Patents
Literature
6104 results about "Maceral" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A maceral is a component, organic in origin, of coal or oil shale. The term 'maceral' in reference to coal is analogous to the use of the term 'mineral' in reference to igneous or metamorphic rocks. Examples of macerals are inertinite, vitrinite, and liptinite.
Vegetable oil hydroconversion process
InactiveUS20060186020A1Improved cetane indexAvoid excessive densityMolecular sieve catalystsBiofuelsVegetable oilHydrogen
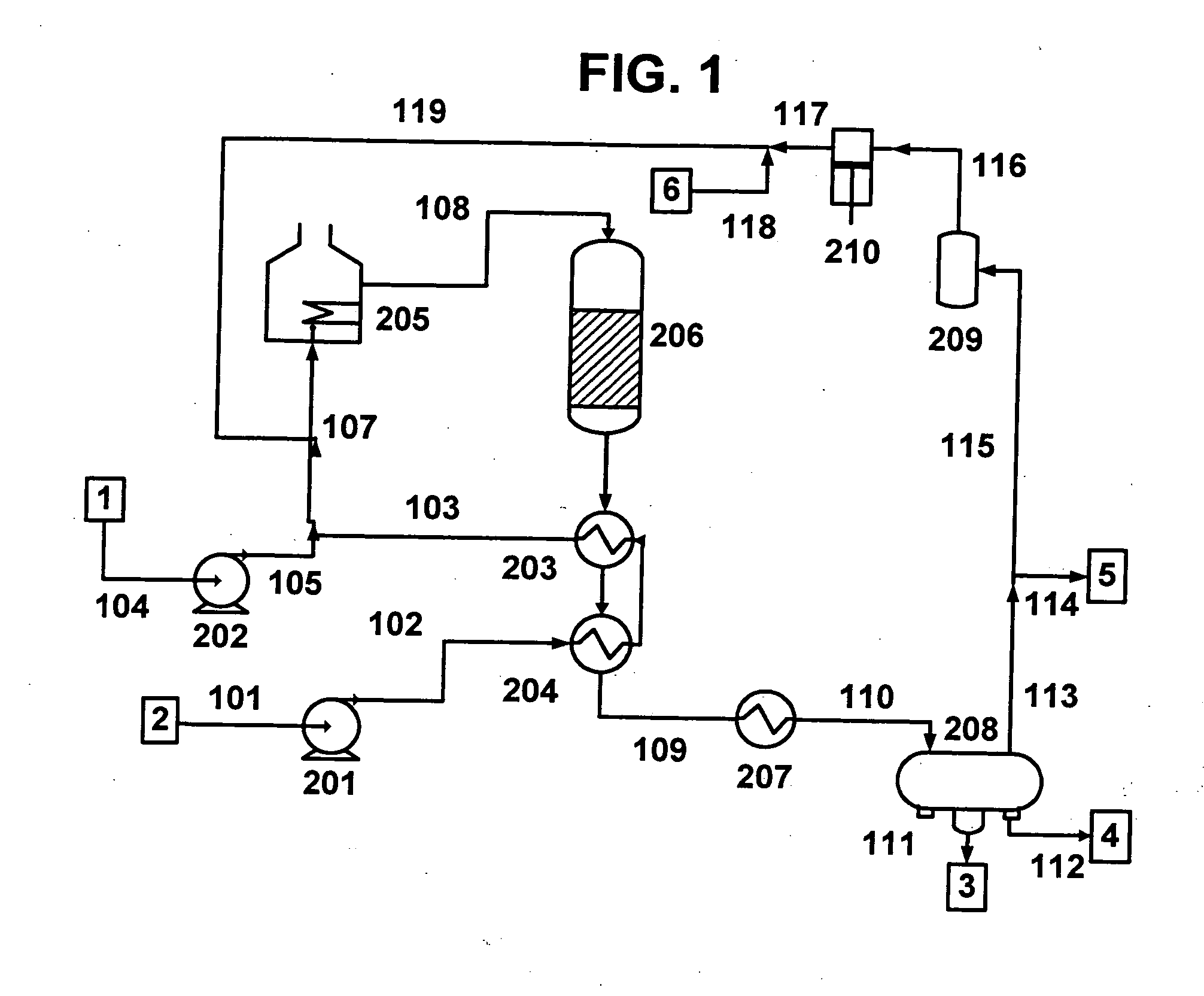
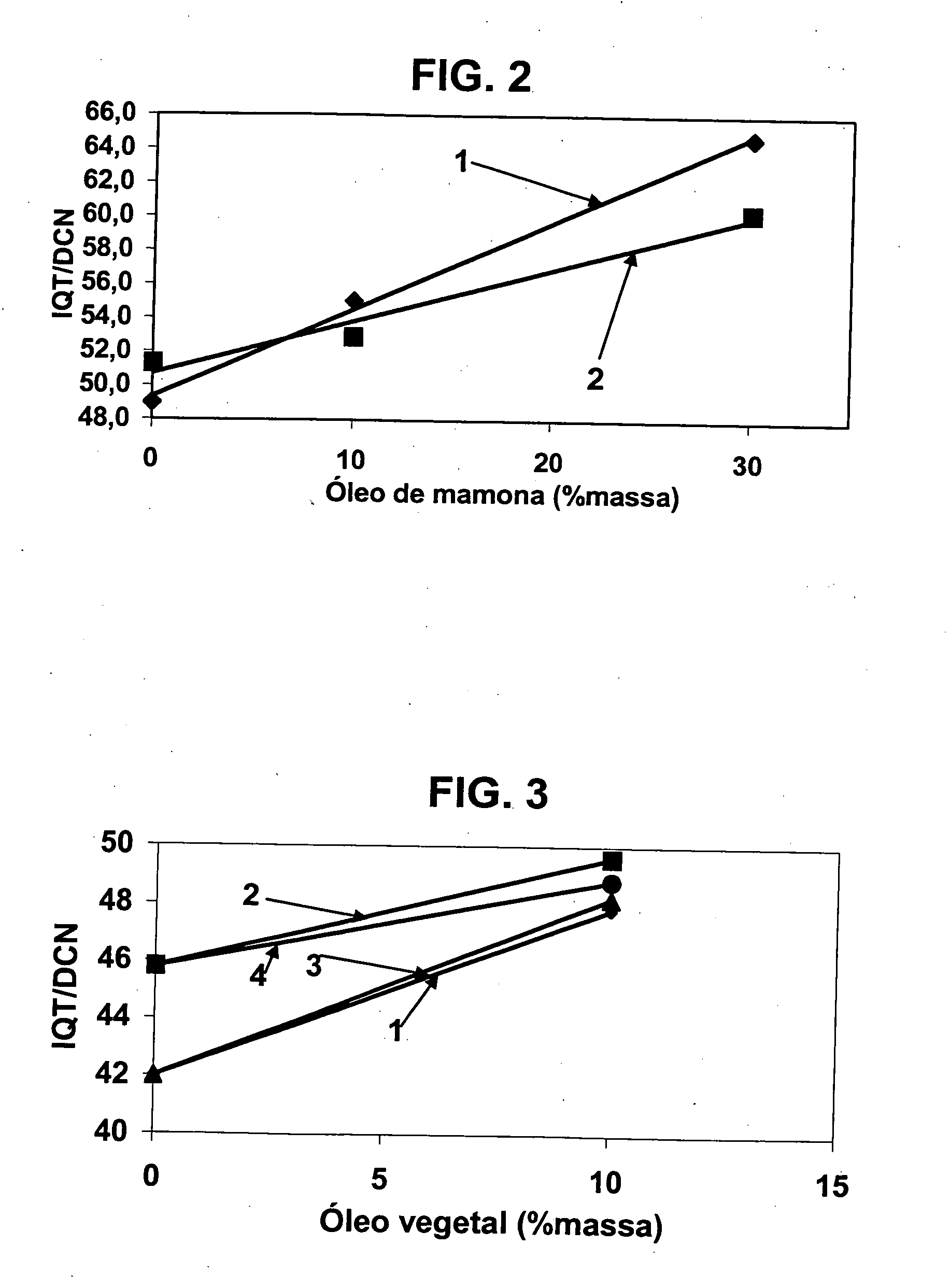
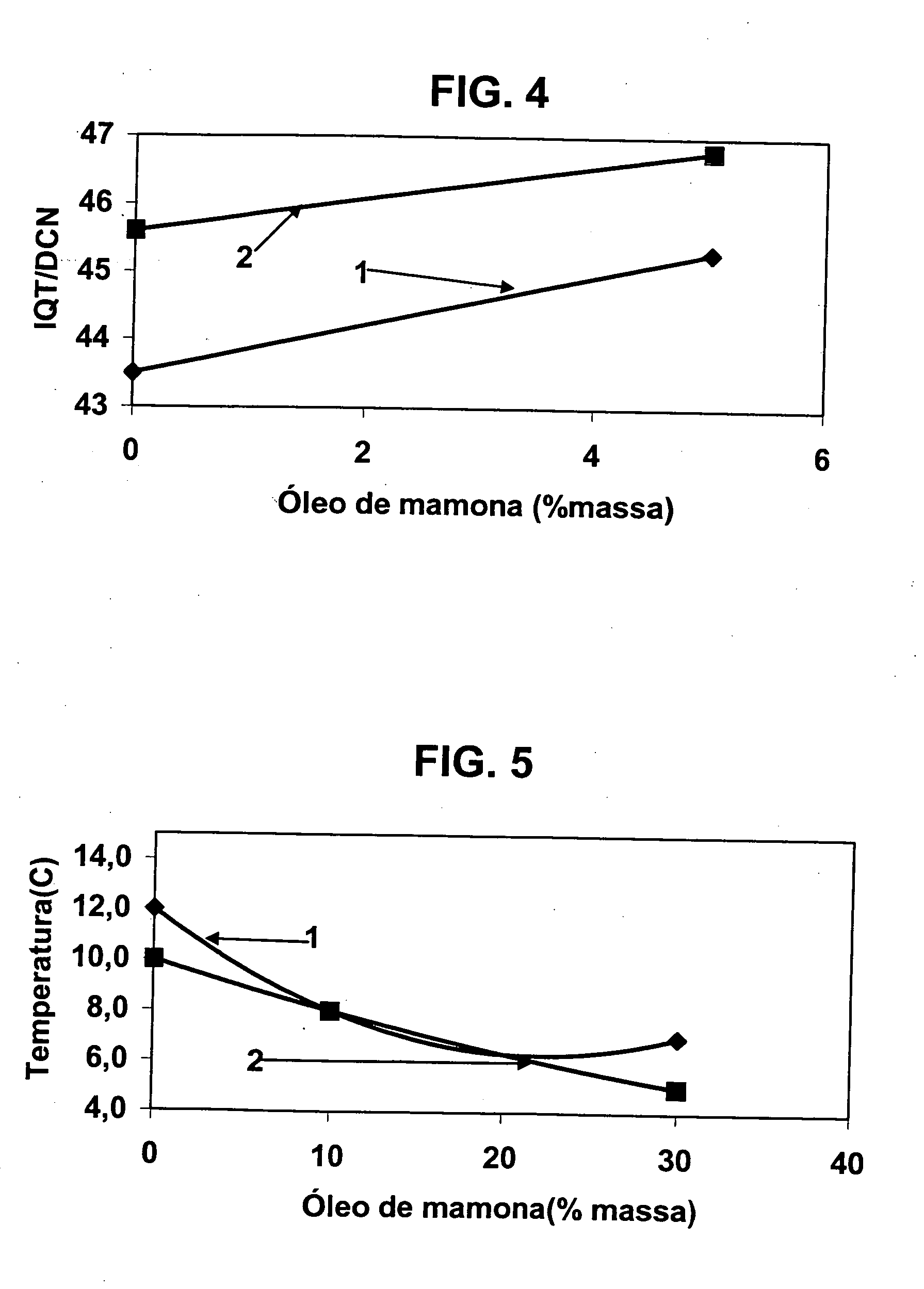
A vegetable oil hydroconversion process is described for hydroconverting a mixture between 1 to 75% in mass of oil or natural fat (1) and the rest mineral oil (2), hydroconverted in a reactor (205) under conditions of pressure, temperature, hydrogen (flow 119) and sulfide catalyst of Groups VIII and VIB, obtaining, after sour water separation (flow 111) and rectification (flow 112), a specified diesel product (4). The product (4) has an ITQ / DCN (cetane number) higher than a product obtained from a pure mineral based oil would have, lower density than from a base oil and a plugging point depending on the mineral oil flow, as well as greater oxidation stability than the base oil.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Mild catalytic steam gasification process
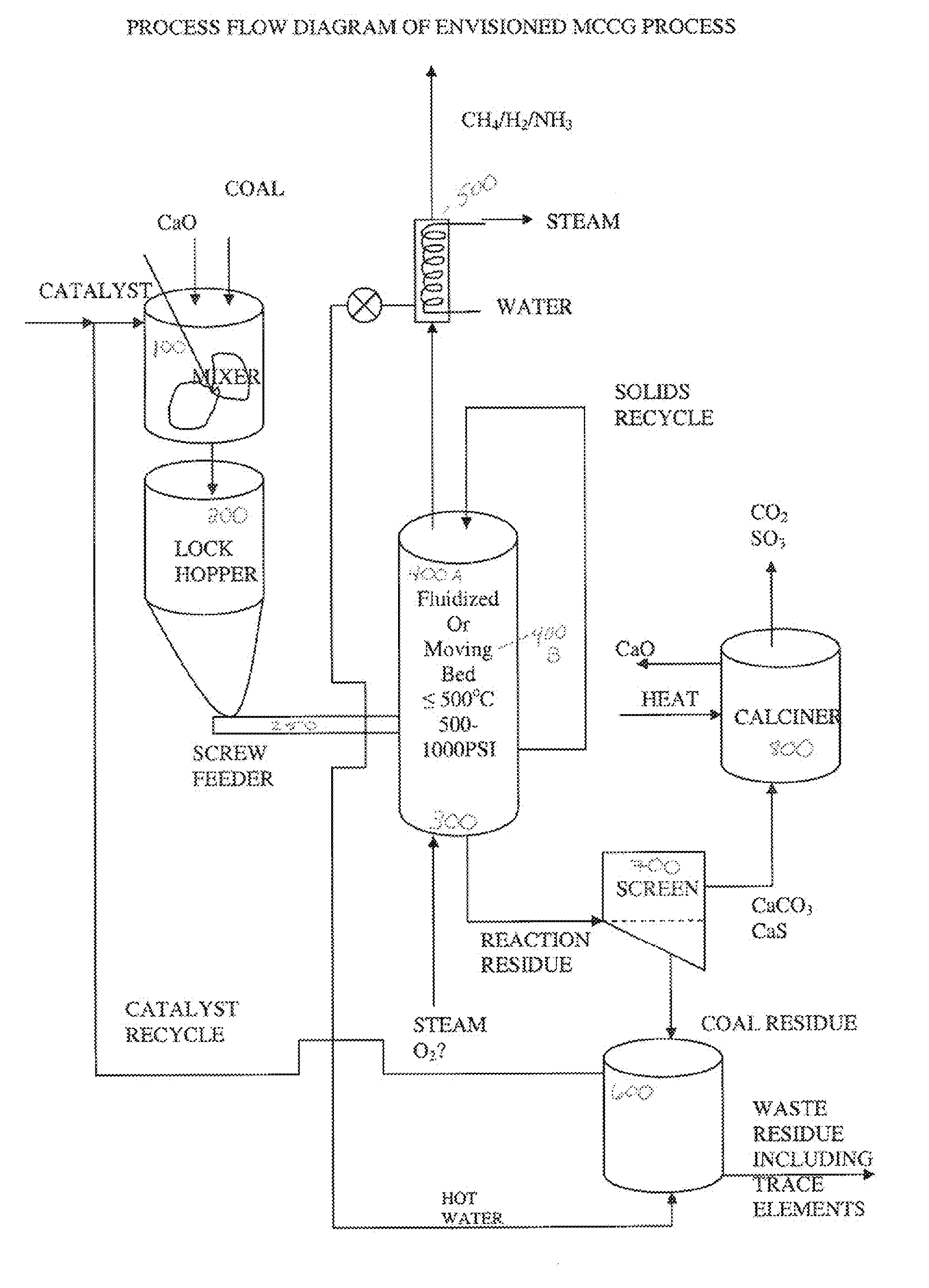
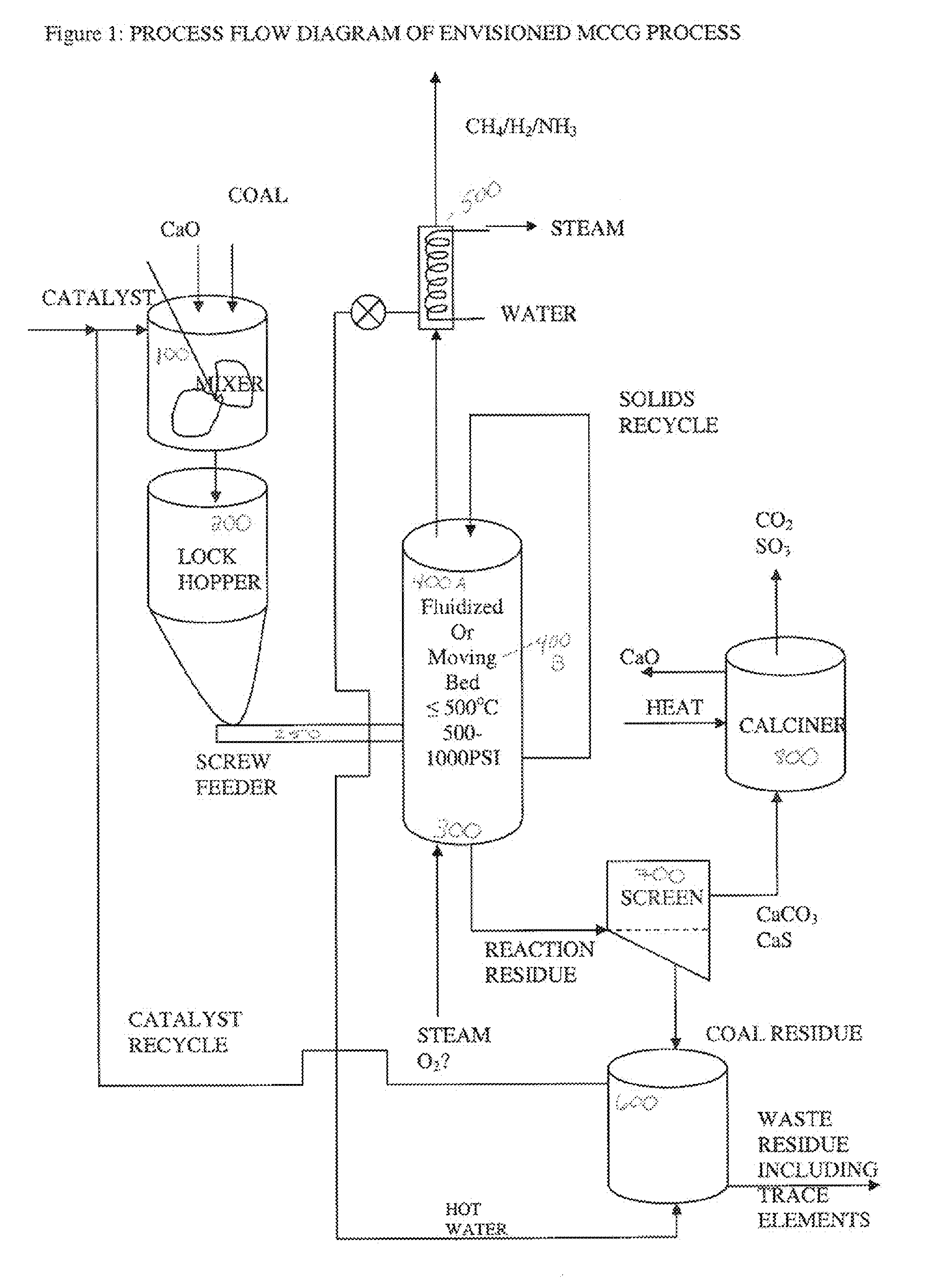
InactiveUS20070000177A1Great carbon conversionLittle additional treatmentGasification processes detailsCombined combustion mitigationMaceralAlkali metal
The present invention provides an improved alkali metal catalyzed steam gasification process that utilizes a CO2 trap material and / or a mineral binder material within the gasifier. The process optimally achieves over 90% carbon conversion with over 80% yield of methane. The raw gas product can be used directly as fuel. The catalyst can be recovered from the solid purge and recycled to the gasifier and / or the CO2 trap can be regenerated and recycled to the gasifier.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
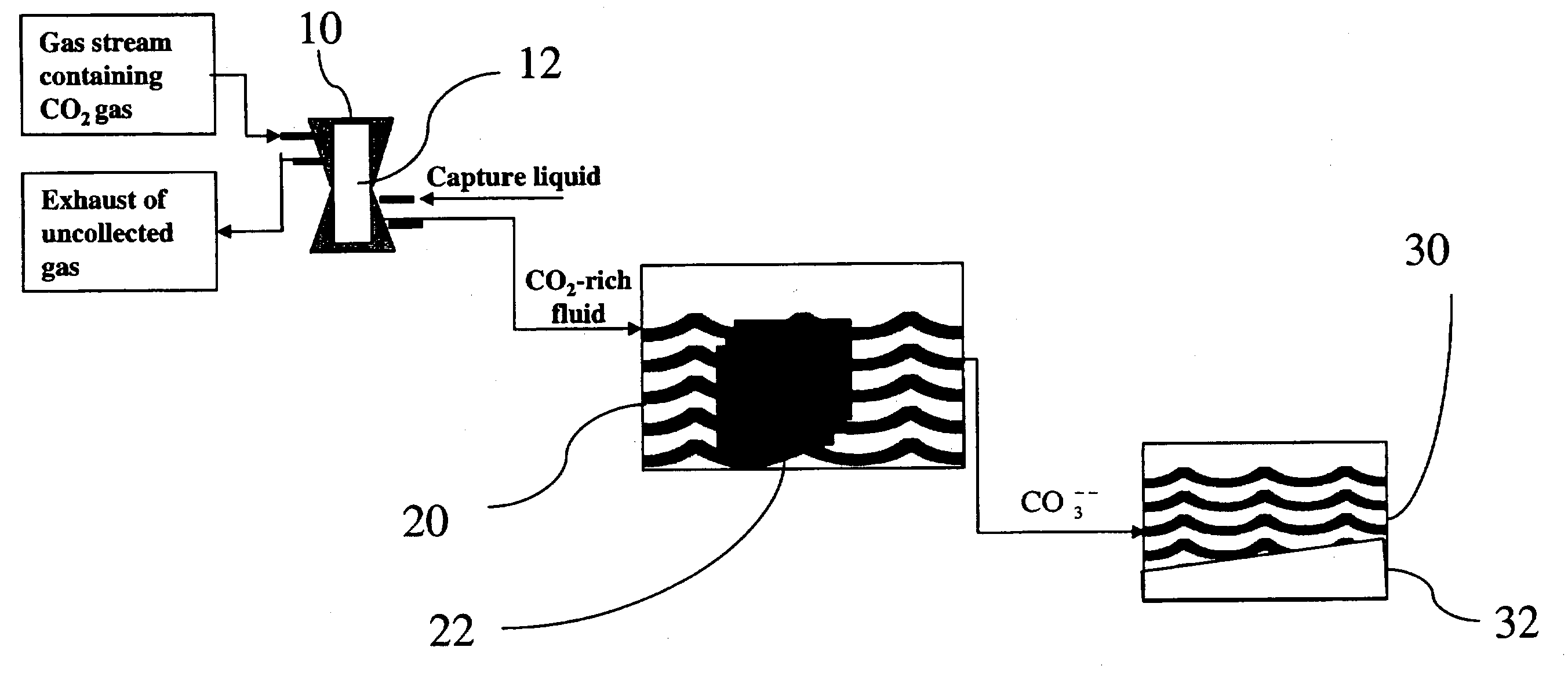
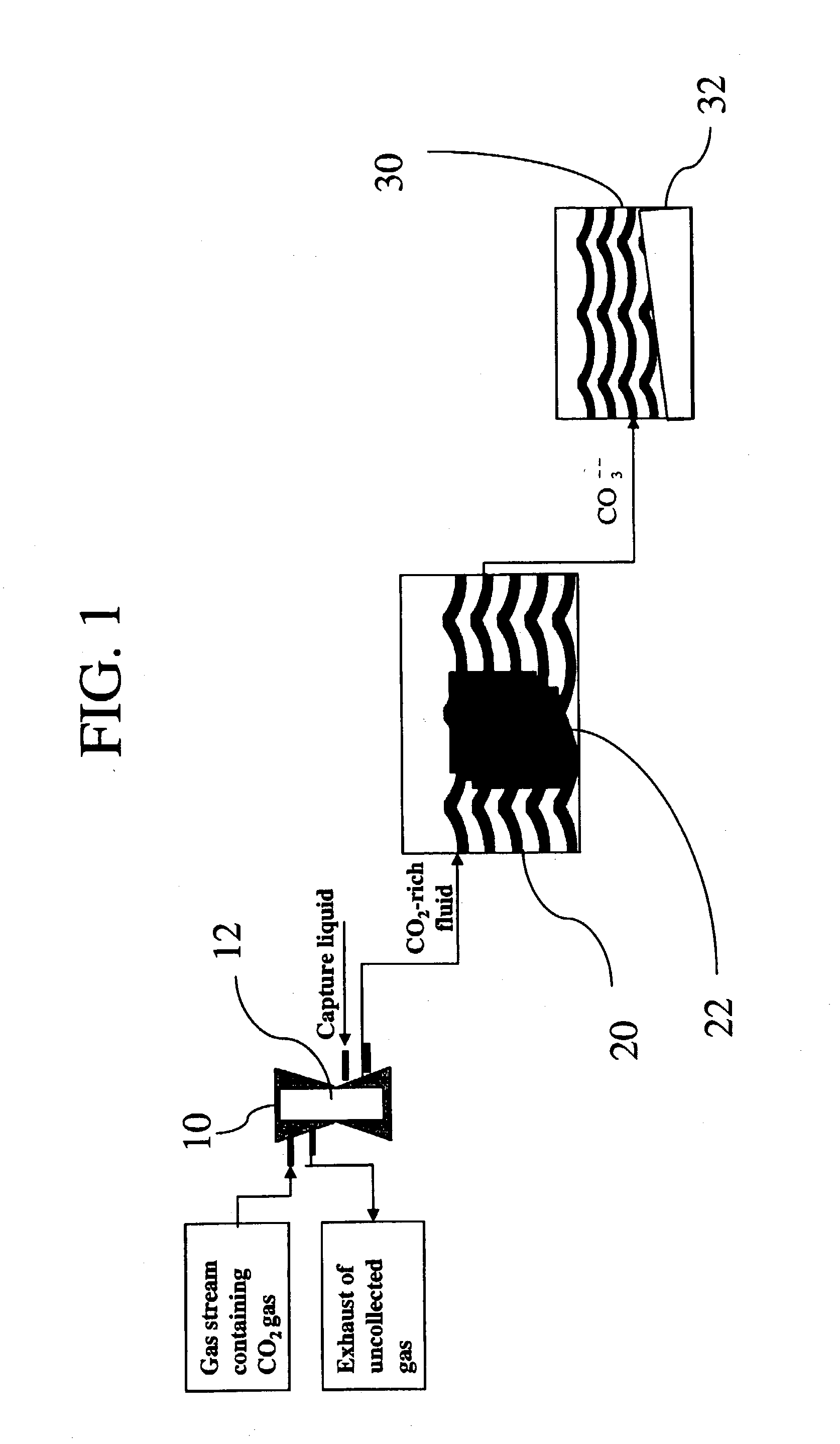
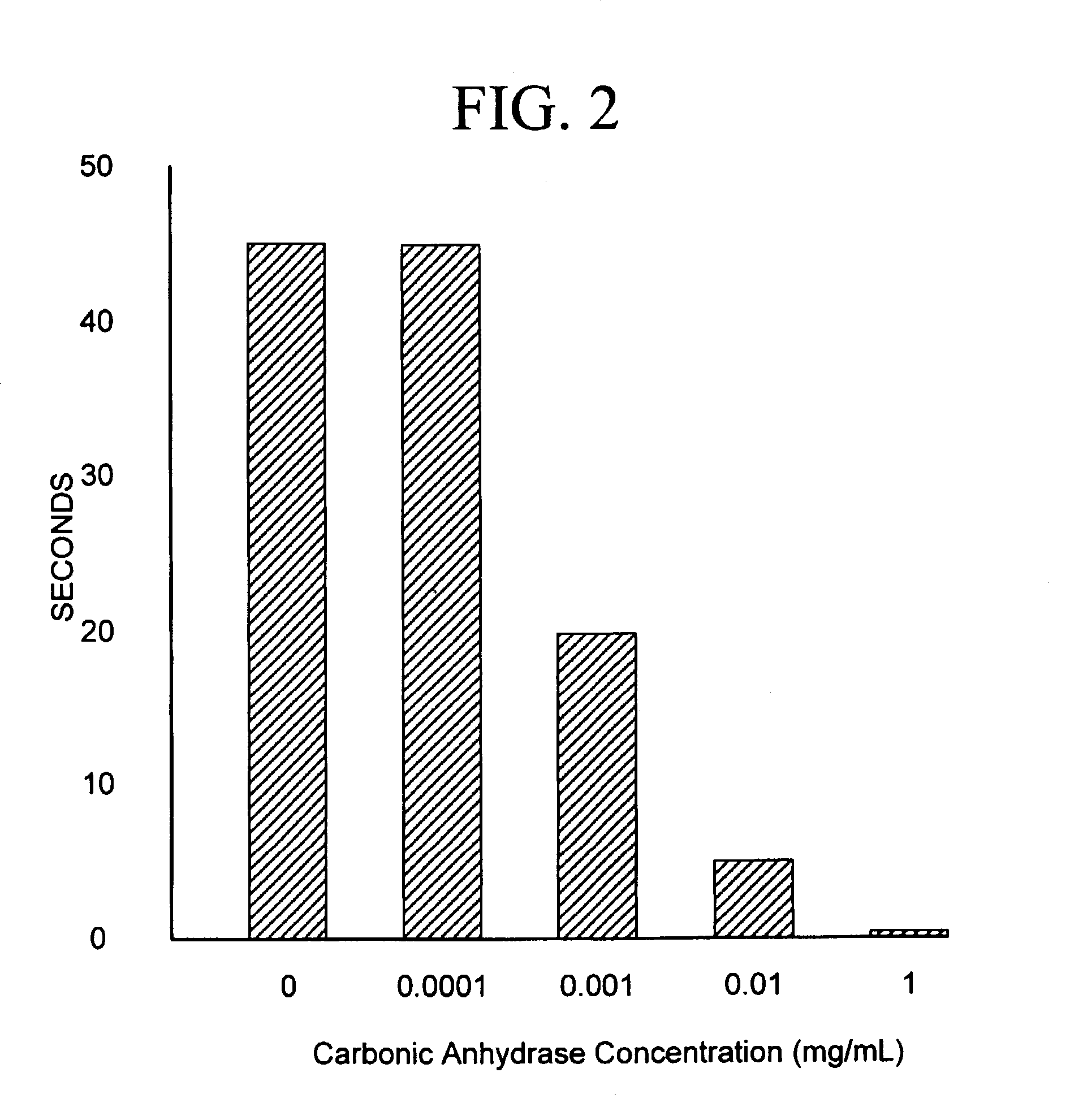
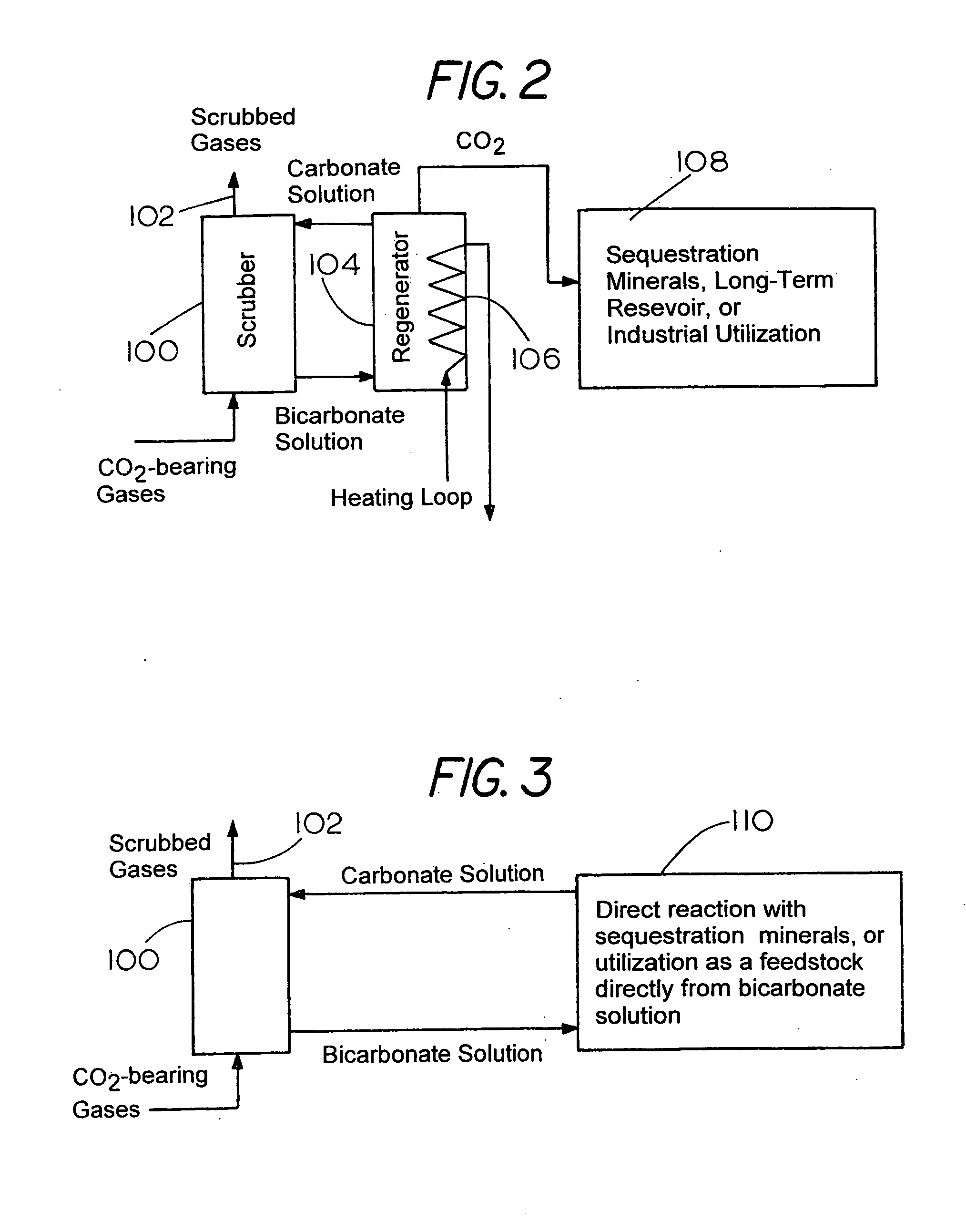
Sequestration of carbon dioxide
ActiveUS7132090B2Safe storageLarge specific surface areaCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesProductsProduct gasMineral ions
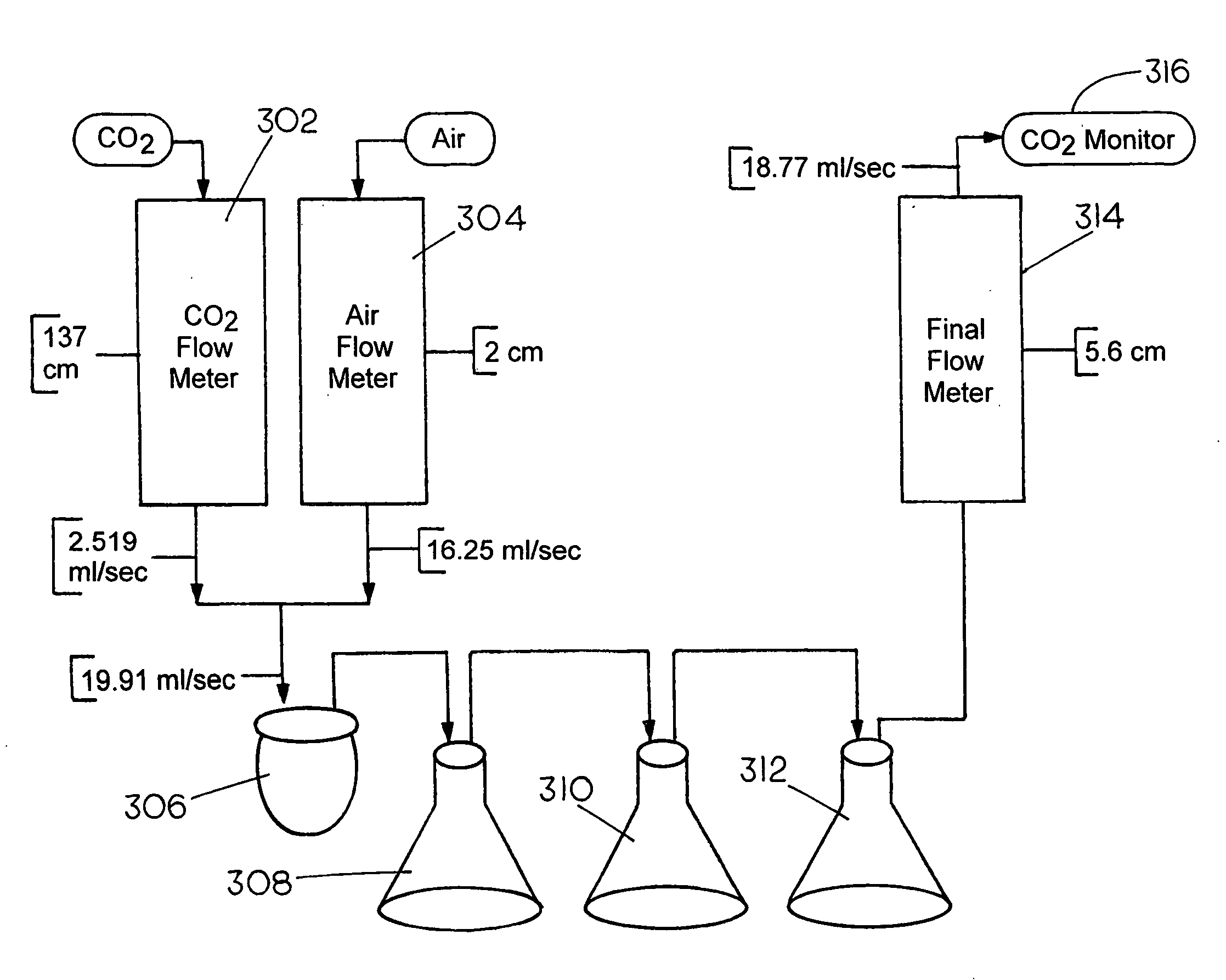
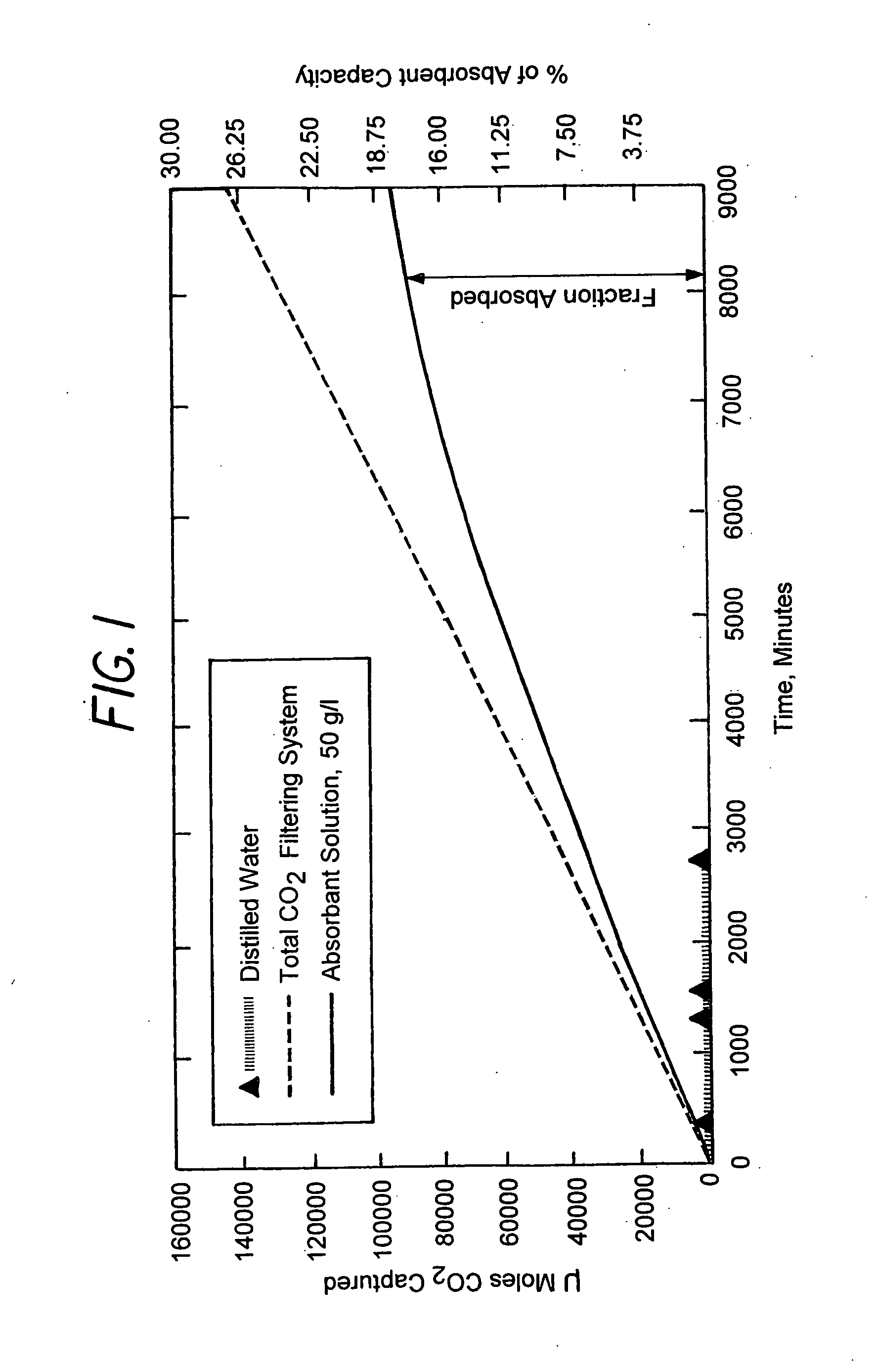
A process for selectively removing carbon dioxide from a gaseous stream by converting the carbon dioxide to a solid, stable form is provided. In a sequestration process, carbon dioxide enriched air is passed through a gas diffusion membrane to transfer the carbon dioxide to a fluid medium. The carbon dioxide rich fluid is then passed through a matrix containing a catalyst specific for carbon dioxide, which accelerates the conversion of the carbon dioxide to carbonic acid. In the final step, a mineral ion is added to the reaction so that a precipitate of carbonate salt is formed. This solid mineral precipitate can be safely stored for extended periods of time, such as by burying the precipitate in the ground or depositing the precipitate into storage sites either on land or into a body of water. An apparatus for removing carbon dioxide from a gaseous stream is also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
