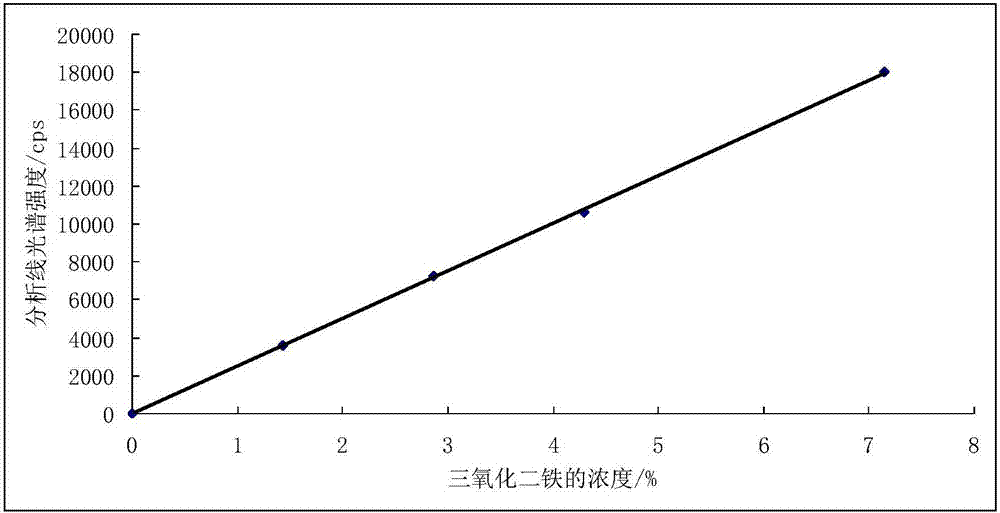
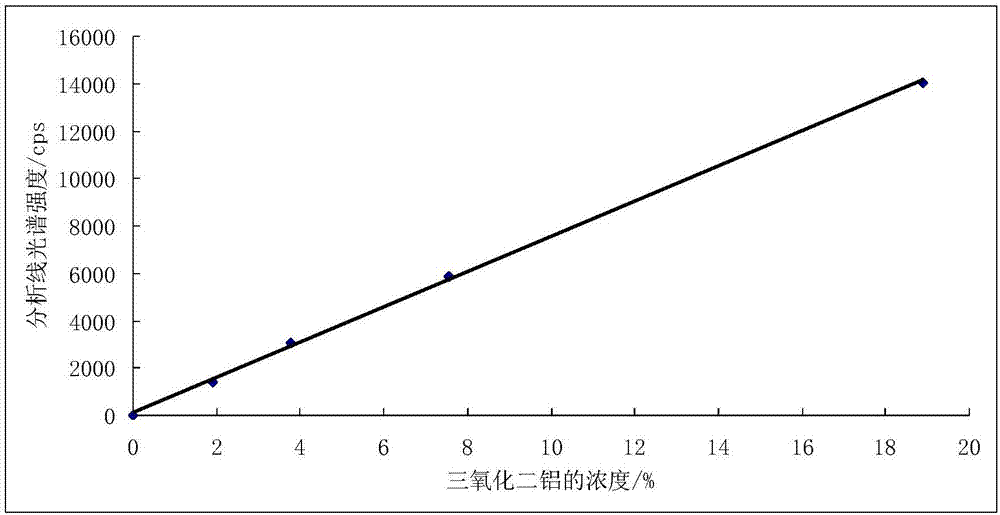
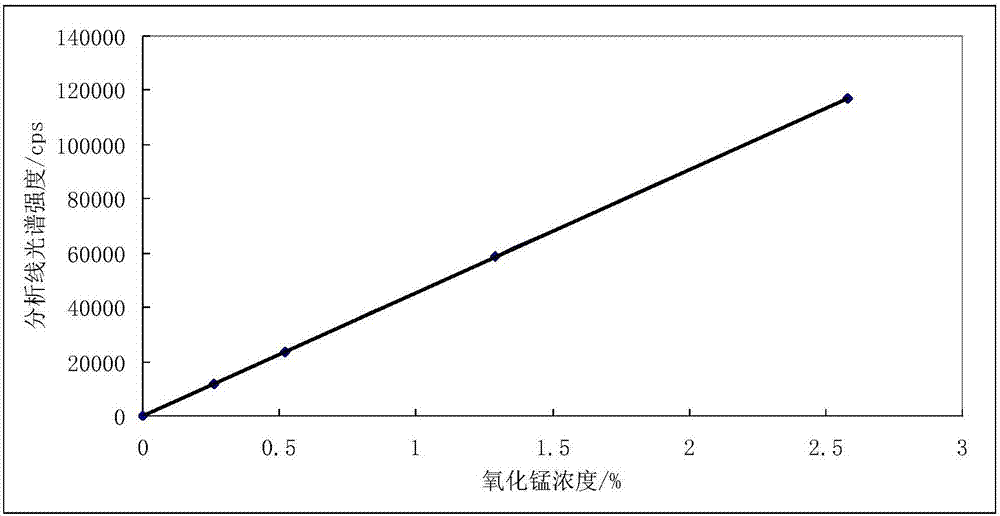
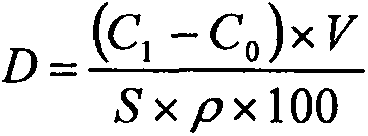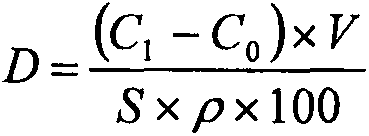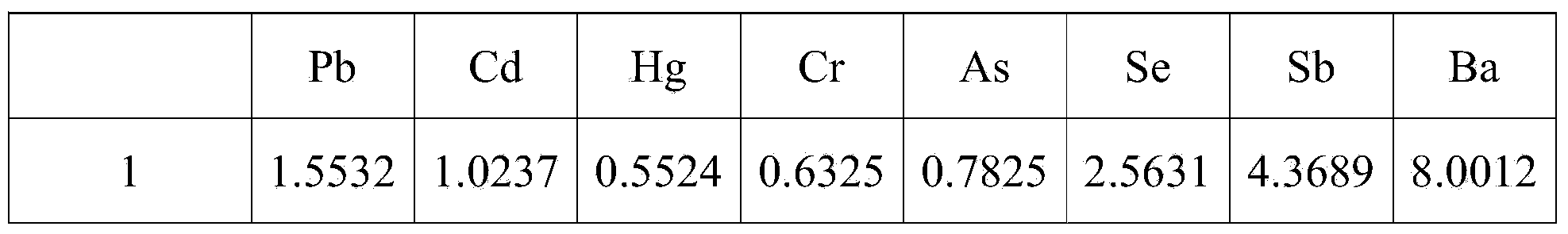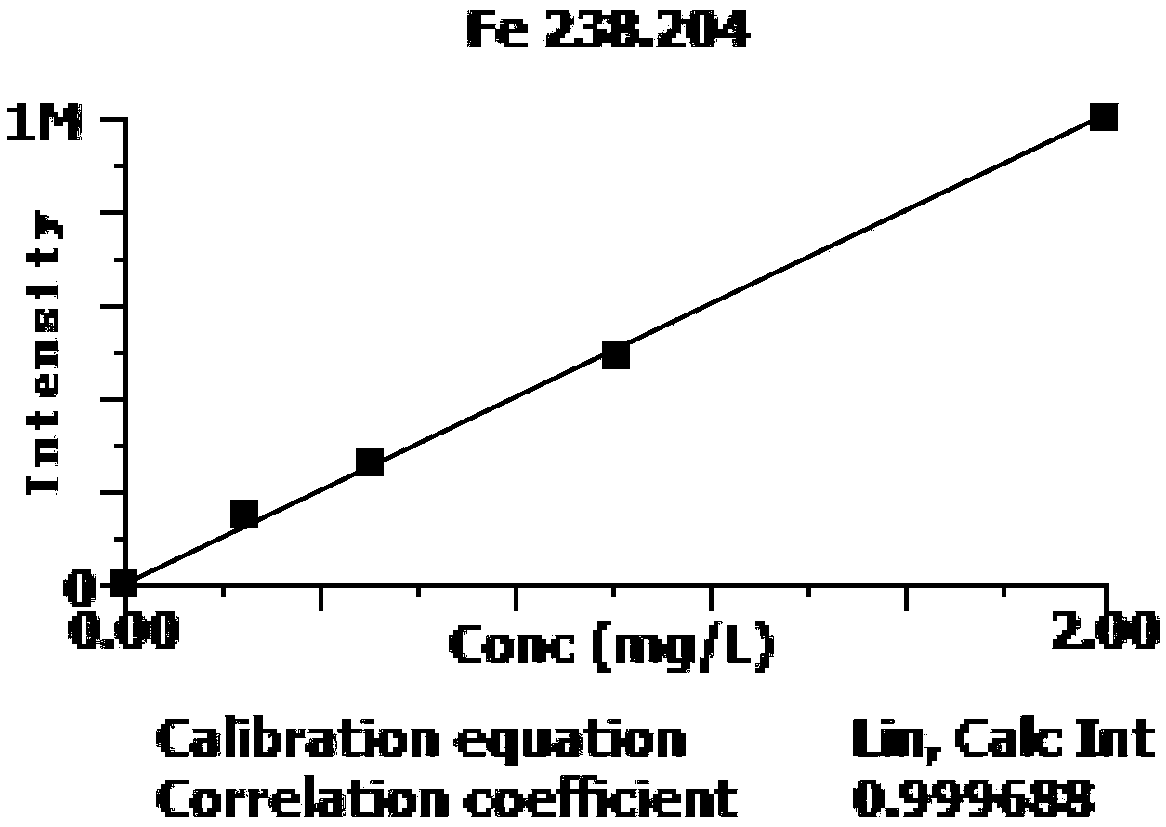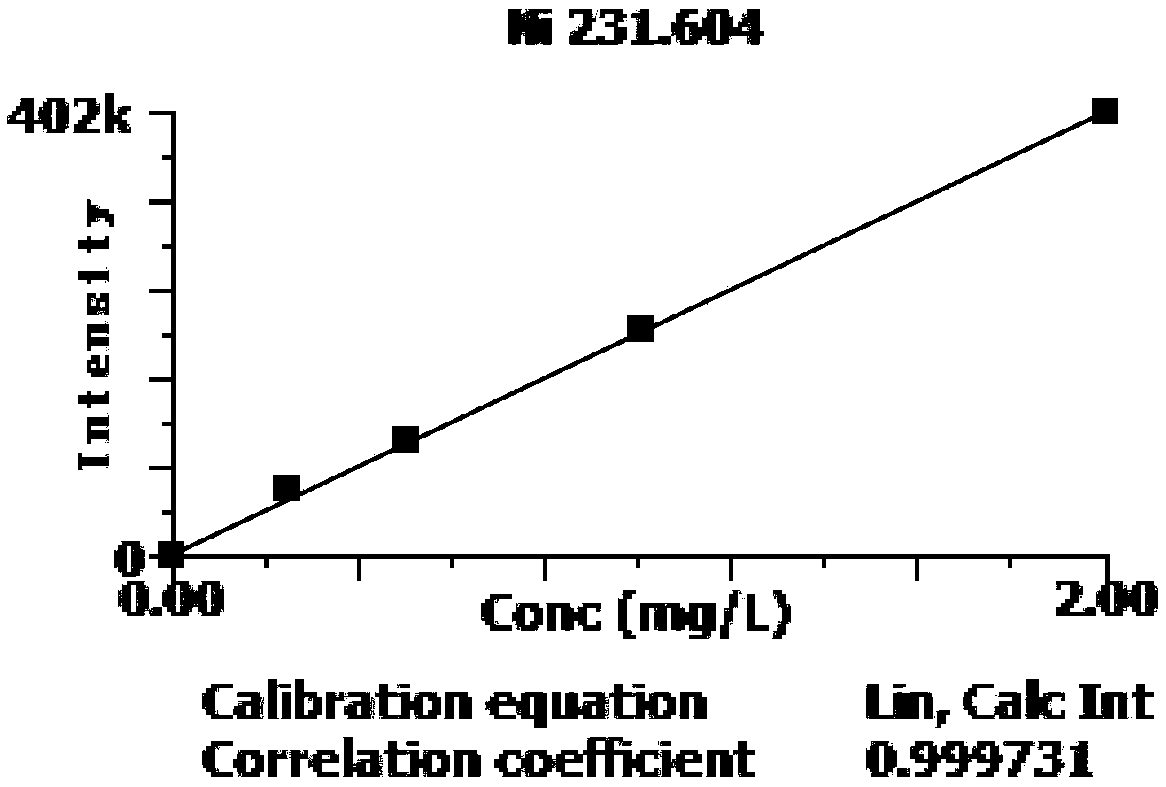Patents
Literature
94 results about "Optical Emission Spectrometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
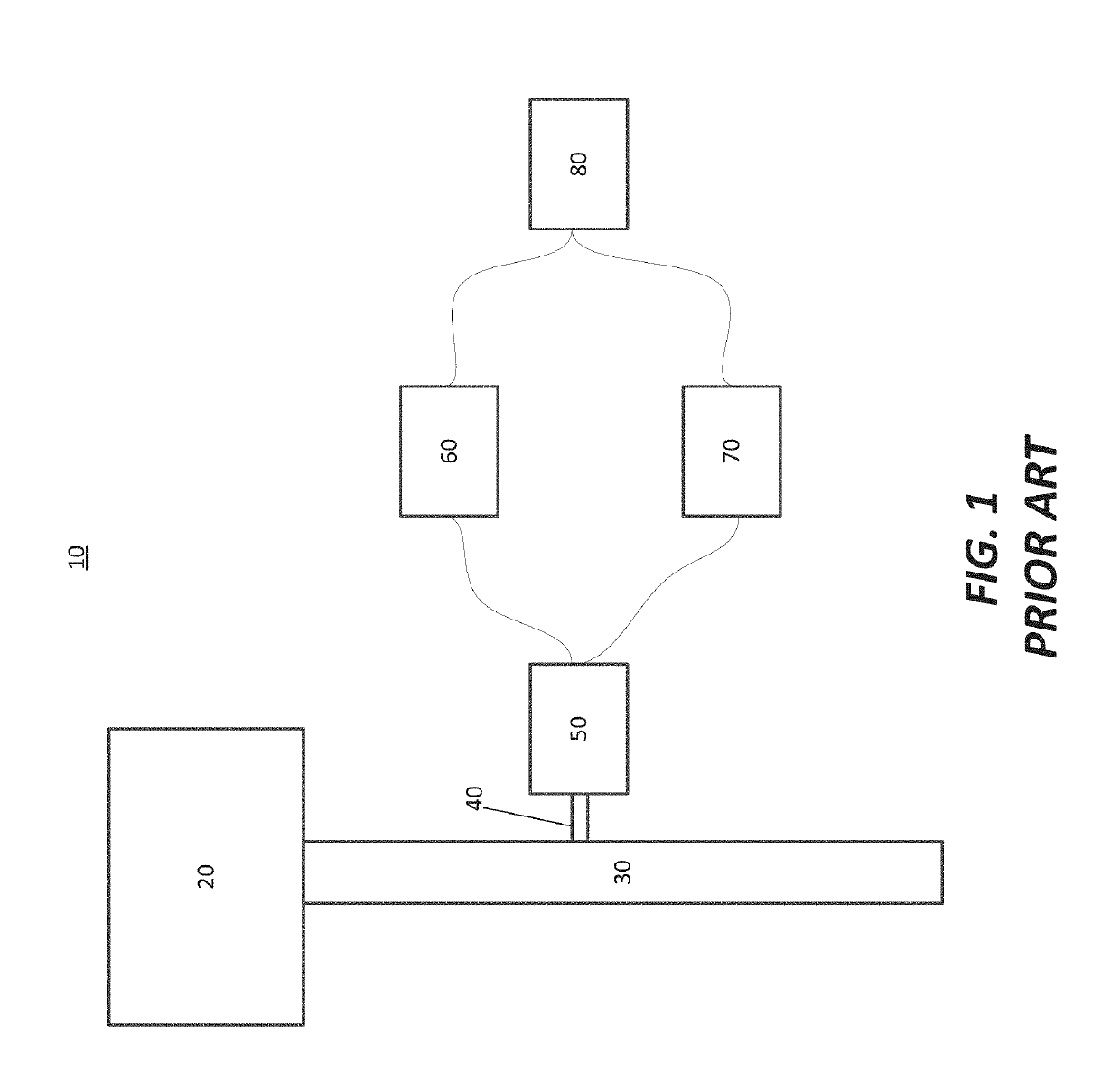
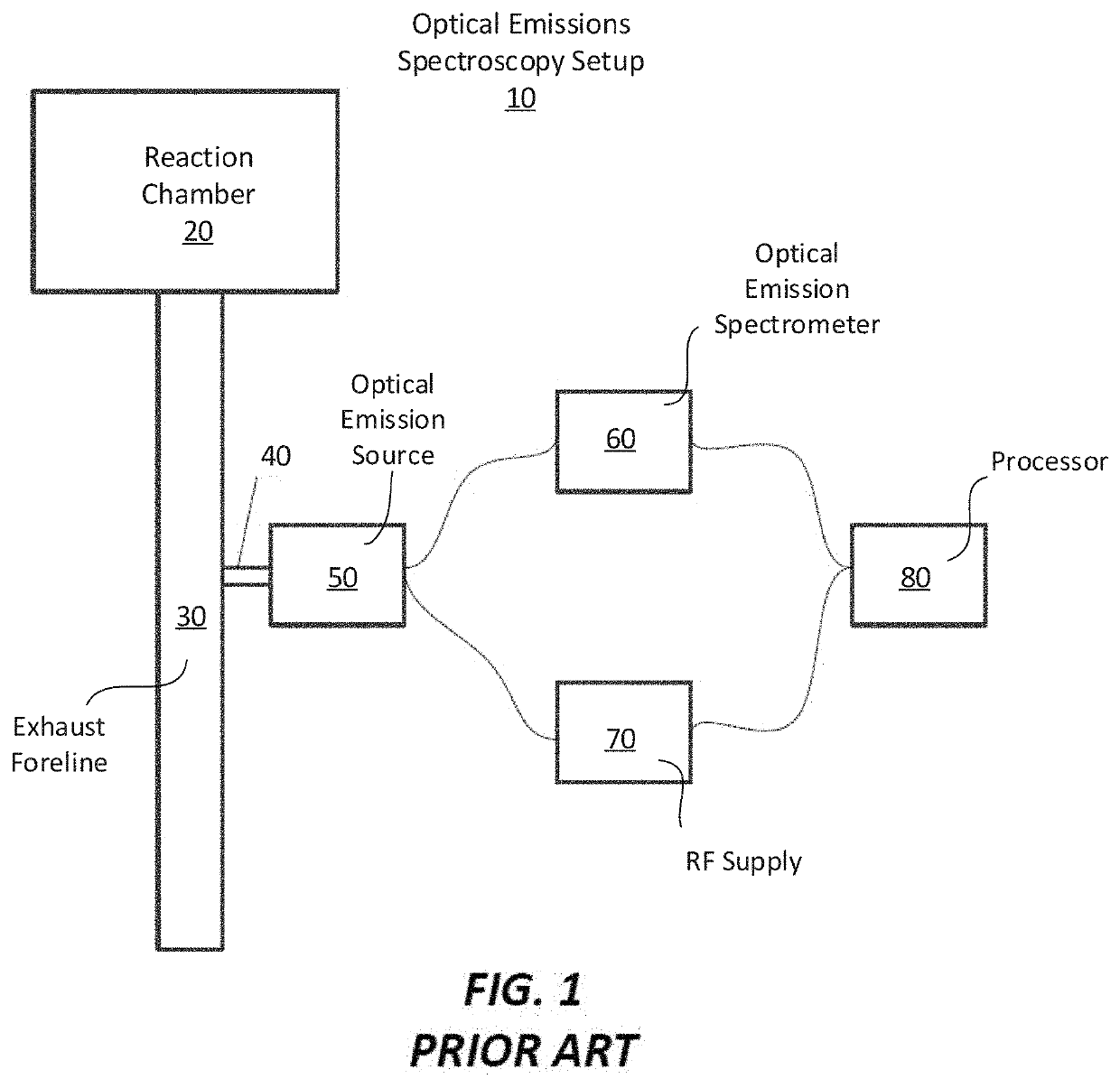
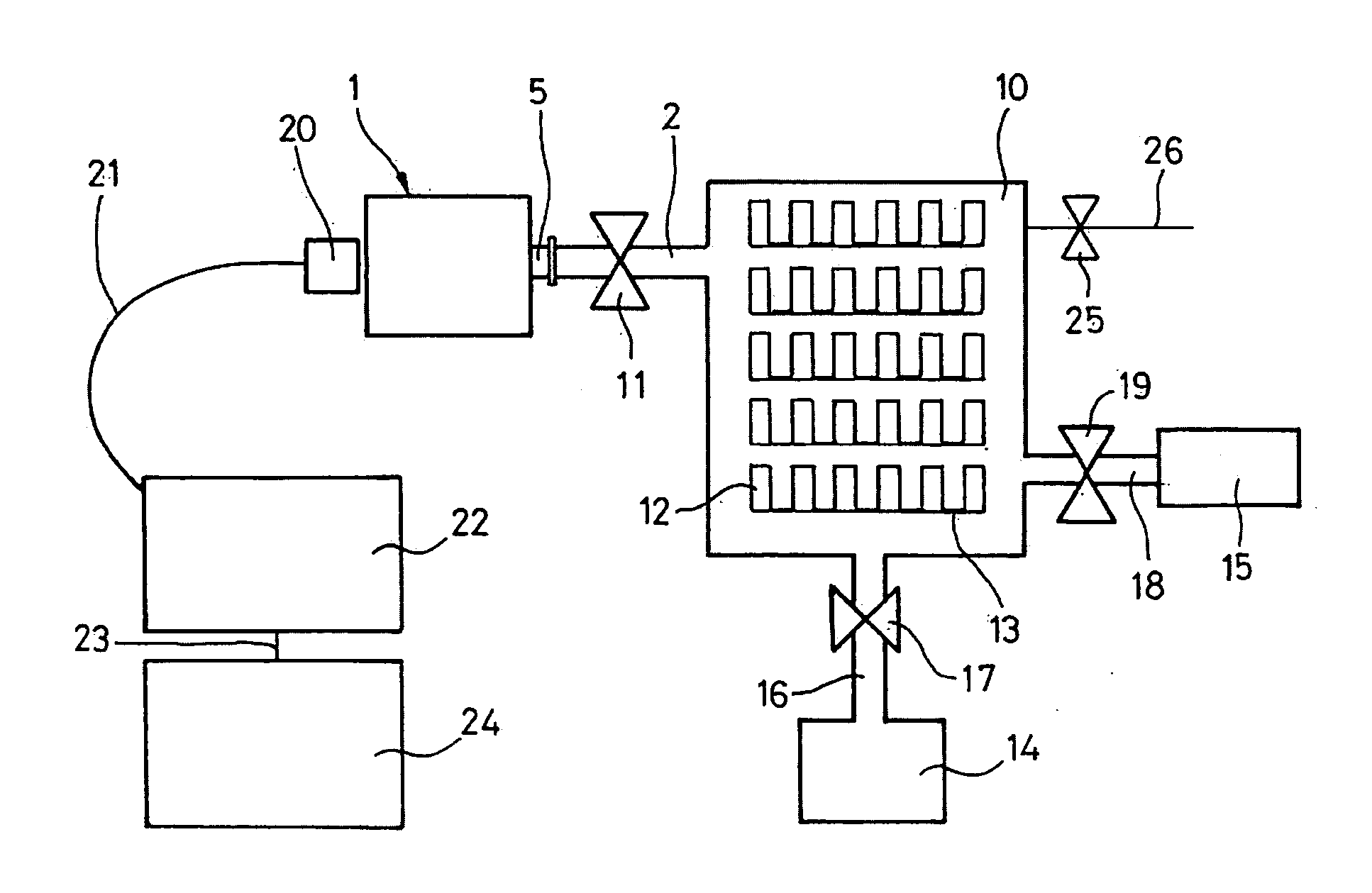
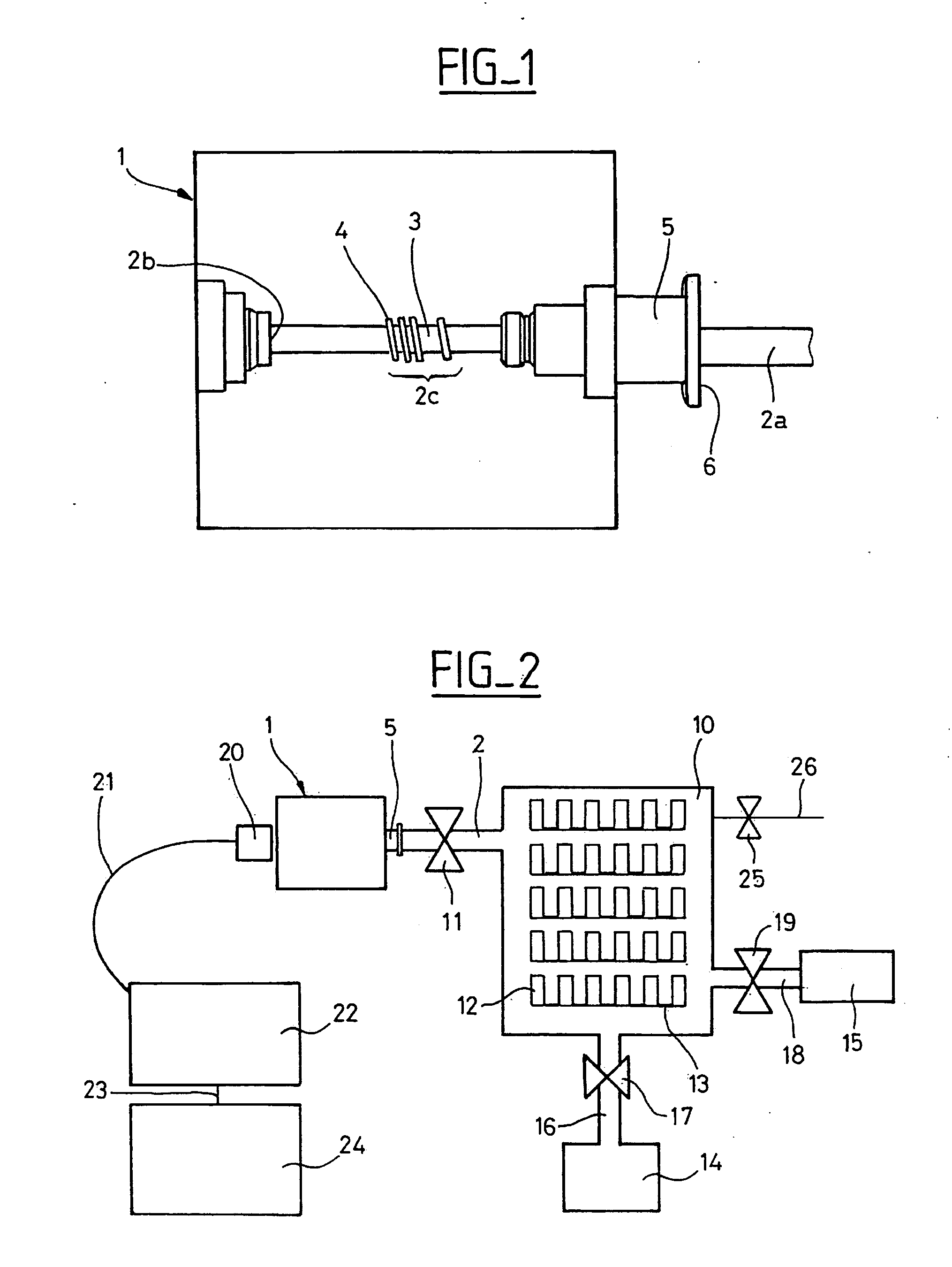
