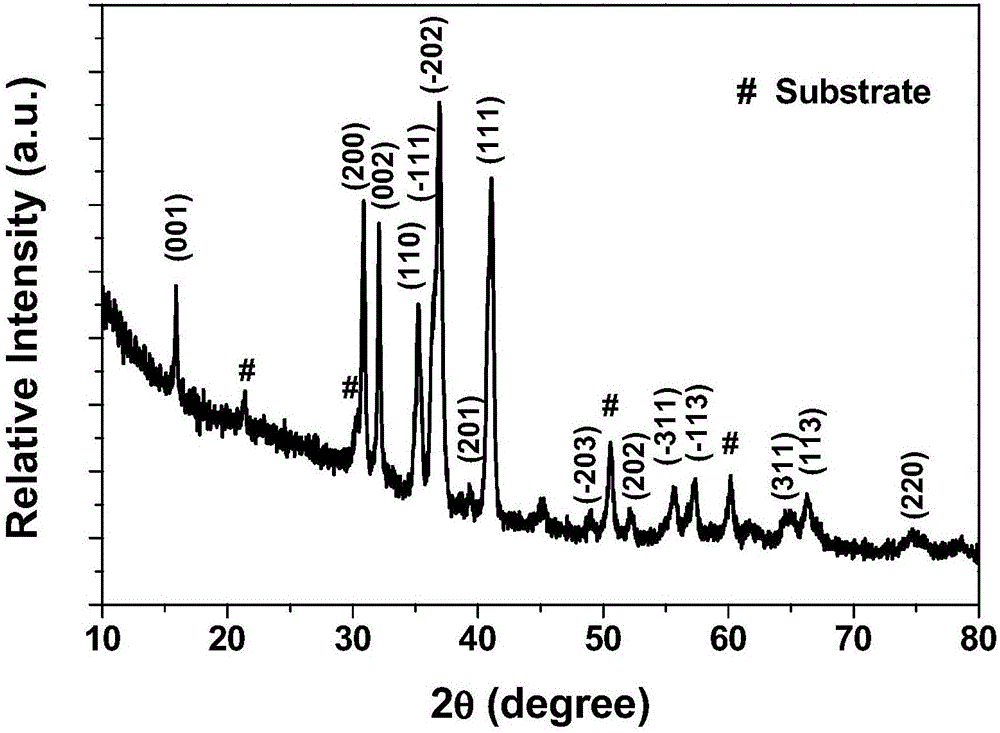
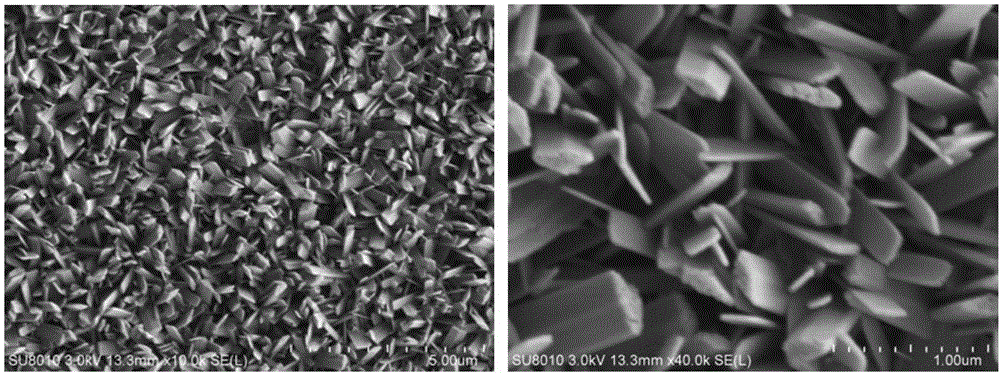
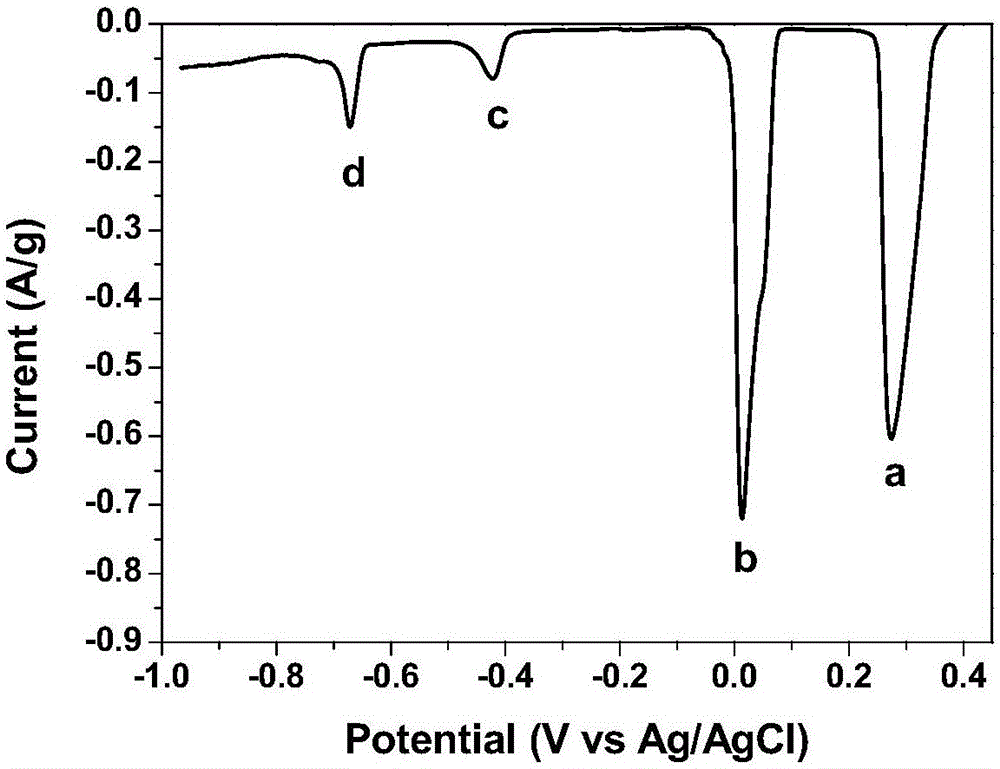
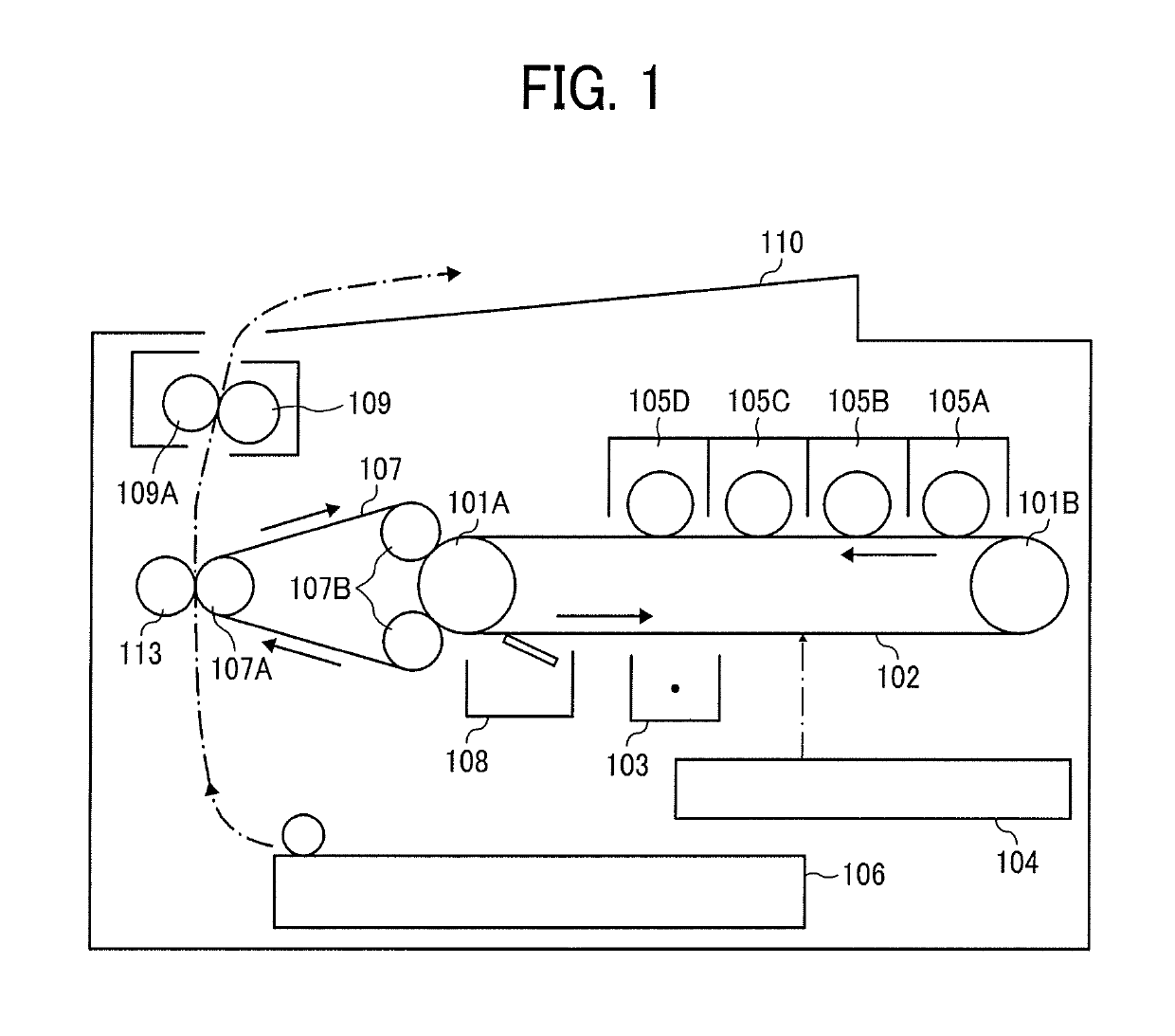
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Field emission scanning electron microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
FIELD EMISSION SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY (FESEM) An electron beam is focused and subsequently raster scanned over a small rectangular area. the beam interacts with the sample it creates various signals like secondary electrons, internal currents, photon emission, etc.), all of which can be appropriately detected.
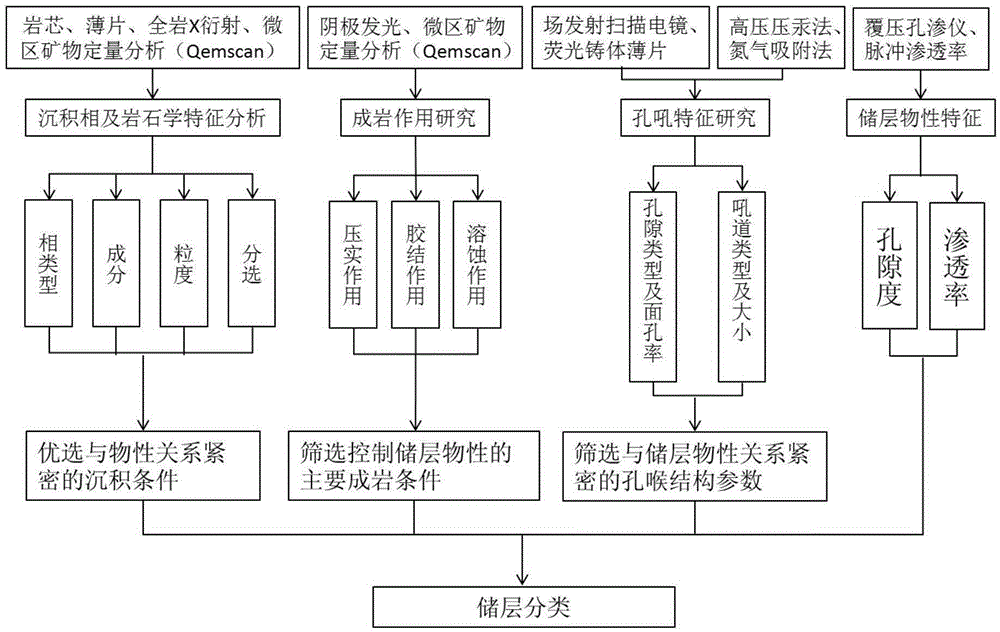
Micro-pore structure evaluation and reservoir classification method for tight reservoirs
InactiveCN105334149ASolve the problem of observationDetermining the cause of densificationEarth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityFluorescence
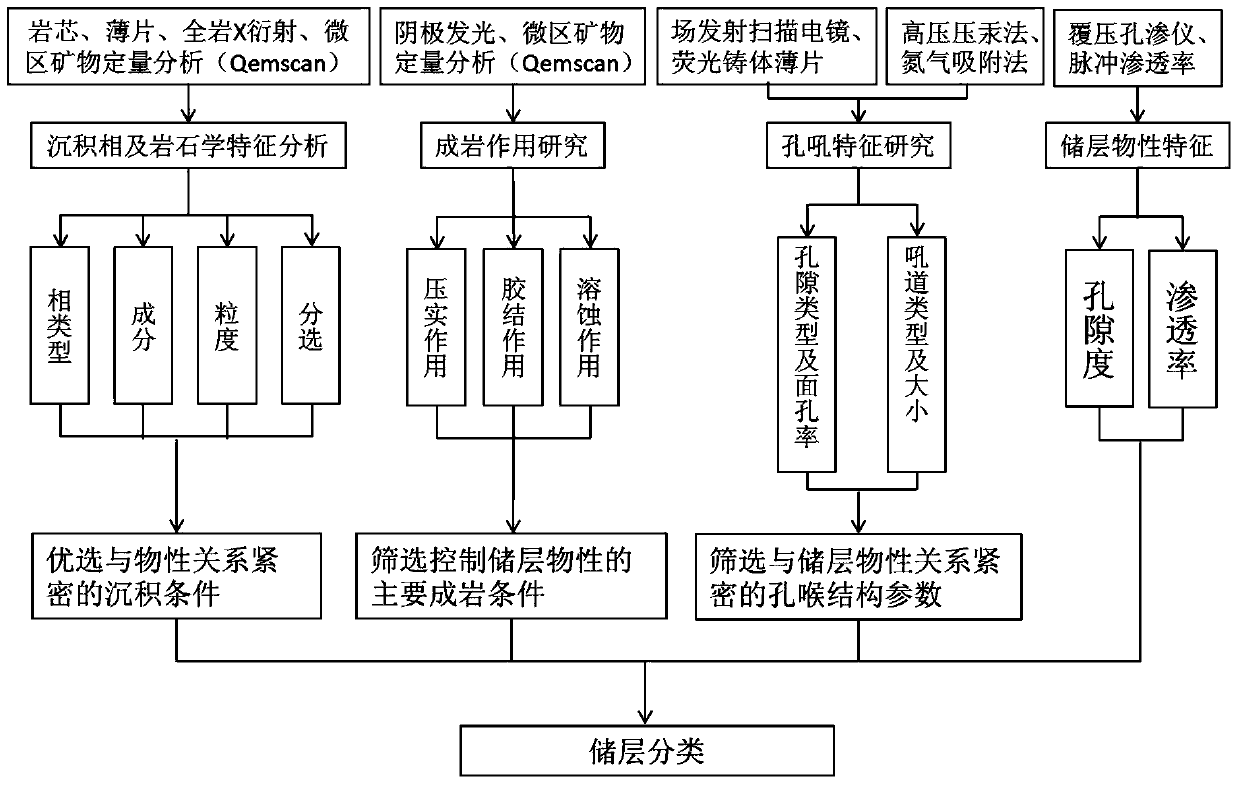
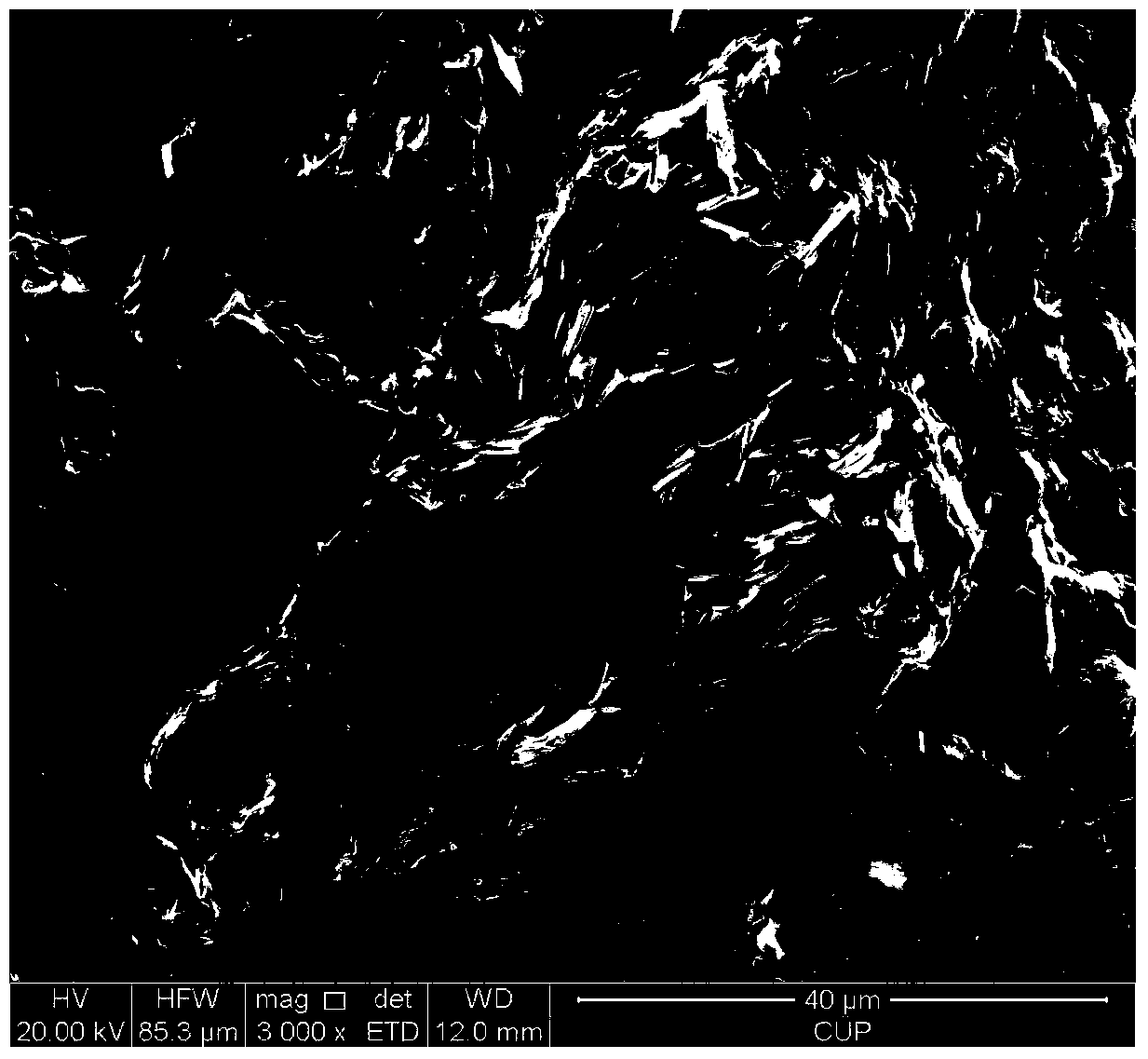
The invention provides a micro-pore structure evaluation and reservoir classification method for tight reservoirs. The method comprises steps as follows: the origin and the petrologic features of each reservoir are analyzed, and the phase type, the content and the like of each reservoir are determined; physical features of each reservoir are analyzed; features of a reservoir space of each reservoir are observed, and the pore type, the surface porosity and the like are determined; pore structure parameters of the reservoirs are measured with a high-pressure mercury intrusion method and a nitrogen adsorption method; the diagenesis is researched, and compaction, cementation and corrosion sequences are determined; physical property control factors of the reservoirs are analyzed; the reservoirs are classified. The method mainly has the effects as follows: the diagenesis and the influences of the diagenesis on the reservoirs are comprehensively reflected through cathode luminescence and micro-area mineral quantitative analysis; micro pores of the tight reservoirs are researched elaborately through fluorescent casting and field emission scanning electron microscopy; the microscopic features of the tight reservoirs are determined accurately through high-pressure mercury intrusion experiments and the nitrogen adsorption experiments; the parameters are optimized for classification and evaluation of the reservoirs, and the method has a great significance in further prediction of beneficial developing stratums or zones.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Diagenetic evolution simulation experiment method for mud shale
The invention discloses a diagenetic evolution simulation experiment method for mud shale and belongs to the field of petroleum exploration and development. The diagenetic evolution of a mud shale reservoir is simulated by using the experiment method, and the problem of evolution of organic matters, mineral components and pores in the mud shale reservoir is solved. The method comprises the following main experiment steps: (1) preparing a sample; (2) performing thermal simulation, (3) collecting and analyzing oil gas; (4) performing experiment sample after-treatment; (5) performing different scales and different ways of comprehensive observation research on the evolution of the organic matters of the sample, the diagenesis of inorganic minerals and the development situation of the pores by utilizing a common polarizing microscope, a fluorescent microscope, a laser scanning confocal microscope, a cathode luminescence microscope and a field emission scanning electron microscopy. The method is used for researching the diagenetic evolution of the mud shale reservoir and determining the evolution characteristics of the organic matters, the mineral components and the pores with different lithofacies, different organic matter types and different organic matter maturity stages in the mud shale reservoir, and plays an important role in research of the characteristics of the mud shale reservoir and the characteristics of an oil-gas enrichment rule.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
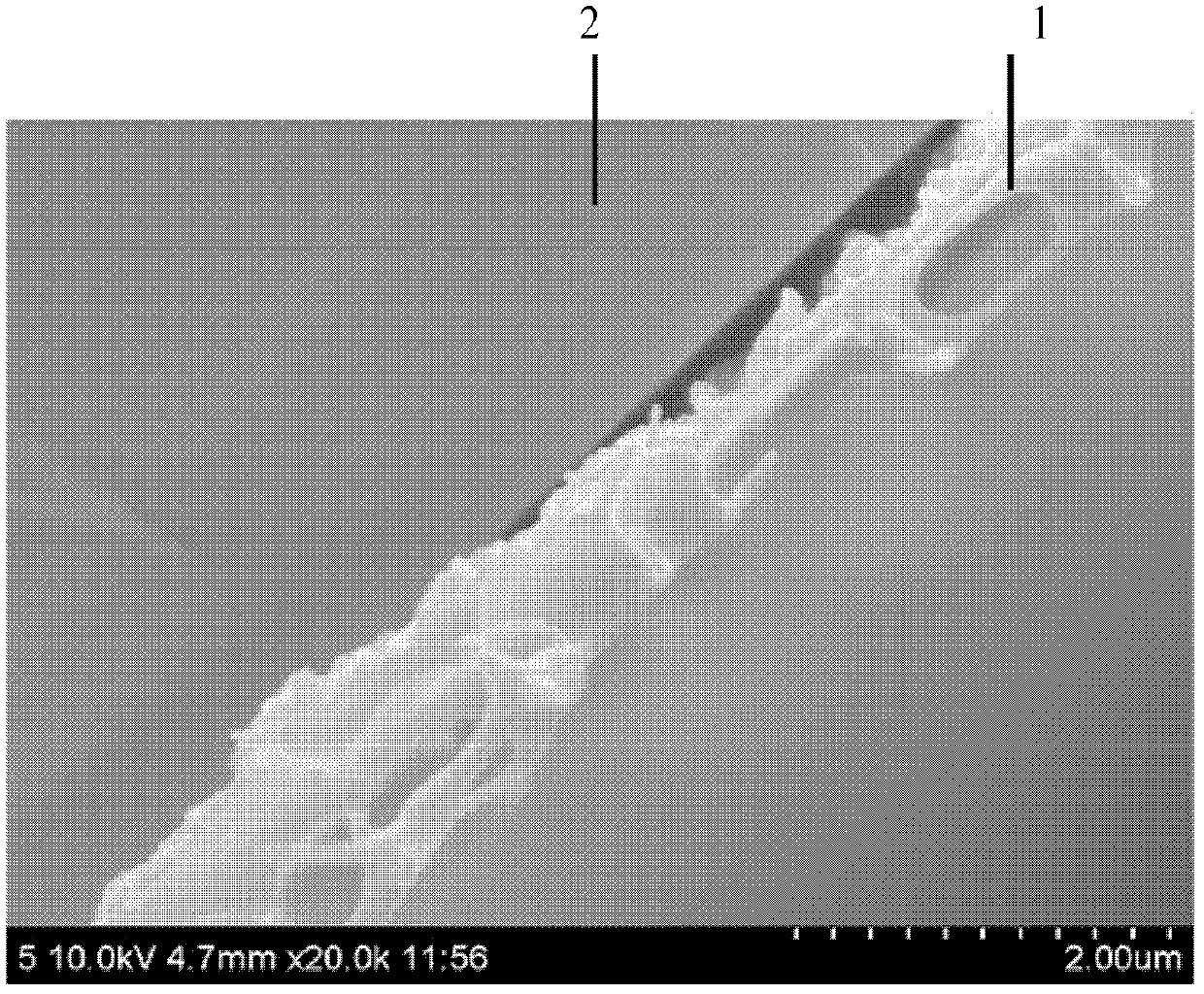
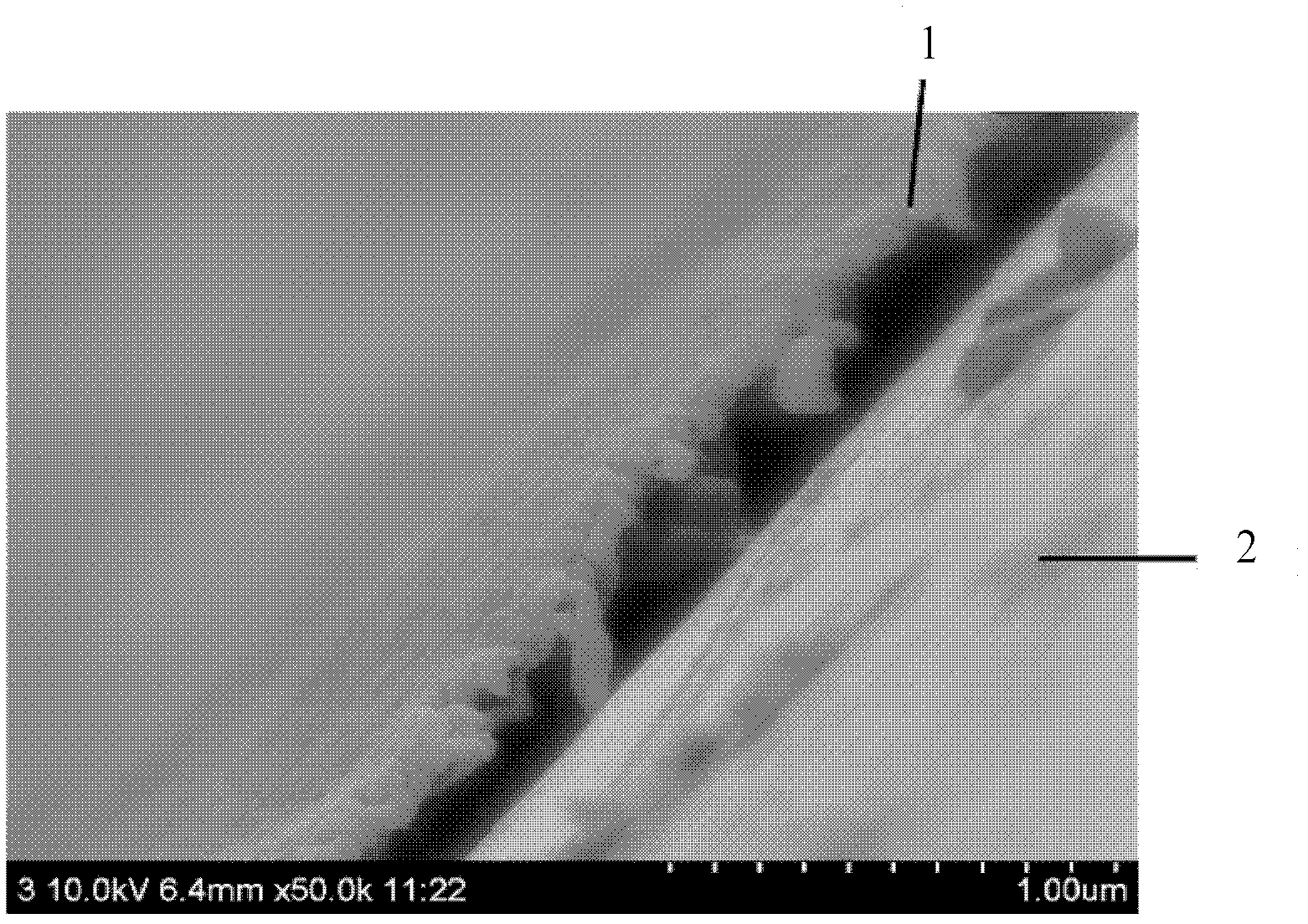
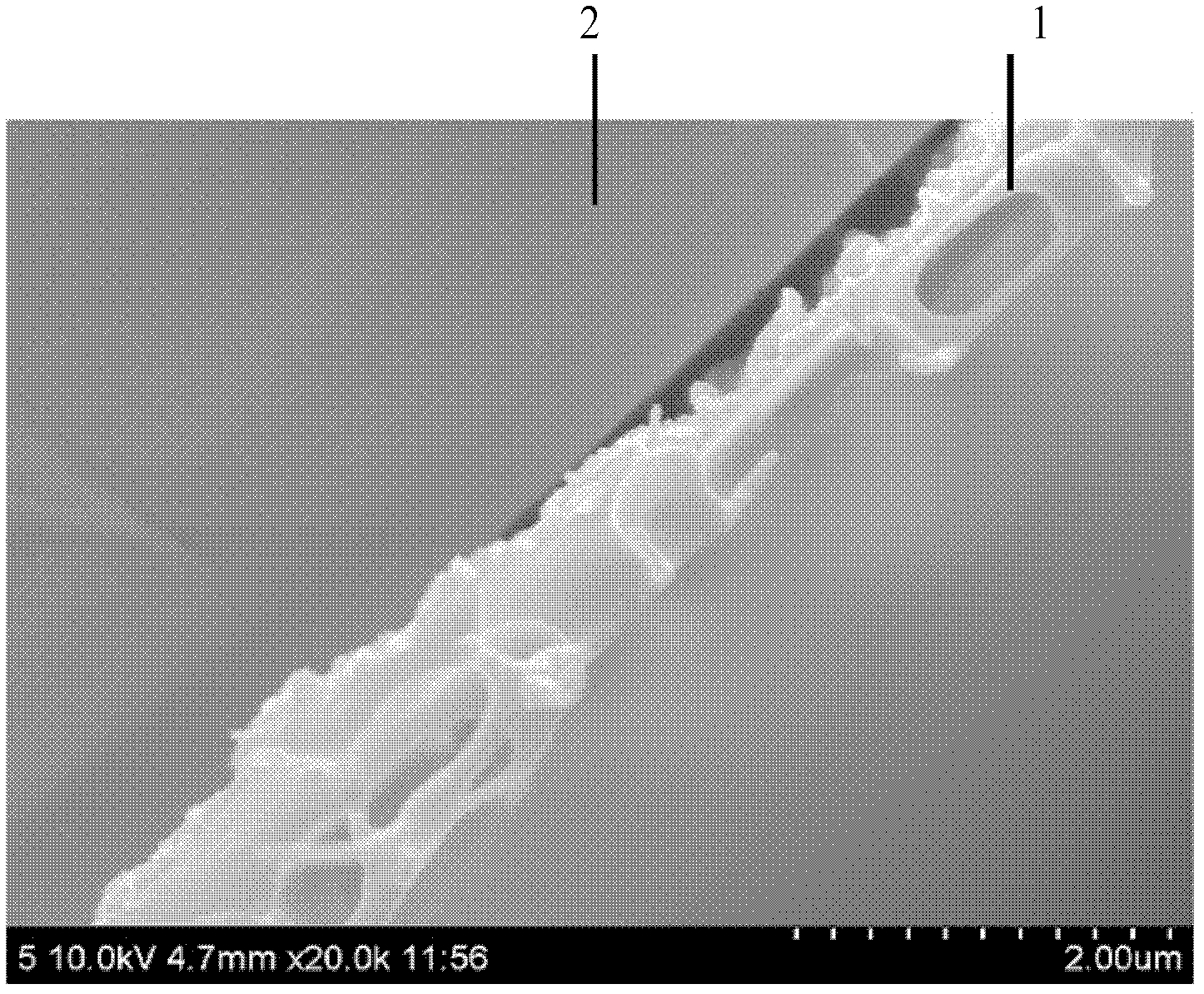
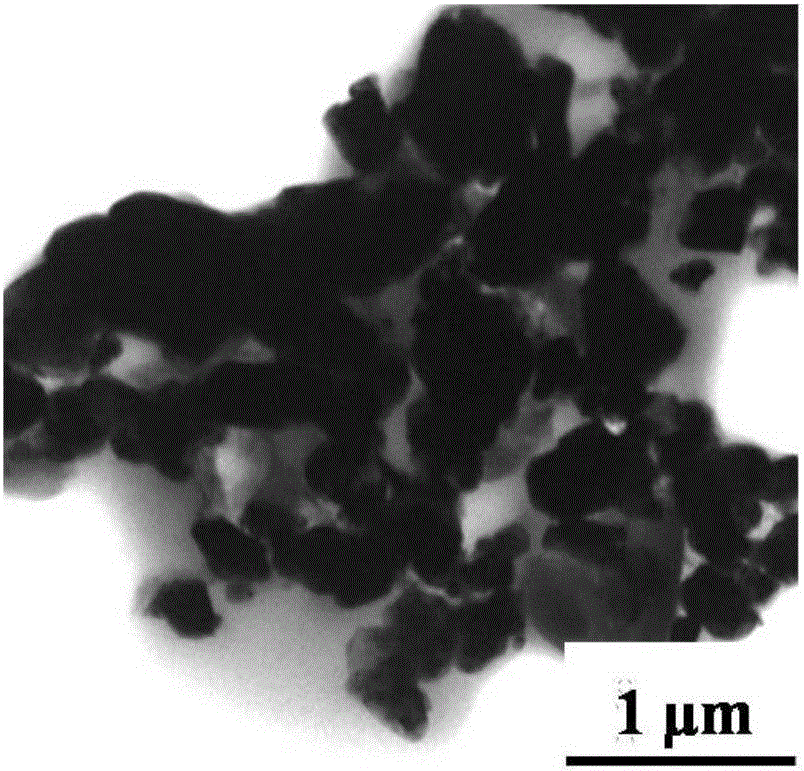
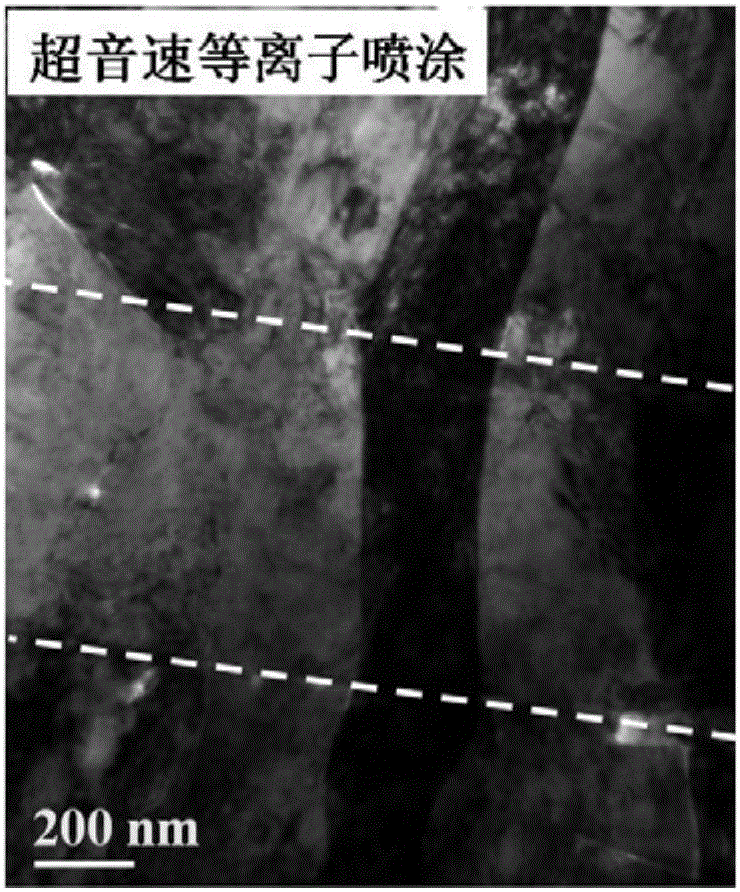
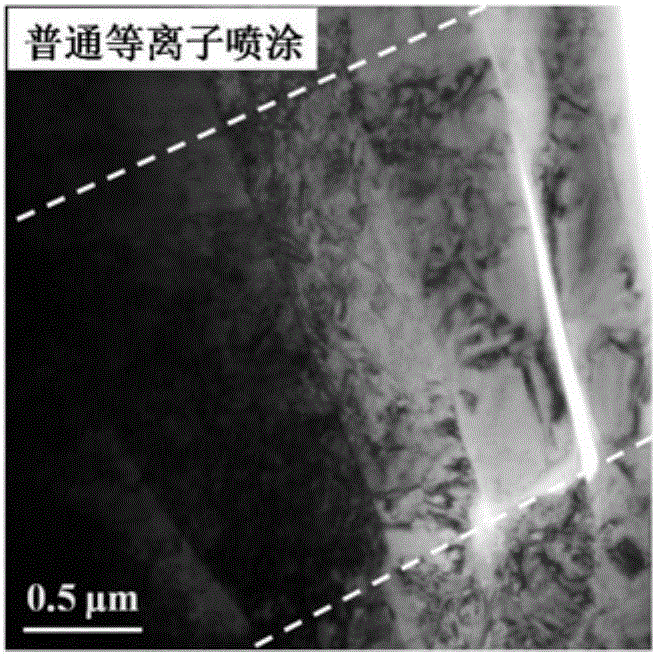
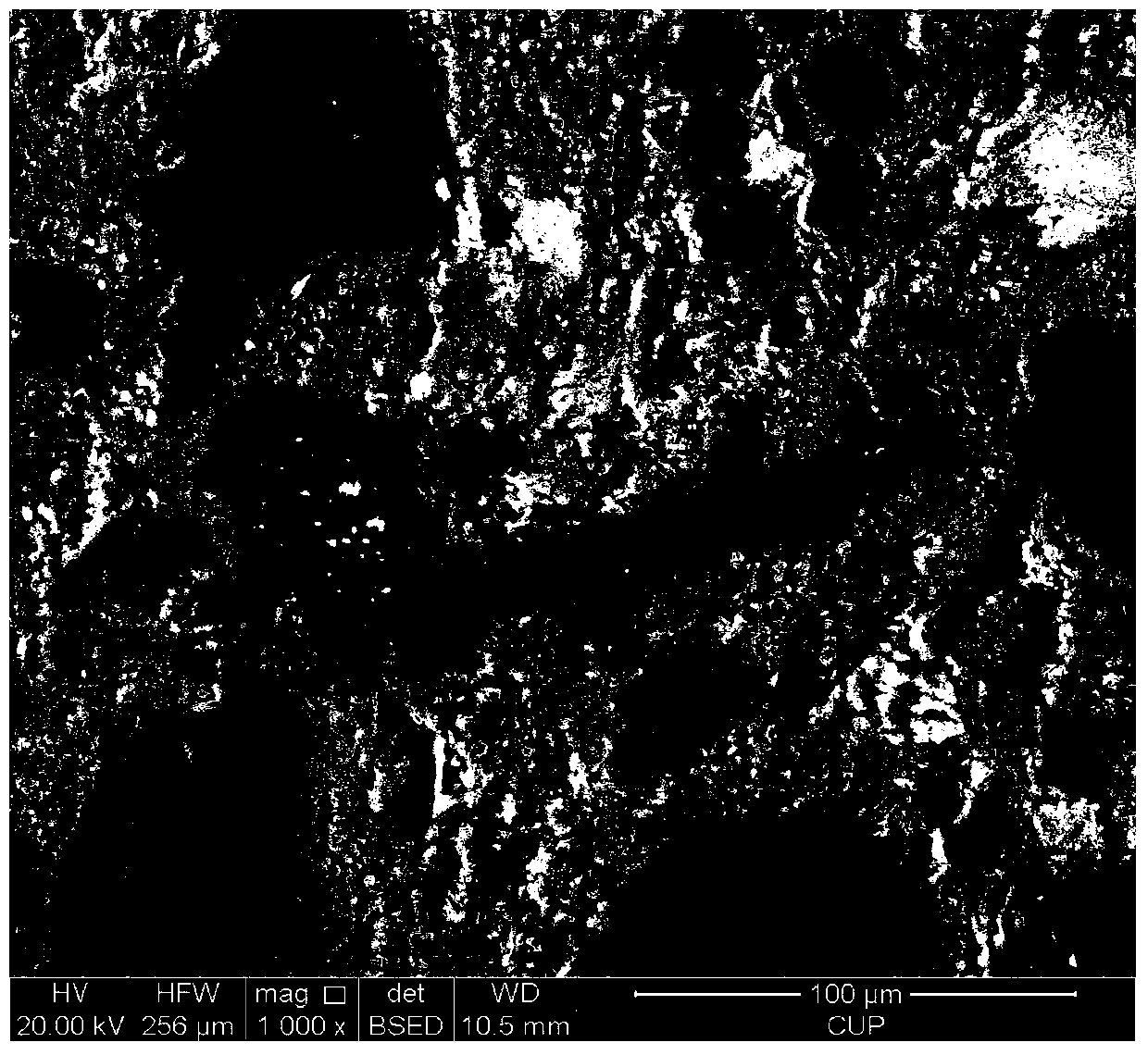
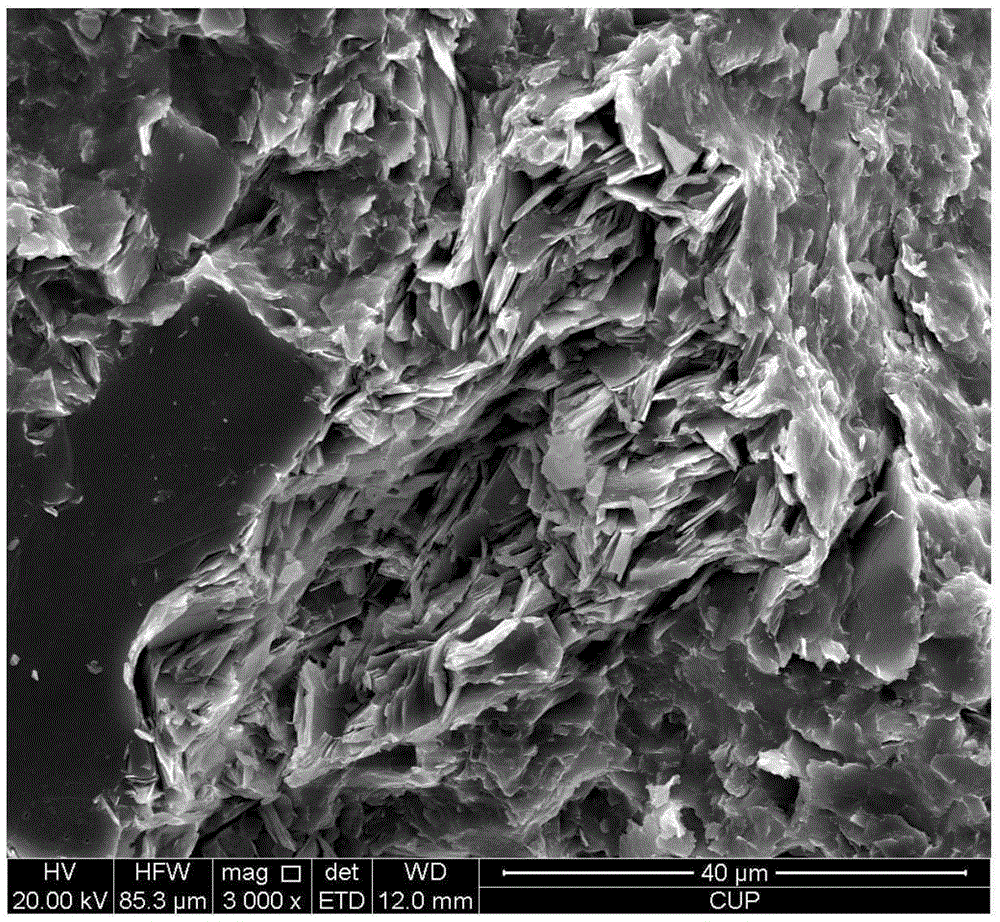
Experimental method for electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure
InactiveCN110186919AImprove performanceReduce energy consumptionAdditive manufacturing apparatusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPower flowExperimental methods
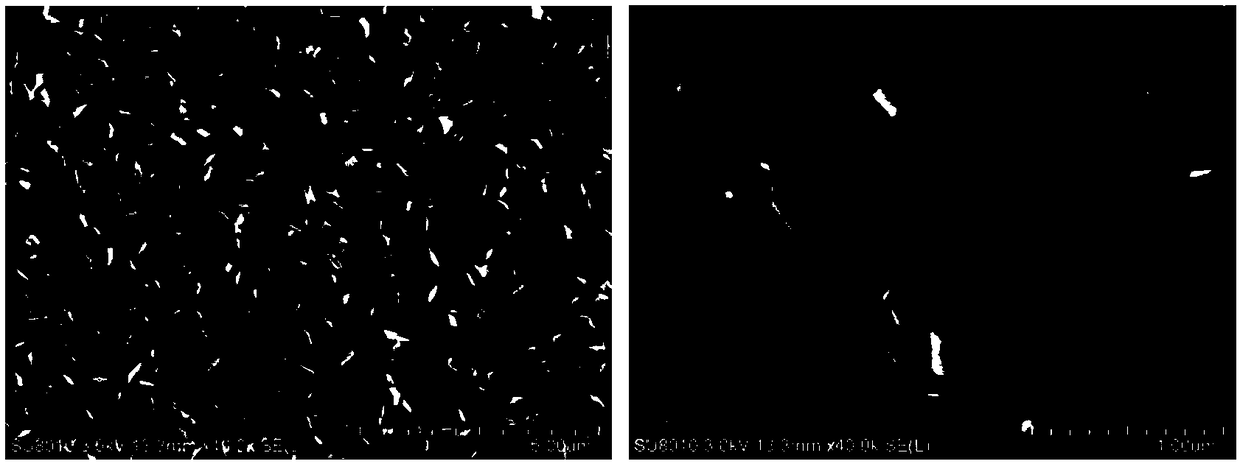
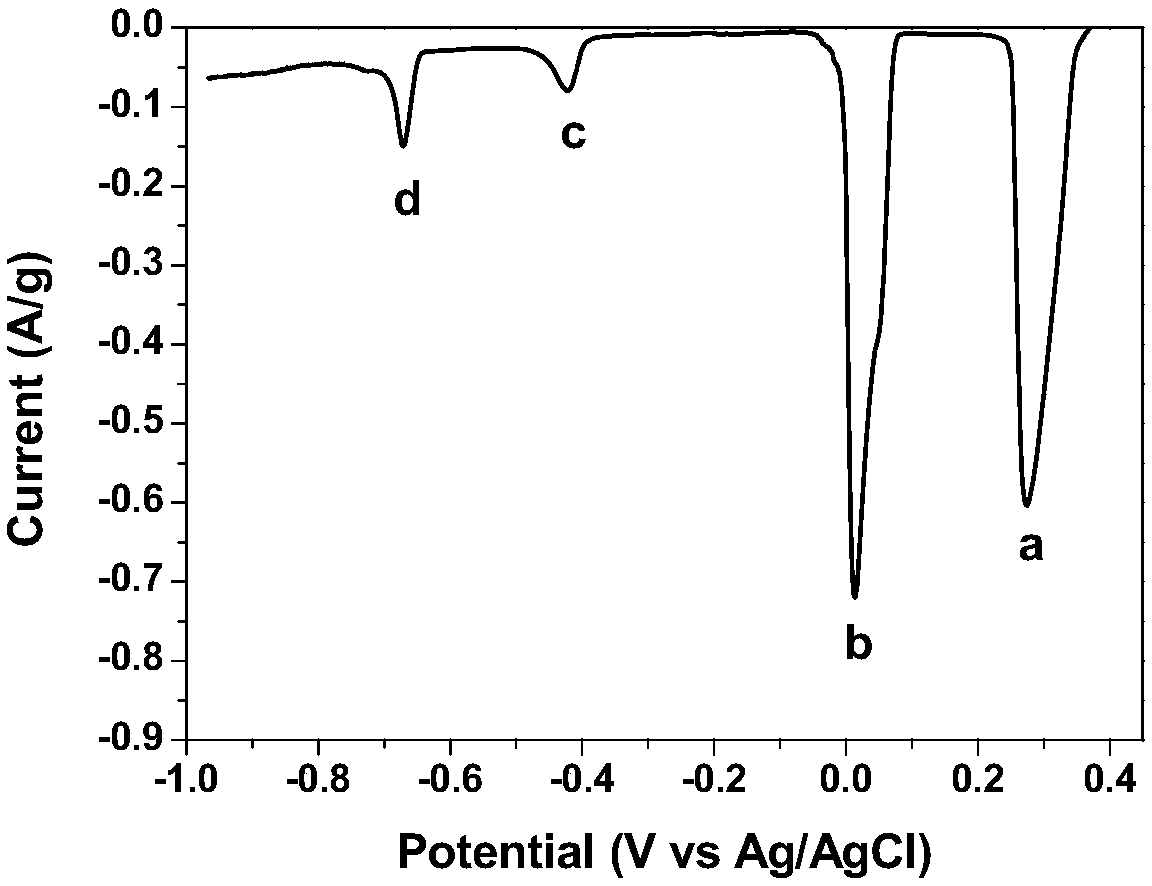
