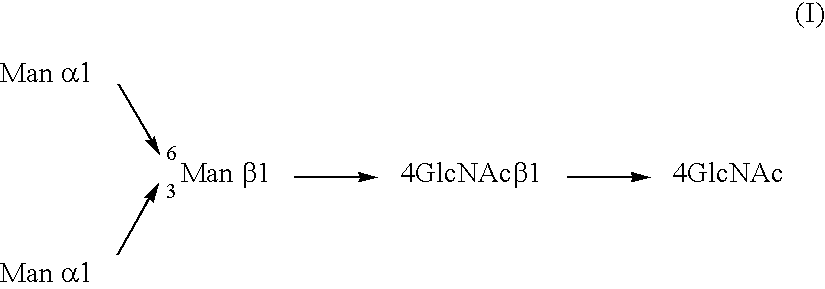Patents
Literature
491results about "Vaccines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cells producing antibody compositions with increased antibody dependent cytotoxic activity
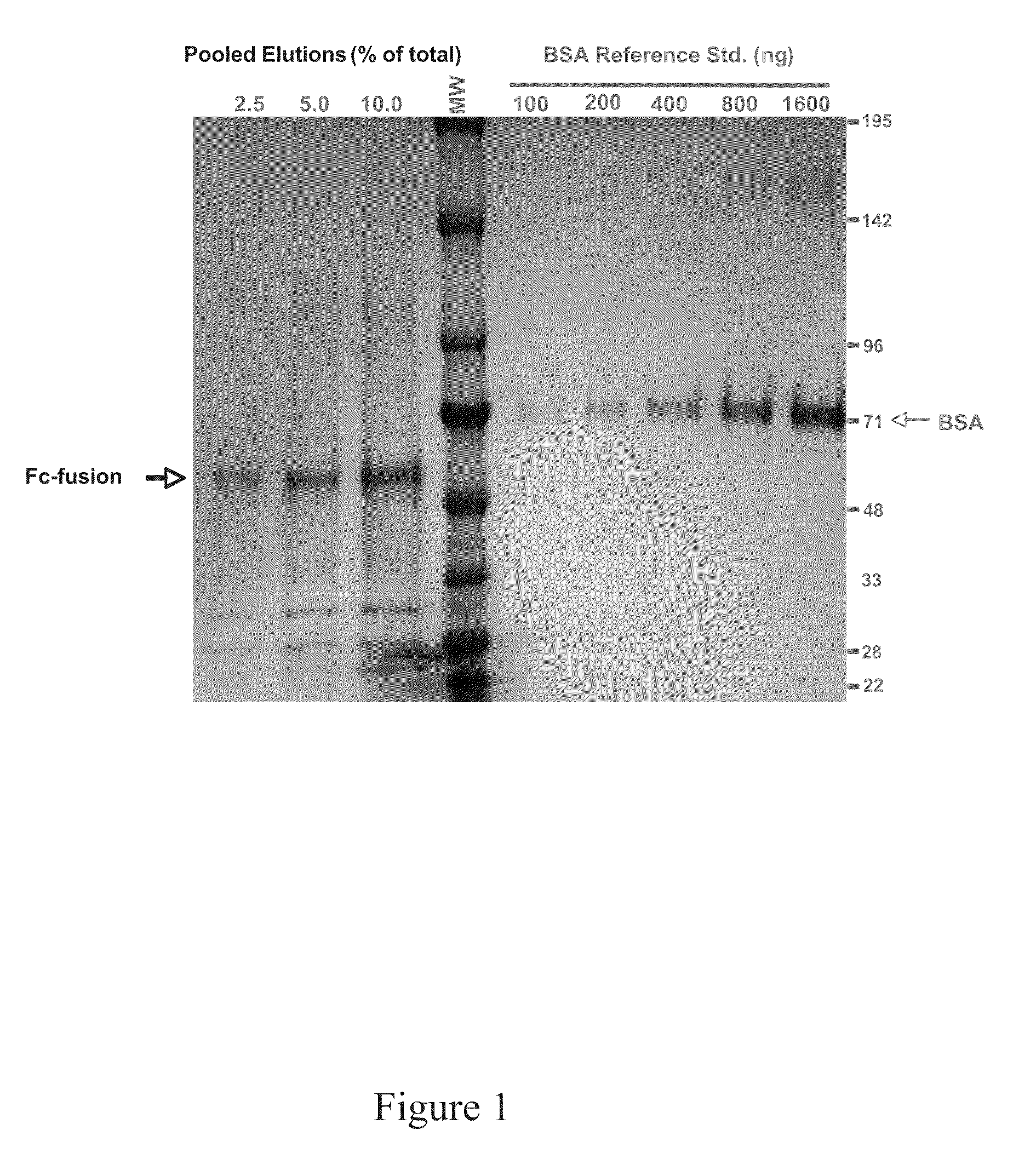
The present invention relates to a cell for the production of an antibody molecule such as an antibody useful for various diseases having high antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity, a fragment of the antibody and a fusion protein having the Fc region of the antibody or the like, a method for producing an antibody composition using the cell, the antibody composition and use thereof.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
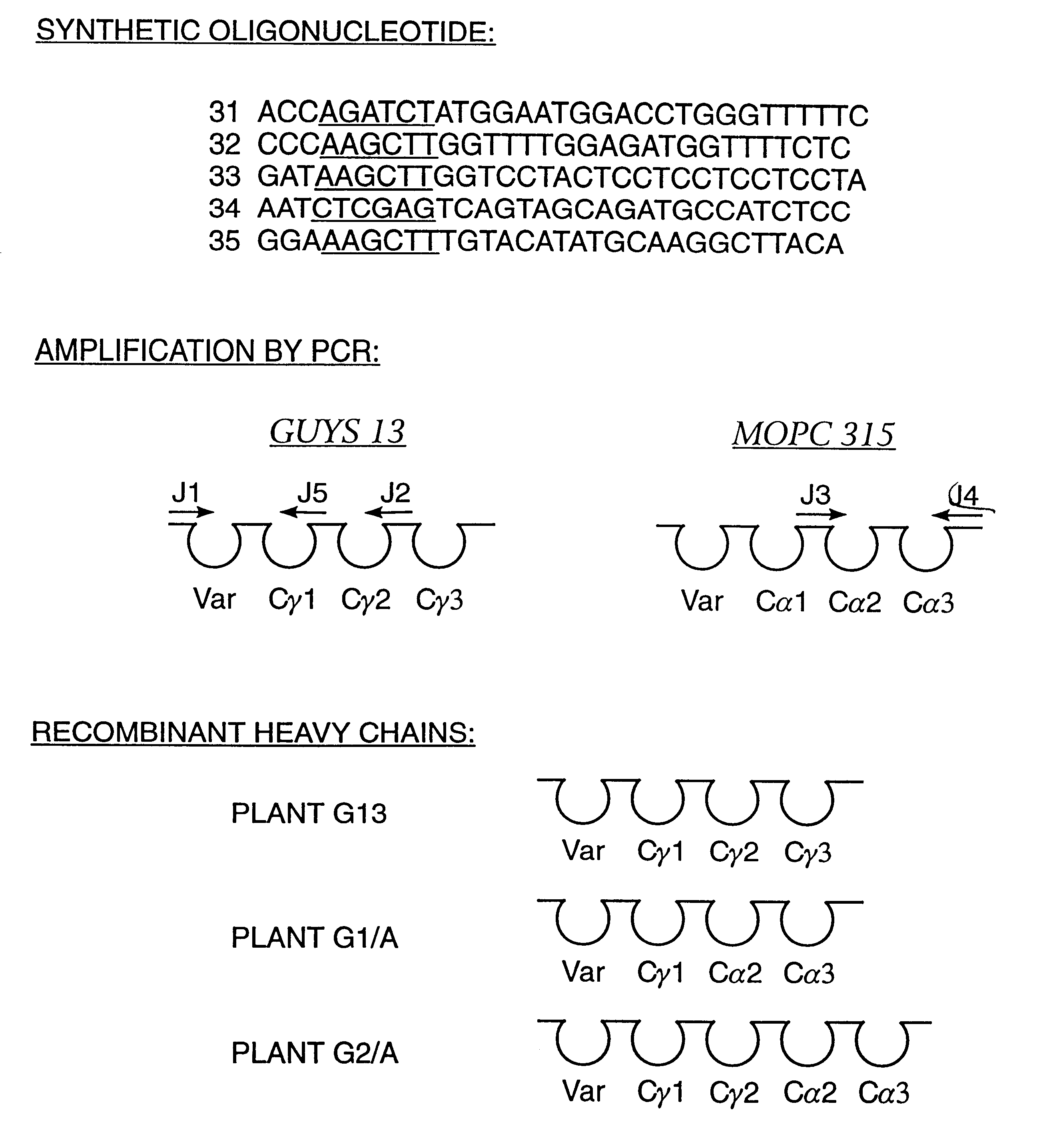
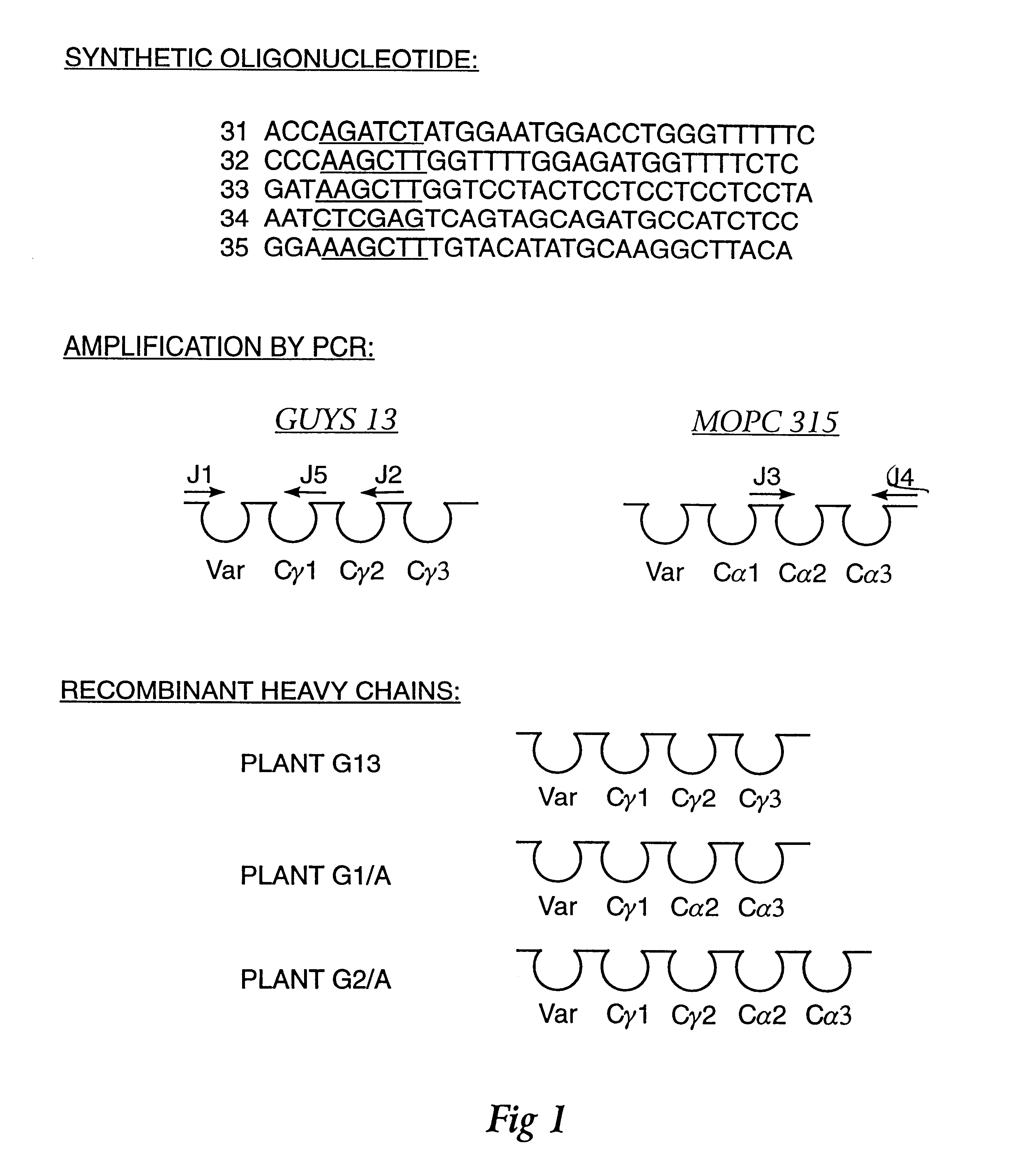
Method for producing immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in plants and their use
The immunoglobulins of the present invention are useful therapeutic immunoglobulins against mucosal pathogens such as S. mutans. The immunoglobulins contain a protection protein that protects the immunoglobulins in the mucosal environment. The invention also includes the greatly improved method of producing immunoglobulins in plants by producing the protection protein in the same cell as the other components of the immunoglobulins. The components of the immunoglobulin are assembled at a much improved efficiency. The method of the invention allows the assembly and high efficiency production of such complex molecules. The invention also contemplates the production of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in a variety of cells, including plant cells, that can be selected for useful additional properties. The use of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins as therapeutic antibodies against mucosal and other pathogens is also contemplated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
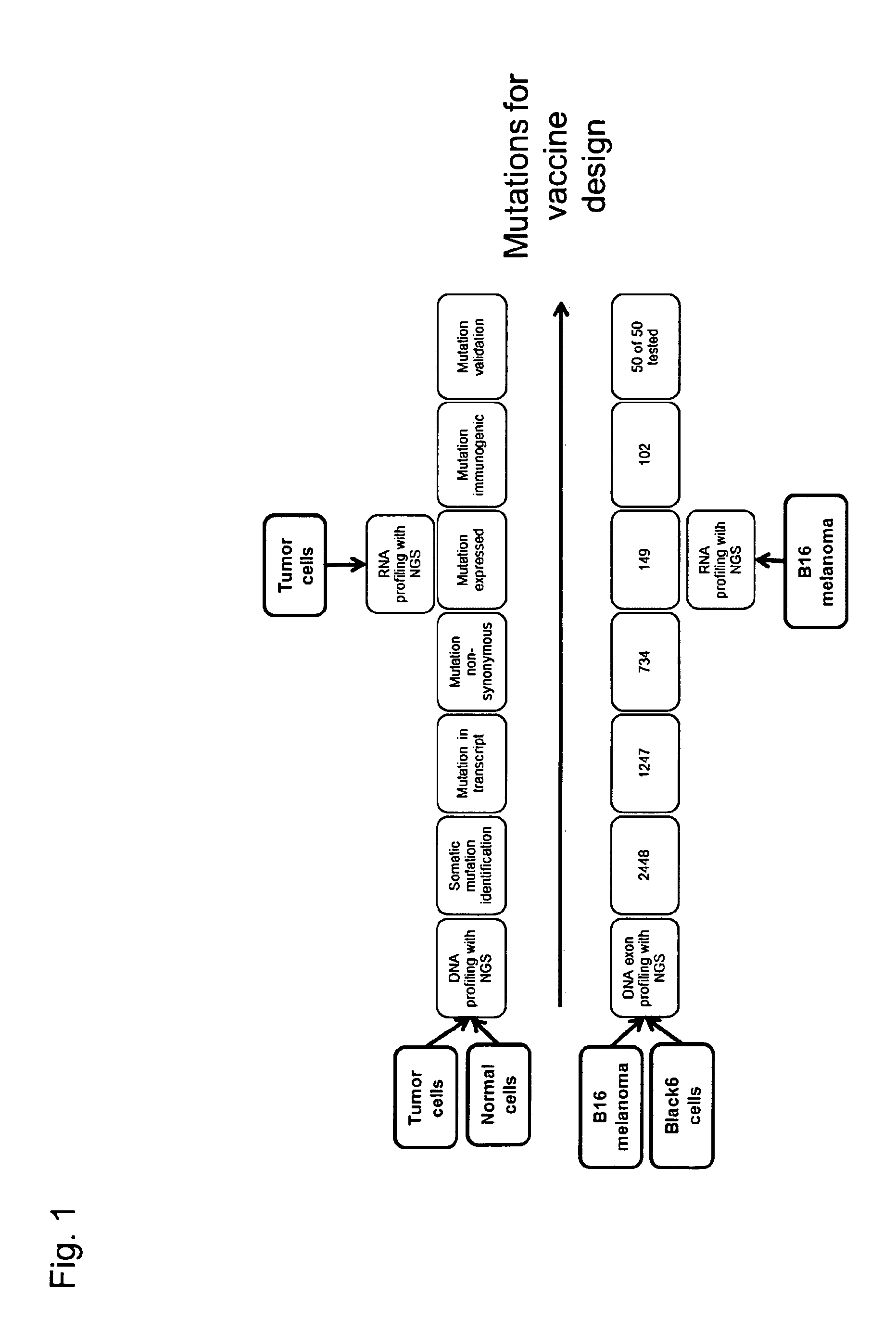
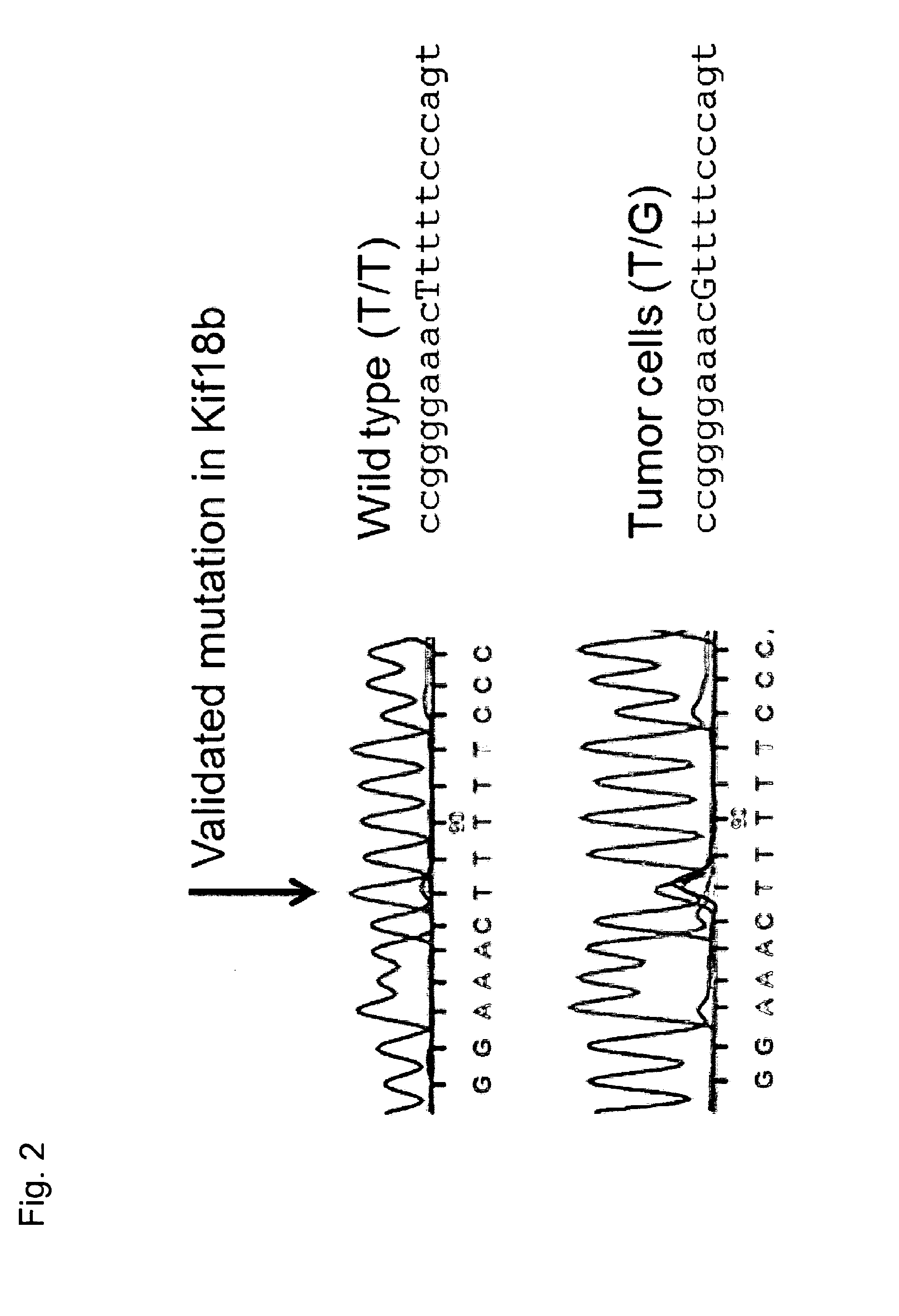
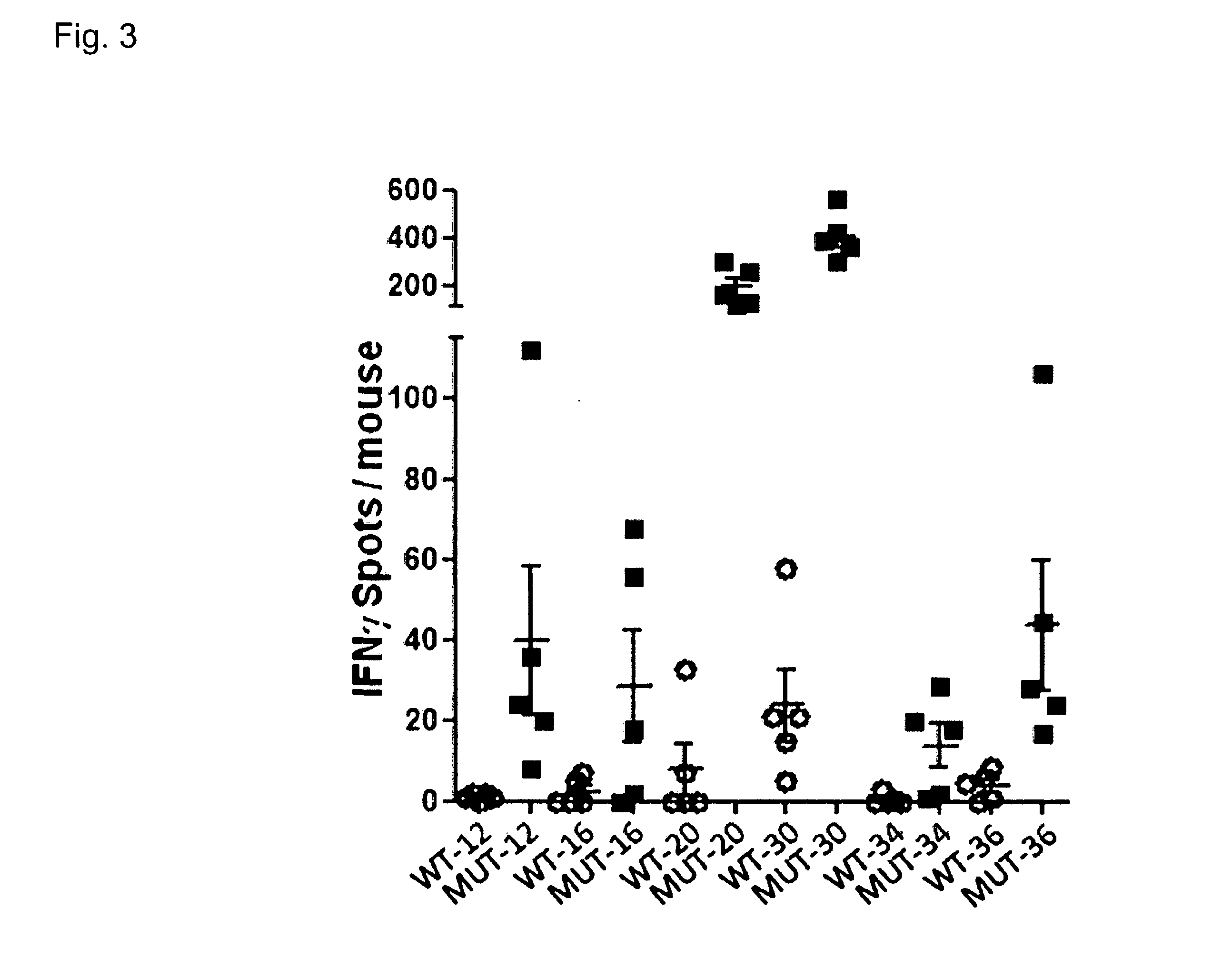
Individualized vaccines for cancer
ActiveUS20140178438A1Reduces steric hindranceImprove translationVaccinesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPrimary tumorTumour metastasis
The present invention relates to the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and are potentially useful for immunotherapy of the primary tumor as well as tumor metastases. In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method for providing an individualized cancer vaccine comprising the steps: (a) identifying cancer specific somatic mutations in a tumor specimen of a cancer patient to provide a cancer mutation signature of the patient; and (b) providing a vaccine featuring the cancer mutation signature obtained in step (a). In a further aspect, the present invention relates to vaccines which are obtainable by said method.