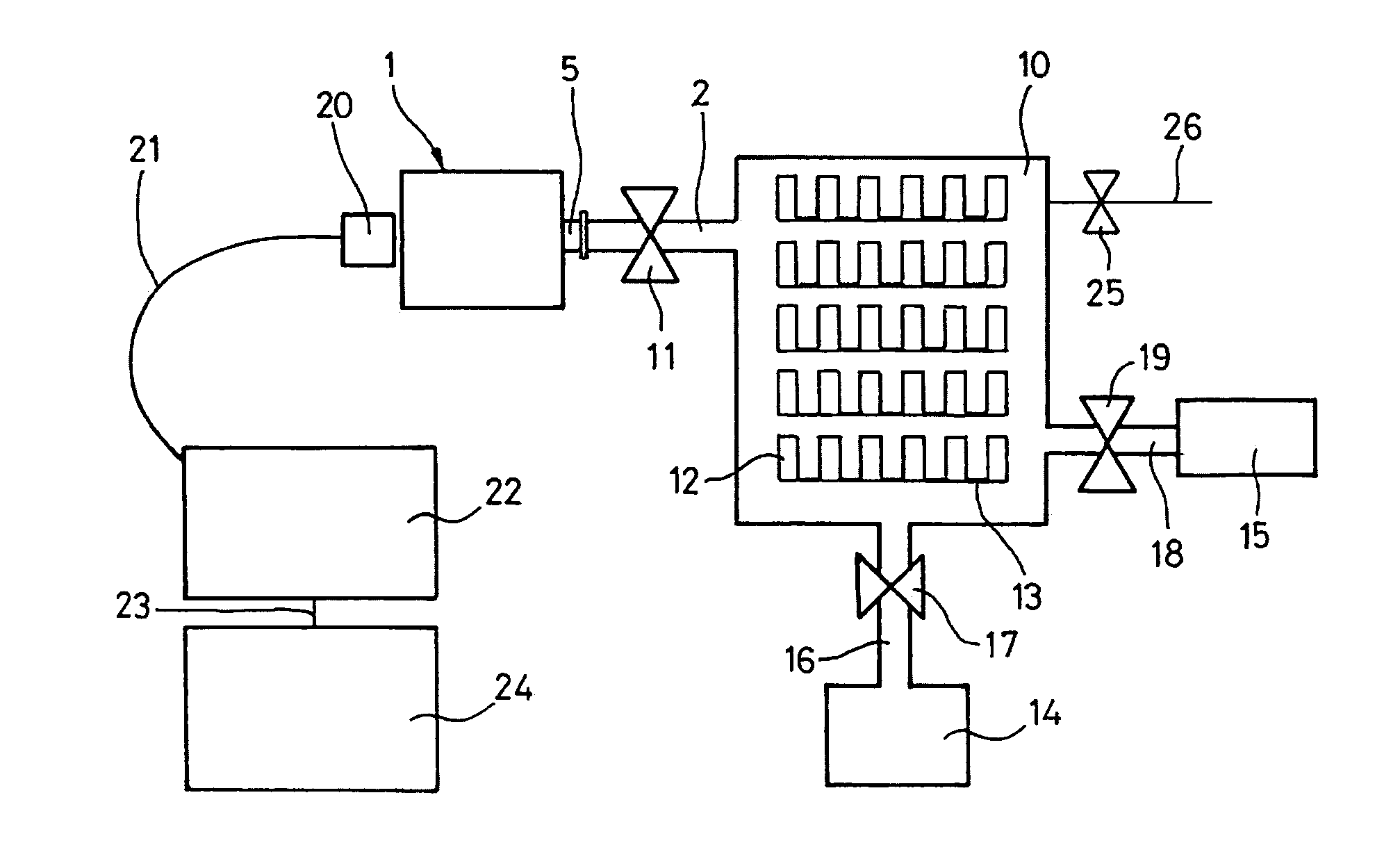
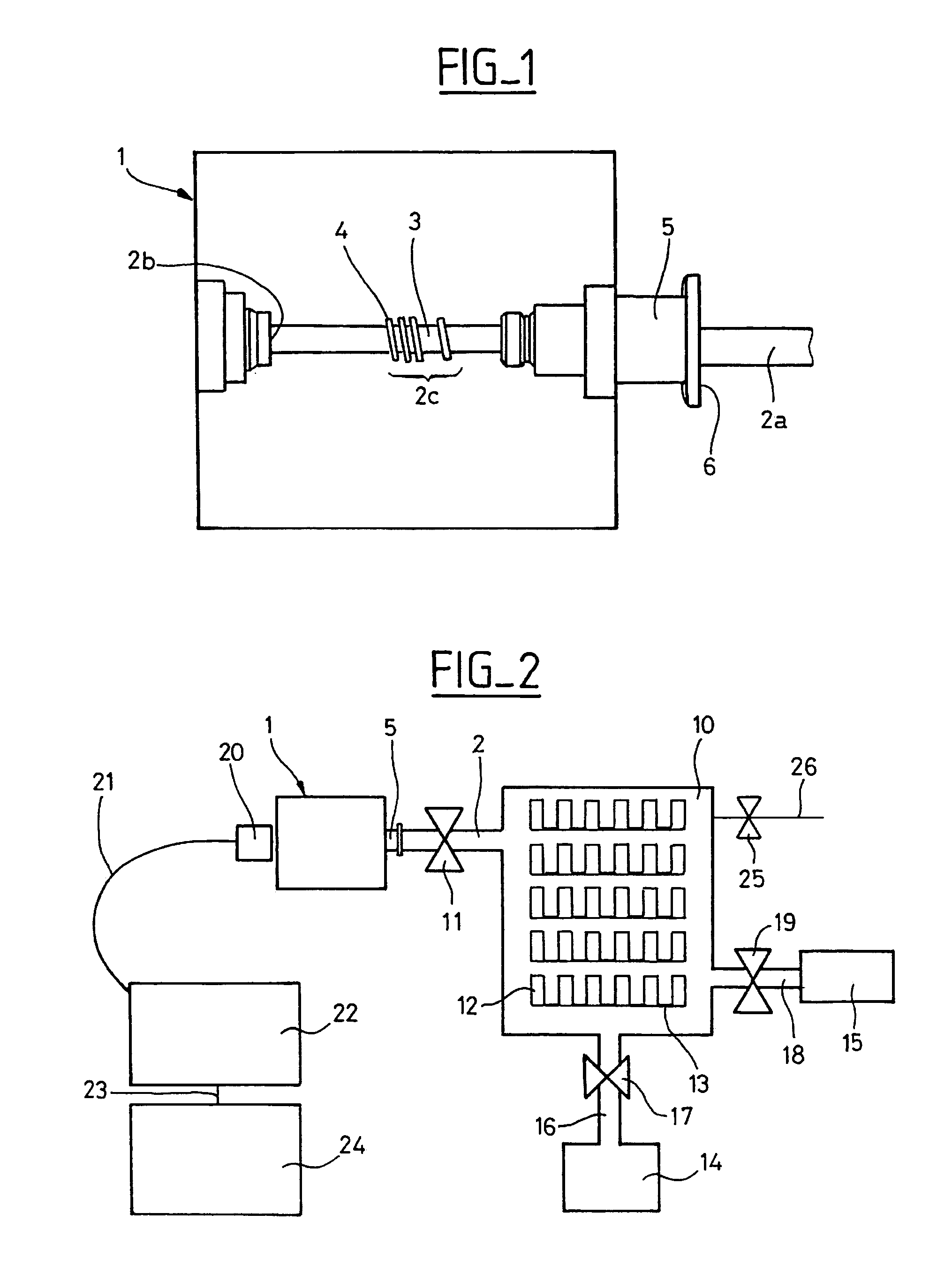
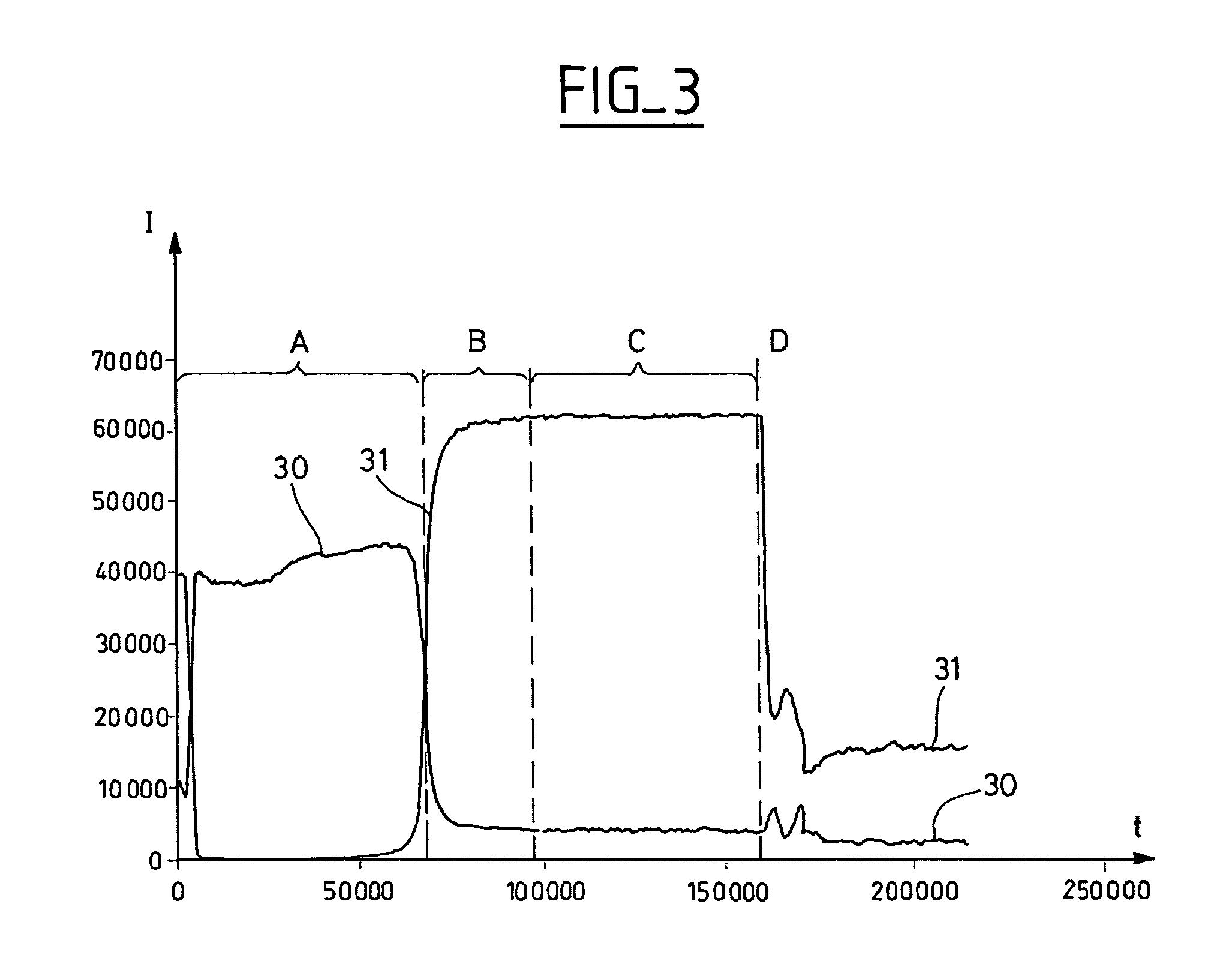
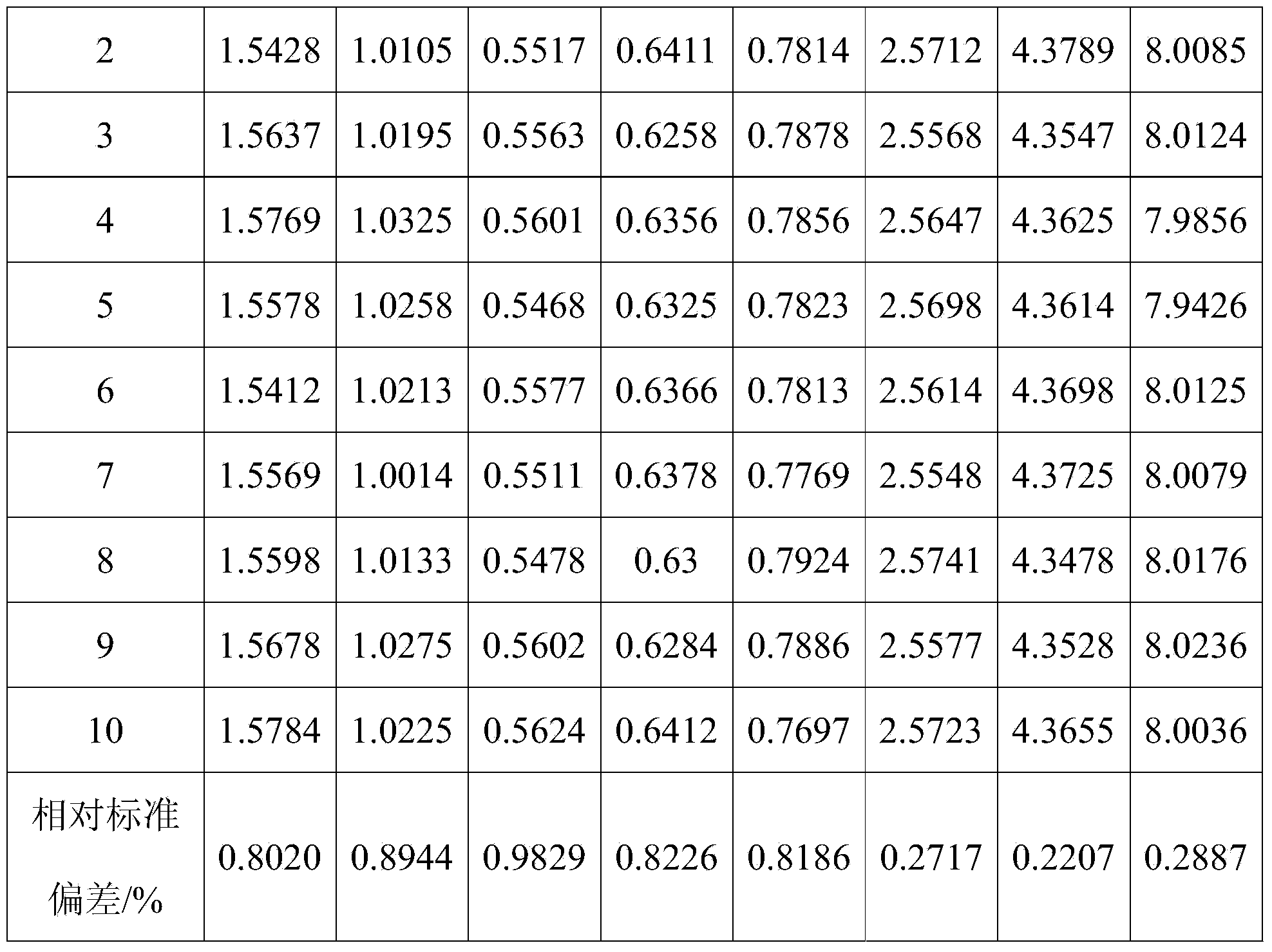
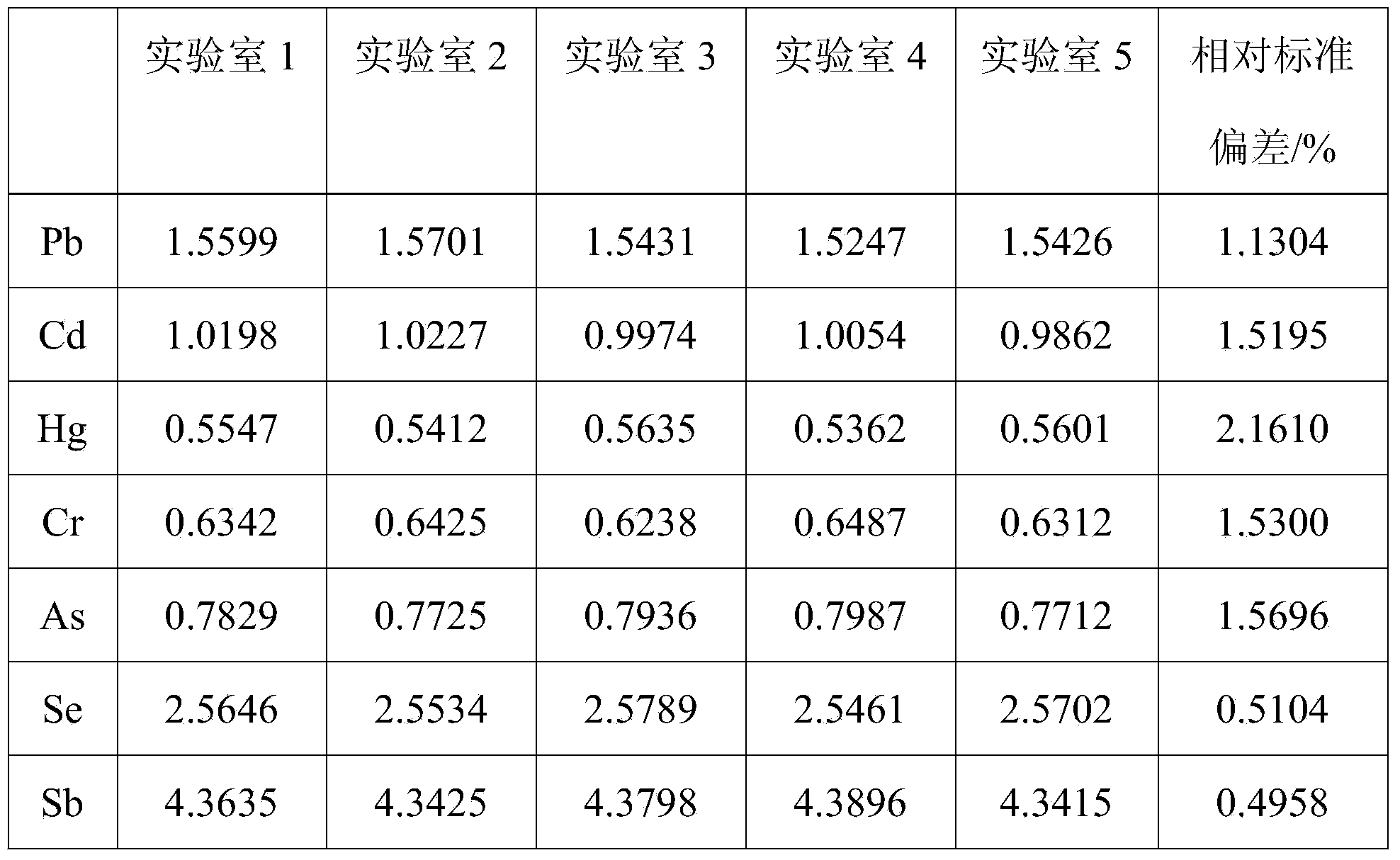
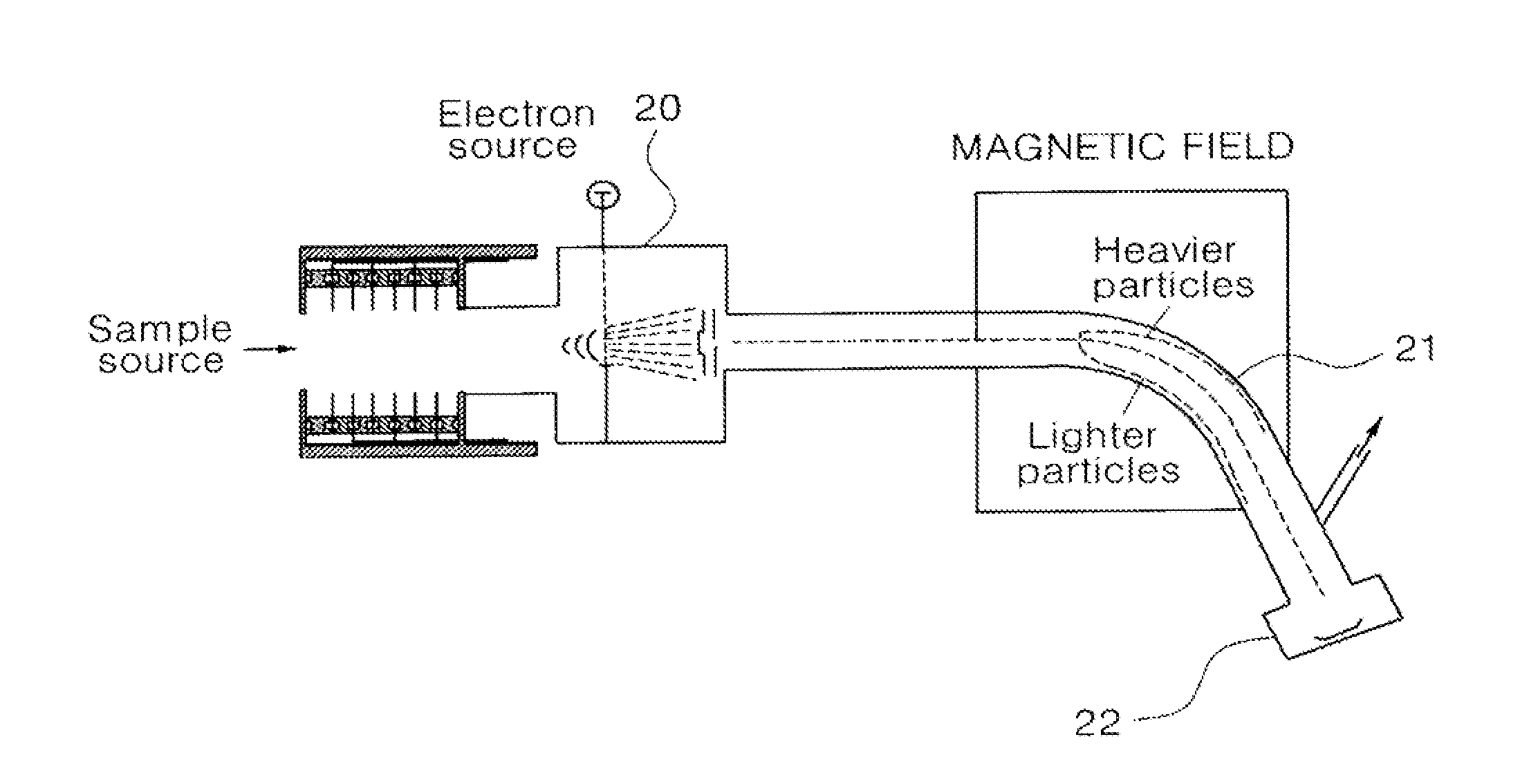
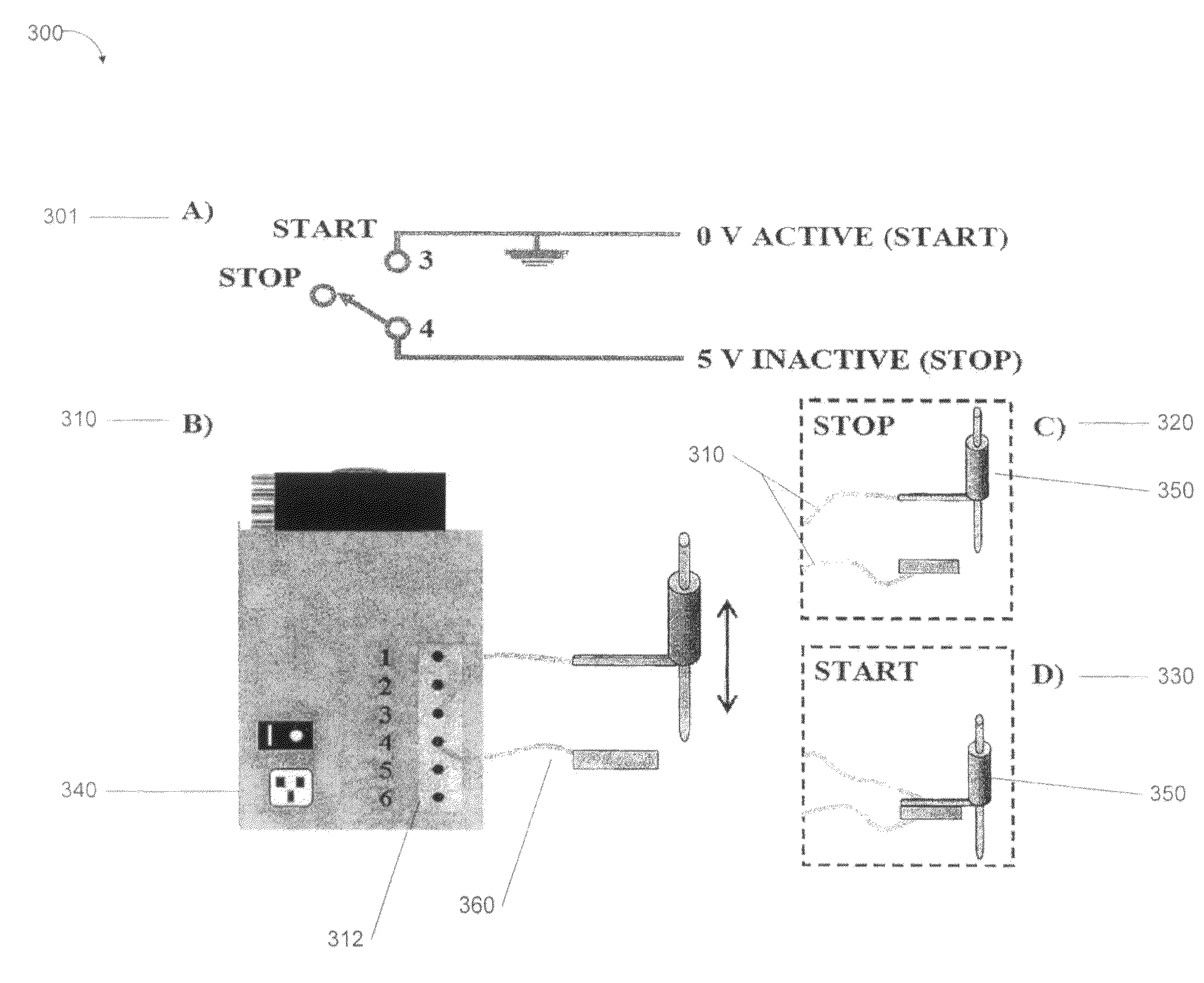
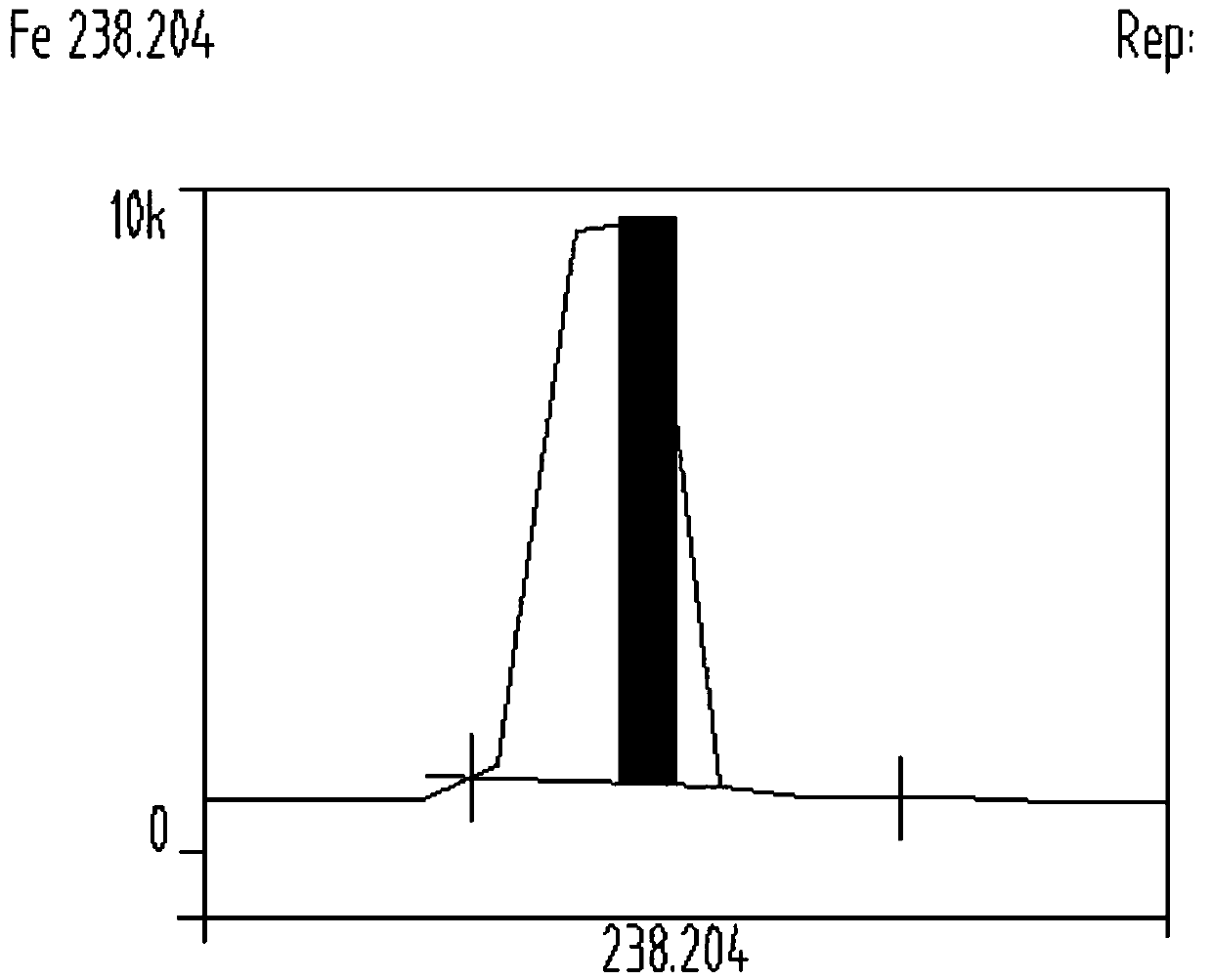
An emission spectrometer that generates a high-energy spark across an argon-filled gap between an electrode and a solid sample, causing emission of radiation from the excited sample surface and resulting in wavelengths characteristic of the elemental composition.
