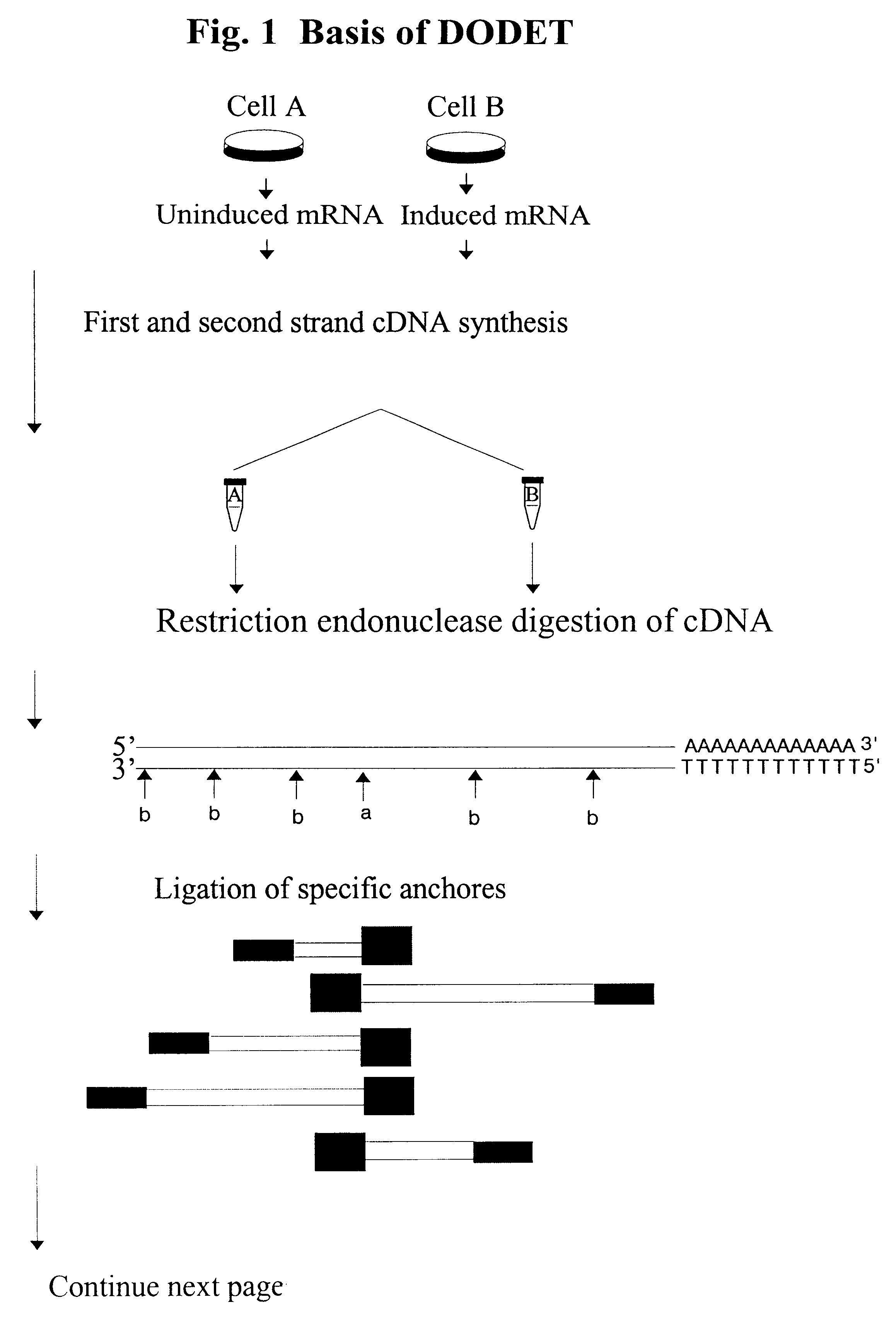
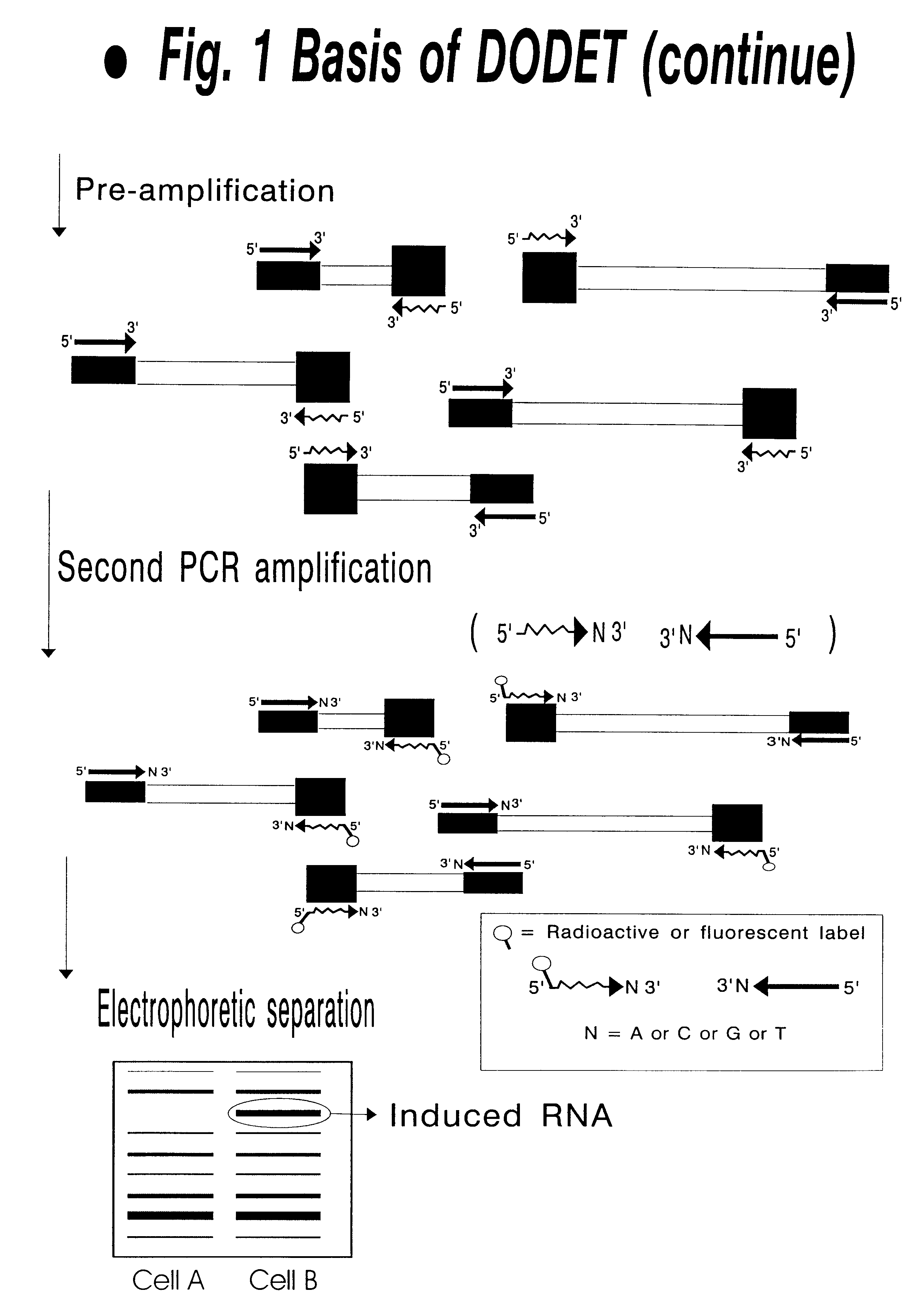
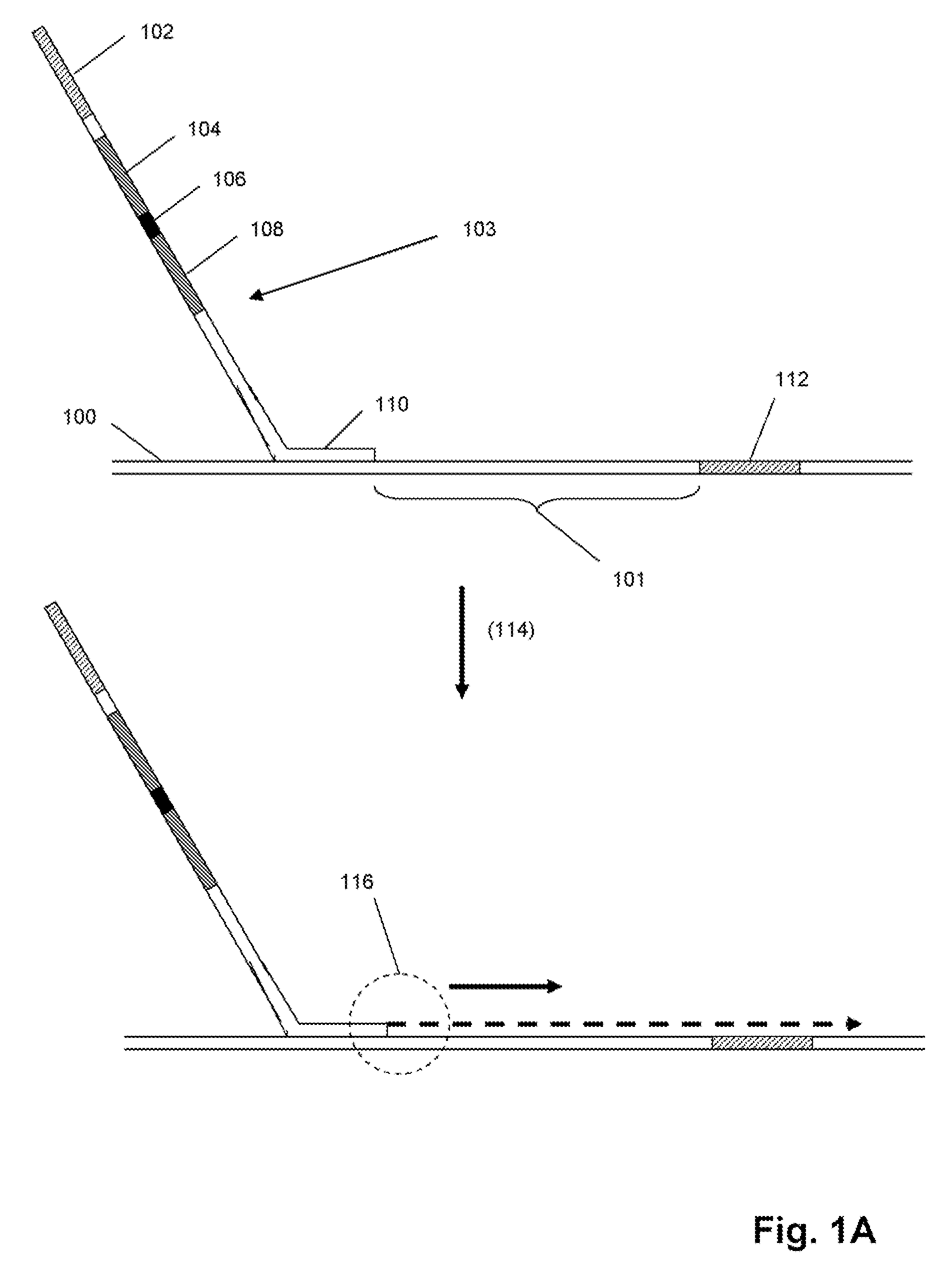
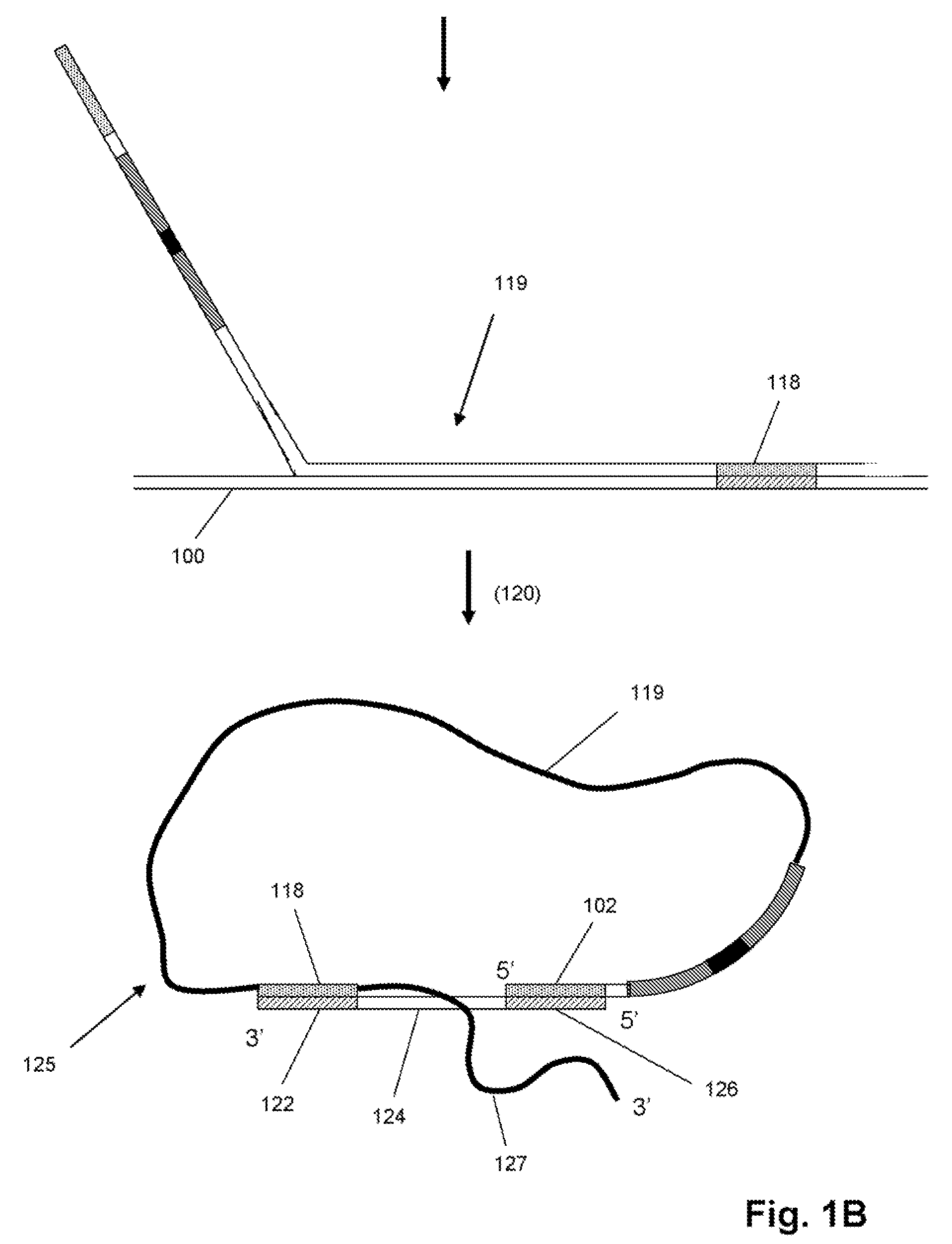
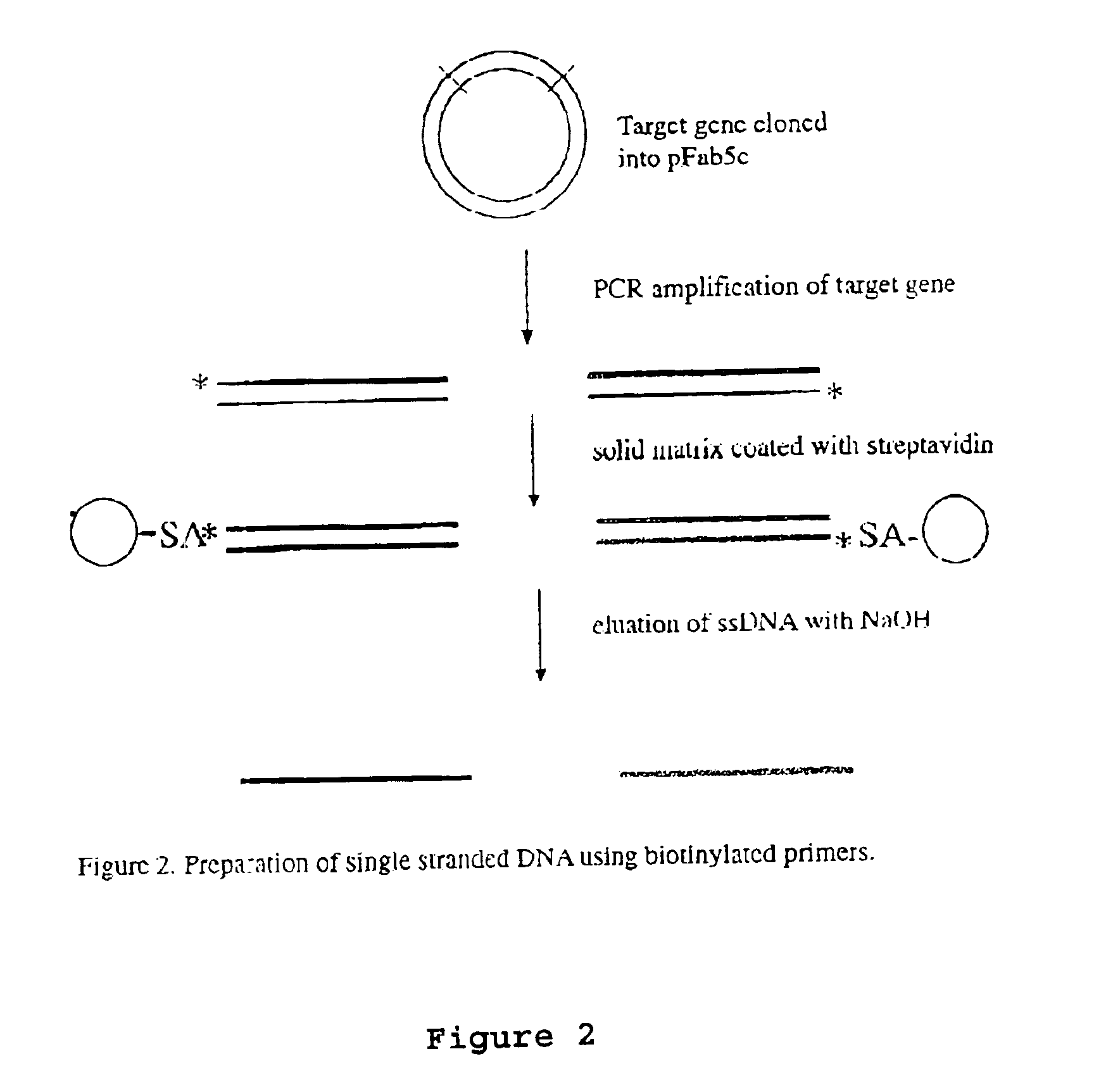
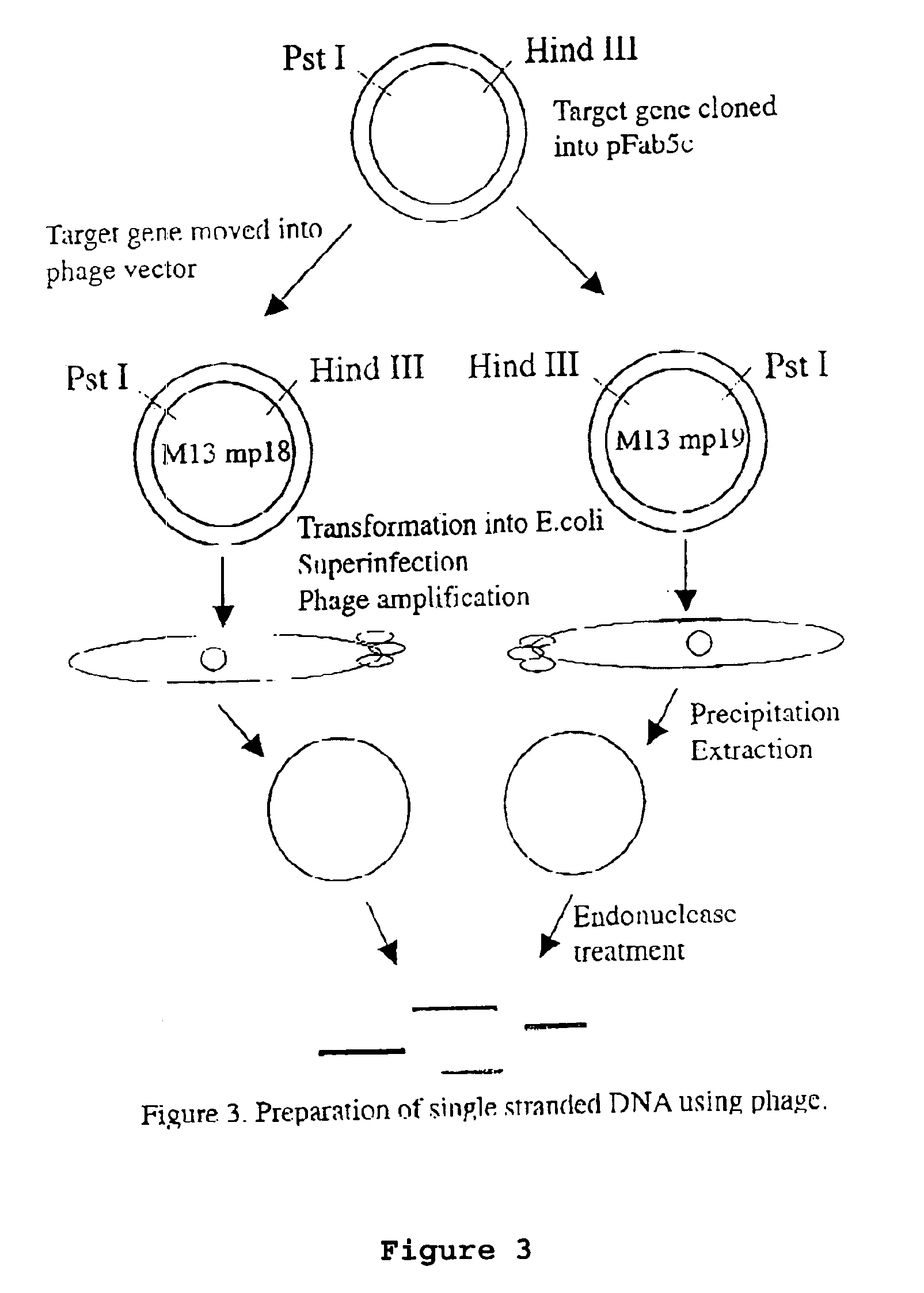
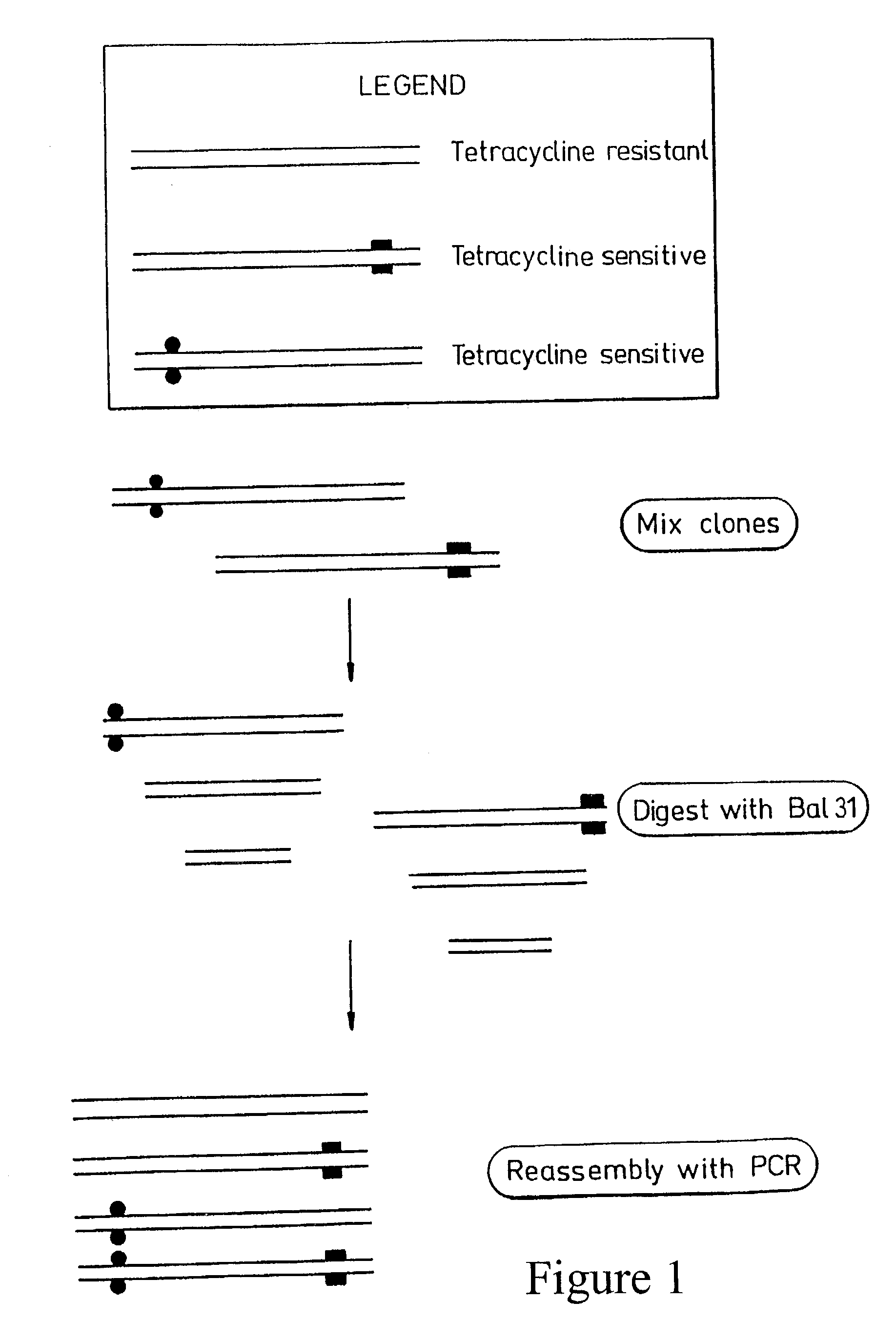
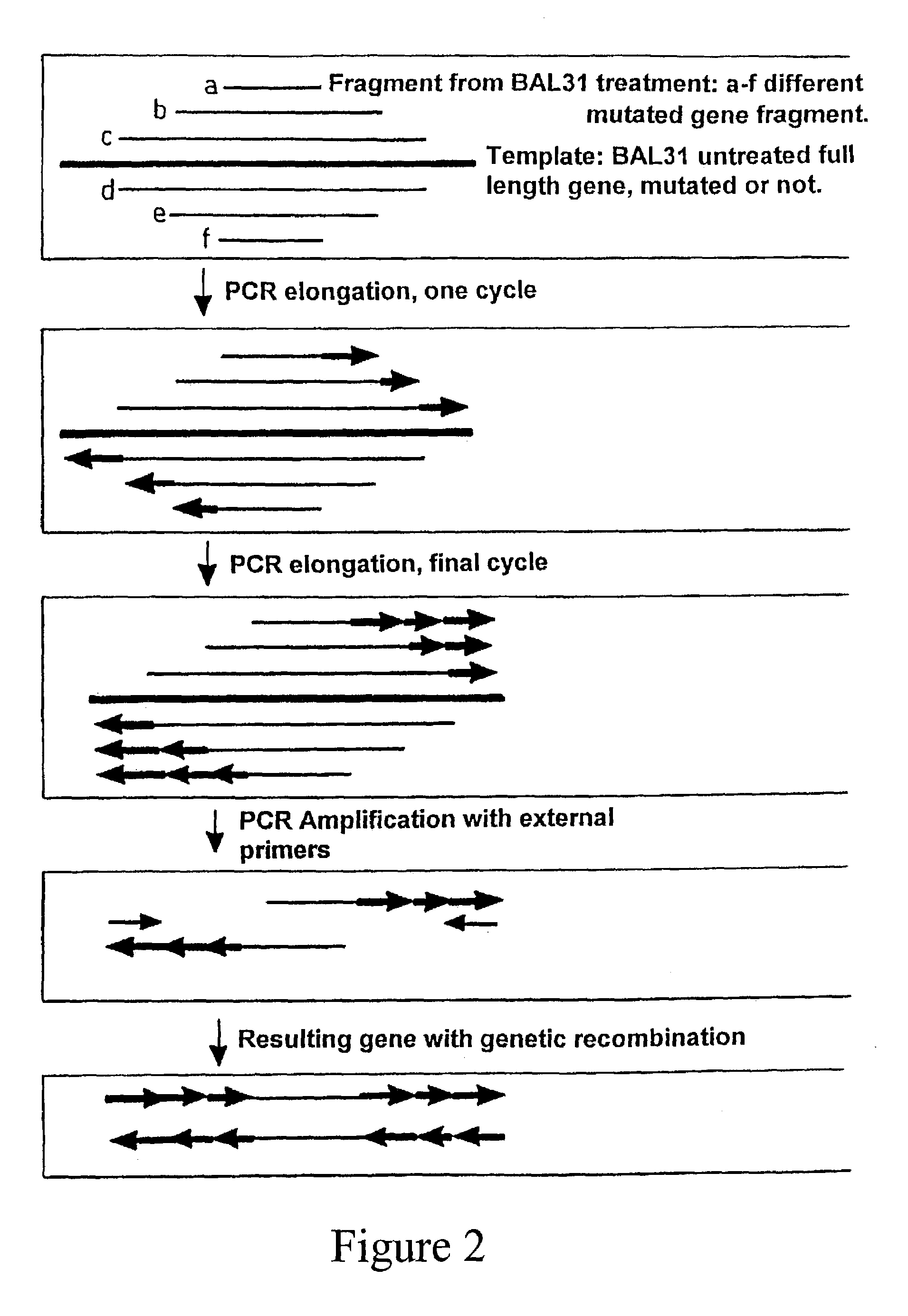
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Nuclease digestion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleases for DNA & RNA Digestion Purification of proteins and specific nucleic acids often requires the digestion of DNA, RNA or both. Viscosity problems resulting from high DNA concentrations and enzymatic cell dissociation methods are often enhanced utilizing DNAse.
Selected amplification of polynucleotides
InactiveUS8137936B2Reducing background and spurious amplificationSave materialMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolynucleotideDouble stranded
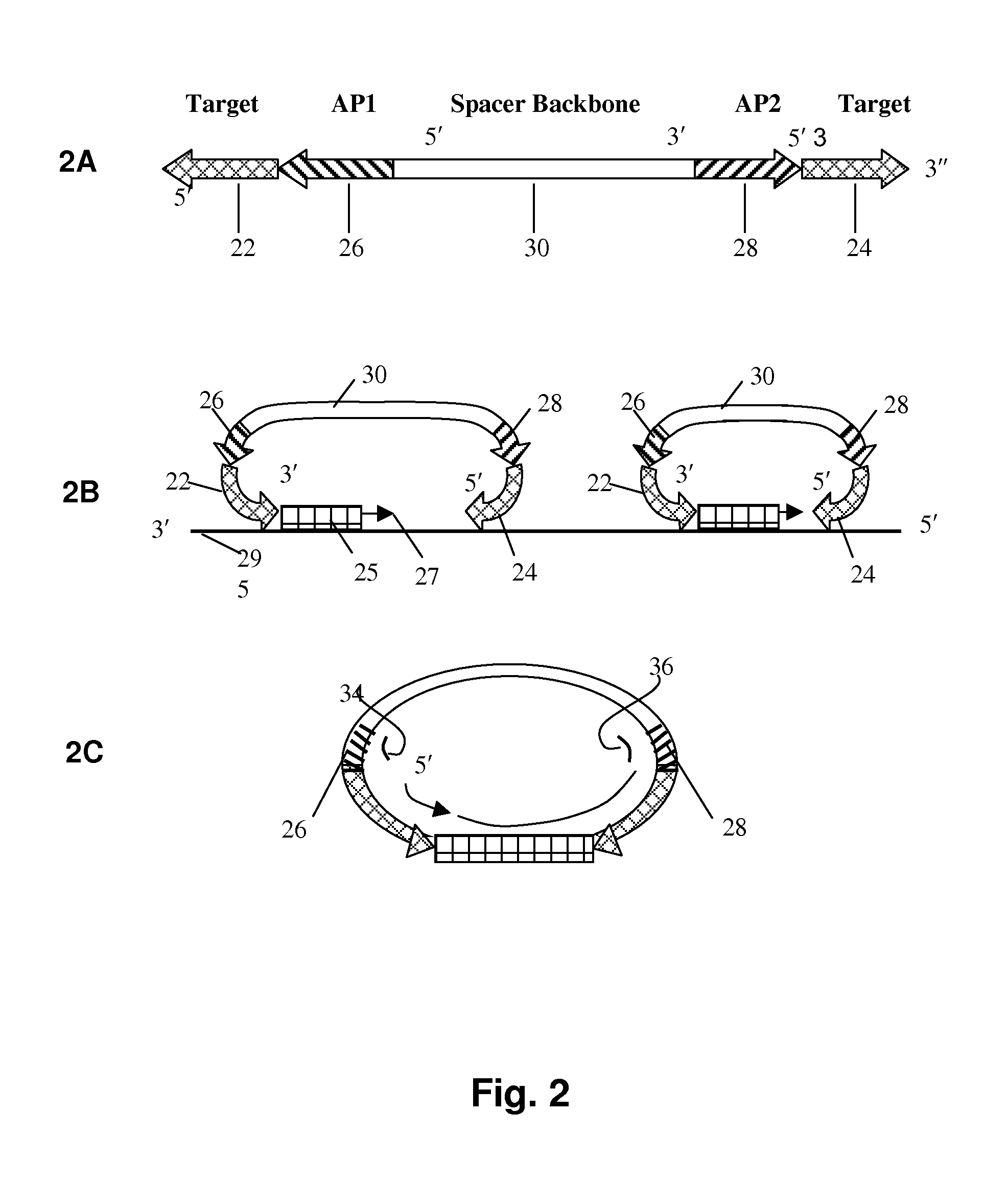
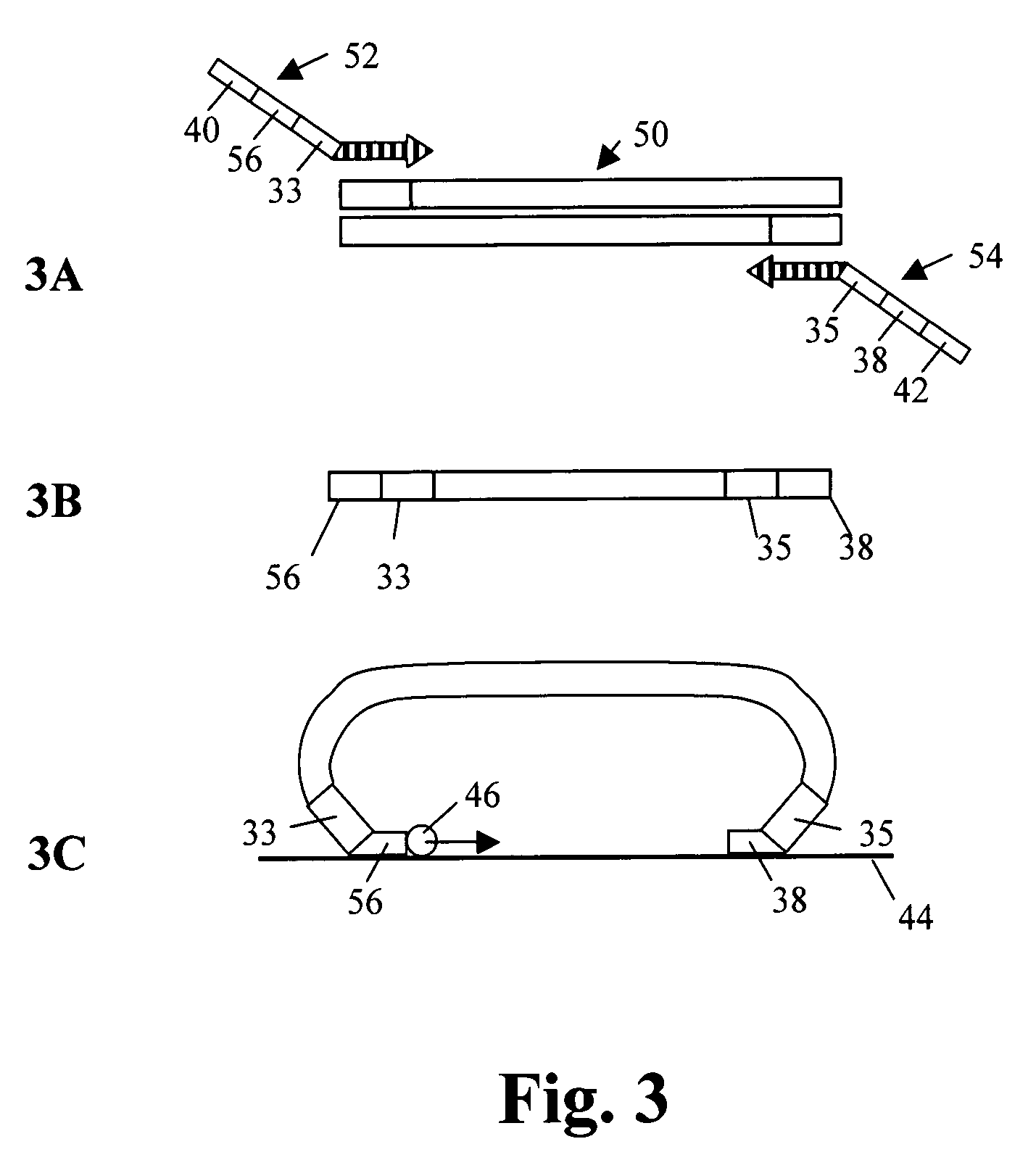
The invention provides methods and compositions for selectively amplifying one or more target polynucleotides in a sample. In one aspect, a plurality of selection oligonucleotides are provided that are capable of simultaneously annealing to separate regions of a target polynucleotide to form a complex that is enzymatically converted into a closed double stranded DNA circle that incorporates the sequence region between the two separate regions. Sequences that fail to form such complexes may be removed by nuclease digestion and the sequences of the remaining DNA circles may be amplified by a variety of techniques, such as rolling circle replication after nicking, PCR amplification after linearization, or the like.
Owner:MACEVICZ STEPHEN C
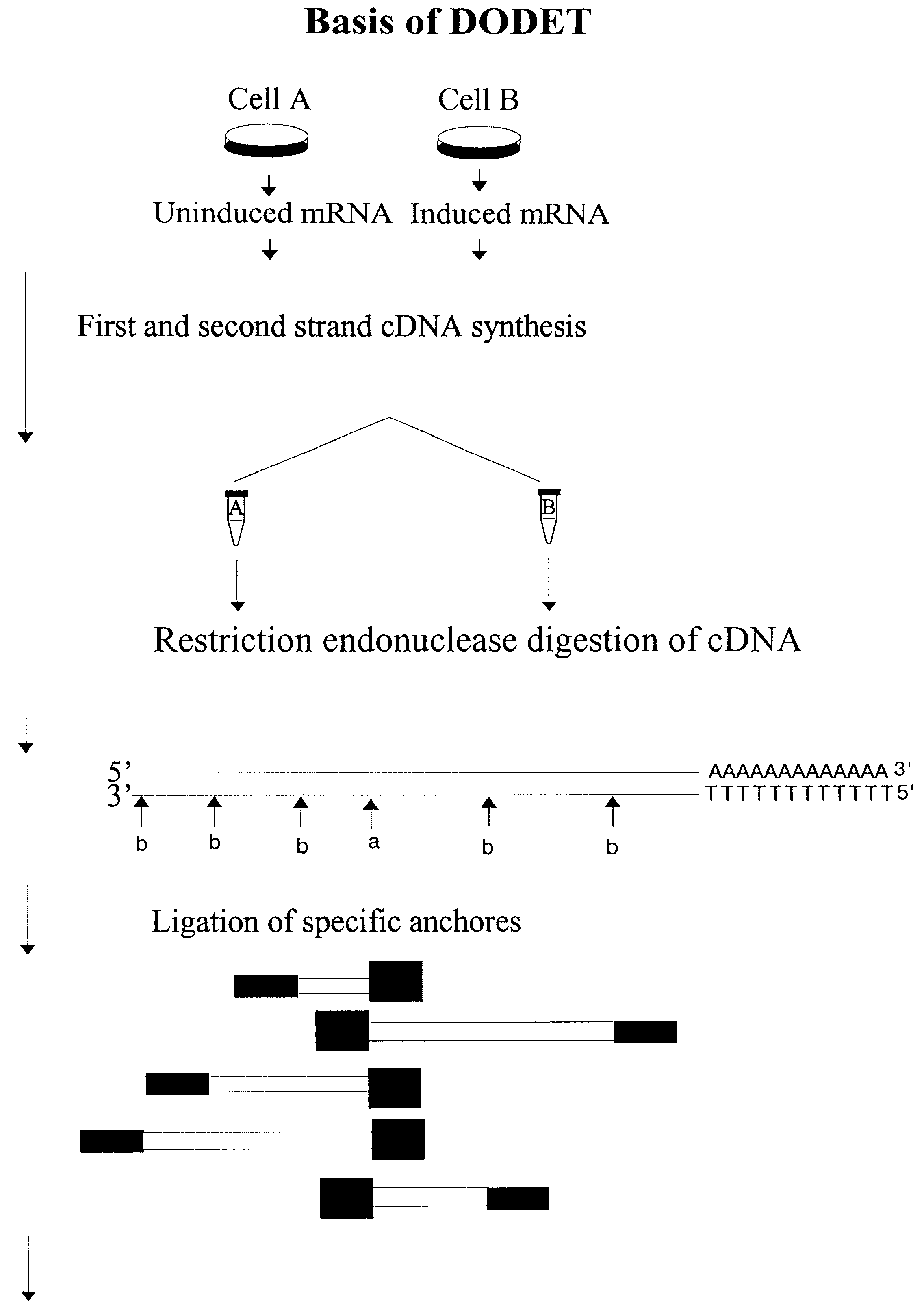
Method to clone mRNAs
InactiveUS6261770B1Convenient verificationHigh homologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Disclosed and claimed is a method for preparing a normalized sub-divided library of amplified cDNA fragments from the coding region of mRNAs contained in a sample. The method includes the steps of: a) subjecting the mRNA population to