Owner:TRANSLATIONALE ONKOLOGIE AN DER UNIVSMEDIZIN DER JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIV MAINZ GGMBH +1
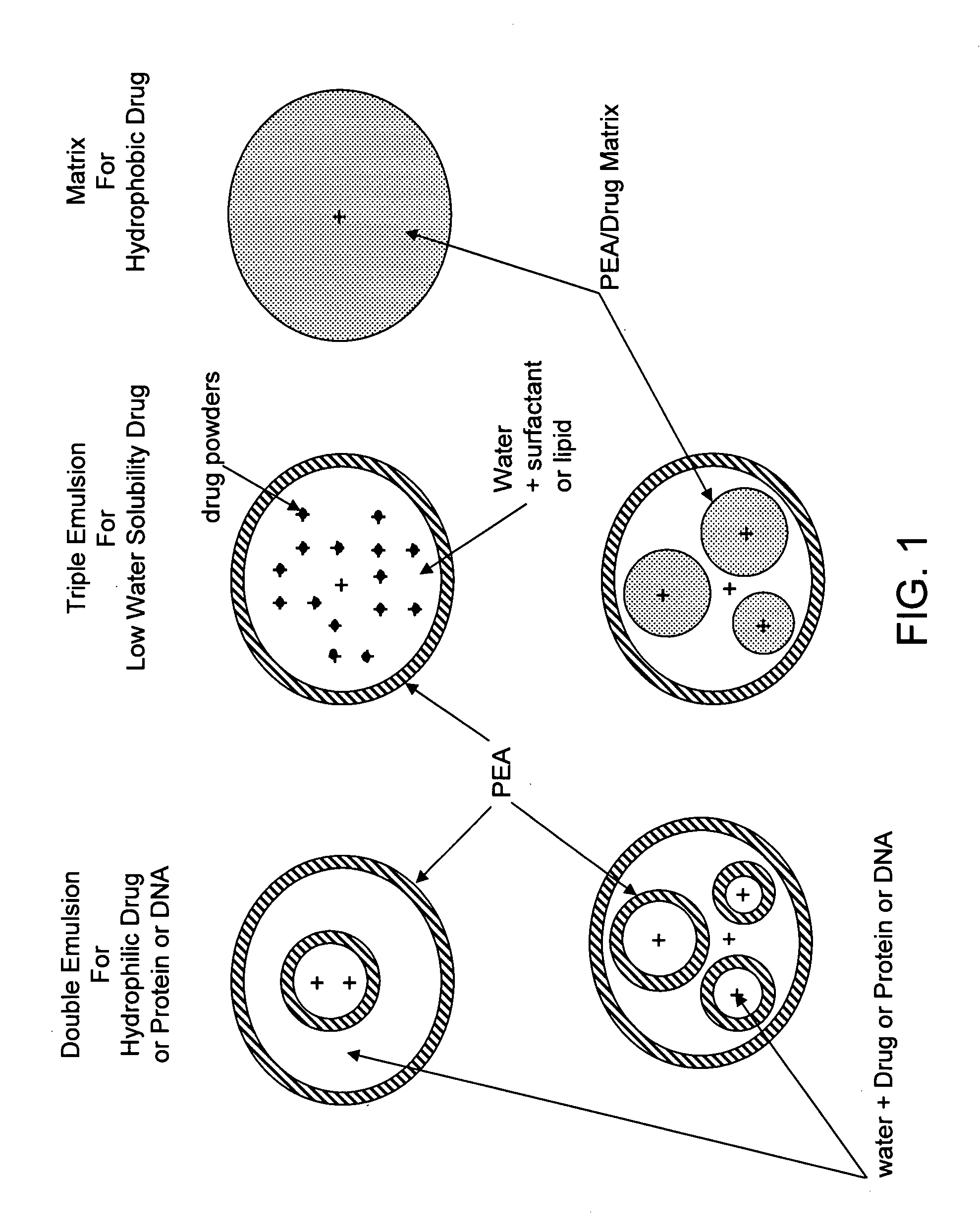
Vaccine delivery compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20080160089A1Easy to produceImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryPolyesterMHC class I
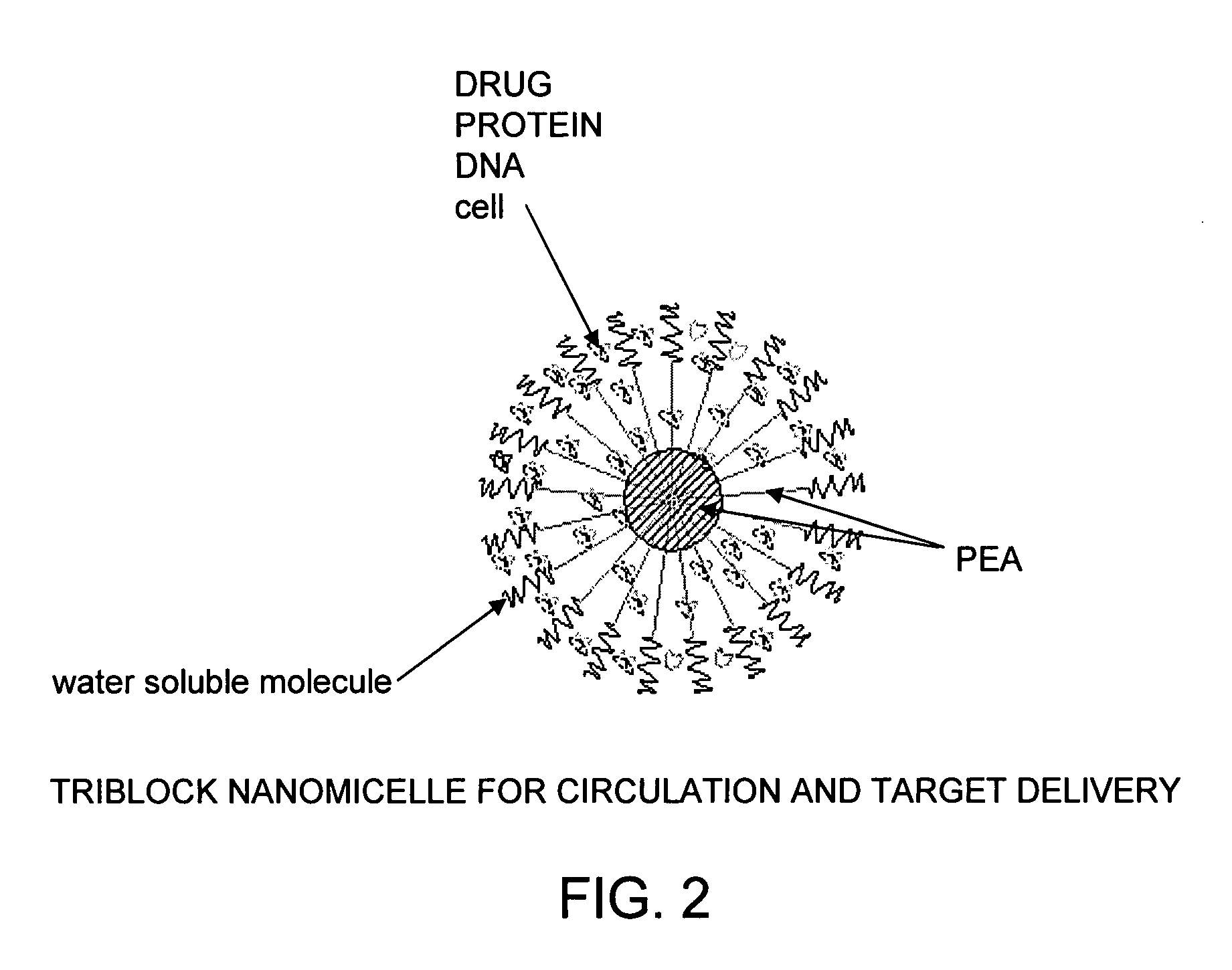
The present invention provides synthetic vaccines against a variety of pathogenic organisms and tumor cells in humans and other mammals based on biodegradable polymers containing polyester amide (PEA), polyester urethane (PEUR), and polyester urea (PEU) and immunostimulatory adjuvants. The vaccines can be formulated as a liquid dispersion of polymer particles or molecules in which are dispersed an immunostimulatory adjuvant, such as a TLR agonist, and whole protein or peptidic antigens containing MHC class I or class II epitopes derived from organism or tumor cell proteins. Methods of inducing an immune response via intracellular mechanisms to the pathogenic organism or tumor cells specific for the antigen in the invention compositions are also included.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Membrane Encapsulated Nanoparticles and Method of Use
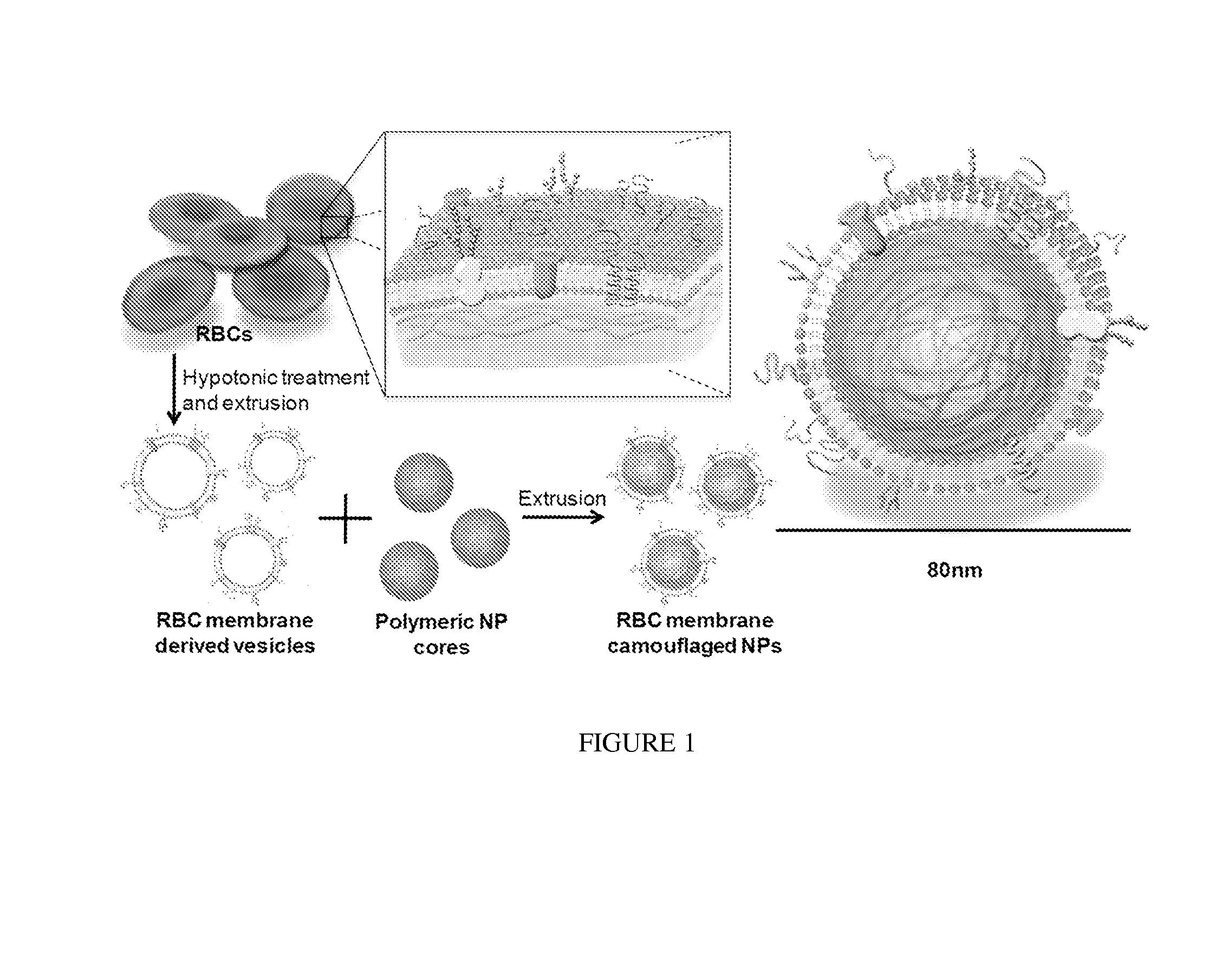
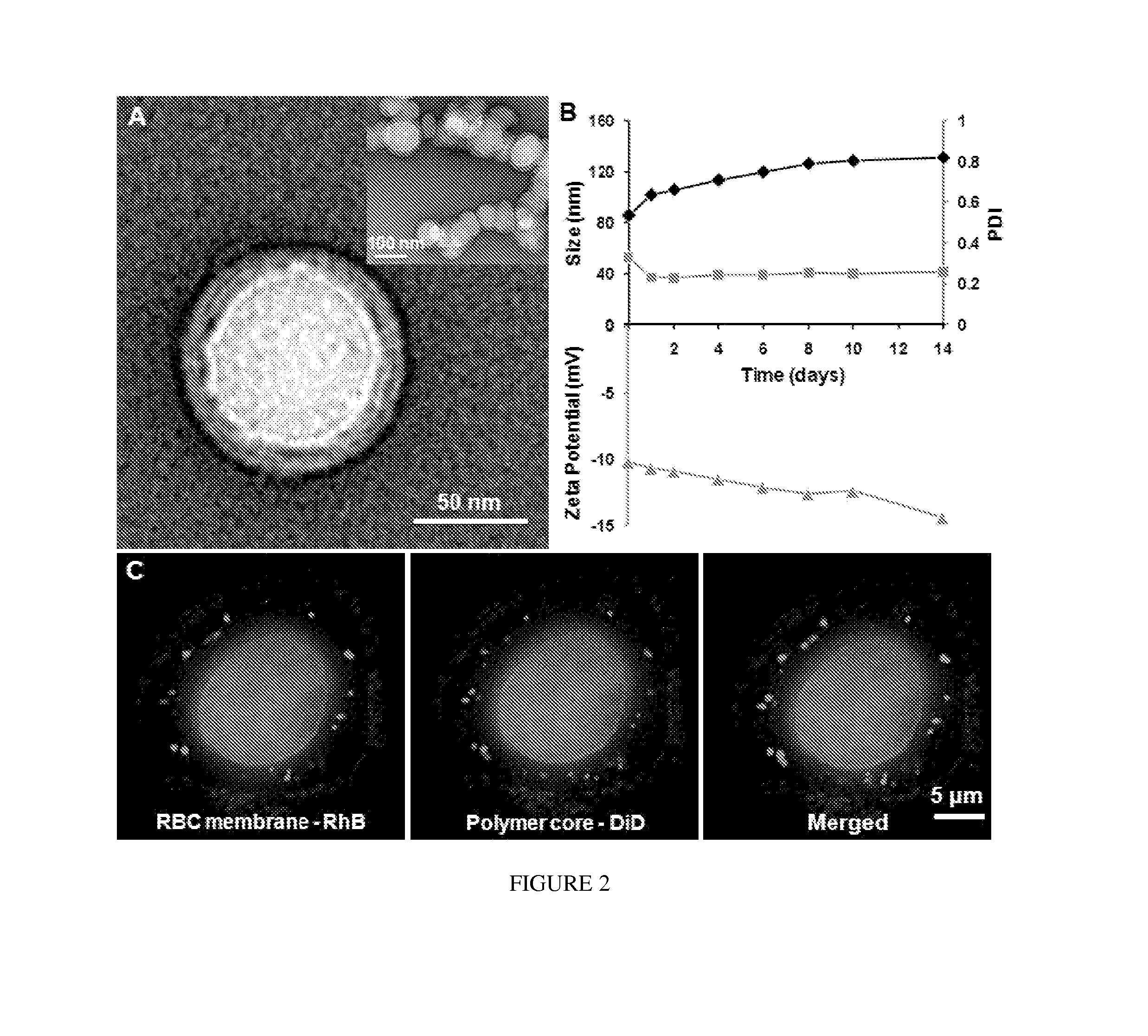
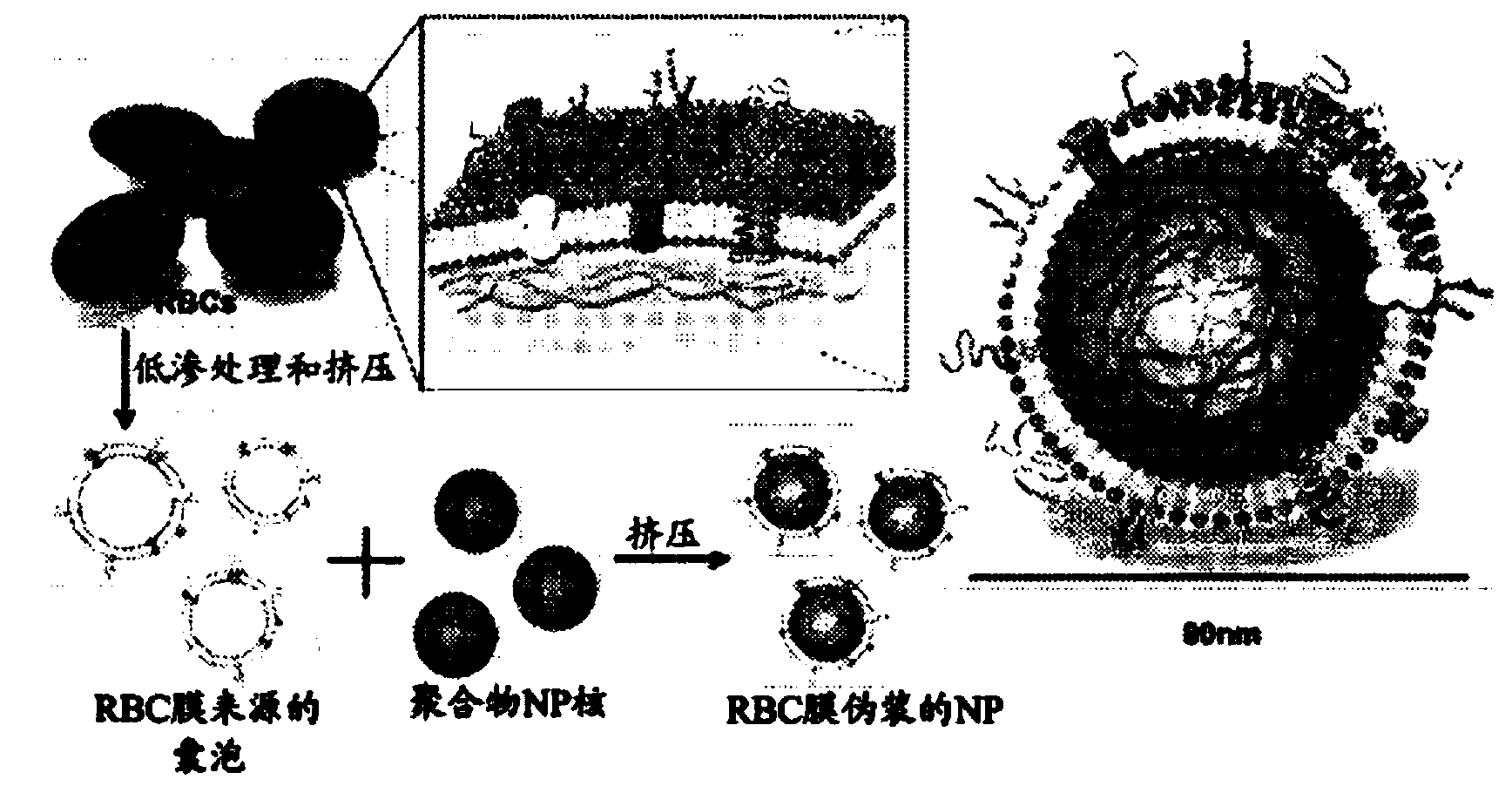
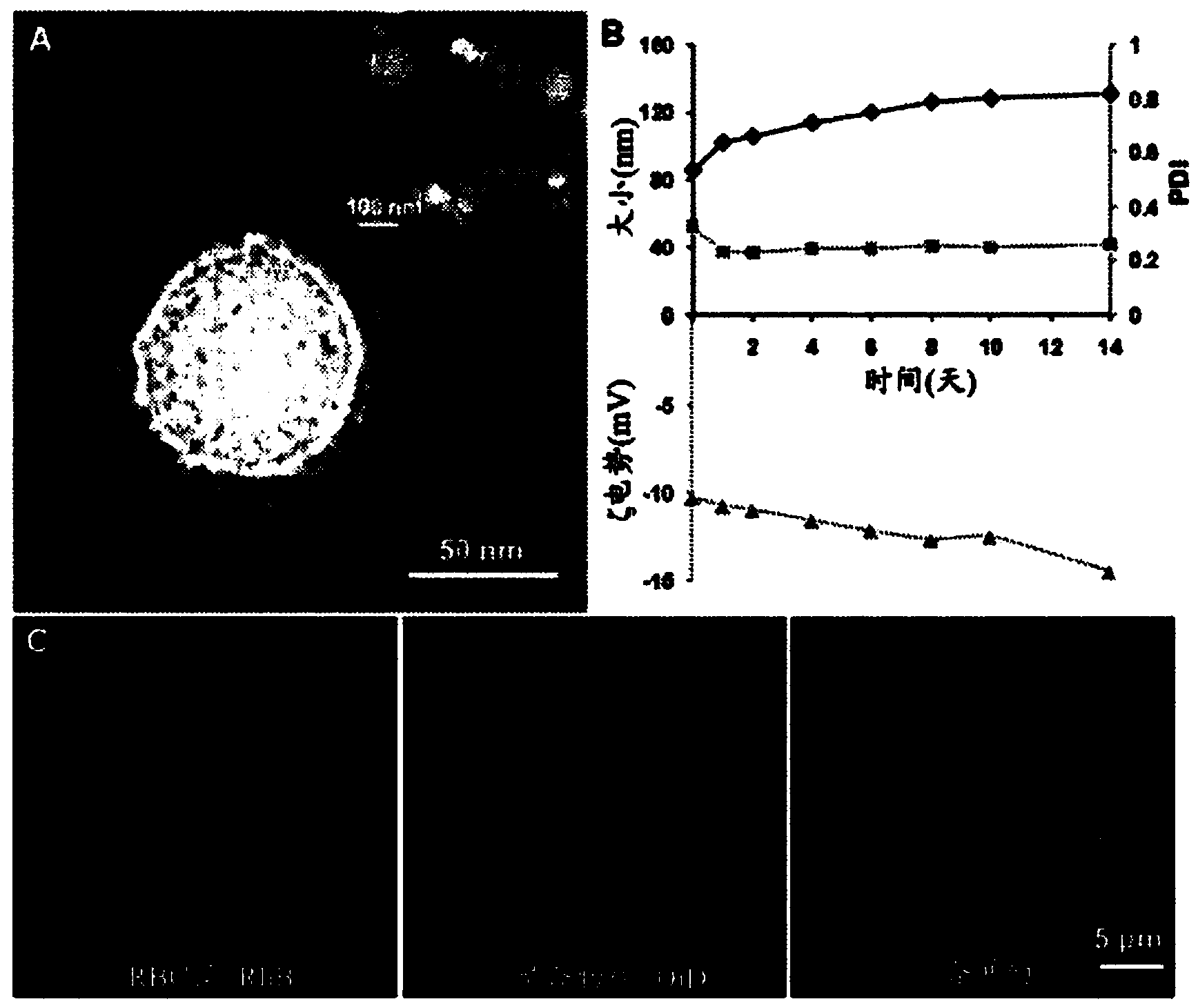
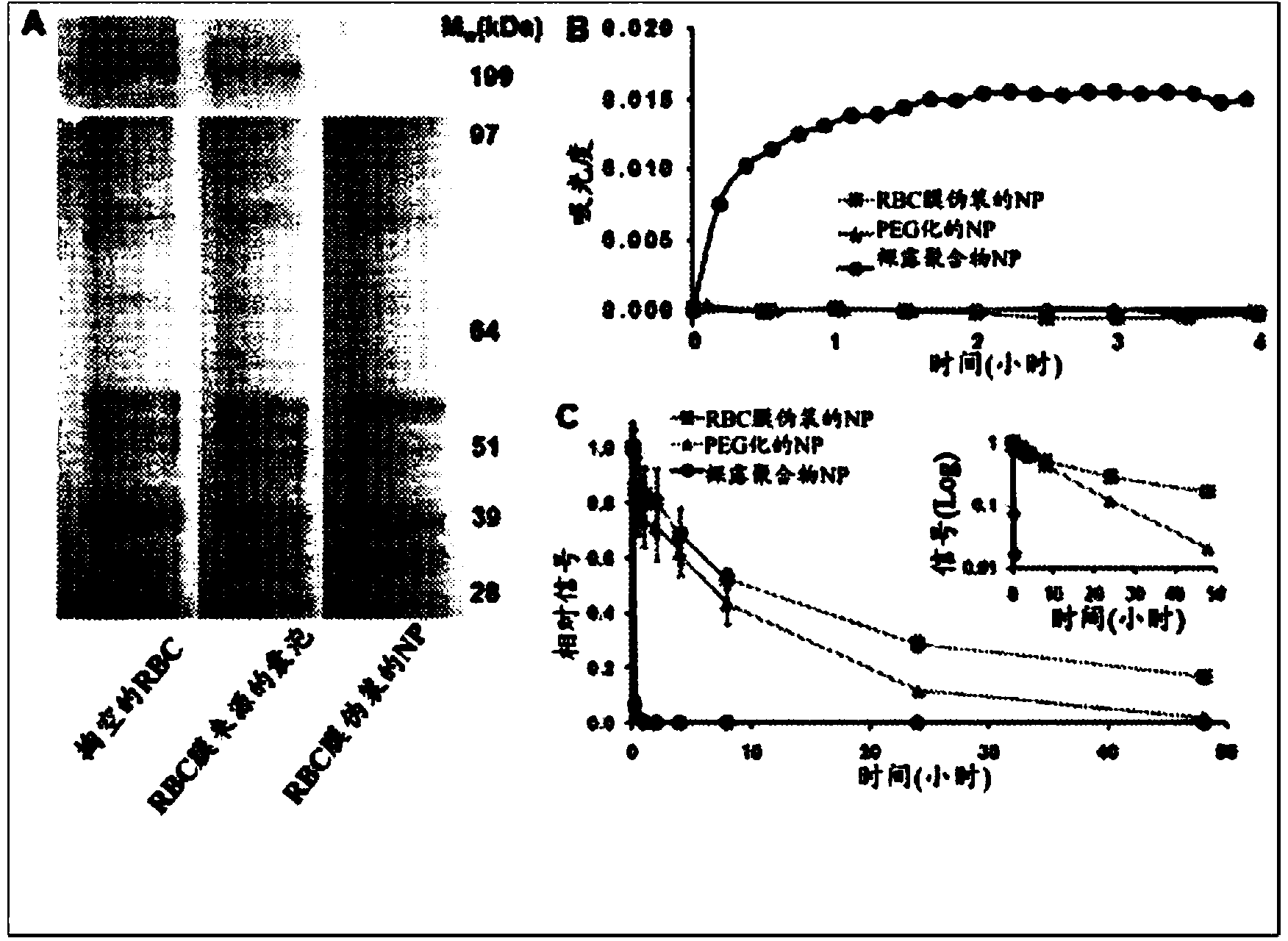
