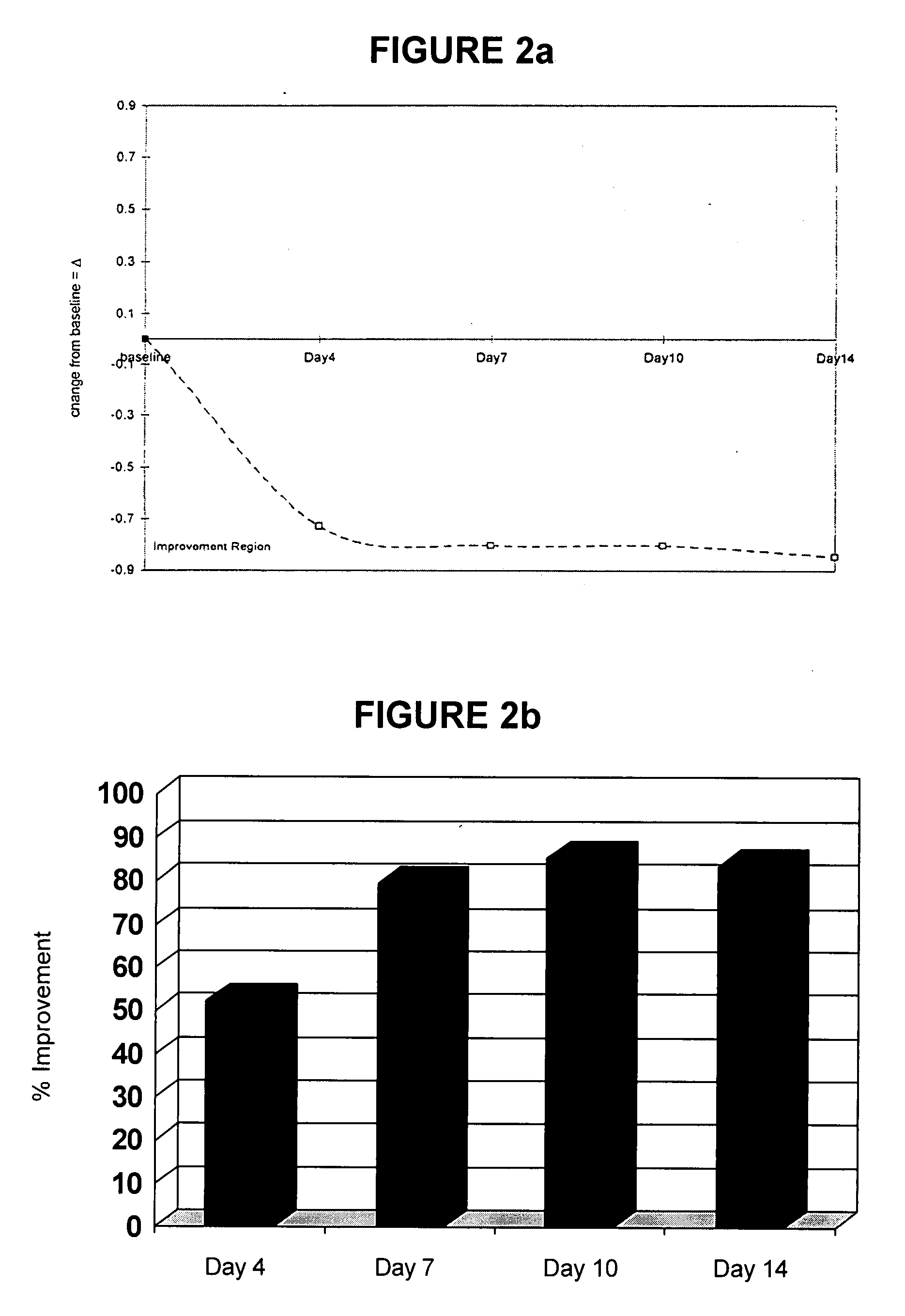
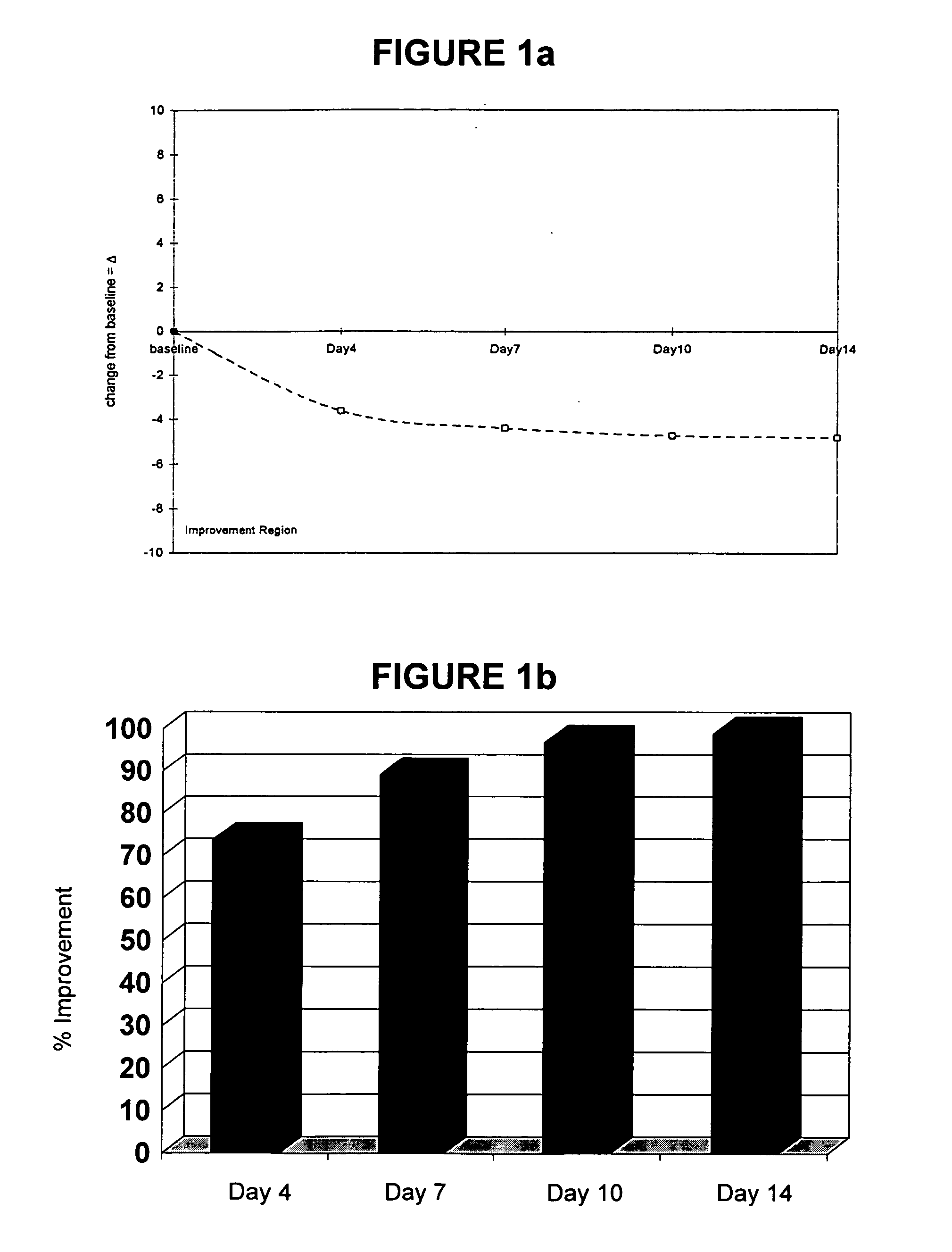
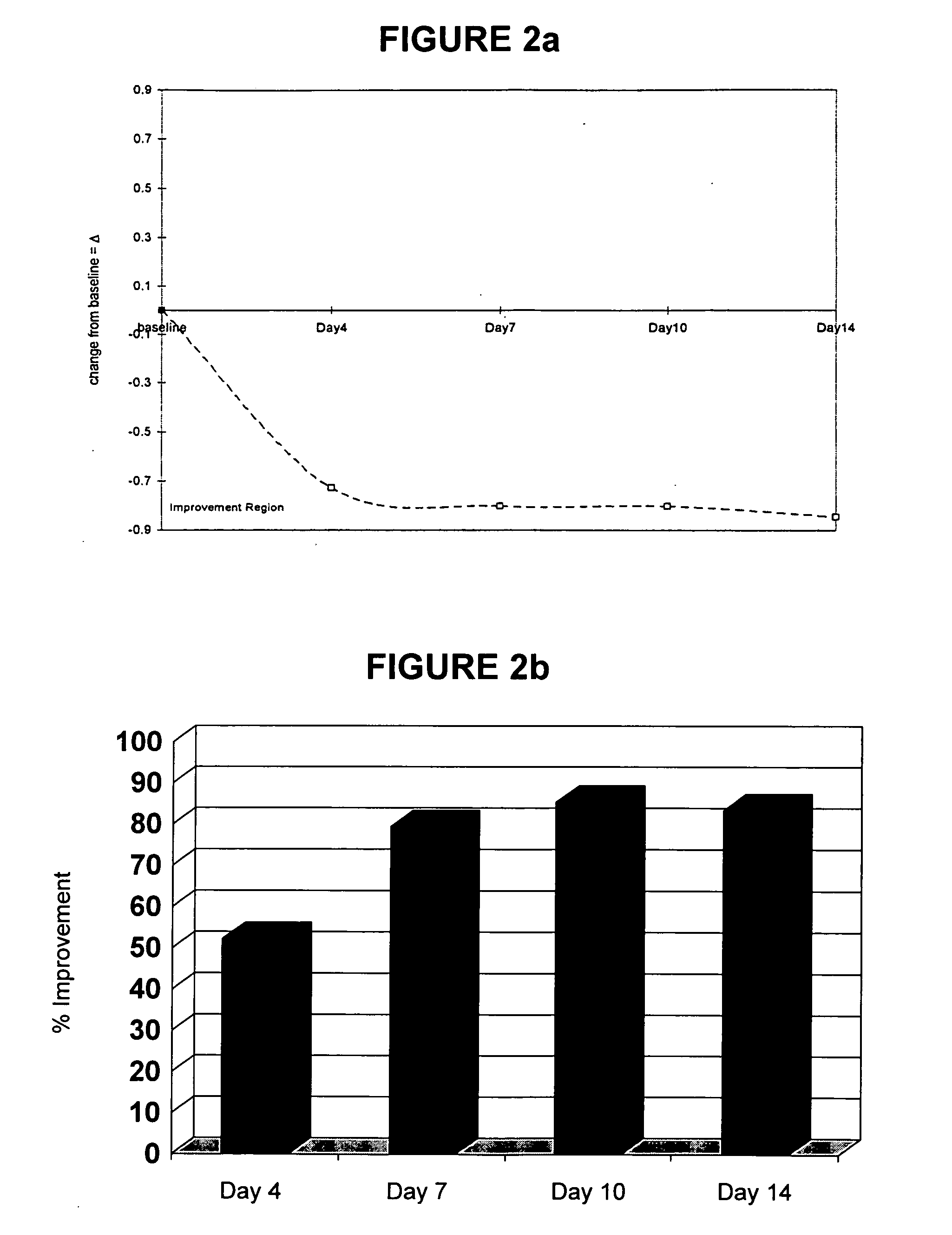
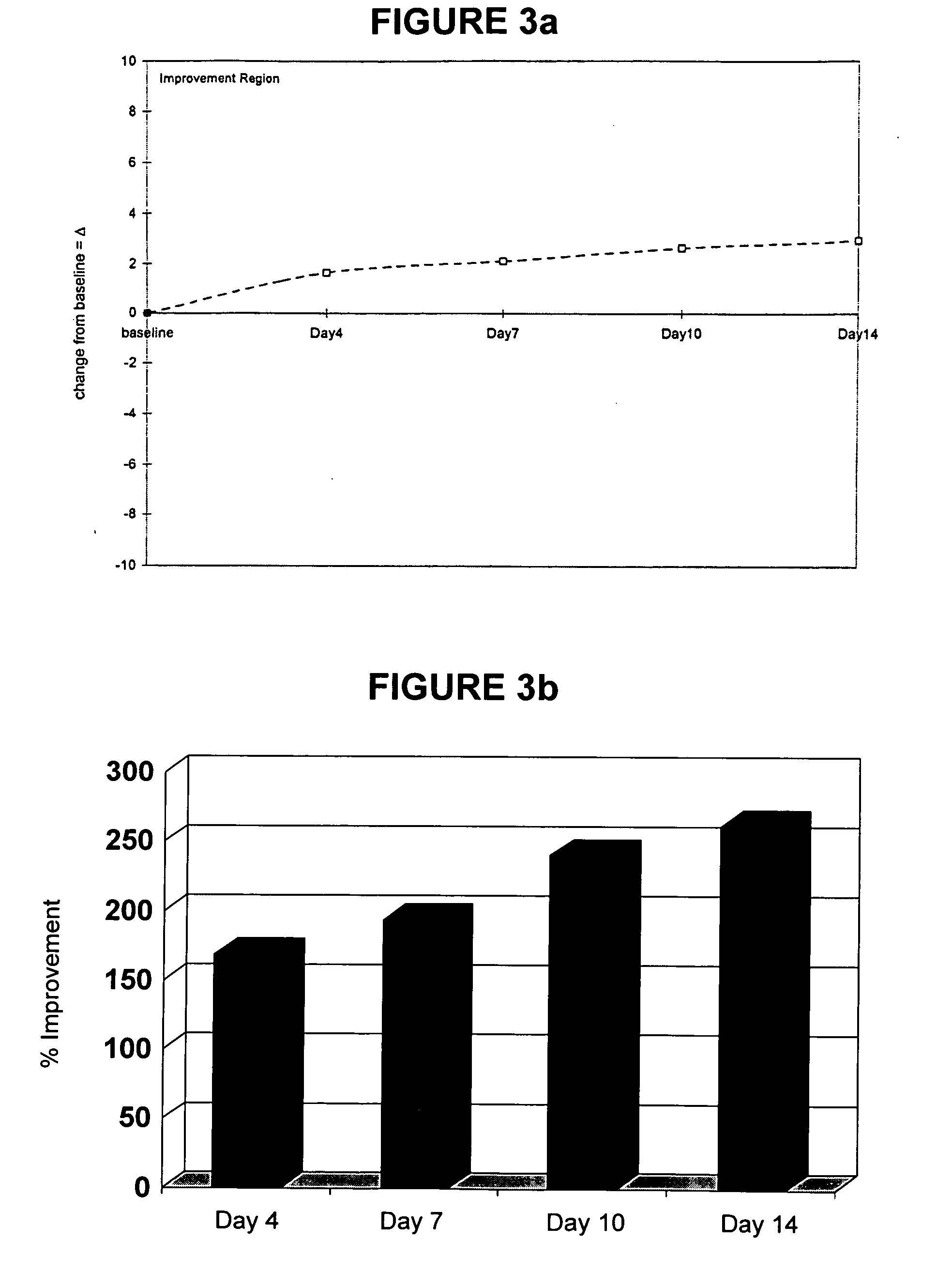
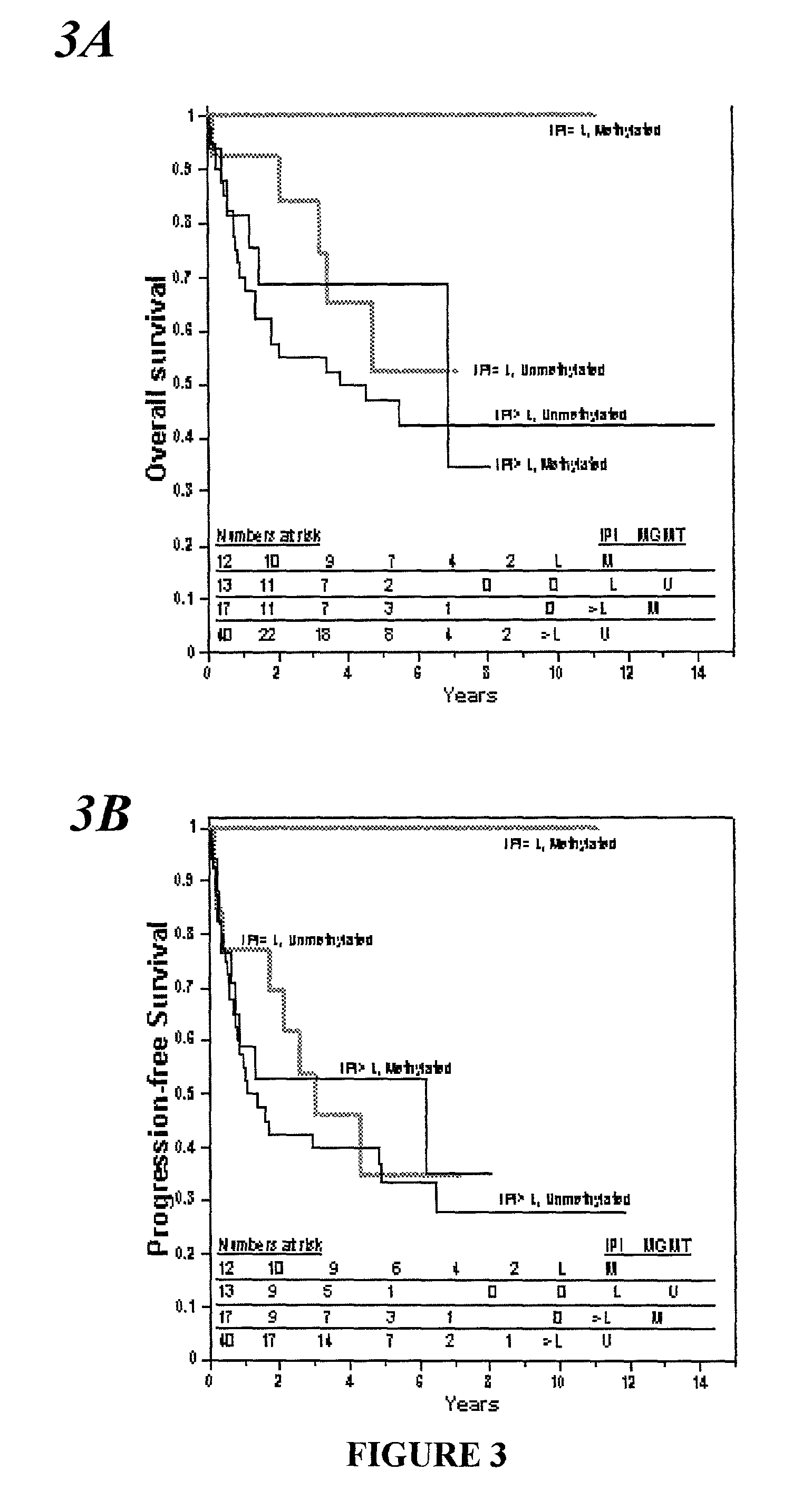
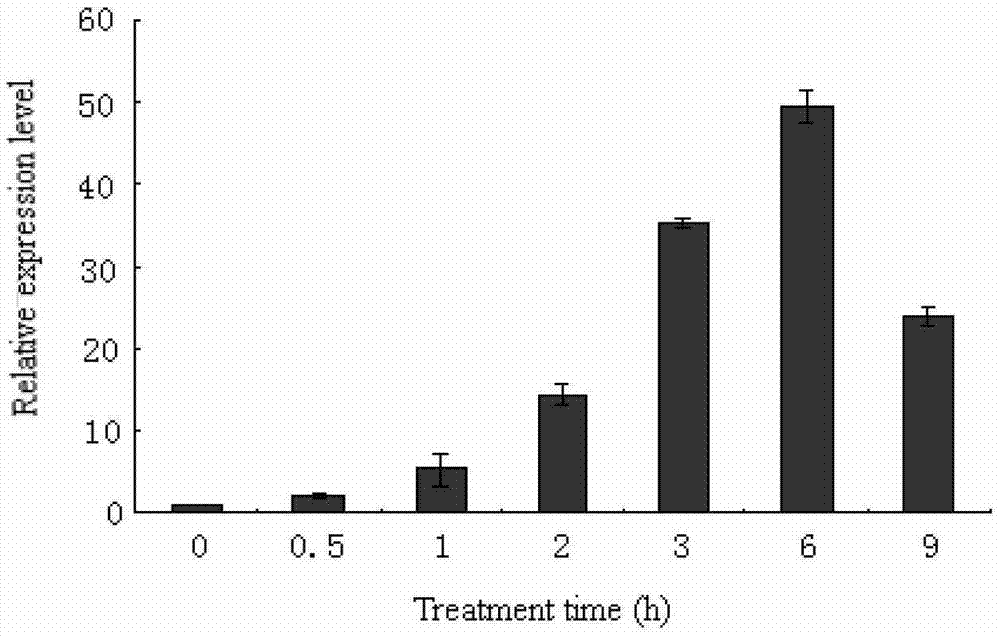
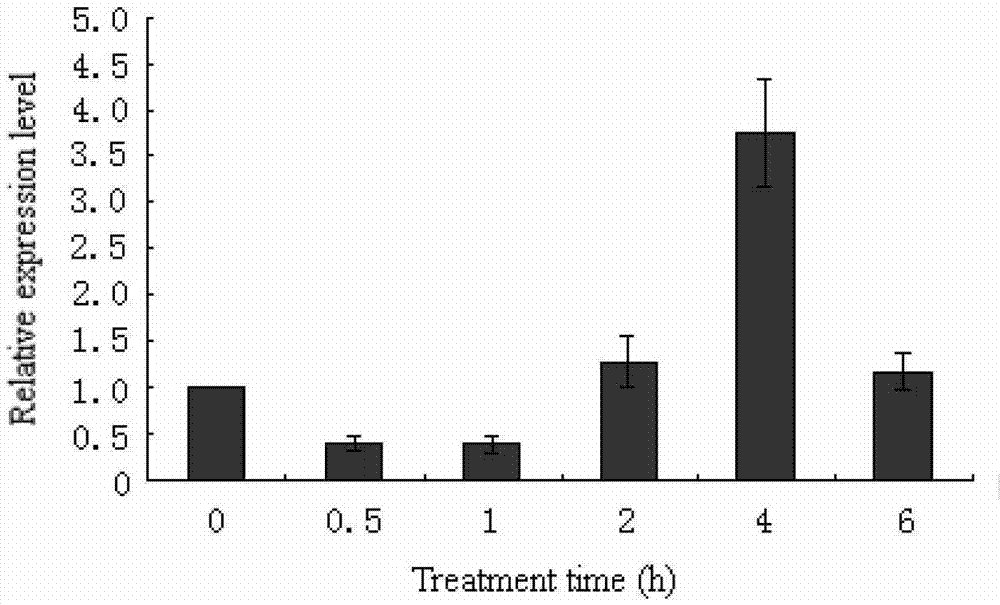
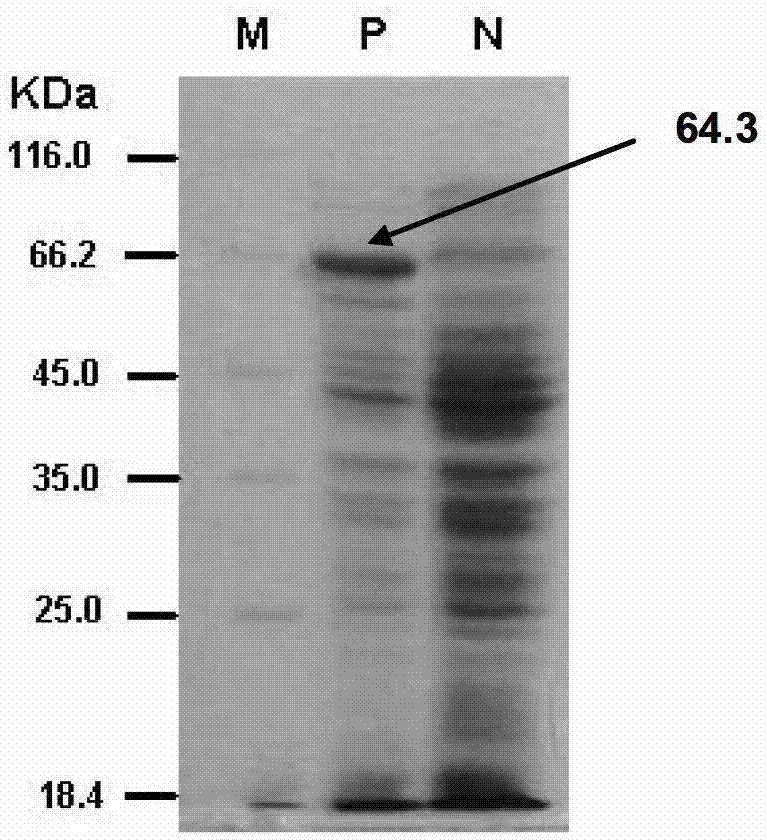
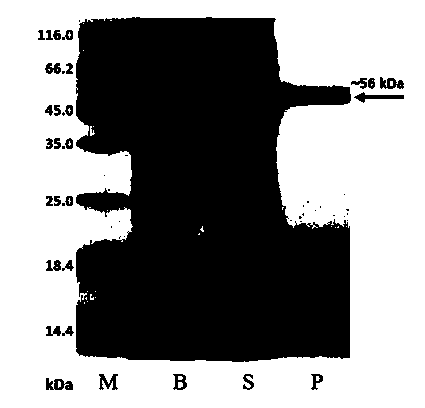
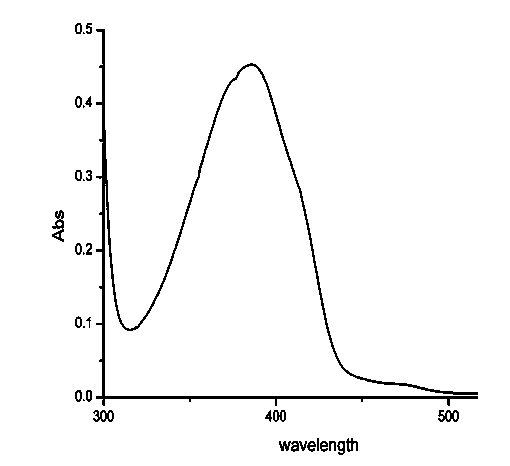
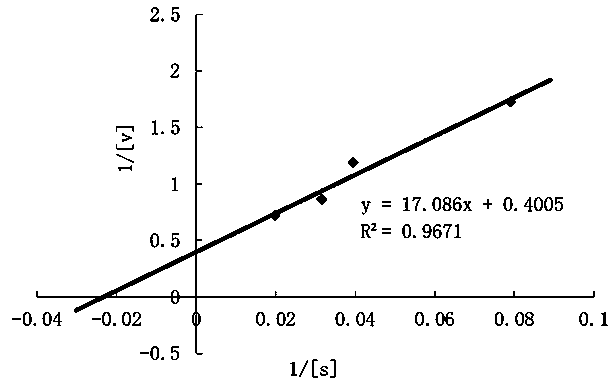
