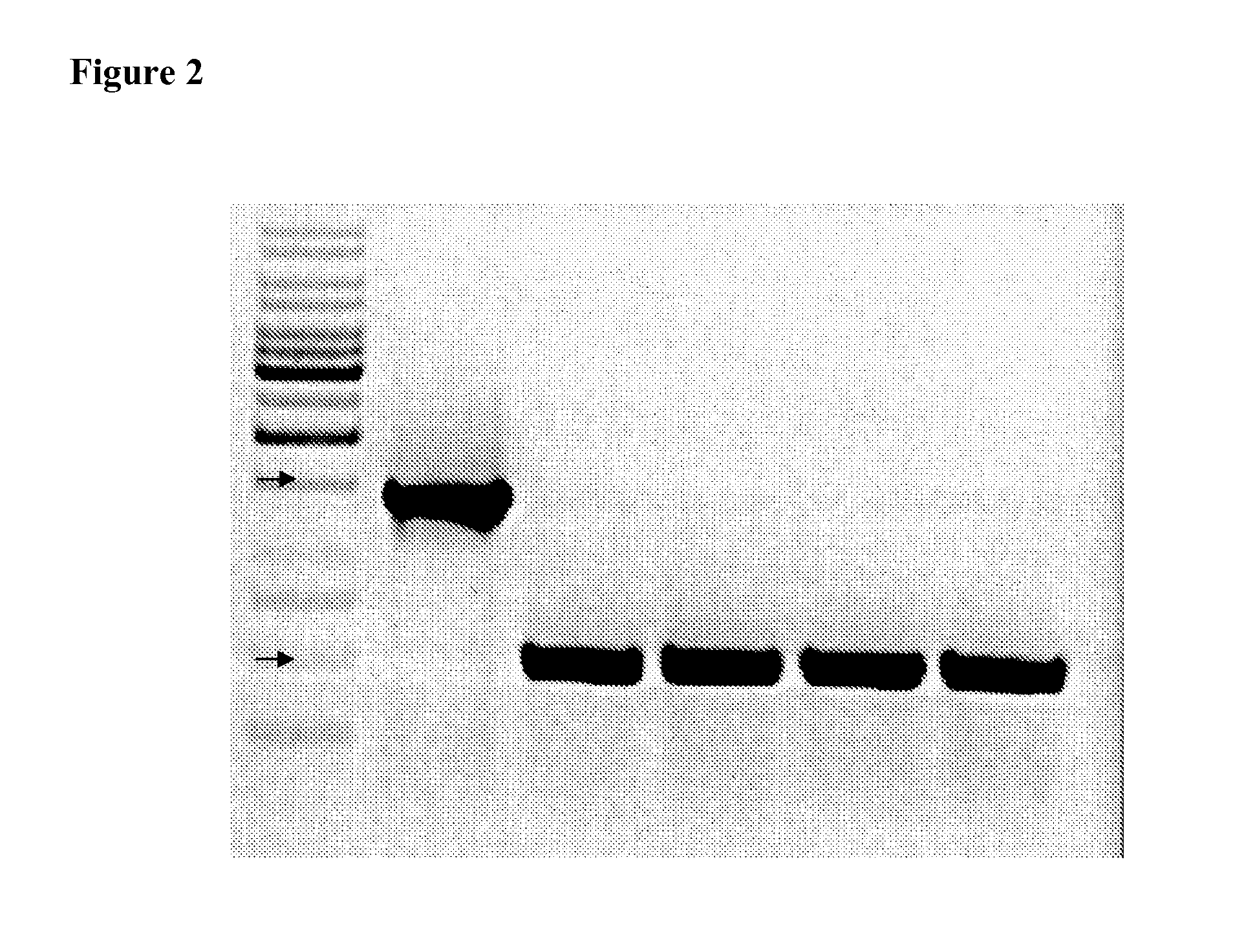
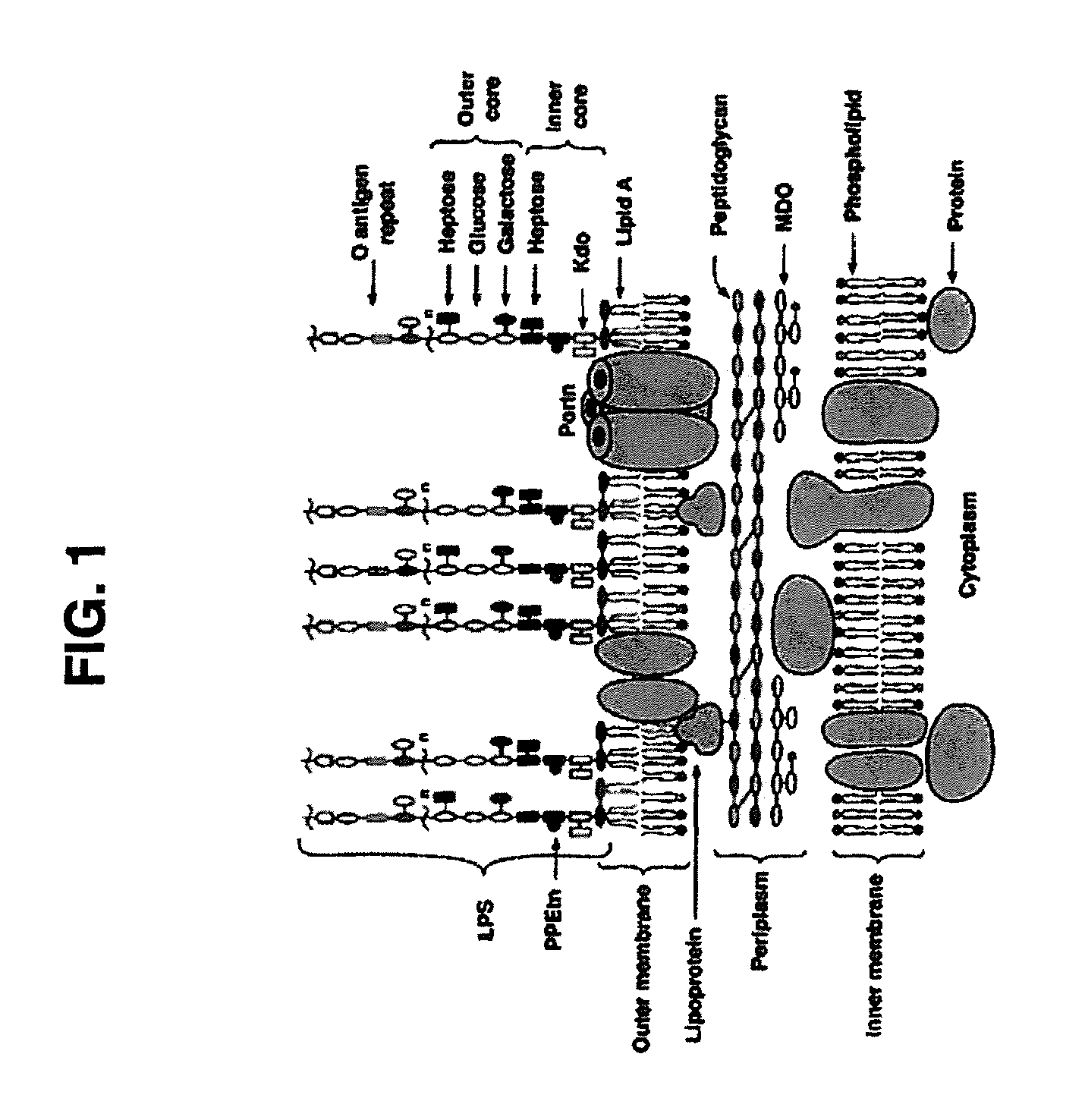
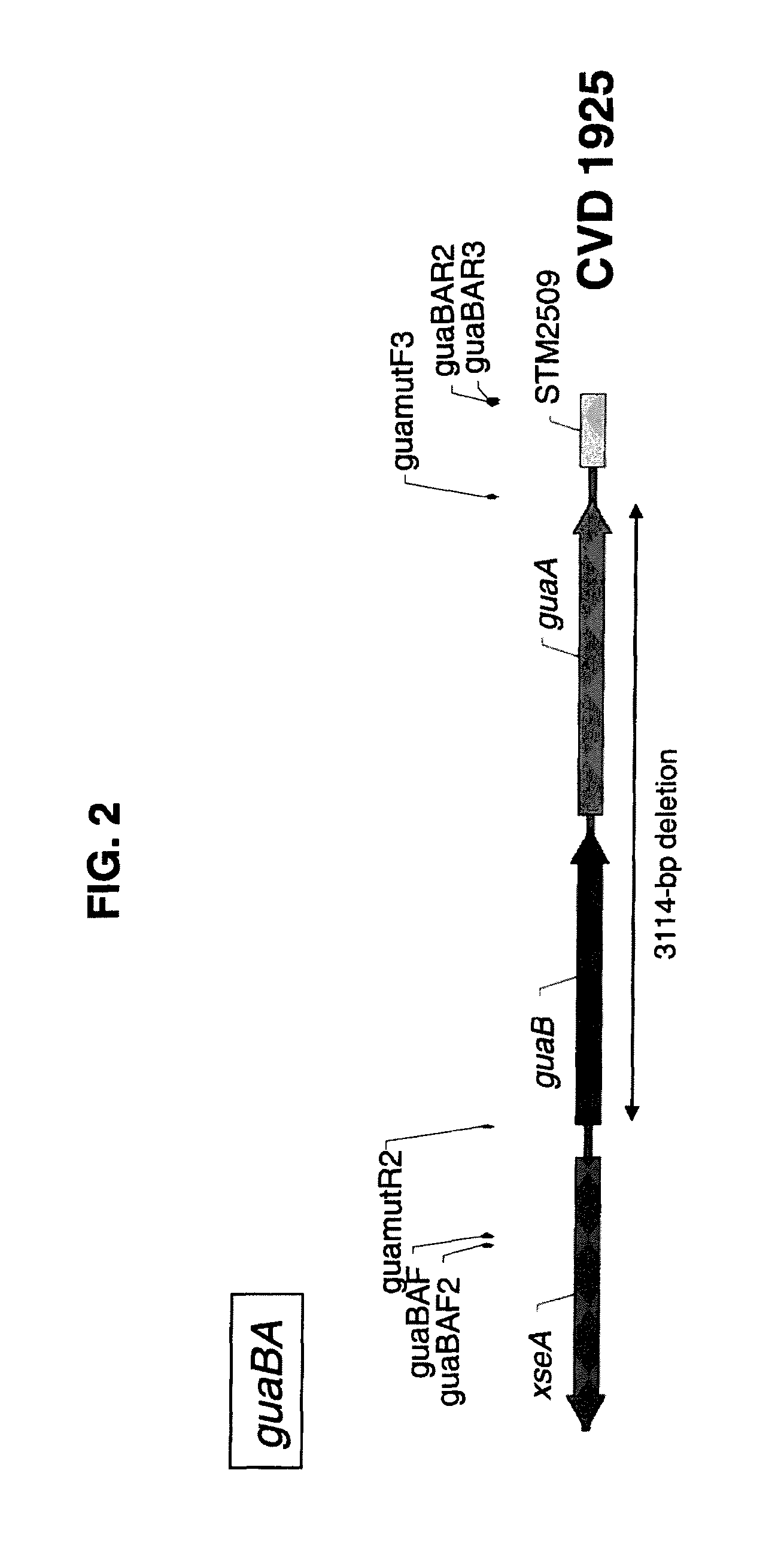
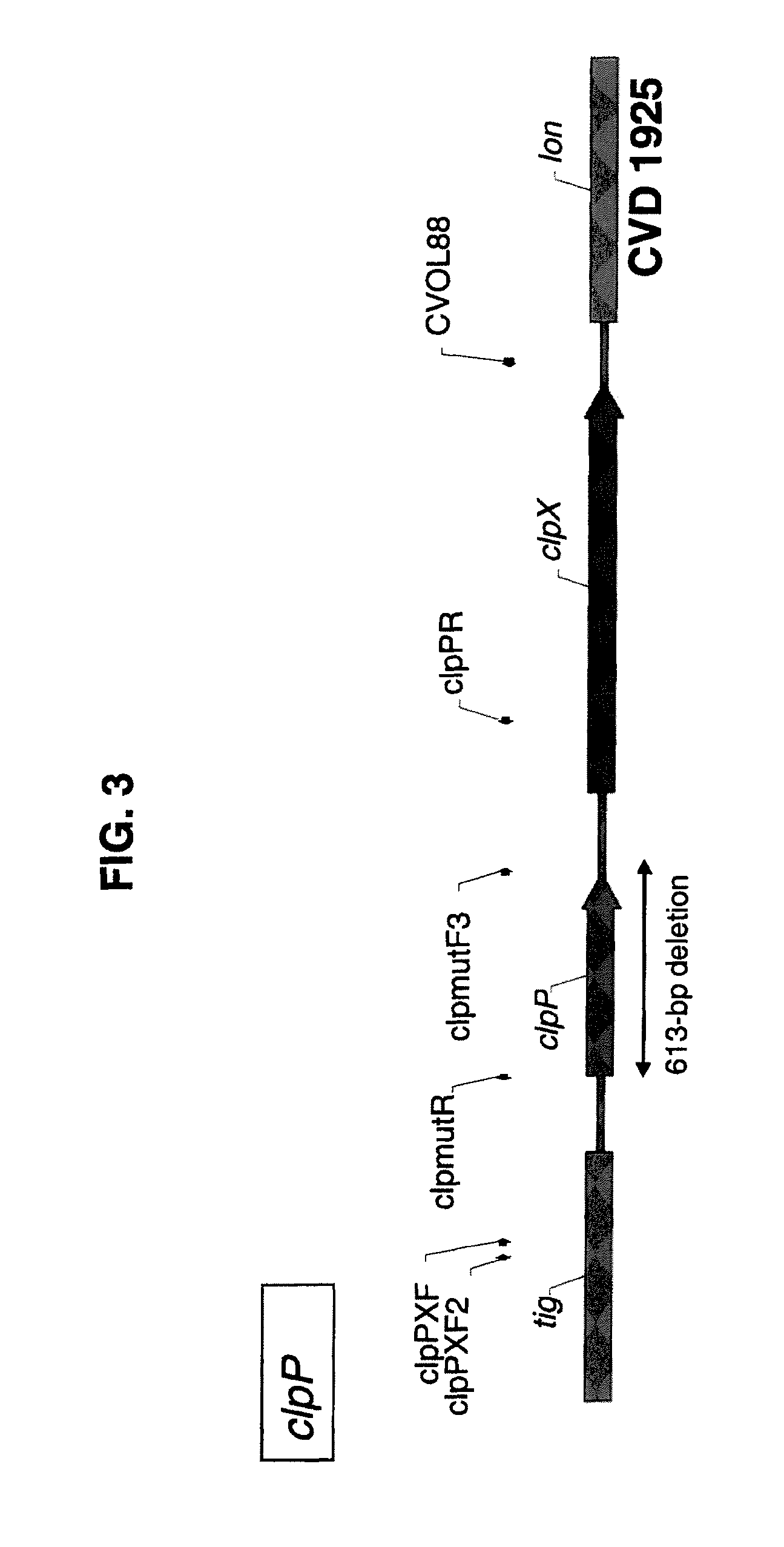
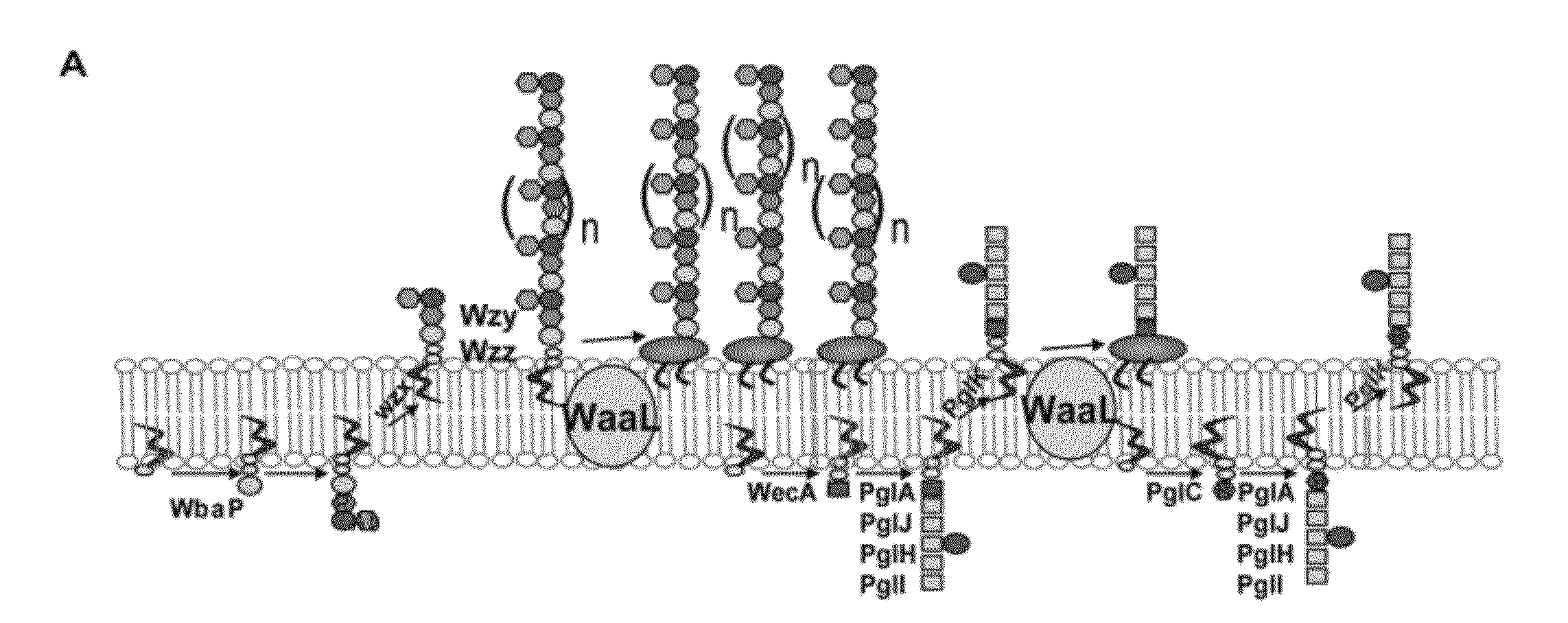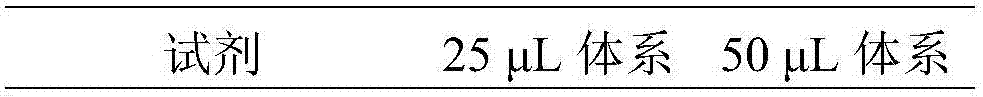Patents
Literature
73 results about "Salmonella enterica" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Salmonella enterica (formerly Salmonella choleraesuis) is a rod-shaped, flagellate, facultative aerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a species of the genus Salmonella. A number of its serovars are serious human pathogens.