reverse transcription using at least one cDNA primer, thereby obtaining first strand cDNA fragments, b) synthesizing second strand cDNA complementary to the first strand cDNA fragments by use of the first strand DNA fragments as templates, thereby obtaining double stranded cDNA fragments, c) digesting the double stranded cDNA fragments with at least one restriction endonuclease, the endonuclease leaving protruding sticky ends of similar size at the termini of the DNA after digestion, thereby obtaining cleaved cDNA fragments, d) adding at least two adapter fragments containing known sequences to the cleaved cDNA fragments obtained in step c), the at least two adapter fragments being able to bind specifically to the sticky ends of the double stranded cDNA produced in step c), the one adapter fragment being able to anneal to the primer having formula I in step f), the second adapter fragment being a termination fragment introducing a block against DNA polymerization in the 5'->3' direction setting out from said termination fragment and the termination fragment being unable to anneal to any primer of the at least two primer sets in step f) during the molecular amplification procedure, the at least two adapter fragments being ligated to the cleaved cDNA fragments obtained in step c) so as to obtain ligated cDNA fragments, e) sub-dividing the ligated cDNA fragments obtained in step d) into 4n1 pools where 1<=n1<=4, and f) subjecting each pool of ligated cDNA fragments obtained in step e) to a molecular amplification procedure so as to obtain amplified cDNA fragments, wherein is used, for an adapter fragment used in step d), a set of amplification primers having the general formula Iwherein Com is a sequence complementary to at least the 5'-end of an adapter fragment which is ligated to the 3'-end of a cleaved cDNA fragment, N is A, G, T, or C, the one primer having the general formula I where n1=0, and the second primer having the general formula I where 1<=n1<=4, the second primer being capable of priming amplification of any nucleotide sequence ligated in its 3'-end to the adapter fragment complementary in its 5'-end to Com.
