Membrane encapsulated nanoparticles and method of use
A nanoparticle and plasma membrane technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as difficulties in nanoparticle functionalization, inability to replicate complex protein composition, and protein denaturation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0141] Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymer nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform
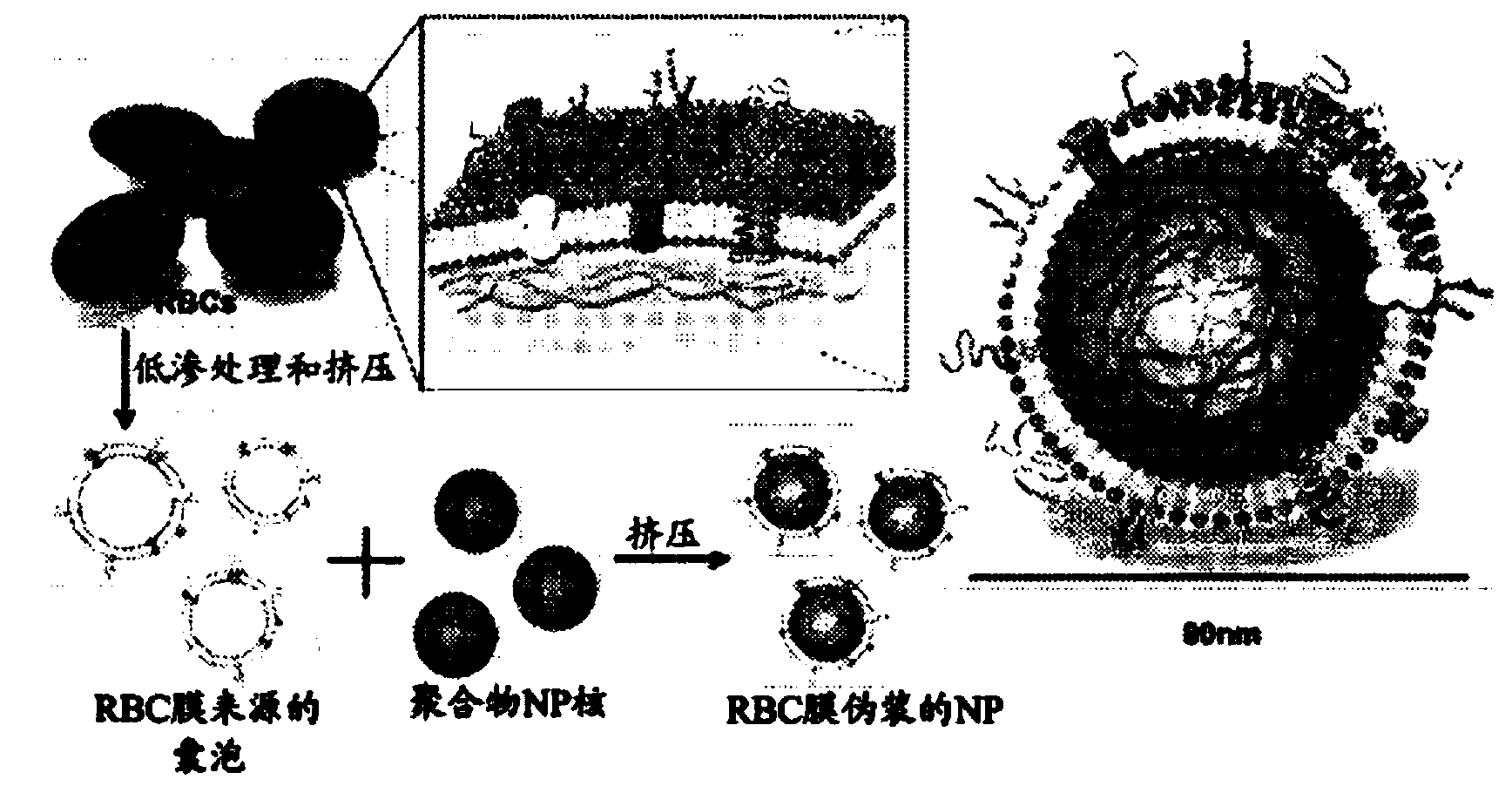
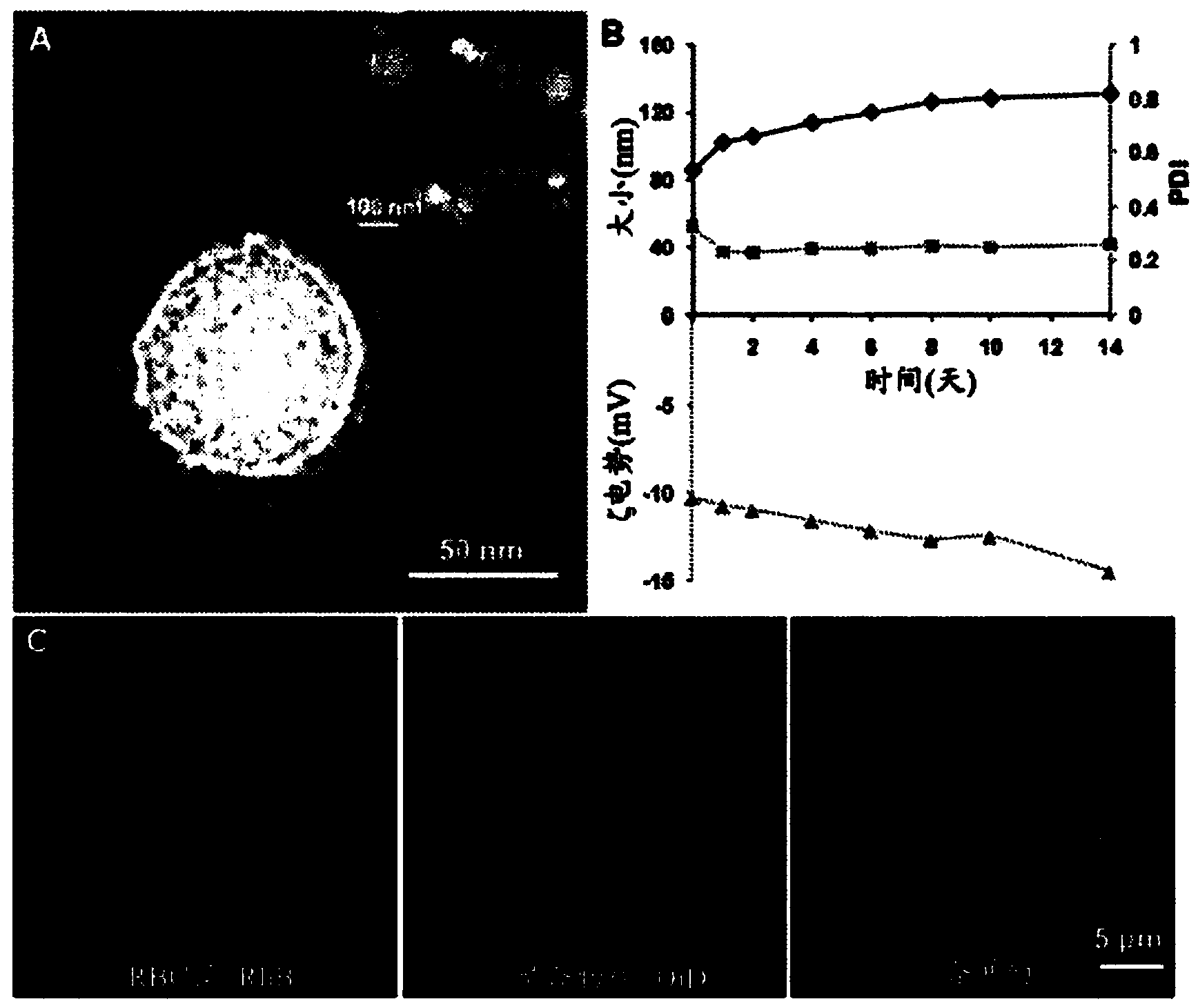
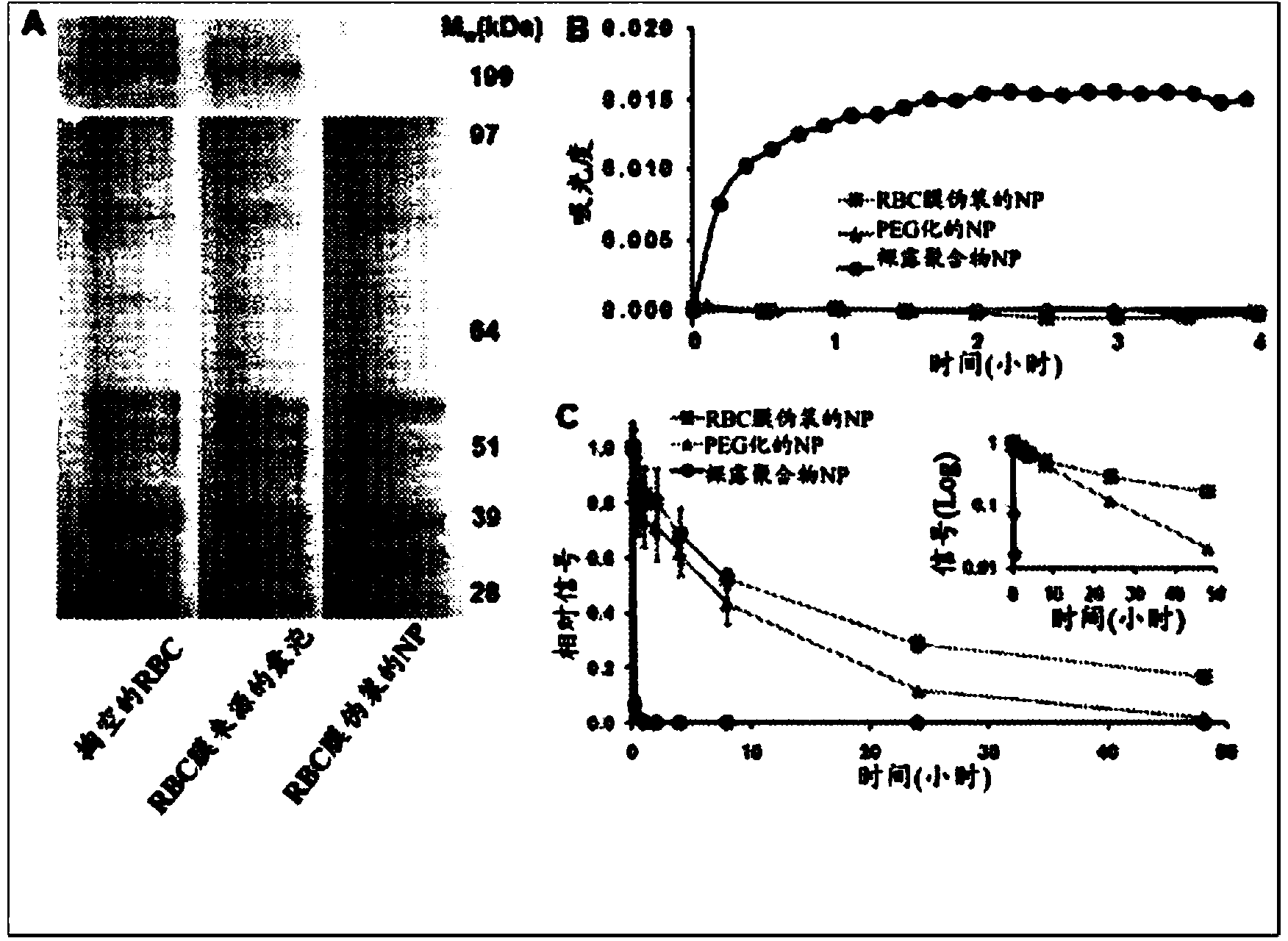
[0142] By extruding poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) particles with preformed RBC membrane-derived vesicles, the inventors coated sub-100 nm polymers with bilayer RBC membranes comprising lipids and corresponding surface proteins particles. This approach aims to camouflage the nanoparticle surface with the erythrocyte exterior for long circulation while retaining the suitability of the polymer core. The inventors report the physical characteristics, physicochemical properties, protein content, pharmacokinetics, and biodistribution of this bioinspired nanoparticle delivery platform.