ActiveUS7335897B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLycopeneElectrospray ionization
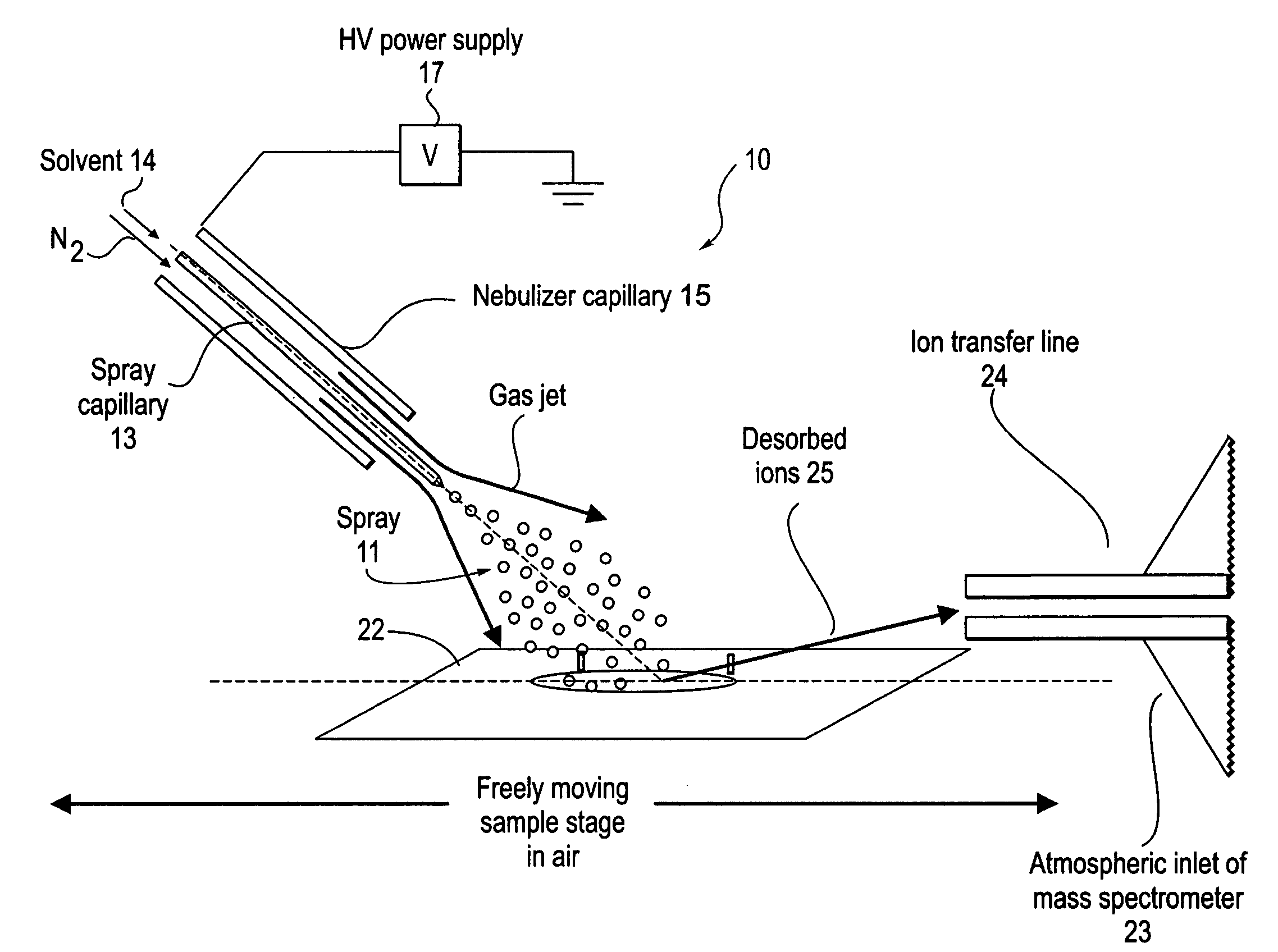
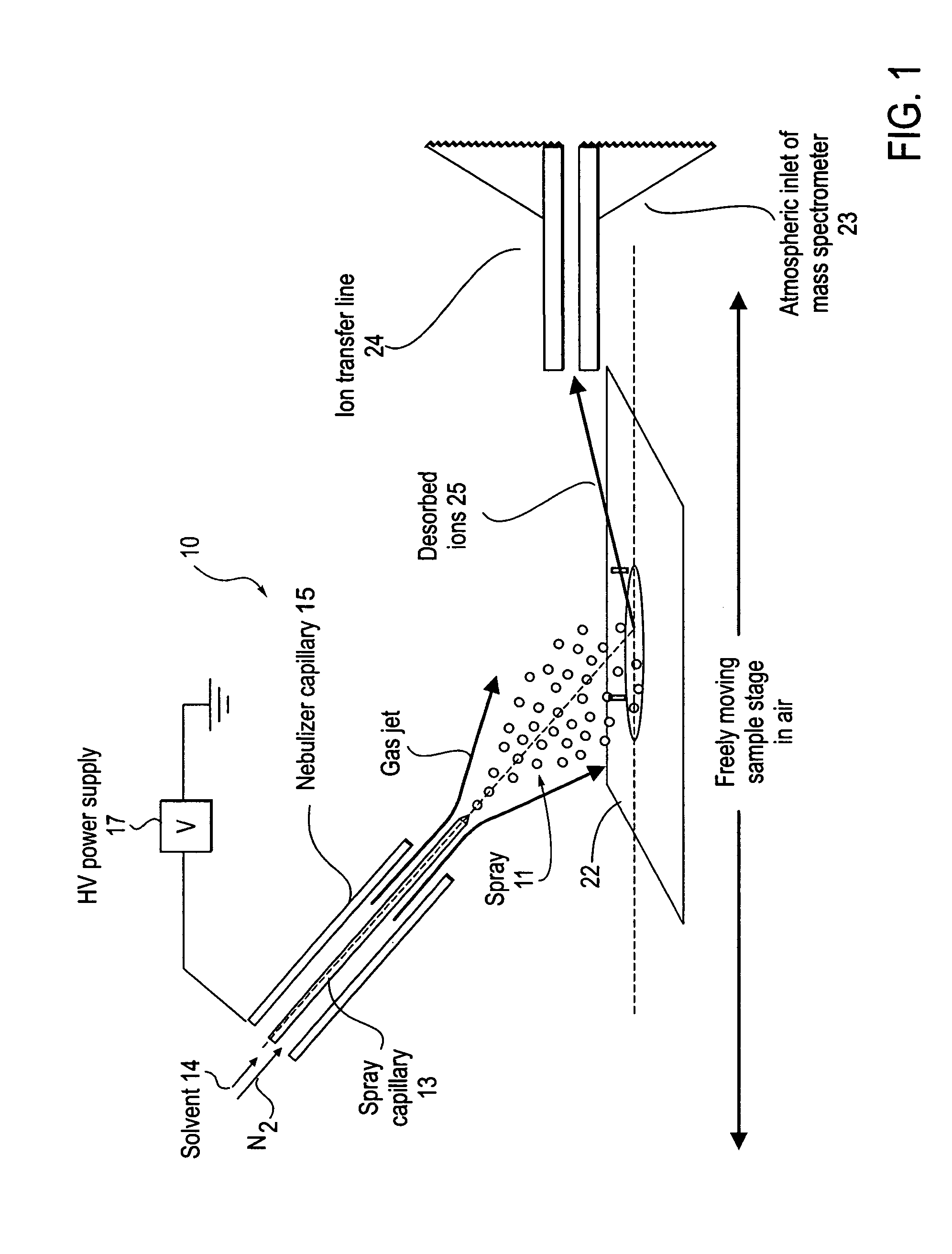
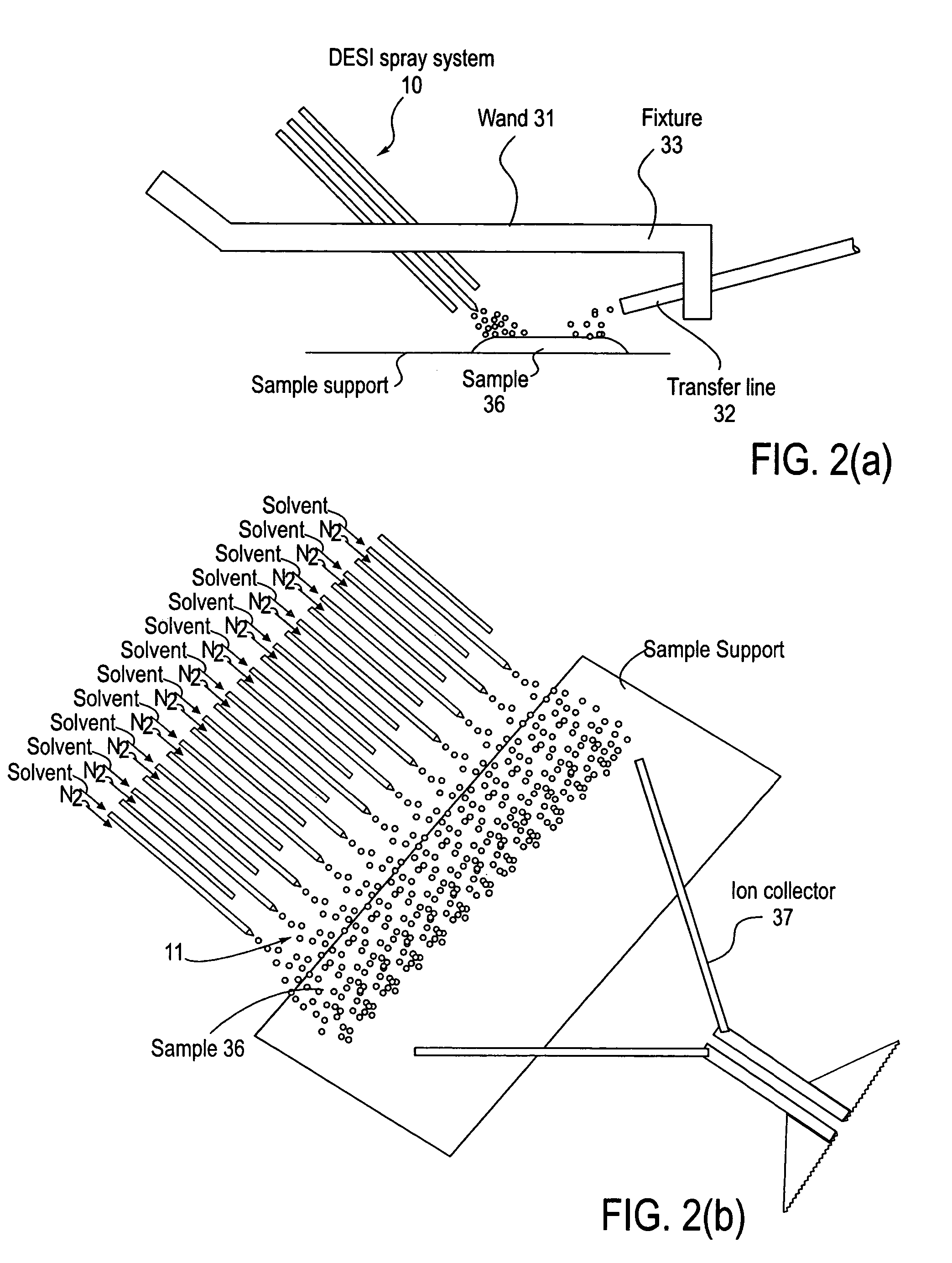
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs, through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Carbon dioxide sequestration using alkaline earth metal-bearing minerals
ActiveUS20050180910A1High dissolution rateEfficient removalCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesProductsParticulatesAlkaline earth metal
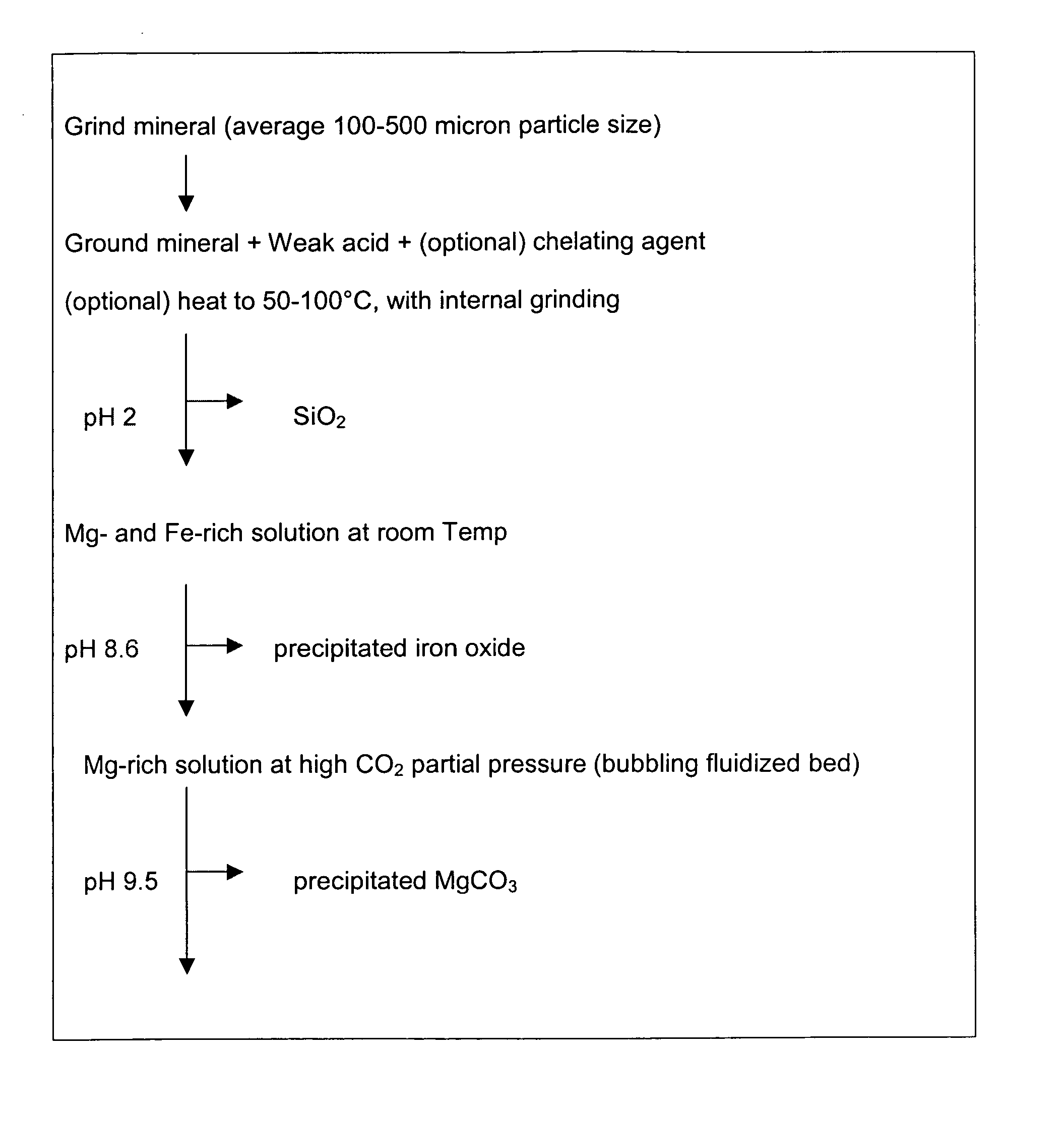
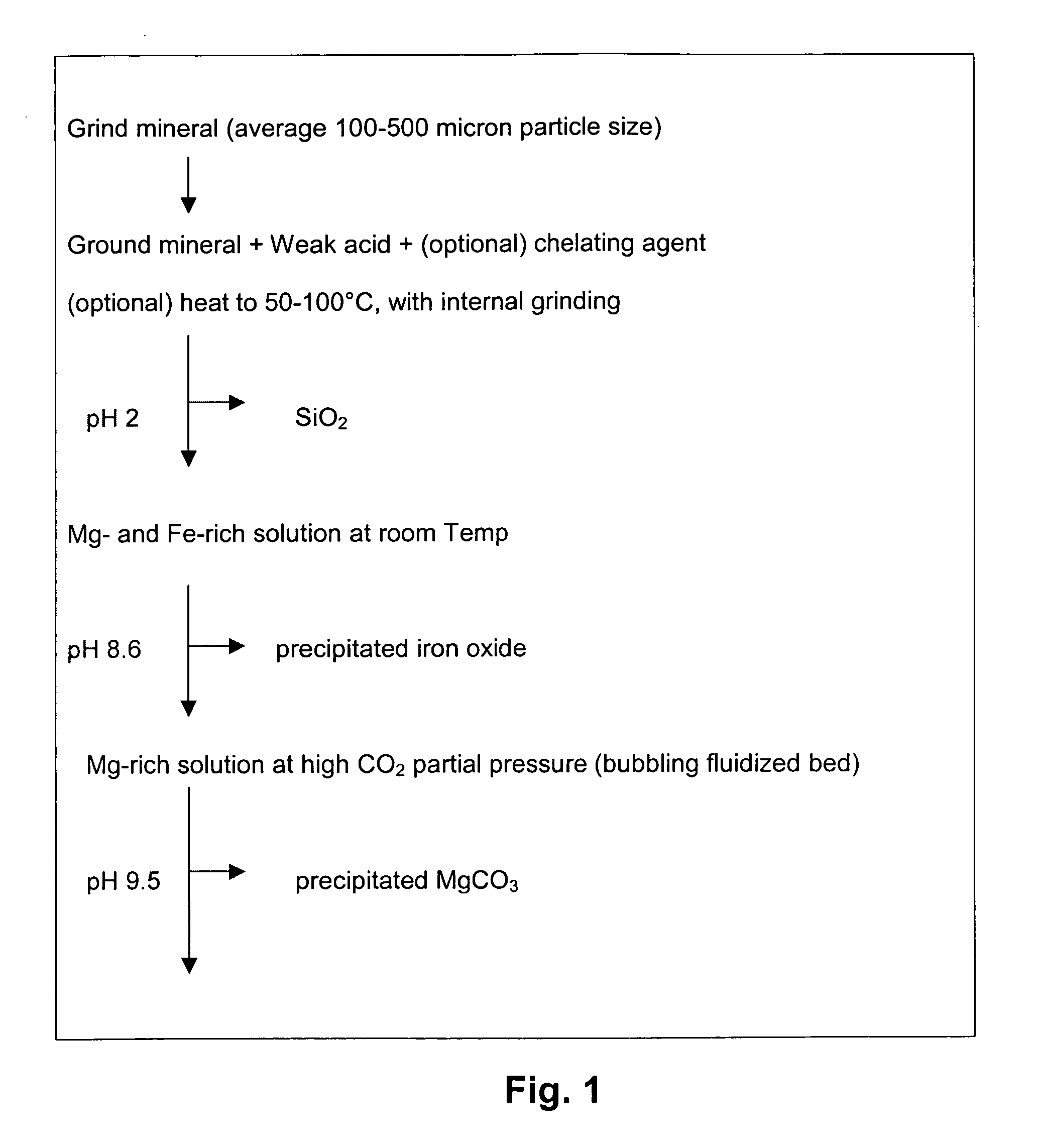
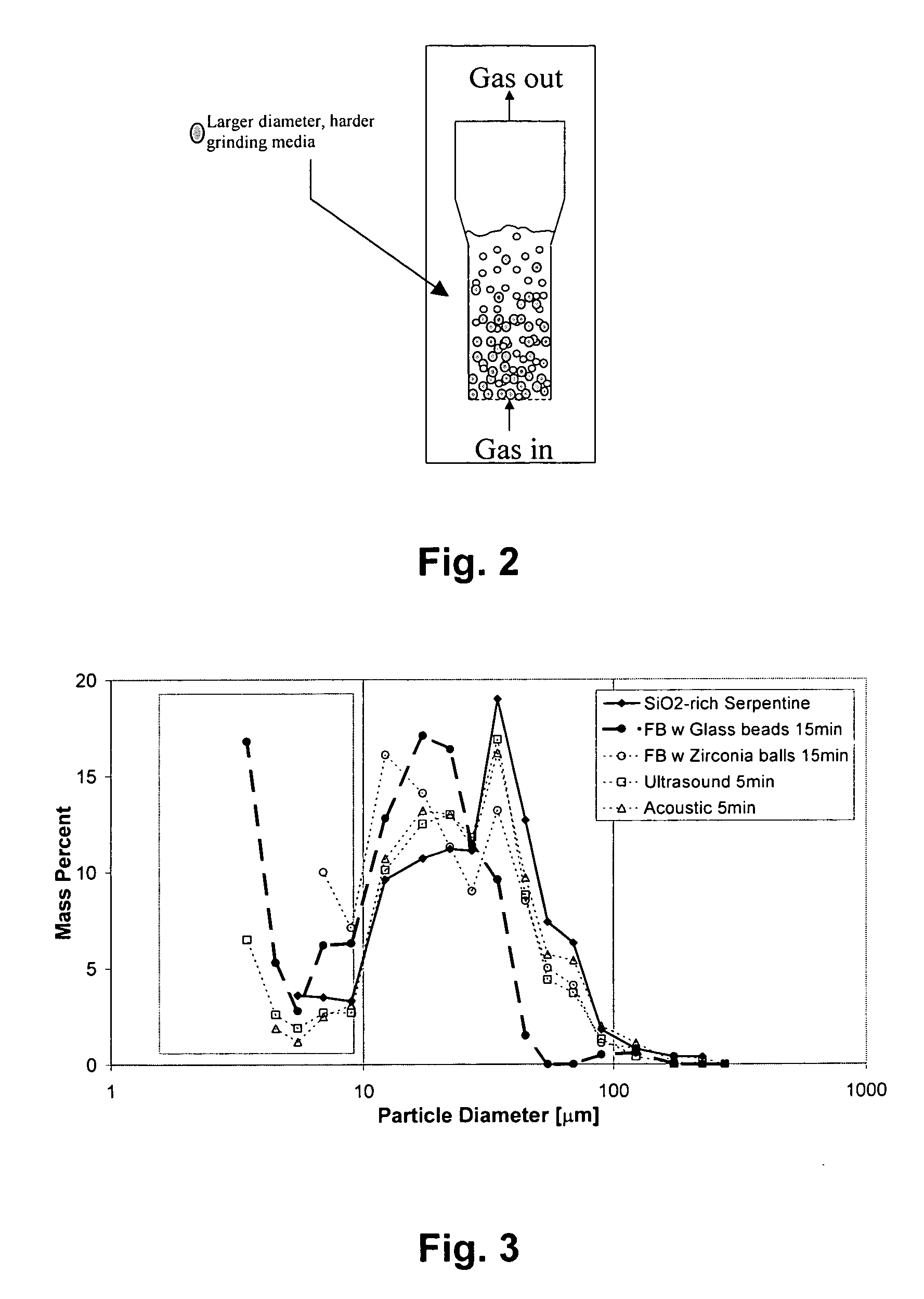
A method for mineral sequestration of pollutant gases resulting from the combustion of carbon-based fuels such as carbon and sulfur dioxides is provided and includes, providing a particulate magnesium-containing mineral and exposing the magnesium-containing mineral to a weak acid to dissolve magnesium from the mineral and form a magnesium-containing solution. The surface of the particulate magnesium-containing mineral is physically activated to expose and dissolve additional magnesium into the solution. Pollutant gases such as carbon dioxide are mixed with the magnesium-containing solution. When the pH of the magnesium-containing solution is increased, solid magnesium carbonate is formed.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide in Flue Gases
ActiveUS20090202410A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentAlkaline earth metalOxidation state
There is provided a process for the capture and sequestration of carbon dioxide that would otherwise enter the atmosphere and contribute to global warming and other problems. CO2 capture is accomplished by reacting carbon dioxide in flue gas with an alkali metal carbonate, or a metal oxide, particularly containing an alkaline earth metal or iron, to form a carbonate salt. A preferred carbonate for CO2 capture is a dilute aqueous solution of additive-free (Na2CO3). Other carbonates include (K2CO3) or other metal ion that can produce both a carbonate and a bicarbonate salt. Examples of suitable metal oxides include several alkaline earths including CaO and MgO. The captured CO2 is preferably sequestered using any available mineral or industrial waste that contains calcium magnesium or iron in non-carbonate forms, or iron in the Fe+2 oxidation state.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Ion mineralization stabilizer for treating soil with heavy metal pollution and application method thereof
InactiveCN102766465AWide range of raw materialsEasy to obtainContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSulfurPhosphor
The invention discloses ion mineralization stabilizer for treating soil with heavy metal pollution and an application method thereof. The ion mineralization stabilizer comprises, by weight percent, 5-30% of sulfur-based compound, 10-50% of phosphor-based compound, 10-50% of calcium-based compound, and 10-30% of silicon-based compound. The materials are respectively ground into powders with particle size not less than 200 meshes, and the powders are proportionally mixed well. The application method of the ion mineralization stabilizer for treating soil with heavy metal pollution includes: detecting arsenic content and leaching toxicity of the soil to be treated, placing the ion mineralization stabilizers in different proportions on the surface of the soil to be treated according to pollution level, well mixing to form mixed soil by ploughing and stirring, adding water to keep the water content of the mixed soil no less than 25%, covering the mixed soil with moisturizing material, curing for at least 5 days to keep heavy metals in the mixed soil to form stable minerals.
Owner:YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
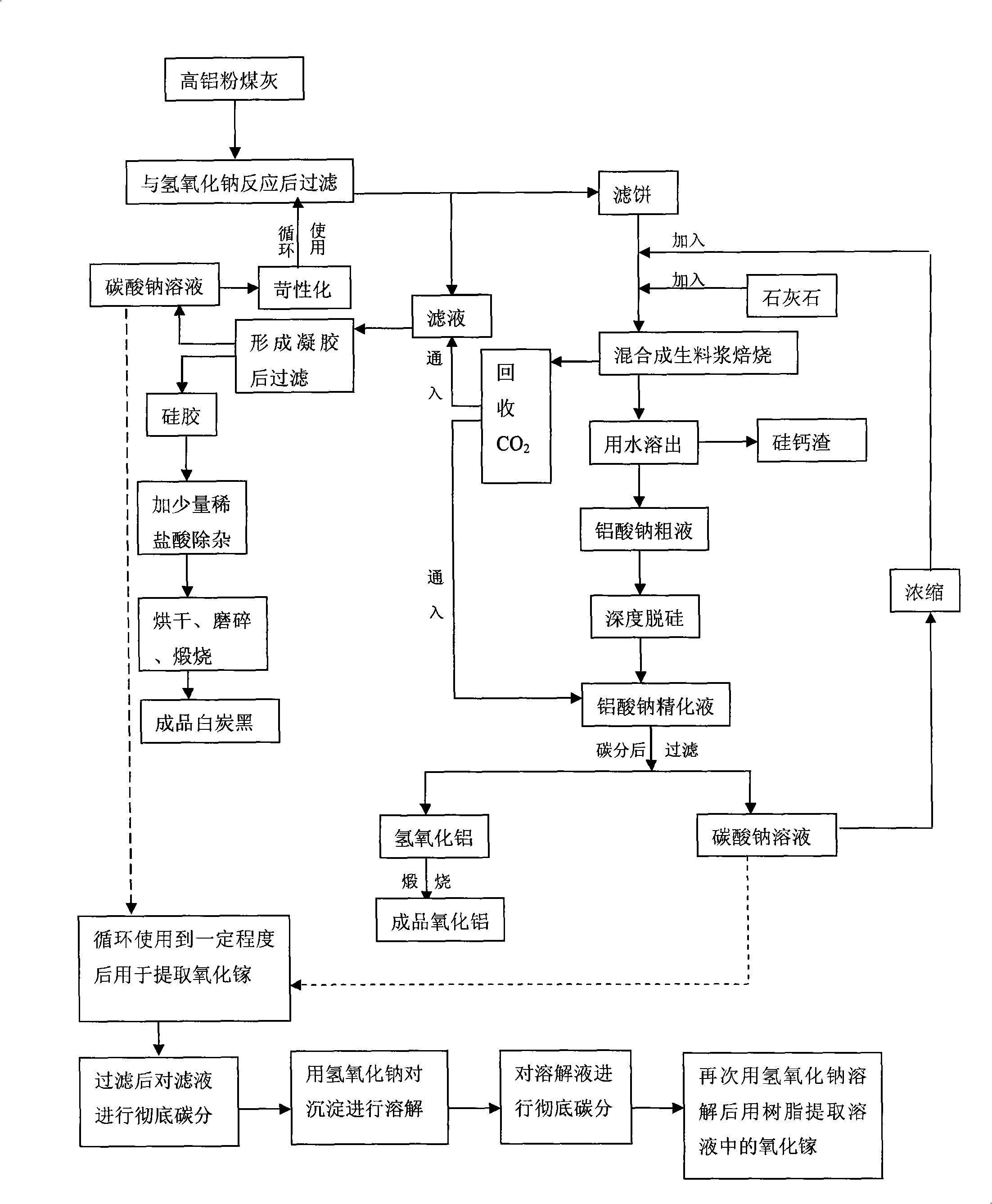
Process for abstracting earth silicon, oxide of alumina and gallium oxide from high-alumina flying ash
ActiveCN101284668AReduce the total massLow firing temperatureGallium/indium/thallium compoundsSilicon oxidesChemical industryFiltration
A method for extracting silicon dioxide, alumina and gallium oxide from high-alumina fly ash relates to the technology fields of environmental mineralogy and material, chemical industry and metallurgy. The method comprises the main steps as follows: causing the high-alumina fly ash to react with sodium hydroxide solution; filtering the solution; introducing CO2 to the filtrate for full gelation; cleaning, purifying, drying, grinding and calcining the silica gel after gel filtration to obtain finished white carbon black; adding limestone and a sodium carbonate solution into the filter mass after the reaction and filtration of the high-alumina fly ash and the sodium hydroxide solution; ball grinding the mixture into raw slurry; dissolving out the clinker obtained by baking the raw slurry; subjecting the filtrate to deep desiliconization to obtain sodium aluminate extraction liquid; filtrating the sodium aluminate extraction liquid after subjecting the sodium aluminate extraction liquid to carbon dioxide decomposition; baking the aluminum hydroxide after washing the filter mass to form the aluminum hydroxide product; and extracting the gallium oxide from the carbon dioxide decomposition mother solution and desiliconized solution. The method has the advantages of low material price, simple operating procedures, low investment, low production cost, low energy consumption and less slag.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Biological fertilizer based on yeasts
The present invention provides biological fertilizer compositions that comprise yeast cells that have an enhanced ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, decompose phosphorus minerals and compounds, decompose potassium minerals and compounds, decompose complex carbon compounds, over produce growth factors, and over produce ATP. The biological fertilizer composition of the invention can replace mineral fertilizers in supplying nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to crop plants. Methods of manufacturing the biological fertilizer compositions and methods of uses are also encompassed.
