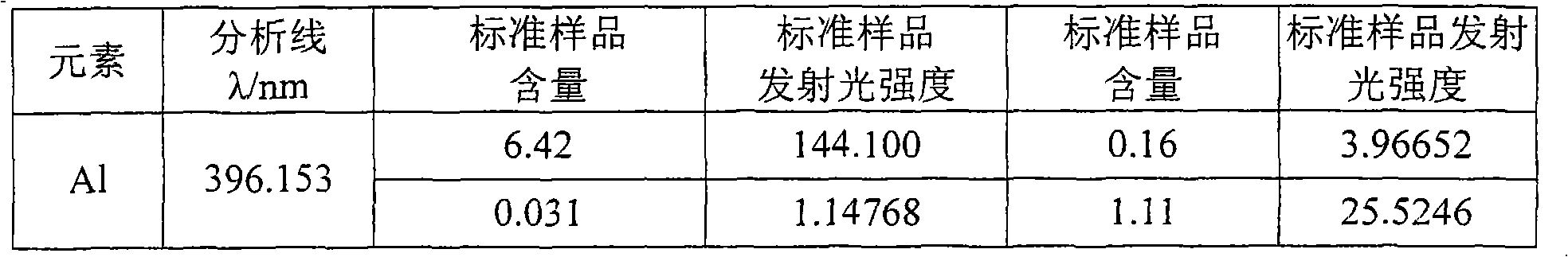
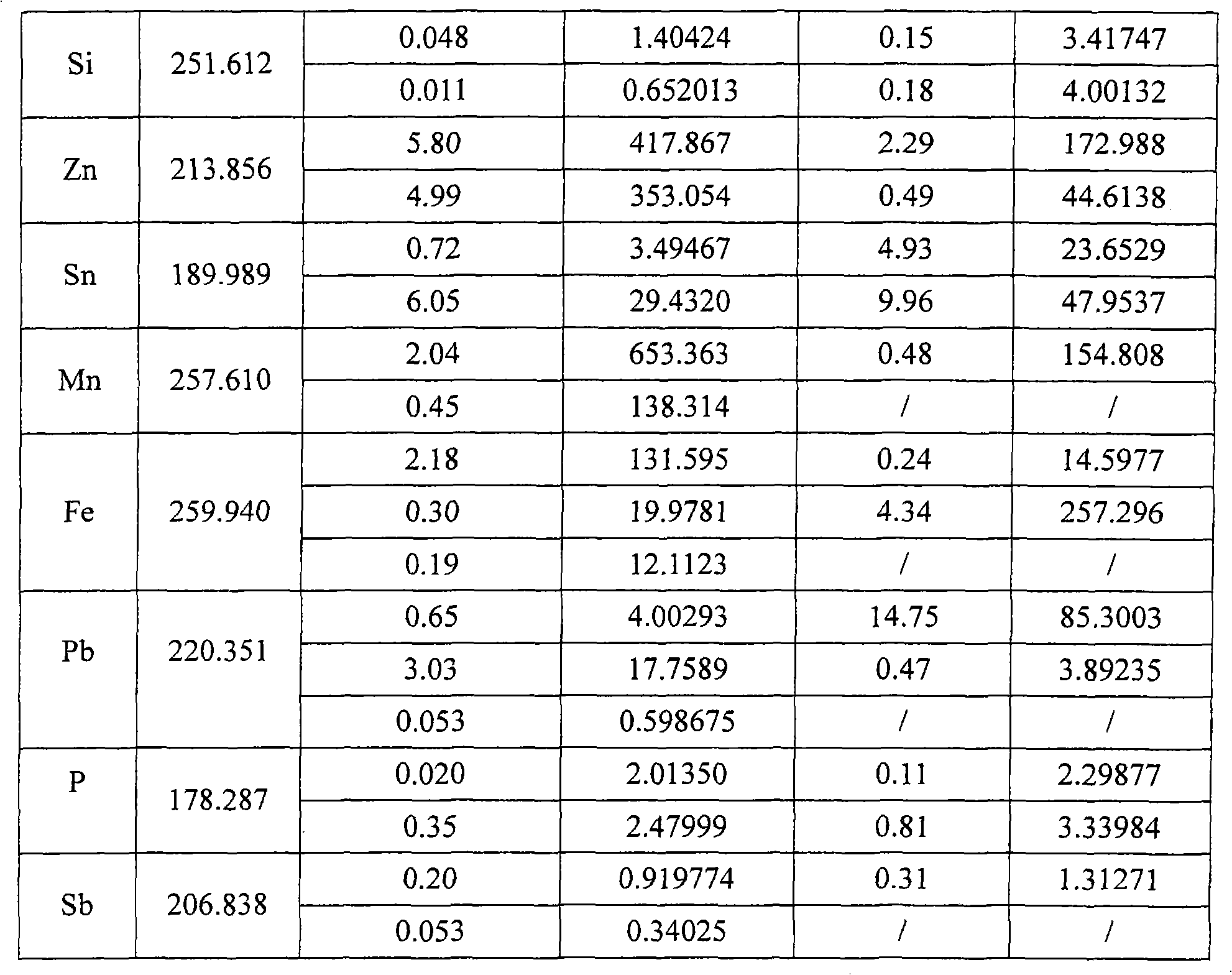
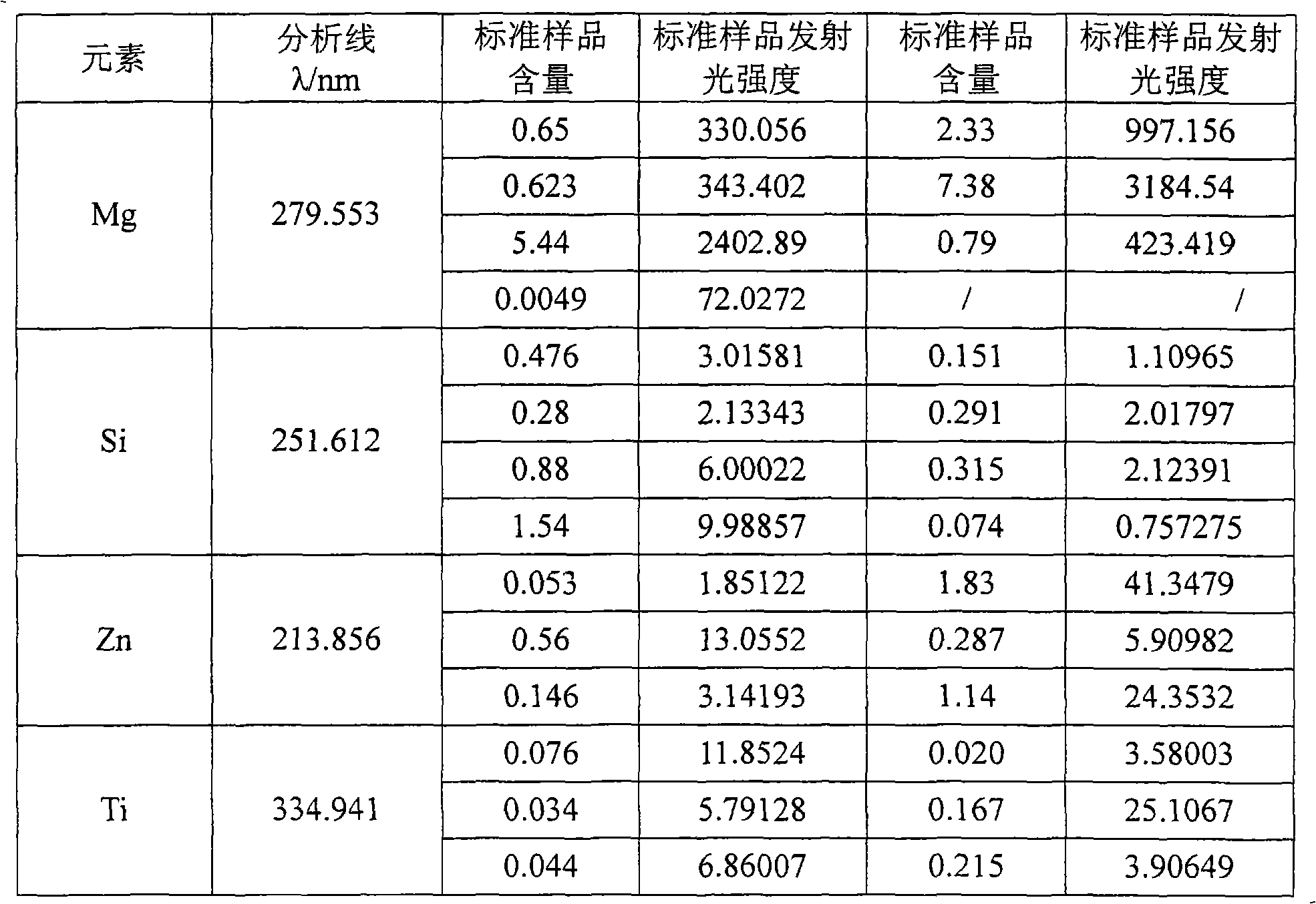
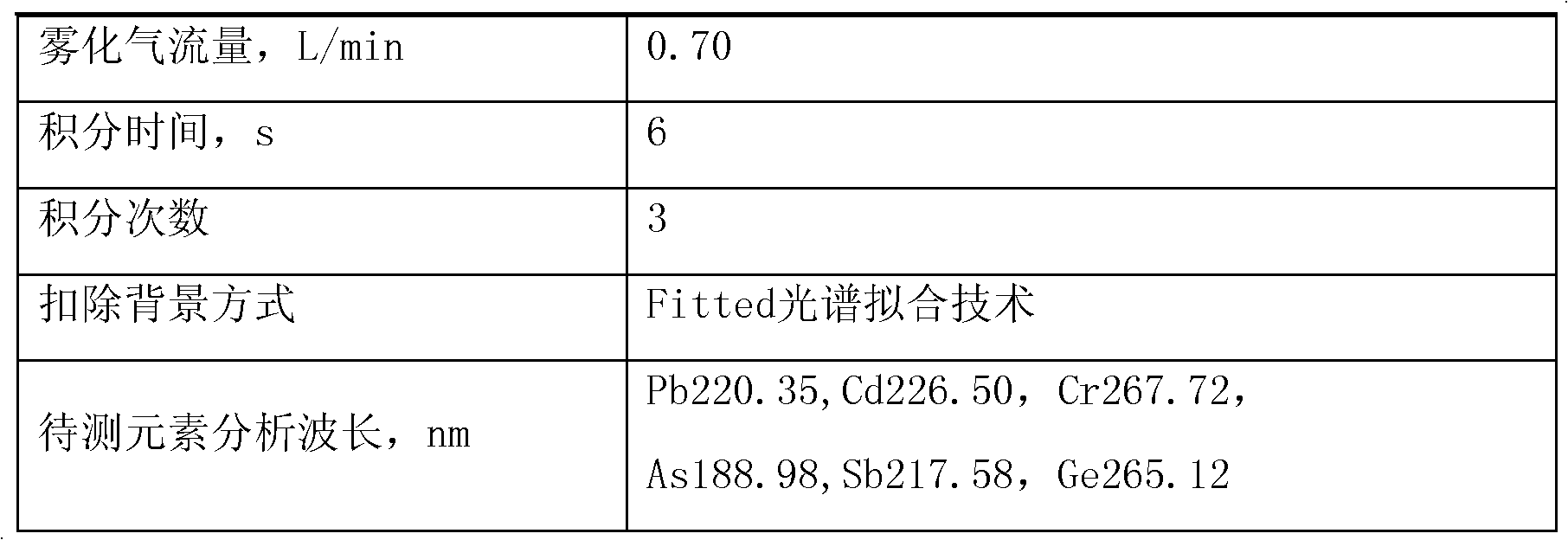
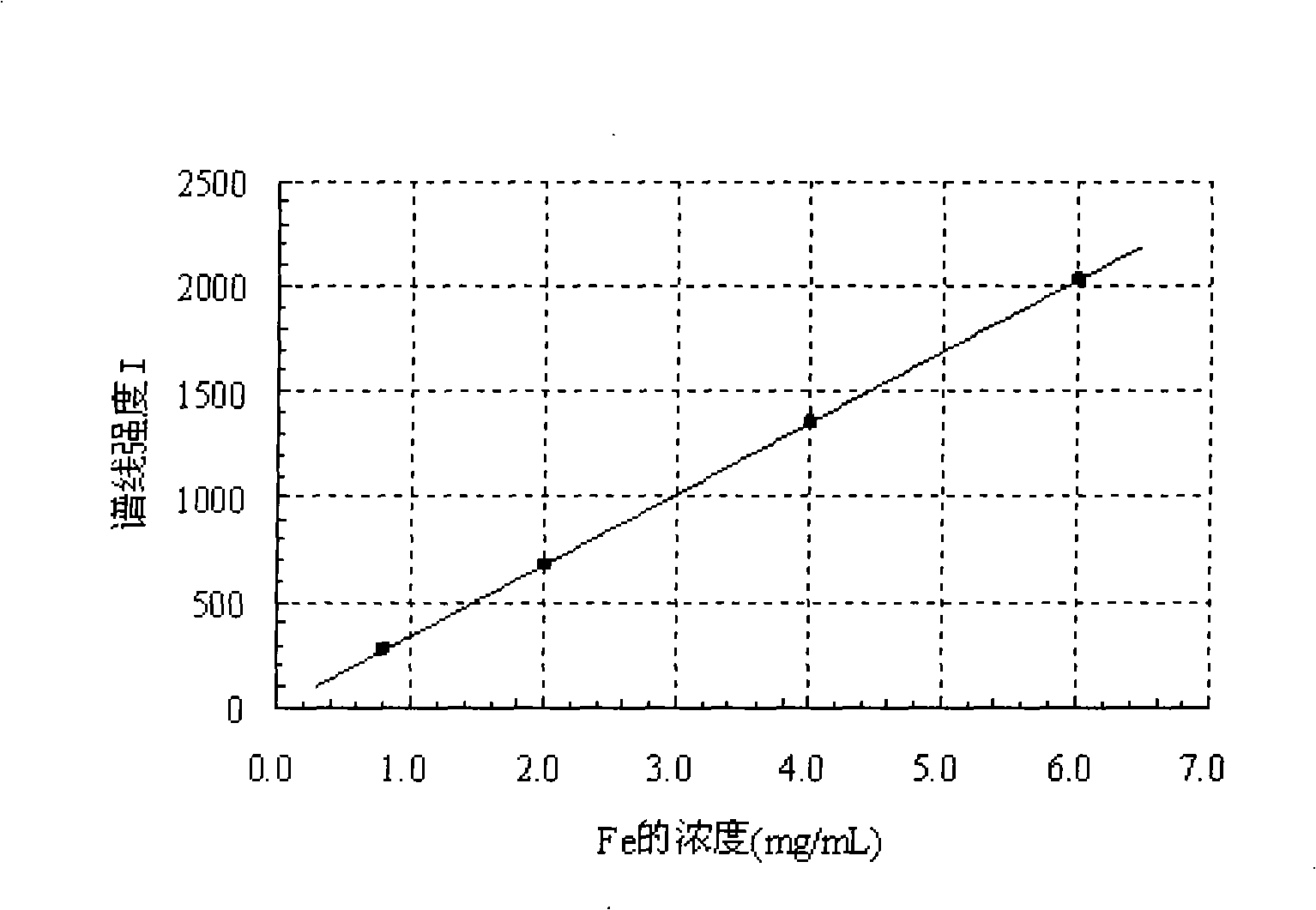
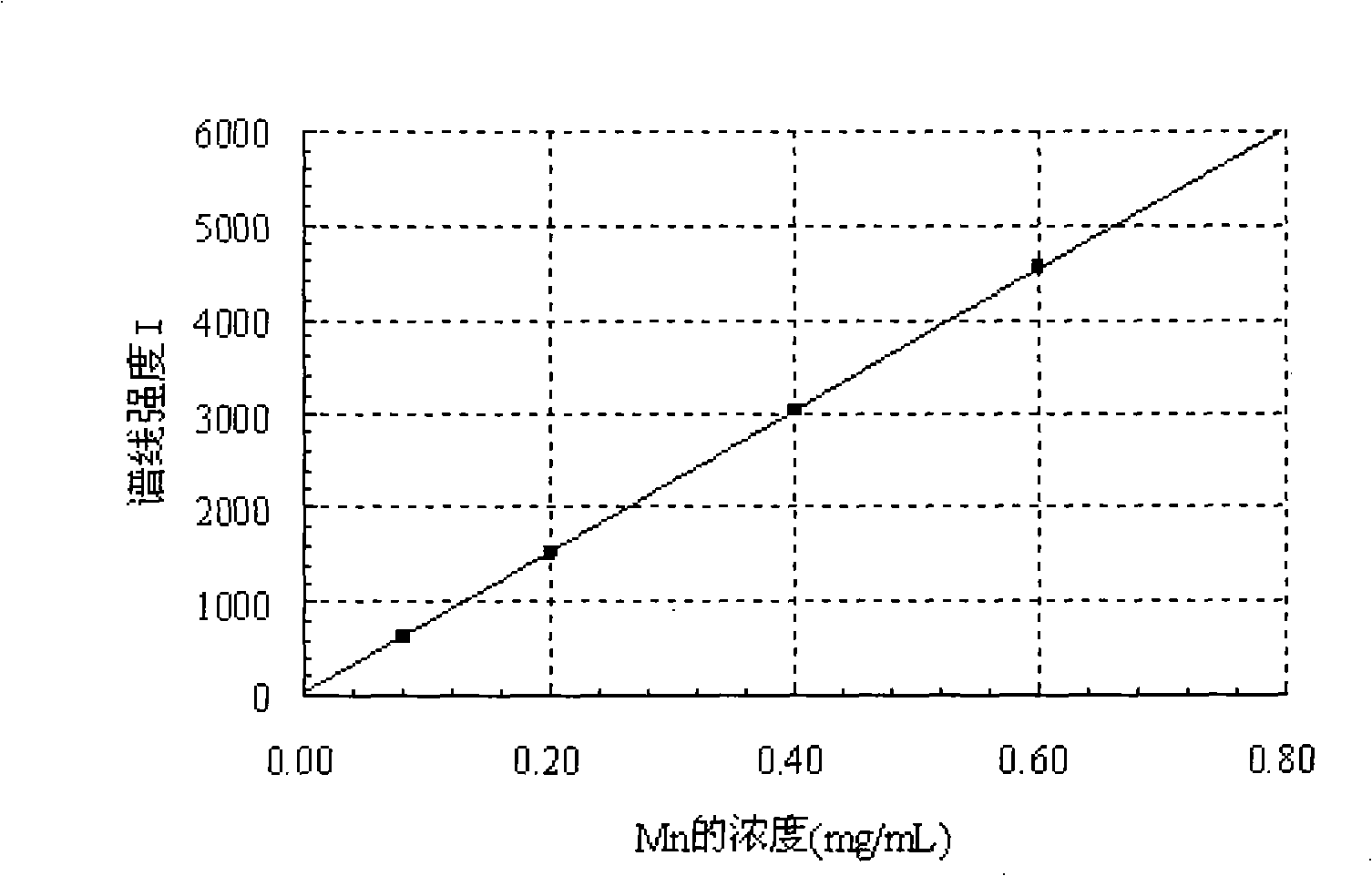
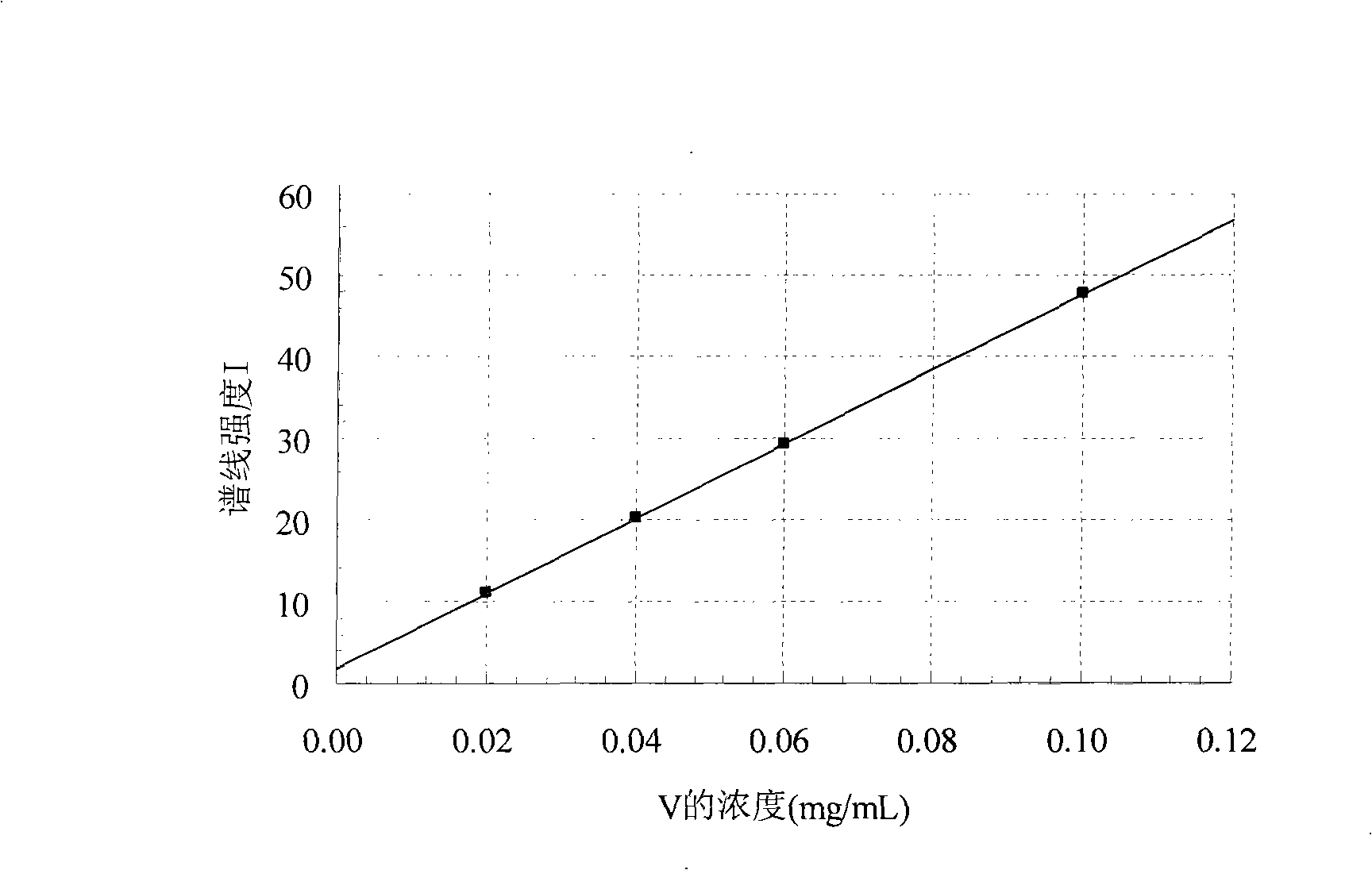
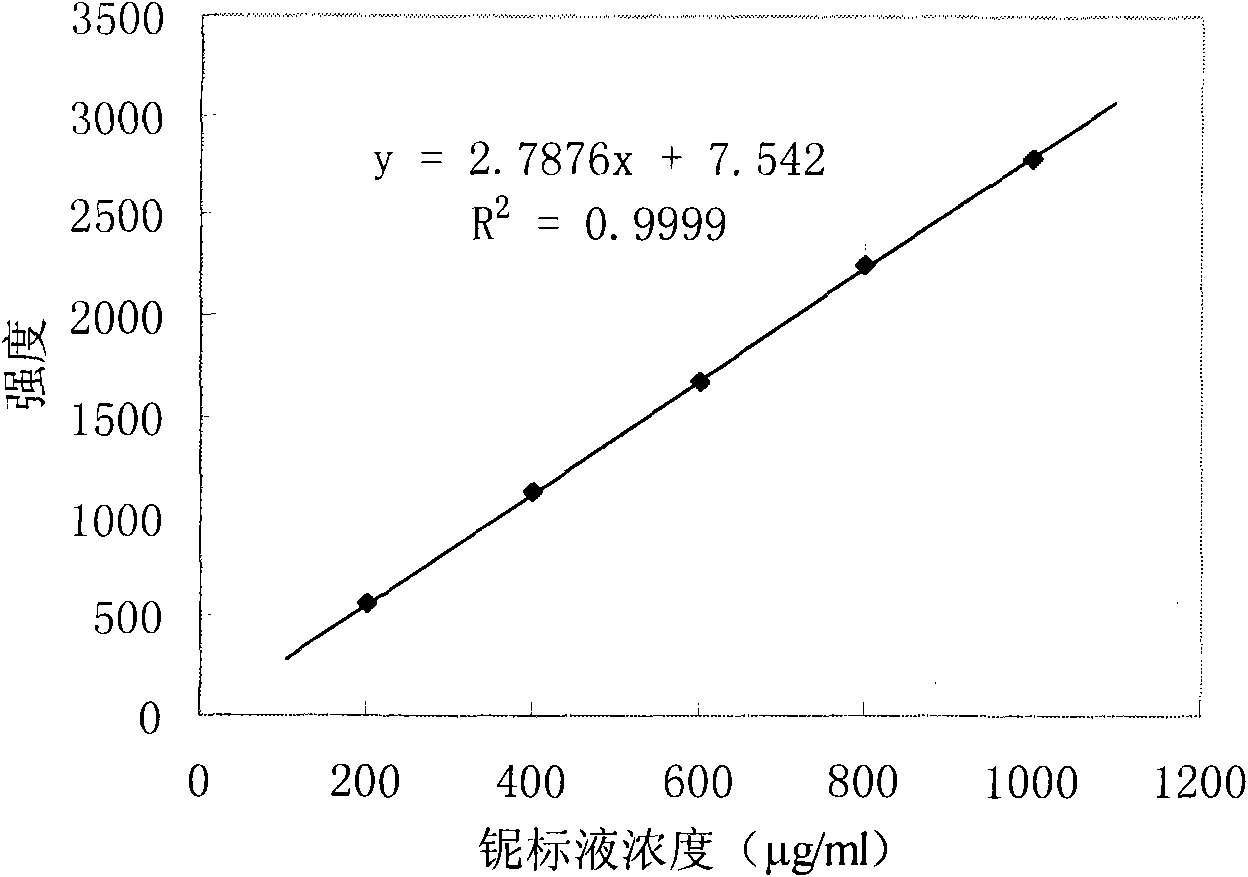
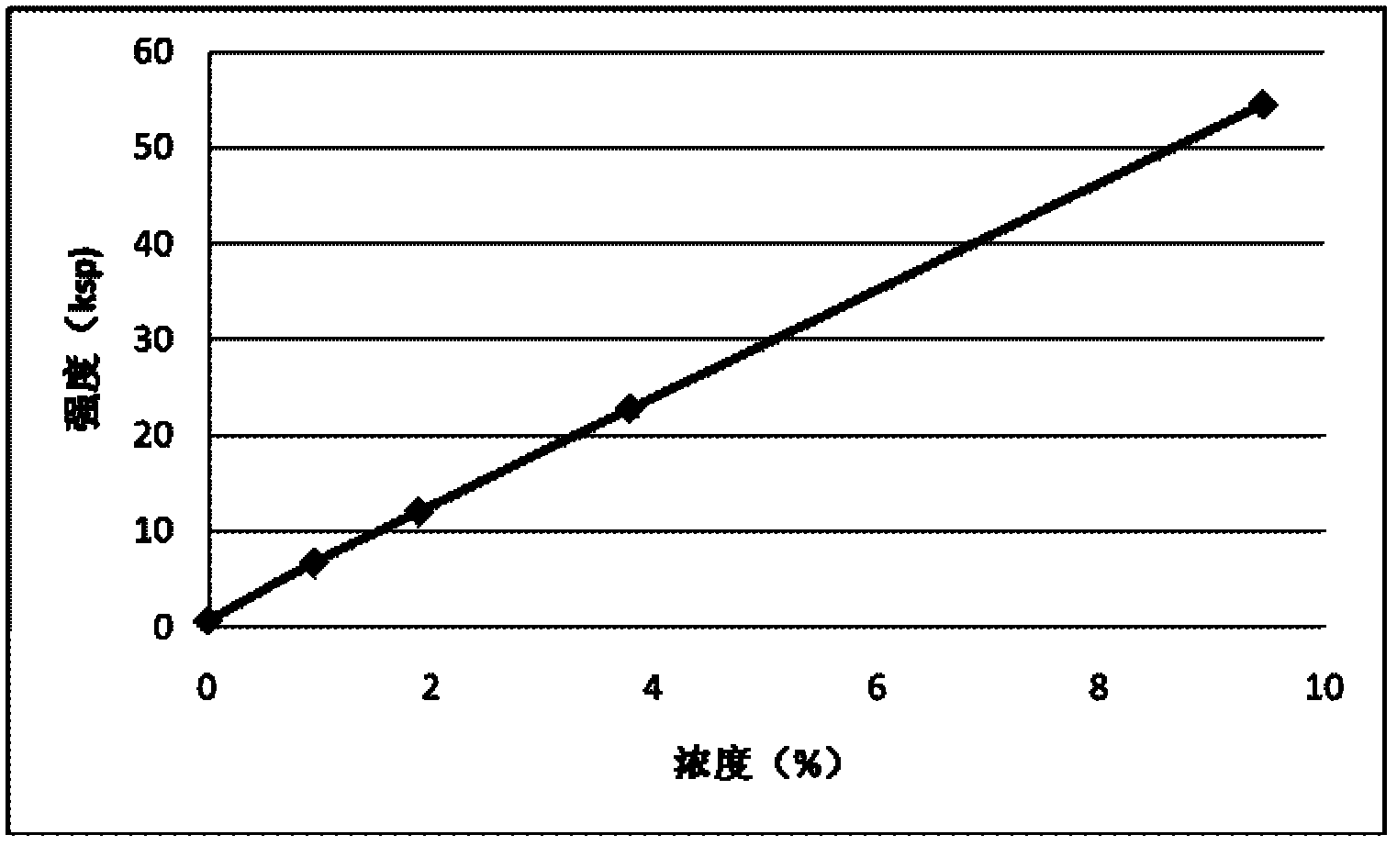
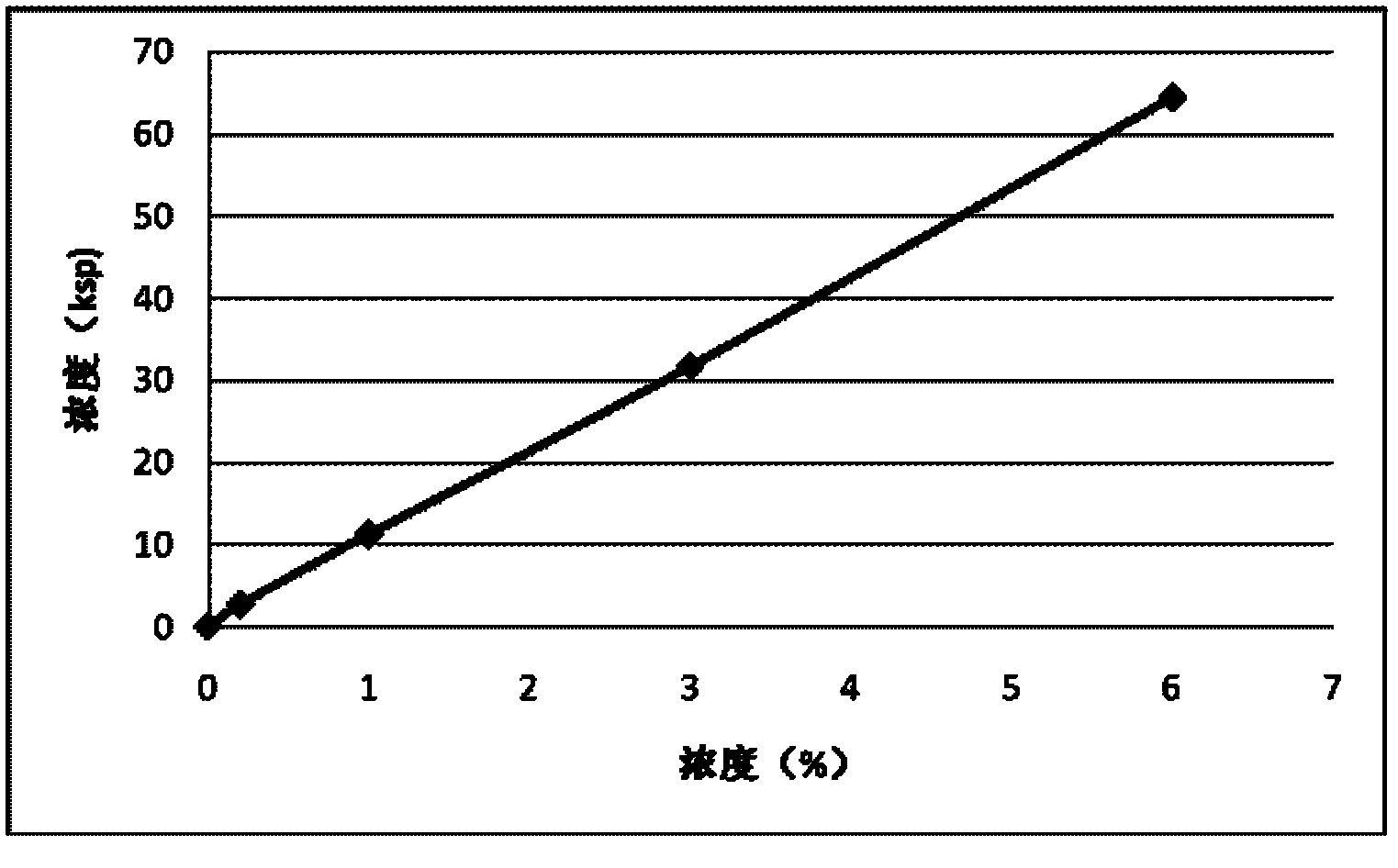
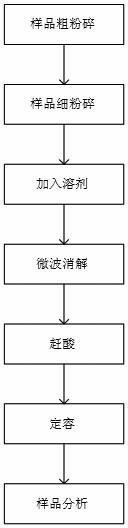
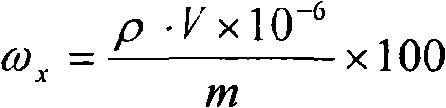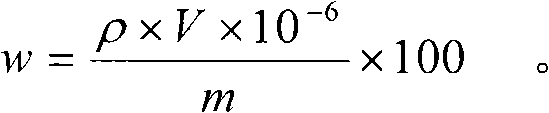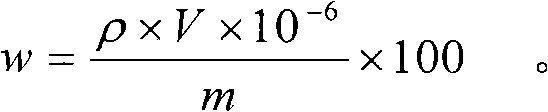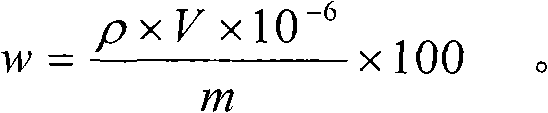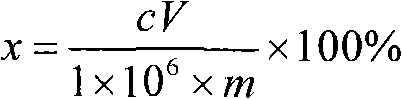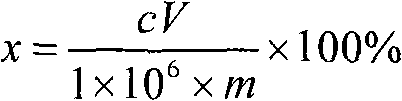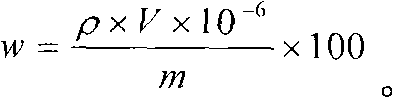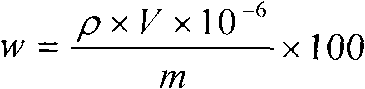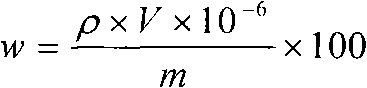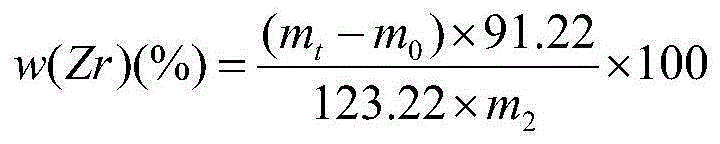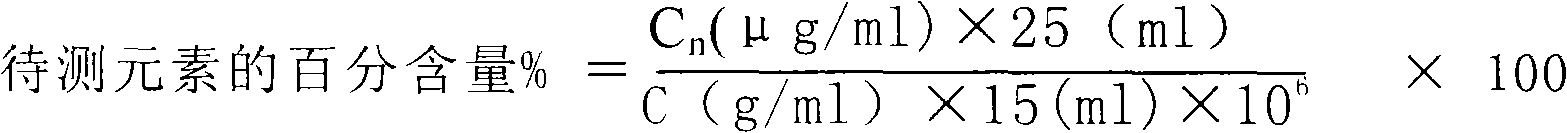Patents
Literature
617 results about "Emission Spectrometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A spectrometer that applies some form of energy to a substance, thereby causing emission of electromagnetic radiation which is then quantified using a detector.
On-site analyzer
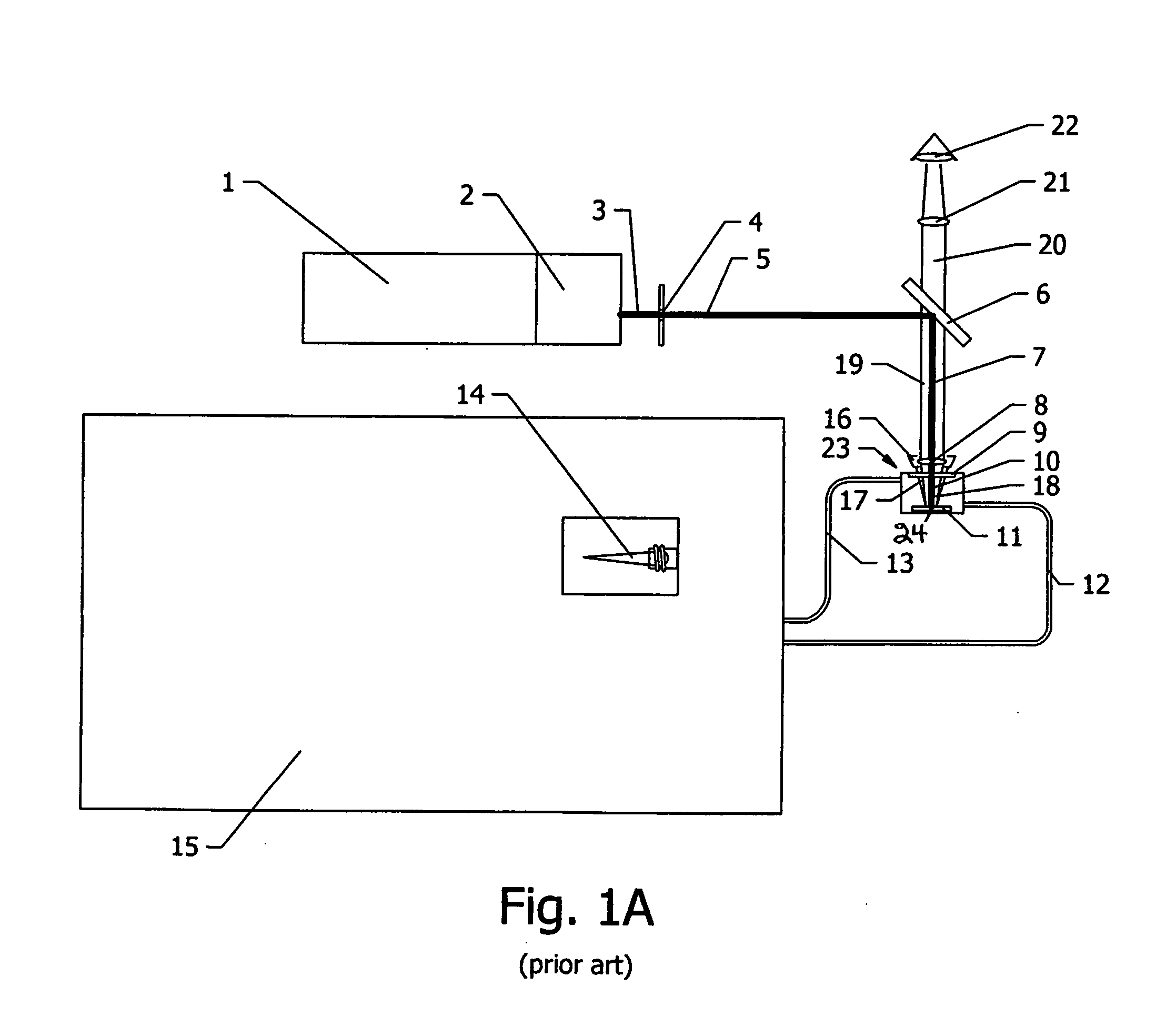
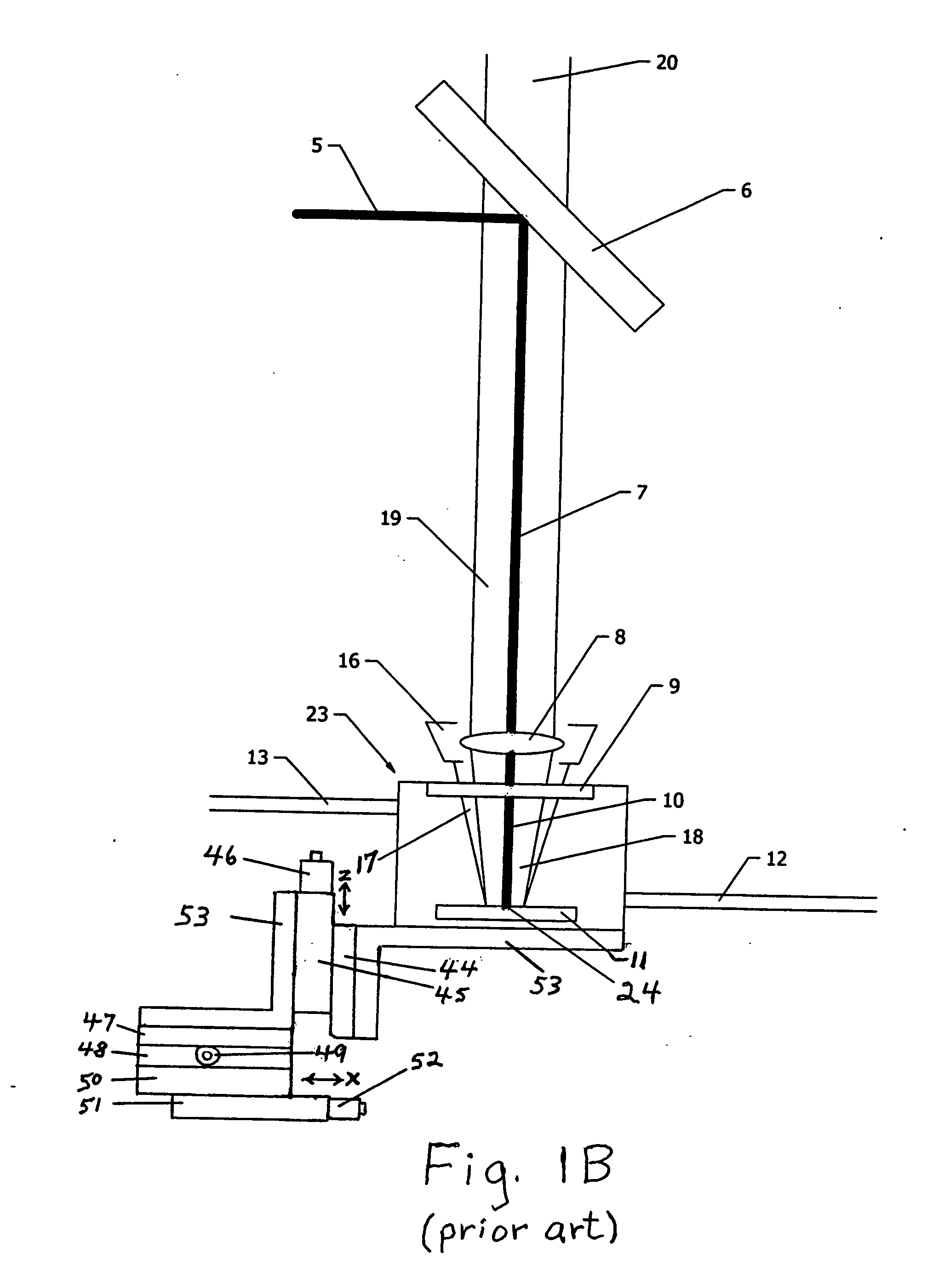
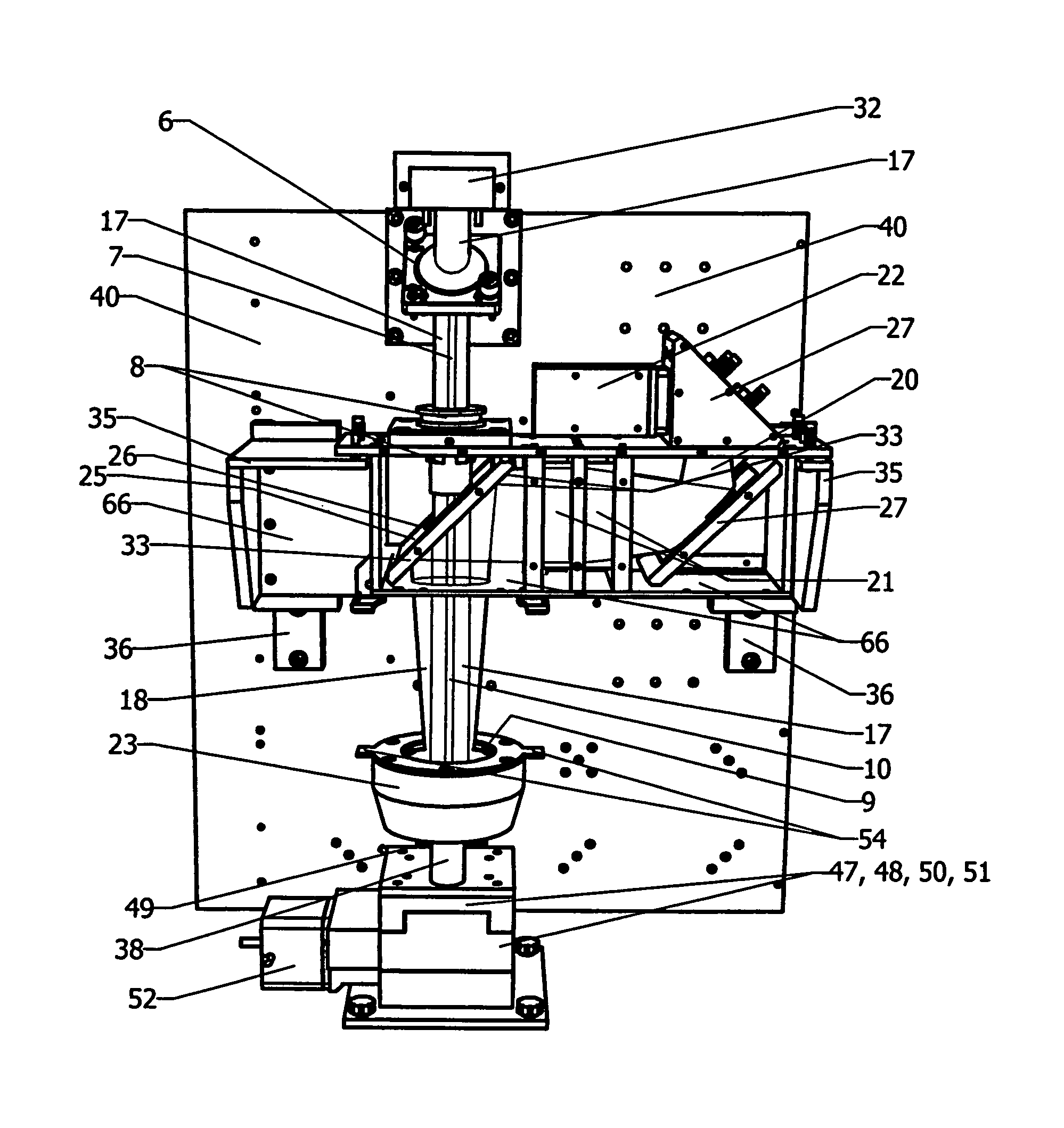
InactiveUS6452179B1Minimizes undesirable effect of fringingEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical spectrometer
