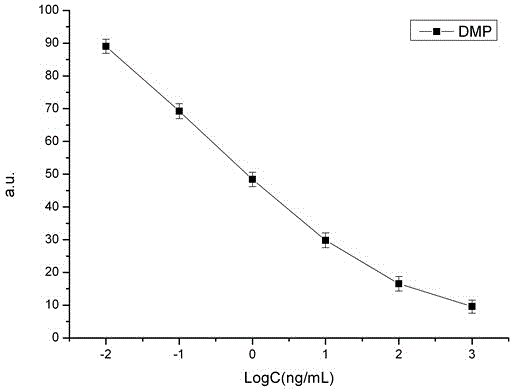
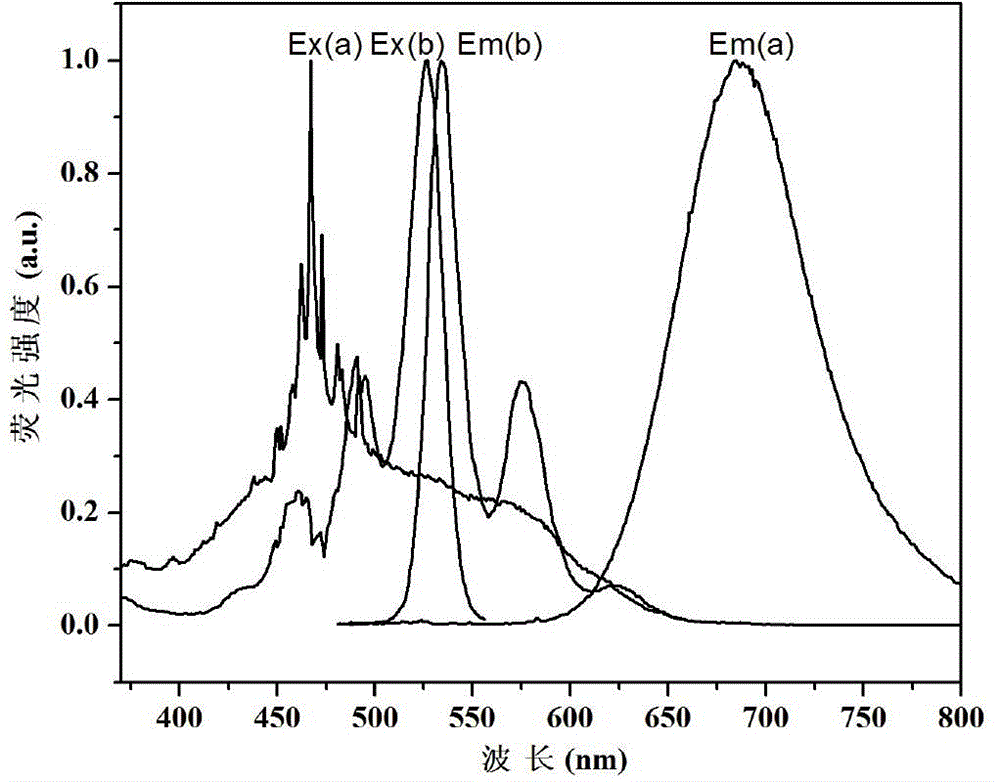
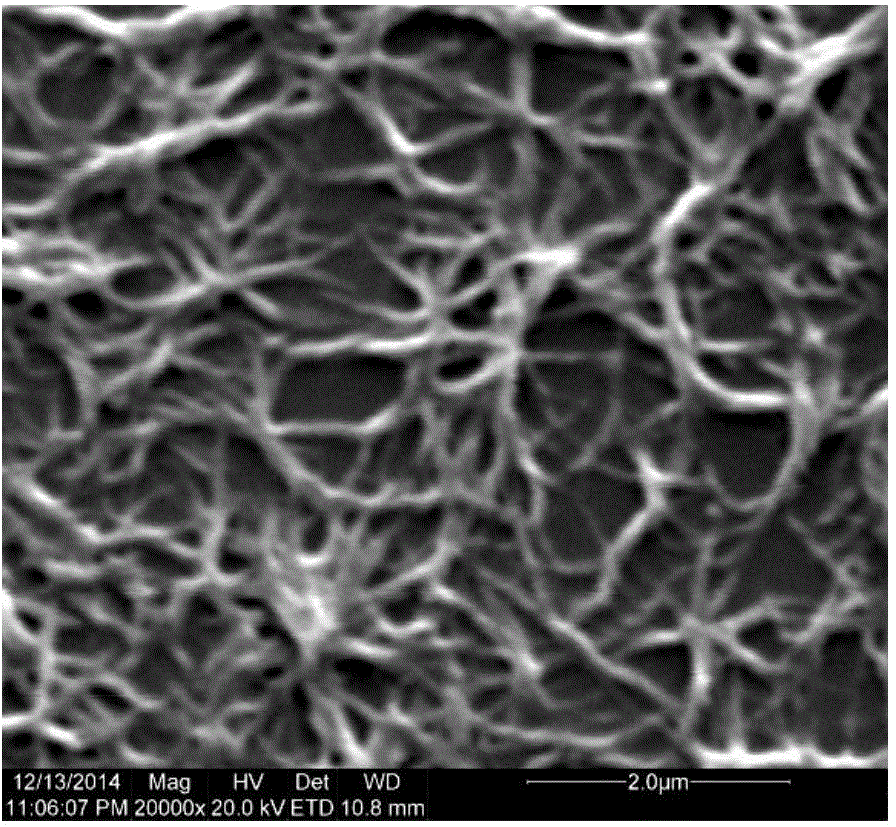
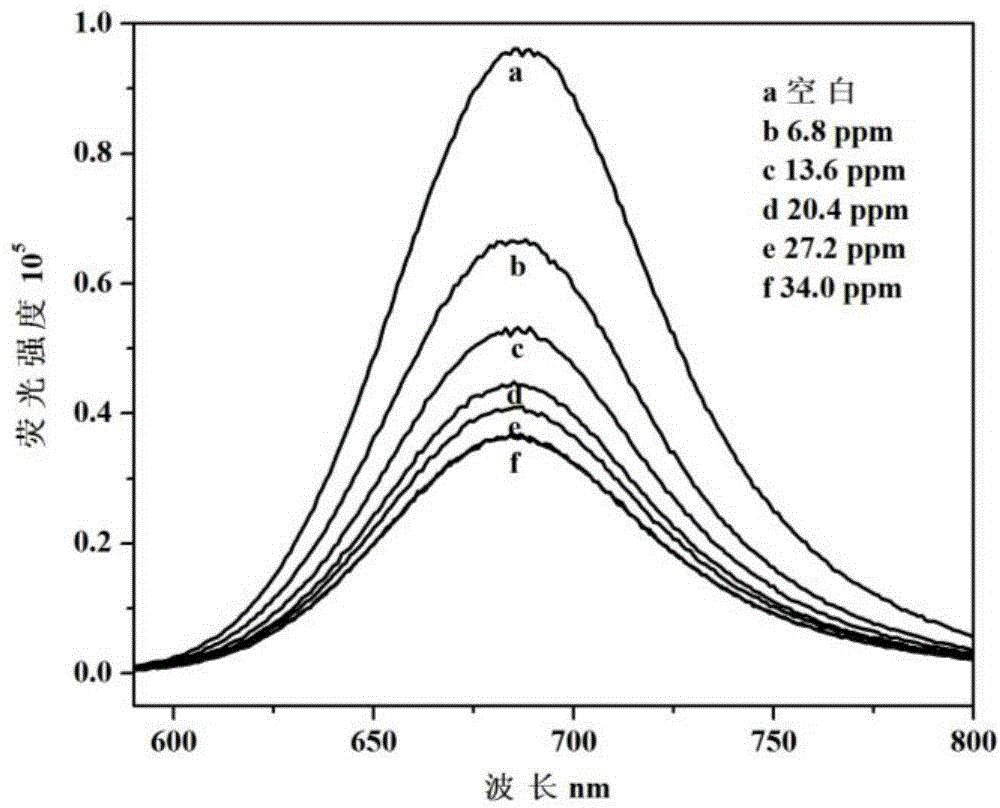
Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Rapid and sensitive detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nanoparticle tracer-based electrochemical DNA sensor for detection of pathogens-amplification by a universal nano-tracer (AUNT)
InactiveUS20110171749A1Rapid and sensitive detectionRapid and sensitive and valid identificationMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicineSalmonella entericaEscherichia coli
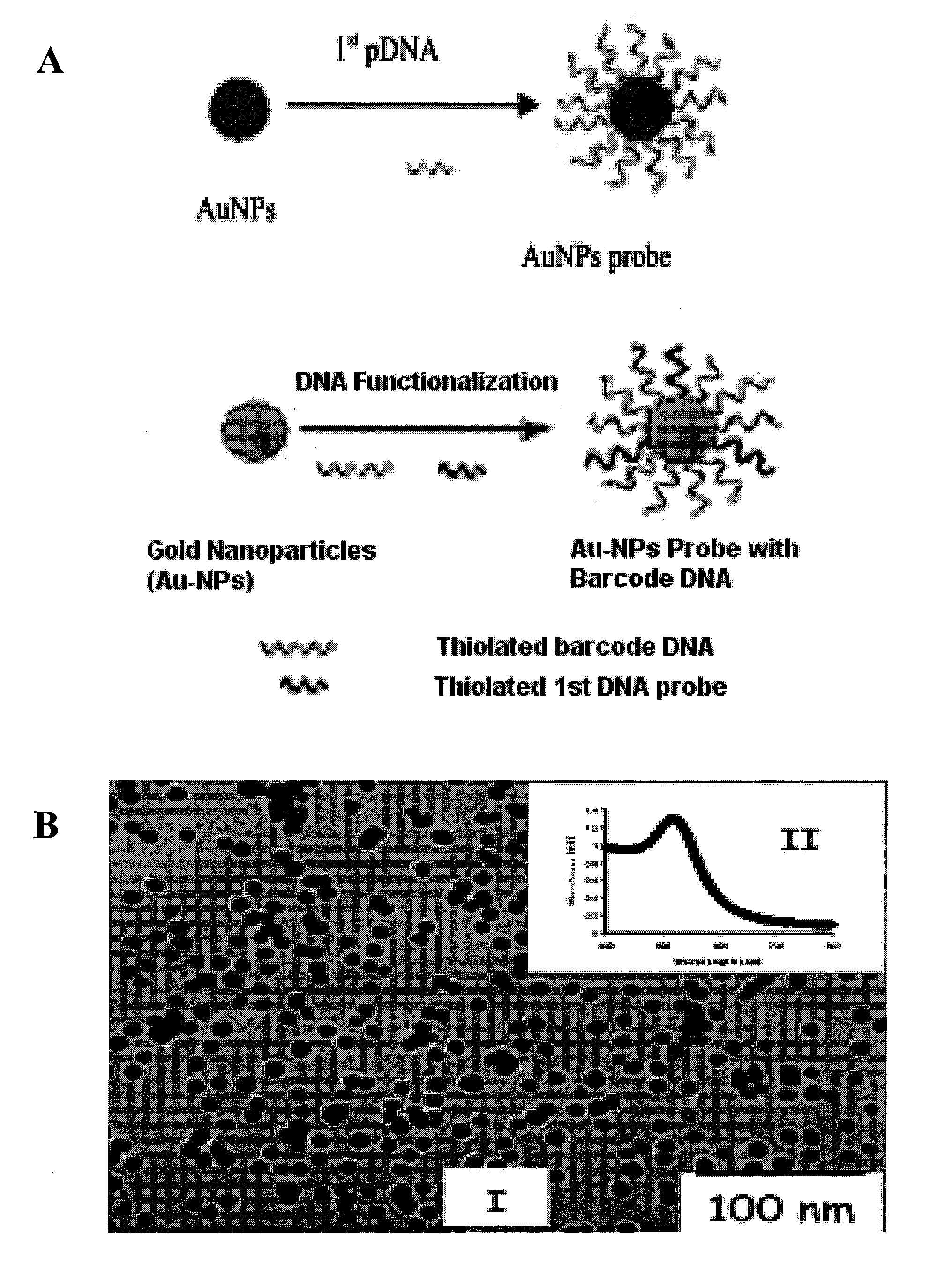
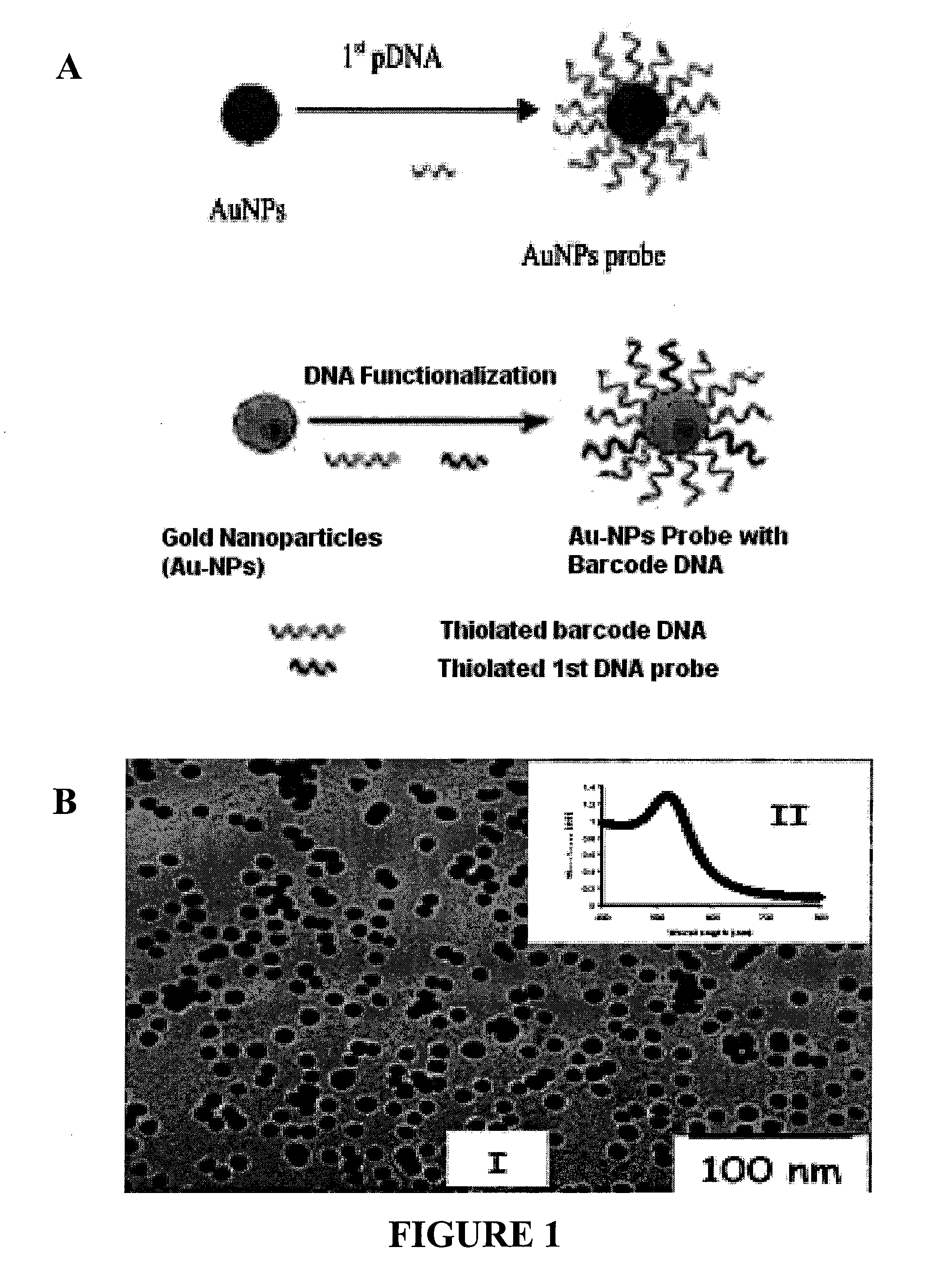
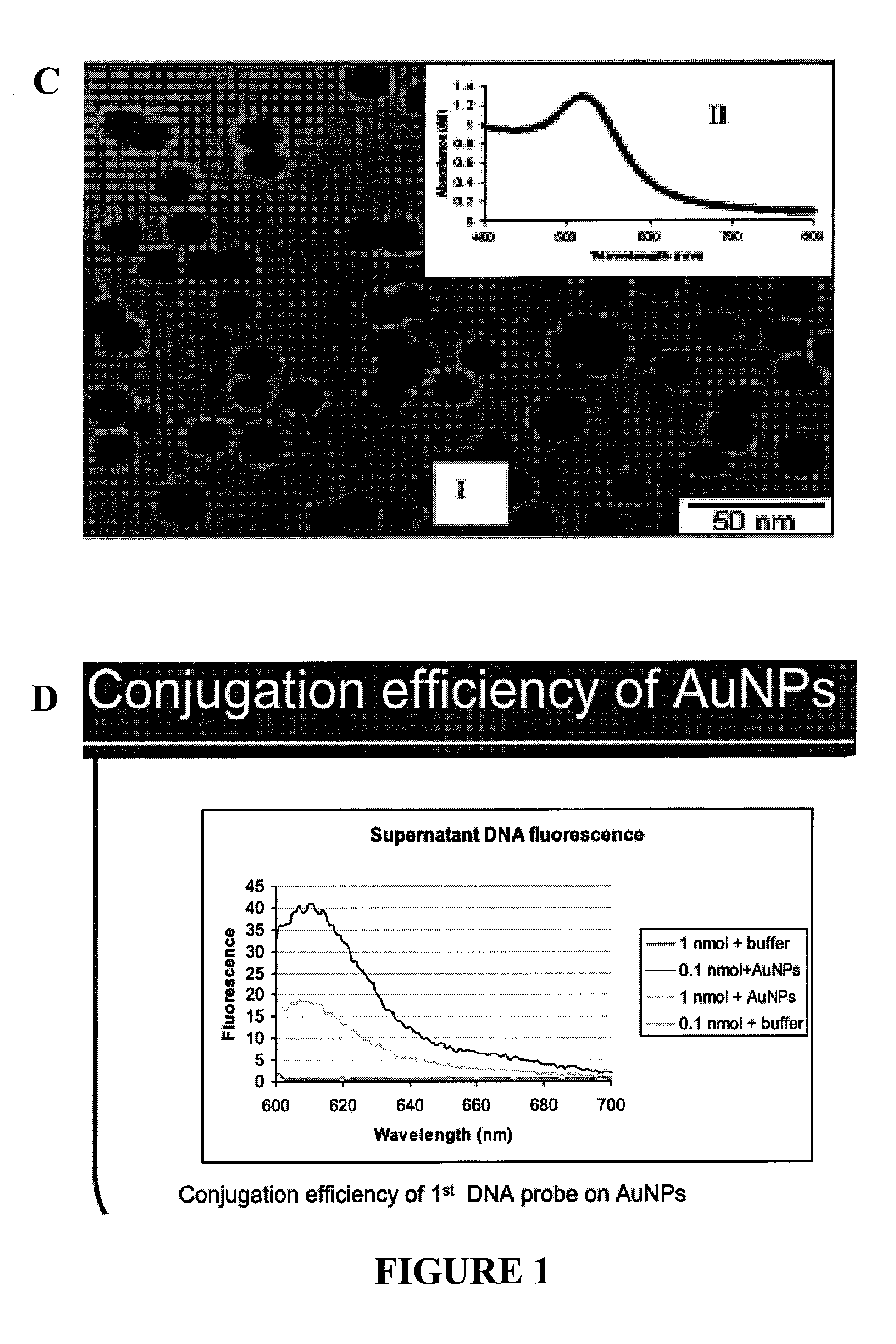
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying a pathogen. The inventions provide an antibody-based biosensor probe comprising (AUNT) in combination with a polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticle. In particular, a nanoparticle-based biosensor was developed for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacterium in food products. Further described are biosensors for detecting pathogens at low concentrations in samples. Even further, a gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensor detection and amplification method for identifying the insertion element gene of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis is described. The present invention provides compositions and methods for providing a handheld potentiostat system for detecting pathogens outside of the laboratory. The AUNT biosensor system has applications detecting pathogens in food, water, beverages, clinical samples, and environmental samples.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
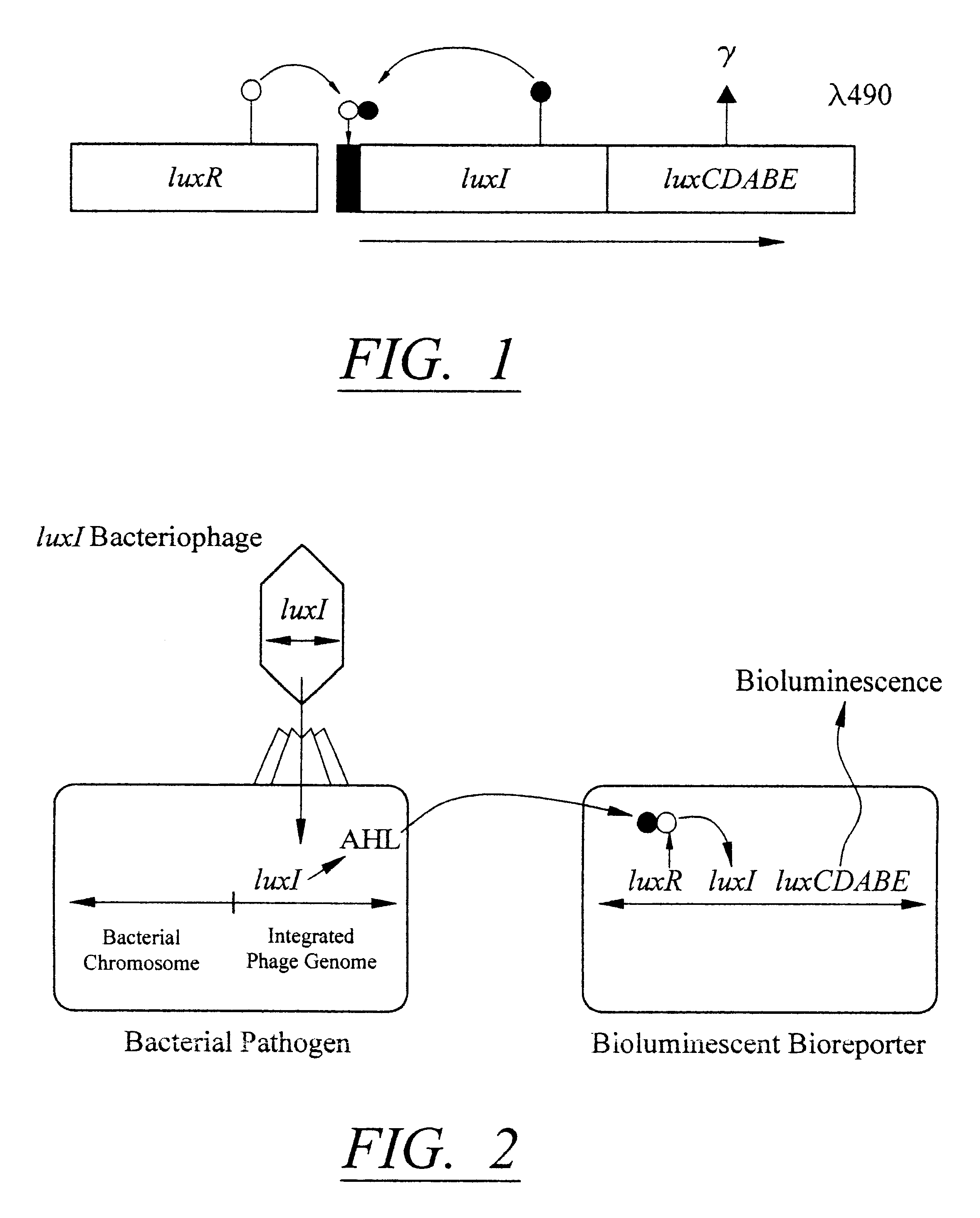
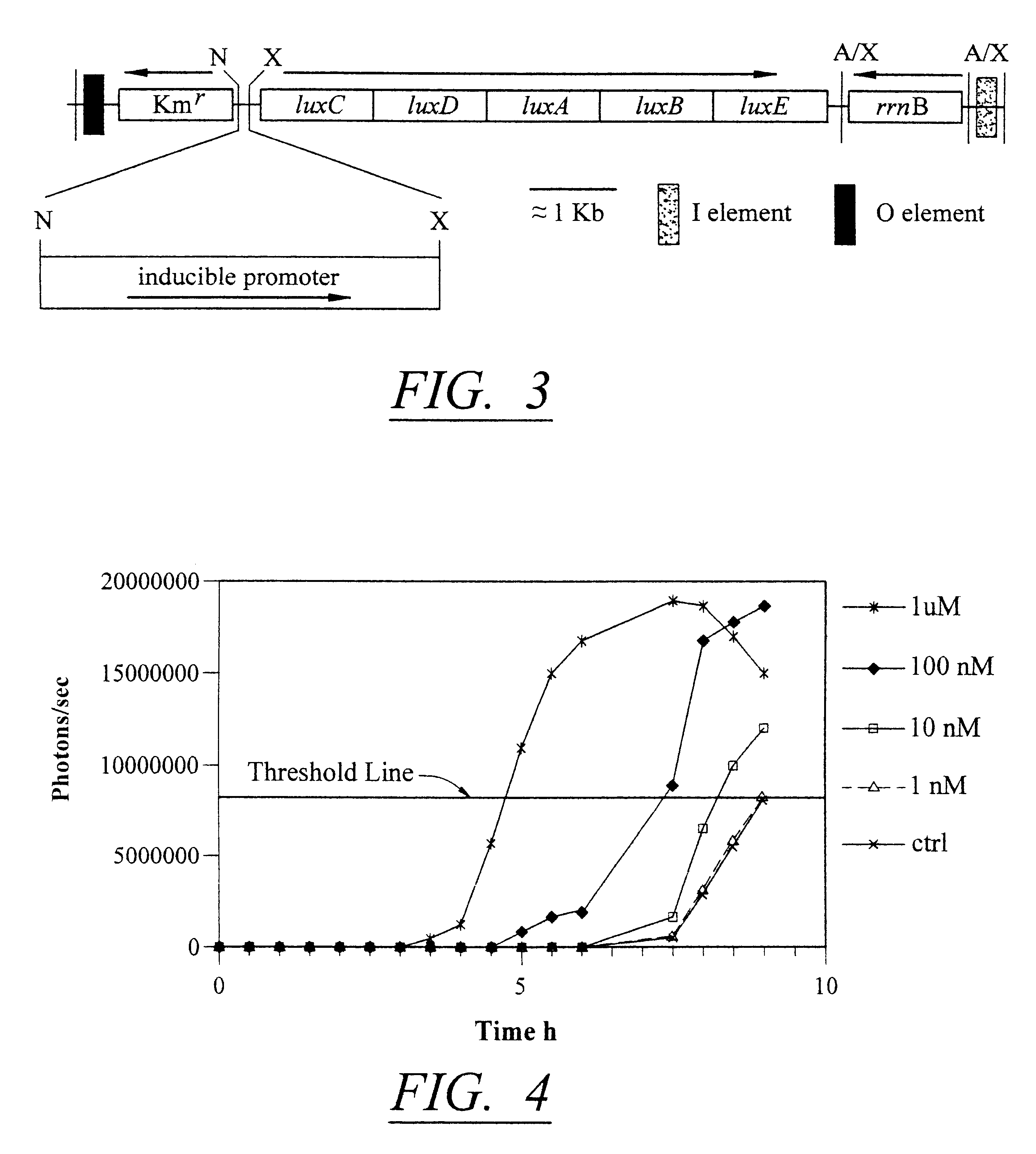
Bioluminescent biosensor device
InactiveUS6544729B2Less stressRapid and sensitive detectionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesBacteroidesBacterial strain
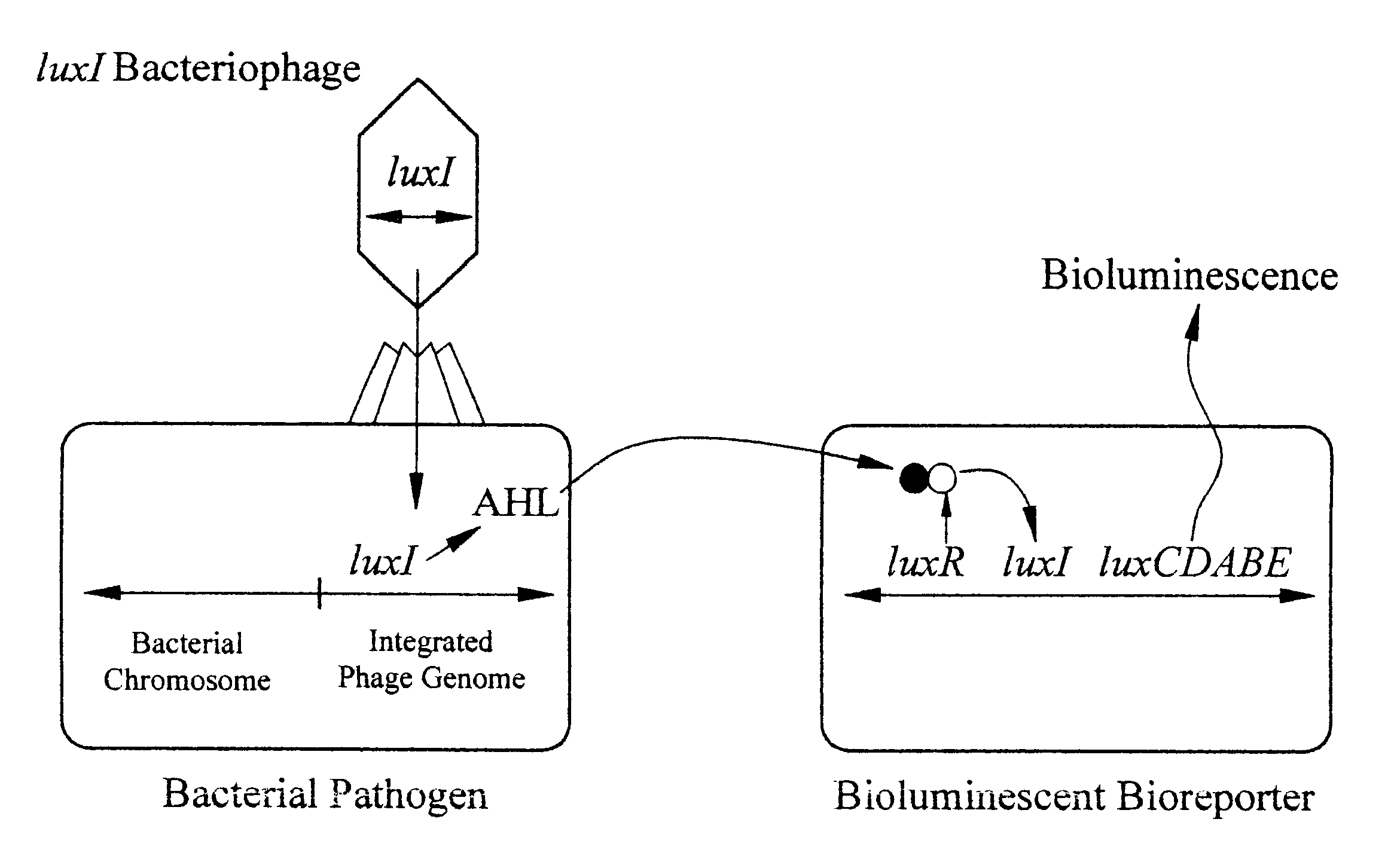
Disclosed are methods and devices for detection of bacteria based on recognition and infection of one or more selected strains of bacteria with bacteriophage genetically modified to cause production of an inducer molecule in the bacterium following phage infection. The inducer molecule is released from the infected bacterium and is detected by genetically modified bacterial bioreporter cells designed to emit bioluminescence upon stimulation by the inducer. Autoamplification of the bioluminescent signal permits detection of low levels of bacteria without sample enrichment. Also disclosed are methods of detection for select bacteria, and kits for detection of select bacteria based on the described technology.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE +1
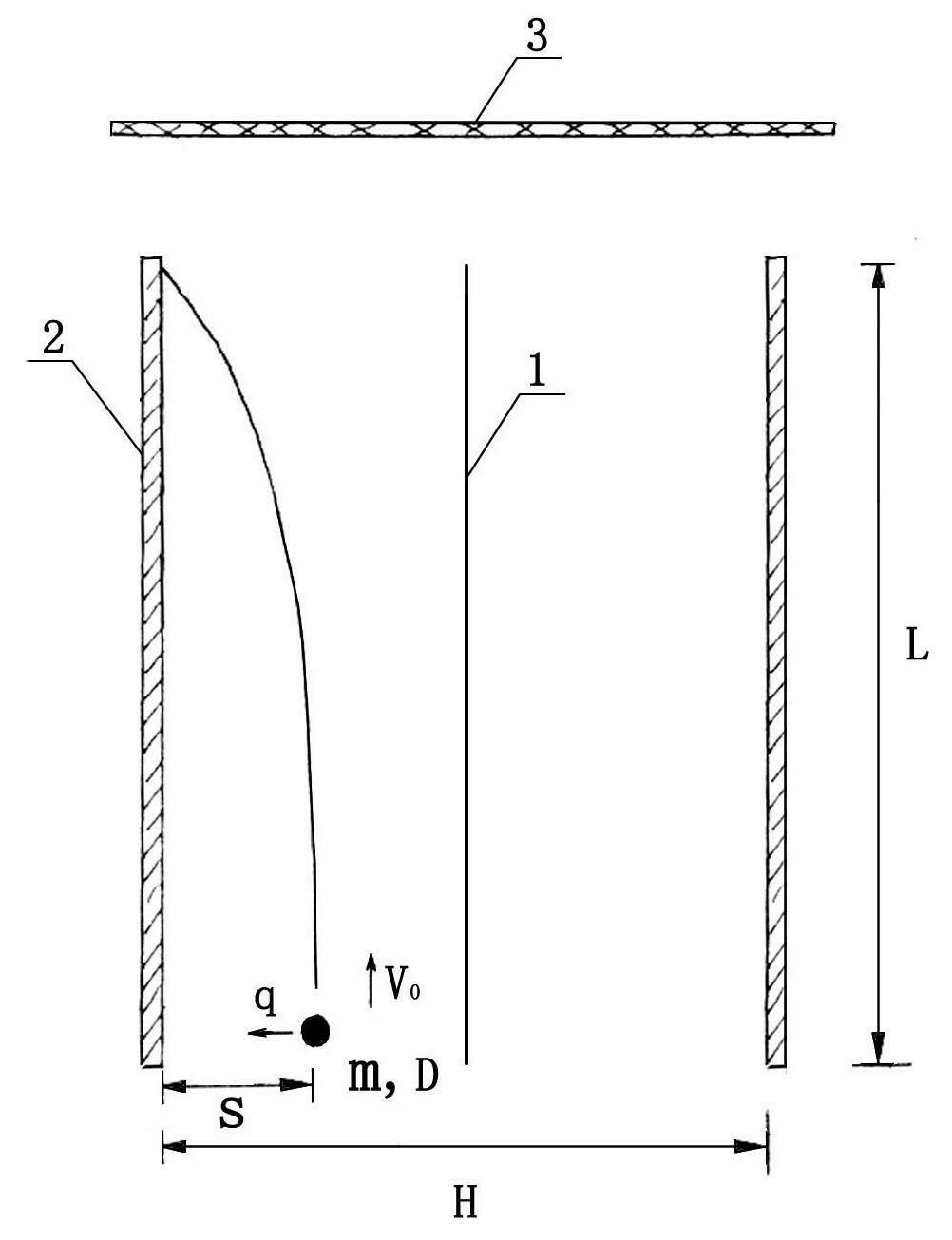
Method and device for fast detection of aerosol particle concentration and size distribution
ActiveCN102147350AEasy to manageUndisturbedParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisChemical physicsSingle mass
The invention discloses a method and a device for fast detection of aerosol particle concentration and size distribution. The method comprises the following steps of: forming a gas flow containing aerosol particles; enabling the gas flow to pass through at least one corona area so that at least partial aerosol particles to be detected in the gas flow are negatively charged; before the actual field measurement, measuring the length L of the corona area, pipe diameter H and gas flow speed v0, searching or measuring the density d of the particles, conducting a calibration experiment for the aerosol particle gas flow having a determined diameter D, then performing an actual measurement and finally calculating the number n of the particles at each level according to the formula YN=22N-2kD2 (22n-2-21-n) nN, in which YN, k, D are known; multiplying the number n of the particles at each level by a single mass of the particles at each level, and then summing the products to obtain a concentration value of the total particles in the gas flow. By the method provided by the invention, the size distribution proportion and the concentration of the aerosol particles in the air or the pipe gas flow can be detected conveniently, sensitively and quickly.
Owner:河北合盛科技有限公司
Nucleic acid amplification method hybridization signal amplification method (HSAM)