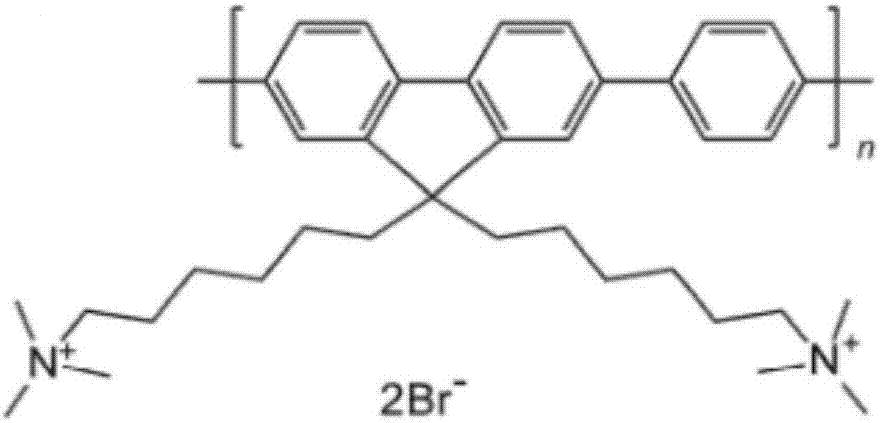
Patents
Literature
61 results about "Repair enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA Repair Enzymes. Structure Function Group. DNA Polymerases Lambda (λ) and Mu (μ) are members of the X Family, and are primarily involved in DNA repair. Both polymerases function in repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs), a particularly toxic type of lesion that can result in cell death if not corrected.