Owner:AZIGN BIOSCI
Selected amplification of polynucleotides
InactiveUS20070128635A1ConservingReduce backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideDouble strand
The invention provides methods and compositions for selectively amplifying one or more target polynucleotides in a sample. In one aspect, a plurality of selection oligonucleotides are provided that are capable of simultaneously annealing to separate regions of a target polynucleotide to form a complex that is enzymatically converted into a closed double stranded DNA circle that incorporates the sequence region between the two separate regions. Sequences that fail to form such complexes may be removed by nuclease digestion and the sequences of the remaining DNA circles may be amplified by a variety of techniques, such as rolling circle replication after nicking, PCR amplification after linearization, or the like.
Owner:MACEVICZ STEPHEN C
Method for building helicobacter pylori nucleic acid fingerprint spectrum and product thereof
ActiveCN102827930AAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEnzymatic digestionMass spectrometry
The invention discloses a method for building a helicobacter pylori nucleic acid fingerprint spectrum, which comprises PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, SAP (severe acute pancreatitis) enzymatic digestion, transcription and nuclease digestion, purification, mass spectrometer detection and the like. A helicobacter pylori nucleic acid fingerprint spectrum database is set up on the basis of the method. According to the generated mass peak spectrum of the experiment, the helicobacter pylori of a sample to be detected can be quickly identified, so the method can be widely applied in the fields of helicobacter pylori types and classification, environmental sanitation, public safety qunarantine and the like.
Owner:BIOYONG TECH
Removal of DNA fragments in mRNA production process
The present invention describes methods of removing DNA from an RNA transcript during the mRNA production process. The method embodies procedures for obtaining an in vitro transcription product, and removing any DNA from the product. The DNA can be removed by adding either free DNase or a resin containing immobilized DNase to the product, and recovering the RNA transcript. Alternatively, the DNA template used in the in vitro transcription reaction is labeled. After transcription, the product is applied to a resin that is configured to bind the label, and the RNA transcript is recovered. To detect whether any residual impurities are left in the RNA transcript product, the product is subjected to nuclease digestion and subsequently to liquid chromato graphy-tandem mass spectrometry analysis to quantitate any residual DNA. The present invention demonstrates efficient and effective methods of isolating an RNA transcript from an in vitro transcription product.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Extraction of duck enteritis virus genom DNA and sequence thereof
InactiveCN101182526AHigh homologyShort copy cycleFermentationGenetic engineeringPUC19Escherichia coli
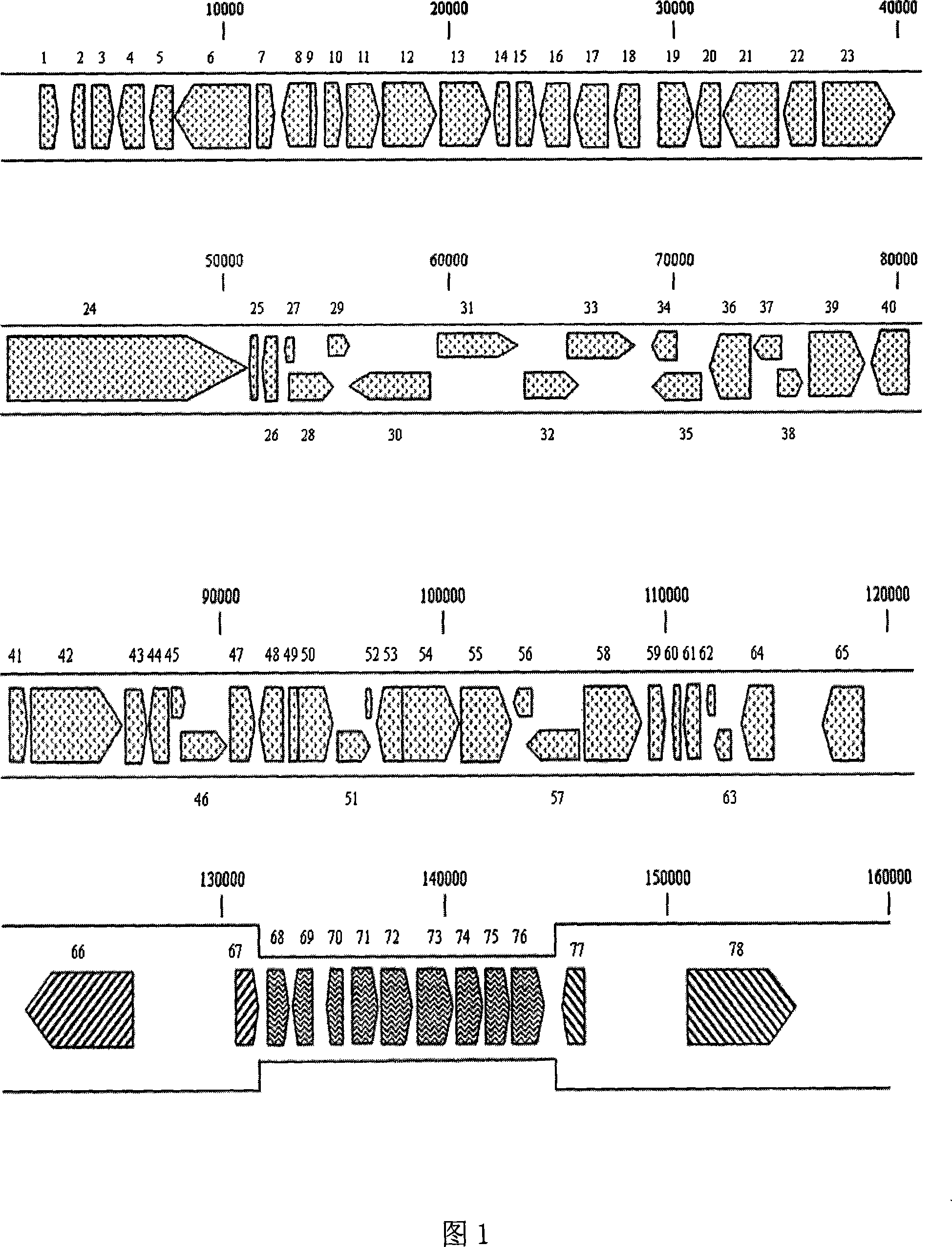
The invention discloses a DNA extraction method of Duck Enteritis Virus genome and the genome sequence. Firstly, the pyrolysis of chicken embryo fibroblast which is infected with DEV is processed by hypertonic buffer; then the nuclease is added for the digestion of cell DNA; and the virus genome DNA is obtained through phenol chloroform extracting method. The obtained sample is broken randomly into 2kb to 2.5kb fragments; the pUC19 vector is linked to transform host E. coli and construct genomic library. The positive clones in the library are randomly sequenced; the total sequence length has 6 times coverage rate for the virus genome. The sequence result is assembled and clustered to obtain the whole DEV genome sequence with the length of156512bp. The analysis shows that the genome structure is the same with that of the members of Varicella virus in Alpha- herpesus subfamily, which provides theoretical basis for the classification of DEV.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for in vitro molecular evolution of protein function
InactiveUS6958213B2Provide effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNegative strandNucleotide
The invention provides a method for generating a polynucleotide sequence or population of sequences from parent single stranded polynucleotide sequences encoding one or more protein motifs, comprising the steps of(a) providing single stranded DNA constituting plus and minus strands of parent polynucleotide sequences;(b) digesting the single stranded polynucleotide sequences with a nuclease other than DNase I to generate populations of single stranded fragments;(c) contacting said fragments generated from the plus strands with fragments generated from the minus strands and optionally, adding primer sequences that anneal to the 3′ and 5′ ends of at least one of the parent polynucleotides under annealing conditions;(d) amplifying the fragments that anneal to each other to generate at least one polynucleotide sequence encoding one or more protein motifs having altered characteristics as compared to the one or more protein motifs encoded by said parent polynucleotides.
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
Method for in vitro molecular evolution of protein function involving the use of exonuclease enzyme and two populations of parent polynucleotide sequence
InactiveUS7153655B2Good effectLonger effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for in vitro evolution of protein function. In particular, the method relates to the shuffling of nucleotide segments obtained from exonuclease digestion. The present inventors have shown that polynucleotide fragments derived from a parent polynucleotide sequence digested with an exonuclease can be combined to generate a polynucleotide sequence which encodes for a polypeptide having desired characteristics. This method may be usefully applied to the generation of new proteins (e.g., antibodies and enzymes) or parts thereof having modified characteristics as compared to the parent protein.
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
Detecting protein of transcriptional factor through probe of digestion FRET marke nucleic acid of nuclease
InactiveCN1727895AEfficient analysisEfficient comprehensive analysis and detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRegulation of gene expressionNucleic Acid Probes
A method for detecting transcription factor protein by nucleic acid probe with nuclease protection PRET label includes preparing fluorescence labeled nucleic acid probe, carrying out combination reaction of nucleic acid probe with transcription factor protein, adding nuclease in combination reaction system to carry out enzyme nick reaction and detecting reaction system by fluorescence to reflect expression and activation level of transcription factor protein.
Owner:王进科 +1
Method for enhancing stability of nano gold and biological detection method adopting the same
ActiveCN101762574AImprove stabilityHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSingle strand dnaNucleic acid
The invention provides a method for enhancing the stability of nano gold and a biological detection method adopting the same. Mononucleotide dNMP can better stabilize the nano gold than single-stranded DNA with the same composition and the same base concentration. Various nucleases with matrix selectivity can digest nucleic acid to form the dNMP. The property of the dNMP, which enables the dNMP to better stabilize the nano gold, is integrated with specific enzyme reaction, and the change of the color of the nano gold can be used to simply and conveniently detect various analytes including enzyme and DNA. The method greatly broadens the range of detected substances biologically detected by the unmodified nano gold, and increases the sensitivity of detection. Taking DNA detection for an example, the mole ratio range of a detecting probe and a target is broadened by three orders of magnitude. The method can be applied to the detection of various types of substances including micromolecules and heavy metal ions.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing subunit vaccine of reovirus antigen for grass carp
InactiveCN1616094AEasy to prepareEasy to operateViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsInfected cellReovirus (antigen)
The preparation process of reovirus antigen subunit vaccine for grass carp includes the following steps: proliferation of GCRV873, which is the Hunan Shaoyang strain of reovirus, in grass carp kidney cell line; centrifugal purification and concentration of GCRV873 infected cell virus suspension; processing purified virus with surfactant to disintegrate complete virus structure to form viral nucleic acid and capsid protein subunit component; digesting with nuclease to degrade free virus genome dsRNA; dialysis to obtain reovirus protein subunit antigen preparation for grass carp containing no nuclease; and diluting with physiological saline to obtain the said vaccine. The vaccine of the present invention has the advantages of containing complete virus protein antigen component, containing no genetic virus matter RNA, simple preparation process, high product purity, etc.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for separating antibiotic peptide and separated antibiotic peptide
InactiveCN1557960AEfficient separationHigh antibacterial activityFermentationHybrid peptidesEscherichia coliLiquid medium
The invention relates to a method of isolating antibacterial peptides and the isolated peptides thereof. The method comprises: constructing a fusion DNA sequence of yeast alpha mating factor leader sequence and a random peptide, inserting the sequence into a saccharomyces cerevisiae vector which contains an inducible promotor, digesting the unlinked linear DNA with exonuclease III and mungbean sprout nuclease, electrotransforming the yeast vector after purification, culturing the transformant 24h and covering the transformant with the upper medium which contains E. coli K12D31, and detecting the bacterial inhibition ring and the bacterial inhibition rate after inducing the expression by liquid medium, selecting the positive clones and amplifying by PCR, and determining the sequence. The method of the present invention can be used easily and effectively to isolate antibacterial oligopeptides and polypeptides and can be used as an alternative way to find antibiotics.
Owner:刘秋云 +1
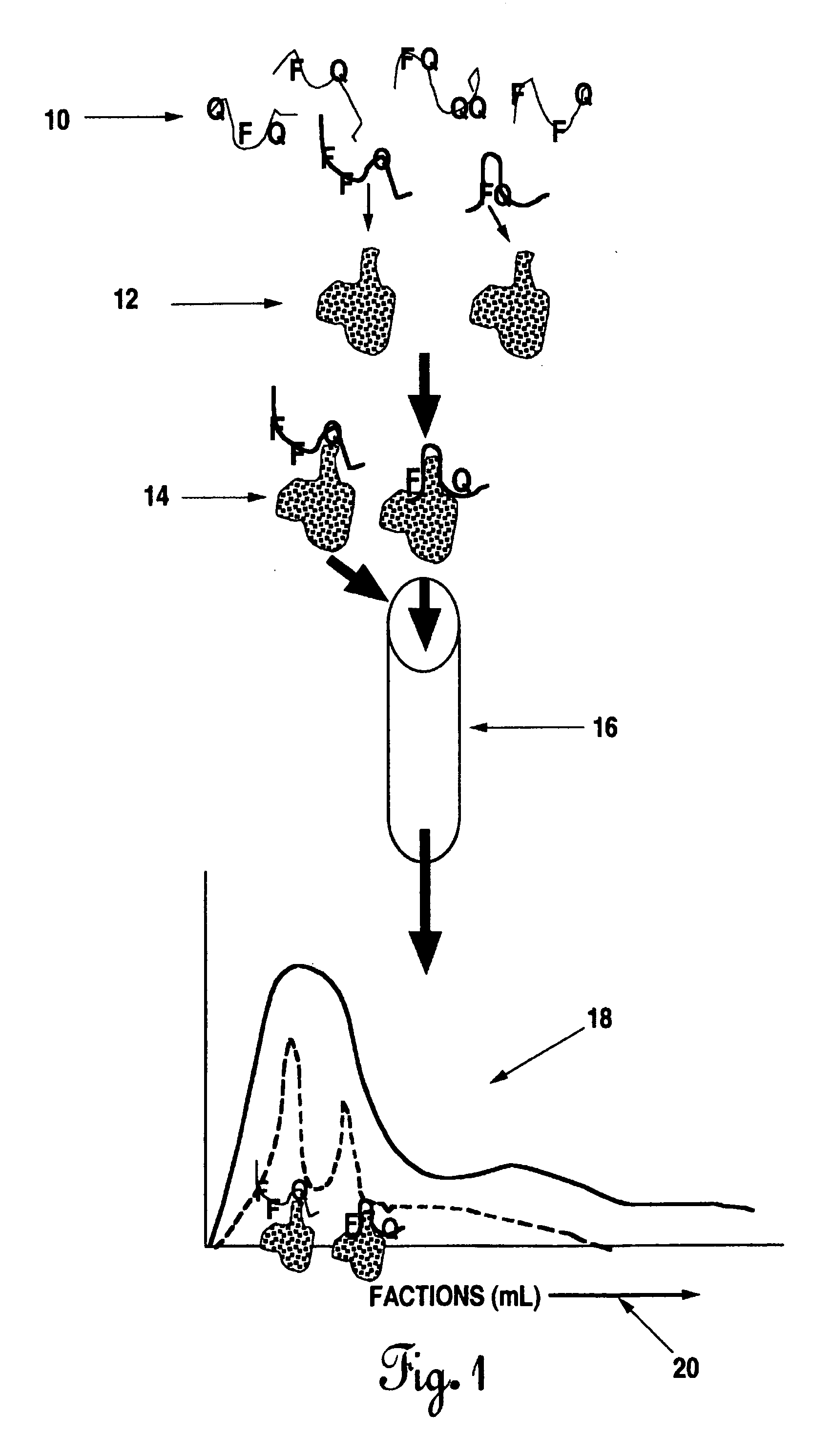
Methods of producing interachain fluorophore-quencher FRET-aptamers and assays
InactiveUS20060257914A1Maximize sensitivityMaximize specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
The present invention describes methods for the production and use of single chain (single-stranded) fluorescence resonance energy transfer (“FRET”) DNA or RNA aptamers containing fluorophores (F) and quenchers (Q) at various loci within their structures, such that when its specific matching analyte is bound and the FRET-aptamers are excited by specific wavelengths of light, the fluorescence intensity of the system is modulated (increased or decreased) in proportion to the amount of analyte added. F and Q are covalently linked to nucleotide triphosphates (NTPs), which are incorporated by various nucleic acid polymerases such as Taq polymerase during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and then selected by affinity chromatographic, size-exclusion or molecular sieving, and fluorescence techniques. Further separation of related FRET-aptamers can be achieved by ion-pair reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or other types of chromatography. Finally, FRET-aptamer structures and the specific locations of F and Q within FRET-aptamer structures are determined by digestion with exonucleases and mass spectral nucleotide sequencing analysis.
