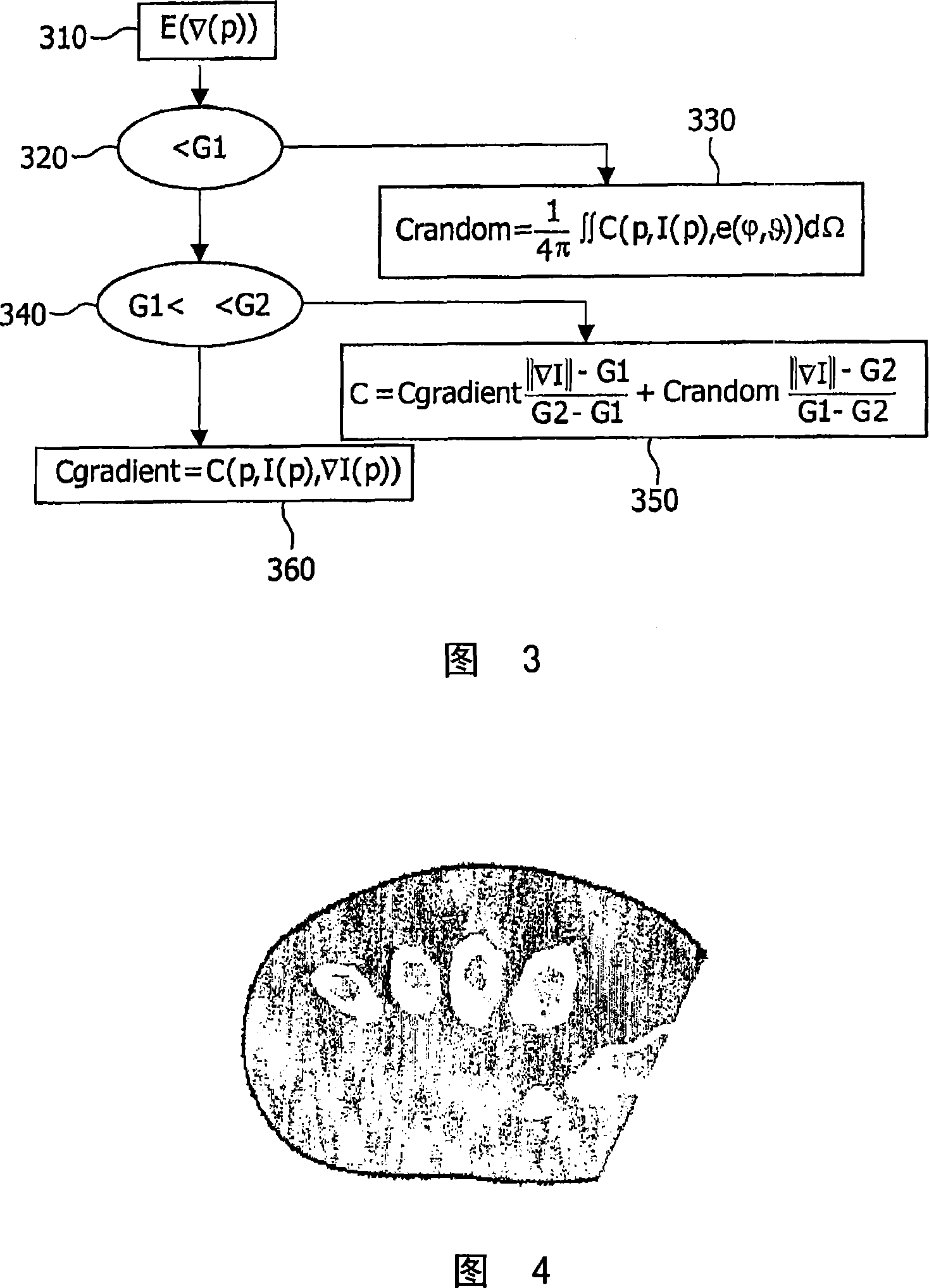
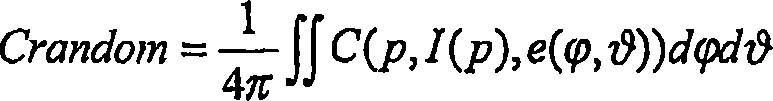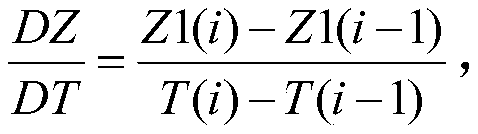Patents
Literature
34 results about "Low gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low-flow, low-gradient (LF-LG) aortic stenosis (AS) may occur with depressed or preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and both situations are among the most challenging encountered in patients with valvular heart disease. In both cases, the decrease in gradient relative to AS severity is due to a reduction in transvalvular flow.
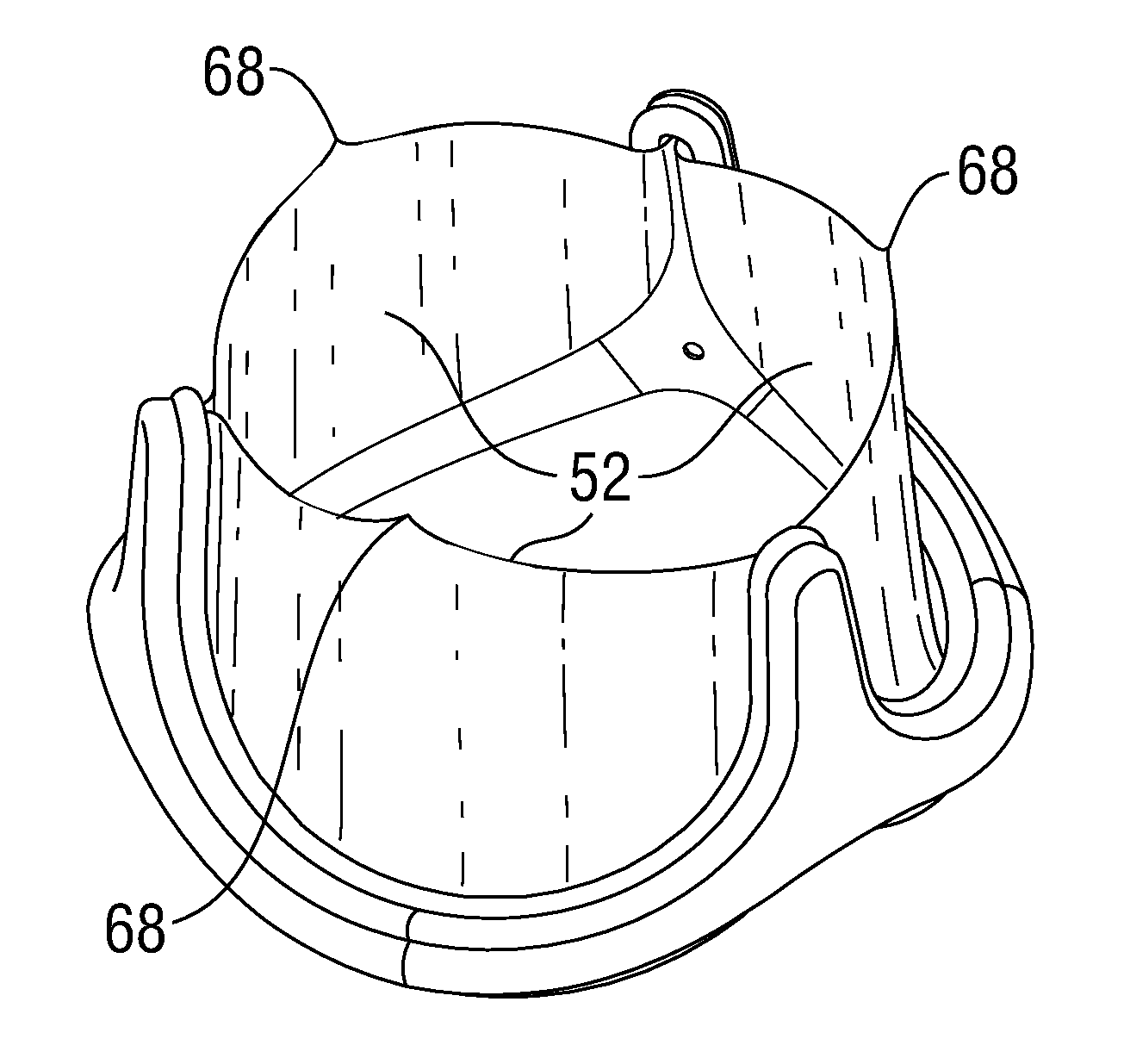
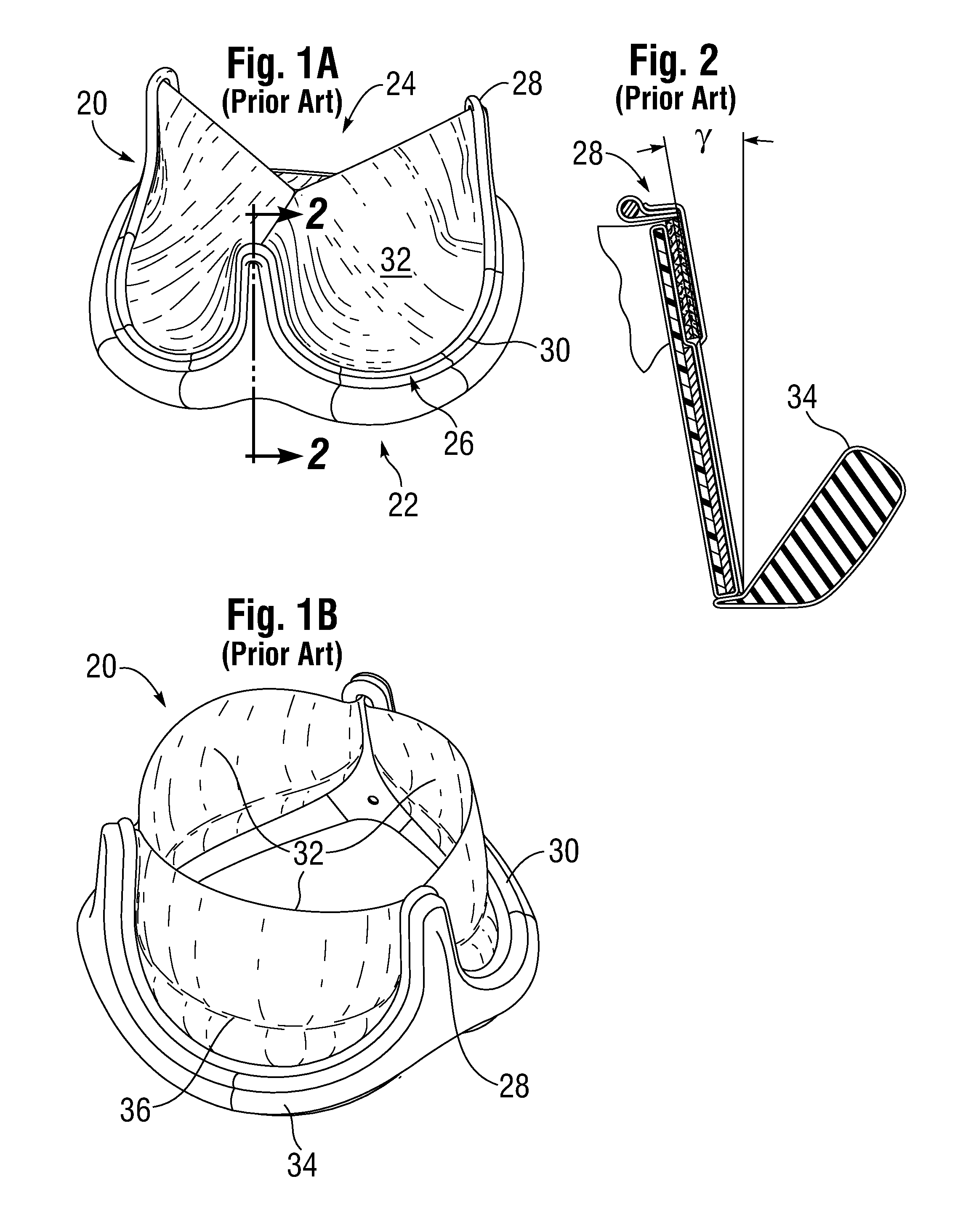
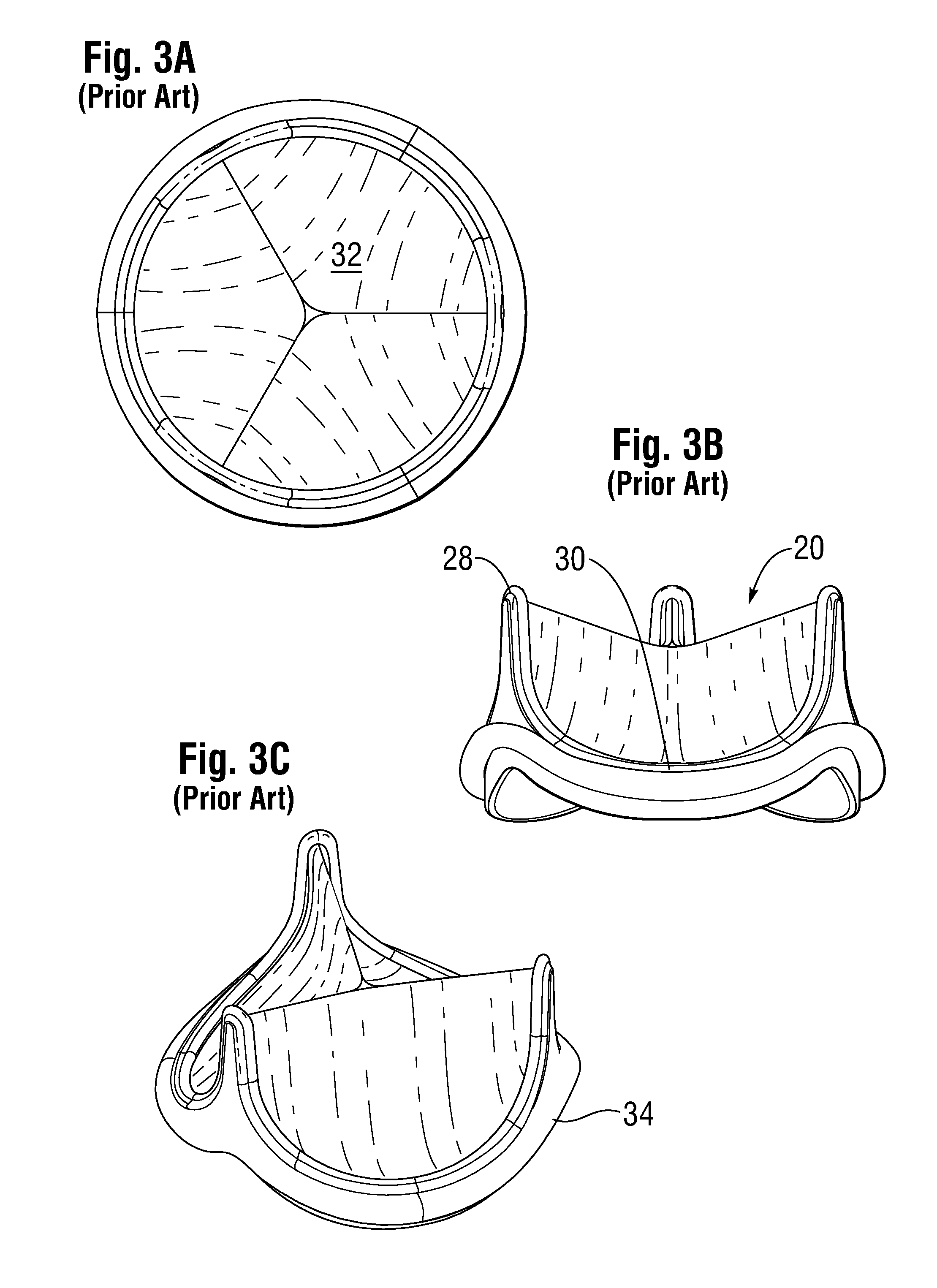
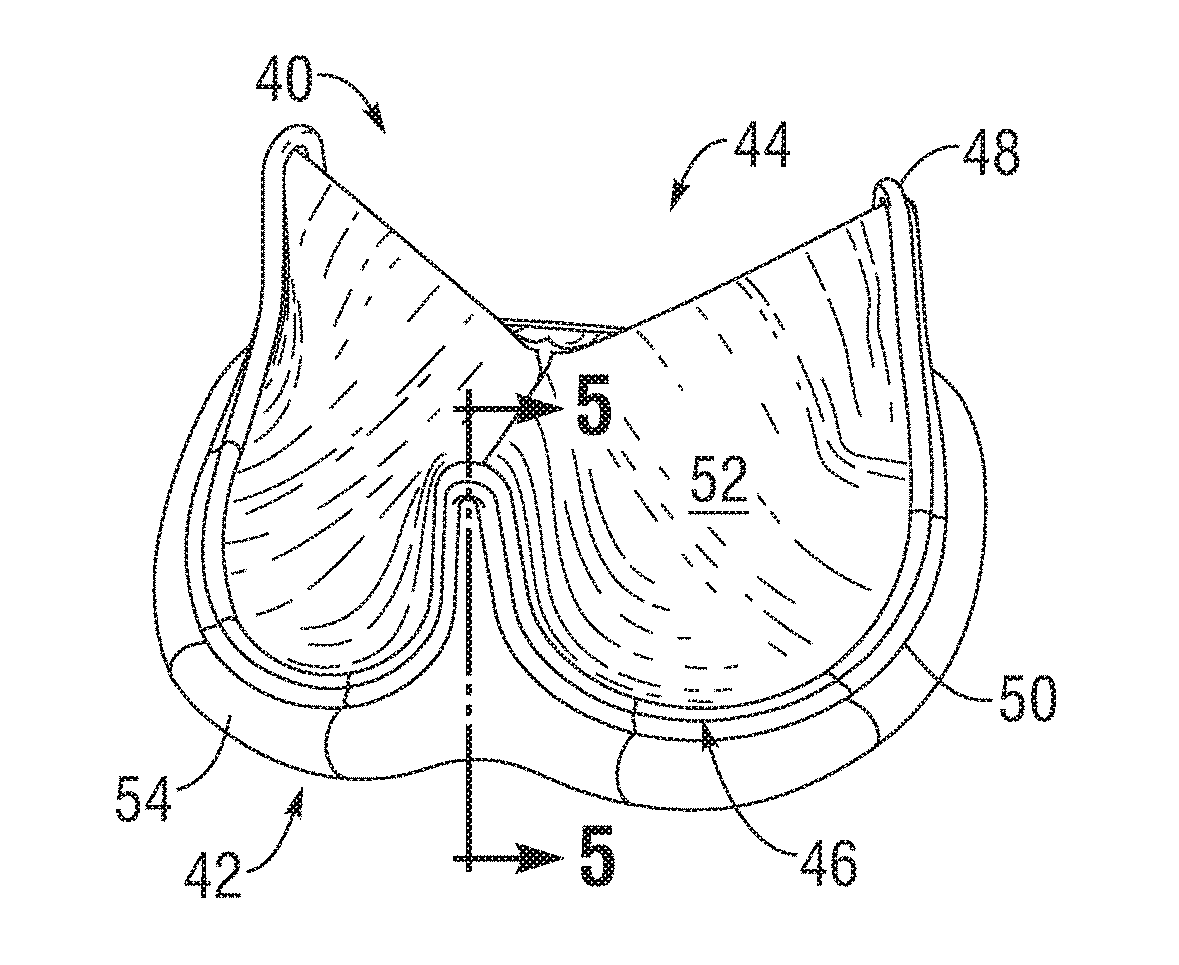
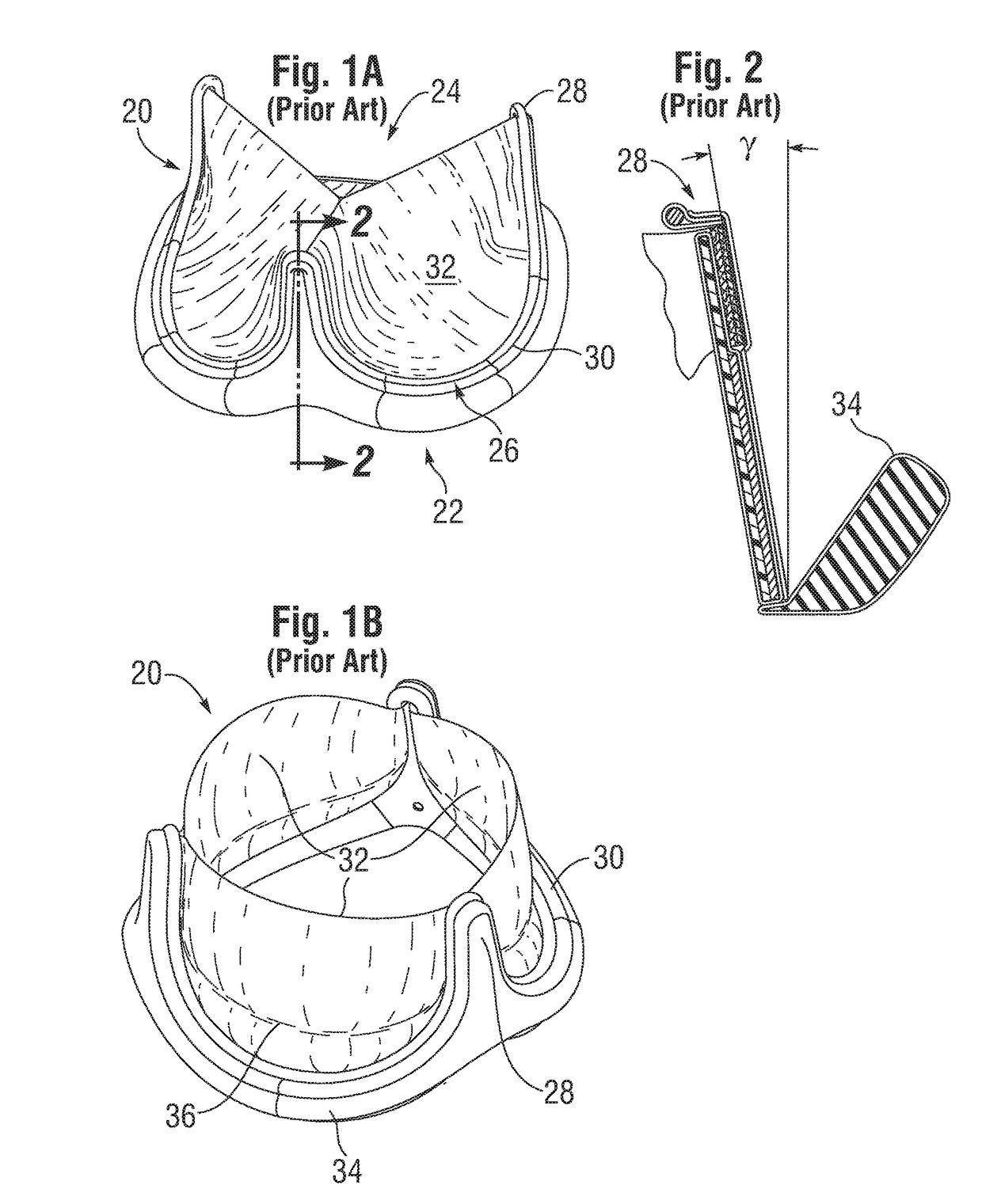
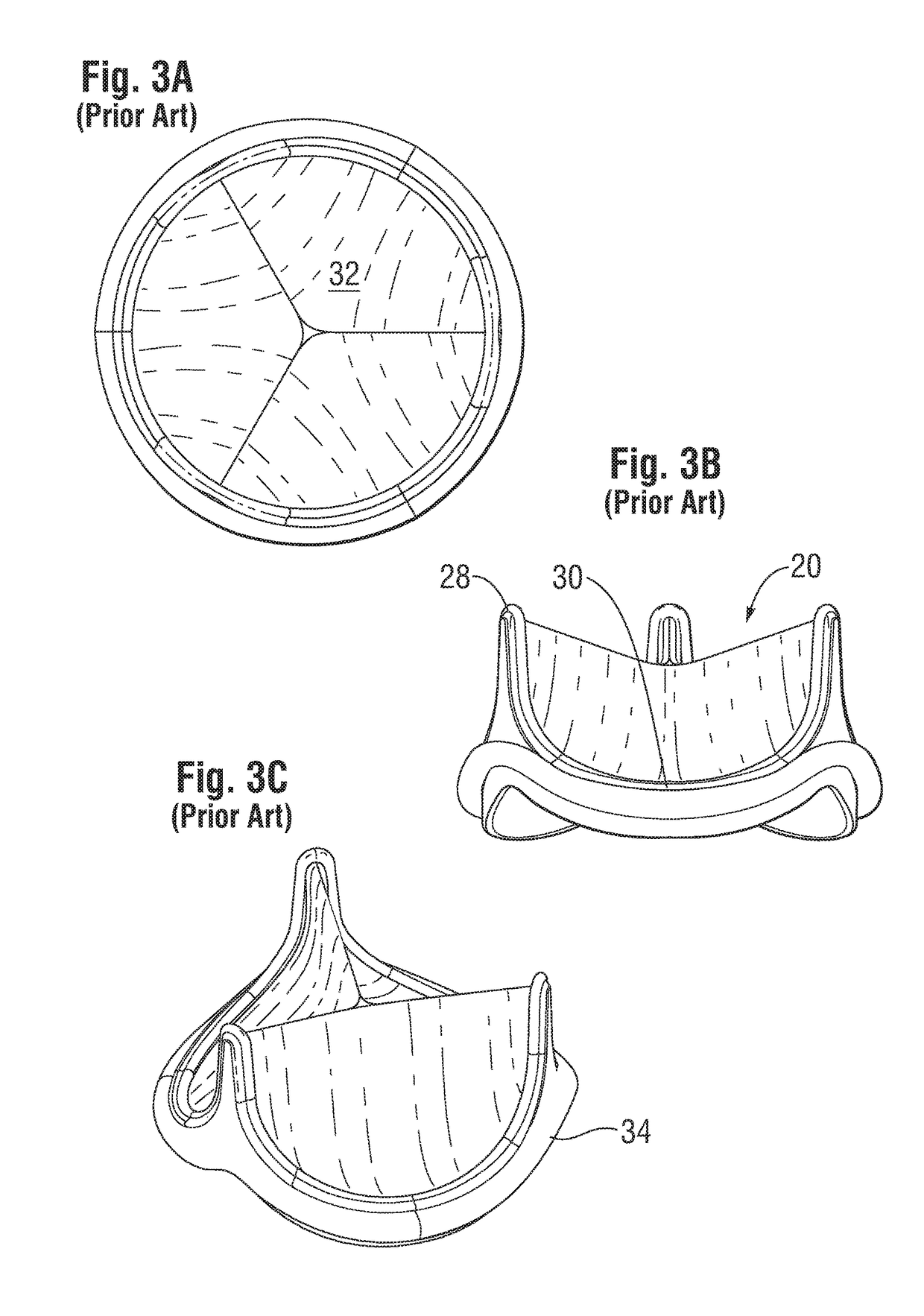
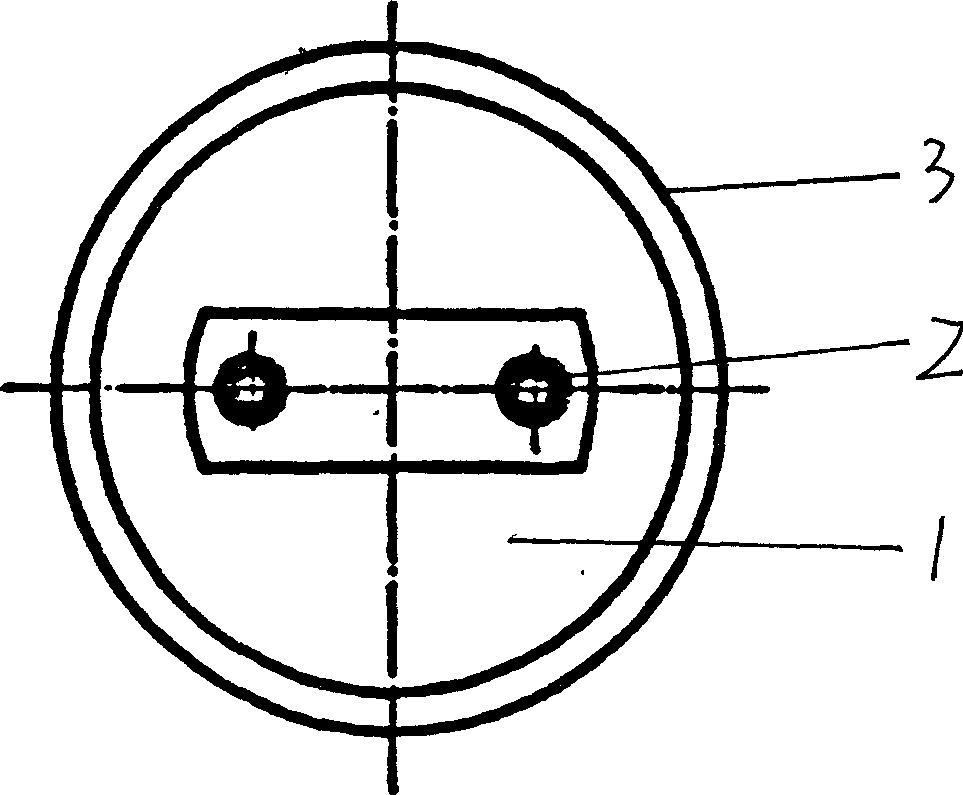
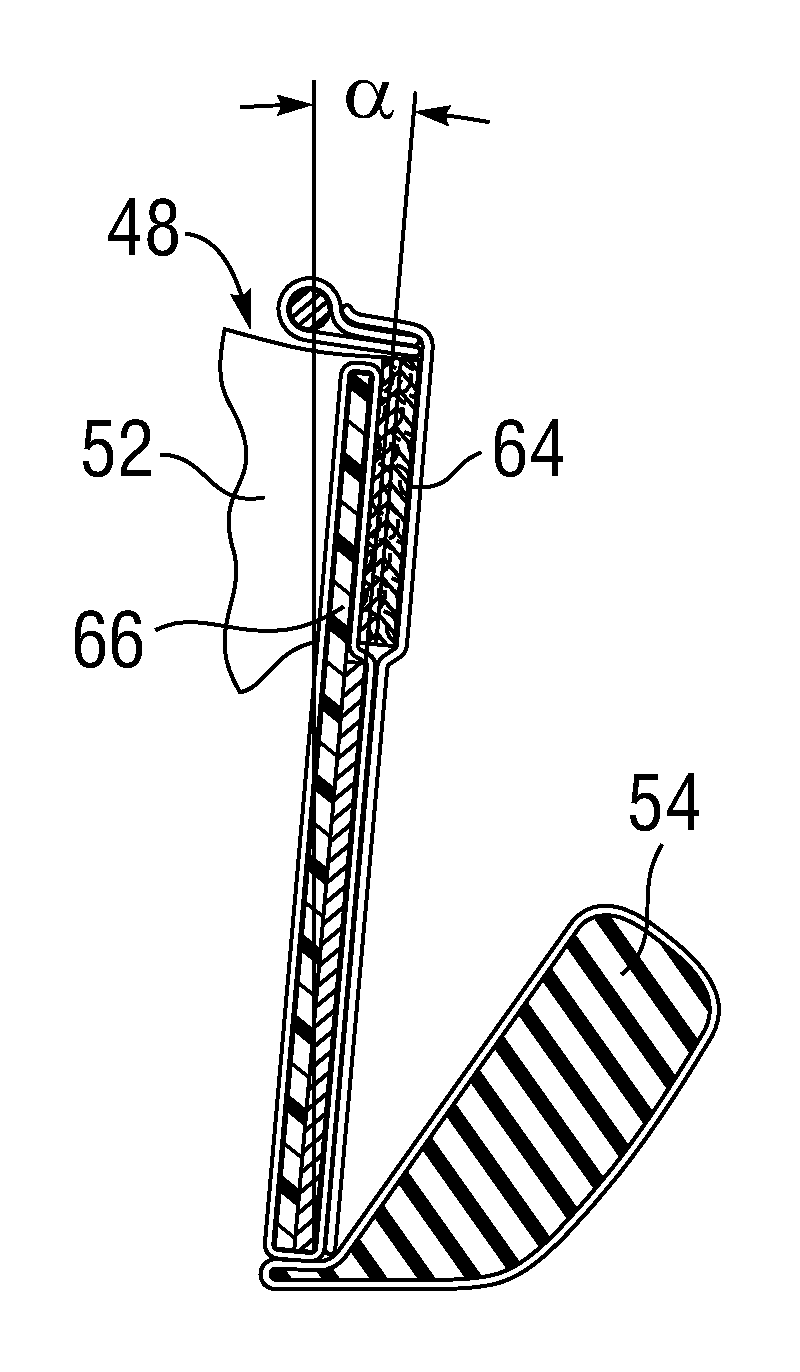
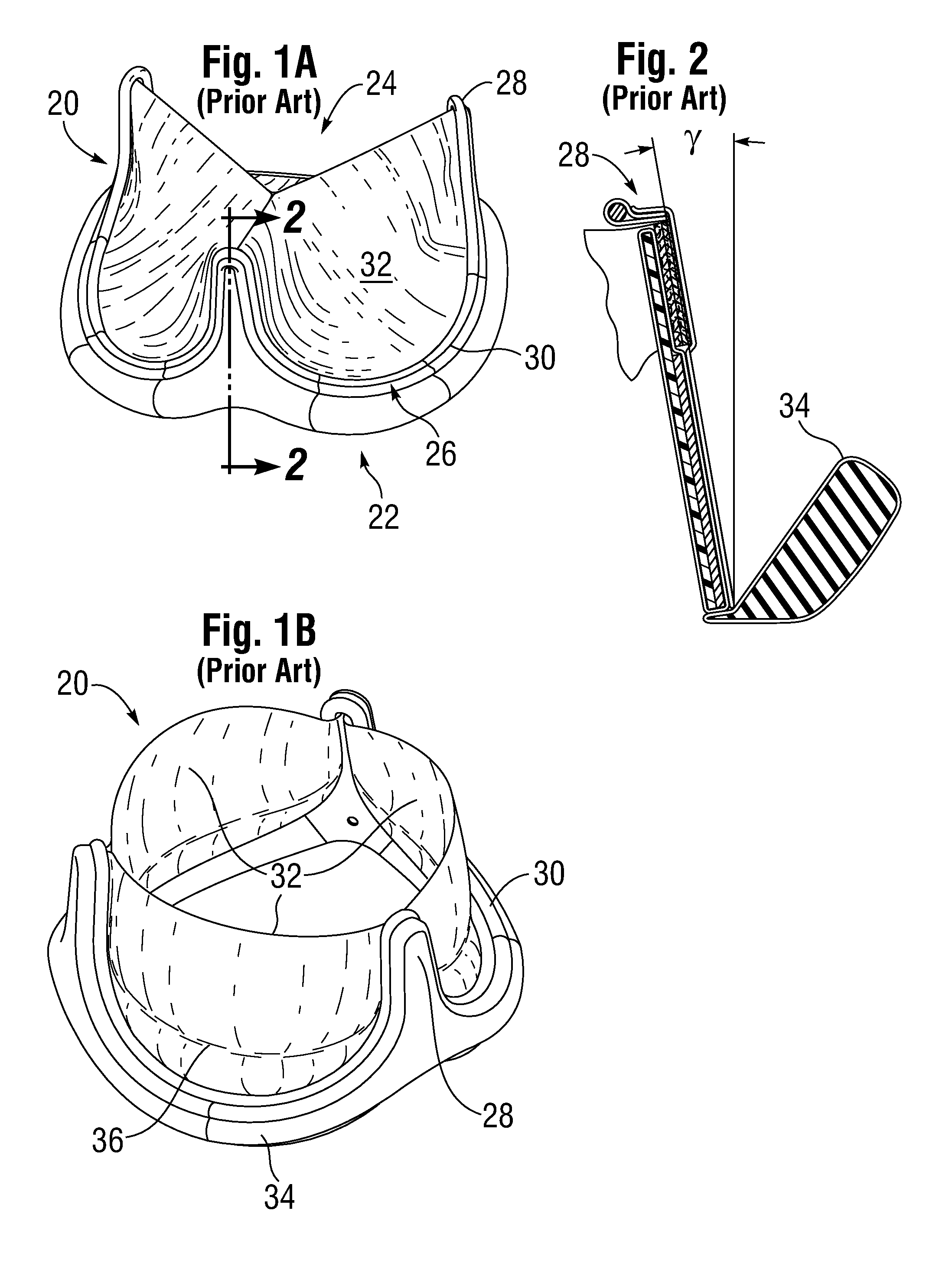
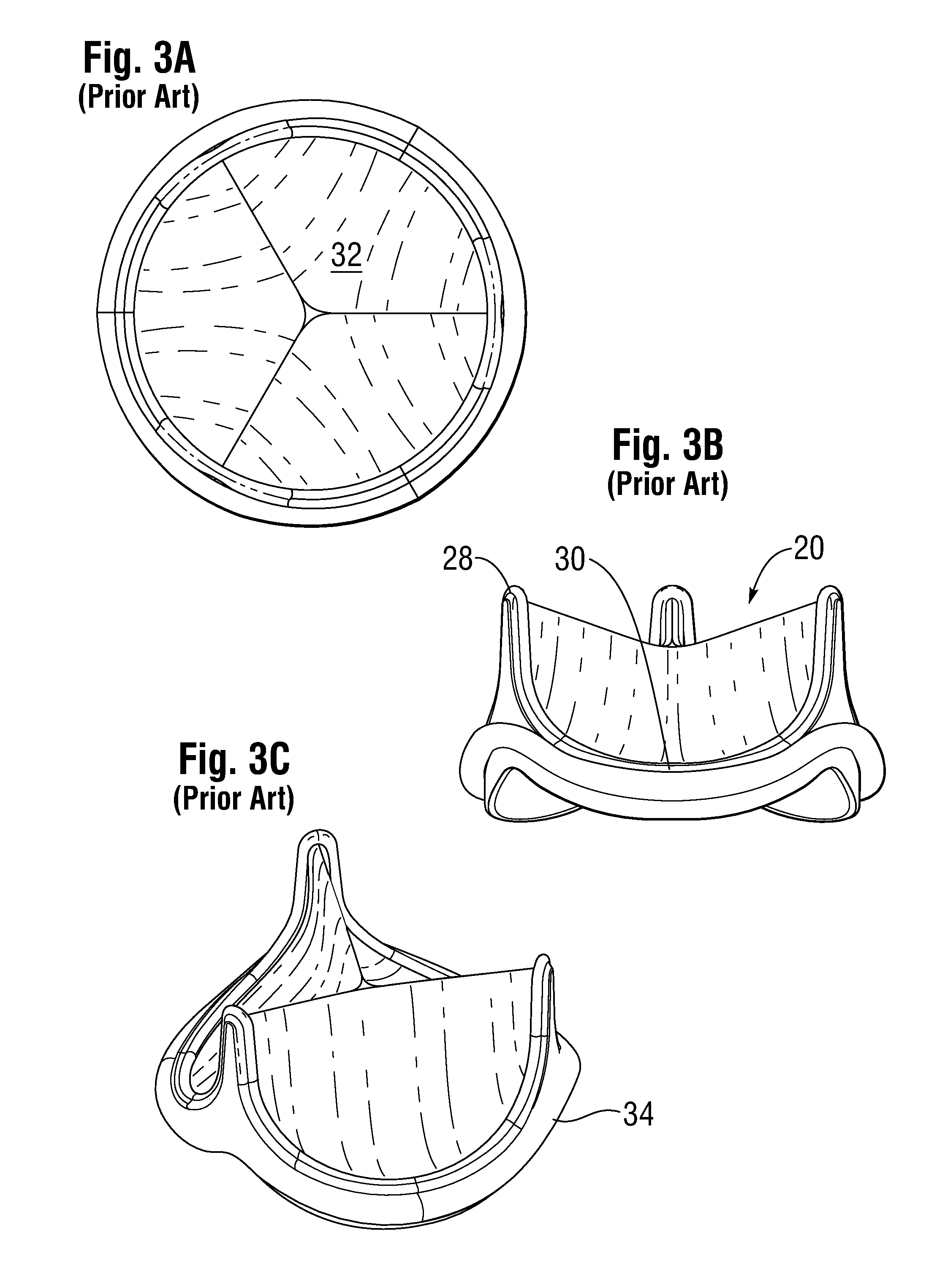
Low Gradient Prosthetic Heart Valve
A low pressure gradient prosthetic heart valve for implant in a human. The valve includes a support frame with undulating inflow cusps and outflow commissure posts to which flexible leaflets attach and coapt in a flow area. The commissure posts angle outward in a neutral state to widen the outflow orifice area. Also, the leaflets are designed to fit within the support frame and expand outward in a valve open state without creating a shelf or belly that would restrict flow.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Processing method for correcting low steepness optical mirror surface error
The invention discloses a processing method for correcting error of a low-gradient optical mirror surface, which comprises the following steps: firstly acquiring a removal function through experiment, then using a wave surface interferometer to acquire a surface shape error function of an element, dispersing the surface shape error function, programming a processing path at the same time, extending the surface shape error function, establishing a model and solving processing residence time, carrying out numerical control processing by using the solved residence time, identifying error and controlling accuracy for the processed result, so as to finish processing. The processing method has the advantages of high process efficiency, low processing cost and good error correction effect, and can effectively correct the surface shape error of the low-gradient optical mirror surface.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Scale-based image filtering of magnetic resonance data
InactiveUS6885762B2Efficient use ofImprove segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDiffusion
The invention provides novel scale-based filtering methods that use local structure size or “object scale” information to arrest smoothing around fine structures and across even low-gradient boundaries. One method teaches a weighted average over a scale-dependent neighborhood; while another employs scale-dependent diffusion conductance to perform filtering. Both methods adaptively modify the degree of filtering at any image location depending on local object scale. This permits a restricted homogeneity parameter to be accurately used for filtering in regions with fine details and in the vicinity of boundaries, while at the same time, a generous filtering parameter is used in the interiors of homogeneous regions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
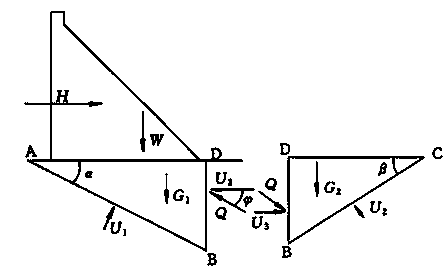
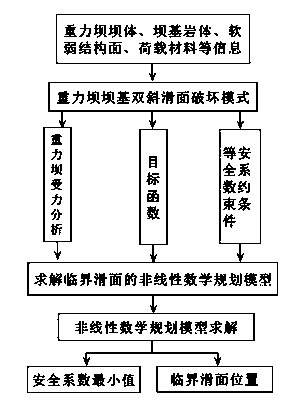
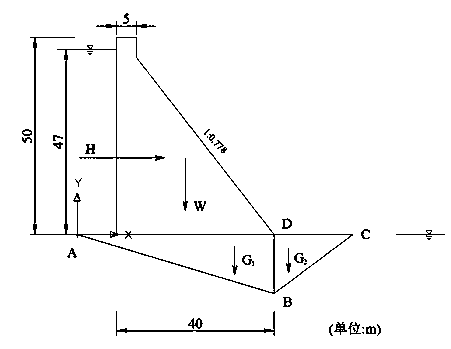
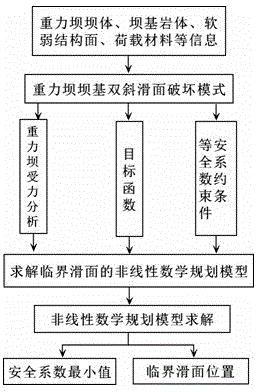
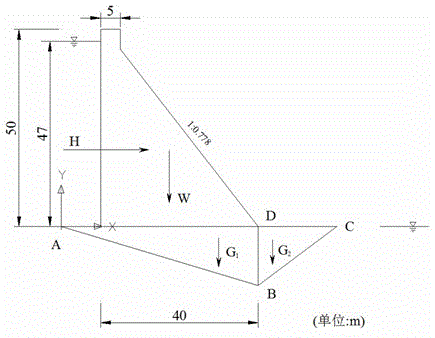
Method of calculating deep antiskid stable critical slipping plane of dam foundation of gravity dam
ActiveCN103469780AMethod concept is clearImprove calculation accuracyIn situ soil foundationBedrockEngineering
The invention discloses a method of calculating a deep antiskid stable critical slipping plane of a dam foundation of a gravity dam and belongs to the field of stability analysis for gravity dams. Aiming at the condition that slip possibly occurs because the low-gradient weak structural plane of the dam foundation of the gravity dam is not exposed but part of downstream bedrock is possibly subjected to clipping, the method comprises the following steps: establishing a nonlinear mathematic programming model of deep antiskid stability analysis for the gravity dam by taking variable of locations subjected to clipping and slipping plane damage on the downstream bedrock as an optimization variable, the deep antiskid stability factor of the gravity dam as an objective function and an equal safety factor normal equation as a constraint condition; solving out a worst critical slipping plane subjected to clipping damage on the downstream rock mass and a safety factor minimal value corresponding to the worst critical slipping plane. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of definite concept, high calculation precision and the like, and can be applied to deep antiskid stability analysis for the gravity dam.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing double-gradient carbide modified C/C composite material