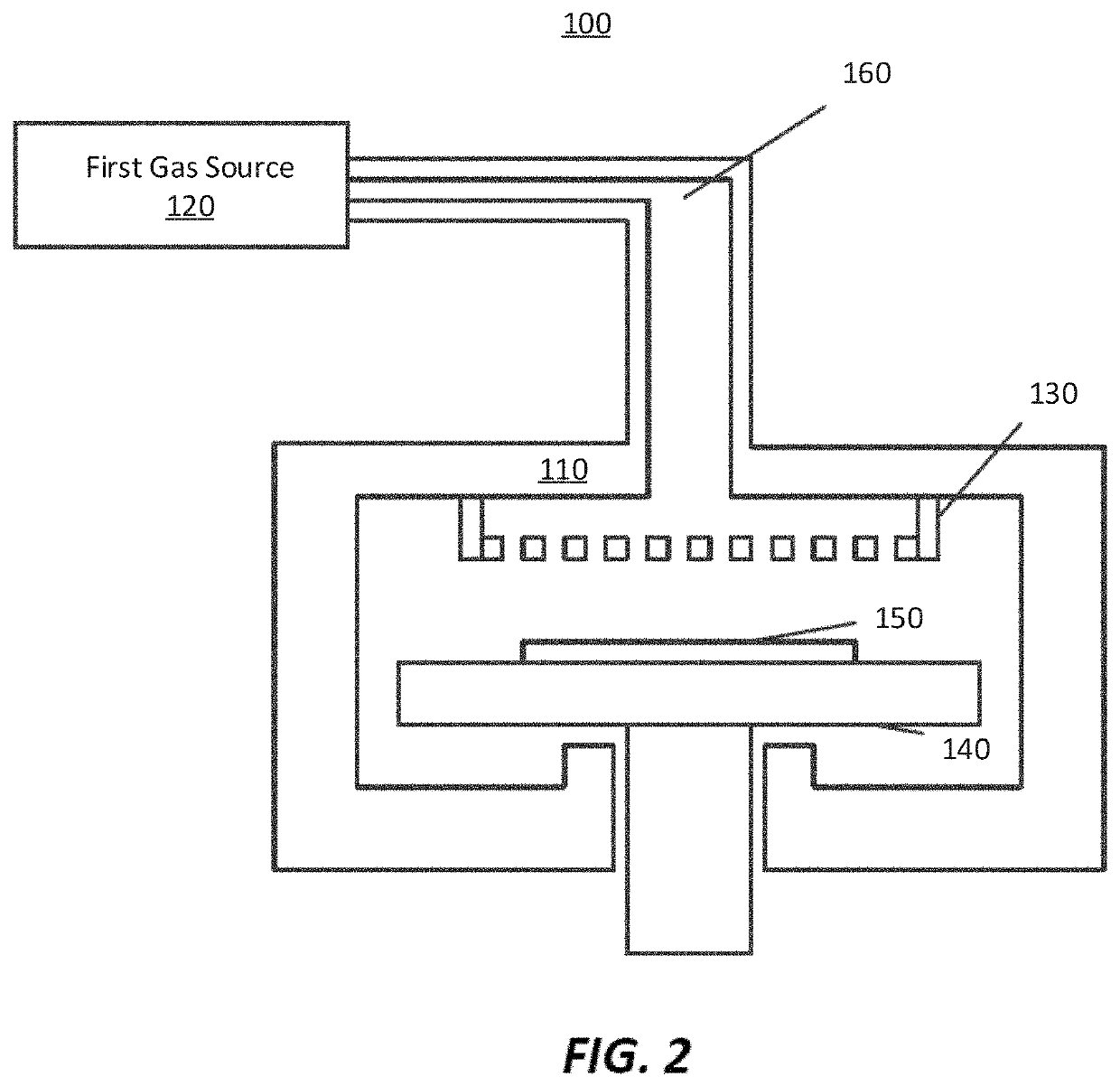
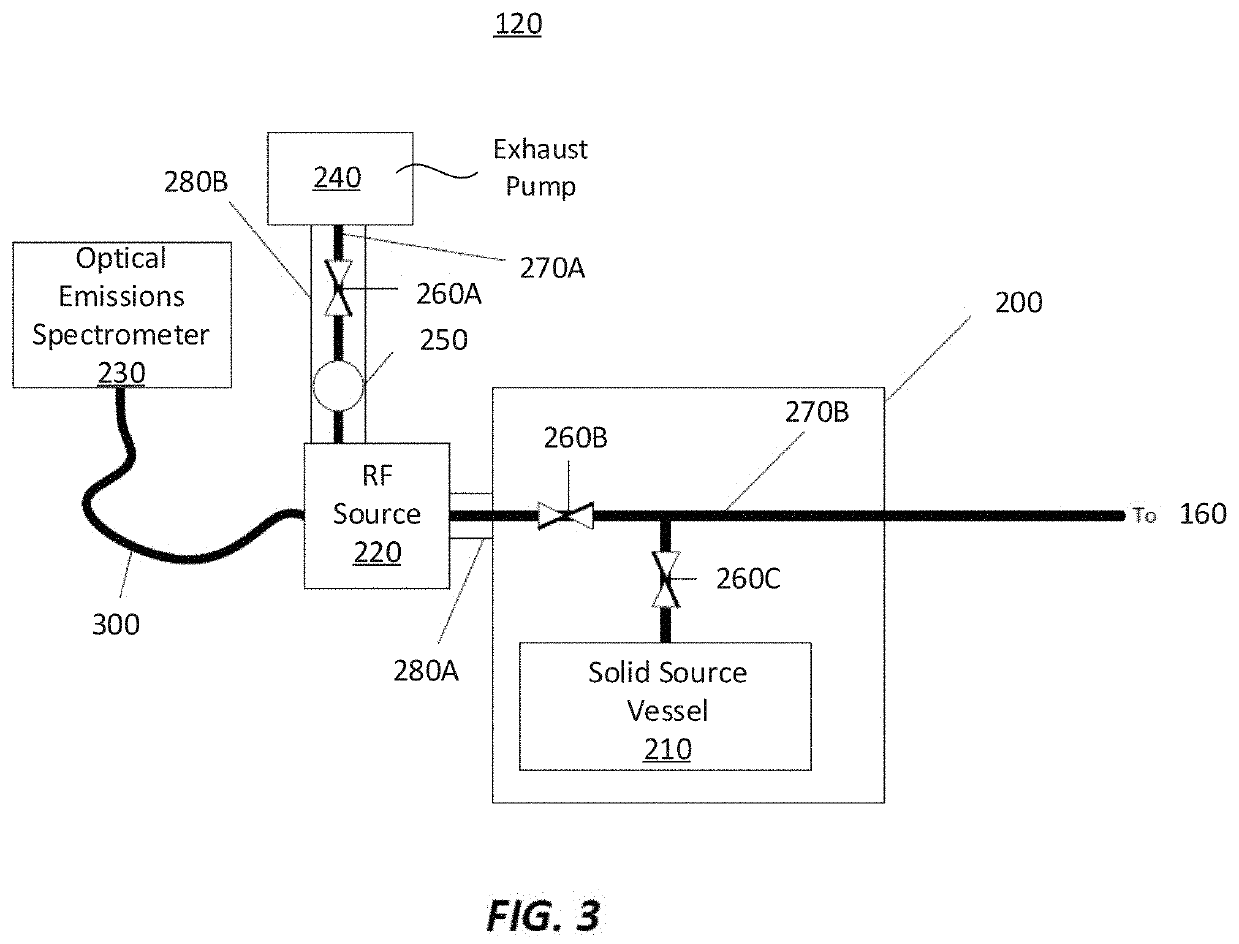
Apparatus for detecting or monitoring for a chemical precursor in a high temperature environment
ActiveUS20190264324A1Emission spectroscopyElectric discharge tubesOptical Emission SpectrometerSmall sample
An apparatus and method are disclosed for monitoring and / or detecting concentrations of a chemical precursor in a reaction chamber. The apparatus and method have an advantage of operating in a high temperature environment. An optical emissions spectrometer (OES) is coupled to a gas source, such as a solid source vessel, in order to monitor or detect an output of the chemical precursor to the reaction chamber. Alternatively, a small sample of precursor can be periodically monitored flowing into the OES and into a vacuum pump, thus bypassing the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Apparatus for detecting or monitoring for a chemical precursor in a high temperature environment
ActiveUS20210180189A1Emission spectroscopyElectric discharge tubesOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical spectrometer
An apparatus and method are disclosed for monitoring and / or detecting concentrations of a chemical precursor in a reaction chamber. The apparatus and method have an advantage of operating in a high temperature environment. An optical emissions spectrometer (OES) is coupled to a gas source, such as a solid source vessel, in order to monitor or detect an output of the chemical precursor to the reaction chamber. Alternatively, a small sample of precursor can be periodically monitored flowing into the OES and into a vacuum pump, thus bypassing the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
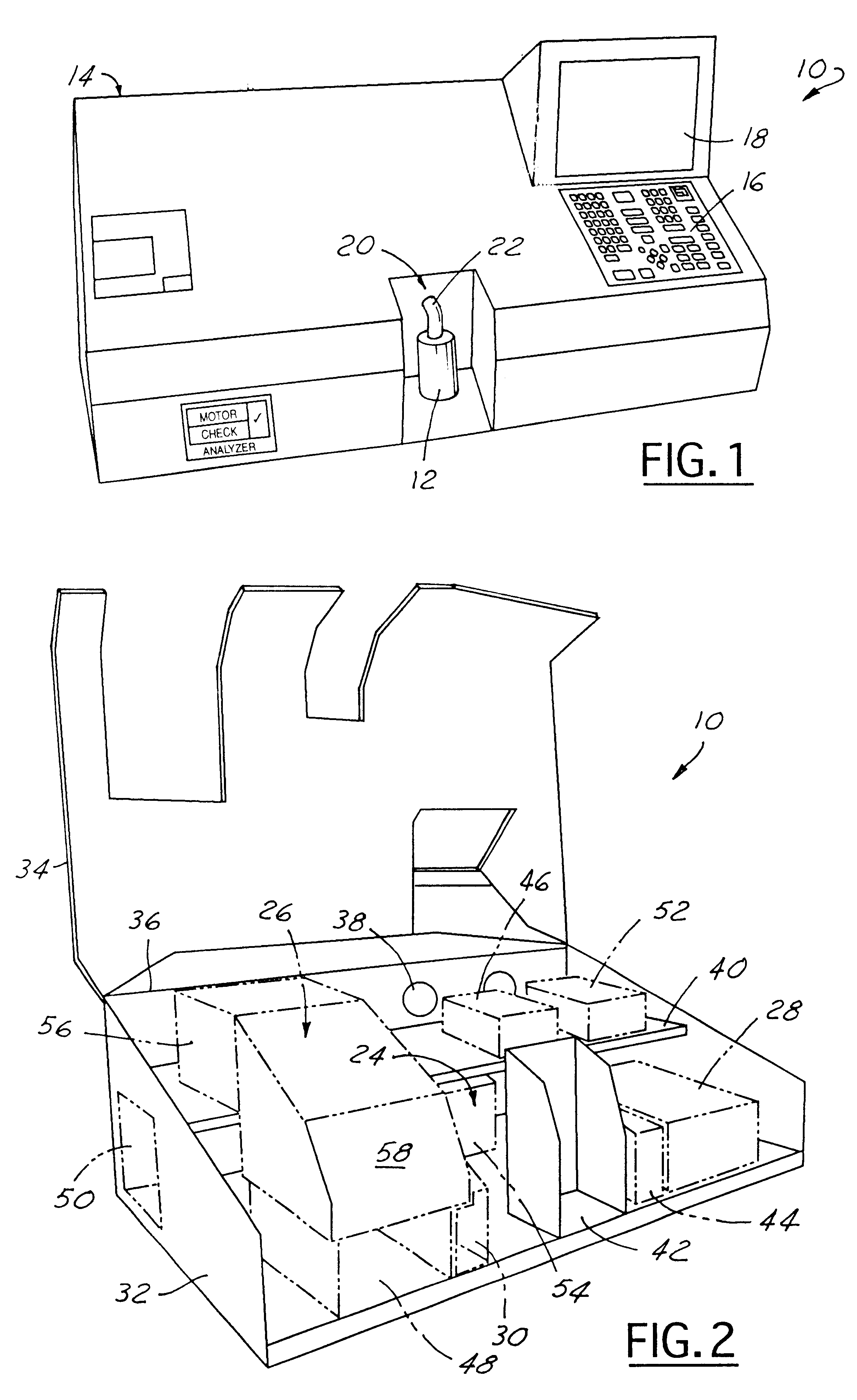
On-site analyzer
InactiveUS6452179B1Minimizes undesirable effect of fringingEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical spectrometer
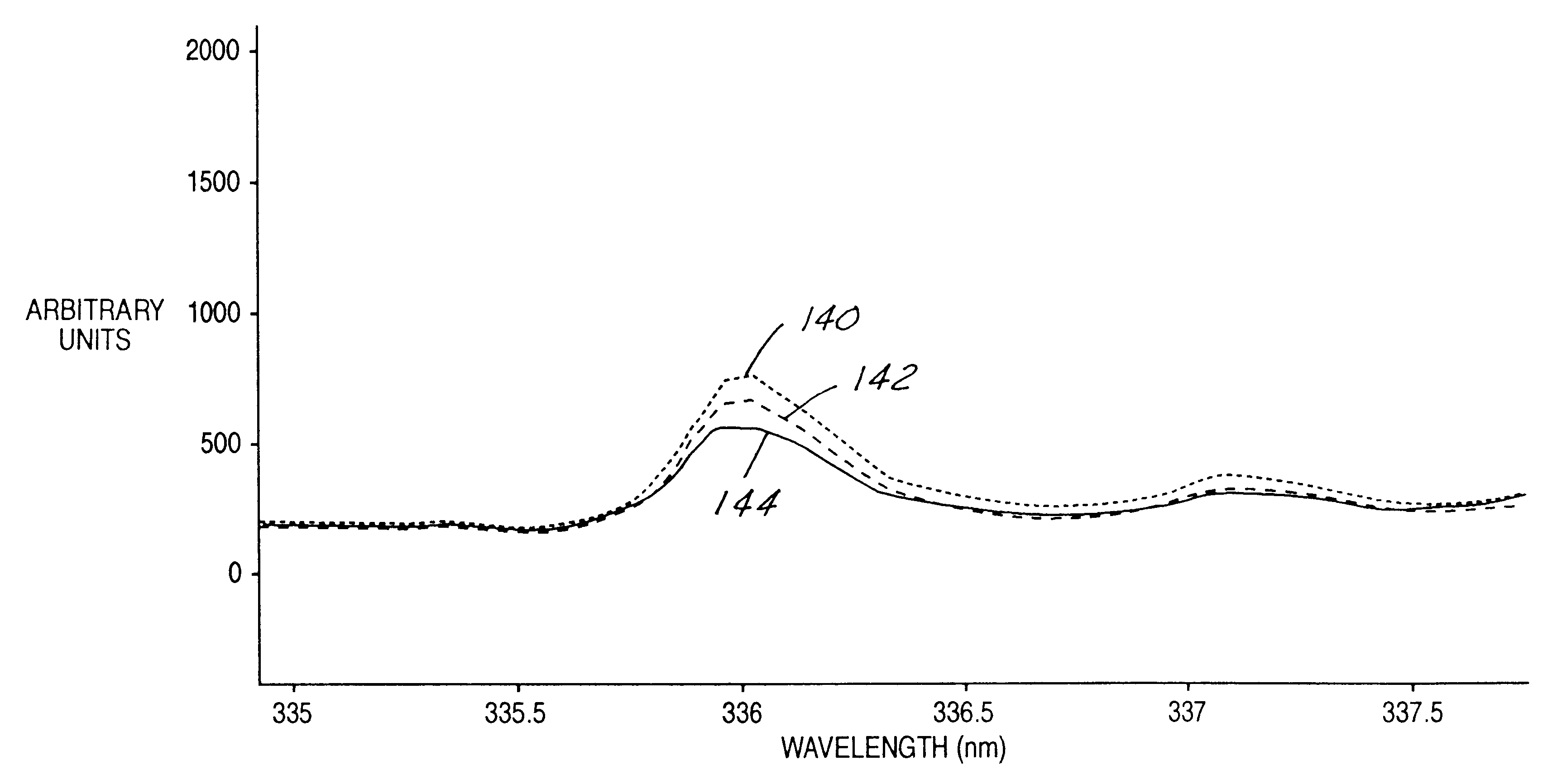
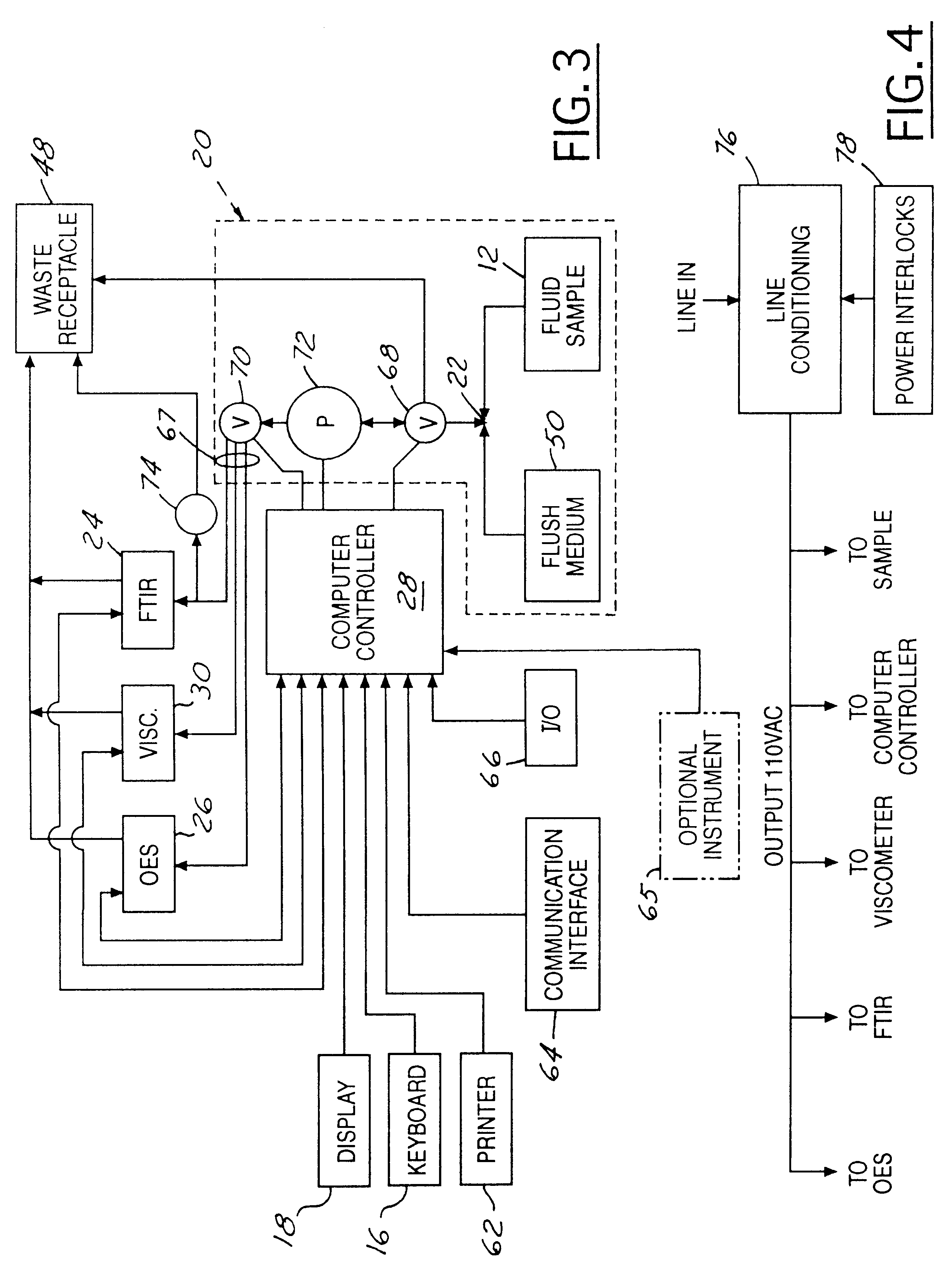
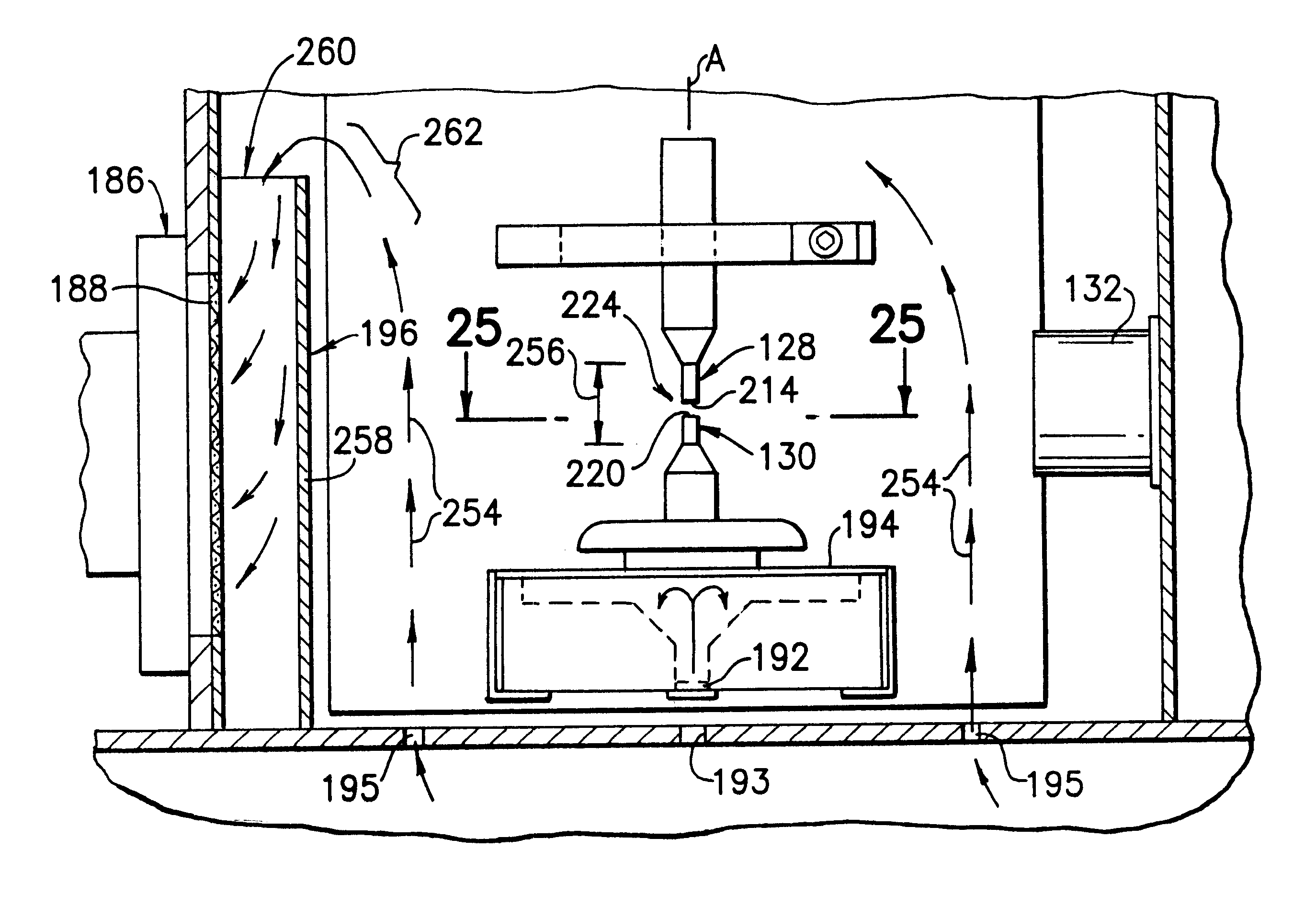
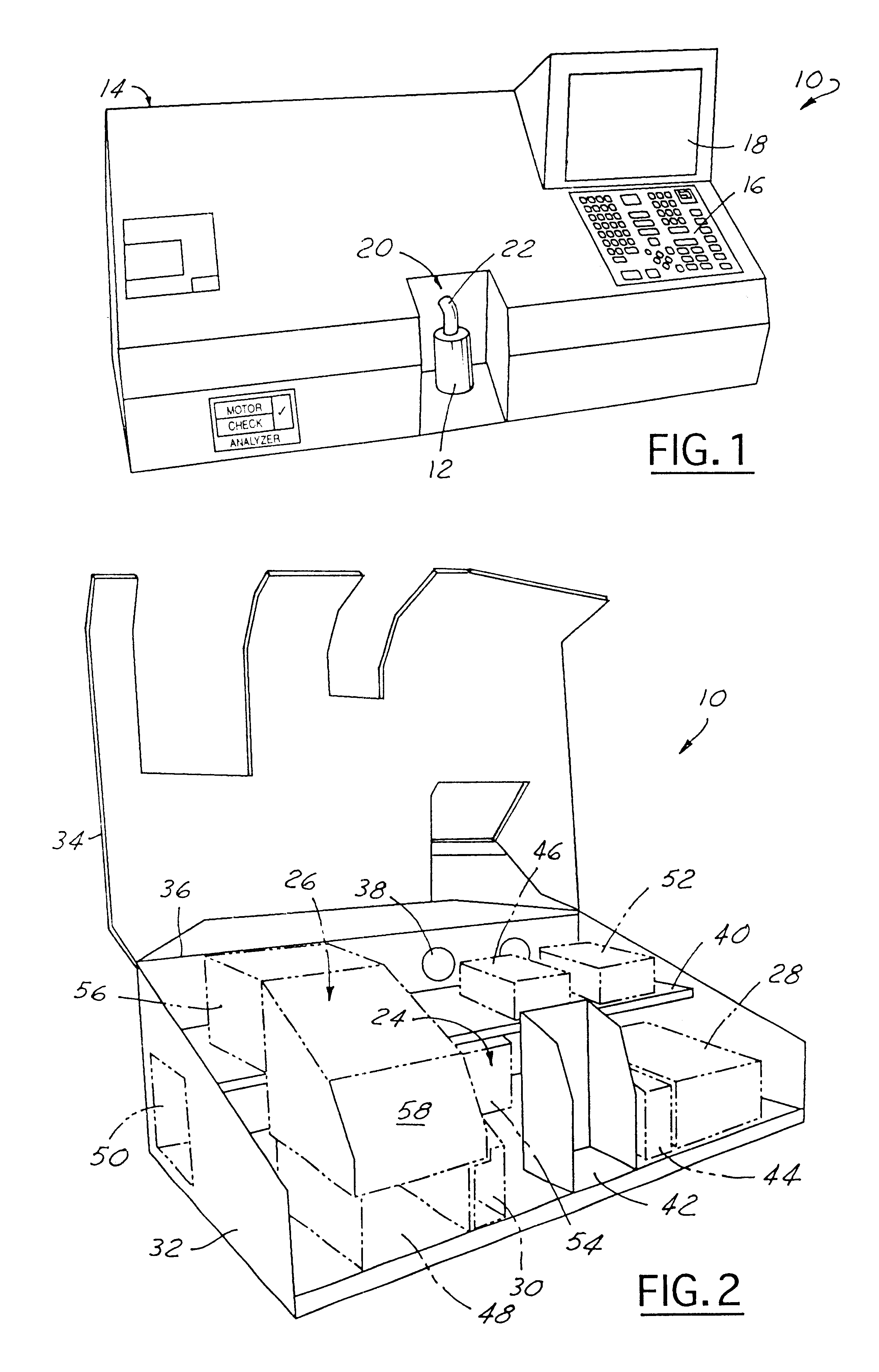
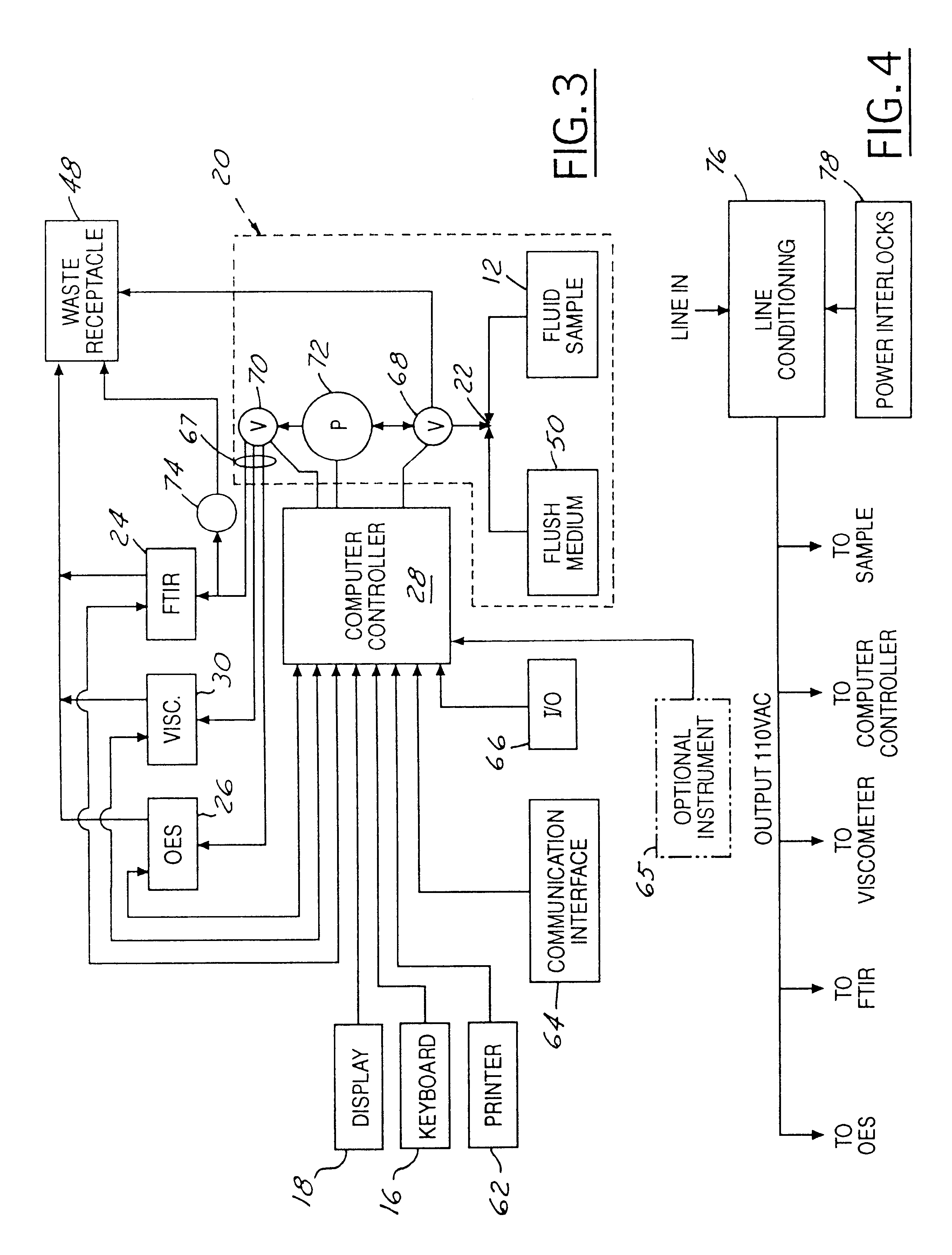
An apparatus (10) for analyzing lubricant oils and functional fluids includes an optical emission spectrometer (OES) (26) having a substantially continuously valued wavelength versus intensity output (140). The OES (26) analyzes light captured from a spark emission stand (58) through which the fluid sample is flowed. An expert system (160-172) operates according to a set of Rules that corrects background influence from the electrodes, and generates diagnostic text (174) for an operator based on the information about the fluid sample provided by the OES (26) and other measurement devices. The apparatus (10) is reduce in size, weight and cost.