Nanoparticle tracer-based electrochemical DNA sensor for detection of pathogens-amplification by a universal nano-tracer (AUNT)
InactiveUS20110171749A1Rapid and sensitive detectionRapid and sensitive and valid identificationMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicineSalmonella entericaEscherichia coli
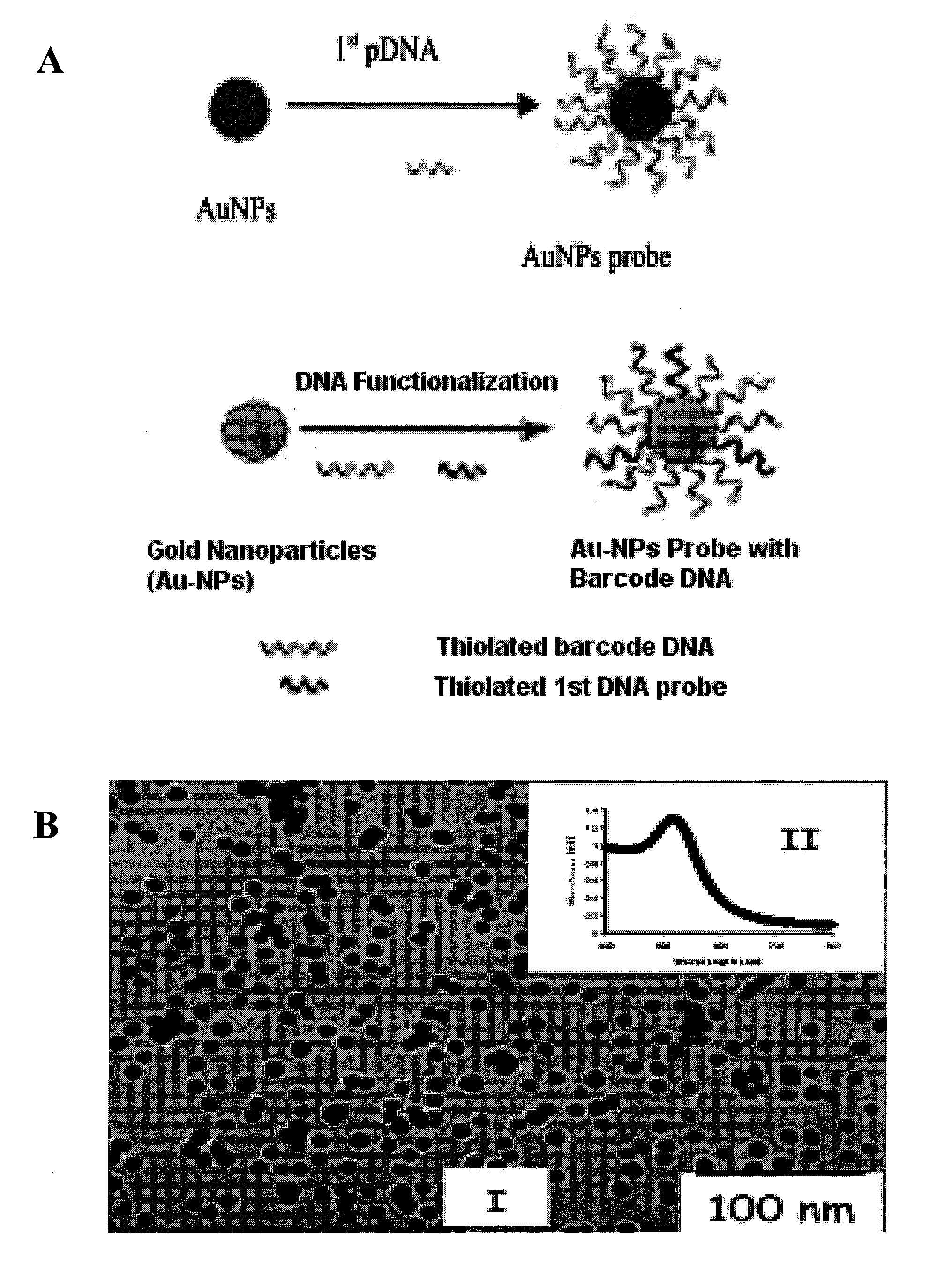
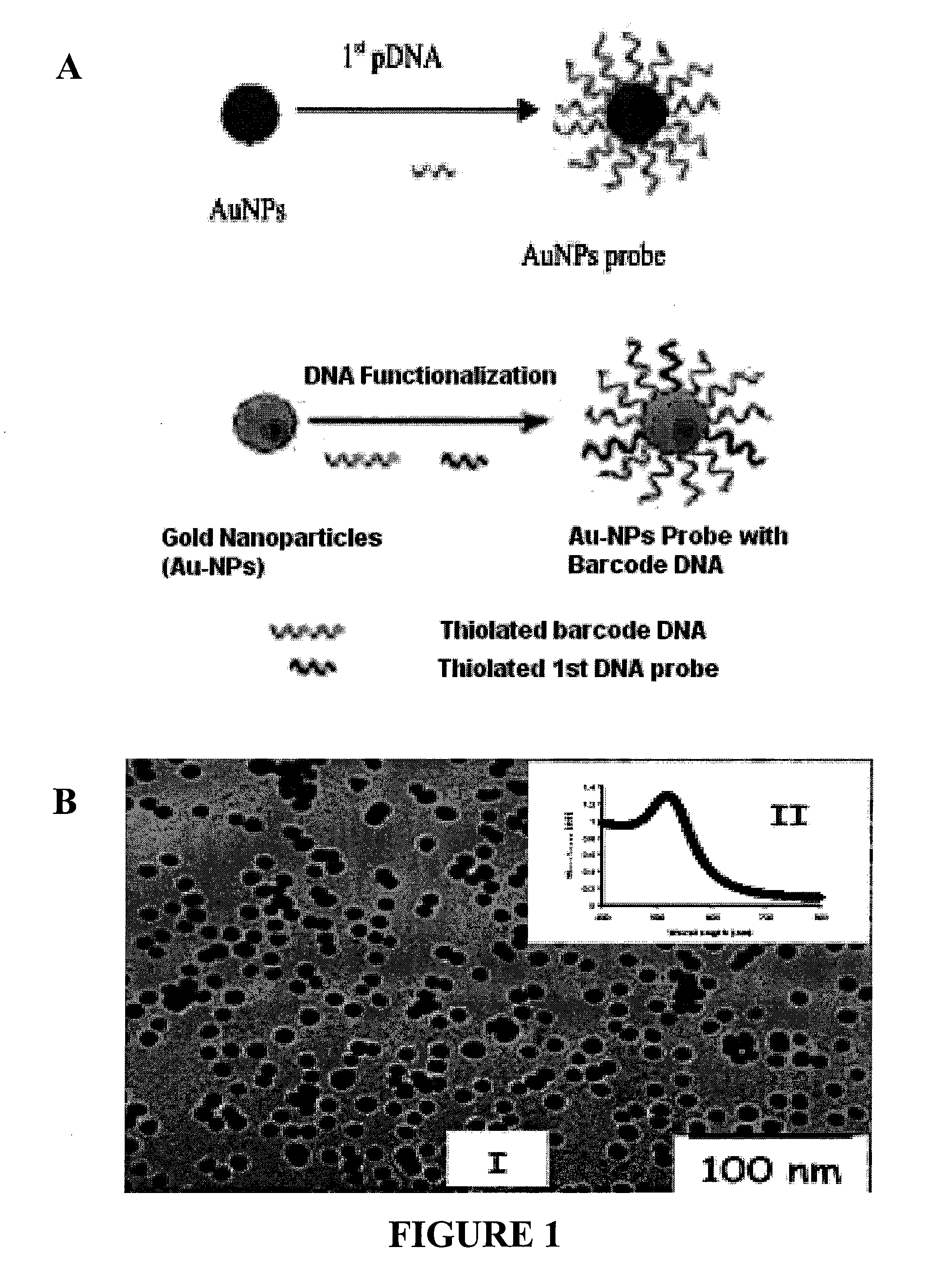
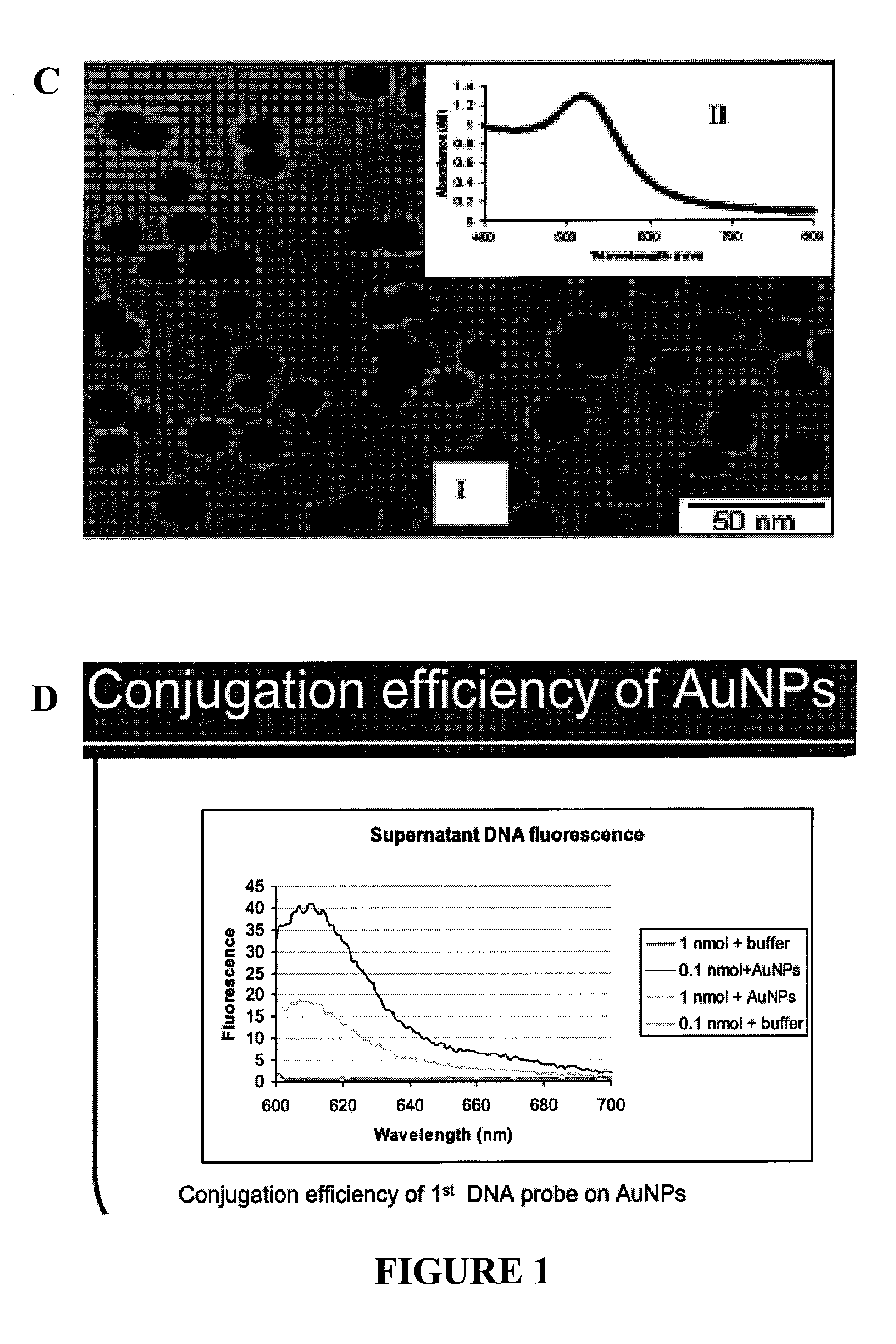
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying a pathogen. The inventions provide an antibody-based biosensor probe comprising (AUNT) in combination with a polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticle. In particular, a nanoparticle-based biosensor was developed for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacterium in food products. Further described are biosensors for detecting pathogens at low concentrations in samples. Even further, a gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensor detection and amplification method for identifying the insertion element gene of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis is described. The present invention provides compositions and methods for providing a handheld potentiostat system for detecting pathogens outside of the laboratory. The AUNT biosensor system has applications detecting pathogens in food, water, beverages, clinical samples, and environmental samples.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
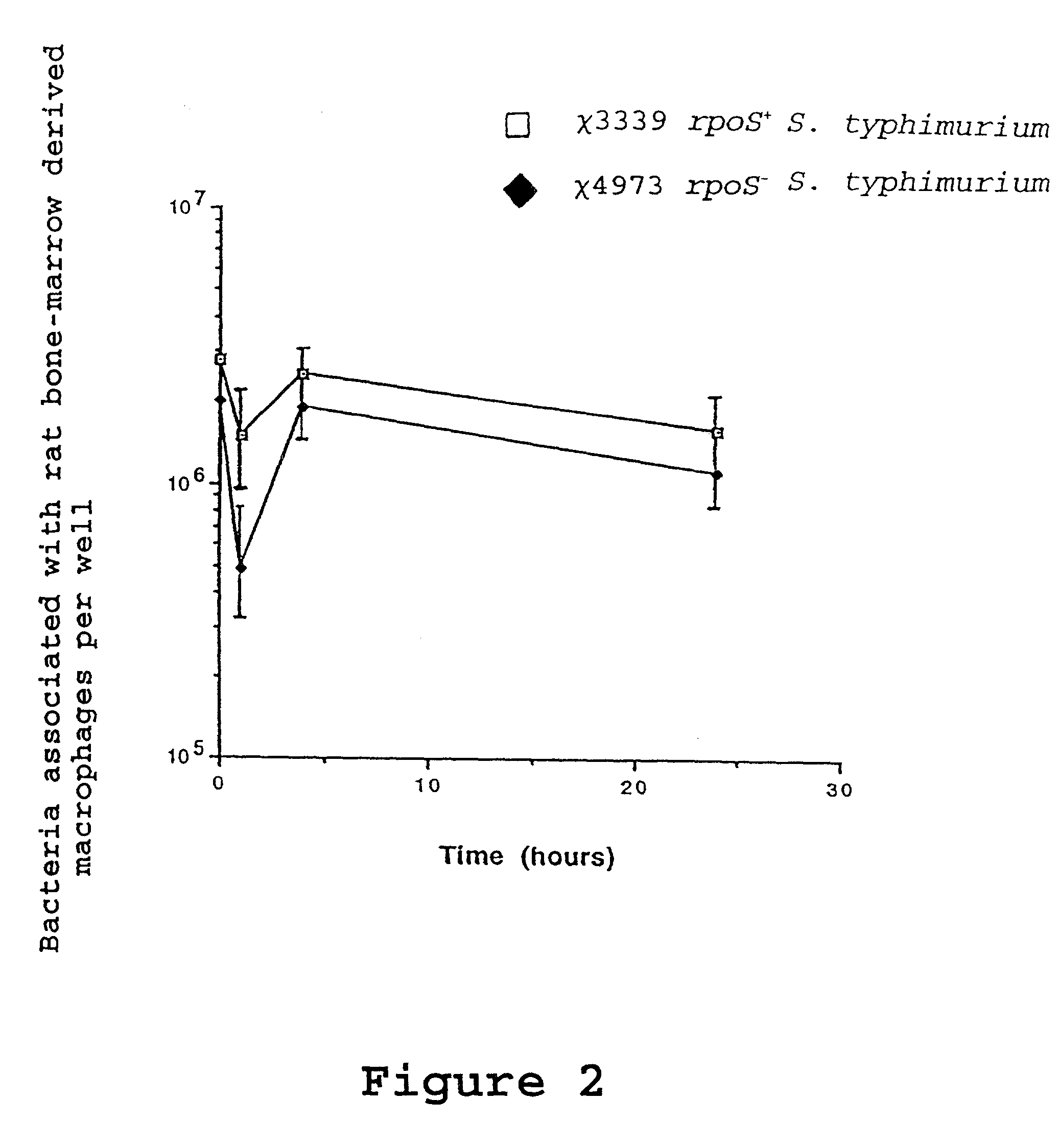
Recombinant vaccines comprising immunogenic attenuated bacteria having RpoS positive phenotype
InactiveUS7083794B2Improve balanceImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSalmonella entericaSalmonella serotype typhi
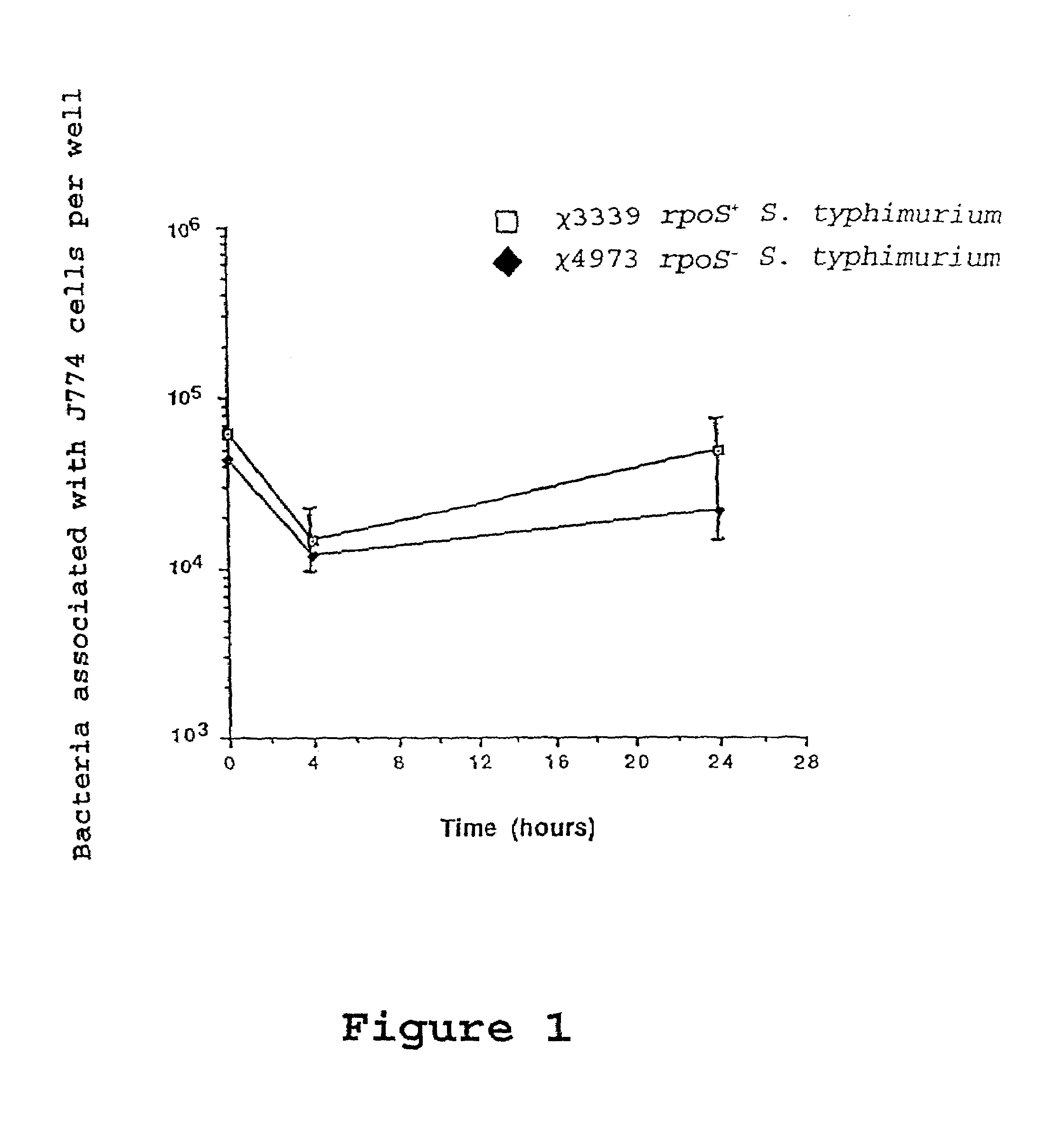
Attenuated immunogenic bacteria having an RpoS+ phenotype, in particular, Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi having an RpoS+ phenotype and methods therefor are disclosed. The Salmonella have in addition to an RpoS+ phenotype, an inactivating mutation in one or more genes which render the microbe attenuated, and a recombinant gene capable of expressing a desired protein. The Salmonella are attenuated and have high immunogenicity so that they can be used in vaccines and as delivery vehicles for genes and gene products. Also disclosed are methods for preparing the vaccine delivery vehicles.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Compositions and methods for mycotoxin decontamination, nucleotide, protein and vitamin enrichment and palatability enhancement of food and animal feed using micronized yeast biomass
InactiveUS20120082759A1Improve performanceWide compatibilityMilk preparationAnimal feeding stuffWeight gainingSalmonella enterica
A method for upgrading human food and animal feed, rendering harmless the contaminating mycotoxins, increasing protein and nucleotide content, providing immuno-modulation, enhancing flavor and palatability is proposed. The method comprises a food functional additive / supplement and feed additive based on yeast biomass processed to enhance the bioavailability and biological activity of its components using dry micron milling with optional agglomeration. The resulting product contains all biologically active components originally present in intact live yeast. Compared to existing practice, the new process is much faster, cheaper, less hardware demanding, less prone to microbial contamination, provides intact biopolymers and results in insoluble product fraction with high surface area. Human food and animal feed containing such additive improves weight gains, feed efficiency, resilience to mycotoxin contamination, improves immunological status, controls intestinal Salmonella and other bacteria and decreases mortality, especially at the young age, replacing antibiotics and growth promoters.
Owner:CUBENA
Compound gene chip for detecting salmonella serotype and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101955993AHigh detection throughputStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSalmonella entericaSalmonella paratyphi A
The invention relates to a compound gene chip for detecting salmonella serotype and a detection method thereof. salmonella paratyphi A, salmonella paratyphi B, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella paratyphi C, salmonella typhisuis, salmonella typhi and salmonella enterica can be identified by integrating probes for detecting salmonella serotype target genes viaB, tyv, filiC-alpha, fliCl, rfbJ, fliC2, invA and hilA on the same chip. The invention can rapidly and accurately carry out the preliminary screening and identification of salmonella and serotype thereof, greatly shortens detection time and is applicable to the requirement of high throughput detection.