InactiveUSRE38442E1Rapid and sensitive detectionRapid and sensitive and standardized detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideSignal amplification
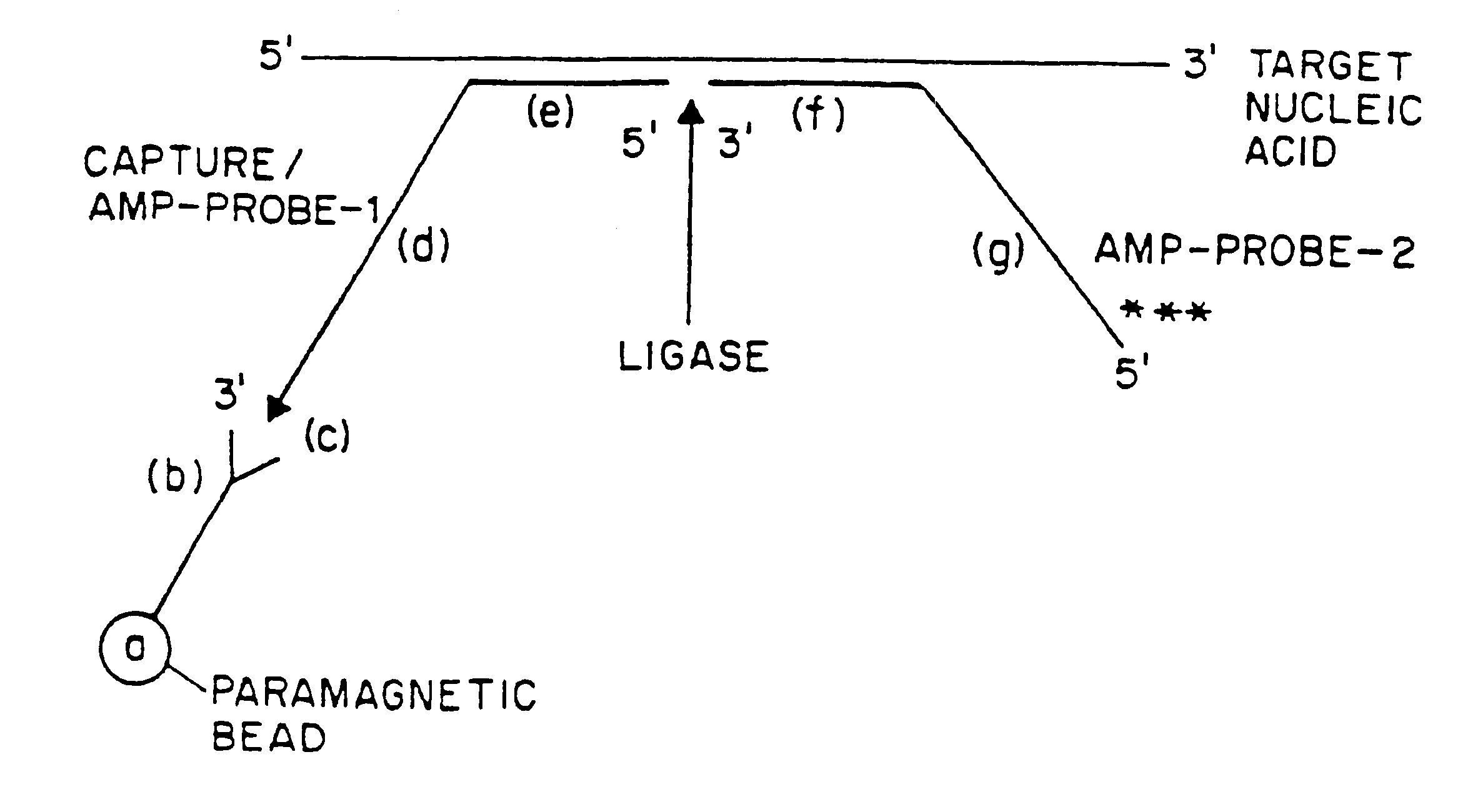
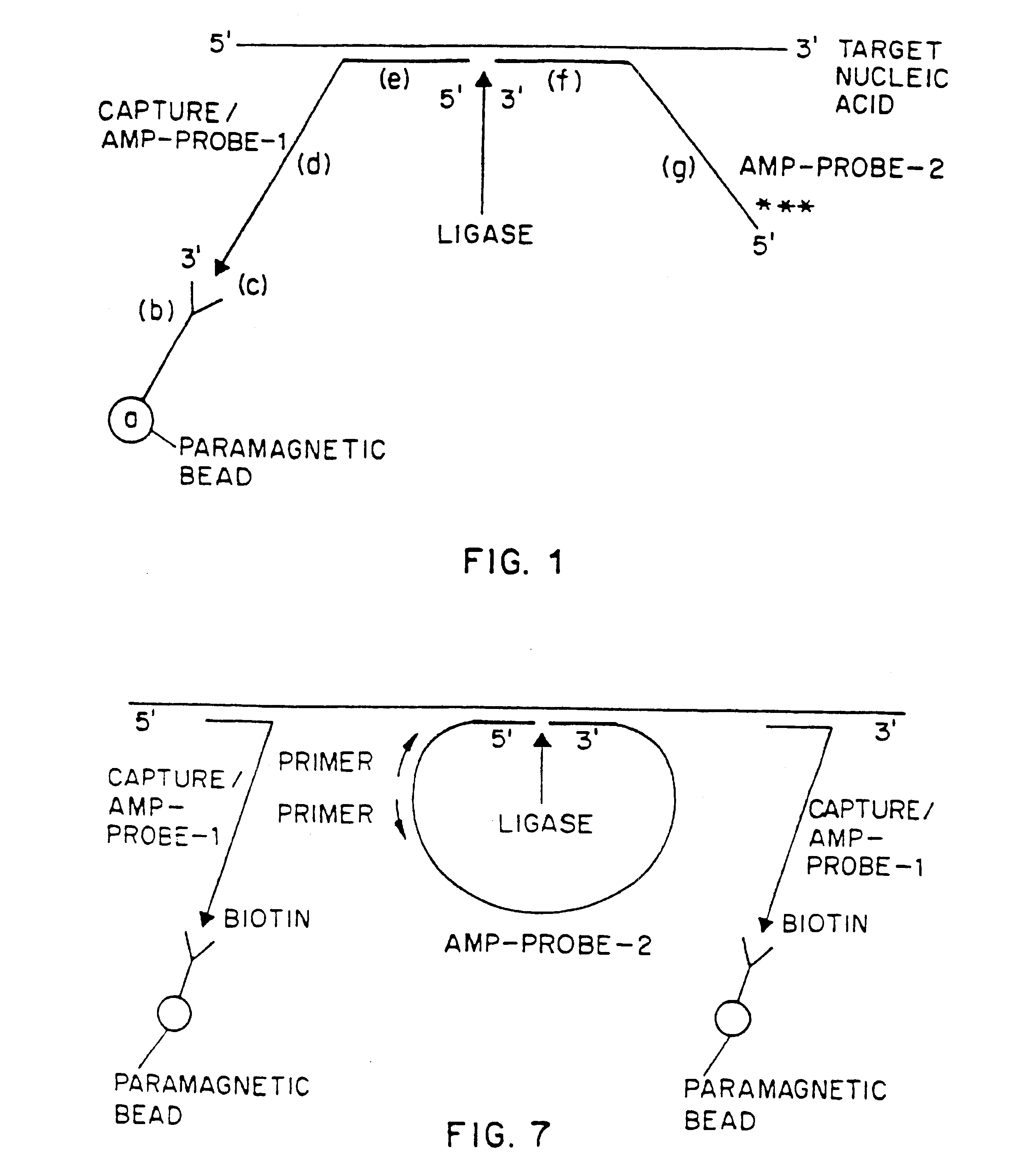
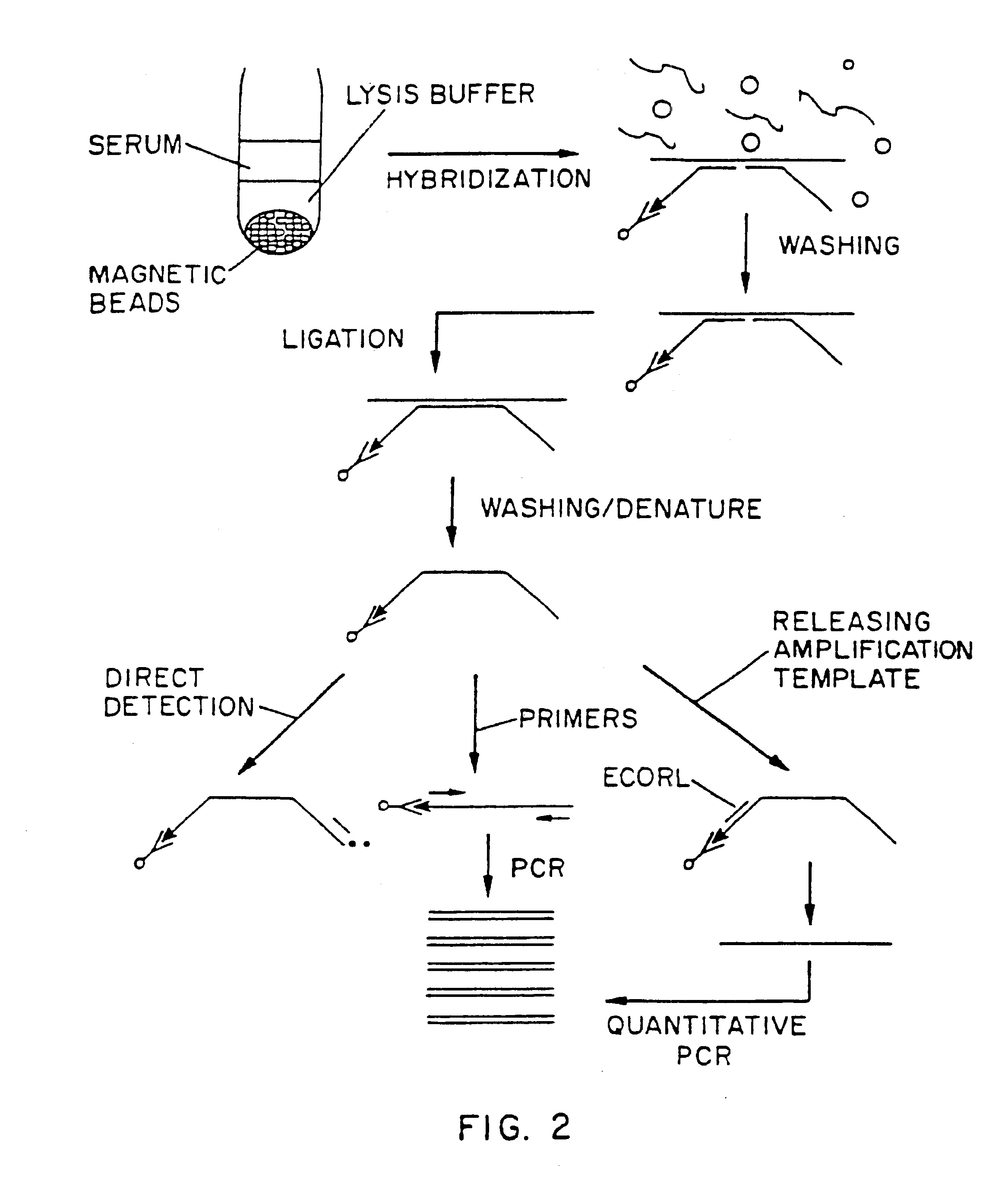
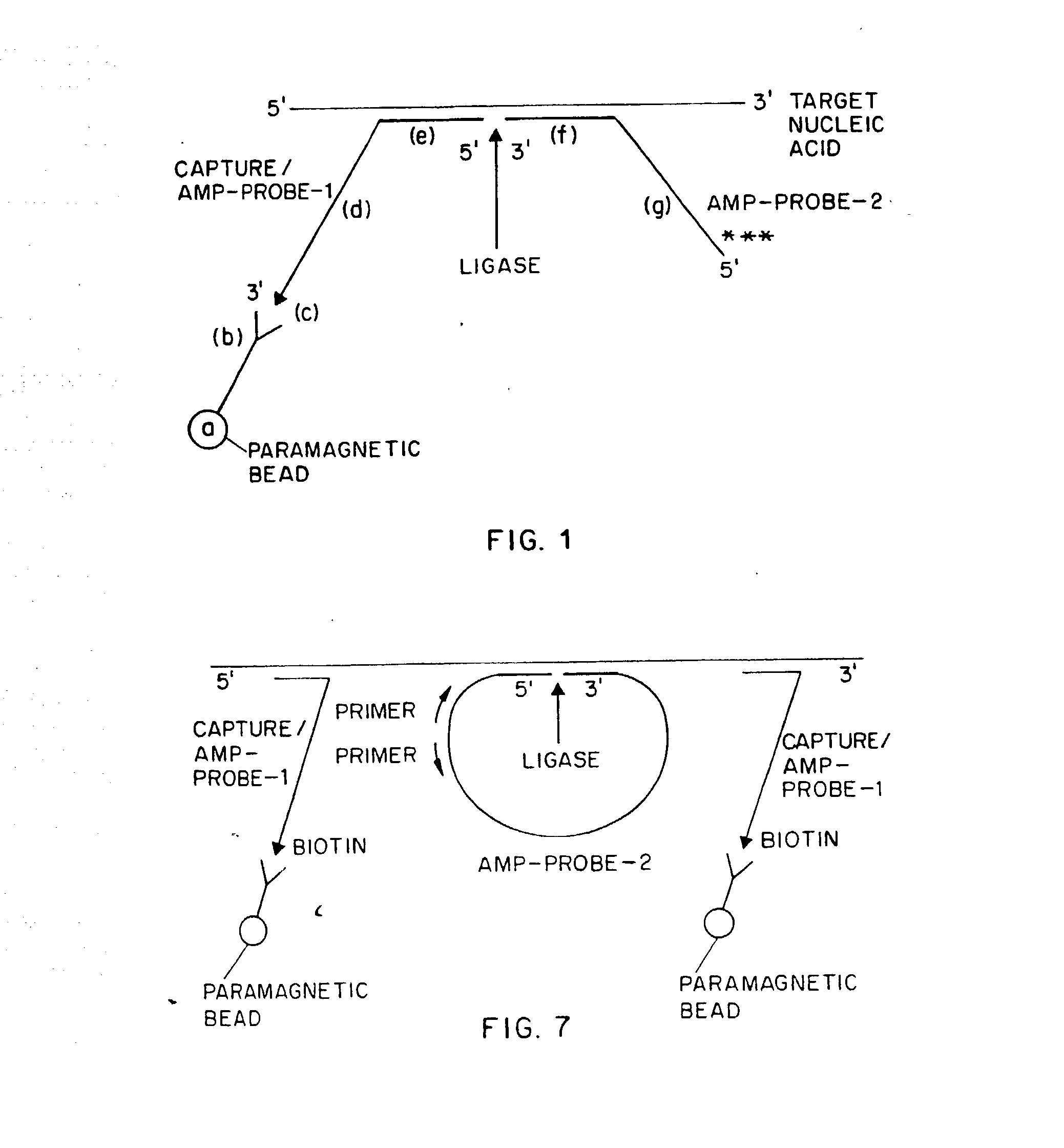
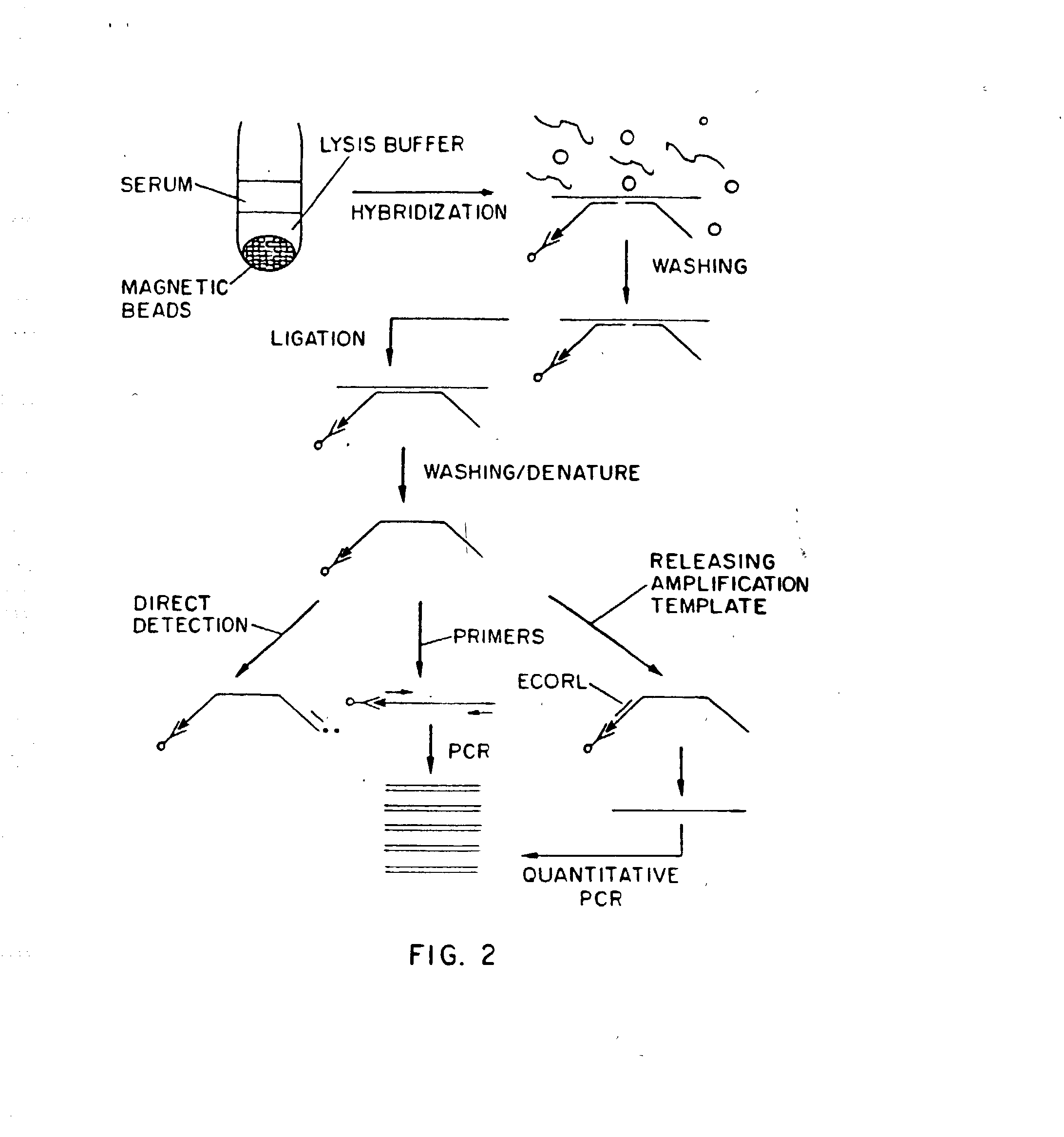
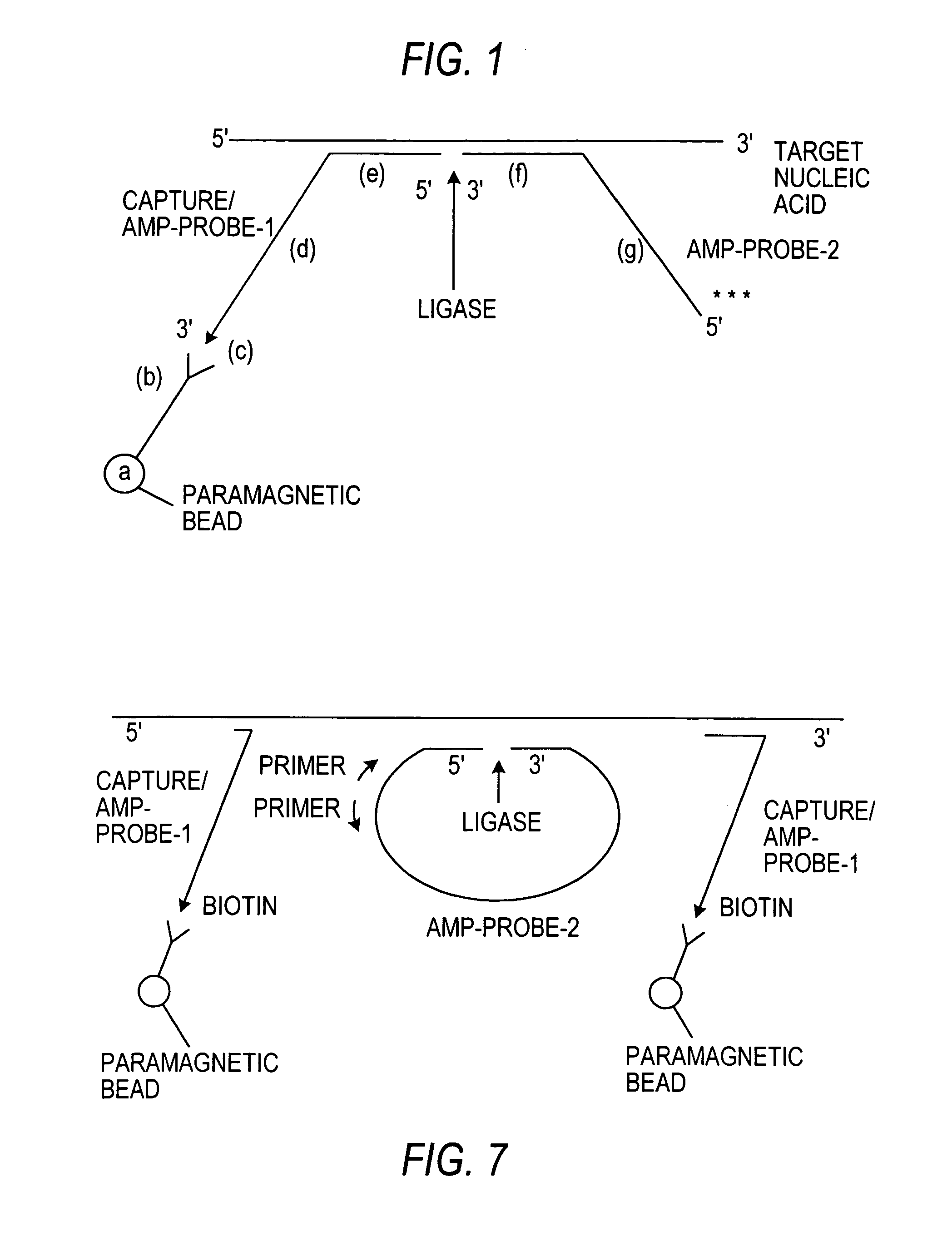
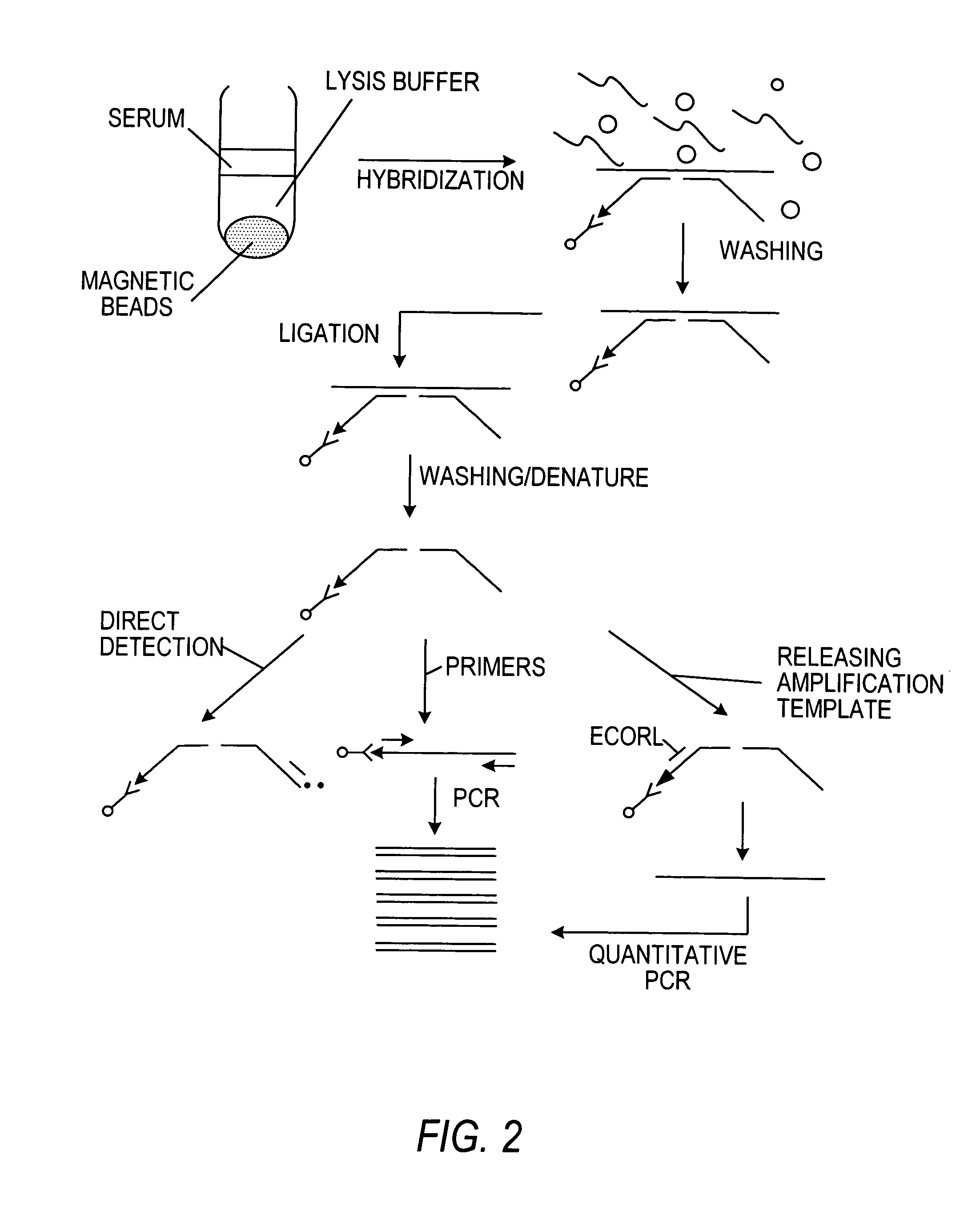
An improved method allowing for rapid sensitive and standardized detection of a target nucleic acid from a pathogenic microorganism or virus or normal or abnormal gene in a sample is provided. The method involves hybridizing a target nucleic acid to several non-overlapping oligonucleotide probes that hybridize to adjacent regions in the target nucleic acid, the probes being referred to capture / amplification probes and amplifications probes, respectively, in the presence of paramagnetic beads coated with a ligand binding moiety. Through the binding of a ligand attached to one end of the capture / amplification probe and the specific hybridization of portions of the probes to adjacent sequences in the target nucleic acid, a complex comprising the target nucleic acid, the probes and the paramagnetic beads is formed. The probes may then ligated together to form a contiguous ligated amplification sequence bound to the beads, which complex may be denatured to remove the target nucleic acid and unligated probes. Alternatively, separate capture and amplification probes may be used which form continuous full-length or circular probes, and may be directly detected or amplified using a suitable amplification technique, e.g., PCR, RAM or HSAM for detection. The detection of the ligated amplification sequence, either directly or following amplification of the ligated amplification sequence, indicates the presence of the target nucleic acid in a sample. Methods for the detection of the ligated amplification sequence, including hybridization signal amplification method and ramification- extension amplification method, are also provided.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Monoclonal antibody of fluoroquinolone medicines as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101921731AIncreased cross-reactivityRapid and Sensitive DetectionTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsFluoro quinolonesAquatic product
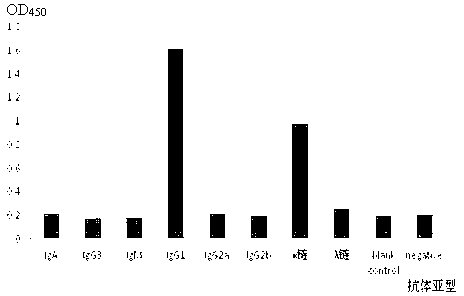
The invention relates to a monoclonal antibody as well as a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to a monoclonal antibody of fluoroquinolone drugs and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of immunochemistry. The monoclonal antibody of fluoroquinolones 4G11' is produced from a mouse hybridoma cell strain 4G11, and the subtype of 4G11 is an IgG1 type. The invention has the advantages that the monoclonal antibody 4G11' produced from the mouse hybridoma cell strain 4G11 has high cross reaction rate with various fluoroquinolone medicines and can be produced in large quantity and used for preparing an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit and colloidal gold test paper for detecting the fluoroquinolone medicines, achieves the purpose of quickly and sensitively detecting the residual fluoroquinolone medicines in milk, muscle and aquatic products and provides a basis for developing a kit for detecting various residual fluoroquinolone medicines.
Owner:深圳市华科瑞科技有限公司
Method for detecting phthalic acid ester compound concentration based on optical fiber immunosense
InactiveCN105424663AWide range of recognitionRealize quantitative detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical compoundAntibody
The invention discloses a method for detecting the phthalic acid ester compound concentration based on optical fiber immunosense. The method includes the steps that firstly, an optical fiber immunosense detection system is established; secondly, a standard inhibition curve is established, wherein (2.1), a fluorescently-labeled antibody solution and a phthalic acid ester compound standard solution with the known concentration are mixed, data obtained after pre-reaction are input to the optical fiber immunosense detection system, and a response signal is obtained; (2.2), the concentration of phthalic acid ester compounds is changed, the step of (2.1) is repeated, and response signals under different concentrations are obtained; (2.3) the standard inhibition curve is drawn according to the concentration logarithm value and the inhibition ratio; (3.1), the step of (2.1) is repeated on the phthalic acid ester compounds to be detected, and a response signal and the inhibition ratio are obtained; (3.2) according to the standard inhibition curve, the concentration of the phthalic acid ester compounds to be detected can be obtained. The method can detect various kinds of PAEs at the same time and is high in sensitivity and precision and fast in detection.