Owner:SPECTRO SCI INC
On-site analyzer having spark emission spectrometer with even-wearing electrodes
InactiveUS6455850B1Easy to measureEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical spectrometer
An apparatus (10) for analyzing lubricant oils and functional fluids includes an optical emission spectrometer (OES) (26) having a substantially continuously valued wavelength versus intensity output (140). The OES (26) analyzes light captured from a spark emission stand (58) through which the fluid sample is flowed. An expert system (160-172) operates according to a set of Rules, and generates diagnostic text (174) for an operator based on the information about the fluid sample provided by the OES (26) and other measurement devices. The apparatus (10) includes an airflow passage (154) in the OES (26) spark enclosure that is characterized by airflow substantially parallel to the spark electrodes (128, 130) promoting even-wear of the electrodes.
Owner:SPECTRO SCI INC
Device and method for controlling dehydration during freeze-drying
InactiveUS20060137212A1Accurate and uniform and sterile method of monitoringImprove productivityParticle separator tubesDrying solid materials without heatOptical Emission SpectrometerFreeze-drying
A device for controlling dehydration during freeze-drying in an enclosure connected to a vacuum line includes an analyzer for analyzing the gases contained in the enclosure, the gas analyzer comprising a system for ionizing the gases comprising a plasma source in contact with the gases combined with a generator adapted to generate a plasma from the gases and a system for analyzing ionized gases comprising a radiation sensor situated in the vicinity of the area of generation of the plasma connected to apparatus for analyzing evolution of the radiation spectrum emitted by the plasma. The plasma source is preferably produced by inductive coupling and the analyzer for analyzing the evolution of the radiation spectrum is preferably an optical emission spectrometer.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Device and method for controlling dehydration during freeze-drying
InactiveUS7334346B2Avoid high ambient temperatureEnvironment safetyDrying solid materials without heatAnalysis by electrical excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerGas analysis
A device for controlling dehydration during freeze-drying in an enclosure connected to a vacuum line includes an analyzer for analyzing the gases contained in the enclosure, the gas analyzer comprising a system for ionizing the gases comprising a plasma source in contact with the gases combined with a generator adapted to generate a plasma from the gases and a system for analyzing ionized gases comprising a radiation sensor situated in the vicinity of the area of generation of the plasma connected to apparatus for analyzing evolution of the radiation spectrum emitted by the plasma. The plasma source is preferably produced by inductive coupling and the analyzer for analyzing the evolution of the radiation spectrum is preferably an optical emission spectrometer.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
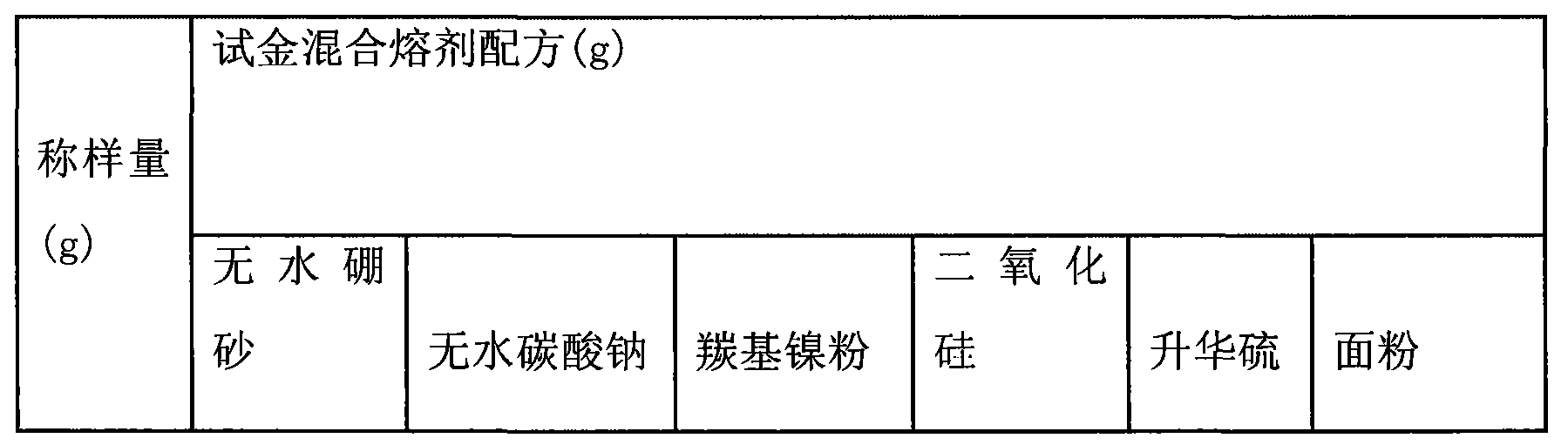
Method for determining precious metal in platinum-palladium ores
InactiveCN103940805AObserve spectral lines in real timeReal-time observation of measurement resultsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWater bathsOptical Emission Spectrometer
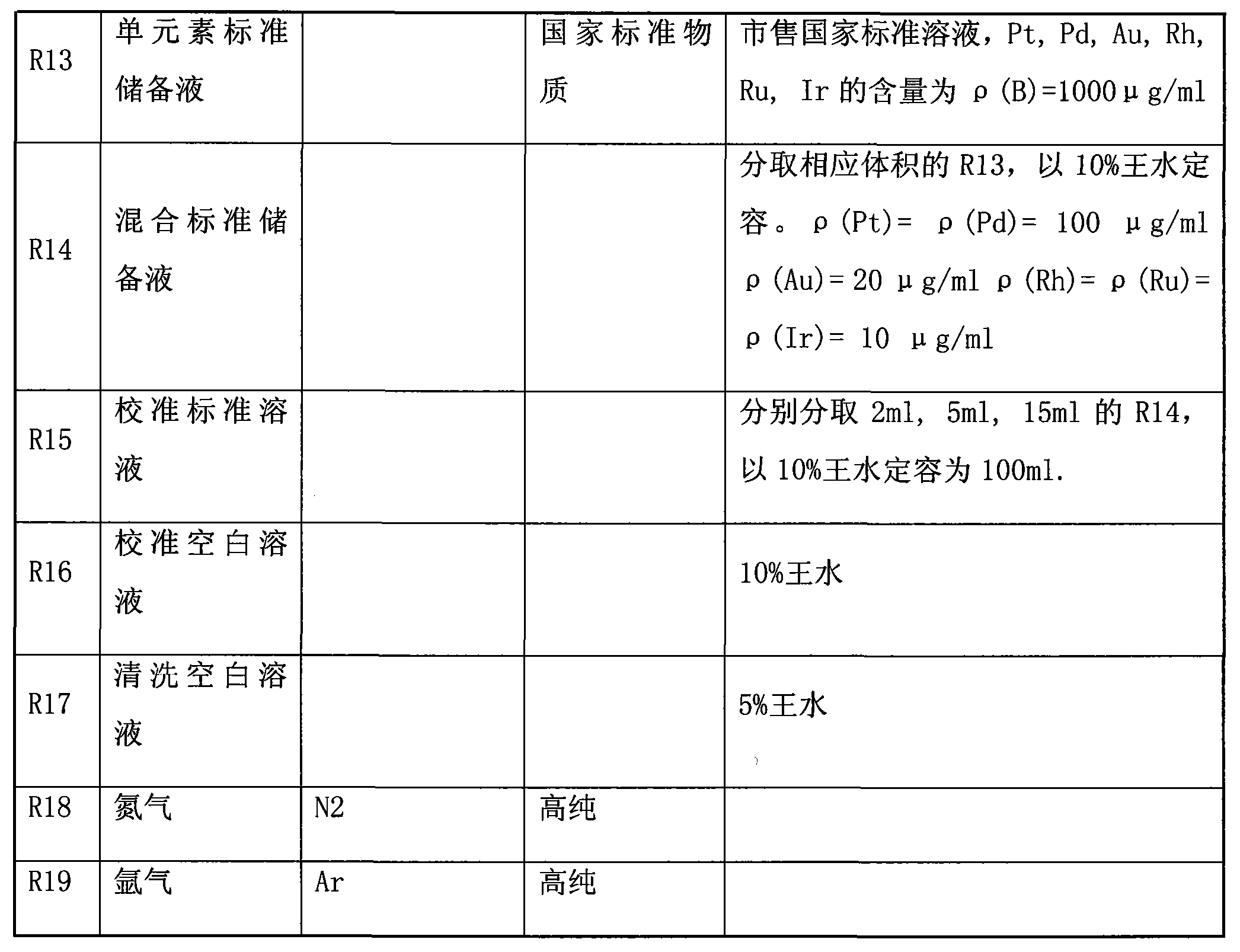
The invention discloses a method for determining precious metal in platinum-group metal ores. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a nickel-sulfonium button from a nickel-sulfonium fire assay enriching sample; (2) grinding the nickel-sulfonium button with a grinder; (3) adding the ground nickel-sulfonium button in a hydrochloric acid solution and heating for dissolving to remove base metal and sulfonium from the nickel-sulfonium button; (4) adding a reductant and a coprecipitator to the solution obtained from the step (3) to recover a small quantity of precious metal lost in the solution; (5) performing suction filtration at negative pressure to obtain a precious metal precipitate; (6) dissolving the precipitate in the step (5) together with a filtering membrane with aqua regia in a water bath and diluting with pure water to a fixed volume; (7) drawing calibration curves of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium by an ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) and determining the intensity of spectral lines of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium in the sample solution; (8) automatically calculating the content of to-be-detected elements by a computer according to the calibration curves and a sample information table. The method has good stability and high result accuracy degree. According to the method, six precious metal elements can be determined simultaneously just by one-time sample weighing and pretreatment, the working efficiency is increased greatly and the detection cost is lowered.
Owner:WANBAO MINING
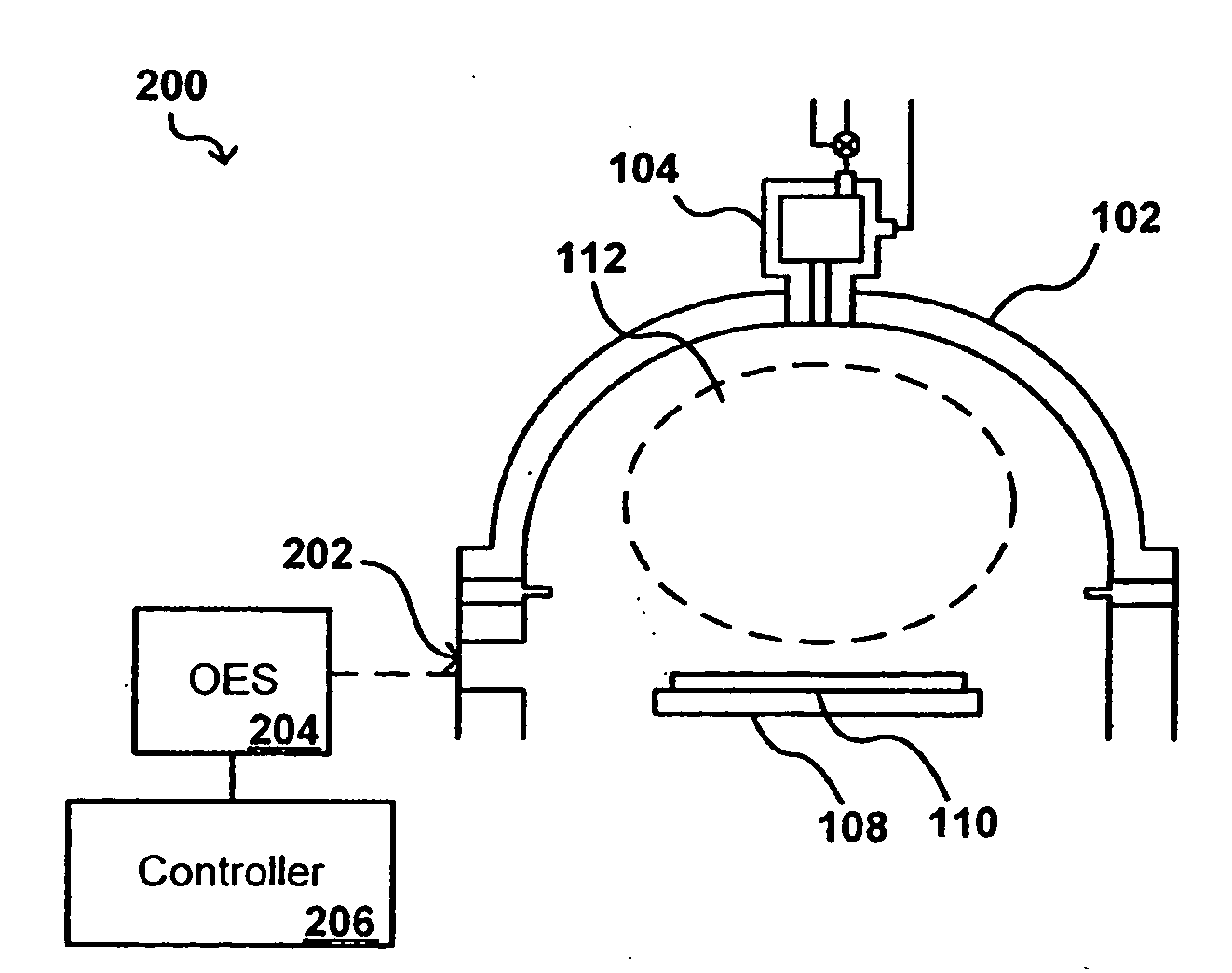
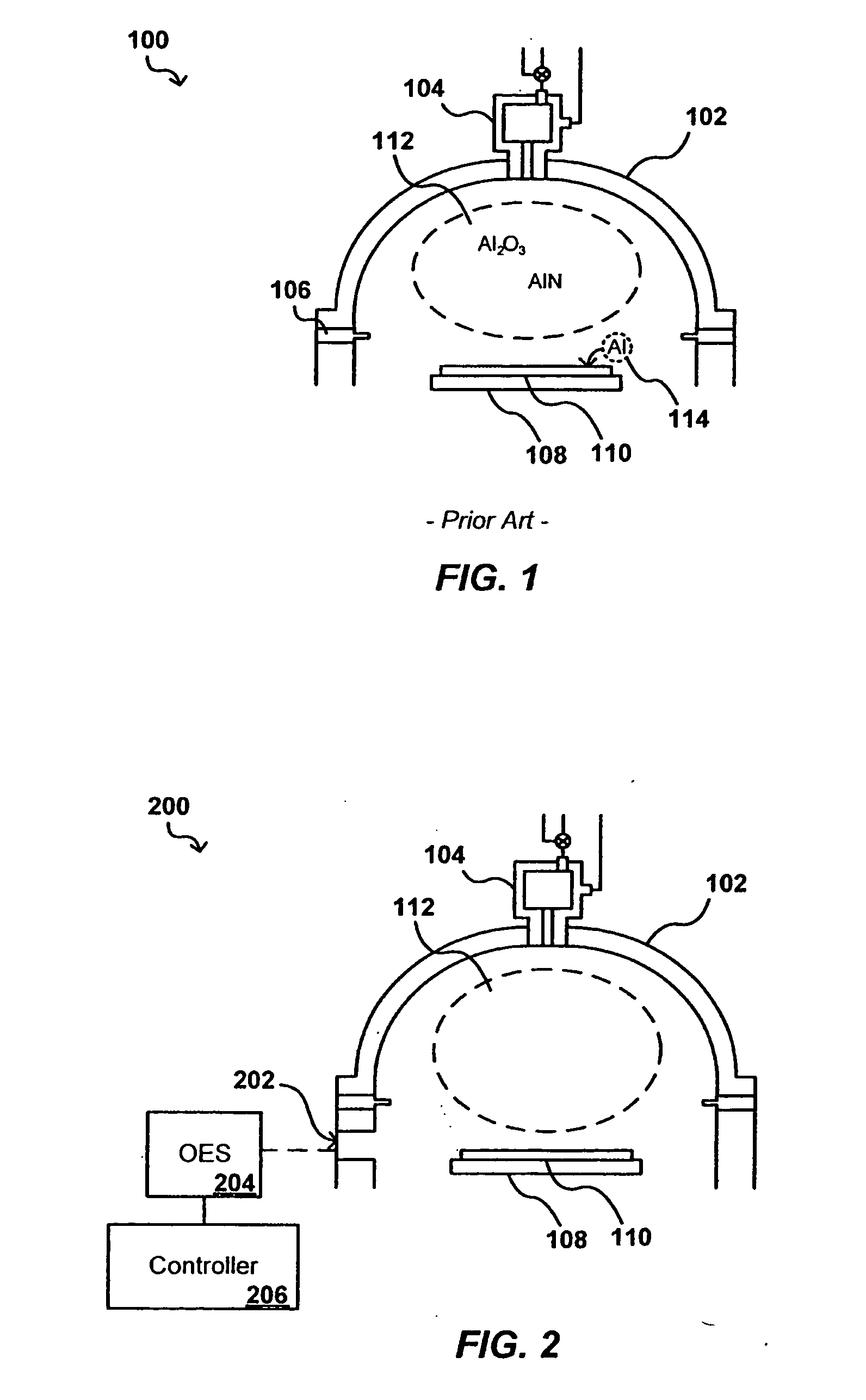
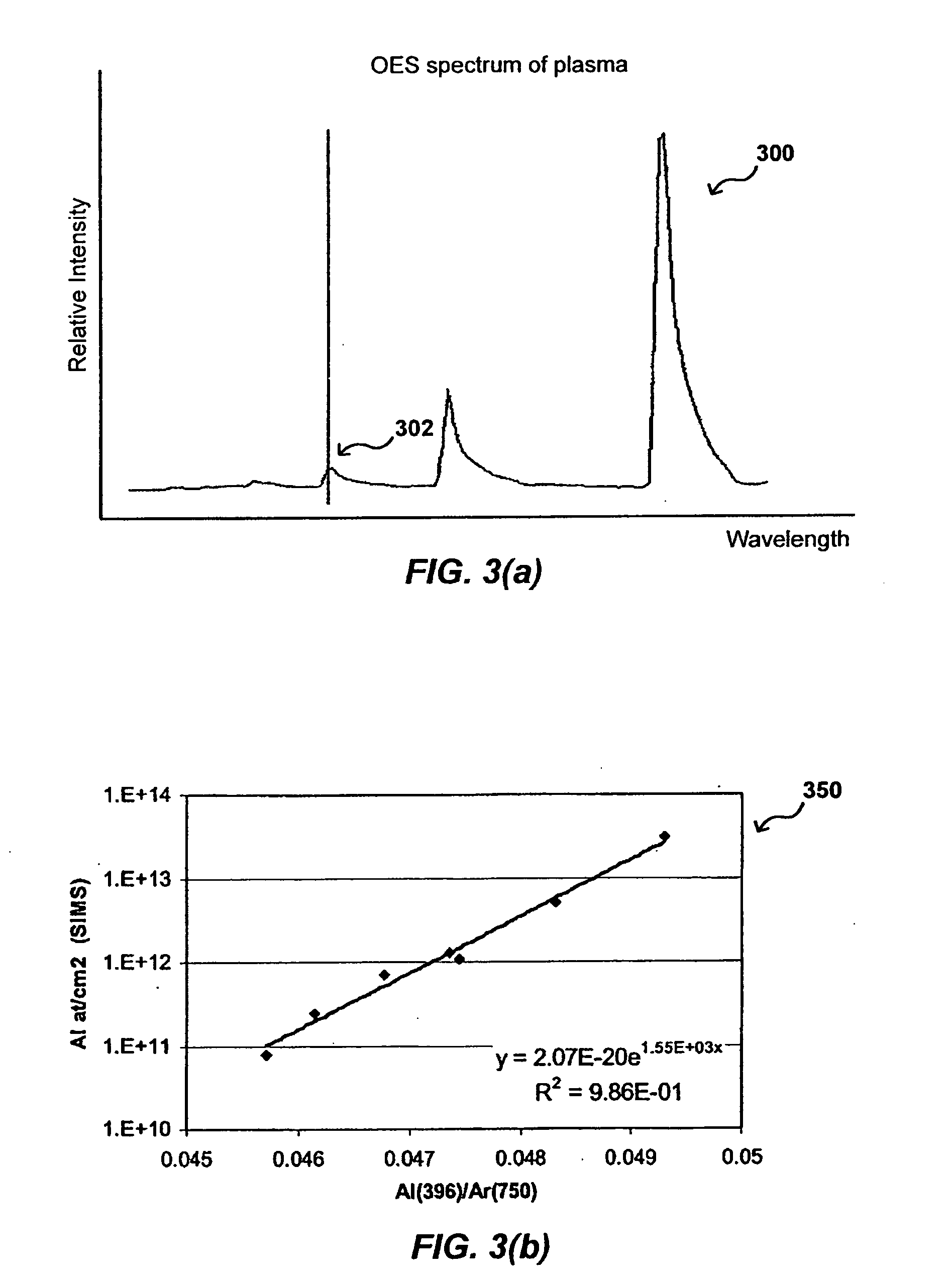
In-situ process diagnostics of in-film aluminum during plasma deposition
InactiveUS20080029484A1Less expensiveReduce the amount requiredElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsOptical Emission SpectrometerPlasma deposition
The concentration of various contaminants in a plasma can be monitored during processing of a substrate such as a silicon wafer, in order to prevent an unacceptable amount of contamination from being deposited on the substrate. The radiation emitted from the plasma through a window in the processing chamber during processing can be detected and measured by a tool such as an optical emission spectrograph (OES) and the relative intensity of peaks in the spectrum corresponding to various contaminants can be analyzed in order to determine contaminant concentration. In one embodiment, the concentration of aluminum in a plasma is monitored during a plasma chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process in order to ensure that the amount of aluminum in the produced device is lower than a maximum threshold amount.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Determination method for iron, aluminum, manganese, calcium, titanium, silicon and magnesium in casting powder
InactiveCN107024468AMeet the comprehensive utilizationFulfil requirementsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerManganese
The invention discloses a determination method for iron, aluminum, manganese, calcium, titanium, silicon and magnesium in casting powder. The method comprises the following steps: melting a test sample, which is subjected to pre-carbon removal treatment, with a sodium carbonate-boric acid mixed flux; dissolving a leached and cooled melted block with hydrochloric acid and heating at low temperature to decompose the melted block; diluting to a specified volume; taking one part of the solution, atomizing the solution and introducing the atomized solution into an inductive coupling plasma optical emission spectrometer; measuring relative intensity of an element to be detected in the solution to a yttrium internal standard element at a selected wavelength; calculating the mass percent of each element to be detected according to a calibration curve manufactured by a standard solution. The determination method provided by the invention is an ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) light spectrum method and the content of various components in the casting powder is determined in one step; the determination method has an accurate and reliable measured result and is simple to operate; the dosage of reagents is greatly reduced and the analysis speed is improved by 70 percent or more, so that a determination period is greatly shortened, and comprehensive utilization of the casting powder and requirements of actual working in a production field are met.
