Method for locating damage and modification sites on genomic DNA
A genome and locus technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and biomedicine, can solve the problems of high experimental cost, low accuracy and low resolution, and achieve the effects of high resolution, high accuracy and easy operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
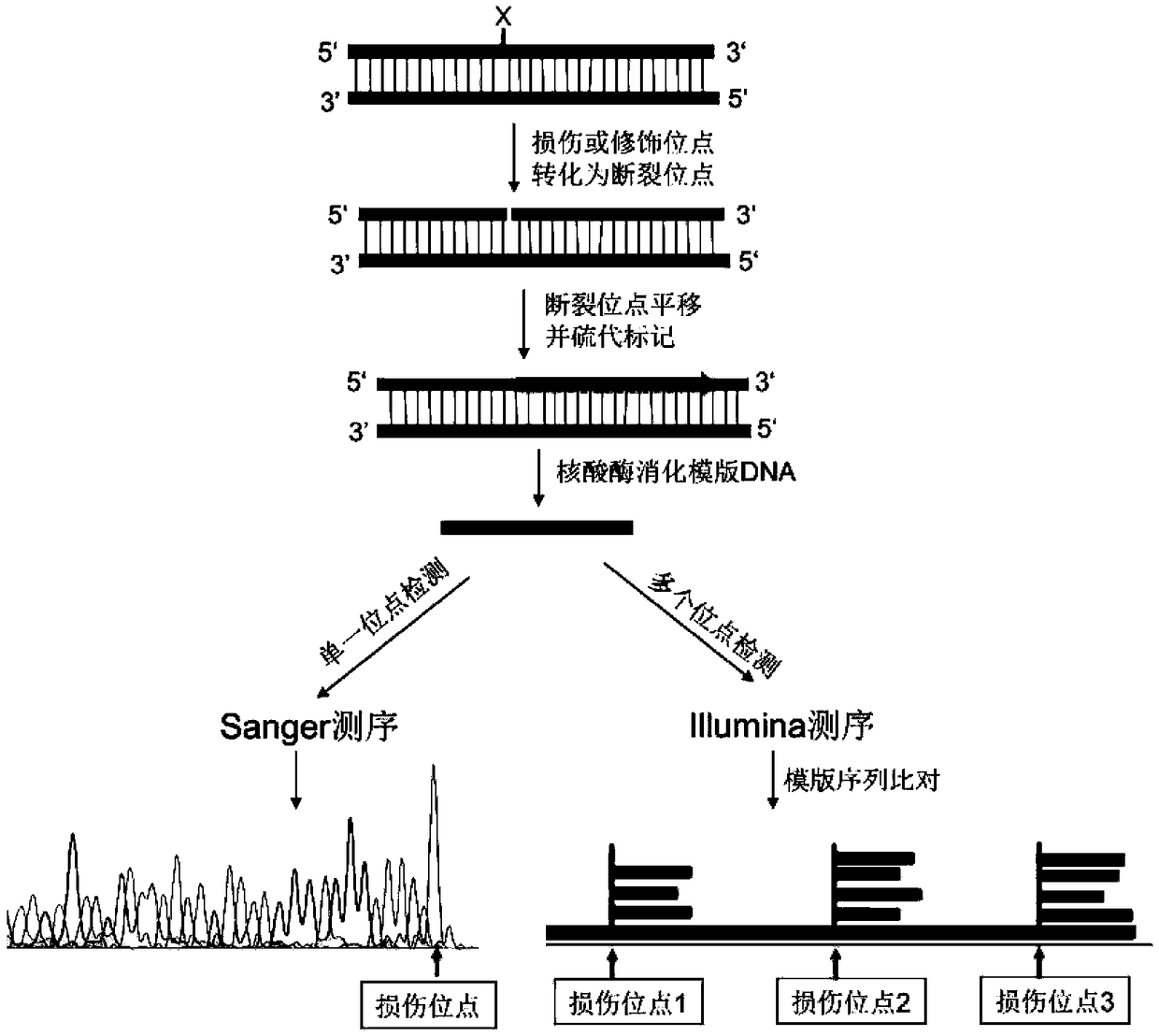
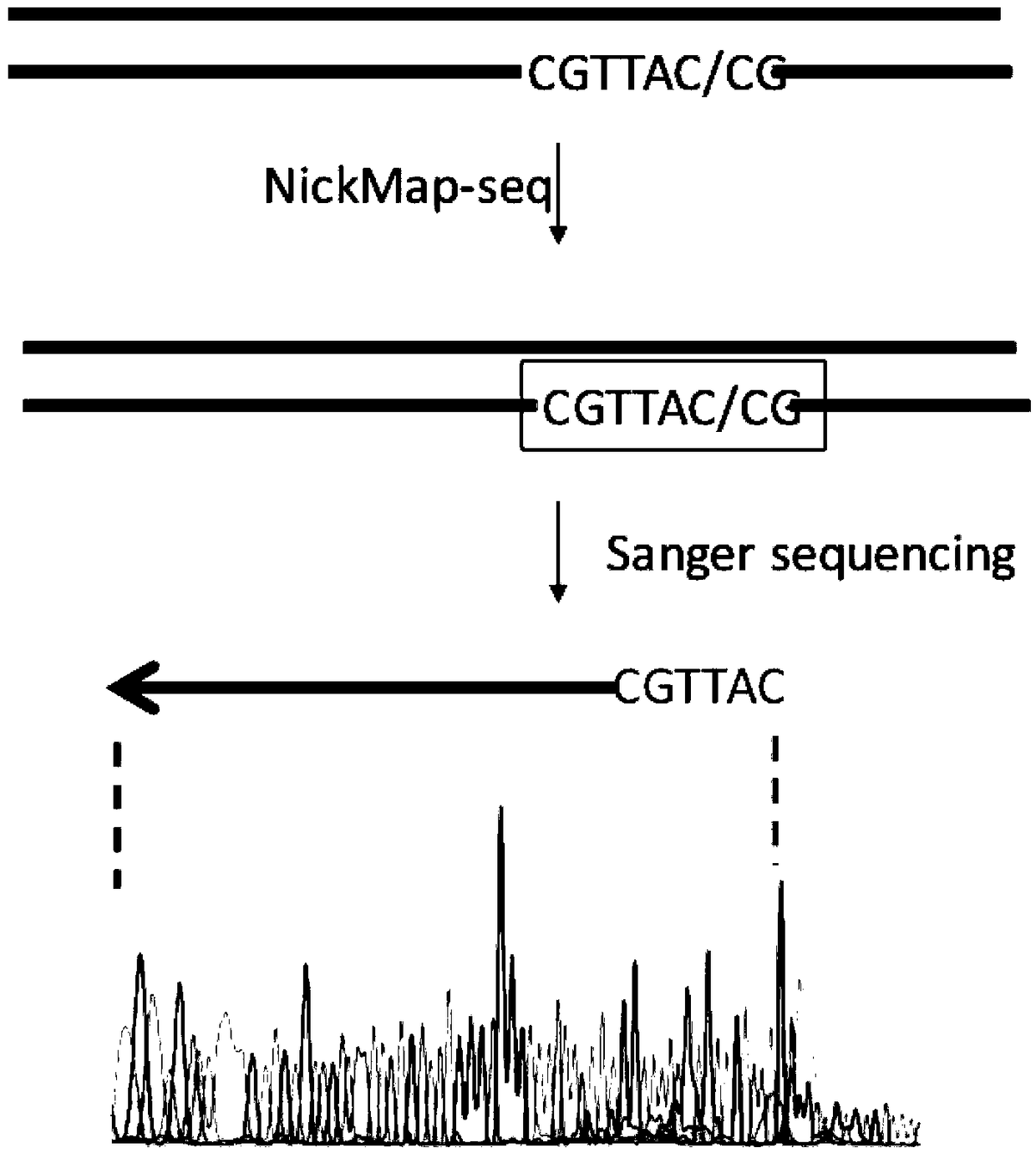
[0029] Example 1 Location of short-strand DNA breakage sites
[0030] 1. Synthesize a DNA double-stranded fragment containing 100 bp by a DNA synthesis company (IDT, USA). The sense strand sequence is:
[0031] ACTGGGGCCAGATG CGTAAGC CCTCCCGTATCGTAGTTATCTACACGACGGGGAGTCAGGATTTCGTTCATCCATAGTTGCCTGACTCCCCGTCGTGTAG, the subscript is DNA single-strand endonuclease Nb.BsrDI site;