Owner:中华人民共和国珠海出入境检验检疫局
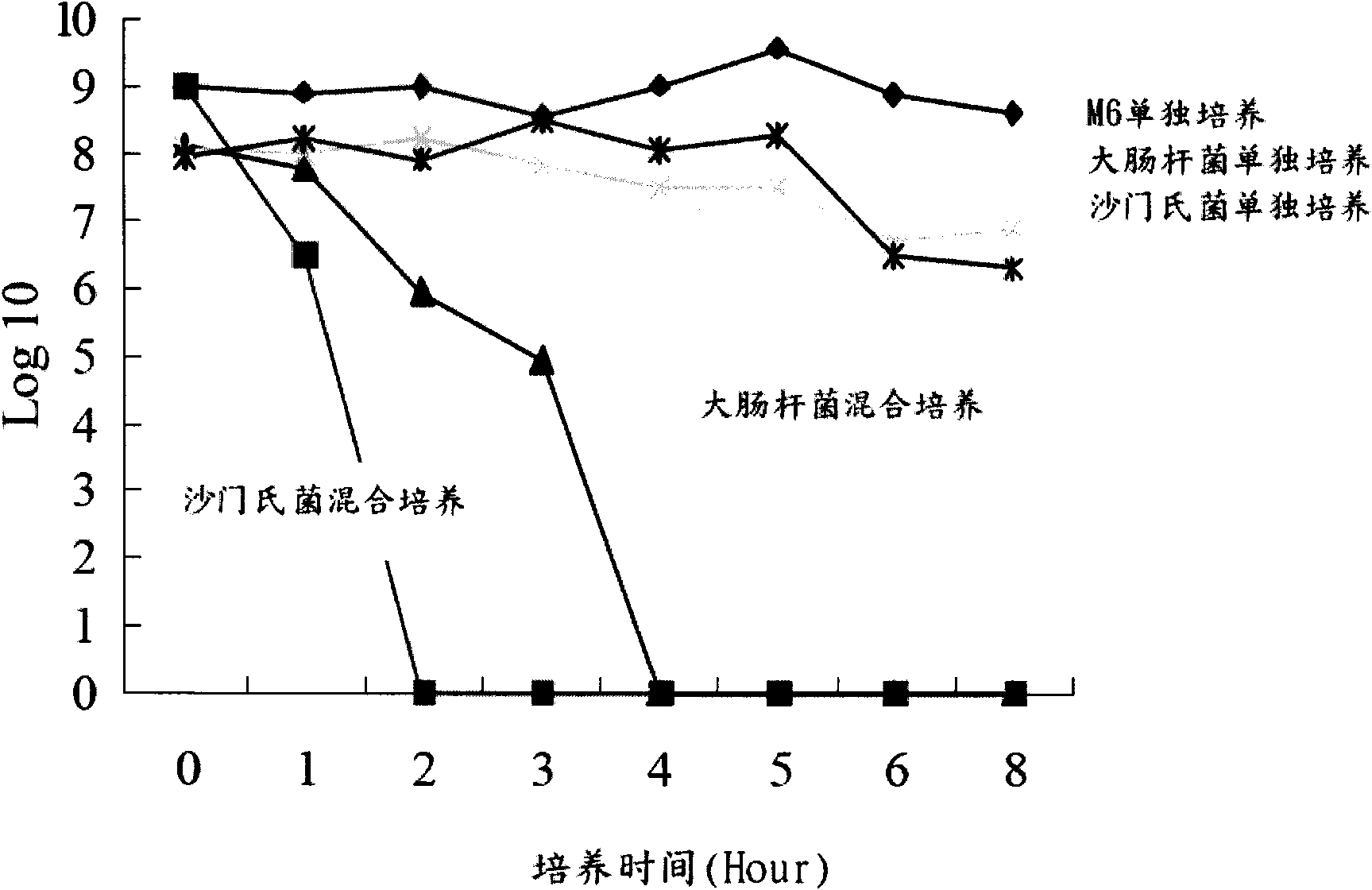
Lactobacillus salivarius M6 and antibacterial composition containing same
ActiveCN102373162ALower doseGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliSalmonella enterica
The invention provides Lactobacillus salivarius M6, which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the number of CGMCC 3505. The invention also provides a lactobacillus which can be mixed with animal feed or added into water, can be used together with antibiotics at the same time, and has antibiotic resistance. The strain can inhibit growth of Salmonella enterica, Escherichia coli and other pathogenic bacteria. The antibacterial composition of the Lactobacillus salivarius M6 can be used in drinking water, drinking water additives, feed and food additives of animals, human and animal medical composition, as well as drinks, drinking additives, foods, food additives and the like of humans. By implementation of the invention, pathogenic bacterium infection of animals or humans can be effectively prevented and treated, and the number of intestinal probiotics can be increased or maintained, so that the growth of pathogenic bacteria is inhibited, the dosage of antibiotics is reduced, and the aim of preventing disease infection of animals and humans can be achieved.
Owner:SYNGEN BIOTECH
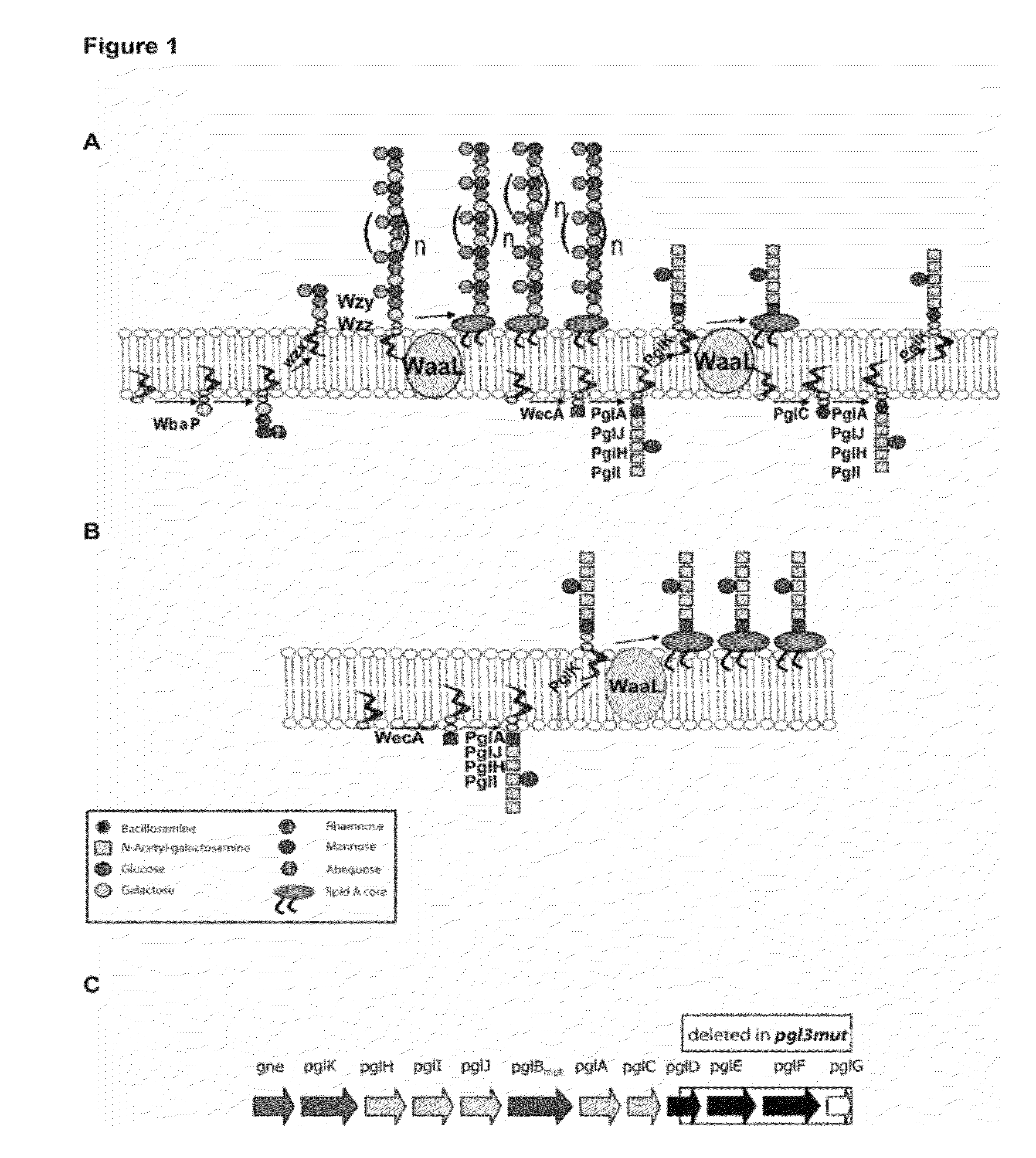
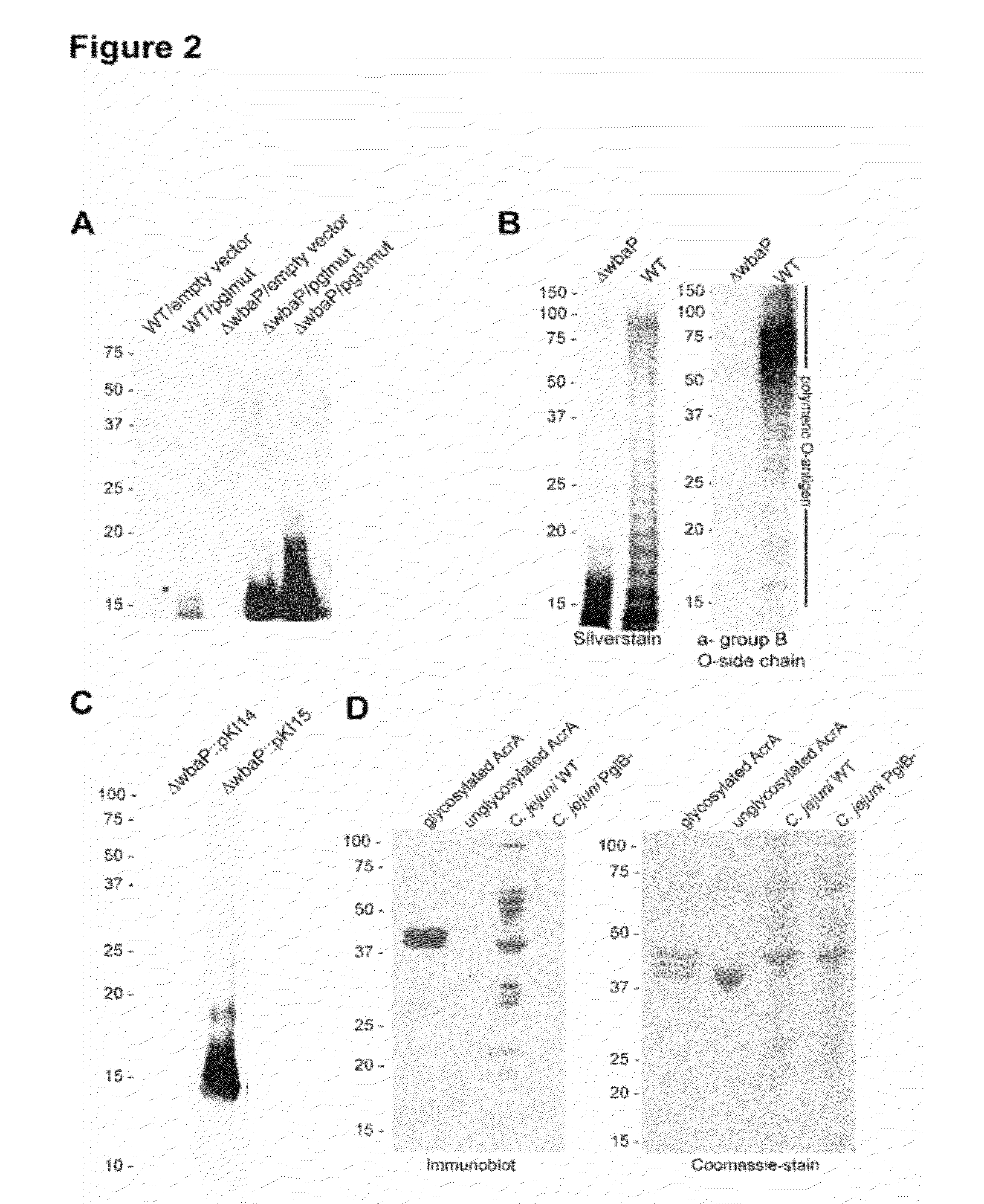
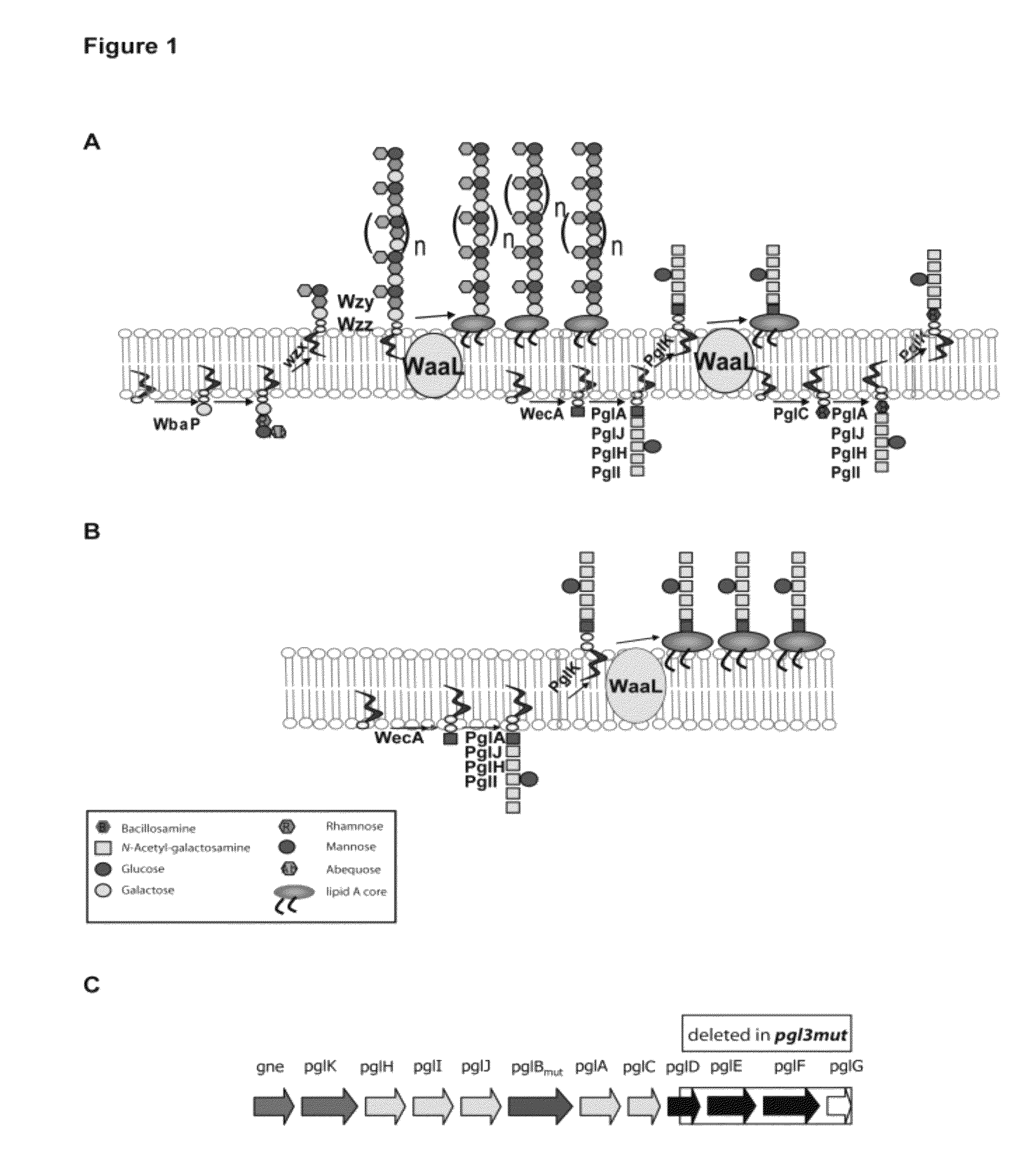
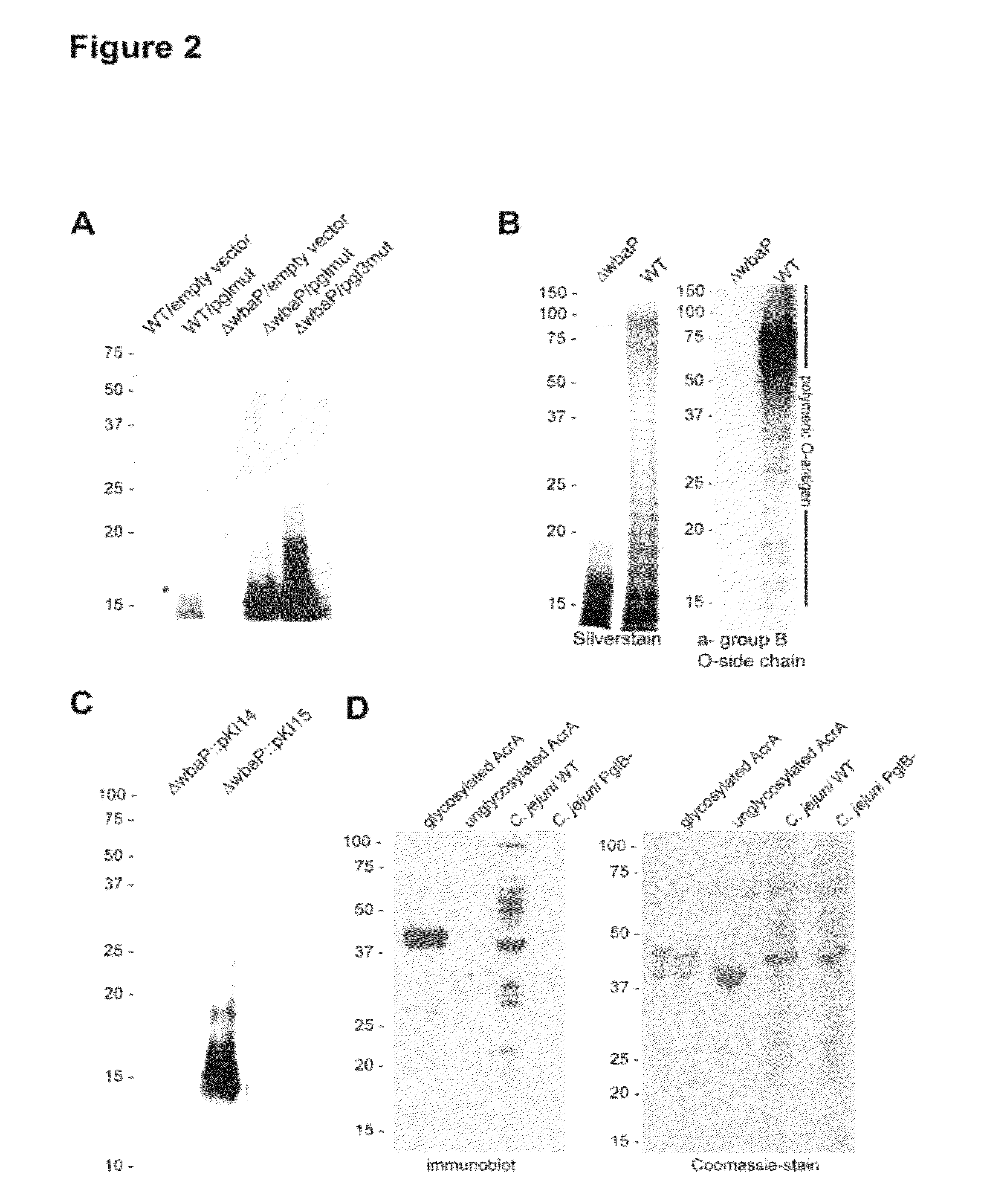
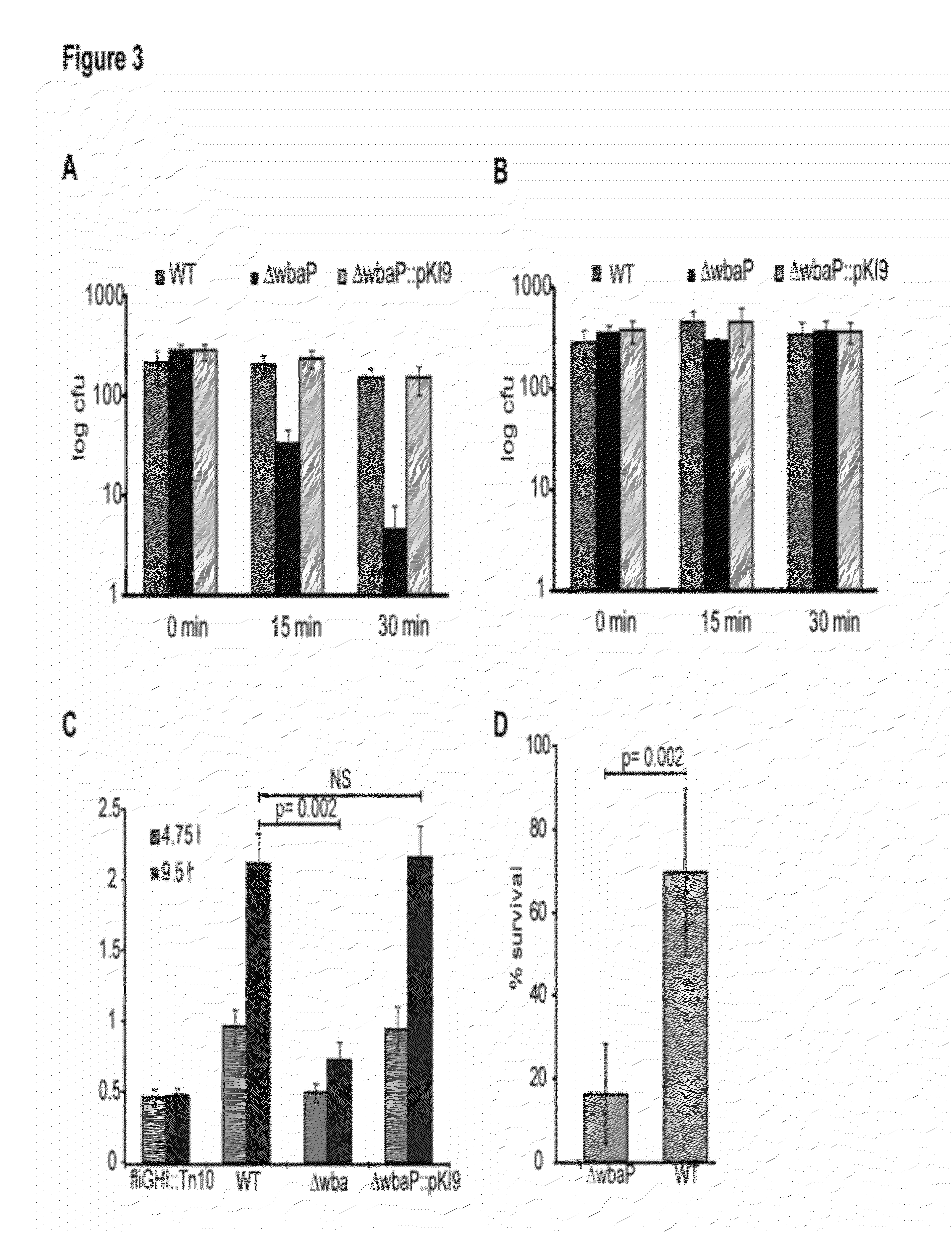
Salmonella enterica presenting c. jejuni n-glycan or derivatives thereof
The present invention relates to Salmonella enterica comprising at least one pgl operon of Campylobacter jejuni or a functional derivative thereof and presenting at least one N-glycan of Campylobacter jejuni or N-glycan derivative thereof on its cell surface. In addition, it is directed to medical uses and pharmaceutical compositions thereof as well as methods for treating and / or preventing Campylobacter and optionally Salmonella infections and methods for producing these Salmonella strains.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
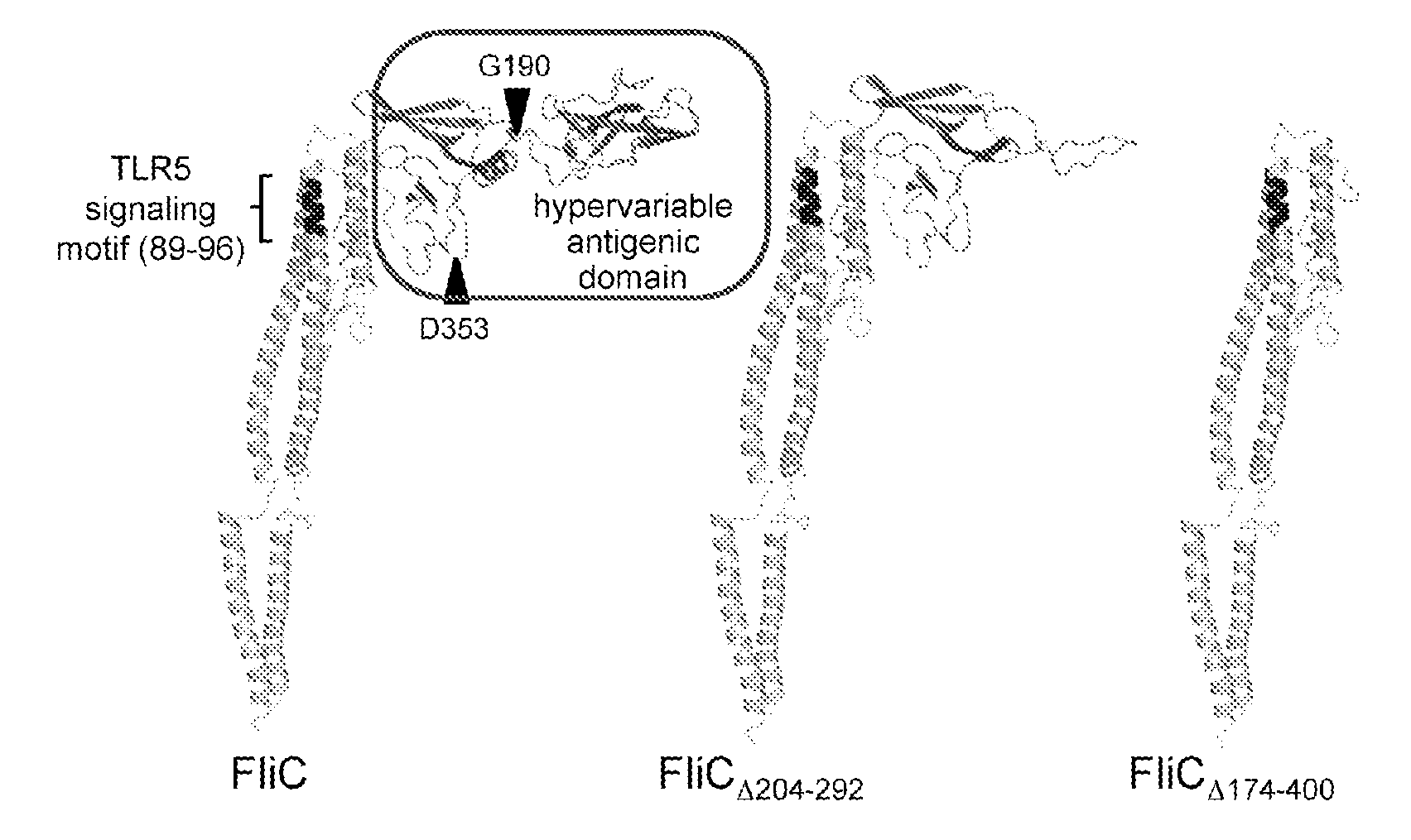
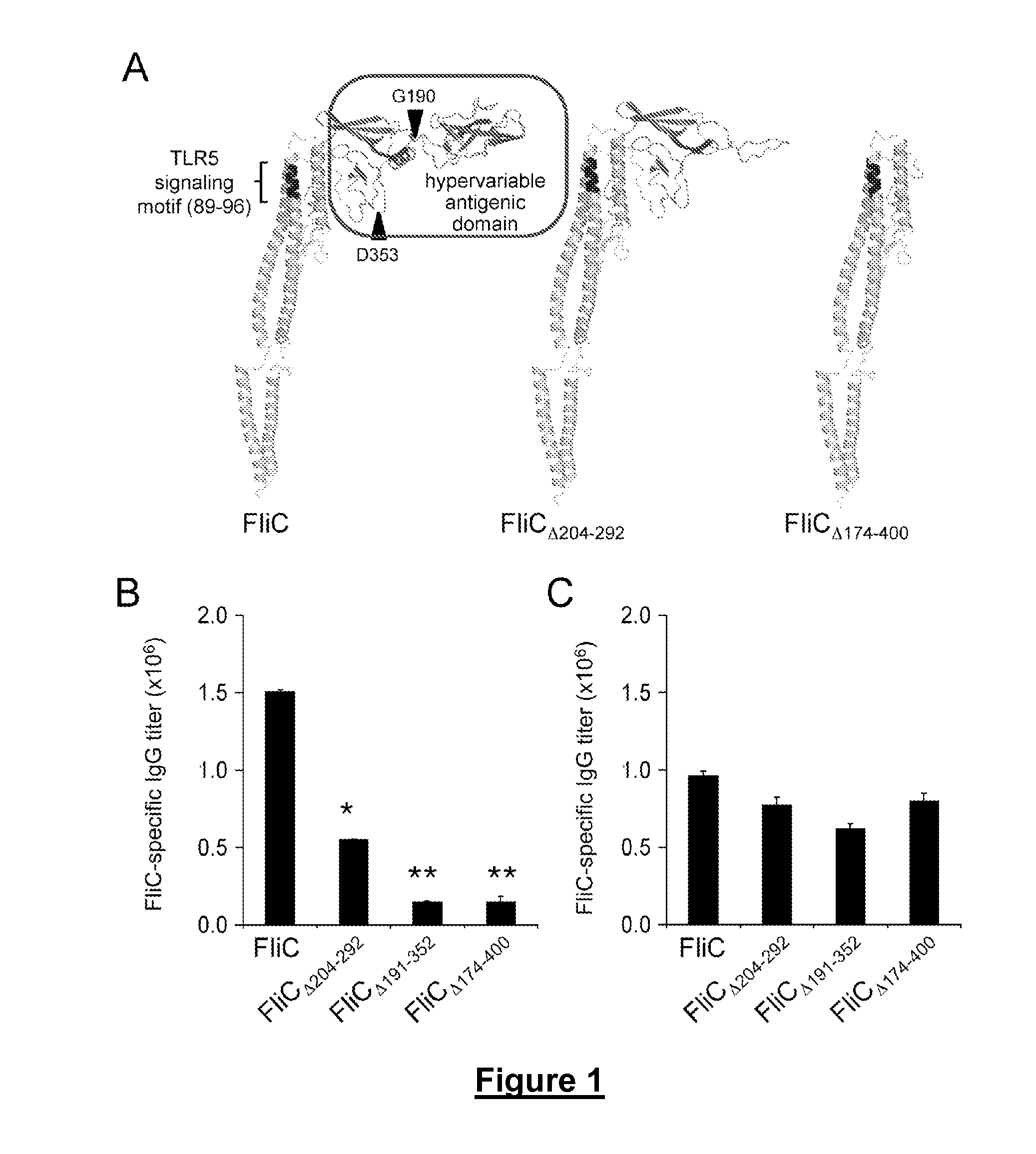
Novel Immunoadjuvant Flagellin-Based Compounds and Use Thereof
The present invention relates to novel peptide compounds derived from flagellin originating from Salmonella enterica that exhibit an in vivo immune adjuvant activity.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar paratyphi A and uses thereof
ActiveUS8137930B2Peptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesSalmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi AConjugate vaccine
The present invention is drawn to a live, attenuated S. Paratyphi A strain, a live, attenuated S. Paratyphi A strain comprising a stabilized plasmid expression system, an S. Paratyphi conjugate vaccine, and methods of using these strains and conjugate vaccine.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
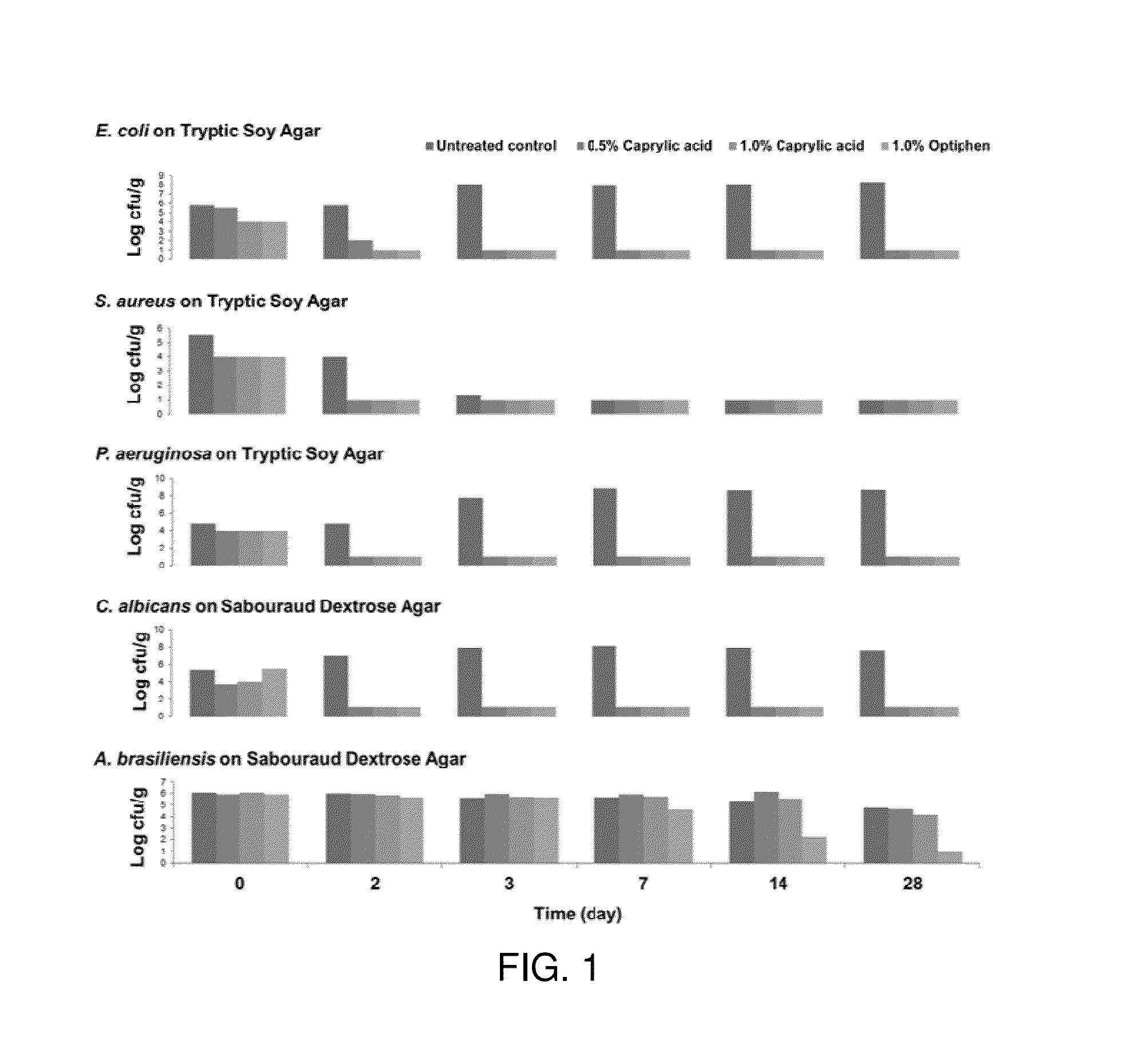
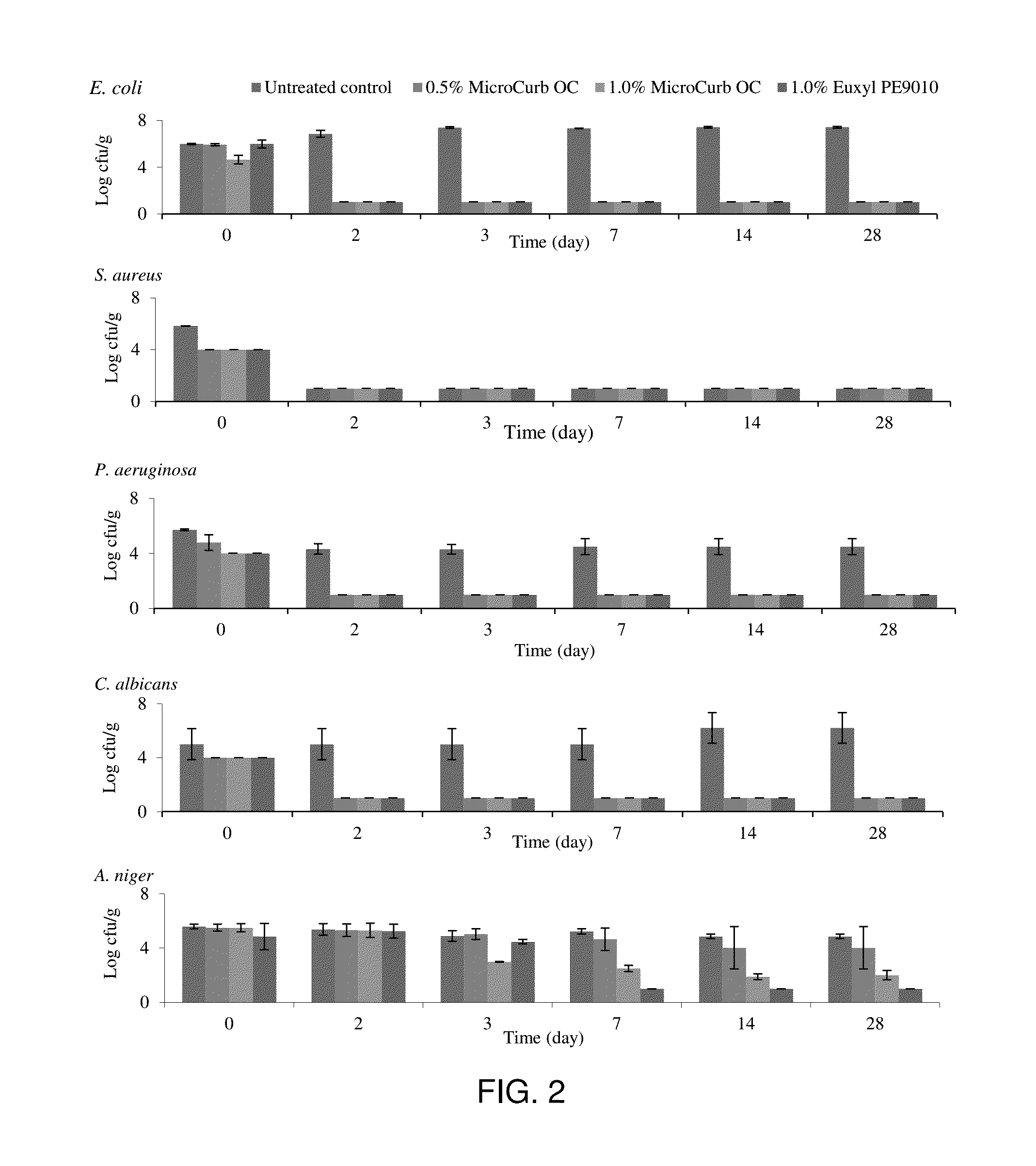