Owner:TANGSHAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
Coating thickness test method
InactiveCN108692664AHigh precisionWide thickness rangeAnalysis by thermal excitationUsing optical meansOptical Emission SpectrometerPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a coating thickness test method. According to the method, a sample to be tested is made into a sample block of which the coating area can be accurately calculated; a coating onthe sample block is completely digested with strong acid, so that a test solution of a certain volume can be prepared; the content of a coating metal component in the solution is measured by an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer; the mass of the coating component is calculated; and the thickness of the coating is calculated on the basis of the measured area of the sample block. The test method of the invention has the advantages of high test accuracy, strong representativeness, less interference, small error, and wide test coating thicknesses range. With the coating thickness test method adopted, the thickness of the coating can be tested in general chemical laboratories, and professional thickness gauges are not required.
Owner:青岛谱尼测试有限公司
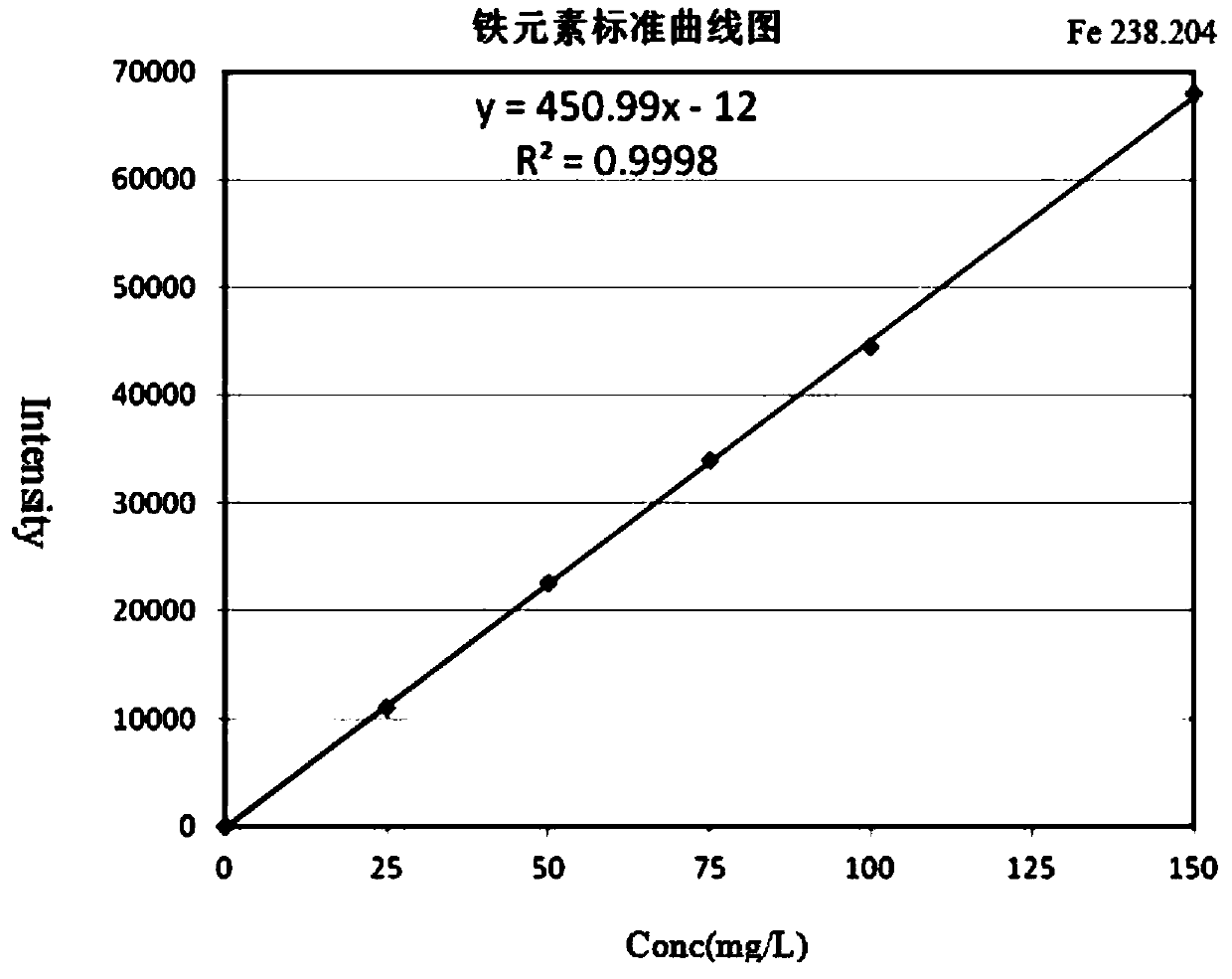
Method for determining impurity elements in high-purity aluminum through microwave digestion-inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer
InactiveCN108375568ALow detection limitAccurate measurementPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerMethod test
The invention provides a method for determining impurity elements in high-purity aluminum through a microwave digestion-inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and belongs to the technical field of analysis and test. The invention provides an analysis method for determining 20 impurity elements including Ag, Ba, Bi, Cd, Co, Cu, Ga, Fe, In, Li, Mg, Mn, Mo, Pb, Sb, Ti, V, Sr, Zn and Zr in the high-purity aluminum through a microwave digester and an inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) by adopting a standard curve method. A sample is dissolved into a sealed high-pressure microwave digestion tank by utilizing a proper amount acid, so as to avoid external factor pollution better. Optimal working parameters of an instrument are determined through a single-factor experiment. A standard curve-method test sample is selected so that matrix interference is reduced. The method is a simple, rapid and accurate modern detection technology capable of determining 20elements in one step.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
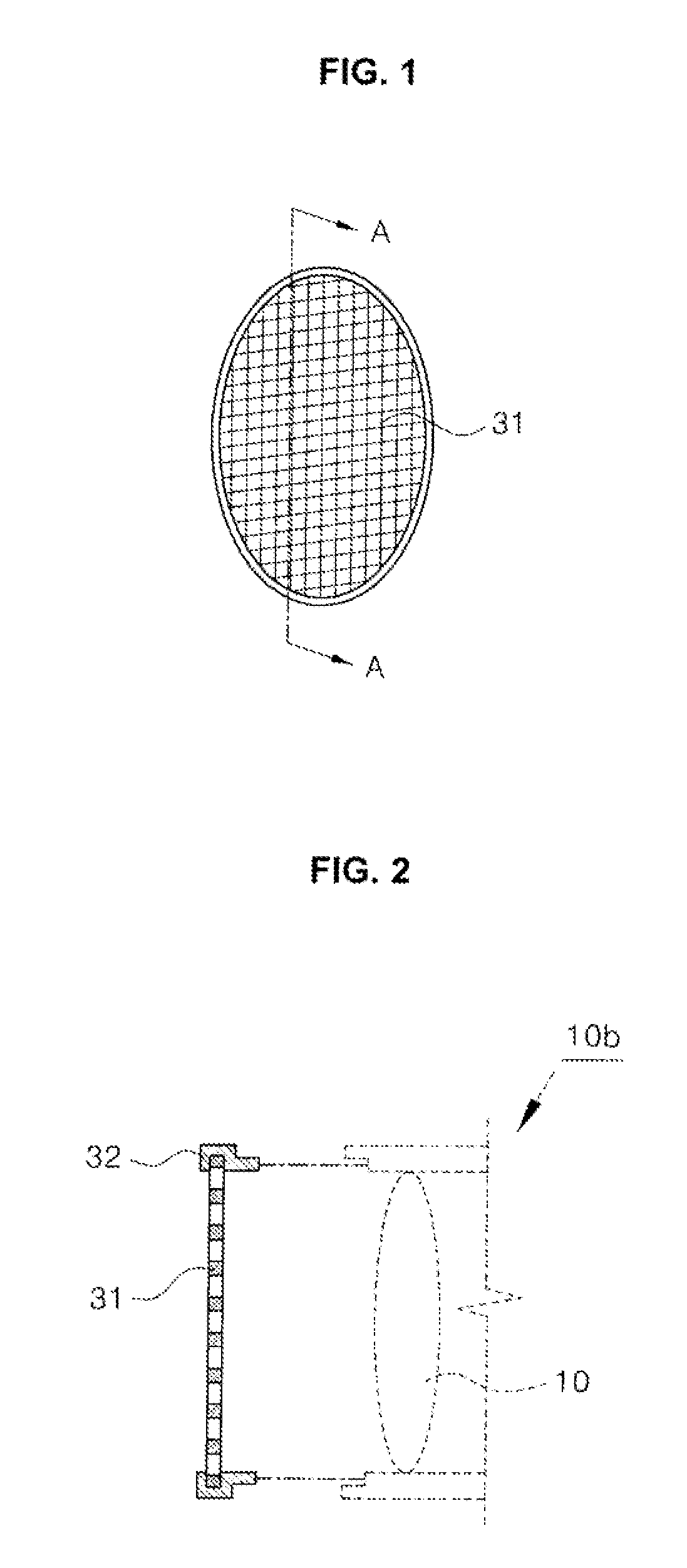
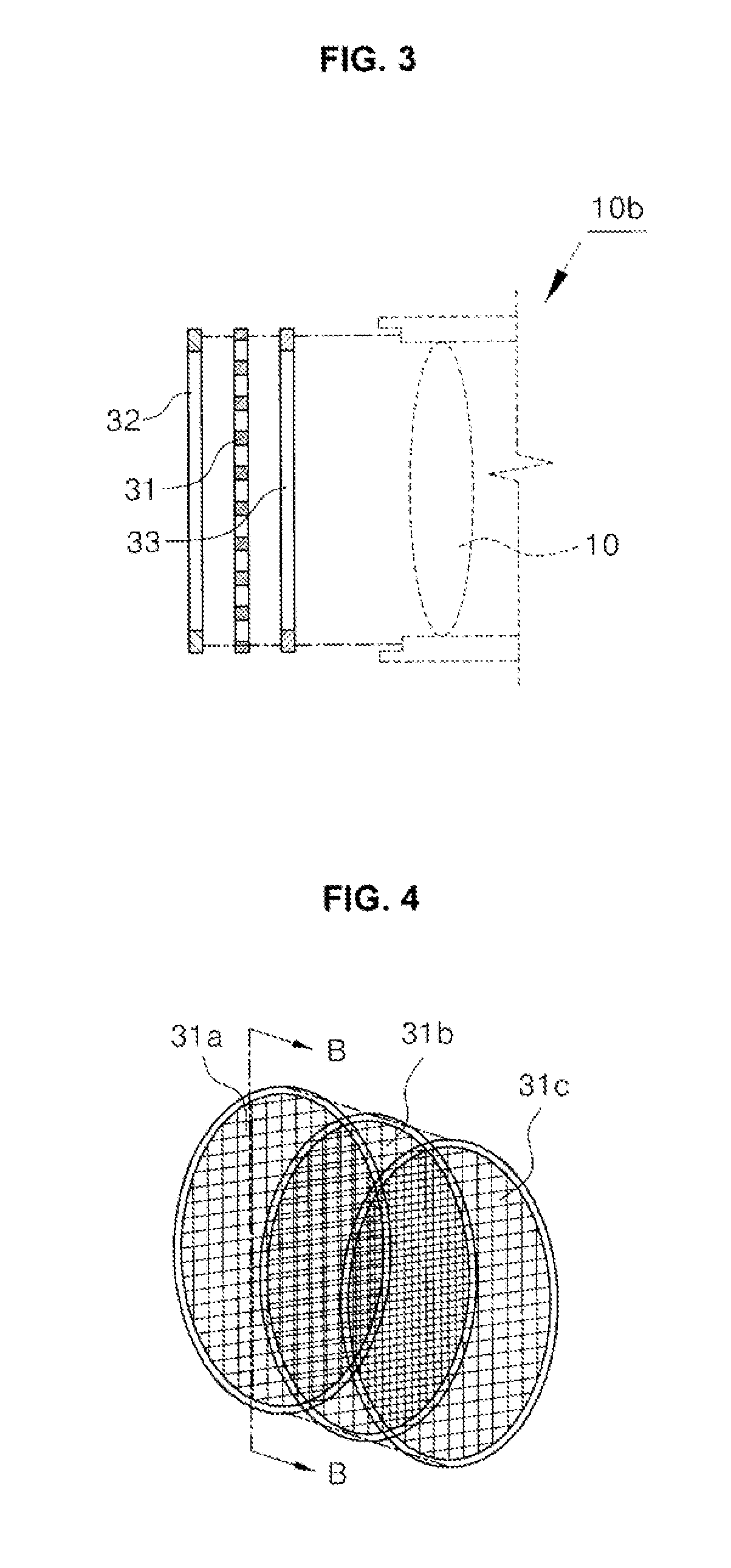
Device for preventing intensity reduction of optical signal, optical emission spectrometer, optical instrument, and mass spectrometer including the same
ActiveUS9025143B2Avoid intensitySolve the real problemEmission spectroscopyShielding materialsOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical emission spectrometry
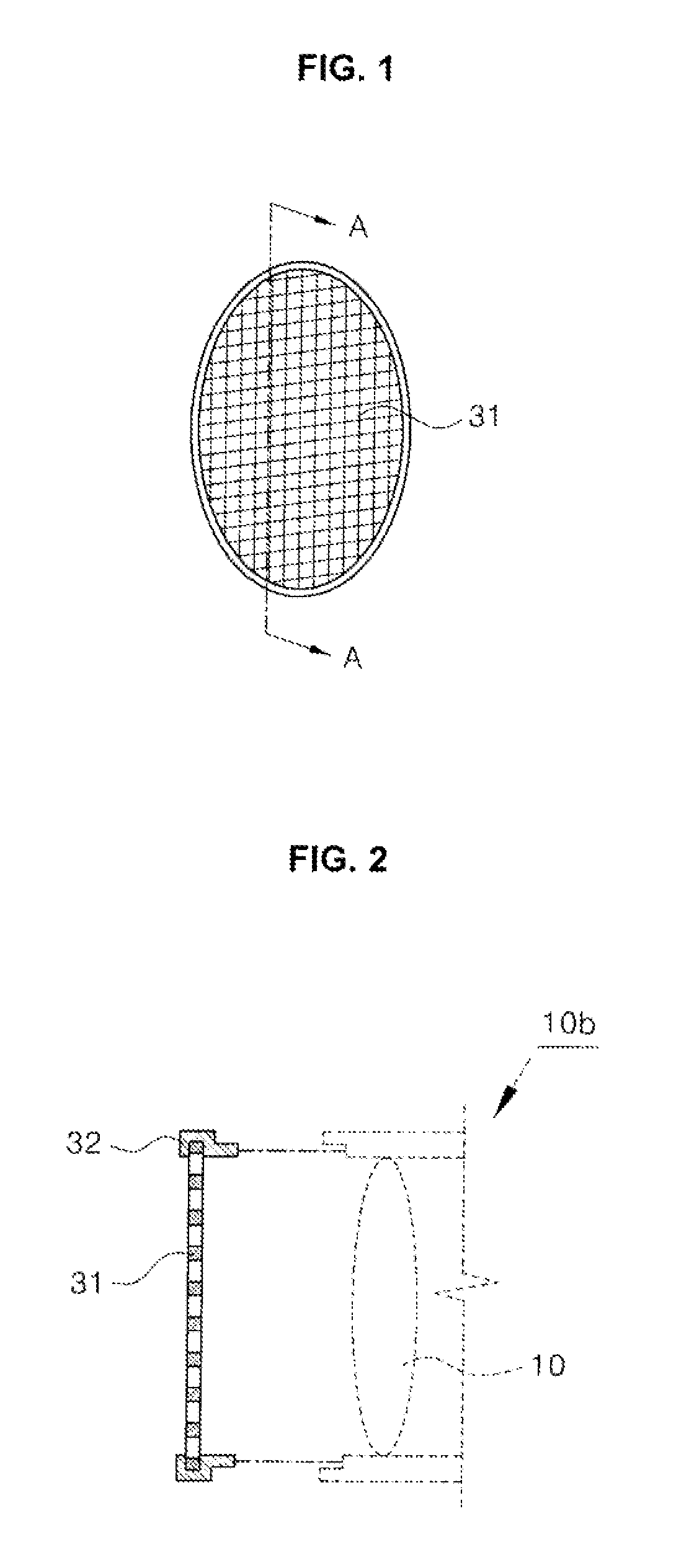
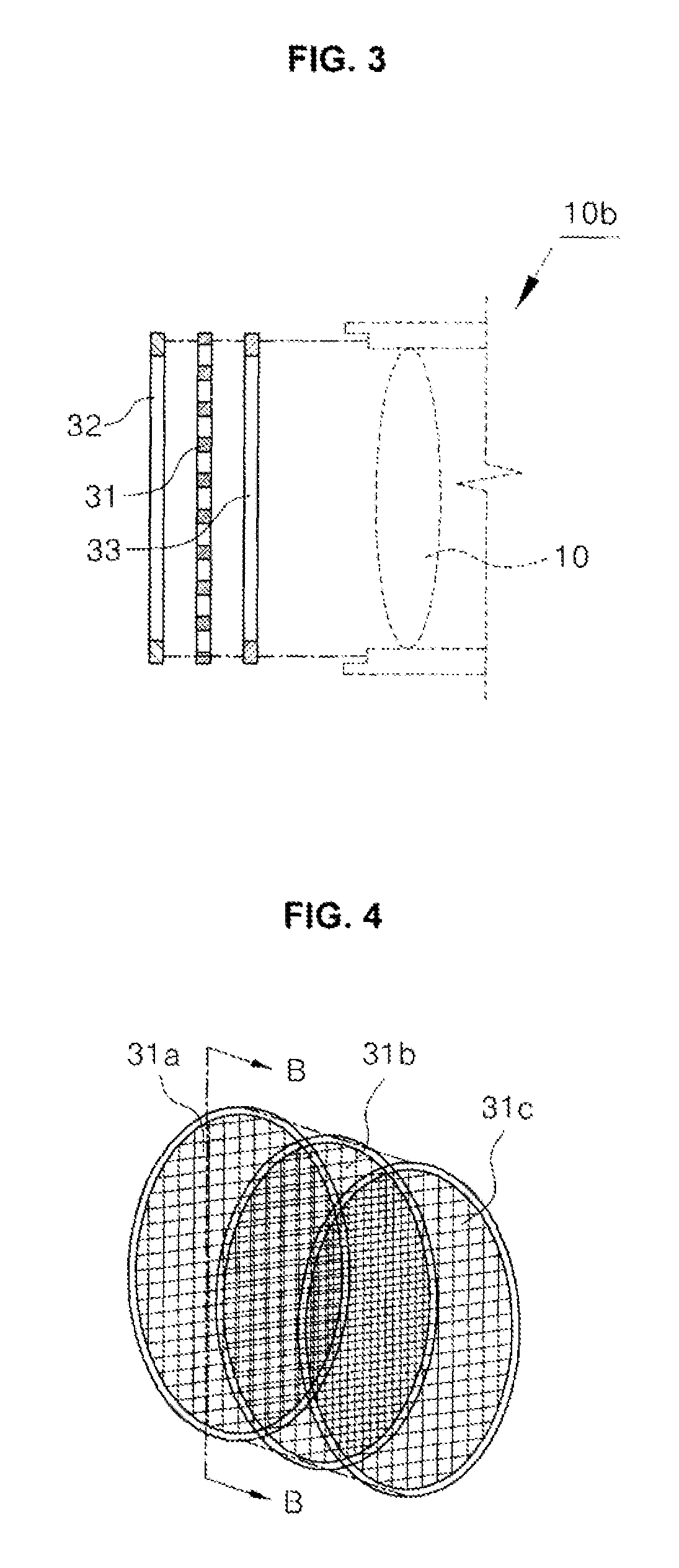
A device for a device for preventing the intensity reduction of an optical signal, an optical emission spectrometer, an optical instrument, and a mass spectrometer including the same are provided. The device for preventing the intensity reduction includes a shielding filter which has a mesh structure capable of blocking RF electromagnetic waves radiated from a plasma field for a wafer processing, is installed in the front of an optical window of an optical emission spectrometer for measuring the plasma field from an emission spectrum image of the plasma field, and collects charging particles passing through the mesh.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Method for detecting heavy metals in plastics
InactiveCN104122253ASolve the influence of measuring timeOvercome the conditionsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWater bathsSolubility
The invention discloses a method for detecting heavy metals in plastics. The method comprises the following steps: S1. putting the plastics to be detected in an airtight container filled with an organic solvent, and carrying out ultrasonic oscillation in a water bath to dissolve the plastics, thus obtaining a plastic dissolution solution; S2. adding dilute nitric acid to the plastic dissolution solution, carrying out ultrasonic oscillation at room temperature, and carrying out filtration, washing and constant volume achievement to extract heavy metals in the plastic dissolution solution, thus obtaining a solution to be detected, containing the organic solvent; S3. qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing the heavy metals in the solution to be detected by adopting an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES). The method has the beneficial effects that by utilizing the characteristic that the plastics have better solubility in the organic solvent, the plastics are dissolved by using the proper organic solvent, and then the heavy metals in the plastics are extracted to form the solution to be detected, containing the organic solvent; then the heavy metals dissolved in the organic solvent are qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by adopting the ICP-OES. The method has the advantages of simple and fast operating process, mild reaction conditions, accuracy in detection, high recovery rate and good stability and is suitable for mass treatment.
Owner:深圳出入境检验检疫局玩具检测技术中心
Method for detecting content of eight heavy metals in plastic
InactiveCN103852463AThe detection work is accurateGet content reliablyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerDigestion
The invention discloses a method for detecting the contents of cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium in plastic. The detection method comprises the following steps of (a) processing a sample into particles, wherein the weight of each particle is not greater than 0.2g; (b) adding nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide in the sample after processing in the step (a) and carrying out microwave digestion, wherein the ratio of the sample to the nitric acid is 1 to 30-50g / ml, the ratio of the sample to the hydrochloric acid is 1 to 10-20g / ml, and the ratio of the sample to the hydrogen peroxide is 1 to 5-10g / ml; and (c) after finishing the digestion, taking out a digestion solution, filtering and carrying out ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) analysis on the digestion solution. The detection method provided by the invention has the advantages that the analytical method is rapid, the accuracy is high, and the repeatability and reproducibility are good.
Owner:昆山洛丹伦生物科技有限公司
Device for preventing intensity reduction of optical signal, optical emission spectrometer, optical instrument, and mass spectrometer including the same
ActiveUS20120120395A1Prevent inflowAvoid intensityEmission spectroscopyShielding materialsOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical emission spectrometry
A device for a device for preventing the intensity reduction of an optical signal, an optical emission spectrometer, an optical instrument, and a mass spectrometer including the same are provided. The device for preventing the intensity reduction includes a shielding filter which has a mesh structure capable of blocking RF electromagnetic waves radiated from a plasma field for a wafer processing, is installed in the front of an optical window of an optical emission spectrometer for measuring the plasma field from an emission spectrum image of the plasma field, and collects charging particles passing through the mesh.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
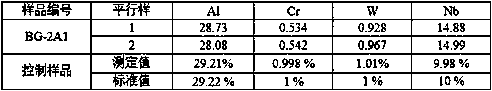
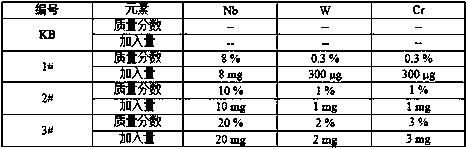
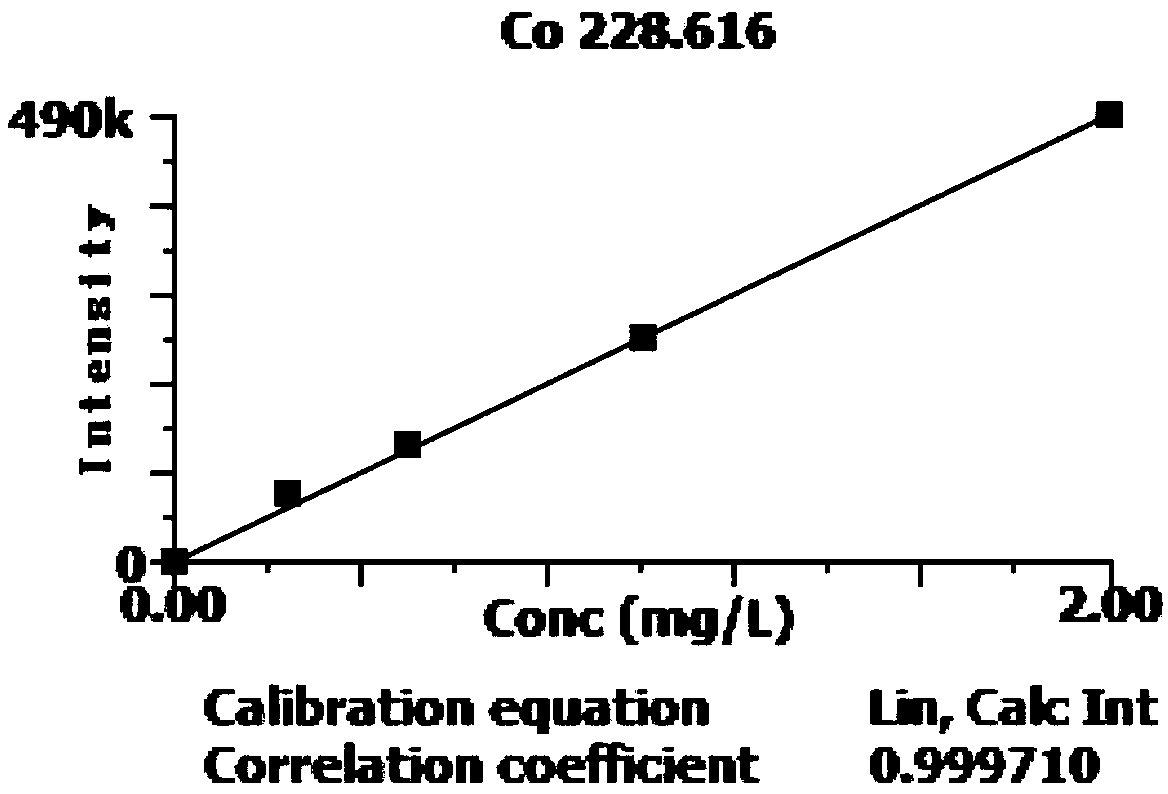
Method for determining contents of aluminum, niobium, tungsten and chromium in high-niobium-aluminum-titanium alloy
InactiveCN108896536AReduce distractionsEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerNiobium
The invention provides a method for determining contents of aluminum, niobium, tungsten and chromium in a high-niobium-aluminum-titanium alloy. The method is used for determining the contents of aluminum, niobium, tungsten and chromium in the high-niobium-aluminum-titanium alloy by adopting inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy, and specifically comprises the following steps: preparing a to-be-determined sample solution, preparing a standard solution, establishing a standard curve, determining the content of each element in the to-be-determined sample solution, and the like.According to the method disclosed by the invention, a series of standard solutions can be prepared by a matrix matching method, matrix interference and interference of inter-element spectral lines canbe reduced, the aluminum, niobium, tungsten and chromium in the high-niobium-aluminum-titanium alloy can be simultaneously analytically determined on an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer, the quantitative range can cover the detection requirement of the high-niobium-aluminum-titanium alloy, the analytical method is simple to operate, and a reliable guarantee is provided forproduction, scientific research, application and quality control of the high-niobium-aluminum-titanium alloy.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Method for determining trace elements in graphite by microwave digestion-ICP-OES (inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer)
InactiveCN108982204AWide linear rangeImprove stabilityPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationHigh temperature storageOptical Emission Spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for determining trace elements in graphite by microwave digestion-ICP-OES (inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer), and relates to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The method comprises the following steps of soaking a graphite sample by aqua regia, and digesting by microwaves, so as to obtain a to-be-determined solution; completely dissolving the metal elements into the to-be-determined solution, guiding the to-be-determined solution into an ICP emission spectrometer, determining the spectrum line intensities of the elements of iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, aluminum, chromium, zinc and the like in the to-be-determined solution, and then determining the specific contents of the elements of iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, aluminum,chromium, zinc and the like in the graphite sample according to the determined standard working curve. The method has the advantages that the defects of the prior art are overcome; the technical blank of using the microwave digestion-ICP atom transmission spectrum technique in determining of the contents of trace elements in the graphite in China is filled; the determining is the quick and precise; the contents of harmful trace elements in the graphite sample can be effectively monitored; a lithium ion battery using the graphite has excellent high temperature storage property.