Provided are nanoparticles and methods of using and making thereof. The inventive nanoparticle comprises a) an inner core comprising a non-cellular material; and b) an outer surface comprising a cellular membrane derived from a cell or a membrane derived from a virus. Medicament delivery systems or pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inventive nanoparticles are also provided. Further provided are immunogenic compositions comprising the inventive nanoparticles, and methods of using the inventive immunogenic compositions for eliciting an immune response, and for treating or preventing diseases or condition, such as neoplasm or cancer, or disease or conditions associated with cell membrane inserting toxin. Vaccines comprising the immunogenic composition comprising the nanoparticles are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for producing immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in plants and their use
The immunoglobulins of the present invention are useful therapeutic immunoglobulins against mucosal pathogens such as S. mutans. The immunoglobulins contain a protection protein that protects the immunoglobulins in the mucosal environment.The invention also includes the greatly improved method of producing immunoglobulins in plants by producing the protection protein in the same cell as the other components of the immunoglobulins. The components of the immunoglobulin are assembled at a much improved efficiency. The method of the invention allows the assembly and high efficiency production of such complex molecules.The invention also contemplates the production of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins in a variety of cells, including plant cells, that can be selected for useful additional properties. The use of immunoglobulins containing protection proteins as therapeutic antibodies against mucosal and other pathogens is also contemplated.