[0032] 2. Single-stranded enzyme-cut DNA fragments: 50 μL reaction system contains: 10 units of single-stranded endonuclease Nb.BsrDI (NEB, USA), 5 μL buffer (NEB cutsmart buffer), 1 μg DNA low-quality substance, and water to make up 50 μL. After reacting at 65°C for 1 hour, inactivate at 80°C for 20 minutes;
[0033] 3. Breakpoint labeling: Add 2 μL of thio-modified nucleotides (10 mM, Trilink), 1 μL of DNA polymerase I to the reaction solution, react at 15 °C for 1 hour, and stop the reaction at 65 °C for 10 min;
[0034] 4. Template elimination: add 10 units of exonuclease III (NEB) and 10 units o...
Embodiment 2
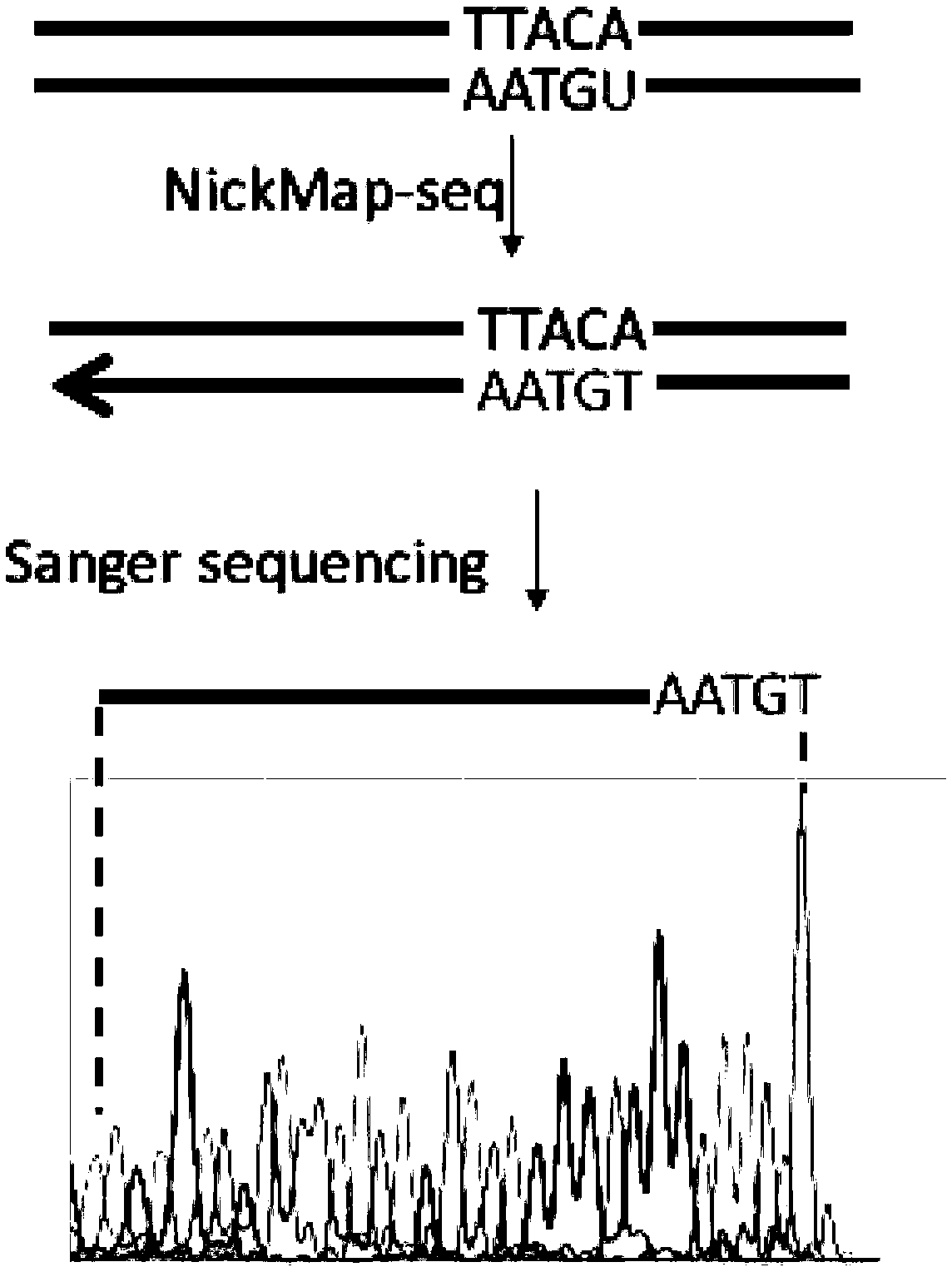
[0037] Example 2 Location of short-strand DNA damage (Uracil) site
[0038] 1. Synthesize a DNA double-stranded fragment containing 100 bp by a DNA synthesis company (IDT, USA). The sense strand sequence is:
[0039] ACTGGGGCCAGATG U GTAAGCCCTCCCGTATCGTAGTTATCTACACGACGGGGAGTCAGGATTTCGTTCATCCATAGTTGCCTGACTCCCCGTCGTGTAG, the subscript is DNA damage (Uracil) site;