Methods and compositions for amplification of dna
InactiveUS20050026147A1Simple methodHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRepair enzymePolymerase L
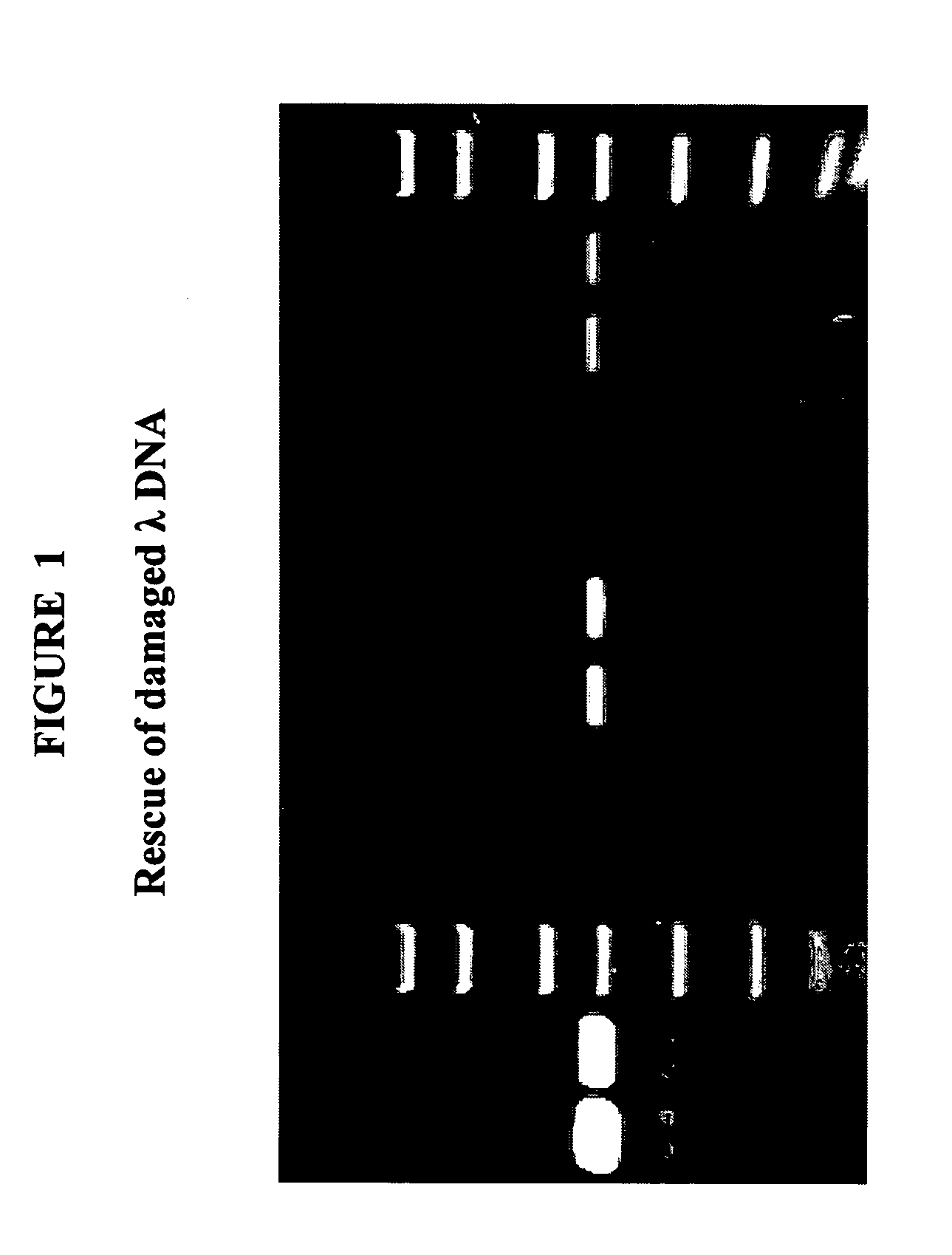
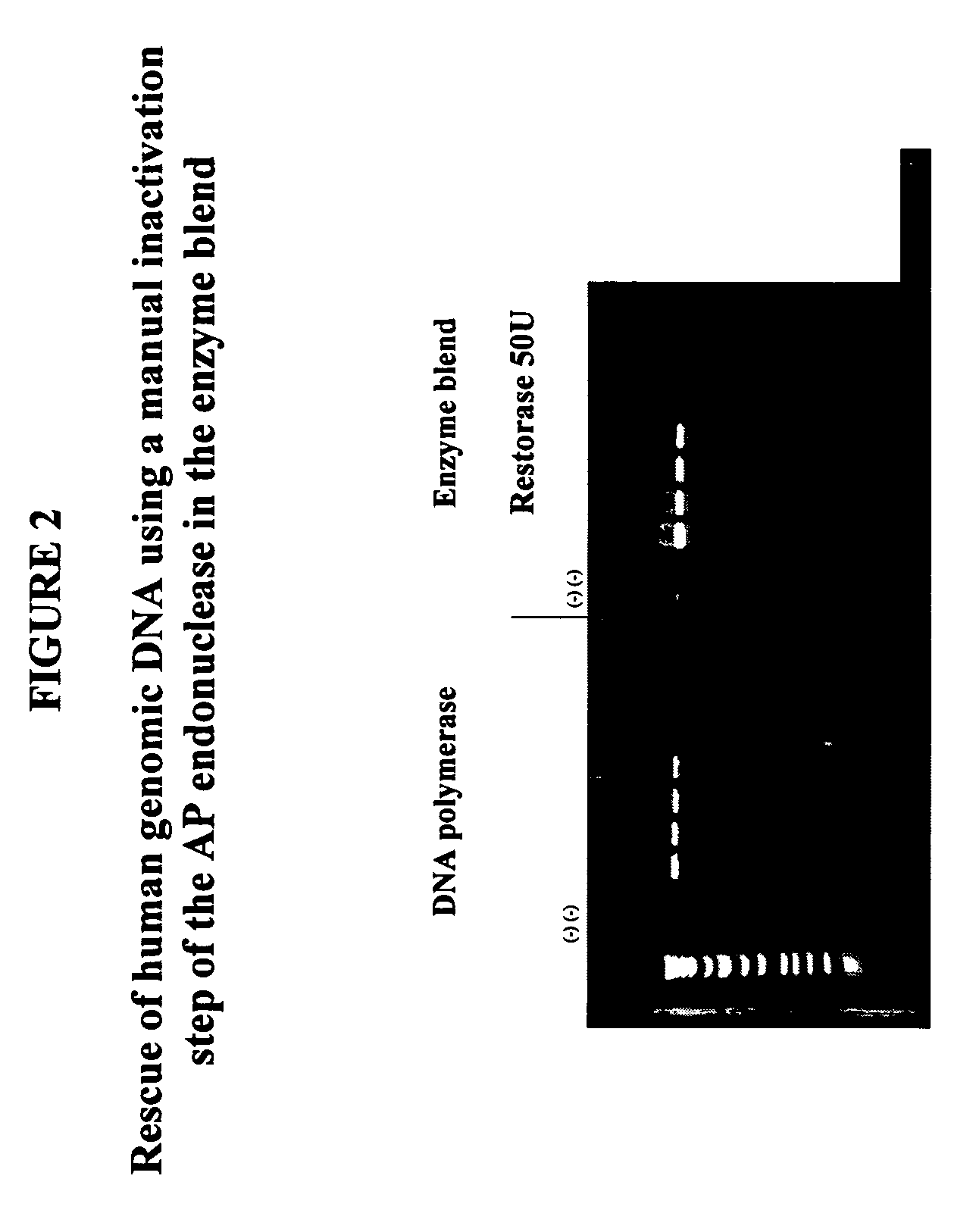
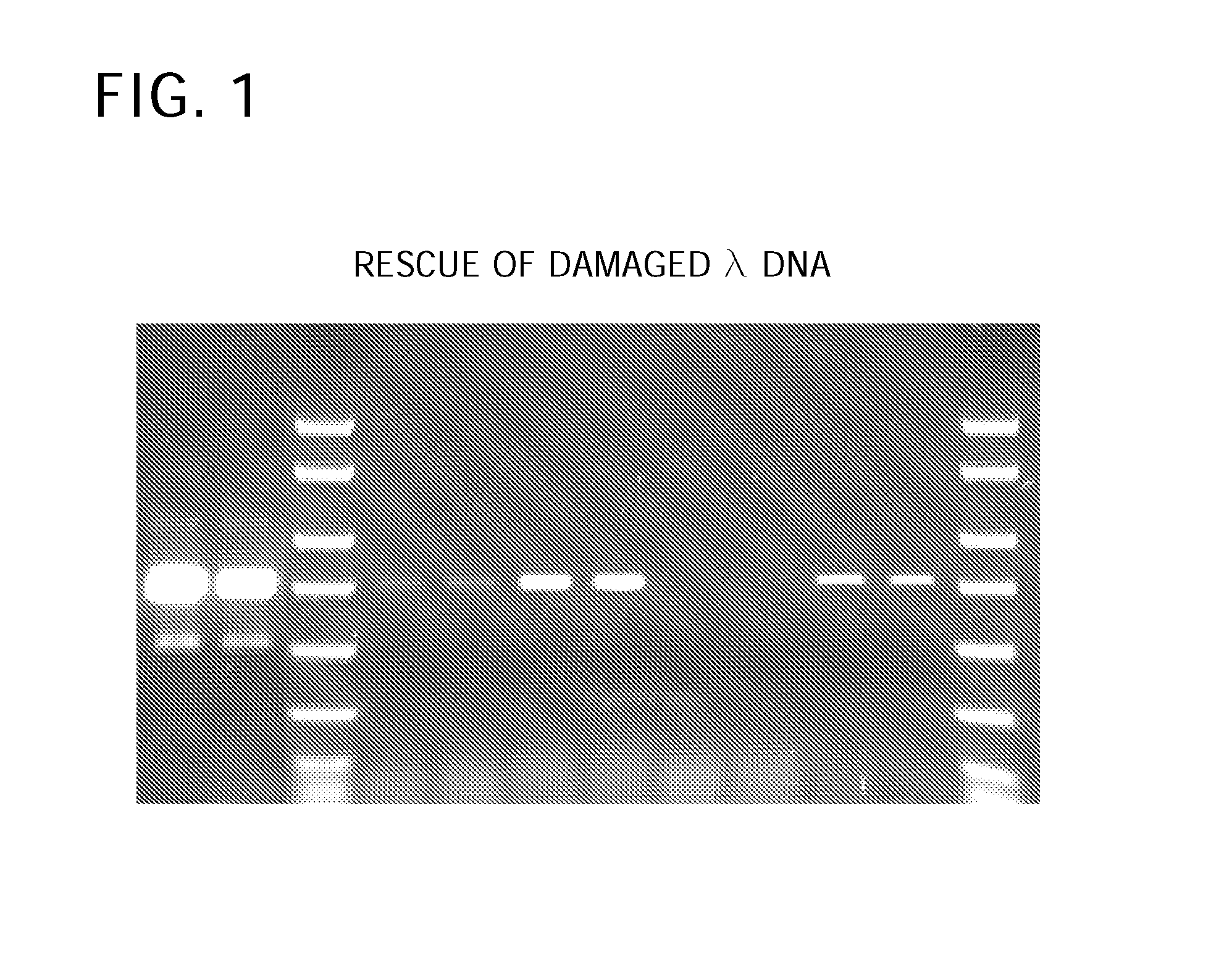
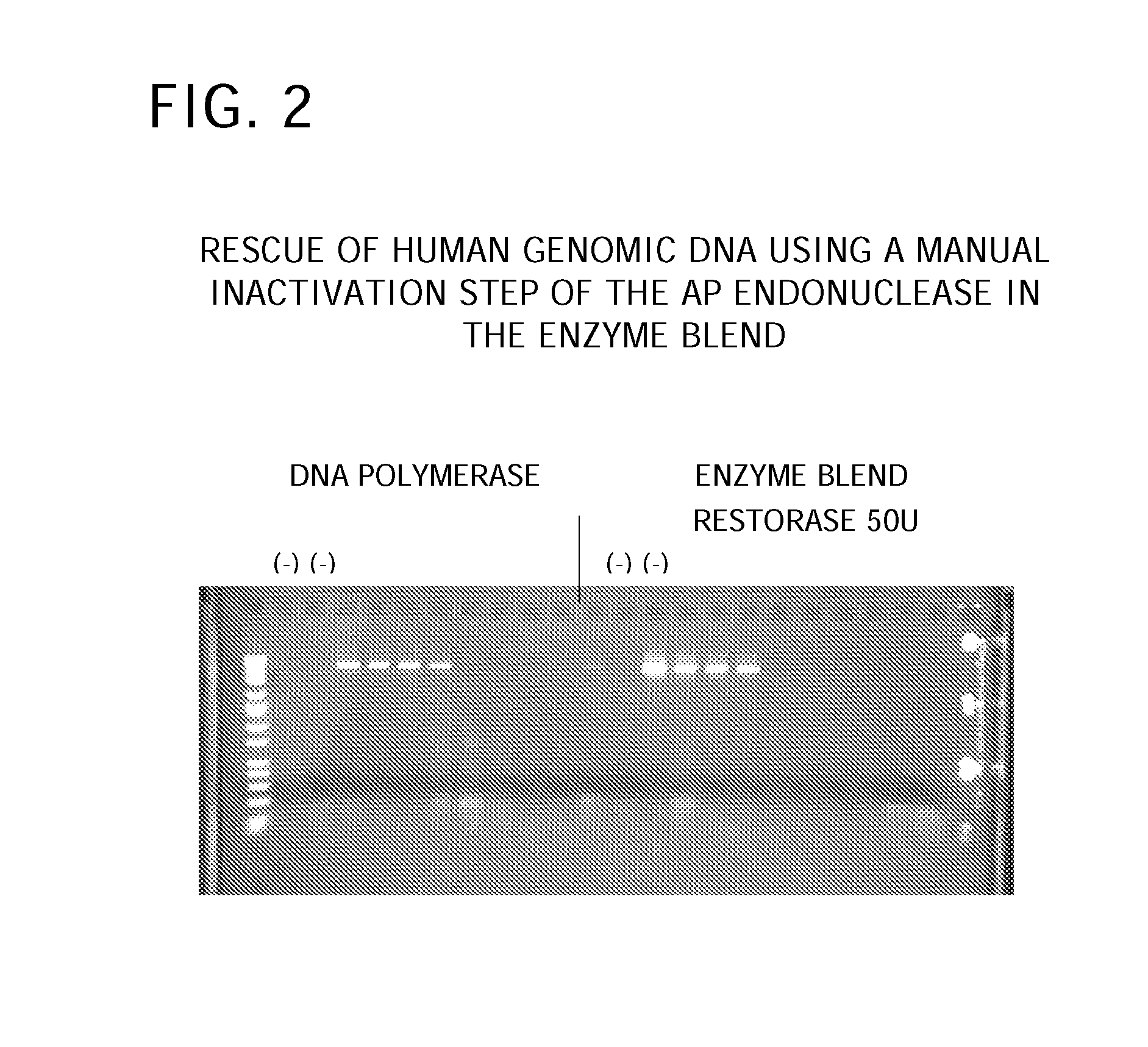
The invention provides an Enzyme Blend comprising a DNA polymerase and a DNA repair enzyme. Methods and kits for amplification of DNA that is damaged, undamaged, or suspected of being damaged are also provided.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Cosmetic treatment system and methods
ActiveUS20070254021A1Improve aestheticsImprove abilitiesCosmetic preparationsBiocideAlpiniaRepair enzyme
A cosmetic treatment system is provided having ingredients that may prevent signs of aging, improve the aesthetic appearance of skin, and promote recovery from environmental stresses. The composition includes natural ingredients, including at least one ingredient or extract from rosemary; at least one ingredient or extract from Centella, Echinacea, Alpinia or mixtures thereof; a DNA repair enzyme; and at least one pharmaceutically or cosmetically acceptable vehicle. The treatment system may further include a patch for applying the cosmetic ingredients and / or a packaging system for holding the components of the cosmetic treatment system.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Cosmetic composition and methods
ActiveUS20060257386A1Improve aestheticsImprove abilitiesAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsMedicineAdditive ingredient
A cosmetic composition is provided having ingredients that may prevent signs of aging, improve the aesthetic appearance of skin, and promote recovery from environmental stresses. The composition includes natural ingredients, including at least one ingredient or extract from rosemary; at least one ingredient or extract from Centella, Echinacea, Alpinia or mixtures thereof; a DNA repair enzyme; and at least one pharmaceutically or cosmetically acceptable vehicle.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Cosmetic treatment system and methods
ActiveUS7758878B2Improve aestheticsImprove abilitiesBiocideCosmetic preparationsCosmetic ingredientAdditive ingredient
A cosmetic treatment system is provided having ingredients that may prevent signs of aging, improve the aesthetic appearance of skin, and promote recovery from environmental stresses. The composition includes natural ingredients, including at least one ingredient or extract from rosemary; at least one ingredient or extract from Centella, Echinacea, Alpinia or mixtures thereof; a DNA repair enzyme; and at least one pharmaceutically or cosmetically acceptable vehicle. The treatment system may further include a patch for applying the cosmetic ingredients and / or a packaging system for holding the components of the cosmetic treatment system.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Poly (adp-ribose) polymerase inhibitor
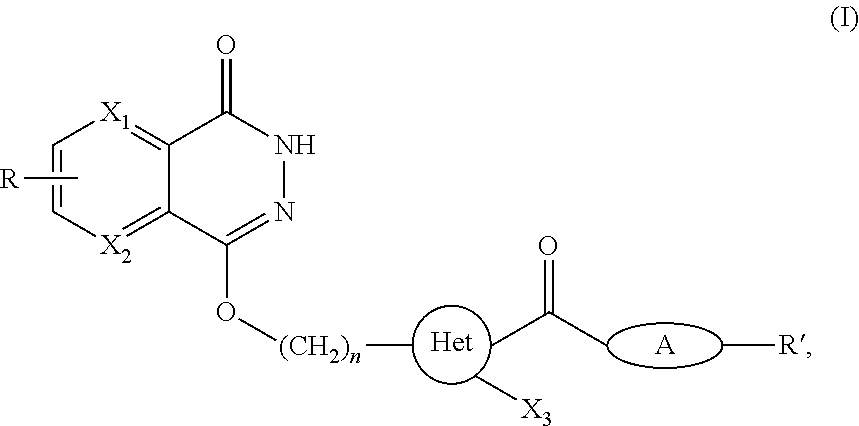