Owner:KEDA (ANHUI) NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
System and Method For Automated Sample Introduction
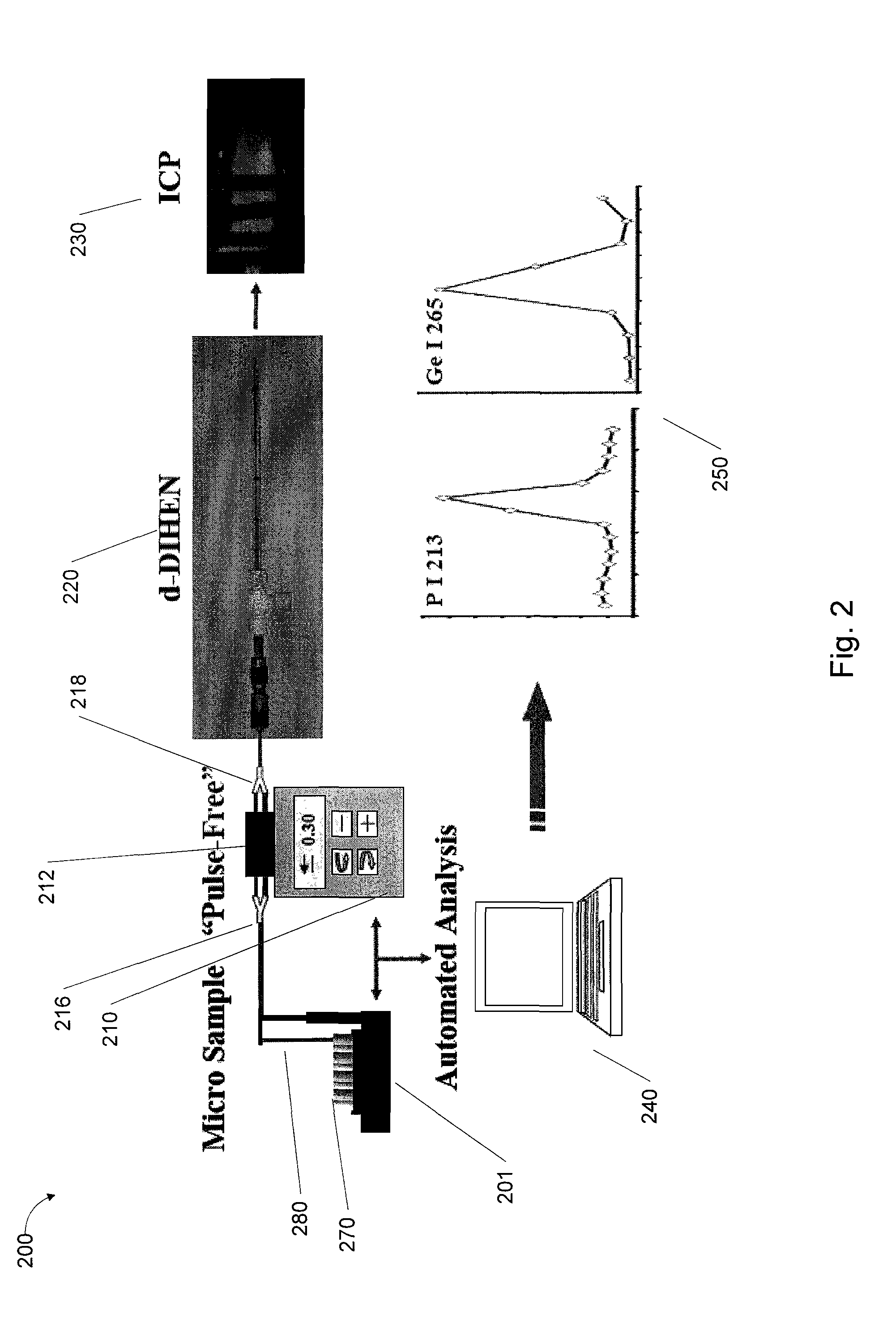
InactiveUS20100229999A1Convenient introductionLimiting sample consumptionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical Emission SpectrometerPresent method
A method, system and apparatus for an automated sample introduction system, utilizing a demountable direct injection high efficiency nebulizer (d-DIHEN) is provided which incorporates an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) for the measurement of the phosphorus content in acid-digested nucleotides and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The solution uptake rate and volume are reduced from 170 μL min−1 to 30 μL min−1 and 10 mL to 2.4 mL, respectively, thereby reducing the required DNA sample mass for solutions containing 3 μg−1 P from 300 μg to 72 μg DNA, in comparison to previous analyses in our lab using a glass, concentric nebulizer with cyclonic spray chamber arrangement. The use of direct injection also improves P (I) 213.617 nm sensitivity by a factor of 4 on average. A high performance (HP) methodology in combination with the previous sample introduction system and ICP-OES provides simultaneous, time-correlated internal standardization and drift correction resulting in relative expanded uncertainties (% U) for the P mass fractions in the range of 0.1 to 0.4 (95% confidence level) for most of the thymidine 5′-monophosphate (TMP), calf thymus DNA (CTDNA), and plasmid DNA (PLDNA) analyses. The d-DIHEN with HP-ICP-OES methodology allows for the quantification of DNA mass at P mass fractions as low as 0.5 μg g−1, further reducing the required DNA mass to 12 μg, with small uncertainty (≦0.4%). The present method, system and apparatus can aide in the development and certification of nucleic acid certified reference materials (CRMs), particularly for these samples that are typically limited in volume.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY +1
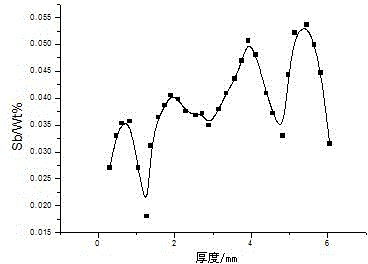
Method for testing element distribution in alloy board
InactiveCN103335999ASimple processValid quantitative dataAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerGlass vessel
The invention relates to a method for testing the element distribution in an alloy board. The technical scheme comprises the following steps of: firstly, taking a board with the diameter of 10-20mm from the test boards as a test sample, except for one surface, sealing other surfaces of the test sample with an adhesion agent; then, mixing a strong acid solution with the concentration of 20-50% and mercuric chloride in a glass vessel according to the volume ratio of 1 to (0.003-0.01) to obtain the test solution; adding 10ml of the test solution into a first beaker, weighing the mass m0 of the test sample, adding the test sample into the first breaker, stirring for 30-240s under ultrasonic shaking, taking out the test sample, washing the test sample with distilled water, drying, and weighing the mass m1 of the dried test sample; testing the concentration of each element in the test solution in the breaker by using an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer, so as to sequentially obtain the thickness delta H1 etched off for the first time and the concentration of each element; repeating the testing process, until the test sample is etched off completely, then, acquiring the element distribution conditions in the alloy board. The method can accurately test the element distribution in the alloy board.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
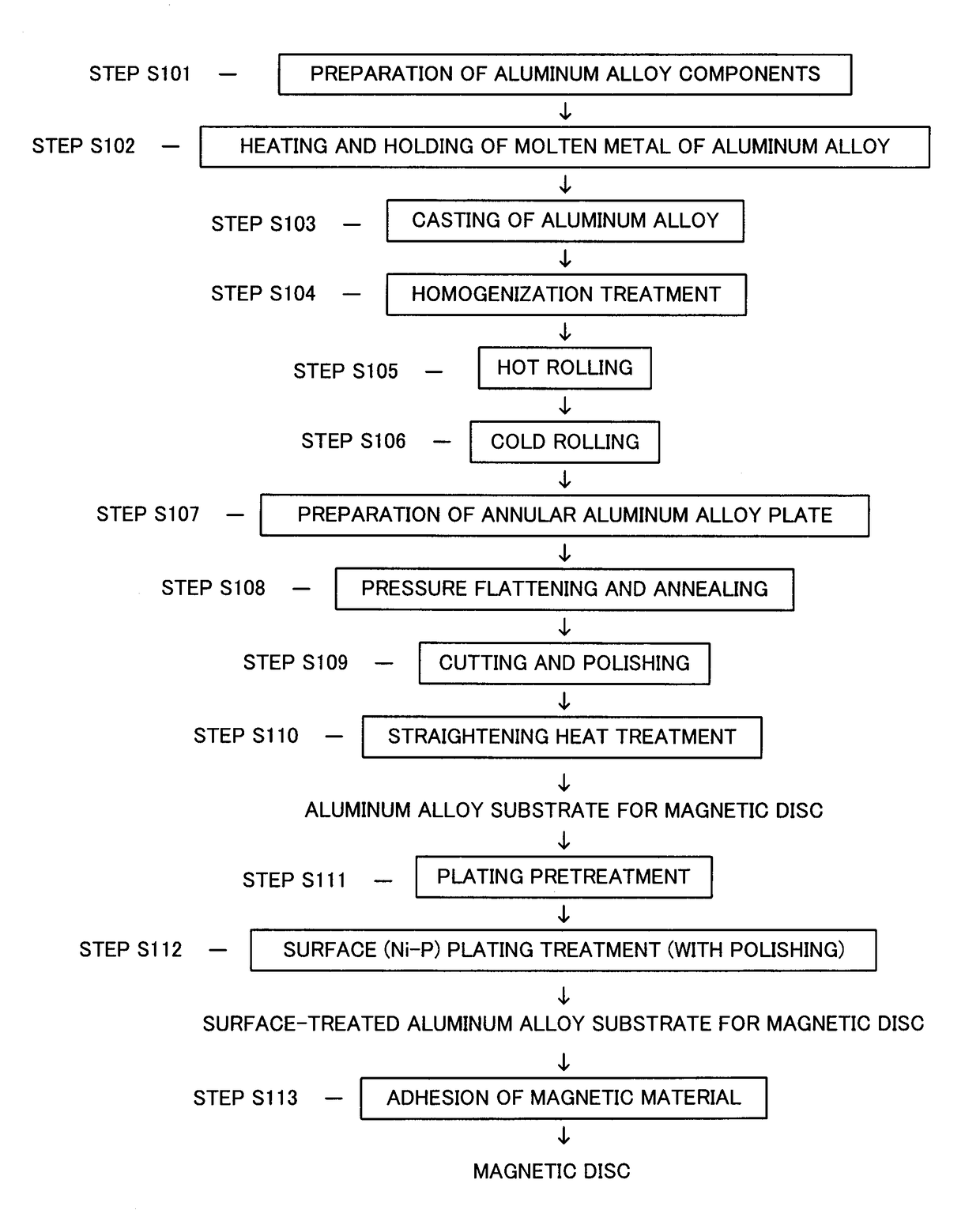
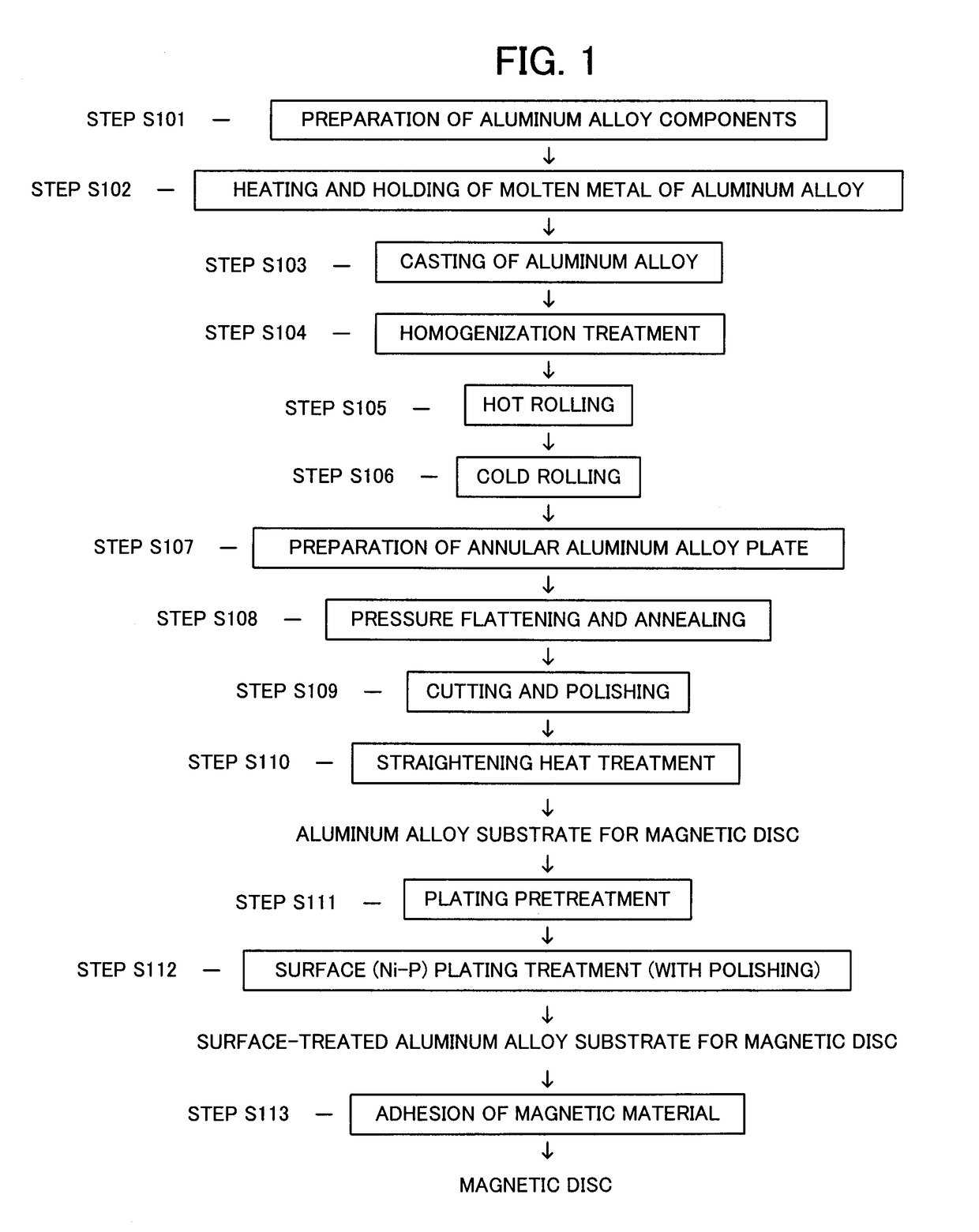
Magnetic disc aluminum alloy substrate and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20180221928A1Improve smoothnessHigh strengthBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageOptical Emission SpectrometerAlloy substrate
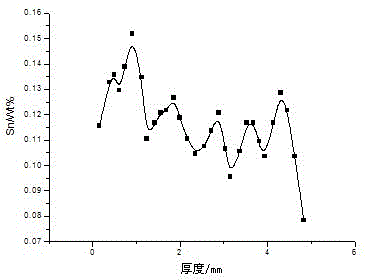
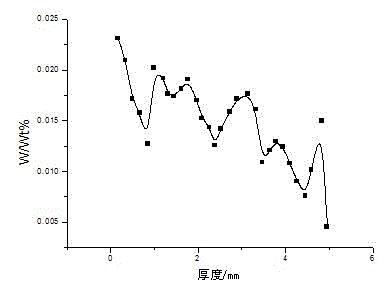
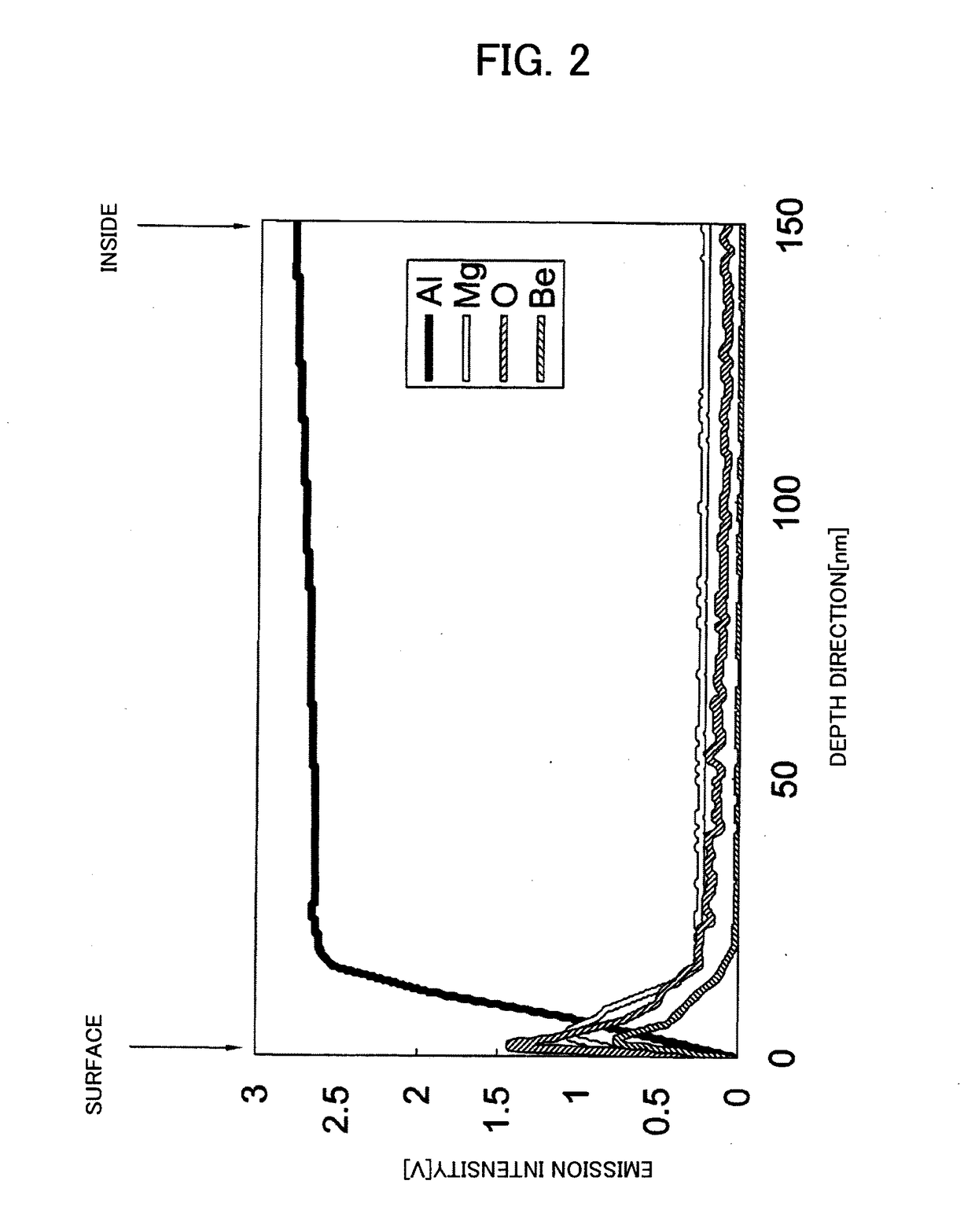
Disclosed are an aluminum alloy substrate for a magnetic disc, which includes an aluminum alloy consisting of Mg:4.5-10.0 mass % (hereinafter referred to as %), Be: 0.00001-0.00200%,Cu: 0.003-0.150%, Zn: 0.05-0.60%, Cr: 0.010-0.300%, Si: 0.060% or less, and Fe: 0.060% or less, with a balance being Al and an unavoidable impurity, an amount of an Mg-based oxide being 50 ppm or less, (IBe / Ibulk)×(CBe)≤0.1000% where (IBe) is a maximum optical emission intensity of Be in a surface depth direction using a glow discharge optical emission spectrometer (GDS) prior to performing a plating pretreatment, (Ibulk) is a mean optical emission intensity of Be in an interior of a base material of the aluminum alloy prior to performing a plating pretreatment, and (CBe) is an amount of the Be, and a method of manufacturing the magnetic disc aluminum alloy substrate.
Owner:FURUKAWA SKY ALUMINUM CORP +1
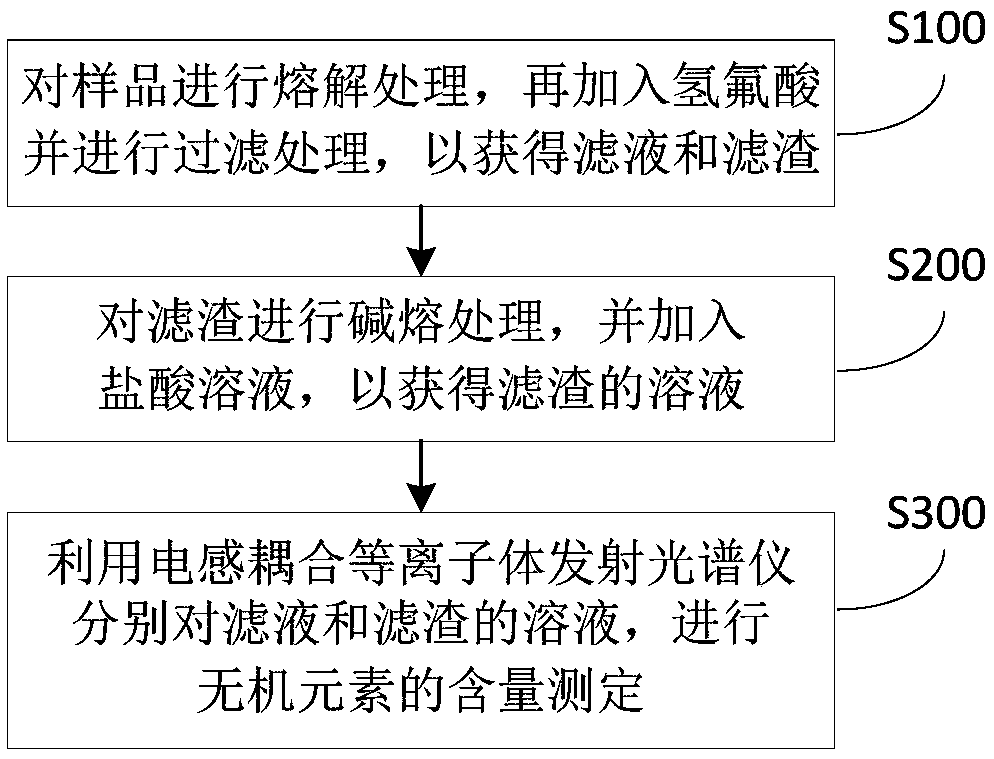
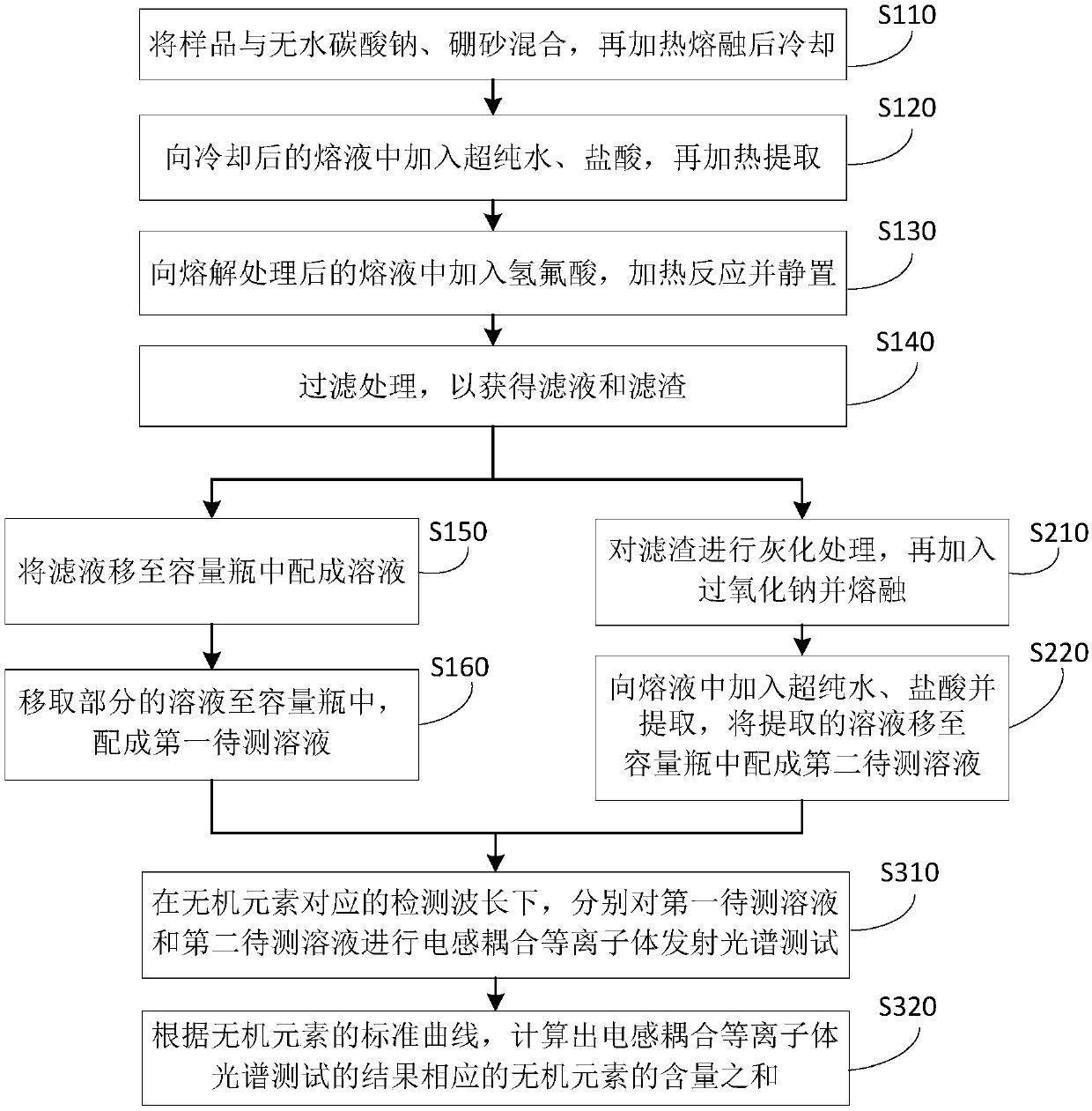
Method for detecting content of inorganic elements in sample of lithium lanthanum zirconium oxide type solid electrolyte
ActiveCN109540874AImprove accuracyEfficient separationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerSolid state electrolyte
The invention provides a method for detecting content of inorganic elements in a sample of a lithium niobium zirconium oxygen type solid electrolyte. The detection method comprises the following stepsof: (1) melting the sample, adding hydrofluoric acid and filtering to obtain filtrate and filter residue; (2) performing an alkali fusion process on the filter residue, and adding a hydrochloric acidsolution to obtain a solution of the filter residue; and (3) measuring the content of the inorganic elements in the filtrate and the solution of the filter residue by an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer. According to the method for detecting the content of inorganic elements in the sample of the lithium niobium zirconium oxygen type solid electrolyte, the content of lithium, lanthanum, and zirconium in the sample of the lithium lanthanum zirconium oxide type solid electrolyte can be detected by the inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer, which has higher accuracy of data, is easier to operate, and is faster and more efficient.