Antimicrobial Efficacy of an Oregano Oil and Caprylic Acid Blend
The purpose of this study was to test the efficacy of an oregano extract containing carvacrol and capyrlic acid blend by screening for inhibition and by conducting a preservative efficacy test, USP 51, in skin creams. Minimum inhibitory concentrations were found for Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonsas aeruginosa, Streptococcus sanguinis, Salmonella enterica, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus brasiliensis.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA N A +1
Method and apparatus for forming of an automated sampling device for the detection of salmonella enterica utilizing an electrochemical aptamer biosensor
ActiveUS9310363B2Improve automationMinimal trainingImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceSalmonella enterica
An aptamer-based solid-state electrochemical biosensor for label-free detection of Salmonella enterica serovars utilizing immobilized aptamers. The device is realized by forming a matrix array of parallel capacitors, thus allowing the realization of low-cost, portable, fully integrated devices. Protein-aptamer binding modulates the threshold voltage of a circuit, changing the impedance (capacitance) of the circuit. This circuit is further characterized by an electrode coded with a p-Si substrate, enhancing the affinity between the Salmonella outer membrane proteins (OMPs) and the aptamer. An aptamer embedded detection plate is configured within a testing lid device that fits a standard, commercially available polymer specimen jar. A sample is mixed with broth for incubation and cultivation of any present Salmonella bacteria to obtain acceptable concentration of the pathogen for testing. The information obtained can then be transmitted by wireless network.
Owner:SENSOR KINESIS
Method and apparatus for forming of an automated sampling device for the detection of Salmonella enterica utilizing an electrochemical aptamer biosensor
ActiveUS9329173B2Improve automationMinimal trainingLibrary screeningBiological material analysisCapacitanceSalmonella enterica
An aptamer-based solid-state electrochemical biosensor for label-free detection of Salmonella enterica serovars utilizing immobilized aptamers. The device is realized by forming a matrix array of parallel capacitors, thus allowing the realization of low-cost, portable, fully integrated devices. Protein-aptamer binding modulates the threshold voltage of a circuit, changing the impedance (capacitance) of the circuit. This circuit is further characterized by an electrode coded with a p-Si substrate, enhancing the affinity between the Salmonella outer membrane proteins (OMPs) and the aptamer. An aptamer embedded detection plate is configured within a testing lid device that fits a standard, commercially available polymer specimen jar. A sample is mixed with broth for incubation and cultivation of any present Salmonella bacteria to obtain acceptable concentration of the pathogen for testing. The information obtained can then be transmitted by wireless network.