The invention discloses a method for preparing a double-gradient carbide modified C / C composite material. A double-element matrix of carbon and carbide is deposited on the surface of carbon fibers in a carbon fiber preformed body by using a chemical vapor infiltration / deposition process; in the prepared composite material, the density of the carbide is in high-low gradient distribution from the inside diameter surface to the outside diameter surface, and the density of the carbon is in low-high gradient distribution from the inside diameter surface to the outside diameter surface, and thus acarbon-ceramic macro gradient is formed; on the surface of the carbon fibers in the composite material, the whole carbon coating is transited to a carbon-carbide co-deposition coating, finally the whole carbide coating is in gradient distribution, and thus a carbon-ceramic micro gradient is formed; and the double-gradient carbide modified C / C composite material is obtained. The material prepared by the method has the characteristics of excellent high-temperature resistance, abrasion resistance, scouring resistance, oxidation resistance, ablation resistance and thermal shock performance. The method is simple, convenient to operate and low in preparation cost; the prepared C / C composite material has excellent ablation resistance and thermal shock performance; and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
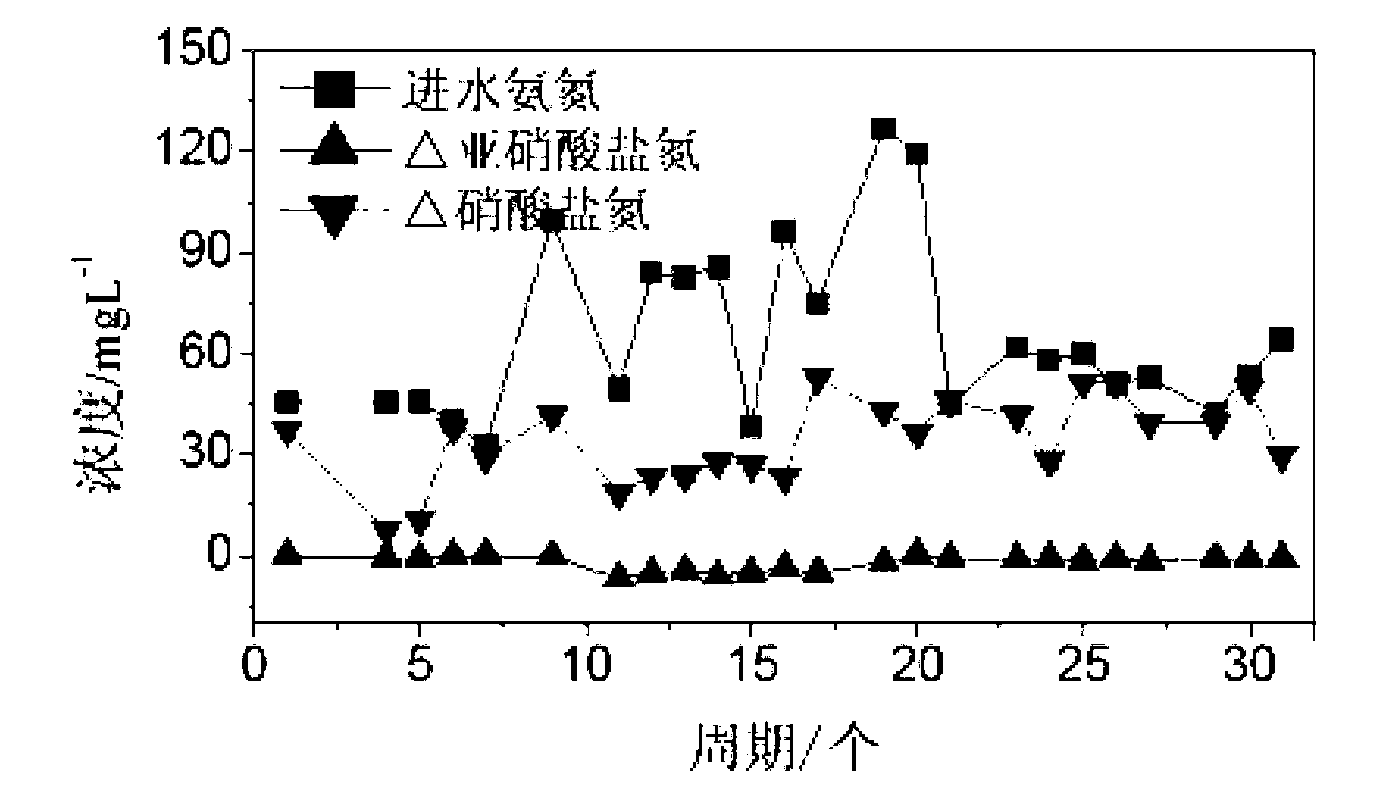
Normal temperature low-ammonia-nitrogen nitrosation starting method
InactiveCN102701438AStart fastHigh speedSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentNitriteResearch Object
A normal temperature low-ammonia-nitrogen nitrosation starting method belongs to the field of urban sewage treatment and reclamation. Researches show that nitrosation starting can be achieved in short time by controlling condition of low dissolved oxygen (DO=0.30mg / L) and inoculating sludge with certain nitrosation effect. If whole course nitration sludge is inoculated, no accumulation of nitrite occurs within 30 days in a water distribution test, no accumulation of nitrite occurs in 30 days in a reactor which utilizes the A / O dephosphorization process processing water as a research object, and the nitrosation starting fails accordingly. Nitrite accumulation can occur by adopting the mode of high-low gradient oxygen limit culture, domesticating the sludge for 10 days under the condition that DO=0.70-0.80mg / L, then controlling condition of low dissolved oxygen (0.30-0.40mg / L) to enable the reactor to discharge water if the whole course nitration sludge is inoculated. Over 90% of nitrosation rate can be achieved within 38 days by continuously domesticating the sludge under the condition of the dissolved oxygen, so that nitrosation can be successfully started.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Leaflet for low gradient prosthetic heart valve
A low pressure gradient prosthetic heart valve for implant in a human. The valve includes a support frame with undulating inflow cusps and outflow commissure posts to which flexible leaflets attach and coapt in a flow area. The commissure posts angle outward in a neutral state to widen the outflow orifice area. Also, the leaflets are designed to fit within the support frame and expand outward in a valve open state without creating a shelf or belly that would restrict flow.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Forest fire smoke detection method based on image segmentation
InactiveCN110222644ASolve the over-segmentation problemAvoid Adaptive EffectsCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageSky
The invention discloses a forest fire smoke detection method based on image segmentation, and belongs to the field. Most traditional forest fire hazard smoke detection algorithms only consider fire hazard detection under an ideal background, analyze images on a pixel level, and are not necessarily suitable for smoke identification under complex environments such as forests. A forest fire smoke detection method based on image segmentation sequentially comprises the following steps of initializing a color image in a CIELAB space a clustering center; moving the clustering center to the lowest gradient of a 3 * 3 neighborhood; performing distribution; updating; when each pixel is classified to the nearest cluster center, updating the cluster center by using the average value of vectors of allpixels in the region; merging the isolated pixel points into the nearest super pixel; combining the superpixels; segmenting the sky and the ground; performing smoke recognition. The limitation that acamera needs to be fixed in a traditional forest fire smoke detection algorithm is broken through, and the method is suitable for dynamic panoramic sampling of the camera on a forest.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Light trap adopted epitaxial material structure of ultrafine divergent angle high-power semiconductor laser
InactiveCN101888056AQuality improvementReduced far-field vertical divergenceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellEpitaxial material
The invention relates to a light trap adopted epitaxial material structure of an ultrafine divergent angle high-power semiconductor laser, which comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an N-type lower limiting layer, a lower gradient light trap layer, an upper gradient light trap layer, an N-type upper limiting layer, an N-type gradient waveguide layer, a quantum well active area, a P-type gradient waveguide layer, a P-type limiting layer and an electrode contact layer, wherein the substrate is used for carrying out the epitaxial growth of all layers of materials of a laser; the buffer layer is prepared on the GaAs substrate; the N-type lower limiting layer is prepared on the buffer layer; the lower gradient light trap layer is prepared on the N-type lower limiting layer; the upper gradient light trap layer is prepared on the lower gradient light trap layer; the N-type upper limiting layer is prepared on the lower gradient light trap layer; the N-type gradient waveguide layer is prepared on the N-type lower limiting layer; the quantum well active area is prepared on the N-type gradient waveguide layer; the P-type gradient waveguide layer is prepared on the quantum well active area; the P-type limiting layer is prepared on the P-type gradient waveguide layer; and the electrode contact layer is prepared on the P-type limiting layer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Differential trajectory jet energy dissipater in absorption basin
The invention relates to a differential trajectory jet energy dissipater in an absorption basin, belonging to the field of engineering hydraulics. The differential trajectory jet energy dissipater comprises the absorption basin and a differential triangular flip bucket energy dissipater arranged in the absorption basin, wherein the differential triangular flip bucket divides the absorption basin into a front basin and a rear basin; and the flip position thereof can be changed in the range of one fourth to two thirds of the length of the absorption basin. The up gradient of the upstream face of the differential triangular flip bucket is incontinuous, the part with higher gradient is a main flip bucket, the part with lower gradient is a trajectory jet groove, and the downstream gradient of the differential triangular flip bucket is continuous. The differential trajectory jet energy dissipater in the absorption basin not only shortens the length of the absorption basin and contributes to the saving of construction cost, but also increases the efficiency of energy dissipation, and has the extremely high ability of anti-cavitation. The differential trajectory jet energy dissipater can be used singly in any normal absorption basin and can also be combined with other assistant energy dissipaters in the normal absorption basin.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Direct volume rendering with shading
InactiveCN101010701AFeel goodReduce complexity3D-image renderingArray data structureComputer graphics (images)
The present invention relates to direct volume rendering based on a light model applied to a 3D array of information data samples. Gradients are first estimated for the individuals samples, and a simple shading is done on the samples with low gradient, i.e. homogenous area.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Rain collecting and irrigating device for fruit trees in hills of loess plateau