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Preparation and application of fluorescent compound having sensing function on methamphetamine and methamphetamine analogues and preparation and application of fluorescent sensing thin film
ActiveCN104892606AStrong supramolecular propertiesRich Assembly BehaviorOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldCholesterol
The invention discloses preparation and an application of a fluorescent compound having a sensing function on methamphetamine and methamphetamine analogues and preparation and an application of a fluorescent sensing thin film, and belongs to the technical field of fluorescent compound preparation. The fluorescent compound contains a cholesterol fragment and a 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic acid anhydride unit, the cholesterol fragment has the advantages of rigid skeleton, multiple chiral centers and strong van der Waals effect and the like, 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic acid anhydride has high fluorescence quantum yield, good photochemistry stability and strong pi-pi stacking interaction, and the construction units make the prepared fluorescent compound have supramolecular characteristics and extremely rich assembly behaviors simultaneously. The prepared sensing thin film has the advantages of controllable micro-morphology, good stability and high sensitivity, and can be used repeatedly; through device formation and combining development with a dedicated fluorescence detection platform, the sensing thin film is expected to be used for a dedicated detector for super sensitive gas-phase detection of methamphetamine and the methamphetamine analogues, and provides a technical support for drug investigation detective works.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Nucleic acid amplification methods
InactiveUS20070269799A9Rapid and sensitive detectionRapid and sensitive and standardized detection and quantitationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayGenomic DNA
The present invention relates to assays and kits for carrying out said assays for the rapid, automated detection of infectious pathogenic agents and normal and abnormal genes. The present invention further relates to methods for general amplification of genomic DNA and total mRNAs and for analyzing differential mRNA expression using the amplification methods disclosed herein.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Enrofloxacin monoclonal antibody and application
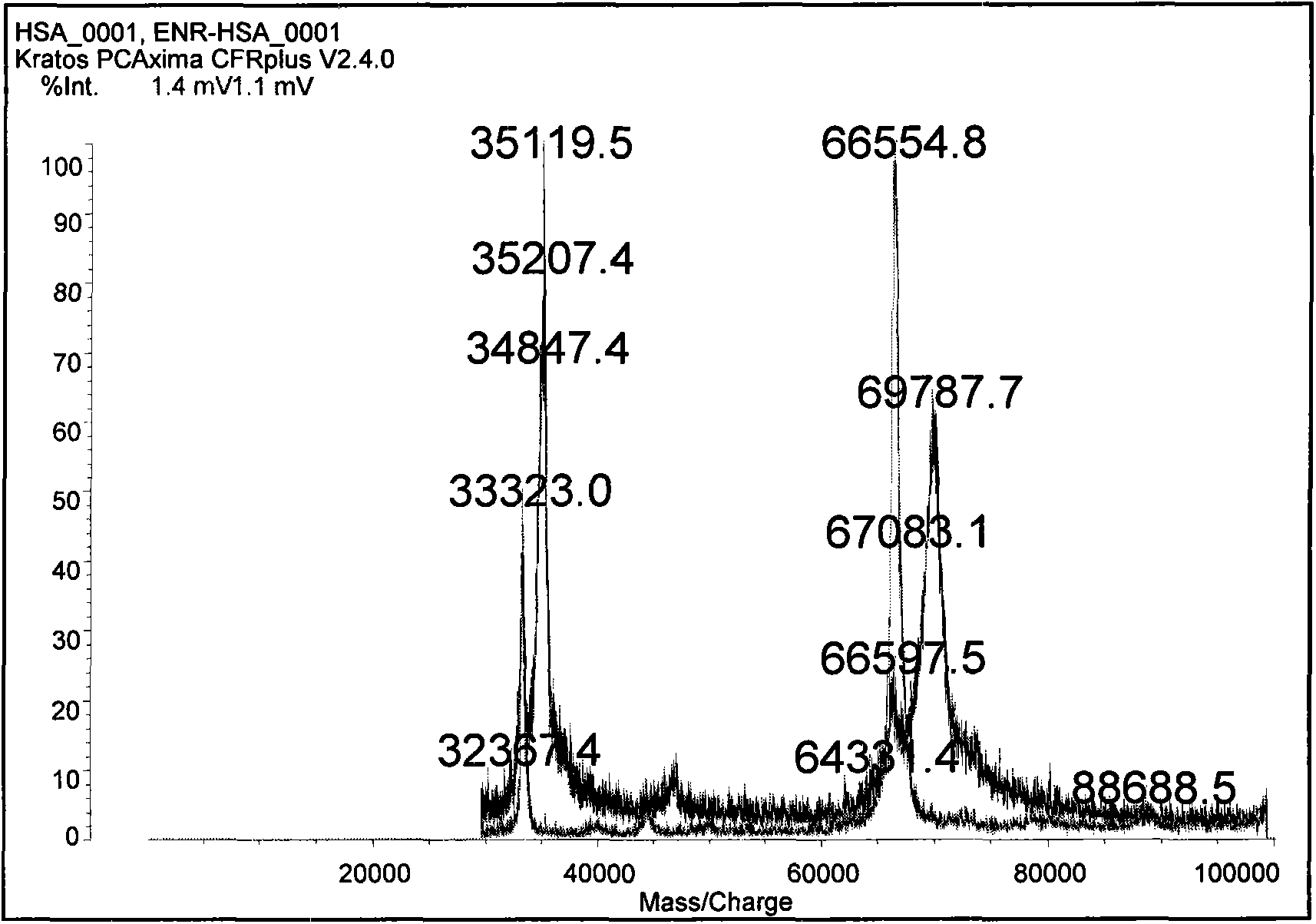
InactiveCN101565690AStrong specificityRapid and Sensitive DetectionTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsBALB/cIon exchange
The invention relates to an enrofloxacin monoclonal antibody and application, relates to hybridoma strains thereof, and belongs to the technical field of immunochemistry. The enrofloxacin monoclonal antibody is generated by mouse hybridoma strains 6A4 and 8E6. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: enrofloxacin and carrier proteins BSA, HAS and OVA are coupled by a carbodiimide method to synthesize artificial immunogens EnR-BSA, EnR-HSA and coatingen EnR-OVA; a Balb / c mouse is immunized by the synthesized artificial immunogens EnR-BSA and EnR-HSA; a spleen cell of the immunized mouse is extracted to be fused with a SP2 / O myeloma cell and coated by the coatingen EnR-OVA; indirect ELISA method and indirect competition ELISA method are established to screen the hybridoma strains which can stably secrete specific antibody; the obtained cell strain immunized Balb / c mouse is used to prepare ascites; the ascites is purified by a caprylic acid-ammonium method and an ion exchange method; and valences of antibodies of two purified cell strains reach over 1.024*10 and 1.28*10. The monoclonal antibody has strong specificity, can be applied to preparation of enrofloxacin residue inspection kit and aerosol test strip, and can sensibly and quickly inspect the enrofloxacin residue.