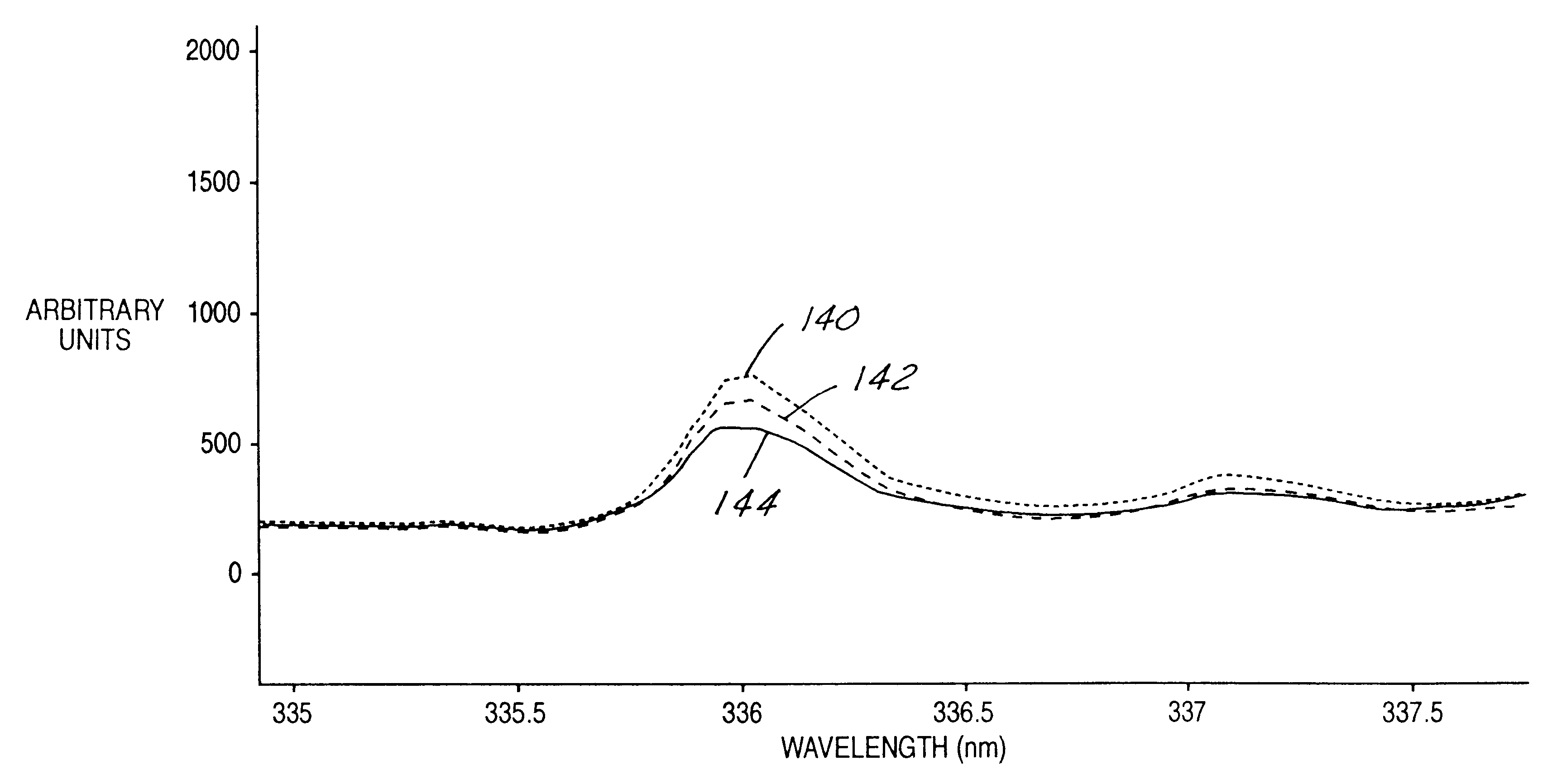
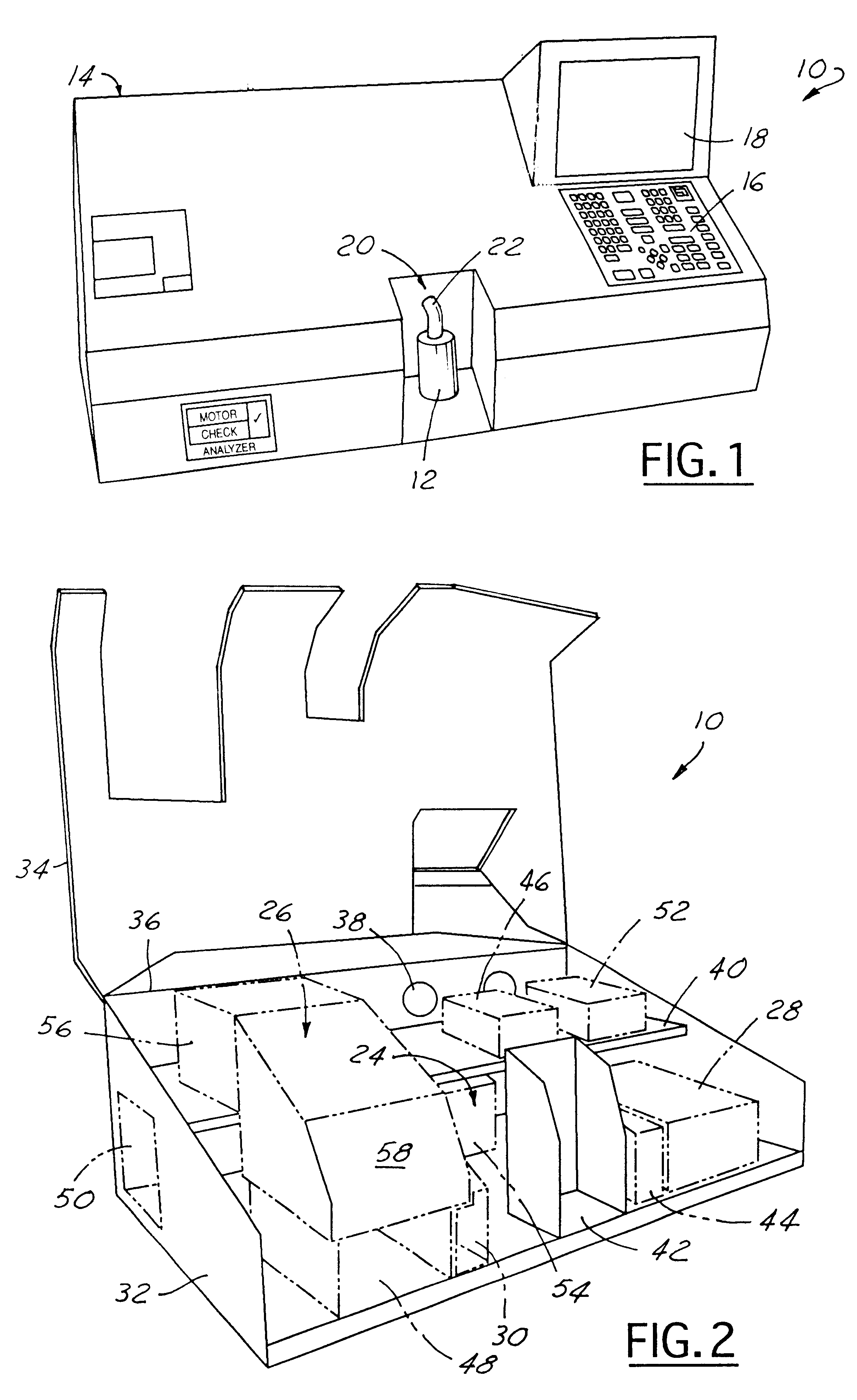
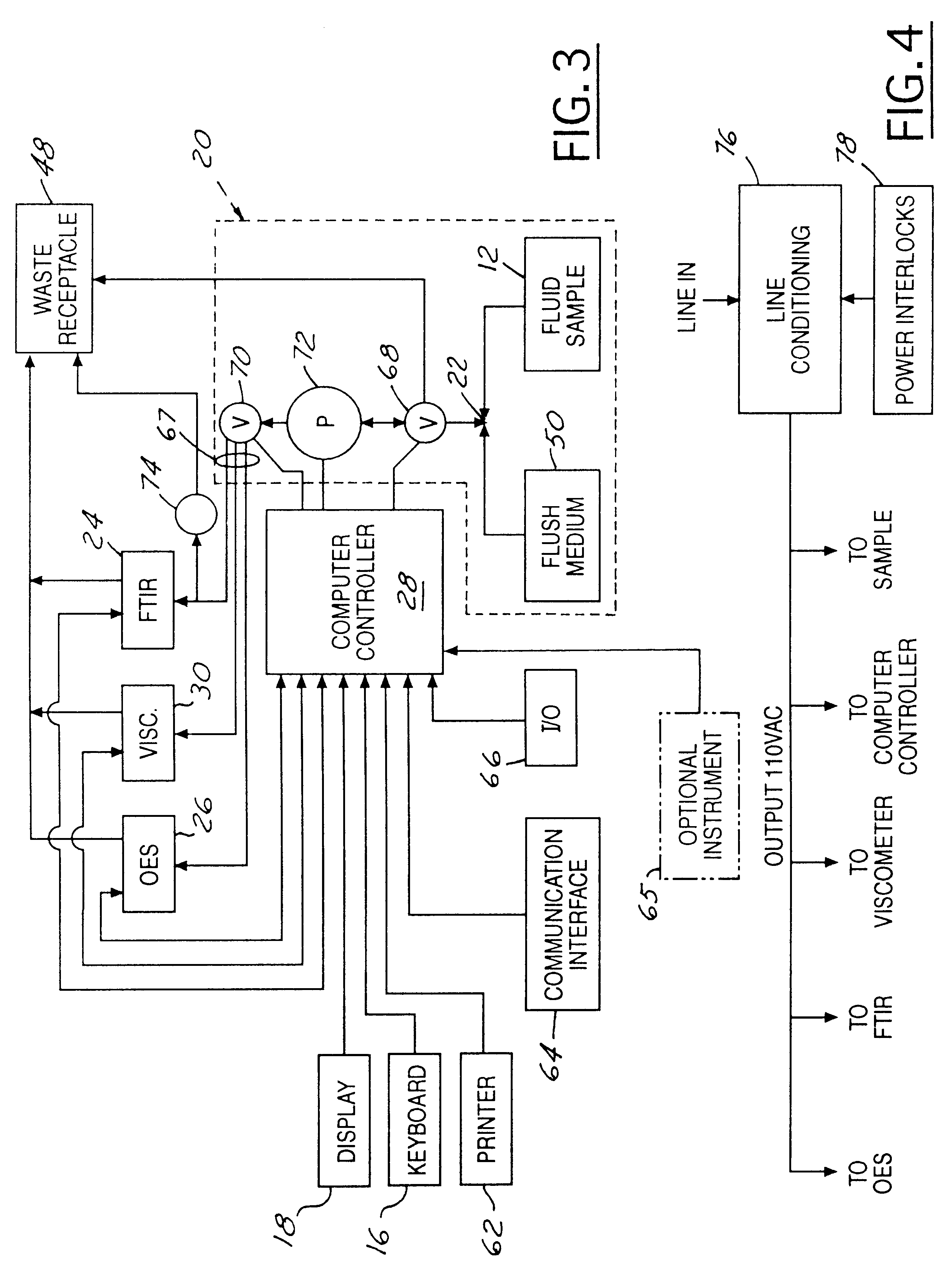
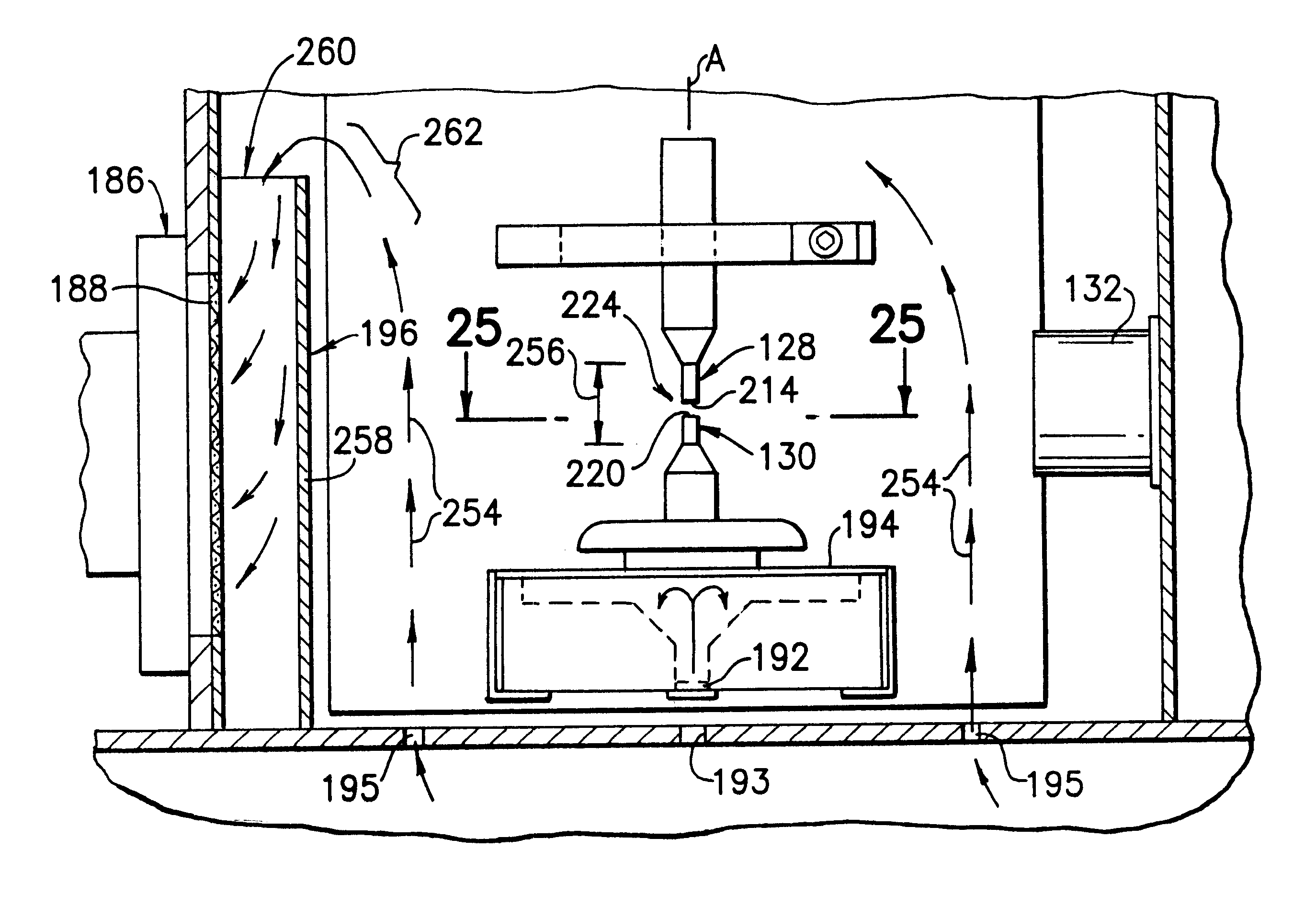
An apparatus (10) for analyzing lubricant oils and functional fluids includes an optical emission spectrometer (OES) (26) having a substantially continuously valued wavelength versus intensity output (140). The OES (26) analyzes light captured from a spark emission stand (58) through which the fluid sample is flowed. An expert system (160-172) operates according to a set of Rules that corrects background influence from the electrodes, and generates diagnostic text (174) for an operator based on the information about the fluid sample provided by the OES (26) and other measurement devices. The apparatus (10) is reduce in size, weight and cost.
Owner:SPECTRO SCI INC
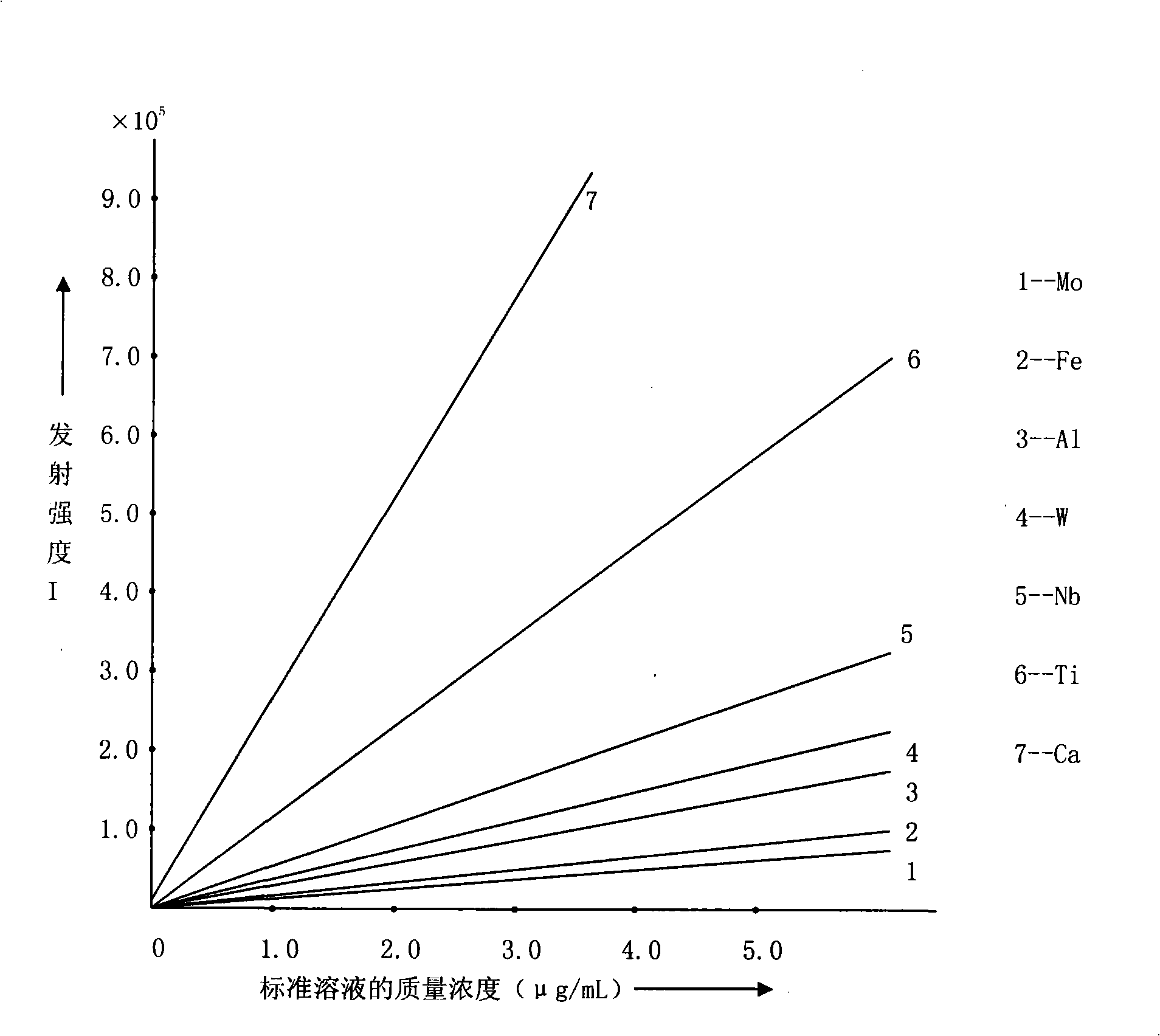
Analyses testing method of aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten impurity elements in chromium carbide
ActiveCN101303307ASolve difficult technical problemsImprove measurement accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationNiobiumDecomposition
The invention discloses an analysis and detection method for impurity elements such as aluminum, calcium, ion, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten and the like in chromium carbide. The method comprises adding a chromium carbide sample into a dissolving cup, adding hydrofluoric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid sequentially, stirring, charging into a sealed high-pressure jar; putting the sealed high-pressure jar into a microwave extinguishing instrument for two times of microwave extinguishment; taking the high-pressure jar out of the microwave extinguishing instrument for cooling, transferring the dissolved chromium carbide liquid sample into a volumeric flask, diluting to a predetermined index, stirring; preparing a chromium substrate matched mixed standard solution series of aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium and tungsten; measuring element emission power of aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten or the like in a blank liquid sample, a chromium carbide liquid sample and the prepared series mixed standard solution by an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer in the same time, obtaining the analysis result by checking a standard working curve or by linear equation calculation. The invention adopts two times of microwave extinguishment using the mixed acid, solves the problem of hardness in chromium carbide decomposition, having a measurement range from 0.010% to 1.00%, which is high in accuracy, and good in precision.