Owner:CIBUSDX INC
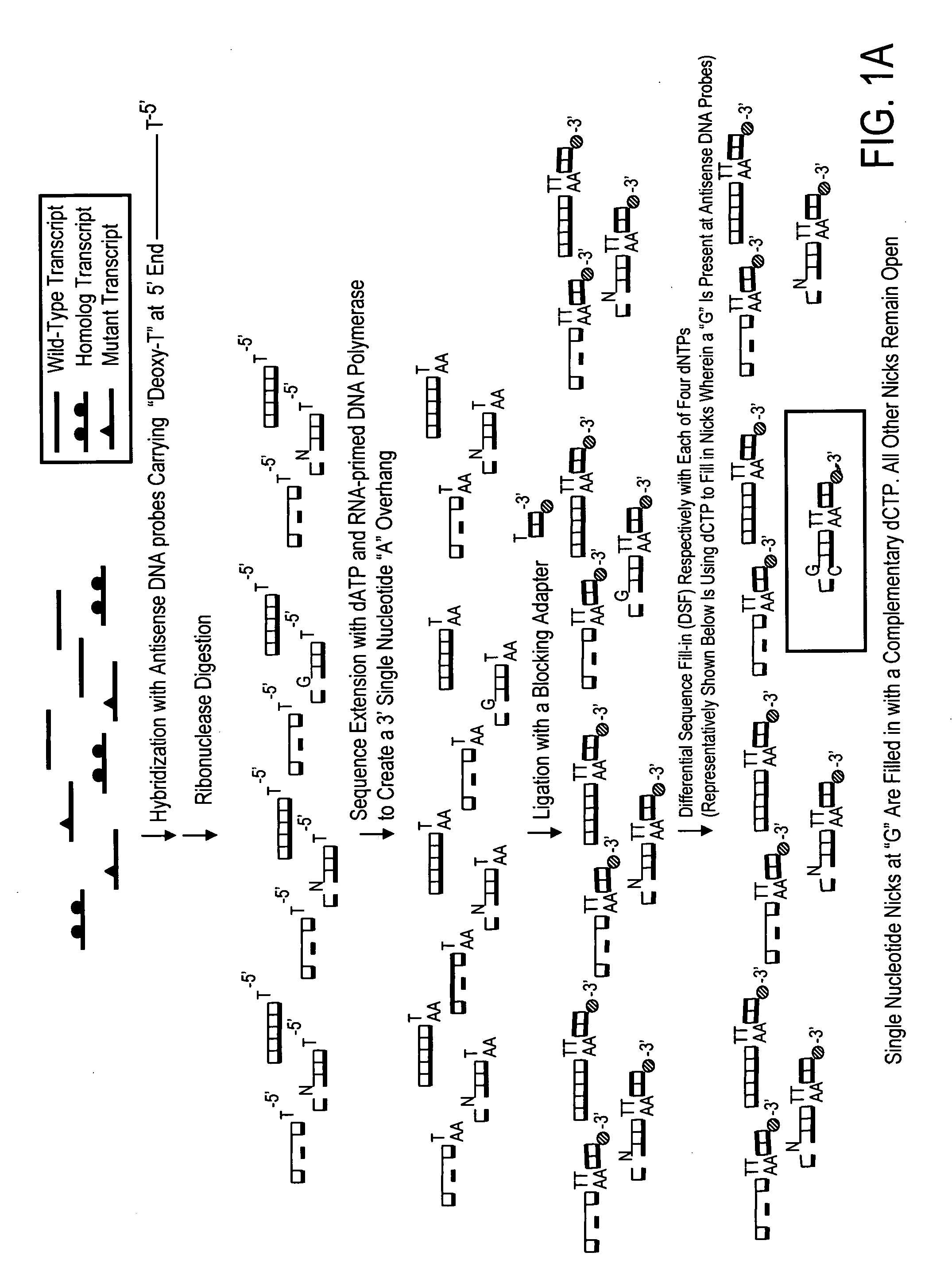
High throughput mutation screening methods and kits using a universalized approach - differential sequence fill-in (dsf)-enabled sequential adapter ligation and amplification
InactiveUS20090075276A1Facilitate simultaneous detectionProhibiting further ligationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationScreening methodSingle strand
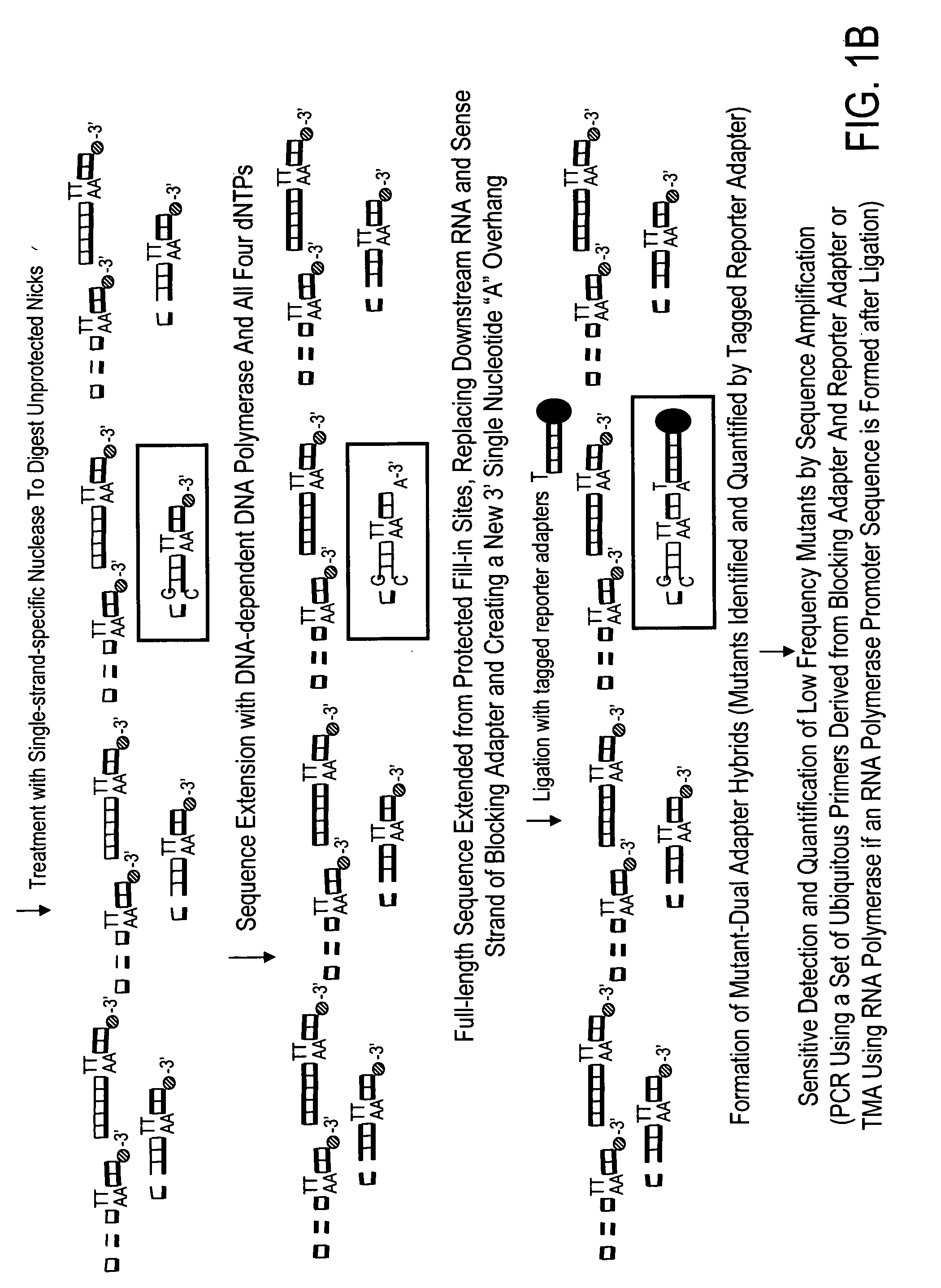
This disclosure teaches high throughput mutation screening methods allowing simultaneous analysis of multiple genetic regions of interest and sensitive detection of very low frequency mutation(s) by the use of a universalized approach. Methods comprise treating RNA:DNA heteroduplexes of interest with a ribonuclease, sequence extension by an RNA-primed DNA polymerase, ligation with a blocking adapter, and differential sequence fill-in followed by single-strand-specific nuclease digestion to permit full-length sequence extension and subsequent ligation with a tagged reporter adapter solely in mutants filled in with a complementary deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate. By forming tagged mutant-dual adapter hybrids or mutant-triple adapter hybrids, the detection and / or quantification of mutants may be directed to the commonly shared tag(s) or flanking adapter sequences for signal detection / enhancement or sequence amplification in all different mutants regardless of the source or the number of mutations involved, thereby avoiding the tremendous effort of multiple target-specific sequence amplifications. Methods may be performed wholly or partially in solution, on solid phase media, in large scale, adapted for automated or semi-automated analysis, and any combinations thereof.
Owner:LEE MING SHENG +2
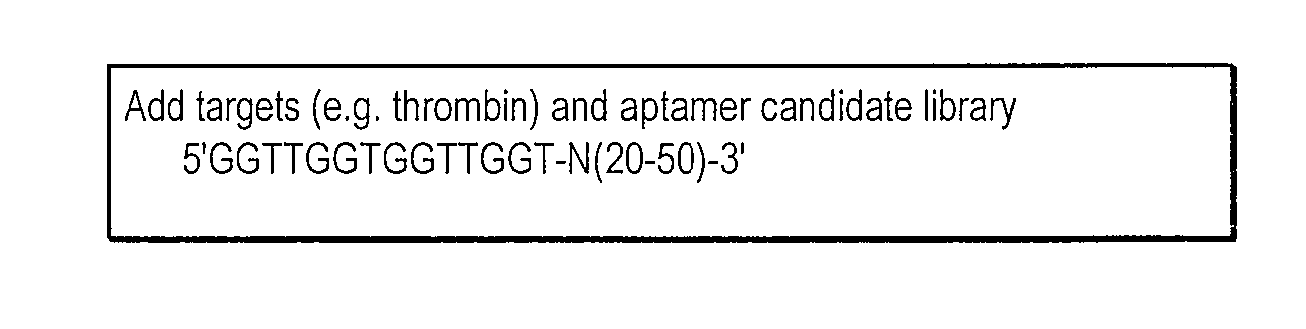
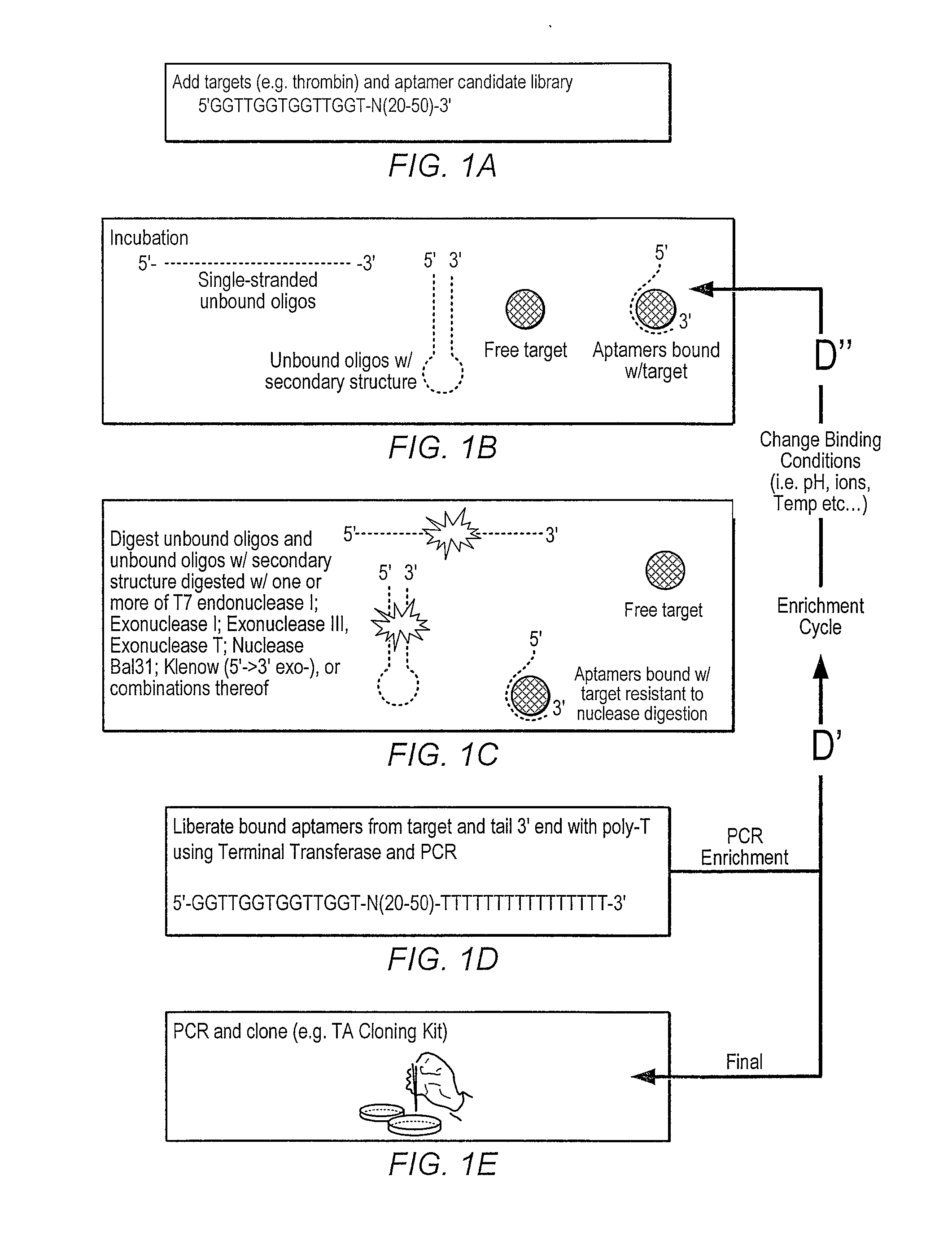
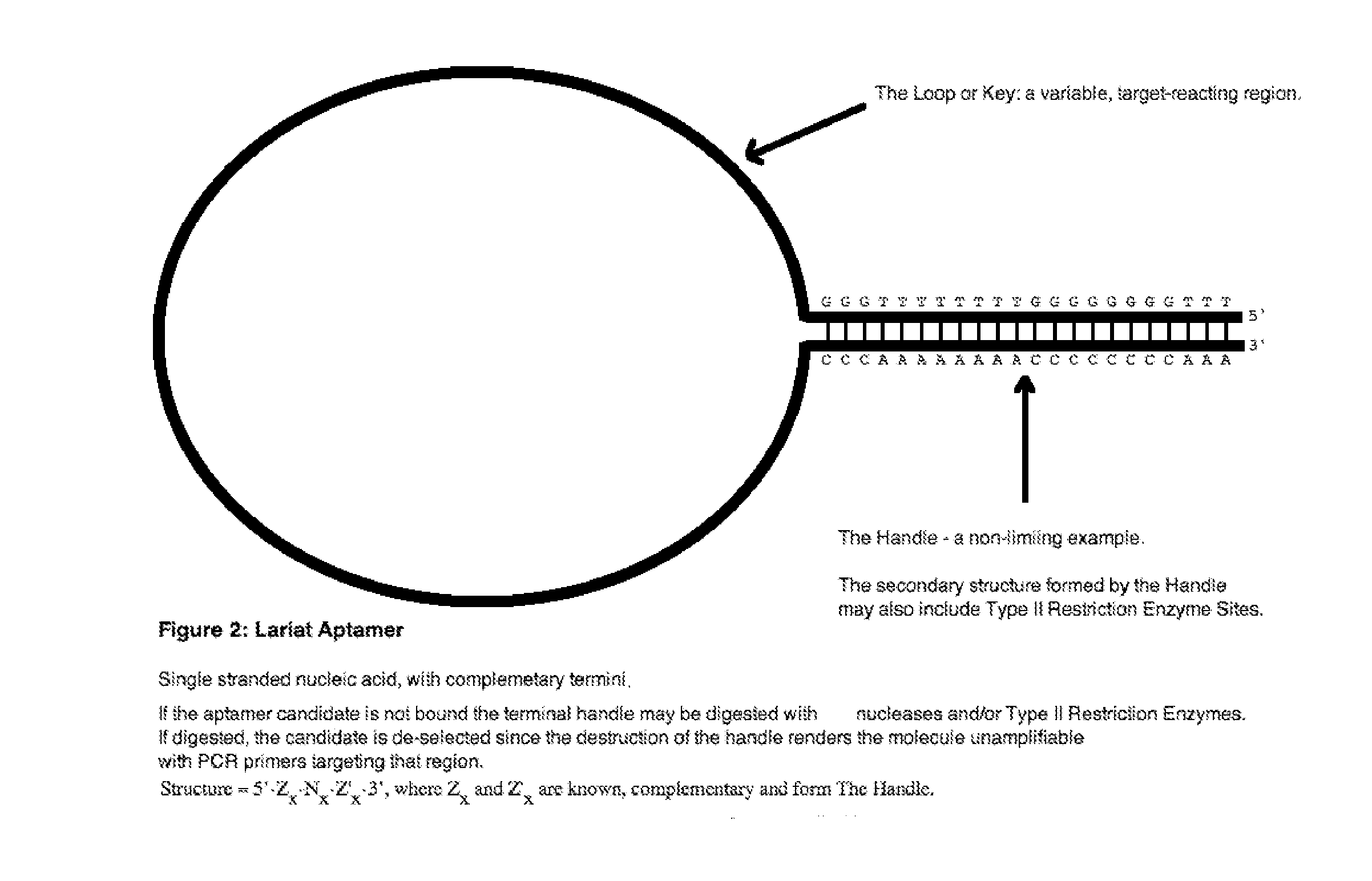
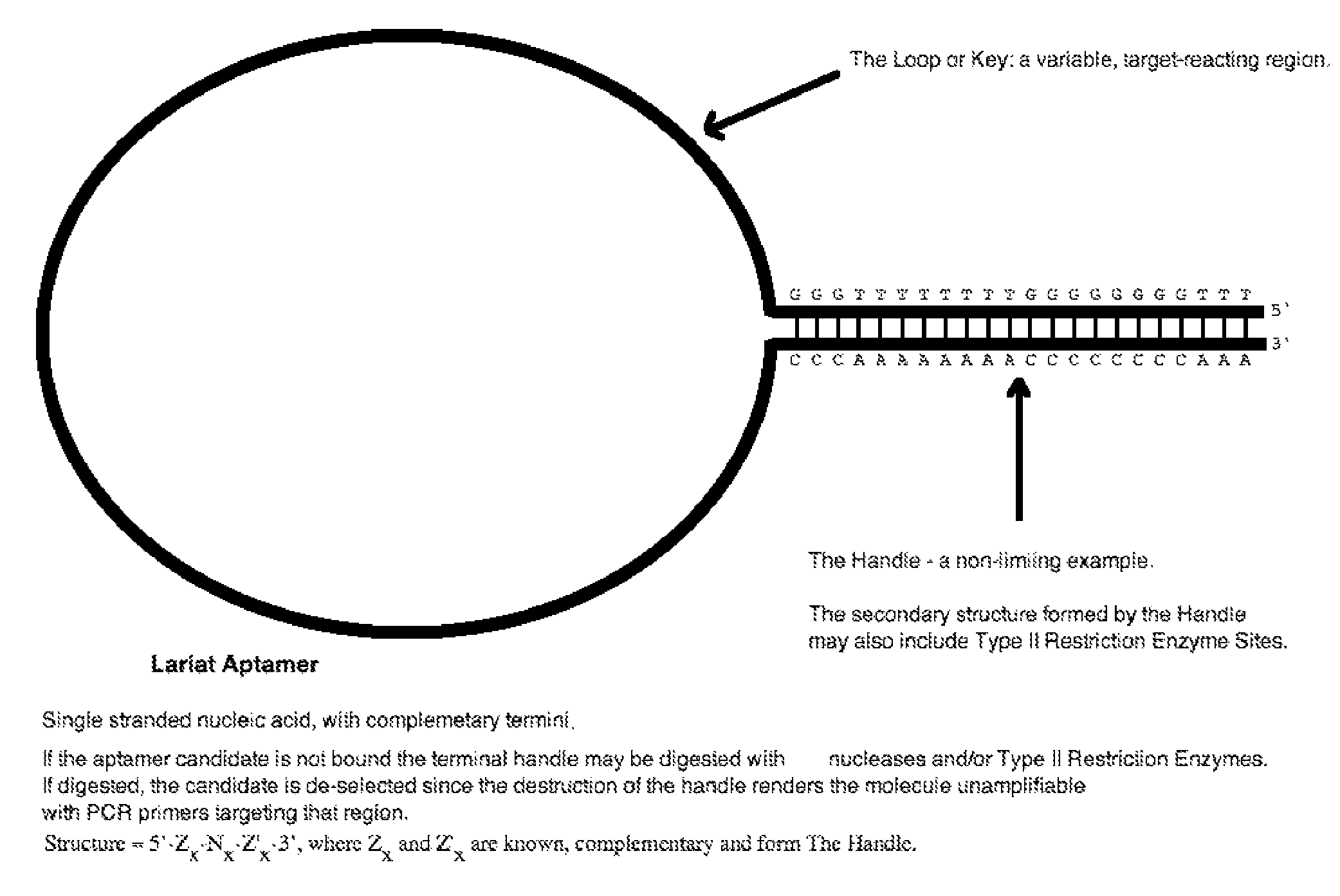
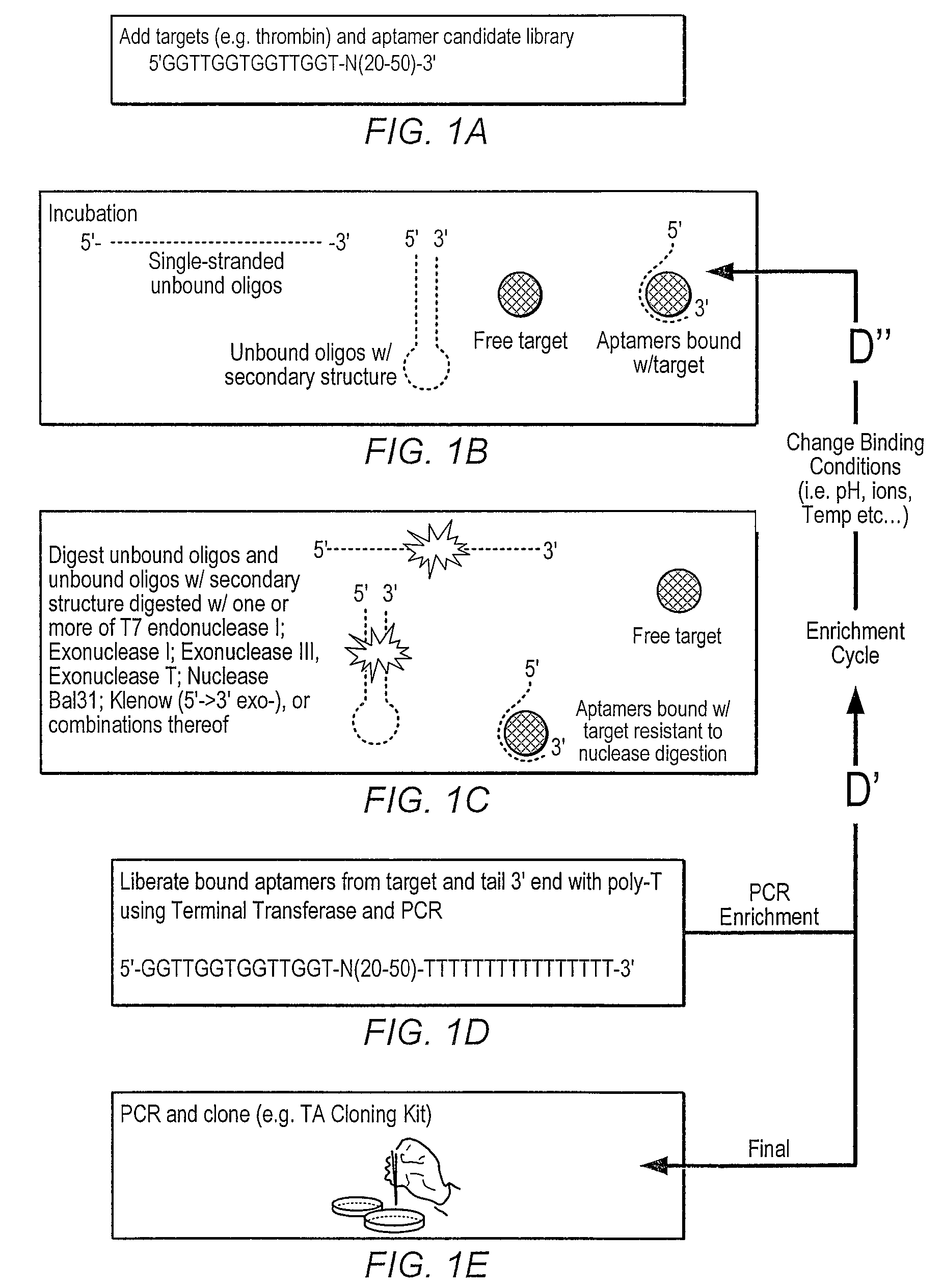
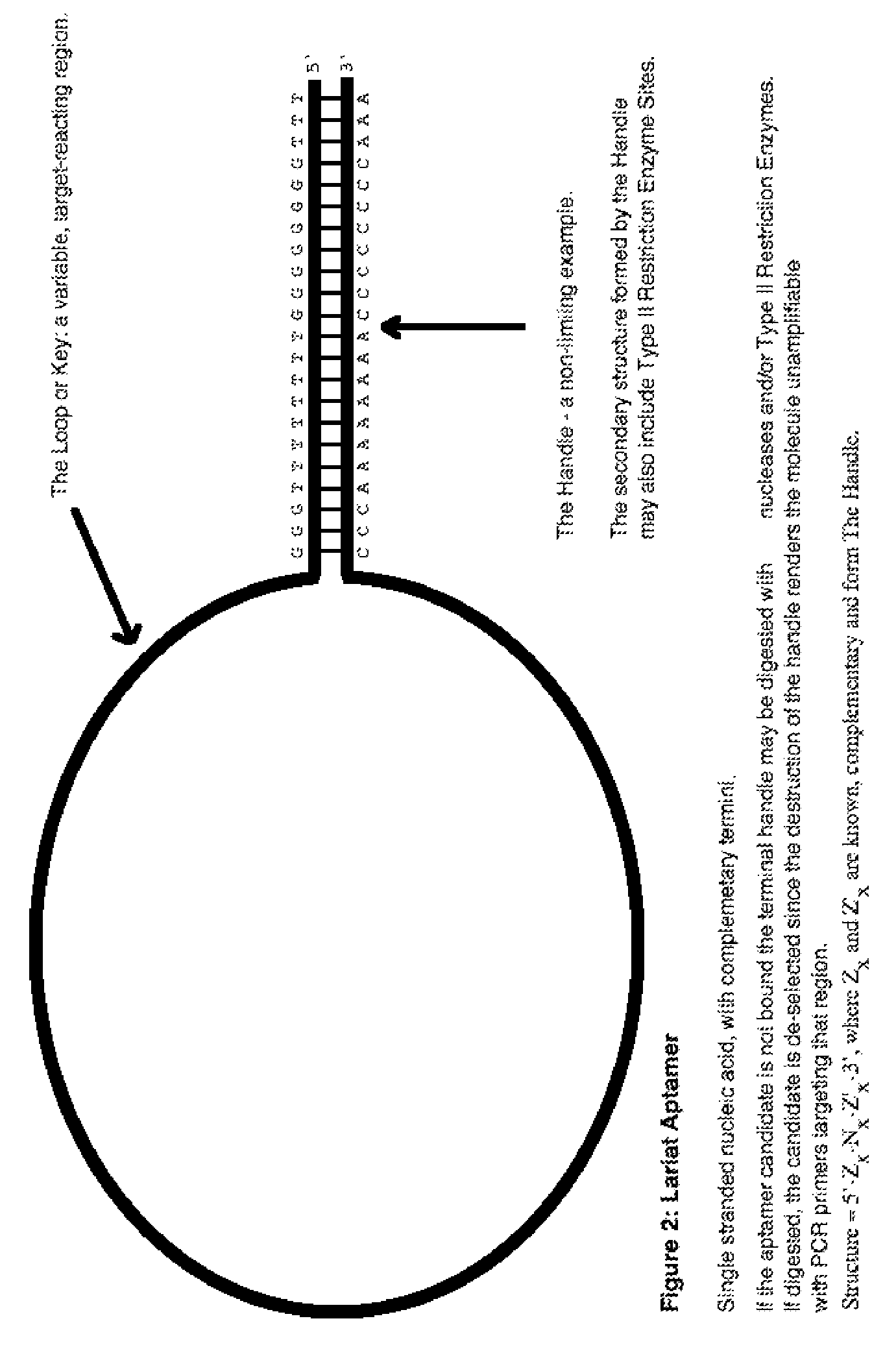
lariat aptamer: aptamer candidate exclusion by nuclease digestion
A method for identifying aptamers that bind to target molecules may include contacting an oligonucleotide library with target molecule and digesting unbound oligonucleotides with one or more endonucleases, one or more exonucleases, or one or more endonucleases in combination with one or more exonucleases. The unbound oligonucletides lend themselves to nuclease digestion because their flanking sequences are complementary and form predictable, terminal, secondary structure (a Lariat Aptamer). Bound molecules (aptamers) are protected from nuclease digestion and become enriched. A method for identifying aptamers may further include optionally subjecting selected aptamers to one or more rounds of selection under conditions of increased stringency. A method for identifying aptamers may include yet further amplifying selected aptamers. The described methods may be performed in a screen for identifying aptamers either alone or in combination with other methods typically employed in the art for selecting aptamers (such as, e.g., SELEX). Also contemplated herein are systems and kits for accomplishing the above.
Owner:LOPREATO GREGORY FRANCIS
Single copy genomic hybridization probes and method of generating same
InactiveUS20050064449A1Eliminates spurious hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
Nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) hybridization probes are described which comprise a labeled, single copy nucleic acid which hybridizes to a deduced single copy sequence interval in target nucleic acid of known sequence. The probes, which are essentially free of repetitive sequences, can be used in hybridization analyses without adding repetitive sequence-blocking nucleic acids. This allows rapid and accurate detection of chromosomal abnormalities. The probes are preferably designed by first determining the sequence of at least one single copy interval in a target nucleic acid sequence, and developing corresponding hybridization probes which hybridize to at least a part of the deduced single copy sequence. In practice, the sequences of the target and of known genomic repetitive sequence representatives are compared in order to deduce locations of the single copy sequence intervals. The single copy probes can be developed by any variety of methods, such as PCR amplification, restriction or exonuclease digestion of purified genomic fragments, or direct synthesis of DNA sequences. This is followed by labeling of the probes and hybridization to a target sequence.