Disclosed are a phthalic hydrazide (phthalazine ketone) compound, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. As a DNA repair enzyme poly (ADP-ribozyme) polymerase inhibitor, the compound and the pharmaceutical composition can effectively treat diseases involving PARP enzymatic activity, including cancer, neural degenerative diseases, inflammation and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU DIAO PHARMA GROUP
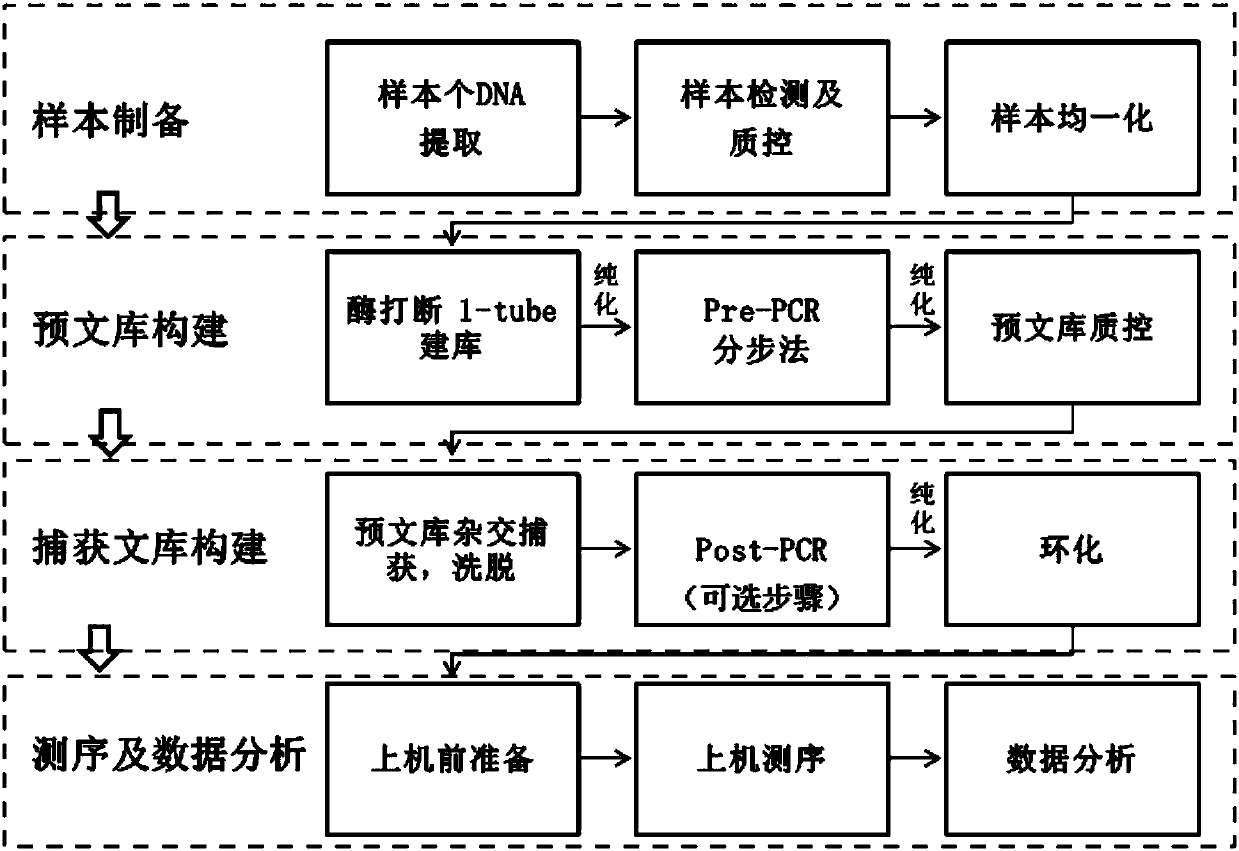
Method and reagent kit for constructing BRCA 1/2 (breast cancer susceptible genes 1/2) detection libraries
InactiveCN106987905AReduce purification operationsReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSingle strandDNA polymerase
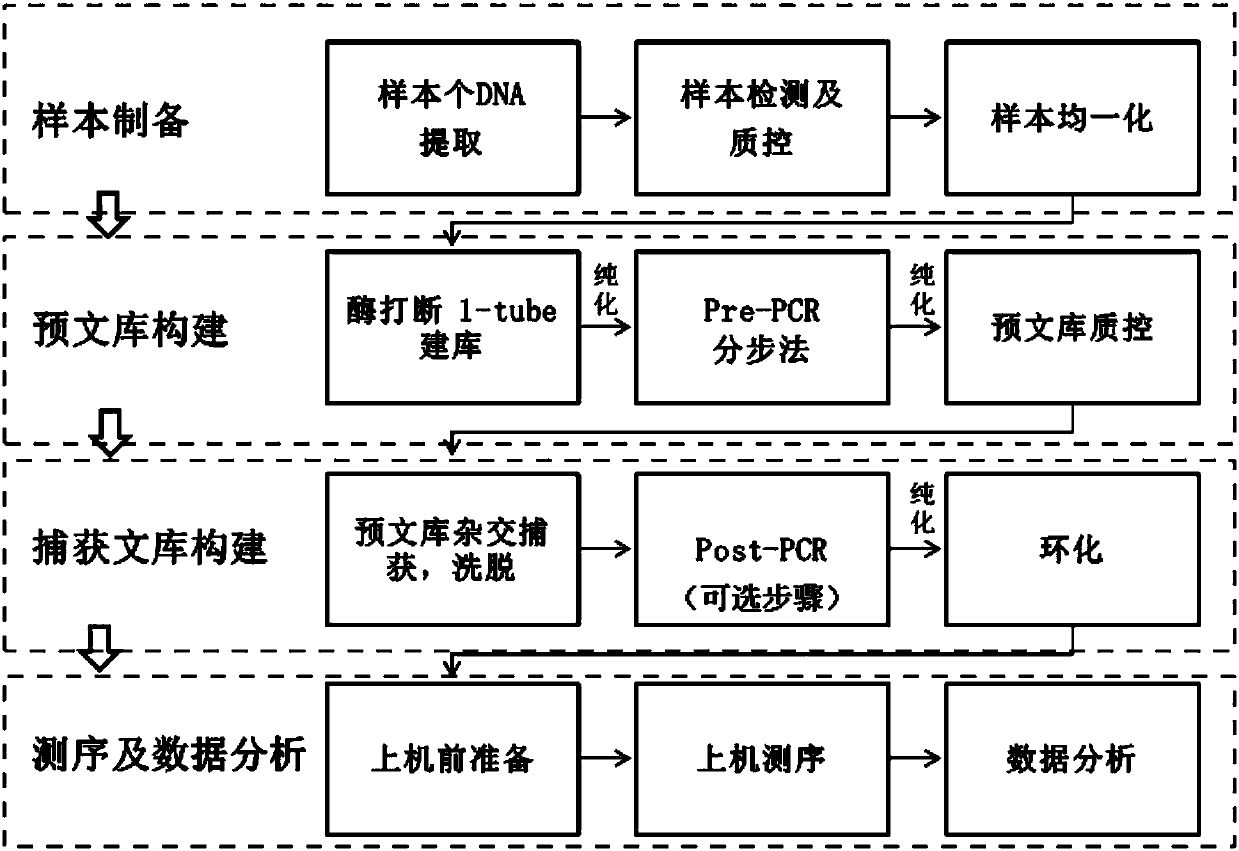
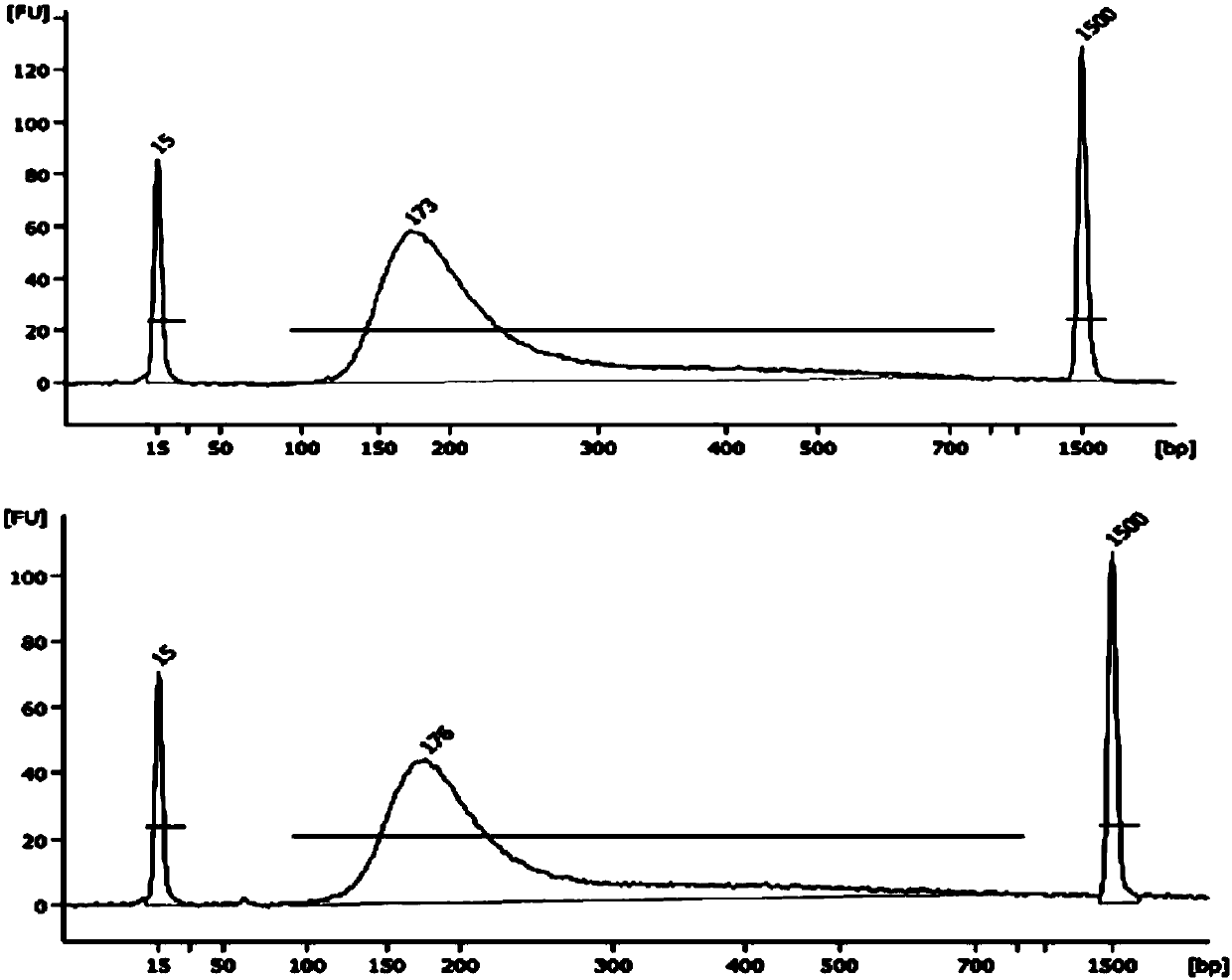
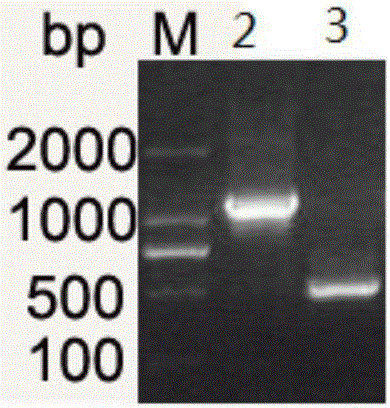
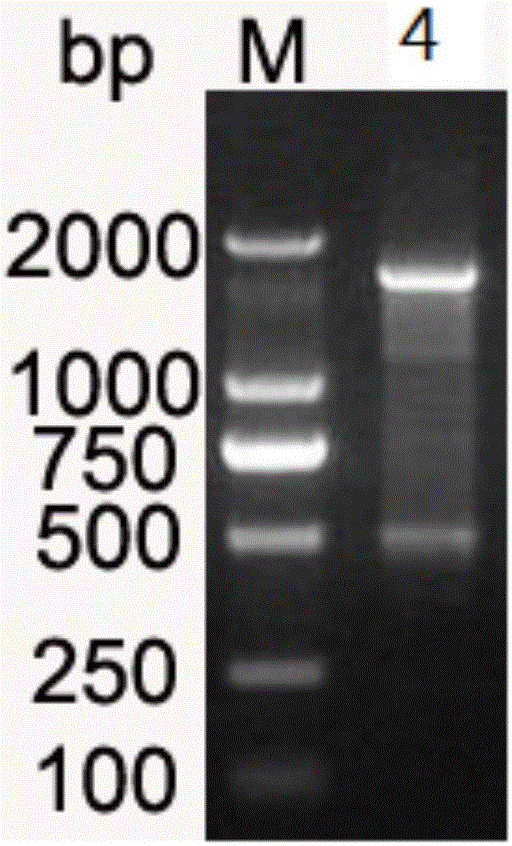
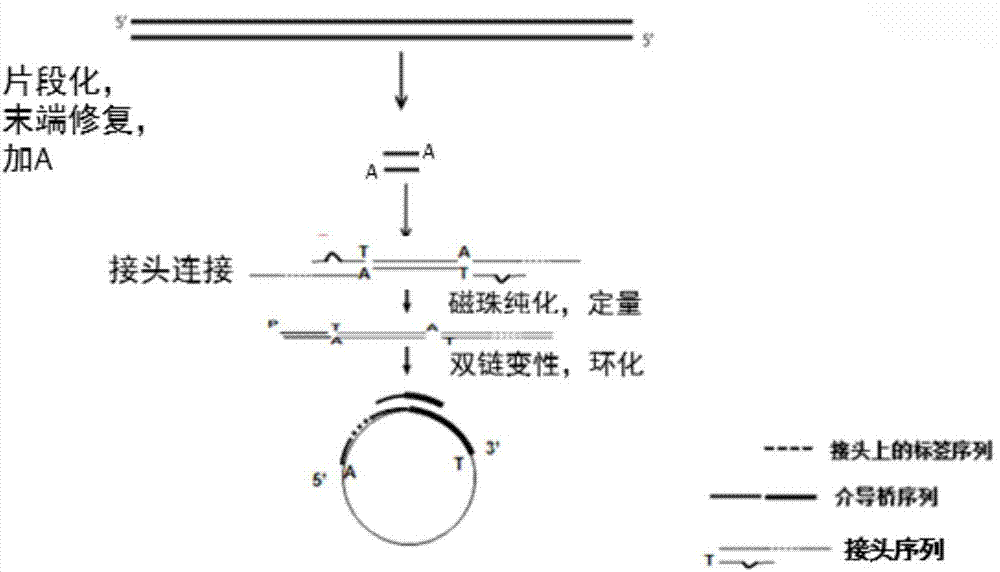
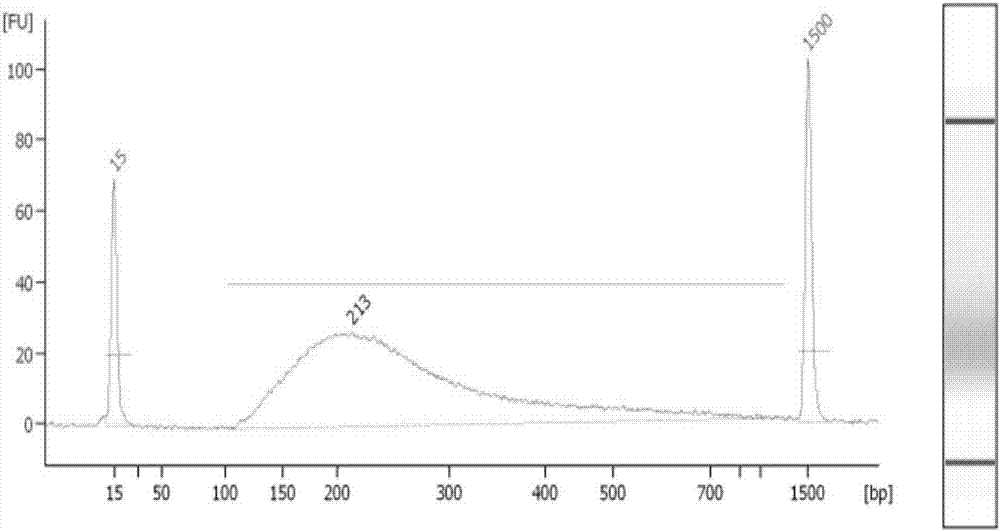
The invention discloses a method and a reagent kit for constructing BRCA 1 / 2 (breast cancer susceptible genes 1 / 2) detection libraries. The method includes carrying out fragmentation and tail-end repair on homogenized DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) samples in DNA fragmentation and tail-end repair systems under the effects of interruption enzymes and tail-end repair enzymes; linking products obtained at the previous step with linker sequences under the effects of DNA ligase; utilizing linker linking products obtained at the previous step as templates and carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by the aid of primers of linker sequences under the effects of DNA polymerases; hybridizing probe sequences with BRCA 1 / 2 and products obtained at the previous step to trap DNA fragments with the BRCA 1 / 2 and carrying out elution to obtain hybridization trapped products; carrying out cyclization on single strands of the hybridization trapped products under the effects of ligase to obtain the BRCA 1 / 2 detection libraries. The method and the reagent kit have the advantages that steps for constructing the libraries are simple, convenient and speedy, the cost can be effectively reduced, workload can be relieved, and variation types are comprehensive and accurate and are high in flux.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +3
Method and test kit for analyzing DNA repair
InactiveUS20020022228A1Solution presentedQuick fixSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JPurine
A method for analyzing the repair of DNA modifications and base mispairings as well as apurinic and apyrimidinic sites by DNA repair enzymes, comprising the following steps: contacting (a) single- or double-stranded DNA molecules which were covalently coupled to a solid-phase matrix carrying primary or secondary amino groups by reaction with a reactive squaric acid derivative, and which have modifications and / or base mispairings and / or apurinic or apyrimidinic sites, with (b) a composition containing DNA repair enzymes; and determining the elimination of the DNA modifications and / or base mispairings and / or apurinic or apyrimidinic sites. The DNA molecules are covalently coupled to the solid state matrix via a primary or secondary amino group incorporated in the DNA molecule at the 5'-end or at the 3'-end of the DNA or in the 2'-position of at least one deoxyribosyl residue.