[0143] The preparation process of RBC membrane-coated nanoparticles is divided into two parts: obtaining membrane vesicles from RBCs and vesicle-particle fusion ( figure 1 ). The derivation of RBC membrane vesicles followed a previously reported method with minor modifications (13). Briefly, R...
Embodiment 2
[0212] Erythrocyte membrane-cloaked polymer nanoparticles for controlled drug loading and release
[0213] Polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) cloaked by red blood cell membranes (RBCm) confer the combined advantages of long circulation life and controlled drug retention and release. In this paper, for the development of this cell-mimicking NP platform for advanced drug delivery applications, the inventors conducted studies to gain a better understanding of its drug loading, drug release kinetics, and cell-based efficacy. Specifically, to study drug release from RBCm-cloaked NPs, the inventors compared two strategies for loading doxorubicin (DOX), a model anticancer drug, into RBCm-cloaked NPs: physical encapsulation and chemical couple couplet. In vitro efficacy was tested by using the acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Kasumi-1 cell line.
[0214]The inventors found that the chemical conjugation strategy resulted in a more sustained drug release profile. Furthermore, by formulating P...
Embodiment 3
[0303] Nanoparticles with cancer cell membranes for personalized immunotherapy
[0304] This example provides an immunotherapeutic system that has several advantages over existing methods.
[0305] 1) Current strategies focus only on individual tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) expressed by the general cancer type in question. Cancer is a heterogeneous disease, and one limitation of such an approach is that the antigen expression of one patient's cancer can be quite different from another patient's. This results in a less than optimal percentage of patients being actual candidates for such treatment. Another problem is that targeting a single TAA results in a weaker overall immune response against the cancer, allowing it to eventually mutate and develop resistance. The described invention addresses these issues by tailoring treatment to each individual patient by collecting membrane material from autologous tumors. This approach allows for the precise re-creation of antigen ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com