Owner:UNTD MED & DENT SCHLS OF GUYS & ST THOMASS HOSP
Antibody composition-producing cell
InactiveUS20060063254A1High activityReduced activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticDisease causeDisease injury
The present invention relates to a cell for the production of an antibody molecule such as an antibody useful for various diseases having high antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity, a fragment of the antibody and a fusion protein having the Fc region of the antibody or the like, a method for producing an antibody composition using the cell, the antibody composition and use thereof.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Anti-glypican-3 antibody having improved kinetics in plasma
InactiveUS20100239577A1Increases tumor proliferation inhibiting activityStrong inhibitory activityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHalf-lifeBlood plasma
A method of modulating the plasma half-life of anti-glypican 3 antibody, a pharmaceutical composition comprising as an active ingredient the anti-glypican 3 antibody that has a plasma half-life that has been modulated, a method of preparing the anti-glypican 3 antibody and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the anti-glypican 3 antibody as an active ingredient are provided. Disclosed is a method of modulating the plasma half-life of anti-glypican 3 antibody by modifying an amino acid residue that is exposed on the surface of the anti-glypican 3 antibody; and anti-glypican 3 antibody that has a plasma half-life that has been modulated by amino acid residue modification, a pharmaceutical composition comprising as an active ingredient the anti-glypican 3 antibody, and a method of preparing the anti-glypican 3 antibody and producing a pharmaceutical composition comprising the anti-glypican 3 antibody as an active ingredient.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Methods for generating or increasing revenues from crops
InactiveUS7193128B2Shorten the timeIncrease incomeData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods of doing business and providing services. For example, methods of increasing the revenue of crops are provided. To this end, the method includes the use of a nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and mini chromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
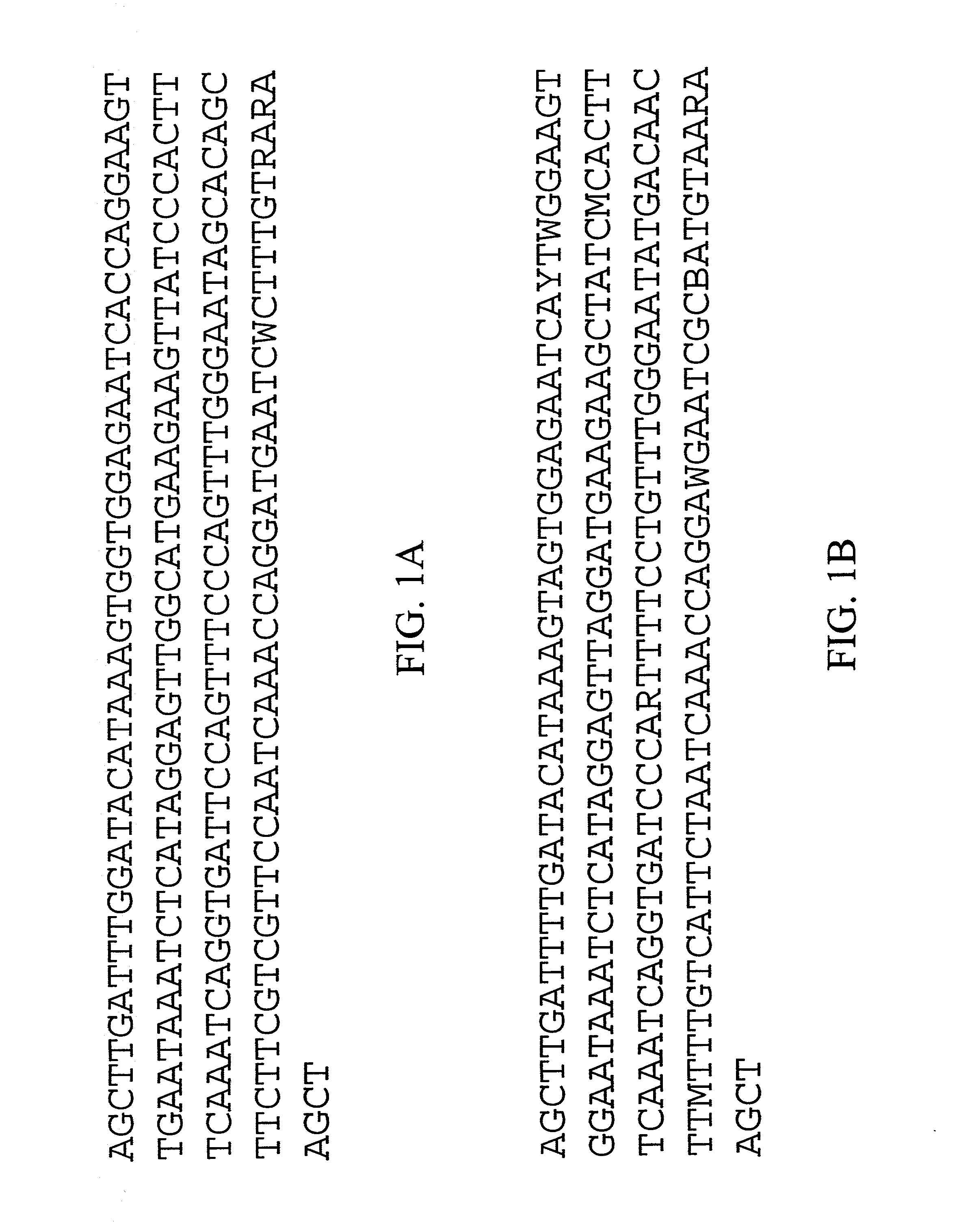
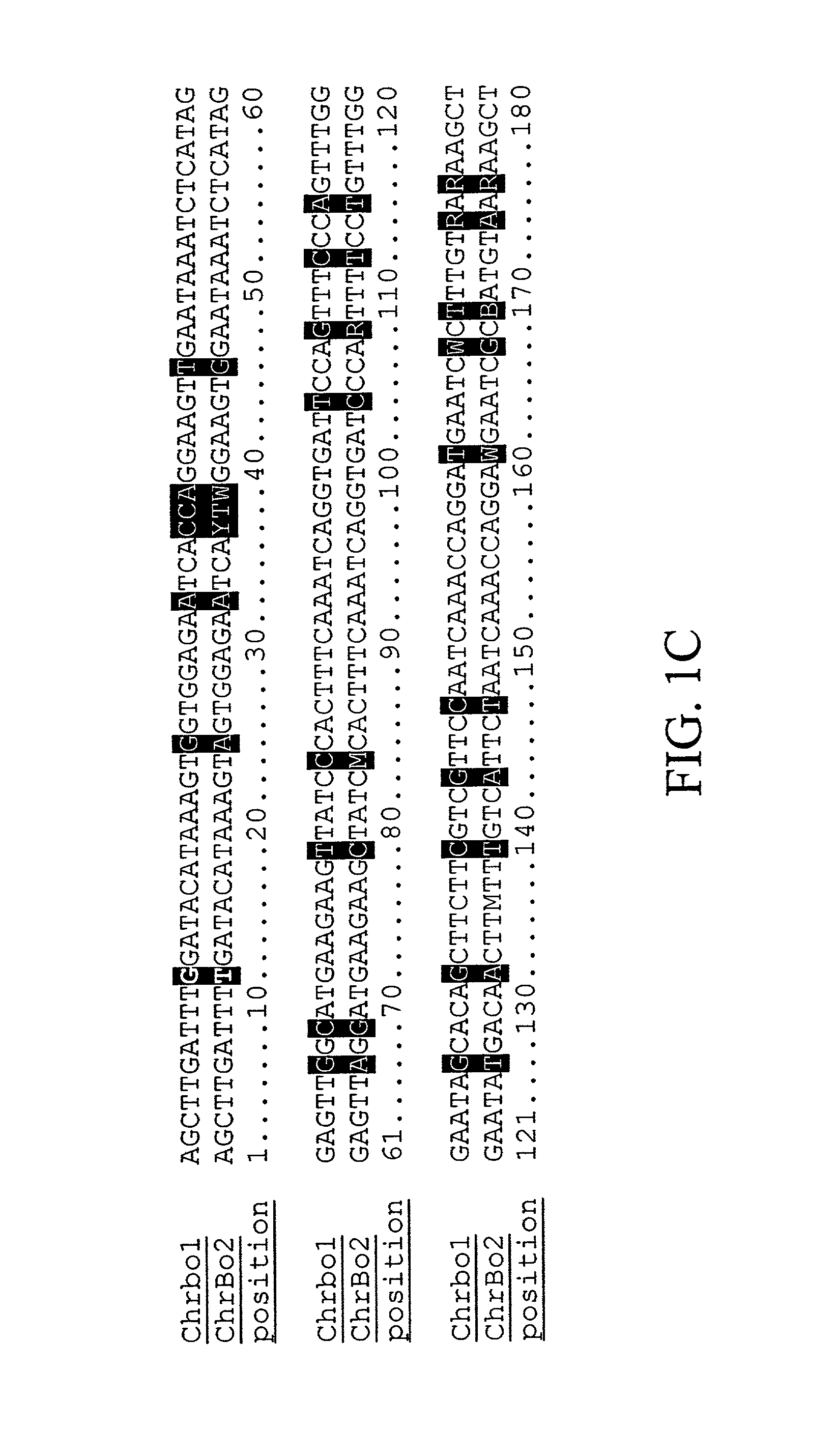
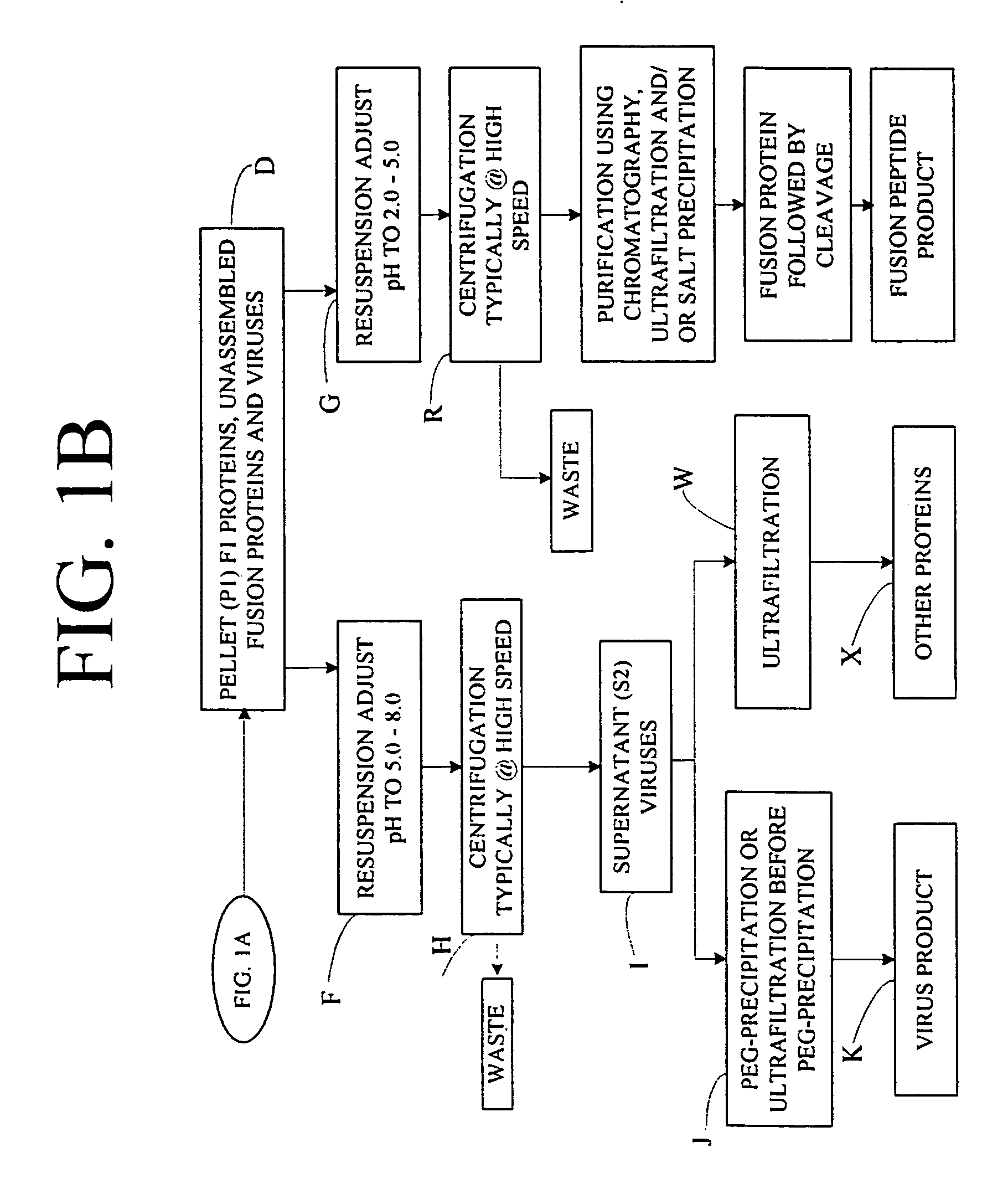
Flexible processing apparatus for isolating and purifying viruses, soluble proteins and peptides from plant sources
InactiveUS7048211B2Efficient and flexibleEasy to processCosmetic preparationsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCentrifugationUltrafiltration
A flexible automated apparatus for isolating and purifying viruses, proteins and peptides of interest from a plant material is disclosed, the apparatus being applicable for large scale purification and isolation of such substances from plant material. The flexible automated apparatus provides an efficient apparatus for isolating viruses, proteins and peptides of interest with little waste material. The automated apparatus for isolating viruses, proteins and peptides of interest includes a grinding apparatus for homogenizing a plant to produce a green juice, a means for adjusting the pH of and heating the green juice, a means for separating the target species, either virus or protein / peptide, from other components of the green juice by one or more cycles of centrifugation, resuspension, and ultrafiltration, and finally purifying virus particles by such procedure as PEG-precipitation or purifying proteins and peptides by such procedures as chromatography and / or salt precipitation.
Owner:KENTUCKY BIOPROCESSING
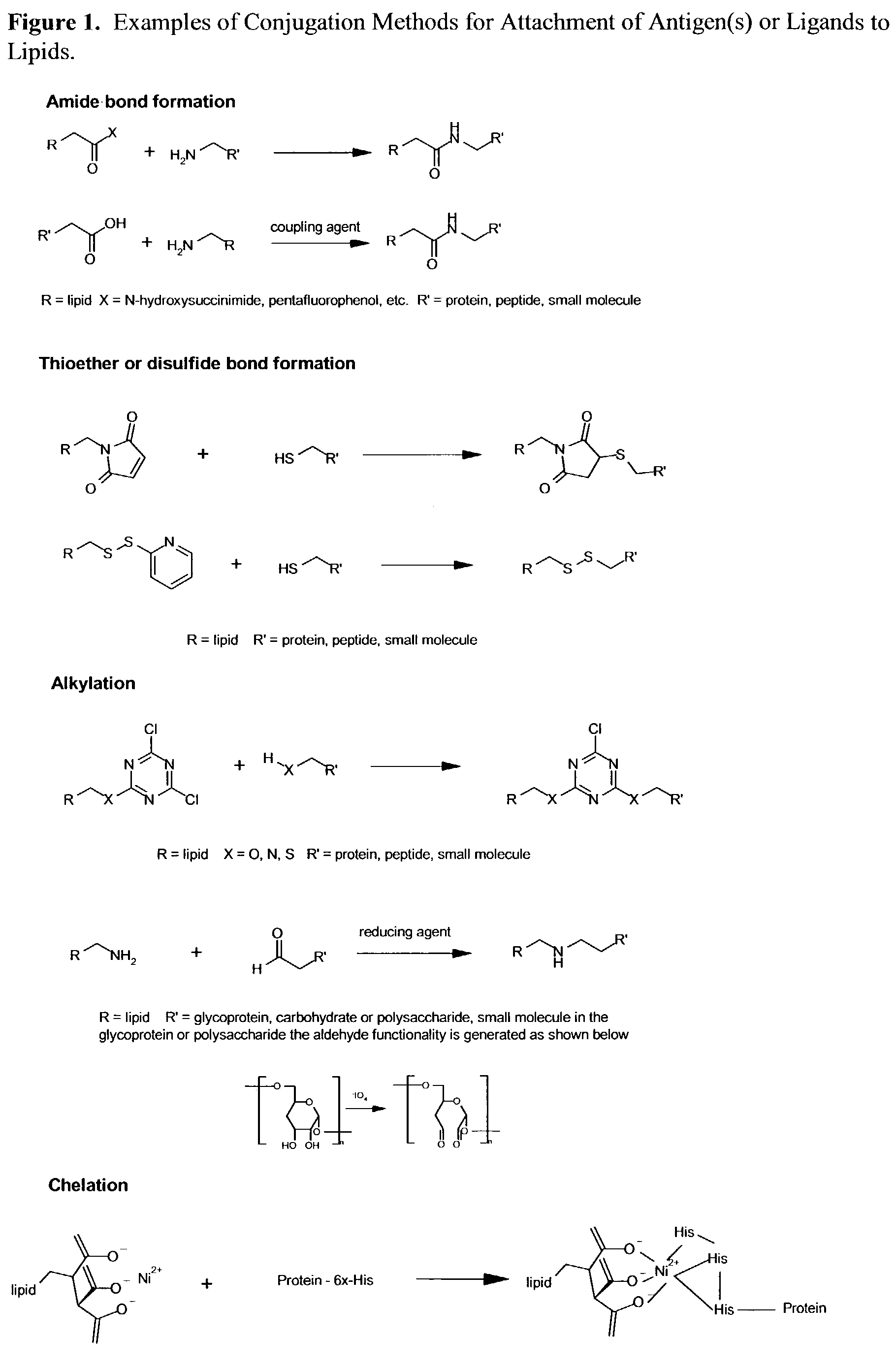
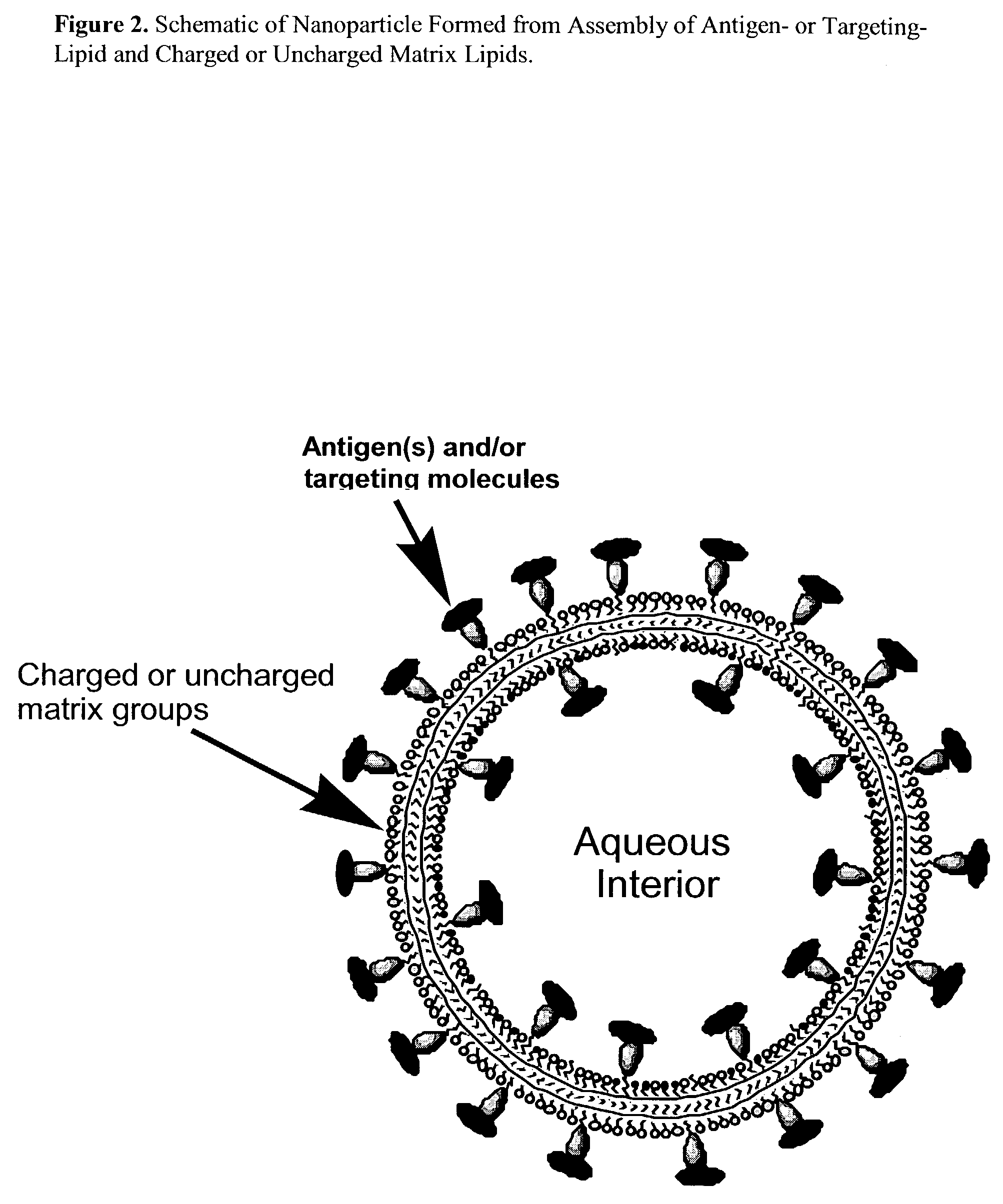
Nanoparticle vaccines
InactiveUS7285289B2Simple and inexpensive to synthesizeEnhance immune responseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryLipid formationAntigen
The present invention relates to nanoparticle vaccines comprised of a carrier, particularly polymerized lipids, having multiple copies of an antigen or combinations of different antigens displayed on the carrier. Such antigen-displaying nanoparticles may also display a targeting molecule on its surface in order to direct it to a specific site or cell type to optimize a desired immune response. The present invention also relates to encapsulating an antigen or combinations of different antigens within such nanoparticles, with or without a targeting molecule displayed on its surface. The antigens used in this invention are effective to produce an immune response against a variety of pathological conditions.