The invention discloses a rain collecting and irrigating device for fruit trees in the hills of loess plateau, which comprises a water collecting surface (1), a water diversion ditch (2), a reservoir (3) and a water delivery irrigation pipeline (4), wherein the water collecting surface (1) is arranged with the gradient of 3-8 degrees; the part with lower gradient on the water collecting surface (1) is provided with the water diversion ditch (2) which is connected with the reservoir (3); and the reservoir (3) is connected with the water delivery irrigation pipeline (4) of which the other end is embedded in the root soil of the fruit trees. The rain collecting and irrigating device in the invention has a simple structure, needs no special construction technology and equipment, is free of power, and is easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
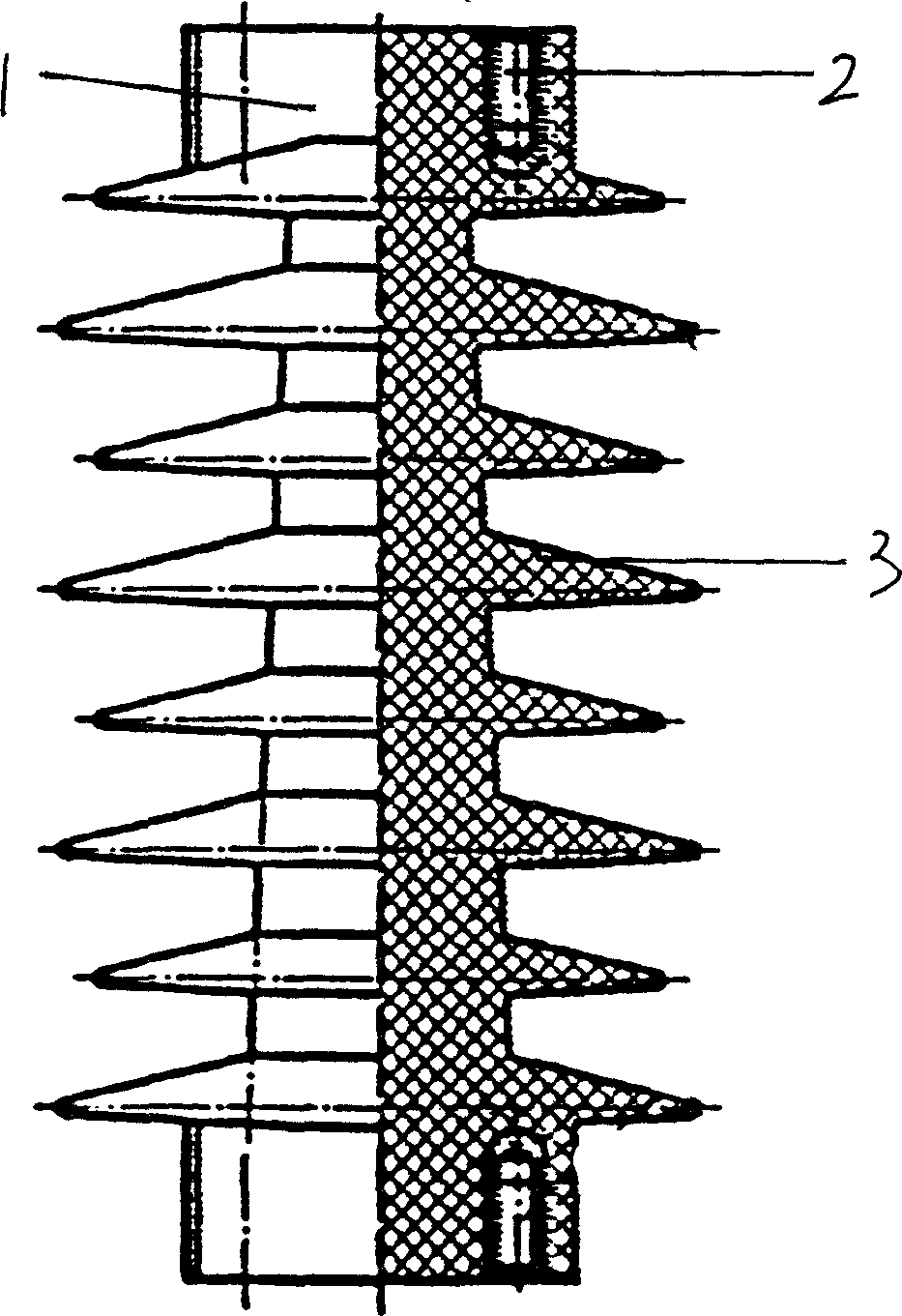
Multi-Layer Cover Dual Core Golf Ball Having A High Acid Casing And Low Gradient Center
A golf ball having an inner core layer having an outer surface and a geometric center and being formed from a rubber composition. An outer core layer surrounds the inner core to form a dual core. An inner cover layer surrounds the dual core, and includes a high-acid ionomer having a hardness of about 66 to 75 Shore D and an acid content of 16 wt. % or greater. An outer cover layer surrounds the inner cover layer, and includes a polyurethane and having a material hardness of about 38 to 56 Shore D. The inner core layer surface hardness is from 0 Shore C to 10 Shore C lower than the geometric center hardness to define a negative hardness gradient and the outer core layer has a surface hardness at least 10 Shore C greater than the geometric center hardness to define a dual core positive hardness gradient.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
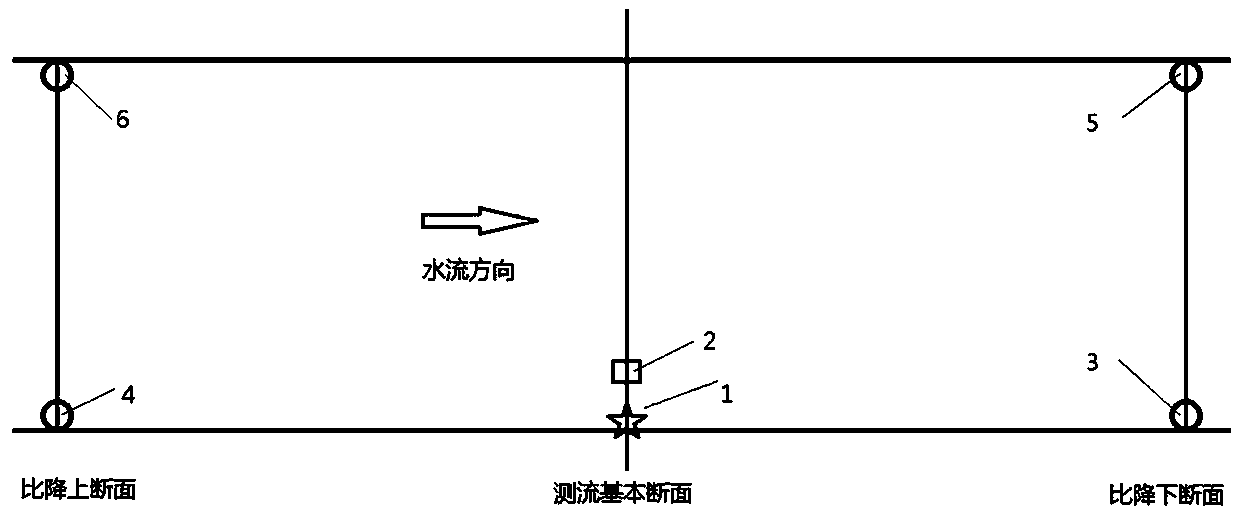
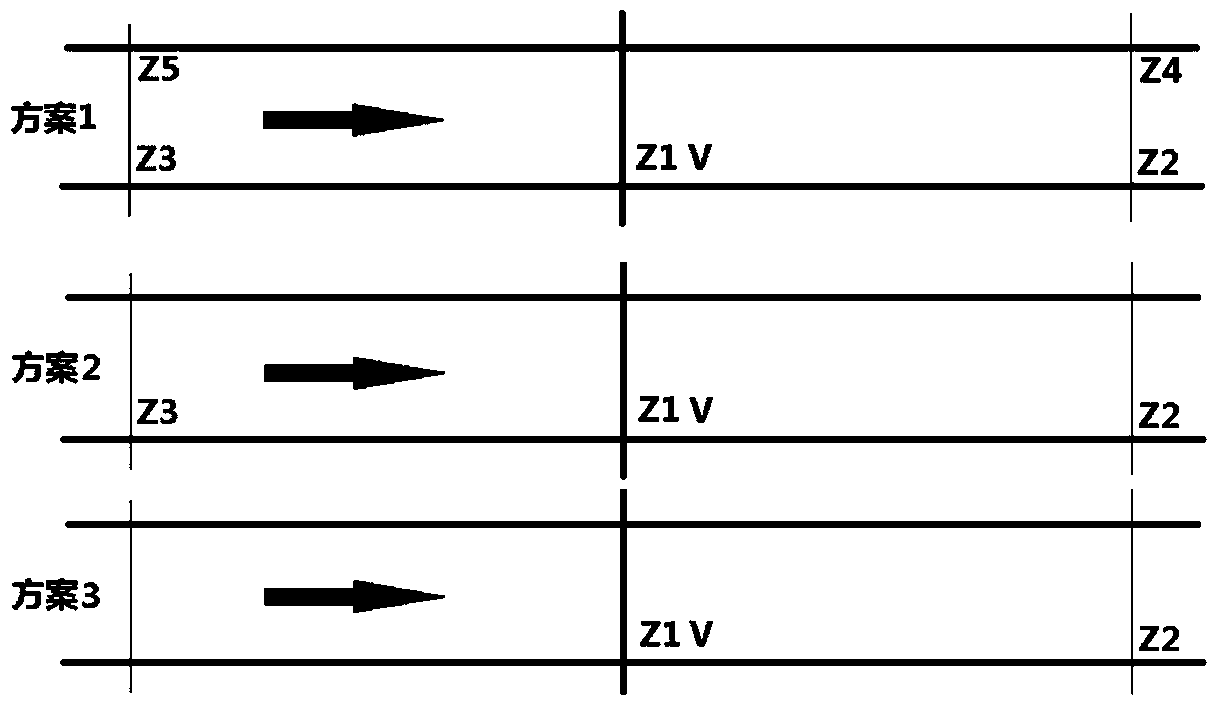
River discharge comprehensive measuring and calculating method and system
ActiveCN110455350AReal-time measurementAccurate calculationVolume/mass flow measurementVolume meteringMaster stationWater level
The invention discloses a river discharge comprehensive measuring and calculating method and system in the technical field of hydrologic survey and aims at solving the technical problems that a discharge online measurement method is high in cost and low in measurement accuracy in the prior art. The river discharge comprehensive measuring and calculating method comprises the following steps: setting up a water level master station, a representative flow velocity station and a water level auxiliary station, acquiring actually measured water level of a cross section, an elevation of the lowest point of a river bottom of the cross section, rate of rise and fall of the water level of the cross section, actually measured flow velocity of a water surface at a representative point as well as waterlevel difference of upper and lower gradient cross sections, substituting the acquired data into a river discharge comprehensive measuring and calculating model, and calculating and obtaining river cross-section discharge.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Tap-hole filling material and filling method thereof
The invention discloses a tap-hole filling material, main raw materials of which are quartz sand, sintered magnesia clinker and waste and old magnesia-chromite bricks and auxiliary materials of which are a carburant and a sintering aid. The raw materials contain, by weight, 25-45% of quartz sand, 30-60% of sintered magnesia clinker, 10-35% of waste and old magnesia-chromite bricks, 0-2% of the carburant and 0-11% of the sintering aid. A filling method of the tap-hole filling material comprises the following step: more than one tap-hole filling material with different ratios undergoes layered filling according to contents of the carburant and the sintering aid from low gradient to high gradient, and the contents of the carburant and the sintering aid at the bottom layer are the lowest. Through compounding of the main raw materials and the auxiliary materials and layered gradient filling, fluidity, sintering property and pouring rate of the filling materials are raised, limitations such as poor fluidity, low free-opening rate and the like of existing tap-hole filling materials are overcome, and technological requirements of converter tapping are met. In addition, cost is low.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Outdoor insulative supporting terminal
ActiveCN1828784AMeet the requirements of overhead layingIncrease productivityInsulatorsPlasticizerUltraviolet
The present invention relates to a outdoors insulation support terminal for fixing 35 cable. It contains outdoors epoxy, modifying acid anhydride used as fixing agent, silicon micro powder used as padding, polyether used as plasticizer, benzyl dimethylamine used as added colour paste, through APG technology and according to certain of proportion, compression casting solidifying two ends metal embedded piece with terminal body. Said Support terminal is low gradient umbrella shape sheet structure with small length dimension and more umbrella skirts, having advantages of compactness, low cost, high mechanical strength, fine electrical performance, and strong anti ultraviolet ray ability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ERG TECH