Owner:ZHUZHOU HARD ALLOY GRP CO LTD
Method for measuring contents of aluminum, titanium, manganese, nickel, tungsten and iron in cobalt-base alloy
ActiveCN101718689AEasy to handlePromote precipitationPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsManganeseMaterials science
The invention belongs to a technique for analyzing elements of an alloy, and relates to a method for measuring the contents of aluminum, titanium, manganese, nickel, tungsten and iron in a cobalt-base alloy. The method adopts an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer and is different according to different measured elements and different tungsten contents; when high-content tungsten is dissolved, the volume of test solution needs to be maintained between 20 and 40 mL, or the tungsten is easy to be separated out; by performing interference experiments and spectrogram analyses, the method finds the optimal analytical line, overcomes the interferences caused by a plurality of elements such as major elements of cobalt, chromium, tungsten and the like in the cobalt-base alloy, and improves the measuring accuracy; the sample dissolving speed is accelerated, and the sample dissolving time is shortened to 2 hours from about two or three days; and the method has wide measuring ranges including: 0.05 to 0.30 percent of the aluminum, 0.05 to 0.30 percent of the titanium, 0.05 to 1.00 percent of the manganese, 0.05 to 24.00 percent of the nickel, 0.05 to 20.00 percent of the tungsten, and 0.05 to 3.00 percent of the iron.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for detecting element content in alloy or ore by utilizing ICP emission spectrometer
InactiveCN101644677AEasy to operateLess distracting factorsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationElement analysisAlloy
The invention relates to a method for detecting the element content in alloy or ore by utilizing an ICP emission spectrometer, comprising the following steps: placing the alloy or the ore in solvent,heating and leading the alloy or the ore to be dissolved fully in solution to obtain mixed solution; diluting the mixed solution to obtain test solution; selecting the optimal analysis line of each element according to the composition of substrate of the alloy or the ore; preparing a set of corresponding standard solutions with the concentration sequencing from low to high according to the concentration index of each element in the alloy or the ore; introducing the standard solutions to the ICP emission spectrometer to measure the emission light intensity of the element analysis line and to draw a standard curve; introducing the test solution to the ICP emission spectrometer to measure the emission light intensity corresponding to each element; and determining the content of each element according to the standard curve. The method can detect simultaneously the content of the required element and oxide only by one solution, therefore, the invention has simple operation, shortened measuring cycle, stable detection results with high accuracy degree.
Owner:DATONG ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE OF NCR
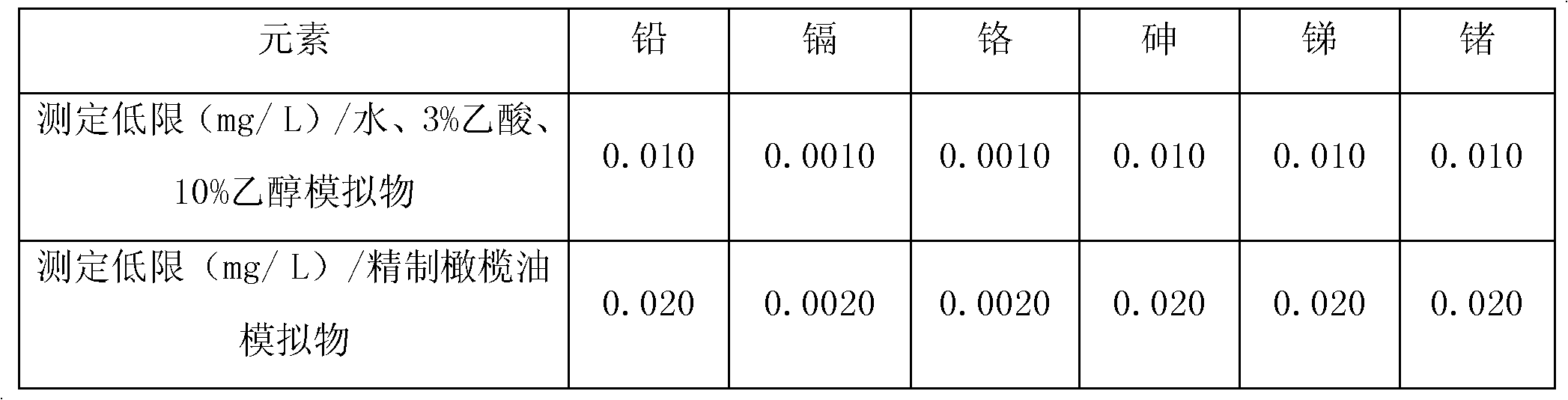
Detection method for simultaneously measuring migrated masses of lead, cadmium, chromium, arsenic, antimony and germanium in plastic packaging container for foods by ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry) method
InactiveCN102023155AEfficient determinationEasy to measurePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical emission spectrometryRadio frequency
The invention relates to a detection method of harmful element migrated masses in a plastic packaging container for foods, in particular to a detection method for simultaneously measuring migrated masses of lead, cadmium, chromium, arsenic, antimony and germanium in a plastic packaging container for foods by an ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry) method. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out a migration test; 2, carrying out a blank test; and 3, carrying out measurement by an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. The ways of RF (radio frequency) power amplification (for a 3% acetic acid simulacrum test solution), ethanol removal (for a 10% ethanol simulacrum test solution) and microwave digestion (for a delicate olive oil test solution) are used to efficiently, simply and quickly measure the migrated masses of various harmful elements in four simulacrums in the plastic packaging container for the foods simultaneously.
Owner:THE INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT ZHEJIANG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Microplasma emission spectrometer
A microplasma emission spectrometer is described that includes a chamber for confining a sample volume of gas. A microplasma source that includes a resonant antenna structure generates a microplasma in the chamber from the sample volume of gas. A RF power supply provides power to the resonant antenna structure that generates the microplasma from the sample volume of gas. A spectrally sensitive detector is optically coupled to the microplasma. The entrance of the spectrally sensitive detector has dimensions and is positioned so that emissions from at least one-tenth of a total volume of the microplasma are transmitted through the entrance of the spectrally sensitive detector.
Owner:INFICON INC
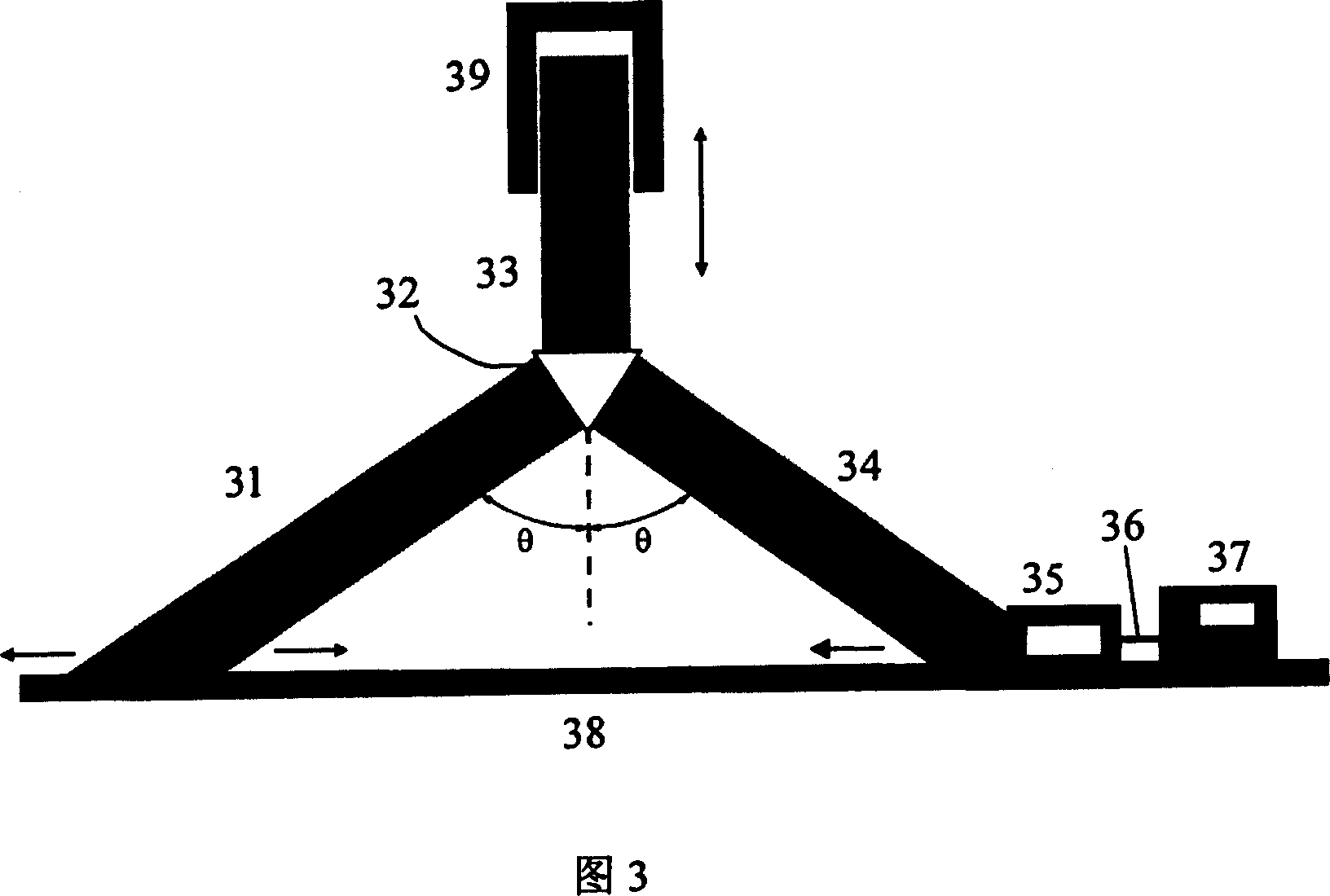
On-site analyzer having spark emission spectrometer with even-wearing electrodes
InactiveUS6455850B1Easy to measureEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical spectrometer
An apparatus (10) for analyzing lubricant oils and functional fluids includes an optical emission spectrometer (OES) (26) having a substantially continuously valued wavelength versus intensity output (140). The OES (26) analyzes light captured from a spark emission stand (58) through which the fluid sample is flowed. An expert system (160-172) operates according to a set of Rules, and generates diagnostic text (174) for an operator based on the information about the fluid sample provided by the OES (26) and other measurement devices. The apparatus (10) includes an airflow passage (154) in the OES (26) spark enclosure that is characterized by airflow substantially parallel to the spark electrodes (128, 130) promoting even-wear of the electrodes.
Owner:SPECTRO SCI INC
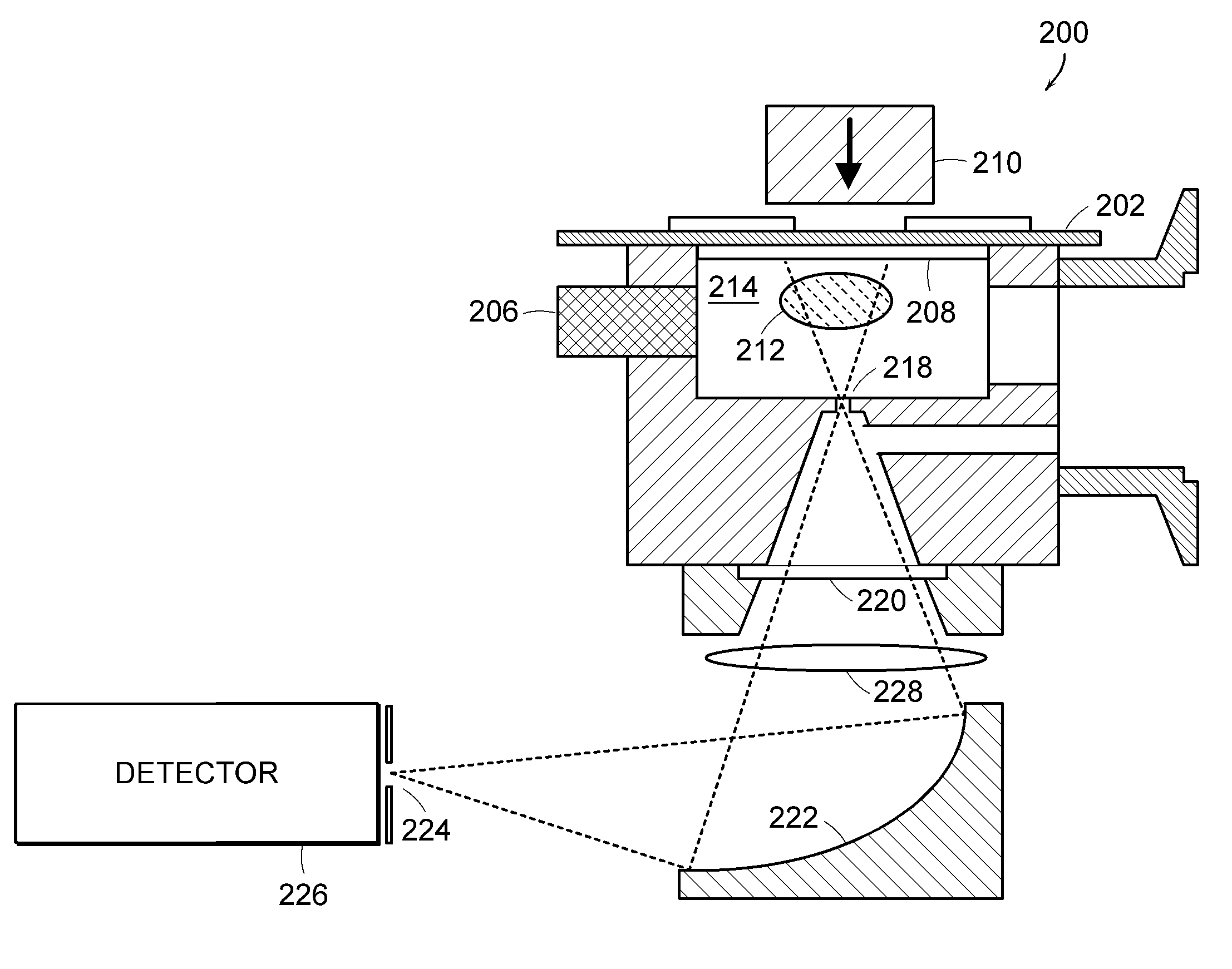
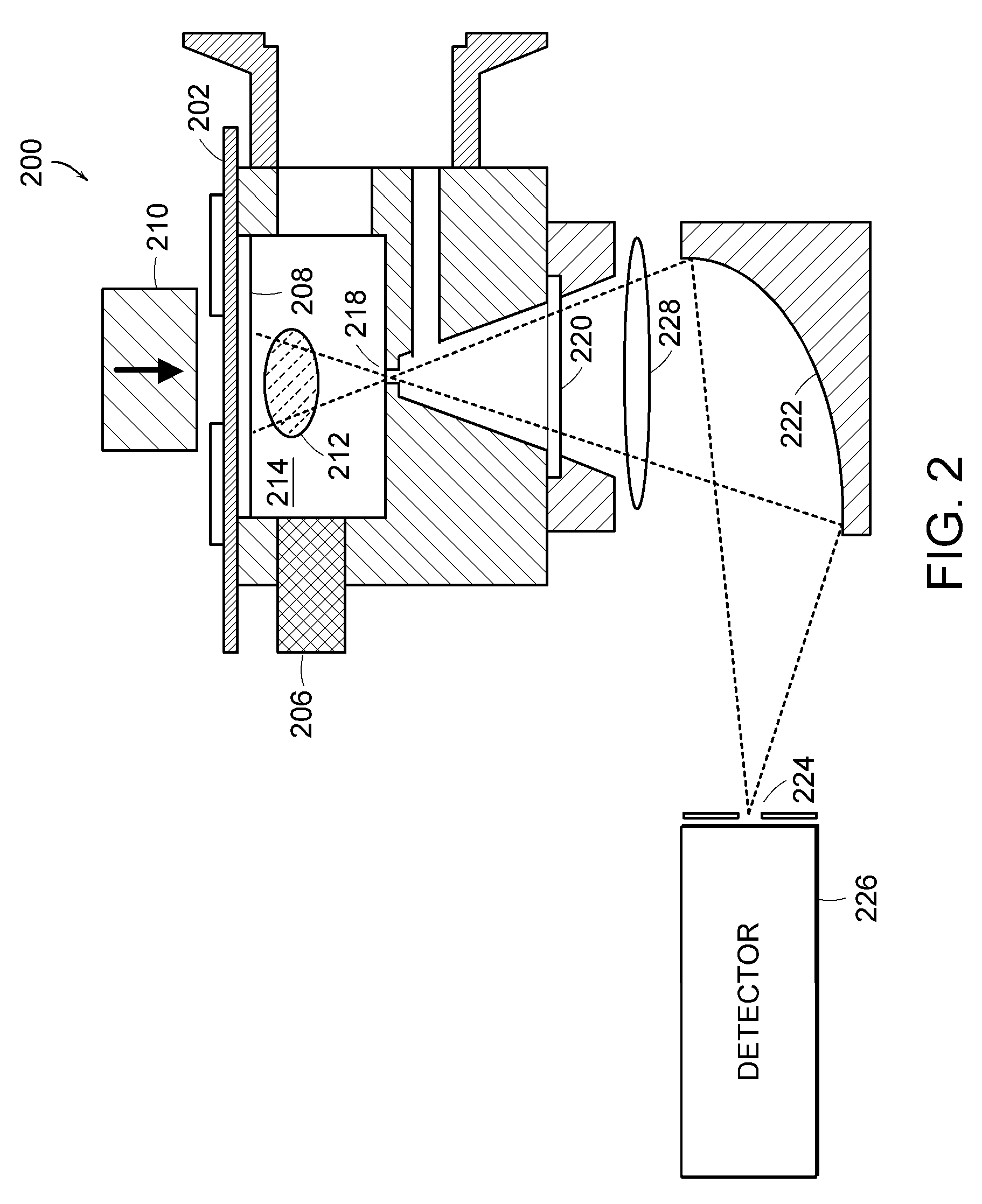
Analytical laser ablation of solid samples for ICP, ICP-MS, and FAG-MS analysis
InactiveUS20090073586A1High sensitivityReduce decreaseMirrorsAnalysis by thermal excitationMolecular analysisPath length
The present invention facilitates improvements in laser ablation of solid samples to be analyzed by an external inductively coupled plasma (ICP) emission spectrometer, ICP / mass-spectrometer (ICP-MS), or flowing afterglow (FAG) mass spectrometer (FAG-MS) for elemental analysis (ICP and ICP-MS) or molecular analysis (FAG-MS). A novel invention mirror-with-hole beam combiner eliminates chromatic aberration in the invention sample view and allows rad-hardening the laser ablation invention for use in a radiation hot cell for analysis of high activity nuclear waste. Many other novel invention rad-hardening attributes facilitate a comprehensive rad-hardened laser ablation system (the world's first). In other embodiments, invention novelties include unusually large homogeneous focused laser spot diameters, unusually long laser objective lens focal length, wide range operationally variable laser path length with built-in re-alignment, operationally variable demagnification ratio and diameter of the focused laser spot, the use of significantly higher powered SMR lasers in a large spot diameter to facilitate high sensitivity bulk analysis of solid samples, a demountable and gravitationally self-sealing stack assembly laser ablation cell, and the world's first auto-samplers (mechanized sample changers) for analytical laser ablation.