Owner:KNOLL JOAN +1
16S rDNA based preparation method of bacteria nucleic acid fingerprint characteristic spectrums and application thereof
InactiveCN103060431AValid identificationUndisturbedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEnzymatic digestionSuper absorbent
The invention discloses a method for preparing bacteria 16S rDNA fingerprint spectrums. The method comprises the steps of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, SAP (super absorbent polymer) enzymatic digestion, transcription and nuclease digestion, purification, mass spectrometer detection and the like. A nucleic acid fingerprint spectrum database of common bacteria is created based on the method. According to the mass spectrum peak chart generated through experiments, the bacteria to be detected can be classified and identified and the results can be widely applied to the fields of bacteria classification and identification, genetic evolution analysis, drug resistance screening application, import and export inspection and the like.
Owner:向华
Method for nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveCN103667491AReduce usageKeep it naturalMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingDigestion
The invention discloses a method for nucleic acid sequencing through adopting nuclease digestion reaction. The method includes the following steps: (1), performing digestion and degradation on a nucleic acid target sequence through an enzyme, so as to generate an enzyme-digested product; (2), detecting the enzyme-digested product, and finally obtaining information of the nucleotide sequence. The method provided by the technical scheme is used for cutting the target sequence and determining an unknown sequence through the exonuclease, and is realized through utilizing the biodegradability of the exonuclease and sequencing the enzyme-digested product generated from degradation, so as to determine the enzyme-digested product.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods for arranging and packing nucleic acids for unusual resistance to nucleases and targeted delivery for gene therapy
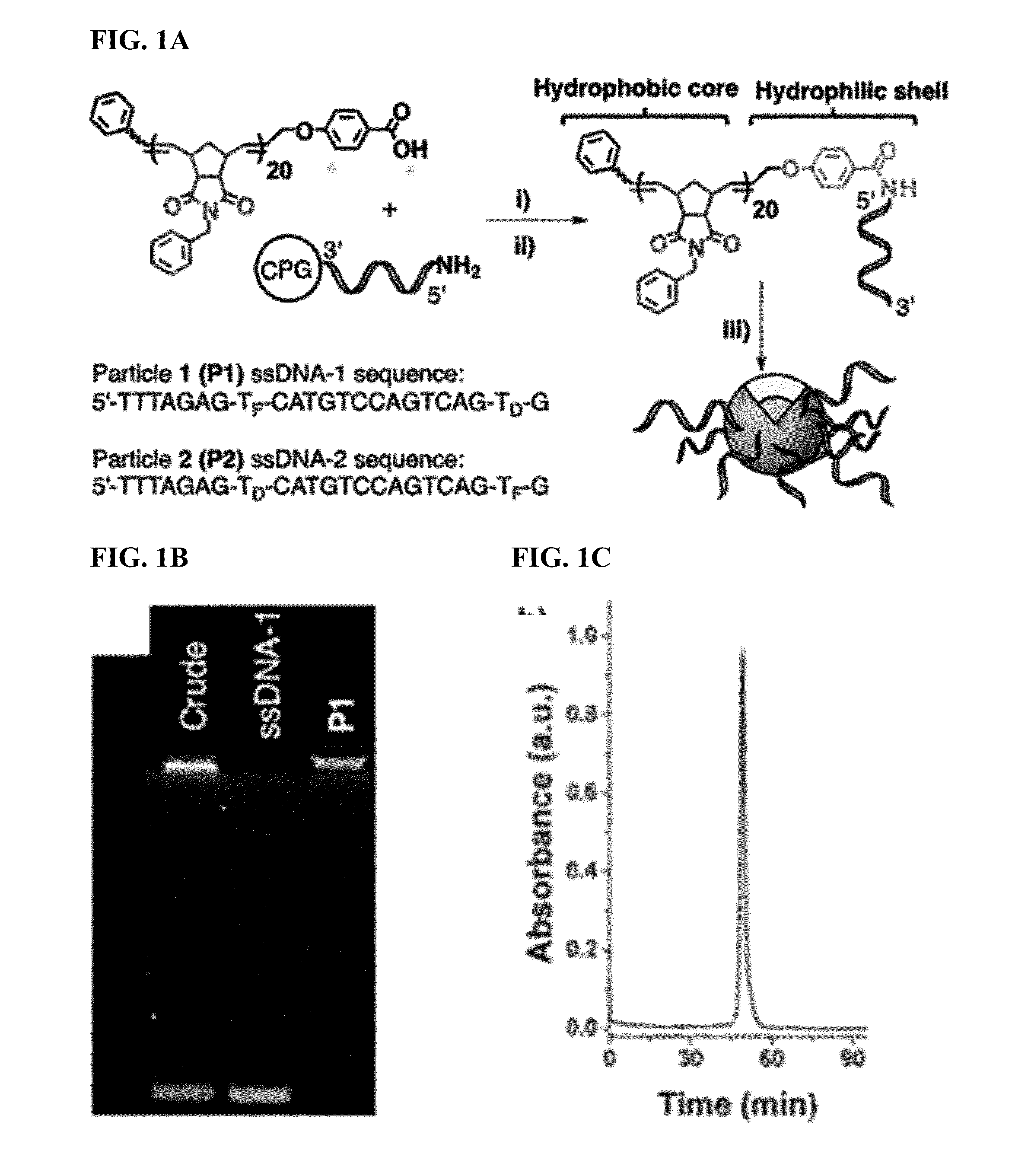
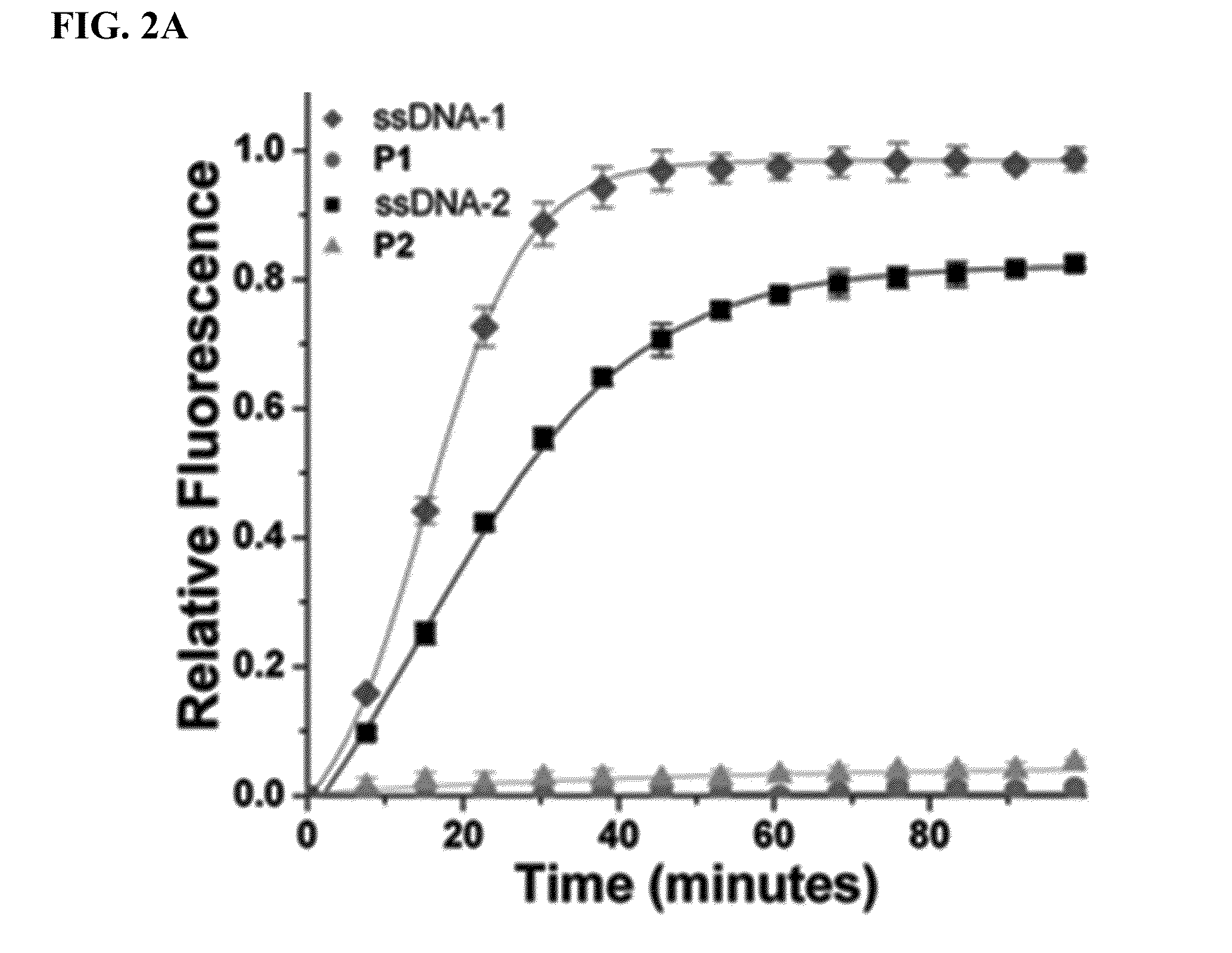
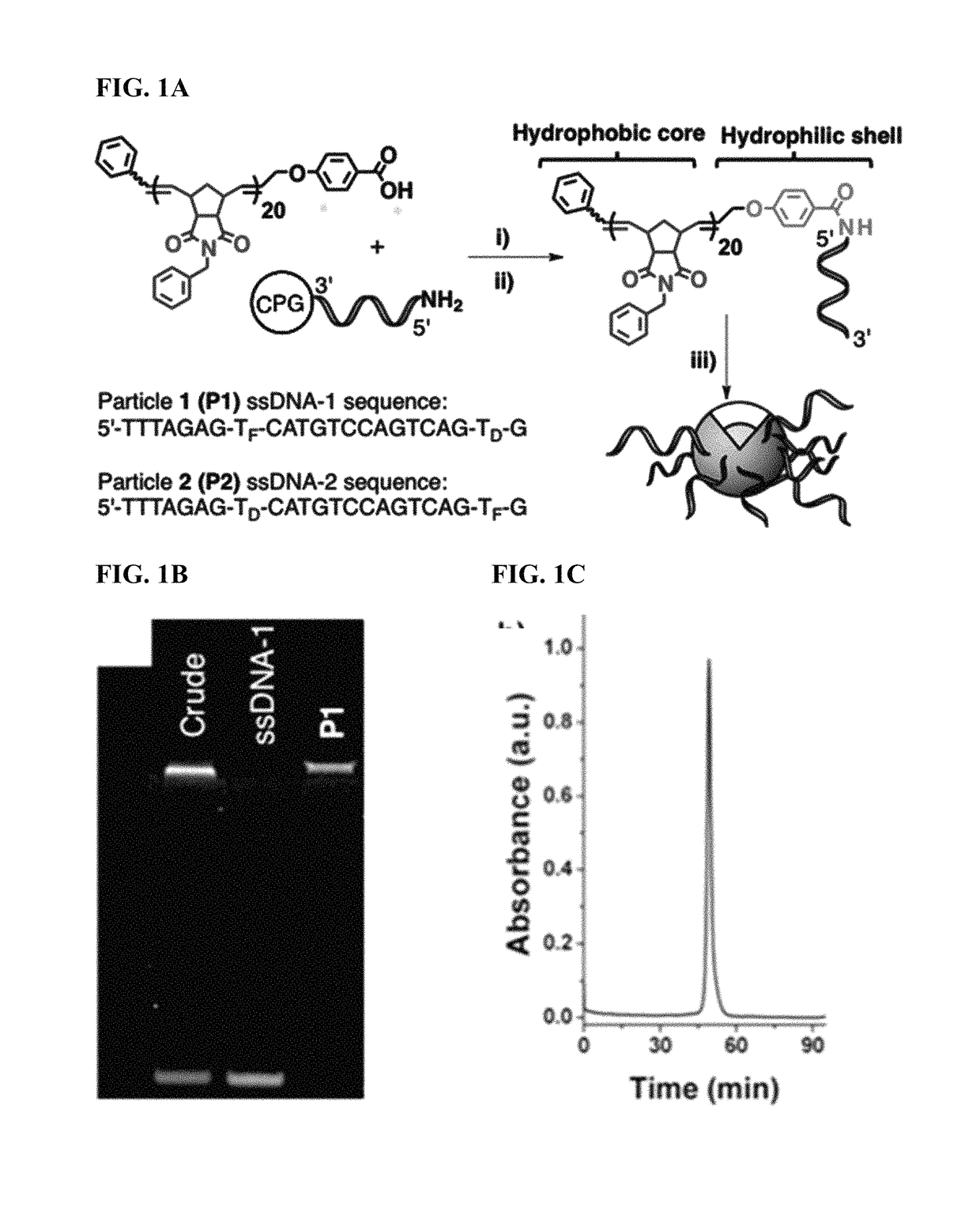
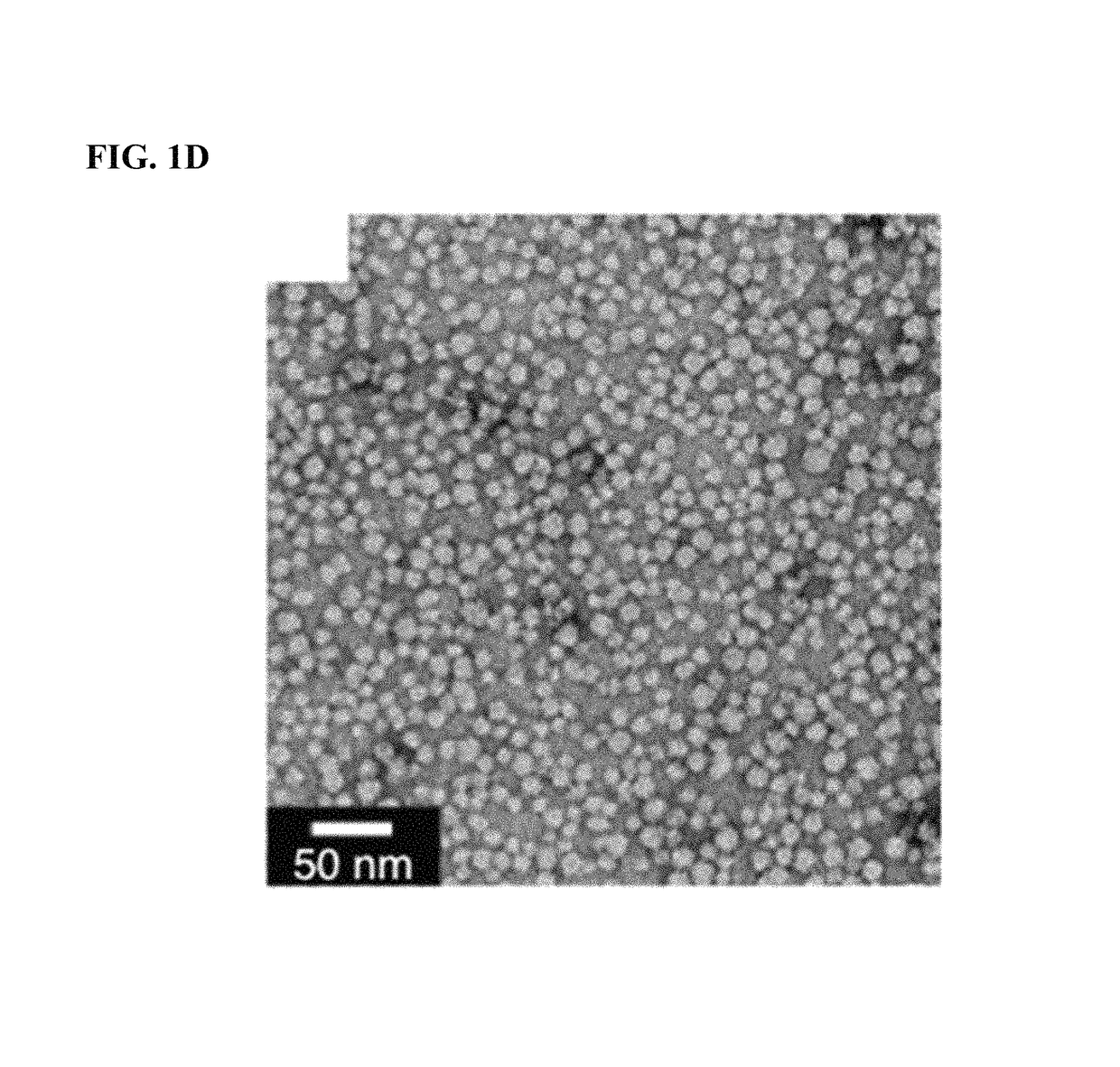
ActiveUS20150190525A1High densityOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryEnzymatic degradationSequence selectivity
There are disclosed compositions and methods to render nucleic acids resistant to nuclease digestion while maintaining sequence selective hybridization competency. The approach relies on utilizing nucleic acids as the polar head group of a nucleic acid-polymer amphiphile in order to assemble well-defined, discrete micellar nanoparticles. Dense packing of nucleic acid in the micelle corona allows for hybridization of complementary oligonucleotides while prohibiting enzymatic degradation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Lariat aptamer: aptamer candidate exclusion by nuclease digestion
A method for identifying aptamers that bind to target molecules may include contacting an oligonucleotide library with target molecule and digesting unbound oligonucleotides with one or more endonucleases, one or more exonucleases, or one or more endonucleases in combination with one or more exonucleases. The unbound oligonucletides lend themselves to nuclease digestion because their flanking sequences are complementary and form predictable, terminal, secondary structure (a Lariat Aptamer). Bound molecules (aptamers) are protected from nuclease digestion and become enriched. A method for identifying aptamers may further include optionally subjecting selected aptamers to one or more rounds of selection under conditions of increased stringency. A method for identifying aptamers may include yet further amplifying selected aptamers. The described methods may be performed in a screen for identifying aptamers either alone or in combination with other methods typically employed in the art for selecting aptamers (such as, e.g., SELEX). Also contemplated herein are systems and kits for accomplishing the above.