Owner:SVOLT ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
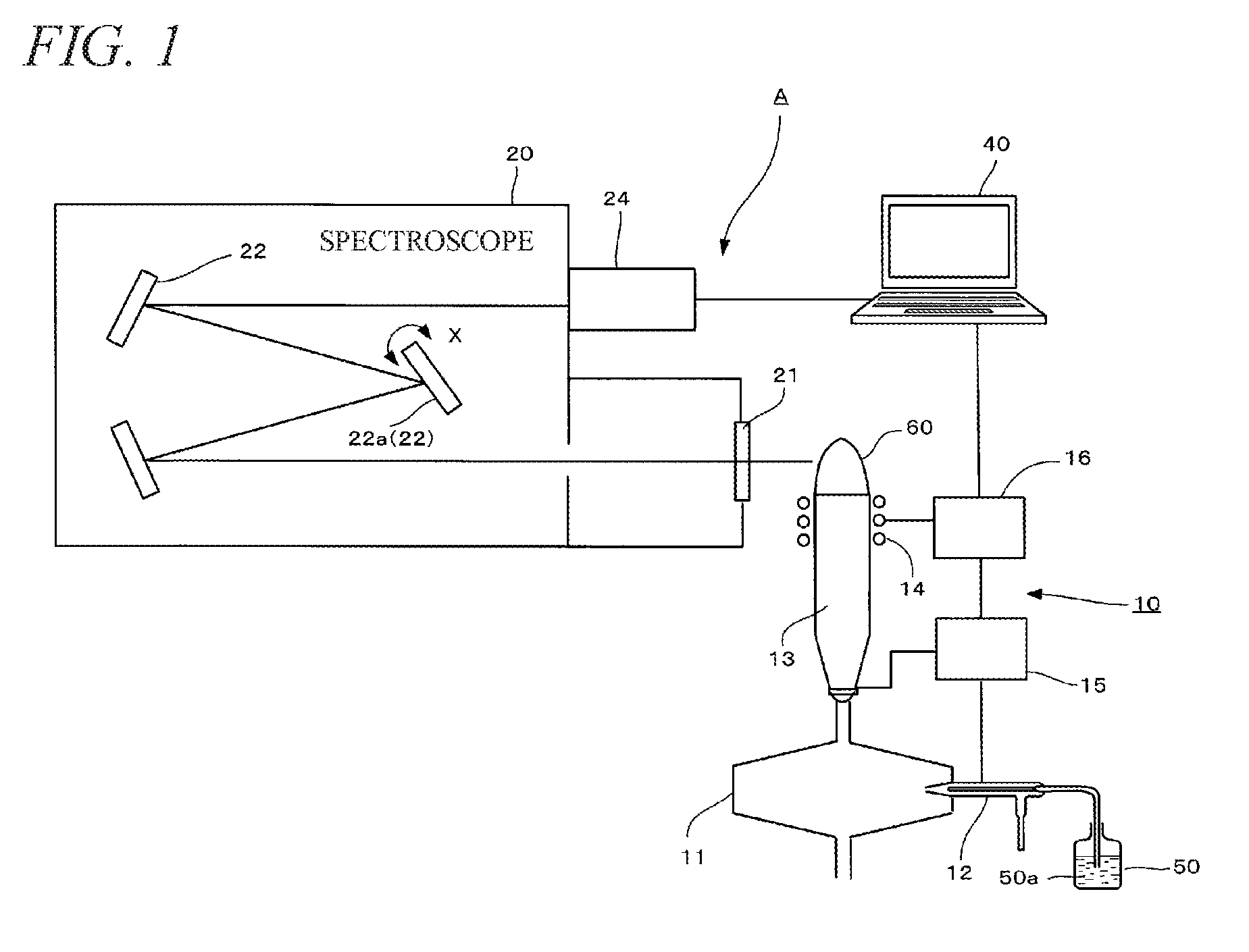
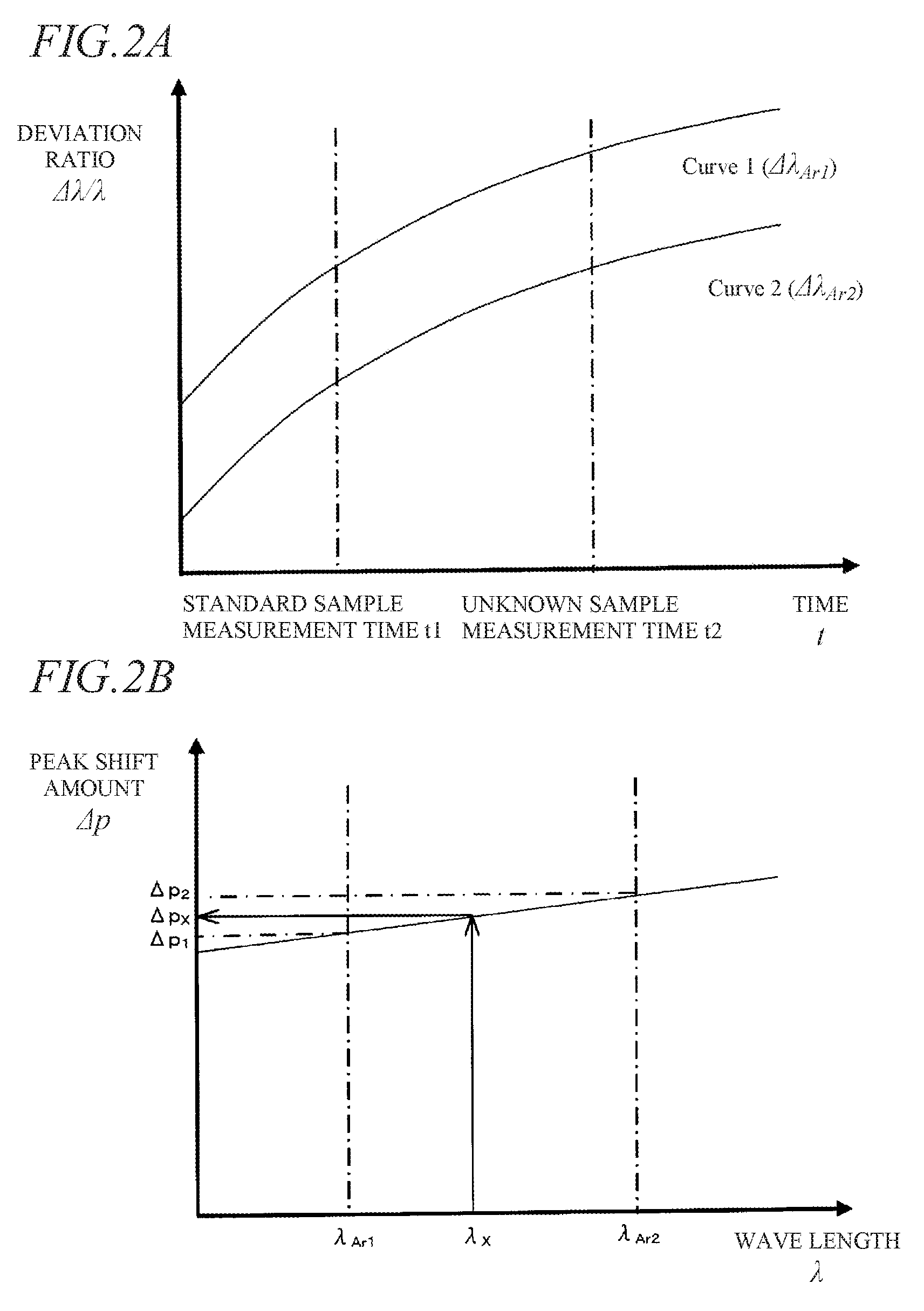
Sequential icp optical emission spectrometer and method for correcting measurement wavelength
InactiveUS20160290862A1Reduce the bodyEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryOptical Emission SpectrometerLength wave
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
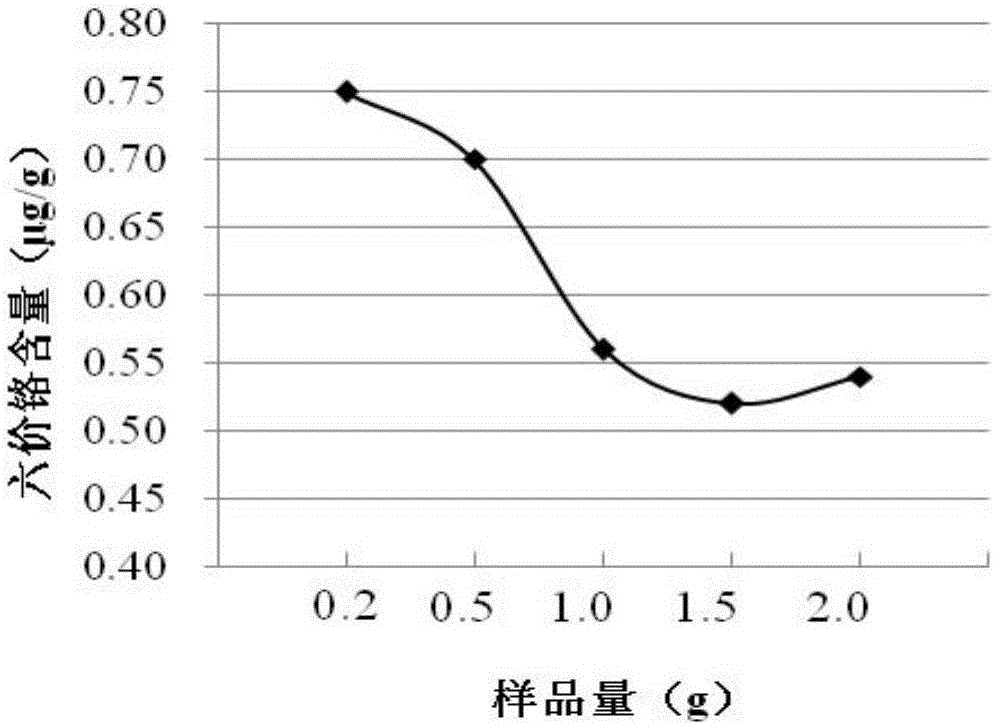
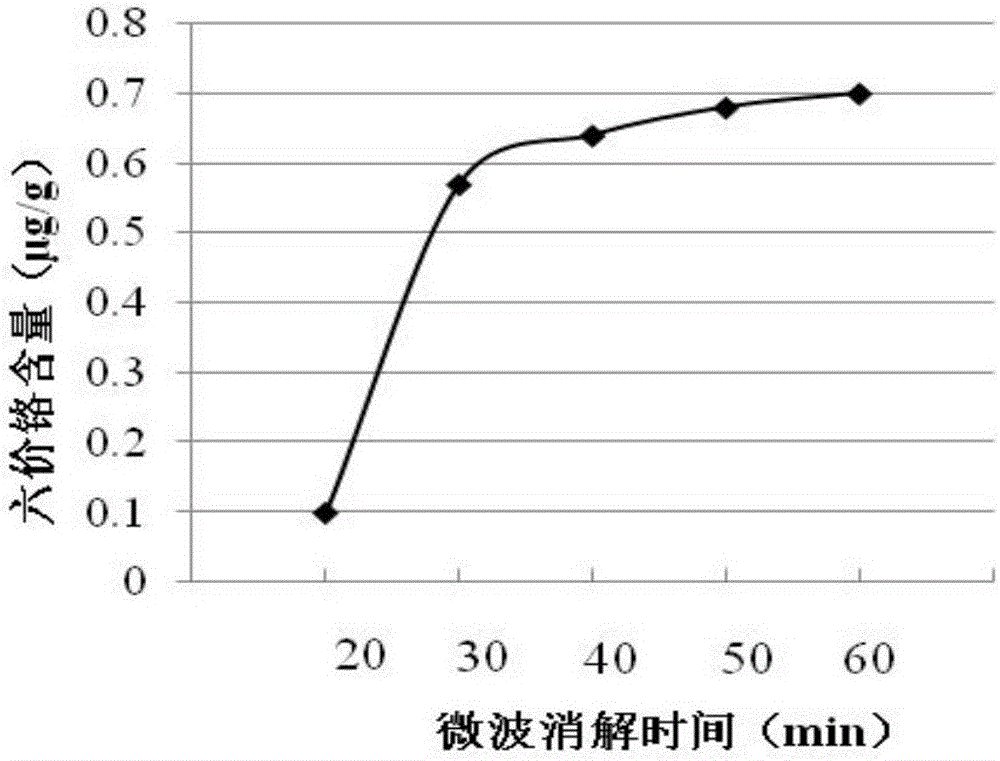
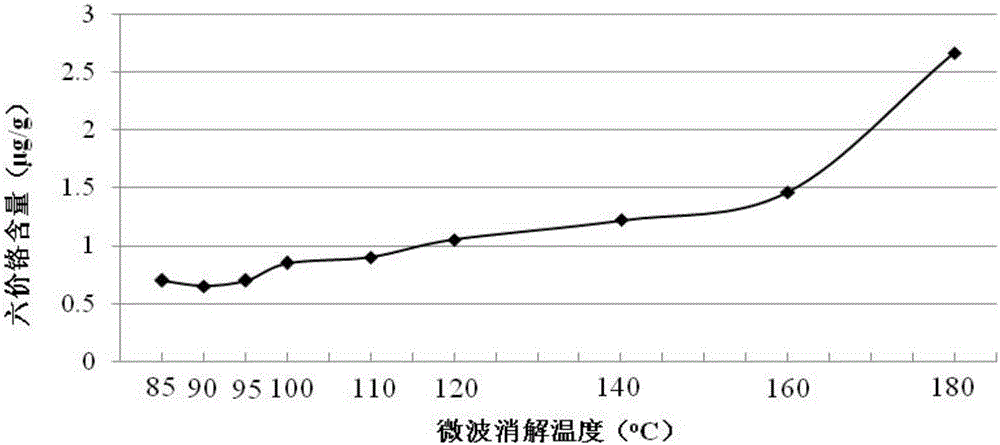
Method for analyzing content of hexavalent chromium in coal ash through ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) method
InactiveCN106770205AReduce distractionsFast analysisPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerMicrowave
The invention provides a method for analyzing the content of hexavalent chromium in coal ash through an ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) method, and relates to the technical field of analyzing testing methods. The method comprises the steps: performing microwave alkaline digestion on a coal ash sample, co-precipitating to separate trivalent chromium, and measuring the content of hexavalent chromium through the ICP-OES. The method has the characteristics of being fast to analyze, high in sensitivity, high in accuracy and precision, small in matrix interference, and wide in linear scope; the average recovering rate reaches 87.2%; and the detection limit is low to 0.00033 mcg / ml.
Owner:淮南市产品质量监督检验所
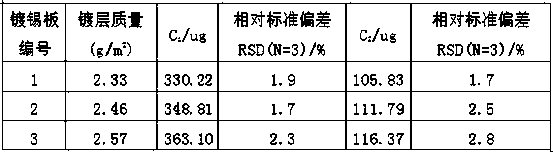
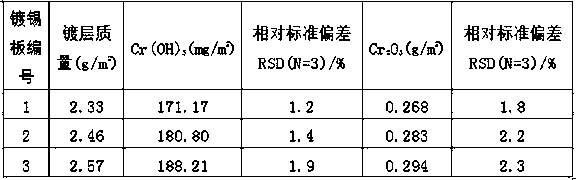
Method for detecting chromium content in surface of cold rolled tin-plated steel sheet
InactiveCN109540875AQuality improvementAvoid affecting the measurement resultsAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerTinning
The invention relates to a method for detecting the chromium content in the surface of a cold rolled tin-plated steel sheet, the method comprises the following steps of: continuously cutting two samples of a certain size on a piece of cold-rolled tin-plated steel sheets without any pollution or corrosion, respectively sealing the surface of one side and four side surfaces of the samples with a resin of high temperature resistance and acid and alkali resistance, immersing, heating and boiling one of the samples with a sulfuric acid solution, and then maintaining the temperature, to prepare a solution 1 to be tested; immersing the other sample with a mixed solution of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate, heating and then maintaining the temperature to prepare a solution 2 to be tested; anddetermining the content of chromium element in the solution 1 and 2 to be tested by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer to calculate the content of chromium hydroxide and chromiumoxide in the surface of the sample. The method of the invention realizes the accurate detection of the total content of chromium, the content of chromium hydroxide, and the content of chromium oxidein the surface passivation layer of the cold-rolled tin-plated steel sheet, and provides conditions for the precise regulation of the passivation process of the cold-rolled tin-plated steel sheet, which is helpful for improving the surface quality of cold-rolled tin-plated steel sheet.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Detection method for authenticating galvanizing method of galvanized steel wire by coating iron content
InactiveCN109557084AAnalysis by thermal excitationColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical Emission SpectrometerDiffusion
The invention provides a detection method for authenticating a galvanizing method of galvanized steel wires by coating iron content, and is proposed to identify zinc electroplating and hot-dip galvanizing from the galvanizing principle. Electroplating is an electrochemical principle. The coating is a pure galvanized layer with no iron. The hot-dip galvanized coating is divided into two layers, a pure zinc layer and a zinc-iron alloy layer formed by thermal diffusion, so that the iron is present in the coating. A chemical method is established to identify the two according to the different chemical elements in the two coatings. The content of iron in the coating is detected by means of an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer or an atomic absorption spectrometer accordingto the test method for the specific detection of iron in the coating. The galvanizing method is identified depending on whether iron is detected in the coating or by its range.
Owner:南通市产品质量监督检验所
Apparatus and Methods for Optical Emission Spectroscopy
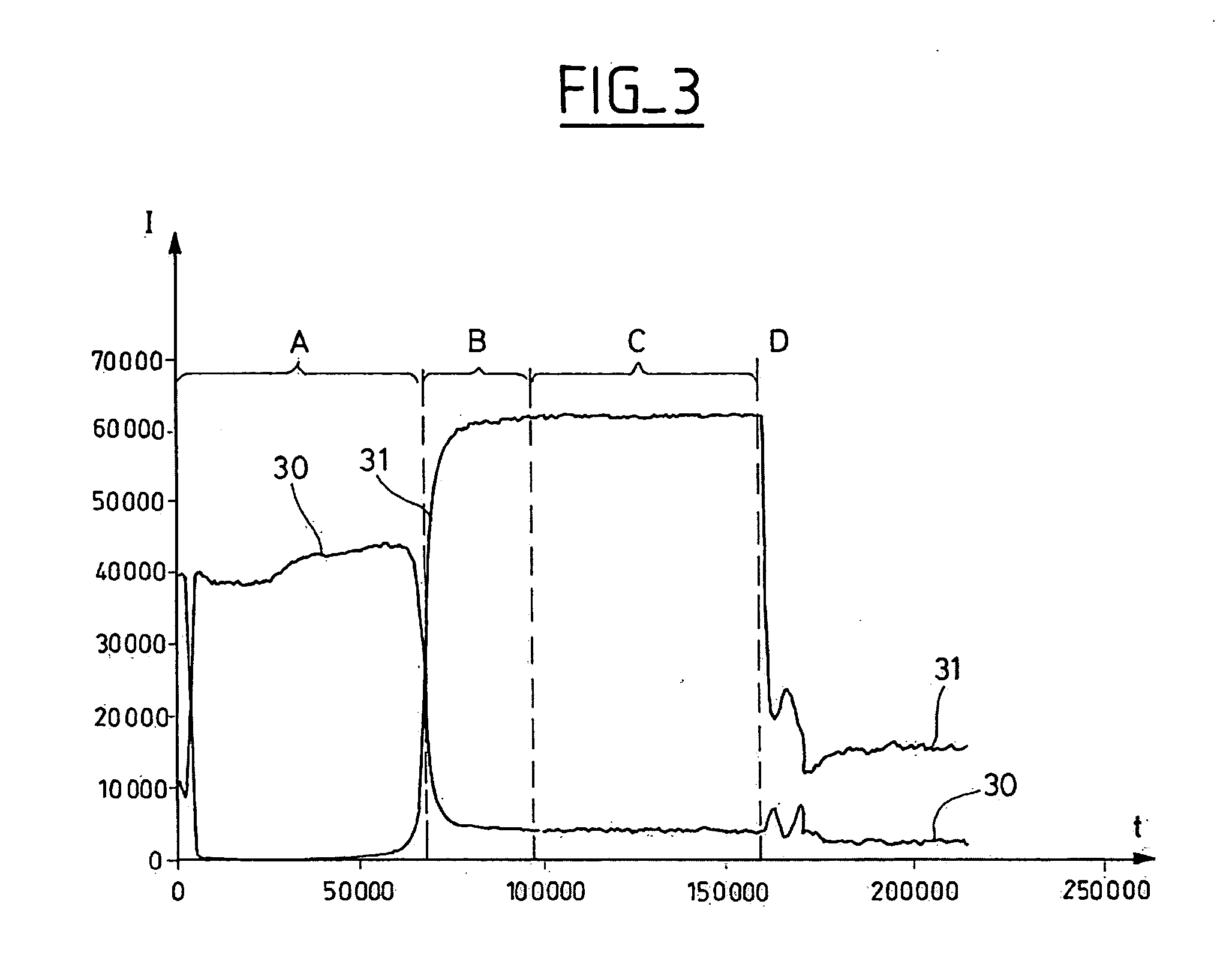
ActiveUS20110228269A1Good precisionHigh energyEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryOptical Emission SpectrometerPeak value
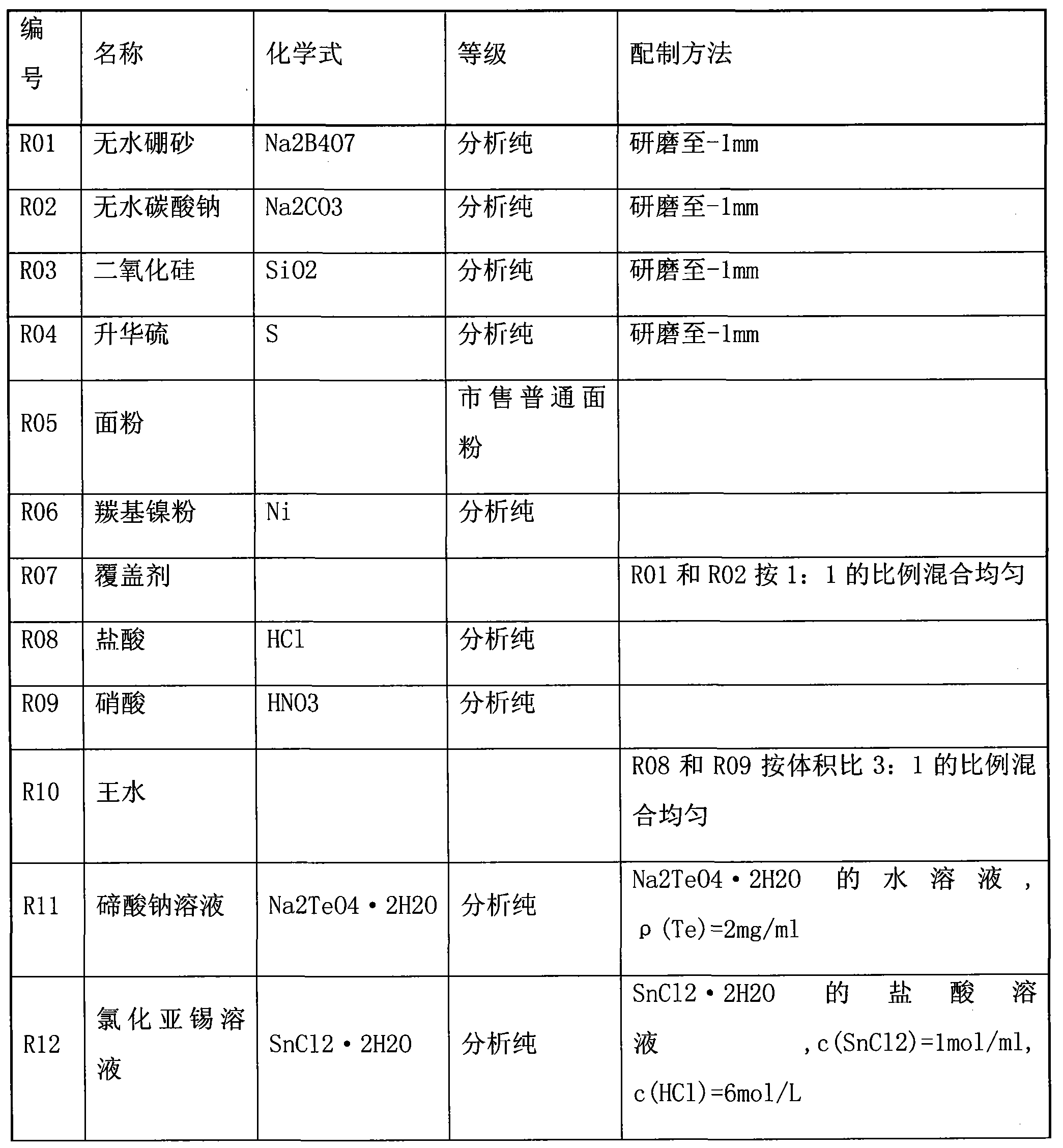
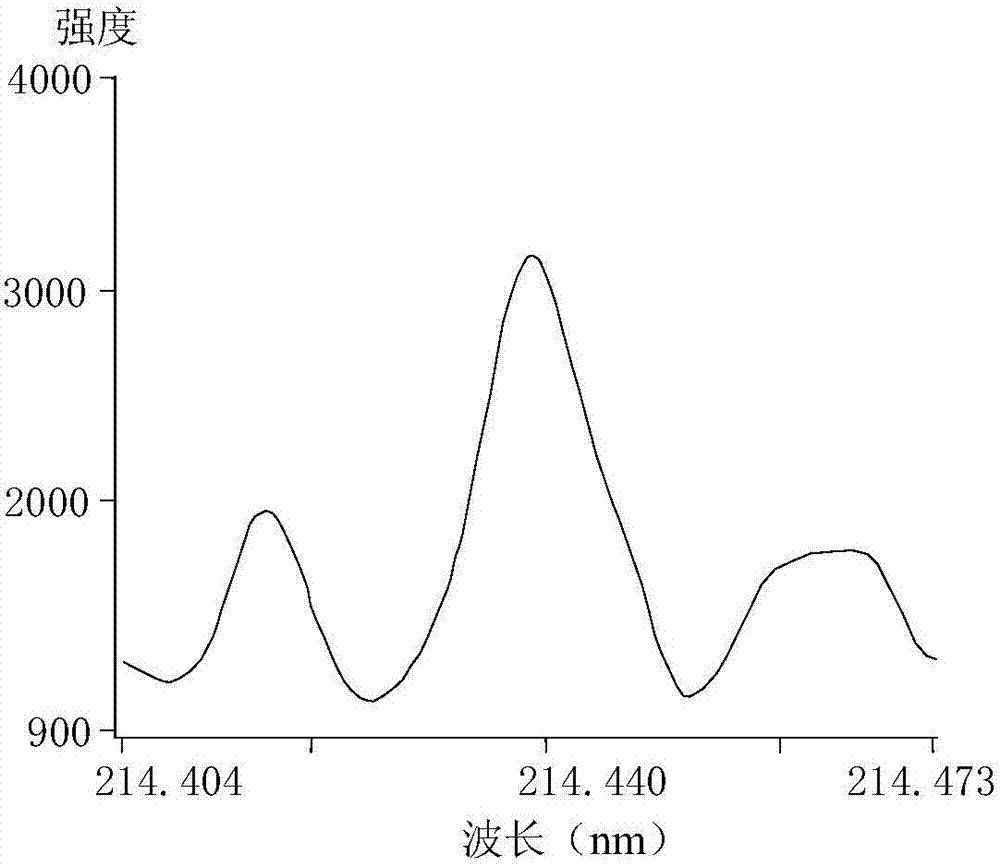
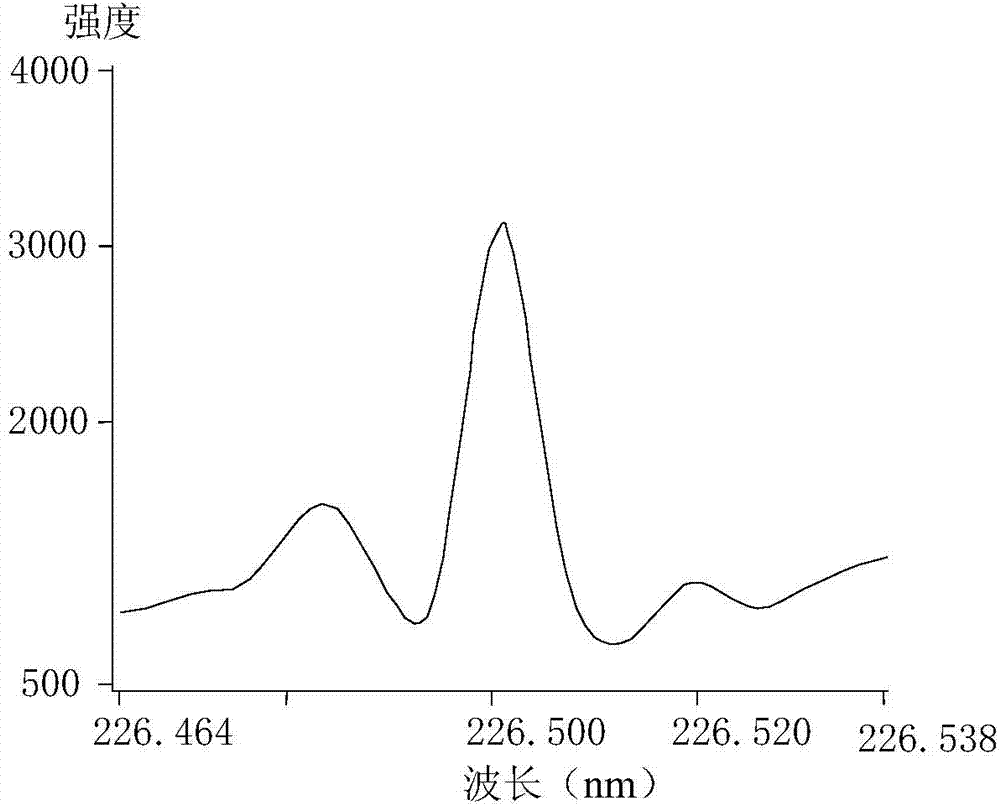
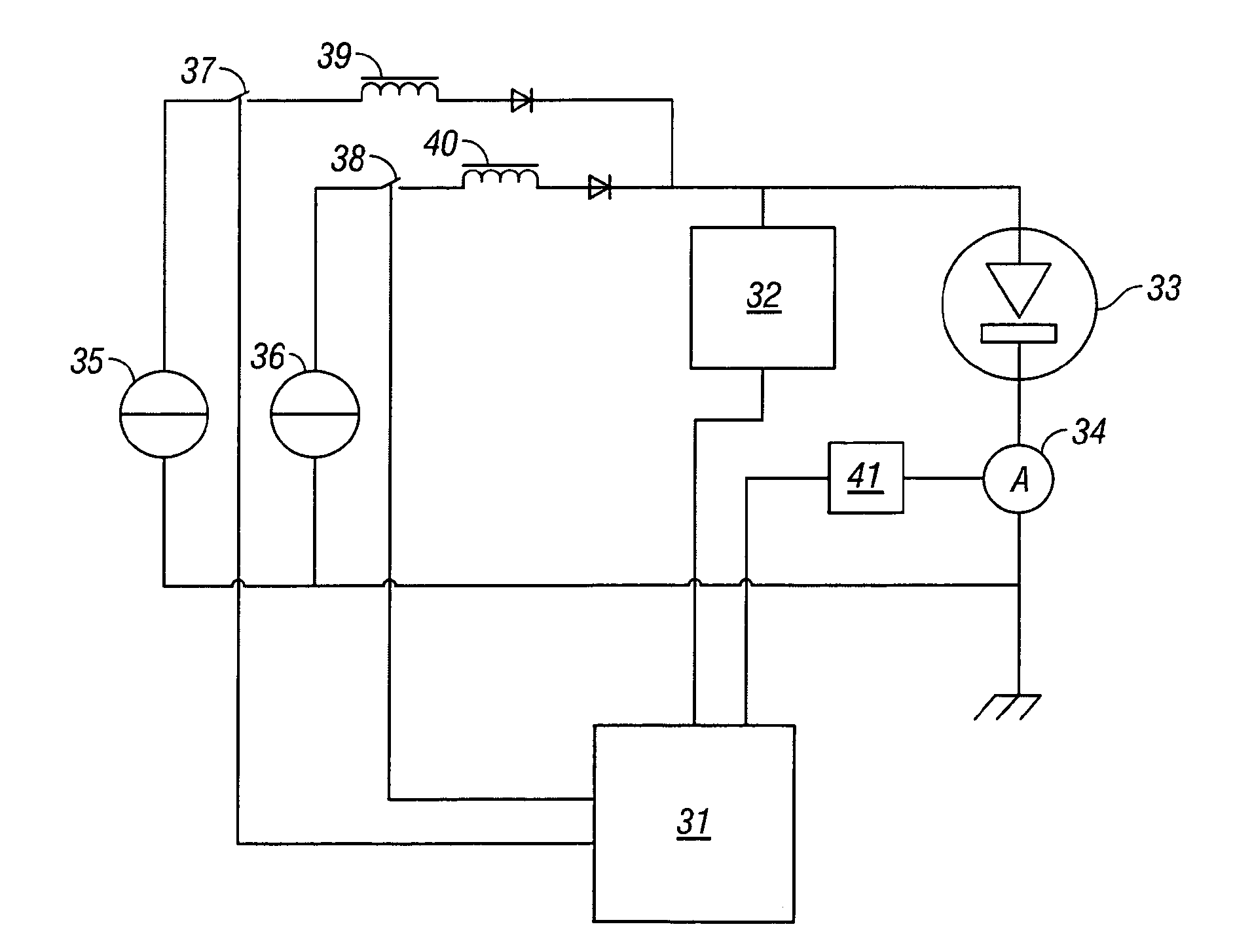
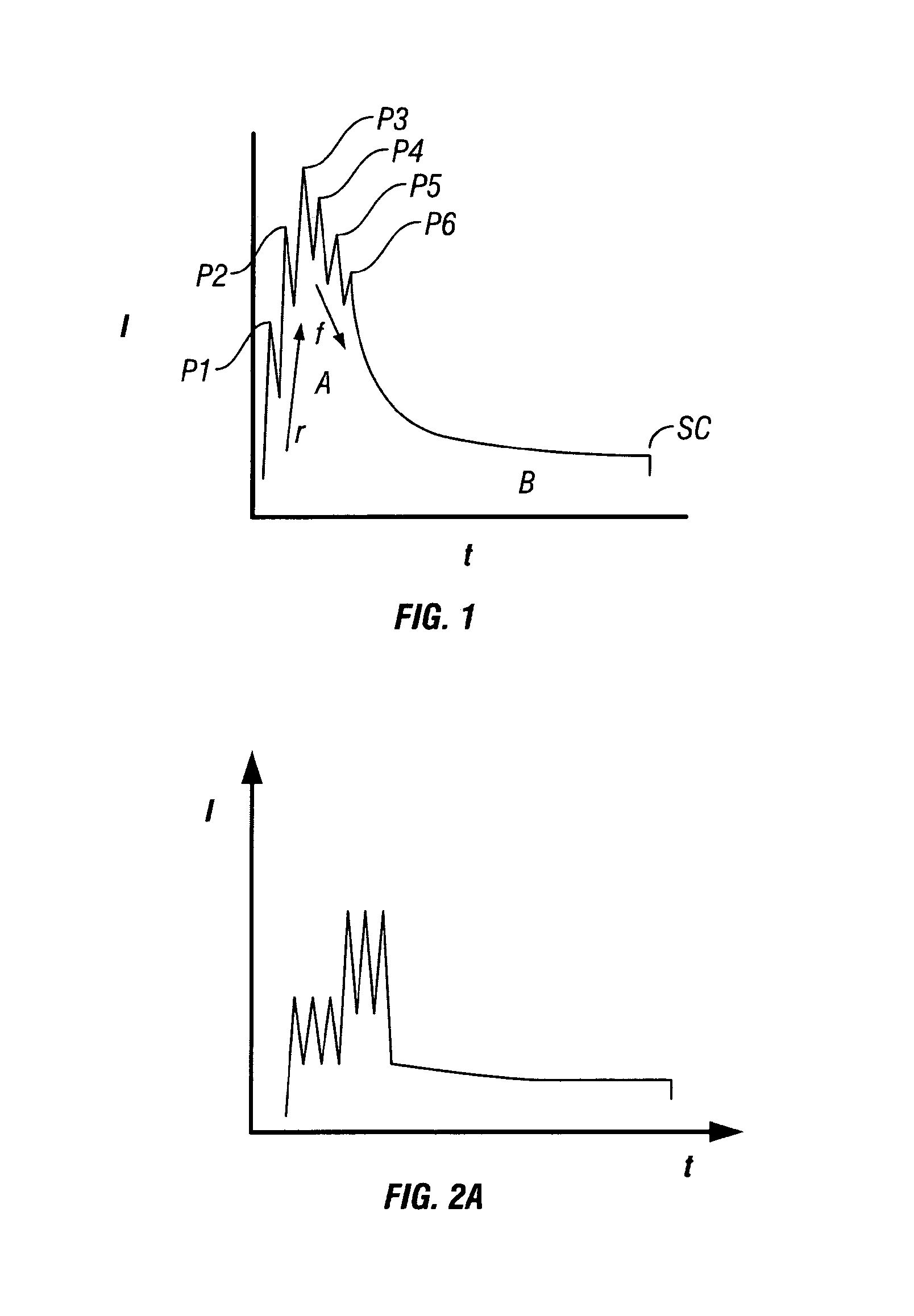
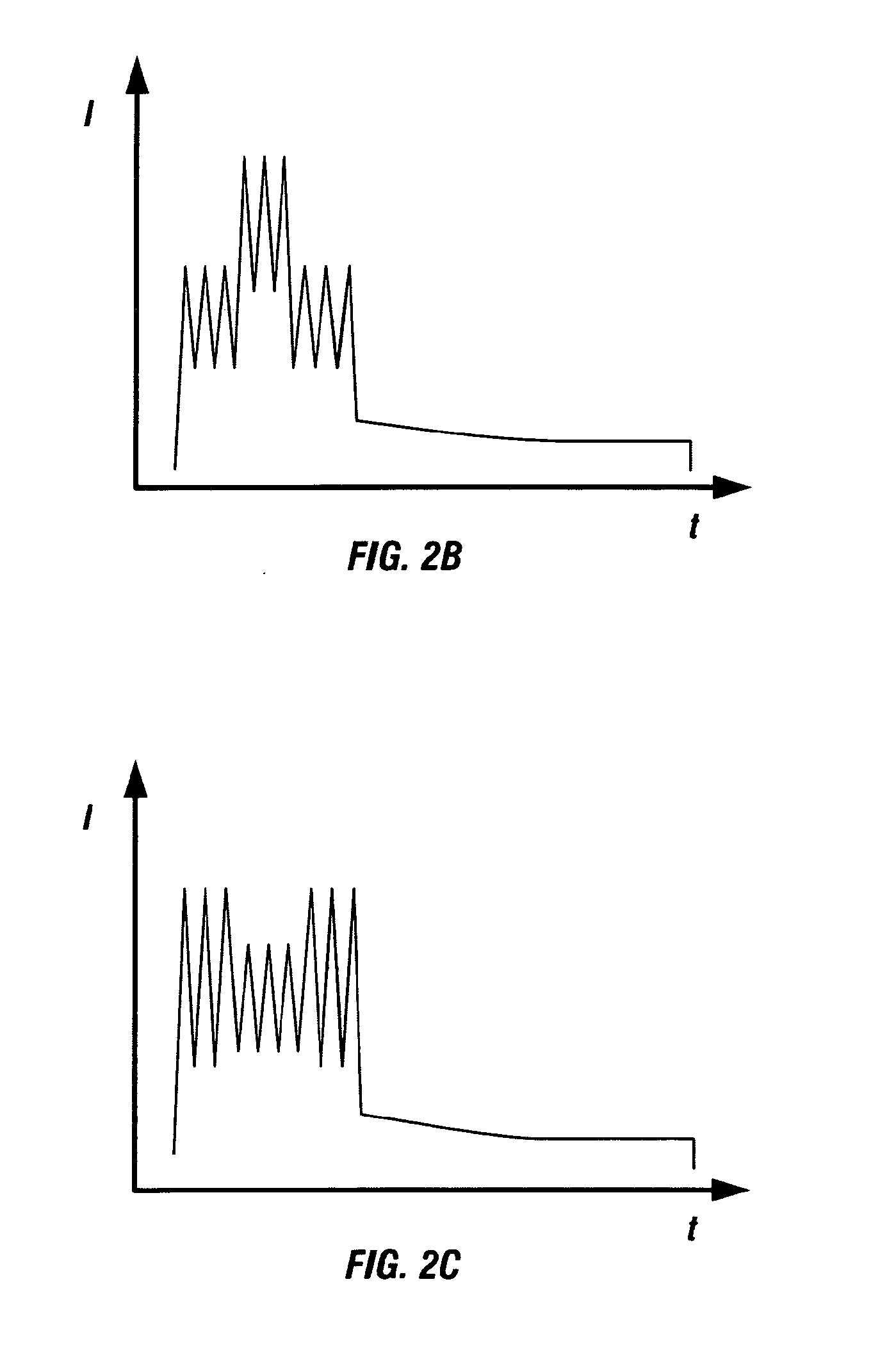
The invention provides a spark generator for generating a spark for optical emission spectroscopy (OES), wherein the spark has a current waveform comprising a first modulated portion which comprises a plurality of relatively high current and high gradient peaks of variable amplitude and / or inter-peak duration and a second modulated portion of relatively low current and low gradient which is substantially without modulated peaks. The spark is preferably generated from two or more programmable current sources. The invention also provides an optical emission spectrometer comprising the spark generator and a method of optical emission spectroscopy using the spark generator.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI ECUBLENS
ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometer) rapid determination method for contents of chromium and iron in nickel-based superalloy
