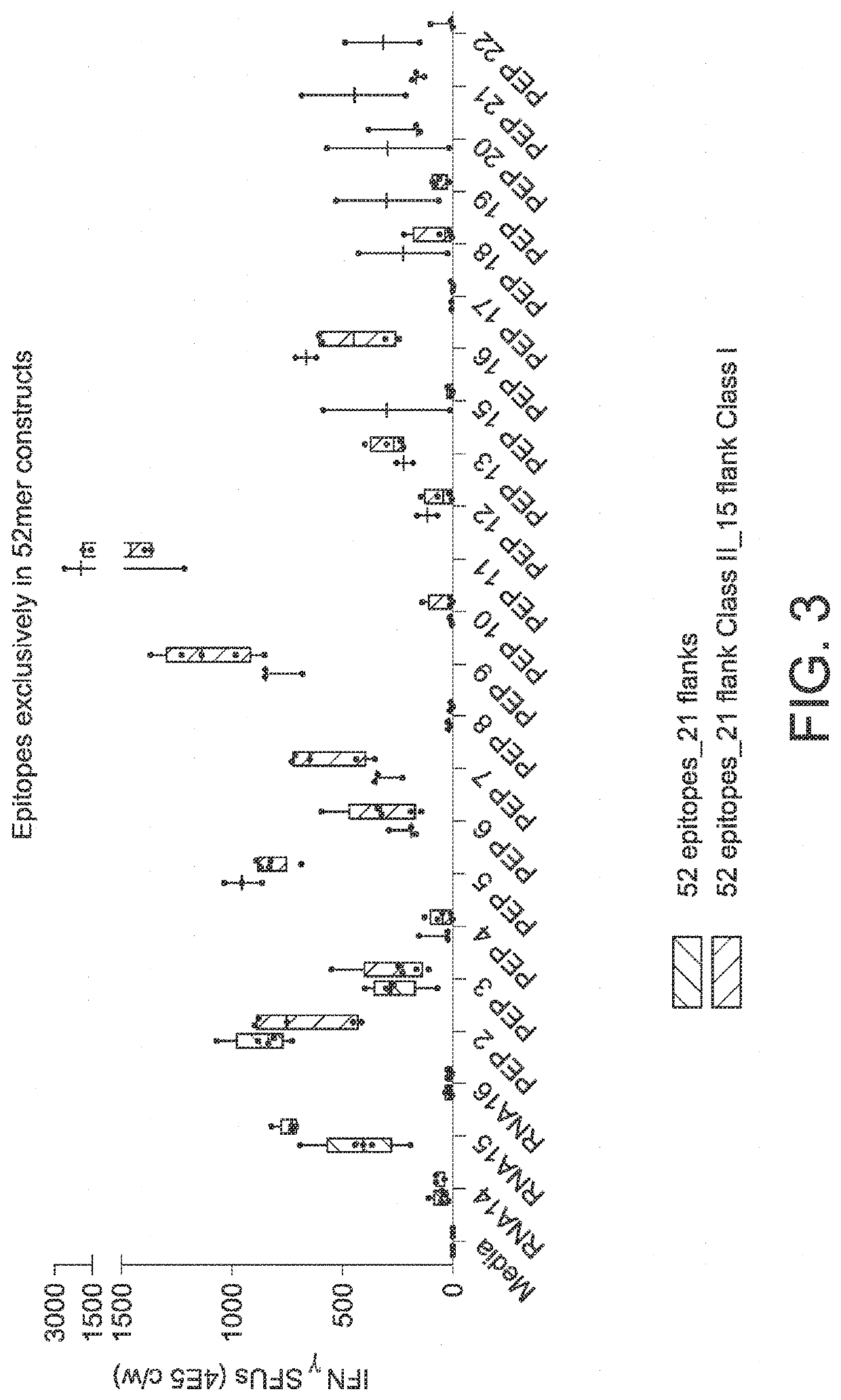
RNA cancer vaccines
PendingUS20190351040A1Balanced immune responseOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsTetanusAdjuvant
The disclosure relates to cancer ribonucleic acid (RNA) vaccines, as well as methods of using the vaccines and compositions comprising the vaccines. In particular, the disclosure relates to concatemeric mRNA cancer vaccines encoding several cancer epitopes on a single mRNA construct, i.e. poly-epitope mRNA constructs or poly-neo-epitope constructs. The disclosure further relates to p53 and KRAS mutations, as well as incorporation of immune enhancers such as STING, e.g. mRNA constructs further encoding an immune stimulator or adjuvant. The disclosure further relates to inclusion of universal T cell epitopes, such as tetanus or diphtheria toxins to elicit an enhanced immune response.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
IL-7 variants with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS7589179B2Low immunogenicityGood biological propertiesHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsVaccine ImmunogenicityInterleukin I
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Immunogenic peptides and their use in immune disorders
ActiveUS20100303866A1High expressionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAuto antigenAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides novel peptides and homologues thereof. The peptides of the invention comprise (i) a T-cell epitope of an antigen (self or non-self) with a potential to trigger an immune reaction presented by a class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) determinant and recognised by CD4+ T cell more specifically of an allergen or auto-antigen, coupled, optionally through the use of a linker to (ii) an amino acid sequence having a reducing activity, such as a thioreductase sequence. The peptides of the invention have been shown to be useful a medicine, more in particular for the prevention or treatment of immune disorders, more specifically of allergic disorders or autoimmune diseases. The present invention thus provides for the use of said peptides for the manufacture of a medicament for the prevention or treatment of an immune disorder and further provides for methods of treatment or preventing immune disorders by using said peptides. The present invention also provides for compositions comprising said peptides.