Owner:ULTRA BIOTECH
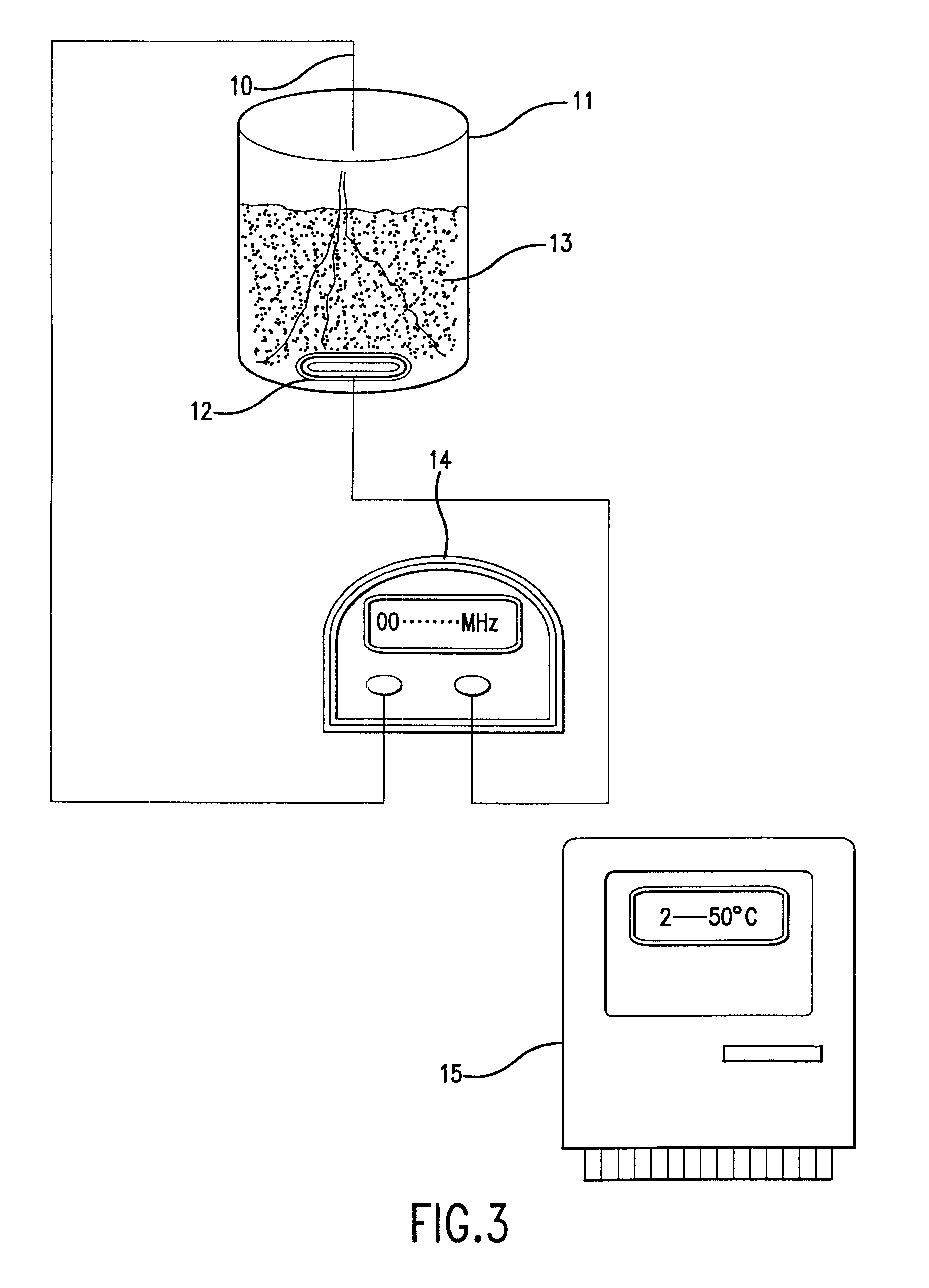
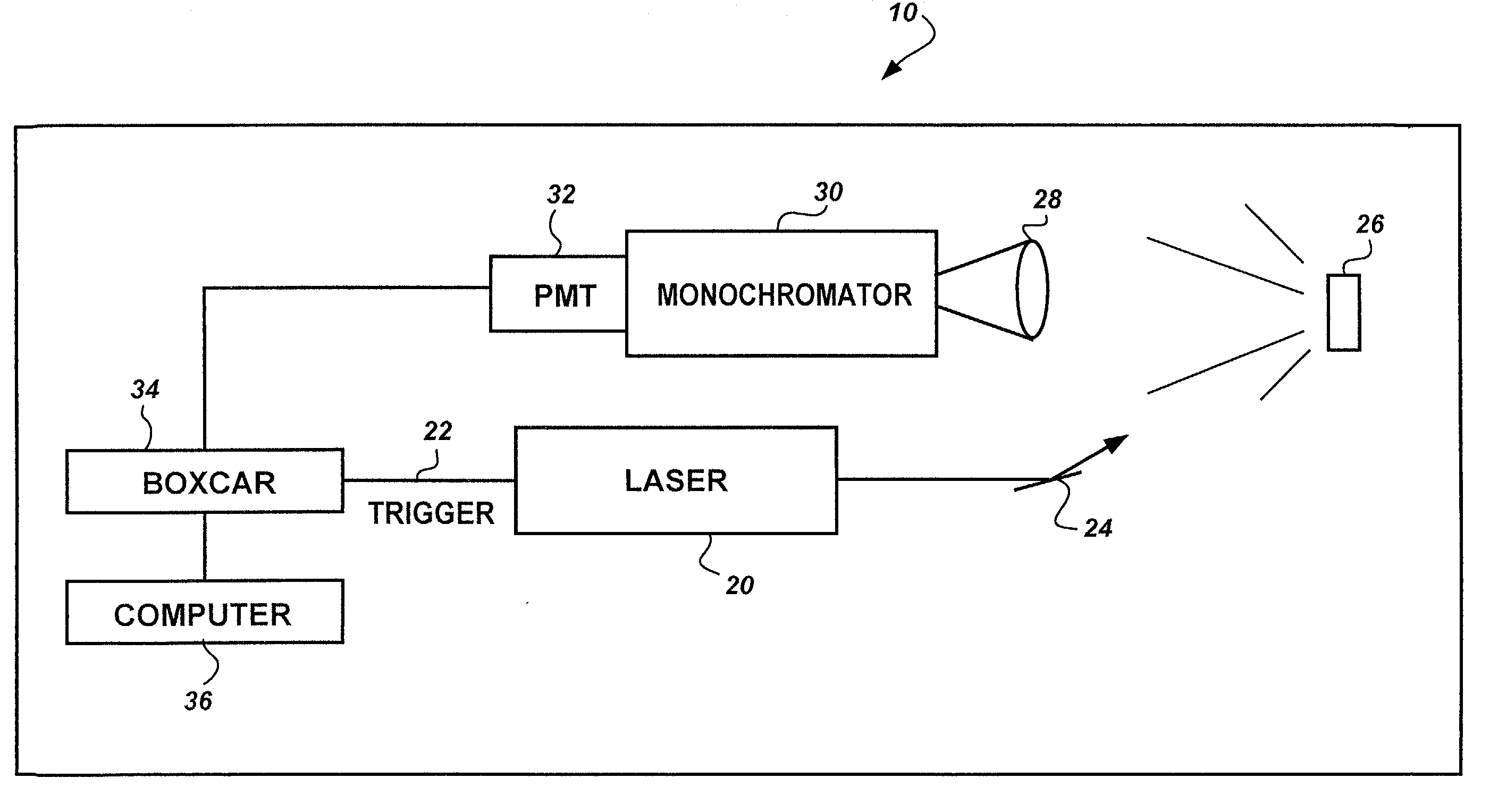
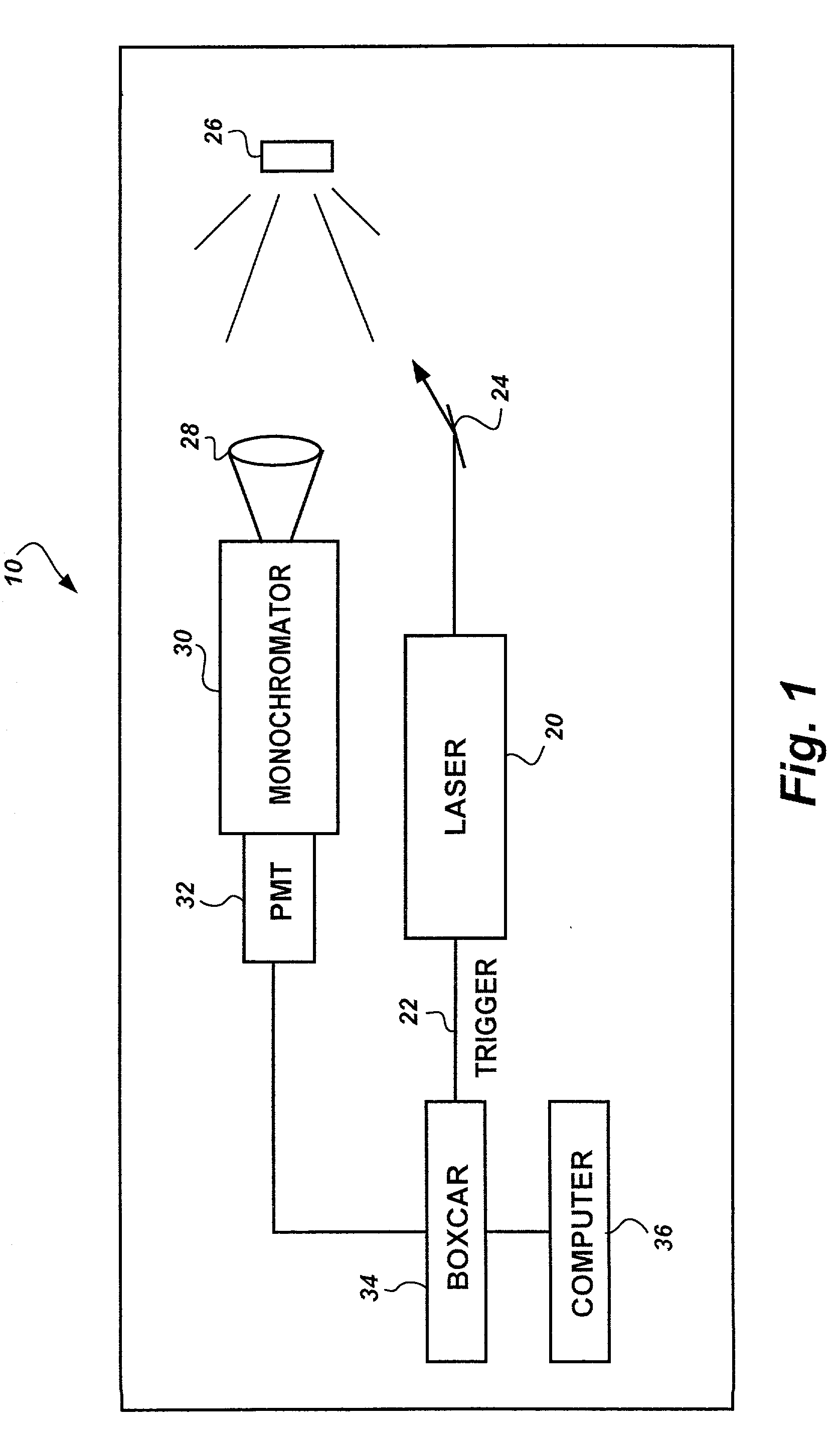
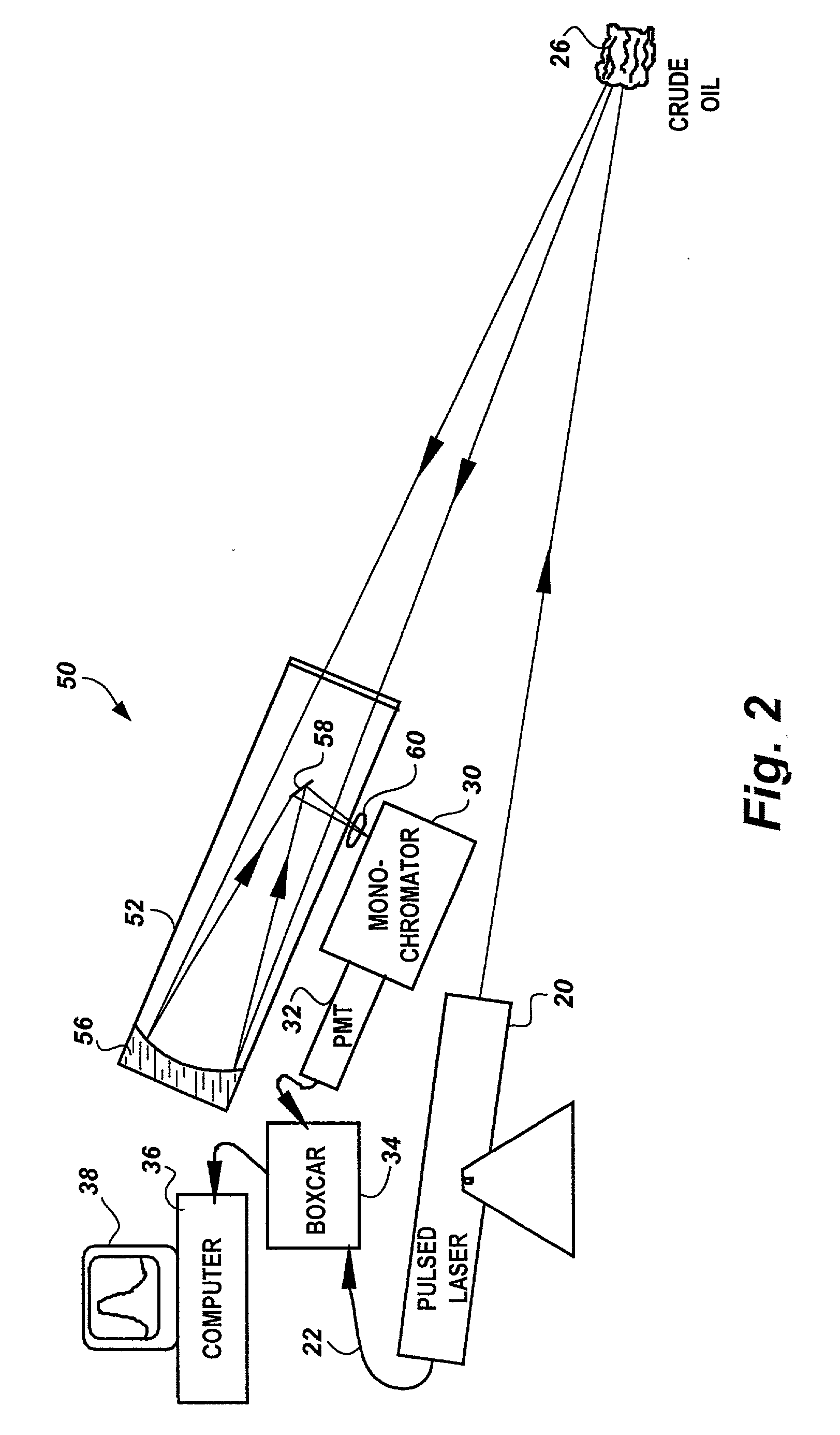
Method for characterization of petroleum oils using normalized time-resolved fluorescence spectra
A method based on time-resolved, laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy for the characterization and fingerprinting of petroleum oils and other complex mixtures. The method depends on exciting the wavelength-resolved fluorescence spectra of samples using ultraviolet pulsed laser radiation, measuring them at specific time gates within the temporal response of the excitation laser pulse, and comparing them in terms of their shapes alone without taking into account their relative intensities. The method provides fingerprints of crude oils without resorting to any kind of approximation, for distinguishing between closely similar crude oils of the same grade, and is useful in remote and non-remote setups, along with applications in fingerprinting blended and non-blended crude oils using different ultraviolet excitation wavelengths. Applications include estimating °API gravity of crude oils and monitoring degradation of mineral oils.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Process for extracting bitumen
Bitumen extraction done using a process comprising: (a) preparing a bitumen froth comprising particulate mineral solids and hydrocarbons dispersed in aqueous lamella in the form of an emulsion; (b) adding a sufficient amount of a paraffinic solvent to the froth to induce inversion of the emulsion and precipitate asphaltenes from the resultant hydrocarbon phase; (c) mixing the froth and the solvent for a sufficient time to dissolve the solvent into the hydrocarbon phase to precipitate asphaltenes; and (d) subjecting the mixture to gravity or centrifugal separation for a sufficient period to separate substantially all of the water and solids and a substantial portion of the asphaltenes from the bitumen; wherein a separation enhancing additive is present in the process. The separation enhancing additive is a polymeric surfactant that has multiple lipophilic and hydrophilic moieties, which can effect easier handling of asphaltene sludges and less foaming during solvent recovery.
Owner:MARATHON OIL SANDS +2
Solid-chemical compositions, geochemical binder system, and improved high-shear granulation process for both conventional and slow-release fertilizer and bioremediation nutrient compositions
InactiveUS20020178772A1Less-expensive to produceWiden meansSolid/semi-solid fertilisersMatrix fertilisersSolubilityAdditive ingredient
This invention discloses advanced means for the formulation and preparation of solid-chemical compositions which provide sources of water-soluble nutrients, electron acceptors and other agents for agriculture and waste-treatment, in particular, the bioremediation of contaminated environmental media. The disclosed formulations and means of production of the slow-release solid-chemical compositions of the present invention utilize a novel and economical "biphasic" chemical-system technology which involves a combination of a first "nutrient" component (1) which comprises water-soluble nutrients and other biologically utilizable substances with a second component (2) which comprises an inorganic geochemical-binder system. The simplest embodiment of the geochemical-binder system comprises one or more salts of phosphoric acid. In the preferred embodiments of the present invention intended for the slow-release of the ingredients contained in the "nutrient" component (1), the geochemical-binder system of component (2) comprises a combination of one or more salts of phosphoric acid with a inorganic binder matrix preferably containing a mixture of low-solubility carbonates, carbonate minerals, phosphates and phosphate minerals. The different embodiments of the geochemical-binder system of this invention allows a wide variation of formulations of the nutrient component (1) to be prepared in both conventional and slow-release forms using an improved high-shear granulation process whereby the dangerous chemicals typically used in the granulation process are largely or completely replaced with water. The present invention discloses means by which such compositions can be economically prepared in large quantities so as to meet the specific needs of different sectors of the agricultural / agribusiness and phytoremediation / bioremediation markets. The disclosed solid-chemical compositions of the present invention provide improved, cost-effective means for slowing and controlling the release-rate profiles of water-soluble nutrients, such as nitrogen- and phosphorus-rich compounds, and improved means for enhanced and / or time-targeted nutrient uptake by plants and microorganisms. The present invention also provides improved means for the reduction of nutrient run-off from agricultural areas into surface waters and means of preventing or minimizing nutrient-contamination of ground-water aquifers.
Owner:HINCE ERIC CHRISTIAN MR
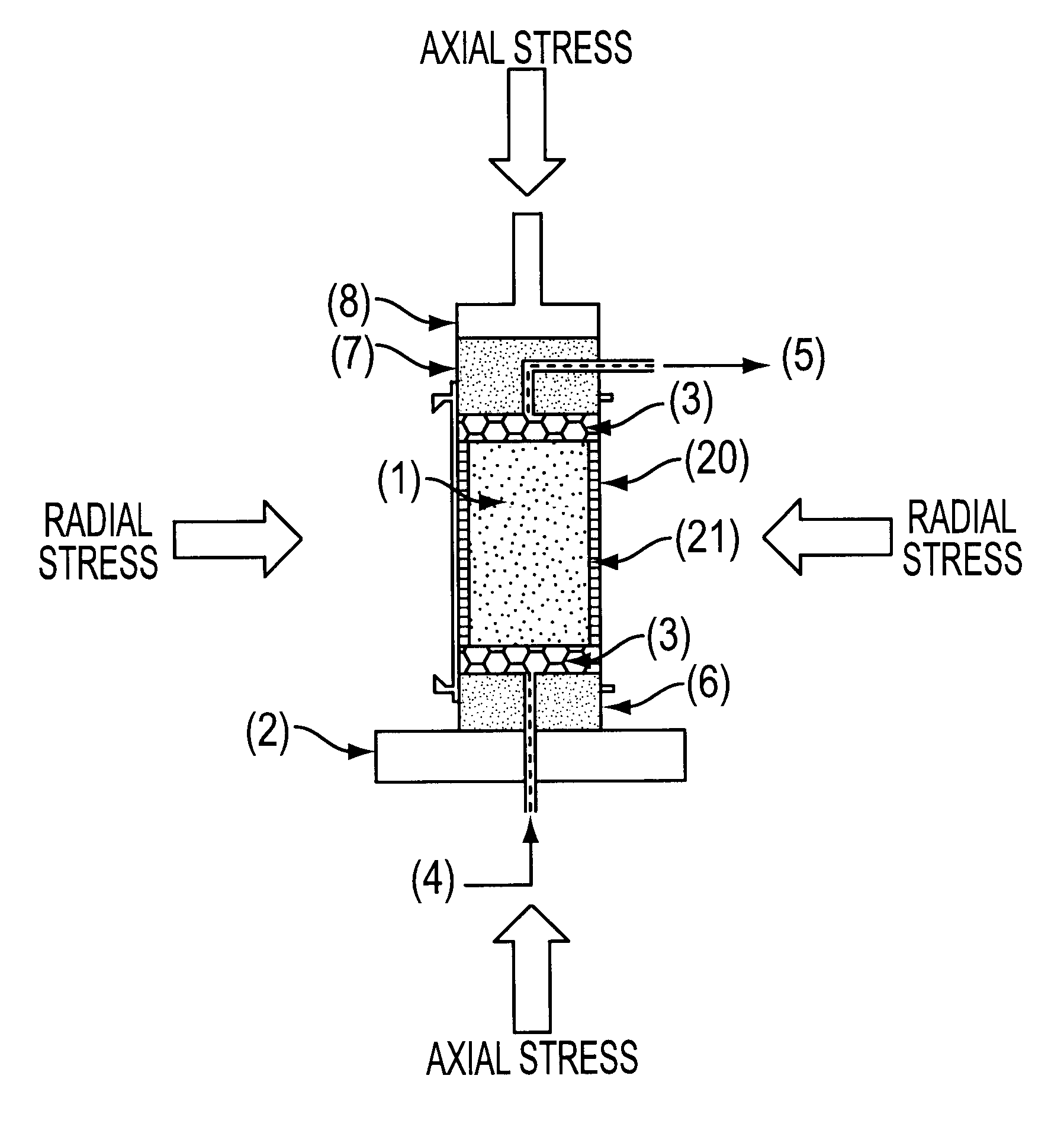
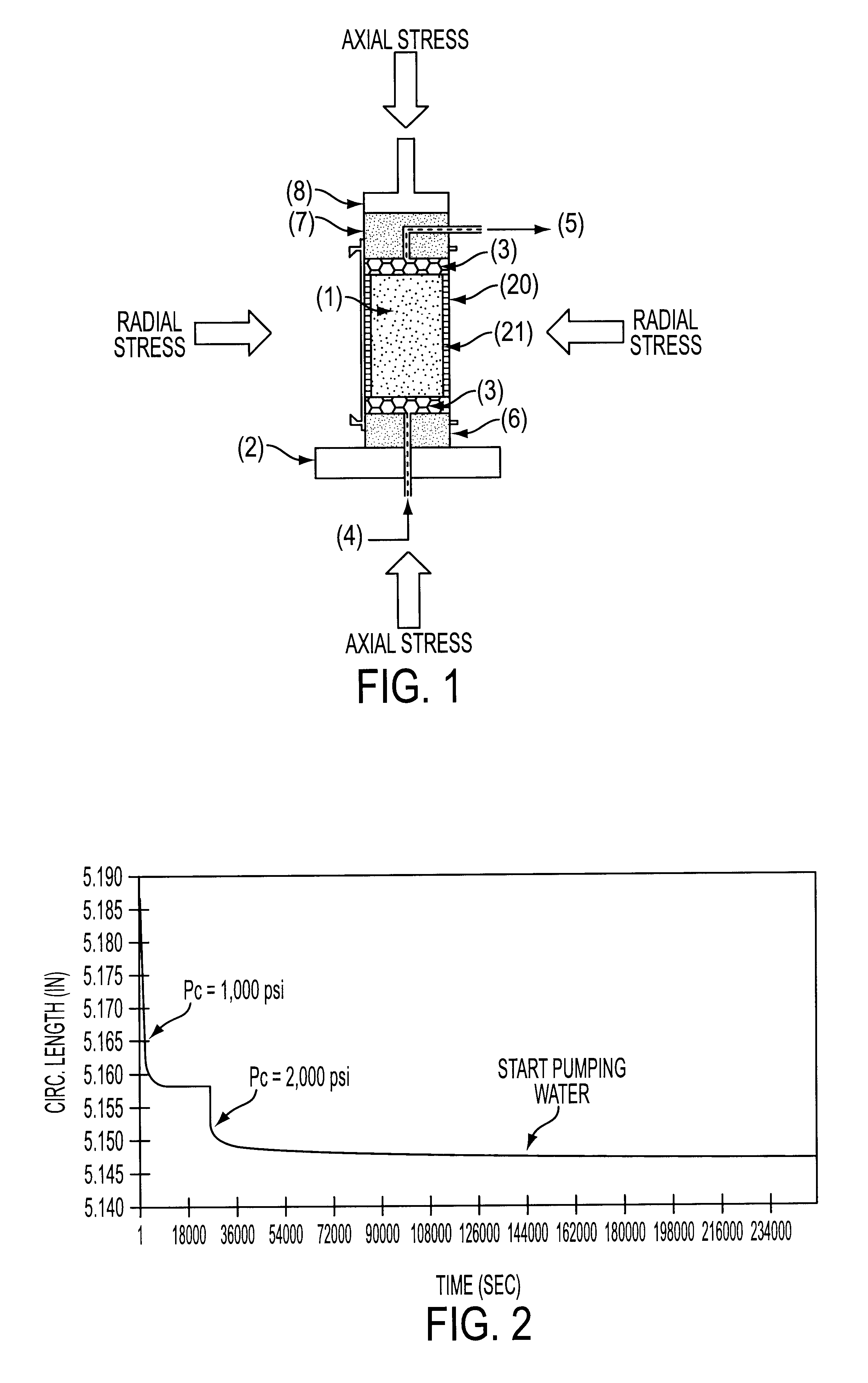
Method for the evaluation of shale reactivity
Shale reactivity is evaluated by testing a preserved test plug of shale sample in a triaxial test machine, the test plug being prepared by collecting a downhole shale sample and keeping it all times immersed in a preserving mineral oil so as to avoid dehydration, then applying radial and axial pressure on the test plug surrounded by mineral oil up to equilibration to overburden pressure, the test fluid being then contacted with the sample and the interaction of fluid and sample being evaluated by axial and radial deformations as measured by a triaxial detector apparatus sensitive to vertical and radial strains occurring across the shale sample, while the shale sample is subjected to any of a set of different conditions including a temperature or thermal potential, a hydraulic potential and / or a chemical potential. Only one fluid is tested on each sample. A sister test at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure is run in order to constitute a visual counterpart of what is occurring in the triaxial test machine.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Biochar complex
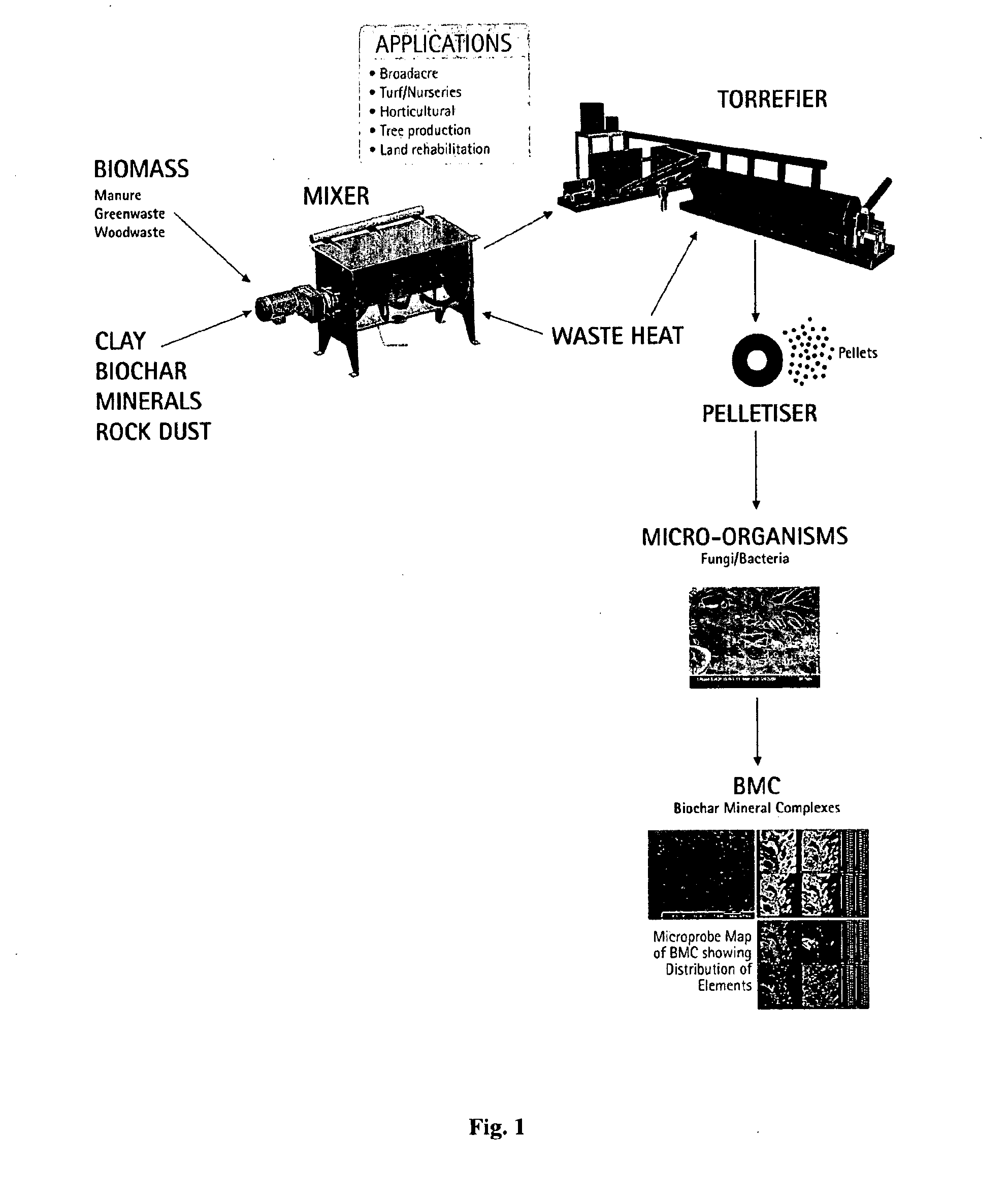
InactiveUS20120125064A1Increase productionLow application rateDirect heating destructive distillationBiofuelsGrowth plantClay minerals
The invention relates to a biochar-containing composition comprising biochar having organic matter therein and / or thereon, clay associated, optionally intercalated, with the organic matter, a non-clay mineral and optionally also a plant growth promoter.