Owner:泰州市蛋白质工程研究院
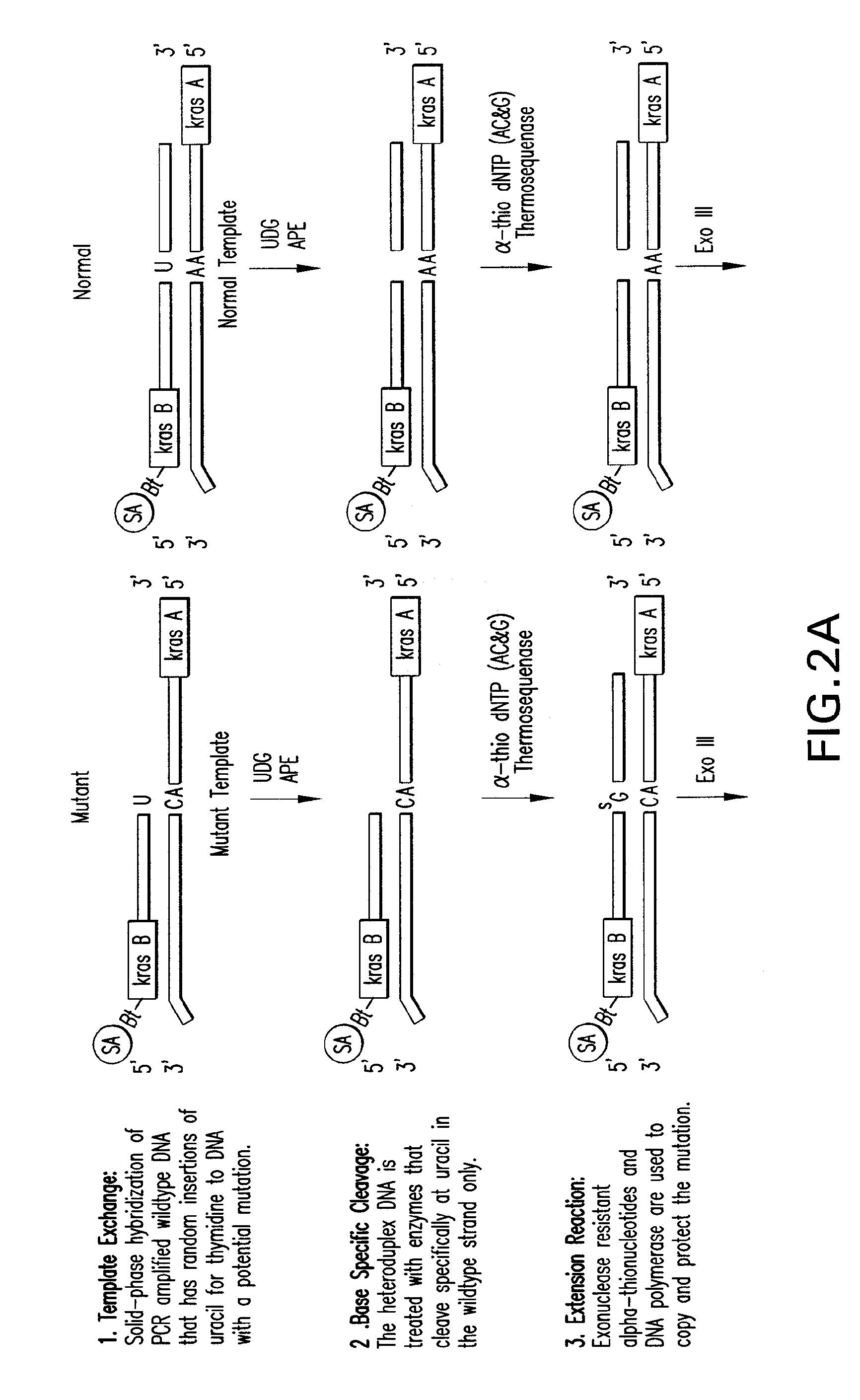
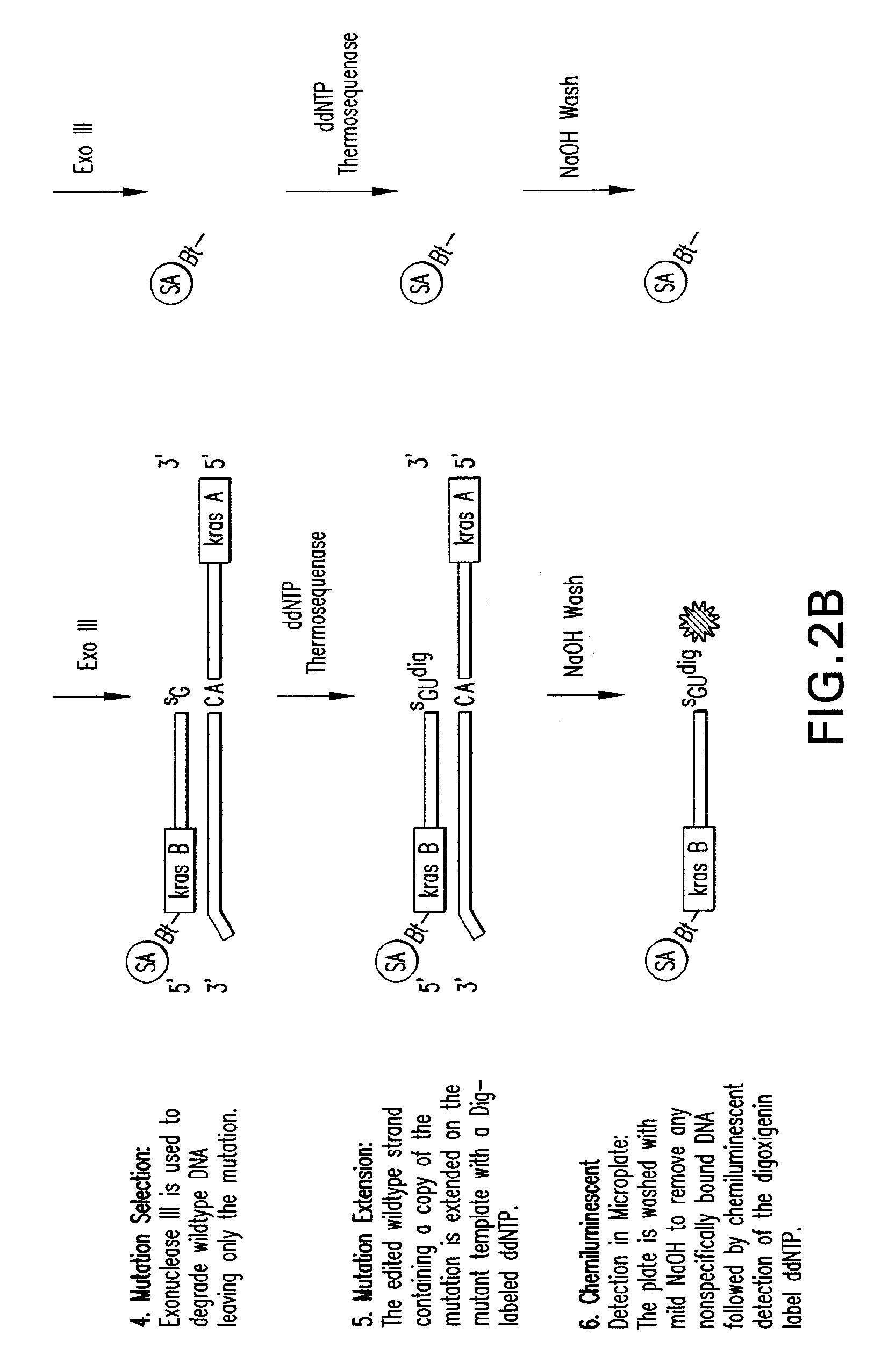
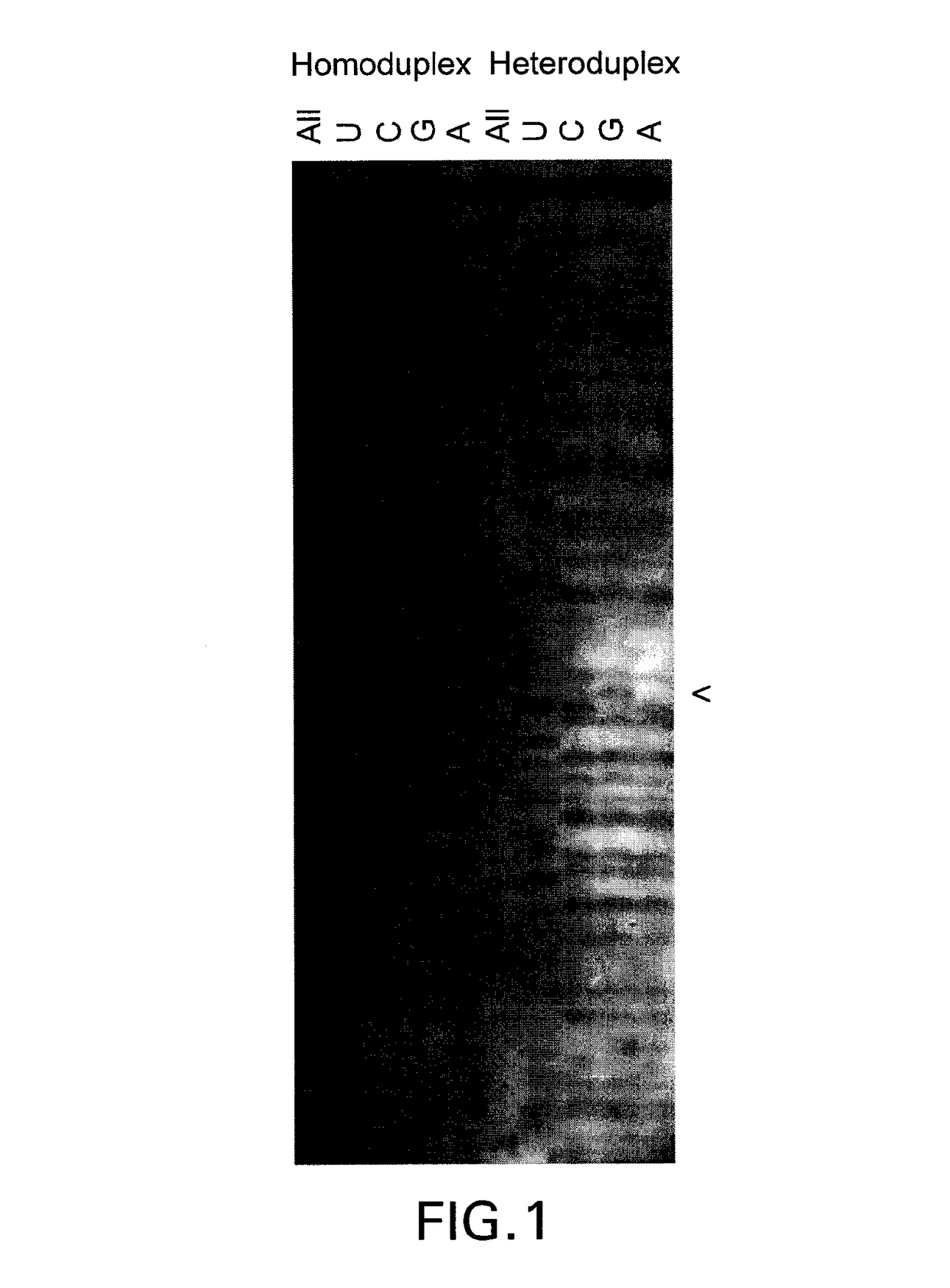
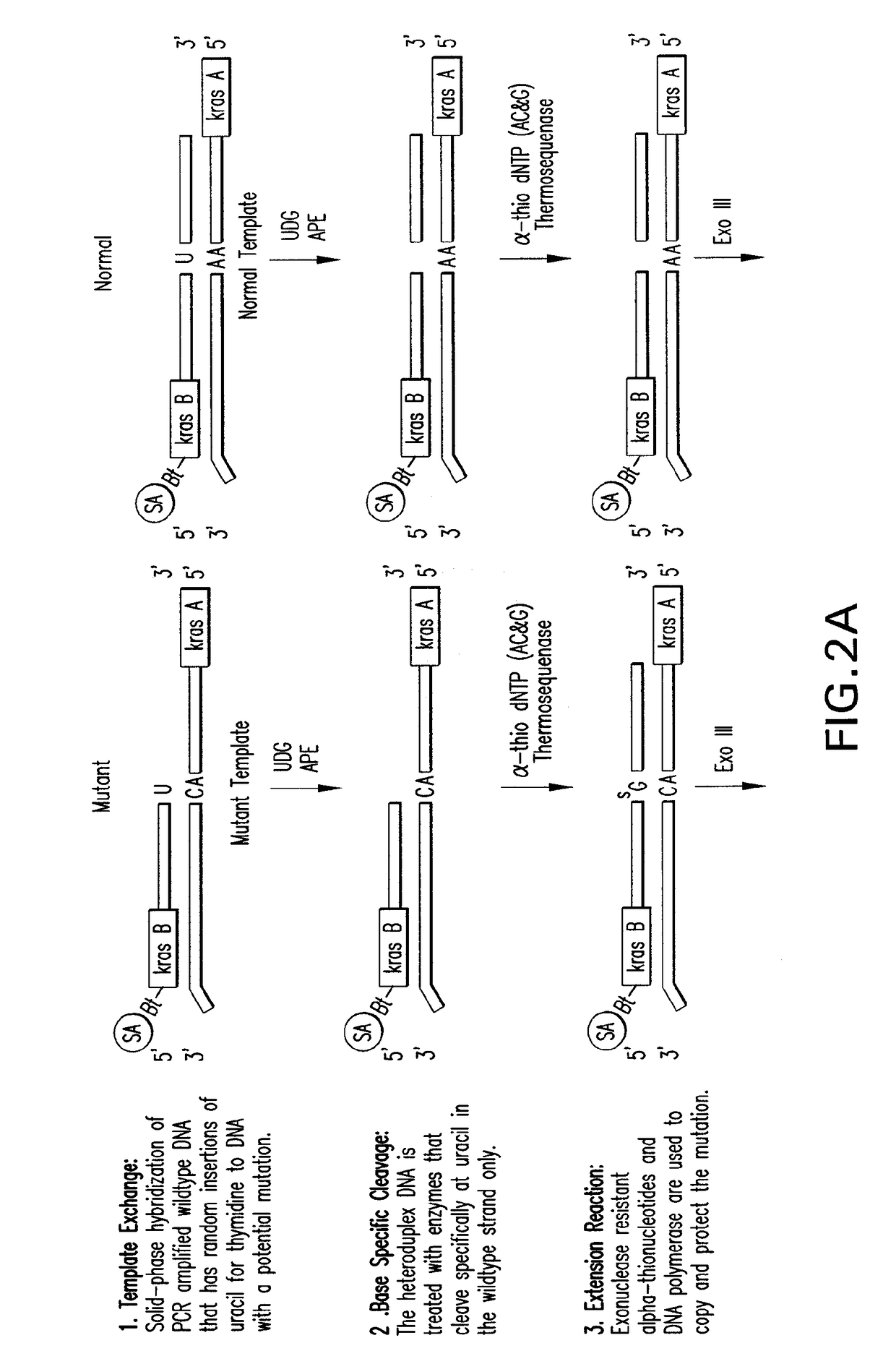
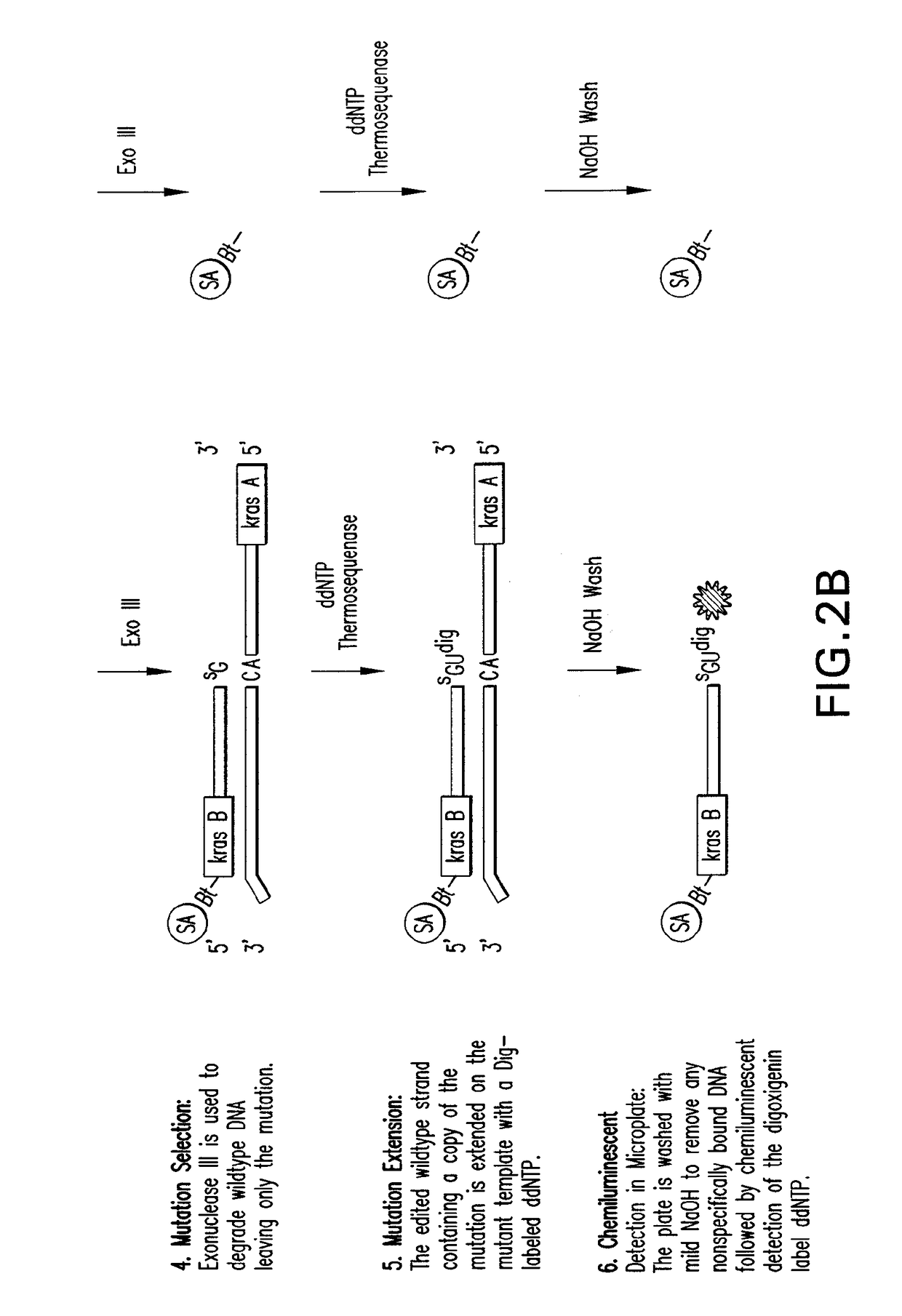
Methods of screening nucleic acids for single nucleotide variations
InactiveUS20090053715A1Rapid and sensitive detectionLimit scopeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsSugar nucleotide
Disclosed are methods and compositions for detecting variation in nucleic acids. The disclosed method compares the sequence of a nucleic acid of interest with the sequence of a reference nucleic acid to sensitively identify variations between the sequence of a nucleic acid of interest and the sequence of a reference nucleic acid. The disclosed method generally involves excision and replacement of selected nucleotides in nucleic acid strands hybridized to other strands. In the method, if the excised nucleotide was mismatched with the nucleotide in the other, hybridized strand, then the replacement nucleotide will not be mismatched. If the excised nucleotide was not mismatched with the nucleotide in the other, hybridized strand, then the excised nucleotide is not replaced. This difference allows detection of variation in the nucleic acid of interest. In some forms of the method, by replacing excised nucleotides with nuclease-resistant nucleotides, strands in which excised nucleotides are replaced will be resistant to nuclease digestion while strands in which excised nucleotides are not replaced will be sensitive to nuclease digestion. By exposing the hybridizing nucleic acids to nuclease following replacement of excised nucleotides, the strands in which excised nucleotides are not replaced can be destroyed by the nuclease while strands in which excised nucleotides are replaced can be preserved. The remaining strands can then be detected and whether the strand survived nuclease digestion can be noted. Strands that survive nuclease digestion are indicative of the presence of variation in the nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:INSIGHT GENETICS INC
Quick nitrite detection method based on nanogold
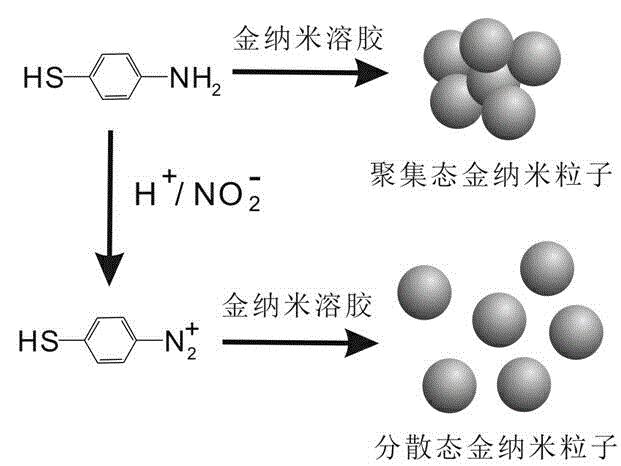
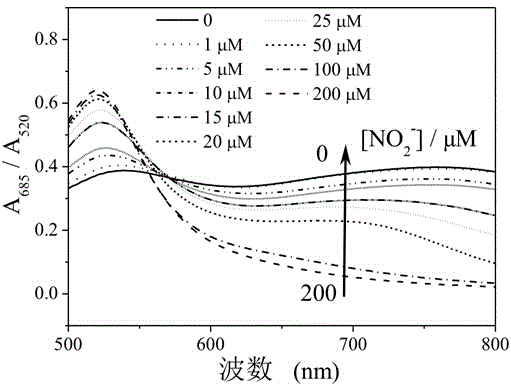
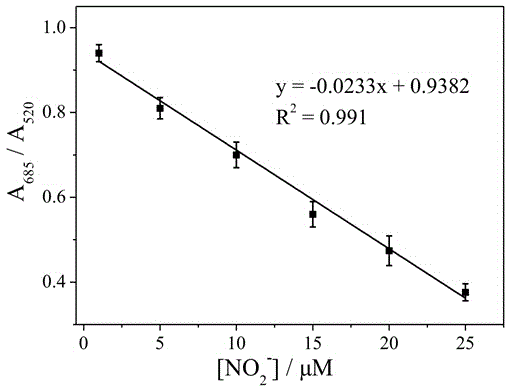
InactiveCN104614370AWide detection rangeGood linear relationshipMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsUv vis absorbanceNitrite concentration
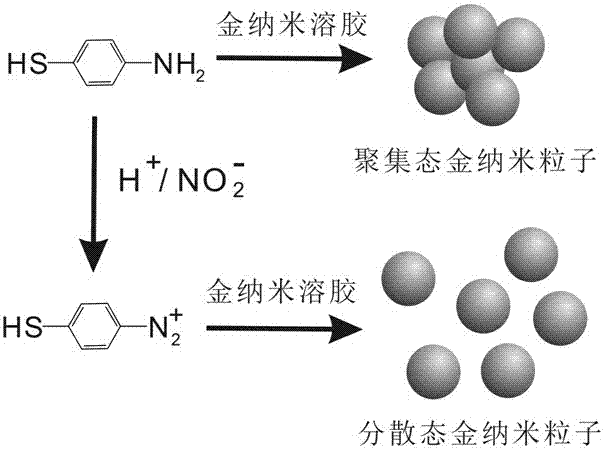
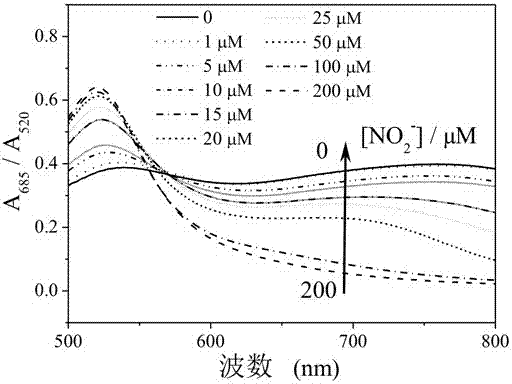
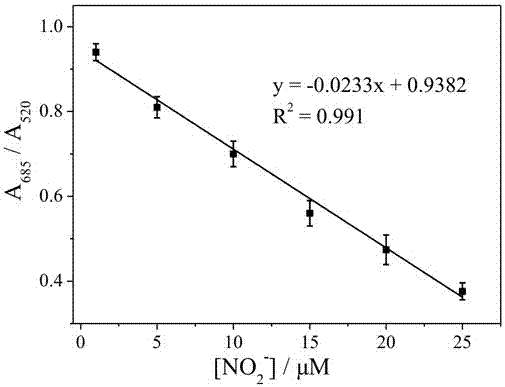
The invention discloses a quick nitrite detection method based on nanogold. The method comprises steps as follows: a standard solution containing nitrite is added to an acid aqueous solution of p-aminothiophenol, nanogold sol is added after a period of incubation, the nanogold sol is detected by an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer, ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum data are acquired, the specific value of the absorbance in 685 nm and 520 nm positions is taken as the longitudinal coordinate, the concentration of the standard solution containing the nitrite is taken as the horizontal coordinate, a standard curve of the nitrite is obtained through fitting, the A685 / A520 value of a to-be-detected solution containing nitrite is introduced into a function relation of the standard curve of the nitrite, and quantitative detection of the nitrite is realized. The method is simple in step, low in cost, good in selectivity, high in detection speed and broad in application prospect, the nanogold is not required to be modified, special instrument equipment is not required, the detection range of the nitrite concentration is wide, and convenient, quick and sensitive detection can be realized.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
Method for authenticating pork, beef, mutton and products thereof
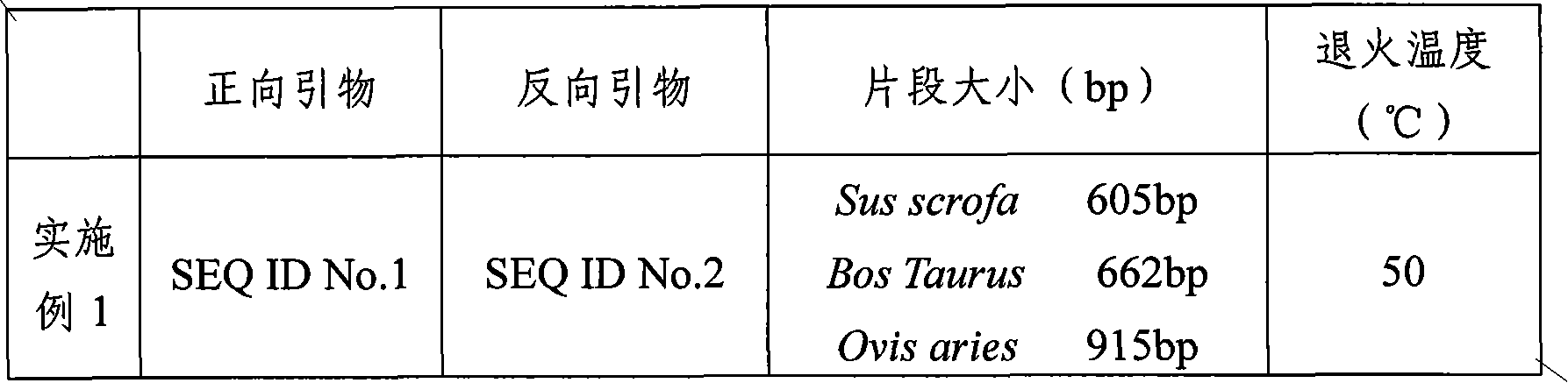
ActiveCN102337328ARapid and Sensitive DetectionThe identification method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
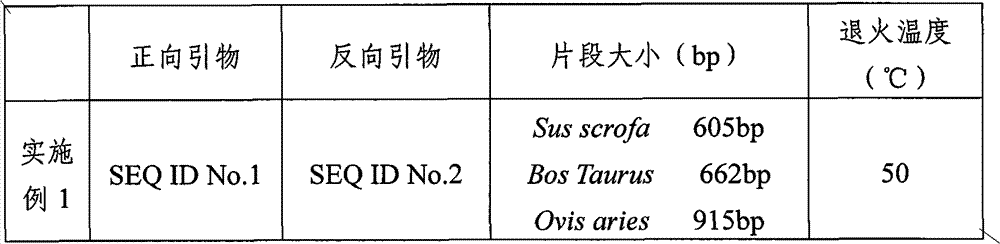