The invention discloses an experimental method for an electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure. The experimentalmethod comprises the following steps that: 1) through additive manufacturing, obtaining a cubic titanium alloy, processing a cylindrical titanium alloy sample of which two end surfaces are flat, and finally, polishing to remove an oxidation layer on the surface of the titanium alloy sample; 2) independently enabling tow end surfaces of the polished titanium alloy sample to be in complete contact with two electrodes of electric pulse processing equipment, regulating the current and the acting time of the electric pulse processing equipment, and carrying out electric pulse processing on the titanium alloy sample; and 3) cutting the titanium alloy sample subjected to the electric pulse processing, through a hot inlay method to prepare a metallographic specimen, polishing, buffing, cleaning and corroding the surface of the metallographic specimen, and utilizing a metallographic microscope and a field emission scanning electron microscopy to represent and analyze the change of an [Alpha] phase and a [Beta] phase before and after electric pulse processing. By use of the method, the additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure is changed and verified with small energy consumption and short time consumption, and the combination property of the additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
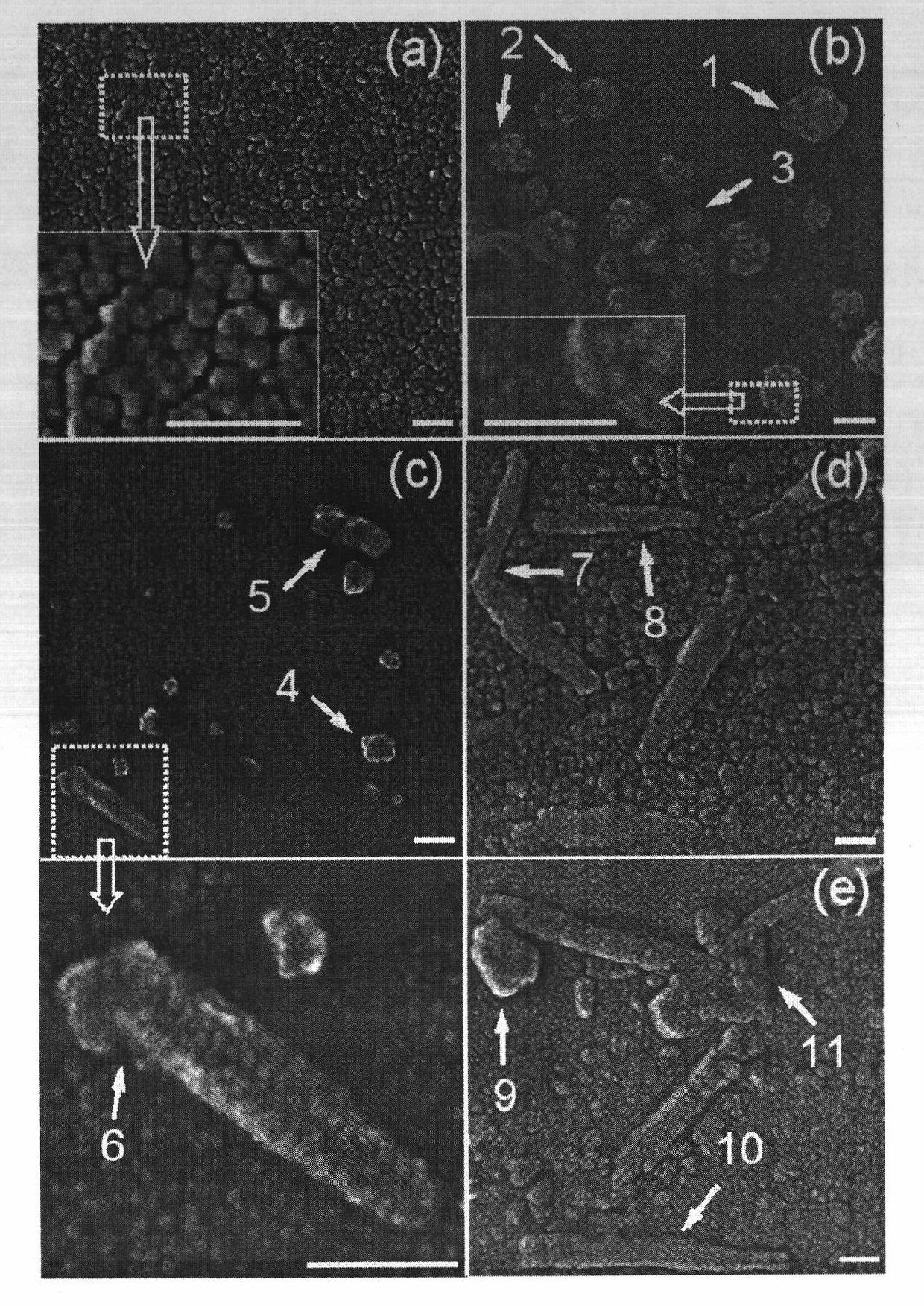
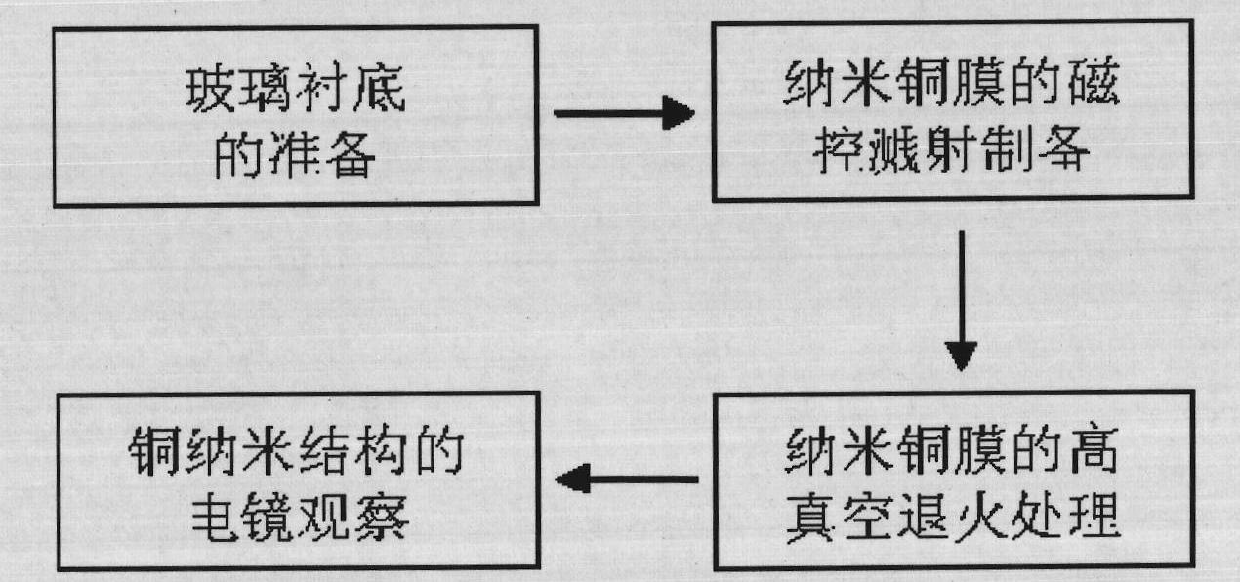
Preparation method of nano copper film-based copper nano structure
InactiveCN101949004AAchieve synthesisRealize the assemblyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNano structuringRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano copper film-based copper nano structure, which relates to a preparation and assembly method of a nano structure. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning glass substrates, placing in a magnetron sputtering chamber, depositing a nano copper film of an appropriate thickness at room temperature, slicing the glass substrates into multiple pieces, carrying out high vacuum annealing of different time lengths, controlling the annealing time to directly form copper nano structures of various shapes on the surface of the nano copper film, and using a field emission scanning electronic microscope to photograph and record the surface topography of the nano copper film in multiple positions on one glass substrate so as to obtain the characteristics of the typical nano copper film and the copper nano structure on the surface thereof. From the perspective of nano curvature effect and thermal activation effect for the first time, the invention realizes the direct controllable preparation of various nano copper film-based copper nano structures on the surface of the nano copper film by carrying out annealing of different time lengths on the nano copper film of an appropriate thickness.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing nanometer CeO2/Zn (cerium oxide/zinc) metal-based composite material in zinc galvanizing layer
InactiveCN104550981AUniform structureImprove performanceHot-dipping/immersion processesNanotechnologyCeriumSteel ball
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nanometer CeO2 / Zn (cerium oxide / zinc) metal-based composite material in a zinc galvanizing layer. The method comprises the following steps of mixing a pure Zn powder with granularity of 47-100m and a CeO powder with average granularity of 30nm according to the weight ratio of 8:1 (wt%), and performing ball milling in a self high-efficiency ball milling machine; using stainless steel balls with diameters of 3mm, 6mm and 10mm as ball milling mediums, wherein the proportion of the three types of steel balls is 3:6:10, and the ratio of ball materials is 30:1 (wt%); before ball milling, sucking vacuum, performing ball milling on the mixed powder under the argon protecting state, setting the rotation speed of the ball milling machine as 120r / min, and sampling after different times. The method has the advantages that the high-efficiency ball milling and the powder metallurgical sintering are the effective methods for preparing the nanometer CeO2 / Zn composite material; after detecting by XRD (X-ray diffraction) and FESEM (field emission scanning electron microscopy), the new alloy phase is not generated in the ball milling and hot pressing sintering processes, namely that the nanometer CeO2 / Zn and Al composite material is obtained; the structure is uniform, and the property is stable.
Owner:QINGDAO HEDELONG MACHINERY
Method for detecting microstructure of reverse osmosis membrane separating layer