Owner:FRY ROBERT C +3
Multifunctional light-absorbing, scattering and transmitting spectrograph based on surface plasma wave
InactiveCN101074921AAchieving Independent AcquisitionPhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsData acquisitionSpectrograph
A multifunction spectrograph based on surface plasma wave consists of light source, modulation unit of incoming light, modulation unit of angle, sample conveying unit, sample electromagnetic coupling reactor, detection unit of emission light, detection unit of reflection light, data collection / management unit and temperature control unit. It is featured as coupling and resonating plasma at surface of incoming-light wave resultant sensing film by said spectrograph for making fade field at surface of said sensing film be intensified so as to excite scattered light by utilizing intensified fade field.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
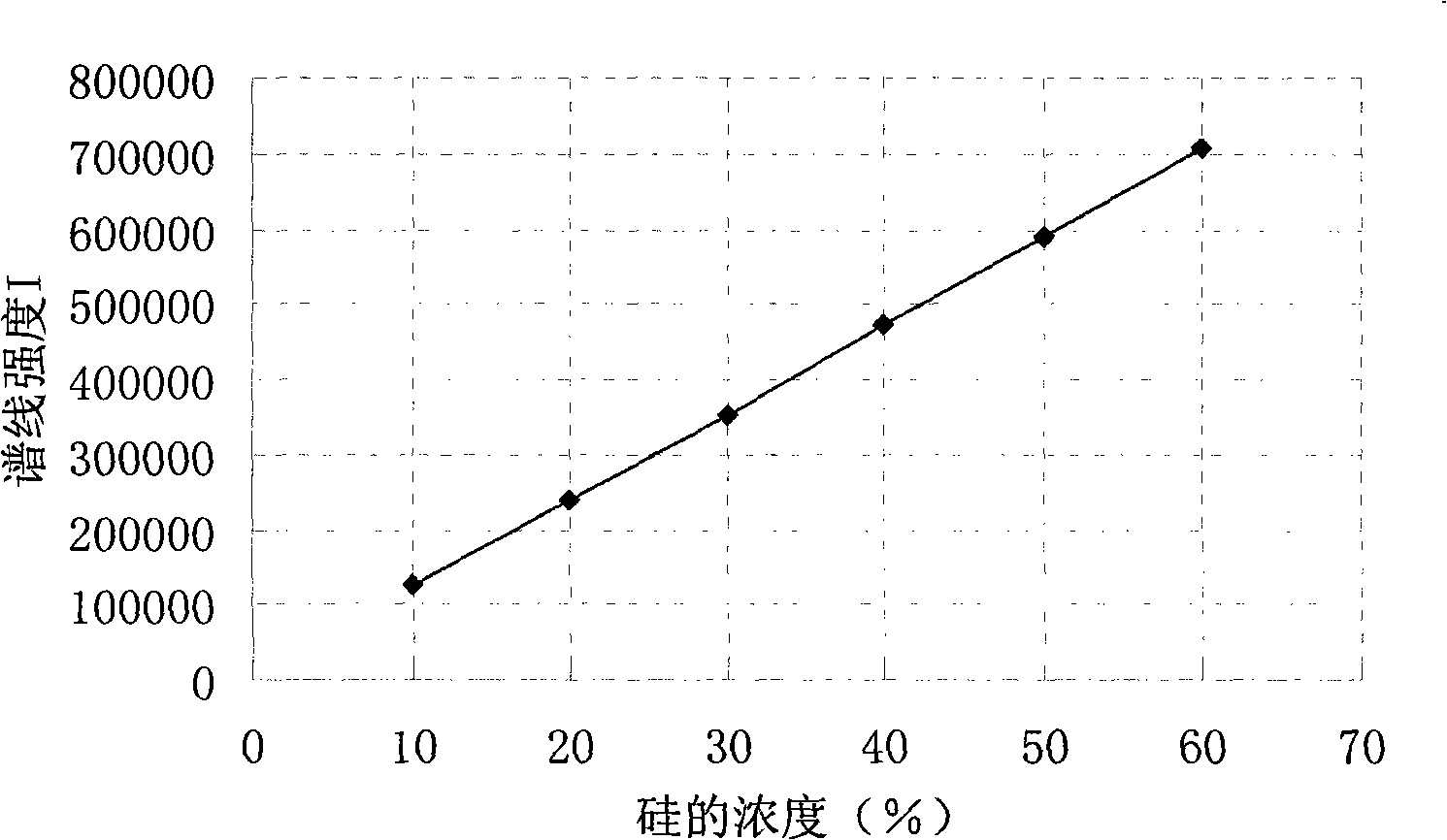
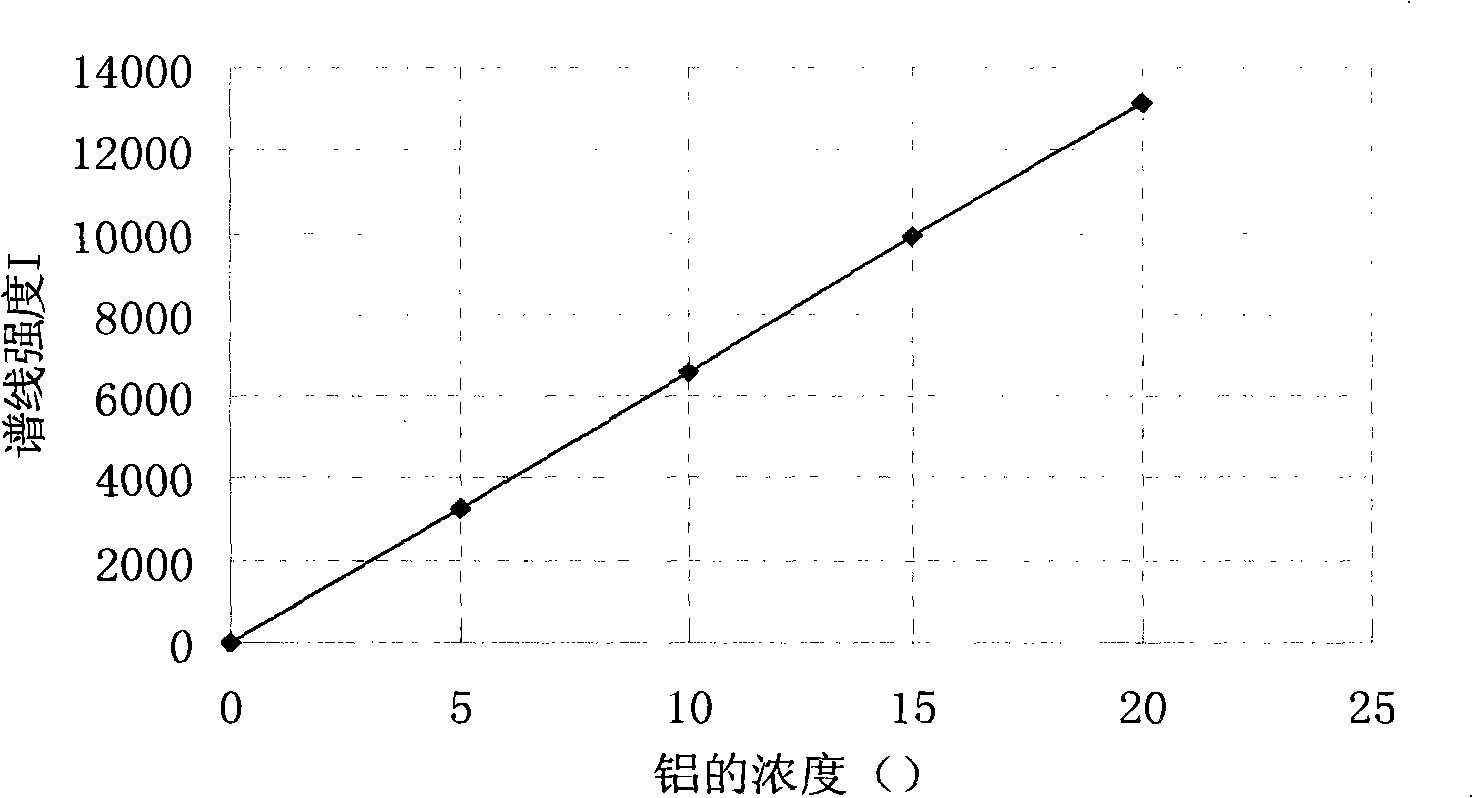
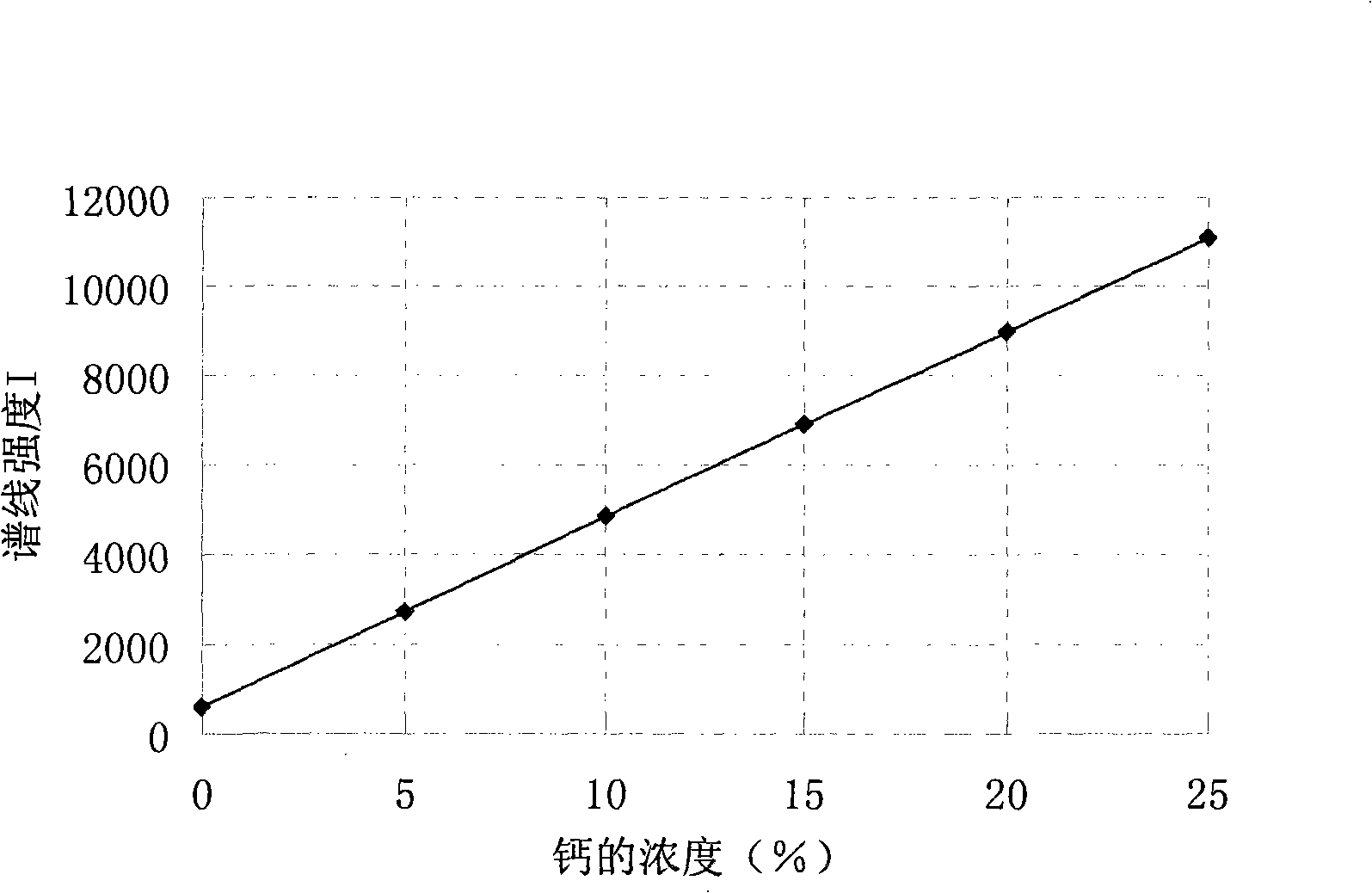
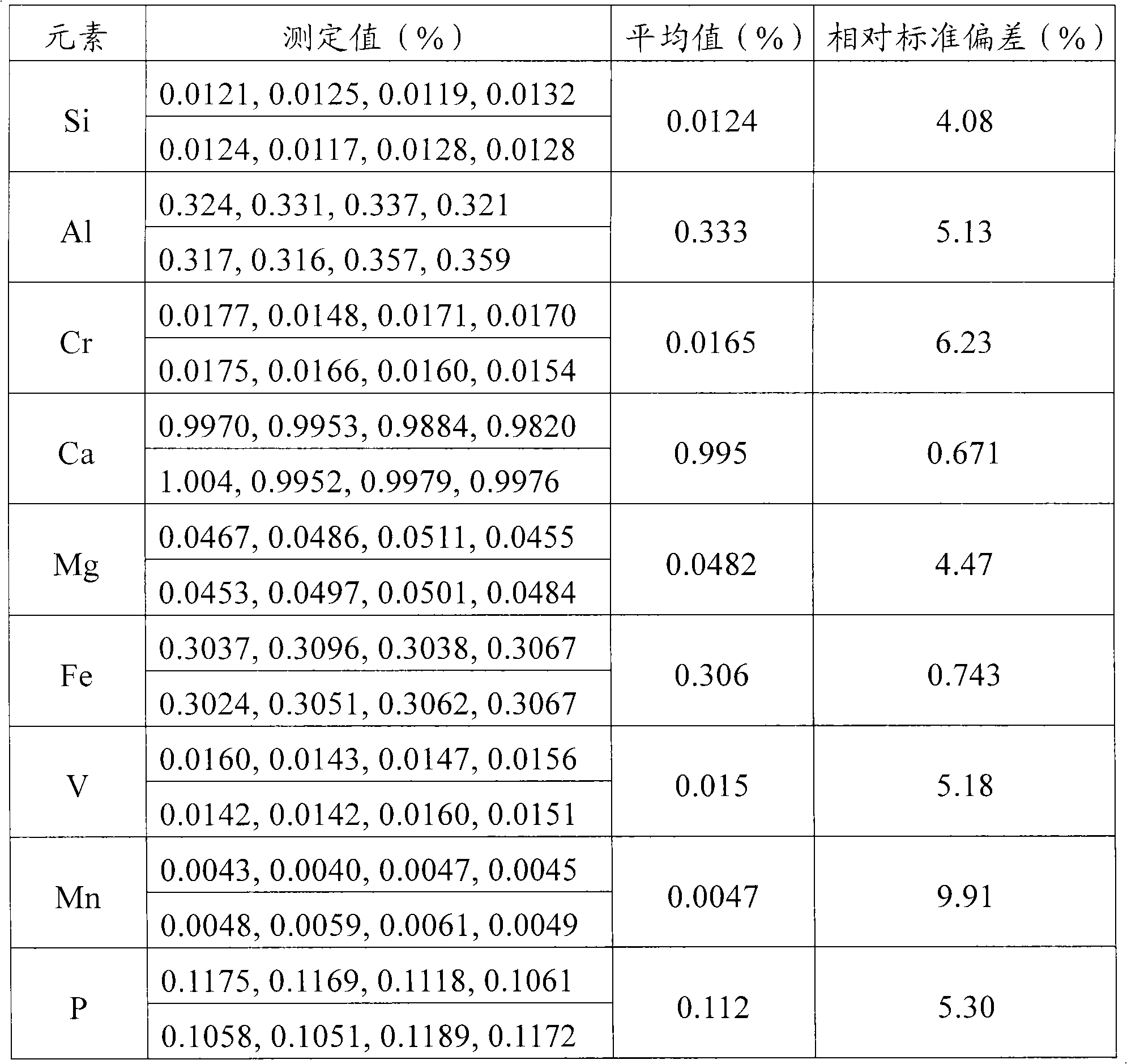
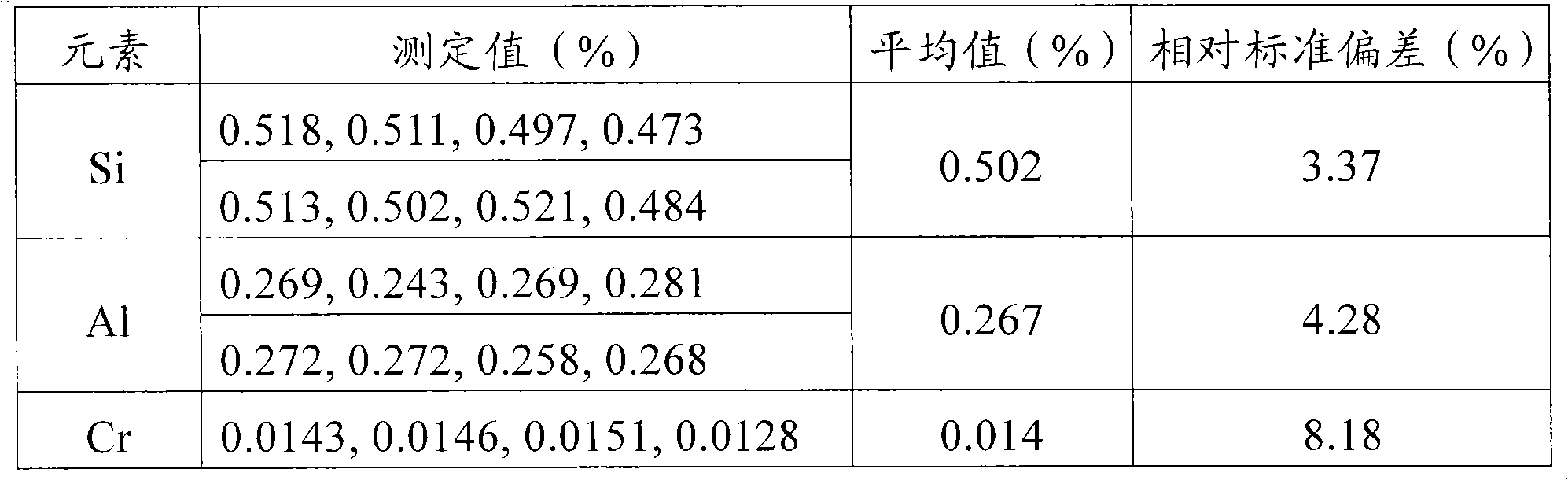
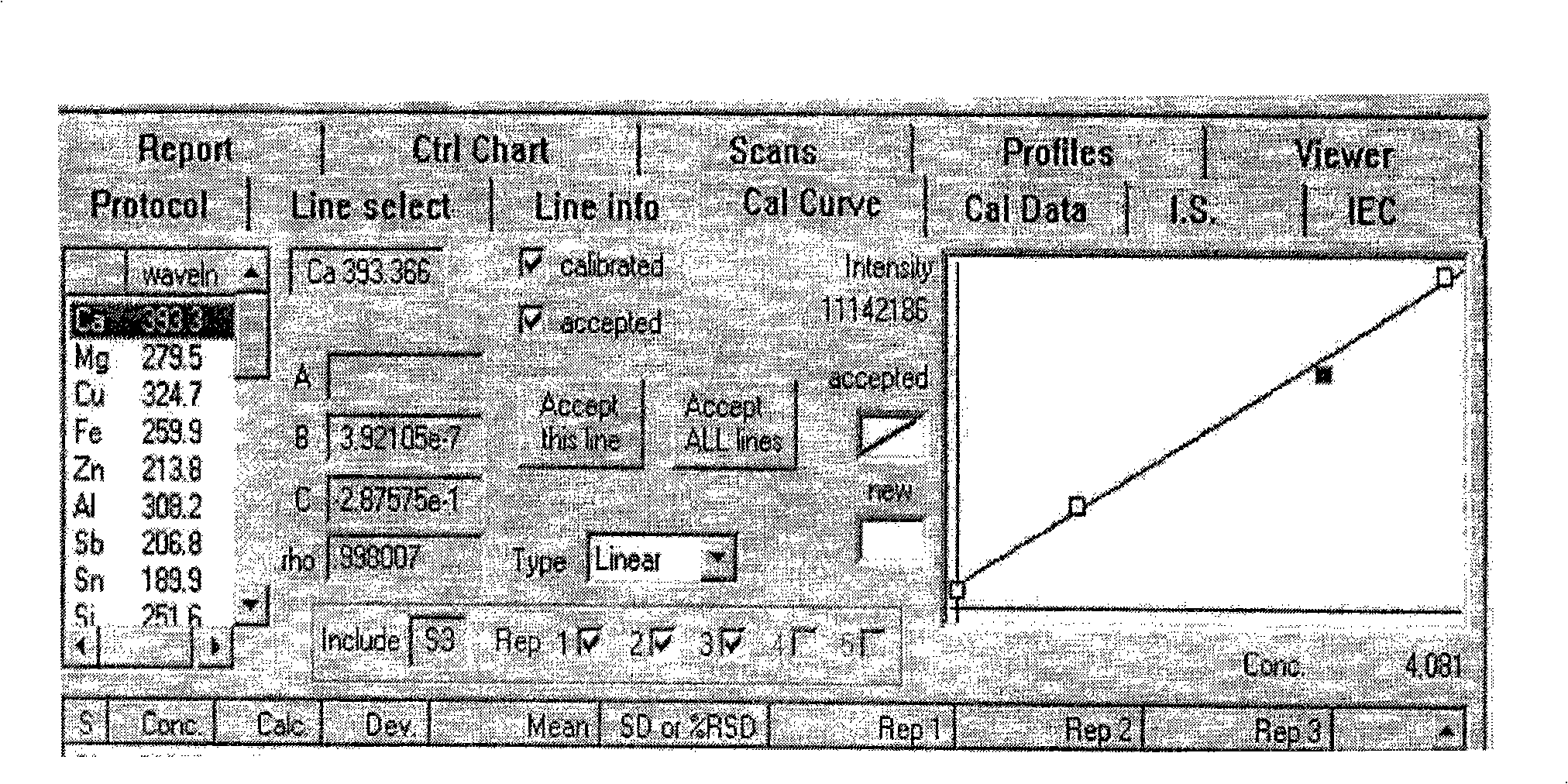
Method for simultaneously measuring elements of silicon, aluminum, calcium and barium
InactiveCN101344487AAccurate measurementReduce pollutionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationRelative standard deviationAcid dissolution
The invention discloses a method that can simultaneously analyze various elements, aims at solving the defects that currently the analysis of various elements cannot be finished at one time, and consequently the analysis time is long and the reagent usage is large, and discloses a method that can simultaneously measure the elements of silicon, aluminum, calcium and barium and comprises the following steps: a test sample is preprocessed through the acid dissolution method, microwave-digested, naturally cooled, and then placed into a volumetric flask with scales, diluted and shaken until well distributed, a solution with a standard working curve is prepared, an atomic emission spectrograph of inductance coupled plasmas is started and led to reach the measurement requirement, a plasma torch is lighted, the relative standard deviation of the plasma torch is led to be less than 5 percent, wavelength of each element is chosen, the working curves are plotted, and the content of each element is computed. The method combines the microwave digesting sample dissolution technique with the atomic emission spectrograph of inductance coupled plasmas, can simultaneously analyze nine elements including silicon, etc., is accurate and quick, has greatly reduced reagent usage, and reduces the environmental pollution that is caused by chemical reagents.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Method for measuring trace elements in high titanium high boiler slag
InactiveCN101349648ABreak down completelyShort processing timeAnalysis by thermal excitationTrace elementBoiler slag
The invention relates to a method for measuring microelements in high titanium blast furnace slag, which comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting an alkali fusion method to pre-process samples, and leading the samples to be totally conversed into soluble salt, and preparing into sample solution, secondly, preparing standard solution of iron, manganese, vanadium and phosphor with different concentrations, thirdly, respectively measuring the spectral line strength of calcium in the standard solution of iron, manganese, vanadium and phosphor with different concentrations, utilizing the concentration of elements to be the abscissa and the spectral line strength to be the longitudinal coordinate to draw a working curve, fourthly, measuring the intensity of the spectral lines of iron, manganese, vanadium and phosphor in sample solution under the condition which is the same to the step three, and calculating and assuring the content of the four elements in each sample solution according to the working curve. The invention has the advantages that the method is simple and fast, which has little dosage of agents and samples, and can simultaneously measure a plurality of elements. The method shortens analysis time, and lowers test cost.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Method for determining niobium element content in ferroniobium
InactiveCN101609048AAvoid hydrolysisBreak down completelyAnalysis by thermal excitationPretreatment methodNiobium
The invention relates to a method for determining niobium element content in ferroniobium, which comprises the following steps: a sample is weighted and put in a polytetrafluoroethylene beaker and deionized water is added for humidifying the sample; hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid are added into the sample, and then are heated so that the sample is slowly dissolved; after the sample is completely dissolved, the breaker is taken down and cooled; after the sample is cooled to room temperature, the volume is metered; reagent blank without the sample is adopted, and then standard solution of niobium element with different volumes is added, and finally deionized water is added and the volume is metered; spectral line strength of niobium element in standard solution is determined under the working condition of a setting inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer and a working curve is drawn; the spectral line strength of niobium element in ferroniobium sample solution to be determined is determined, and then a computer automatically determines the concentration of niobium element in sample solution according to the working curve. The method mainly solves problems of long operational process, narrow measuring range and the like, determines appropriate sample processing methods and analytic conditions of instruments, and realizes effectively, rapidly and accurately measuring niobium element in ferroniobium.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Digestion method and detection method of titanium-rich material
InactiveCN101315316AEfficient and fast digestionReduce salt concentrationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationHydrofluoric acidMicrowave
The invention provides a method for digesting a rich titanium product and a method for detecting the rich titanium product. The method comprises the following steps: placing a sample of the rich titanium product in a container; adding nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid into the container; sealing the container; conducting digestion with microwave to obtain a digestion solution. The method comprises the step of adopting an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer to detect the digestion solution prepared through the above steps. According to the digesting method and the detecting method, a plurality of key impurities with the content ranging from 15% to 0.001%, which determine the quality of the rich titanium product, can be simultaneously detected. Furthermore, the accuracy, the precision and the working efficiency of detection data are greatly improved.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +2
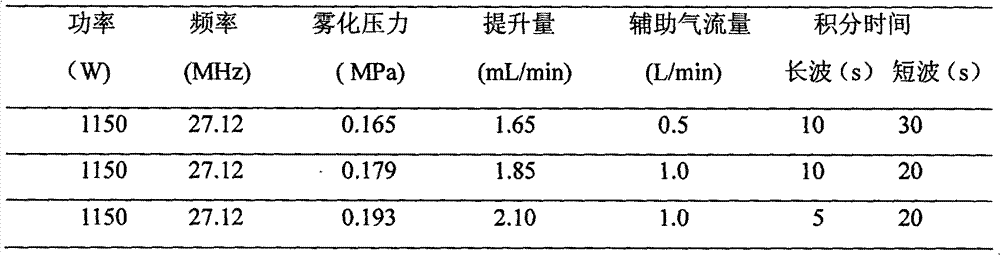
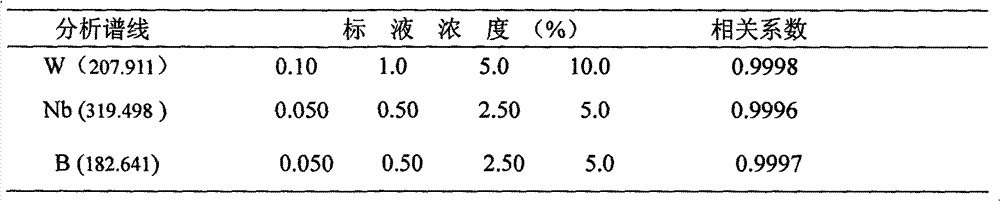
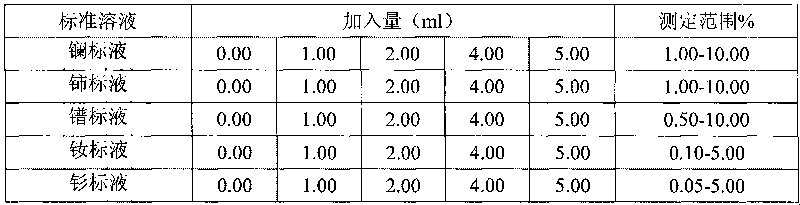
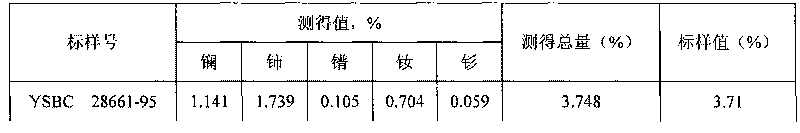
Method for simultaneously determining W, B and Nb in high-alloy deposited metal
ActiveCN102954958AIntensity automatically determinedAvoid hydrolysisPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationAlloySolvent
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining W, B and Nb in a high-alloy deposited metal. The method comprises the following steps: placing a high-alloy deposited metal sample in a mixed acid solvent comprising hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, digesting through utilizing a microwave digestion instrument to prepare a W, B and Nb simultaneously-dissolved solution to be tested, selecting the optical analytic spectral lines of all elements according to the matrix of the sample and the composition of coexistence elements, determining a spectral interference correcting method, preparing a group of standard solutions having concentrations from the low to the high through a coupling method of a matrix close to the sample matrix, introducing the standard solutions to ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometer) under optimized apparatus working parameters, drawing a working curve according to the concentrations and the intensities of elements to be tested, introducing the sample solution to the ICP-AES, testing to obtain the intensities to be tested, and determining the contents of W, B and Nb in the sample solution according to the working curve. The method has the advantages of less reagent application amounts, reduction of the pollution of chemical reagents to the environment, and effective satisfying of the practical needs of the scientific research and the production.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Method for measuring rare earth component in rare earth magnesium alloy