Owner:LOPREATO GREGORY FRANCIS
Nucleic acid fingerprint feature spectrum database of mycobacterium tuberculosis and usage of nucleic acid fingerprint feature spectrum database
ActiveCN102808223AAccurate identificationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyTuberculosis mycobacterium
The invention discloses a method for rapidly classifying and identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis by the aid of the mass-spectrometric technique. The method includes the steps of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, SAP (severe acute pancreatitis) enzymatic digestion, transcription and nuclease digestion, purification, mass spectrometer detection and the like. A nucleic acid fingerprint spectrum database of the mycobacterium tuberculosis is established based on the method. The mycobacterium tuberculosis in samples to be detected can be rapidly identified according to mass spectrum peak diagrams generated by experiments, and results can be widely applied to typing and classification of the mycobacterium tuberculosis and the fields of environmental sanitation, public security quarantine and the like.
Owner:重庆黄嘉生物技术有限公司
Method for extracting and enriching phage in soil
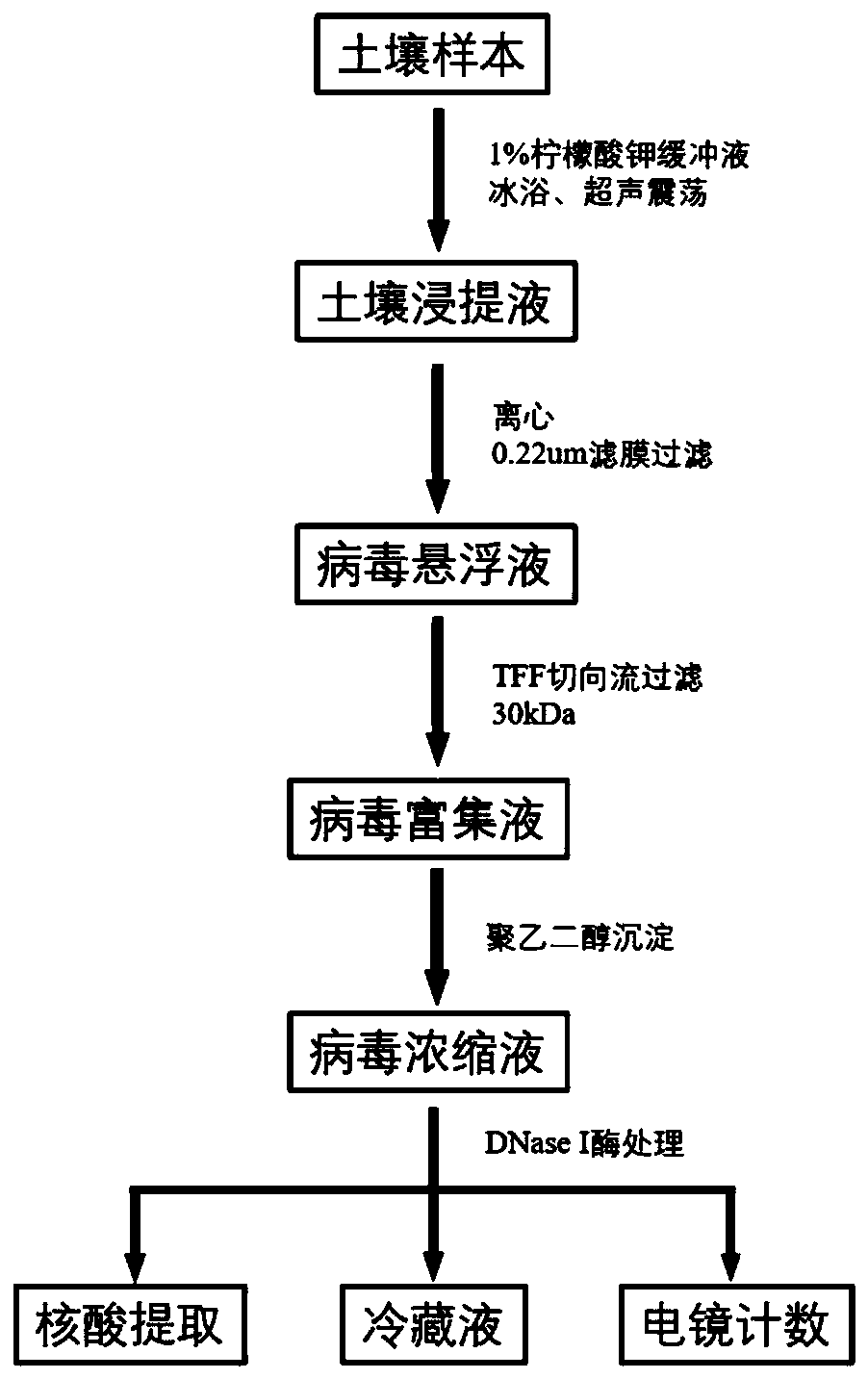
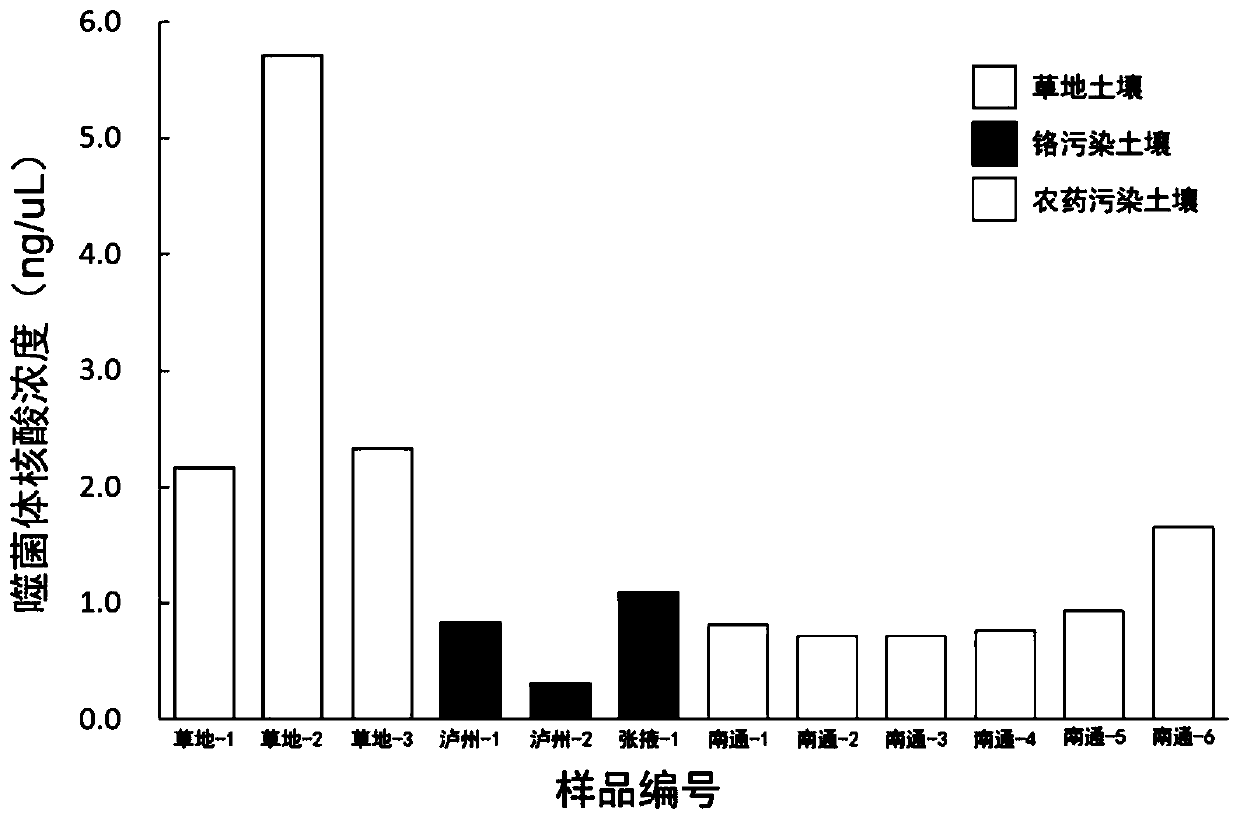
InactiveCN110904057AIncrease concentrationHigh purityMicroorganism based processesBacteriophagesTE bufferUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a method for extracting and enriching phage in soil, which comprises the following steps: mixing fresh soil with a potassium citrate buffer solution according to a certain ratio, incubating the materials at low temperature for a period of time, and carrying out ultrasonic oscillation treatment on an extracting solution to extract the phage in soil from soil particles, centrifuging soil turbid liquid for multiple times to obtain a supernatant, sequentially filtering and degerming by using a sterilization filter membrane, reducing the volume of a filtrate by using a tangential flow filtration / ultrafiltration technology, and enriching bacteriophage; recovering bacteriophage in a polyethylene glycol precipitation manner, performing standing overnight at a low temperature, centrifuging the next day, dissolving the bacteriophage in a TE buffer solution, filtering the solution by using a filter membrane again for sterilization, and digesting impurities DNA and RNA ina sample by using nuclease; and finally performing subsequent DNA extraction, sample fixation and other operations on the obtained concentrated solution.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enzyme digestion based preparation method of bacteria nucleic acid fingerprint characteristic spectrums and application thereof
InactiveCN103060926AValid identificationUndisturbedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEnzymatic digestionSuper absorbent
The invention discloses a method for preparing bacteria nucleic acid fingerprint spectrums. The method comprises the steps of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, SAP (super absorbent polymer) enzymatic digestion, transcription and nuclease digestion, purification, mass spectrometer detection and the like. A nucleic acid fingerprint spectrum database of common bacteria is created based on the method. According to the mass spectrum peak chart generated through experiments, the bacteria to be detected can be classified and identified and the results can be widely applied to the fields of bacteria classification and identification, genetic evolution analysis, drug resistance screening application, import and export inspection and the like.
Owner:BIOYONG TECH
Polymorphic DNA fragments and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060199198A1Resistance and susceptibilityEasy to addMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein nucleotide librariesGenomic DNASingle strand
The invention provides methods and materials for generating a reference library of restriction fragments from pooled nucleic acids that contain a sequence polymorphism. Preferably, such a library is formed by digesting genomic DNA from a pool of individuals with a first and a second restriction endonuclease to form a population of restriction fragments; isolating restriction fragments of the population digested by both the first and second restriction endonucleases and forming a first single stranded fragment population therefrom; separately isolating restriction fragments from the population digested by the first restriction endonuclease but not the second restriction endonuclease and forming a second single stranded fragment population therefrom; hybridizing the first and second single stranded fragment populations to form a population of duplexes; and isolating the population of duplexes to form a reference library of restriction fragments that contain sequence polymorphism. An important aspect of the invention is the use of the reference population of restriction fragments to compare the frequencies of polymorphic sequences between different population pools. Such comparisons may be accomplished by competively hybridizing DNA from the respective pools which has been enriched for the presence of a restriction site polymorphism with DNA from the reference population. Preferably, such competitive hybridization reactions are carried out the reference library attached to one or more solid phase supports. Most preferably, members of the reference library are attached to individual microparticles so that each microparticle has a unique fragment attached. After competitive hybridization, the microparticles may be analyzed and sorted for identifying those microparticles carrying sequences for which the pools being compared exhibit different polymorphic frequencies.