[0040] 2. Enzyme cutting DNA damage site: 50 μL reaction system contains: 10 units of Uracil repair enzyme UDG and endonuclease IV (NEB, USA), 5 μL buffer (NEB cutsmart buffer), 1 μg DNA low content, make up 50 μL with water. After reacting at 37°C for 1 hour, inactivate at 75°C for 20 minutes;
[0041] 3. Breakpoint labeling: Add 2 μL of thio-modified nucleotides (10 mM, Trilink), 1 μL of DNA polymerase I to the reaction solution, react at 15 °C for 1 hour, and stop the reaction at 65 °C for 10 min;
[0042] 4. Template elimination: add 10 units of exonuclease III (NEB) and 10 units of exonuclease RecJ (NEB) to th...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Locating Genomic DNA Fracture Sites
[0046] 1. Cultivate E. coli DH10B strain overnight at 37°C in 10 mL of LB medium. Collect 1mL of bacteria, and use OMEGAbacterial DNA extraction kit (OMEGA Company, USA) to extract genomic DNA, and the method is carried out according to the product instructions;
[0047] 2. Enzyme cutting DNA fragmentation site: 50 μL reaction system contains: 10 units of DNA single-strand nicking enzyme Nb.BsrDI (NEB, USA), 5 μL buffer (NEB cutsmart buffer), 1 μg genomic DNA low content, make up 50 μL with water . After reacting at 37°C for 1 hour, inactivate at 75°C for 20 minutes;
[0048] 3. Breakpoint labeling: Add 2 μL of thio-modified nucleotides (10 mM, Trilink) and 1 μL of DNA polymerase I to the reaction mixture, react at 15°C for 1 hour, and stop the reaction at 65°C for 10 minutes.
[0049] 4. Template elimination: add 10 units of exonuclease III (NEB) and 10 units of exonuclease RecJ (NEB) to the reaction solution, and reac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com