The invention relates to the technical field of ferrous metallurgical analysis, and discloses a method for measuring a rare earth component in a rare earth magnesium alloy. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a sample through a nitric acid and a hydrofluoric acid; fuming the sample through a perchloric acid; diluting the sample to a certain volume; introducing atomization solution into an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer; measuring the intensity of a spectral line to be tested; and calculating the concentration of the corresponding element of the substance to be tested according to the intensity of the spectral line which is measured by the standard substance at known concentration. The method has the advantages of conveniently, quickly and accurately analyzing the rare earth component in the rare earth magnesium alloy and ensuring smooth production.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Analytical laser ablation of solid samples for ICP, ICP-MS, and FAG-MS analysis
InactiveUS8274735B2Eliminate chromatic aberrationMirrorsAnalysis by thermal excitationMolecular analysisPath length
The present invention facilitates improvements in laser ablation of solid samples to be analyzed by an external inductively coupled plasma (ICP) emission spectrometer, ICP / mass-spectrometer (ICP-MS), or flowing afterglow (FAG) mass spectrometer (FAG-MS) for elemental analysis (ICP and ICP-MS) or molecular analysis (FAG-MS). A novel invention mirror-with-hole beam combiner eliminates chromatic aberration in the invention sample view and allows rad-hardening the laser ablation invention for use in a radiation hot cell for analysis of high activity nuclear waste. Many other novel invention rad-hardening attributes facilitate a comprehensive rad-hardened laser ablation system (the world's first). In other embodiments, invention novelties include unusually large homogeneous focused laser spot diameters, unusually long laser objective lens focal length, wide range operationally variable laser path length with built-in re-alignment, operationally variable demagnification ratio and diameter of the focused laser spot, the use of significantly higher powered SMR lasers in a large spot diameter to facilitate high sensitivity bulk analysis of solid samples, a demountable and gravitationally self-sealing stack assembly laser ablation cell, and the world's first auto-samplers (mechanized sample changers) for analytical laser ablation.
Owner:FRY ROBERT C +3
Method for determining impurity content in high-titanium slag
InactiveCN102253030AEasy to measureAccurate measurementPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationFritImpurity
The invention discloses a method for determining the impurity content in high-titanium slag, and belongs to the metallurgical chemical field. According to the method, a high-titanium slag sample is molten by a mixed flux; a frit is leached by a sulfuric acid solution to prepare a test solution; and the impurity component in the diluted high-titanium slag test solution is determined by an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer. With the invention, the content of the impurity component in high-titanium slag can be determined accurately, simply, and rapidly.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Method for measuring content of boron in cobalt-base alloy
ActiveCN101718688AAvoid interferenceImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsElement analysisMaterial resources
The invention belongs to a technique for analyzing trace elements of an alloy, and relates to a method for measuring the content of boron in a cobalt-base alloy. By adopting an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and treating a sample of the cobalt-base alloy in particular a high-tungsten sample by using 20mL of hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, the method solves the puzzling problems that the past dissolved sample has large reagent dosage and high reagent blank and cannot be measured normally by an instrument; by performing interference experiments and spectrogram analyses, the method finds the optimal analytical line, overcomes the interferences caused by a plurality of elements such as major elements of cobalt, chromium, tungsten and the like in the cobalt-base alloy, and improves the measuring accuracy; the method has wide measuring ranges, the measuring lower limit is 0.002 percent, and the measuring upper limit is 0.20 percent and is 101 times of the measuring lower limit; and the method can perform measurement quickly, is simple and convenient to operate, and saves a large quantity of manpower and material resources.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
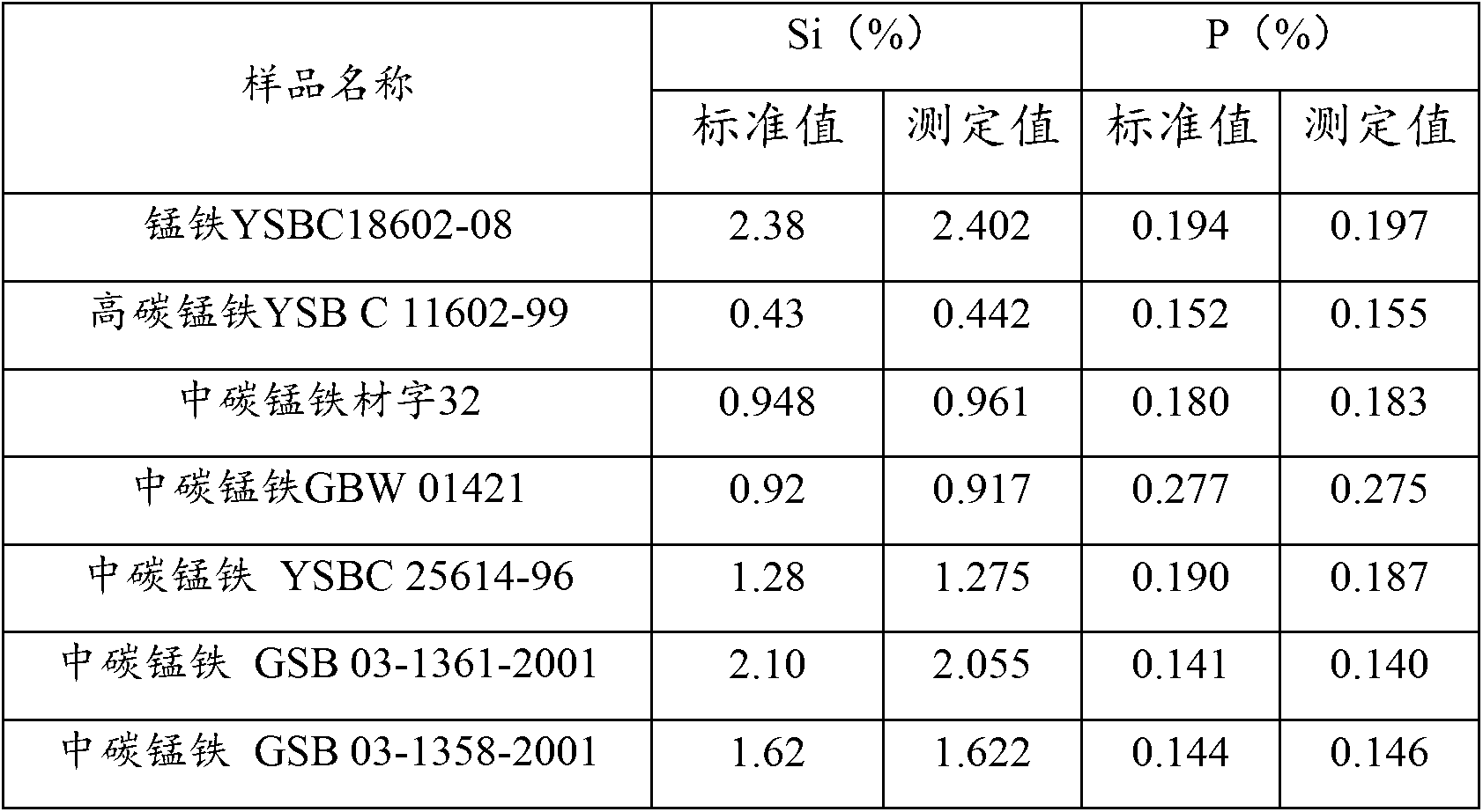
Method for measuring content of silicon and phosphorus in ferromanganese iron by inductively coupled plasma spectrum emission instrument
ActiveCN103175824AImprove accuracyRapid determinationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationUltimate tensile strengthInductance
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of silicon and phosphorus in ferromanganese iron by an inductively coupled plasma spectrum emission instrument. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing an atomized solution of a ferromanganese iron sample and standard solutions comprising a manganese standard solution, a phosphorus standard solution and a silicon standard solution; and introducing the atomized solution into an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, and measuring the spectral line intensity of an element to be measured, thus obtaining the content of silicon and phosphorus in the ferromanganese iron sample according to the spectral line intensity measured via the standard solutions with given concentrations. Due to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the content of silicon and phosphorus in ferromanganese iron can be rapidly and accurately measured.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Method for analyzing and measuring typical metal in circuit board of discarded electrical equipment
InactiveCN102169091ADosage ratio optimizationWith strong acidPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationDigestionRefrigerated temperature
The invention relates to a method for analyzing and measuring typical metal in a circuit board of discarded electrical equipment and relates to the technology for pre-treating the circuit board of discarded electrical equipment and detecting and analyzing the content of the typical metal element. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a sample of the circuit board part of discarded electrical equipment and then performing the operations of surface dressing, cleaning, and rough and fine grinding on the sample; adding a proper amount of digestion reagent into the prepared sample, digesting the prepared sample by using a microwave digestion device and then extracting metal matter from the discarded circuit board; and using an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer to analyze the nature and quantity of the digested sample. According to the method, the operations of sample grinding and digesting are simple, the reagent consumption is less, the analysis result is accurate and reliable, the detection concentration range is wide, the technical problem of difficultly pre-treating the circuit board sample is solved, and the method is suitable for quickly identifying and accurately measuring the typical metal elements in the circuit boards of various discarded electrical products (such as televisions, refrigerators, washing machines, computers, printers, and the like) and the typical metal elements in the corner wastes generated in the circuit board production process.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for detecting content of main element in carbon coated lithium iron phosphate or lithium manganese ferric phosphate
InactiveCN105372229AUse less consumablesLess acid consumptionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationLithium iron phosphatePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for detecting the content of a main element in carbon coated lithium iron phosphate or lithium manganese ferric phosphate. The method comprises the steps of 1 sample pretreatment, wherein a sample to be detected is cleared up through acid and transferred, volume metering and still standing are carried out, and after a solution is layered, a middle clear part is sucked as liquid to be detected; 2 standard curve drawing, wherein a series of mixed standard solutions are prepared according to the variety of the main element to be detected, an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer is utilized for carrying out testing, and a standard curve is drawn; 3 main element content measuring, wherein the inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer is used for measuring the content of the main element in the solution to be detected. The pretreatment process is simple, the analysis result is accurate, the content of the main element in carbon coated lithium iron phosphate or lithium manganese ferric phosphate can be measured fast, accurately and quantitatively, and reliable guarantees are provided for improving the product quality of lithium iron phosphate and lithium manganese ferric phosphate and controlling the intermediate technological process.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Detection method for micronutrient levels in liquid milk or milk powder