Owner:SOLEXA
Removal of DNA fragments in mRNA production process
ActiveUS20190100748A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnologyDNA fragmentation
Owner:MODERNATX INC
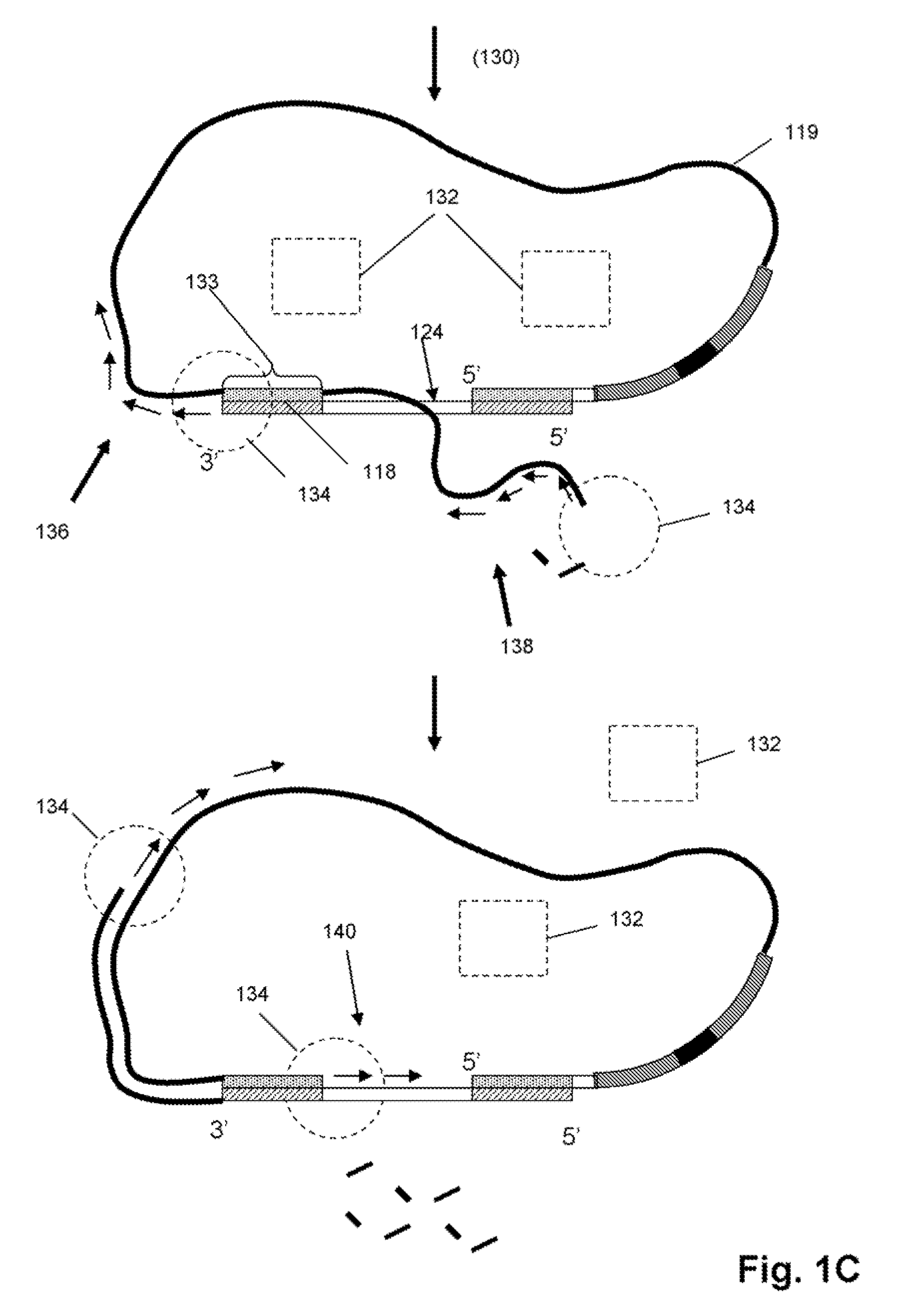
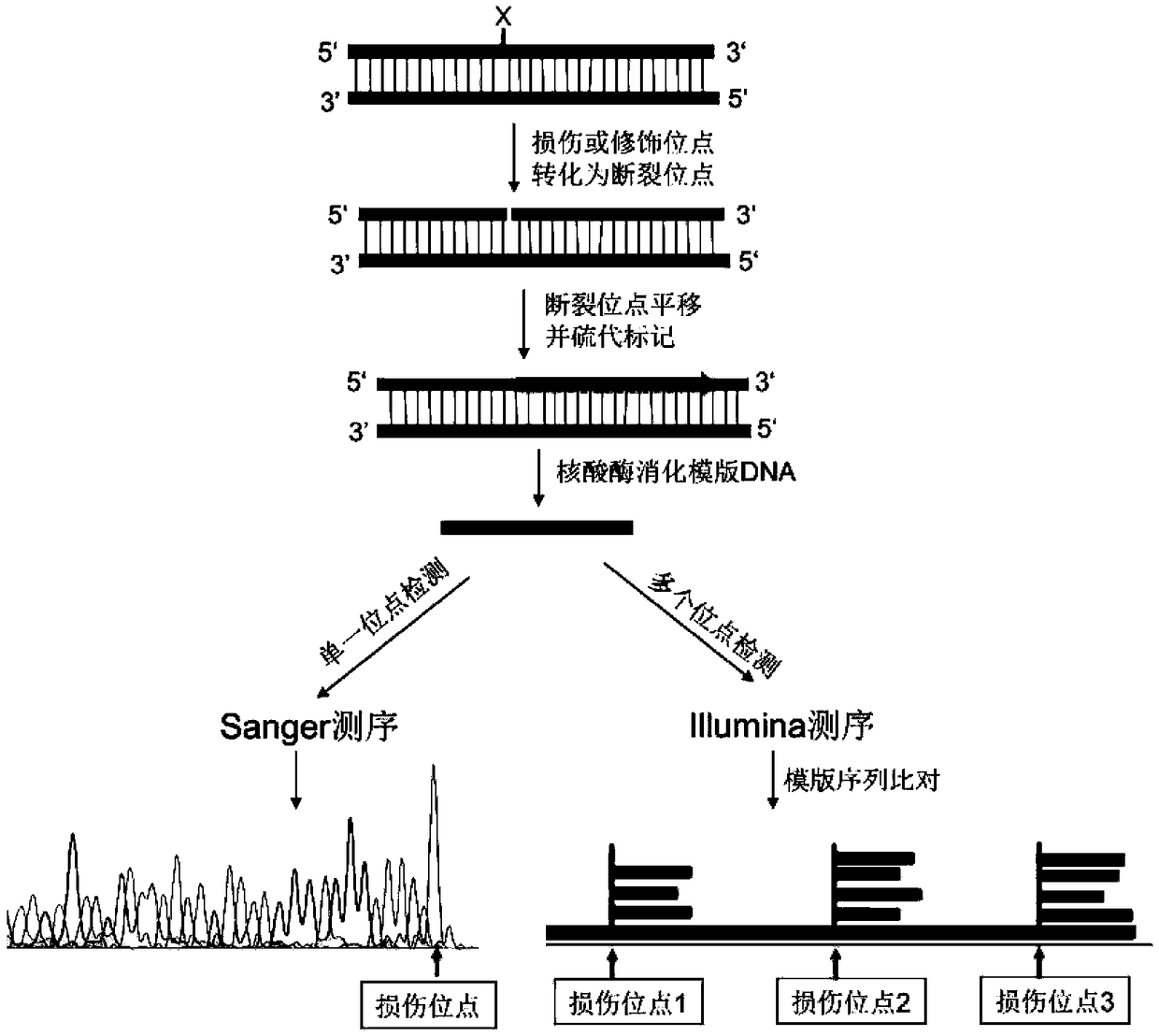
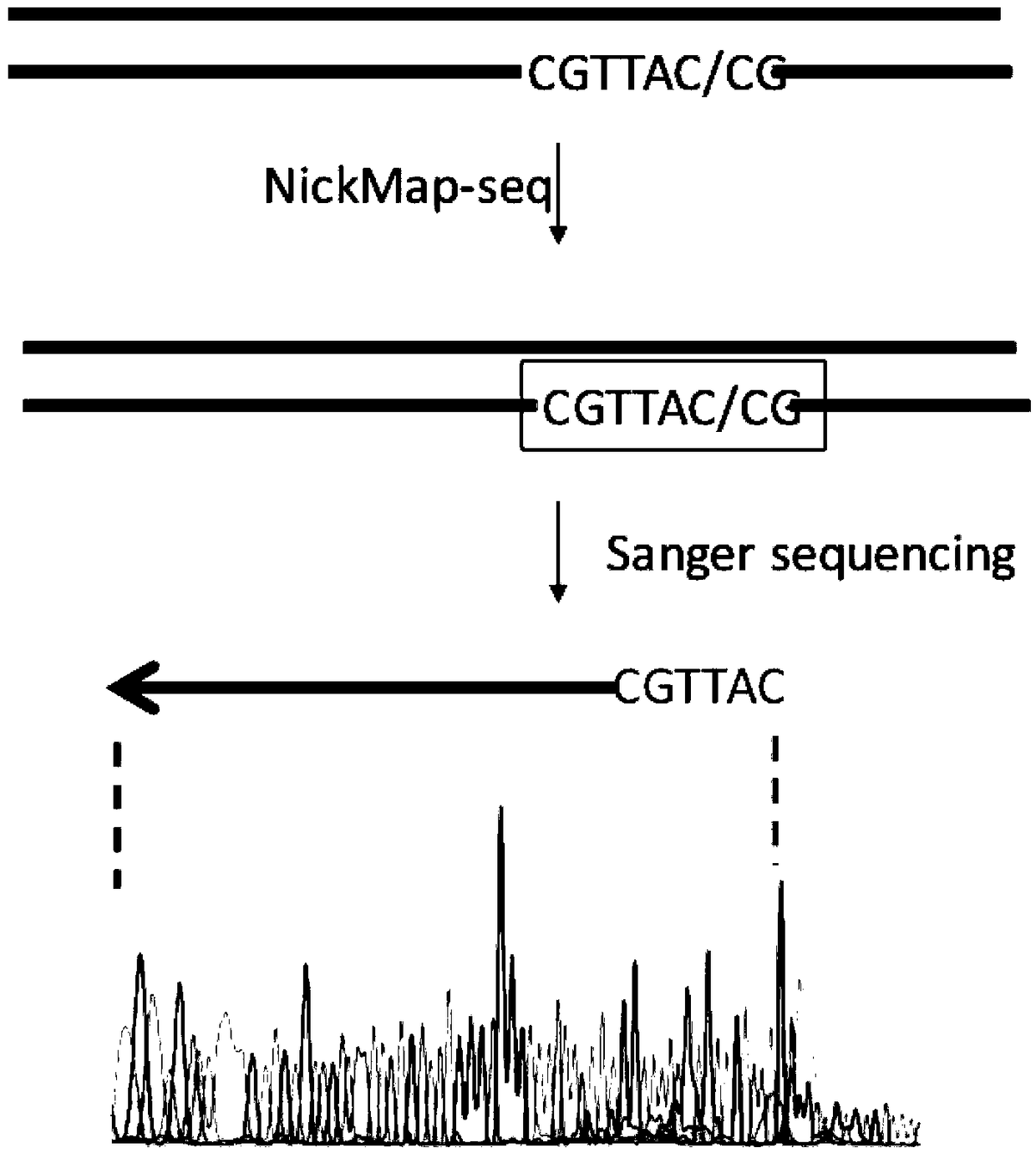
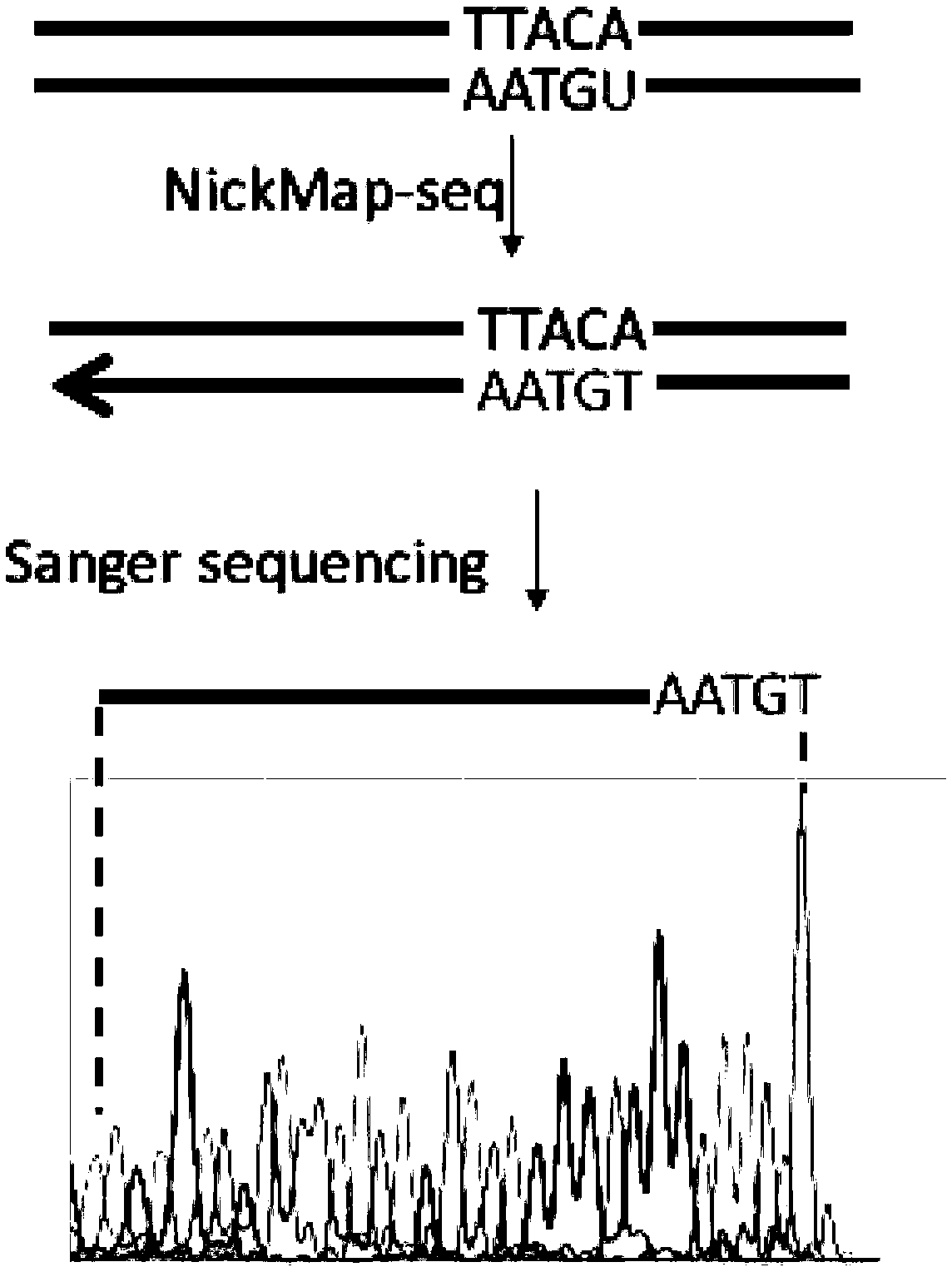
Method for locating damage and modification sites on genomic DNA
ActiveCN109266728AEasy to useEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaDNA polymerase I
The invention provides a method for locating damage and modification sites on genomic DNA. Firstly, a damage or modification site of a DNA sample is converted into a breakpoint. Then thionucleotide and DNA polymerase I were added for incision translation. The sample obtained after the reaction is terminated is added with a nuclease digestion template sensitive to phosphorothioylation modificationDNA. Finally, the phosphorothioyl modified DNA was sequenced, and the 5'end of the obtained sequence was the original damaged or modified site. The method provided by the invention, the invention fills in the blank that the existing technology at home and abroad can not accurately locate the damage site on the genomic DNA, and can realize the quantitative and positioning analysis of the damage andmodification sites of DNA samples with different lengths and different sources. The invention is simple to use, easy to operate, and has no special requirements on the samples, high accuracy, low detection background influence and high resolution.
Owner:中磷科技深圳有限公司
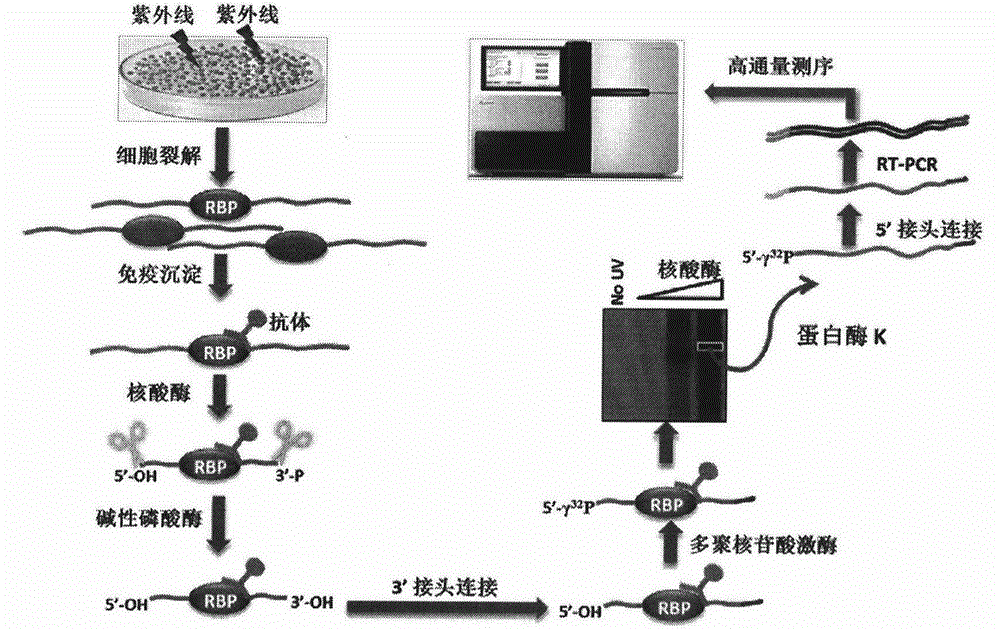
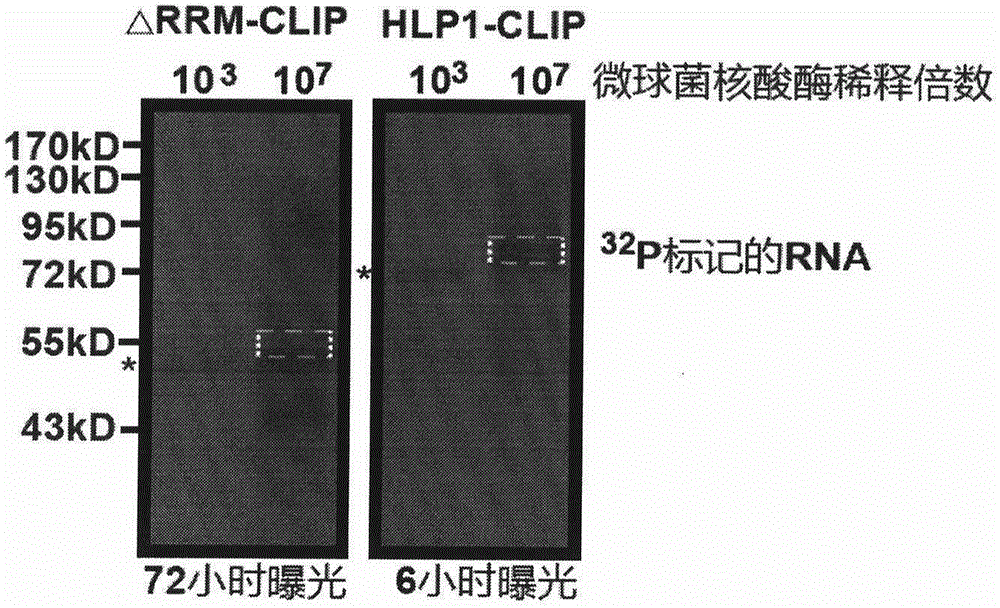
Method for identifying type and site of RNA binding with protein in plant
The invention relates to a method for identifying the type and site of a RNA binding with protein in a plant. The method mainly comprises the following steps: immobilizing the in-vivo binding state of protein and nucleic acid through ultraviolet crosslinking; subjecting immunoprecipitated RNAs to digestion with nuclease into small fragments; removing non-specifically bound RNAs by using SDS-PAGE and transferring methods; and carrying out reverse-transcription PCR amplification and large-scale sequencing by using adaptors connected with two ends of the RNA. The method has the advantages that 1) ultraviolet crosslinking is carried out in vivo, so real in-vivo binding conditions can be reflected; 2) since a covalent bond formed by ultraviolet crosslinking is irreversible, the length of nucleic acid binding with protein can be reduced through digestion by nuclease, and subsequent multi-step purification can greatly improve a ratio of signal to noise; 3) most non-specifically bound RNAs in a precipitation sample are removed through SDS-PAGE separation and subsequent transferring process removes free RNAs; and 4) the two ends of the RNA are connected with the adaptors, which makes subsequent PCR amplification and large-scale sequencing to be possible.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
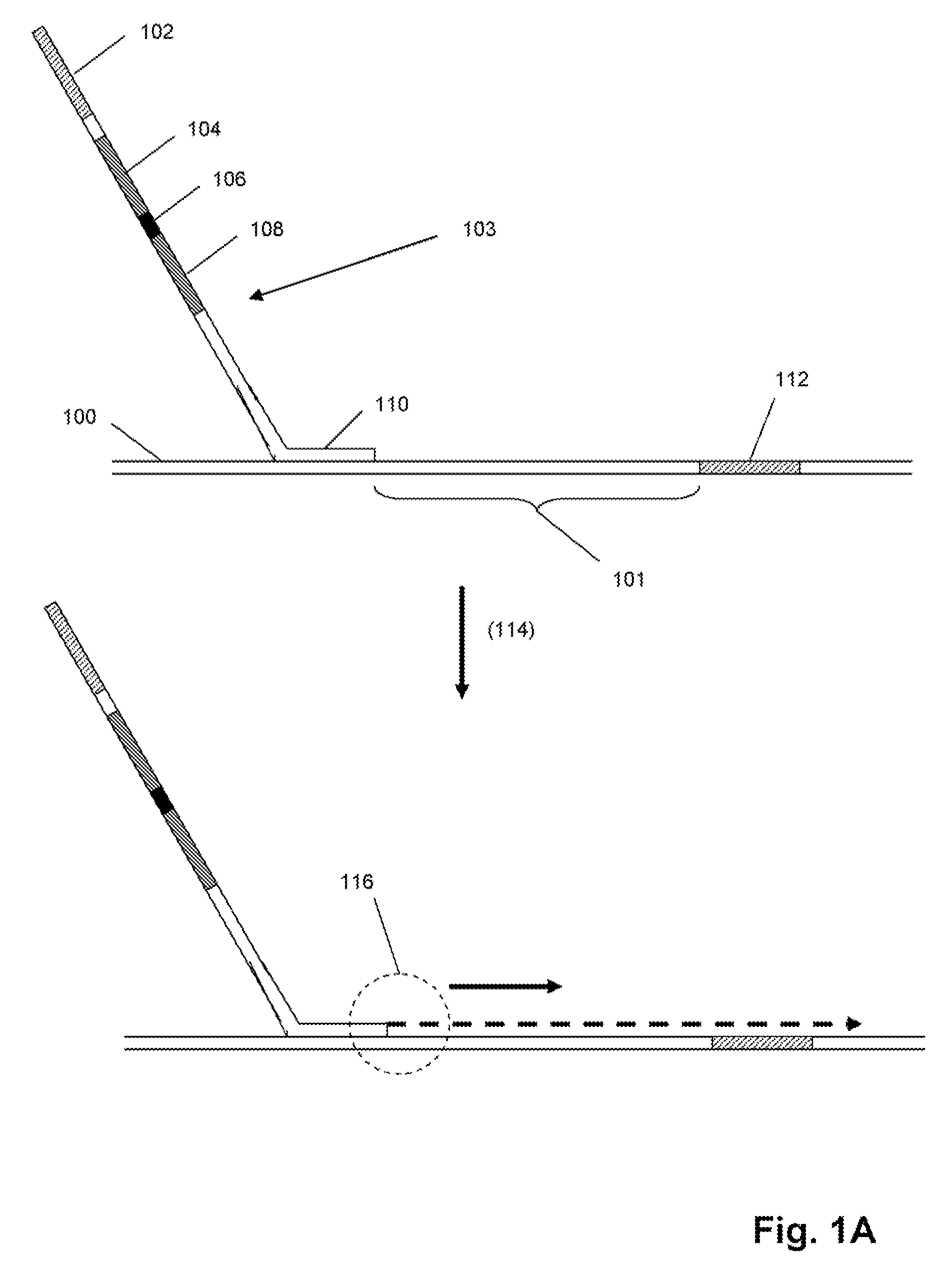
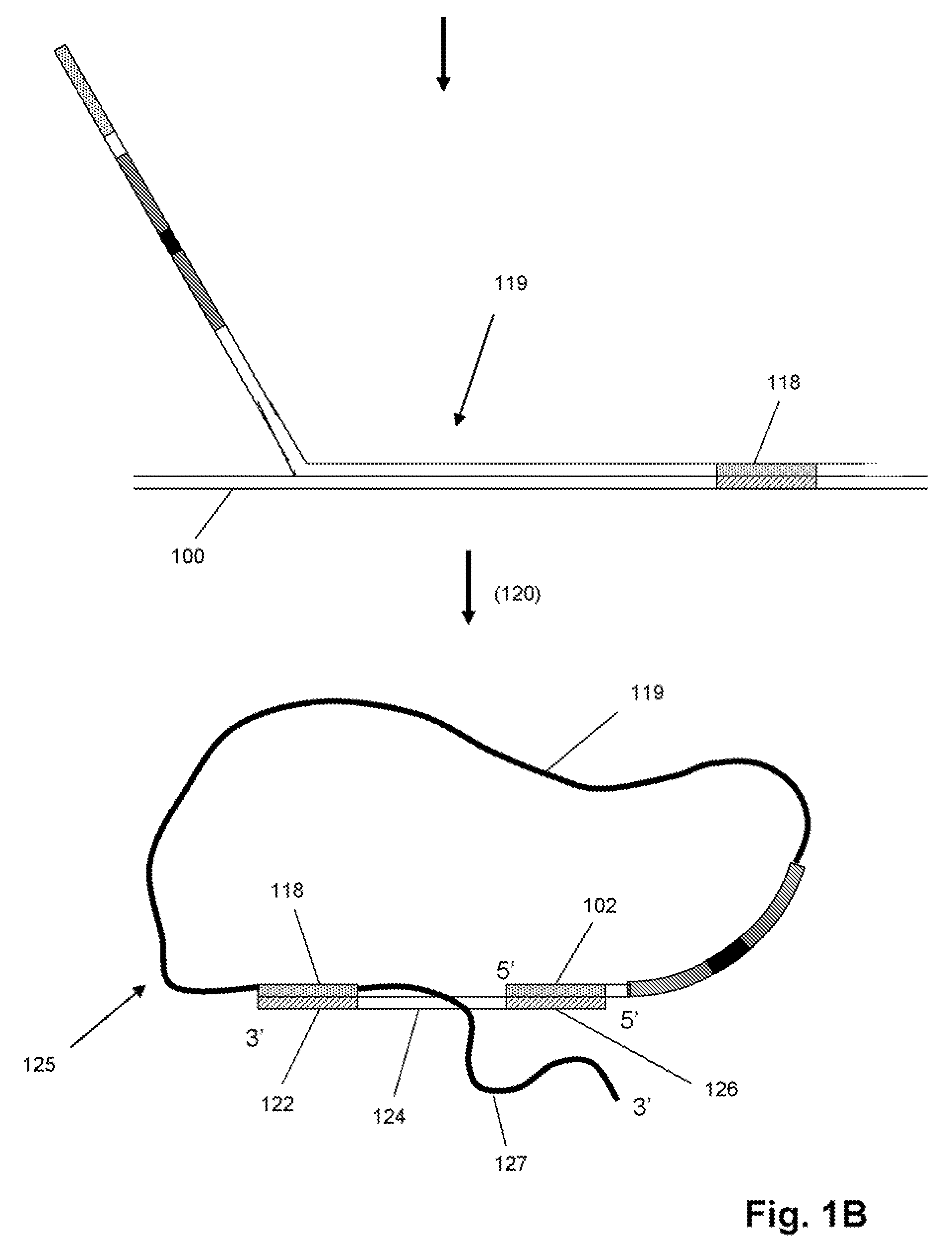
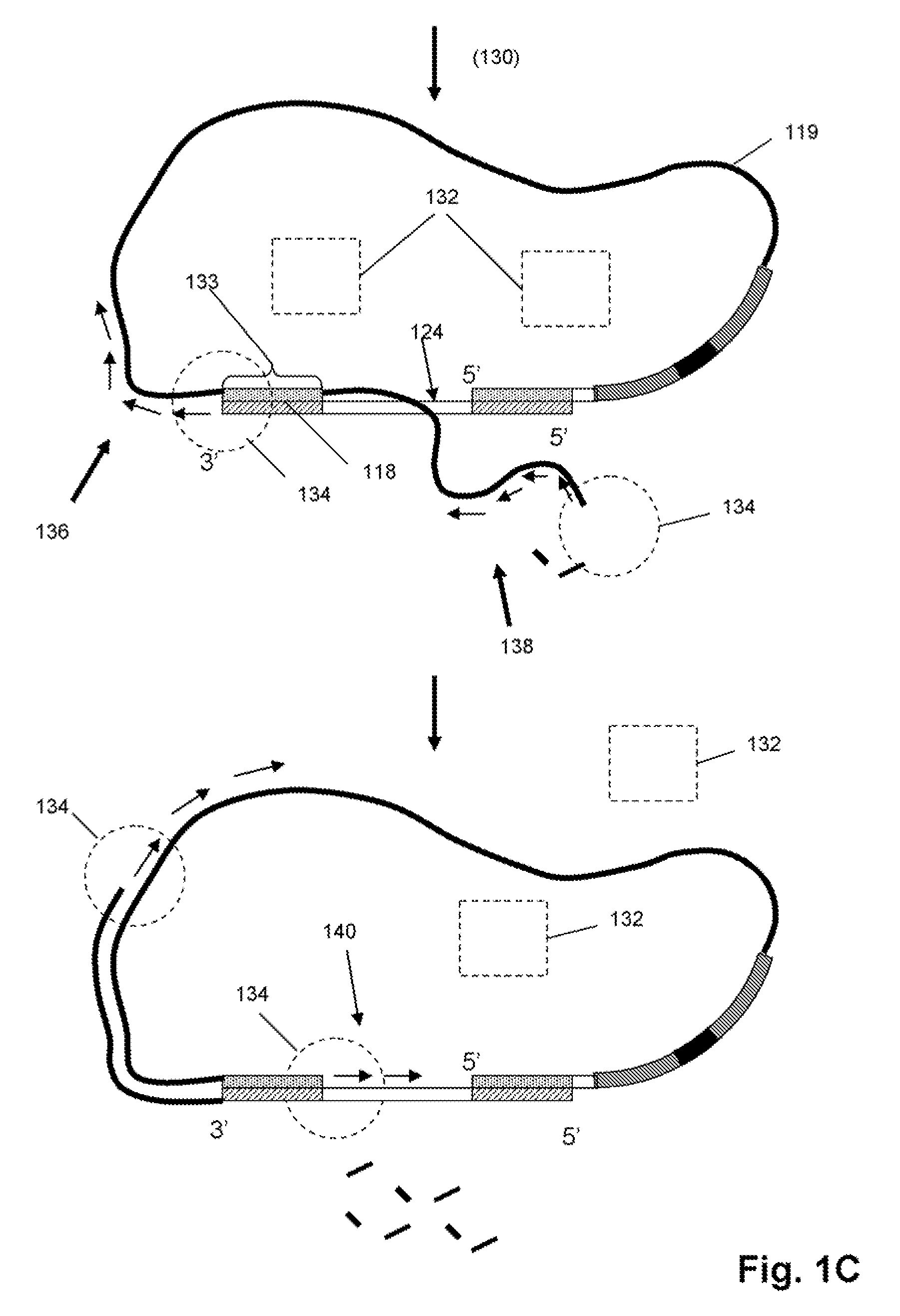
Method to produce single stranded DNA of defined length and sequence and DNA probes produced thereby
ActiveUS7897747B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical synthesisDefining length