Owner:NANOVALENT PHARMA
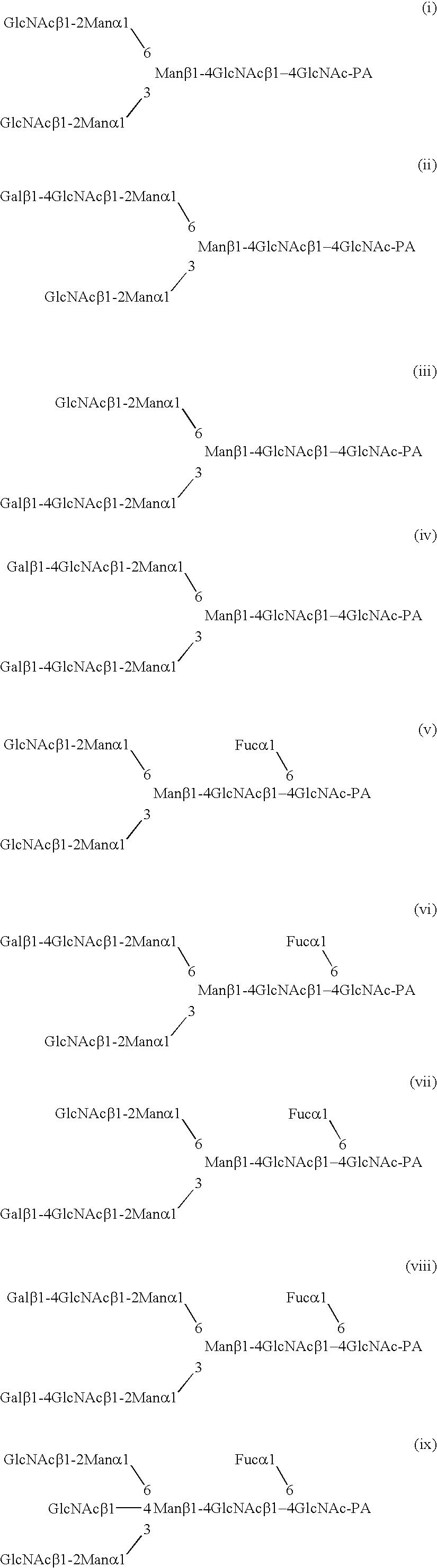
Optimizing glycan processing in plants
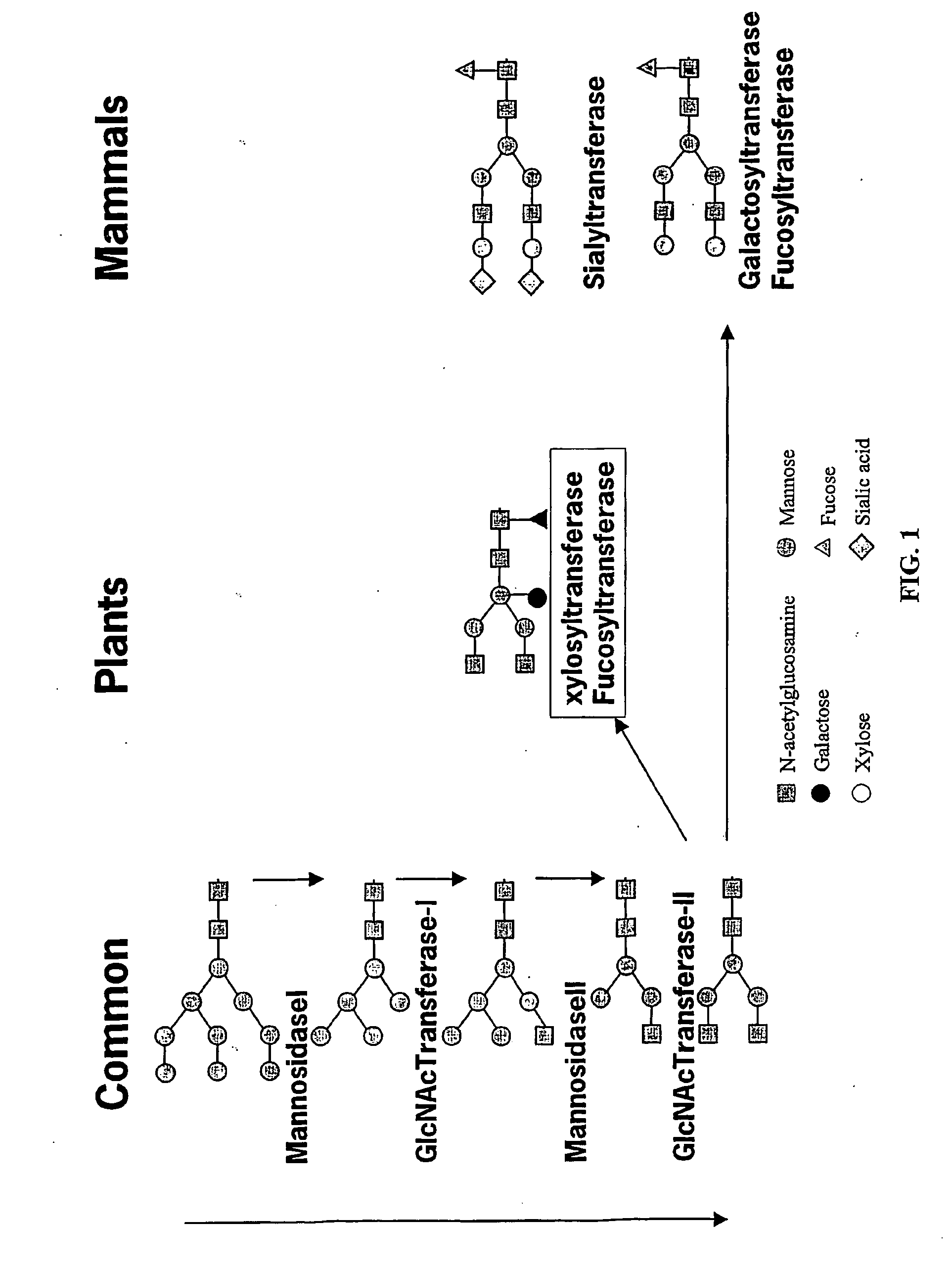
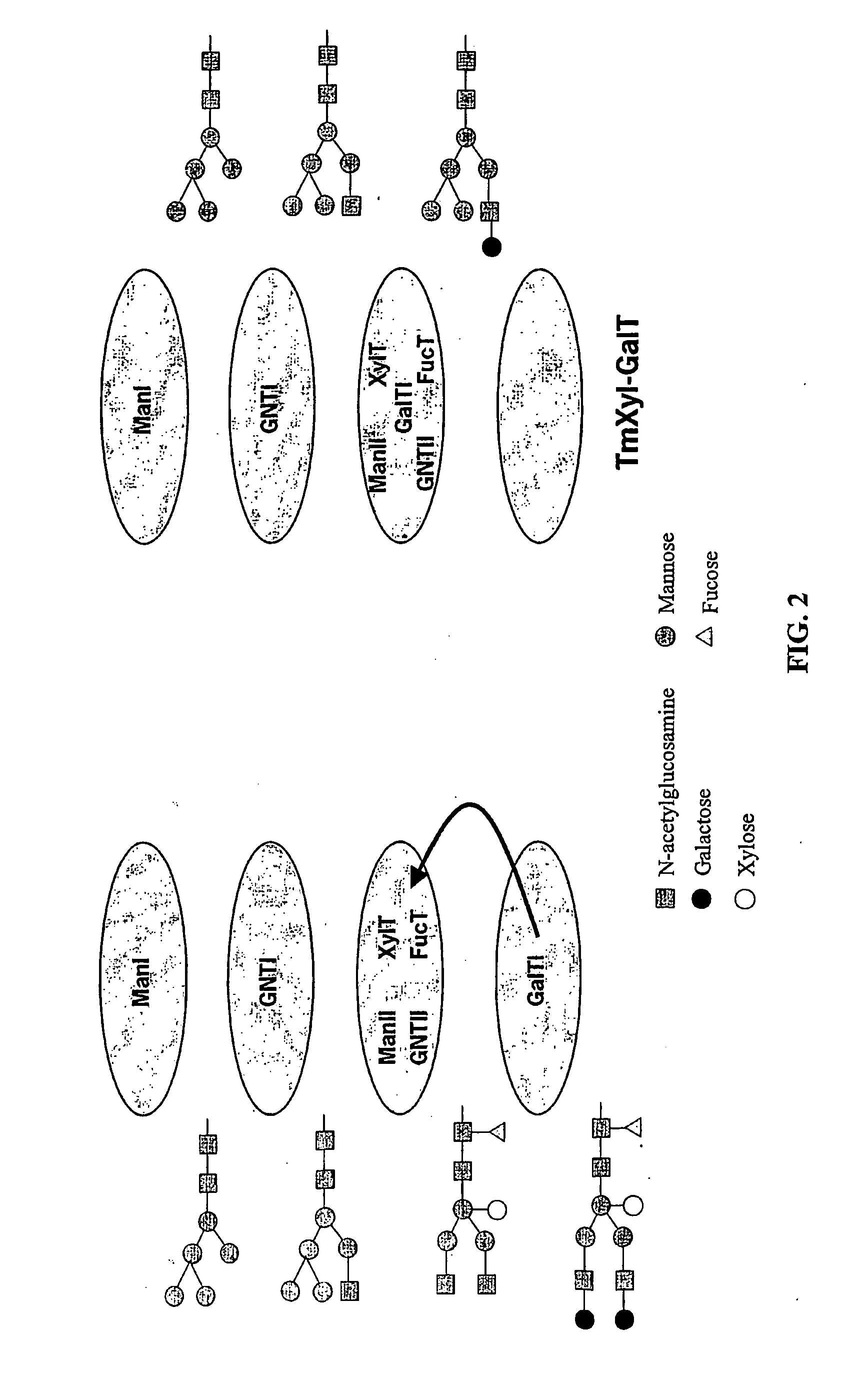
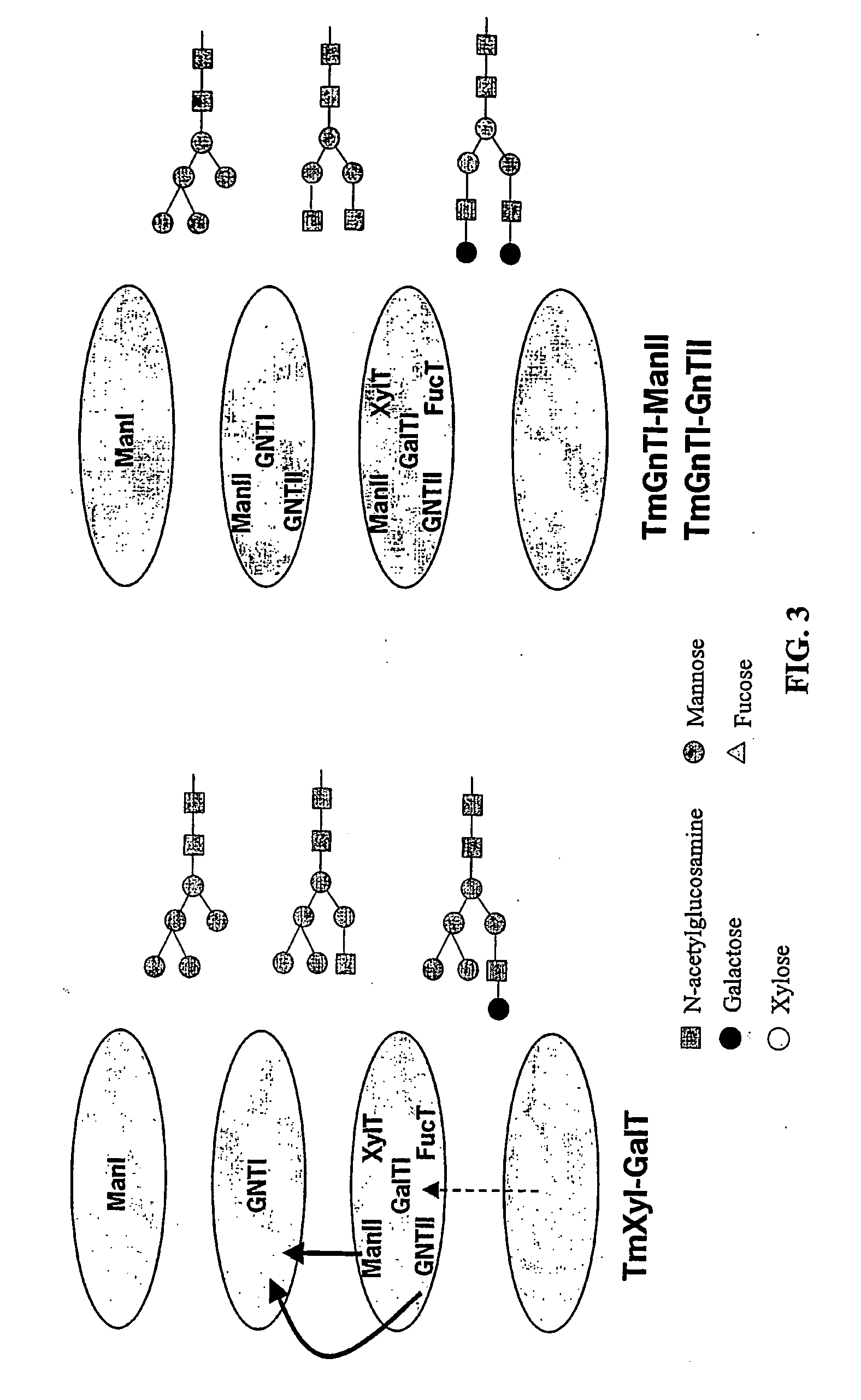
InactiveUS20060253928A1Reduce diversityGalactosylation is improvedFungiBacteriaBiological bodyComplex type
The invention is directed to methods for optimizing glycan processing in organisms (and in particular, plants) so that a glycoprotein having complex type bi-antennary glycans and thus 5 containing galactose residues on both arms and which are devoid of (or reduce in) xylose and fucose can be obtained. The invention is further directed to said glycoprotein obtained and host system comprising said protein.
Owner:STICHTING DIENST LANBOUWKUNDIG ONDERZOEK
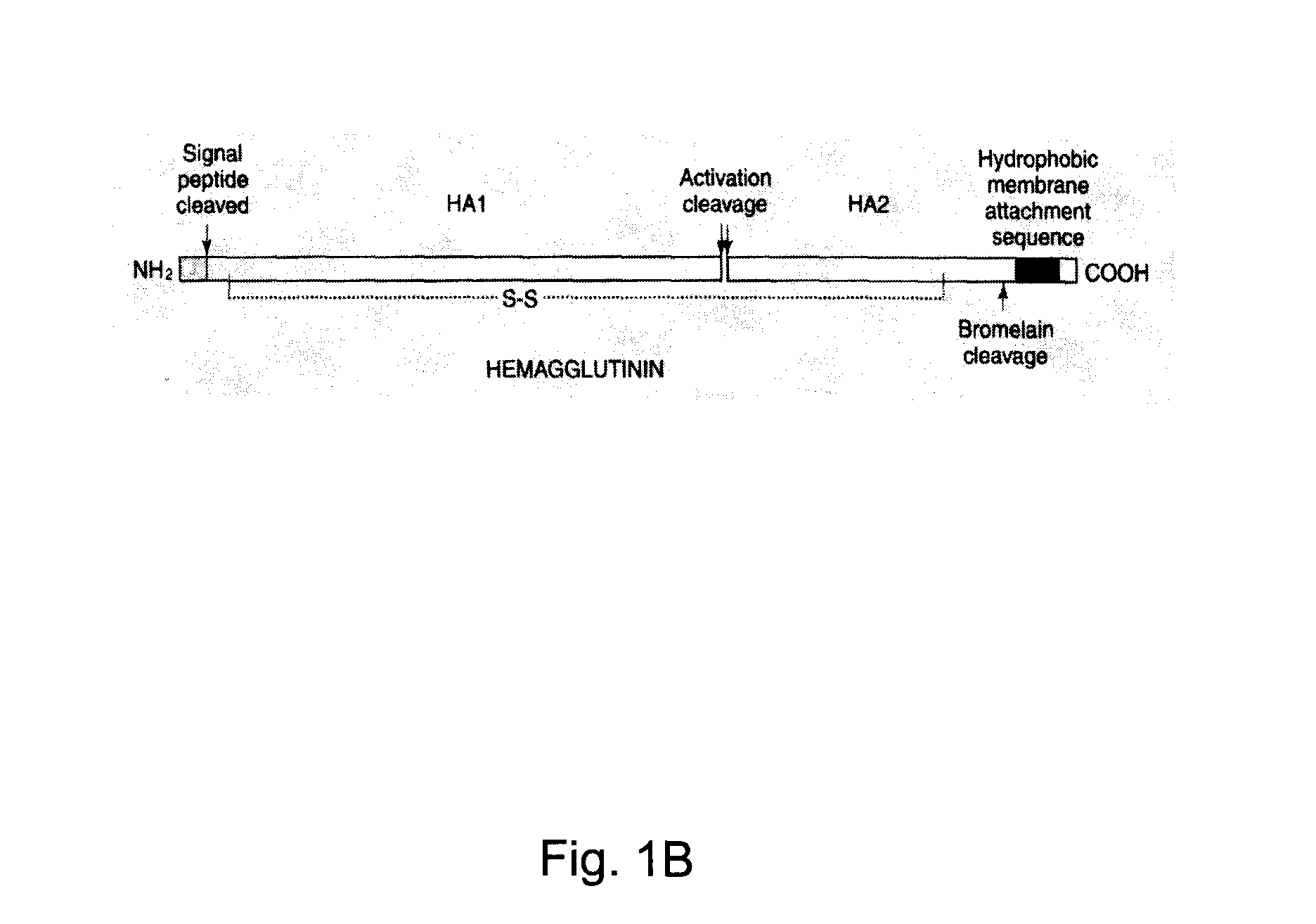
Influenza virus-like particles (VLPS) comprising hemagglutinin produced within a plant
InactiveUS20100239610A1Enhance immune responseEasy to captureSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesHemagglutininLipid formation
A method for synthesizing influenza virus-like particles (VLPs) within a plant or a portion of a plant is provided. The method involves expression of influenza HA in plants and the purification by size exclusion chromatography. The invention is also directed towards a VLP comprising influenza HA protein and plants lipids. The invention is also directed to a nucleic acid encoding influenza HA as well as vectors. The VLPs may be used to formulate influenza vaccines, or may be used to enrich existing vaccines.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
System and method for production of antibodies in plant cell culture
ActiveUS20090082548A1Rapid and consistent reproductionLack of uniformityVaccinesFused cellsBiotechnologyHigh level expression
A system and method for production of antibodies in plant cell culture, which results in highly functional antibodies, produced with a high level of expression efficiency. The present invention also encompasses host cells, vectors and methods for mass production of full size assembled immunoglobulins.
Owner:PROTALIX
Compositions and methods for humanization and optimization of n-glycans in plants
InactiveUS20080060092A1Enhanced effector functionHigh antibody activityAntipyreticAnalgesicsGrowth plantGlycan
Methods for altering the N-glycosylation pattern of proteins in higher plants are provided. The methods comprise introducing into the plant a recombinant construct that provides for the inhibition of expression of α1,3-fucosyltransferase (FucT) and β1,2-xylosyltransferase (XylT) in a plant. Use of these constructs to inhibit or suppress expression of both of these enzymes, and isoforms thereof, advantageously provides for the production of endogenous and heterologous proteins having a “humanized” N-glycosylation pattern without impacting plant growth and development. Stably transformed higher plants having this protein N-glycosylation pattern are provided. Glycoprotein compositions, including monoclonal antibody compositions, having substantially homogeneous glycosylation profiles, and which are substantially homogeneous for the G0 glycoform, are also provided.
Owner:BIOLEX INC +1
Glycan-optimized Anti-cd20 antibodies
InactiveUS20090060921A1High antibody activityEnhanced effector functionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansVaccinesAntigenFucosylation
Glycan-optimized monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind CD20 antigen and which have improved effector function are provided. The anti-CD20 antibodies of the invention have a glycosylation pattern that results in an antibody composition having predominately the G0 glycoform, and thus comprise N-glycans that lack fucose (i.e., afucosylated) and galactose residues attached thereto. In some embodiments, these anti-CD20 antibodies comprise the light chain and heavy chain sequences of the rituximab anti-CD20 antibody, and thus represent afucosylated rituximab. Methods for producing these glycan-optimized anti-CD20 antibodies are also provided.