Owner:RUBYCON CORPORATION
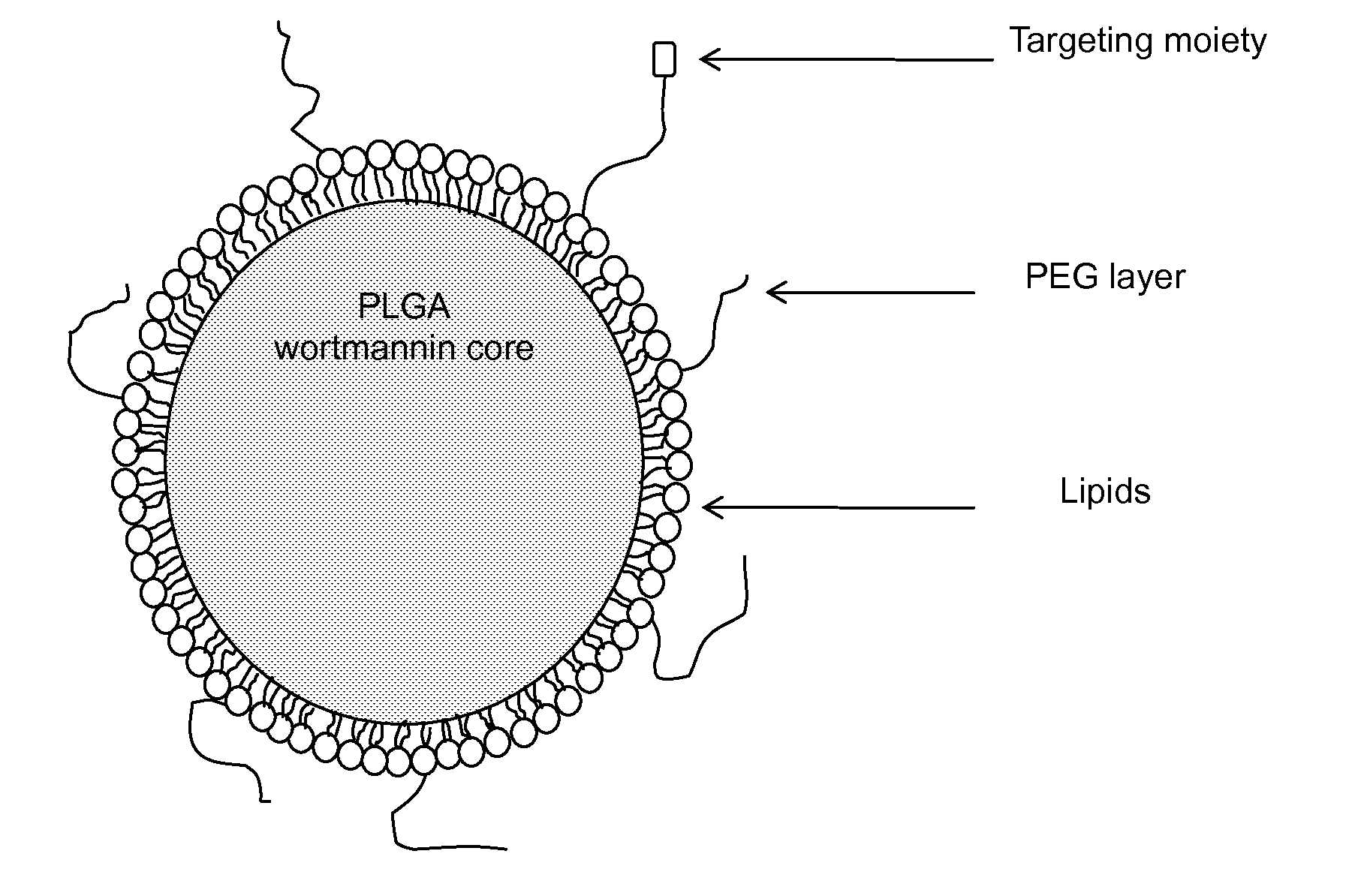
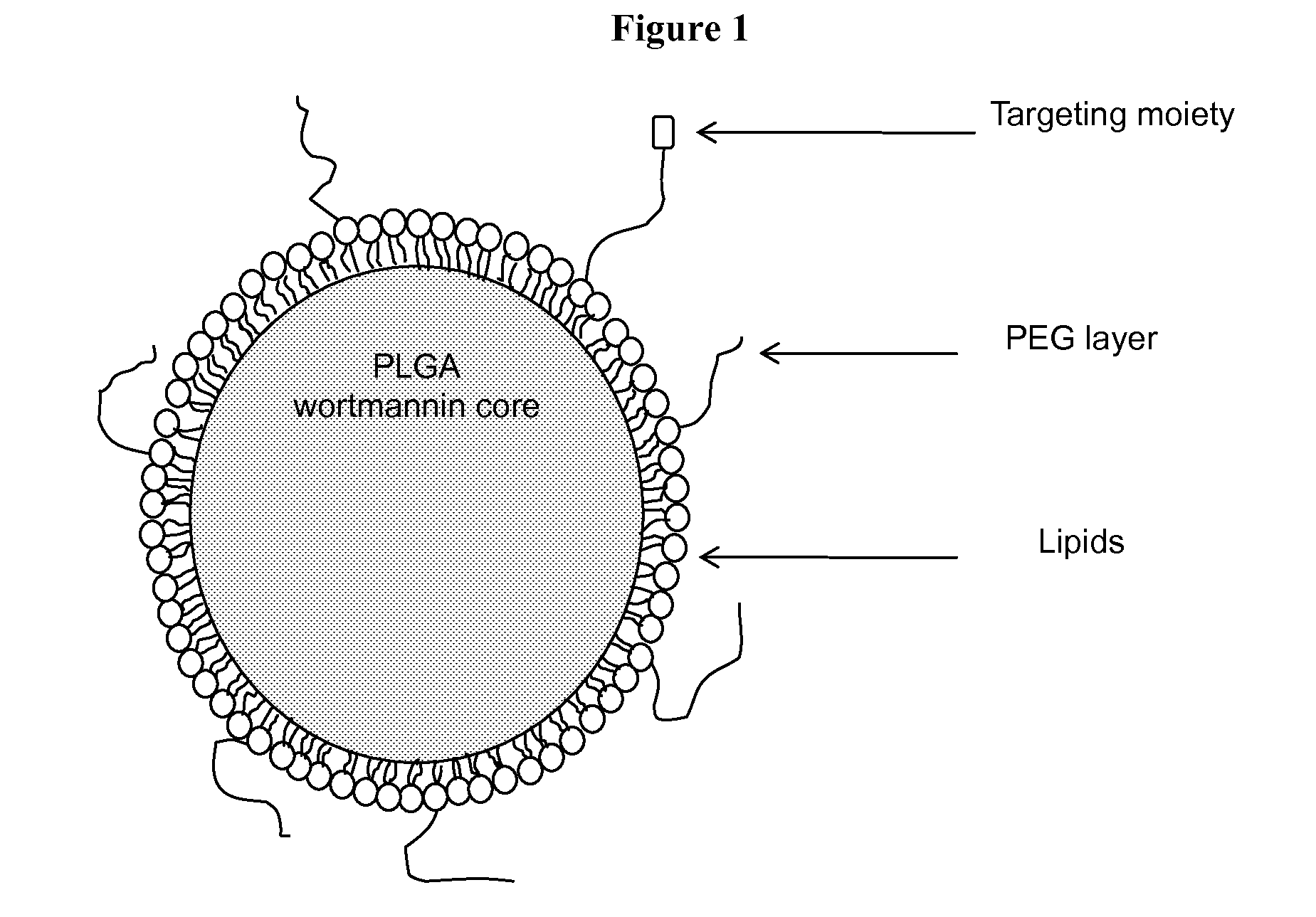
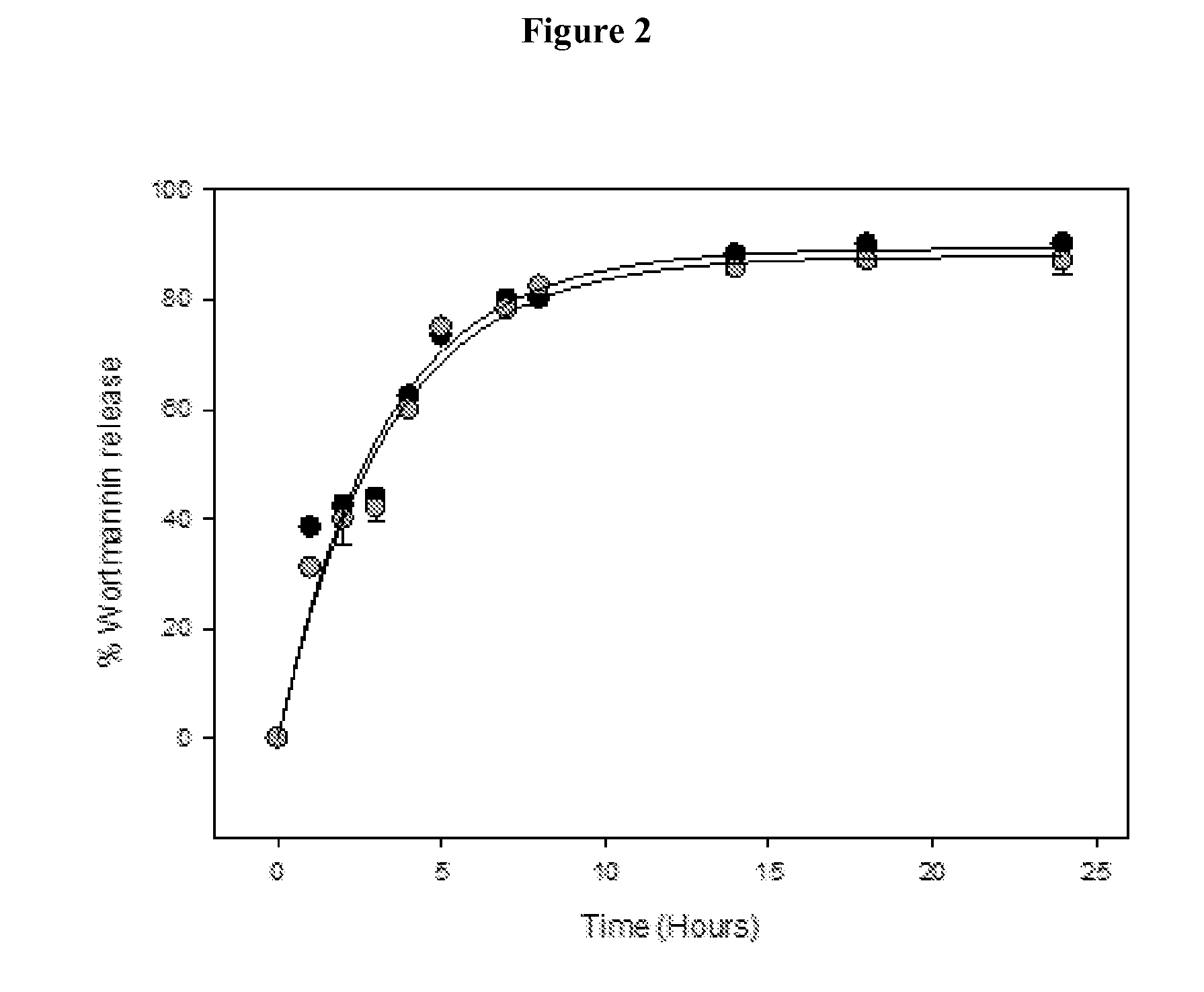
DNA repair enzyme inhibitor nanoparticles and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140017165A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocidePolyethylene glycolRepair enzyme
This invention relates generally to the discovery of novel nanoparticles for delivery of DNA double-stranded break (DSB) repair enzyme inhibitors such as wortmannin or wortmannin analogues. In one embodiment, these nanoparticles comprise a polylactide polyglycolide (PLGA) copolymer and a polyethylene glycol (PEG). In addition methods of treatment and methods of enhancing radiation treatments are also provided.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Anti-aging composition for improving co-enzyme I, preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109045037AIncrease contentPromote energy metabolismHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsArray data structureRaw material
The invention discloses an anti-aging composition for improving co-enzyme I, a preparation and a preparation method thereof. The anti-aging composition is prepared from the following raw materials andcomponents in parts by weight: 0.005 to 0.02 part of methylpyridine chromium, 0.05 to 0.2 part of folic acid, 100 to 250 parts of quercetin, 30 to 80 parts of resveratrol, 10 to 100 parts of niacinamide, 10 to 300 parts of niacin, 10 to 50 parts of soluble magnesium, and 300 to 600 parts of leucine. The anti-aging composition and the preparation have the advantages that the content of the coenzyme I (NAD) in cells is effectively increased; by compounding with other natural components, the histone deacetylase family (SIRT 1-7) for cell growth, metabolism and survival can be more effectively activated, the health of mitochondria is maintained, the energy metabolism of the cells is optimized, the activity of the gene repair enzyme PARP1 is maintained, the injury of the cells is restored, thegeneration of the cells is enhanced, and the functions of a human body are regulated and optimized; a user can reach the purposes of more effectively resisting aging, and reducing deteriorative disease risk of the patient.