Low gradient prosthetic heart valve
A low pressure gradient prosthetic heart valve for implant in a human. The valve includes a support frame with undulating inflow cusps and outflow commissure posts to which flexible leaflets attach and coapt in a flow area. The commissure posts angle outward in a neutral state to widen the outflow orifice area. Also, the leaflets are designed to fit within the support frame and expand outward in a valve open state without creating a shelf or belly that would restrict flow.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Aerial shooting traffic video frequency vehicle rapid checking method
InactiveCN100545867CImprove real-time performanceAvoid the problem of inaccurate segmentation or even wrong segmentationImage analysisTelevision systemsMotion vectorGround segment
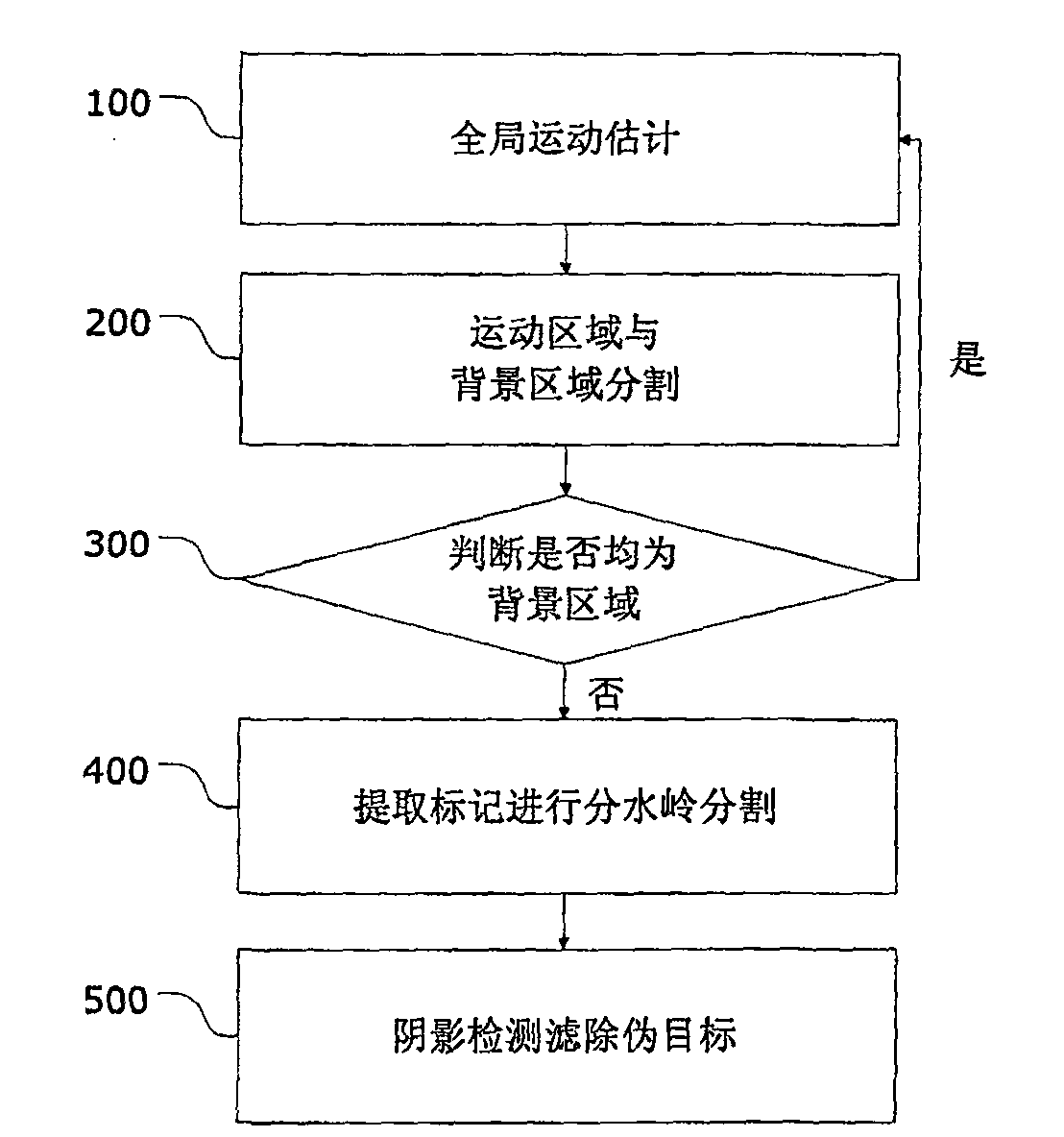
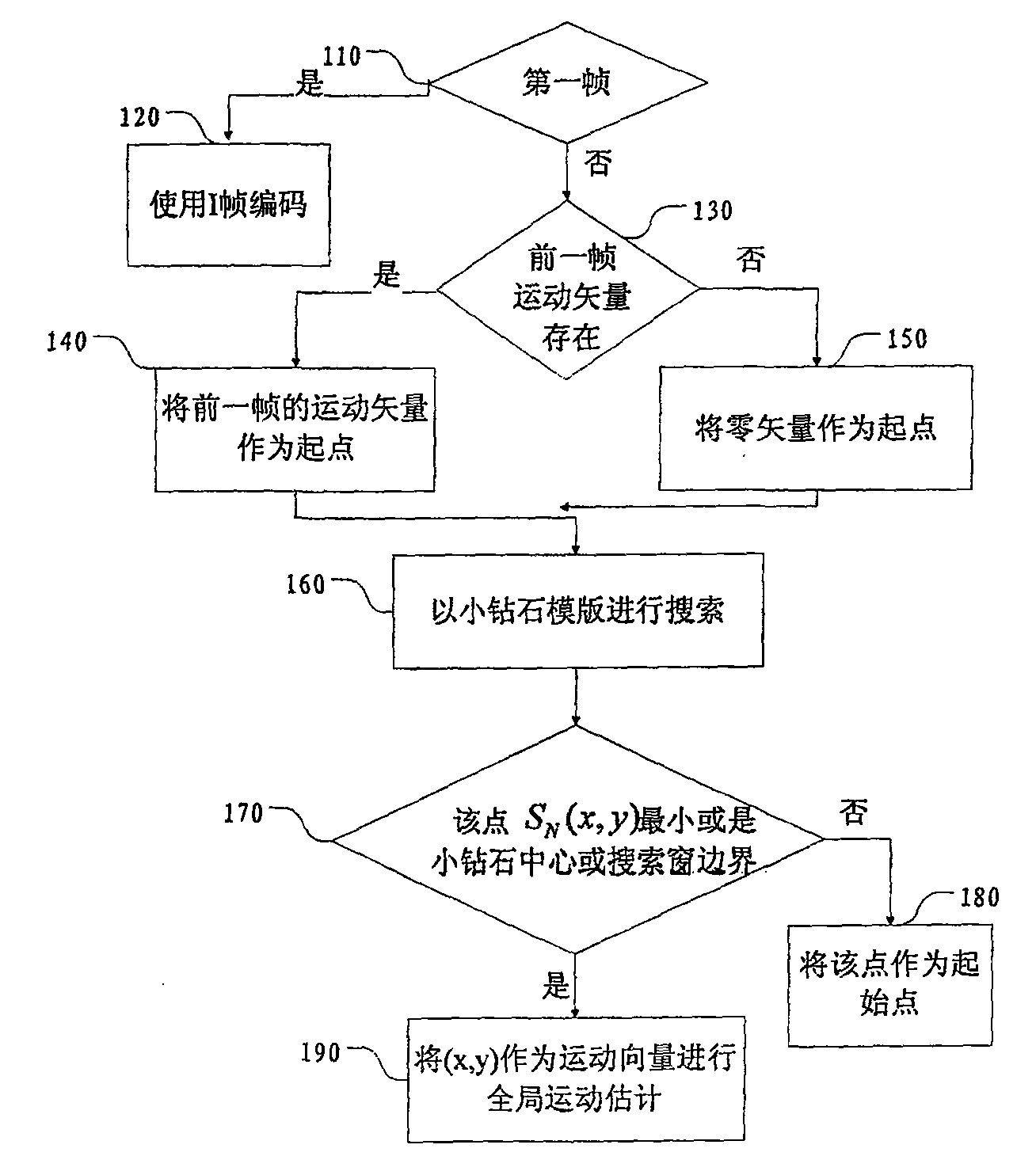
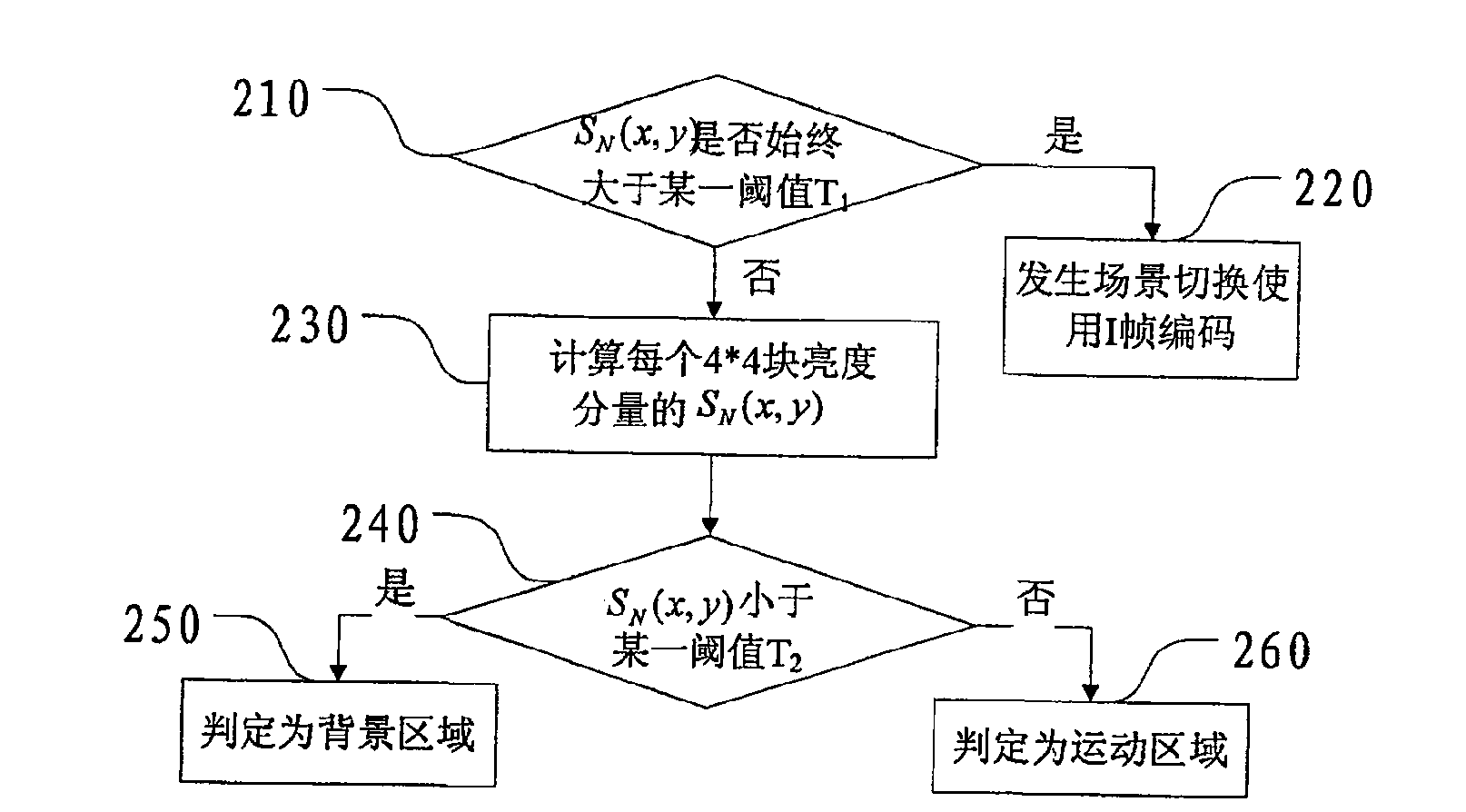
The method for quickly detecting vehicles in aerial traffic video, the steps are as follows: step 100, adopt global motion estimation in the space-based encoding part, determine the global motion vector of the background; step 200, calculate the residual value according to the global motion vector, and segment the background area and the motion area ; Step 300, judge whether they are all background areas, transfer to the next frame for the images that are all background areas, and perform step 100; otherwise, for the motion area of the image, perform step 400; step 400, first determine an offset on the ground part Low but still able to correctly segment the adaptive gradient threshold of each object, and perform preliminary marker extraction; then introduce the two parameters of area and catchment depth, and further screen the extracted markers to determine the final marker points; then use the marker points as The minimum value of the area is divided by VS watershed; finally, the area is merged according to the texture information of the area; step 500, the shadow is detected in the HSV color space, the false target is filtered out, and the vehicle is finally detected. The invention solves the problem that the calculation amount is large when decompressing the aerial image and detecting the moving target, and it is difficult to meet the requirements of real-time and robustness at the same time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Photovoltaic waterproof system used for low-gradient roof
PendingCN110541526AImprove waterproof performancePlay the role of guiding water leakagePhotovoltaic supportsRoof covering using slabs/sheetsWater flowEngineering
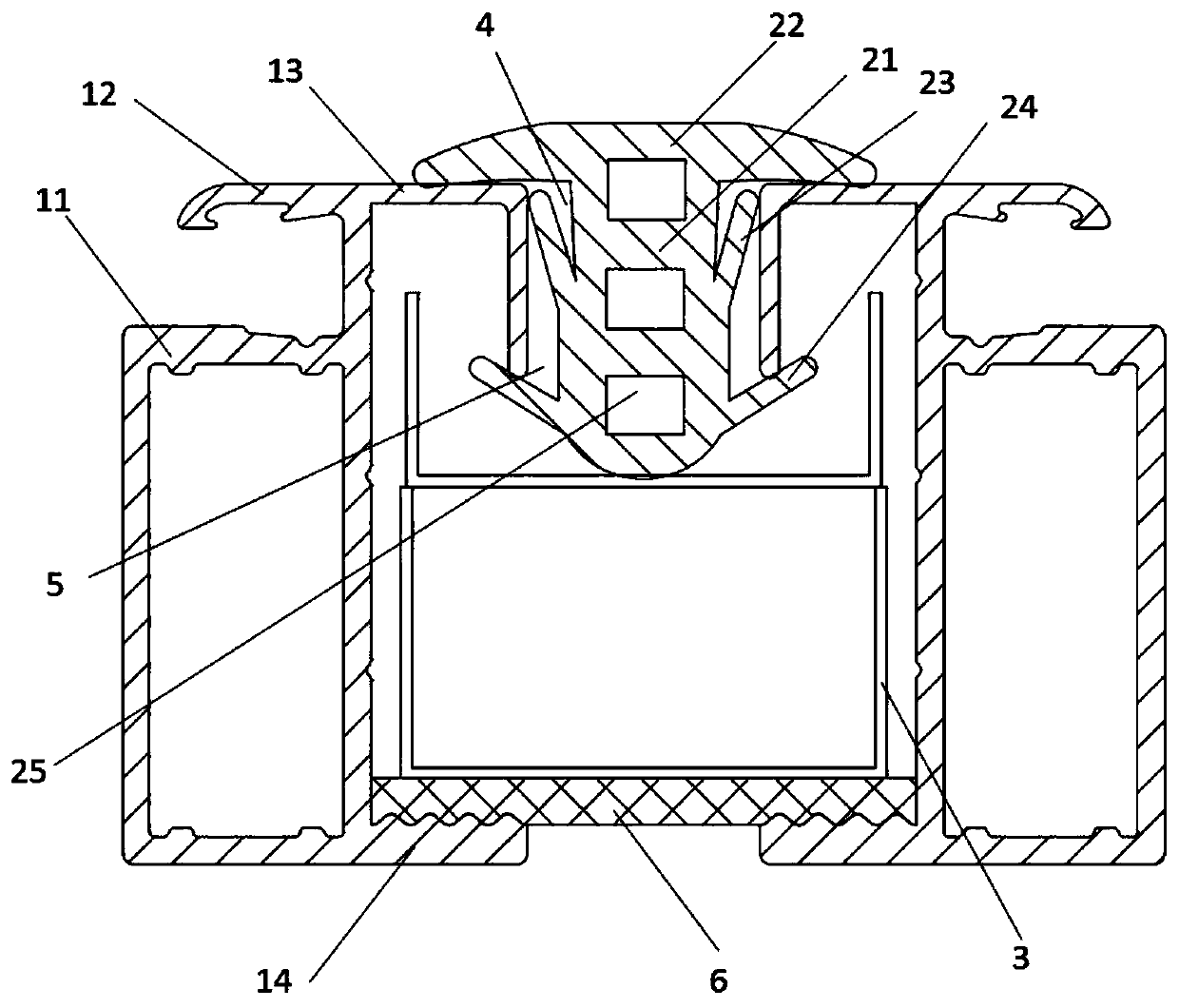
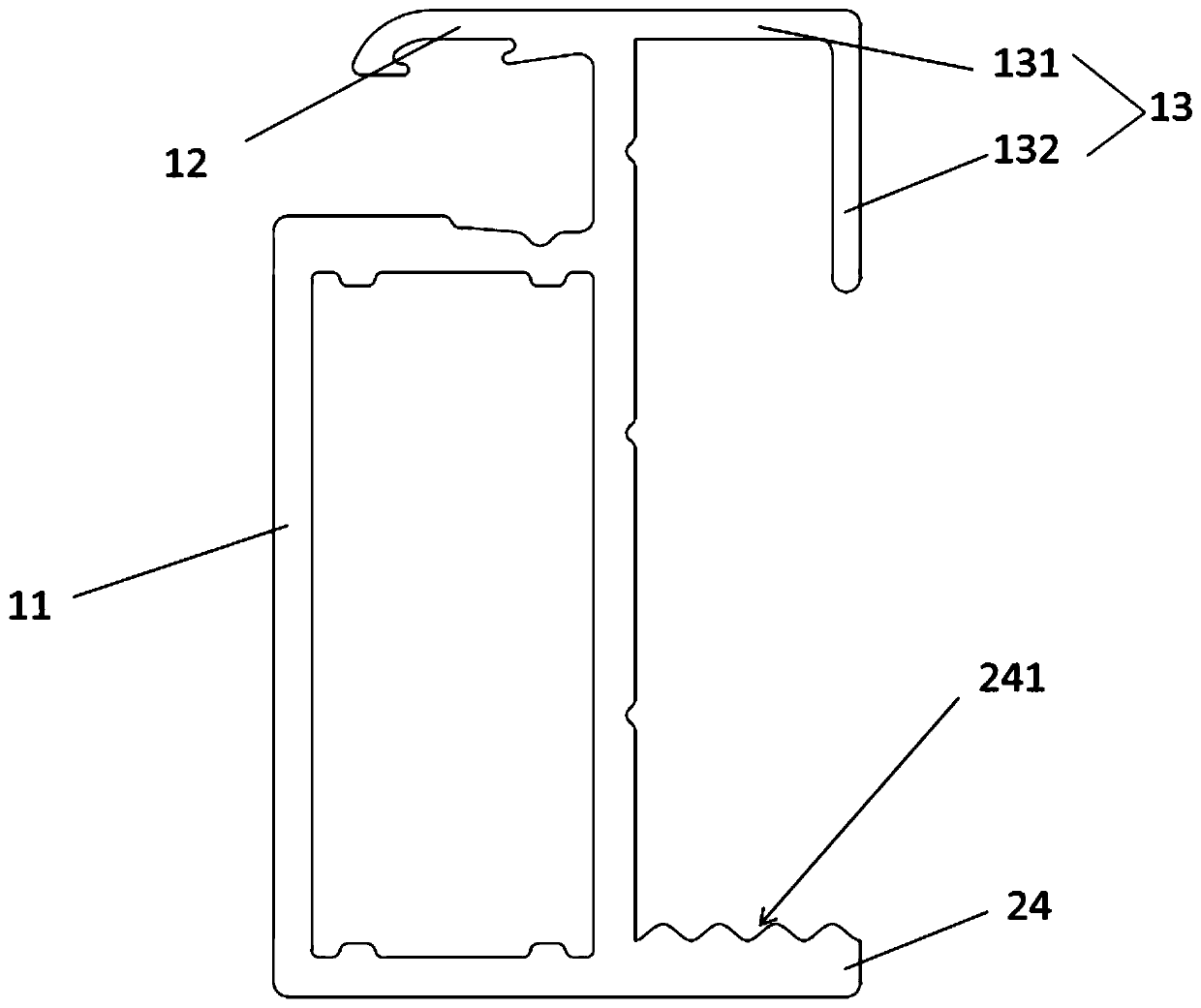
A photovoltaic waterproof system used for a low-gradient roof comprises a supporting structure, sealing strips and flow guide strips. The supporting structure is composed of multiple section bars. Each section bar comprises a section bar body and clamping hooks on the section bar body. Each sealing strip is arranged between the two corresponding section bar bodies. Each sealing strip comprises a plunger and a first umbrella sheet kept being connected with the two corresponding section bar bodies in an abutting manner. A second umbrella sheet of a V-shaped structure is further arranged on eachplunger. The edge of each second umbrella sheet is connected with the corresponding section bar bodies in an abutting manner, and a first flow guide groove is formed among each plunger, the corresponding second umbrella sheet and the corresponding section bar body. Each flow guide strip is arranged on the end portion of the corresponding sealing strip. When rainwater seeps in the photovoltaic waterproof system, because the second umbrella sheets are connected with the section bar bodies in the abutting manner, water seeping into every two corresponding section bar bodies is guided through thecorresponding first flow guide grooves to flow into the corresponding flow guide strips, the first flow guide grooves formed through the sealing strips are more convenient to implement, and the construction quantity of supporting structure laying is decreased. The flow guide strips arranged on the end portions of the sealing strips can converge the water flowing out of the sealing strips togetherand guide the water to be discharged out of the roof.