Owner:SENSOR KINESIS
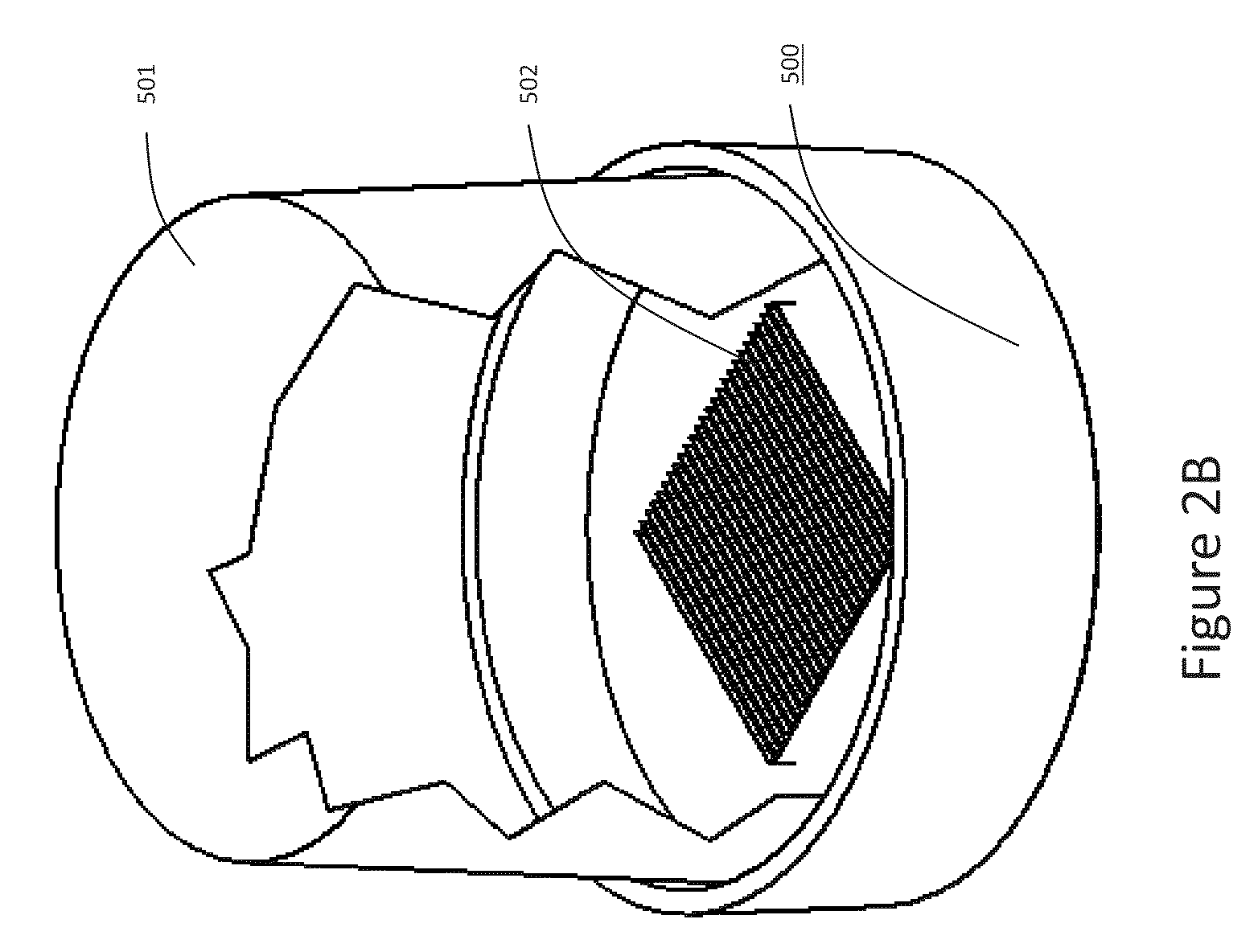
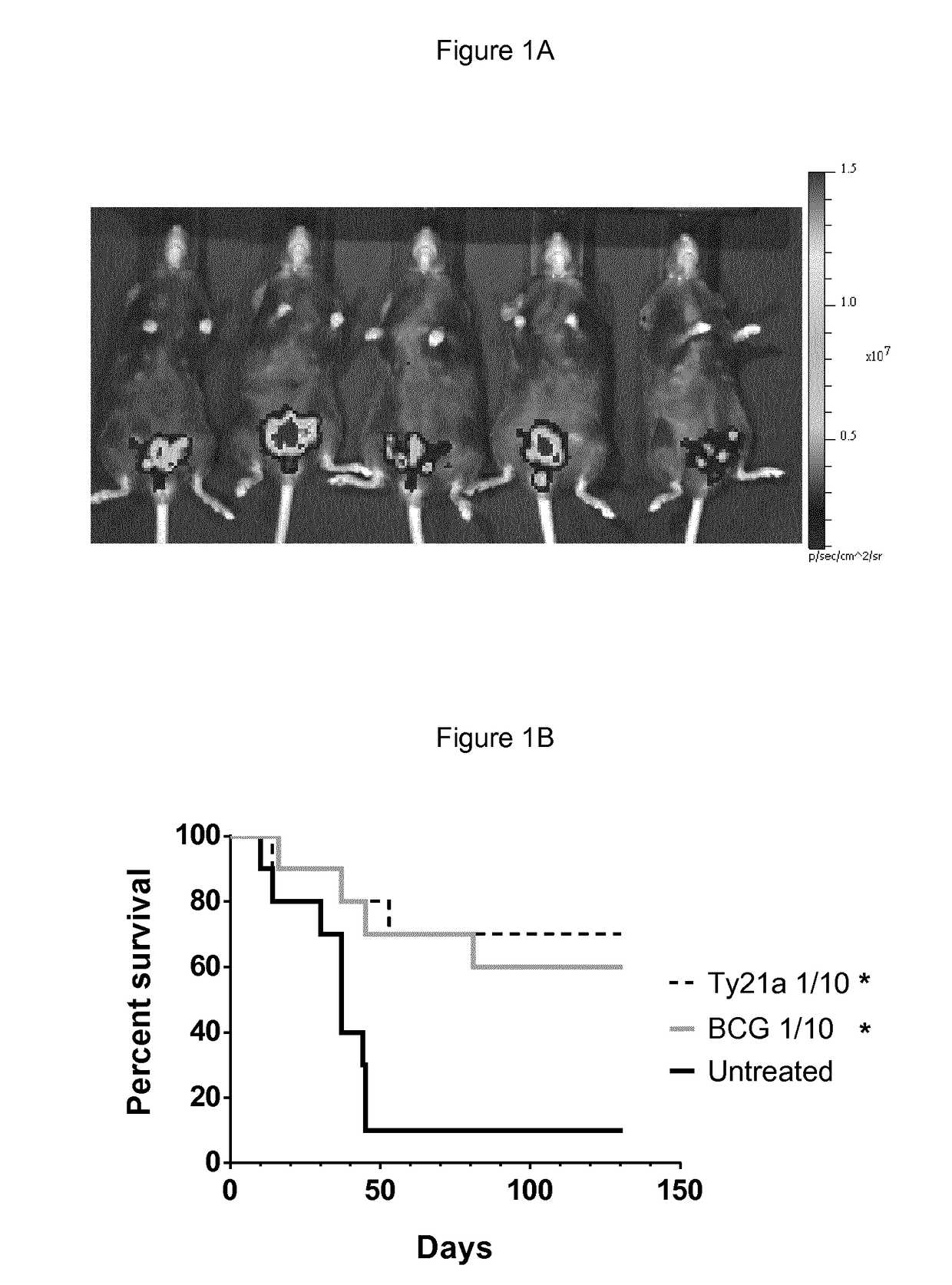
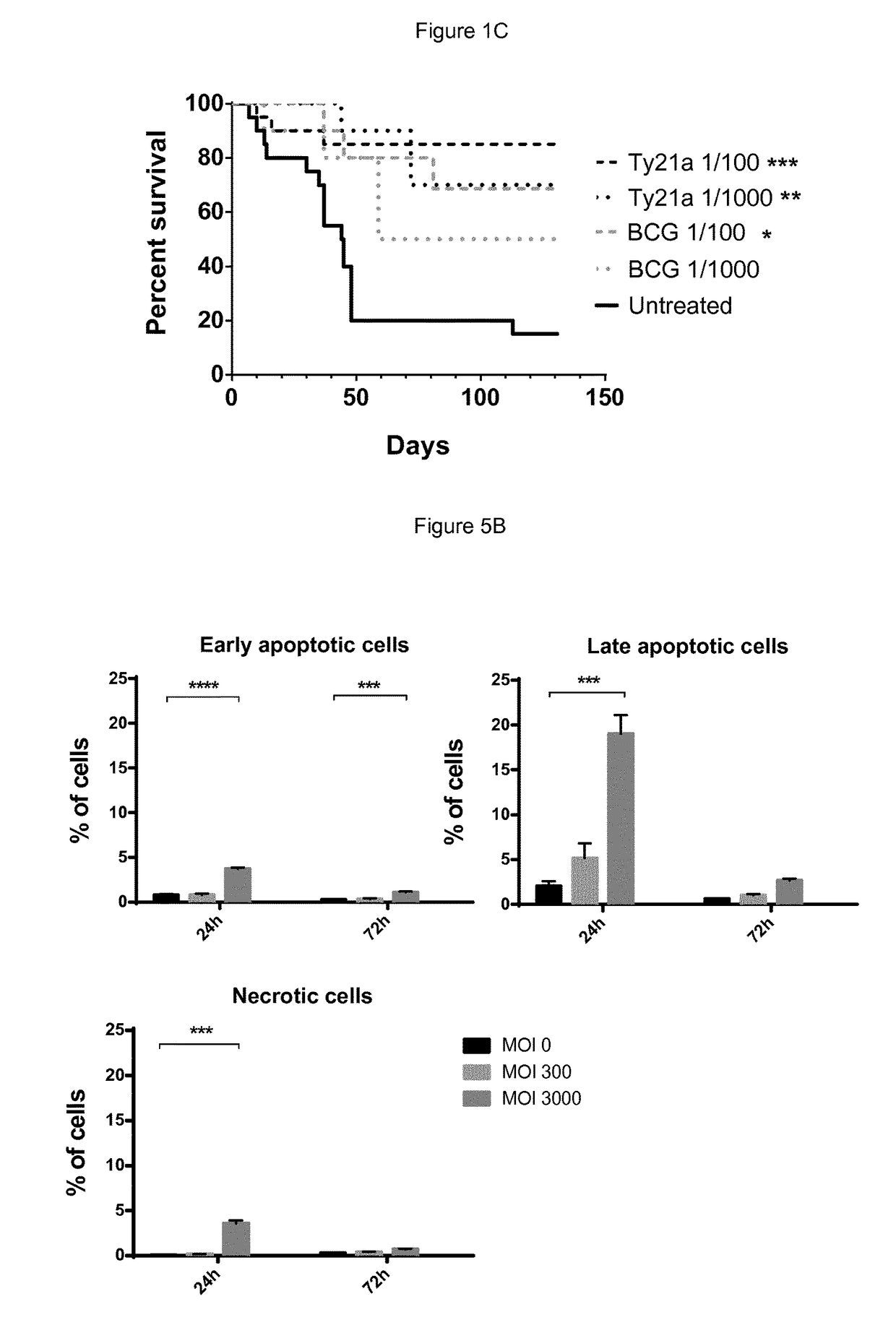
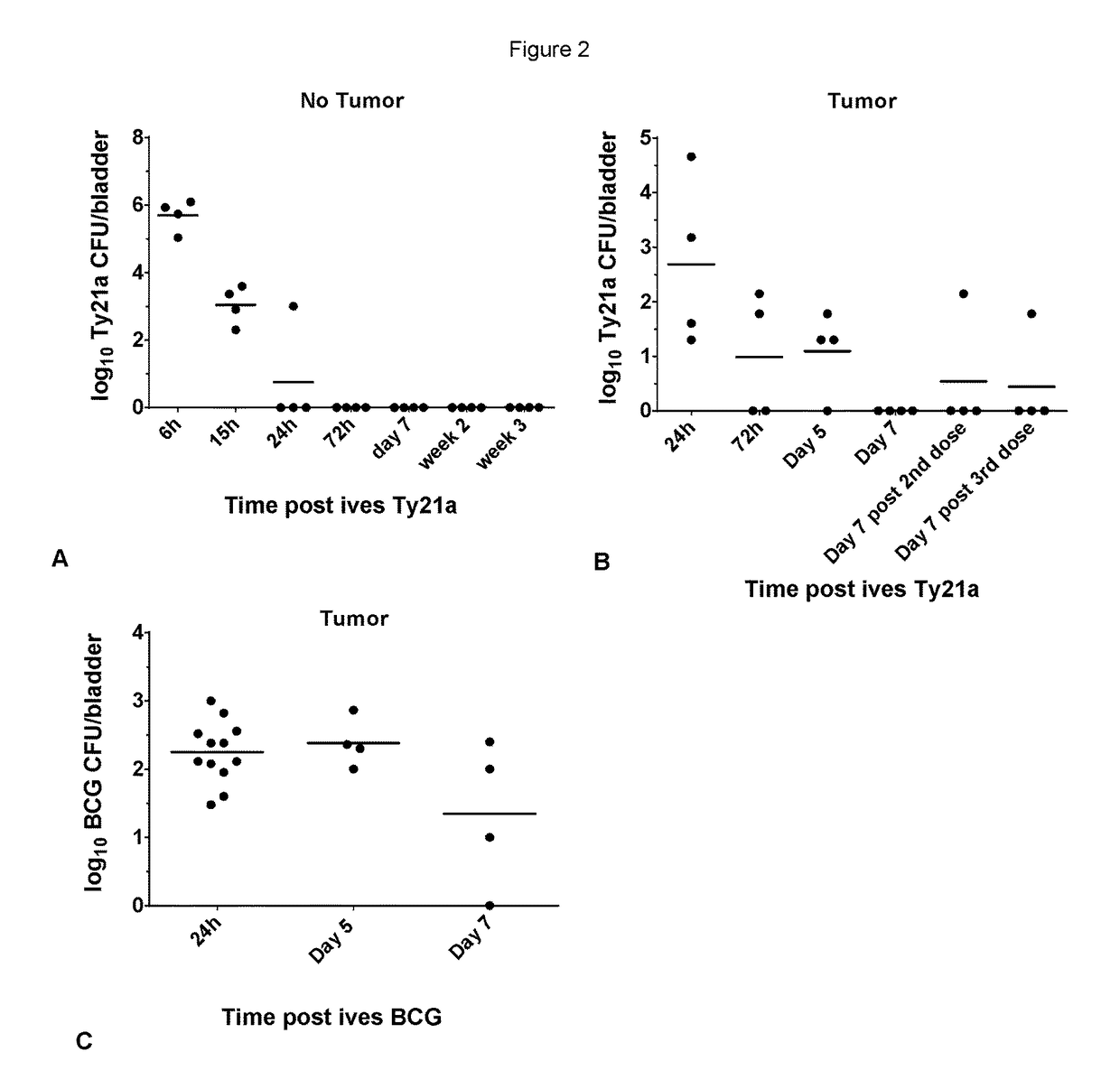
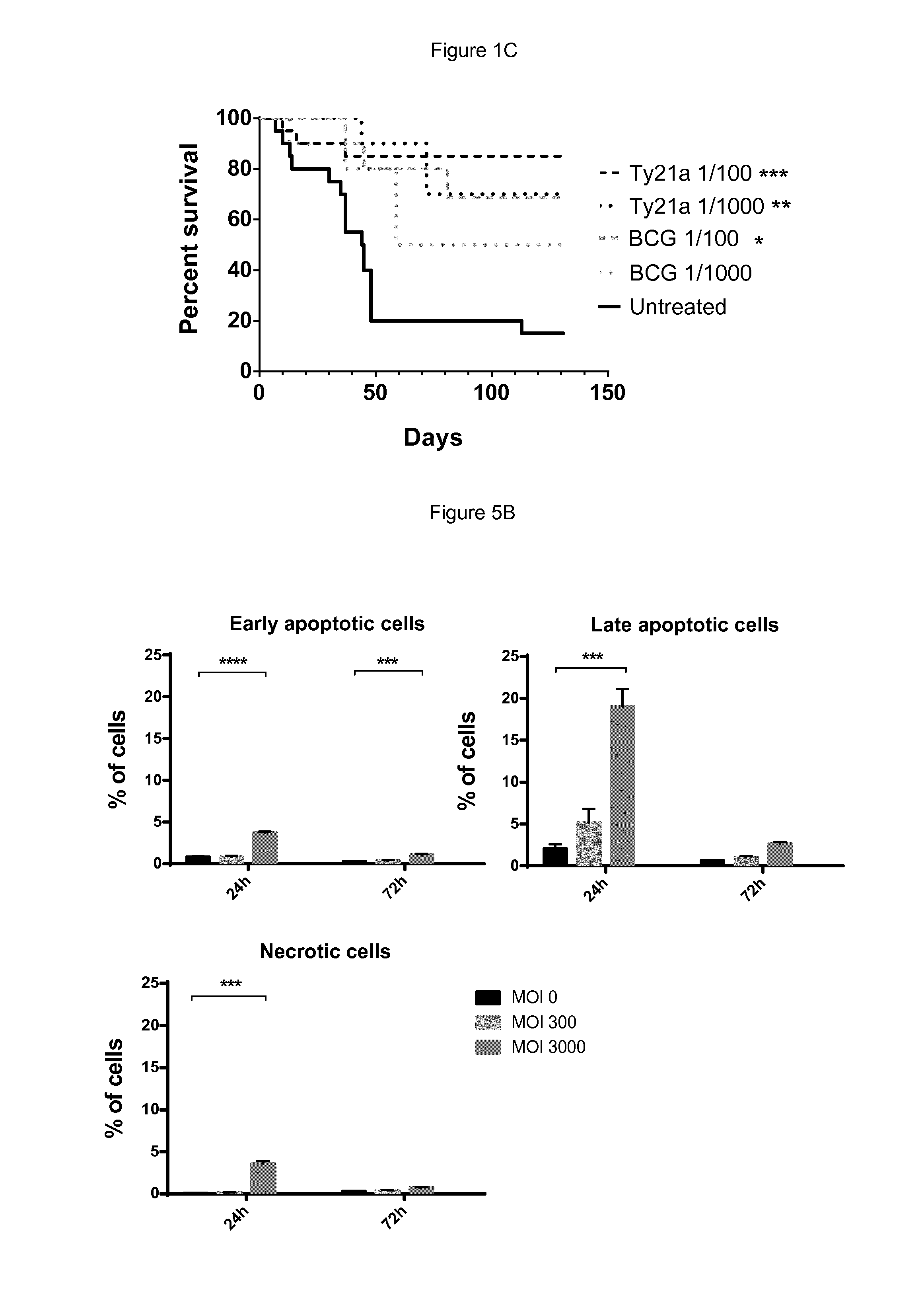
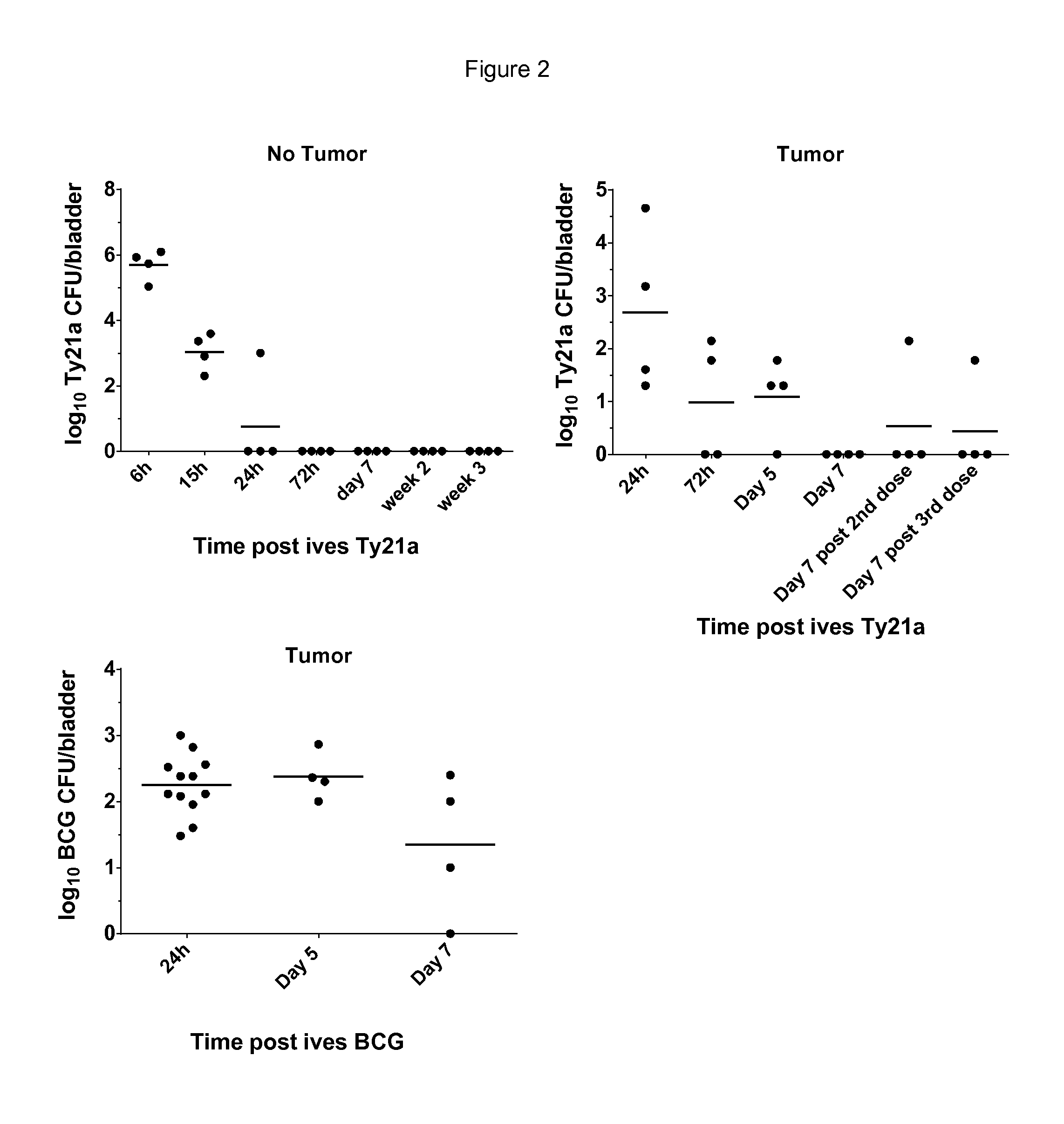
Salmonella strains for use in the treatment and/or prevention of cancer
ActiveUS9795641B2Bacteria material medical ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBladder cancerSalmonella enterica
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a live attenuated non-recombinant mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi strain and / or a non-viable attenuated non-recombinant mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi strain for use the treatment of cancer recurrence / progression. Preferably the cancer is bladder cancer.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV VAUDOIS C H U V
Construction and fermentation method of artificial strain with high yield of fengycin
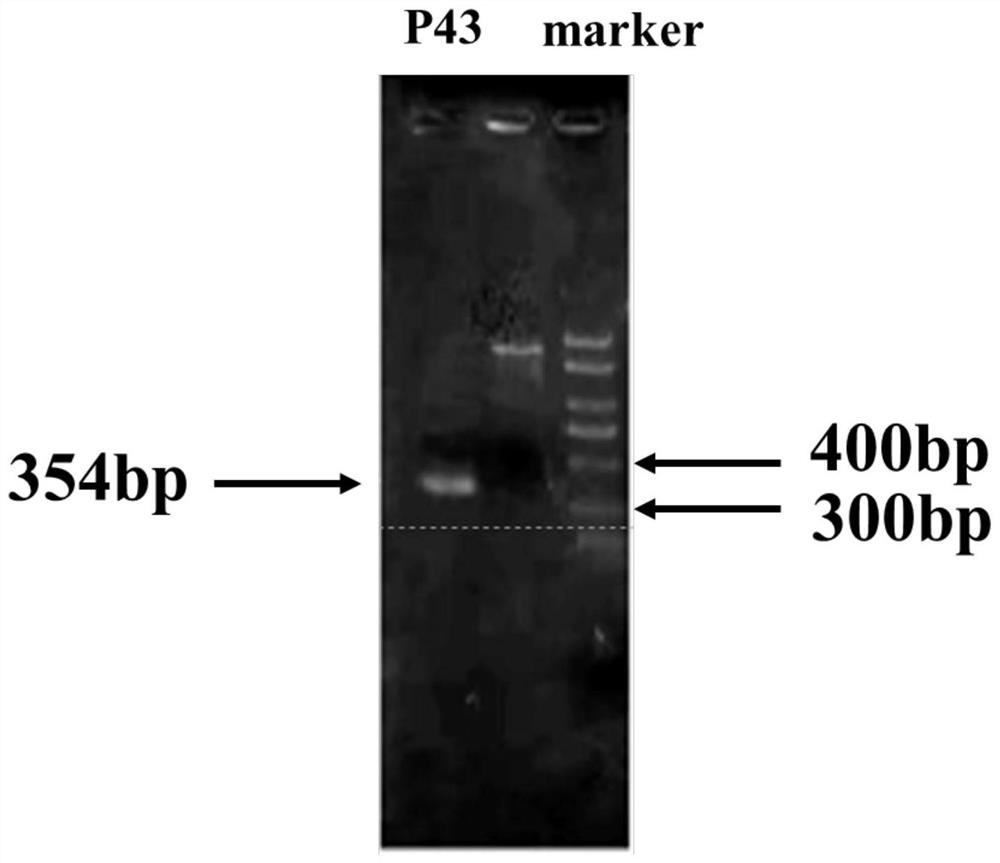
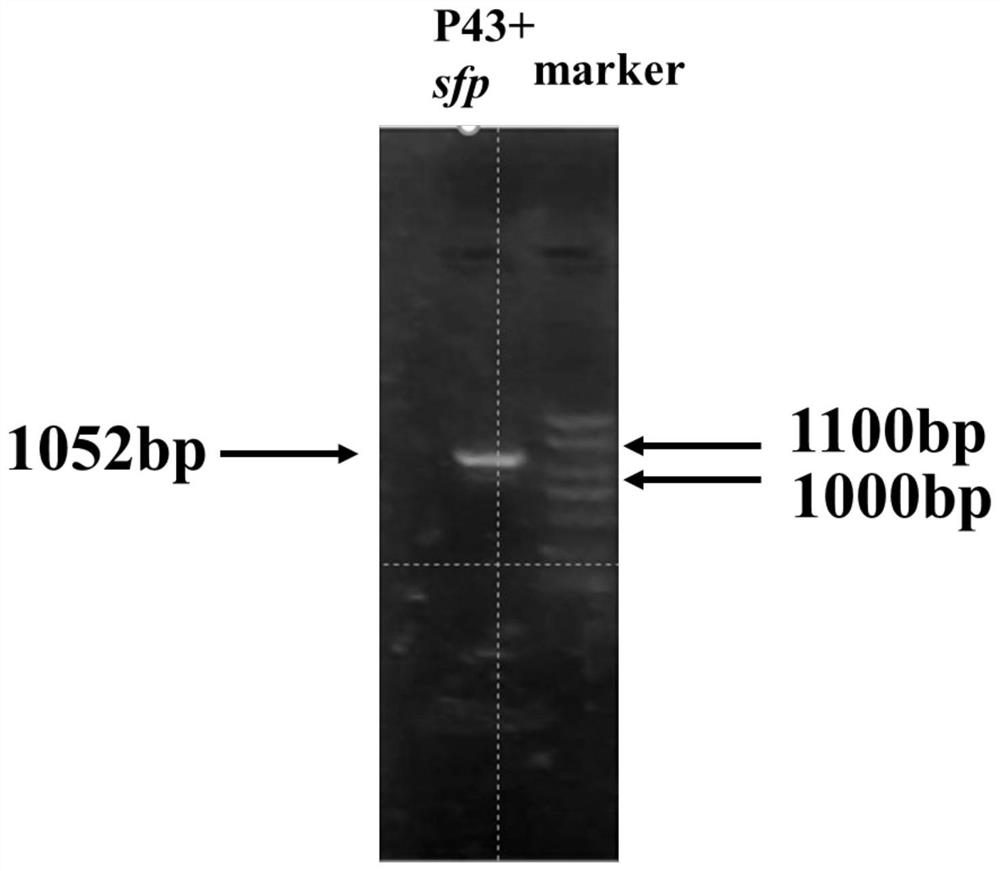
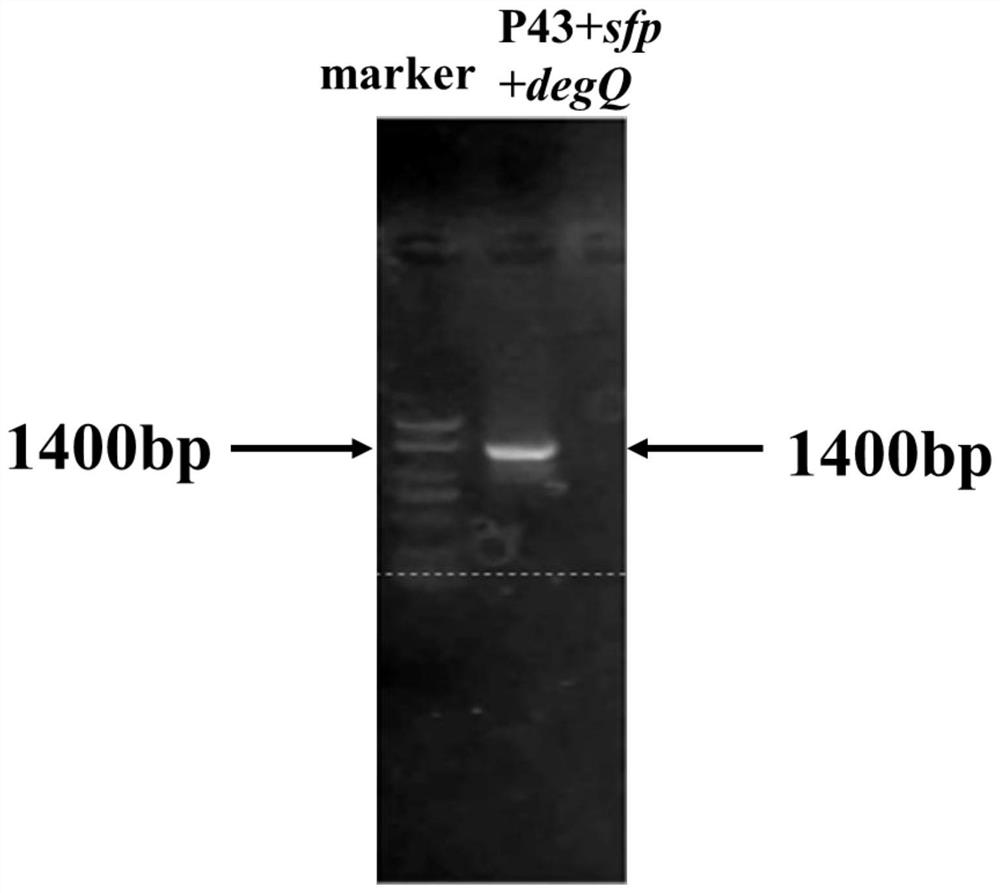
The invention provides a construction and fermentation method of an artificial strain with high yield of fengycin. The 4'-phosphoric acid pantetheinyl transferase gene sfp from bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, a multi-effect factor gene degQ from bacillus subtilis 168 and a strong promoter P43 are integrated in series onto a genome of the bacillus subtilis 168 by utilizing CRISPR gene editing to construct a strain B.subtilis ds; an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs of Escherichia coli BL21, an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene accACD of Salmonella enterica and a biotin ligase gene bisA of Corynebacterium glutamicum are connected in series to an expression vector pHT43, and the expression vector pHT43 is introduced into a fengycin synthesis strain B.subtilis ds, so that a fengycin high-yield strain B.subtilis dspabacd is constructed; the constructed engineering strain is fermented and cultured in a shake flask to produce the fengycin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Salmonella enterica presenting C. jejuni N-glycan or derivatives thereof
The present invention relates to Salmonella enterica comprising at least one pgl operon of Campylobacter jejuni or a functional derivative thereof and presenting at least one N-glycan of Campylobacter jejuni or N-glycan derivative thereof on its cell surface. In addition, it is directed to medical uses and pharmaceutical compositions thereof as well as methods for treating and / or preventing Campylobacter and optionally Salmonella infections and methods for producing these Salmonella strains.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Pullorum disease agglutination antigen and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107446851ALow variabilityGood antigenicityBacteriaBiological material analysisSalmonella entericaBacteroides
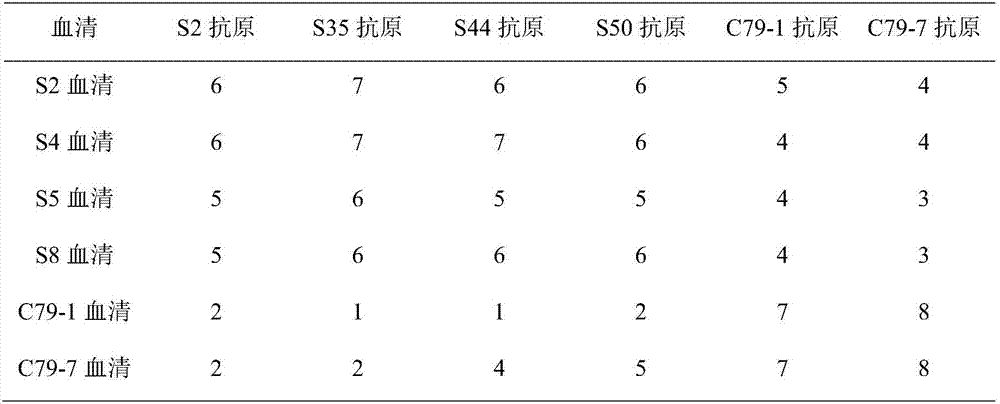
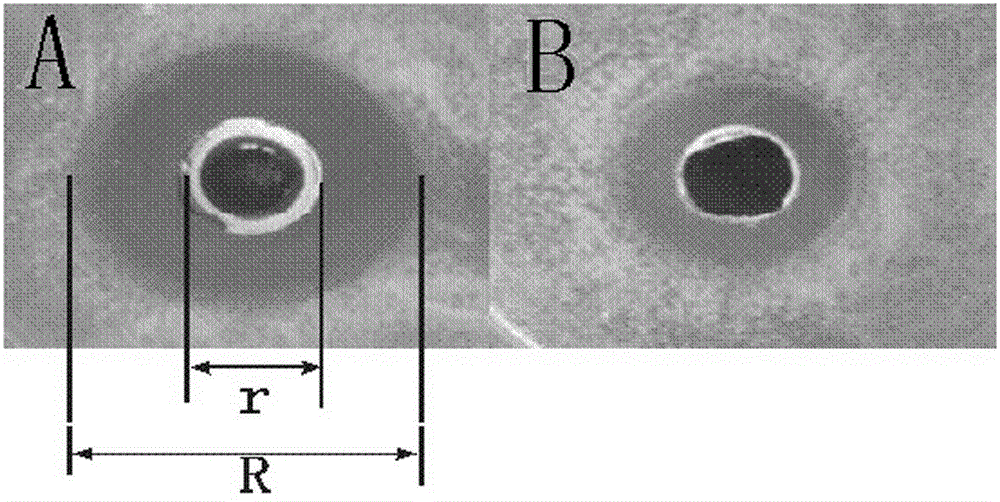
The invention relates to a pullorum disease agglutination antigen and a preparation method thereof and mainly relates to a bacterial strain which is salmonella pullorum standard strain C79-1 and a screened wild isolated strain S44. The wild isolated strain S44 of salmonella pullorum is classified and named as follows: salmonella enterica intestinal sub-salmonella pullorum, of which the Latin name is Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica pullorum, which is screened from the salmonella pullorum separated from chicken and which is collected at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the collection No.: CGMCC No. 14258. The method provided by the invention is scientific and reasonable, stable in production and low in cost; the selected pullorum disease agglutination antigen production strain is high in antigenicity and low in aberration rate; and the prepared pullorum disease agglutination antigen product has the advantages of high sensibility, high specificity, quick diagnosis, easiness in observing agglutination effect, and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for the detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis
Described herein is the identification of a novel Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis locus that serves as a marker for DNA-based identification of this bacterium. In addition, three primer pairs derived from this locus that may be used in a nucleotide detection method to detect the presence of the bacterium are also disclosed herein.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
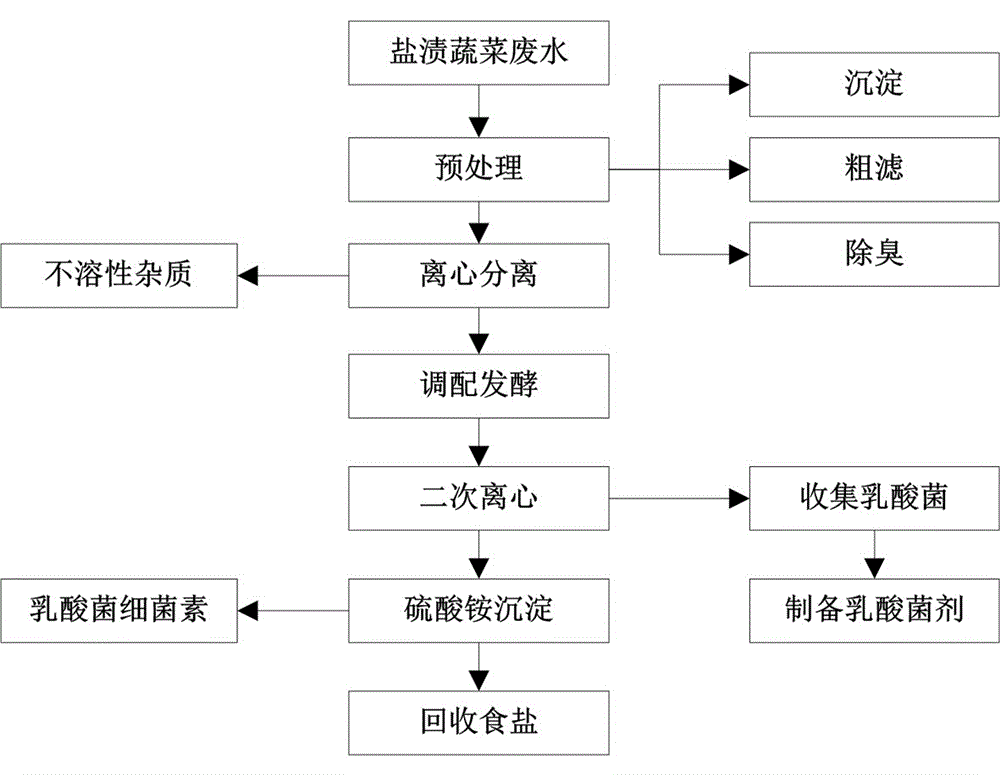
Method for producing lactic acid bacteria agent and bacteriocin by using salted vegetable wastewater
ActiveCN104988099AEmission reductionReduce processing difficultyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalmonella entericaEscherichia coli
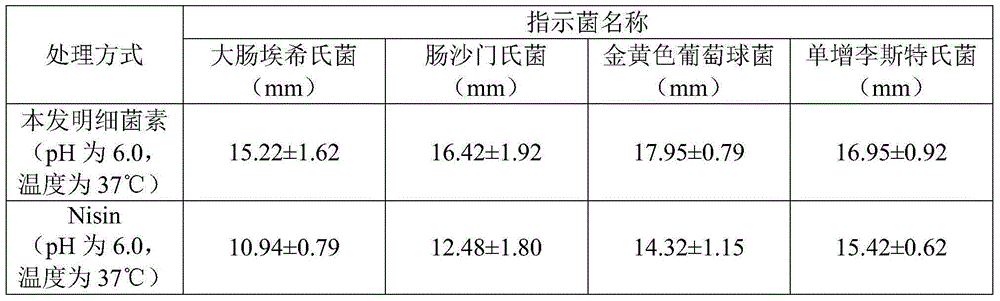
The present invention discloses a method for producing lactic acid bacteria agent and bacteriocin by using salted vegetable wastewater. The method comprises the production steps of pretreatment, centrifugal separation, blending fermentation, preparation of lactic acid bacteria agent and recovery of bacteriocin. The invention has simple operation, low production costs, environmental protection, low energy consumption, high added value, and important economic value and environmental value. The invention has the beneficial effects that: yield of lactobacillus cell is high, and the obtained lactic acid bacteria has significant inhibition effect on Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica, Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes bacteria, and shows more significant inhibitory effect in an acidic environment.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Uses of Phyllanthus emblica, and Phyllanthus emblica composition and uses thereof
InactiveCN109276602AExpand the scope of antibacterial applicationGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses applications of Phyllanthus emblica or Phyllanthus emblica and a Phyllanthus emblica composition in preparation of products for preventing and / or treating at least one of mastitis, diarrhea and porcine respiratory diseases, and further provides antibacterial effects of Phyllanthus emblica or Phyllanthus emblica extract and the Phyllanthus emblica composition, wherein the Phyllanthus emblica or Phyllanthus emblica extract and the Phyllanthus emblica composition can effectively inhibit the growth of one or a variety of bacteria selected from Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Pseudomonas, Salmonella choleraesuis, Escherichia coli, Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, Streptococcus suis, Bordetella, Pasteurella multocida, Salmonella enterica, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Enterococcus faecalis and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, and the effectiveness of the uses are proved through experiments so as to expanded the applications of Phyllanthus emblica andthe Phyllanthus emblica composition.
Owner:SICHUAN ANIMAL SCI ACAD
Method and Apparatus for Forming of an Automated Sampling Device for the Detection of Salmonella Enterica Utilizing an Electrochemical Aptamer Biosensor
ActiveUS20110166033A1Minimal trainingEasy to handleLibrary screeningBiological material analysisCapacitanceSalmonella enterica
An aptamer-based solid-state electrochemical biosensor for label-free detection of Salmonella enterica serovars utilizing immobilized aptamers. The device is realized by forming a matrix array of parallel capacitors, thus allowing the realization of low-cost, portable, fully integrated devices. Protein-aptamer binding modulates the threshold voltage of a circuit, changing the impedance (capacitance) of the circuit. This circuit is further characterized by an electrode coded with a p-Si substrate, enhancing the affinity between the Salmonella outer membrane proteins (OMPs) and the aptamer. An aptamer embedded detection plate is configured within a testing lid device that fits a standard, commercially available polymer specimen jar. A sample is mixed with broth for incubation and cultivation of any present Salmonella bacteria to obtain acceptable concentration of the pathogen for testing. The information obtained can then be transmitted by wireless network.