Owner:IMCYSE
Immunogenic peptide composition comprising measles virus Fprotein Thelper cell epitope (MUFThl-16) and N-terminus of β-amyloid peptide
InactiveUS6906169B2Increase the gapHigh cross reactivityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrilDisease patient
The present invention relates to a composition comprsing a peptide immunogen useful for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. More particularly, the peptide immunogen comprises a main functional / regulatory site, an N-terminal fragment of Amyloid β (Aβ) peptide linked to a helper T cell epitope (Th) having multiple class II MHC binding motifs. The peptide immunogen elicit a site-directed immune response against the main functional / regulatory site of the Aβ peptide and generate antibodies, which are highly cross-reactive to the soluble Aβ1-42 peptide and the amyloid plaques formed in the brain of Alzheimer's Disease patients. The antibodies elicited being cross reactive to the soluble Aβ1-42 peptide, promote fibril disaggregation and inhibit fibrillar aggregation leading to immunoneutralization of the “soluble Aβ-derived toxins”; and being cross-reactive to the amyloid plaques, accelerate the clearance of these plaques from the brain. Thus, the composition of the invention comprising the peptide immunogen is useful for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:UNITED NEUROSCIENCE LIMITED
Immunotherapeutic methods and systems
InactiveUS20060024334A1Easy to produceReduced responseSenses disorderNervous disorderPeptide antigenPharmaceutical drug
Methods for desensitising an individual to a selected polypeptide antigen are provided. The methods entail administration of T cell epitope containing peptides from a polypeptide antigen in such a way as to establish a tolergeneic environment, that is, a state of hyporesponsiveness to the peptides. The selected polypeptide antigen is then administered such that the state of hyporesponsiveness and co-administration of the selected antigen are sufficient to desensitise the individual to the polypeptide antigen. Also provided are therapeutic systems useful in the methods of the invention, and the use of polypeptide antigens and peptides in the manufacture of medicaments in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CIRCASSIA
Antigen-Specific T Cell Receptors and T Cell Epitopes
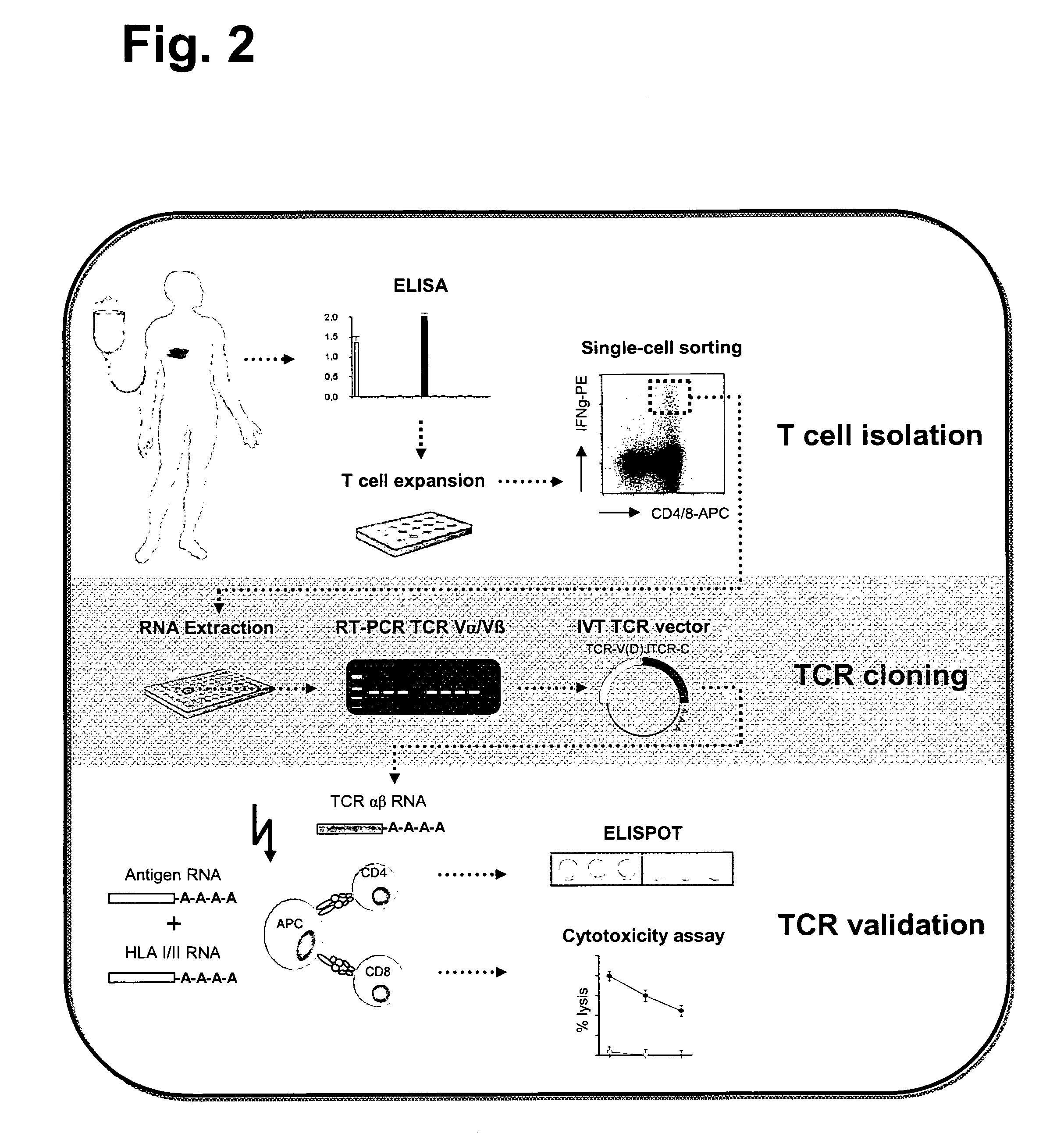
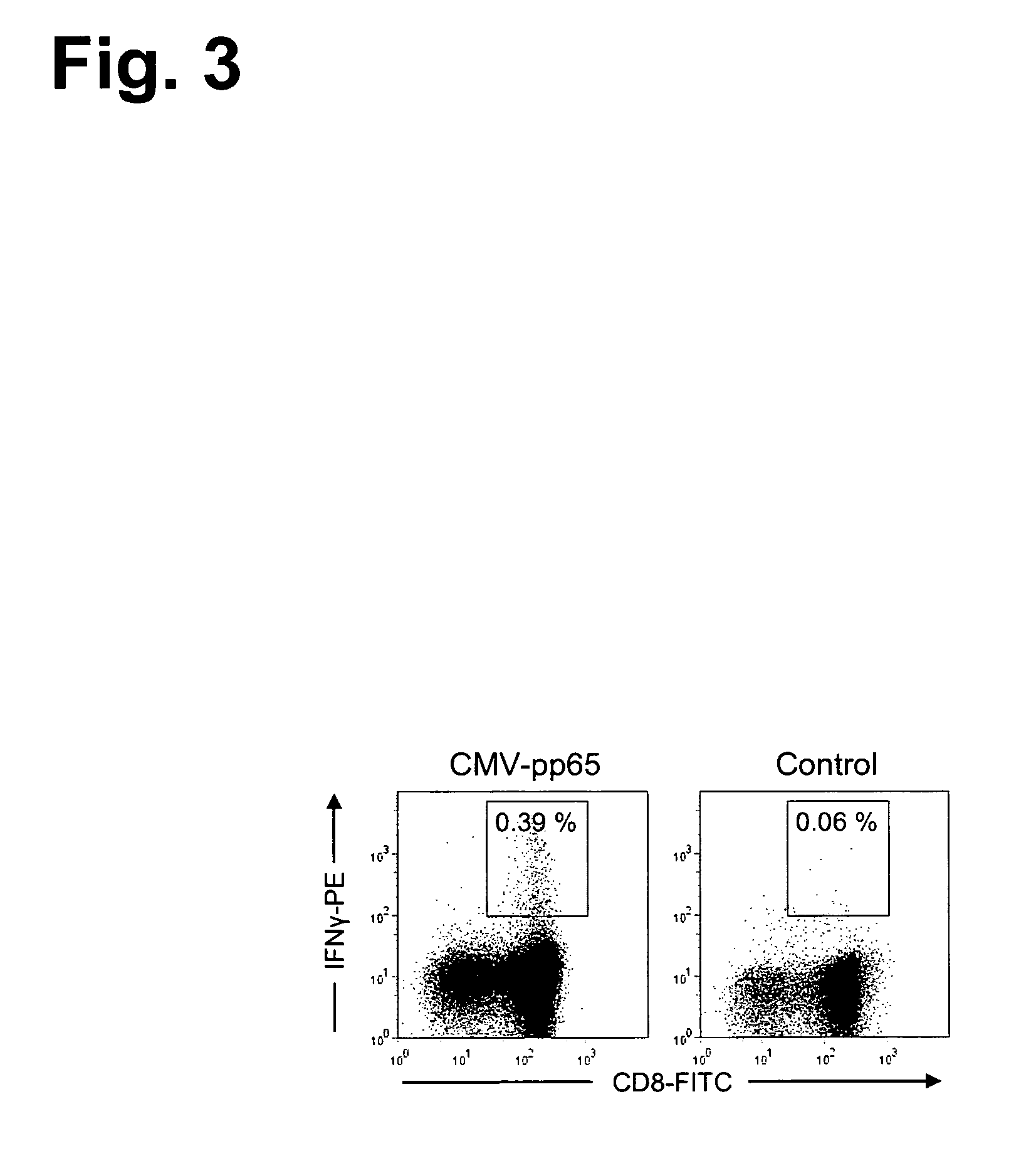
ActiveUS20130273647A1Reliable detectionMeasureVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsMHC restrictionCellular receptor
The present invention relates to efficient methods for providing antigen-specific lymphoid cells. These lymphoid cells may be used to provide antigen specific T cell receptors having a defined MHC restriction and to identify immunologically relevant T cell epitopes. Furthermore, the present invention relates to antigen-specific T cell receptors and T cell epitopes and their use in immunotherapy.
Owner:TRON TRANSLATIONALE ONKOLOGIE AN DER UNIVERSITATSMEDIZIN DER JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIVERS +1
Methods and reagents for vaccination which generate a CD8 T cell immune response
New methods and reagents for vaccination are described which generate a CD8 T cell immune response against malarial and other antigens such as viral and tumour antigens. Novel vaccination regimes are described which employ a priming composition and a boosting composition, the boosting composition comprising a non-replicating or replication-impaired pox virus vector carrying at least one CD8 T cell epitope which is also present in the priming composition.
