Site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase and construction method thereof
A technology of Escherichia coli and photorepair enzymes, applied in recombinant DNA technology, botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low antioxidant capacity and poor stability, and achieve stable activity and antioxidant effects Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] 1. Obtain the photorepair enzyme gene phr of WT Escherichia coli
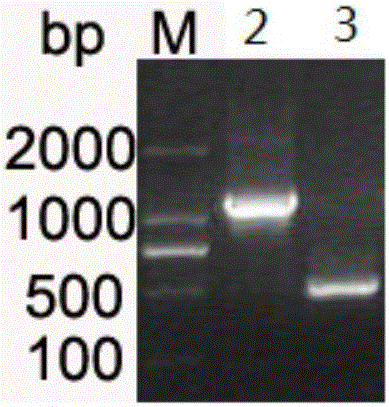
[0029] Primers were designed through the known Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) photorepair enzyme (cyclobutanepyrimidinedimerphotolyase, CPDase, EC4.1.99.3) (WT) gene, using E.coli genomic DNA as a template, the target fragment was amplified by PCR (such as figure 1 ). The phr amplification primers and PCR conditions were as follows:
[0030] phrF(NdeI): 5′-CTCCATATGACTACCCATCTGGTCTG-3′
[0031] phrR(XhoI): 5'-GTGCTCGAGTTTCCCCCTTCCGCGCC-3'
[0032] Pre-denature at 95°C for 5 minutes; cycle 30 times at 94°C for 30s, 60°C for 30s, and 72°C for 2 minutes; fully extend at 72°C for 10 minutes.
[0033] 2. Construction of recombinant vector pET22b-phr
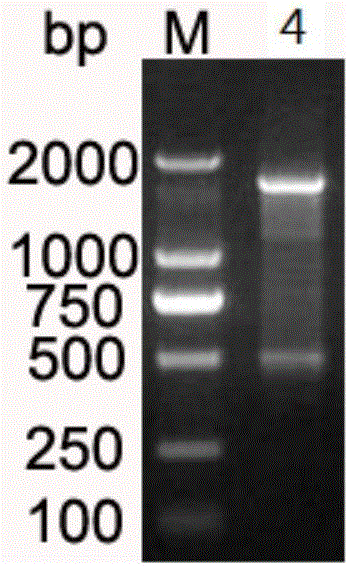
[0034] The amplified gene fragment and plasmid pET22b were digested with NdeI and XhoI, ligated at 16°C for 20h, and transformed into E.coliDH5α. Positive transformants were screened out to obtain recombinant plasmid pET22b-phr. After double-enzyme di...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: A377N activity experiment.
[0045] Escherichia coli DNA photorepair enzyme contains two coenzymes, which are methenyltetrahydrofolate (MTHF) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). MTHF can enhance the activity of photorepair enzymes. While FAD enables the enzyme to have photorepair activity, there are three forms of FAD, oxidized state, free radical state and reduced state. So E.coliCPDase type can be divided into oxidation type, free radical type and reduction type. Among the three types of E.coliCPDase, only the reduced E.coliCPDase has photorepair activity, and the specific absorption wavelength is about 360nm visible light; while the oxidized and free radical types of E.coliCPDase have no photorepair enzyme activity. The oxidized E.coliCPDase specifically absorbs visible light with a wavelength of about 450nm, and does not absorb visible light with a wavelength above 550nm. The free radical type E.coliCPDase specifically absorbs visible light with a w...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Antioxidative ability of A377N.
[0050] In the air, the oxidation process of Escherichia coli DNA photorepair enzyme changed from free radical E.coliCPDase to oxidized E.coliCPDase, that is, the free radical E.coliCPDase decreased continuously, while the oxidized E.coliCPDase increased continuously. The oxidized E.coliCPDase specifically absorbs visible light with a wavelength of about 450nm, and does not absorb visible light with a wavelength above 550nm. The free radical type E.coliCPDase specifically absorbs visible light with a wavelength of about 580nm. Therefore, the photorepair enzyme oxidation process includes two characteristics, one is that the absorbance of visible light with a wavelength of about 580nm gradually decreases until it becomes stable; the other is that the absorbance of visible light with a wavelength of about 450nm gradually increases until it becomes stable. Store the purified DNA photorepair enzyme at 4°C. At regular intervals, d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com