Owner:SENSOR KINESIS
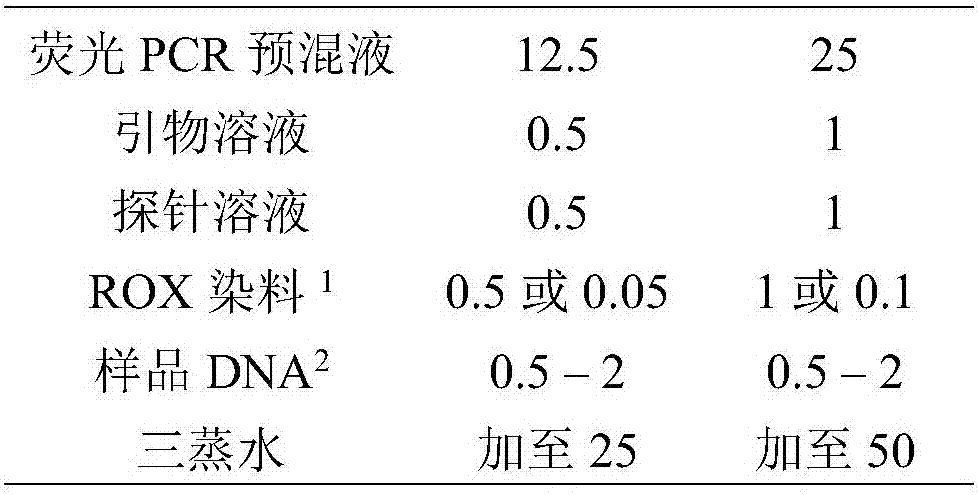
Quadruple real-time fluorescence PCR method for detecting four types of pathogenic bacteria
InactiveCN107338294AReduce generationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSalmonella entericaPositive control
The invention discloses a quadruple fluorescence PCR method for detecting four types of pathogenic bacteria. The four types of pathogenic bacteria are staphylococcus aureus, salmonella enterica, listeria monocytogenes and vibrio parahemolyticus. Four elements, namely sample DNA, a pair of universal primers and four probes, fluorescence PCR premix liquid and positive control are adopted in the method. The method comprises the following steps: designing the primers and the probes in accordance with 16S rRNA genes of the four types of bacteria, implementing amplification on a target sequence and exciting corresponding fluorescence signals; and preparing a kit from the to-be-detected sample DNA in accordance with a reagent formula and amplification conditions of the fluorescence PCR amplification; and specifically, the method comprises the following steps: establishing a quadruple fluorescence PCR primer system for detecting the four types of bacteria; establishing the quadruple fluorescence PCR kit for detecting the four types of bacteria; and determining the quadruple fluorescence PCR identification method for detecting the four types of bacteria. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being low in standard error, short in detection time, and being capable of simultaneously detecting a plurality of target genes and reducing reagent cost; and the method is applicable to detection of pathogenic bacteria in food and cosmetics.
Owner:GUIZHOU PROVINCIAL PRODUCT QUALITY SUPERVISION AND INSPECTION INSTITUTE
Salmonella strains for use in the treatment and/or prevention of cancer
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a live attenuated non-recombinant mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi strain and / or a non-viable attenuated non-recombinant mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi strain for use the treatment of cancer recurrence / progression. Preferably the cancer is bladder cancer.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV VAUDOIS C H U V
Method for constructing negative bacterium capable of expressing positive bacterium polysaccharide and mutant obtained by same
ActiveCN106191091AEasy to trainReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalmonella entericaMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for constructing a gram-negative bacterium capable of expressing a gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide. The method comprises the following steps: transforming a low-copy expression plasmid of the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide into an asd and rfbP gene-deletion gram-negative bacterium, screening by a balanced lethal system to obtain the gram-negative bacterium capable of producing the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide. The invention also provides the gram-negative bacterium capable of producing the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide prepared by the method. The invention also provides a mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium P0005, which is named as Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium P0005, and has the CCTCC NO: M 2016344. The gram-negative bacterium can express the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide, and the method provided by the invention does not contain any resistance marker and meets the biosafety requirements of subsequent vaccines and other application.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
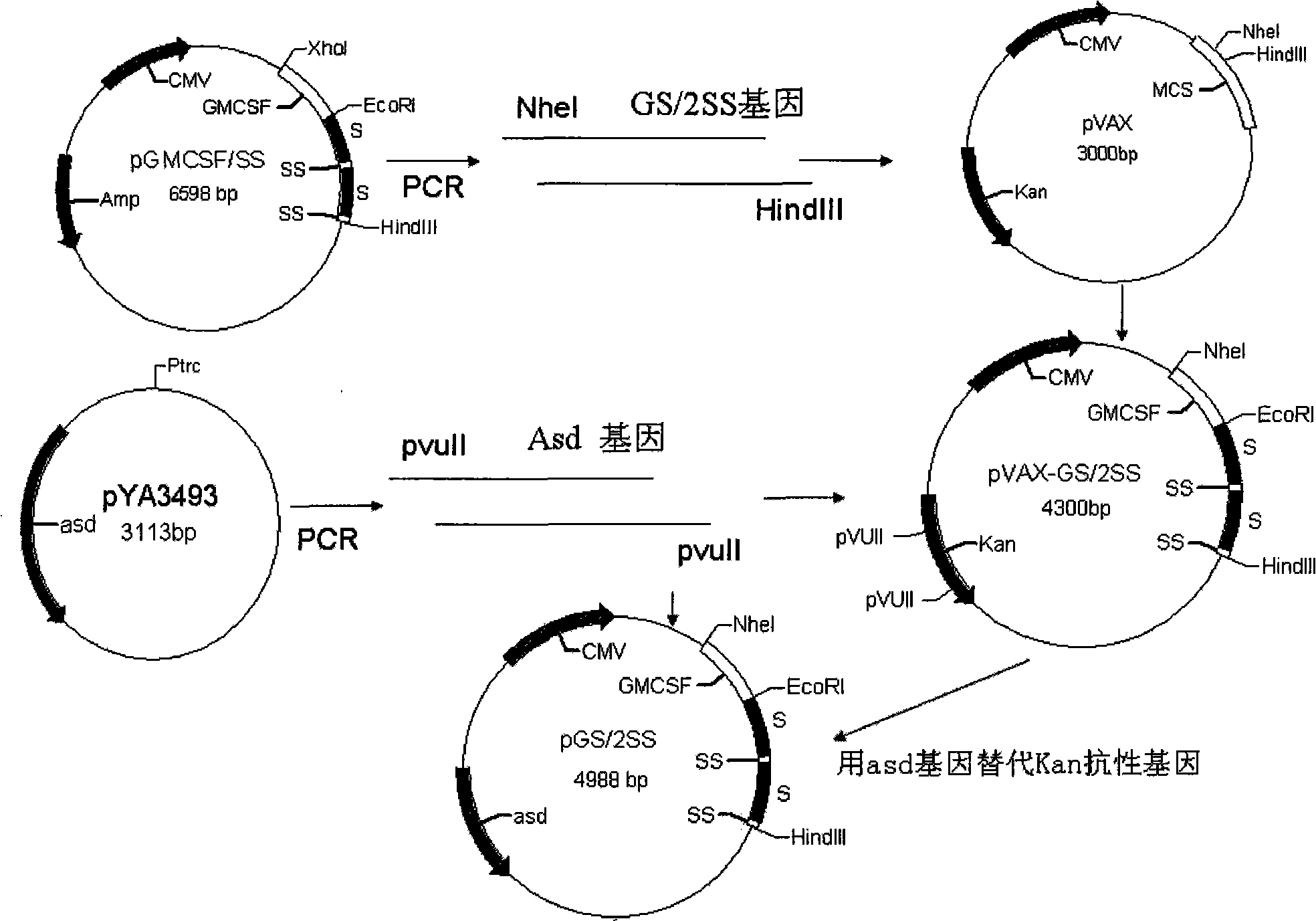
Oral DNA vaccine for promoting growth of animal by non-antibiotics resistance gene screening, and preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101407782AWon't spreadEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalmonella entericaKanamycin
The invention belongs to the preparation field of animal vaccines, and particularly relates to a non-antibiotically screened animal growth promotion oral DNA vaccine as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. A somatostatin with a GMCSF cell gene and a hepatitis b surface antigen fusion gene GS / 2SS are cloned to a plasmid vector pVAX1 for obtaining a middle plasmid pVAX-GS / 2SS; an aspartic acid Beta-galactose dehydrogenase gene (asd) is used for replacing a kanamycin (Kan) gene in the middle plasmid pVAX-GS / 2SS to obtain an eukaryotic expression plasmid pGS / 2SS of the non-antibiotically screened somatostatin; and then the plasmid pGS / 2SS is converted into a pig cholera salmonella C500 lack of asd and crp genes for obtaining the non-antibiotically screened animal growth promotion oral DNA vaccine. The pig cholera salmonella (Salmonella enterica sv. Choleraesuis) C500 / pGS / 2SS which comprises the eukaryotic expression plasmid of the somatostatin is preserved in the China Center for Type culture collection (CCTCC) and the preservation number thereof is CCTCC NO: M208194. The method also discloses the preparation method of the vaccine and the applications thereof in the aspect of promoting the growth of the animals.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
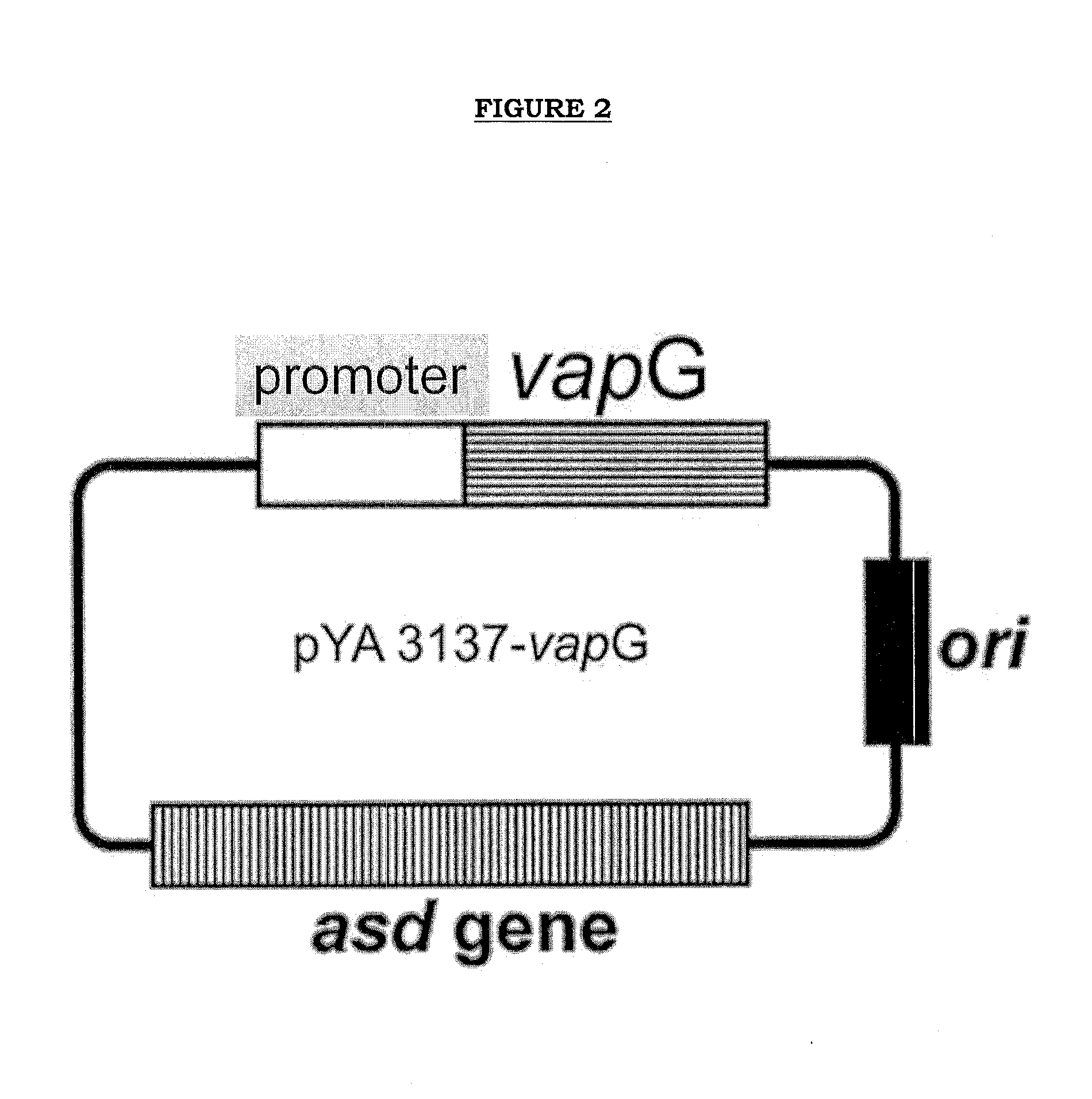
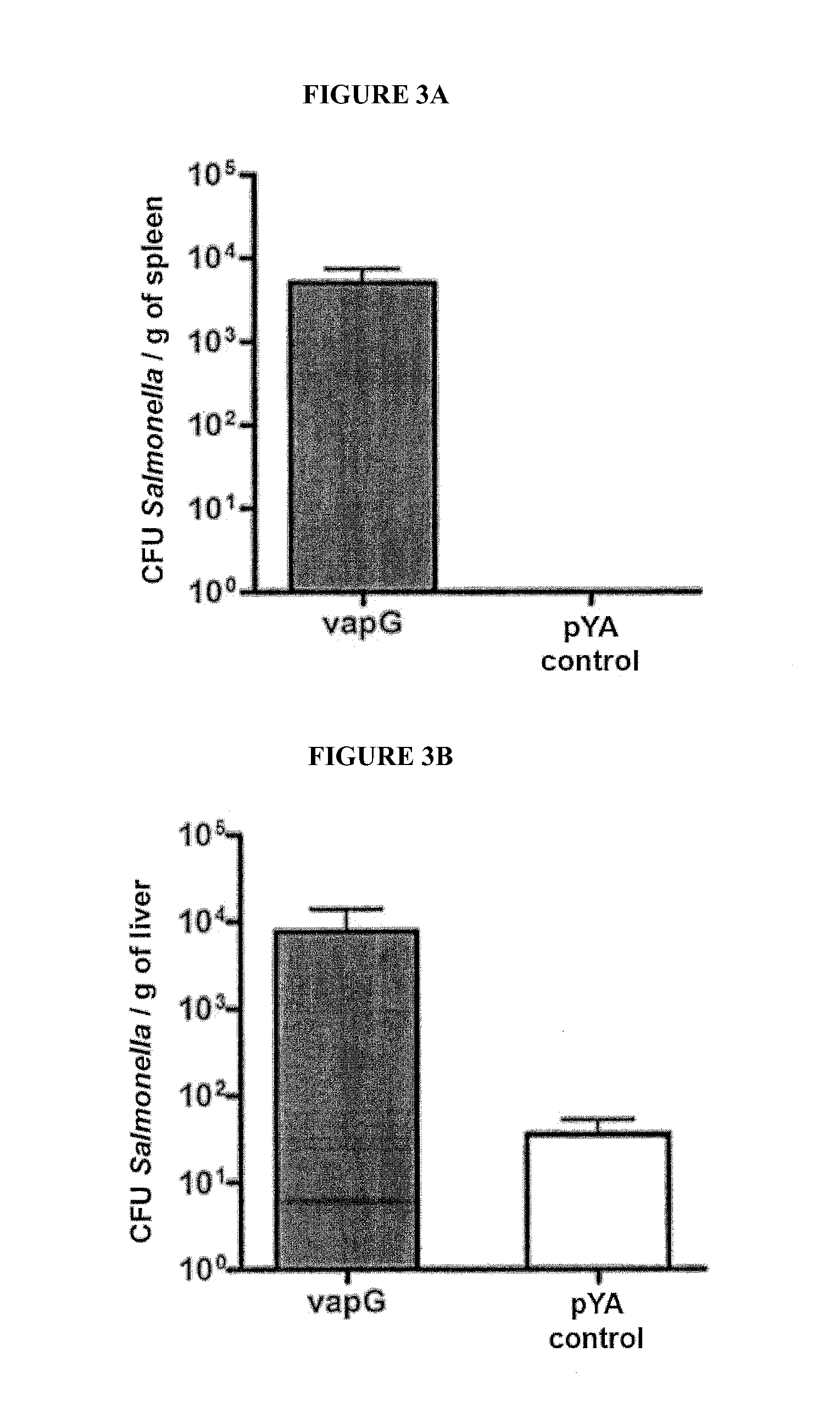
Recombinant microorganisms and uses thereof
The present invention provides live recombinant microorganisms such as prokaryote organisms, particularly enterobacteria, preferably Salmonella enterica, containing SEQ. ID. no. 1 and SEQ. ID. no. 2 capable of expressing VapG and / or VapA / VapG lipoproteins (SEQ. ID. no. 3 and SEQ. ID. no. 4), optionally in combination with other active ingredients, methods for preparing vaccine strains, antigens (SEQ. ID. no. 3 and SEQ. ID. no. 4) and vaccine compositions, preferably vectored vaccines. Additionally, the present patent application relates to the use of the vaccine vectors in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions, particularly vaccines indicated for the prevention and / or treatment of infections by Rhodococcus equi, its antibodies and / or antisera, diagnostic kits and methods for the prophylaxis and / or treatment of infections by R. equi.