Owner:董玲
Methods and Compositions for Amplification of DNA
The invention provides an Enzyme Blend comprising a DNA polymerase and a DNA repair enzyme. Methods and kits for amplification of DNA that is damaged, undamaged, or suspected of being damaged are also provided.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Development of a novel assay for mgmt (methyl guanine methyl transferase)
InactiveUS20070264672A1Shorten the timeLower potentialBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceRepair enzyme
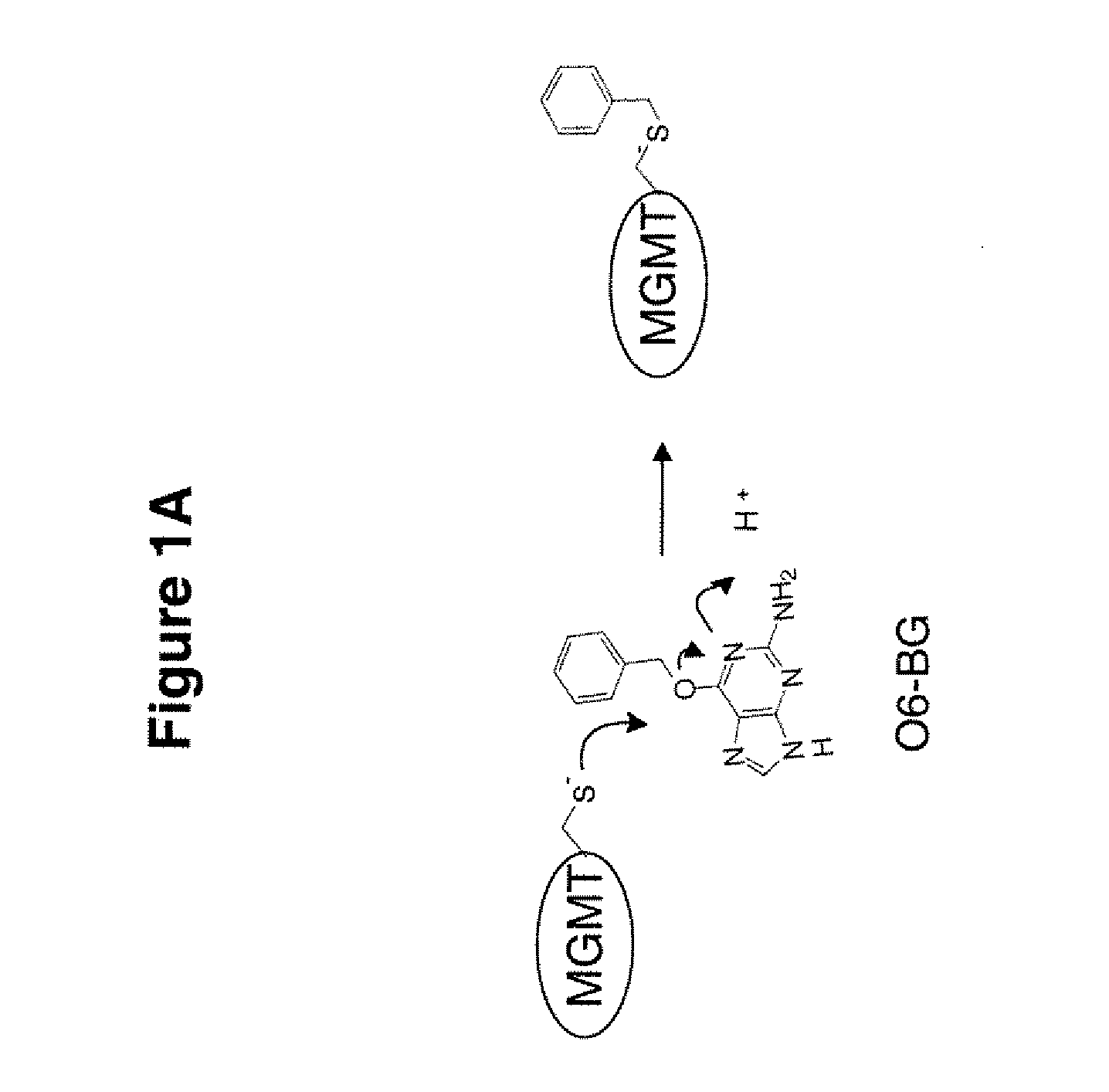
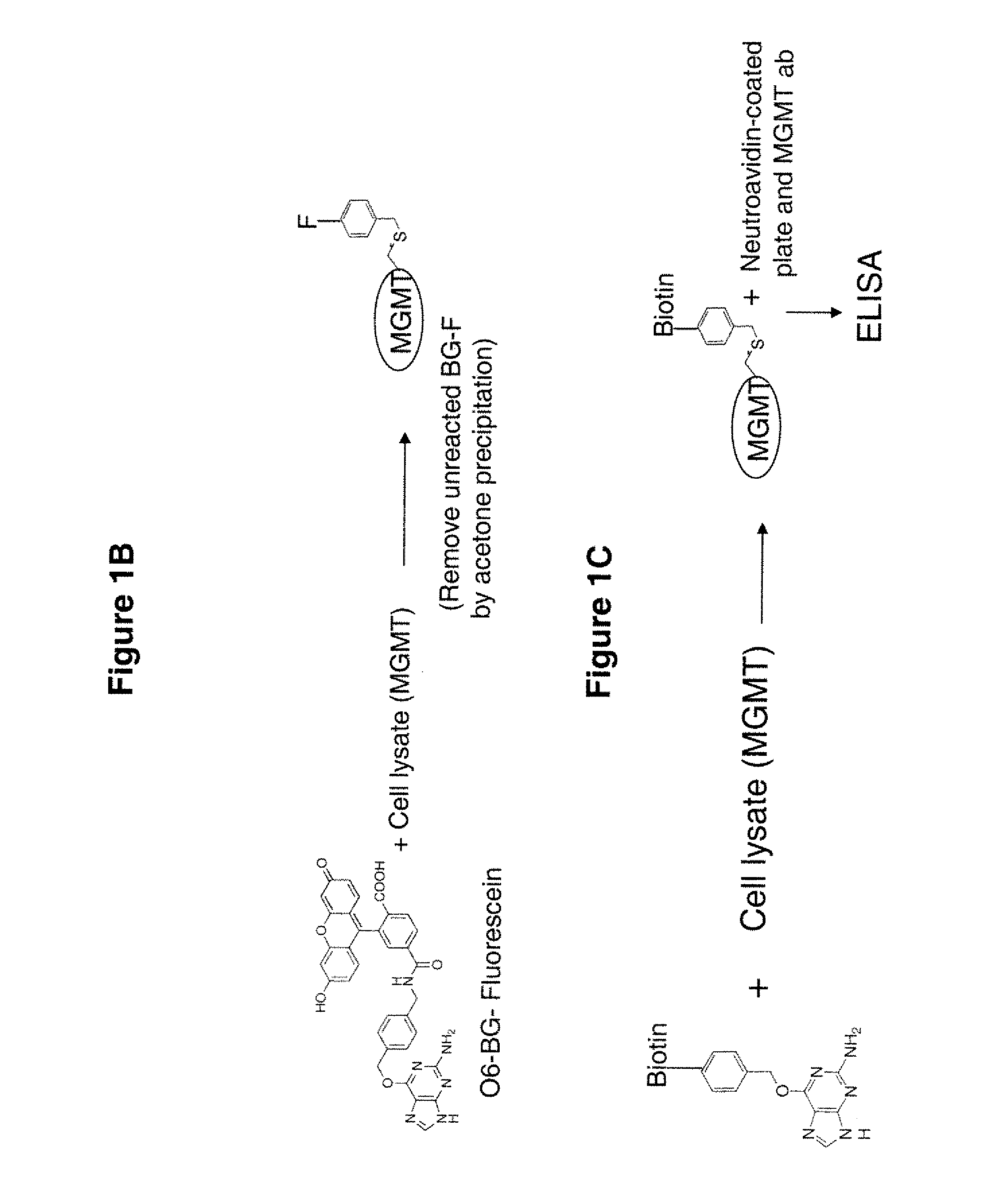
The present invention provides improved methods for assessing the level of MGMT activity in a variety of biological preparations. MGMT, a DNA repair enzyme, can reduce the chemotherapeutic efficacy of alkylating agents by repairing the damage that alkylating agents do to tumor cell DNA. The methods of the present invention can be used, inter alia, to measure MGMT levels and to thereby predict the clinical response to alkylating agents. The present invention includes three preferred assays for assessment of MGMT activity: (1) the immunoassay technique, (2) the labeled O6—BG technique, and (3) the fluorescence polarization technique. Kits useful for the performance of such assays are also provided.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Kit for genetic detection of colorectal cancer
InactiveCN101608224AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceFhit gene
The invention discloses a kit for genetic detection of colorectal cancer. The kit comprises a specific primer pair and a specific probe pair which are used for detecting the mononucleotide polymorphism loci genotype of a 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene (MTHFR), a glutathione-s-transferase T1 gene (GSTT1), a glutathione-s-transferase M1 gene (GSTM1), a cytochrome P450 2E1 gene (CYP2E1), and a mismatching repair enzyme gene (hMLH1), a fluorescent quantitative PCR general component, a PCR reaction component and the like. The kit can evaluate the genetic risk of individuals suffered from the colorectal cancer by detecting the polymorphism loci genotype of the genes closely related to the genetic risk of the colorectal cancer at the same time.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
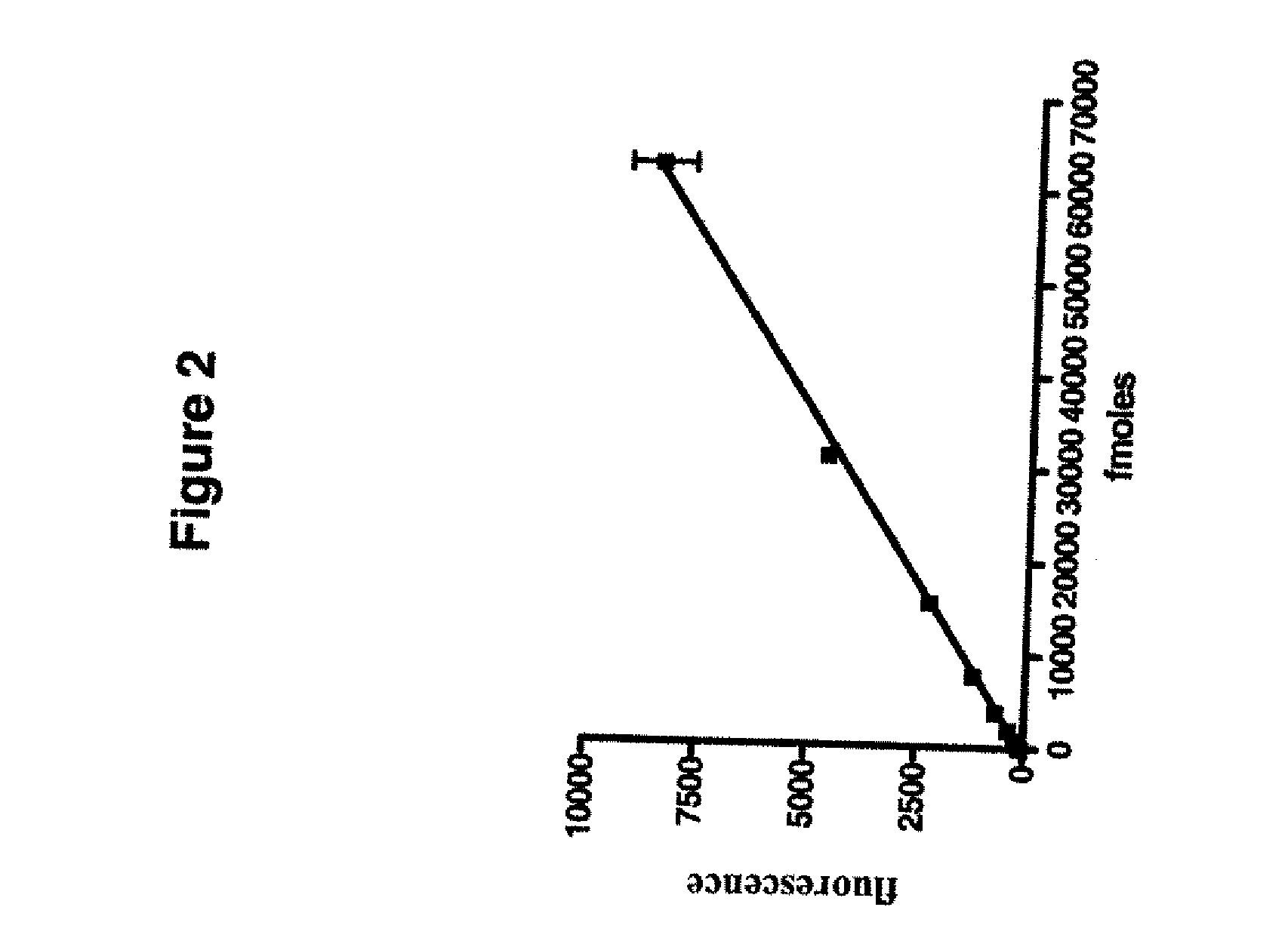
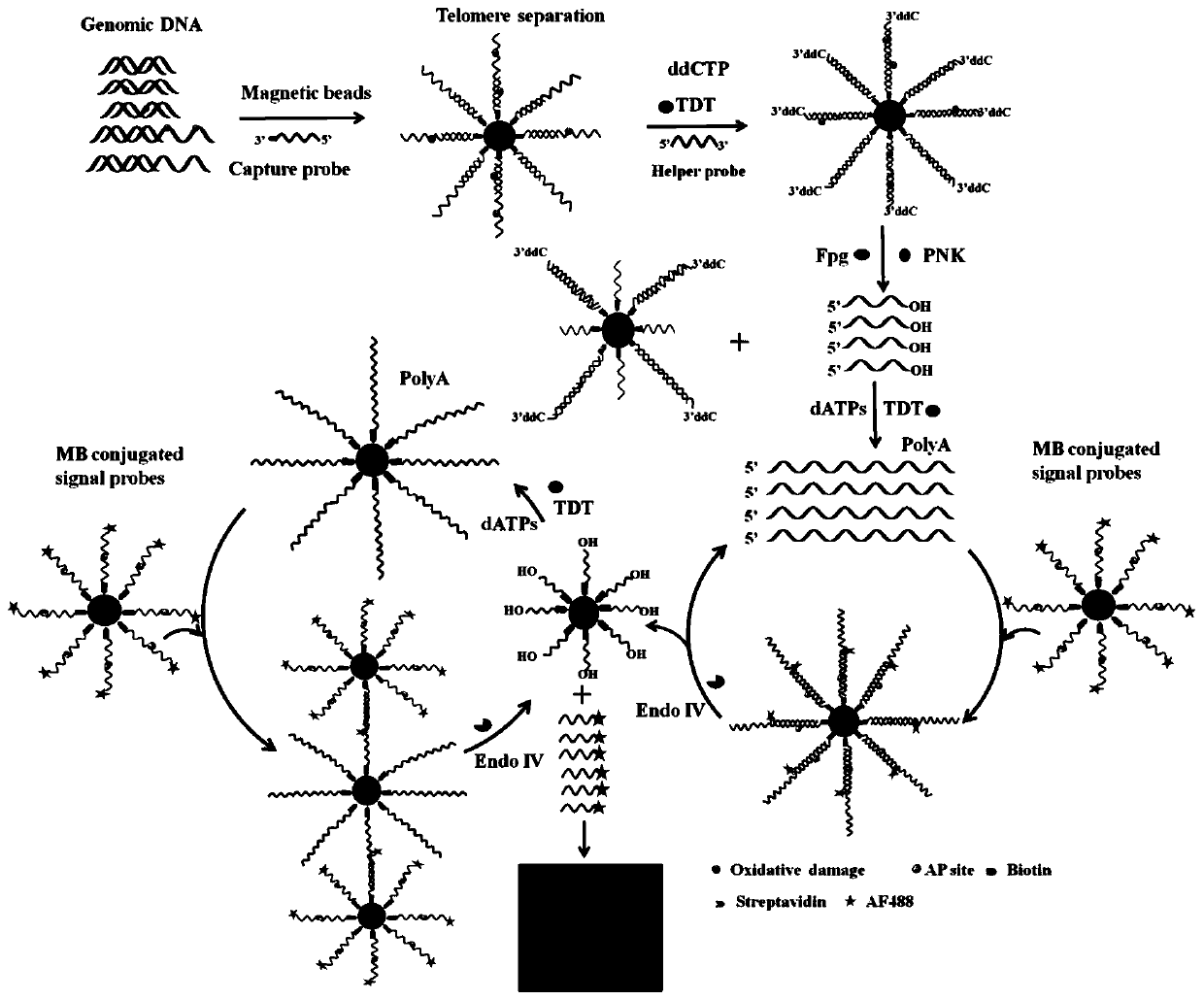
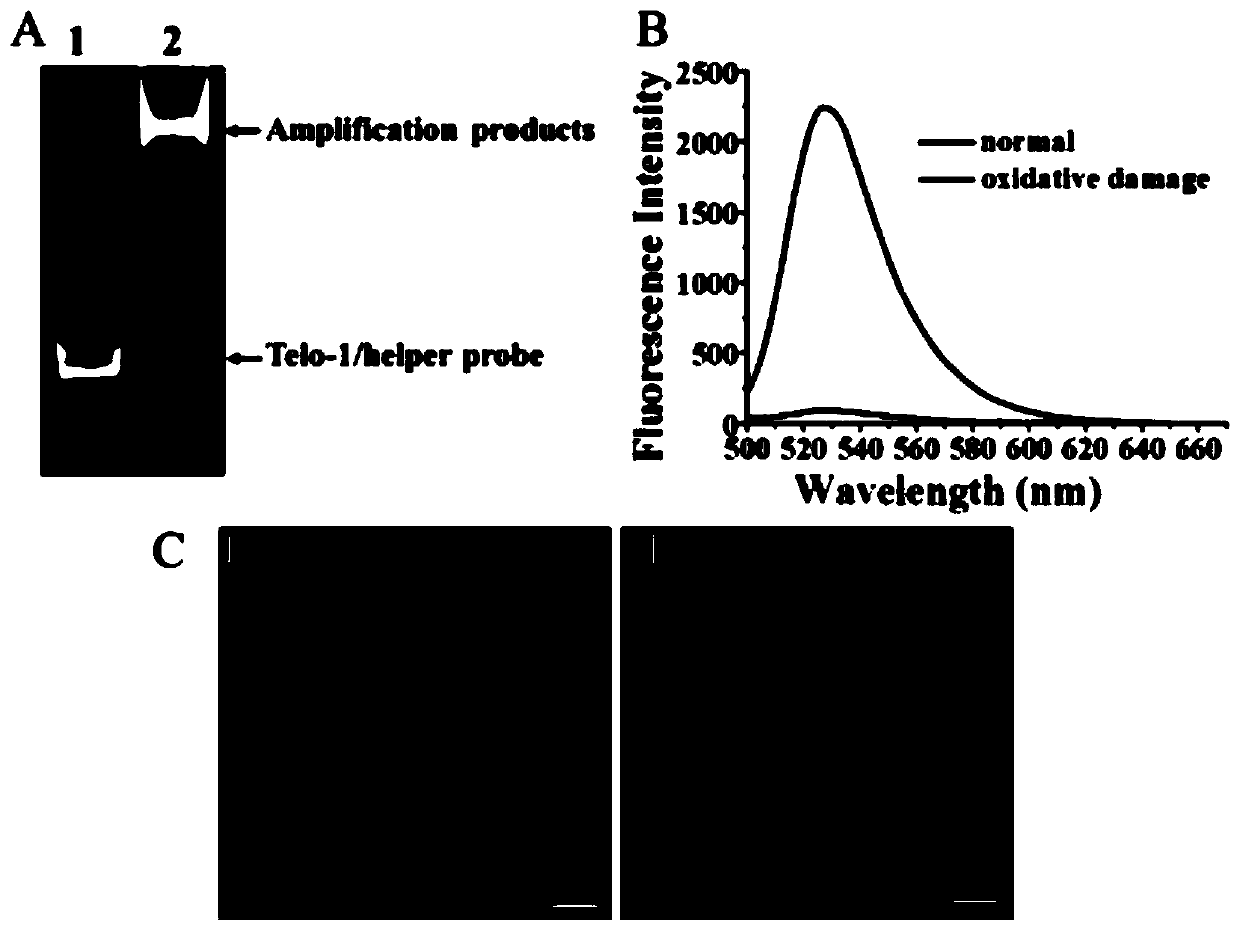
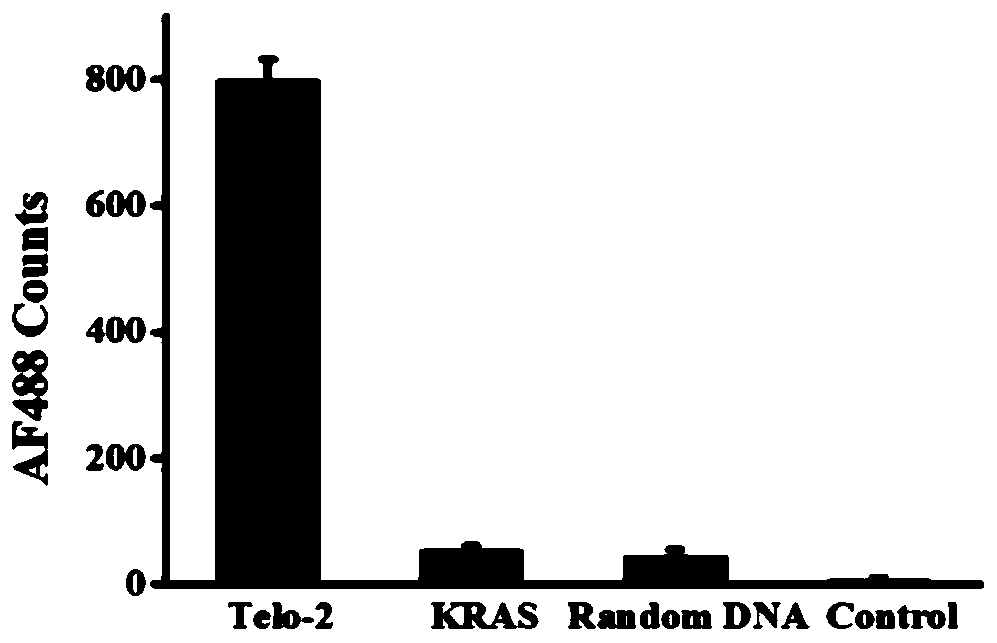
Fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method for detecting oxidative damage in telomeres and application of fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method
ActiveCN110144384AReduce consumptionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorophoreRepair enzymes
The invention provides a fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method for detecting oxidative damage in telomeres and an application of the fluorescent chemical sensor and the detection method. Specificity of a repair enzyme and polymerization mediated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase are combined so as to start a cycle cutting signal probe induced by endonuclease IV, induce an AP sitein an Endo IV splitting signal probe, cause release of AF488 fluorophore on the signal probe, and besides, generate a signal probe having free 3'-OH end. Each signal probe having free 3'-OH can be effectively extended through TdT to generate a long poly-A sequence. The released poly-A sequence and a newly-generated poly-A sequence can induce the repeated cycle cutting of the signal probe so as torelease more AF488 fluorophore. Under magnetic separation, the fluorophore in supernatant can be imaged and quantified by unimolecule. The fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method have favorable actual application value.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Method for determining activity of nucleic-acid-repair enzyme