The invention provides a pair of PCR primers used for authenticating pork, beef, mutton and products thereof. The nucleotide sequences of the primers are represented by SEQ ID No.1 and No.2. The invention also provides a kit comprising the primers, and a method for authenticating pork, beef, mutton and products thereof. The method provided by the invention is characterized in accurate result and high sensitivity. With the method provided by the invention, adulterate fresh meats in markets can be rapidly detected. Also, the method plays an important role in individual discriminating and origintracing researches. According to the authenticating method provided by the invention, only one pair of PCR primers is required for authenticating fresh pork, beef, and mutton, such that the authentication is simple and rapid. With the method, adulterate fresh meats in markets can be rapidly and sensitively detected, and great significance is provided for pig individual discriminating and origin tracing researches.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
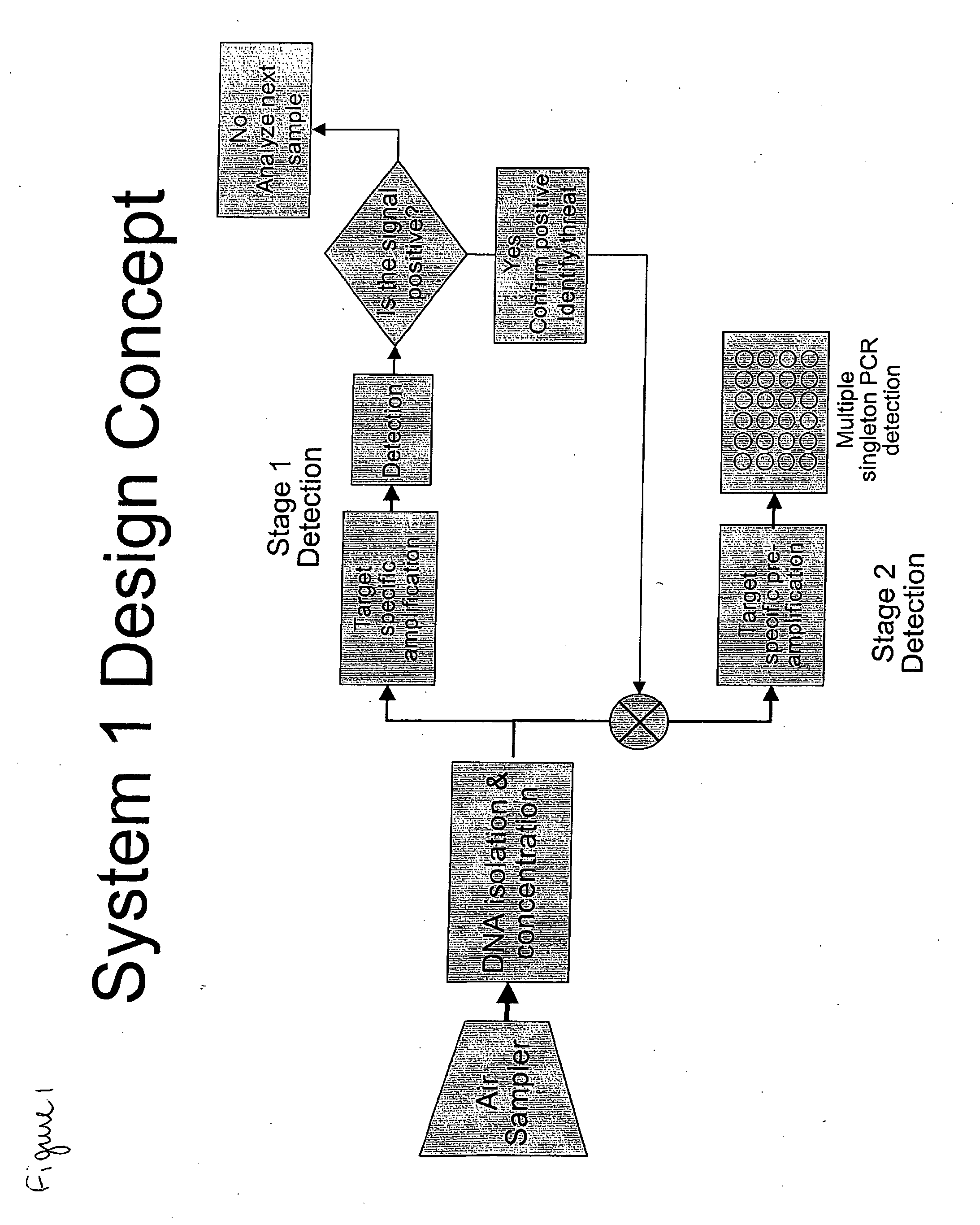
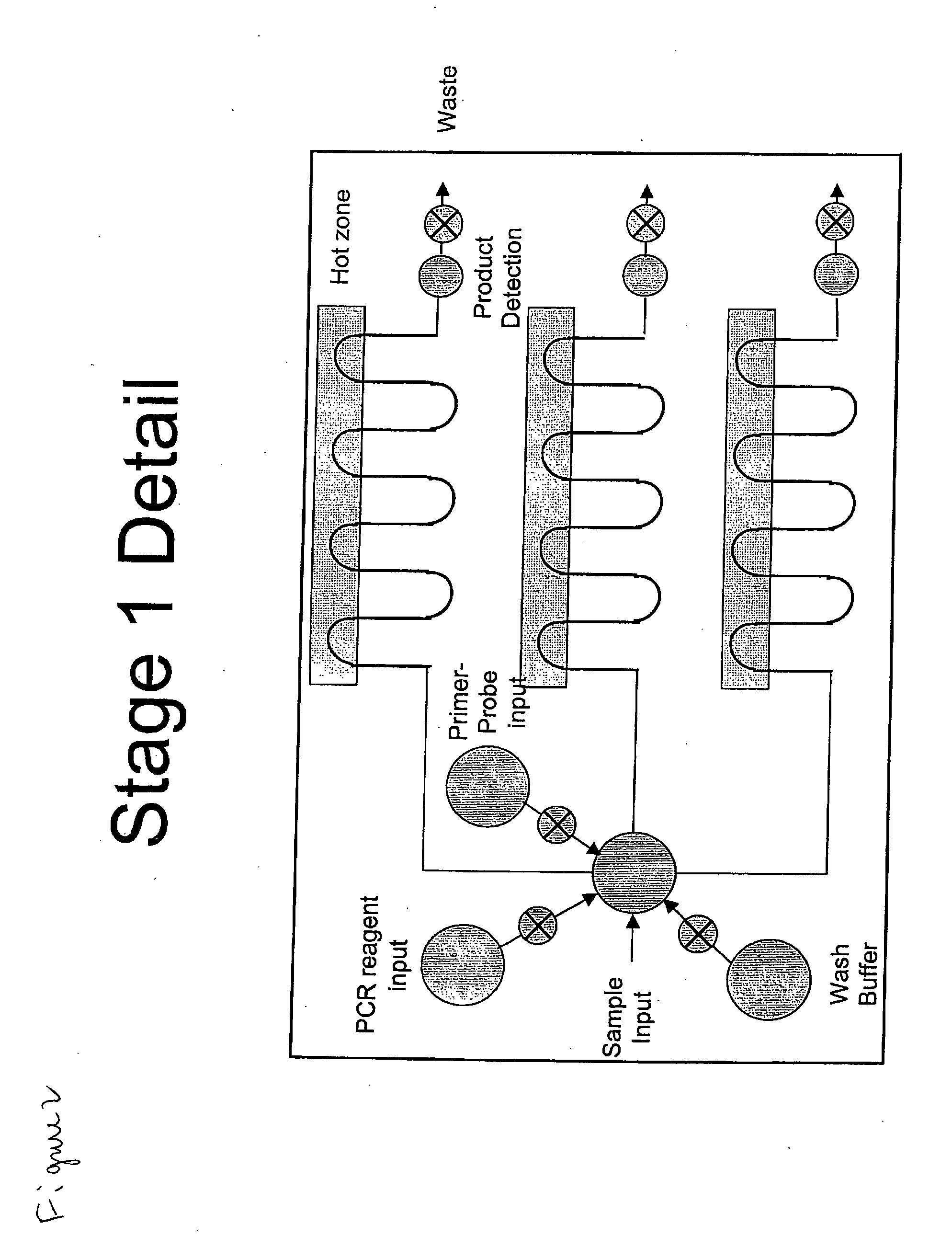
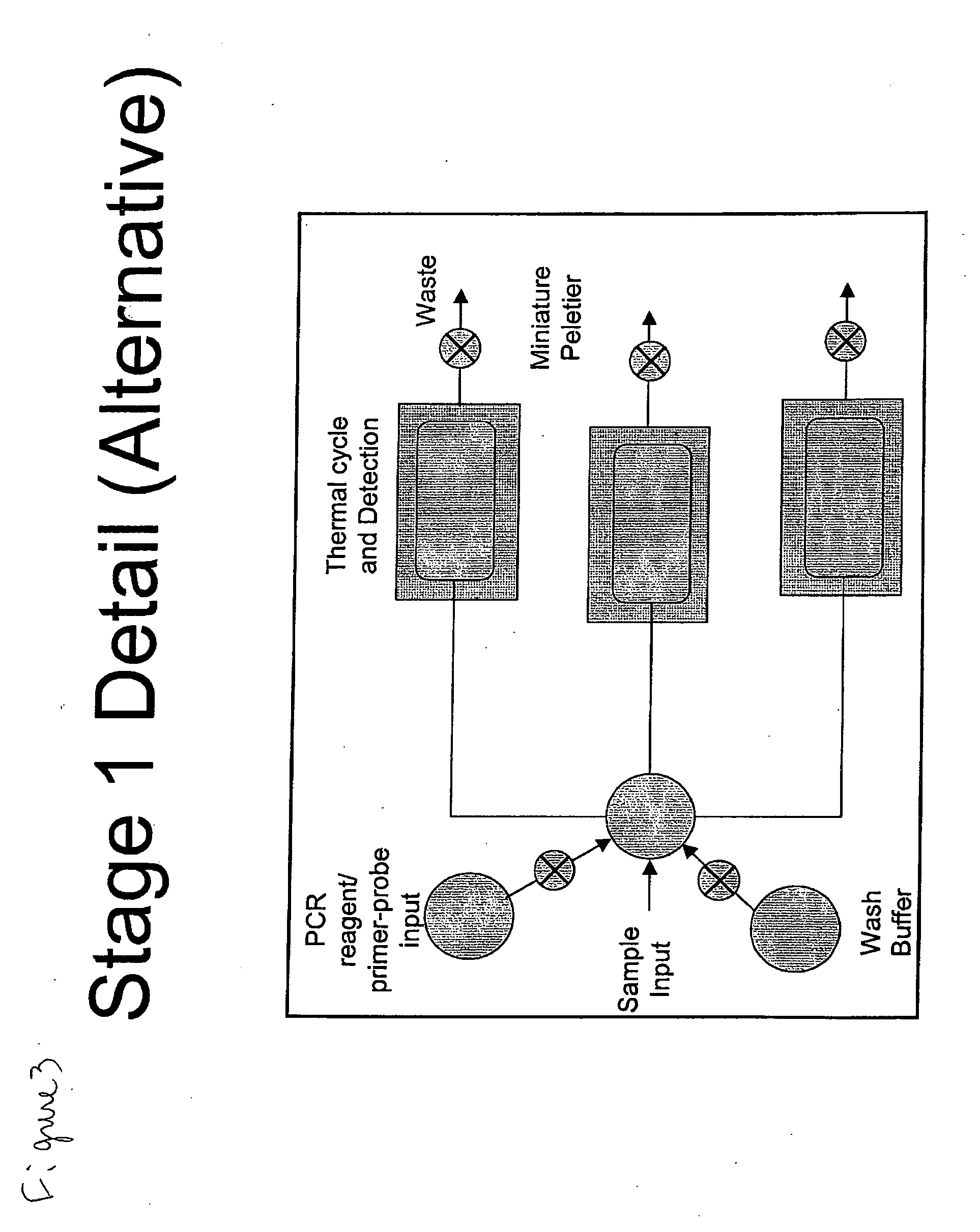
System for the Detection of a Biological Pathogen and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20110251084A1Rapid and sensitive detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTarget analysisAnalyte
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for detecting hemoglobin based on GQDs (graphene quantum dots)
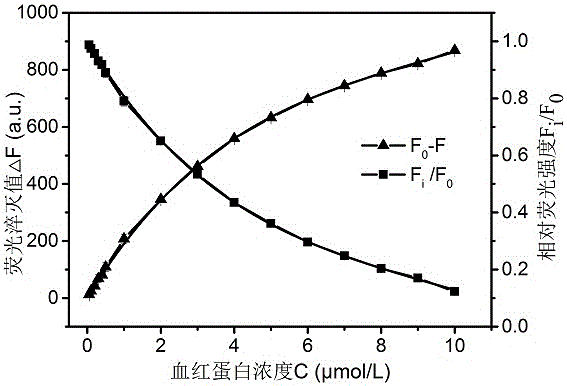
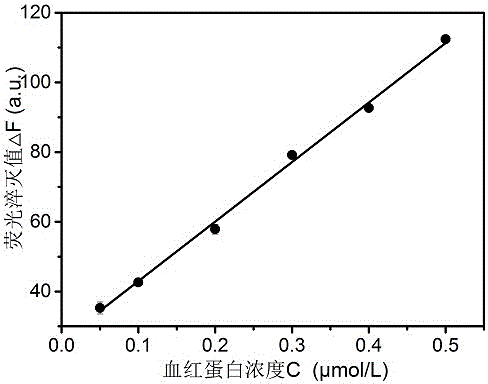
InactiveCN106770100AEasy to operateEfficient and accurate operationFluorescence/phosphorescencePhysical chemistryFluorescence spectrometry
The invention relates to a method for detecting hemoglobin based on GQDs (graphene quantum dots). The method comprises two main points as follows: (1) establishment of a linear relation: the fluorescence intensity of the GQDs is weakened with an increase of the concentration of a hemoglobin solution according to a fluorescence spectrogram, and a fluorescence quenching value and the concentration of the hemoglobin solution have a good linear relation; (2) detection of a simulation sample: the fluorescence intensity of a to-be-detected hemoglobin solution is detected, and the content of hemoglobin in the to-be-detected hemoglobin solution is determined according to the linear relation. Meanwhile, the method can also be applied to content detection of hemoglobin in a mixed system, and a result proves that the method has the advantage of high-sensitivity detection, thereby having a broad application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Nucleic acid amplification methods
InactiveUS20140038238A1Rapid and sensitive and standardized detection and quantitationRapid and sensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyGeneMrna expression
The present invention relates to assays and kits for carrying out said assays for the rapid, automated detection of infectious pathogenic agents and normal and abnormal genes. The present invention further relates to methods for general amplification of total mRNAs and for analyzing differential mRNA expression using the amplification methods disclosed herein.
Owner:ZHANG DAVID Y
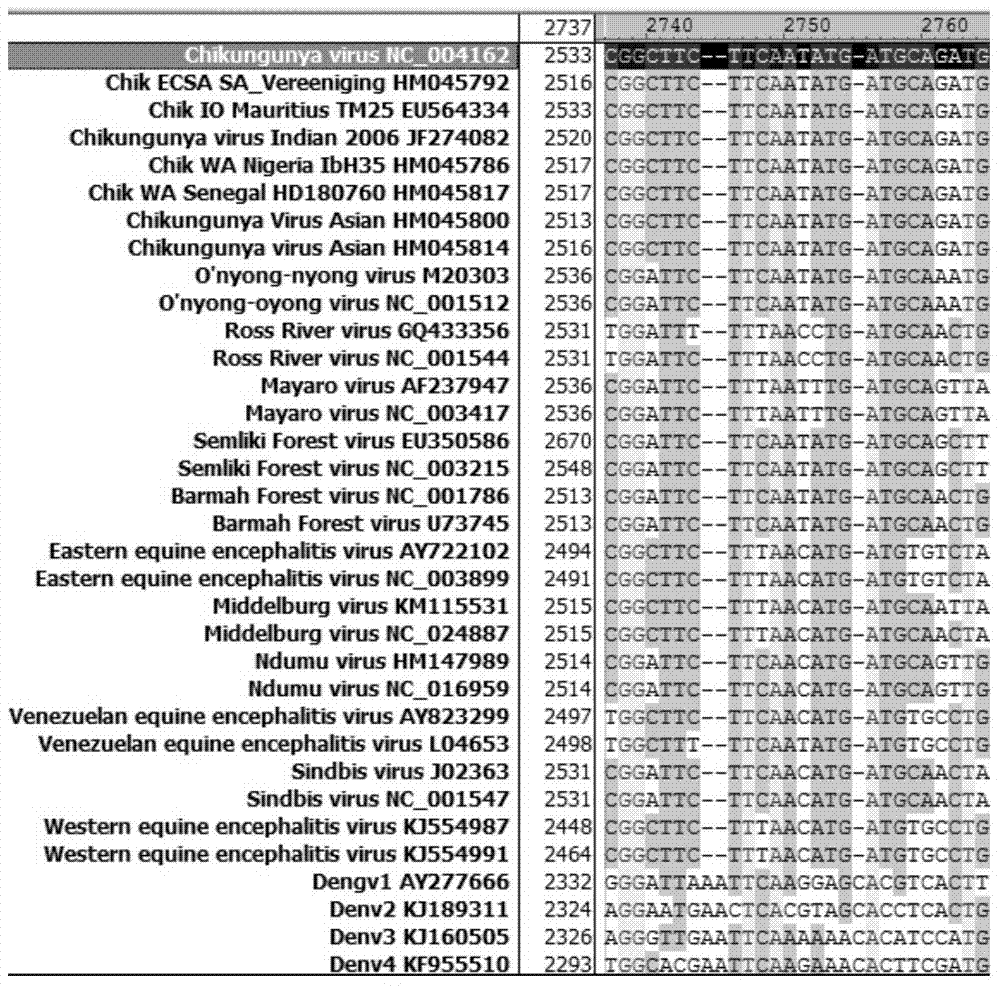
Kit and detection method for inverse transcription PCR detection of chikungunya virus
InactiveCN104513865AReduce contentHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleotideChikungunya virus RNA
The invention discloses a kit and detection method for inverse transcription PCR detection of chikungunya virus, the kit for inverse transcription PCR detection of chikungunya virus comprises primers, probes and a FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer)-PCR standard substance, the primers are an upstream primer and a downstream primer; the probes comprise 6-FAM (carboxyfluorescein) probe and a LCRed640 probe; the upstream primer has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No.1, the 6-FAM probe has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No.2; the LCRed640 probe has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No.3, and the downstream primer has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No.4. The inverse transcription PCR system can effectively amplify RNA, namely can fast and efficiently amplify chikungunya virus RNA nucleic acid in clinical samples.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for detecting stannous ions by using rhodamine fluorescence probe