Owner:UNIV DE SAO PAULO +1
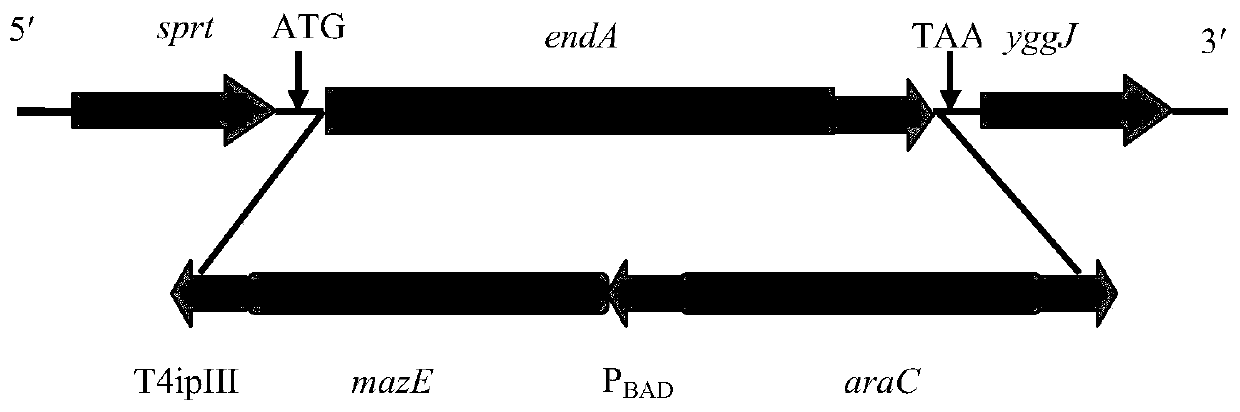
Recombinant lysed Salmonella enterica and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110373422AEnsure safetyIncrease concentrationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaSalmonella entericaAgricultural science
The invention discloses recombinant lysed Salmonella enterica and a construction method and application thereof. The elements introduced to genome of the recombinant lysed Salmonella enterica include:a mazE expression element including antitoxin gene mazE and its upstream promoter PBAD, and positive-negative regulator gene araC that encodes the promoter PBAD; an lacI expression element includinga gene lacI and its upstream promoter PBAD, and a positive-negative regulator gene araC that encodes the promoter PBAD; and an mazF expression element including toxin gene mazF and its upstream promoter Plac. The invention also discloses a construction method and application of the recombinant lysed Salmonella enterica. A Salmonella vector is modified through the combination of an arabinose promoter regulatory gene technology and an MazEF system so that programmed death occurs to the Salmonella vector due to immunostimulation; safety is good; allowing Salmonella to serve as a biosafe controllable polyvalent vaccine vector to deliver an exogenous antigen is guaranteed.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Primer and kit for detecting salmonella and use method of primer and kit
PendingCN114196769AImprove detection accuracyHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSalmonella entericaExpression gene
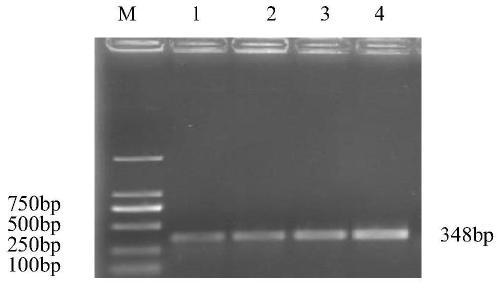
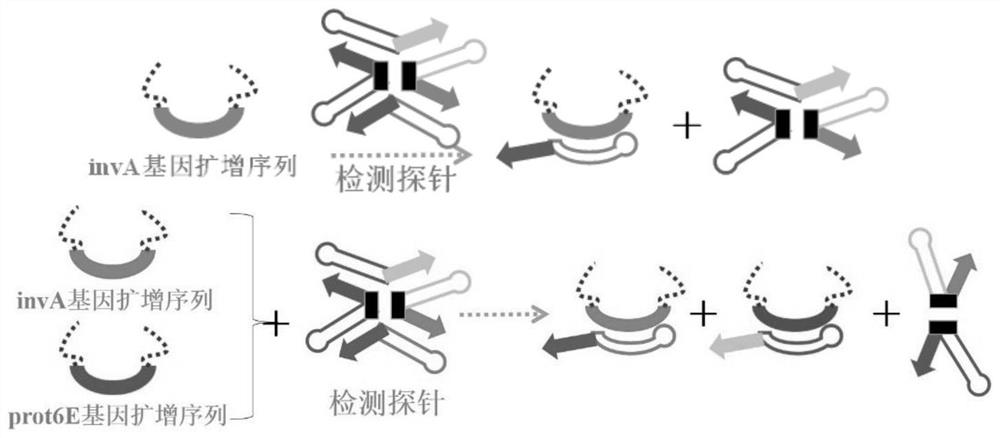
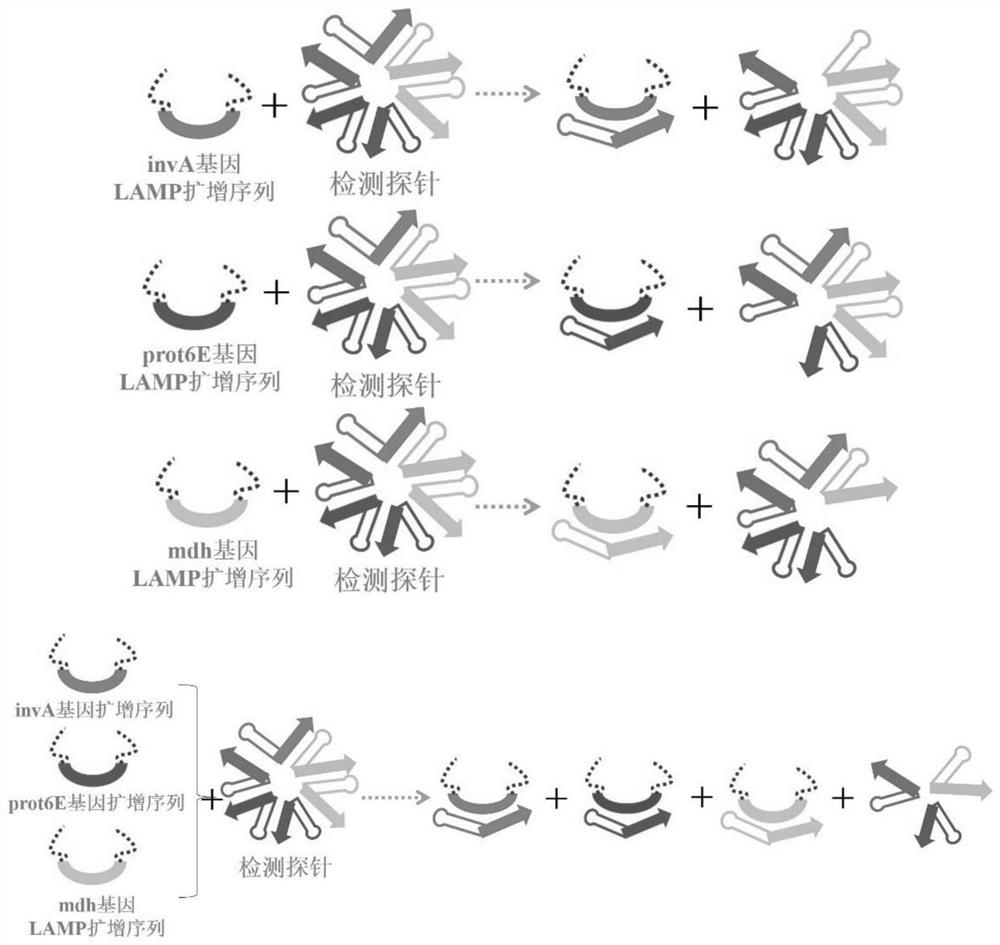
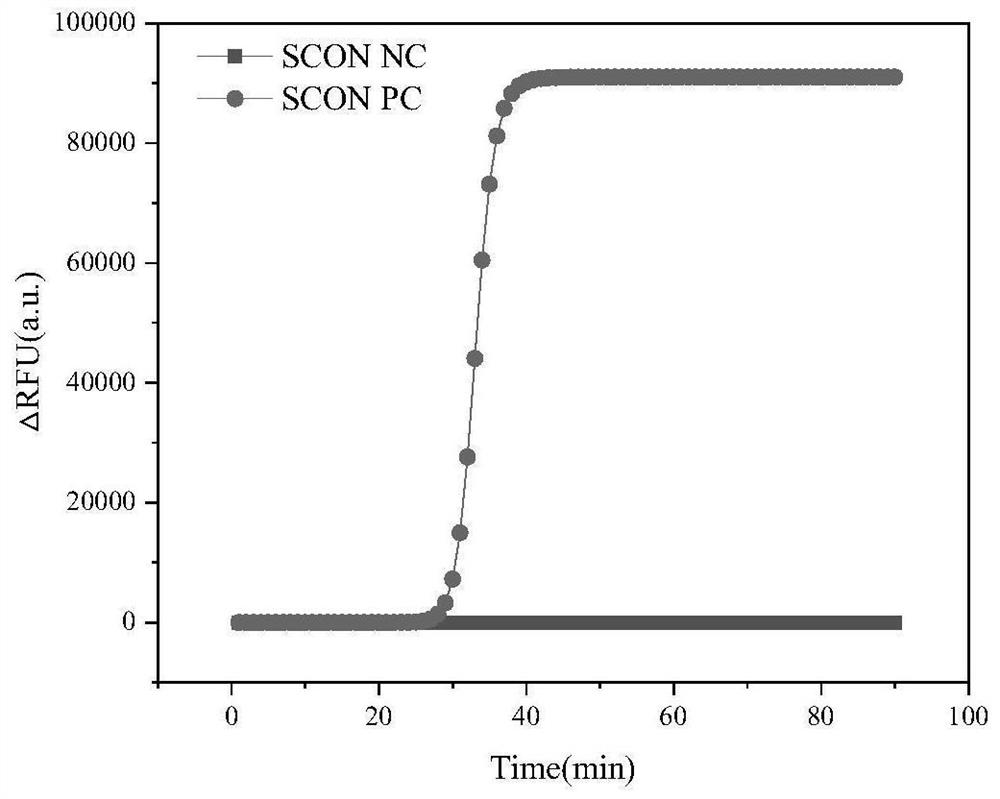
The invention discloses a primer and a kit for detecting salmonella and a use method of the kit, and belongs to the field of bacterial detection. The problems that a salmonella detection method in the prior art is low in detection sensitivity, low in accuracy and high in cost, and false negative and false positive results are likely to occur are solved. The kit disclosed by the invention comprises LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) primers of a salmonella conserved gene invA, an enteritis serotype specific expression gene prot6E of salmonella enterica, a specific expression gene mdh of salmonella typhimurium, a probe SC-E6 and a probe SC-E6-TM. The kit for detecting salmonella has very high detection accuracy and sensitivity, is convenient to operate and low in cost, and can avoid aerosol pollution in the detection process.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
ATP-bioluminescence immunoassay
InactiveUS8518658B1Wide applicationWeak matrixMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSalmonella entericaBacteroides
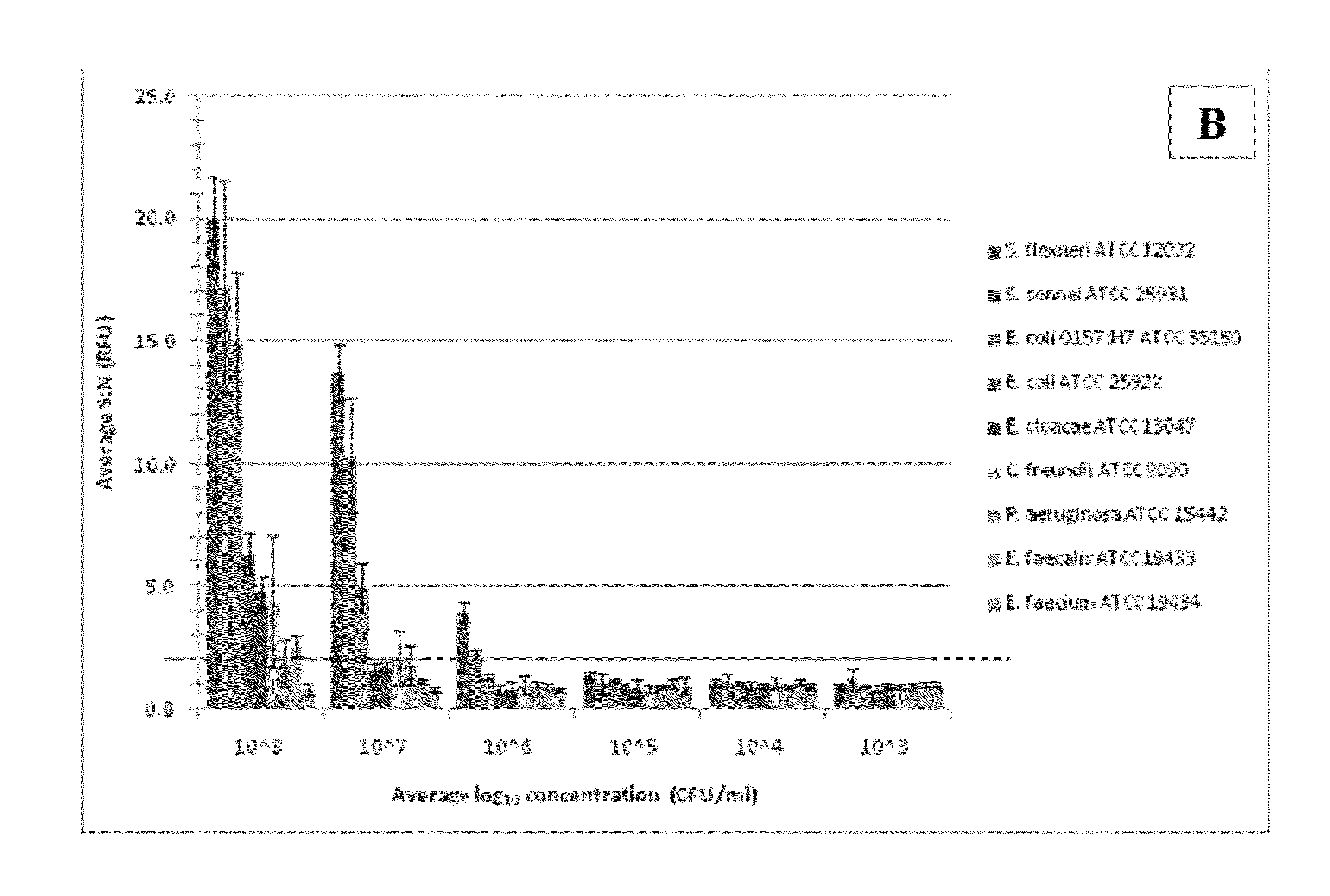
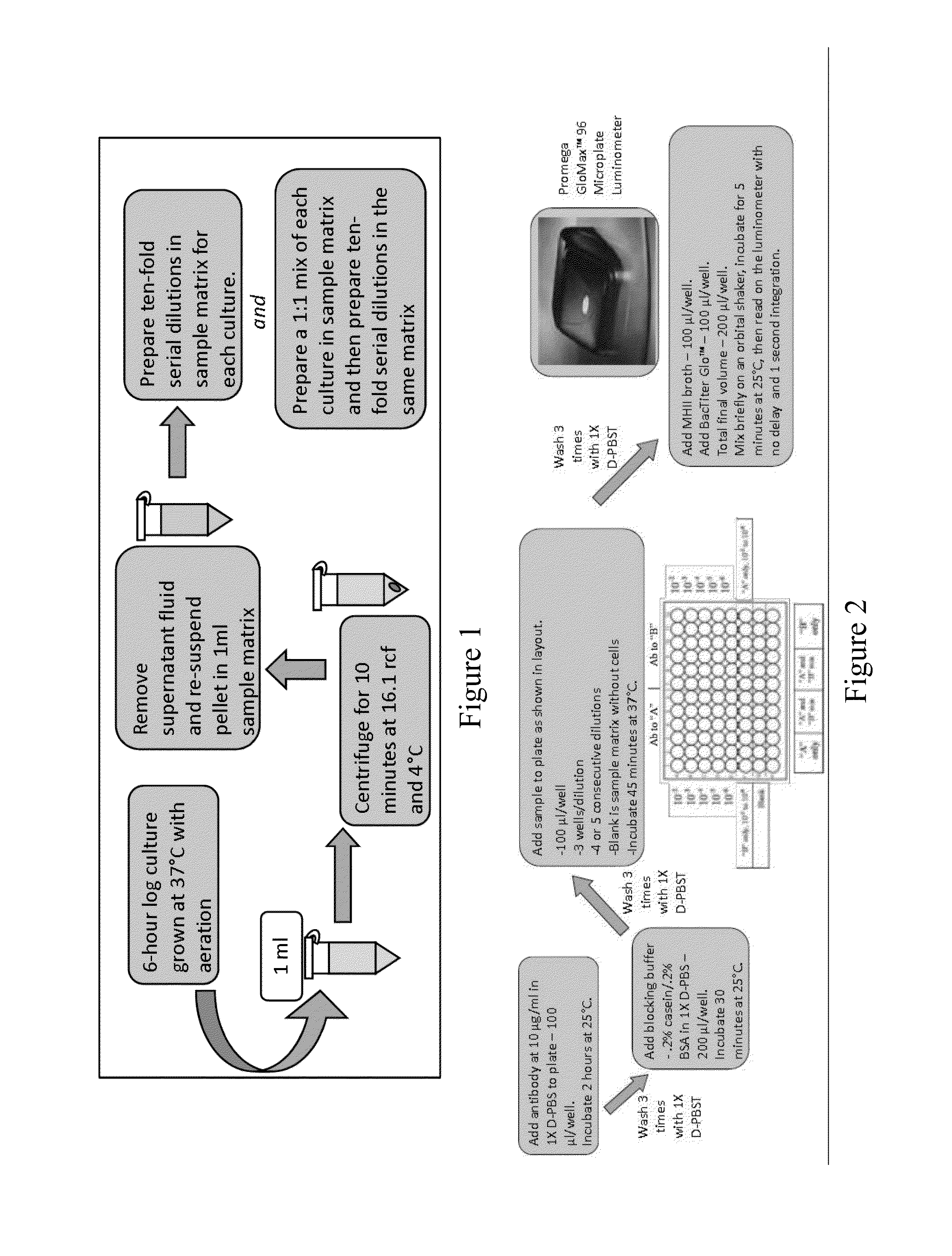
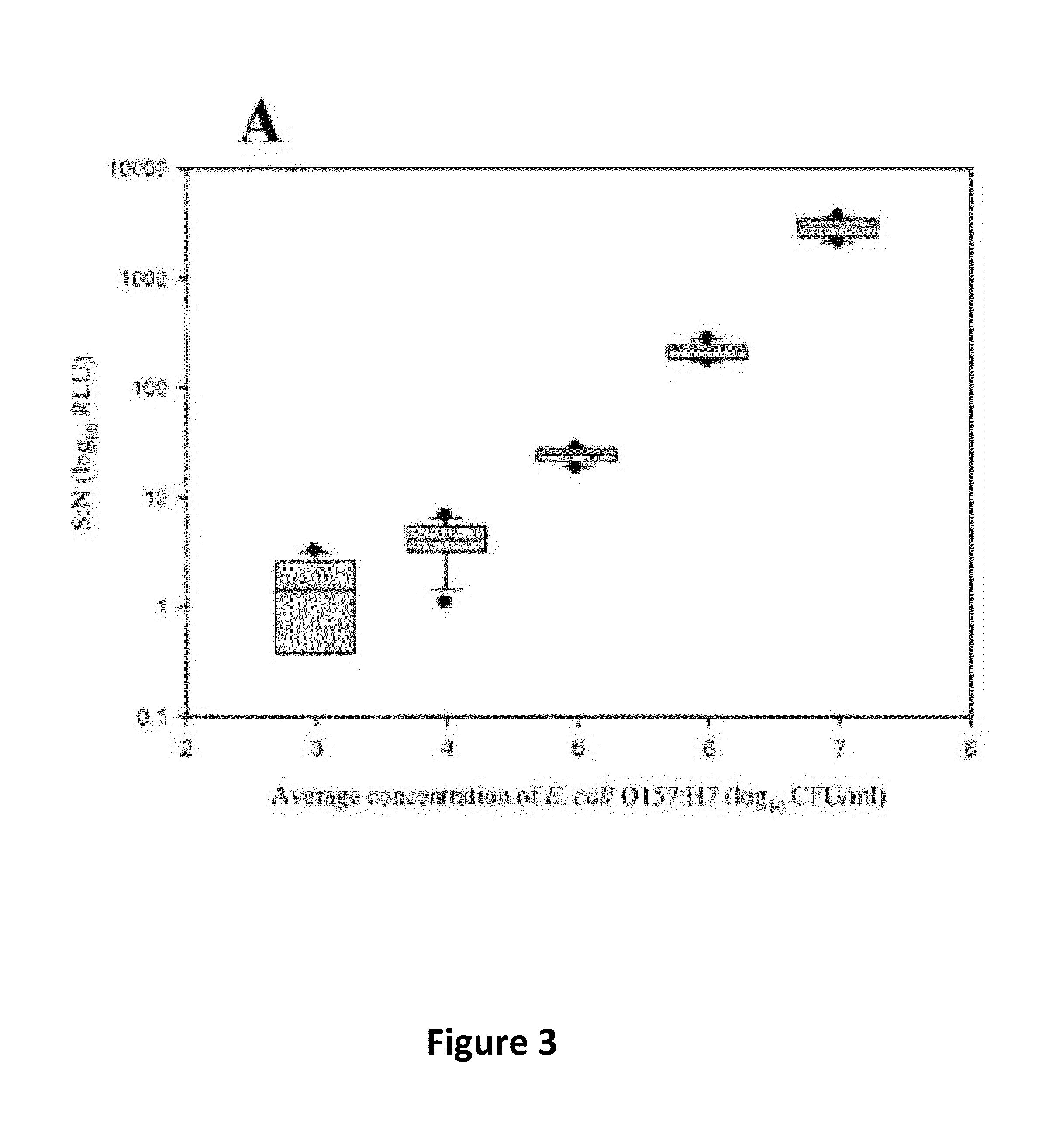
Disclosed is a method and associated device for the rapid identification of viable bacterial contaminants in food products. The method detects viable microbes by using a combined ATP-bioluminescence immunoassay. Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium were selected as target organisms in various matrices including ground beef homogenate, apple juice, milk, and phosphate-buffered saline. Specific antibodies were immobilized on the surface of well plates in which the sample matrices were incubated. The plates were washed, and the wells were incubated with BacTiter-Glo reagent in Mueller-Hinton II broth. Bioluminescent output was measured with a luminometer and signal-to-noise ratios were calculated. The LOD was not affected by the presence of non-target cells. A strong linear correlation was observed between the number of cells and luminescent output over 4 orders of magnitude. This method provides a means of simultaneously detecting and identifying viable pathogens in complex matrices.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Attenuated salmonella enterica serovar paratyphi a and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120029173A1Peptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesSalmonella enterica serovar Paratyphi AConjugate vaccine
The present invention is drawn to a live, attenuated S. Paratyphi A strain, a live, attenuated S. Paratyphi A strain comprising a stabilized plasmid expression system, an S. Paratyphi conjugate vaccine, and methods of using these strains and conjugate vaccine.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Broad spectrum vaccine against typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella disease
ActiveUS9011871B2Snake antigen ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsAntigenSalmonella enterica
The present invention is drawn to multivalent Salmonella enterica serovar conjugate vaccines comprising conjugates of S. Typhimurium, S. Enteritidis, S. Choleraesuis, S. Typhi, S. Paratyphi A and optionally S. Paratyphi B, wherein the conjugates comprise a hapten antigen and a carrier antigen, wherein at least one of the hapten antigens or carrier antigens is characteristic of the Salmonella enterica serovar. The present invention also provides Salmonella enterica serovar reagent strains to produce the multivalent conjugate vaccines and attenuated Salmonella enterica serovars for use as vaccines.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com