Owner:SYNTHON BIOPHARMACEUTICALS BV
T cell regulation
InactiveUS20060240024A1Increases magnitudeSimple methodAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderRegulatory T cellAutoimmune responses
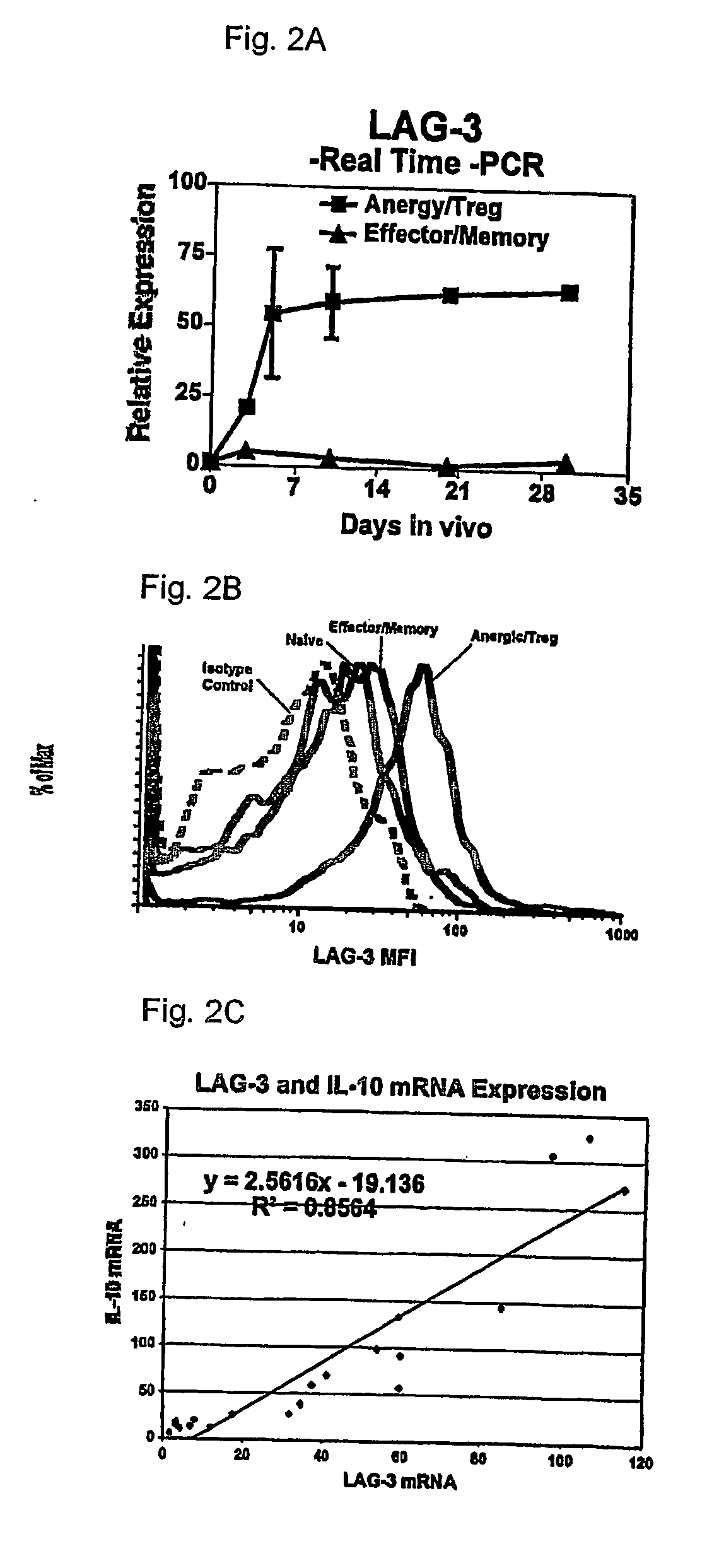
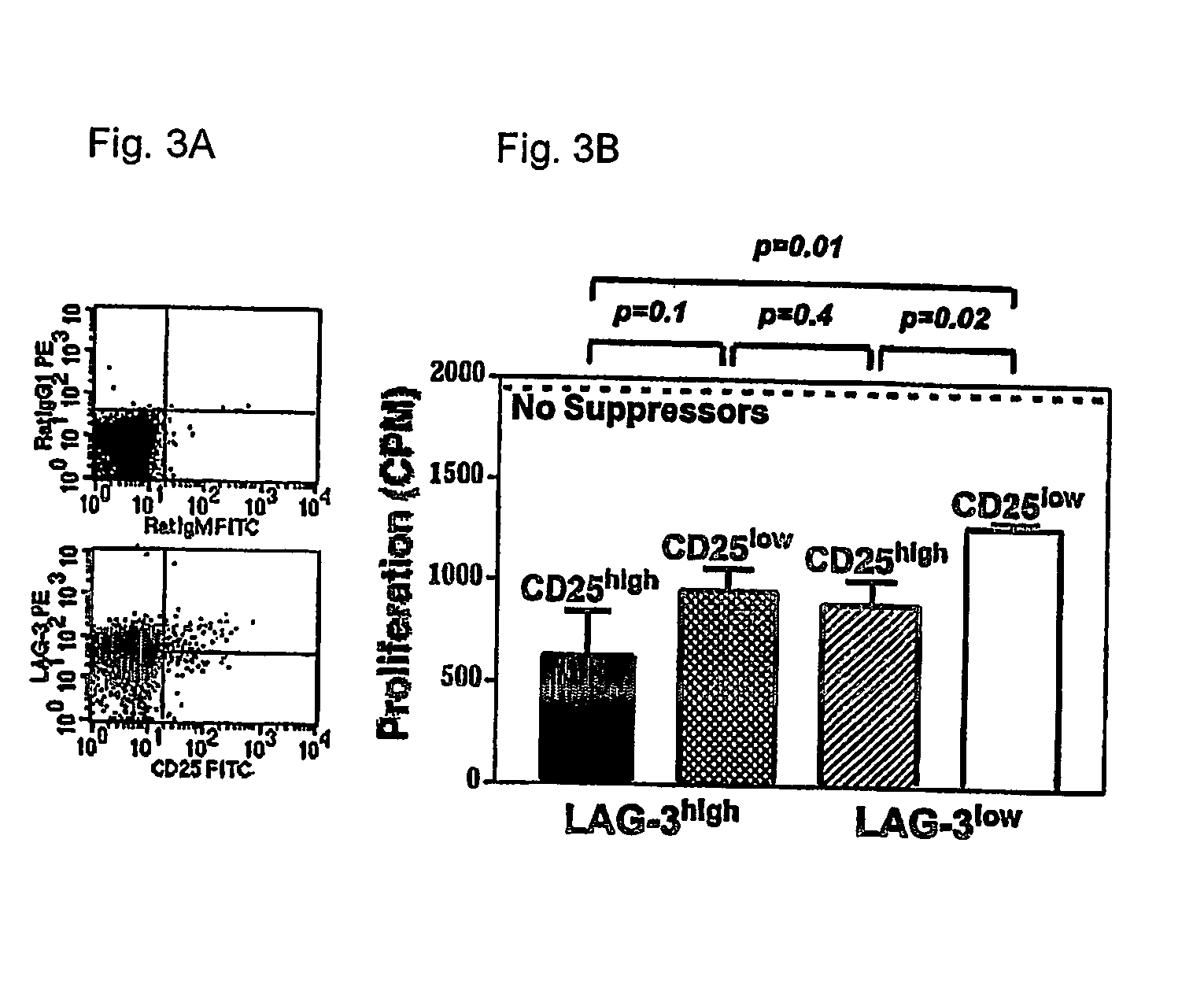
Regulatory T cells (Treg) limit autoimmunity but can also attenuate the magnitude of anti-pathogen and anti-tumor immunity. Understanding the mechanism of Treg function and therapeutic manipulation of Treg in vivo requires identification of Treg selective receptors. A comparative analysis of gene expression arrays from antigen specific CD4+ T cells differentiating to either an effector / memory or a regulatory phenotype revealed Treg selective expression of LAG-3 (CD223), a CD4-related molecule that binds MHC class II. LAG-3 expression on CD4+ T cells correlates with the cells' in vitro suppressor activity, and ectopic expression of LAG-3 on CD4 T cells confers suppressor activity on the T cells. Antibodies to LAG-3 inhibit suppression both in vitro and in vivo. LAG-3 marks regulatory T cell populations and contributes to their suppressor activity.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC +1
Production of fc-fusion polypeptides in eukaryotic algae
InactiveUS20110151515A1Increase serum stabilityEfficient separation and purificationUnicellular algaeVaccinesHeterologousProtein regulation
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer plastids comprising heterologous genes encoding immuno-activating domains fused to an extracellular domain (ECD) of a receptor or surface glycoprotein, a growth factor or an enzyme and produced within a subcellular organelle, such as a chloroplast. The immuno-activating domains may include those regions of a protein capable of modulating the interaction between immune effector cells via proteins containing stereoselective binding domains and specific ligands, such as the Fc regions of antibodies. The present disclosure also demonstrates the utility of plants, including green algae, for the production of complex multi-domain fusion proteins as soluble bioactive therapeutic agents.
Owner:SAPPHIRE ENERGY
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS7235716B2Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHROMATIN
Novel peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against breast cancer and other cancers
ActiveUS20170173132A1High error rateImmunoglobulin superfamilyTumor rejection antigen precursorsAdditive ingredientNeoplasm
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Membrane encapsulated nanoparticles and method of use
Provided are nanoparticles, method of using and making thereof. The invention nanoparticle comprises a) an inner core comprising a non-cellular material; and b) an outer surface comprising a cellular membrane derived from a cell or a membrane derived from a virus. Medicament delivery systems or pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inventive nanoparticles are also provided. The present invention further provides immunogenic compositions comprising the inventive nanoparticles, and methods of use the inventive immunogenic compositions for eliciting an immune response and for treating or preventing disease or condition, such as neoplasm or cancer, or disease or conditions associated with cell membrane inserting toxin. Vaccines comprising the immunogenic composition comprising the nanoparticles of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
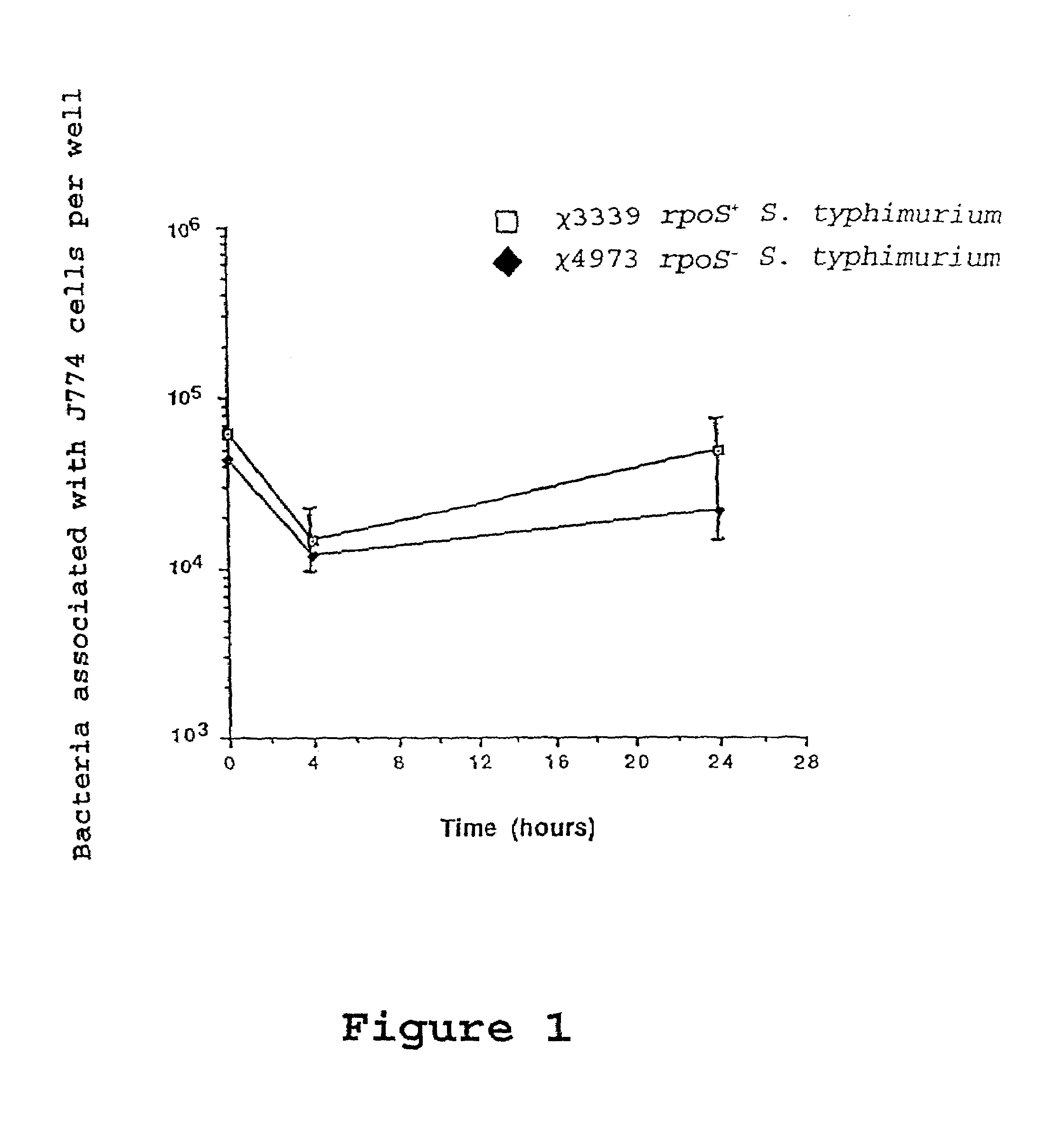
Recombinant vaccines comprising immunogenic attenuated bacteria having RpoS positive phenotype
InactiveUS7083794B2Improve balanceImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSalmonella entericaSalmonella serotype typhi