InactiveCN105907387AUndisturbedHigh fluorescence intensityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceLength waveUltimate tensile strength
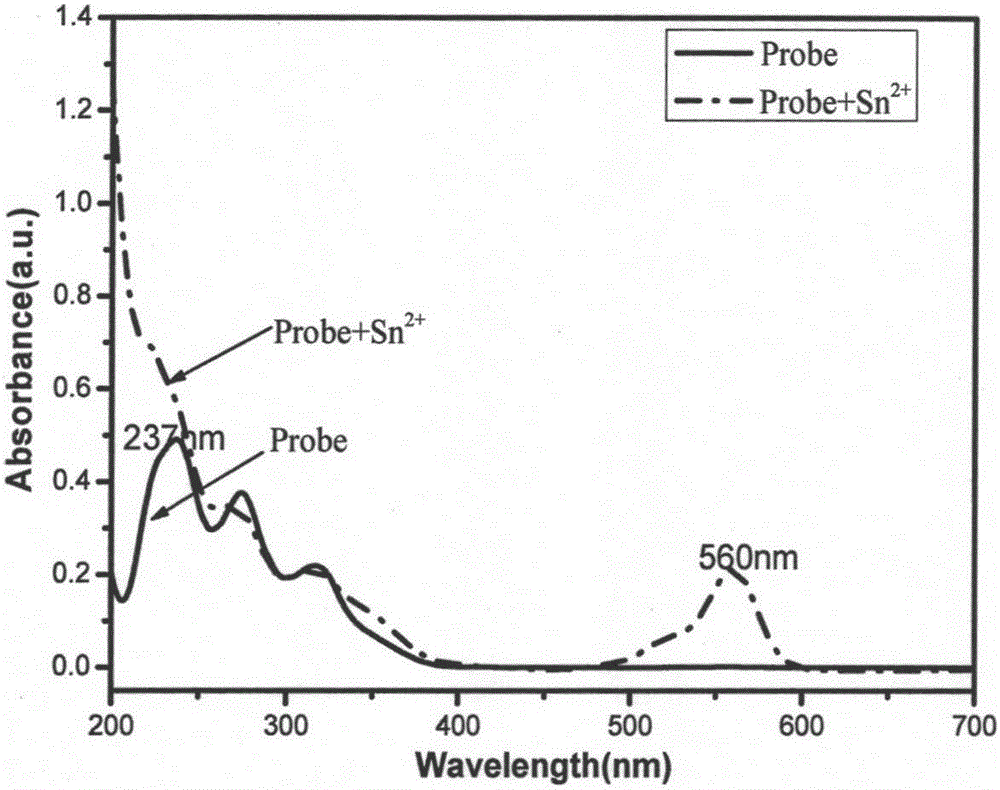
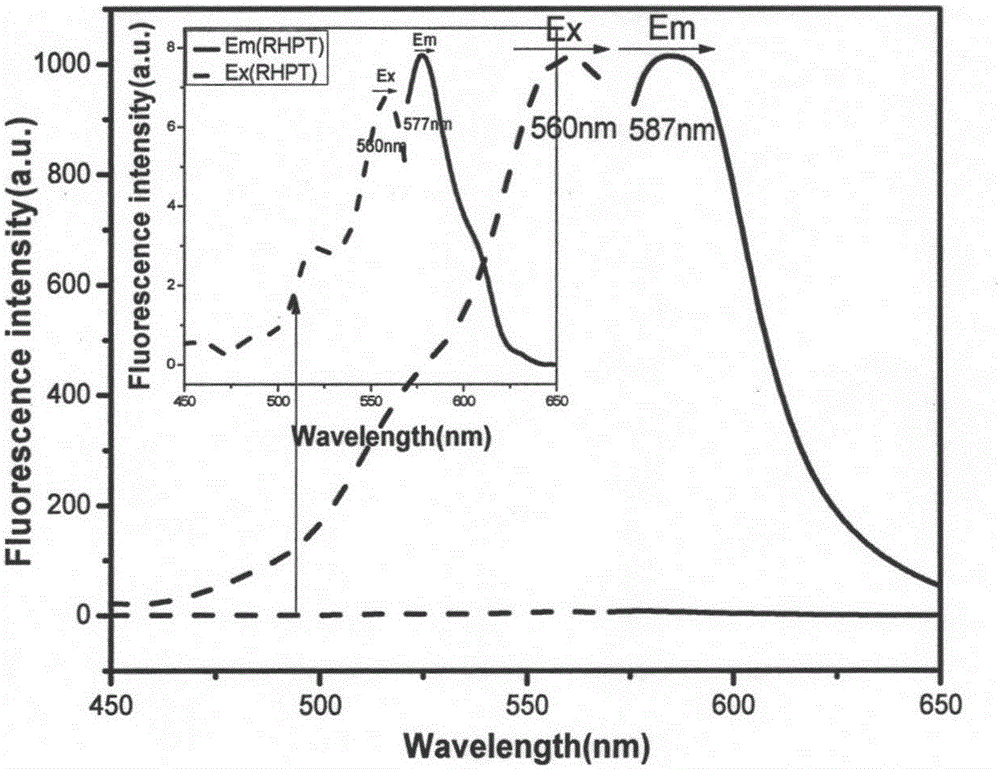
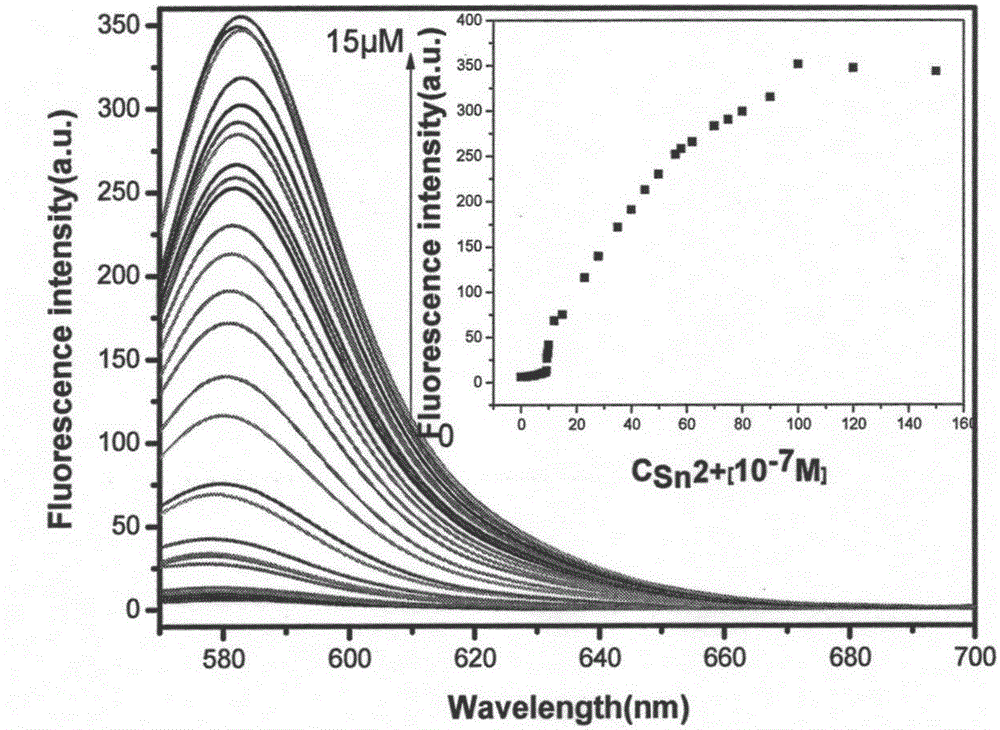
The invention provides a method for detecting stannous ions by using a rhodamine fluorescence probe. The method comprises the following steps: adding a rhodamine fluorescence probe solution to a NaOH / NaH2PO4 buffer solution to obtain multiple fluorescence probe-containing buffer systems, respectively adding different volumes of a stannous ion solution to obtain stannous ion solutions with different concentrations, standing the stannous ion solutions, detecting the fluorescence intensity at an emission wavelength of 587nm under an excitation wavelength of 560nm, and mapping through adopting the concentration of the stannous ions as abscissa and the fluorescence intensity as ordinate to obtain a linear relation curve; and adding the rhodamine fluorescence probe solution to the NaOH / NaH2PO4 buffer solution to obtain a fluorescence probe-containing buffer system, adding a stannous ion solution to be detected, standing the obtained system, detecting the fluorescence intensity at an emission wavelength of 587nm under an excitation wavelength of 560nm, and calculating the concentration of the stannous ions. The method has the advantages of simple operation, fast detection, high sensitivity and good selectivity.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
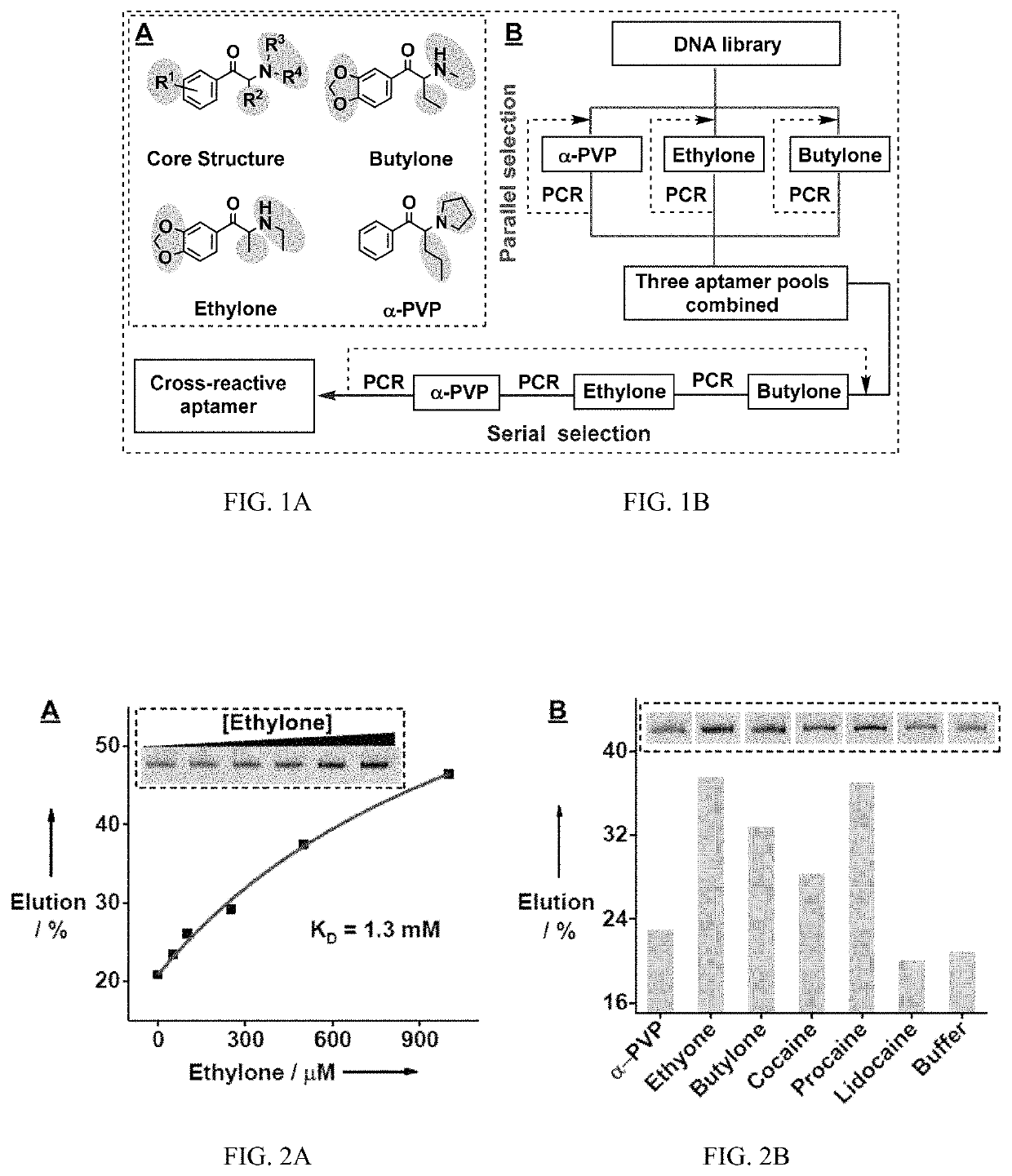
Method for isolating cross-reactive aptamer and use thereof
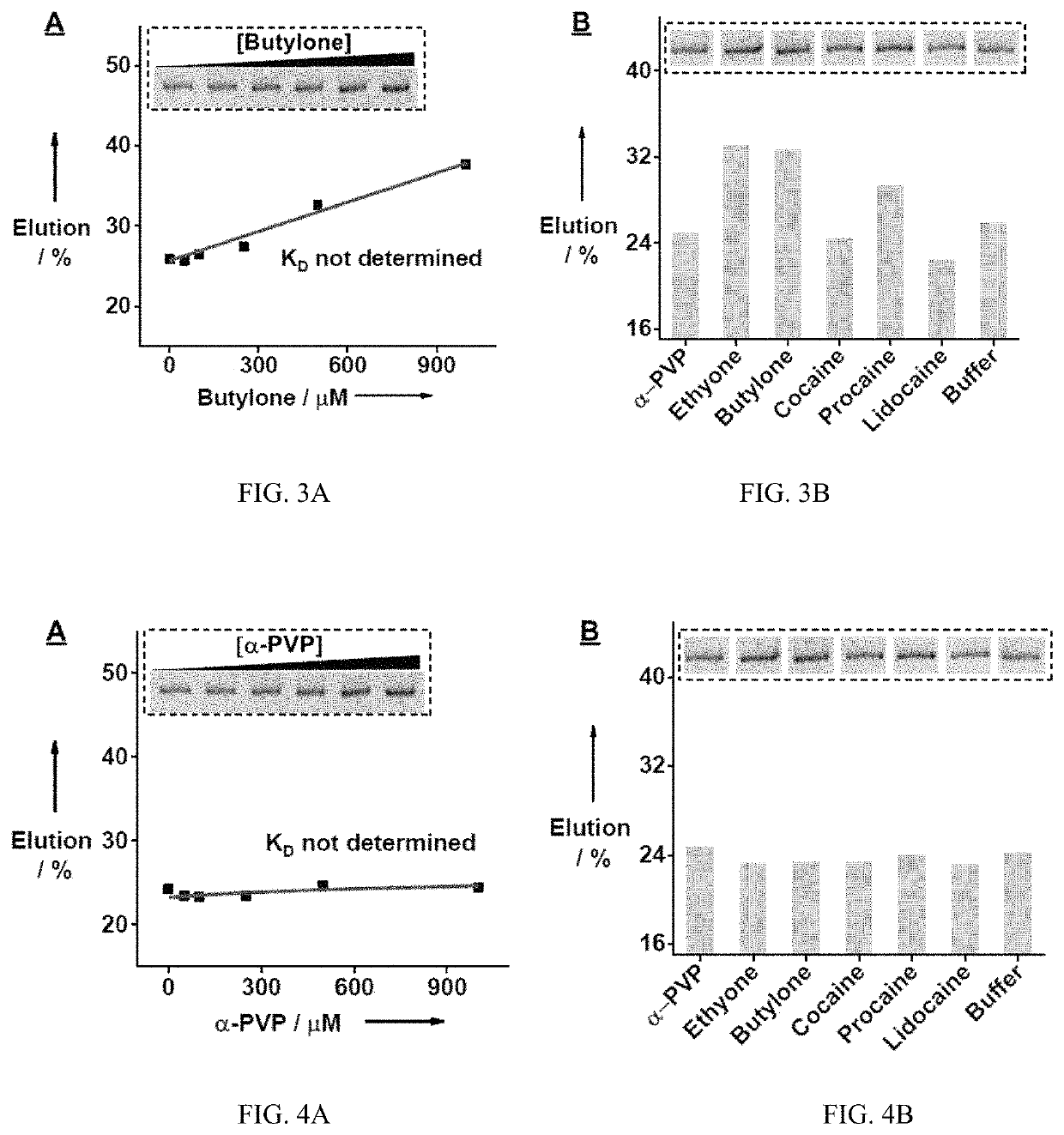
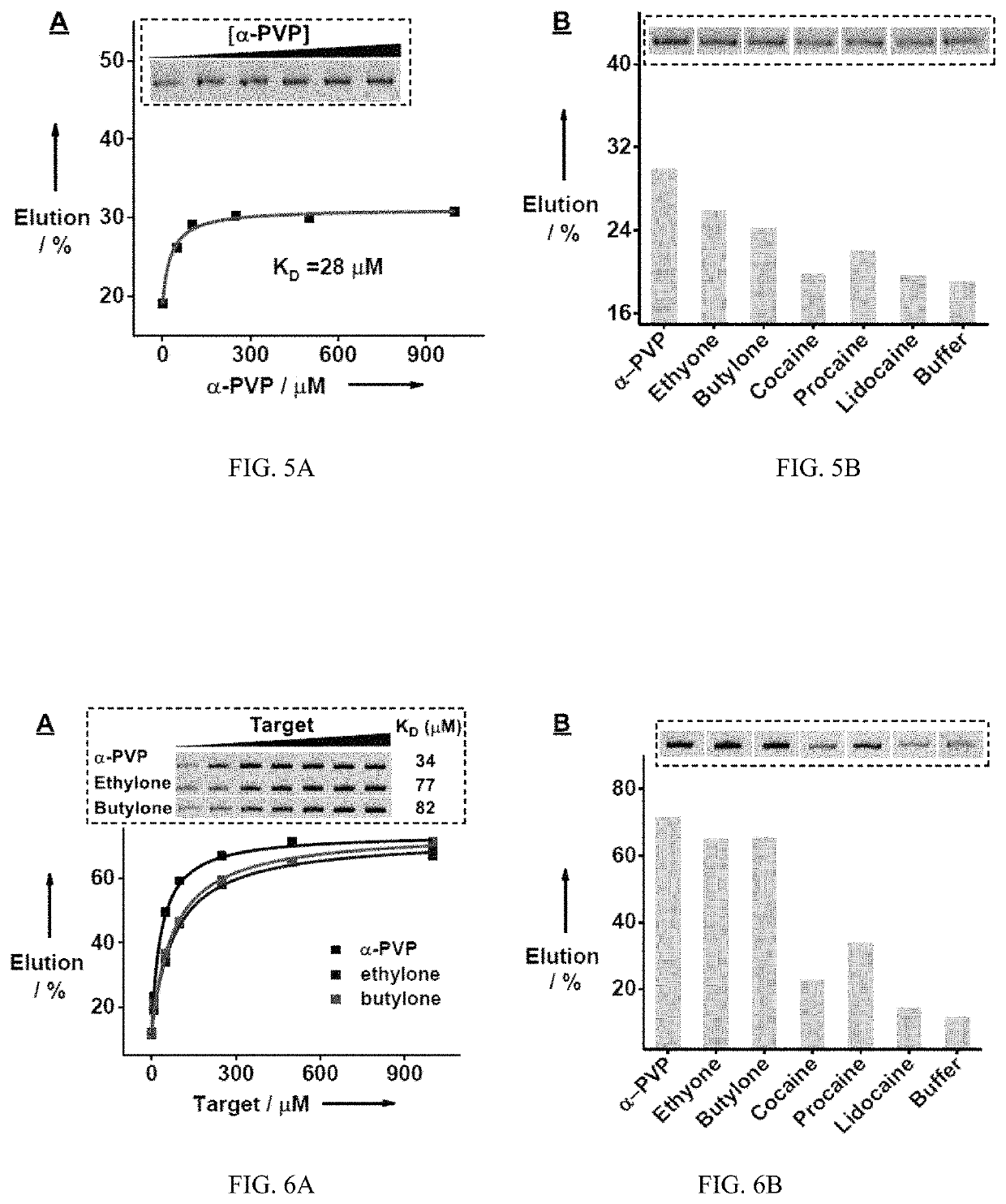
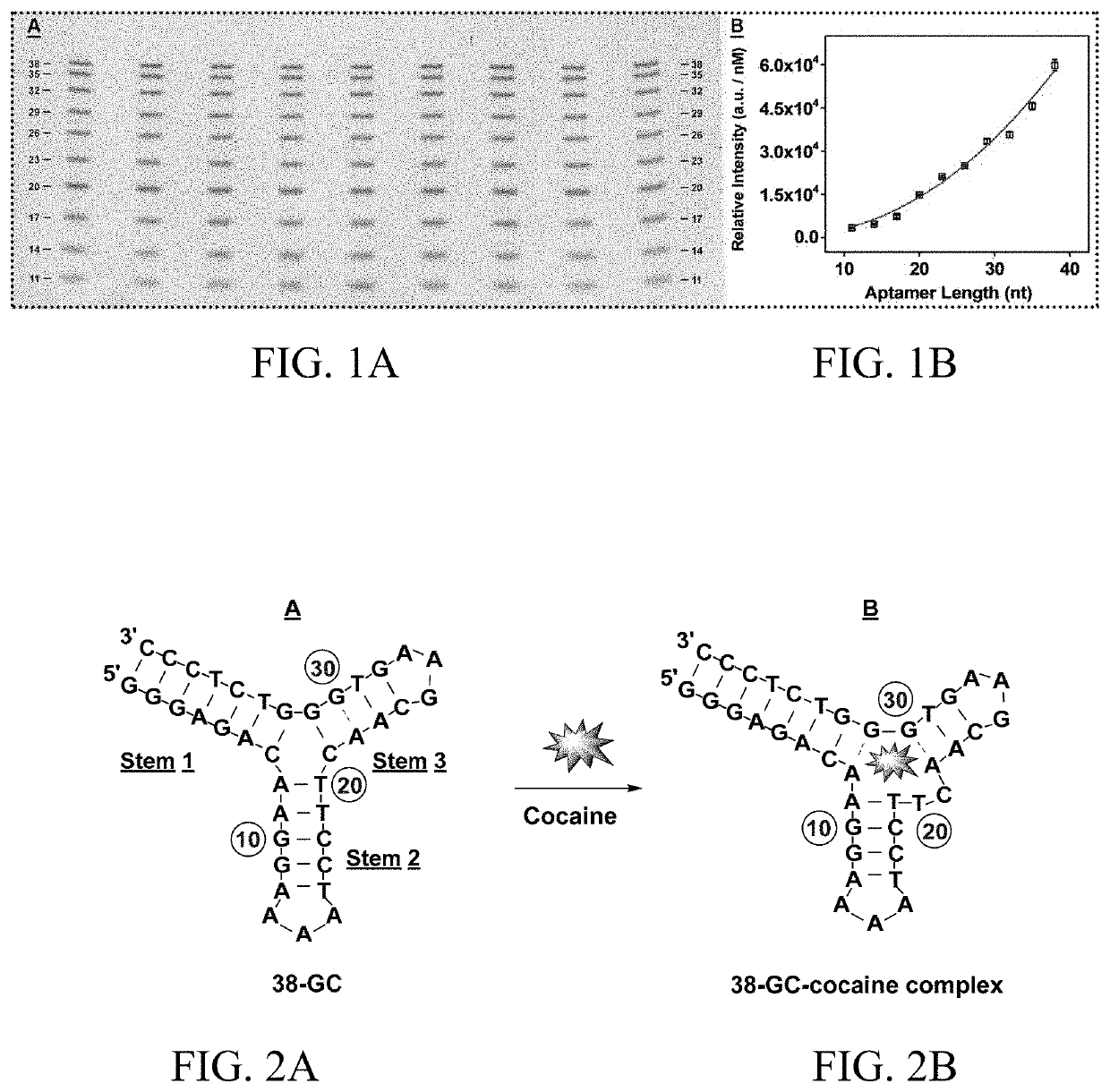
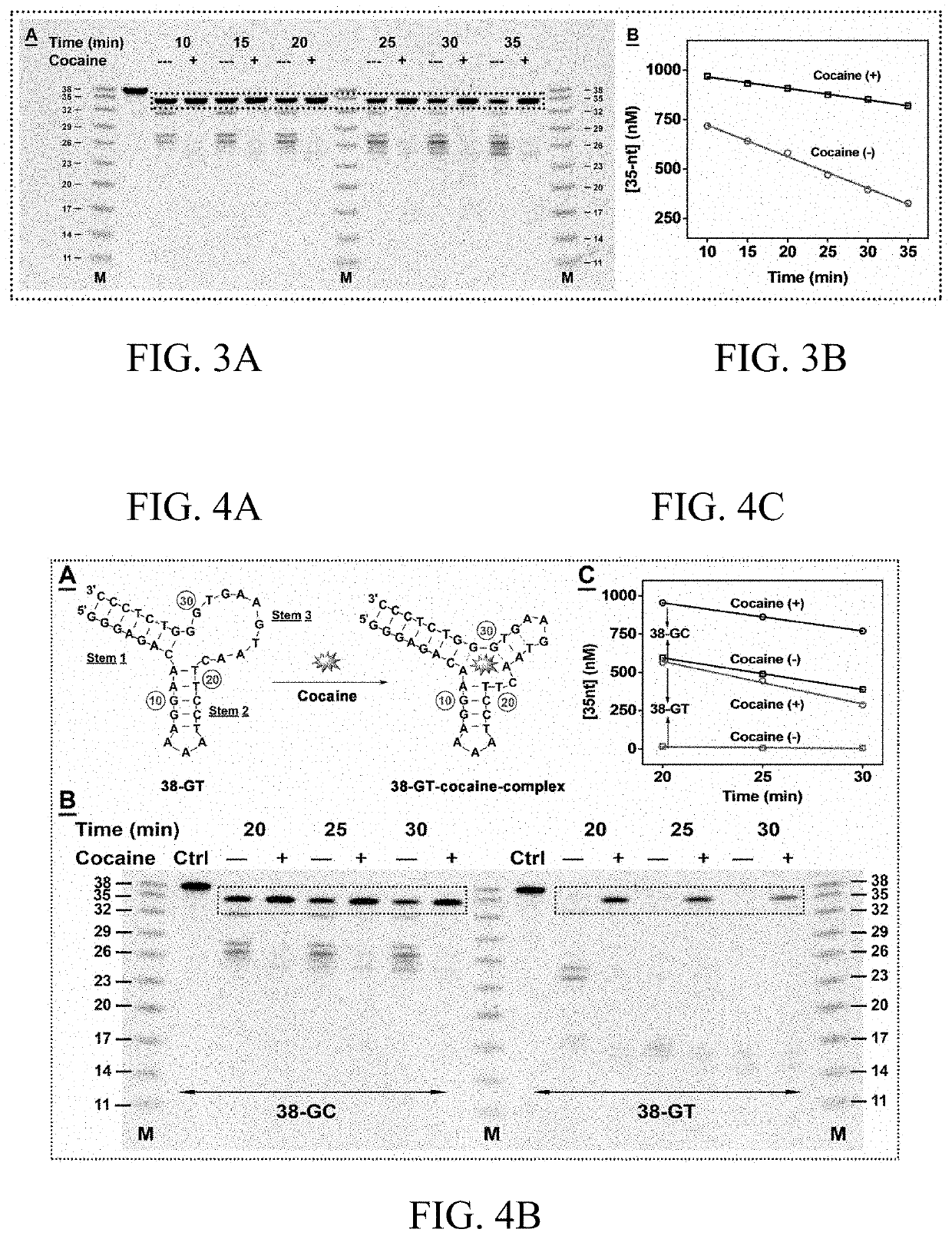
ActiveUS10655132B1Rapid and sensitive detectionImprove performanceOrganic active ingredientsScreening processAptamerAssay
The subject invention provides a novel SELEX strategy for isolating cross-reactive aptamers that recognize a core structure of a small-molecule family and bind to each structurally-similar molecule in said family. The subject invention also provides methods, assays, and products for detecting small-molecule targets of the family in a sample in both clinical and field settings. Such method is based on an aptamer sensor that reports the presence of small-molecule targets via a sensitive colorimetric signal for naked-eye detection. The subject invention further provides exonuclease-based methods for generating structure-switching aptamers from fully folded aptamers and developing electrochemical aptamer-based (E-AB) sensors for rapid and sensitive detection of synthetic cathinones.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for generating structure-switching aptamers and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190376987A1Rapid and sensitive detectionImprove performanceActivity regulationHydrolasesBioinformaticsSmall molecule
The subject invention provides methods, assays, and products for detecting small-molecule targets in a complex sample in both clinical and field settings. The subject invention provides aptamer-based sensors and methods of use thereof. The subject invention provides exonuclease-based methods for generating structure-switching aptamers from fully folded or pre-folded aptamers and developing aptamer-based sensors for small-molecule detection. The method for detecting one or more small-molecule targets in a sample comprises contacting the sample with one or more aptamer-based sensor selective for each of the small-molecule targets, and detecting the small-molecule target in the sample.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for measuring methanol concentration in alcohols solution
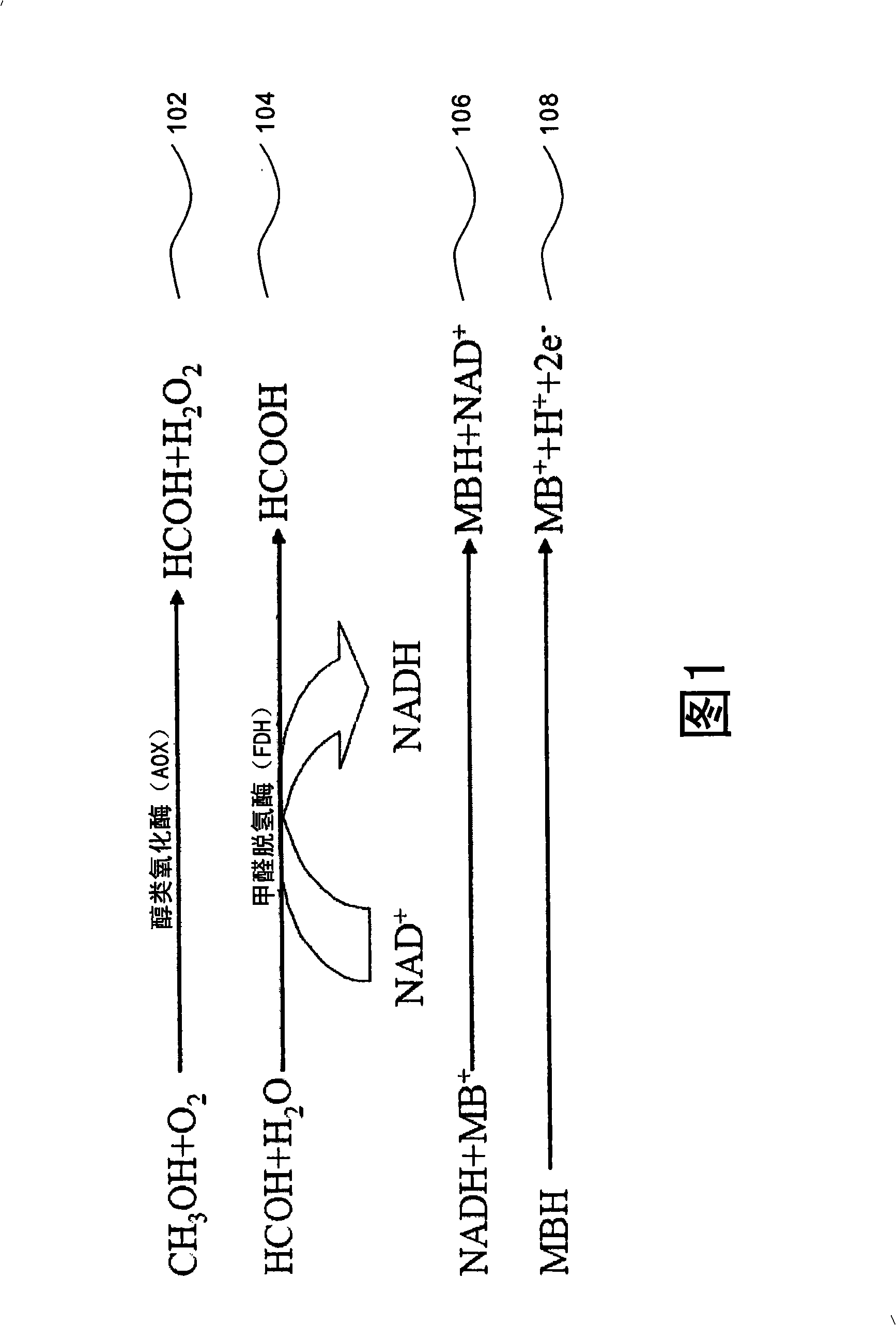
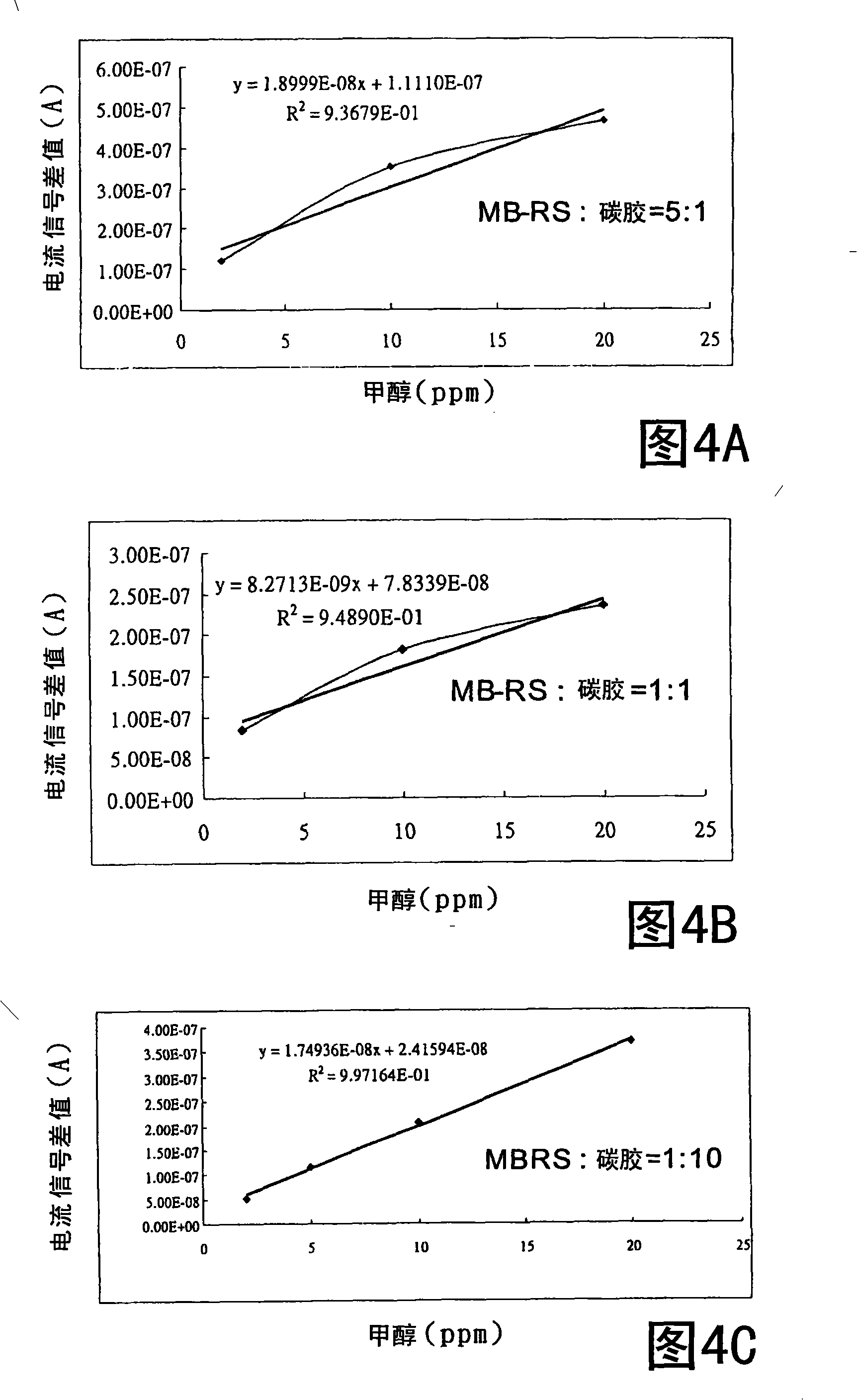