Owner:PERLIGHT SOLAR
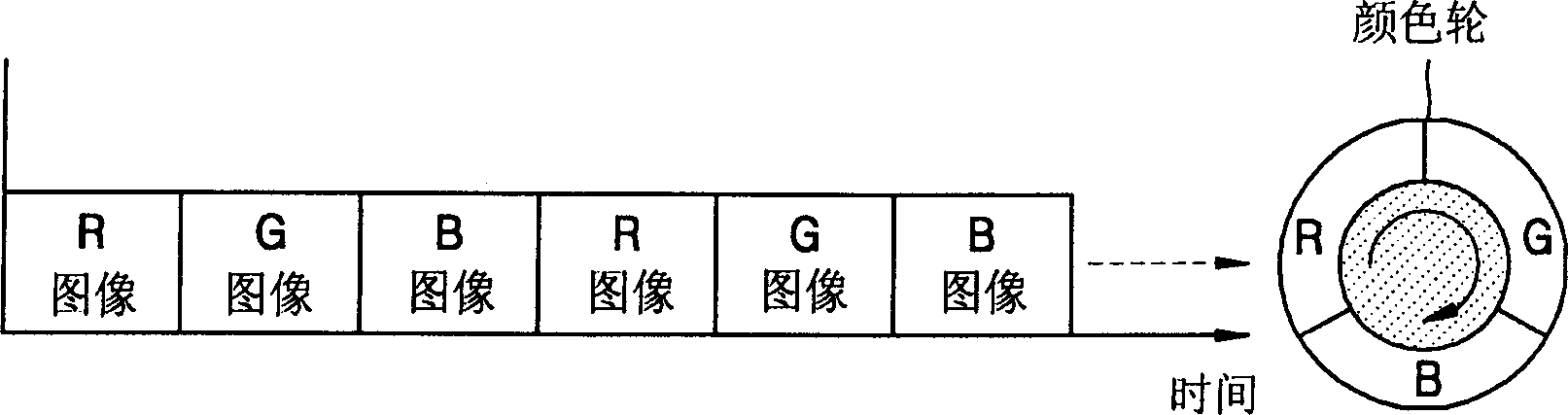
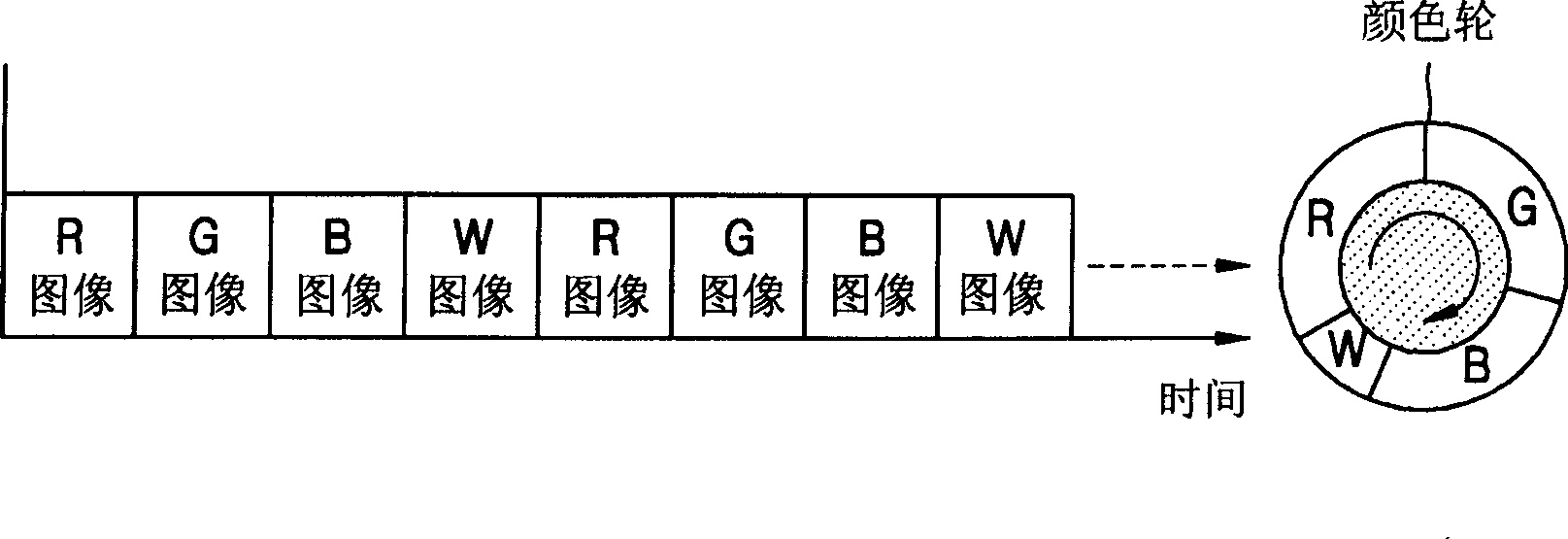
Method of displaying image in image display device using sequential driving method
InactiveCN1722856APicture reproducers using projection devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor imageDisplay device
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A maternal and fetal blood group incompatibility immunosorbent therapeutic apparatus
InactiveCN109157694ASpeed can be adjustedEasy to transportOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
A maternal-fetal blood group incompatibility immunosorbent therapy apparatus used in the medical field is characterized in that a blood separator and a plasma adsorber are connected through a circulation line to form a cardiopulmonary bypass adsorption device, wherein the blood separator is used for separating blood cells and plasma, as the separated plasma flows through and filters through the plasma adsorber, wherein the pathogenic antibody is adsorbed, the filtered plasma is combined with the separated blood cells and then re-enters a cardiopulmonary bypass adsorption device for circulatingadsorption to achieve the purpose of cleaning the pathogenic antibody, and the plasma adsorber is filled with a solid-phase carrier coated with blood group antigen or anti-blood group antibody with high to low gradient titer from an inlet to an outlet in a layered manner.
Owner:翁炳焕
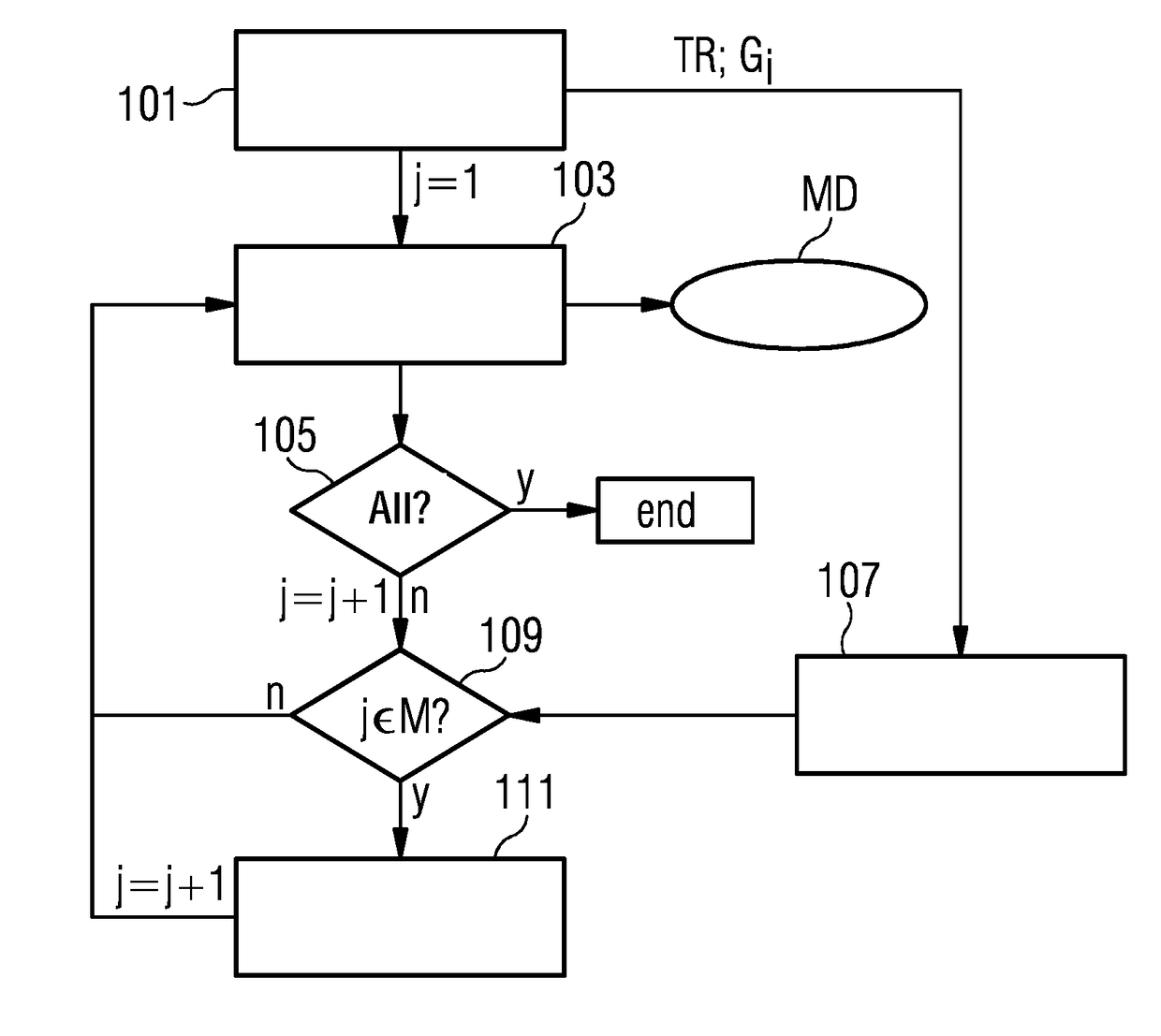
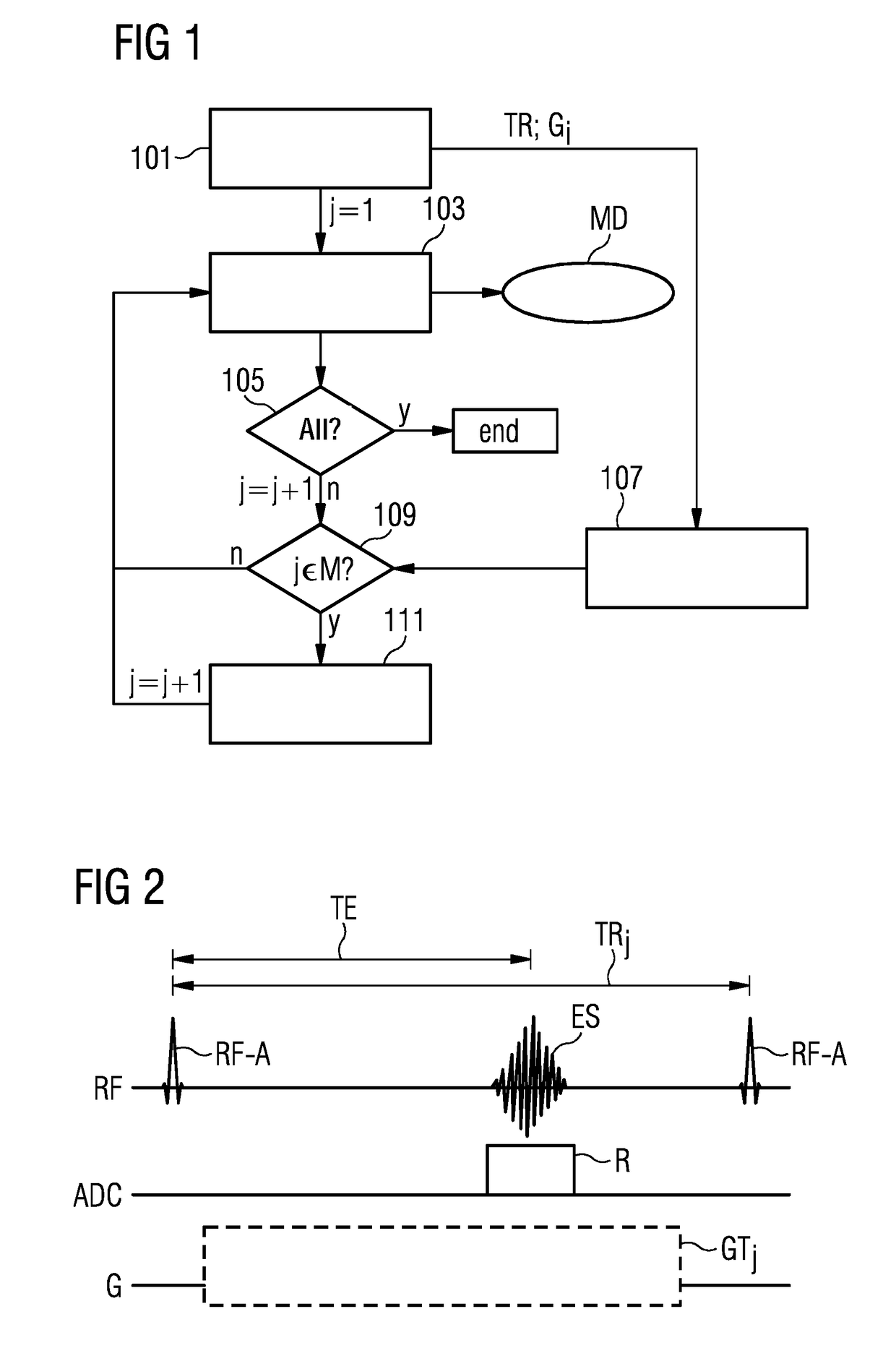
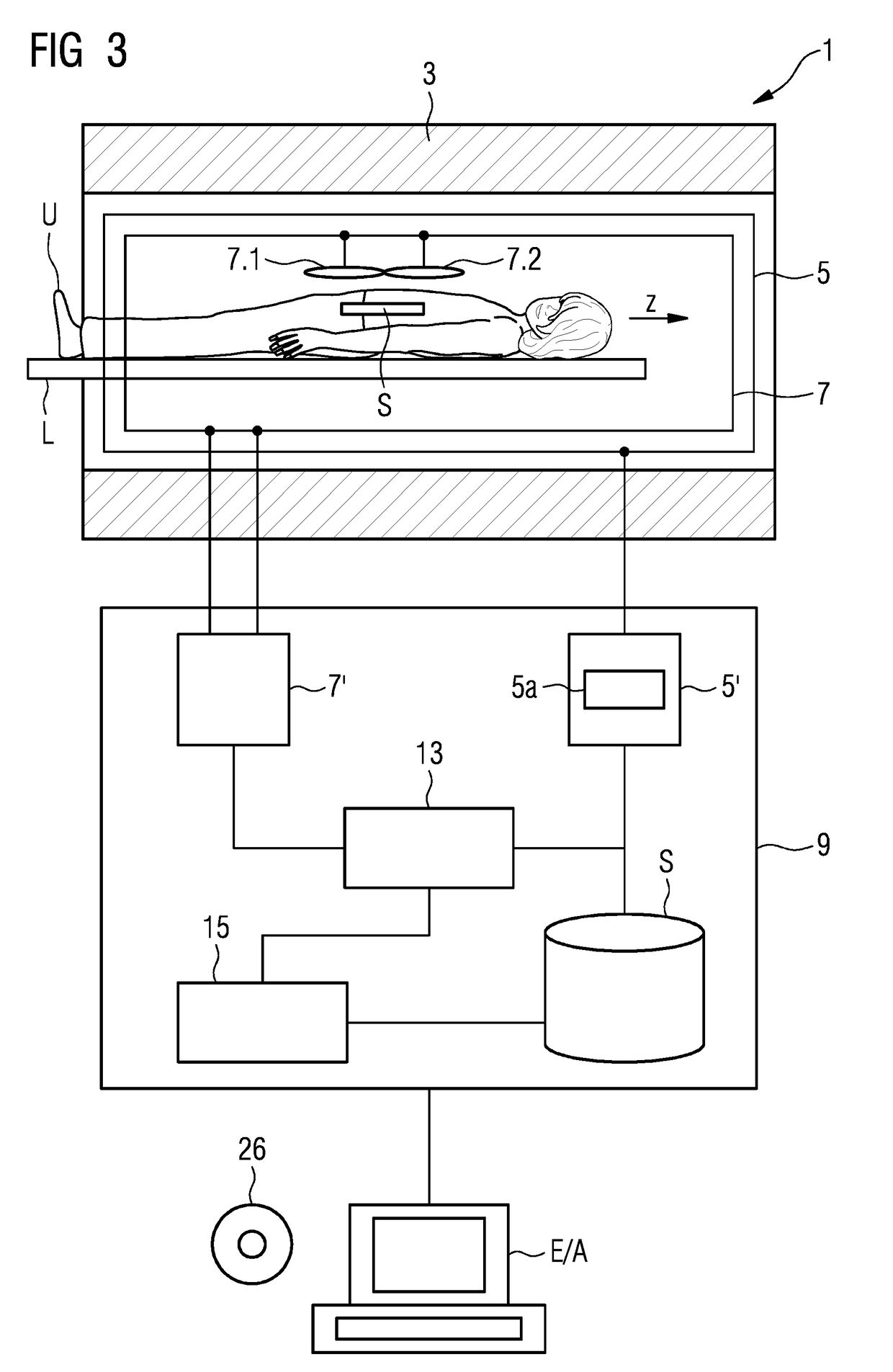
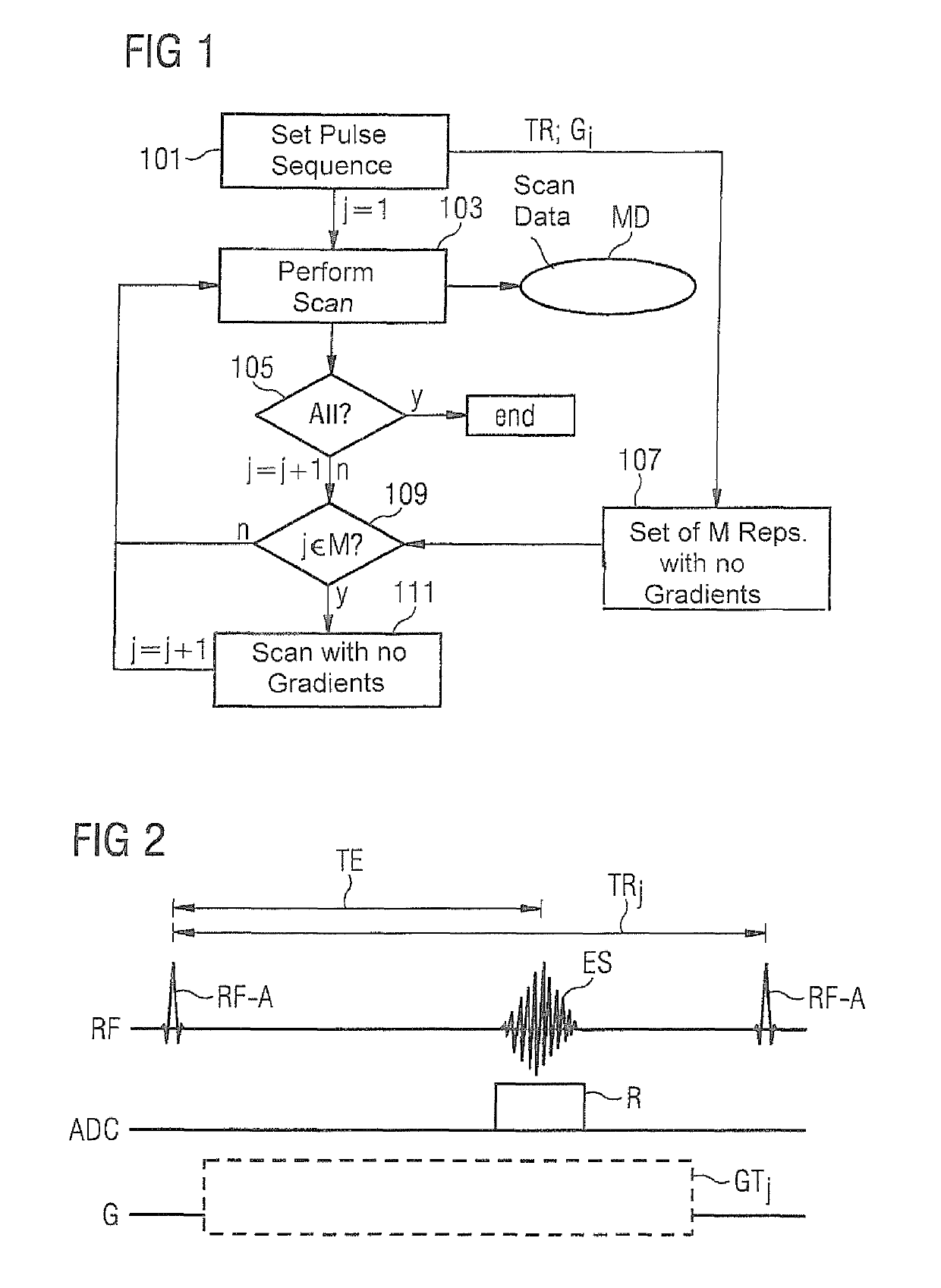
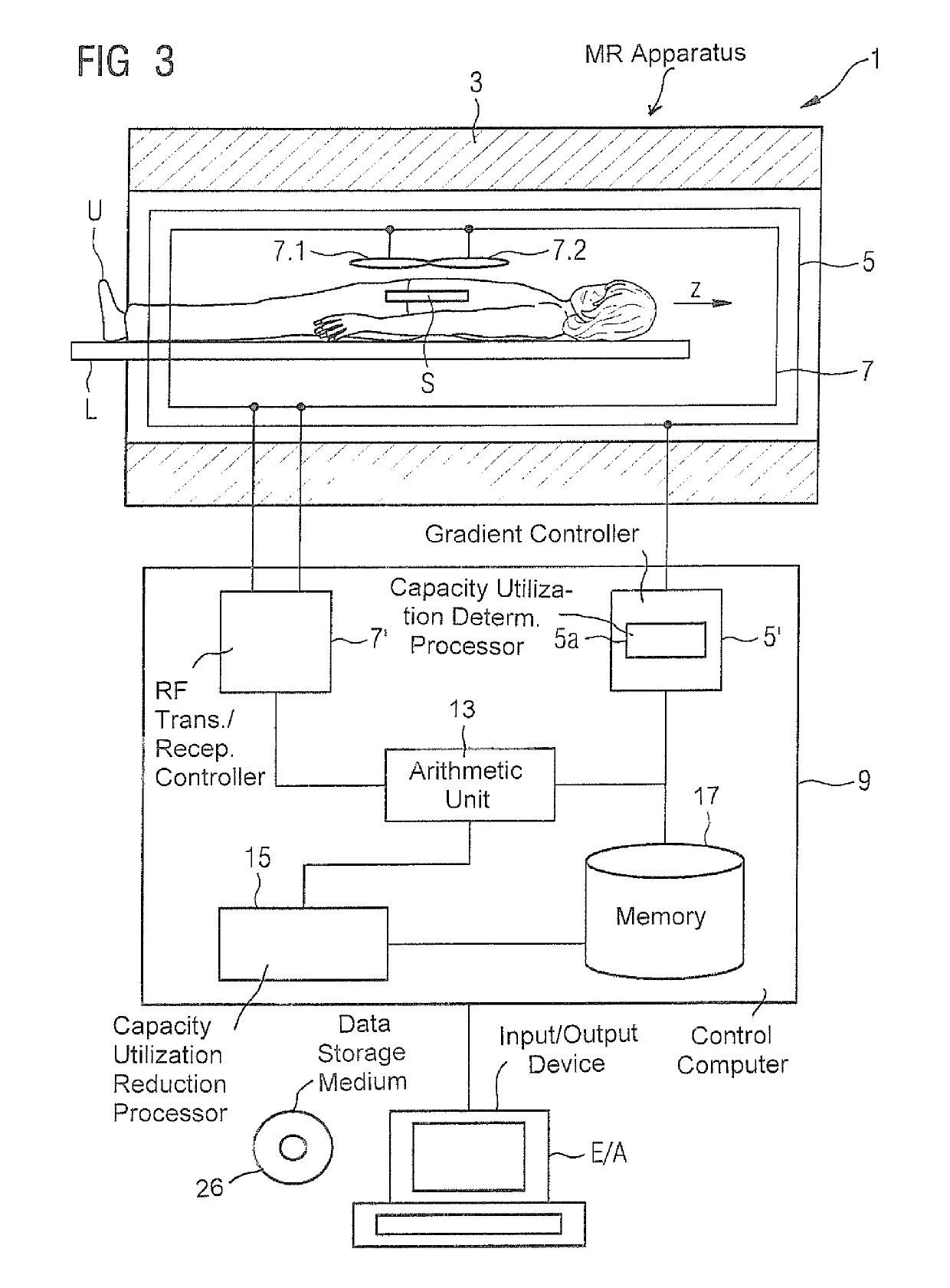
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for reducing the repetition time without increasing the gradient capacity utilization
ActiveUS20180088196A1Short repetition time TRImproved reproducibility and comparabilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceBiological activation
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) apparatus for generating scan data of an examination object, radiation of RF pulses, activation of gradients, and reading out of MR signals generated by the radiated RF pulses and the activated gradients occur according to a pulse sequence. The signals that are stored as scan data. Repetition of the pulse sequence activating respective other gradients takes place until all the desired scan data are stored, wherein for determined repetitions, no gradients are activated. By the performance of repetitions in which no gradients are switched, a minimum repetition time, which is restricted by the utilized gradient unit due to hardware limitations thereof, can be further reduced. Thus repetition times can be selected more freely, e.g. according to a desired contrast, including on magnetic resonance systems with a low gradient output.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