Attenuated immunogenic bacteria having an RpoS+ phenotype, in particular, Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi having an RpoS+ phenotype and methods therefor are disclosed. The Salmonella have in addition to an RpoS+ phenotype, an inactivating mutation in one or more genes which render the microbe attenuated, and a recombinant gene capable of expressing a desired protein. The Salmonella are attenuated and have high immunogenicity so that they can be used in vaccines and as delivery vehicles for genes and gene products. Also disclosed are methods for preparing the vaccine delivery vehicles.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Use of cell adhesion inhibitor for the mobilization of antigen presenting cells and immune cells in a cell mixture (AIM) from the peripheral blood and methods of use
Disclosed is a method to recover an antigen presenting cells (APCs) and immune cells rich mixture (AIM) from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) mobilized with one or more cell adhesion inhibitors for the preparation of an AIM vaccine or an AIM adoptive immunotherapy preparation. In addition, AIM mobilization can be enhanced by priming, simultaneously or in sequence, one or more of a combination of different chemical compounds, cytokines, hormones, growth factors, etc. The interaction of chemokines and chemokine receptors enable tumor cells attachment or in close proximity to antigen presenting cells and immune cells which possess similar receptors in a micro niche environment. Severing the chemokine / chemokine receptor linkage by a cell adhesion inhibitor will release these specifically primed cell mixtures into the peripheral blood. The collection of these cells from the peripheral blood has never been described and is the basis of this invention. AIM cells can either be used alone or better still, be induced into more target specific preparations with additions, modifications and incubation, pre or post cell adhesion inhibitors mobilization, with vaccines, different target specific antigens, peptides, chemotherapeutic agents, oncolytic viral therapeutic agents, cytokines, co-stimulatory molecules, anti-regulatory T cell therapeutic agents, anti-CTLA4, anti-PD1 molecules and other methodologies of immunological enhancement known to the art. The AIM vaccine or AIM adoptive immunotherapy preparation can then be used, but not limited to, the treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:YEUNG ALEX WAH HIN +1
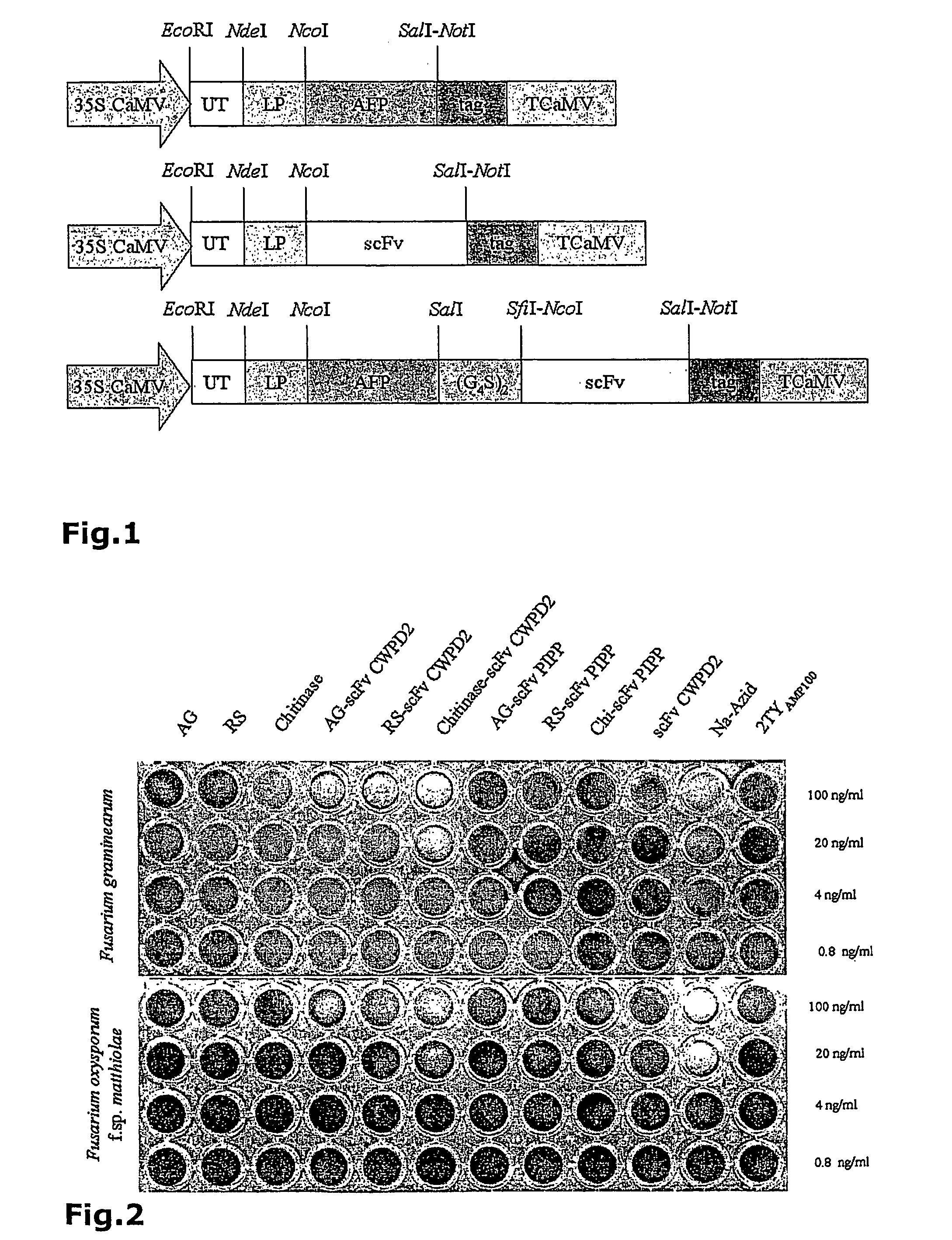
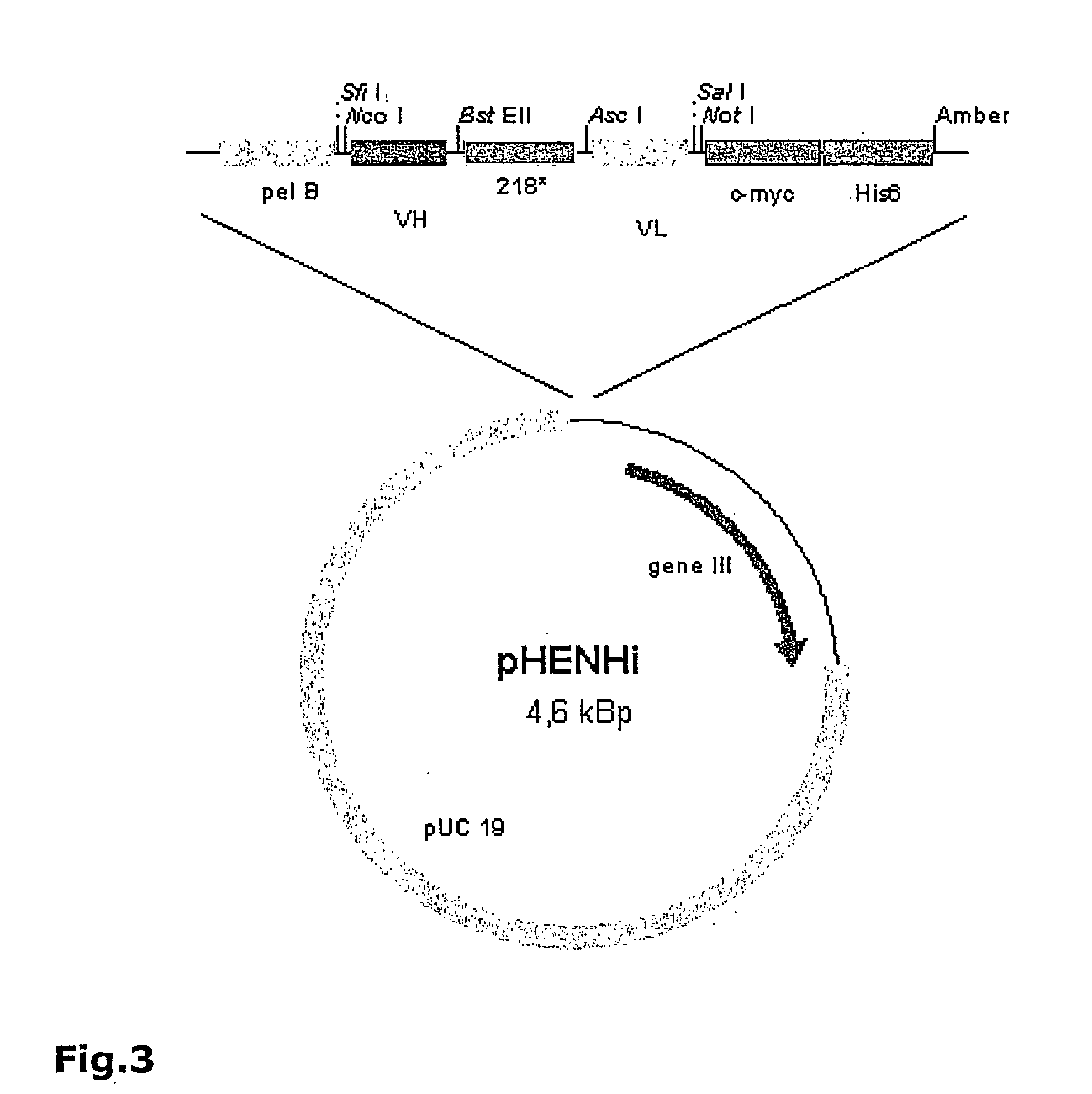
Recombinant antibodies to sclerotinia antigens
InactiveUS20080104734A1Sugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansSclerotiniaAnti fungal
The invention is directed to recombinant antibodies which bind to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum antigens and comprise a single chain variable fragment (scFv). The antigen may be selected from SSPG1d or a portion thereof, aspartyl protease or a portion thereof, or whole Sclerotinia sclerotiorum mycelium. The invention also provides an antibody linked to an anti-fungal polypeptide. The invention extends to nucleic acid sequences encoding the antibodies, and expression vectors comprising the nucleic acid sequences. The invention is also directed to transgenic plants, seeds, tissues or cells transformed with the expression vectors. Methods for producing a transgenic plant that is resistant to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, and for detecting Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in a biological sample utilizing an antibody which binds to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum antigen, and immunoassay kit for same are also provided.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Plant centromere compositions
InactiveUS20050268359A1Shorten the timeOvercome limitationsBacteriaVaccinesBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides for the nucleic acid sequences of plant centromeres. This will permit construction of stably inherited recombinant DNA constructs and minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF +1
Protein expression system
ActiveUS20100287670A1Improve expression levelBoost protein levelsVirus peptidesVaccinesStart codonForeign protein
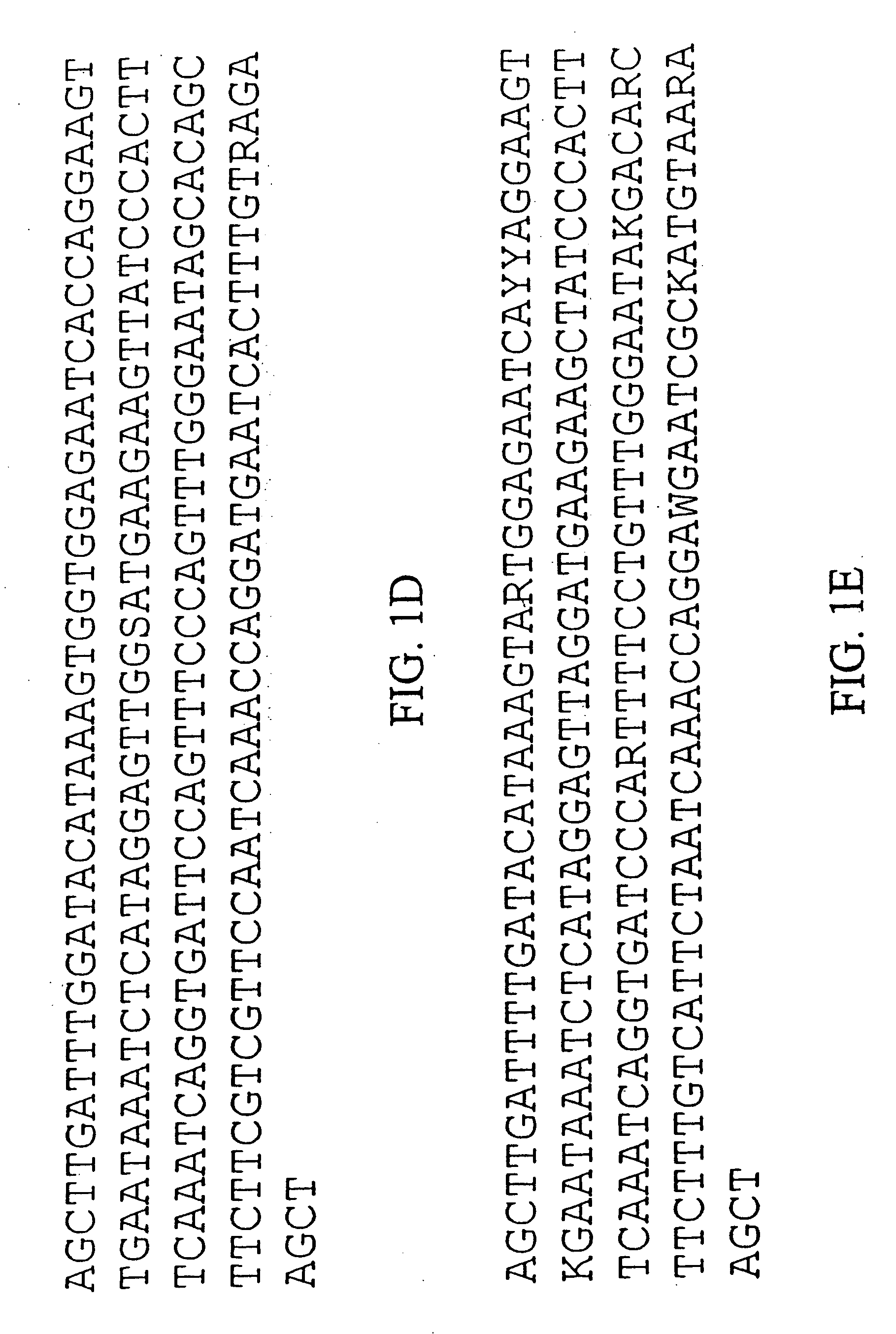
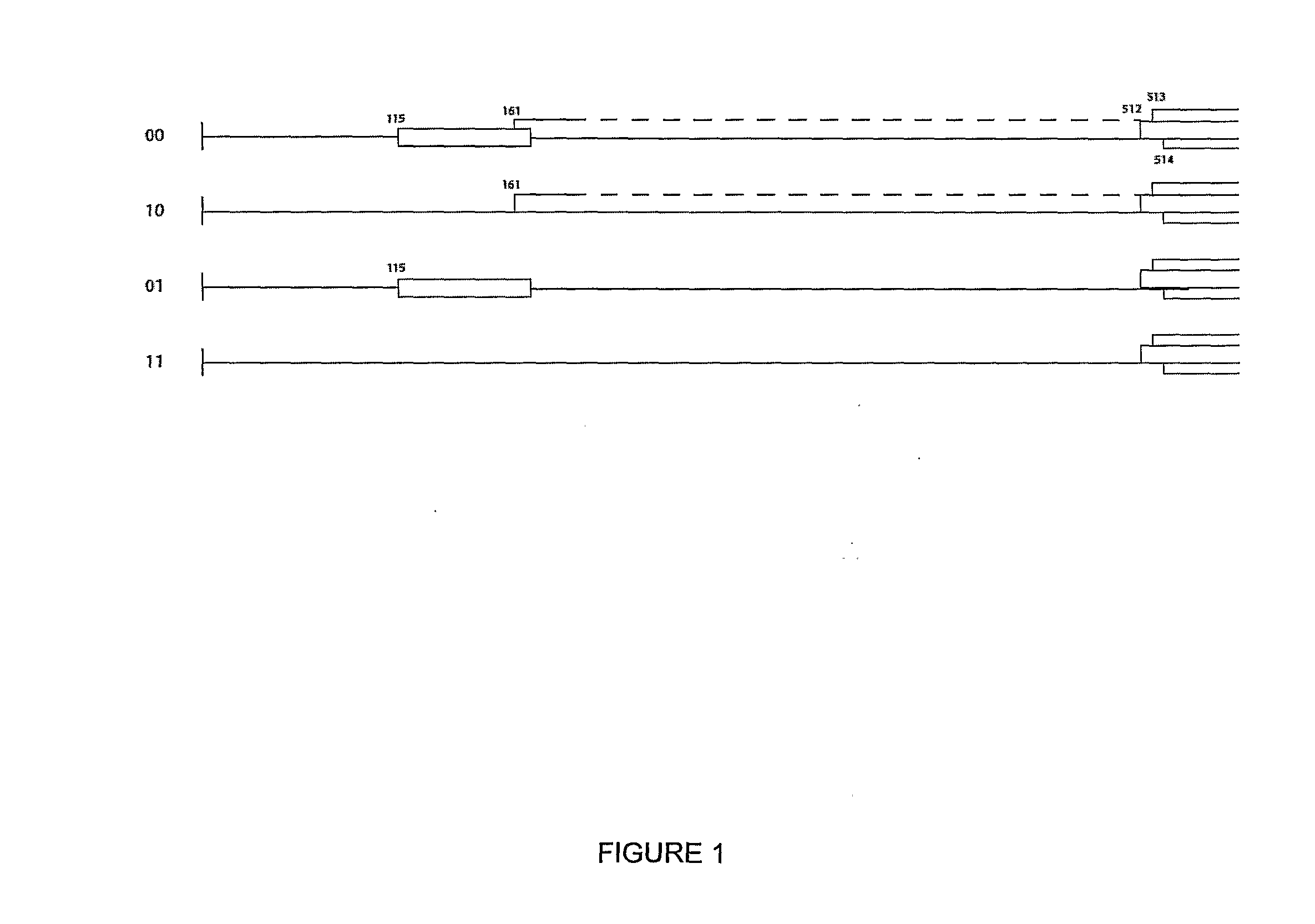
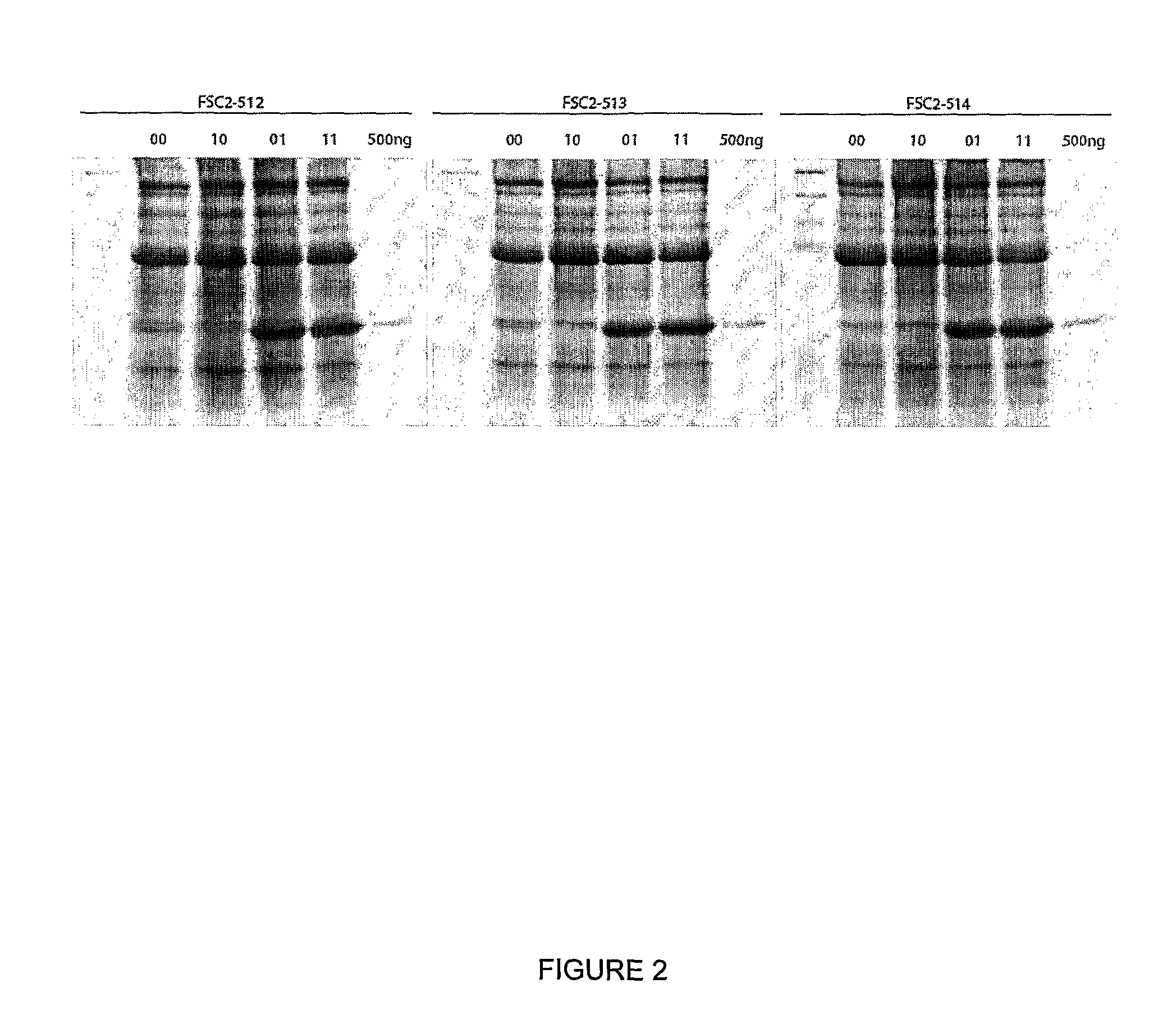