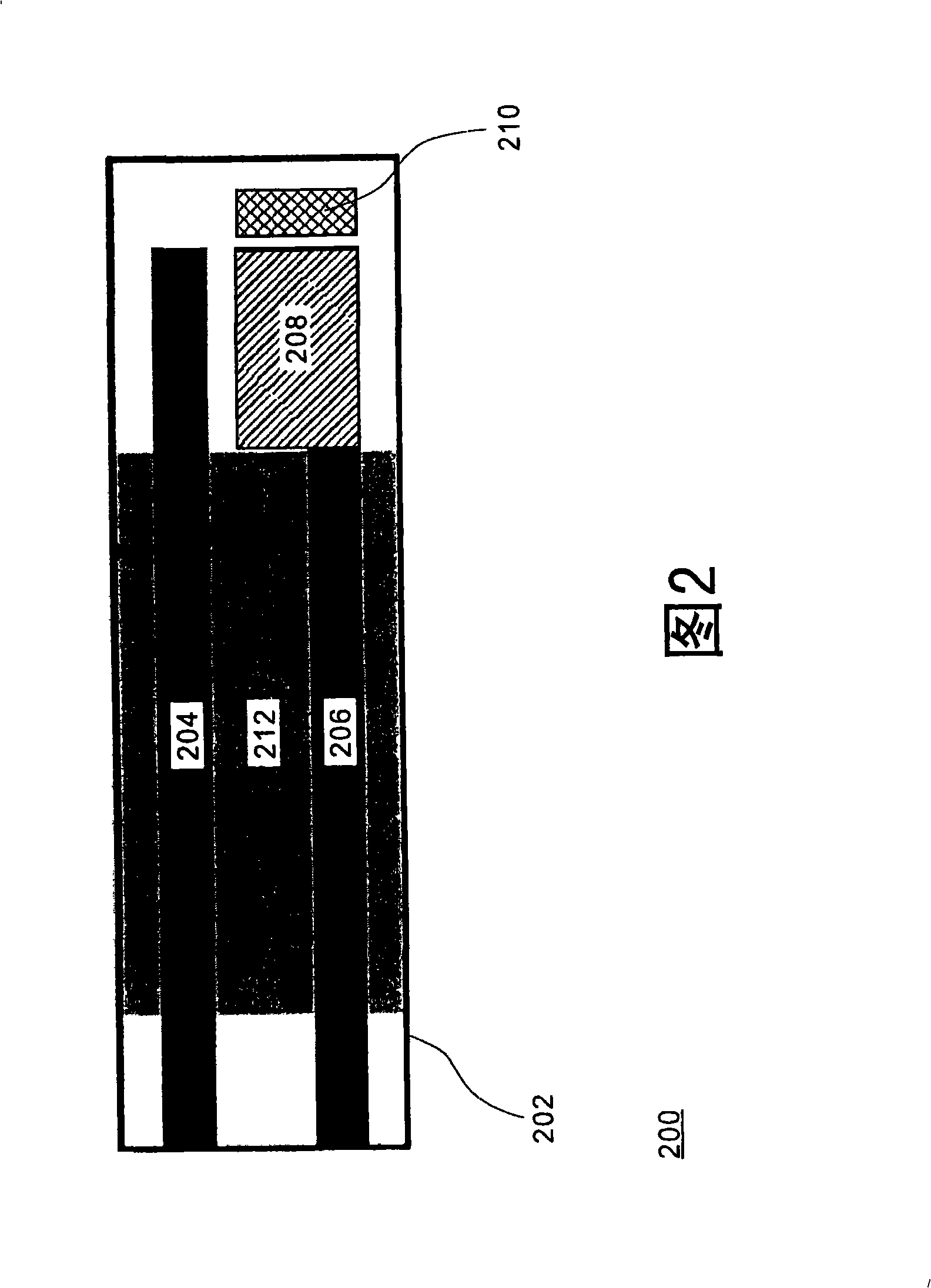
InactiveCN101329298ATo achieve the purpose of health maintenanceImprove convenienceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAlcoholEnzyme
The invention provides a method and device used for measuring carbinol content in alcoholic solutions. The device of the invention is a biological micro-sensor which is used for electrochemical carbinol measurement and based on enzyme reaction, can carry out quick and sensitive detection aiming at the content of the carbinol in real alcohol samples, achieve the effect of saving time and cost, and greatly improve the convenience in use. The method and device of the invention can be directly used for the screening and checking of the false wine, thus achieving the aim of avoiding the generation of false wine poisoning events.
Owner:DEV CENT FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY
Primer, probe and kit for detecting and typing rickettsia by virtue of real-time FRET-PCR (Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer-Polymerase Chain Reaction) and nested PCR
InactiveCN103789442AEasy to findEasy to knowMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPositive sampleEnergy transfer
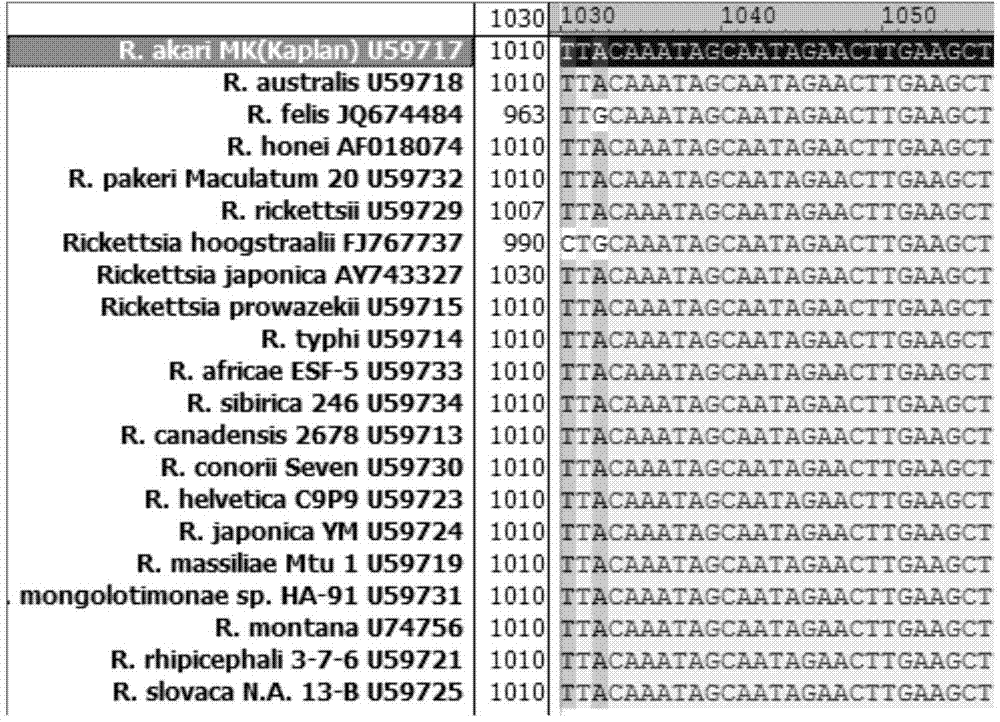
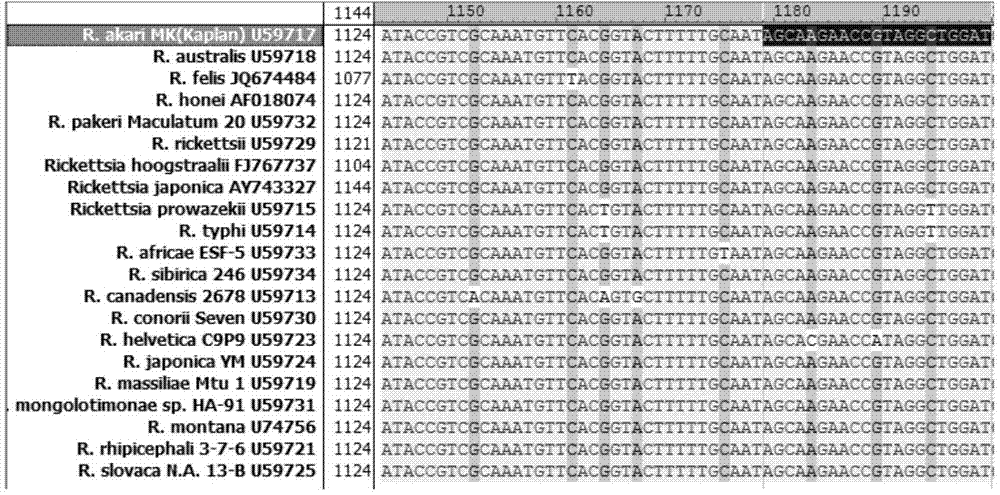
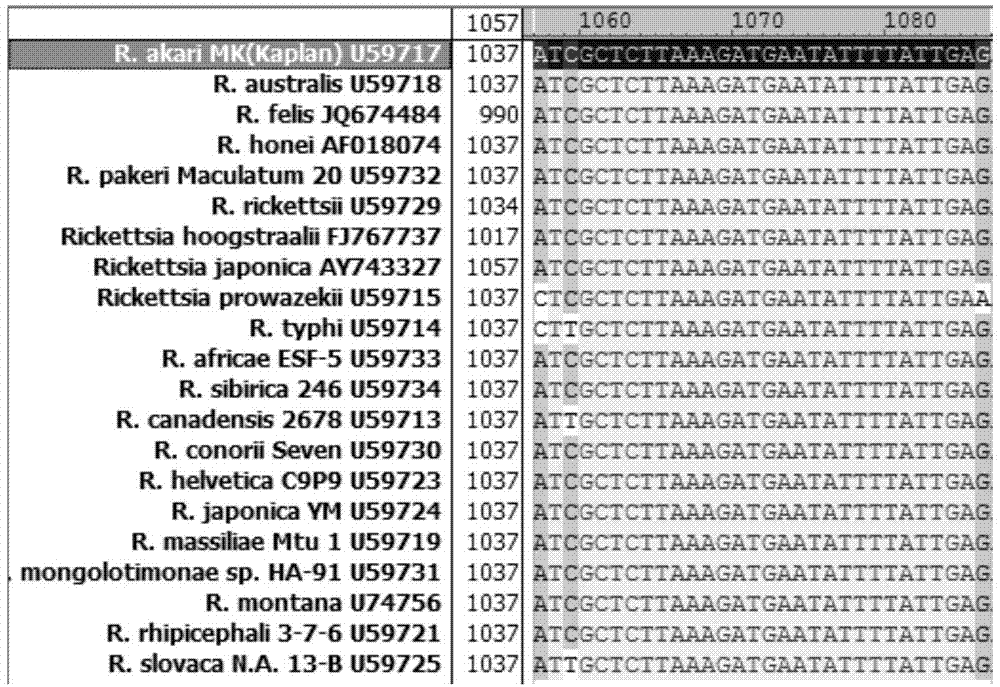
The invention relates to a primer, a probe and a kit for detecting and typing a rickettsia by virtue of real-time FRET-PCR (Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer-Polymerase Chain Reaction) and nested PCR. The primer and the probe are shown as sequences 1-8. By virtue of designing the primer and the probe of the FRET-PCR, nucleinic acids of all Rickettsiaes can be specifically amplified, thus fast judging positive samples; then two pairs of primers of the nested PCR can be designed by selecting other conservative intervals of the same gene, and the Rickettsiae of the corresponding positive samples can be determined by virtue of nested PCR, agarose gel electrophoresis and sequencing. Therefore, the system not only can fast and specifically detect the rickettsia organisms of all the Rickettsiaes, but also can confirm the Rickettsiae.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
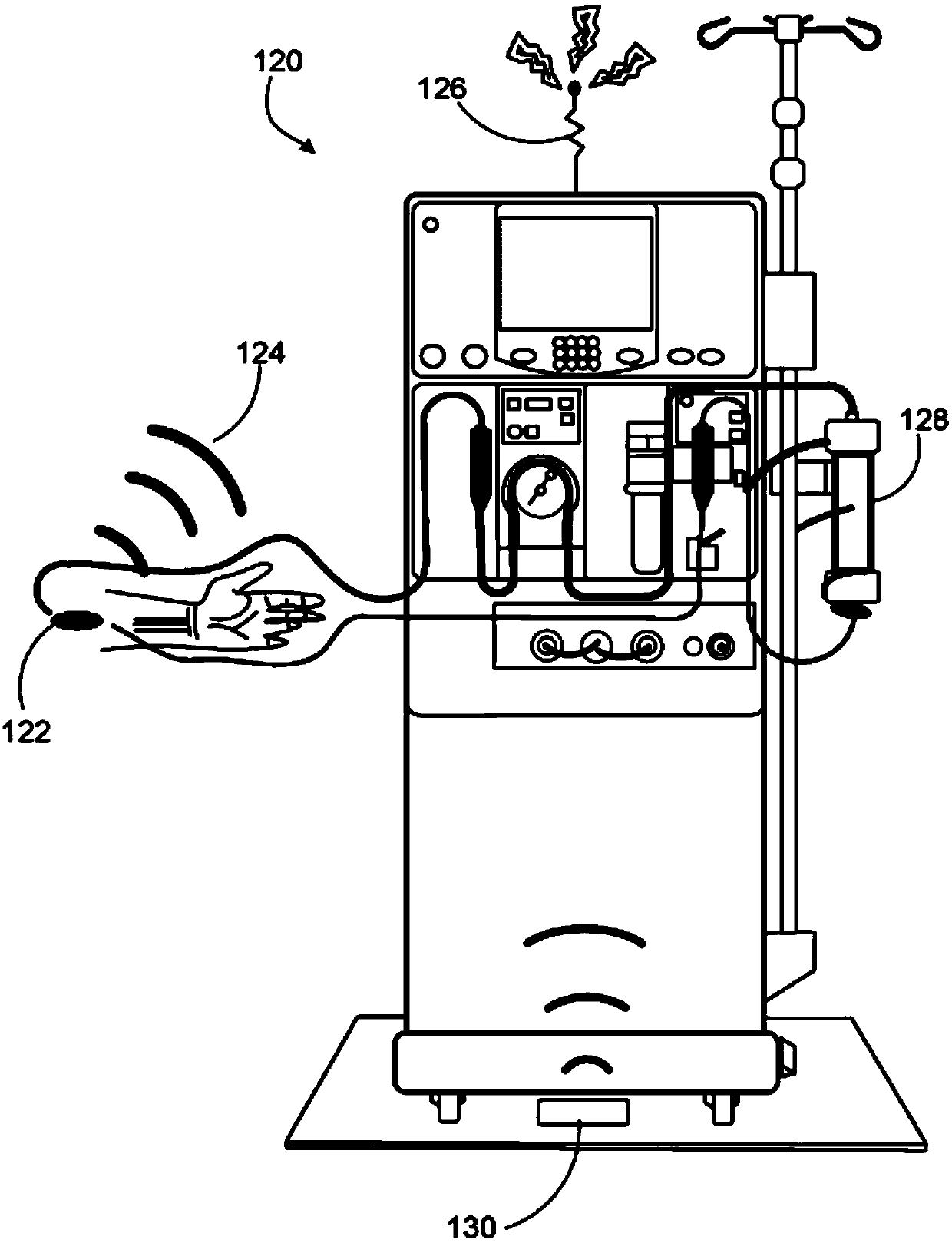
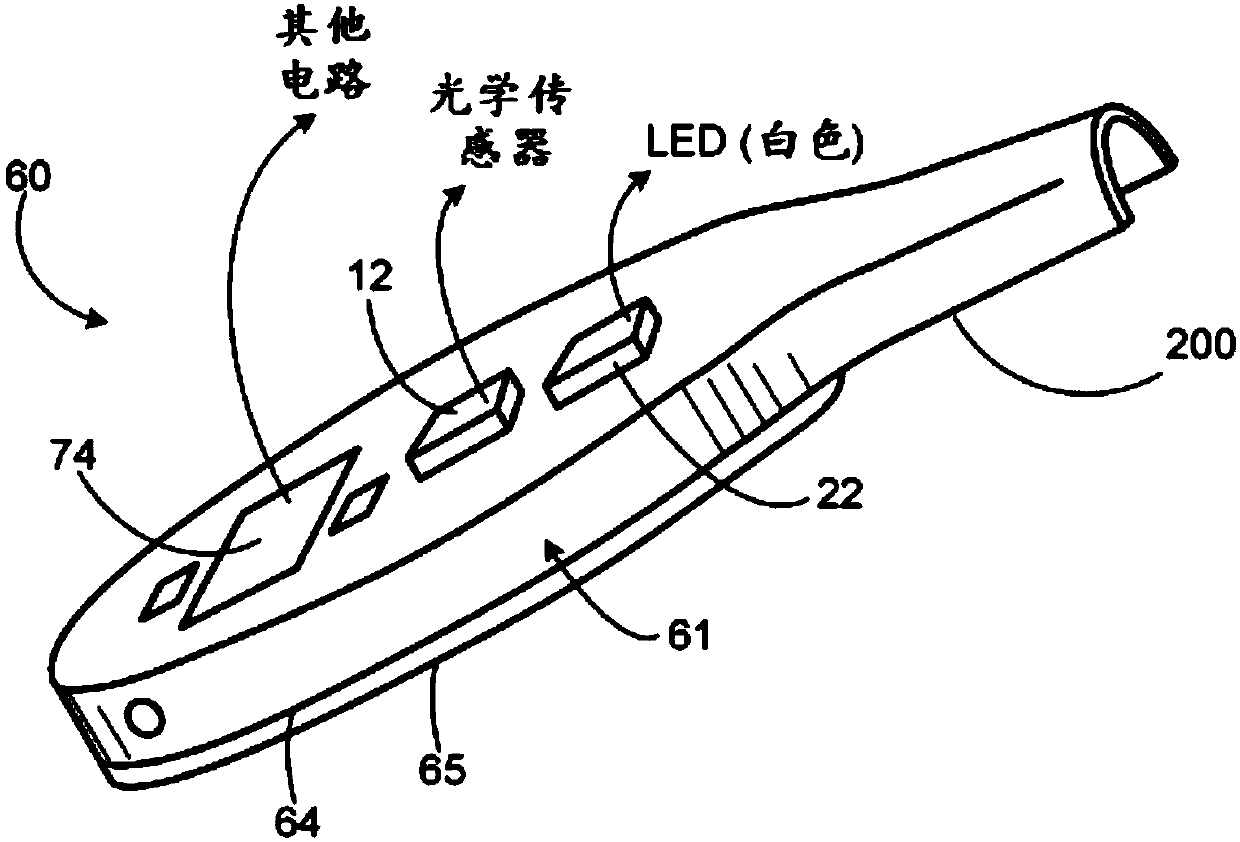
Optical blood detection system
PendingCN109689127ARapid and Sensitive DetectionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesIntravenous needlesBlood treatments
An optical blood detector system is described that rapidly detects the presence of blood due to a blood leak in a system. The blood detector system contains a reusable blood sensor that is able to accurately detect the presence of blood in, for example, an extracorporeal blood treatment system by optically sensing light from a sensing region and determining if the light came from a leaked blood. The blood sensor may be responsive to reflected light or light emitted from blood due to bio-fluorescence excited by a light source in the blood detector system. The blood detector system can be placedagainst absorbent material adjacent to an intravenous needle injection site and quickly detect any blood wicked into the absorbent material. The blood detector system can eliminate the need for medical personnel to continuously inspect numerous patients visually for potentially fatal blood leaks due to needle dislodgement.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Docking station with waveguide enhanced analyte detection strip
ActiveUS20210293716A1High sensitivityRapid and sensitive detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLaboratory glasswaresDocking stationWireless transmission
This disclosure presents a docking station into which a test card can be inserted for rapid analyte detection and reporting. This docking station has portable capability and can include wire or wireless transmission to a local server or cloud-based server. A test card that has a test structure located on the test structure that includes a modified waveguide can be inserted into the and a docking station that includes a laser and interferometer provides for accurate and rapid detection of a test sample.