Owner:VENEARTH GRP
Use of high carbon coal ash
InactiveUS6755905B2Avoid insufficient heatingReduce flowCharge manipulationHandling discharged materialSlagHigh carbon
A synthetic slag is produced by a high temperature combustion reaction between coal ash having a high carbon content, and a source of lime such as cement kiln dust. The carbon content of the coal ash is oxidized by oxygen gas, which typically is derived from air or an air / oxygen combination in an exothermic reaction and the heat generated is exploited in the melting process. In this way the gaseous products will typically comprise nitrogen, unreacted oxygen and carbon dioxide, and heat energy can be readily recovered from the hot off gas products evolving during the combustion reaction. The synthetic slag may be pelletized and employed as lightweight mineral aggregate or milled to cement fineness to provide slag cement.
Owner:LAFARGE CANADA INC
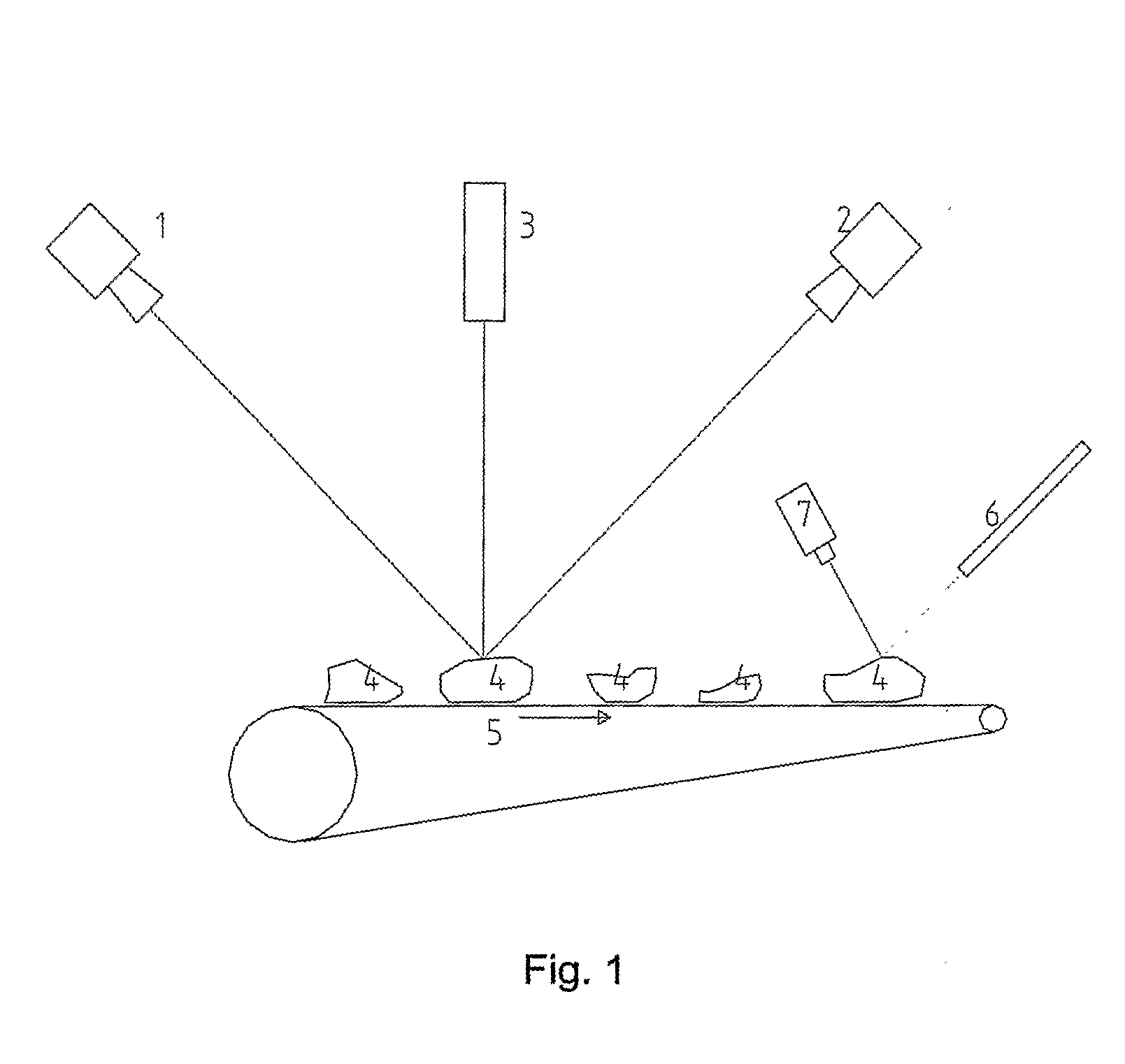
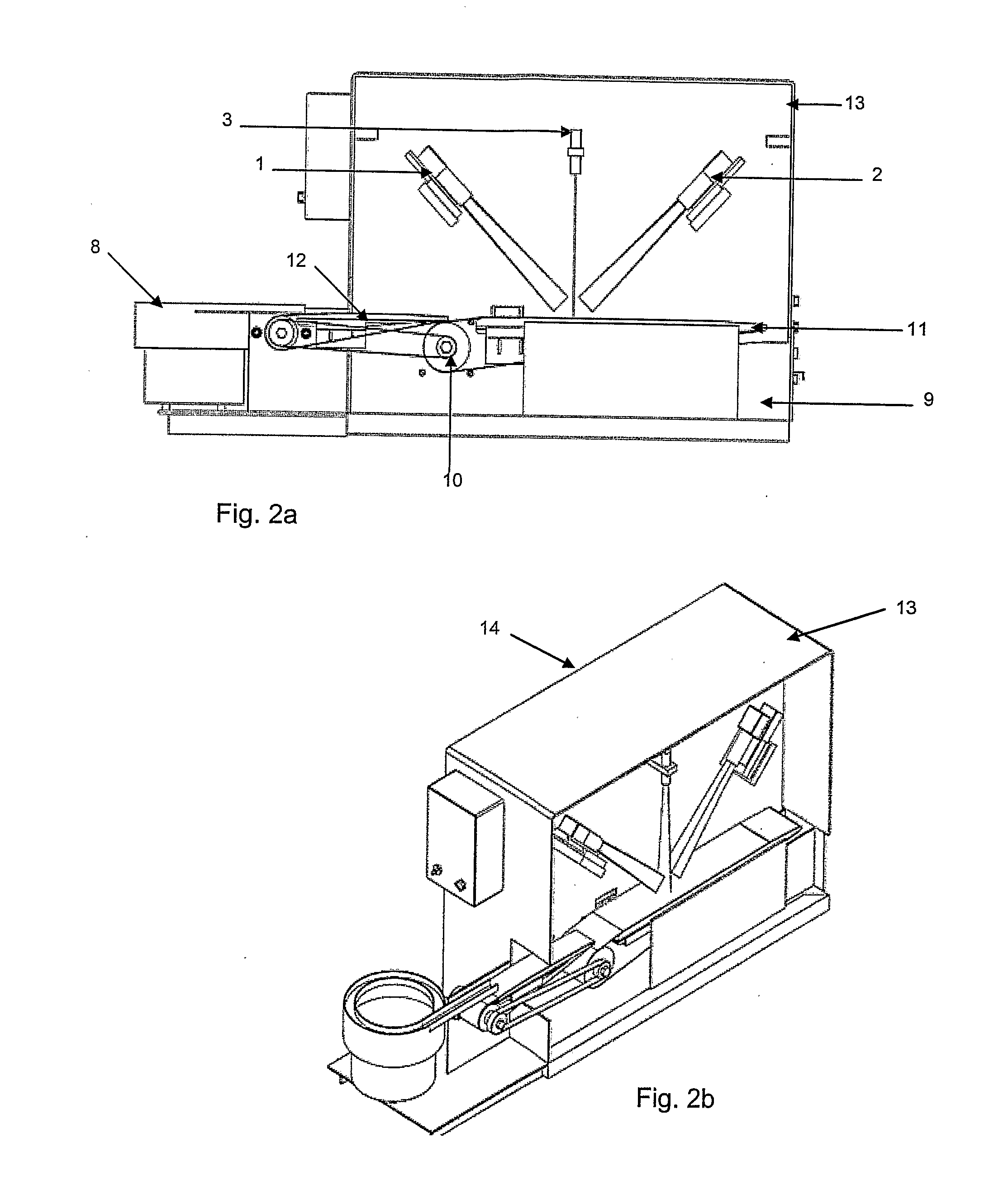
Apparatus and Method For Analysis of Size, Form and Angularity and For Compositional Analysis of Mineral and Rock Particles
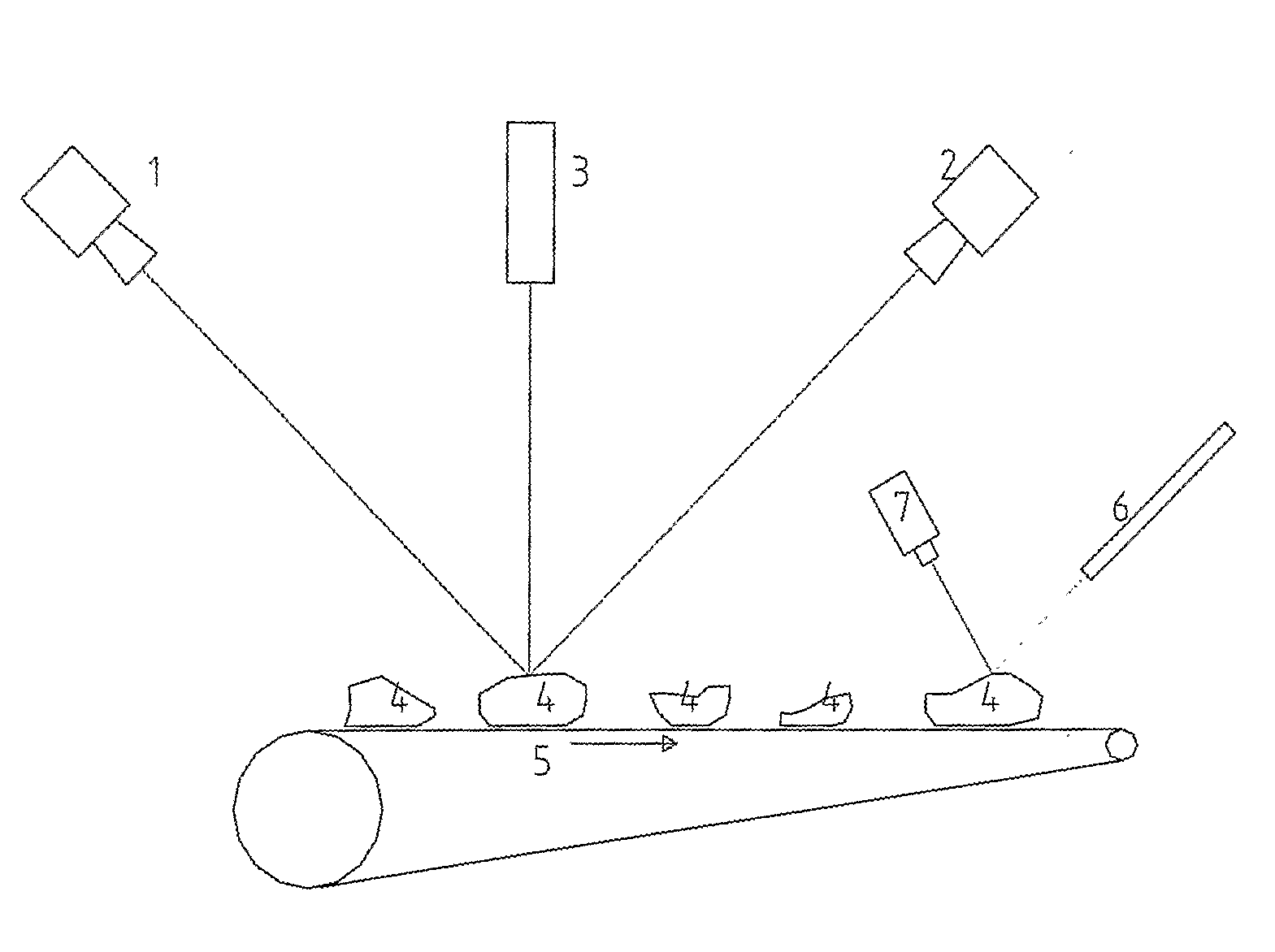
ActiveUS20080192987A1Automatically and rapidly analyzeEarth material testingCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine visionThree dimensional measurement
Equipment and process for three-dimensional measurement of size and shape and for compositional analysis of mineral and rock particles and the like objects. A mixture of particles or objects of same or different sizes of minerals or rocks or the like are fed individually and automatically onto a conveyor belt for three-dimensional machine vision measurements using laser and two cameras and subsequently for spectroscopic measurements using visible and infrared light and are then collected at the end of the conveyor. Computer software is used to perform the measurement automatically and to calculate size, form, roundness, and preferably petrographic composition and other characteristics or properties of each individual object and the statistical distribution of relevant properties, either according to built-in measurement processes or user specific methods.
Owner:PETROMODEL EHF
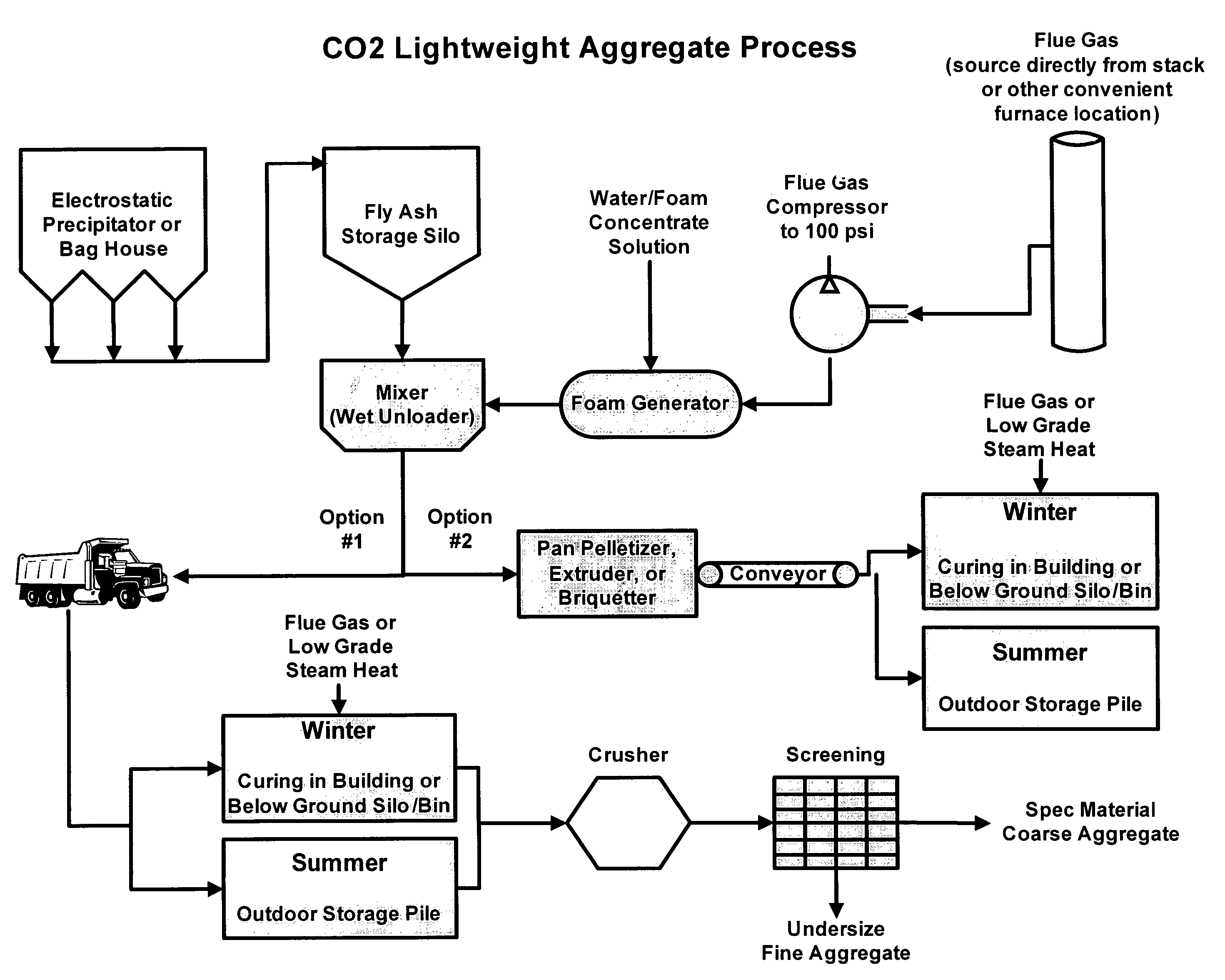
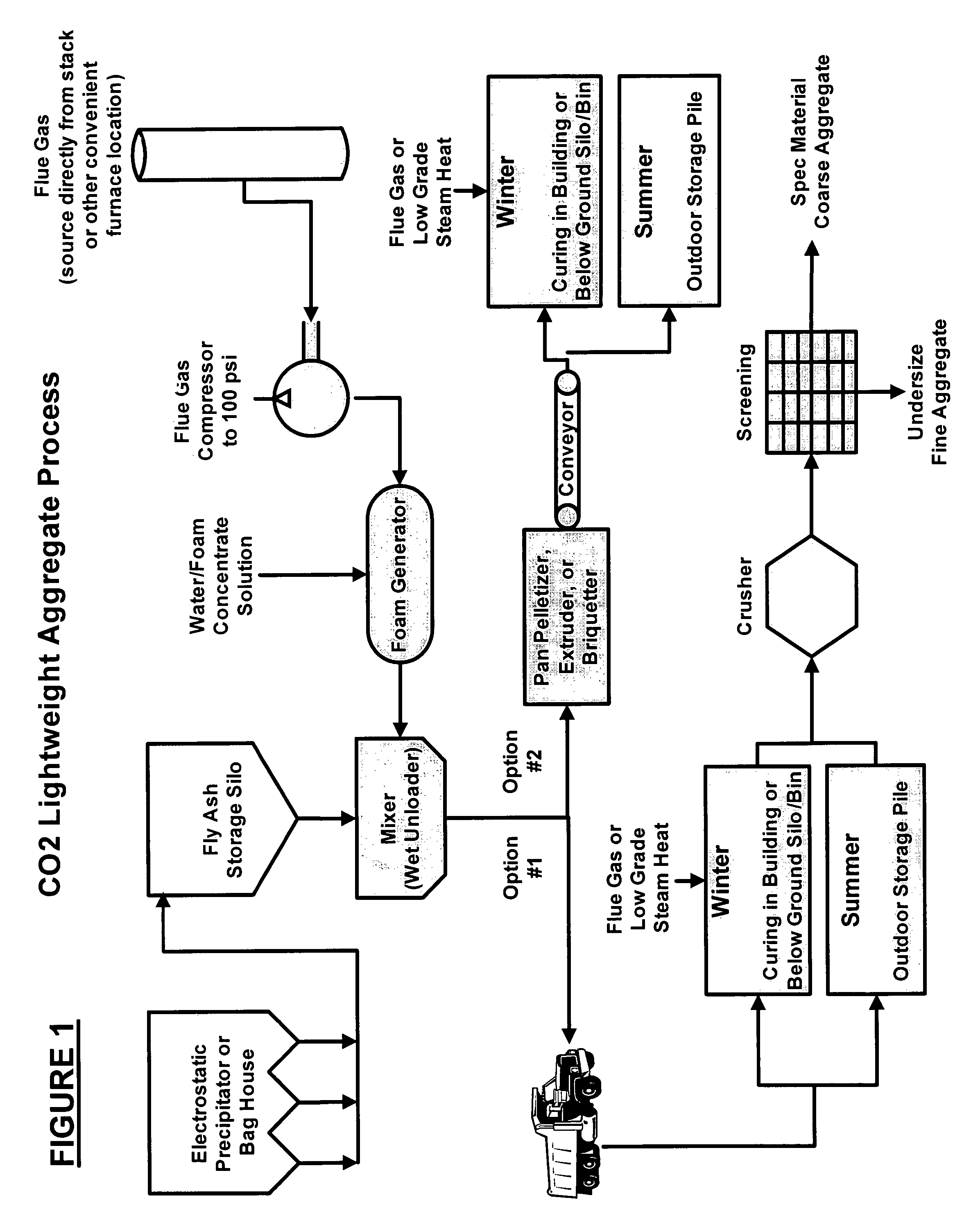
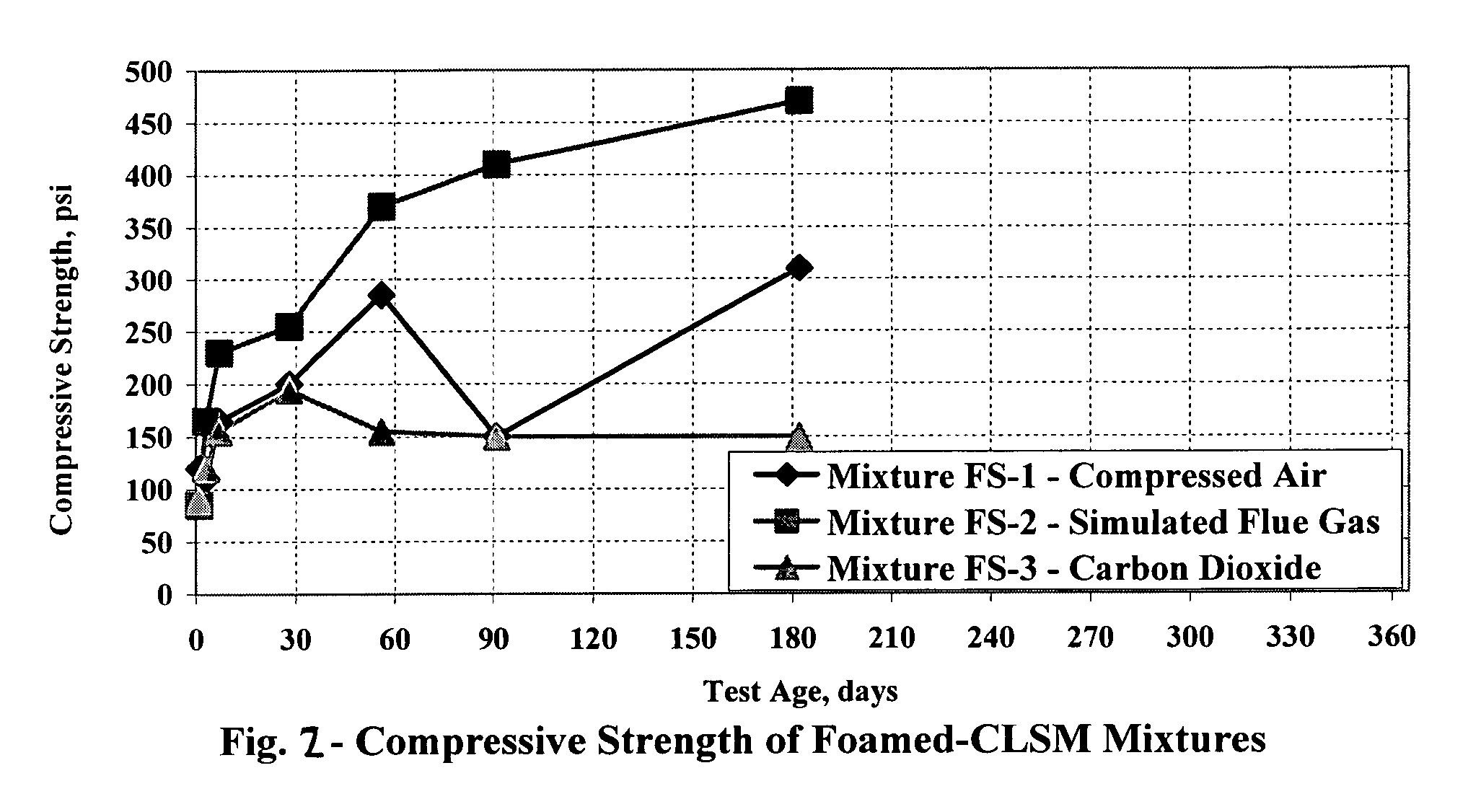
Carbon dioxide sequestration in foamed controlled low strength materials
A process for sequestering carbon dioxide from the flue gas emitted from a combustion chamber is disclosed. In the process, a foam including a foaming agent and the flue gas is formed, and the foam is added to a mixture including a cementitious material (e.g., fly ash) and water to form a foamed mixture. Thereafter, the foamed mixture is allowed to set, preferably to a controlled low-strength material having a compressive strength of 1200 psi or less. The carbon dioxide in the flue gas and waste heat reacts with hydration products in the controlled low-strength material to increase strength. In this process, the carbon dioxide is sequestered. The CLSM can be crushed or pelletized to form a lightweight aggregate with properties similar to the naturally occurring mineral, pumice.