InactiveCN102302900AObserving the microstructureThe pre-processing process is simpleSemi-permeable membranesSolubilityOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for detecting a microstructure of a reverse osmosis membrane separating layer. The method comprises the following steps of: completely peeling a non-woven layer of a reverse osmosis membrane sheet; remaining a separating layer and a supporting layer and flatly paving the separating layer and the supporting layer on a glass sheet and adhering the separating layer and the supporting layer to the glass sheet, so that the supporting layer is upward and the separating layer contacts with the glass sheet; according to the solubility difference between the separatinglayer and the supporting layer, dissolving and removing the supporting layer by selecting a proper volatile organic solvent; removing the organic solvent from the separating layer through vacuum drying; cutting the glass sheet with the separating layer into small blocks according to the size of a scanning electronic microscope sample platform; spraying gold; and observing the microstructures of the reverse side and the section of the separating layer by using a field emission scanning electronic microscope. By the method, the microstructures of the reverse side and the section of the separating layer of the reverse osmosis membrane can be observed clearly. The method is simple in pretreatment process of samples, low in cost, high in operability and easy in popularization. By the method, the microstructures of the reverse side and the section of the separating layer of the reverse osmosis membrane can be observed by using the scanning electronic microscope at home and abroad.
Owner:TIANJIN SEA WATER DESALINATION & COMPLEX UTILIZATION INST STATE OCEANOGRAPHI
Preparation method of YSZ thermal barrier coating of sheet micro-nano column crystal structure
InactiveCN105970145AIncrease cooling rateImprove structural stabilityMolten spray coatingEfficient propulsion technologiesMicroscopic scaleSupersonic speed
The invention discloses a preparation method of a YSZ thermal barrier coating of a sheet micro-nano column crystal structure. The average thickness of laminated structures (or spreading sheets) formed in different embodiments is measured, so that the thickness of each spreading sheet of the obtained supersonic speed plasma spray coating is approximately one third that of a common plasma spray coating. The structure of the supersonic speed plasma spray coating is represented through a field emission scanning electronic microscope, so that a double-mode microstructure with submicron crystals and nanocrystals coexisting therein appears inside each spreading sheet; and the content of different submicron crystals and nanocrystals inside each spreading sheet is further disclosed through a thermal etching displaying method and a quantitative statistic method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing cathode material AgCuO2 through anodic oxidation electrodeposition
InactiveCN106637332ASimple and fast operationLow costElectrolytic inorganic material coatingCell electrodesWater bathsThin film electrode
The invention discloses a method for preparing cathode material AgCuO2 through anodic oxidation electrodeposition. The method is characterized in that in strong alkaline mixed electrolyte, ammonia water and Ag + are complexed and ammonia water and Cu2 + are complexed through an anodic electrodeposition method, constant current electrodeposition is carried out in a water bath at the temperature of 40 DEG C, an AgCuO2 thin film electrode which has the sheet-like morphology and is deposited on ITO conductive glass is obtained in a short period of time, and then tests of X-ray powder diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy representation and a discharging experiment in an alkaline solution are conducted on the deposited AgCuO2 thin film electrode. The method has the beneficial effects that the used raw materials are low in cost, equipment is simple, operation is easy, convenient and fast, and meanwhile the environmental friendliness is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
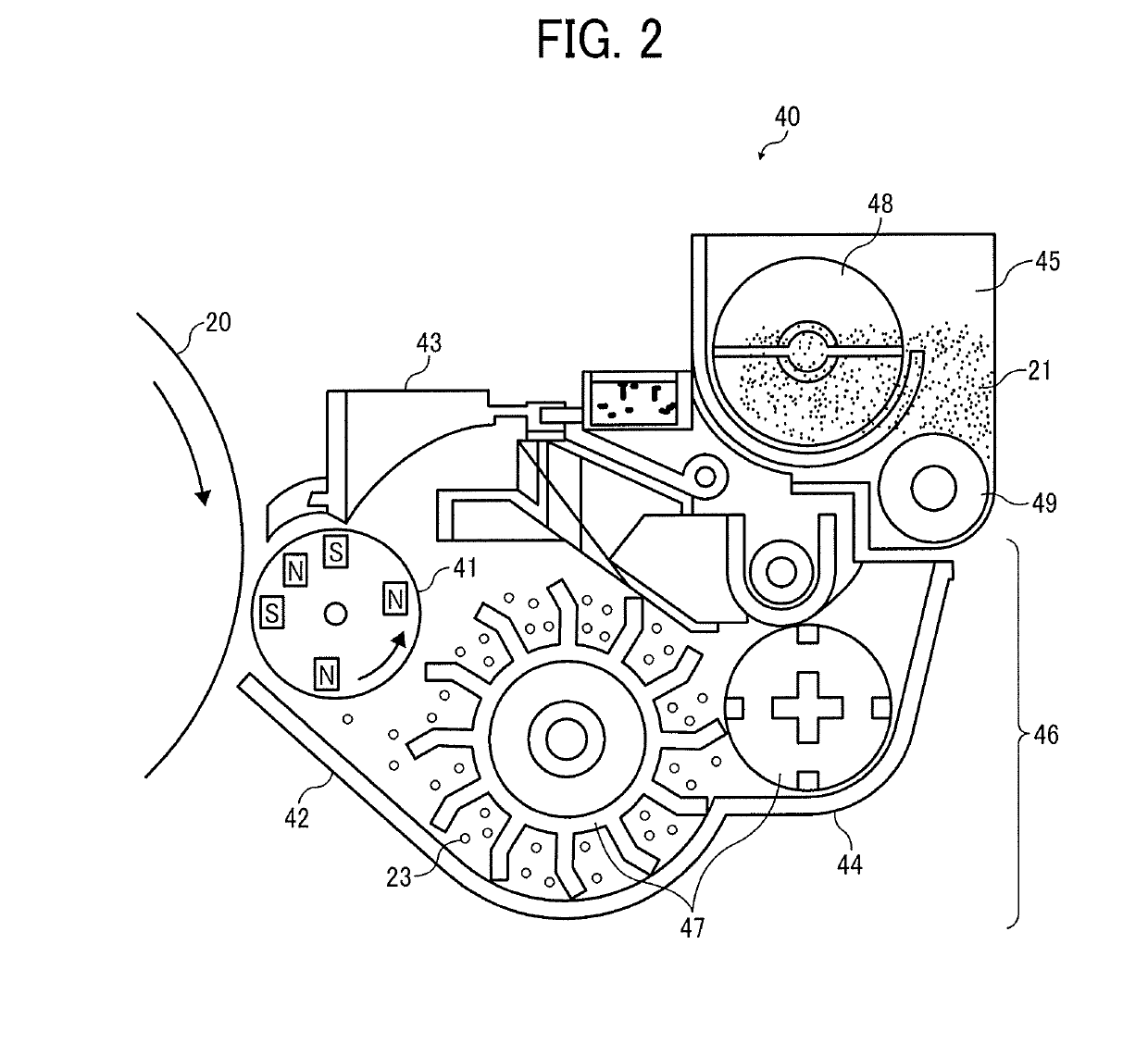
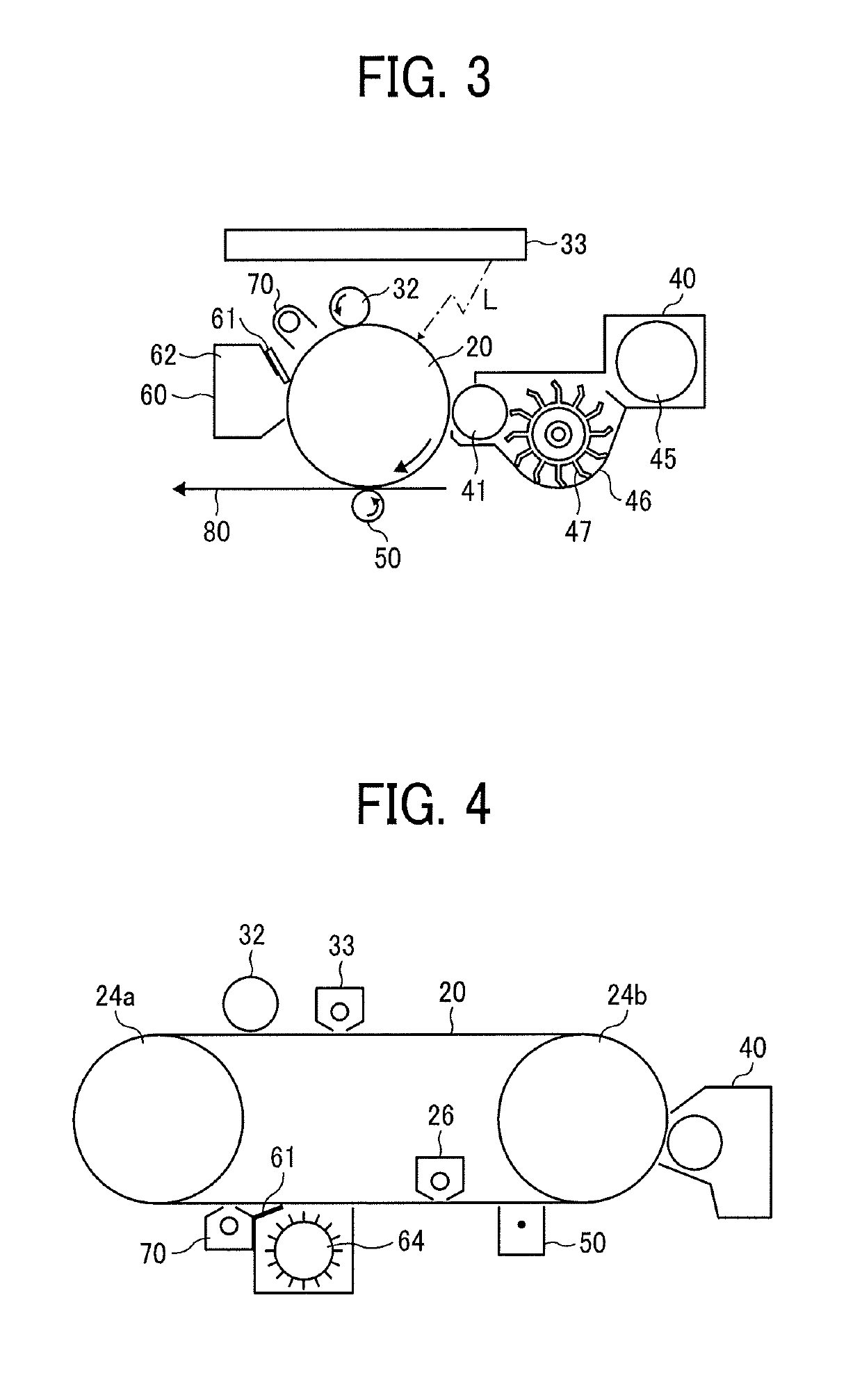
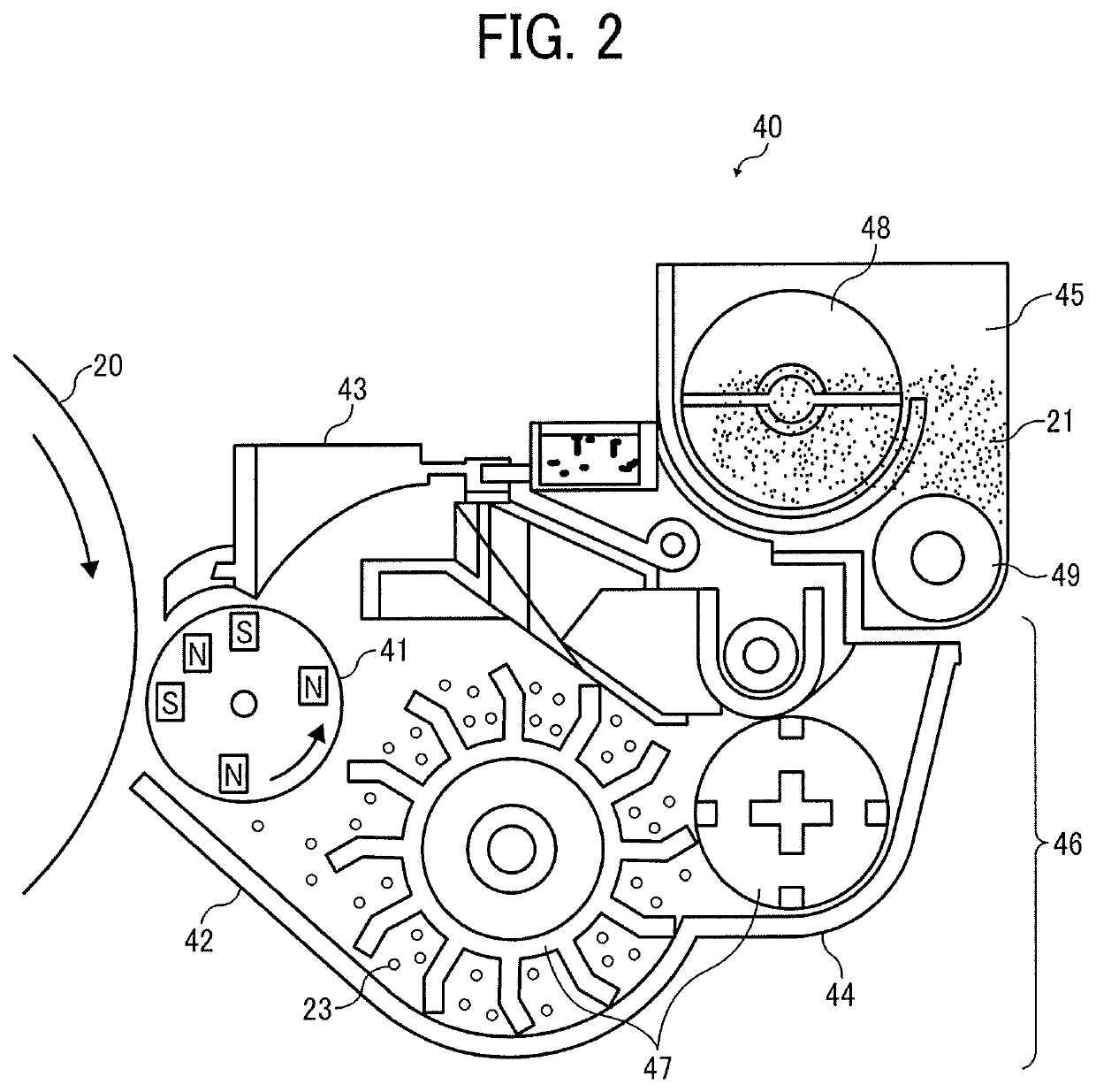
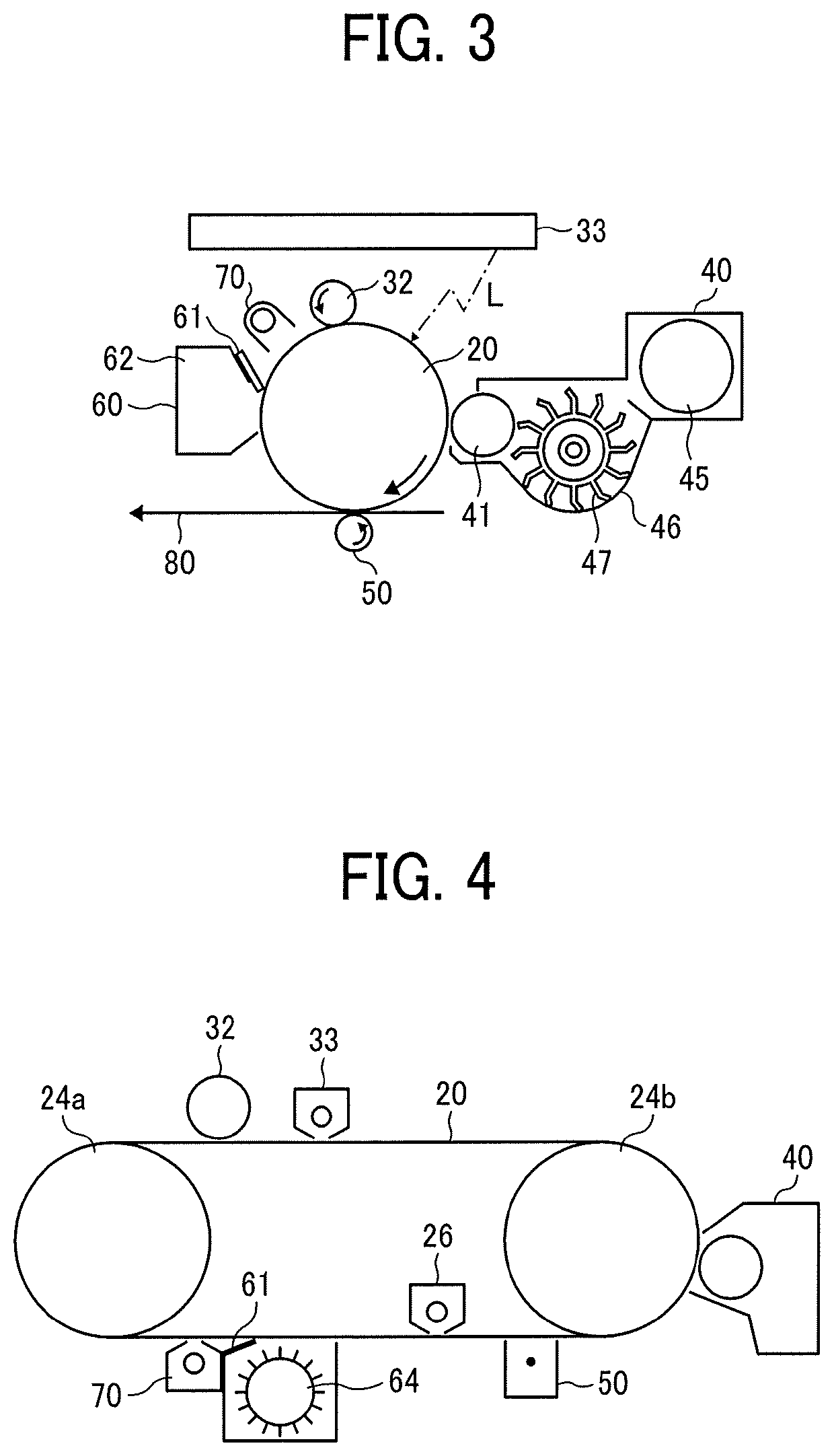
Toner, image forming apparatus, image forming method, and toner storage unit
A toner is provided. The toner comprises mother particles and an external additive covering the mother particles. The mother particles comprise a binder resin, and the external additive comprises inorganic particles. The inorganic particles comprise small-size inorganic particles having an equivalent circle diameter of from 30 to 70 nm and large-size inorganic particles having an equivalent circle diameter of from 150 to 200 nm and a circularity of 0.85 or more. The large-size inorganic particles are 20 to 70 in number per 100 μm2 image area of the toner observed with a field-emission scanning electron microscope.