Owner:STRIKE PHTONICS INC
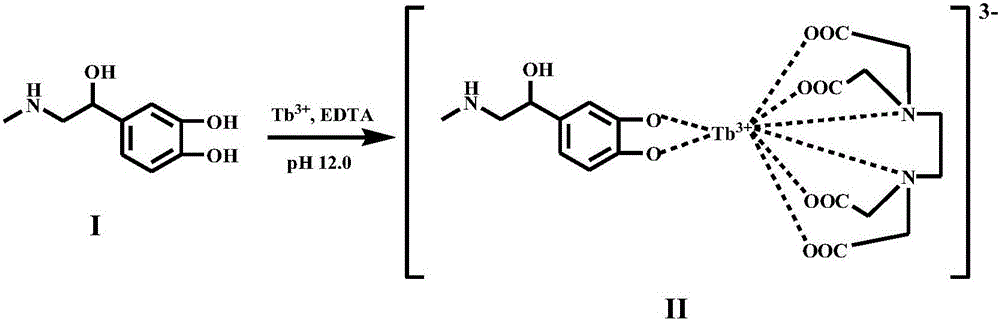
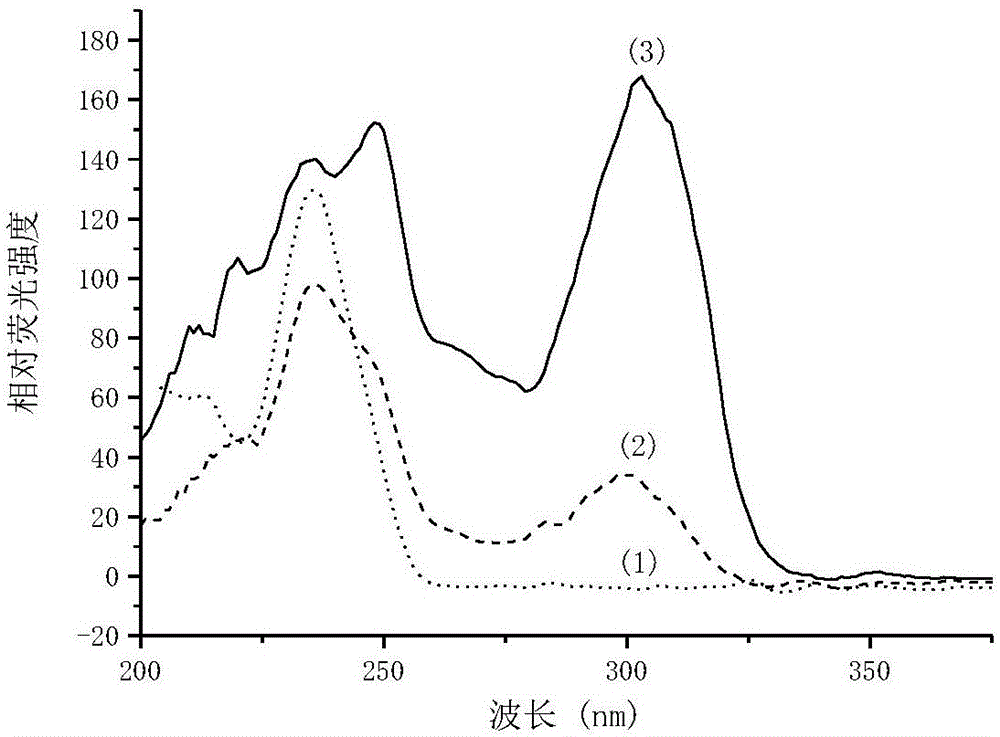
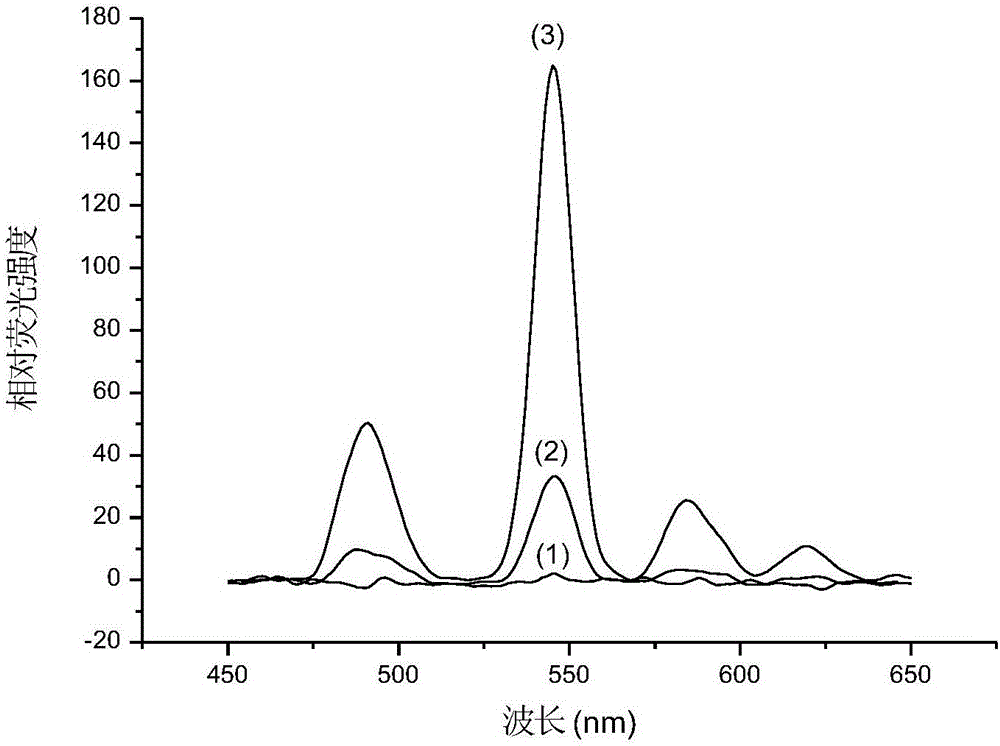
Method for detecting adrenaline by metal-terbium fluorescent probe and use of method
InactiveCN106770129AHighly sensitive fluorescence detectionWide detection rangeFluorescence/phosphorescenceRare-earth elementTerbium
The invention relates to a method for detecting adrenaline by a metal-terbium fluorescent probe and use of the method. According to the method, the adrenaline, disodium edetate and a rare-earth element terbium form a stable ternary complex in an alkaline solution, and the ternary complex can emit characteristic fluorescence of Tb(III). Through adding hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride, which serves as a sensitizing agent, into the ternary complex, the fluorescence intensity of the ternary complex can be remarkably enhanced. The relative fluorescence intensity of the ternary complex is proportional to adrenaline concentration in the adrenaline concentration range of 7.0*10<-8>mol / L to 5.0*10<-5>mol / L, and the detection limit is 2.1*10<-8>mol / L. According to the method, the interference resulting from common metal ions and drug excipients can be eliminated; the method is high in sensitivity, simple in operation and low in detection limit; the result is good when the method is applied to the detection on adrenaline injections.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Methods of screening nucleic acids for single nucleotide variations
InactiveUS7906287B2Rapid and sensitive detectionLimit scopeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide variation
Disclosed are methods and compositions for detecting variation in nucleic acids. The disclosed method compares the sequence of a nucleic acid of interest with the sequence of a reference nucleic acid to sensitively identify variations between the sequence of a nucleic acid of interest and the sequence of a reference nucleic acid. The disclosed method generally involves excision and replacement of selected nucleotides in nucleic acid strands hybridized to other strands. In the method, if the excised nucleotide was mismatched with the nucleotide in the other, hybridized strand, then the replacement nucleotide will not be mismatched. If the excised nucleotide was not mismatched with the nucleotide in the other, hybridized strand, then the excised nucleotide is not replaced. This difference allows detection of variation in the nucleic acid of interest. In some forms of the method, by replacing excised nucleotides with nuclease-resistant nucleotides, strands in which excised nucleotides are replaced will be resistant to nuclease digestion while strands in which excised nucleotides are not replaced will be sensitive to nuclease digestion. By exposing the hybridizing nucleic acids to nuclease following replacement of excised nucleotides, the strands in which excised nucleotides are not replaced can be destroyed by the nuclease while strands in which excised nucleotides are replaced can be preserved. The remaining strands can then be detected and whether the strand survived nuclease digestion can be noted. Strands that survive nuclease digestion are indicative of the presence of variation in the nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:INSIGHT GENETICS INC
Detection of targets
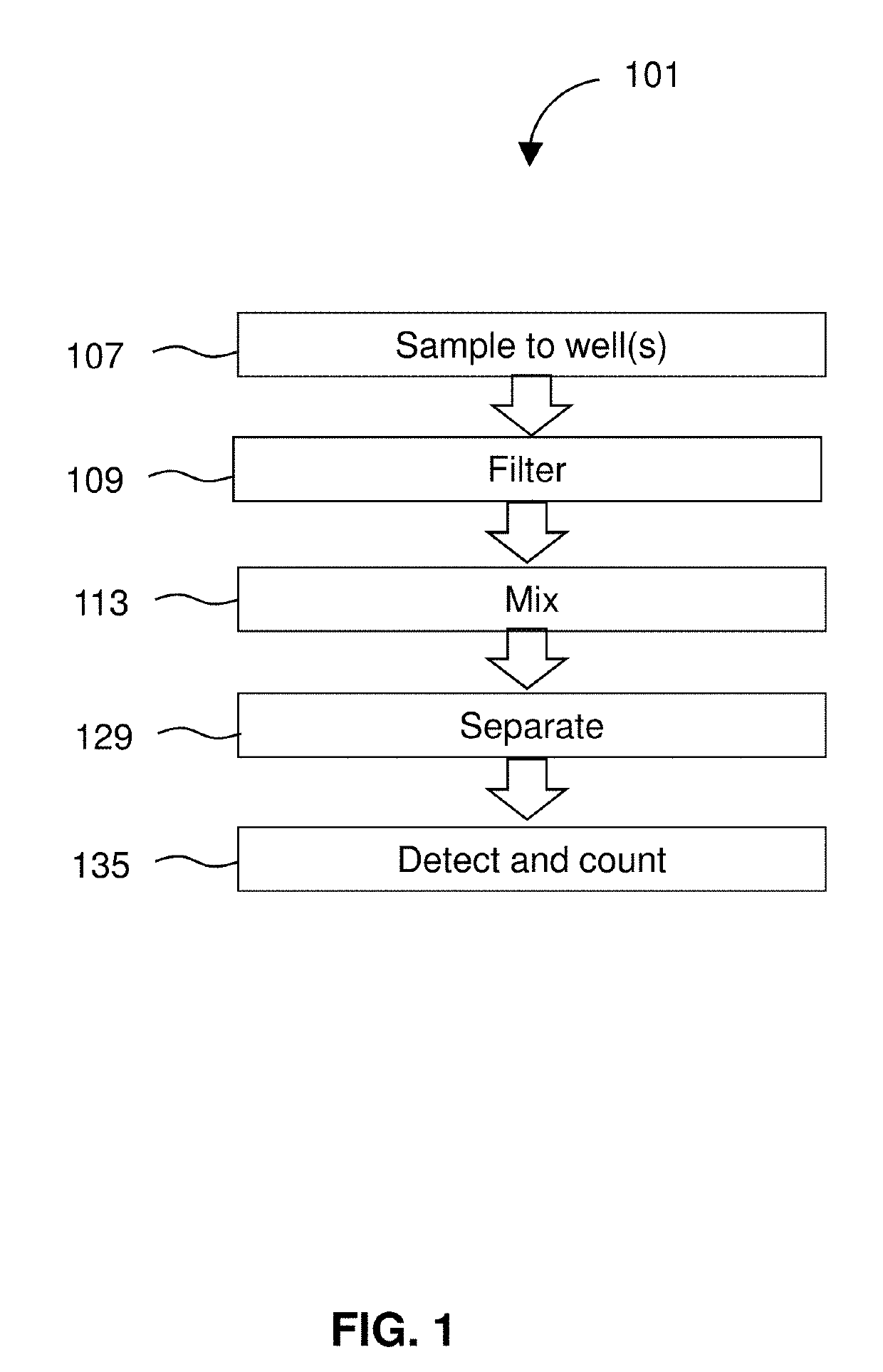
PendingUS20190324034A1Rapid and sensitive detectionLow costLaboratory glasswaresDisease diagnosisParticulatesLiquid layer
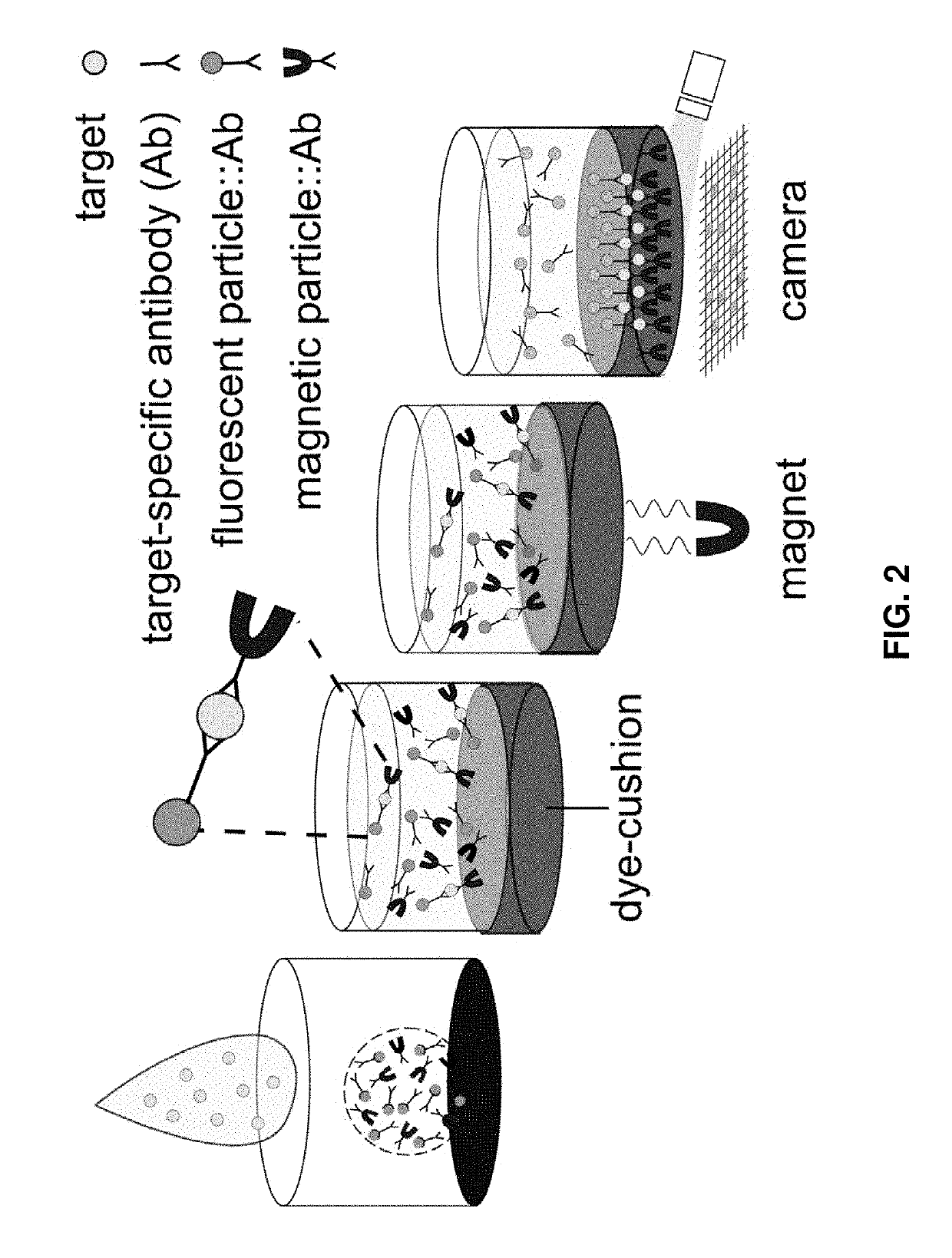
Methods and cartridges for detecting targets are provided. A biological sample is introduced to a cartridge. Targets in the sample are photonically labeled with fluorescent particles in a first liquid layer in the cassette. Photonically-labeled targets are separated out of the sample into a second liquid layer within the cassette, detected, and counted to show presence of the targets in the subject. Cartridges include a receiving reservoir, a mixing well for introducing the sample to photonic labels and magnetic particles, and an imaging well for detecting and counting targets from the sample. The sample may be a human stool sample. A filter may be used to filter particulates out of the sample.
Owner:FIRST LIGHT BIOSCI INC
Histamine Detection Method of Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Biosensor
ActiveCN107421937BEasy to synthesizeQuick checkFluorescence/phosphorescenceMaterials scienceFluorescence intensity
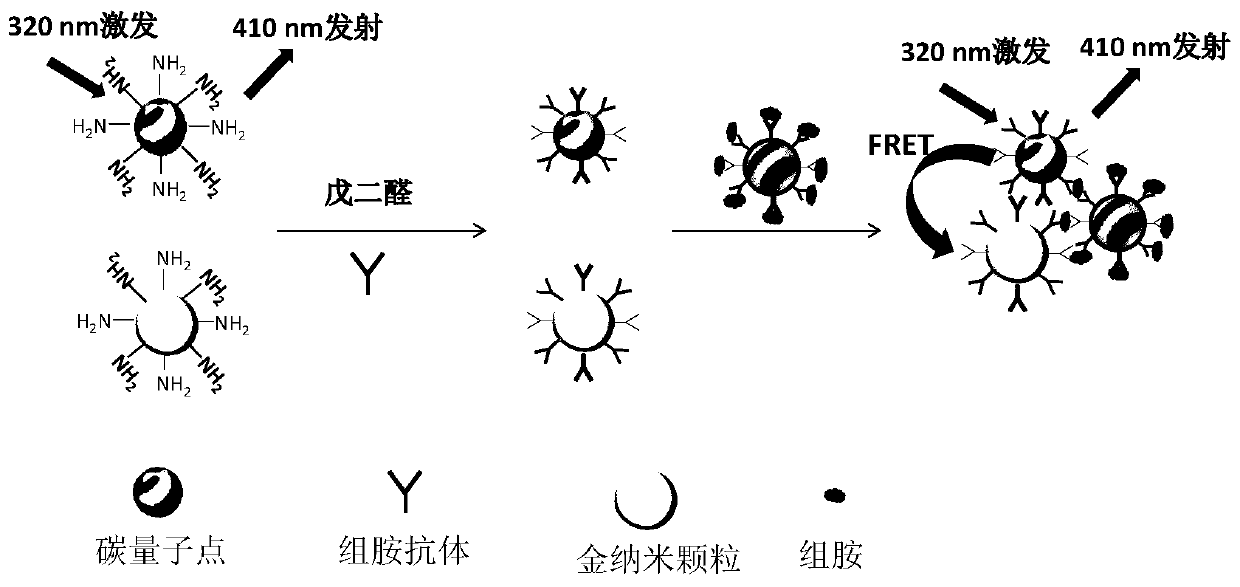
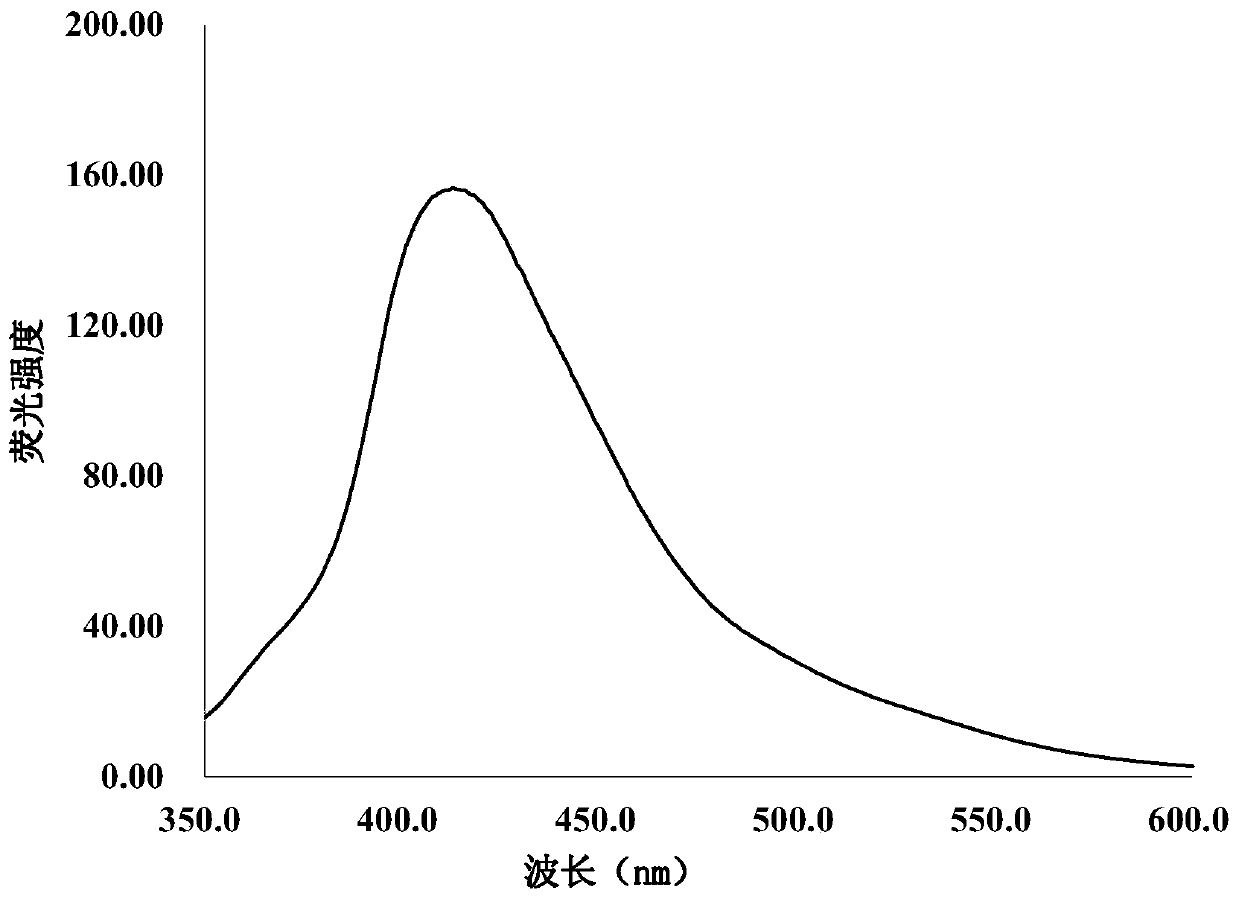
The invention discloses a histamine detection method for a fluorescence resonance energy transfer biosensor based on magnetic nano-particle separation. The method comprises the following steps: respectively immobilizing histamine antibodies on surfaces of magnetic nano-particles, graphene quantum dots subjected to surface amino functionlization and gold nanoparticles in a covalent binding manner; and adding the histamine enriched and separated by the magnetic nano-particles into a mixed solution of the graphene quantum dots and the gold nanoparticles. Because the histamine on the magnetic nano-particles can be in specific binding with the surfaces of the graphene quantum dots and the gold nanoparticles modified by the histamine antibodies, the distance between the graphene quantum dots and the gold nanoparticles is narrowed, and under ultraviolet excitation of the wavelength of 320nm, due to fluorescence resonance energy transfer, fluorescence of the graphene quantum dots is quenched by the gold nanoparticles. The content of the histamine is determined by detecting the fluorescence signal intensity. The detection limit in the method reaches 24pM. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the histamine can be rapidly, sensitively and accurately detected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A method for rapid detection of nitrite based on nano-gold
InactiveCN104614370BWide detection rangeGood linear relationshipMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsNanoparticleUv vis absorbance
The invention discloses a quick nitrite detection method based on nanogold. The method comprises steps as follows: a standard solution containing nitrite is added to an acid aqueous solution of p-aminothiophenol, nanogold sol is added after a period of incubation, the nanogold sol is detected by an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer, ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum data are acquired, the specific value of the absorbance in 685 nm and 520 nm positions is taken as the longitudinal coordinate, the concentration of the standard solution containing the nitrite is taken as the horizontal coordinate, a standard curve of the nitrite is obtained through fitting, the A685 / A520 value of a to-be-detected solution containing nitrite is introduced into a function relation of the standard curve of the nitrite, and quantitative detection of the nitrite is realized. The method is simple in step, low in cost, good in selectivity, high in detection speed and broad in application prospect, the nanogold is not required to be modified, special instrument equipment is not required, the detection range of the nitrite concentration is wide, and convenient, quick and sensitive detection can be realized.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
Hybridoma cell strain, anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody generated by hybridoma cell strain and application
ActiveCN103343109AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesElisa kitMicrobiology
The invention provides a hybridoma cell strain, an anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody generated by the hybridoma cell strain and application, and belongs to the technical field of immunochemistry. The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain 8D7 which generates the anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody and is stored with a number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No., 7953, an anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody 8D7' secreted by the hybridoma cell strain 8D7, and application of the anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody in preparation of an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit and a colloidal gold test strip used for detecting salbutamol. The hybridoma cell strain 8D7 can efficiently and stably secrete the anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody; the anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody has high titer, specificity and sensitivity, can be produced as mass, and realizes the effect of quickly and sensitively detecting a salbutamol medicine residual in urine, muscle and viscera. By adopting the anti-salbutamol monoclonal antibody for detecting the salbutamol residual in a sample, toxic agents are not needed during treating the sample, and the operation is simple.
Owner:江苏奥的特生物技术有限公司
Method for authenticating pork, beef, mutton and products thereof
ActiveCN102337328BRapid and Sensitive DetectionThe identification method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a pair of PCR primers used for authenticating pork, beef, mutton and products thereof. The nucleotide sequences of the primers are represented by SEQ ID No.1 and No.2. The invention also provides a kit comprising the primers, and a method for authenticating pork, beef, mutton and products thereof. The method provided by the invention is characterized in accurate result and high sensitivity. With the method provided by the invention, adulterate fresh meats in markets can be rapidly detected. Also, the method plays an important role in individual discriminating and origintracing researches. According to the authenticating method provided by the invention, only one pair of PCR primers is required for authenticating fresh pork, beef, and mutton, such that the authentication is simple and rapid. With the method, adulterate fresh meats in markets can be rapidly and sensitively detected, and great significance is provided for pig individual discriminating and origin tracing researches.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com