Owner:WISCONSIN ELECTRIC POWER
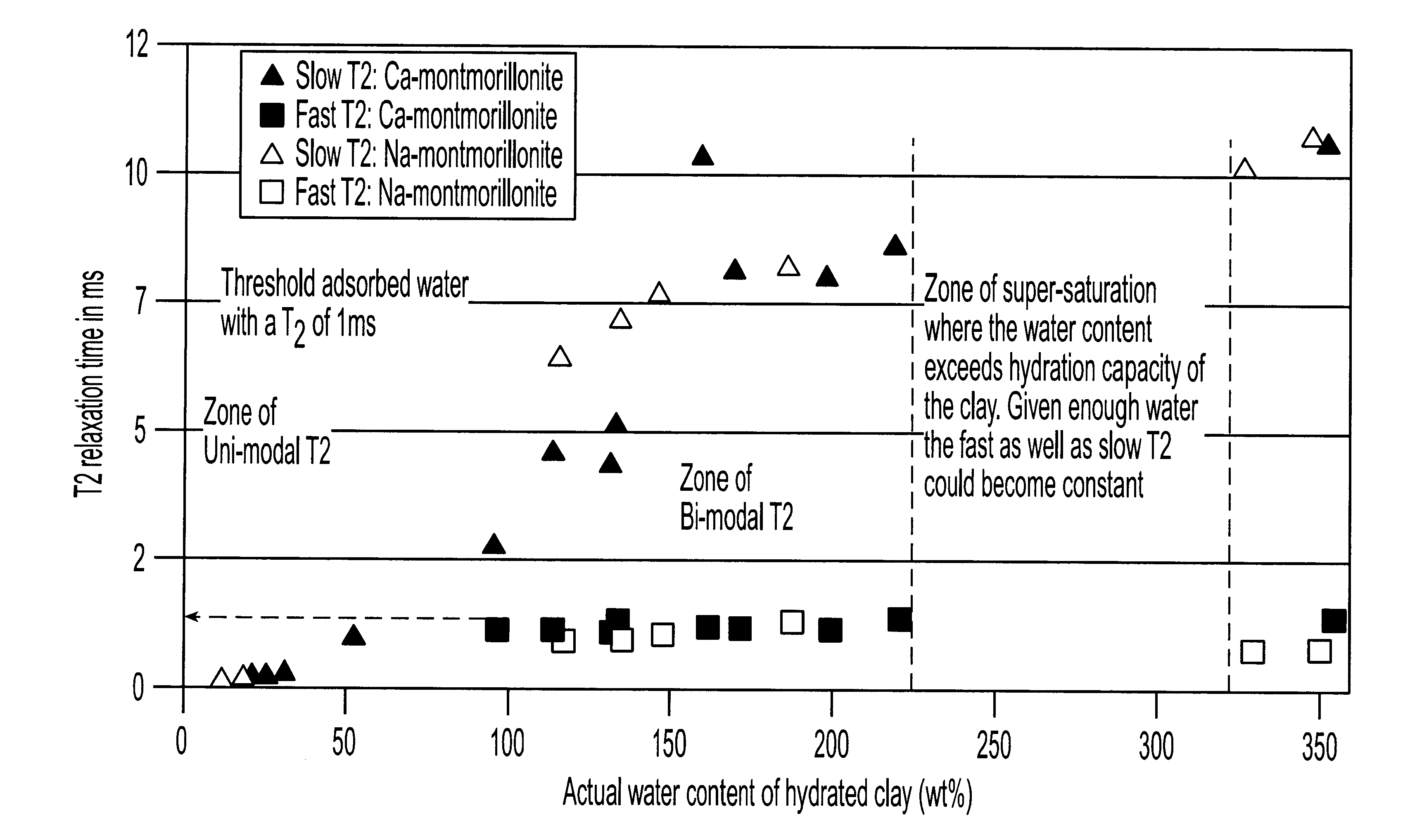
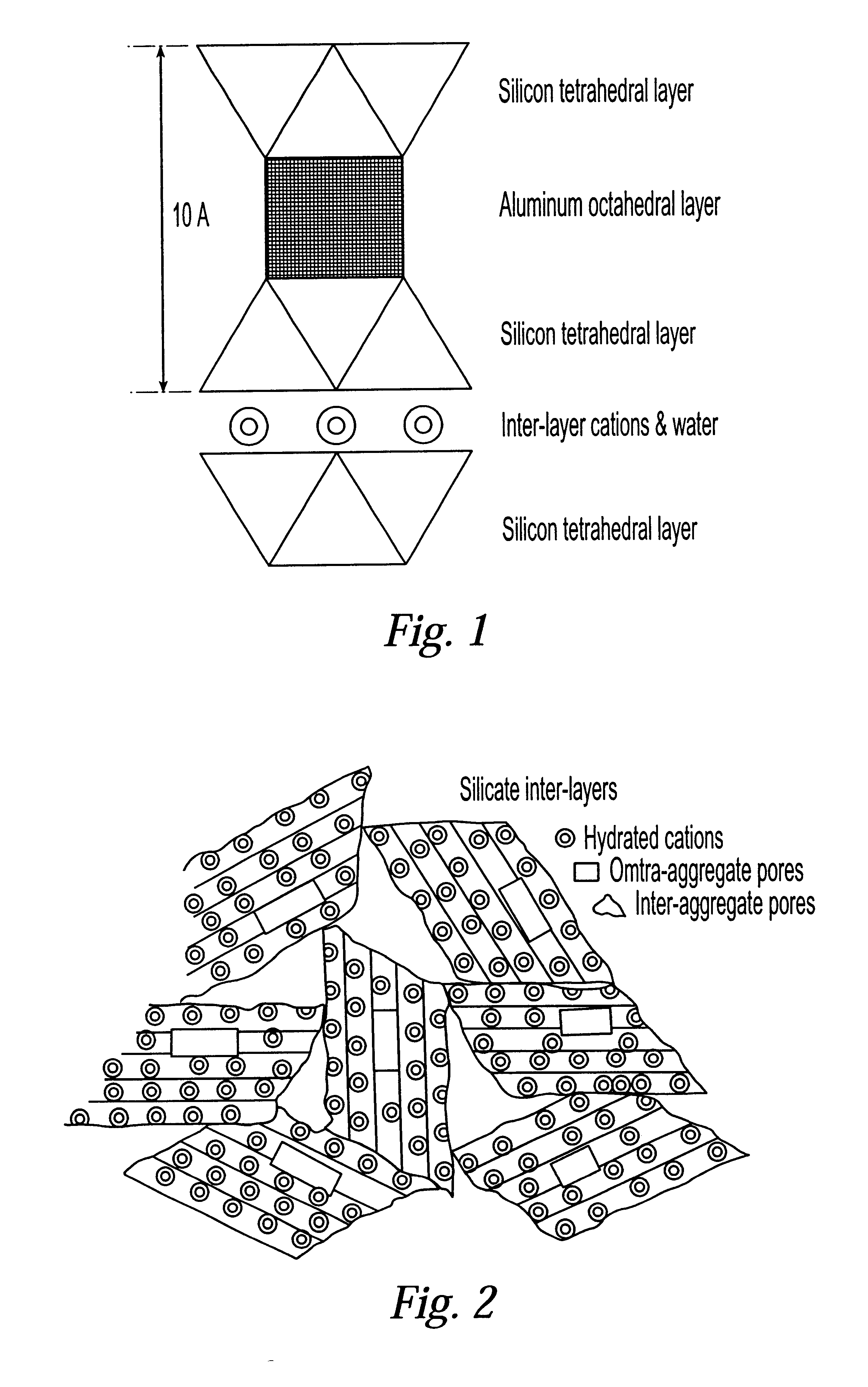
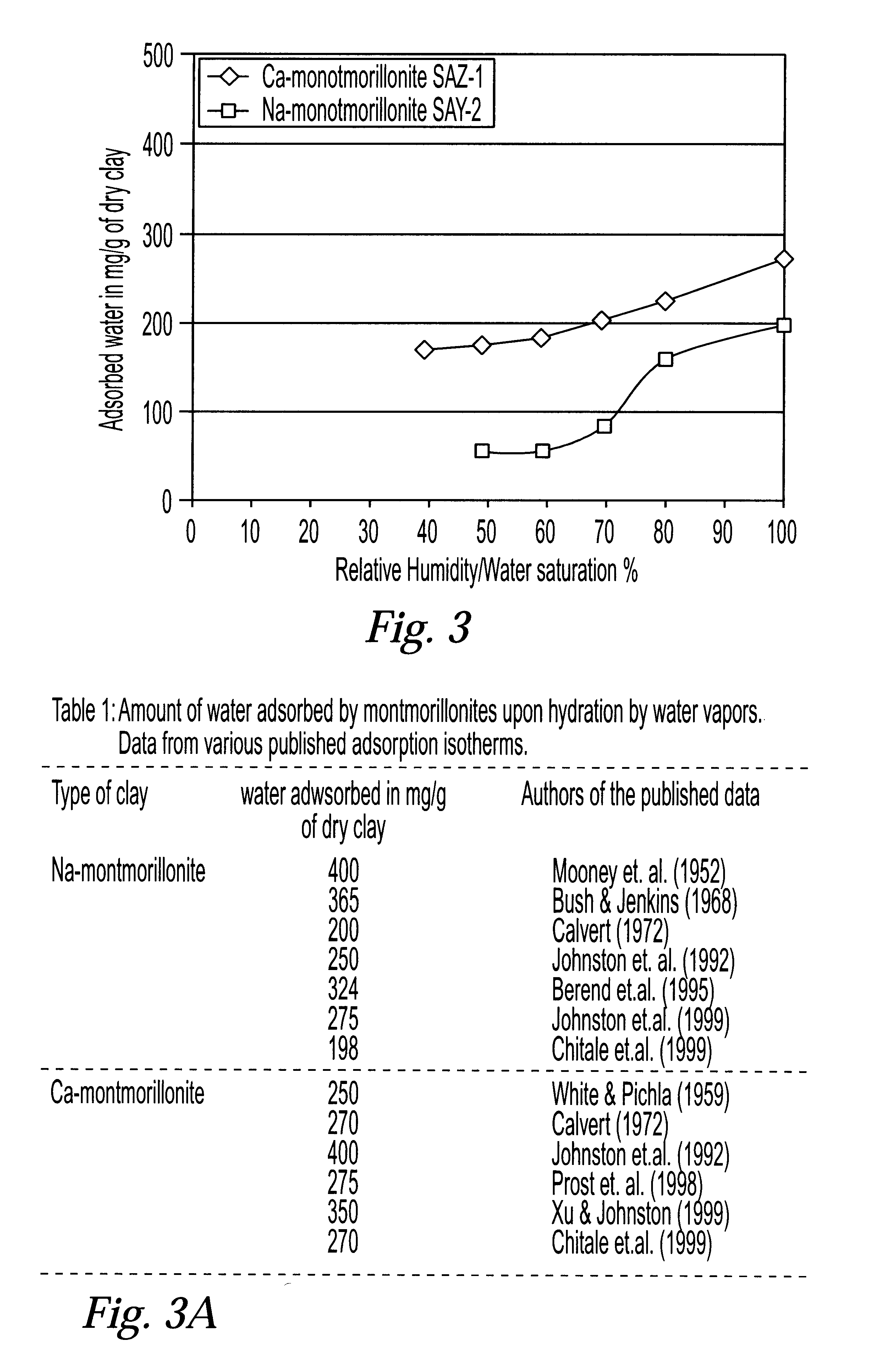
System and method for clay typing using NMR-based porosity modeling
InactiveUS6646437B1Good estimateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingClay mineralsTyping
System and method for characterizing formation properties based on NMR measurements. NMR clay measurements of this invention distinguish between interstitial pore water and the water adsorbed by the clay minerals. The measurements can be used to determine the quantity of adsorbed water in different clays and correct previously available data obtained using conventional density and neutron porosity logs. A new petrophysical parameter wetness clay is defined as an intrinsic parameter for clays, and its value is computed for members of the smectite group of clays, such as montmorillonite. The wet clay values for the density, neutron logs based on the adsorbed water in clays are used to enhance the quality and accuracy of the overall log interpretation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
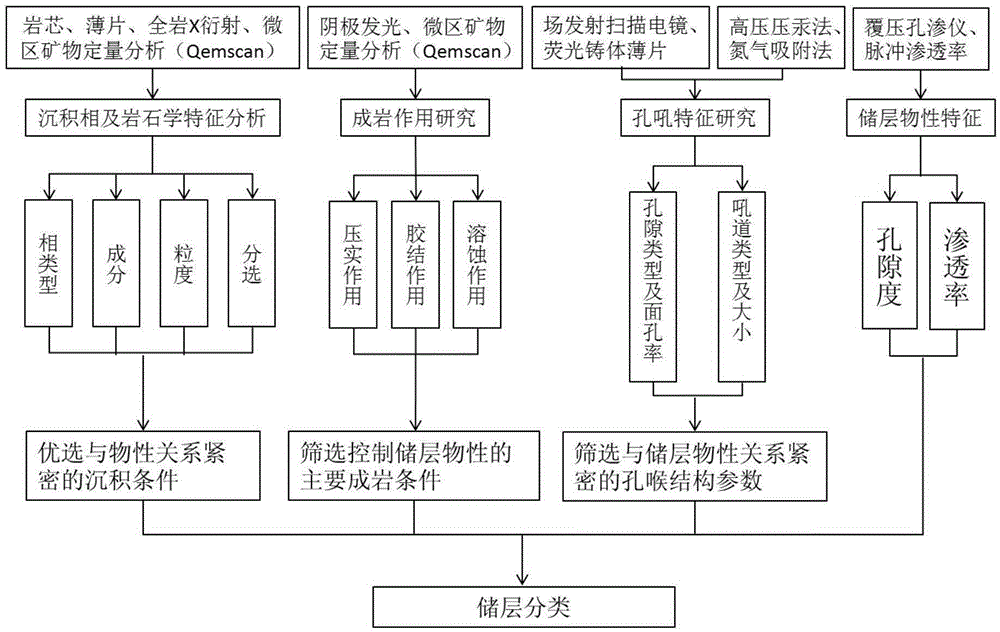
Micro-pore structure evaluation and reservoir classification method for tight reservoirs
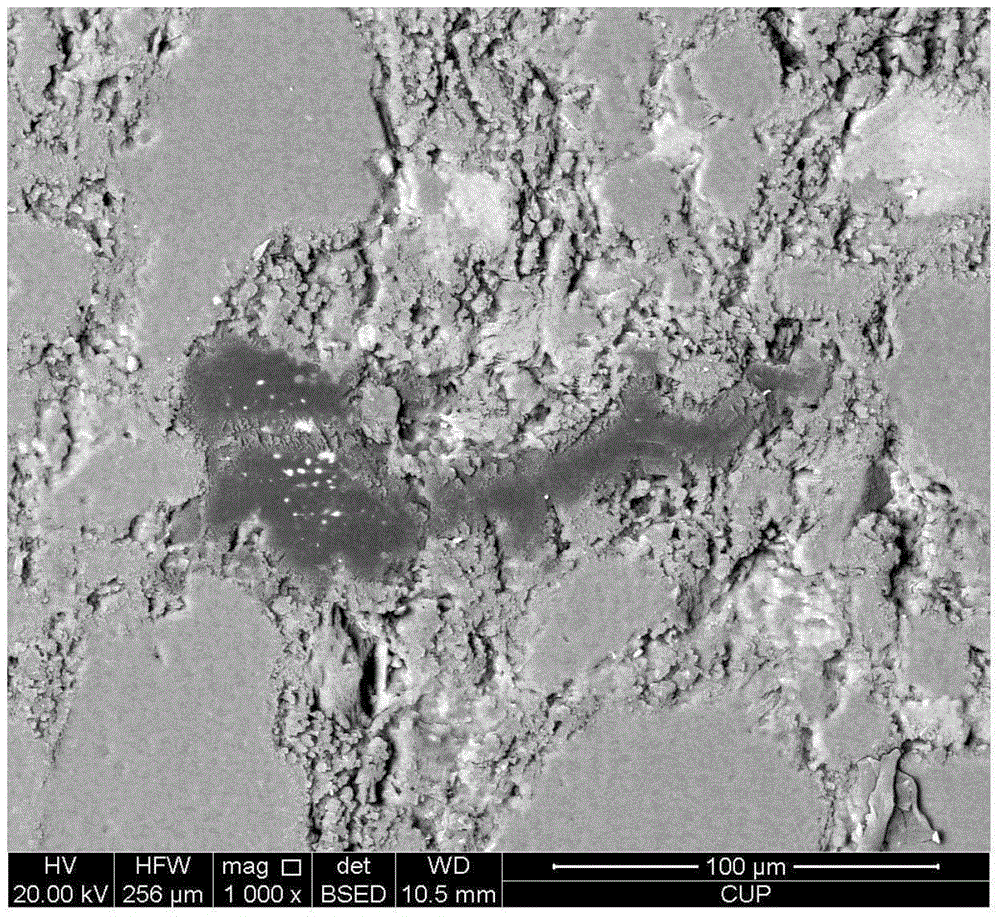
InactiveCN105334149ASolve the problem of observationDetermining the cause of densificationEarth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityFluorescence
The invention provides a micro-pore structure evaluation and reservoir classification method for tight reservoirs. The method comprises steps as follows: the origin and the petrologic features of each reservoir are analyzed, and the phase type, the content and the like of each reservoir are determined; physical features of each reservoir are analyzed; features of a reservoir space of each reservoir are observed, and the pore type, the surface porosity and the like are determined; pore structure parameters of the reservoirs are measured with a high-pressure mercury intrusion method and a nitrogen adsorption method; the diagenesis is researched, and compaction, cementation and corrosion sequences are determined; physical property control factors of the reservoirs are analyzed; the reservoirs are classified. The method mainly has the effects as follows: the diagenesis and the influences of the diagenesis on the reservoirs are comprehensively reflected through cathode luminescence and micro-area mineral quantitative analysis; micro pores of the tight reservoirs are researched elaborately through fluorescent casting and field emission scanning electron microscopy; the microscopic features of the tight reservoirs are determined accurately through high-pressure mercury intrusion experiments and the nitrogen adsorption experiments; the parameters are optimized for classification and evaluation of the reservoirs, and the method has a great significance in further prediction of beneficial developing stratums or zones.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
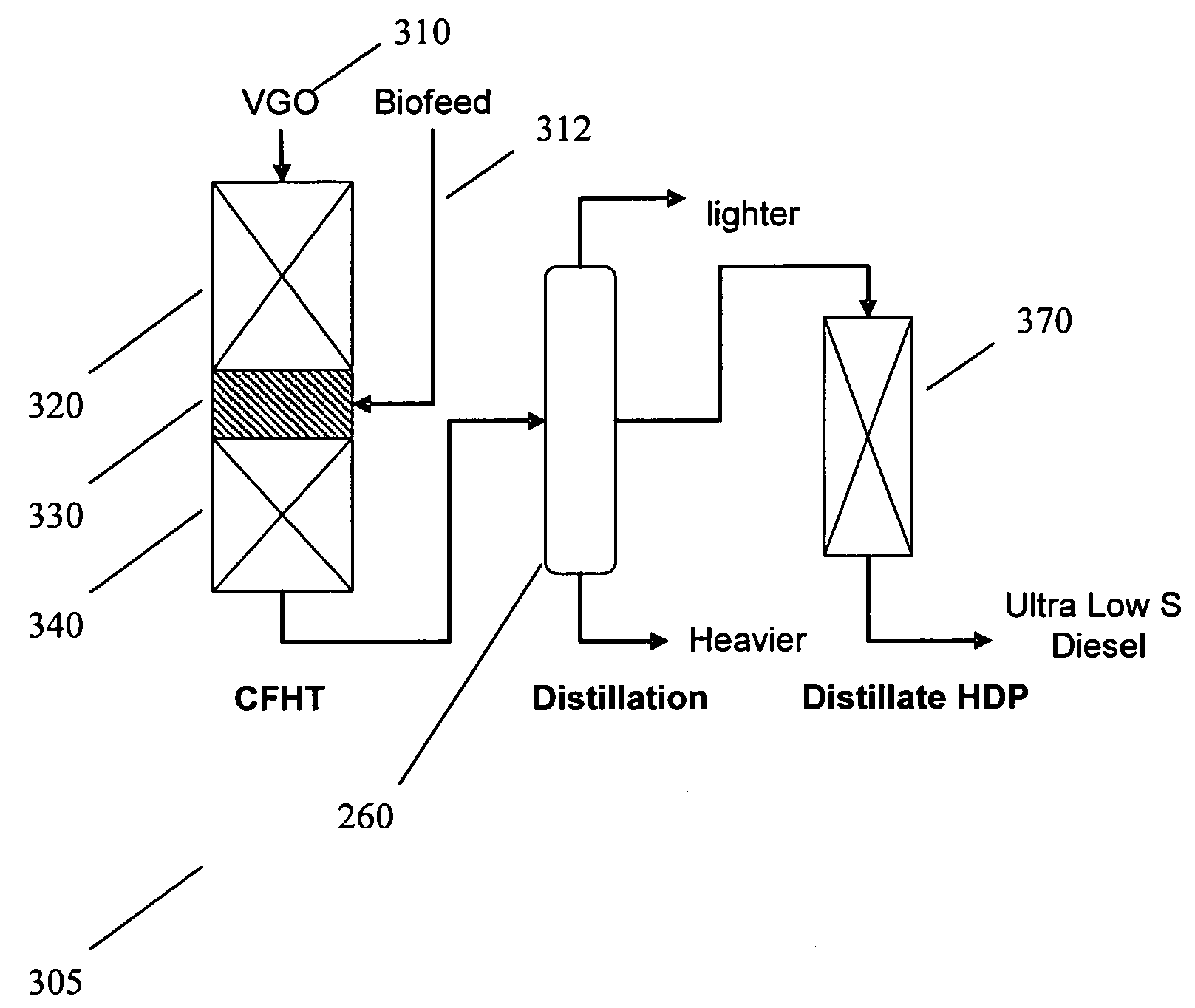
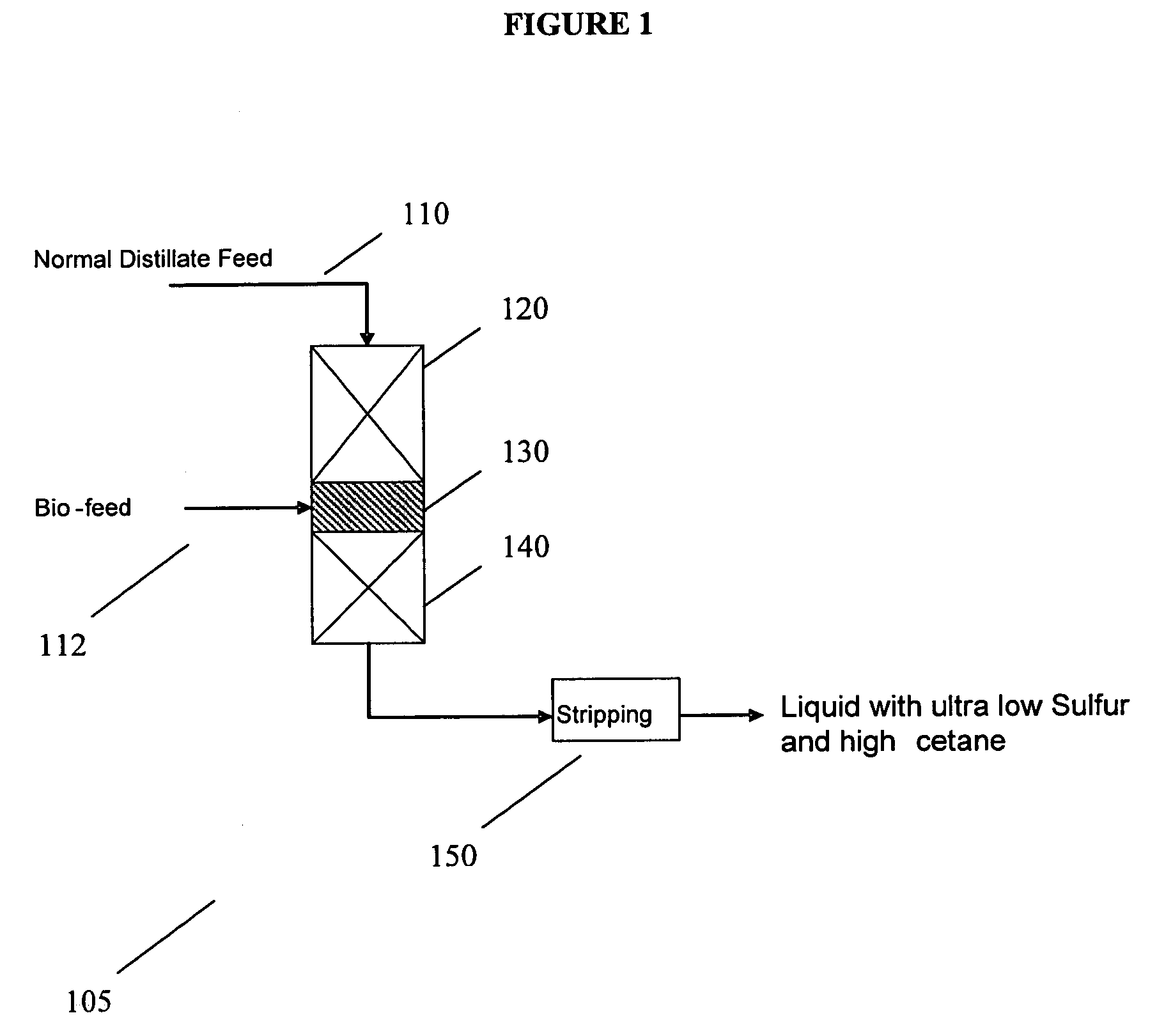
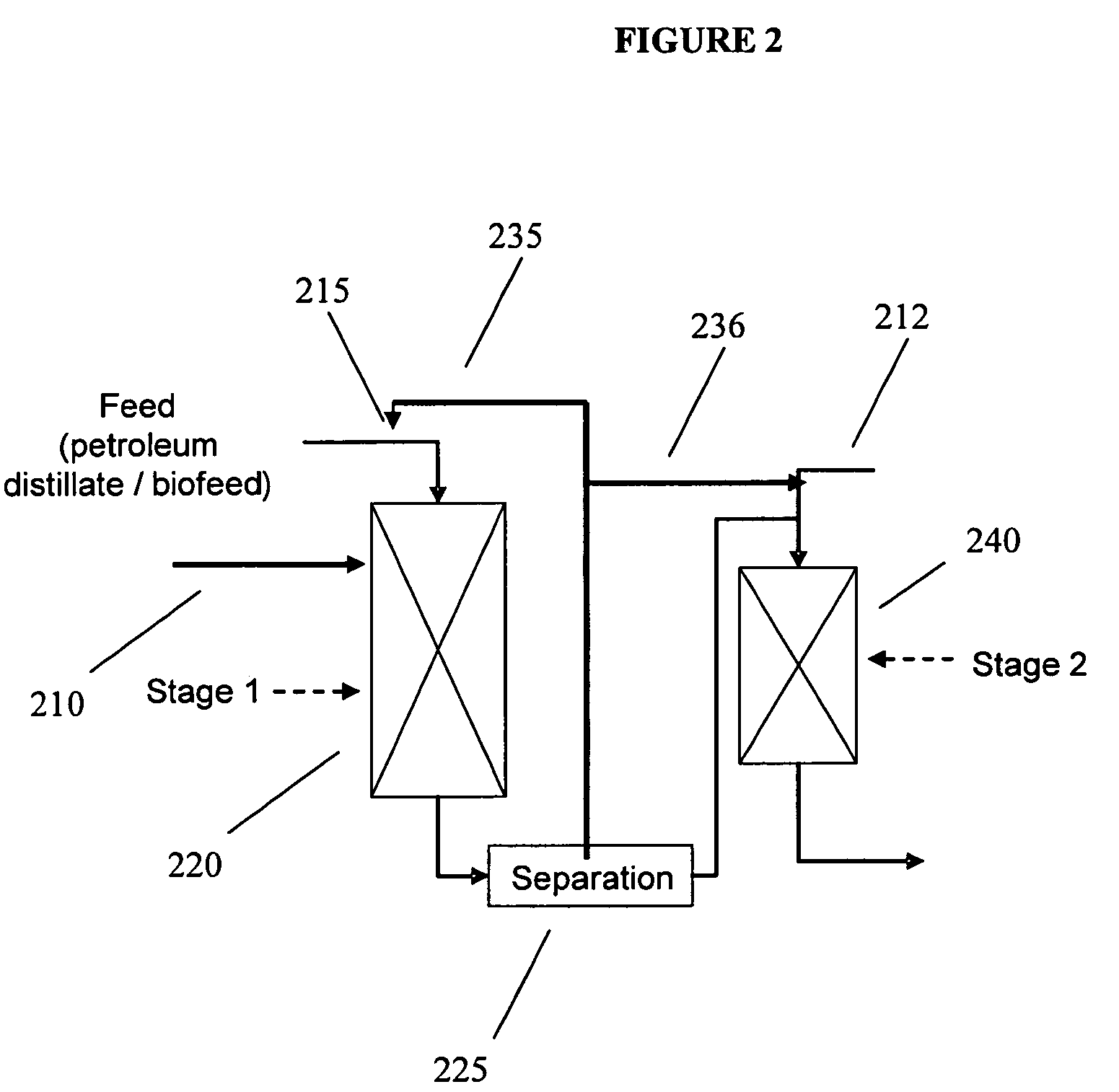
Staged co-processing of biofeeds for manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20090166256A1Liquid hydrocarbon mixture productionTreatment with hydrotreatment processesCo-processingMaceral
Processes are provided for producing a diesel fuel product having a sulfur content of 10 ppm by weight or less from feed sources that include up to 20% by weight of a biocomponent feedstock. The mineral hydrocarbon portions of the feed sources can be distillate or heavier feed sources.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Method for evaluating shale gas reservoir and searching sweet spot region
InactiveCN104853822AImprove fidelityEstimates are stable and accurateEntertainmentBorehole/well accessoriesWell loggingElastance
The present invention discloses a method for evaluating shale gas reservoirs and searching sweet spot regions, which includes steps as follows: drilling corestone columns with different directions and measuring dynamic and static parameters of the corestone columns after saturation to obtain a transformable relational expression of dynamic and static elasticity modulus, processing physical simulation of anisotropic rocks, and calculating elastic parameters; intersecting to obtain related relationship corresponding to elastic and sensitive parameters or the combination of the elastic and sensitive parameters and parameters of shale gas sweet spot regions, getting and predicating the parameters or parameter combination of the shale gas sweet spot regions; correcting log data to obtain optimal well log; utilizing multi-mineral analysis and corestone test analysis methods to obtain a model and processing in series; inverting three-dimensional high resolution post-stack seismic data; synthesizing obtained various favorable parameters of the shale gas reservoirs and combining the accurate burial depth, thickness, occurrence and planar distribution of the shale gas reservoirs to obtain the gas bearing characteristic prospect of the shale gas reservoirs and outline the sweet spot regions for shale gas exploration and development.