PendingCN112834487AEliminate the effects ofFully affectedPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerElemental analysis
The invention relates to an ICP-OES rapid determination method for contents of chromium and iron in nickel-based superalloy, belongs to the technical field of chemical analysis test. The method comprises steps of dissolving pure nickel to serve as a matrix, adding different amounts of chromium and iron standard solutions to prepare a calibration solution, and adding an yttrium internal standard solution; simultaneously measuring the intensity ratio of the internal marking line of the internal standard element to the analysis line of the element to be measured in the calibration solution by using ICP-OES to make a calibration curve; dissolving a to-be-measured sample with nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid, adding an yttrium internal standard solution with the same content as the standard solution, diluting with water to a fixed volume, introducing the solution into ICP-OES to measure the spectral line intensity of the to-be-measured element, and calculating the content of the to-be-measured element on the calibration curve. The calibration solution prepared by the method is similar to a sample solution in matrix, so that the matrix effect is eliminated; and a high-precision analysis instrument is used, so that the problems of complicated chemical analysis operation and low analysis speed are solved, and the method has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness, high accuracy, high precision and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU LONGDA SUPERALLOY MATERIAL CO LTD
Systems and methods for rapid elemental analysis of airborne particles using atmospheric glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy
InactiveUS20200132606A1Analysis by electrical excitationParticle size analysisOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical spectrometer
The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for performing elemental analysis of airborne aerosols. The systems comprise an aerosol collection device for accumulating aerosol particles in a flow of aerosol particles, a radio frequency power supply for providing a glow discharge current to ablate the aerosol particles accumulated in the aerosol collection device, and an optical emission spectrometer or a mass spectrometer for analyzing elements in the ablated aerosol particles. Several types of aerosol collection devices are described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Detecting method for contents of cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium in plastic
InactiveCN103852464AThe detection work is accurateThe detection method is simplePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerEthylene diamine
The invention discloses a detecting method for contents of cadmium, lead, mercury and chromium in plastic. The detecting method comprises the following steps of (a) treating a sample to form particles, wherein the weight of each particle is not larger than 0.2g; (b) adding sulfuric acid into the sample treated in the step (a), heating at the temperature of higher than 250 DEG C for more than 15min, and adding nitric acid into the sample until the sample is completely digested, wherein the ratio of the sample to the sulfuric acid is 1: (15-35)g / ml; (c) stopping heating, standing and cooling, then, slowly adding preoxyhydrochloric acid and an EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid)-2Na solution, continuously heating until the solution is boiled, and keeping the solution boiling for more than 1min, wherein the ratio of the volume of the added preoxyhydrochloric acid to the quantity of the sample is (40-60):1ml / g, and the ratio of the volume of the added EDTA-2Na solution to the quantity of the sample is (40-60):1ml / g; (d) filtering the solution obtained in the step (c), and analyzing by using an ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer). The analysis method provided by the invention is rapid, high in accuracy and good in repeatability and reproducibility.
Owner:昆山洛丹伦生物科技有限公司
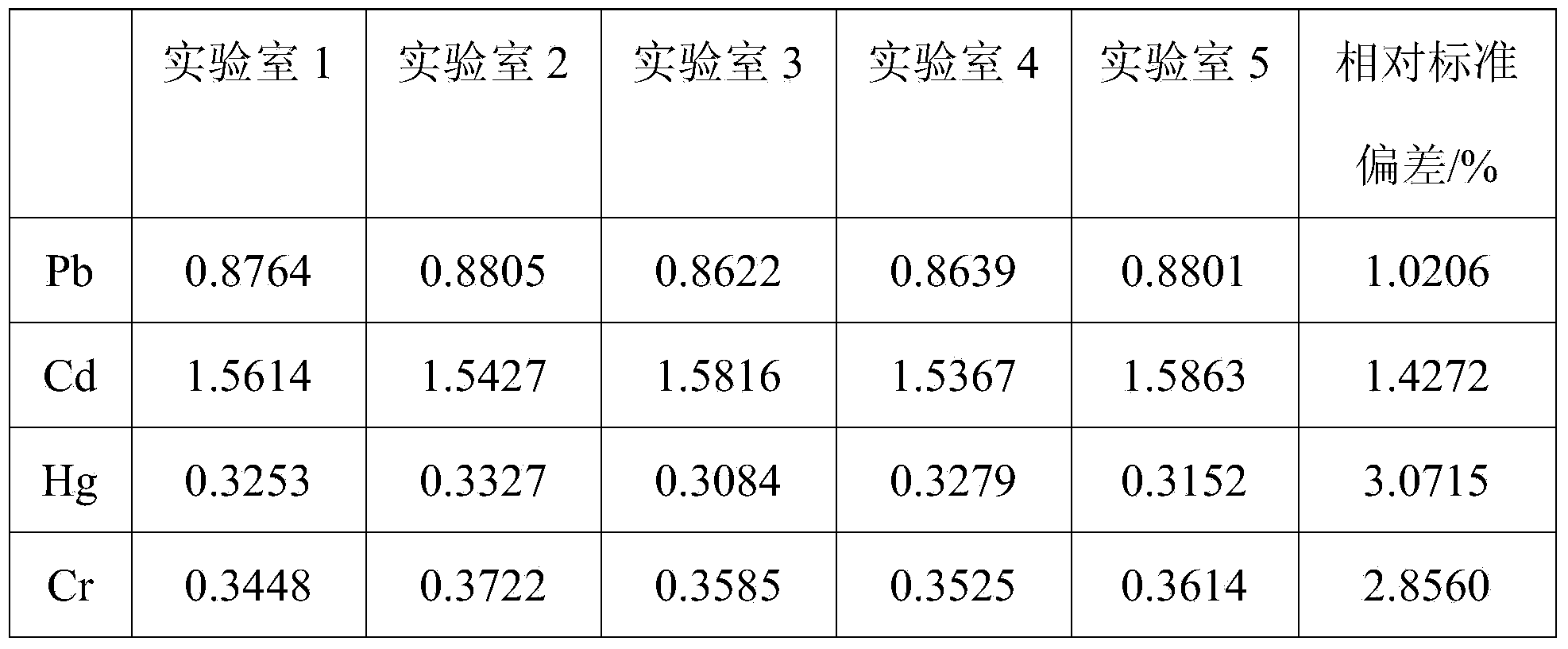
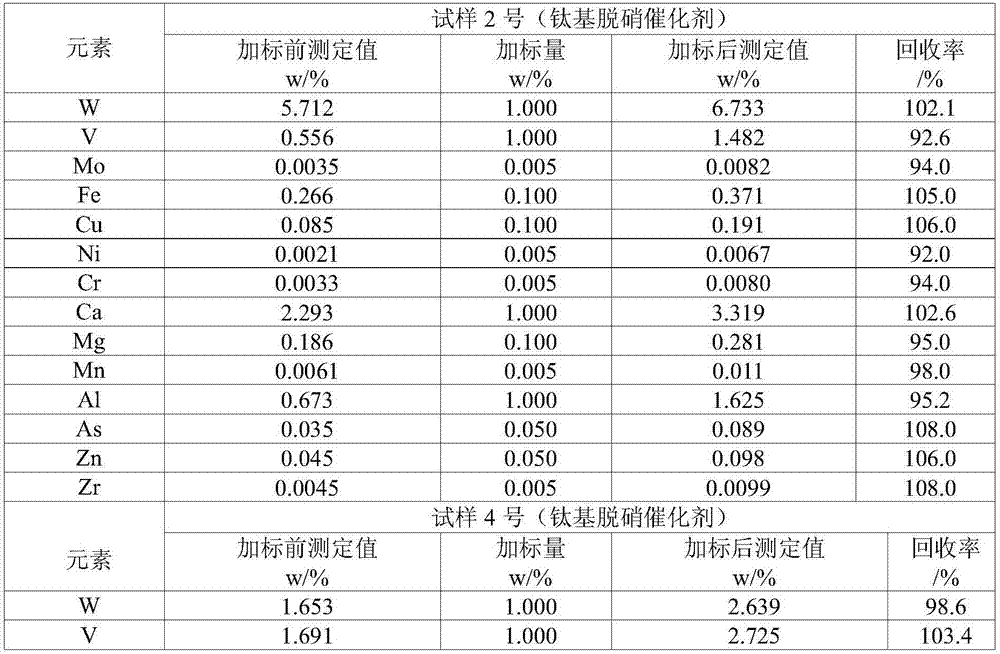
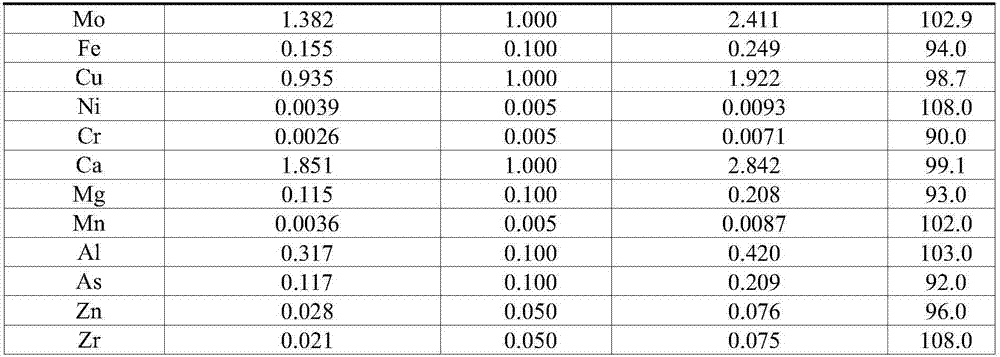
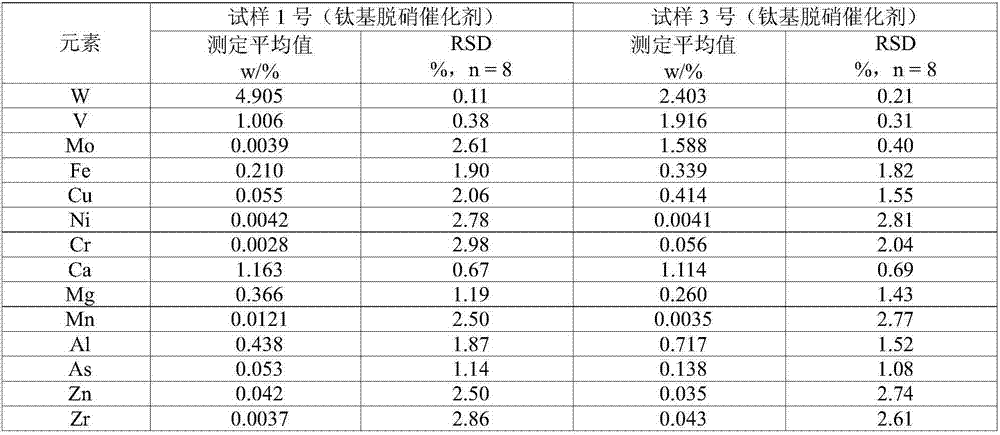
Method for resolving titanium base denitration catalyst and detection method for resolving solution
InactiveCN106872258AGuaranteed validityKeep alivePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerHigh concentration
The invention relates to the technical field of macroelement or microelement detection, in particular to a method for resolving a titanium base denitration catalyst and a detection method for resolving solution. The method for resolving the titanium base denitration catalyst comprises the following steps: adding hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid and water into the titanium base denitration catalyst, and heating until solution is boiling; then, adding the mixed solution of sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid and water, continuously heating to enable the solution to boil, and resolving a sample until the sample completely disappears and the solution is clear; then, continuously heating until white smoke appears, finishing heating, and cooling the solution to a room temperature; adopting an existing conventional detection method or ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) to detect the resolving solution. According to the method for solving the titanium base denitration catalyst, the quick and complete resolving of complex insoluble oxides, including titanium dioxide, tungsten trioxide and the like, of a coexistence system in the titanium base denitration catalyst can be solved; through the complexing stability function of sulfate radical and phosphate radical, side reactions which include high titanium base hydrolysis and the precipitation of high-concentration tungsten by tungstic acid and affect detection result accuracy are respectively avoided.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com