Owner:RICOH KK
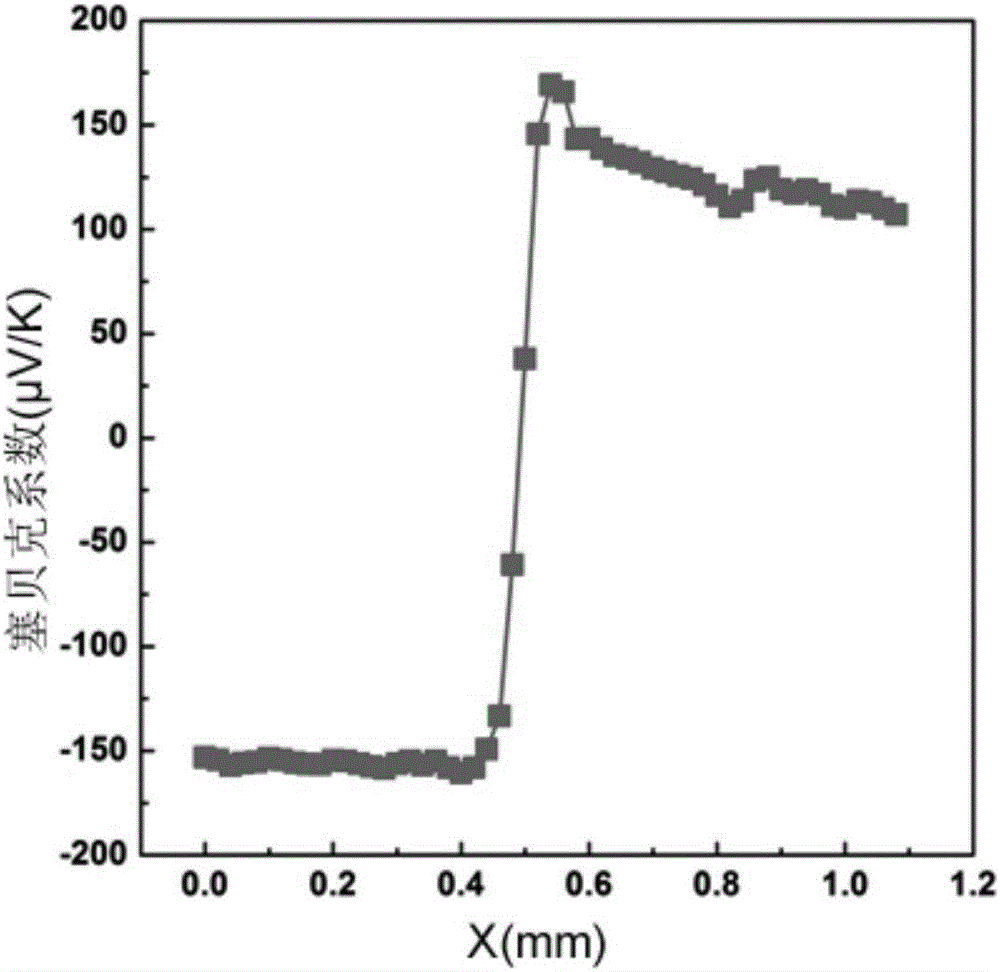
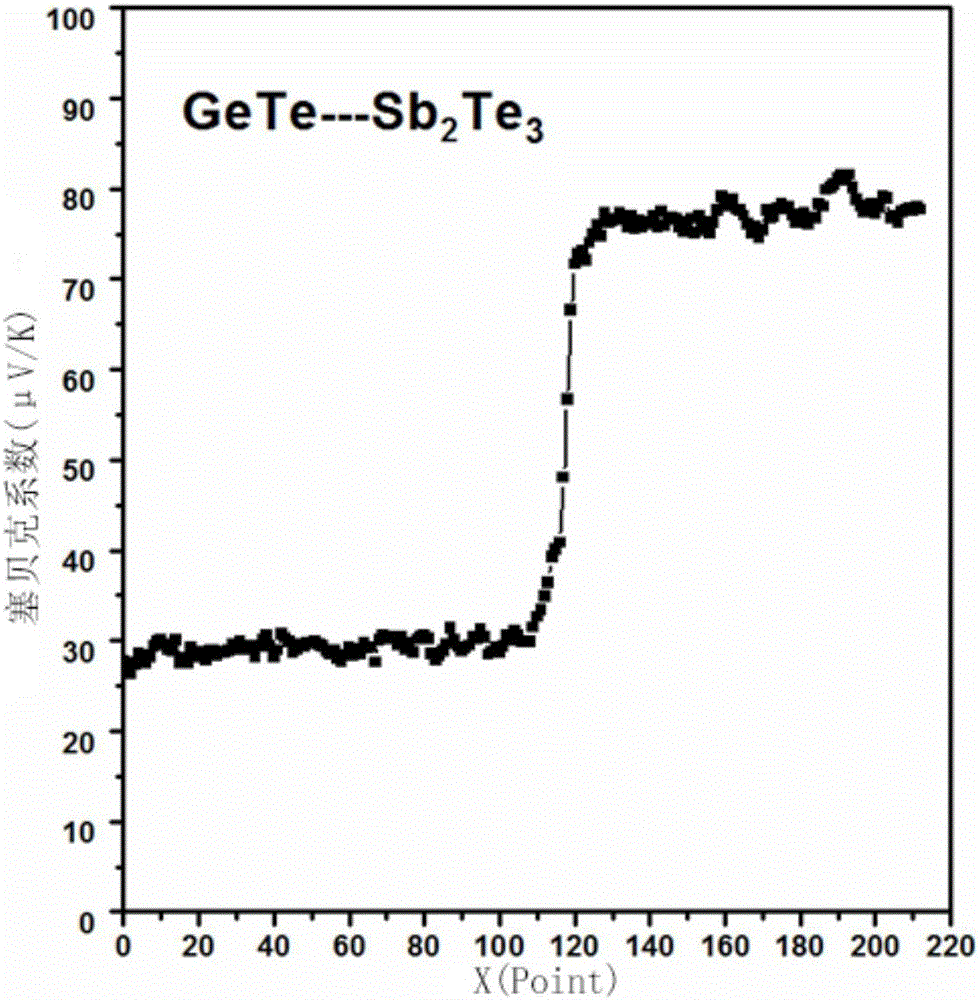
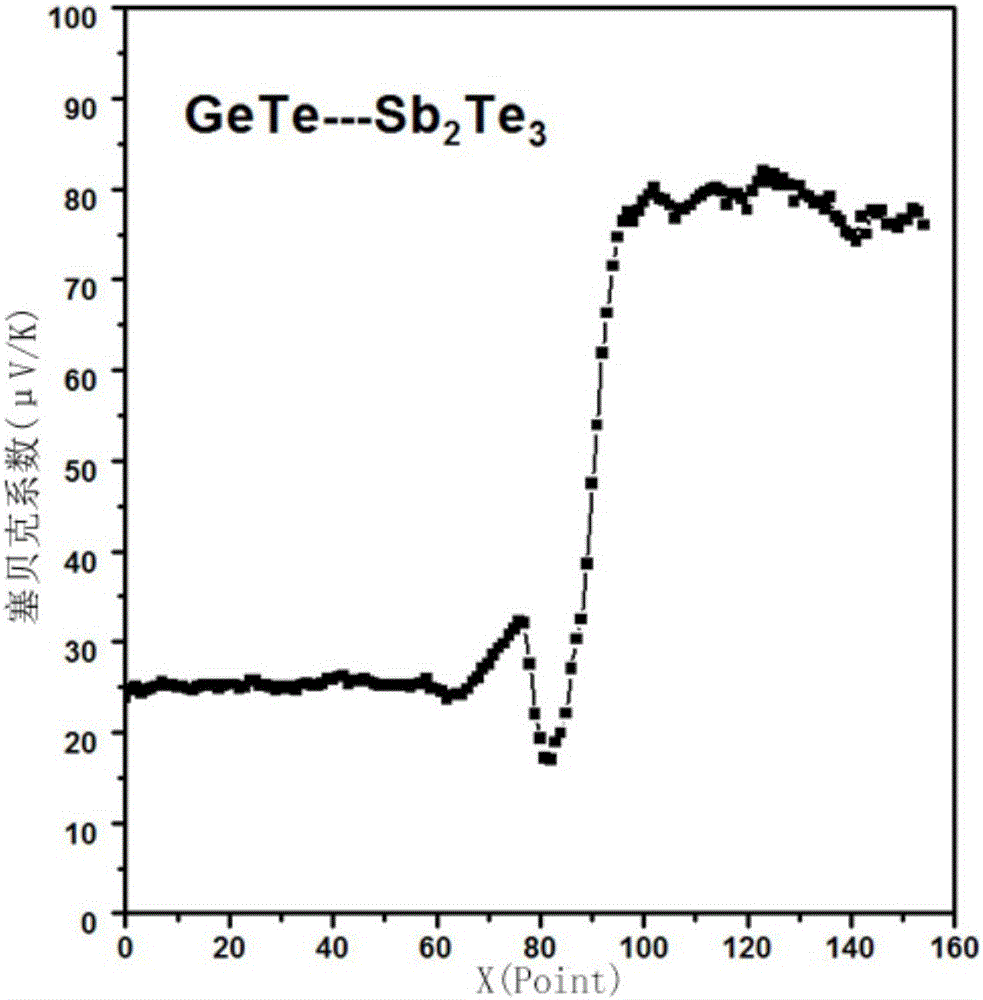
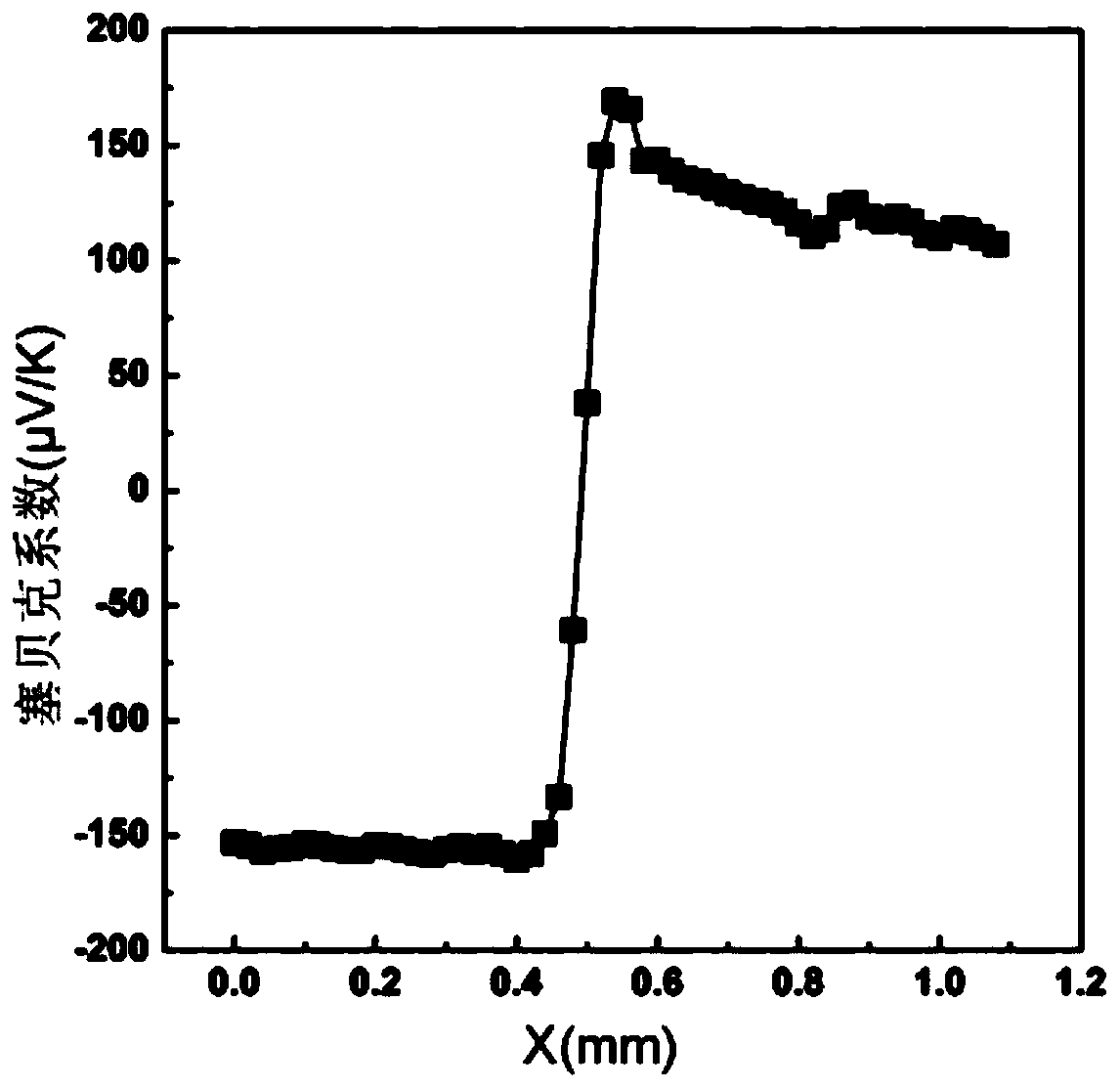
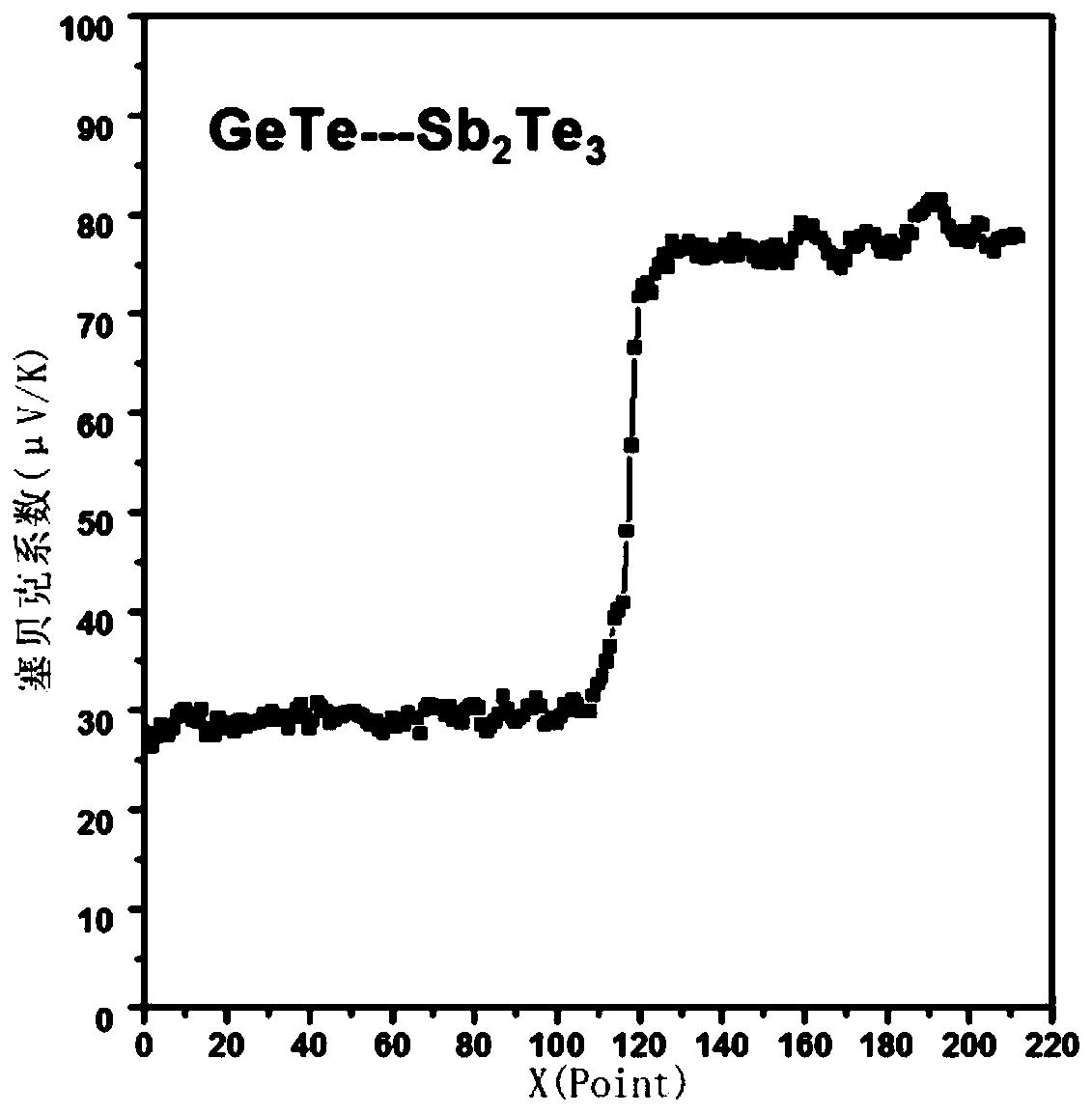
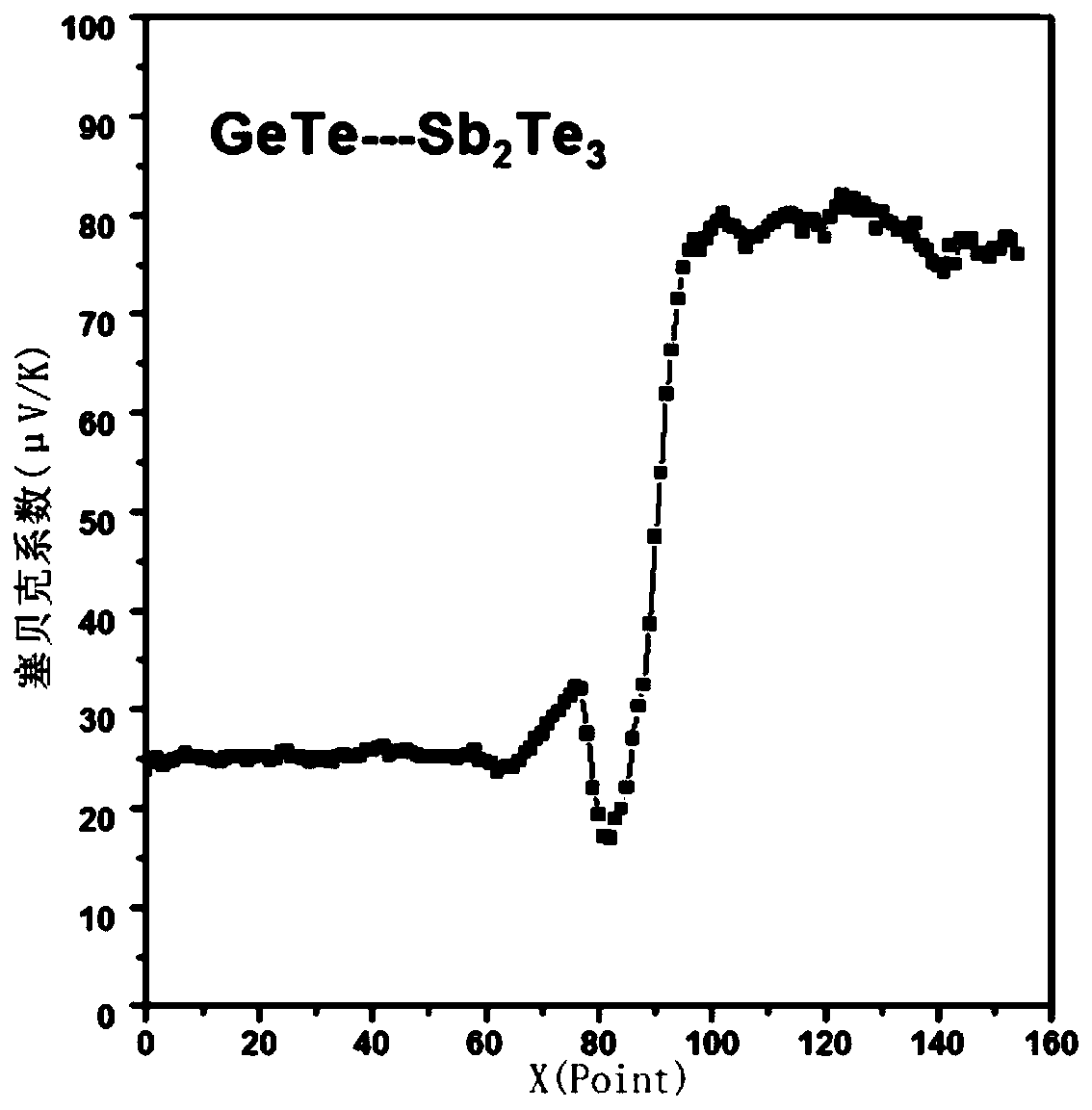
Rapid screening method of thermoelectric material with optimized performance
ActiveCN106771706ARich in microstructureShort manufacturing cycleElectrical testingScreening methodX-ray
The invention discloses a rapid screening method of the thermoelectric material with optimized performance; the method comprises the following steps: firstly using a plasma activation sintering technology to prepare a multi-element chalcogenide system diffusion couple, thus obtaining a block material sample bank with rich compositions and microstructures; combining an EPMA (electron probe X ray microscopic analyzer), a FESEM (field emission scan electron microscope) with a PSM (conductivity-Seebeck coefficient scan probe microscope) symptom technologies so as to study the relations between the sample bank composition, structure and thermoelectricity performance, thus screening out the high performance thermoelectric material with specific compositions and microstructures with high flux. The method can effectively improve the information density and efficiency obtained by tests, thus obvious reducing test needing manpower, material resources and cost, and searching the thermoelectric material with excellent performance with high efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
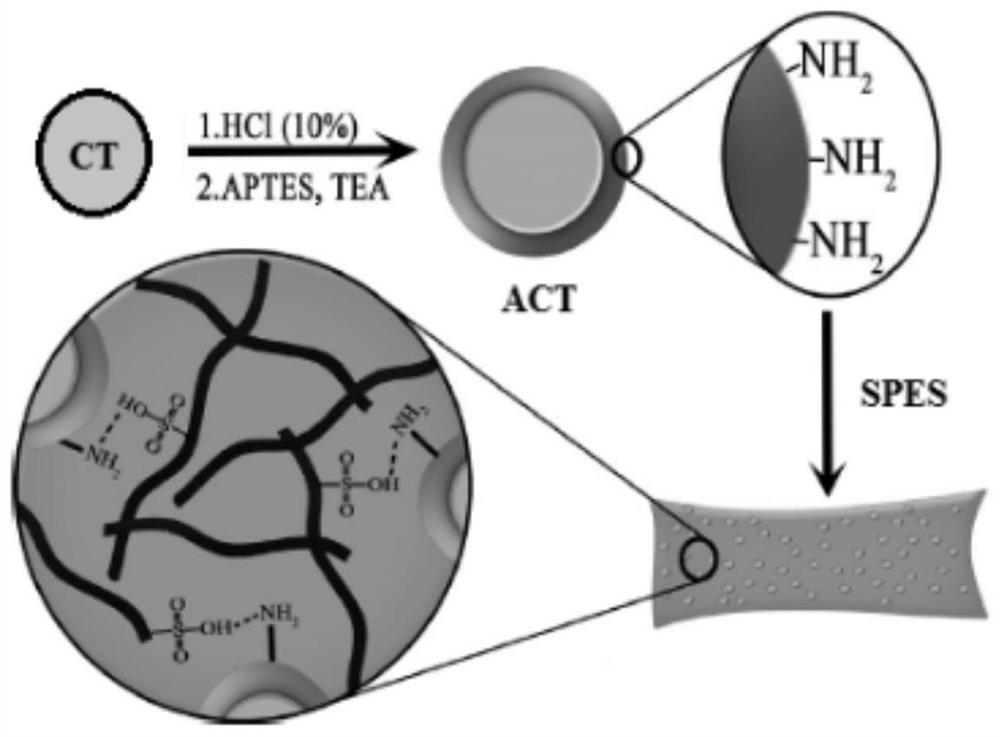
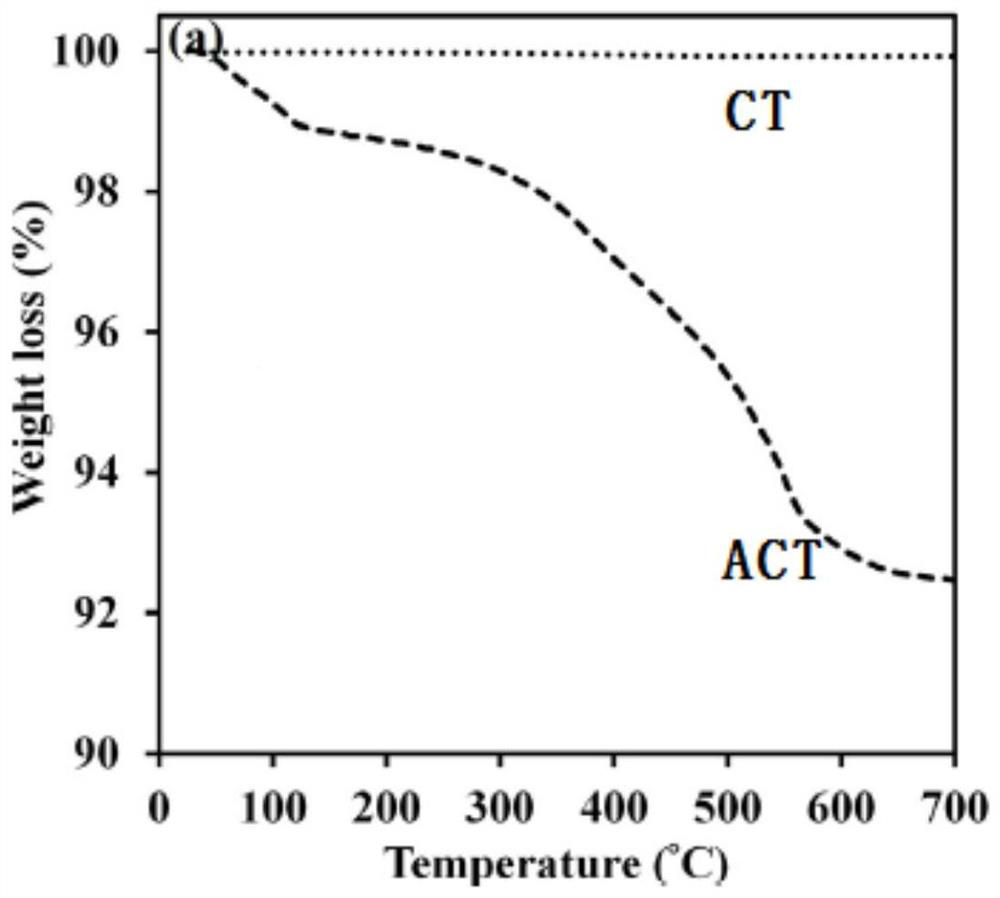
Proton exchange membrane applied to fuel cell and preparation method of proton exchange membrane
InactiveCN113193218AImprove stabilityImprove water retentionFuel cellsCompatibilizationField emission scanning electron microscopy
The invention discloses a proton exchange membrane applied to a fuel cell and a preparation method of the proton exchange membrane. The proton exchange membrane is prepared from the following raw materials: 0.005 g-0. 03g of functionalized cobalt titanate nano particles and 0.97 g-0.995 g of sulfonated polyethersulfone. The novel proton exchange membrane is prepared by combining amine functionalized cobalt titanate nanoparticles with a sulfonated polyethersulfone polymer matrix; surface modification is carried out on cobalt titanate nano particles by adopting grafted (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane; the interfacial compatibility of the ACT nano particles subjected to surface modification and the SPES is improved, so that the ACT nano particles can be uniformly dispersed in the SPES film; the prepared nano composite film is characterized by adopting technologies such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, a universal testing machine, a field emission scanning electron microscope and an atomic force microscope; the obtained nano composite film shows better stability and good water retention performance.
Owner:深圳氢时代新能源科技有限公司
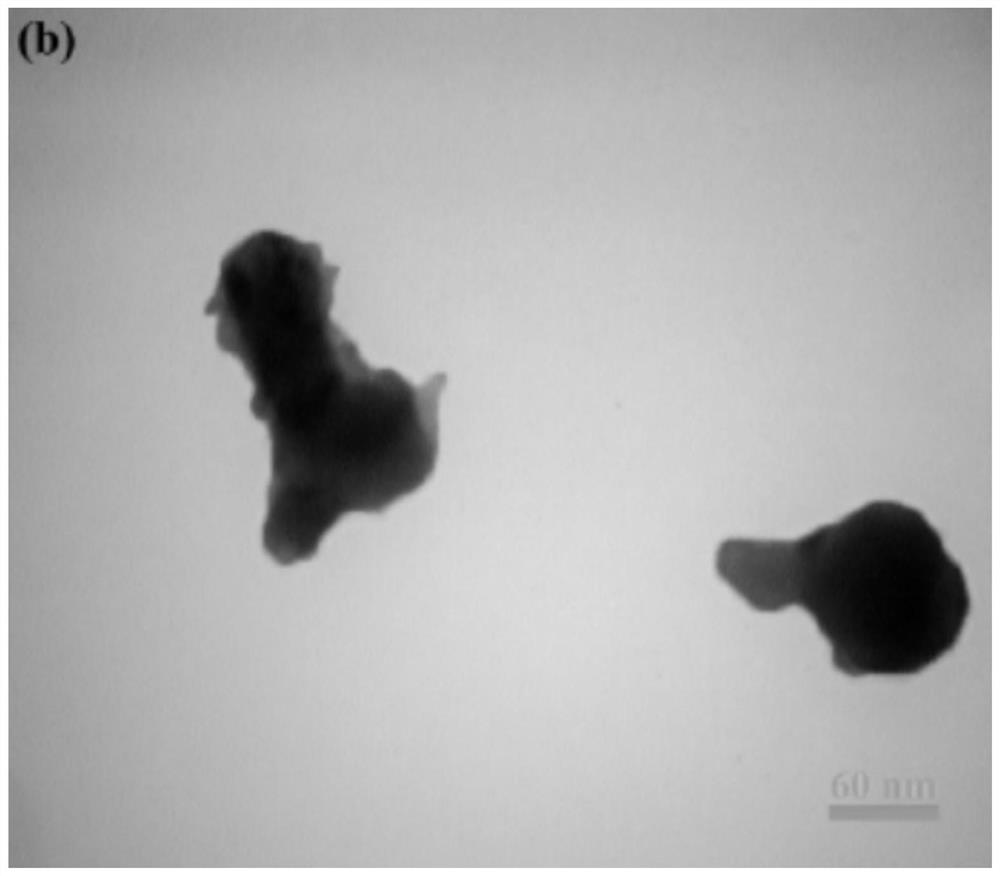