A method for producing a single stranded DNA (ssDNA) molecule of a defined length and sequence is disclosed. This method enables the preparation of, inter alia, probes of greater length than can be chemically synthesized. The method starts with a double stranded molecule, such as genomic, double stranded DNA (dsDNA) from any organism. A fragment of the starting molecule (dsDNA) is amplified by specific primers engineered to introduce cleavage sites on either side of the desired sequence. Cleavage steps on the amplified, engineered fragment are combined with a phosphate removal step, thereby creating a construct that can be digested with an exonuclease without damage to the desired ssDNA. Probes, which hybridize with large gaps between the ends of the probes, are also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for arranging and packing nucleic acids for unusual resistance to nucleases and targeted delivery for gene therapy
There are disclosed compositions and methods to render nucleic acids resistant to nuclease digestion while maintaining sequence selective hybridization competency. The approach relies on utilizing nucleic acids as the polar head group of a nucleic acid-polymer amphiphile in order to assemble well-defined, discrete micellar nanoparticles. Dense packing of nucleic acid in the micelle corona allows for hybridization of complementary oligonucleotides while prohibiting enzymatic degradation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
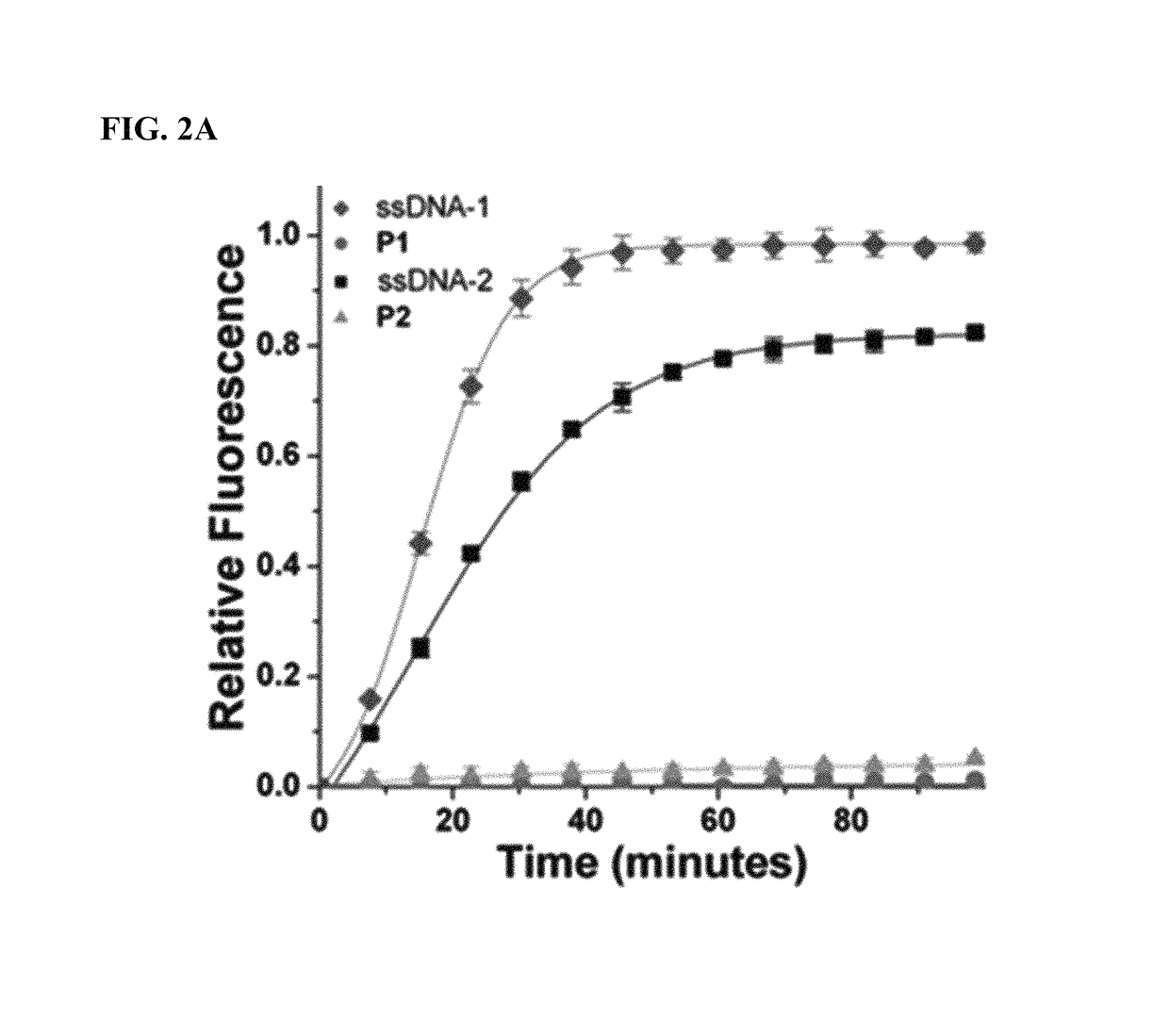
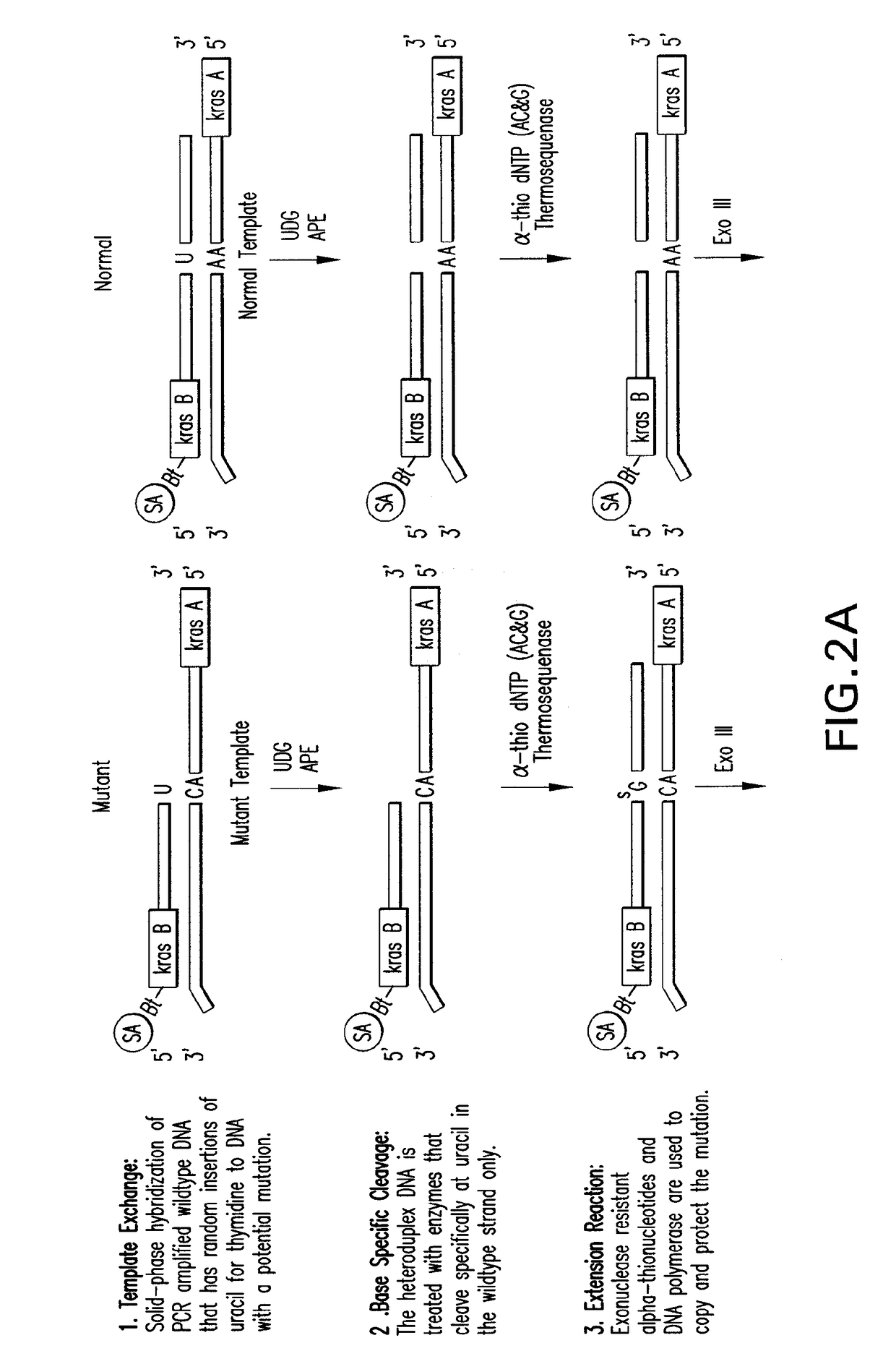
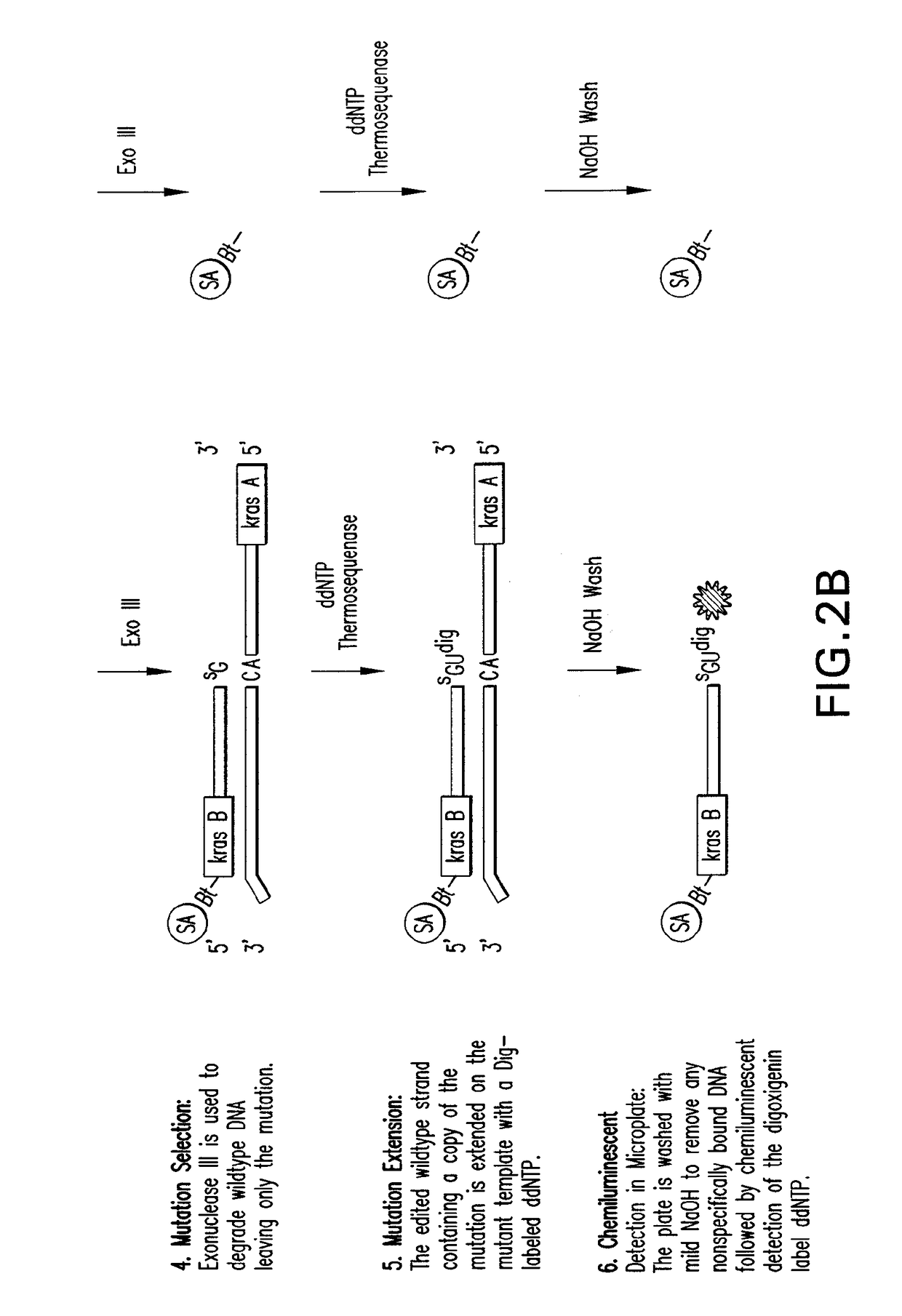
Methods of screening nucleic acids for single nucleotide variations
InactiveUS7906287B2Rapid and sensitive detectionLimit scopeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide variation
Disclosed are methods and compositions for detecting variation in nucleic acids. The disclosed method compares the sequence of a nucleic acid of interest with the sequence of a reference nucleic acid to sensitively identify variations between the sequence of a nucleic acid of interest and the sequence of a reference nucleic acid. The disclosed method generally involves excision and replacement of selected nucleotides in nucleic acid strands hybridized to other strands. In the method, if the excised nucleotide was mismatched with the nucleotide in the other, hybridized strand, then the replacement nucleotide will not be mismatched. If the excised nucleotide was not mismatched with the nucleotide in the other, hybridized strand, then the excised nucleotide is not replaced. This difference allows detection of variation in the nucleic acid of interest. In some forms of the method, by replacing excised nucleotides with nuclease-resistant nucleotides, strands in which excised nucleotides are replaced will be resistant to nuclease digestion while strands in which excised nucleotides are not replaced will be sensitive to nuclease digestion. By exposing the hybridizing nucleic acids to nuclease following replacement of excised nucleotides, the strands in which excised nucleotides are not replaced can be destroyed by the nuclease while strands in which excised nucleotides are replaced can be preserved. The remaining strands can then be detected and whether the strand survived nuclease digestion can be noted. Strands that survive nuclease digestion are indicative of the presence of variation in the nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:INSIGHT GENETICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com