A Calculation Method of Critical Sliding Surface of Deep Anti-sliding Stability of Gravity Dam Foundation
ActiveCN103469780BMethod concept is clearImprove calculation accuracyIn situ soil foundationBedrockStructure of the Earth
The invention discloses a method of calculating a deep antiskid stable critical slipping plane of a dam foundation of a gravity dam and belongs to the field of stability analysis for gravity dams. Aiming at the condition that slip possibly occurs because the low-gradient weak structural plane of the dam foundation of the gravity dam is not exposed but part of downstream bedrock is possibly subjected to clipping, the method comprises the following steps: establishing a nonlinear mathematic programming model of deep antiskid stability analysis for the gravity dam by taking variable of locations subjected to clipping and slipping plane damage on the downstream bedrock as an optimization variable, the deep antiskid stability factor of the gravity dam as an objective function and an equal safety factor normal equation as a constraint condition; solving out a worst critical slipping plane subjected to clipping damage on the downstream rock mass and a safety factor minimal value corresponding to the worst critical slipping plane. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of definite concept, high calculation precision and the like, and can be applied to deep antiskid stability analysis for the gravity dam.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
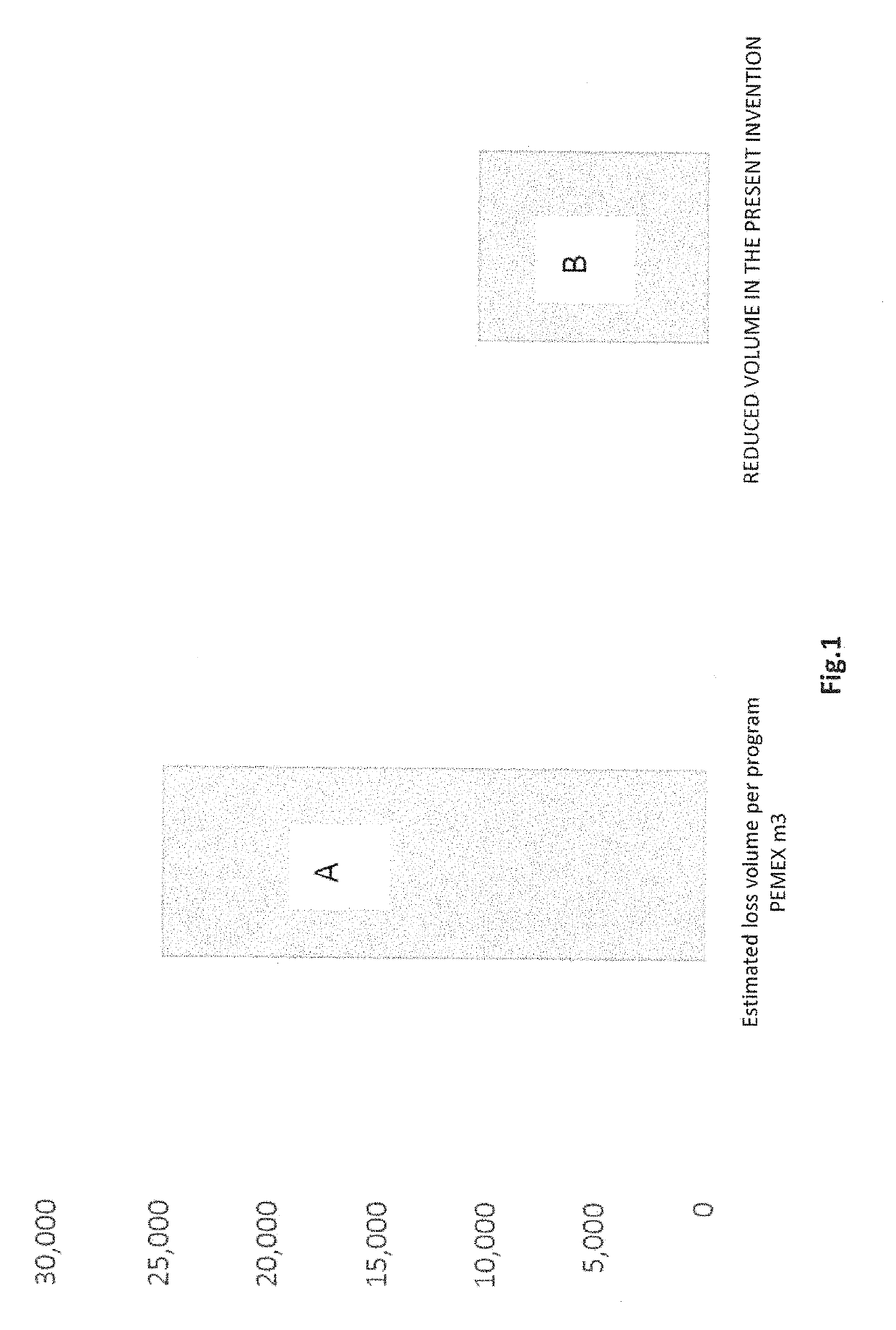
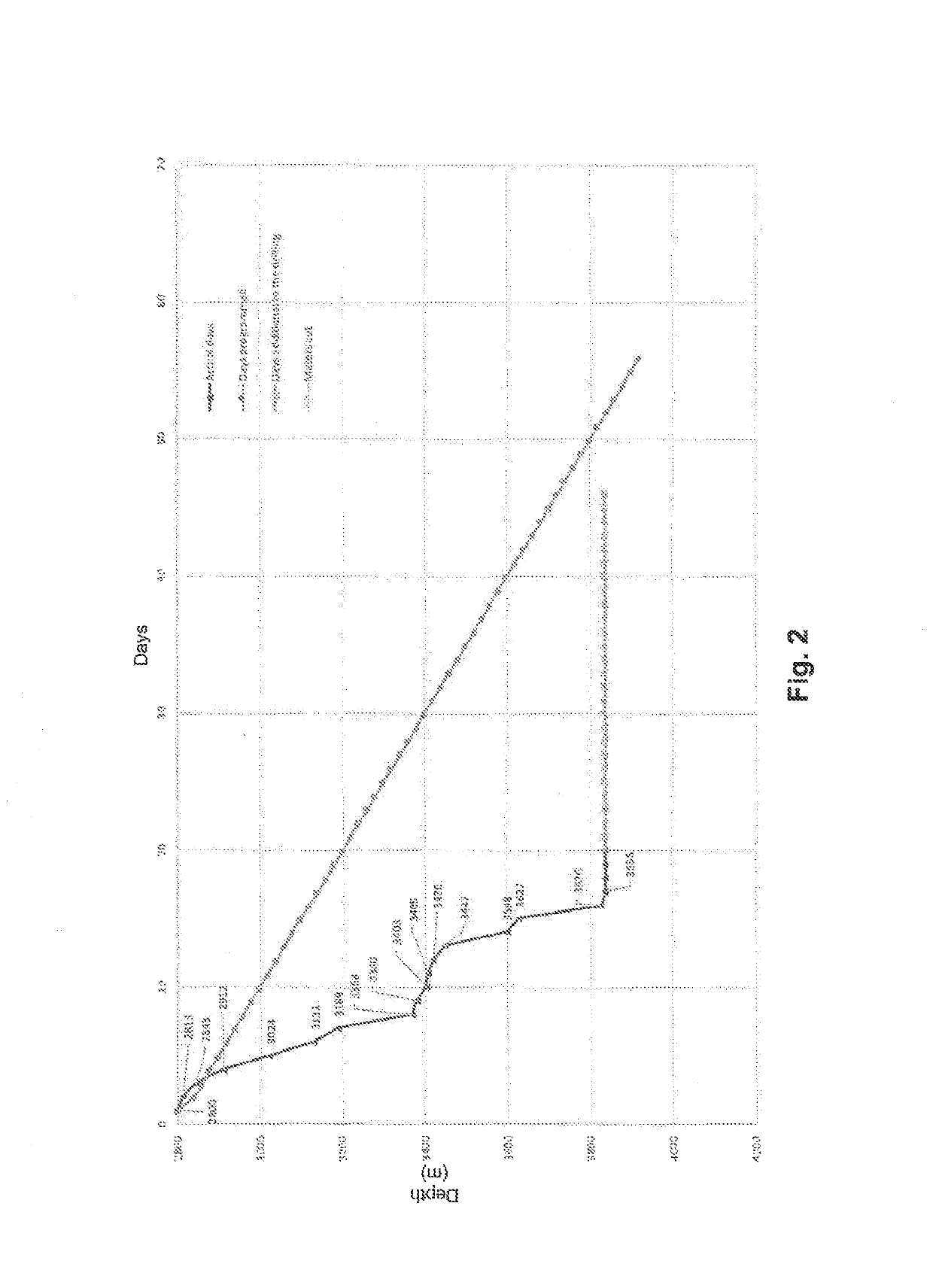
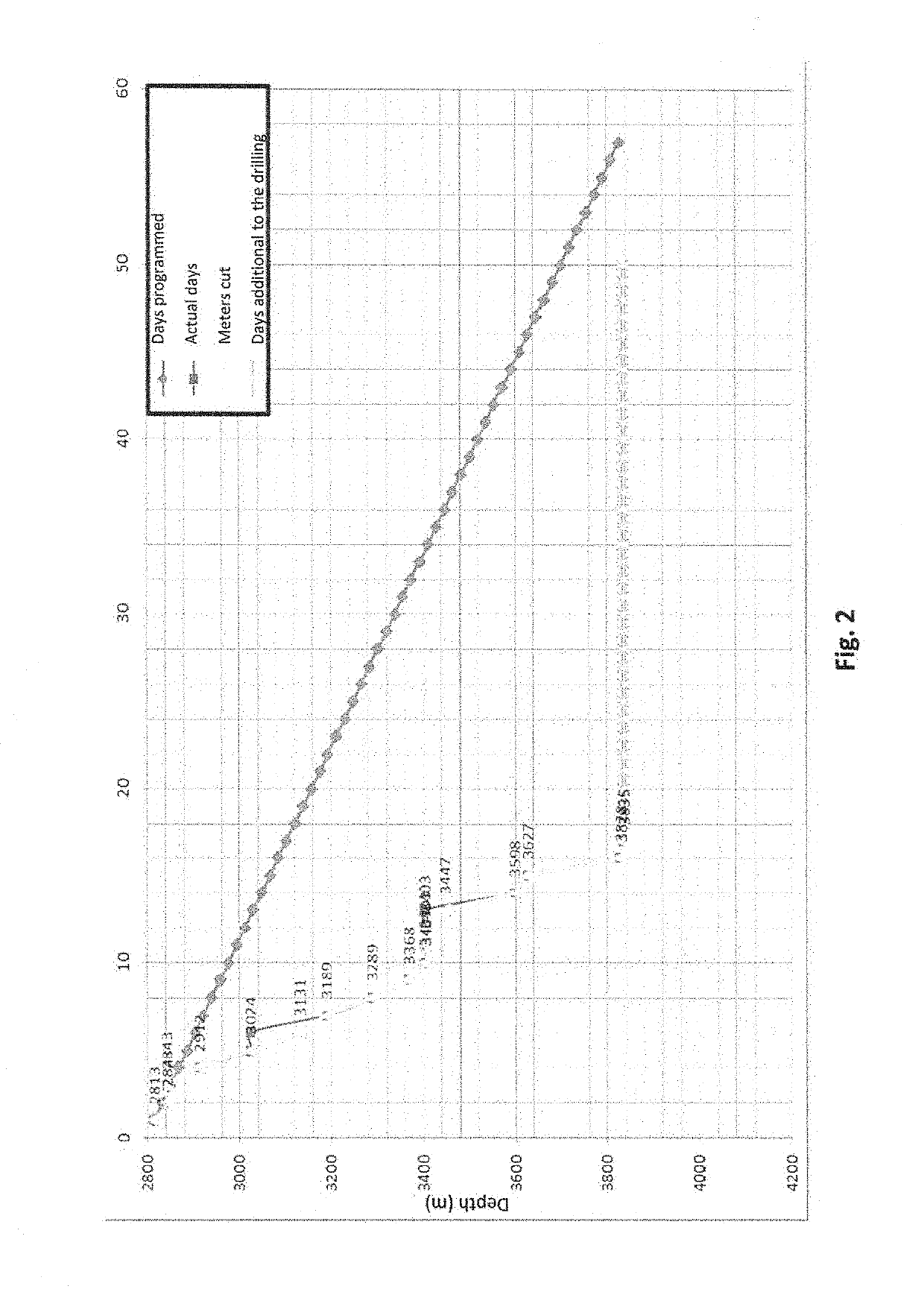
High-Performance Aqueous-Phase Polymer Fluid for Drilling Well Bores in Low-Gradient Formations
The present invention relates to a high performance aqueous phase polymer fluid, which is a seawater-based drilling fluid for well drilling in low gradient formations. It is formulated based on liquid state polymer chemical products, easy to aggregate, and quickly mixed; a preparation and homogenization that reduces preparation times, designed to drill hydrocarbon-producing deposits, focusing on minimizing damages to the producing formations, with a high rate of circulation loss in naturally-fractured deposits. The system is environmentally-friendly, it complies with the required main functions of the drilling fluids while also providing a high inhibition control by swelling and dispersion of clay zones, due to the polymeric nature of the materials with which it is formulated. It is a fluid that does not contain solids in its formulation and provides an excellent transport and cleaning of the drilling shears in the well.