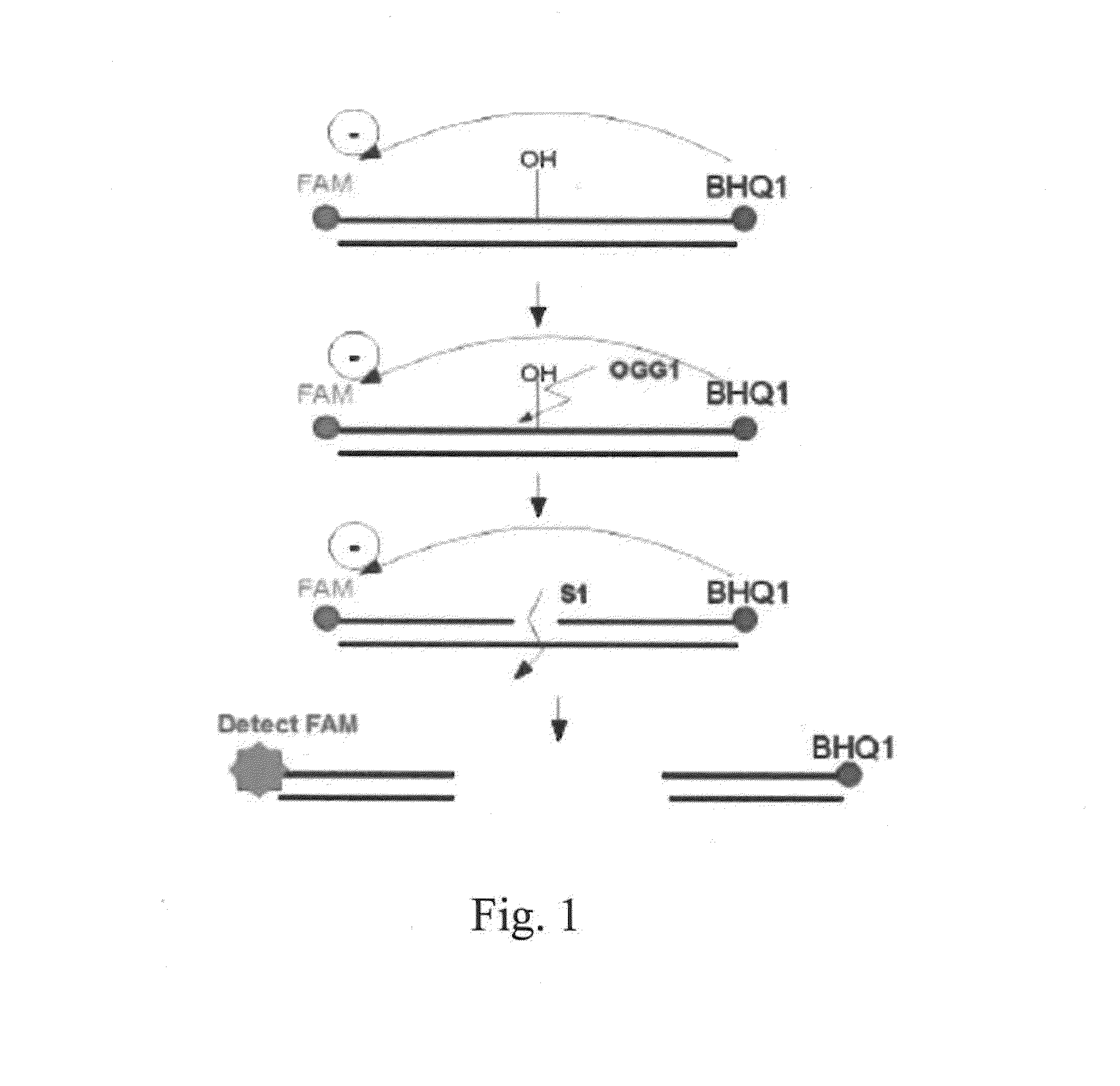
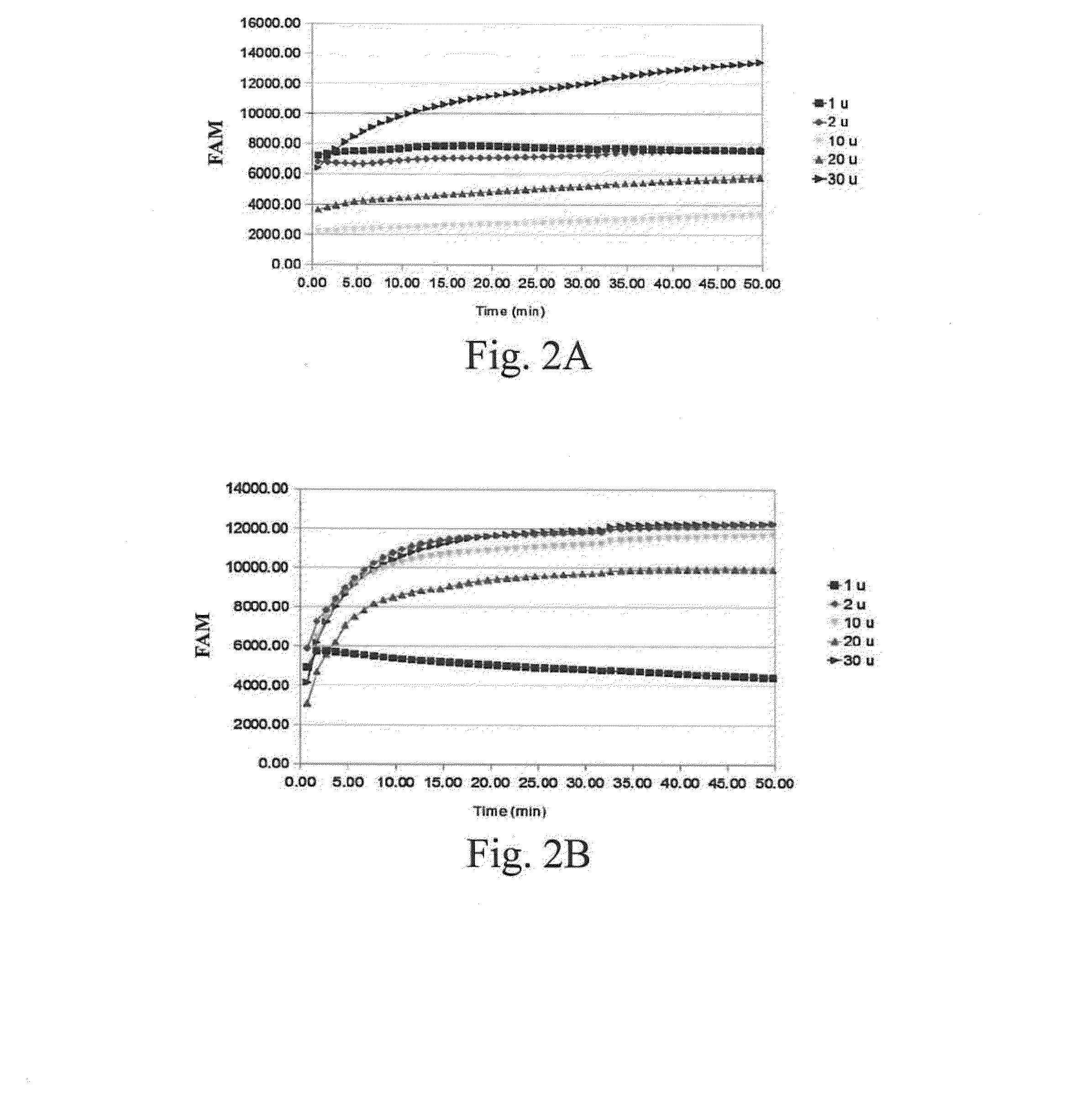
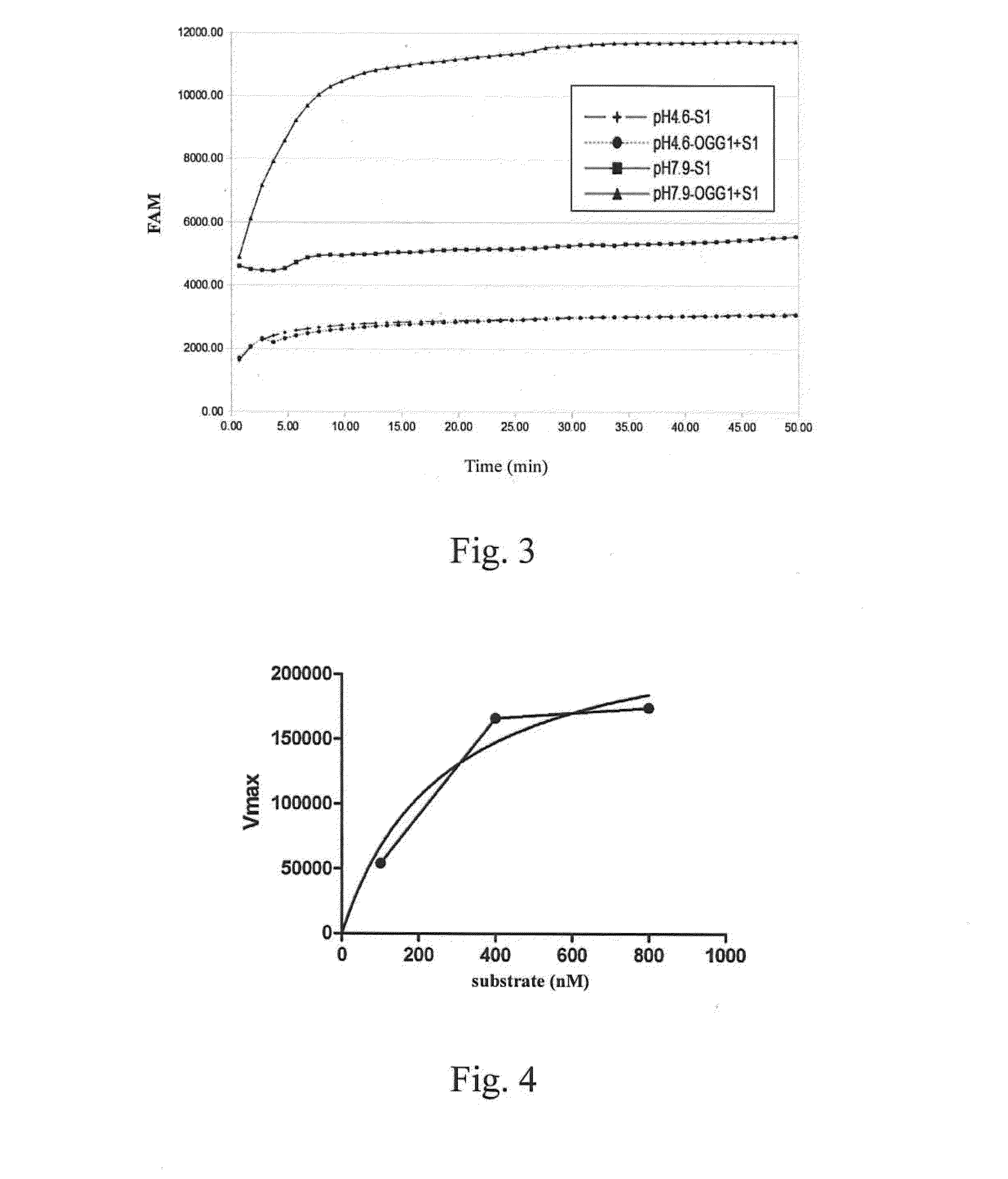
InactiveUS20150226671A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisS1 nucleaseNucleotide
A method for determining the activity of a nucleic-acid-repair enzyme is provided. The method comprises the following steps: (i) providing a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule, which is labeled with a fluorophore and a quencher and has at least one mutated nucleotide in either strand; (ii) mixing the double-stranded nucleic acid molecule, S1 nuclease, and the sample to obtain a mixture; and measuring the fluorescence intensity of the mixture.
Owner:TAIWAN SUGAR CORP
Compound recipe anti-cancer drugs slow release agent comprising anticancer antibiotics and booster thereof
Disclosed is a compound anticancer slow release agent which comprises slow release microspheres and dissolvent, wherein the slow release microballoons comprise anti-cancer active constituents and slow release auxiliary materials, the dissolvent being specific dissolvent containing suspension adjuvant. The anticancer effective ingredients include Aclarubicin, Idarubicin, Doxorubicin, Epirubicin, Valtaxin, Pirarubicin, Losaxantrone, Losoxantrone and / or anticancer antibiotic synergistic agents selected from phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analogues and / or DNA restoration enzyme inhibitor, the slow release auxiliary materials are selected from polylactic acid copolymer EVAc, or sebacic acid copolymer, the viscosity of the suspension adjuvant is 100-3000cp (at 20-30 deg C). The slow release microspheres can also be prepared into slow release implanting agent for lowering down the whole body toxicity reaction of the medicament when locally dispensing on the tumor, and for selectively increasing the tumor local medicinal concentration.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA
Escherichia coli DNA photolyase and construction method thereof
ActiveCN105062999AHigh activityImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention discloses escherichia coli DNA photolyase and a construction method thereof. The enzyme has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (in the description). The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a DNA photolyase gene from the conventional WT escherichia coli; designing a mutation primer to obtain a mutational gene segment; connecting the mutational gene segment with pET22b plasmid; constructing recombinant expression plasmid pET22b-A377S; converting the recombinant expression plasmid into a competent cell of escherichia coli; constructing genetically engineered bacterium BL21 (DE3) / pET22b-A377S for mutant enzyme expression. According to the invention, better expression is achieved under the conditions of 18 DEG C and 1 mM ITPG; the expressed photolyase is more stable in activity, and the antioxidant effect of the enzyme is remarkably improved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Slow-releasing injection contg. vasoinhibitor and potentiator type anticarcinogen
InactiveCN1861047AIncreased sensitivityGrowth inhibitionSolution deliveryEmulsion deliverySolventErlotinib
A slow-release anticancer injection contains the slow-release microspheres and solvent. Said slow-release microsphere contains the active anticancer component chosen from 16 vascula inhibitors including gefitinib, angiostatin, etc and 3 cytotoxins including phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analog or DNA repairase inhibitor, and the slow-release auxiliary.