Owner:杨顺伟
Composite heavy metal polluted soil in-situ fixing method
ActiveCN102303041APromote mineralization reactionQuick fixContaminated soil reclamationWater insolubleMagnesium sulfite
The invention discloses a composite heavy metal polluted soil in-situ fixing method. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a heavy metal polluted soil restoration agent by using 80 to 90 weight parts of bentonite or kaolin serving as a filling agent, 0.5 to 15 weight parts of ferrous sulfide, 0.5 to 5 weight parts of magnesium sulfate, 1.5 to 8 weight parts of magnesium sulfite, 1 to 5 weight parts of magnesium oxide, 2 to 10 weight parts of calcium hydroxide and 1 to 5 weight parts of phosphorus-containing preparation; and mixing the components and heavy metal polluted soil according to the weight ratio of 1:(5-20), and uniformly stirring to make the humidity of the soil kept between 15 and 30 percent, wherein heavy metal ions in the polluted soil are converted into water-insoluble metal sulfides, hydroxides, multi-metal co-precipitates, basic carbonates and phosphate minerals, the biological activity of heavy metal is lost, and the heavy metal is fixed in the soil. The restored soil meets the requirement of second-level standard values of 'Environmental Quality Standard for Soil' (GB 15618-1995) in China.
Owner:刘阳生
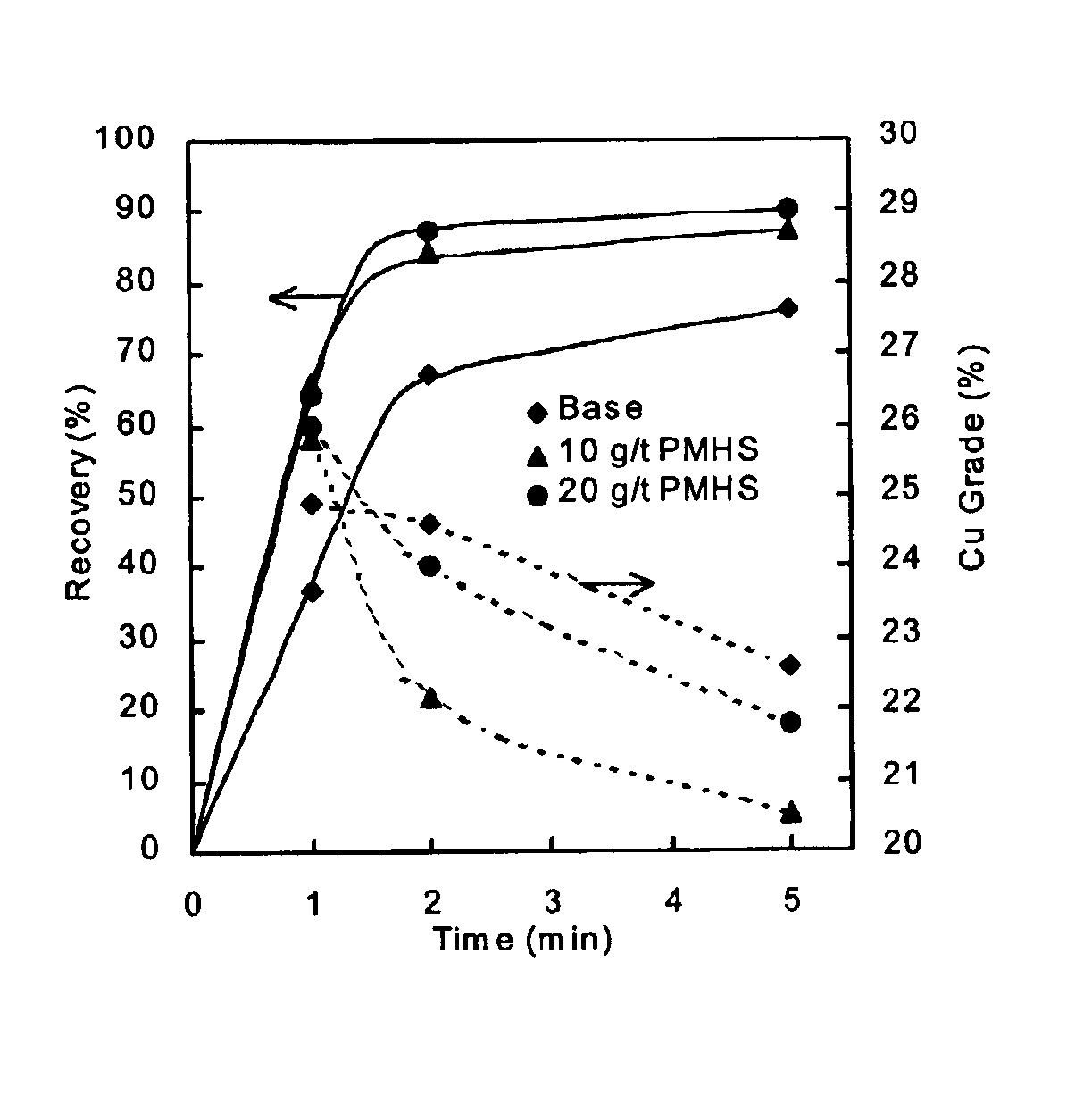
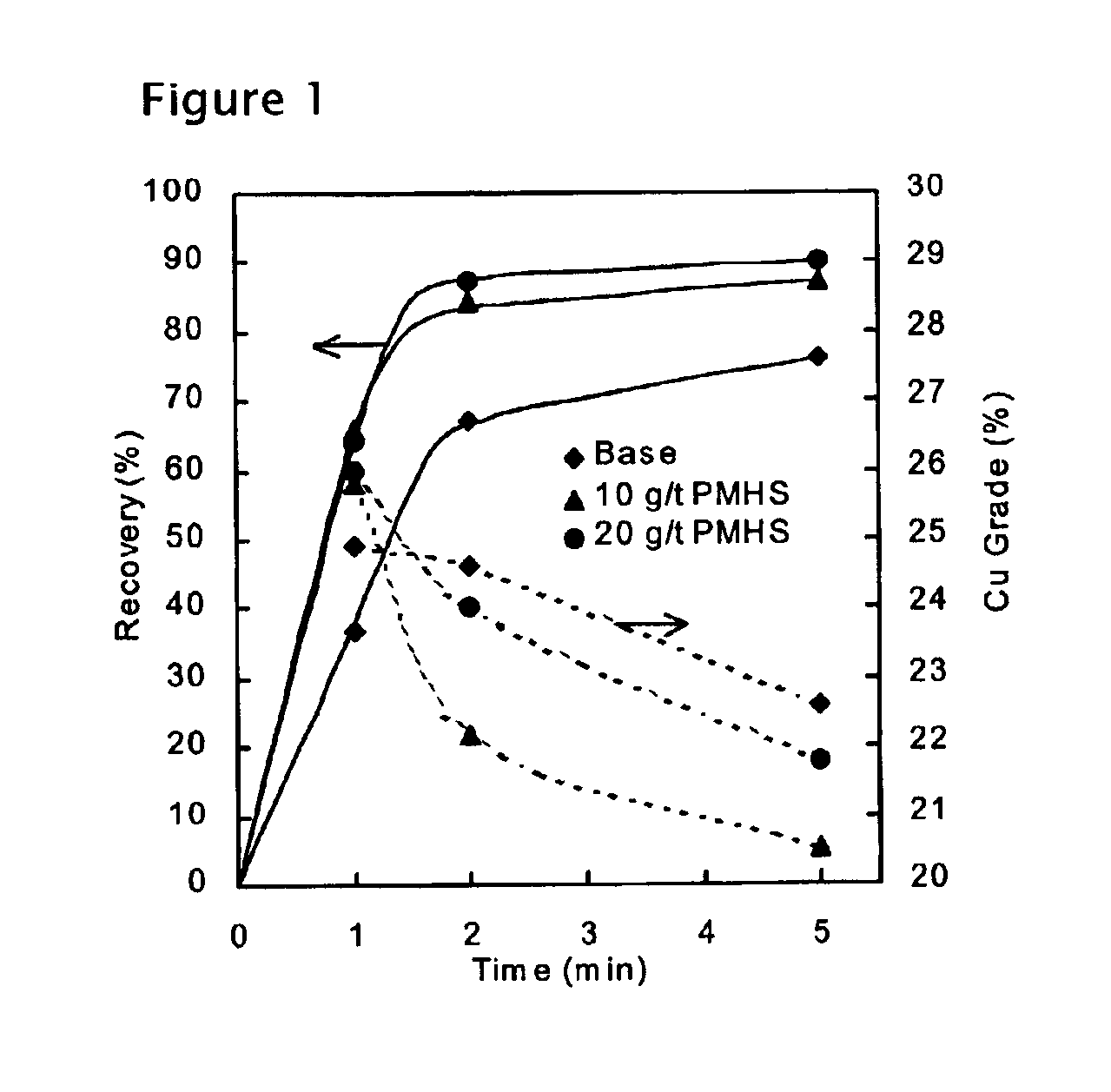
Methods of increasing flotation rate
Methods of increasing the rate of separating hydrophobic and hydrophilic particles by flotation have been developed. They are based on using appropriate reagents to enhance the hydrophobicity of the particles to be floated, so that they can be more readily collected by the air bubbles used in flotation. The hydrophobicity-enhancing reagents include low HLB surfactants, naturally occurring lipids, modified lipids, and hydrophobic polymers. These methods can greatly increase the rate of flotation for the particles that are usually difficult to float, such as ultrafine particles, coarse particles, middlings, and the particles that do not readily float in the water containing large amounts of ions derived from the particles. In addition, new collectors for the flotation of phosphate minerals are disclosed.
Owner:MINERAL & COAL TECH
Beneficiation method for removing long quarry impurities by adopting strong magnetic flotation
InactiveCN101898168AIncrease production capacityImprove grinding efficiencyFlotationMagnetic separationEngineeringBall mill
The invention relates to a beneficiation method for removing long quarry impurities by adopting strong magnetic flotation, comprising the steps of crushing, grinding, sieving, desliming, strong magnetically floating, floating, concentrating and dewatering. The concrete beneficiation method comprises the following steps of: breaking and grinding ore in a ball mill; grading ground minerals by a spiral grader and a hydraulic hydrocyclone twice; combining with the ball mill into a closed cycle; respectively mounting high-frequency linear vibration sieves in overflows graded twice; respectively removing impurities over 3 mm and 1 mm, such as mica, grass-roots bark, and the like; removing most of muddy substances from minerals through desliming equipment after the impurities are removed; removing mechanical iron, weakly magnetic iron ore, tourmaline and partial mica in a strong magnetic flotation machine; floating the minerals passing through the strong magnetic flotation machine again to remove residual iron minerals, mica and black minerals; and finally, concentrating and dewatering the minerals to form a product.
Owner:衡阳县湘雁矿业有限公司
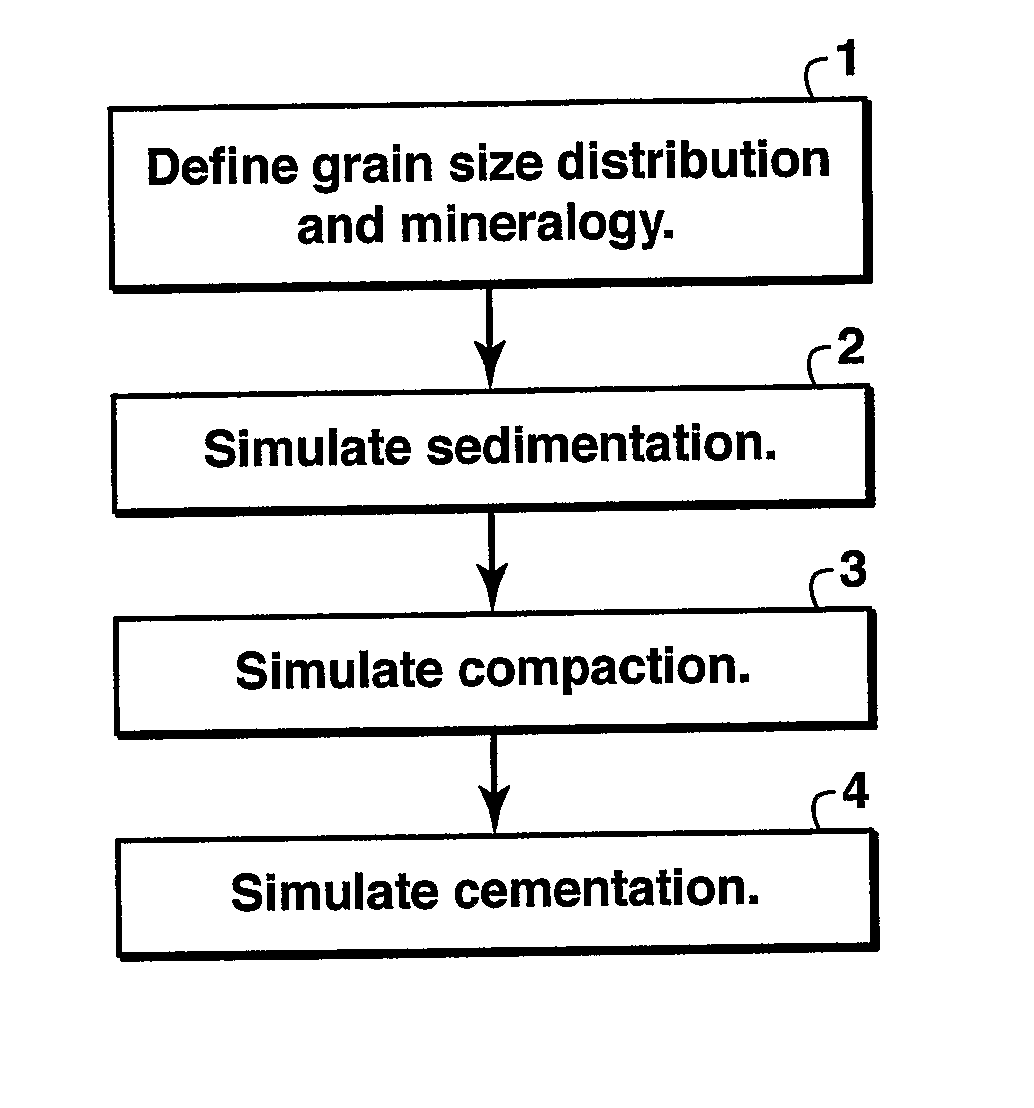
Method For Simulating And Estimating Sandstone Properties
InactiveUS20070203677A1Computation using non-denominational number representationGeological measurementsPorosityMaceral
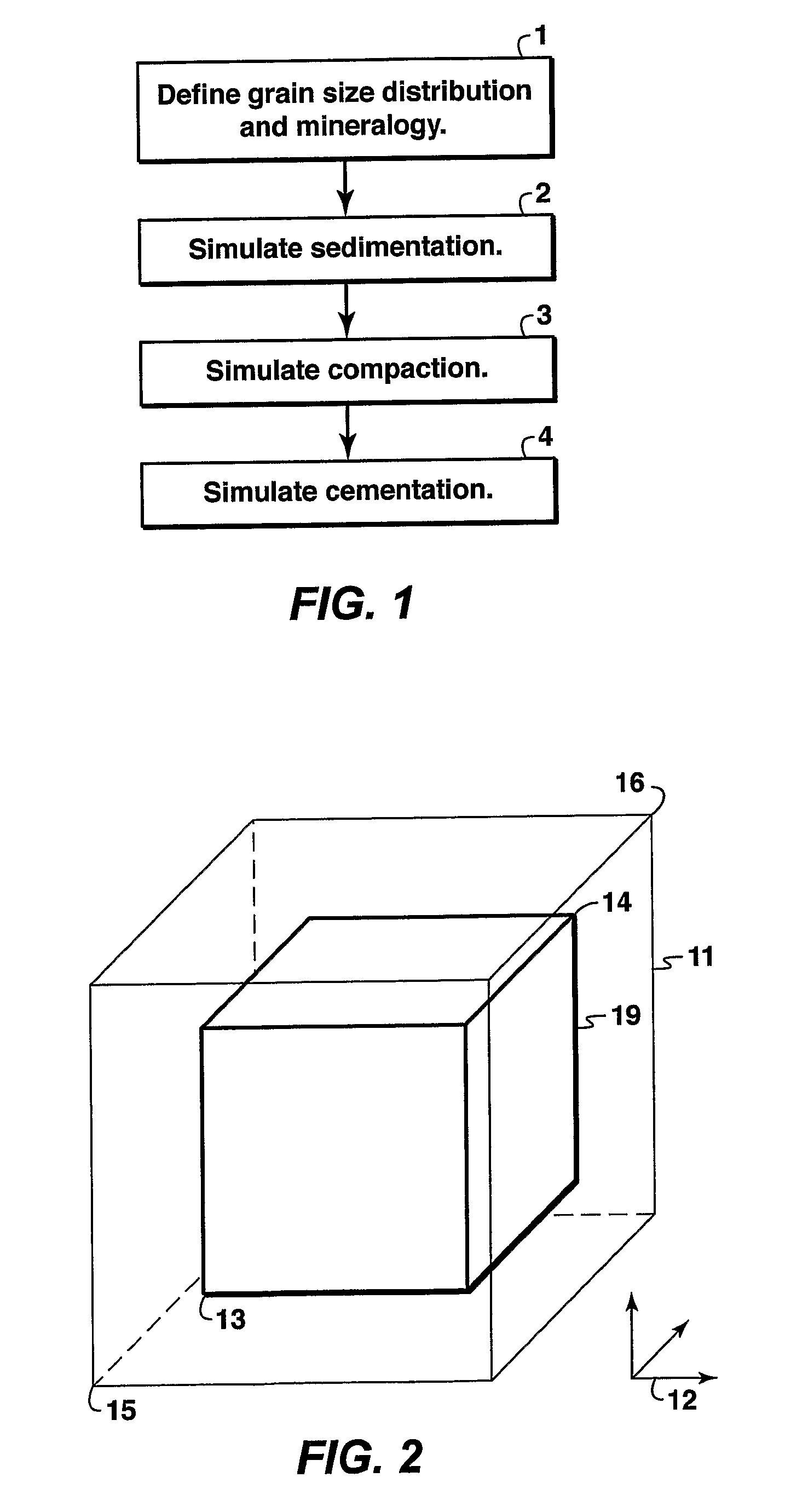
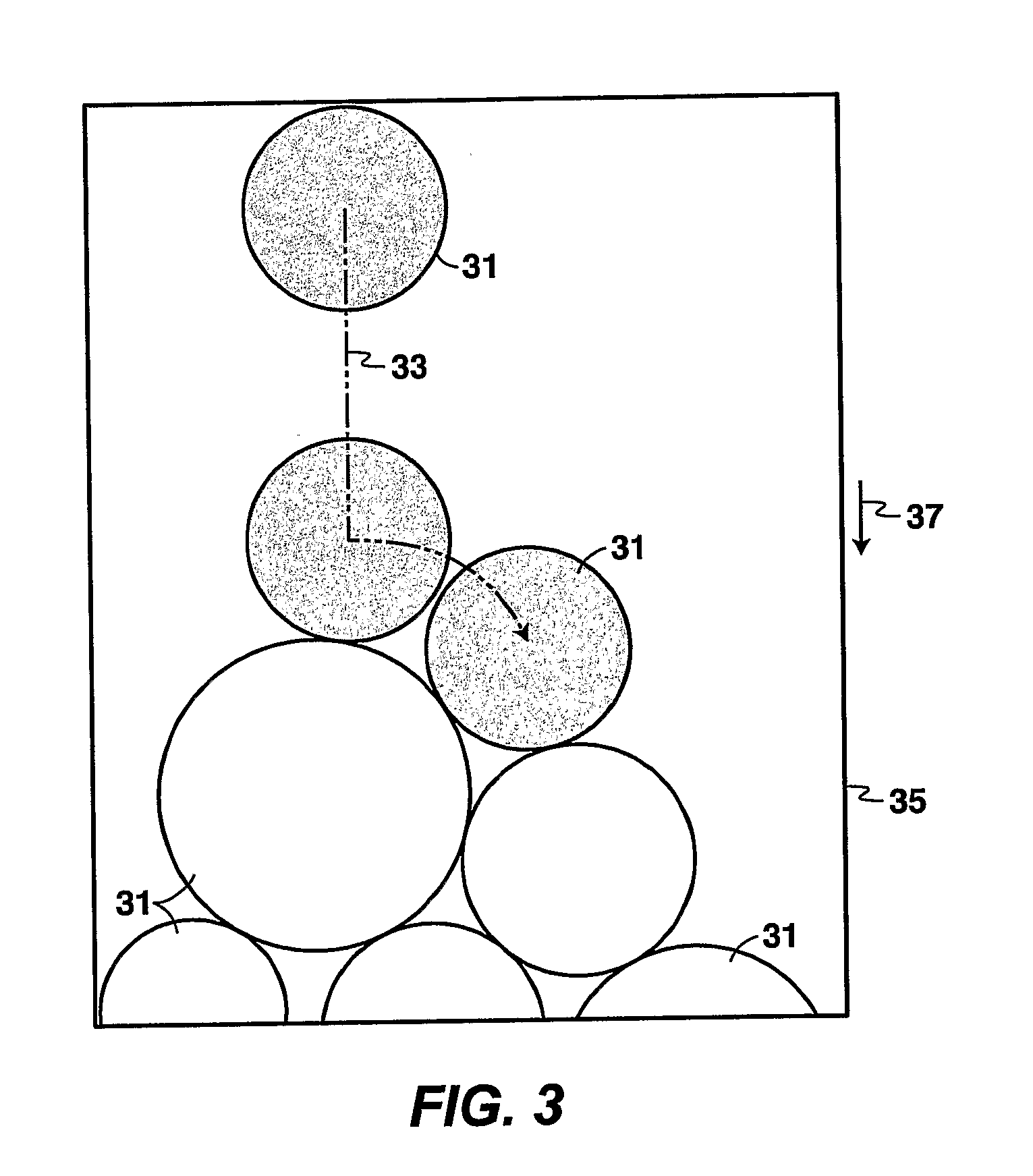
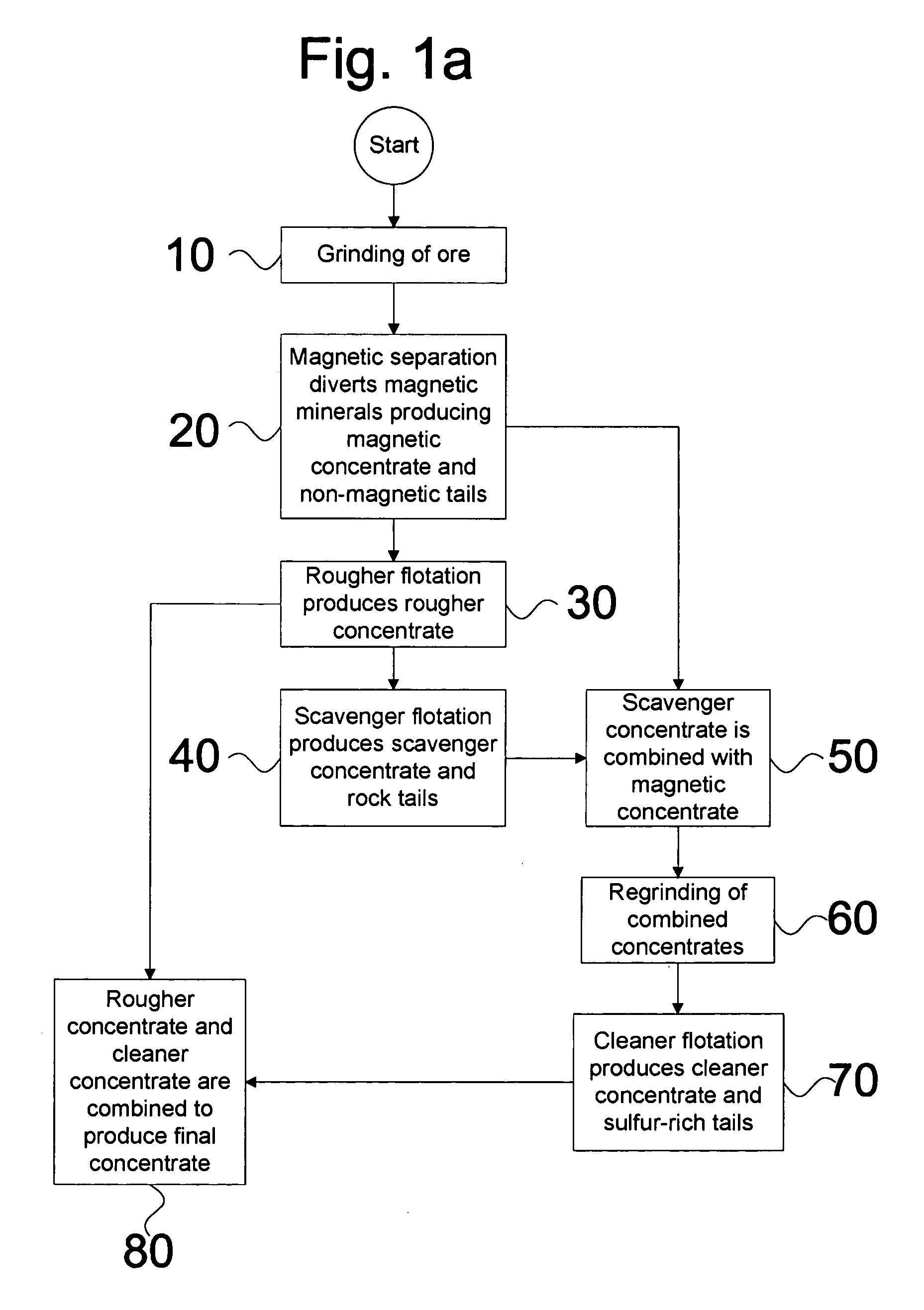
The invention is a method for simulating sandstone deposition. The sandstone is simulated by estimating the grain size distribution and mineral composition of grains in the sandstone, simulating sedimentation of grains from the grain size distribution and mineral composition of the grains, simulating compaction of the grains, and simulating cementation of the grains. Properties of the sandstone such as porosity and permeability may be estimated from the simulated sandstone. The method permits multiple mineralogies to be simulated during the burial history of sedimentation, compaction and cementation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method of removing arsenic species from an aqueous medium using modified zeolite minerals
InactiveUS6042731AComprehensive understandingHigh affinityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsArsenateMaceral
A method for removing arsenic species from an aqueous medium with modified zeolite minerals comprising providing an aqueous medium containing arsenic species in the form of both arsenate and arsenite, contacting the aqueous medium with an iron (II) laden zeolite mineral so that arsenic in the form of at least one of arsenate and arsenite contained in the aqueous medium can be adsorbed onto the iron (II) laden zeolite mineral forming an arsenic adsorbed iron (II) laden zeolite mineral, and separating the arsenic adsorbed iron (II) laden zeolite mineral from the aqueous medium.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIV OF ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF THE BOARD OF REGENTS A PUBLIC OF THE STATE OF FLORIDA
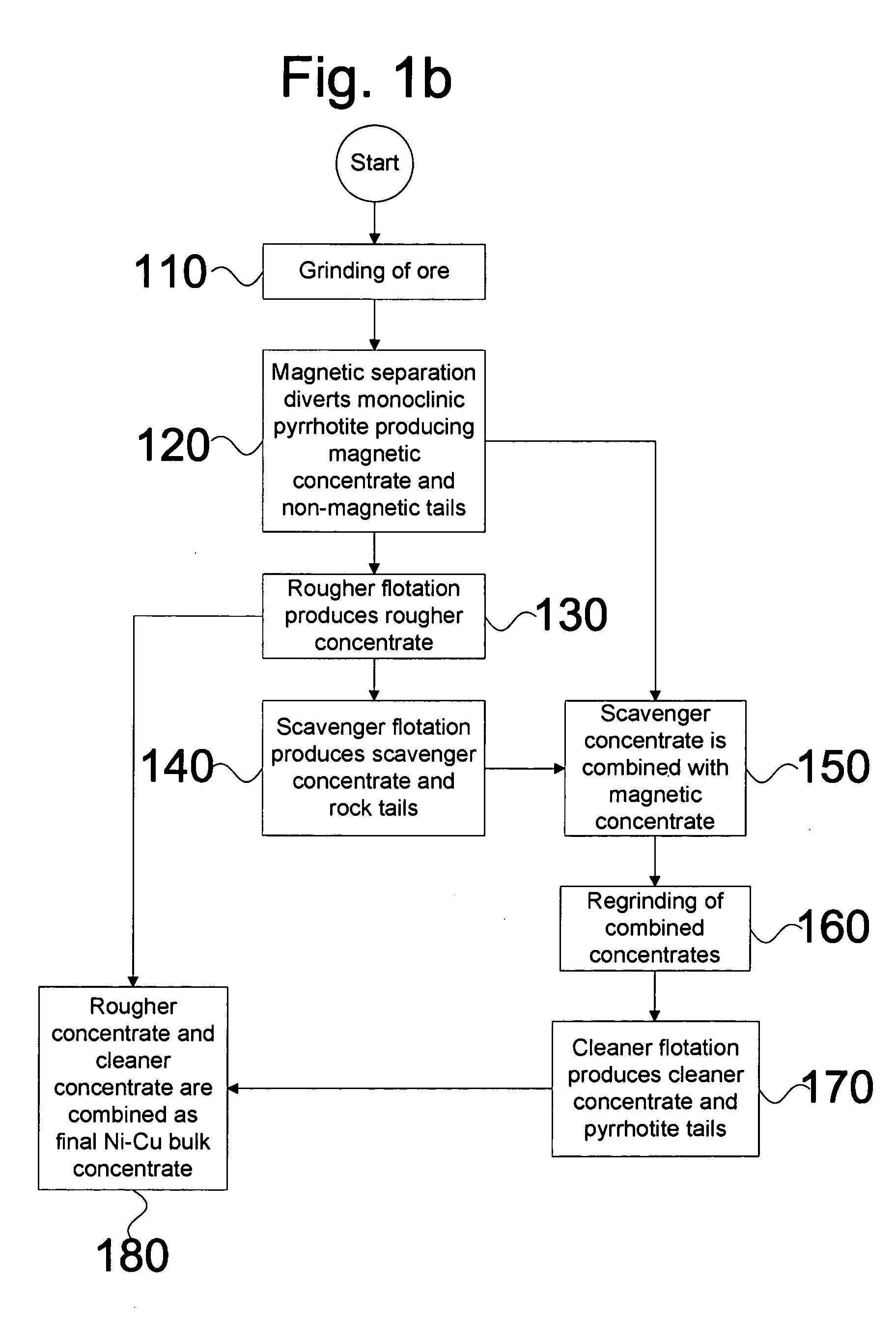
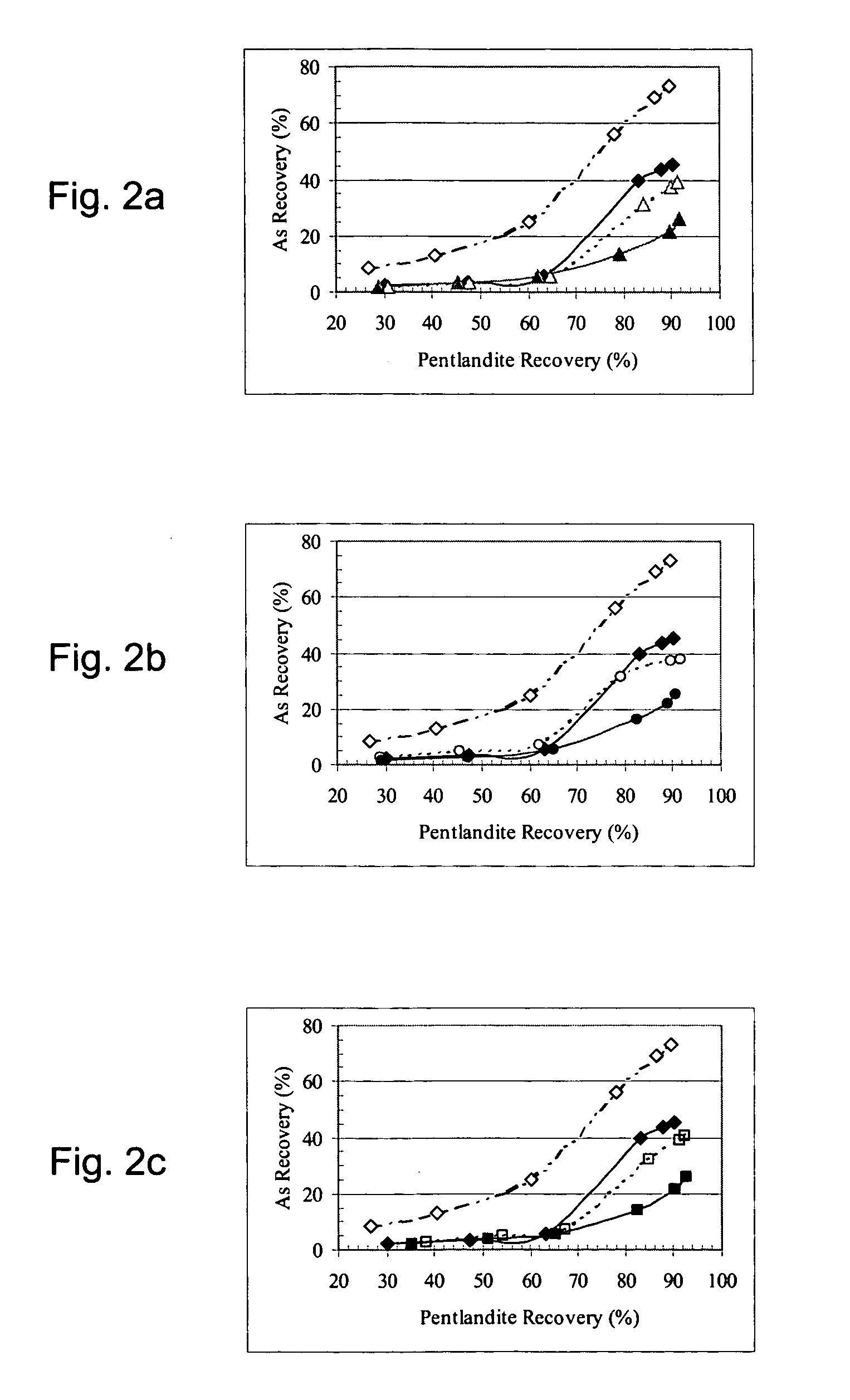
Arsenide depression in flotation of multi-sulfide minerals
A mineral separation process includes wet-grinding the ore to liberation of minerals, oxidizing the slurry using air, hydrogen peroxide or other oxidants and floating the valuable minerals at a pH between about 9.0 and 10.0 with a xanthate as collector, and a combination of a polyamine and a sulfur containing species as depressants for arsenide minerals. This depressant suite effectively depresses the flotation of arsenide minerals with no effect on the flotation of the valuable minerals.
Owner:INCO
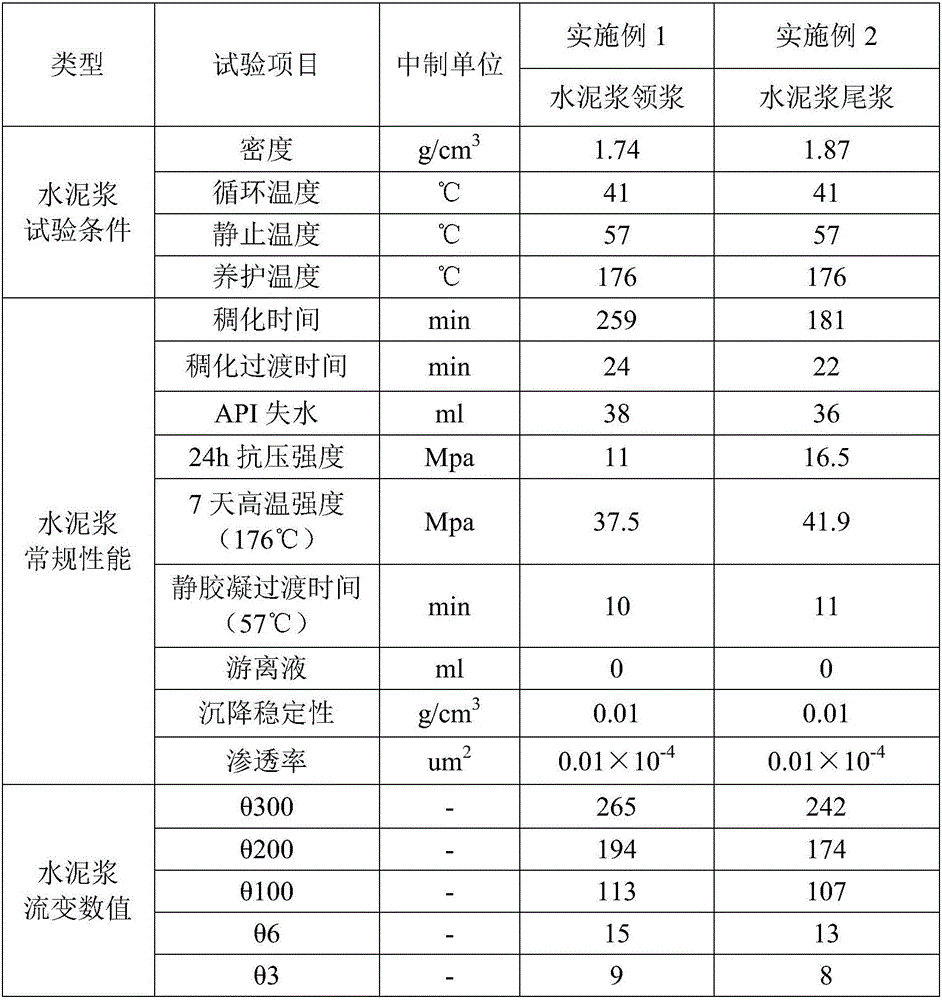
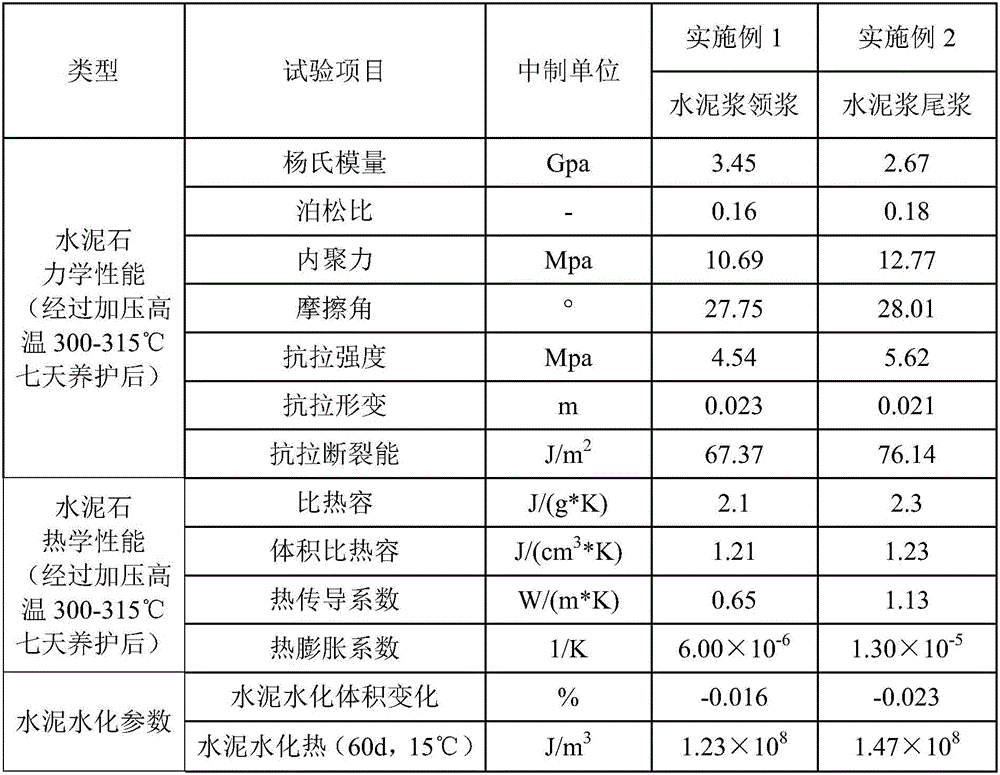
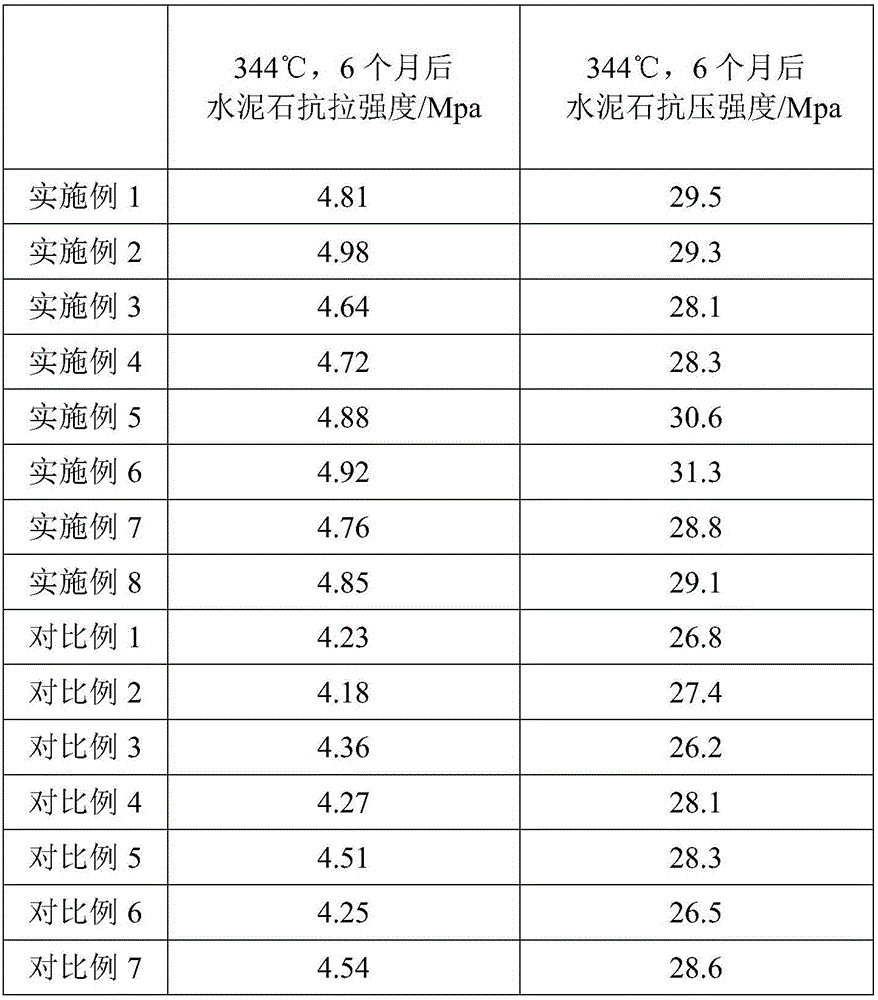
Cement slurry with long-term-integrity cement sheath for heavy-oil thermal-recovery well and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106007545AGuaranteed general performanceEnsure that the cement slurry system has conventional comprehensive performanceDrilling compositionFiberClay minerals
The invention provides a cement slurry with long-term-integrity cement sheath for a heavy-oil thermal-recovery well. The cement slurry comprises, by weight, 100 parts of thermally responsive cement, 25 to 65 parts of water and 0.2 to 8 parts of a cement slurry aid. The thermally responsive cement comprises 30 to 60 parts of oil well cement, 10 to 20 parts of active silicon powder, 0 to 10 parts of hollow glass beads and 10 to 50 parts of a thermally responsive composite material. The thermally responsive composite material comprises 20 to 30 parts of clay mineral, 10 to 20 parts of fly ash and / or vulcanic ash, 5 to 20 parts of rubber powder and / or latex powder, 3 to 10 parts of carbon fiber, 10 to 15 parts of nanometer silicon dioxide, 5 to 10 parts of calcined magnesia, 10 to 20 parts of ultrafine superfine slag powder and 5 to 10 parts of inorganic whiskers. The cement slurry provided by the invention can solidify at normal temperature; and set cement can resist long-term high temperature, and the mechanical properties and thermal properties of the set cement in a high temperature environment are integrally adaptive to strata and casing pipes.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
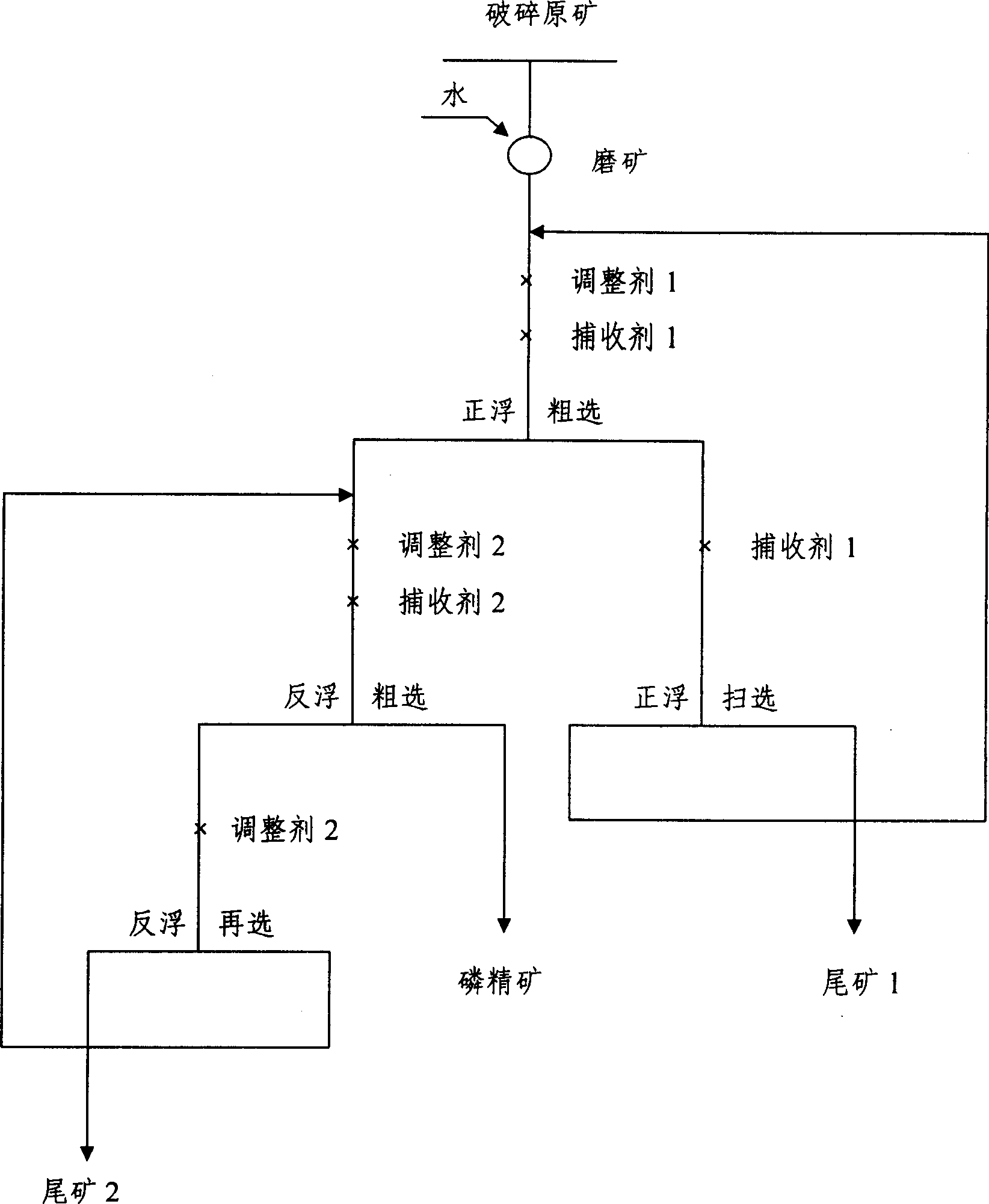
Collophanite direct flotation and reverse flotation technique
The invention relates to a positive-negative floatation technology for cellophane, which comprises the following steps: subjecting siliceous-calcareous collophane ore to breaking and grinding process to dissociate ore monomer; adding water to it get ore pulp with concentration of 20 -50%; Leading the mixture to agitated tank; adding modifying agent sodium silicate and positive collector agent to ore pulp; processing the mixture in positive floating system to get foamed product; adding negative floatation agent inorganic acid and collector agent to the foamed product in negative flotation agitated tank; processing the mixture in negative floating system with carbonate vein mineral negative flotation to get foamed product as negative flotation debris and product in tank as clean ore. The invention can simplify process, deduce cost and recycle the water.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Process for preparing biological diesel oil from waste animal and plant oil
InactiveCN1382762AEliminate emissionsSimple production processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockOil and greaseBiodiesel
A process for preparing biologic diesel oil from waste plant or animal oil includes alcoholysis and esterifying reactions under the existance of acidic catalyst, separating out the excessive non-product part to obtain coarse product, adding saturated equeous solution of edible salt containing sodium carbonate (10%), neutralizing reaction, adding industrial sodium carbonat4e, heating distillation and collecting the gas-phase fraction at 22-320 deg.C to obtain biologic diesel oil. Its advantages are high performance no pollution, and simple preparing process.
Owner:叶活动 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com