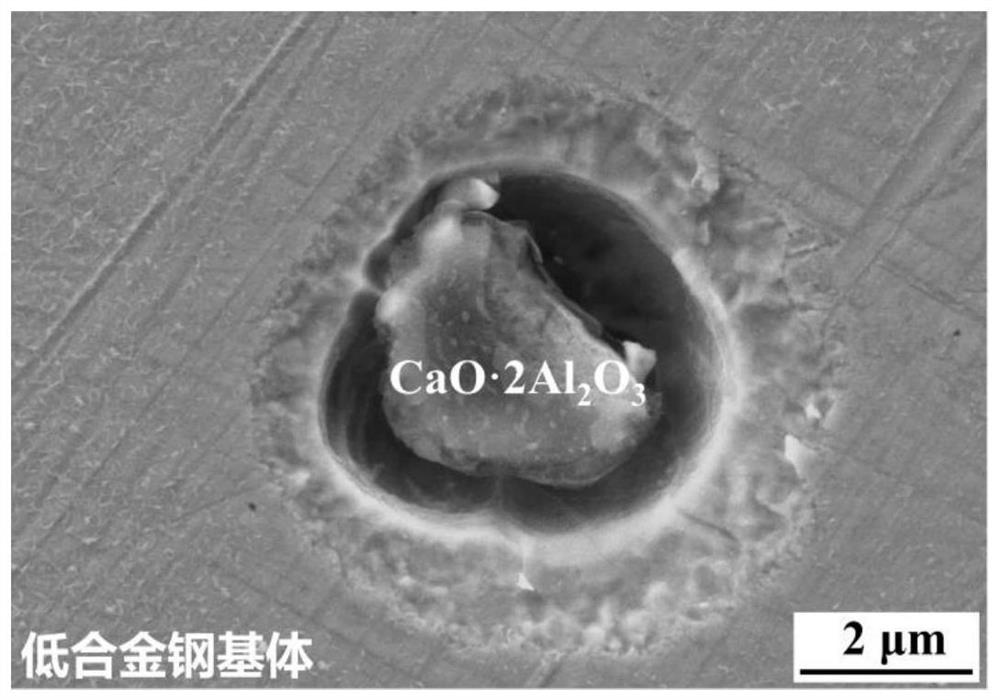
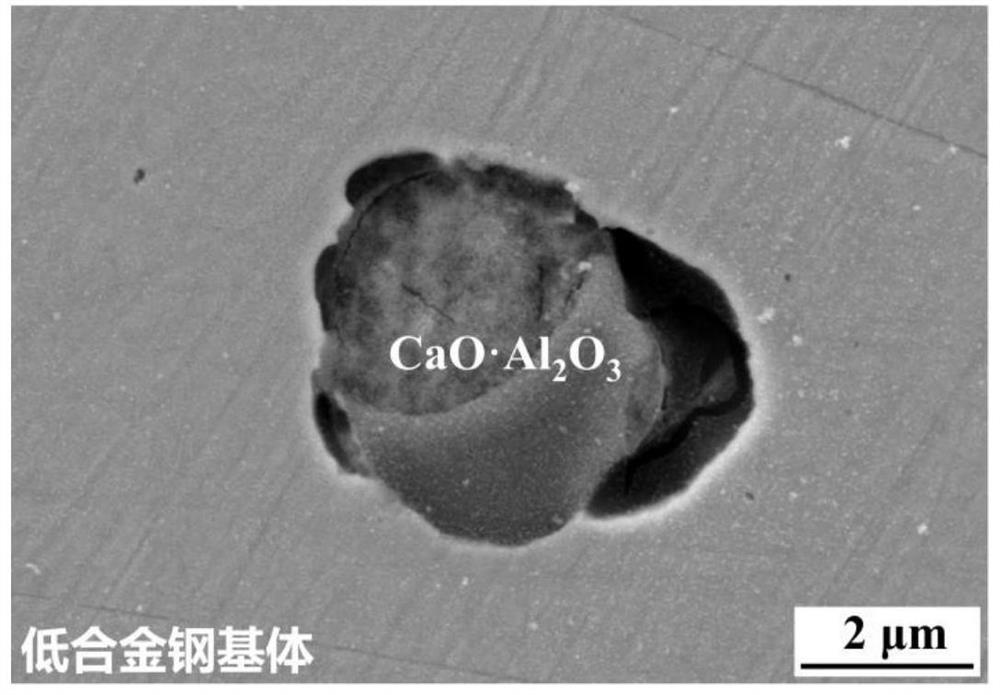
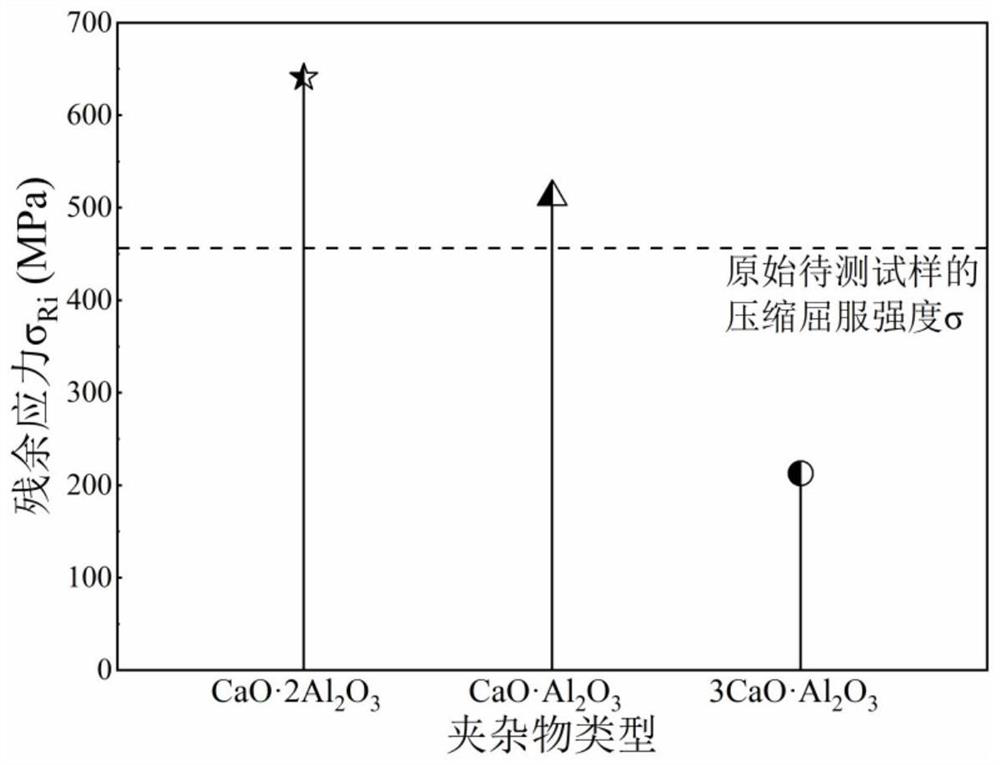
Method for detecting corrosion activity of inclusions in low alloy steel
PendingCN113030143ASimple and convenient observation and analysisEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning electron microscopeUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a method for detecting corrosion activity of inclusions in low alloy steel. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of grinding, polishing, cleaning and blow-drying a low-alloy steel sample, sequentially putting the sample into a full-automatic inclusion analyzer and a field emission scanning electron microscope, measuring the type number of inclusions in the sample to be measured, selecting one inclusion from each type of inclusions, and sequentially recording the radius of the inclusion, then obtaining the residual stress sigmaRi at the interface of the ith type of inclusion and the steel substrate by utilizing the measurement result and combining with the physical property parameters of different types of inclusions, if the residual stress sigmaRi is greater than the compression yield strength sigmas of the low alloy steel, determining that the ith type of inclusions are corrosive active inclusions, otherwise, determining that the ith type of inclusions are non-corrosive active inclusions, and acquiring the corrosive activity of various selected inclusions in sequence. The method is simple to operate and reliable in data, and the capacity of inducing pitting corrosion by the inclusion in the low alloy steel can be accurately evaluated without corrosion treatment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
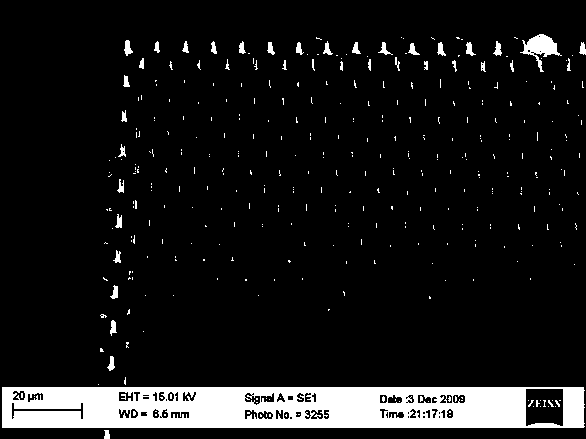
Method for detecting wall breaking rate of plant cells by utilizing field emission scanning electron microscopy
The invention discloses a method for detecting a wall breaking rate of plant cells by utilizing field emission scanning electron microscopy. The cell wall breaking rate is detected by utilizing the field emission scanning electron microscope, the method can be used for accurately and rapidly realizing the field emission scanning electron microscope imaging technology to detect the wall breaking rate of the dried plant cells; and the method is simple, visual and rapid. The sample preparation process is simple, only a conductive adhesive needs to be adhered to a sample table, a cell suspension liquid is dropped on the conductive adhesive, and the whole can be placed into the field emission scanning electron microscope to be observed. The magnification factor of the scanning electron microscope can be adjusted randomly from 40 times to 1 million times, imaging is clear and cell characteristics can be observed; and the method is suitable for all dry plant raw materials, as long as the drying degree of the raw materials can be crushed by a common pulverizer to obtain more than 100 meshes, and the method is wide in application range.