Owner:JINAN SHUAIHUA PHARMA TECH
Reagent box for detecting chromosome aneuploidy and preparing method and application thereof
PendingCN107083440AReduce biasNo separationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadDNA polymerase I
The invention relates to the technical field of biological detection, and relates to a reagent box for detecting chromosome aneuploidy and a preparing method and an application thereof. The reagent box comprises a first reagent, a third reagent with purification magnetic beads or a second reagent, and a third reagent with the purification magnetic beads; the first reagent comprises a breaking repairing buffer solution, a breaking repairing enzyme, a dATP, a dNTP, a DNA polymerase I and a rtaq enzyme; the second reagent comprises the breaking repairing buffer solution, the breaking repairing enzyme, the dATP, the dNTP, a klenow enzyme and the rtaq enzyme; the third reagent comprises T4 DNA ligase, a PNK buffer solution and a junction. According to the reagent box, through an efficient and precise building database method, chromosome abnormity is detected, the comparison rate is increased, the GC deviation is reduced, the dup rate is lowered, meanwhile 10bp fluctuation before sequencing can be reduced, and the situation of AT separation can be avoided.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Slow-releasing injection contg. platinum compounds and its potentiator type anticarcinogen
InactiveCN1861050AEasy to operateGood repeatabilitySolution deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAnticarcinogenMicrosphere
A slow-release anticancer injection contains the slow-release microspheres and solvent. Said slow-release microsphere contains the active anticancer component chosen from 6 Pt compounds including bicycloplatinum, etc and 3 cytotoxins including phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analog or DNA repairase inhibitor, and the slow-release auxiliary.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
Site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase and construction method thereof
ActiveCN105087535AHigh activityImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention discloses a site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase and a construction method thereof. The photolyase has an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a DNA photolyase gene from the existing WT escherichia coli, designing a mutation primer to obtain a mutated gene fragment, and connecting the mutated gene fragment with a pET22b plasmid to construct a recombinant expression plasmid pET22b-A377N; and converting the recombinant expression plasmid into an escherichia coli competent cell to construct a genetic engineering bacterium BL21(DE3) / pET22b-A377N for mutant enzyme expression. The site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase obtains better expression under a 1mM ITPG condition at 18 DEG C. The expressed photolyase is more stable in activity, and the antioxidation effect of the photolyase is significantly improved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Slow-releasing injection contg anticarcinogen of Jixitabin
A slow-release anticancer injection contains the slow-release microspheres and solvent. Said slow-release microsphere contains the active anticancer component chosen from 13 antimetabolic medicines including gemcitabine, zalcitabine, etc and 3 cytotoxins including phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analog or DNA repairase inhibitor, and the slow-release auxiliary.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
Method of predicting the clinical response to chemotherapeutic treatment with alkylating agents
InactiveUS20020127572A1Low levelPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthNervous system
The present invention provides methods relating to chemotherapeutic treatment of a cell proliferative disorder. In particular, a method is provided for predicting the clinical response to certain types of chemotherapeutic agents. Alkylating agents, used for the treatment of certain types of tumors including tumors of the nervous system and lymph system, are efficacious agents when the damage they do to tumor cell DNA is not repaired by cellular DNA repair mechanisms. The present invention provides a method for determining the activity of a gene encoding a DNA repair enzyme, thus providing a prediction of the clinical response to alkylating agents.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Anti-cancer medicine sustained-released injection loaded with platinum compound and synergist thereof
InactiveCN101380303AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEptaplatinPicoplatin
A anticarcinogenic slow release injection carrying platinum compounds and a synergist thereof is composed of slow release microspheres and a dissolvant, wherein, the slow release microspheres comprise anticancer active components and a slow release adjuvant, and the dissolvant is a special dissolvant containing a suspending agent. The anticancer active component comprises platinum compounds such as sunpla, dicycloplatin, eptaplatin, (cis-amminedichloro(2-methylpyridine) platinum, camphoramine chloroacetic platinum or picoplatin, and the like, and a cytotoxic drug selected from a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analogue and / or a DNA repair enzyme inhibitor; the slow release adjuvant is biocompatible macromolecules such as polylactic acid and copolymer thereof, polyethylene glycol, carboxyl end polylactic acid copolymer, copolymer of dienoic fatty acid and sebacic acid, poly (erucic acid dimer-sebacic acid), poly (fumaric acid-sebacic acid), polifeprosan, polylactic acid, EVAc, and the like, and the suspending agent has the viscosity of 100cp-3,000cp (at the temperature of 20-30 DEG C) and is selected from sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, and the like. The slow release microspheres can also be made into a slow release implant. The slow release injection is injected or placed in tumors or around the tumors, which can improve the curative effects of non-operative therapies such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
A kind of Antarctic ice alga cpd photorepair enzyme, its coding gene and expression vector and the application of the enzyme
Disclosed is an Antarctic ice algae CPD photolyase, a protein as set out in (a) or (b): (a) an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2; (b) a protein derivative of (a) having CPD photolyase activity, the amino acid sequence of which having been subjected to substitution, deletion or addition of 1 to 10 amino acid residues. Also disclosed are an Antarctic ice algae CPD photolyase coding gene and expression vector, and application of the Antarctic ice algae CPD photolyase in fields relating to cosmetics and biopharmaceuticals. The present invention clones the Antarctic ice algae CPD photolyase gene for the first time, successfully cloning said gene into the expression vector, and thereby obtaining a large quantity of CPD photolyase. The CPD photolyase has applications within fields relating to cosmetics and biopharmaceuticals, and may actively repair disorders caused by ultraviolet rays, thus being of great significance and benefit to society.
Owner:QINGDAO HENGSHENG BIOLOGICAL PHARMA TECH DEV
Spirulina platensis CPD (cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer) photolyase and application thereof
InactiveCN103966193ARepair DNA damageRepair damageCosmetic preparationsBacteriaNucleotideCyclobutane
The invention discloses spirulina platensis CPD (cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer) photolyase and an application thereof. The CPD photolyase has a polypeptide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2 or a polypeptide sequence which has CPD photolyase activity and is formed by replacing and / or losing and / or adding 1-10 amino acid residues in the polypeptide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2; and polynucleotide used for encoding the spirulina platensis CPD photolyase can have a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 or a nucleotide sequence which has higher than 90% of homology with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 and can encode active protein of photolyase. According to the spirulina platensis CPD photolyase and the application thereof, a spirulina platensis CPD photolyase gene applicable to prokaryotic expression is optimized and artificially synthesized for the first time and is successfully cloned to an expression vector, a large amount of spirulina platensis CPD photolyase is acquired, spirulina platensis CPD photolyase can initiatively repair skin diseases caused by ultraviolet light when applied to related fields such as cosmetics, biological medicine and the like, and the spirulina platensis CPD photolyase has huge social benefits and economic values as well as great significance.
Owner:ANHUI BIOYEARNING BIO ENG
Oxidative damage DNA detection method
InactiveCN106939336AInjury mitigation steps are cumbersomeEase sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
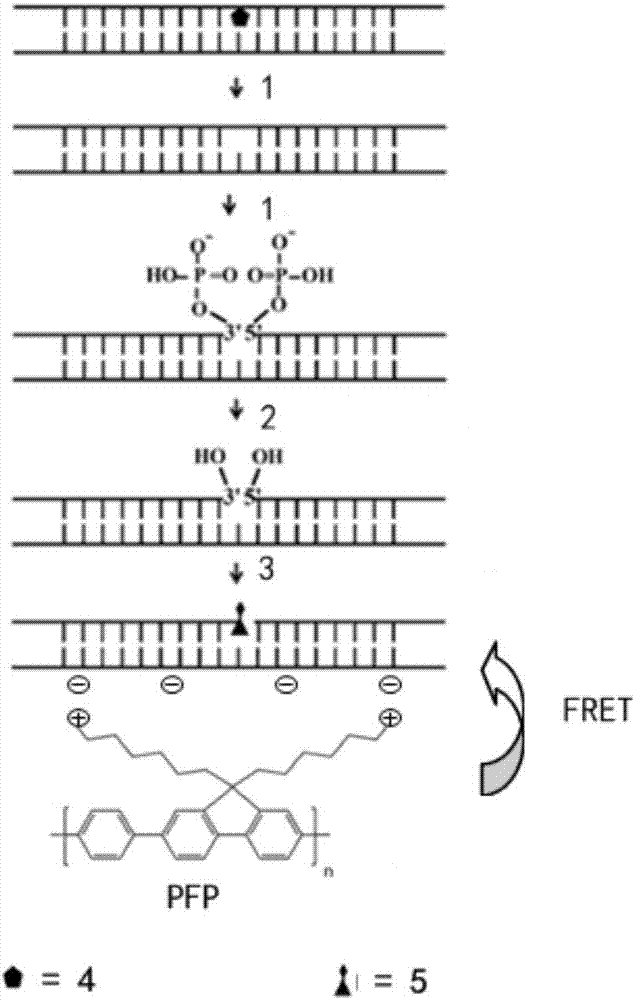
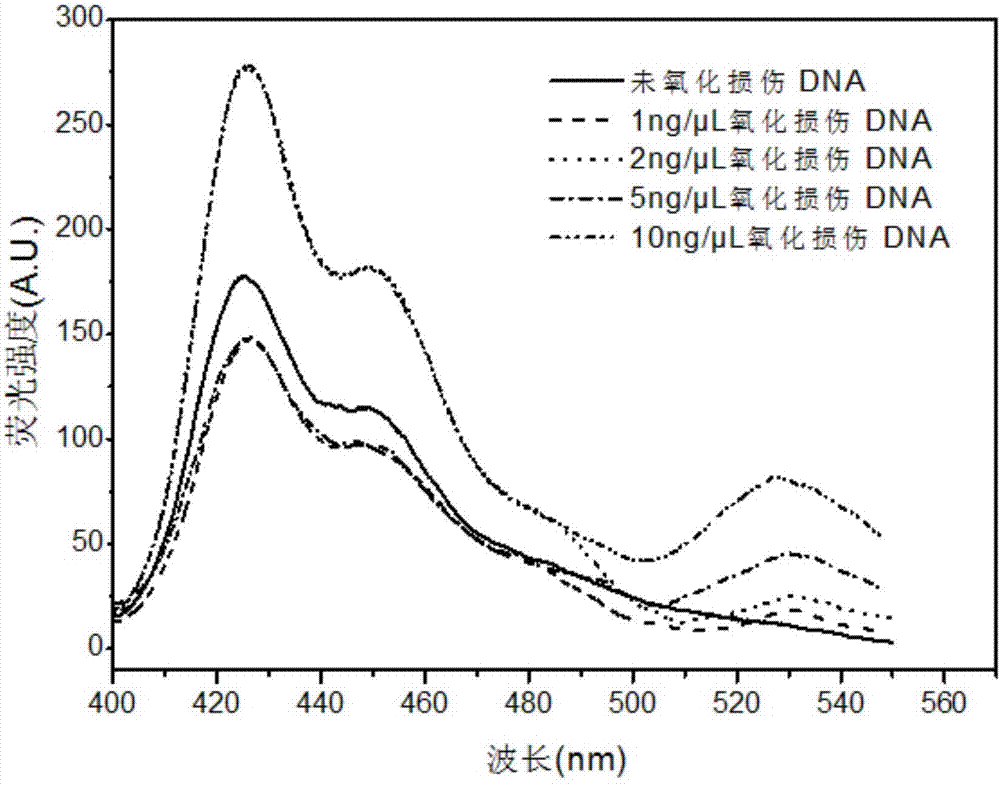
The invention discloses an oxidative damage DNA detection method, and relates to the technical field of DNA oxidative damage detection. The method comprises (a) obtaining of DNA containing 3 ', 5'-phosphate group nucleotide voi, to be more specific, adding a DNA repair enzyme for recognition and cutting of oxidized DNA bases; (b) introduction of hydroxyl into 3 ', 5' site, to be more specific, adding alkaline phosphatase for dephosphorylation to obtain the DNA containing 3 ', 5'-hydroxyl group nucleotide voids; (c) introduction of a fluorescent marker, to be more specific, adding DNA polymerase I and the fluorescent marker to obtain fluorescence-labeled DNA; (d) formation of a PFP-DNA complex, to be more specific, adding PFP to obtain the PFP-DNA complex; and (e) oxidative damage DNA detection, to be more specific, detecting damage DNA by FRET. The method alleviates the disadvantages of tedious steps, low sensitivity and low selectivity of DNA damage detection in the prior art. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity and high accuracy.
Owner:CHINA INST OF SPORT SCI
Anticancer sustained-released formulation loaded with blood vessel inhibitor and synergist thereof
InactiveCN101380304AIncreased sensitivityGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAngiostatinDepressant
An anticarcinogenic slow release injection carrying an angiogenesis inhibitor and a synergist thereof is made from slow release microspheres and a dissolvant. The slow release microspheres comprise anticancer active components and a slow release adjuvant, and the dissolvant is a special dissolvant containing a suspending agent. The anticancer active components are angiogenesis inhibitors such as gefitinib, erlotinib, lapatinib, vatalanib, pelitinib, thalidomide, ranolamine, angiostatin, endostatin, imatinib, thalidomide, ranolamine, simatinib, dasatinib, avastin, kanatini, sorafenib, sunitinib, telstar or panitoma, and the like, and / or cytotoxic drugs selected from a phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analogue and / or a DNA repair enzyme inhibitor; the slow release adjuvant is biocompatible macromolecule; the viscosity of the suspending agent is 100cp-3,000cp (at the temperature of 20-30 DEG C), and the suspending agent is selected from sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, and the like. The slow release microspheres can be also made into a slow release implant, and the curative effects of non-operative therapies such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and the like, can be improved when the slow release injection is injected or placed in tumors or around the tumors.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
Compositions for protecting skin comprising DNA repair enzymes and phycobiliprotein
ActiveUS20180207079A1Improve protectionEnhanced restorative activityCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineRepair enzyme
Owner:ALGAKTIV SL
Slow-released prepn containing taxane and its synergist
The slow released injection containing taxane and its synergist consists of slow released microballoon and solvent. The slow released microballoon includes effective anticancer component and slow releasing supplementary material, and the solvent is common solvent or special solvent containing suspending agent. The effective anticancer component is taxane and / or taxane synergist of phosphorinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analogue and / or DNA repair enzyme inhibitor; the slow releasing supplementary material is PLA, PLGA, EVAc, etc or their composition; and the suspending agent is sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, etc. The slow released microballoon may be also prepared into implantation preparation. Implanting or injecting the slow released preparation to local tumor part can lower the systematic toxic reaction of the medicine and raise the medicine concentration of local tumor part selectively to raise the treating effect.
Owner:JINAN KANGQUAN PHARMA TECH
Gene combination, primer and probe for detecting gastric cancer susceptibility and application
InactiveCN101962667AImprove accuracyImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationXRCC1 GeneMetabolic enzymes
The invention discloses a gene combination, a primer and a probe for detecting gastric cancer susceptibility and application. The gene combination comprises a combination of four genes closely related with a gastric cancer, namely an MTHFR gene, a CYP2E1 metabolic enzyme gene, an XRCC1 repairase gene and an ADPRT repairase gene. The gene combination comprises the following SNP sites: rs1801133 site of the MTHFR gene, rs2031920 site of the CYP2E1 gene, rs25478 site of the XRCC1 gene and rs1136410 site of the ADPRT gene. Whether the detected crowds carry 'gastric cancer susceptible genes' are comprehensively detected and analyzed by detecting a group of genes and sites related with the gastric cancer susceptibility, using the specific primer and the probe and combining a mononucleotide extending technique and a micro array chip technique so as to screen the gastric cancer susceptible crowd from the crowds, change unhealthy lifestyles and fulfill the purpose of preventing.
Owner:NANJING WEIYU GENETIC ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com