The inventions is based on an expression enhancer sequence derived from the RNA-2 genome segment of a bipartite RNA virus, in which a target initiation site in the RNA-2 genome segment has been mutated. Deletion of appropriate start codons upstream of the main RNA2 translation initiation can greatly increase in foreign protein accumulation without the need for viral replication. Also provided are methods, vectors and systems, including the ‘hyper-translatable’ Cowpea Mosaic Virus (‘CPMV-HT’) based protein expression system.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Recombinant antibodies to sclerotinia antigens
The invention is directed to recombinant antibodies which bind to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum antigens and comprise a single chain variable fragment (scFv). The antigen may be selected from SSPG1d or a portion thereof, aspartyl protease or a portion thereof, or whole Sclerotinia sclerotiorum mycelium. The invention also provides an antibody linked to an anti-fungal polypeptide. The invention extends to nucleic acid sequences encoding the antibodies, and expression vectors comprising the nucleic acid sequences. The invention is also directed to transgenic plants, seeds, tissues or cells transformed with the expression vectors. Methods for producing a transgenic plant that is resistant to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, and for detecting Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in a biological sample utilizing an antibody which binds to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum antigen, and immunoassay kit for same are also provided.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Predicting immunogenicity of t cell epitopes
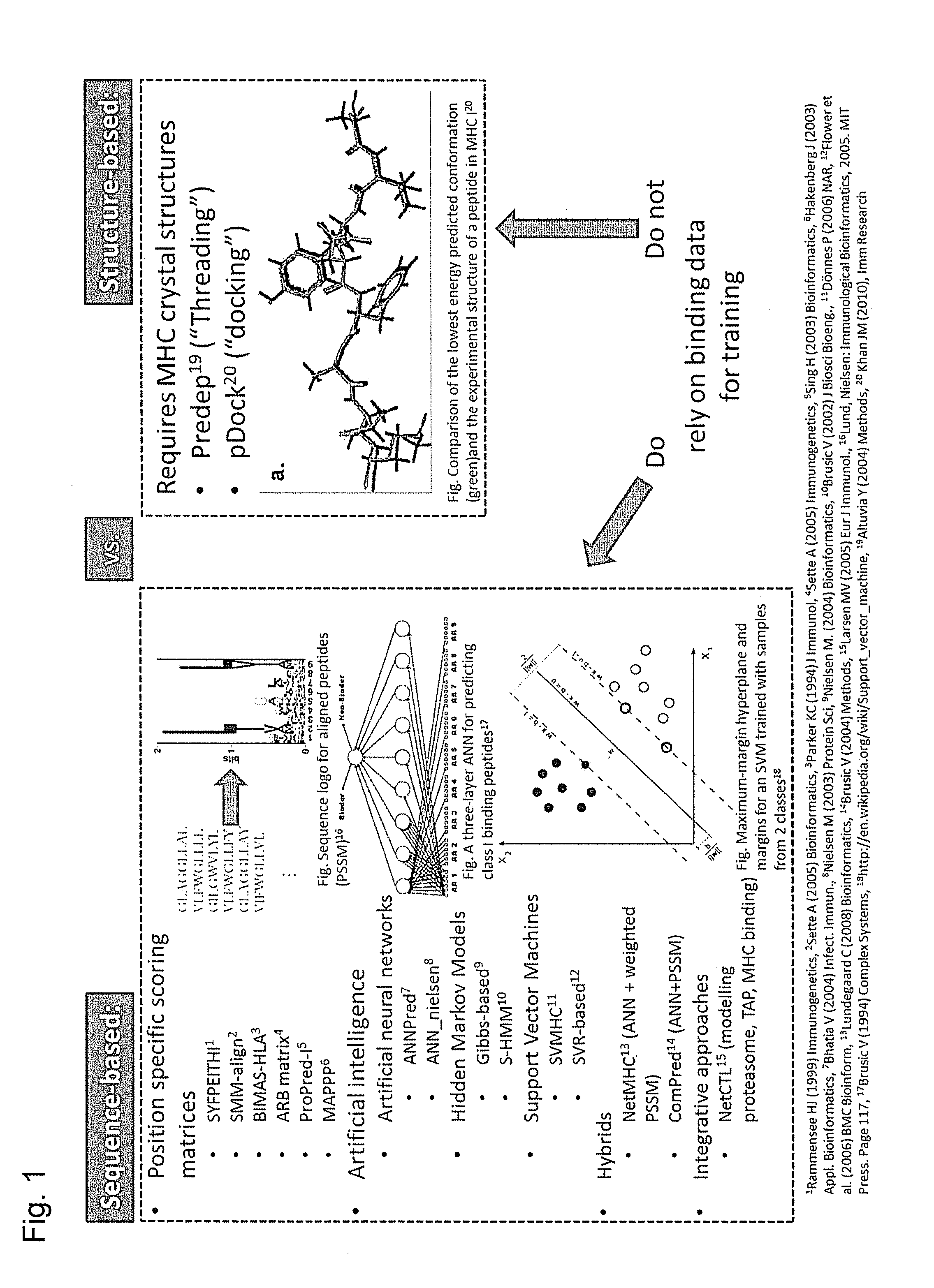
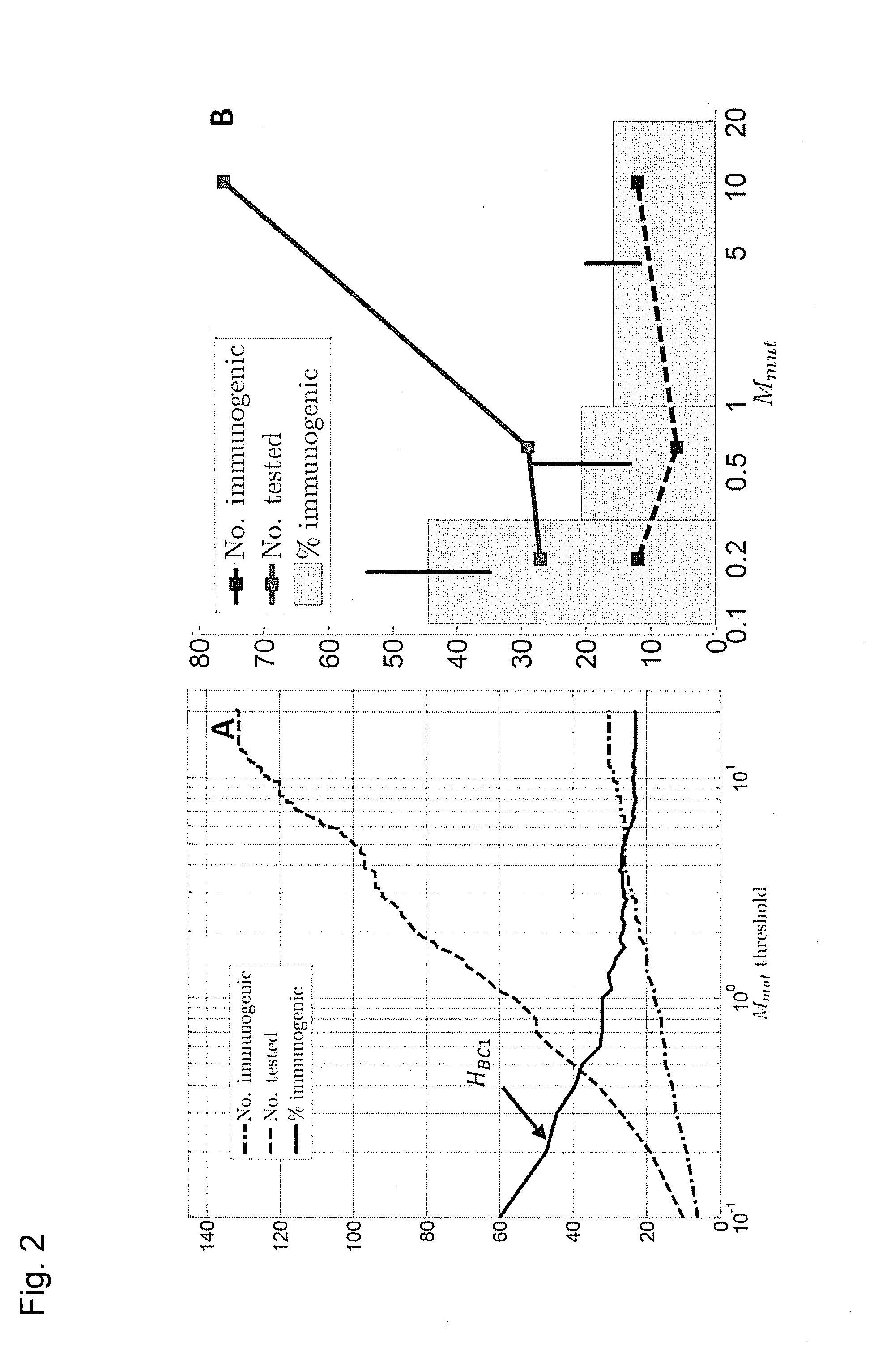
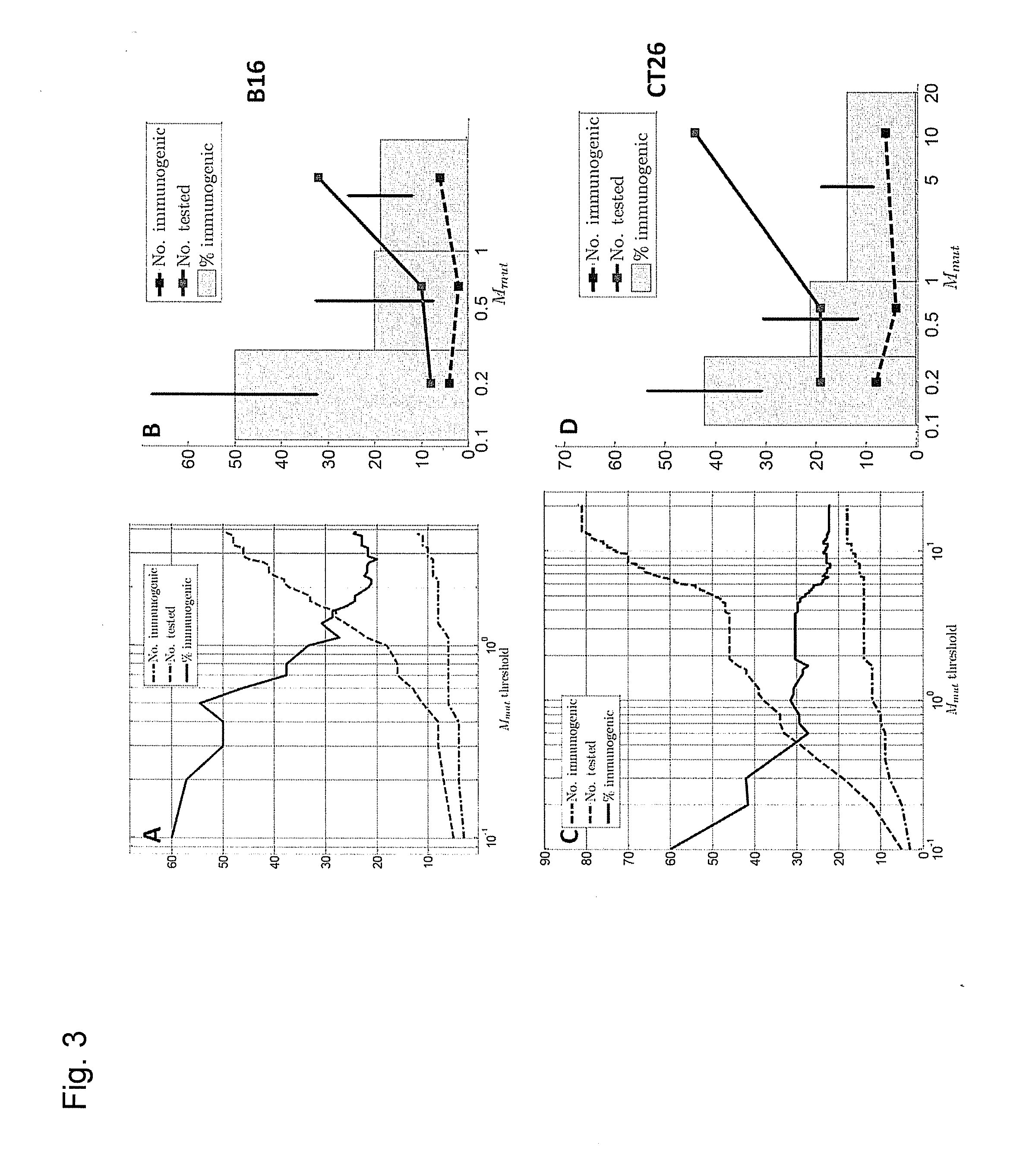
ActiveUS20160125129A1Minimizing chanceDevelopmental delayMicrobiological testing/measurementVaccinesOncologyImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to methods for predicting T cell epitopes. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for predicting whether modifications in peptides or polypeptides such as tumor-associated neoantigens are immunogenic or not. The methods of the invention are useful, in particular, for the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and, thus, in the context of personalized cancer vaccines.
Owner:BIONTECH SE +1
Vaccines expressed in plants
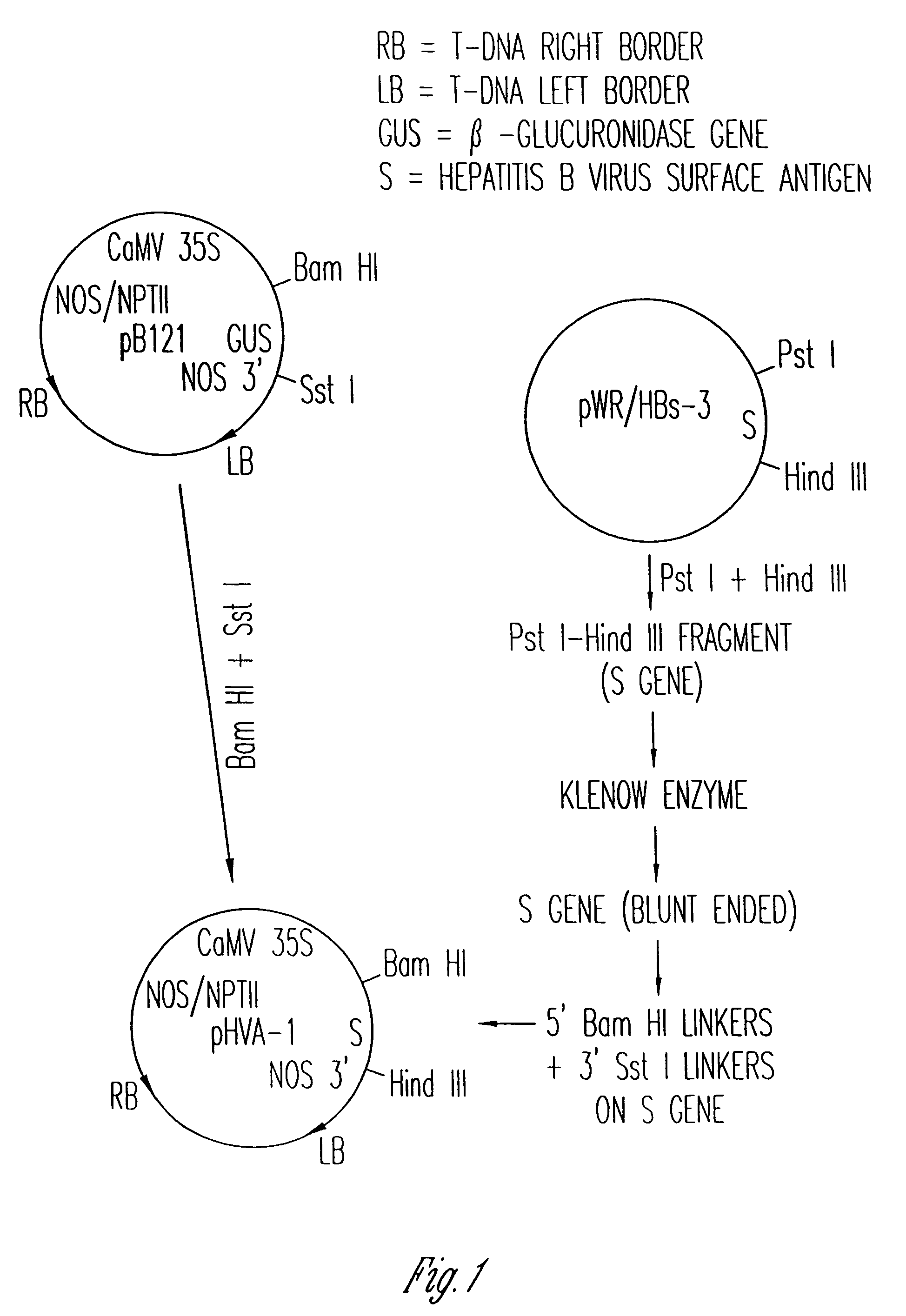
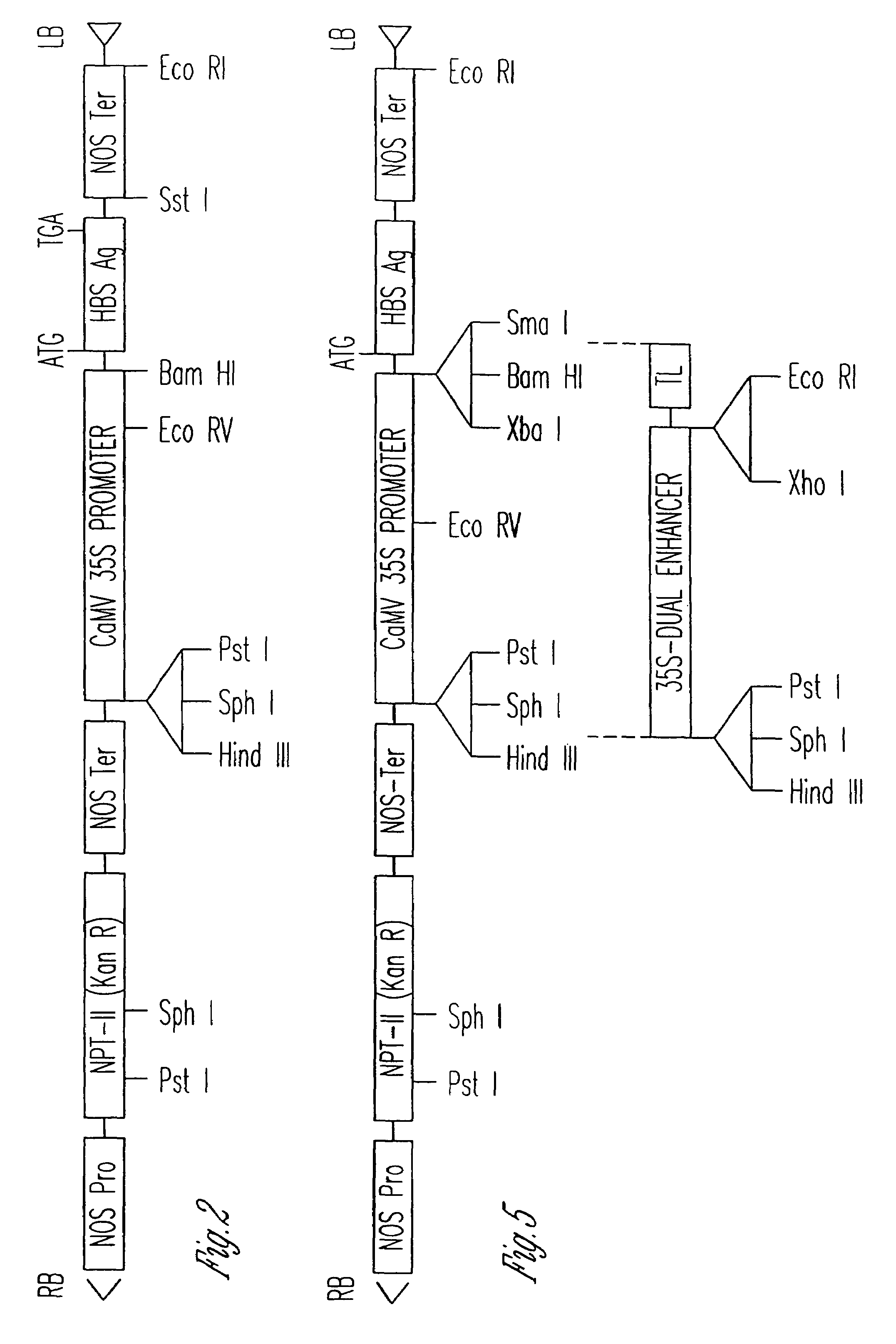
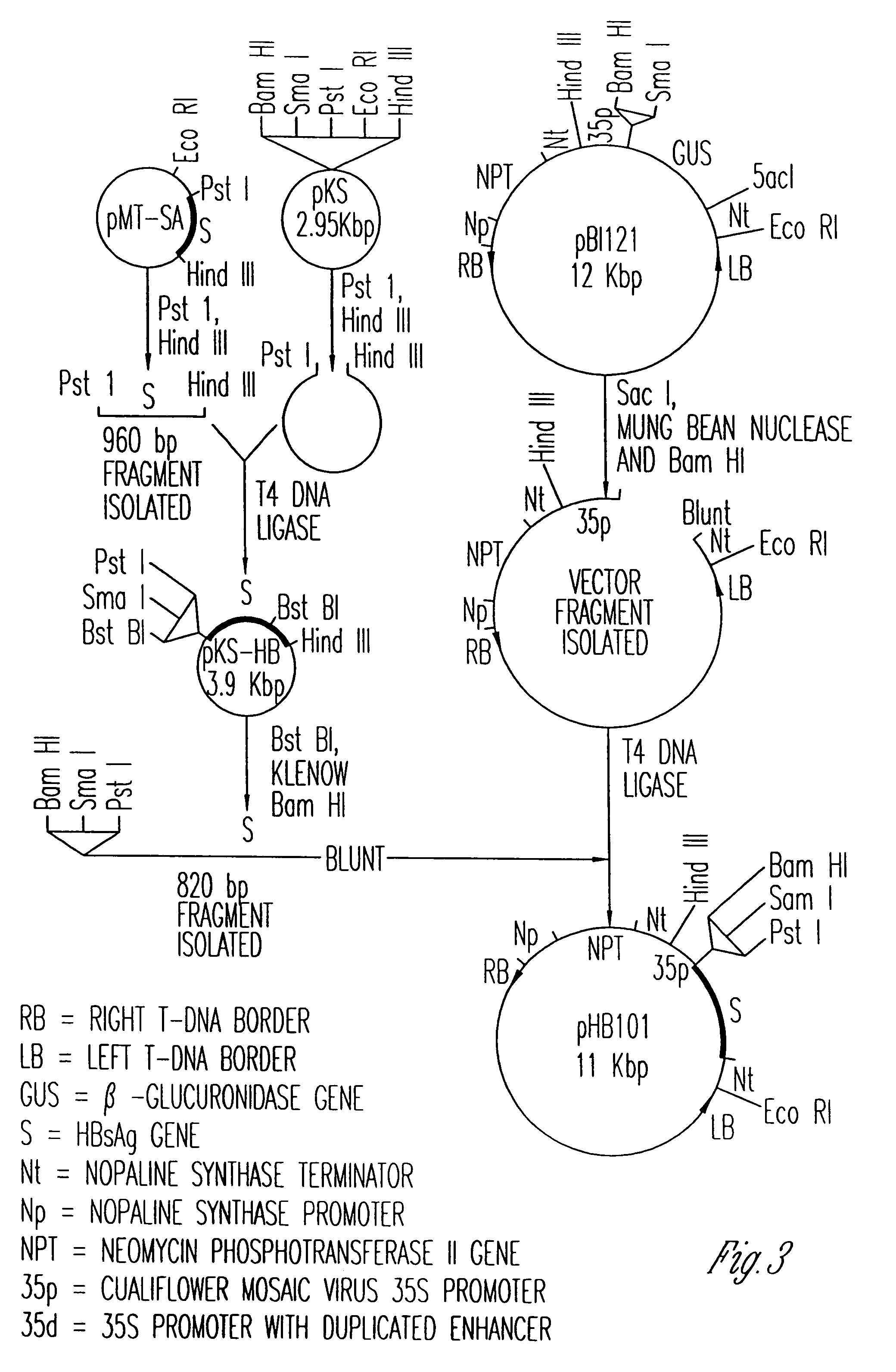
The anti-viral vaccine of the present invention is produced in transgenic plants and then administered through standard vaccine introduction method or through the consumption of the edible portion of those plants. A DNA sequence encoding for the expression of a surface antigen of a viral pathogen is isolated and ligated to a promoter which can regulate the production of the surface antigen in a transgenic plant. This gene is then transferred to plant cells using a procedure that results in its integration into the plant genome, such as through the use of an Agrobacterium tumenfaciens plasmid vector system. Preferably, the foreign gene is expressed in an portion of the plant that is edible by humans or animals. In a preferred procedure, the vaccine is administered through the consumption of the edible plant as food, preferably in the form of a fruit or vegetable juice which can be taken orally.
Owner:PRODI GENE INC
Antibodies, recombinant antibodies, recombinant antibody fragments and fusions mediated plant disease resistance against fungi
InactiveUS20050244901A1Efficient mannerImprove the immunityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroencapsulation basedPlant tissueFungal microorganisms
A method for the production of fungus resistant transgenic plants, plant cells or plant tissue comprising the introduction of an Ab, rAb, rAb fragment or fusion or vector of the invention or the vectors of the composition of the invention into the genome of a plant, plant cell or plant cell tissue and a transgenic plant cell comprising stably integrated into the genome a polynucleotide or vector of the invention or the vectors of the composition of the invention.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com