Owner:湖南航天天麓新材料检测有限责任公司
Method for characterizing morphologies of particulate matters in diesel
InactiveCN106596357AIntuitive reflectionReliable reflectionParticle size analysisAdhesiveScanning electron microscope
The invention discloses a method for characterizing morphologies of particulate matters in a diesel. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting particulate matters with different aerodynamic diameters in an exhaust passage of the diesel in a grading manner as samples to be measured; extracting the samples to be measured by an ultrasonic oscillation and centrifugation method by using an acetone reagent; adhering a particulate-containing dissolved solution to the surface of the surface of conductive adhesive, performing metal spraying to obtain particulate analysis samples, and analyzing the samples by using a field emission scanning electron microscope to obtain electron microscope gray scale images with the gray scale values of 0-255; with a maximum interclass variance method, determining the thresholds to obtain binary images; extracting the boundaries of the target areas of the images by a multi-level edge detection algorithm; with an arithmetic order meshing method, dividing contour boundaries by using a matrix containing delta*delta pixel points; establishing some squares or boxes with the side length of delta, and then calculating the number of intersections of the boxes with different delta values and a plane set F to obtain dimensions of the boxes. The method is simple, convenient and fast; the calculated dimensions of the boxes can clearly and intuitively reflect fractal characteristics of the particulate matters in the diesel.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
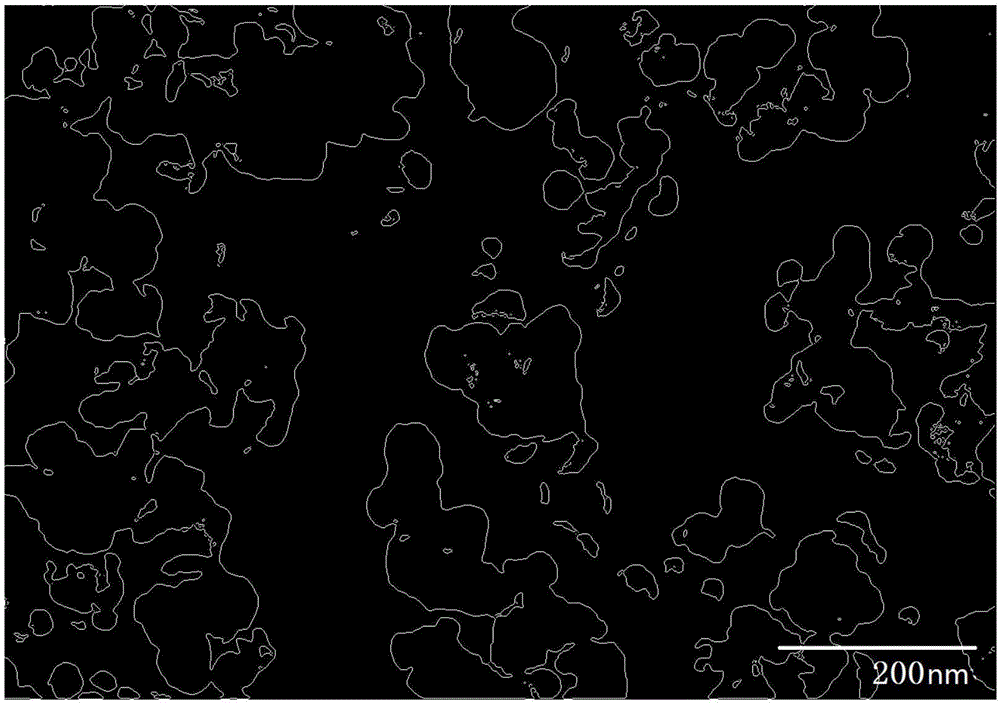
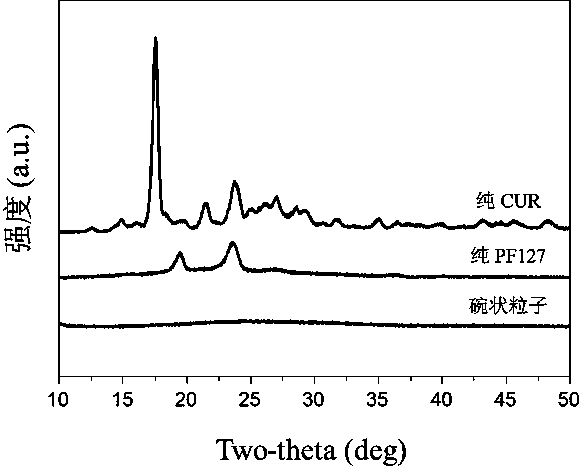
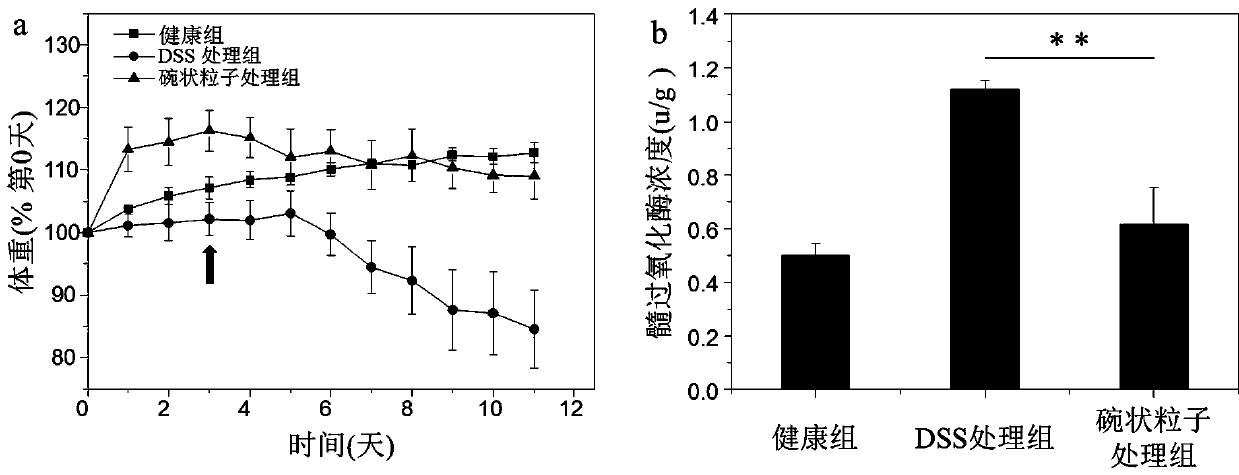
Preparation method and application of novel medicine-carrying bowl-shaped particle
InactiveCN107595804AEasy and quick to makeShort preparation cycleDigestive systemKetone active ingredientsCarrying capacityUlcerative colitis
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of novel medicine-carrying bowl-shaped particle. According to the preparation method and the application, the medicine-carrying bowl-shapedparticle is prepared by virtue of a water-in-oil-in-water emulsified solvent evaporation method and is subjected to a series of characterizations. Field emission scanning electron microscopy finds that the particle size of the prepared bowl-shaped particle is 1.86+ / -0.20 microns, and the bowl-shaped particle has relatively narrow size distribution and relatively high medicine-carrying capacity (4.48+ / -0.12%). After the medicine-carrying bowl-shaped particle is orally taken by a mouse with ulcerative colitis, a result shows that the bowl-shaped particle has a good treatment effect on ulcerative colitis, and furthermore, the bowl-shaped particle has very good medical application prospects.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
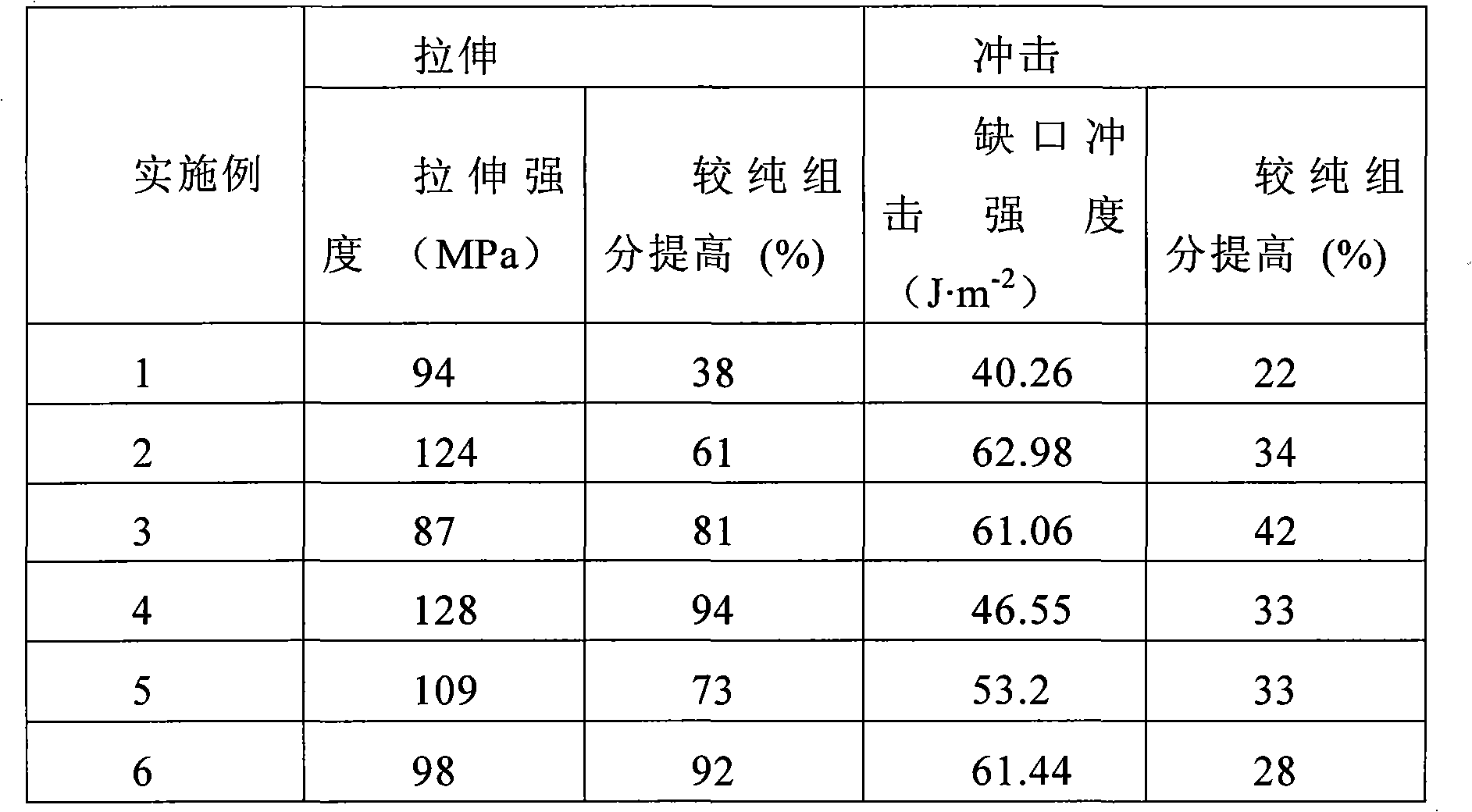
Silicon dioxide nano rod enhanced and toughed polyester compound material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a silicon dioxide nano rod enhanced and toughed polyester compound material and a preparation method thereof. The compound material mainly consists of aromatic dioctyl phthalate dimethyl, alpha, omega-diol and inorganic filler presoma, and rod-like silica in the compound material is formed by collosol in a polymerization system by sol-gel transformation. The nano rod is generated in site, thereby avoiding the large-scale agglomeration phenomenon caused in the addition process. Observed by a field-emission scanning electron microscope, the nano rod is regularly dispersed in a matrix. Compared with pure polyester, the mechanical property of the composite material is greatly improved, 1 percent of nano rod by weight can improve the tensile property by 80 percent and improve the impact performance by 50 percent. The composite material can be used as a high-polymer composite, and high-polymer matrix can be removed by a high-temperature erosion method to extract silicon dioxide nano rod, wherein the extracted silicon dioxide nano rod can be applied in the field of semiconductor devices.
Owner:HEFEI GENIUS NEW MATERIALS
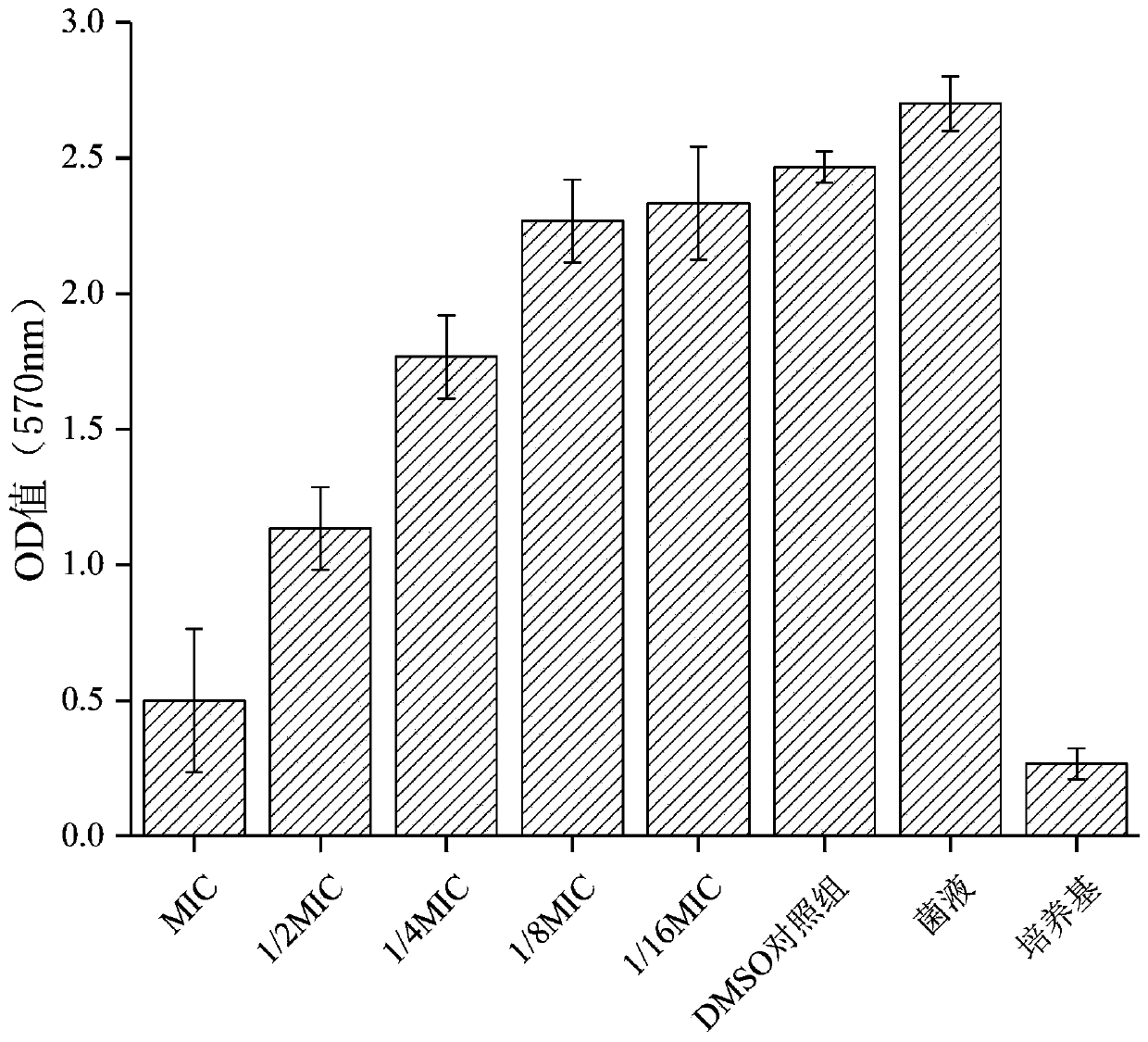
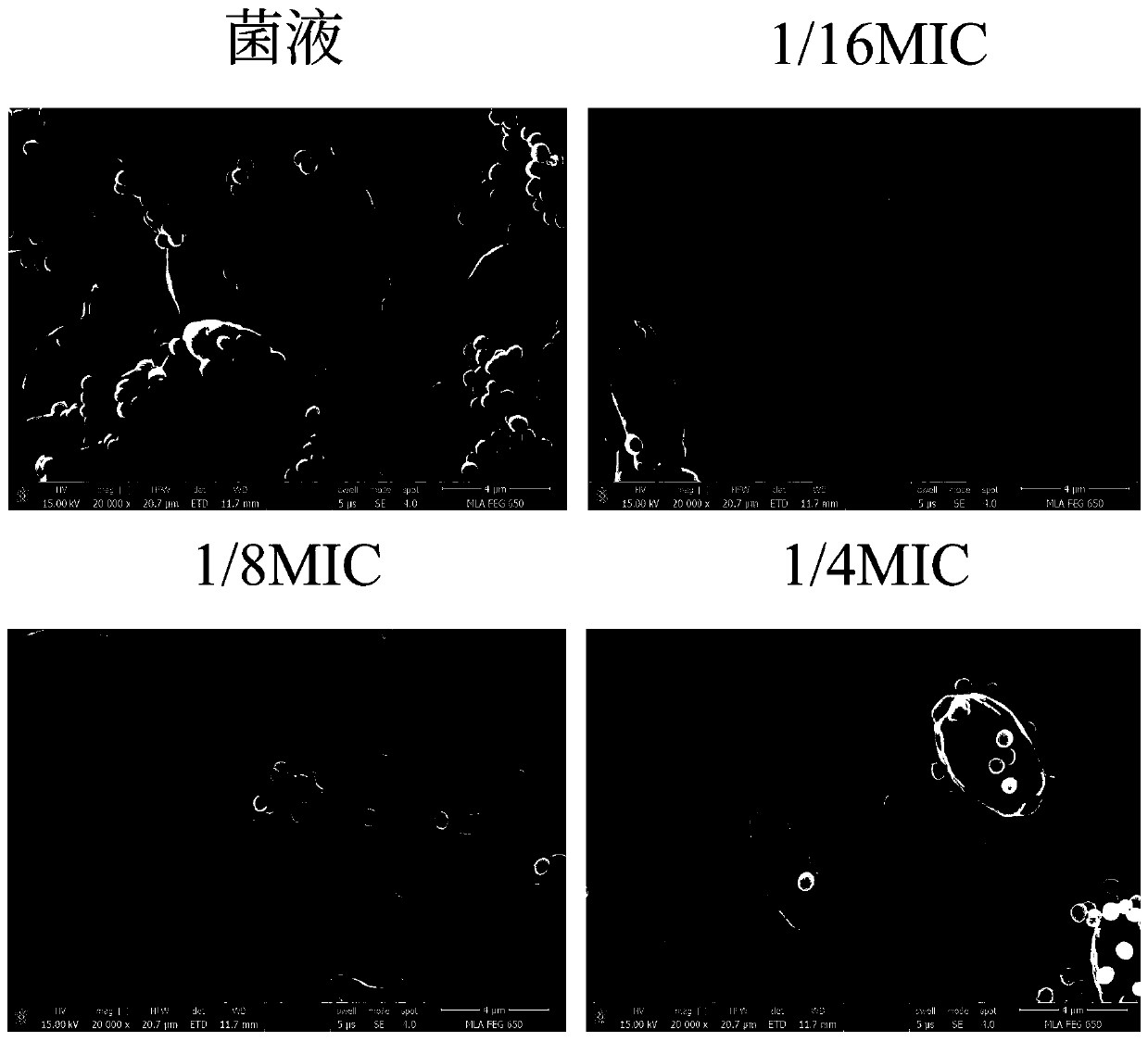
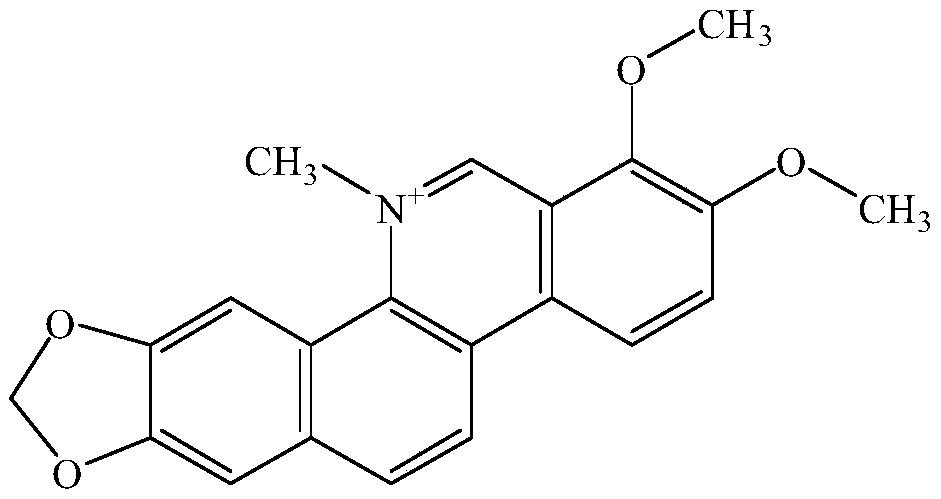
Application of chelerythrine to preparation of medicine for inhibiting blastomyces albicans and staphylococcus aureus bi-species biofilm
InactiveCN110812359AForm an effective interventionInterventionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyStaphyloccocus aureus
The invention discloses application of chelerythrine to preparation of a medicine for inhibiting blastomyces albicans and staphylococcus aureus bi-species biofilm. By adopting a blastomyces albicans and staphylococcus aureus bi-species biofilm in vitro model, an in vitro intervention effect of the chelerythrine on the bi-species biofilm is researched; through observation of a crystal violet method, the phenomenon that the chelerythrine can effectively intervene formation of the blastomyces albicans and staphylococcus aureus biofilm is found; and through observation of field emission scanning electron microscope, the phenomenon that the chelerythrine has obvious inhibition and clearing effects on the blastomyces albicans and staphylococcus aureus in the biofilm is found; and therefore, thechelerythrine has definite effects on inhibition of the blastomyces albicans and staphylococcus aureus bi-species biofilm, and can be applied to preparing the medicine for inhibiting or clearing the blastomyces albicans and staphylococcus aureus bi-species biofilm; and therefore, the application of the chelerythrine has an effective meaning.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