Owner:OXXON THERAPEUTICS LTD
Multi oligosaccharide glycoconjugate bacterial meningitis vaccines
InactiveUS6656472B1Inhibition effectWeight increaseAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticSerotypeTumor antigen
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Modified factor VIII
InactiveUS20050256304A1Modify characteristicReduce in quantityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vivoVaccine Immunogenicity
The invention relates to the modification of human Factor VIII (FVIII) to result in FVIII proteins that are substantially non-immunogenic or less immunogenic than any non-modified counterpart when used in vivo. The invention relates furthermore to T-cell epitope peptides derived from said non-modified protein by means of which it is possible to create modified FVIII variants with reduced immunogenicity.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Allergenic proteins and peptides from Japanese cedar pollen
InactiveUS6982326B1Diagnosing, treating, and preventing Japanese cedar pollinosisSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectNucleic acid sequencing
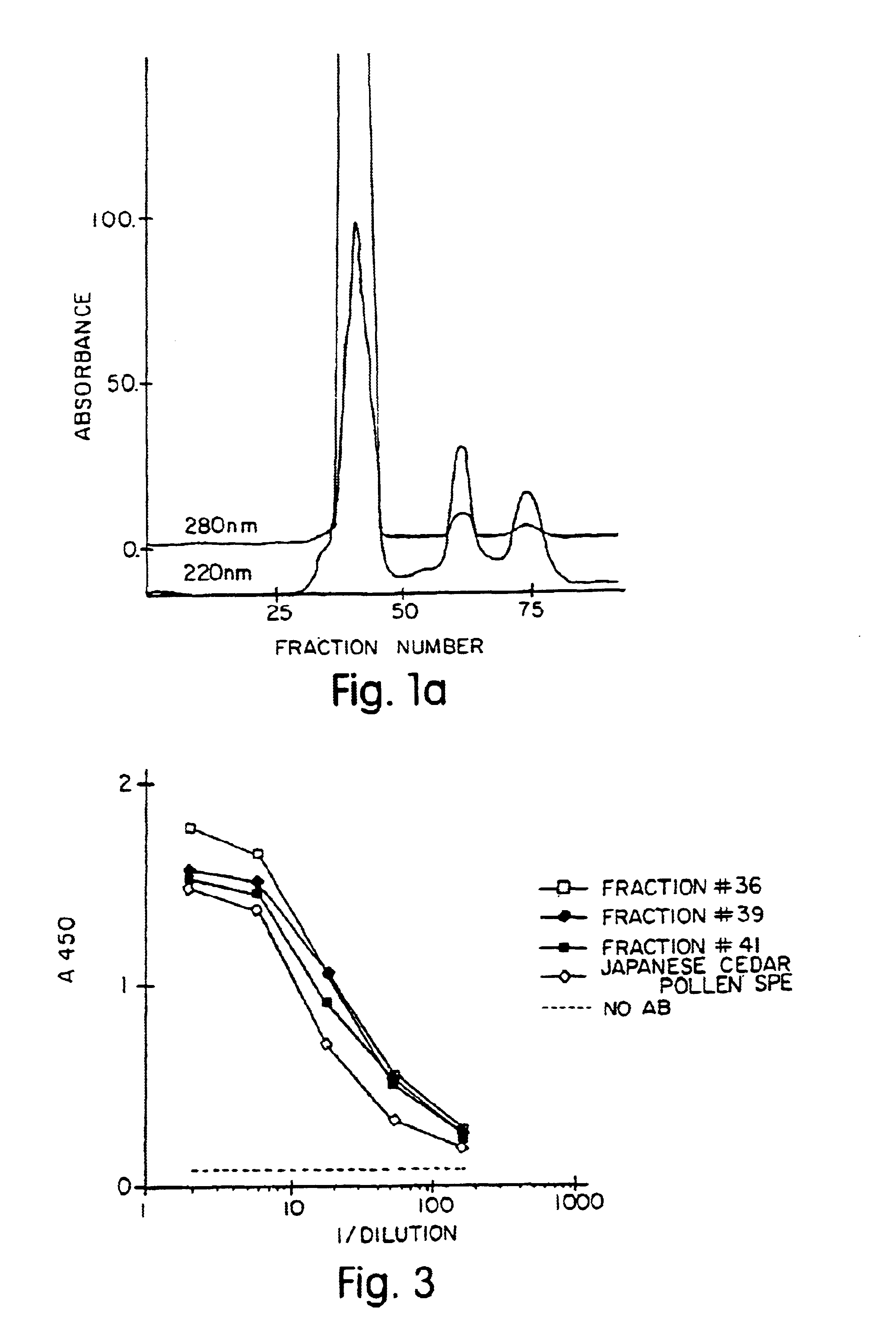
The present invention provides nucleic acid sequences coding for the Cryptomeria japonica major pollen allergen Cry j I, Cry j II, Jun s I and Jun v I and fragments or peptides thereof. The present invention also provides purified Cry j I, Cry j II, Jun s I and Jun v I and at least one fragment thereof produced in a host cell transformed with a nucleic acid sequence coding for Cry j I, Cry j II, Jun s I and Jun v I or at least one fragment thereof, and fragments of Cry j I, Cry j II, Jun s I or Jun v I or at least one fragment thereof, and fragments of Cry j I, Cry j II, Jun s I or Jun v I prepared synthetically. Cry j I, Cry j II, Jun s I and Jun v I and fragments thereof are useful for diagnosing, treating, and preventing Japanese cedar pollinosis. The present invention also provides isolated peptides of Cry j I and Cry j II. Peptides within the scope of the invention comprise