InactiveCN101315387AEasy to handleProcess loss is smallAnalysis by thermal excitationBiological testingDiffusion functionLiquid milk
The invention relates to a method for detecting the microelement content of liquid milk or milk powder. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, a standard curve is made; secondly, a sample is detected; thirdly, the detected result of the sample is compared with the standard curve, and the content of the microelement in the sample is obtained; and a detection apparatus is an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer. Through the diffusion function of cesium chloride, the surface activity of the sample is changed by utilizing triton x-100, and the sample is added to beryllium standard liquid to be compared, and atomized through an instrument atomizing chamber and is quantified by adopting a multi-reaction monitoring mode. The instrument detection limit of the method is 0.024 to 0.21 Mu g / ml, in an element linear range, a correlation coefficient r is above 0.999, and the recovery rate is 86.8 percent to 103.8 percent. The method has the advantages that the content of microelements in the liquid milk and the milk powder can be rapidly and accurately measured by the method, the probability of the element loss and the element pollution in the sample preparation process is low, results are accurate and reliable, the repeatability is good, and the sensitivity is high.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA MENGNIU DAIRY IND (GRP) CO LTD
Method for measuring contents of aluminum, calcium, barium, strontium, and phosphorus in silicon-calcium-barium alloy by ICP (inductively coupled plasma)
The invention relates to the technical field of ferrous metallurgical analysis, in particular to a method for measuring contents of aluminum, calcium, barium, strontium, and phosphorus in silicon-calcium-barium alloy by ICP (inductively coupled plasma). The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving a sample with nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, fuming with sulfuric acid, diluting to a certain volume, and introducing an atomized solution into an inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometer to measure the intensity of a spectral line to be measured; and solving the concentration of elements corresponding to substances to be measured based on the measured spectral line intensity of known concentration standard substances. The method has the advantages of no pollution and capability of analyzing and determining the content of the calcium, the barium, the aluminum, the phosphorus and the strontium in the silicon-calcium-barium alloy and meanwhile, separating the barium and the strontium which can not be separated by a chemical analytical method.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
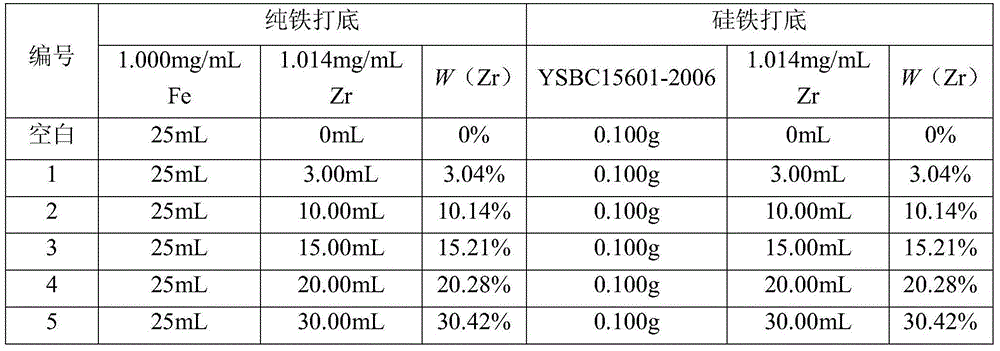
Method for determining zirconium content in silicon-zirconium alloy
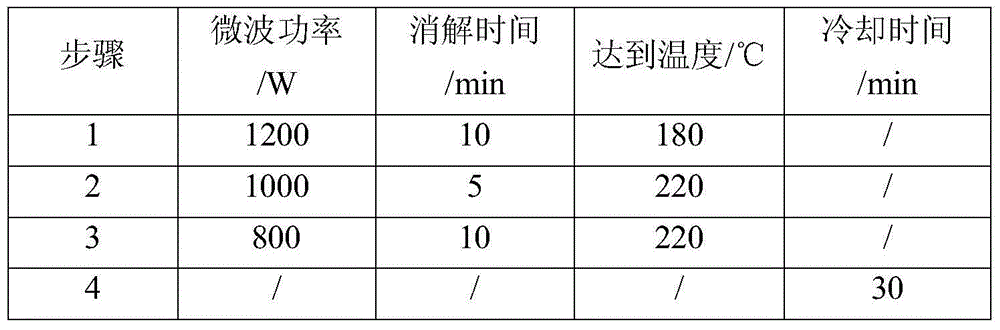
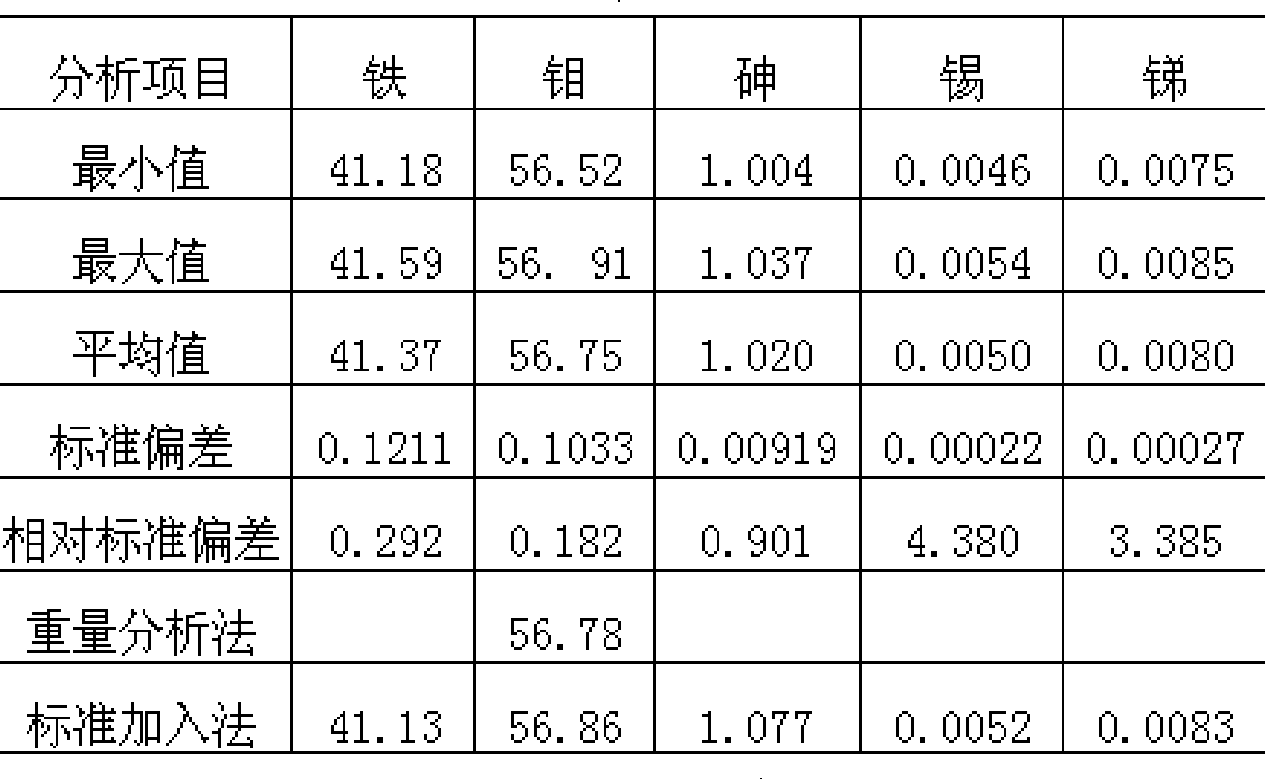
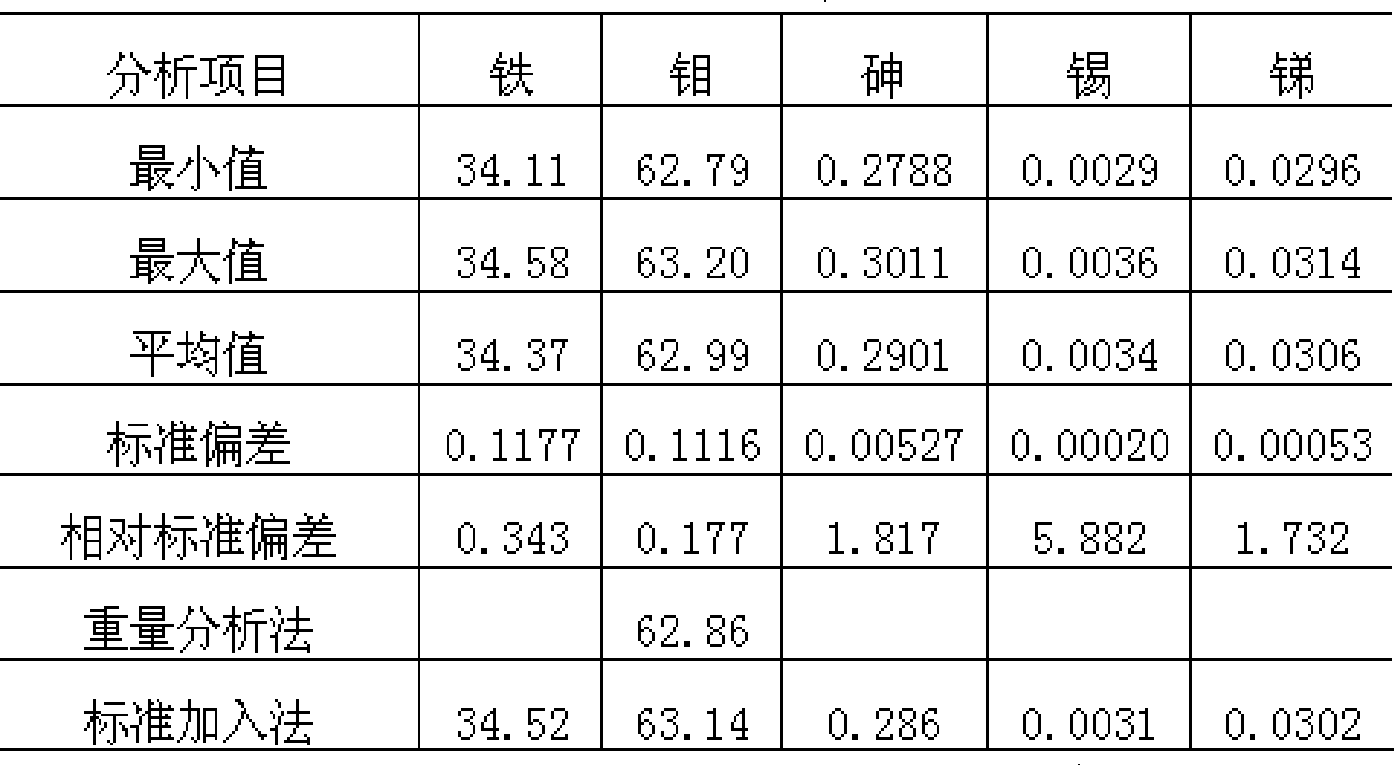
InactiveCN104597037ASolve the problem of cumbersome analysis operation and slow analysis speedReduce dosageAnalysis by thermal excitationFerrosiliconZirconium alloy
The invention relates to a method for rapidly determining zirconium content in silicon-zirconium alloy, belonging to the technical field of chemical analysis tests. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving pure iron or silicon iron as matrix, adding standard solutions with different amounts of zirconium to prepare a standard solution; determining the standard solution by virtue of an ICP-OES to prepare a standard curve; dissolving a sample with one or more of nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid and perchloric acid, and diluting with water to achieve a certain volume; introducing the solution into the ICP-OES to determine to-be-determined spectral line intensity; determining the concentration of a to-be-determined element on a calibration curve. The zirconium content range in the silicon-zirconium alloy can be determined to be 0-30%; the standard solution prepared by the method is similar to sample solution matrix; the matrix effect is removed; the problems of fussy chemical analysis operation and slow analysis speed are solved by virtue of a high-precision analysis instrument; and the method has the advantages of being simple, fast, high in accuracy and precision and the like.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
Method for measuring impurity elements arsenic, tin antimony in ferromolybdenum
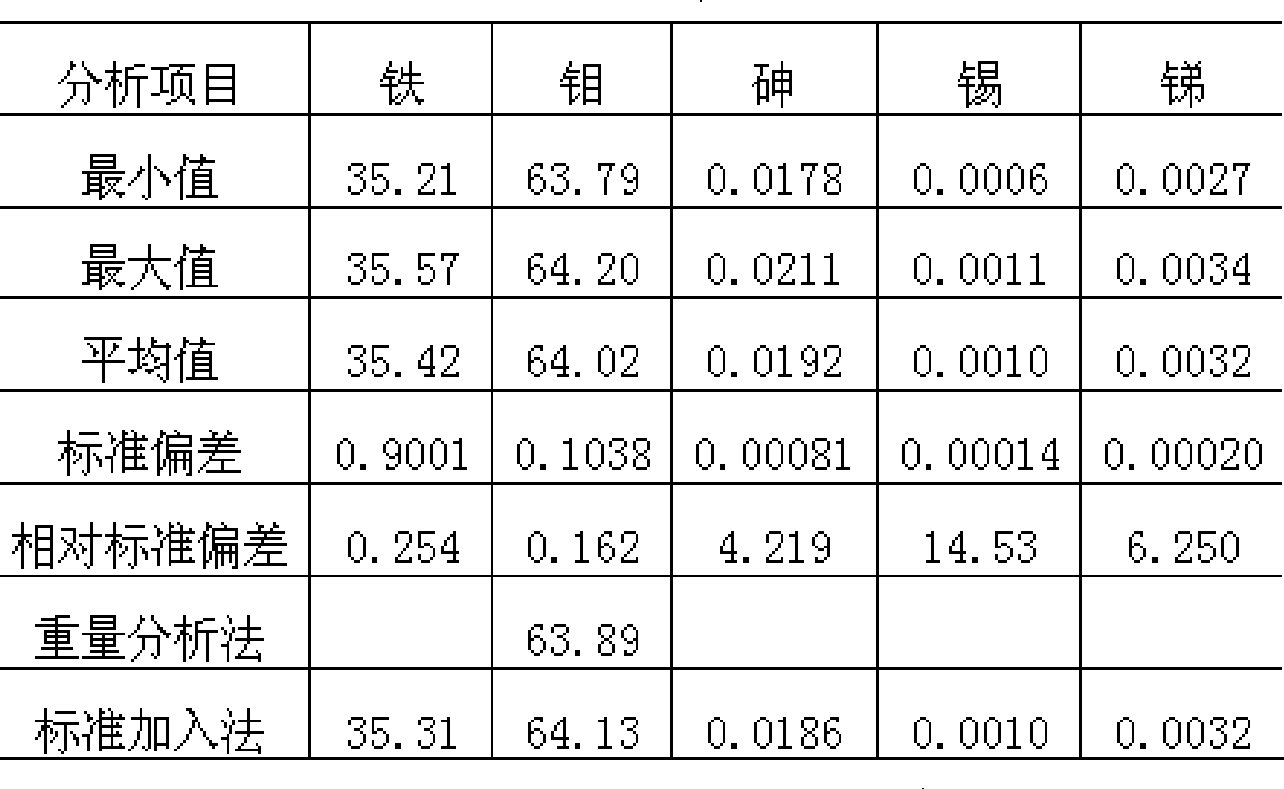
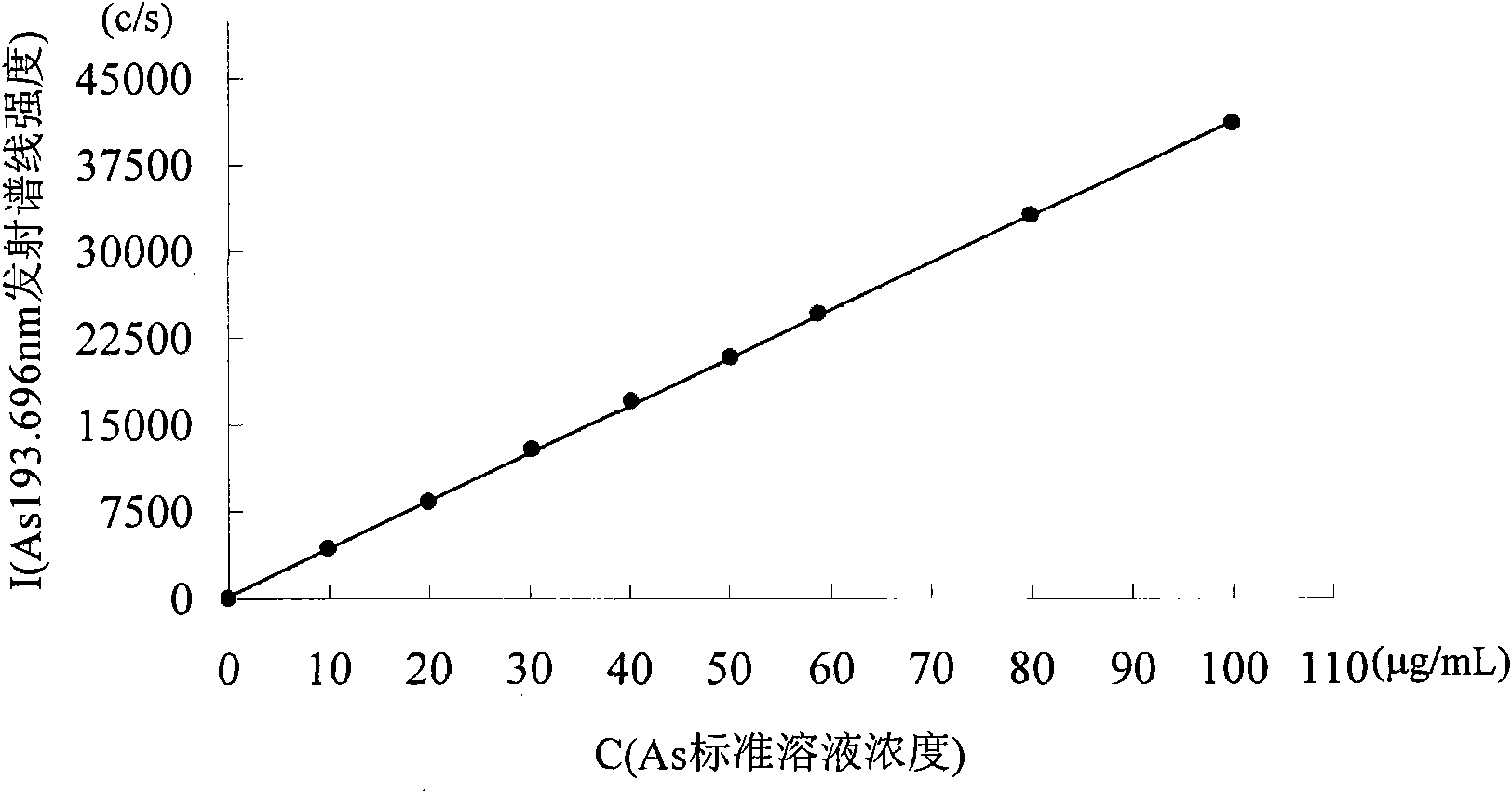
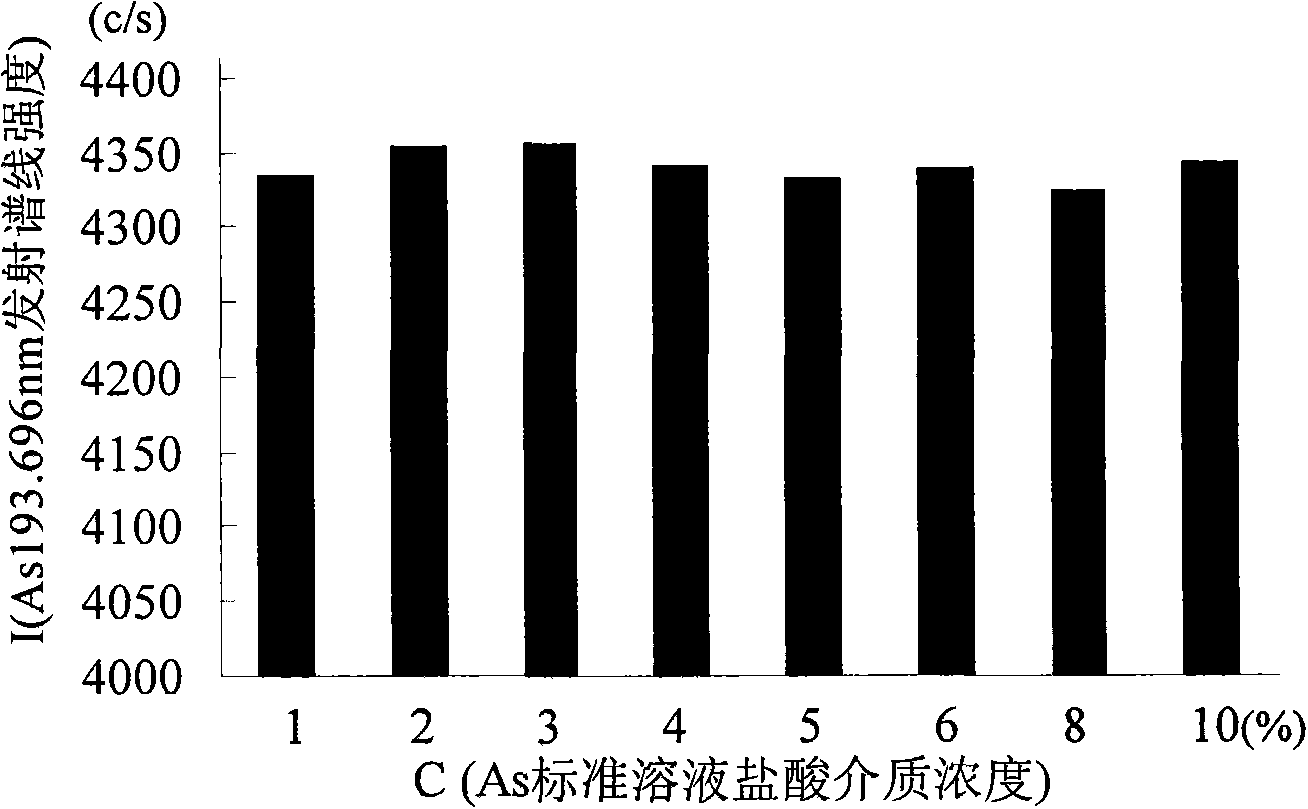
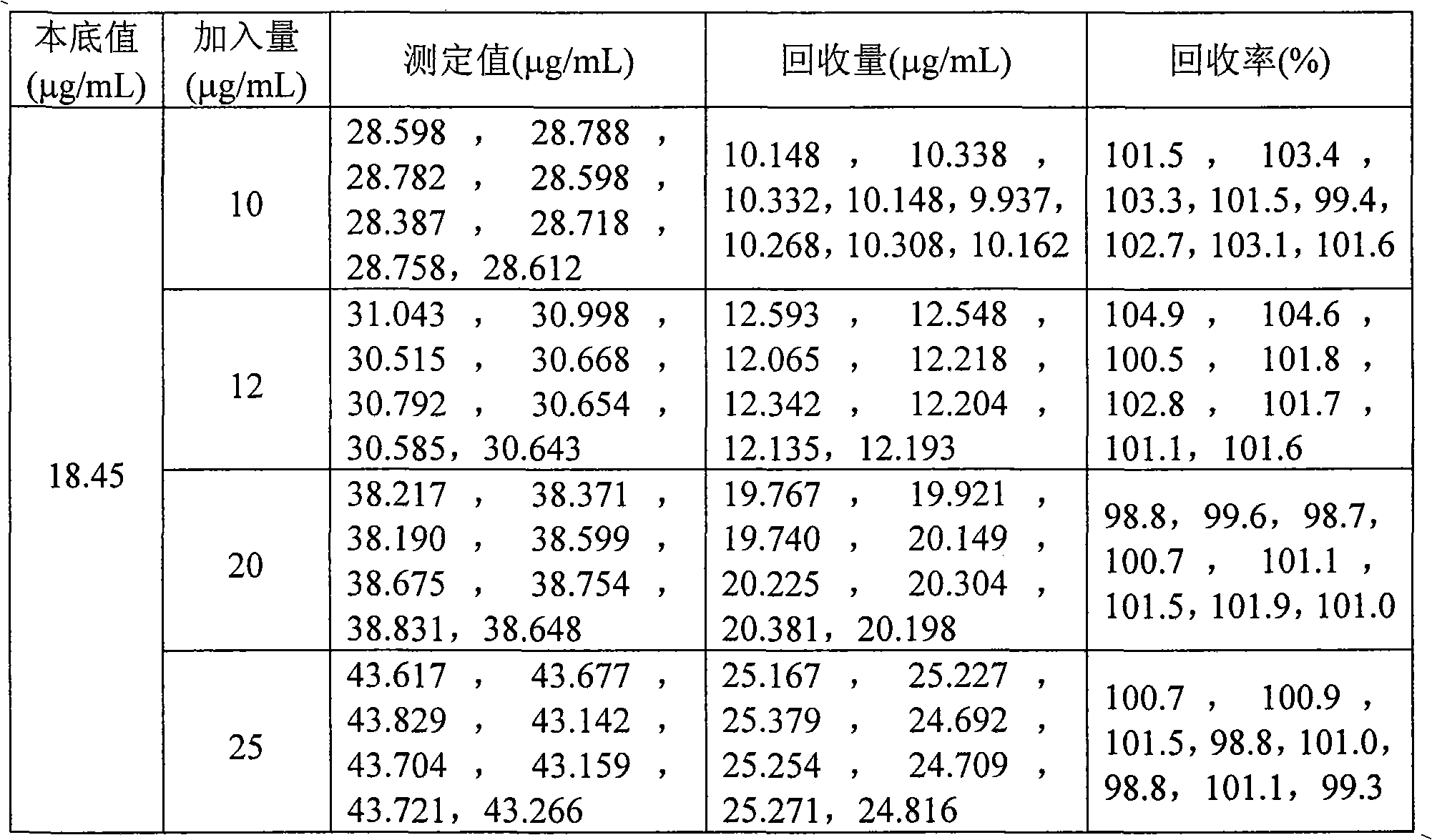
ActiveCN101435775AEasy pretreatmentSuitable for mass production inspectionAnalysis by thermal excitationImpurityAntimony
The invention provides a method for determining arsenic, tin and antimony in ferromolybdenum, which belongs to the field of quantitative analysis in analytical chemistry. The method for determining arsenic, tin and antimony in ferromolybdenum comprises the steps of dissolving a ferromolybdenum specimen in mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, using standard serial solutions to draw a working curve on an inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, deducting interference among elements and background interference through a computer program correction mode and determining arsenic, tin and antimony which are trace detrimental impurity element in a specimen solution. The method does not need to perform separation, enrichment and other fussy operation during specimen pretreatment and only needs to suck the ferromolybdenum specimen solution into an instrument for determination, and the percentage content of trace arsenic, tin and antimony in the specimen can be simultaneously displayed after tens of seconds. The content range that can be directly determined by the method is as follows: 0.005 to 1.00 percent of arsenic, 0.001 to 0.20 percent of tin and 0.001 to 0.10 percent of antimony.
Owner:CHINA ERZHONG GRP DEYANG HEAVY IND
Method for analyzing arsenic content in glass refining agent
InactiveCN101620186AAvoid volatile lossSimplify the analysis processAnalysis by thermal excitationOperabilityDigestion
The invention discloses a method for analyzing arsenic content in a glass refining agent, which comprises the following steps: processing samples by a potassium permanganate preoxidation-hydrofluoric acid wet digestion method to obtain a sample digestion solution; measuring the content of arsenic in the digestion solution by an inductance coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry. By using potassium permanganate as a pre-oxidizing agent to carry out routine wet acid digestion on glass refining agent samples, the method can effectively avoid volatilizable loss of low-valent arsenic components in the preliminary processing of the samples, therefore, a routine inductance coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometer can be used to directly measure the content of the effective content-arsenic in the glass refining agent without allocating a hydride generator or an atomic fluorescence spectrometer. The method has the advantages of high operability, high analysis speed, high accuracy and favorable sensitivity and repetitiveness.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for determining precious metal in platinum-palladium ores
InactiveCN103940805AObserve spectral lines in real timeReal-time observation of measurement resultsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWater bathsOptical Emission Spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for determining precious metal in platinum-group metal ores. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a nickel-sulfonium button from a nickel-sulfonium fire assay enriching sample; (2) grinding the nickel-sulfonium button with a grinder; (3) adding the ground nickel-sulfonium button in a hydrochloric acid solution and heating for dissolving to remove base metal and sulfonium from the nickel-sulfonium button; (4) adding a reductant and a coprecipitator to the solution obtained from the step (3) to recover a small quantity of precious metal lost in the solution; (5) performing suction filtration at negative pressure to obtain a precious metal precipitate; (6) dissolving the precipitate in the step (5) together with a filtering membrane with aqua regia in a water bath and diluting with pure water to a fixed volume; (7) drawing calibration curves of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium by an ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) and determining the intensity of spectral lines of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium in the sample solution; (8) automatically calculating the content of to-be-detected elements by a computer according to the calibration curves and a sample information table. The method has good stability and high result accuracy degree. According to the method, six precious metal elements can be determined simultaneously just by one-time sample weighing and pretreatment, the working efficiency is increased greatly and the detection cost is lowered.