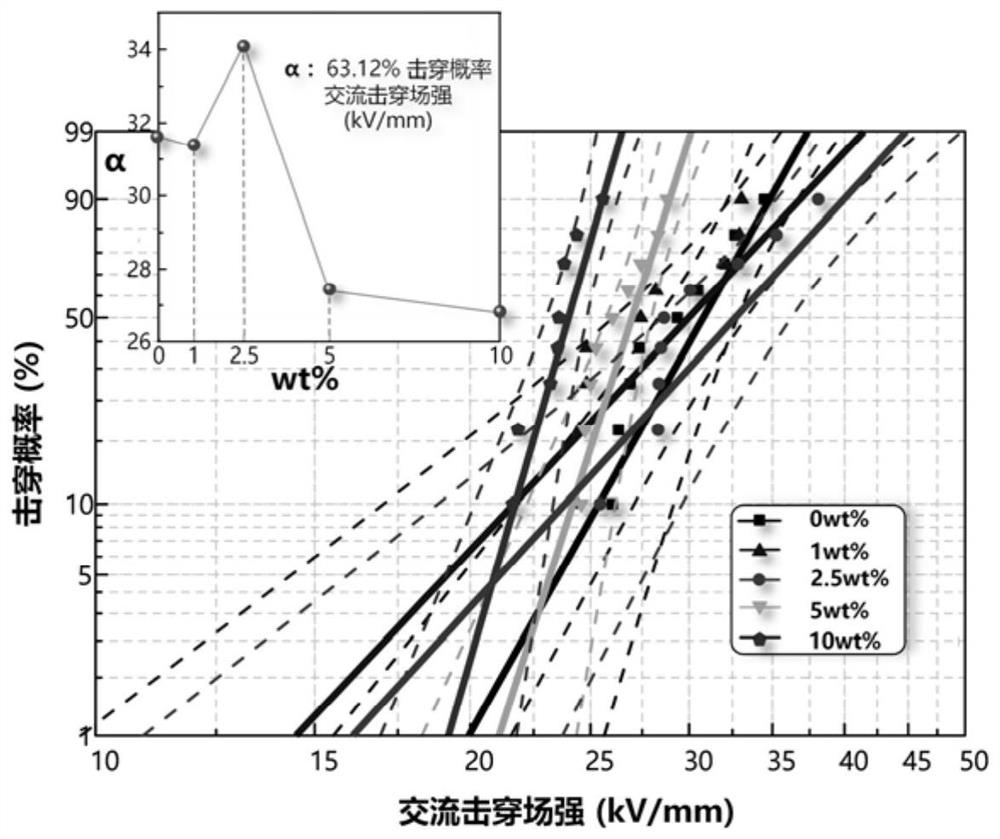
Epoxy resin composite insulating material with mechanical damage targeted self-healing performance
PendingCN114874587ANo degradation in electrical performanceElectrical performance degradationMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of an epoxy resin composite insulating material with mechanical damage targeted self-healing performance, and belongs to the field of materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, weighing microcapsules, dispersing the microcapsules in epoxy resin to obtain a mixture, adding methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride, a diethylenetriamine curing agent and a catalyst 2, 4, 6-tri (dimethylaminomethyl) phenol into the mixture, uniformly mixing, and reacting; carrying out vacuum degassing on a product obtained after the reaction is finished, pouring the product into a stainless steel mold, driving the magnetic core microcapsule to move towards an easily damaged area by utilizing a high-density directional magnetic field, and completing migration of the microcapsule after 20-40 minutes; and after the permanent magnet is removed, curing for 1-3 hours at 80-100 DEG C, then heating to 100-110 DEG C, continuing curing for 1-3 hours, and taking out the epoxy resin composite insulating sheet. The method is based on the self-repairing performance test of the epoxy resin composite insulating material, and the targeted mechanical damage repairing function of the epoxy resin composite insulating material is proved through a field emission scanning electron microscope and an inverted multi-photon confocal microscope.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for testing fertilizer efficiency of fine garbage compost
InactiveCN101887021AReduce conductivityReduce voidsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerCompost
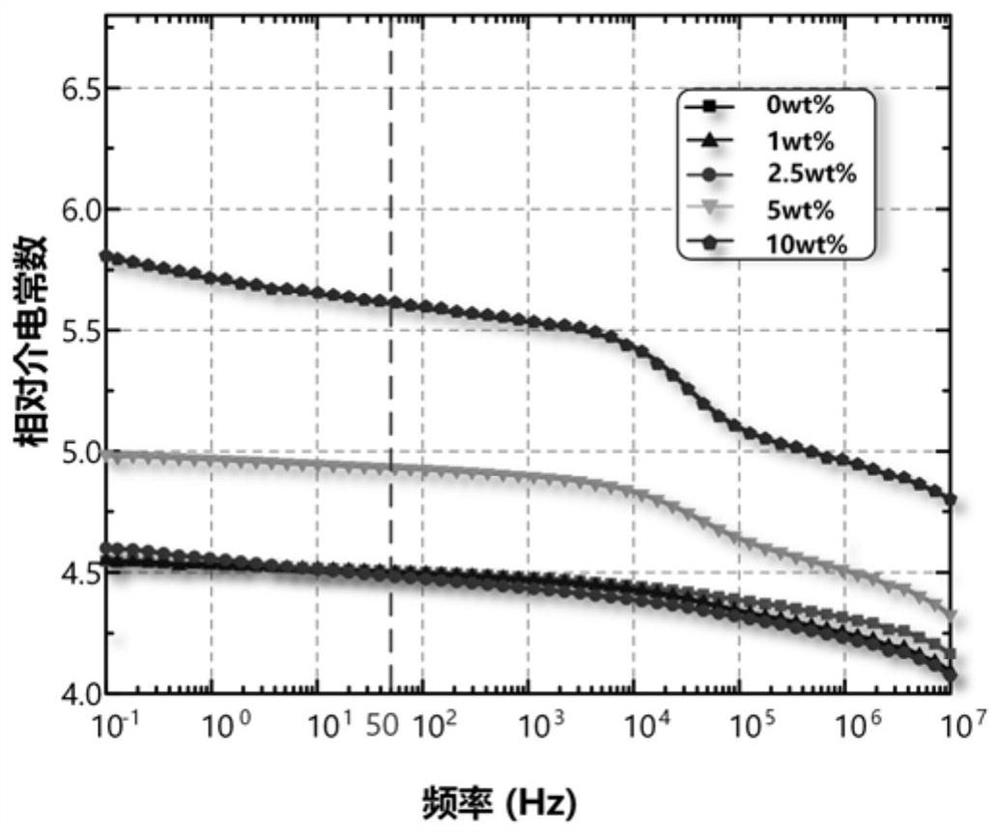
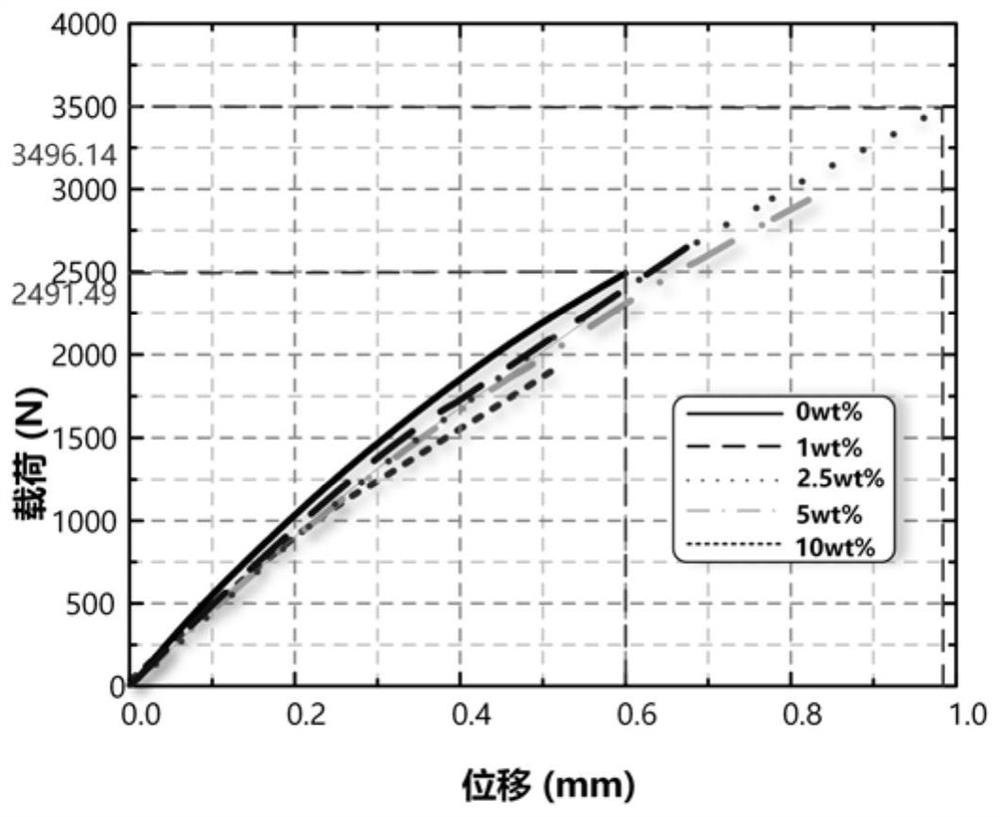
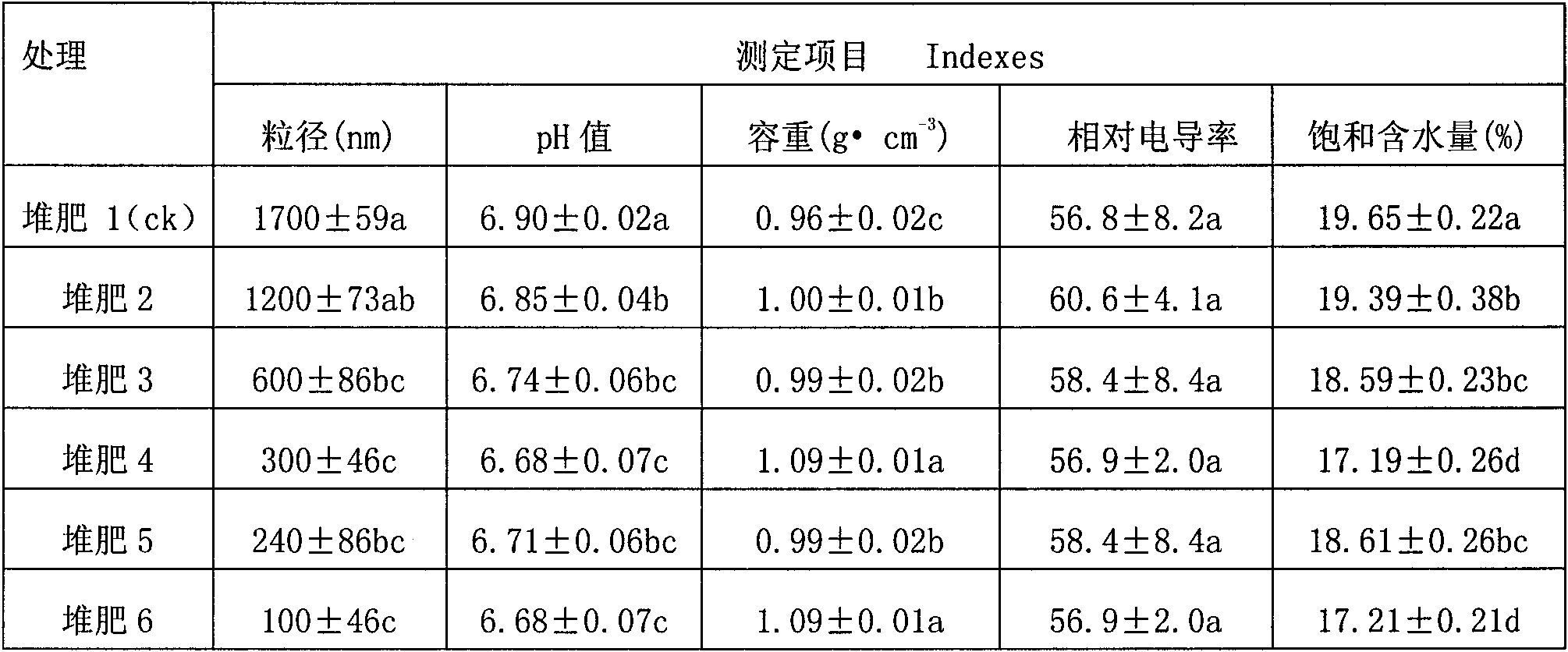
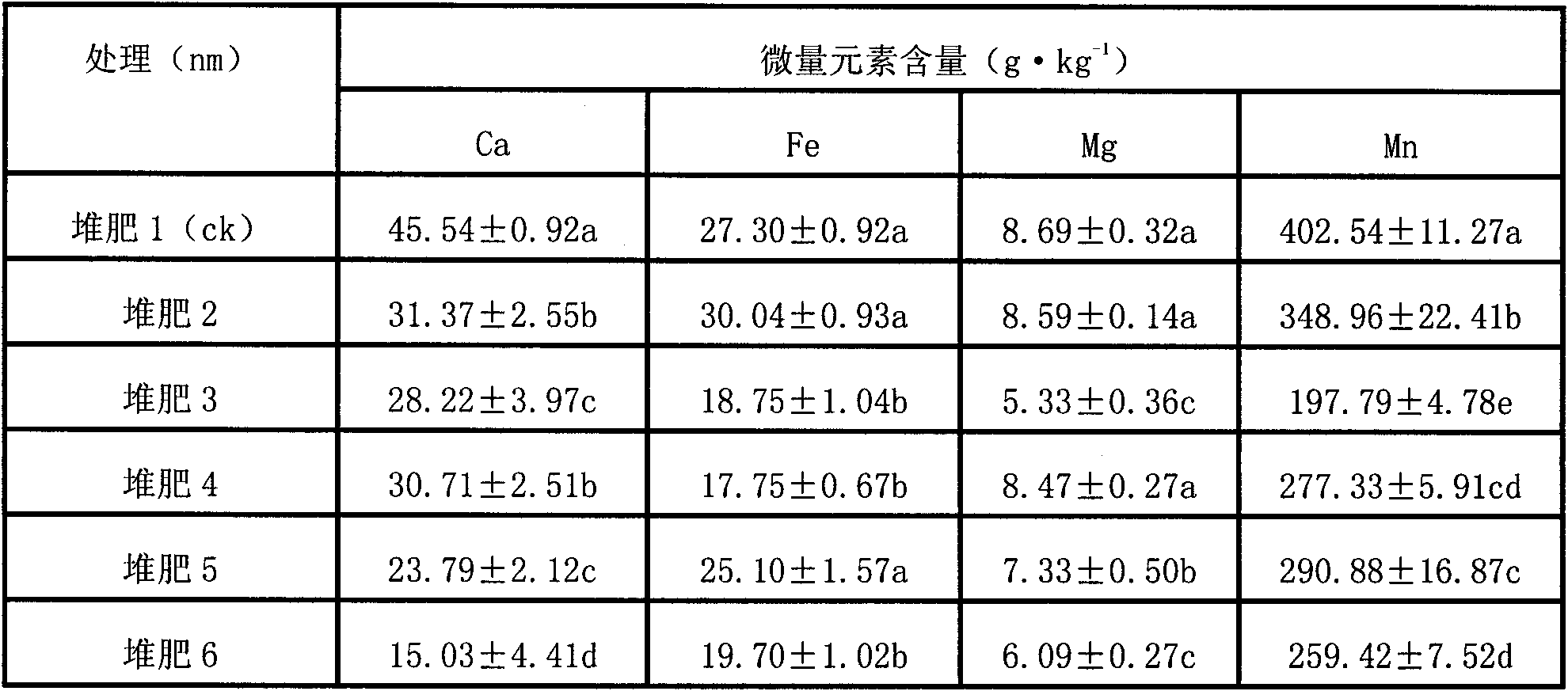
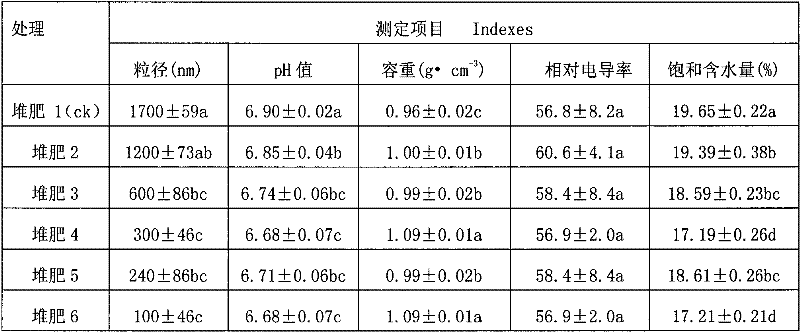
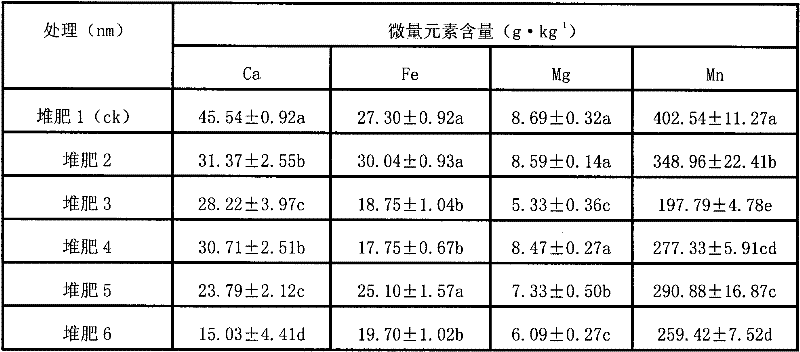
The invention relates to a method for testing the fertilizer efficiency of fine garbage compost. The method comprises the following steps of: removing impurities from the compost, drying the compost at the temperature of 105 DEG C to constant weight, screening the compost of which the particle size is 1,700 nanometers, smashing the screened compost at the speed of 24,000 revolutions per minute for 9 minutes, 6 minutes, 3 minutes, 2 minutes and 1 minute respectively to prepare the compost with different particle sizes, putting the compost with the different particle sizes into alcohol, and uniformly dispersing the compost with the different particle sizes by using an ultrasonic oscillator to prepare suspension; dipping a toothpick with a small amount of suspension, coating a layer of suspension on the surface of a sample platform, drying the suspension by using electric heating air, sucking the dried suspension by using a dust collector for half a minute and measuring the particle sizes by using an S4800 field-emission scanning electron microscopy, wherein the particle sizes of the obtained compost are 1,700 nanometers, 1,200 nanometers, 600 nanometers, 300 nanometers, 240 nanometers and 100 nanometers respectively; and weighing 0.5 grams of garbage compost to determine a digest volume respectively and testing the fertilizer efficiency of the fine garbage compost by using an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for testing fertilizer efficiency of fine garbage compost
InactiveCN101887021BReduce conductivityReduce voidsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerCompost
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
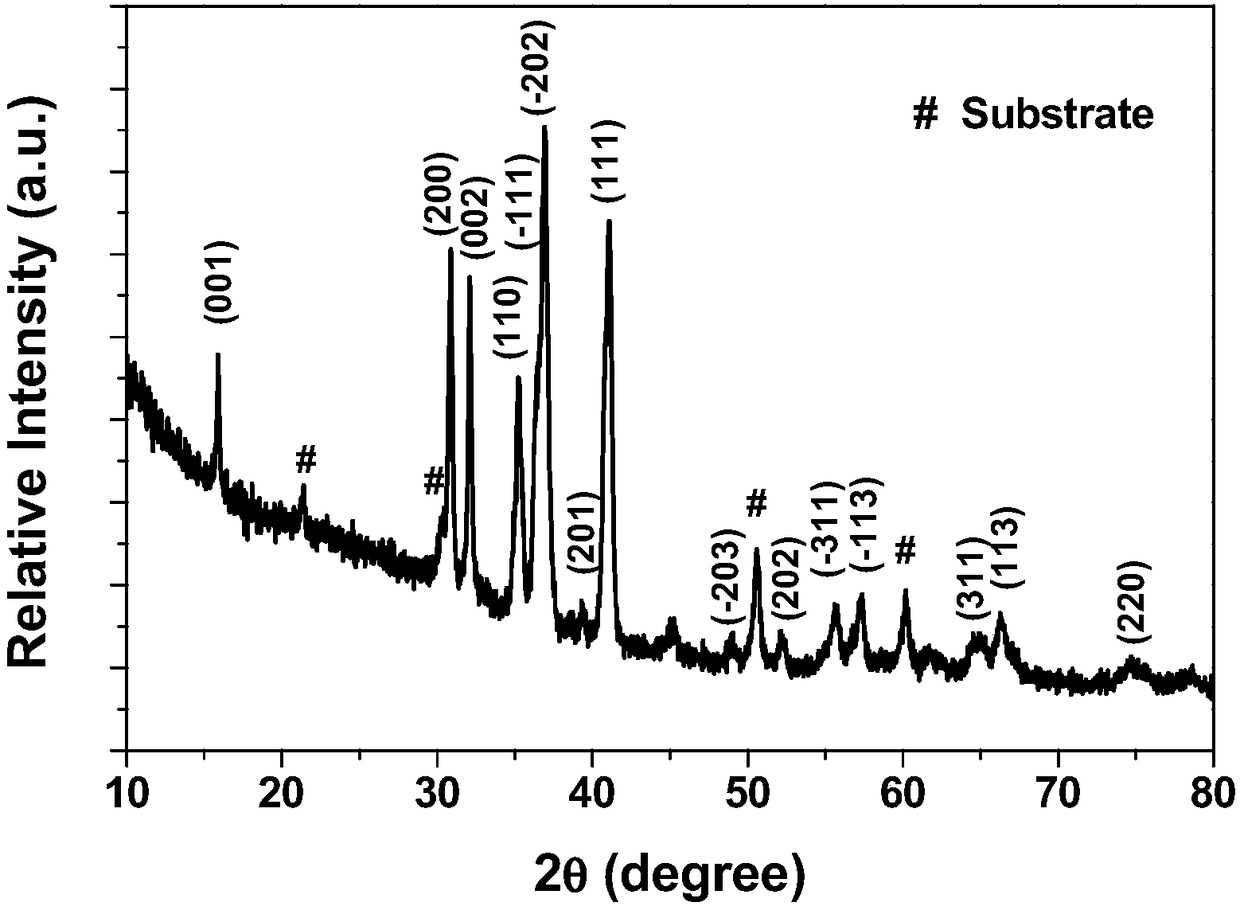
ZnO/CdO composite film with low resistivity
The invention discloses a ZnO / CdO composite film with low resistivity. The film is mainly prepared by the following steps: using pulsed laser deposition equipment with four target holders, wherein the target holders adopt high-purity metal Zn targets and Cd targets; depositing 10 layers of ZnO films and CdO films at intervals by the pulsed laser deposition equipment under the atmosphere of 10 pascal oxygen and 300DEG C of the base temperature so as to form a composite film structure. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the ZnO / CdO composite film is prepared on a quartz glass substrate by a pulsed laser deposition method; the phase composition, the crystal structure and the crystal of the film are identified by an X-ray diffractometer, and the best film is selected; an JSM6700F field emission scanning electron microscope which is produced by the Japanese Shi-madzu company is used to observe the surface appearance of the film, and besides, an energy spectrum which is matched with the field emission scanning electron microscope is used to analyze the component content of the film. The film consists of ZnO and CdO two-phase nano crystalline grains, and the size of the crystalline grains gradually decreases while the CdO increases; all the ZnO / CdO has high transmittance within a visible light range. The more important is that the ZnO / CdO composite film keeps the light-emission characteristic of ZnO, namely the conventional ultraviolet light-emission characteristic is presented, and the position of a photoluminescence peak is not changed; besides, the optical characteristic of the ZnO is maintained, the ZnO / CdO composite film has low resistivity, and the resistivity can reach 10-2-10-3 omega.cm, which is close to the resistivity of a pure CdO film.