Owner:TECHA INTEGRAL & FLUIDOS DE PERFORACION S A DE
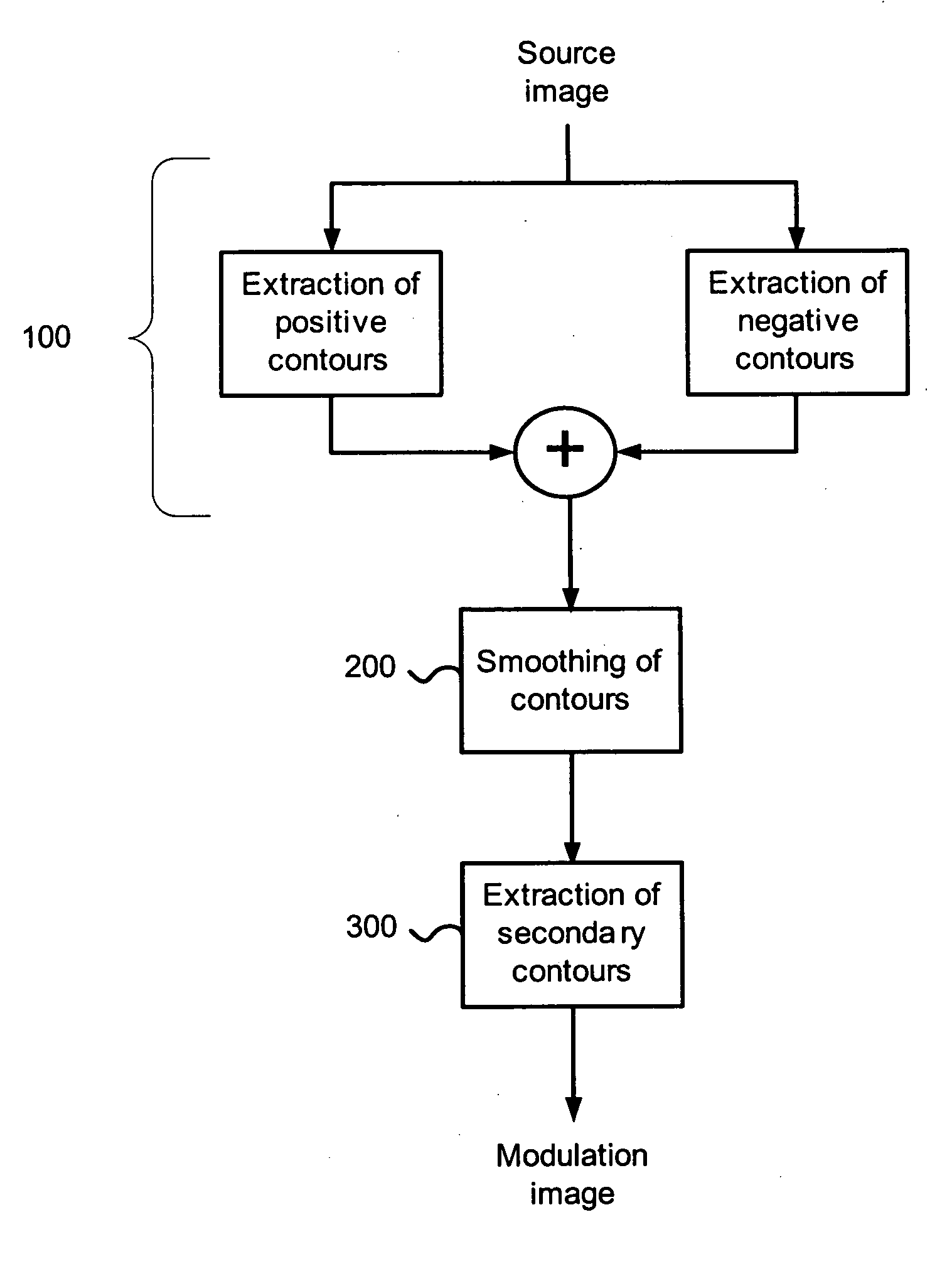
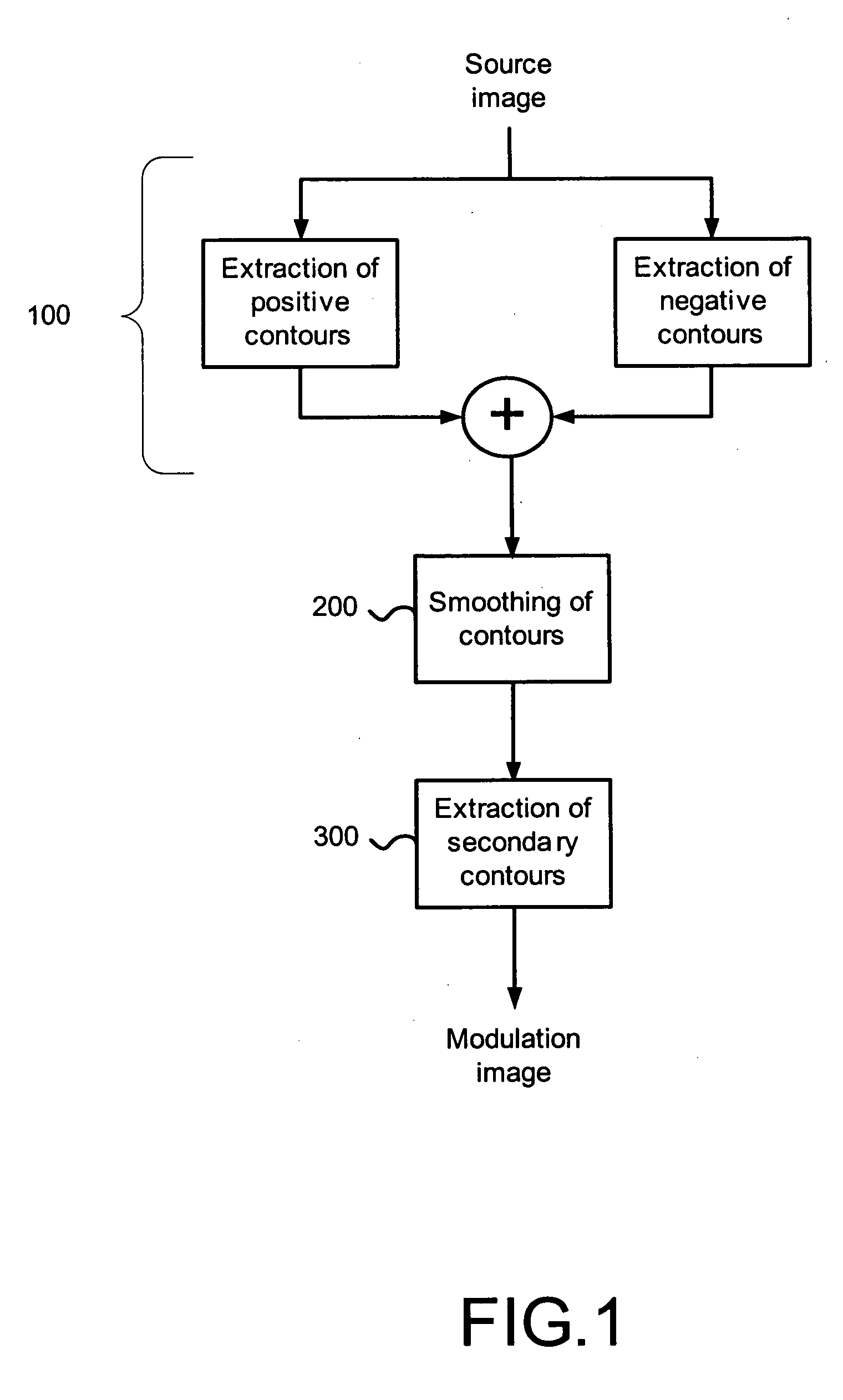
Image processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050270547A1Possible to createTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus and device intended to temporally modulate a sequence of source images with a modulation image comprising at least one anti-copy pattern. According to the invention, it is proposed that the modulation image be generated on the basis of the source image to be modulated in such a way as to place the patterns at locations of the image that may hinder the person watching an illicit copy of the video sequence (filmed for example by a camcorder). The modulation image is for example an image of the secondary contours of the image. The patterns are therefore placed in the low-gradient zones of the source image.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
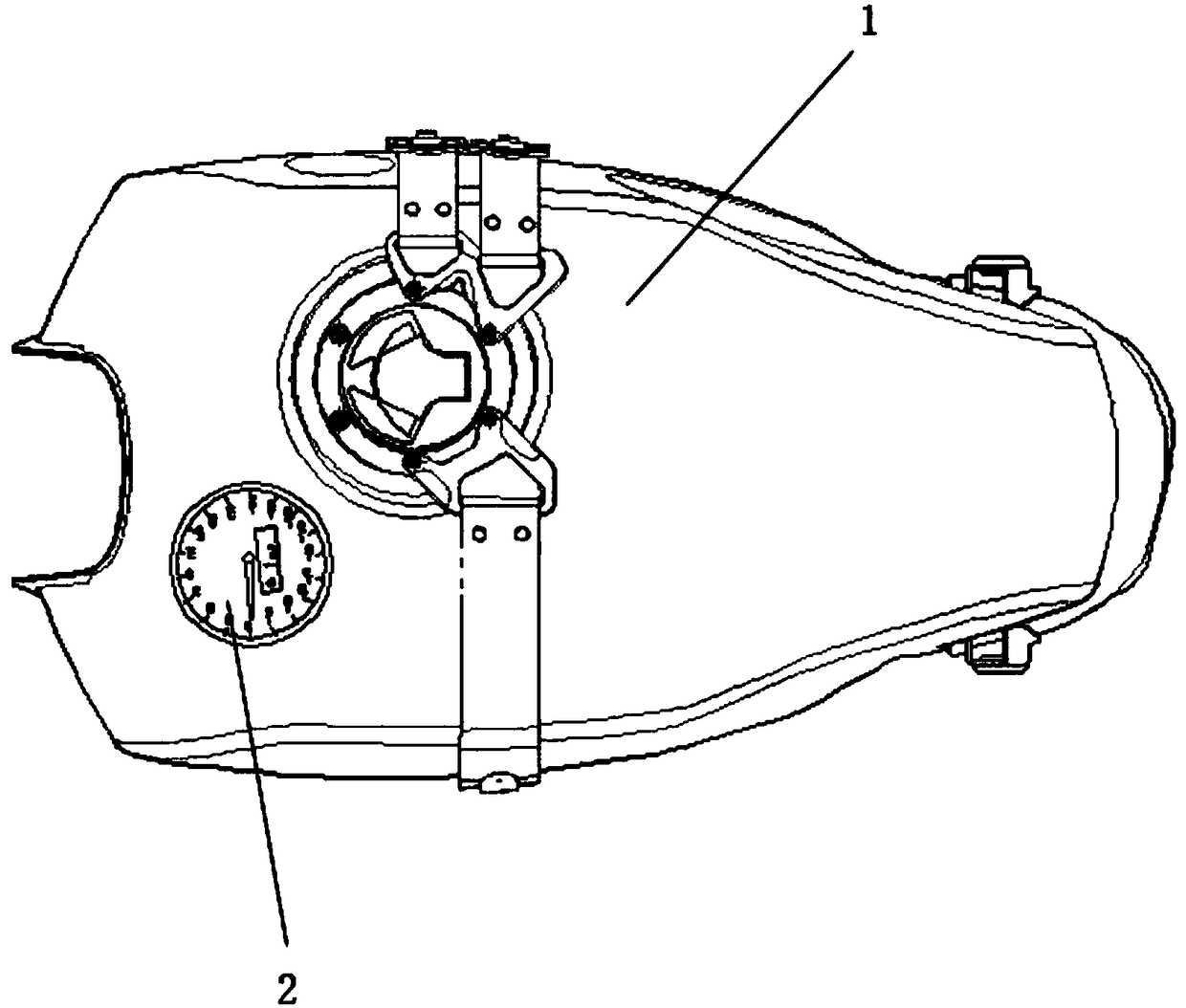
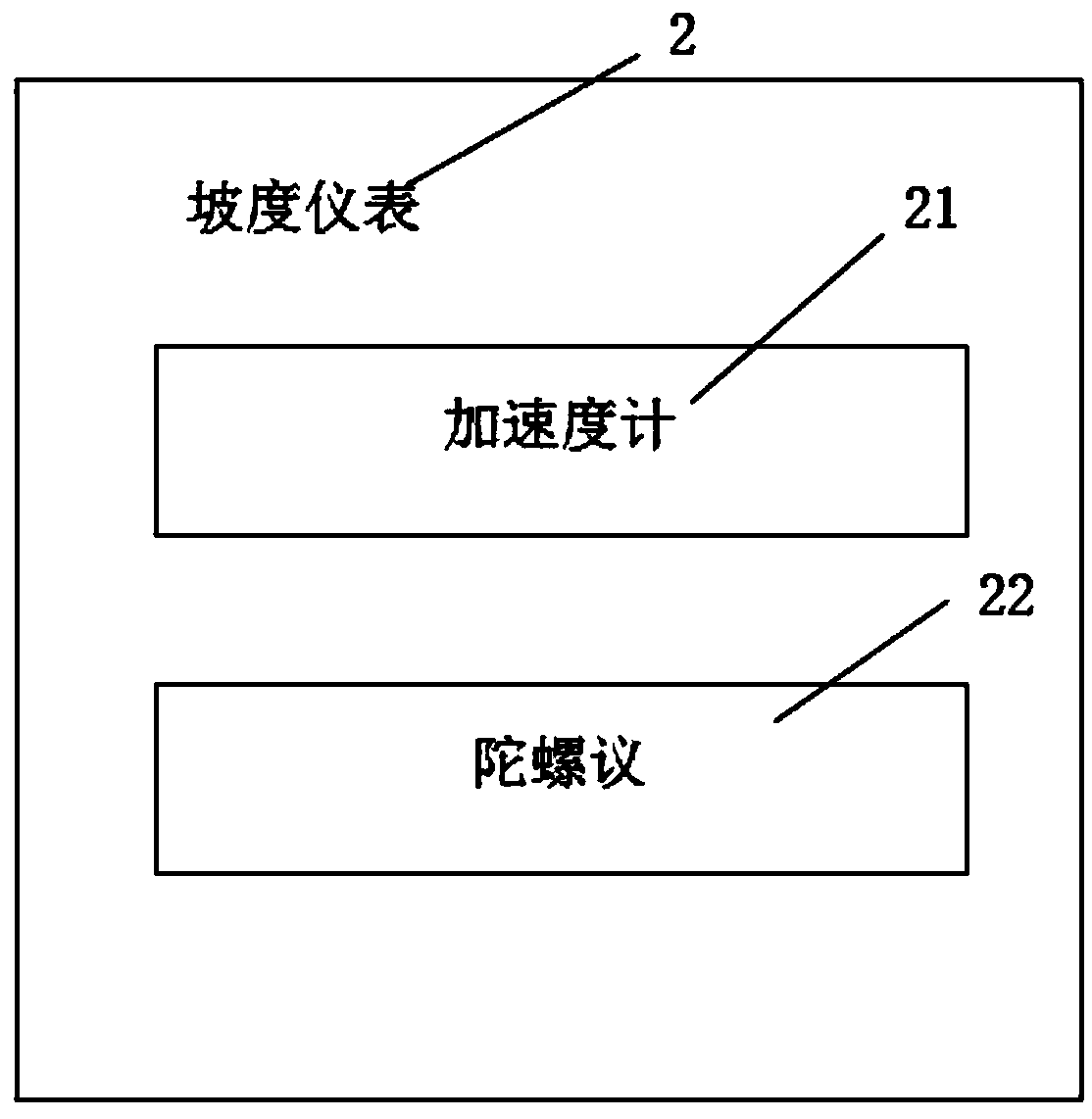
A fuel tank with a gradient meter
PendingCN109263771ASafe drivingQuickly master driving skillsFuel tanksCycle sensorsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention relates to a fuel tank with a gradient meter. The fuel tank with the gradient meter comprises a fuel tank body and a gradient meter. The gradient meter is fixed on the oil tank body; theslope meter comprises an accelerometer, a gyroscope and a display device; the accelerometer is used for detecting the inclination angle of the tank body; the gyroscope detects the change of the angular acceleration, and gives the display device a matching gear and a gradient according to the change of the angular acceleration. The invention has the advantages that the fuel tank with the gradientmeter can provide a matching gear when driving on the high and low gradient road surface, thus ensuring the safe driving of the new rider, so that the new rider can master the driving technology morequickly.
Owner:力帆科技(集团)股份有限公司
High-performance aqueous-phase polymer fluid for drilling well bores in low-gradient formations
The present invention relates to a high performance aqueous phase polymer fluid, which is a seawater-based drilling fluid for well drilling in low gradient formations. It is formulated based on liquid state polymer chemical products, easy to aggregate, and quickly mixed; a preparation and homogenization that reduces preparation times, designed to drill hydrocarbon-producing deposits, focusing on minimizing damages to the producing formations, with a high rate of circulation loss in naturally-fractured deposits. The system is environmentally-friendly, it complies with the required main functions of the drilling fluids while also providing a high inhibition control by swelling and dispersion of clay zones, due to the polymeric nature of the materials with which it is formulated. It is a fluid that does not contain solids in its formulation and provides an excellent transport and cleaning of the drilling shears in the well.
Owner:TECHA INTEGRAL & FLUIDOS DE PERFORACION S A DE
Method for forming a high-performance aqueous-phase polymer fluid and system for drilling well bores in low-gradient formations
The present invention relates to a method to form or obtain a high performance aqueous phase polymer fluid, which is a seawater-based drilling fluid for well drilling in low gradient formations. It is formulated based on liquid state polymer chemical products, easy to aggregate, and quickly mixed; a preparation and homogenization process that reduces preparation times, designed to drill hydrocarbon-producing deposits, focusing on minimizing damages to the producing formations, with a high rate of circulation loss in naturally fractured deposits. The system is environmentally-friendly, it complies with the main functions required of drilling fluids, while also providing a high inhibition control by swelling and dispersion of clay zones, due to the polymeric nature of the materials with which it is formulated. It is a fluid that does not contain solids in its formulation and provides an excellent transport and cleaning of drilling shears in the well.
Owner:TECHA INTEGRAL & FLUIDOS DE PERFORACION S A DE
Method for reducing and controlling bamboo forest nitrogen runoff loss by utilizing charcoal and buffer zone coupling
InactiveCN106416498AIncrease carbon to nitrogen ratioEasy to fixSoil-working methodsBuffer stripWater discharge
The invention discloses a method for reducing and controlling bamboo forest nitrogen runoff loss by utilizing charcoal and buffer zone coupling and belongs to the field of agroecological environment protection. The method comprises a step (1) of applying charcoal: applying the charcoal in a runoff producing area of a bamboo forest, wherein the application quantity of the charcoal is 0.5-3 kg / m2; a step (2) of arranging a buffer zone: lining out the buffer zone at the low-gradient water discharging end of a bamboo forest runoff area, wherein the specification design of the buffer zone is that the length is consistent with the length of the runoff area and the width is 0.5-3.5 m, and planting lolium perenne, cynodon dactylon or zoysia japonica in the buffer zone. Based on a charcoal and buffer zone coupling technology, the effect of applying the method to an intensively managed bamboo forest to reduce and control the soil nitrogen runoff loss is monitored, mechanism analysis is performed, so that the bamboo forest soil nitrogen runoff loss is reduced from two links which are source decrement and process blockage more effectively, and the goal of improving utilization efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer input into the bamboo forest and protecting the water environment is achieved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for reducing the repetition time without increasing the gradient capacity utilization
ActiveUS10459050B2Improved reproducibility and comparabilityKeep for a long timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceBiological activation
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com