at least one T cell epitope, or preferably at least two T cell epitopes of Cry j I or Cry j II. The invention also pertains to modified peptides having similar or enhanced therapeutic properties as the corresponding naturally-occurring allergen or portion thereof but having reduced side effects. Methods of treatment or of diagnosis of sensitivity to Japanese cedar pollens in an individual and therapeutic compositions, and multipeptide formulations comprising one or more peptides of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
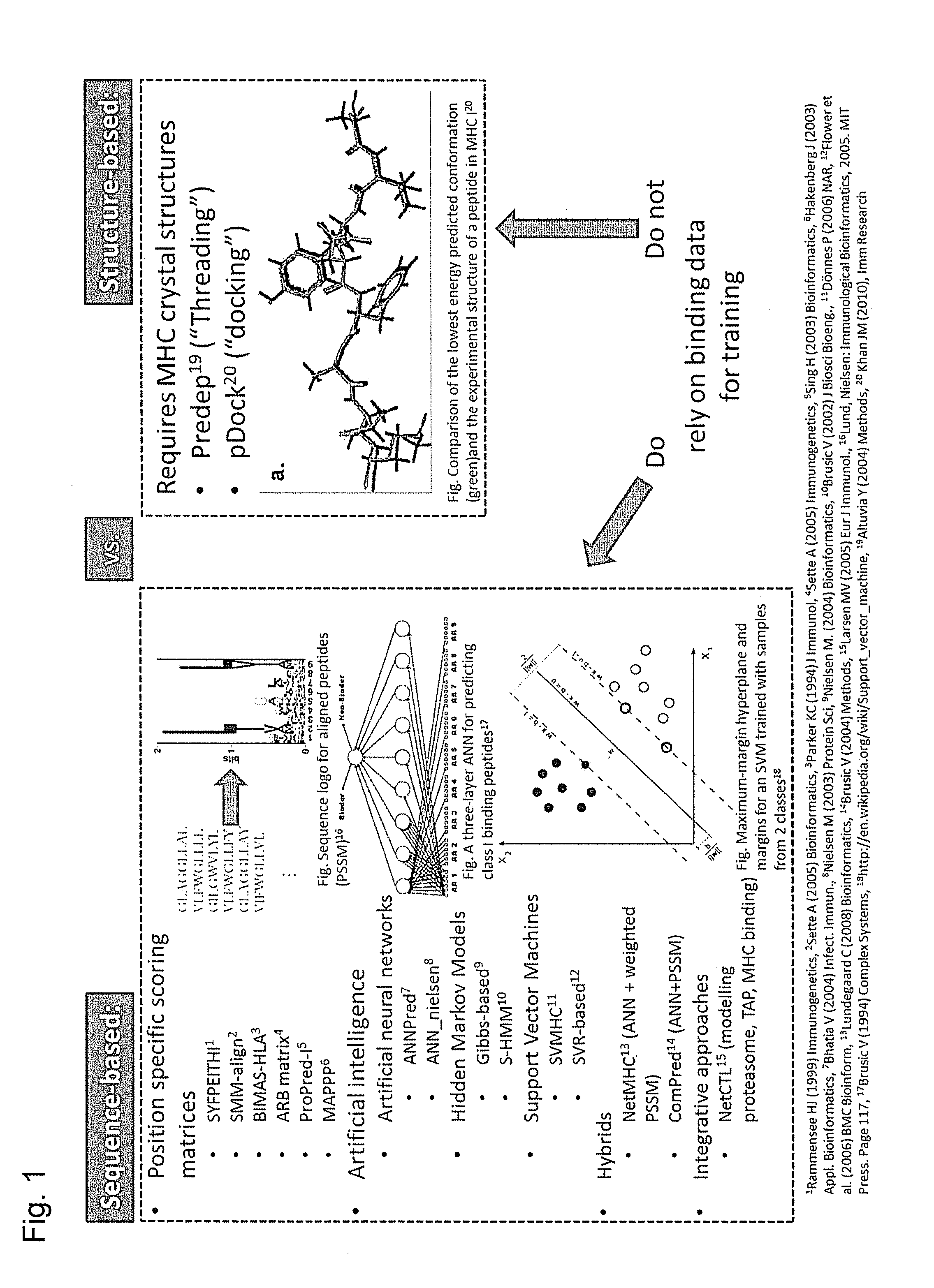
Predicting immunogenicity of t cell epitopes
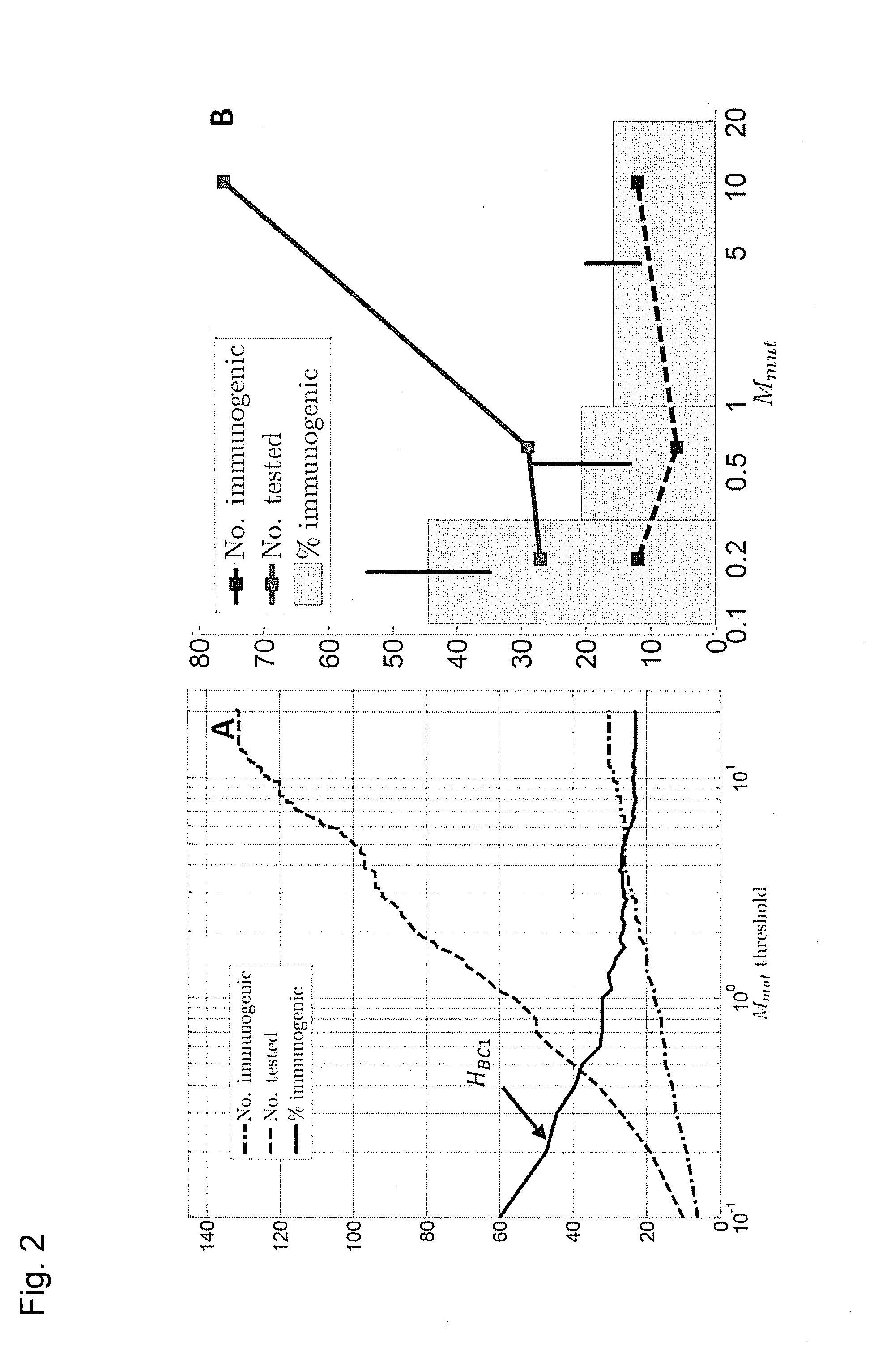
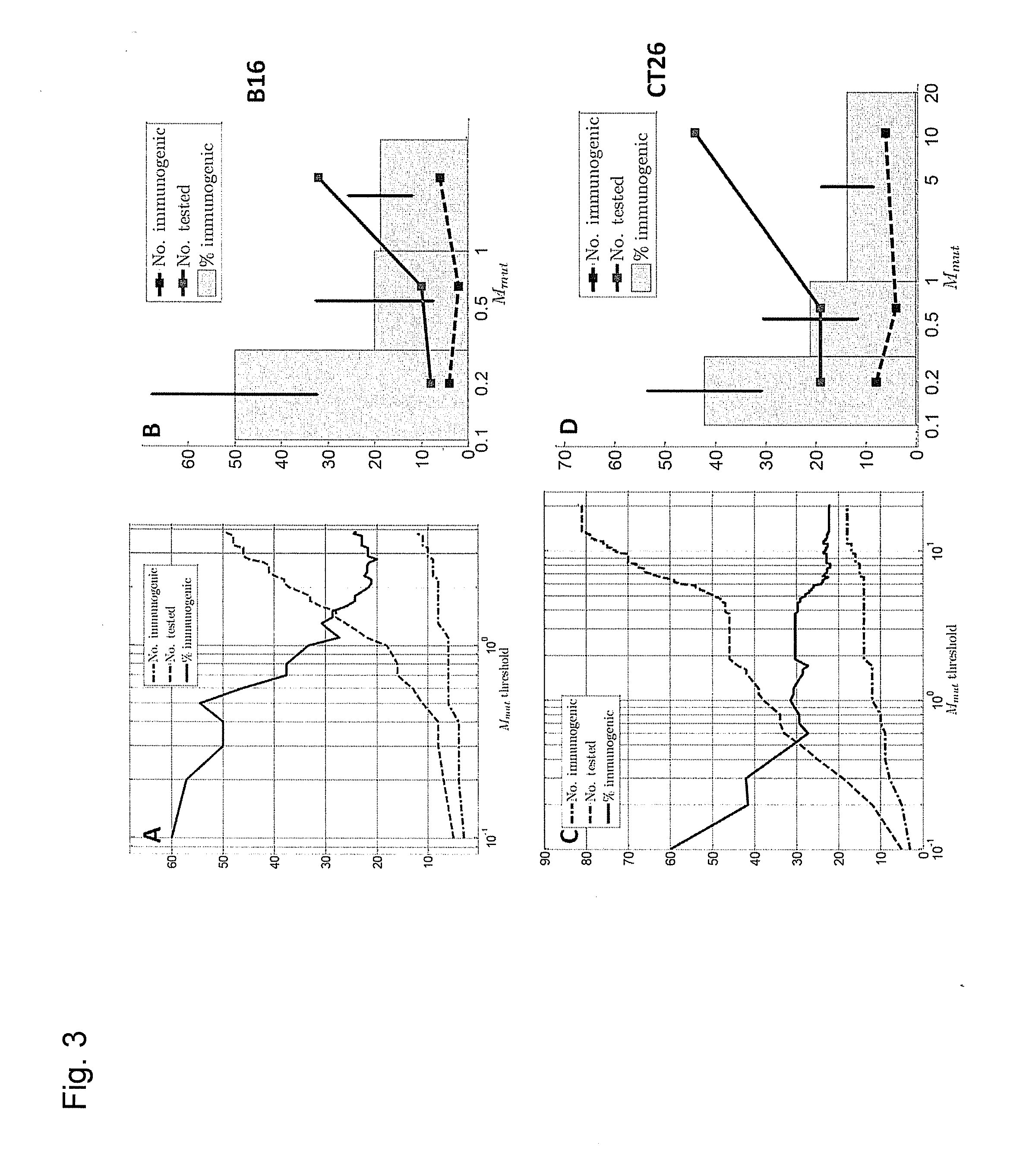
ActiveUS20160125129A1Minimizing chanceDevelopmental delayMicrobiological testing/measurementVaccinesOncologyImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to methods for predicting T cell epitopes. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for predicting whether modifications in peptides or polypeptides such as tumor-associated neoantigens are immunogenic or not. The methods of the invention are useful, in particular, for the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and, thus, in the context of personalized cancer vaccines.
Owner:BIONTECH SE +1
Subtilisin carlsberg proteins with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS20050239043A1Low immunogenicityReduced immunogenic responseCosmetic preparationsHydrolasesWild typeCD4 antigen
The present invention provides methods for the identification of CD4+ T-cell epitopes in subtilisin Carlsberg proteins. The present invention also provides for the production of altered peptides which, when incorporated into a wild-type subtilisin Carlsberg protein produce an altered immunogenic response, preferably a low immunogenic response in humans. In particular, the present invention provides means, including methods and compositions suitable for reducing the immunogenicity of ALCALASE® enzyme.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com