Owner:鲍云根
A method for evaluating the microscopic pore structure of tight reservoirs and classifying them
InactiveCN105334149BSolve the problem of observationDetermining the cause of densificationEarth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityFluorescence
The invention provides a micro-pore structure evaluation and reservoir classification method for tight reservoirs. The method comprises steps as follows: the origin and the petrologic features of each reservoir are analyzed, and the phase type, the content and the like of each reservoir are determined; physical features of each reservoir are analyzed; features of a reservoir space of each reservoir are observed, and the pore type, the surface porosity and the like are determined; pore structure parameters of the reservoirs are measured with a high-pressure mercury intrusion method and a nitrogen adsorption method; the diagenesis is researched, and compaction, cementation and corrosion sequences are determined; physical property control factors of the reservoirs are analyzed; the reservoirs are classified. The method mainly has the effects as follows: the diagenesis and the influences of the diagenesis on the reservoirs are comprehensively reflected through cathode luminescence and micro-area mineral quantitative analysis; micro pores of the tight reservoirs are researched elaborately through fluorescent casting and field emission scanning electron microscopy; the microscopic features of the tight reservoirs are determined accurately through high-pressure mercury intrusion experiments and the nitrogen adsorption experiments; the parameters are optimized for classification and evaluation of the reservoirs, and the method has a great significance in further prediction of beneficial developing stratums or zones.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
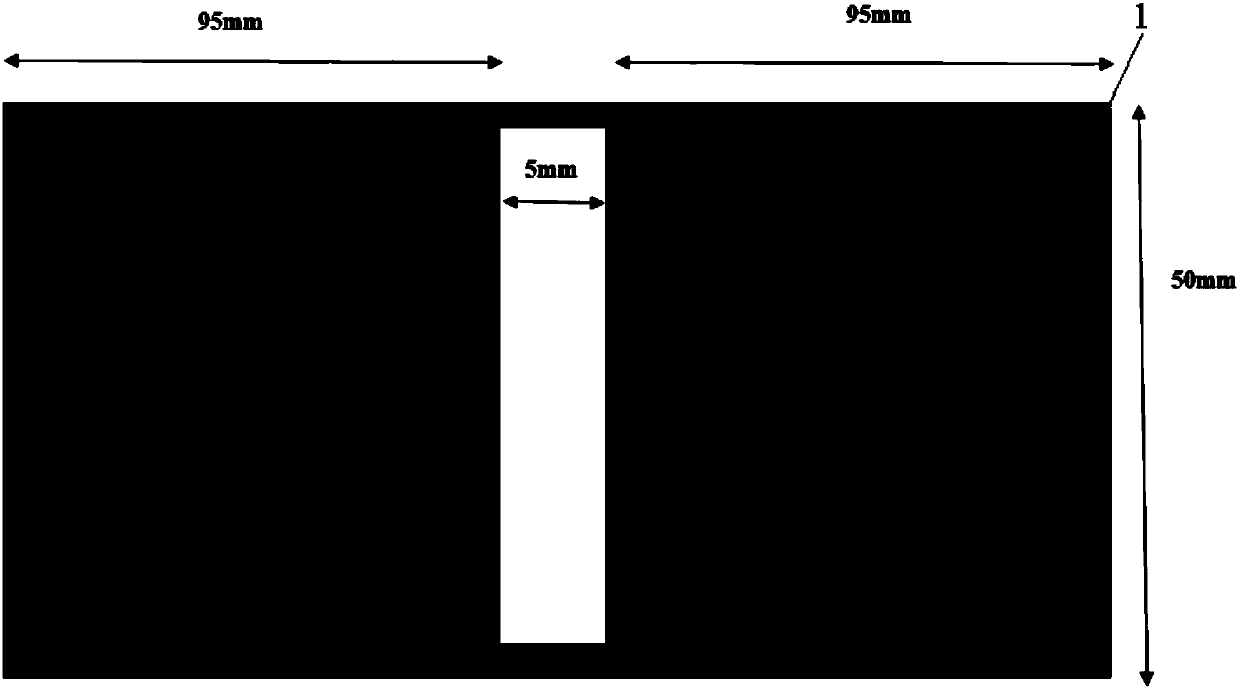
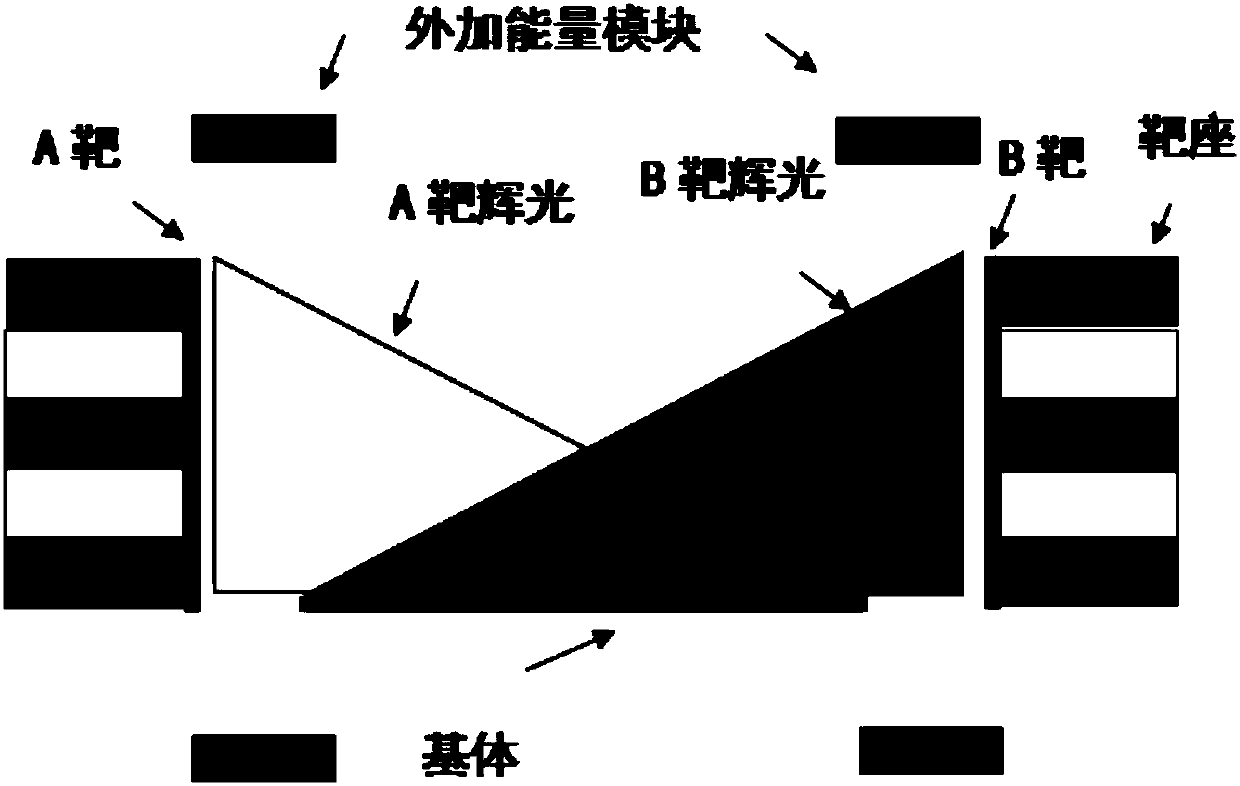
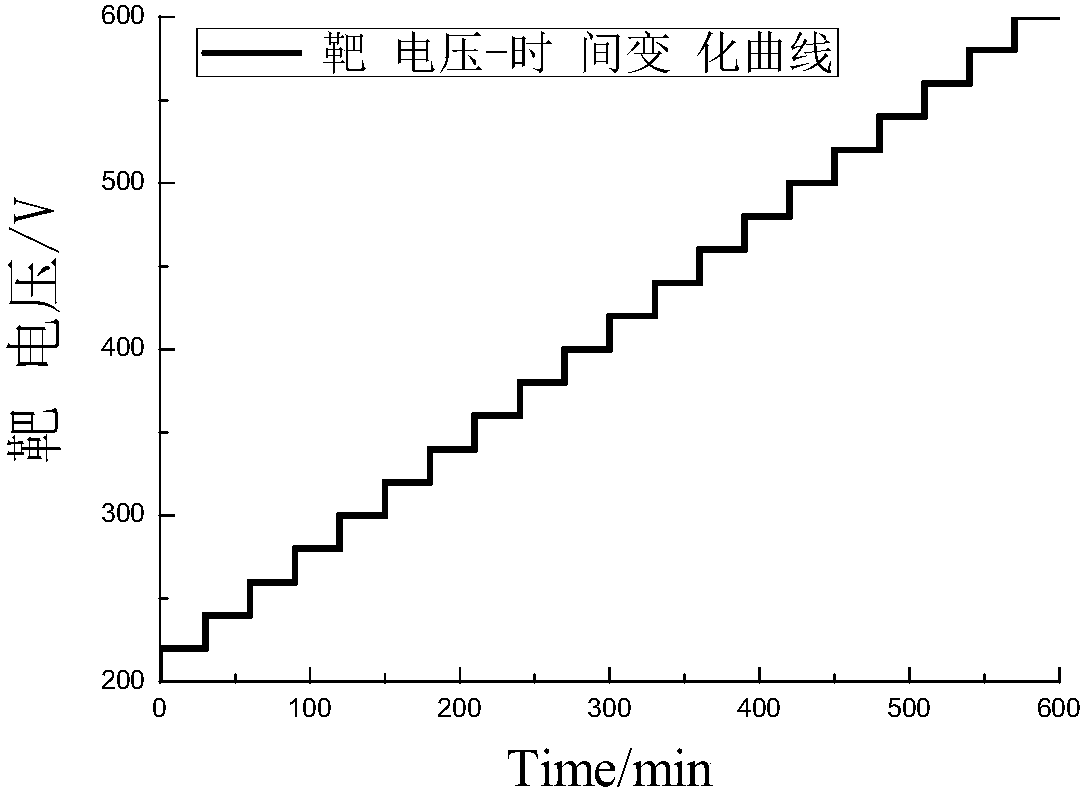
Texture regulation and control method and device of external energy field module to high throughput thin film
InactiveCN107858657ASequential depositionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingExternal energyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a high throughput preparation method for thin film ingredients and textures by adding an energy field module to complete high throughput thin film ingredient and microscopic structure regulation and control in the thin film sedimentation process, and in particular to a texture regulation and control method and device of the external energy field module to high throughput thin films. High throughput screening of the high throughput thin film ingredients and textures is achieved. Test instruments include a mask control system, an external energy field controller, an XRDanalysis meter and a field emission scanning electron microscope. A double-target magnetic control co-sputtering method is adopted for preparing thin film samples with the ingredients and textures changed in a gradient manner, the thin films at different positions on a base surface are subject to sedimentation at different times through mask motion and external energy field changes, the thin filmssubject to sedimentation firstly and the thin films subject to sedimentation secondly have different ingredients and microscopic structures, and finally the ingredients and texture structures with the best performance are screened according to the using performance high throughput characterization technique.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A method for rapid screening of performance-optimized thermoelectric materials
ActiveCN106771706BRich in microstructureShort manufacturing cycleElectrical testingScreening methodX-ray
The invention discloses a rapid screening method of the thermoelectric material with optimized performance; the method comprises the following steps: firstly using a plasma activation sintering technology to prepare a multi-element chalcogenide system diffusion couple, thus obtaining a block material sample bank with rich compositions and microstructures; combining an EPMA (electron probe X ray microscopic analyzer), a FESEM (field emission scan electron microscope) with a PSM (conductivity-Seebeck coefficient scan probe microscope) symptom technologies so as to study the relations between the sample bank composition, structure and thermoelectricity performance, thus screening out the high performance thermoelectric material with specific compositions and microstructures with high flux. The method can effectively improve the information density and efficiency obtained by tests, thus obvious reducing test needing manpower, material resources and cost, and searching the thermoelectric material with excellent performance with high efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Toner, image forming apparatus, image forming method, and toner storage unit
A toner is provided. The toner comprises mother particles and an external additive covering the mother particles. The mother particles comprise a binder resin, and the external additive comprises inorganic particles. The inorganic particles comprise small-size inorganic particles having an equivalent circle diameter of from 30 to 70 nm and large-size inorganic particles having an equivalent circle diameter of from 150 to 200 nm and a circularity of 0.85 or more. The large-size inorganic particles are 20 to 70 in number per 100 μm2 image area of the toner observed with a field-emission scanning electron microscope.
Owner:RICOH KK
Orientated-growth latticed high-performance carbon nano-tube field emission array and preparation method
InactiveCN102324350BImprove structural stabilityEnhance the edge effectDischarge tube/lamp detailsField emission deviceX-ray
The invention discloses an orientated-growth latticed high-performance carbon nano-tube field emission array, which comprises a conductive substrate and latticed orientated carbon nano-tube arrays grown on the substrate, wherein the carbon nano-tube arrays are distributed into a latticed shape and form an integral structure. By the technical scheme, the structural stability of small-size carbon nano-tube arrays is improved, the edge effect of the carbon nano-tube arrays is enhanced, and then a turn-on electric field and a threshold electric field are reduced to improve the emission current density. The orientated-growth latticed high-performance carbon nano-tube field emission array is suitable for field emission devices having high requirements on current emission performance, such as electron sources in an X ray source, a microwave amplifier, a field emission scanning electron microscope and the like.
Owner:上海康众光电科技有限公司
A method for preparing cathode material agcuo2 by anodic oxidation electrodeposition
InactiveCN106637332BSimple and fast operationLow costElectrolytic inorganic material coatingCell electrodesWater bathsThin film electrode
The invention discloses a method for preparing cathode material AgCuO2 through anodic oxidation electrodeposition. The method is characterized in that in strong alkaline mixed electrolyte, ammonia water and Ag + are complexed and ammonia water and Cu2 + are complexed through an anodic electrodeposition method, constant current electrodeposition is carried out in a water bath at the temperature of 40 DEG C, an AgCuO2 thin film electrode which has the sheet-like morphology and is deposited on ITO conductive glass is obtained in a short period of time, and then tests of X-ray powder diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy representation and a discharging experiment in an alkaline solution are conducted on the deposited AgCuO2 thin film electrode. The method has the beneficial effects that the used raw materials are low in cost, equipment is simple, operation is easy, convenient and fast, and meanwhile the environmental friendliness is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting microstructure of reverse osmosis membrane separating layer
InactiveCN102302900BObserving the microstructureThe pre-processing process is simpleSemi-permeable membranesSolubilityOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for detecting a microstructure of a reverse osmosis membrane separating layer. The method comprises the following steps of: completely peeling a non-woven layer of a reverse osmosis membrane sheet; remaining a separating layer and a supporting layer and flatly paving the separating layer and the supporting layer on a glass sheet and adhering the separating layer and the supporting layer to the glass sheet, so that the supporting layer is upward and the separating layer contacts with the glass sheet; according to the solubility difference between the separating layer and the supporting layer, dissolving and removing the supporting layer by selecting a proper volatile organic solvent; removing the organic solvent from the separating layer through vacuum drying; cutting the glass sheet with the separating layer into small blocks according to the size of a scanning electronic microscope sample platform; spraying gold; and observing the microstructures of the reverse side and the section of the separating layer by using a field emission scanning electronic microscope. By the method, the microstructures of the reverse side and the section of the separating layer of the reverse osmosis membrane can be observed clearly. The method is simple in pretreatment process of samples, low in cost, high in operability and easy in popularization. By the method, the microstructures of the reverse side and the section of the separating layer of the reverse osmosis membrane can be observed by using the scanning electronic microscope at home and abroad.
Owner:TIANJIN SEA WATER DESALINATION & COMPLEX UTILIZATION INST STATE OCEANOGRAPHI
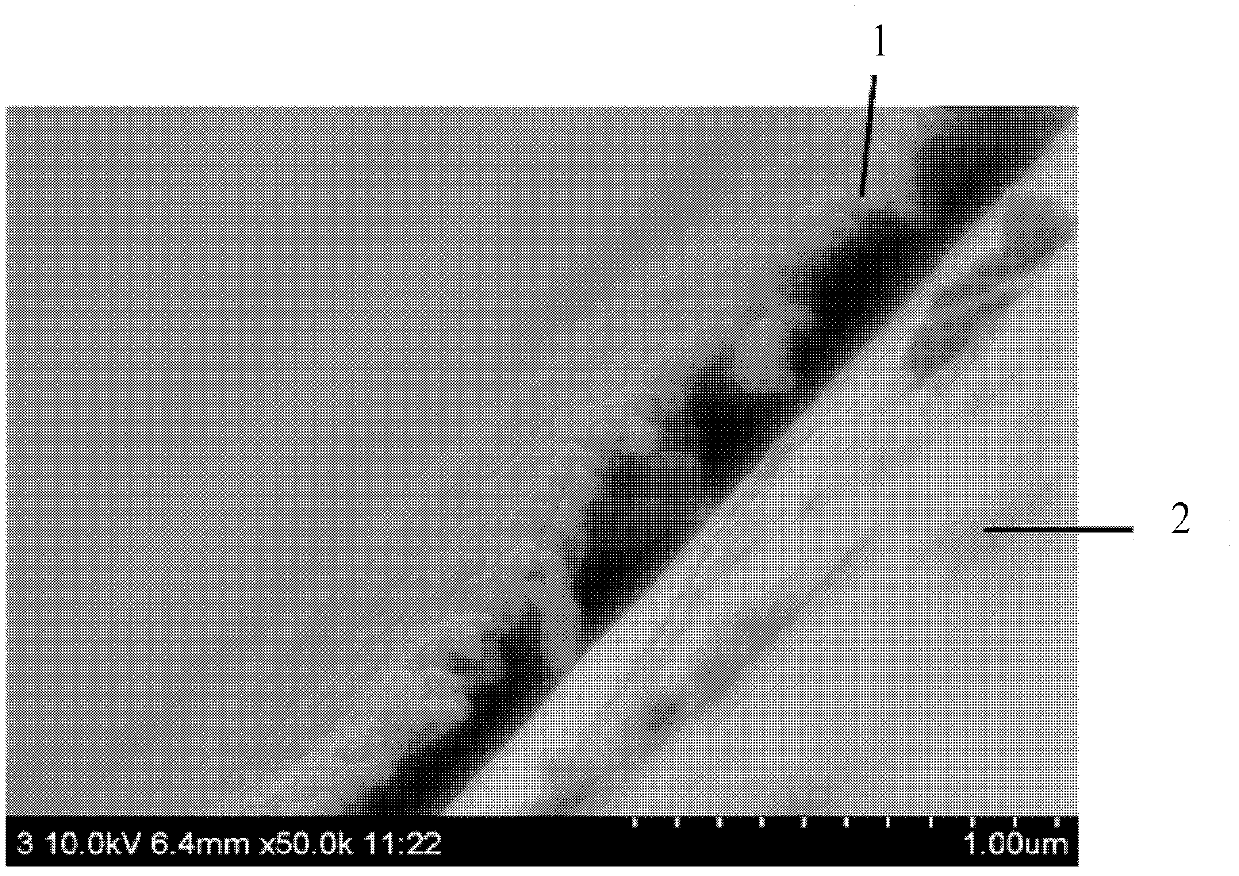
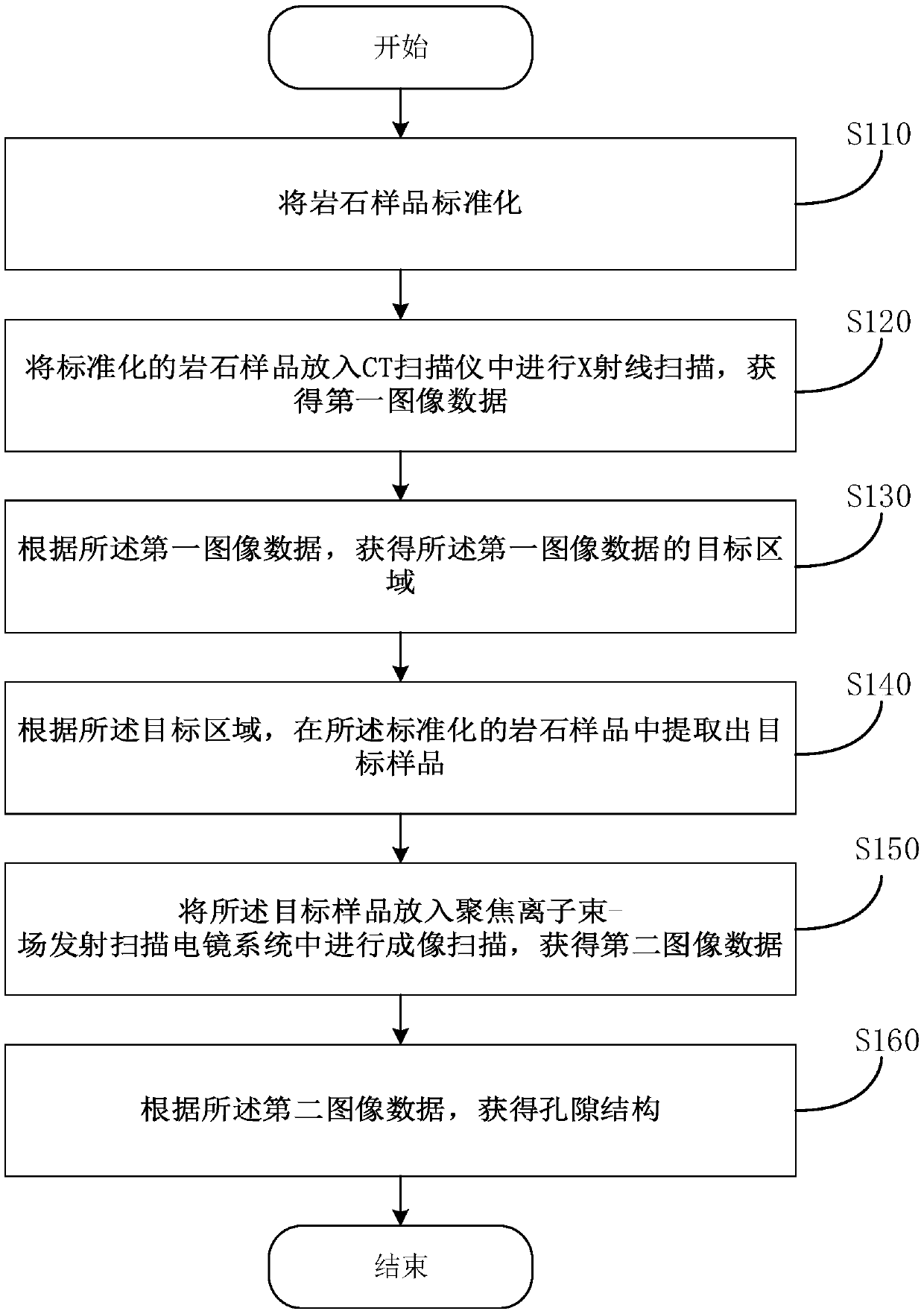
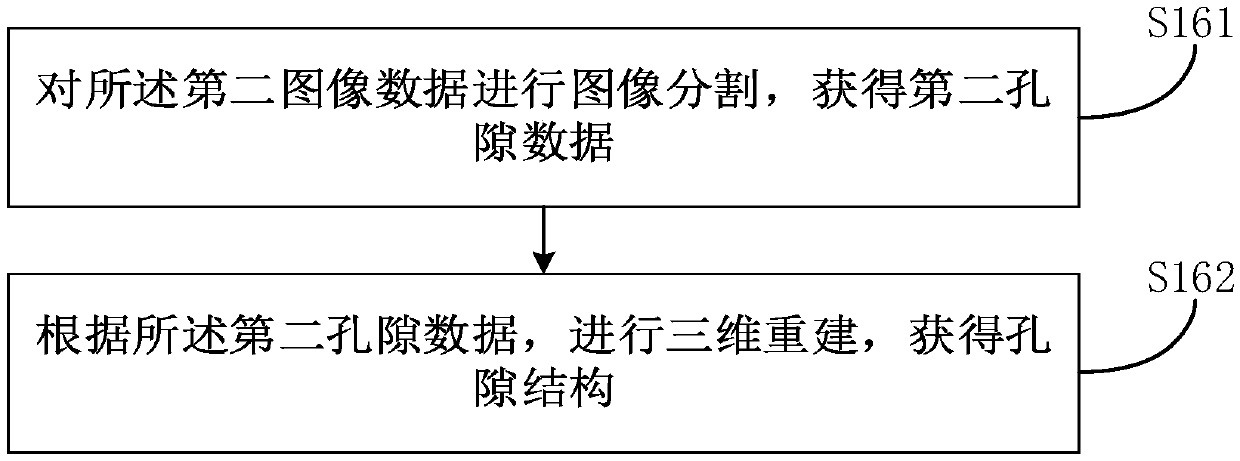
A method and device for acquiring pore structure
InactiveCN106918607BAccurate observationAccurate researchMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionCt scannersX-ray
The invention provides a pore structure obtaining method and device, and belongs to the technical fields of geological exploration and physical geography. The method comprises the steps: standardizing a rock sample; placing the standardized rock sample into a CT scanner, and carrying out X ray scanning to obtain first image data; according to the first image data, obtaining a target area of the first image data; according to the target area, extracting a target sample from the standardized rock sample; placing the target sample into a focused ion beam-field emission scanning electron microscopy system, and carrying out imaging scanning, to obtain second image data; and according to the second image data, obtaining a pore structure. The method can be used for acquiring and characterizing the pore structure of the rock sample and the pore structure of a specified area or an unclear area. The pore structure of rock is specifically and systematically acquired and characterized so as to accurately observe and study the pore structure in the rock sample and the dependence relationship between pores in the rock sample.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
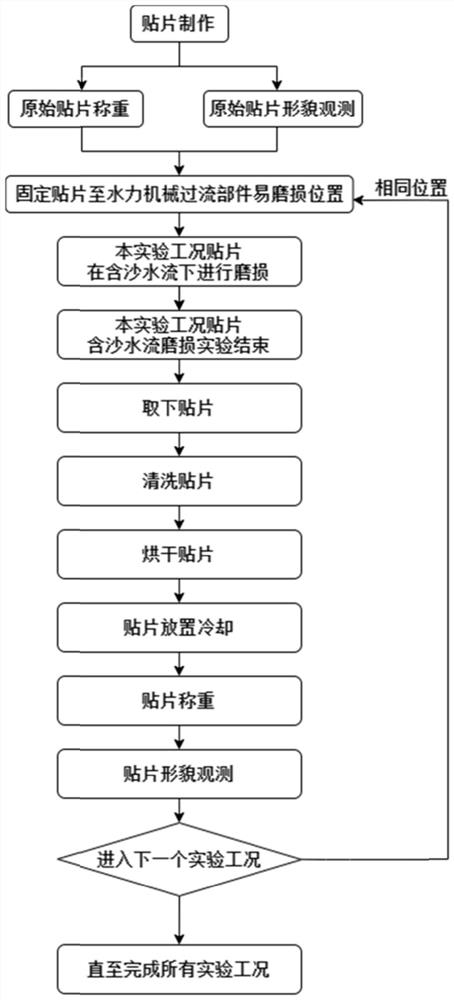
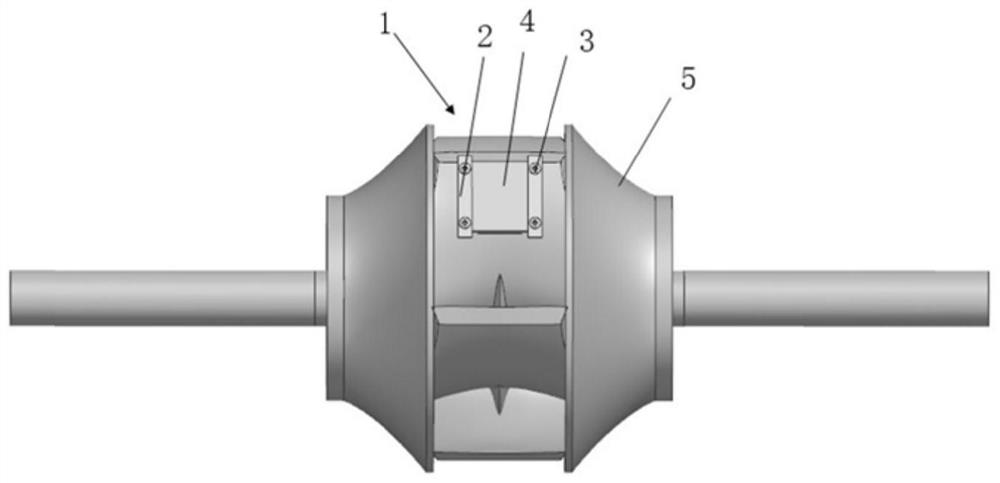
Hydraulic machinery sediment wear experiment method and application
PendingCN114839100AVisually reflect the amount of wearVisually reflect the characteristicsWeighing by removing componentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoil scienceField experiment
The invention discloses a hydraulic machinery sediment wear experiment method and application. The method can be used for a hydraulic machinery sediment wear mesoscopic quantitative experiment. According to the invention, a patch which is easy to wear and bend is fixed at a position where the flow passage component of the hydraulic machinery is seriously worn, after each experimental working condition is completed, the patch is taken down, cleaned, dried and weighed, and is put under a field emission scanning electron microscope for morphology observation, so that the sand wear loss weight and the sand wear surface morphological characteristics are directly reflected. The method is not only suitable for hydraulic machinery indoor model experiments, but also suitable for engineering field experiments, can carry out hydraulic machinery silt wear mesoscopic quantitative research, visually reflects wear loss weight and silt wear characteristics, and provides a new method for hydraulic machinery silt wear research.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Experimental method for electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure Experimental method for electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1739d857-3770-452a-ba3b-bc82905dd293/HDA0002065859030000011.png)
![Experimental method for electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure Experimental method for electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1739d857-3770-452a-ba3b-bc82905dd293/HDA0002065859030000012.png)
![Experimental method for electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure Experimental method for electric pulse auxiliary regulation and control additive manufacturing near-[Beta] type titanium alloy metallographic structure](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1739d857-3770-452a-ba3b-bc82905dd293/HDA0002065859030000013.png)