Owner:WANBAO MINING
Method for determination of silicon content in ferro-aluminum manganese
InactiveCN102565026AAnalytical data is reliableFew kindsAnalysis by thermal excitationLinear correlationManganese
The invention provides a method for determination of silicon content in ferro-aluminum manganese, comprising the following steps: dissolving a sample to be tested with hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, introducing the solution into an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrograph, and automatically calculating and displaying the concentration of silicon in the sample of ferro-aluminum manganese according to the standard working curve for silicon stored in the spectrograph. The method of the invention implements the working curves comparison and automatic analysis and verification with the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrograph, so that the working process is greatly simplified with high analysis speed and high accuracy. The standard working curve for calibration of silicon solution is automatically drawn by an analysis software, and the linear correlation coefficient between the sample of ferro-aluminum manganese and the standard working curve is greater than 99.9% so as to provide reliable analytical data for manufacturing plants in a fast and accurate manner; moreover the reagents are less used in terms of category and dosage so as to relatively reduce the environmental pollution.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
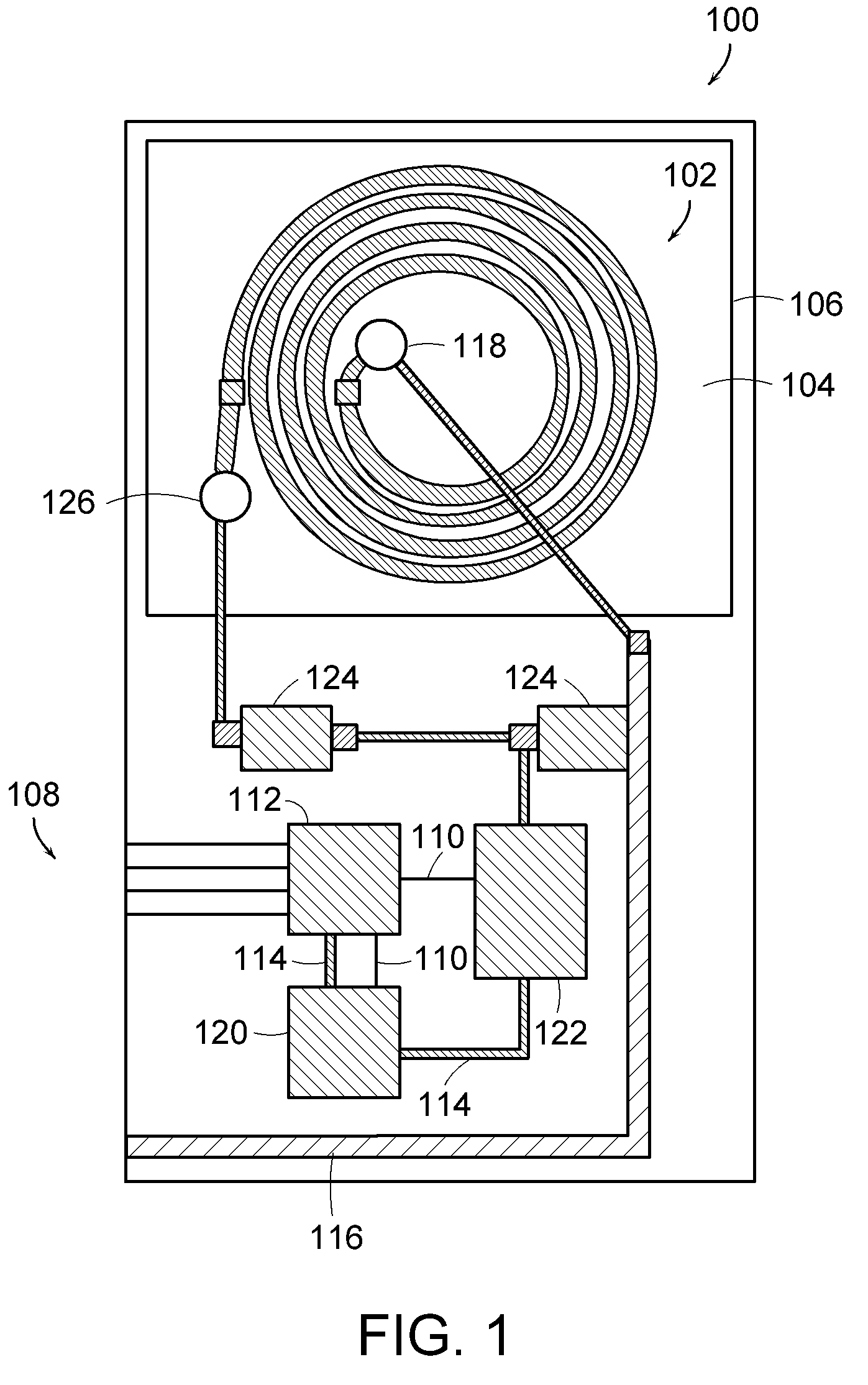
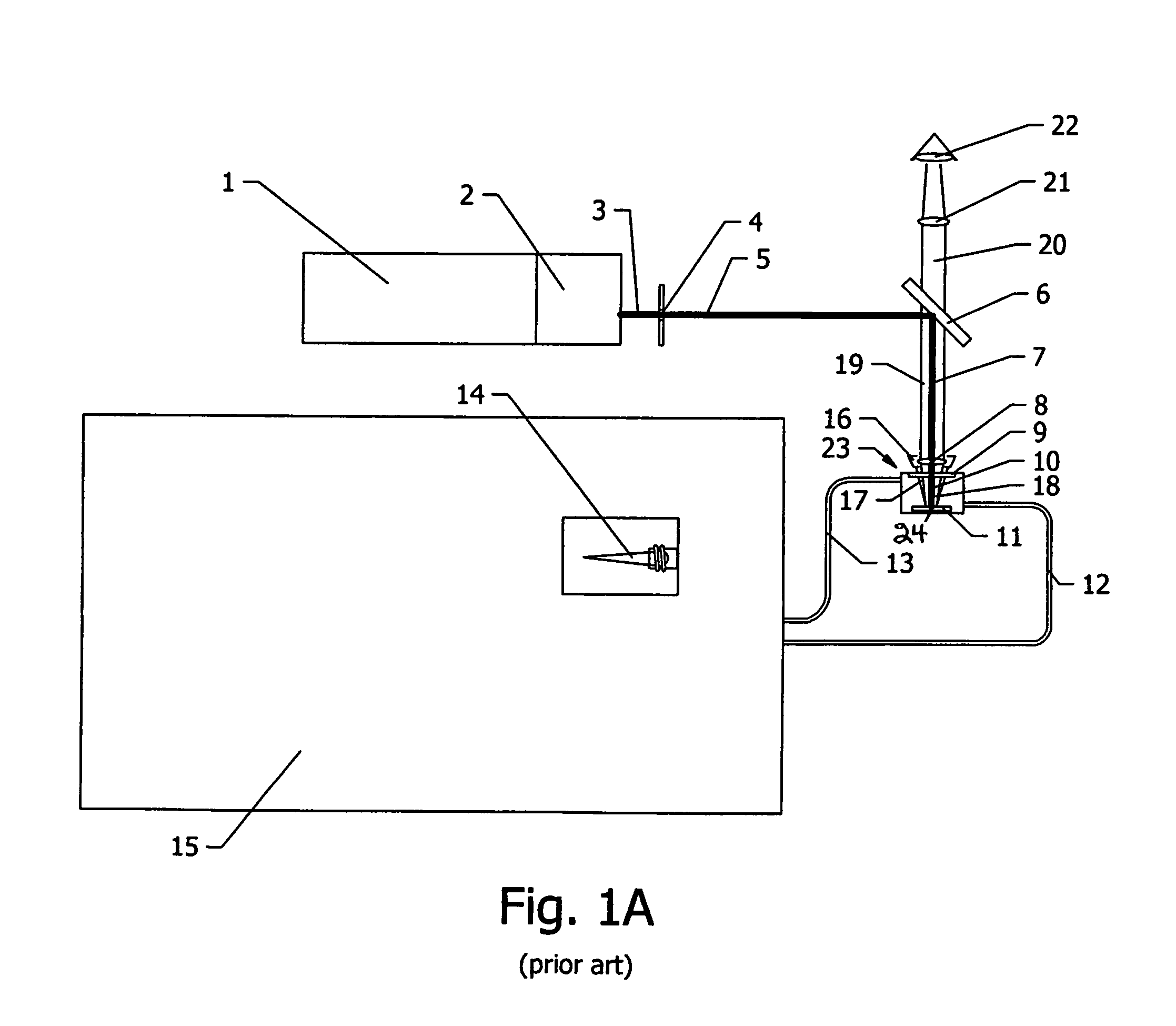
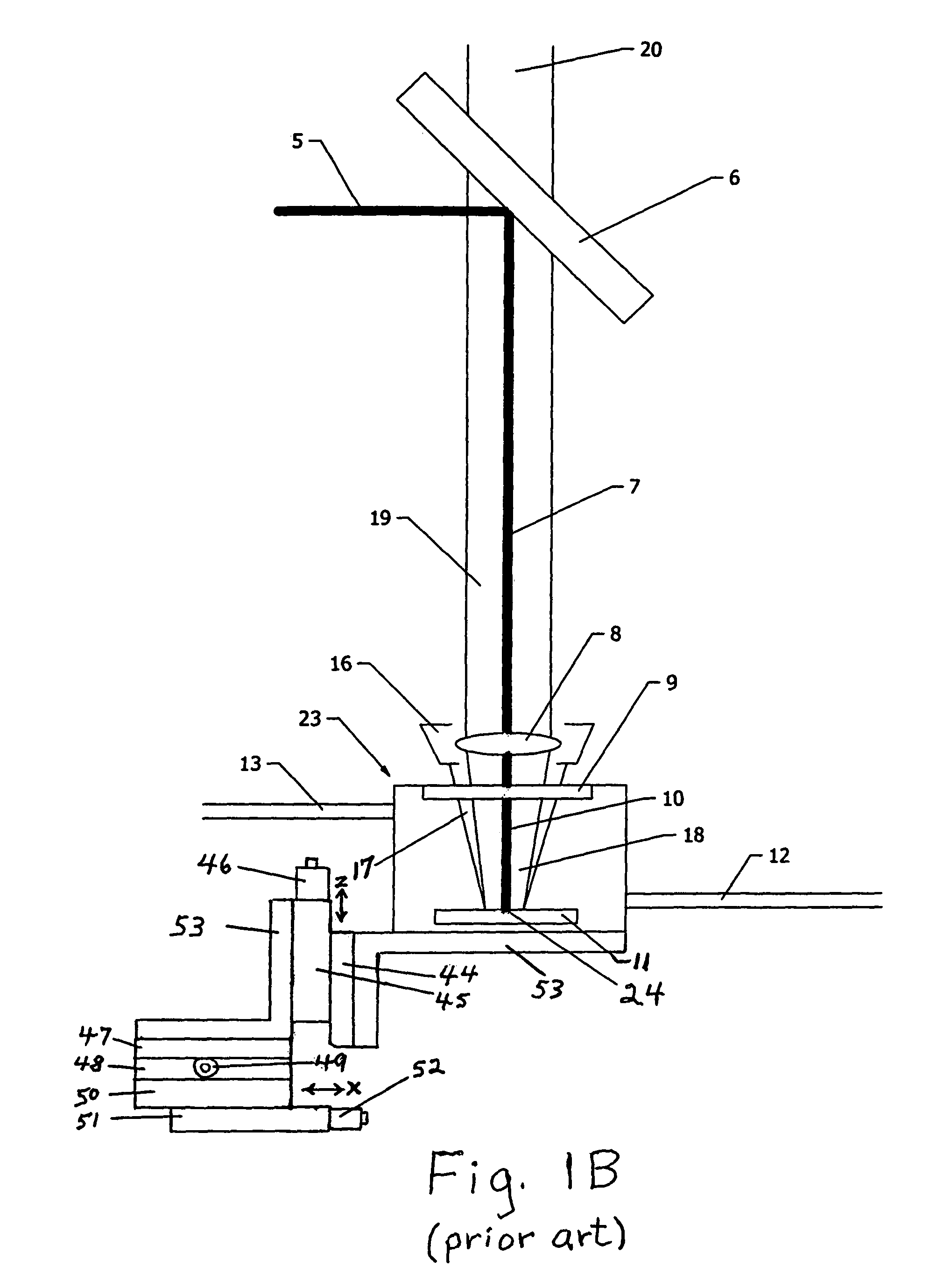
Method for analysis of a molten material, device and immersion sensor
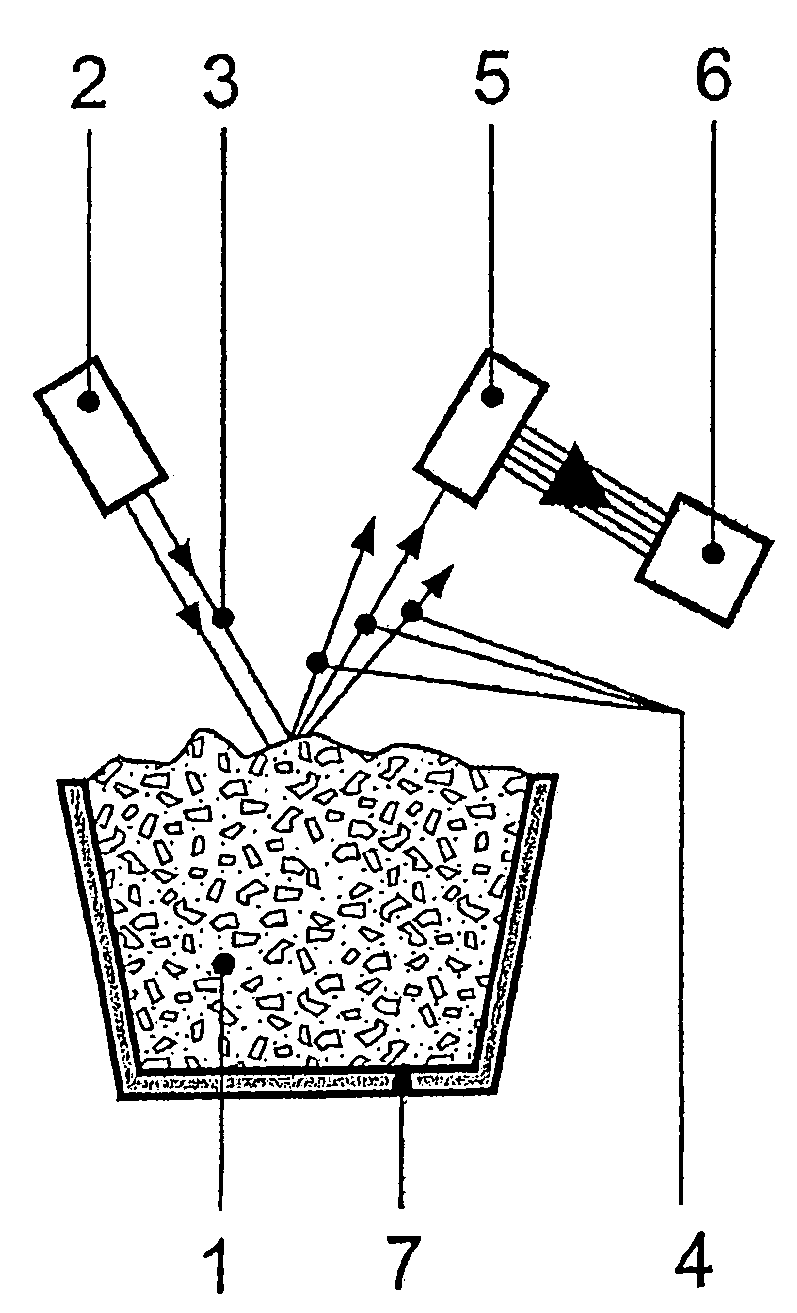
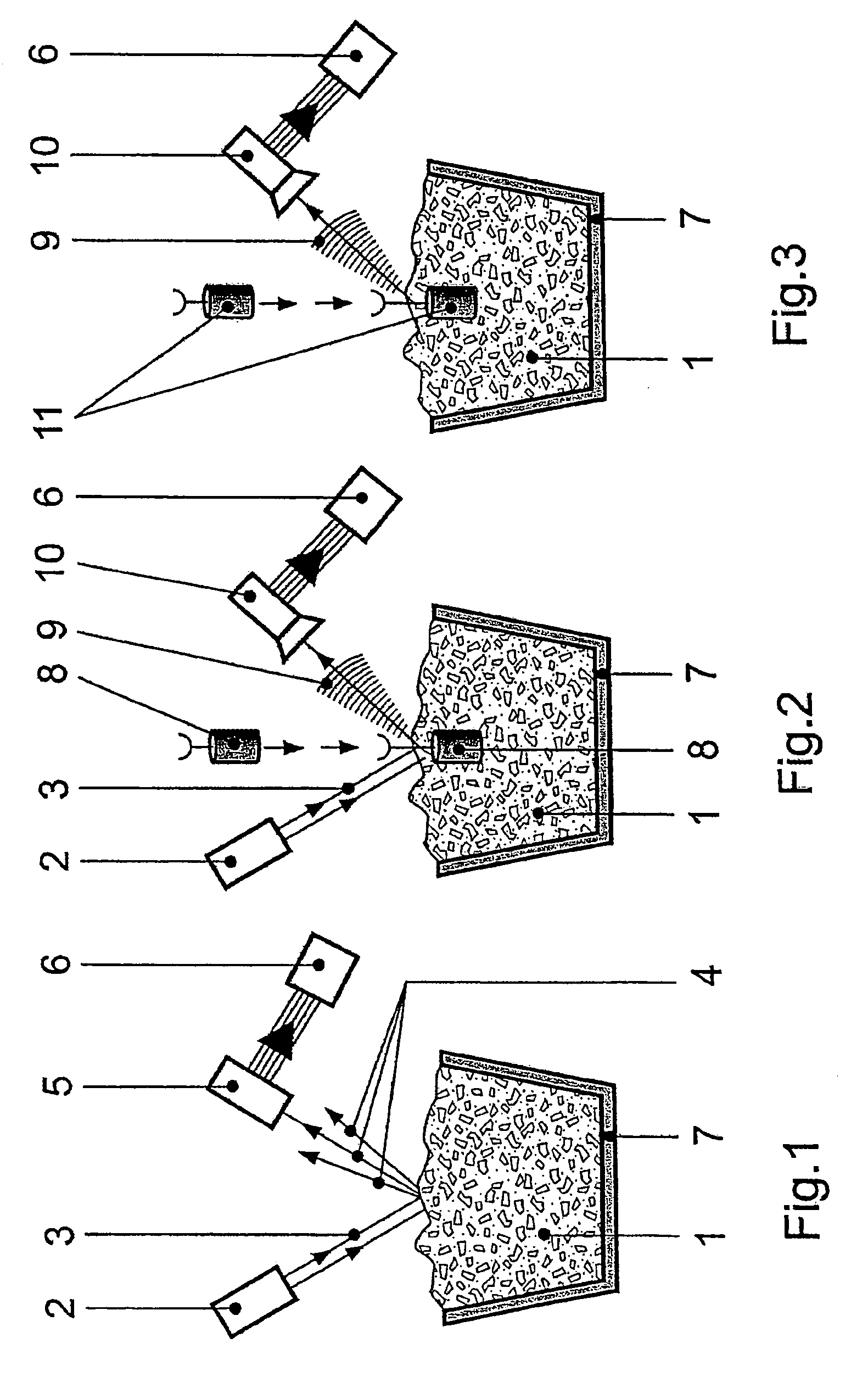
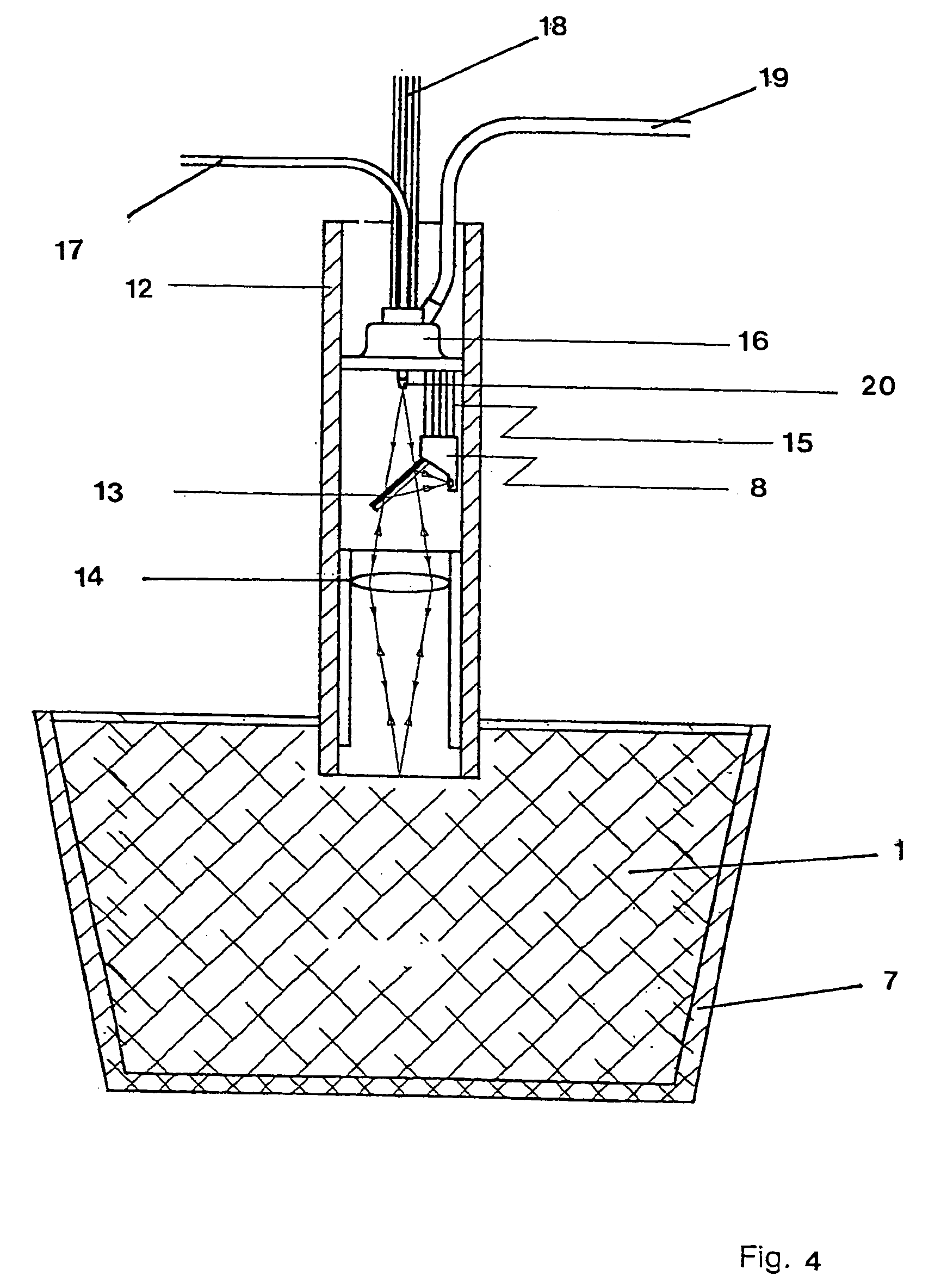
InactiveUS20060250614A1Easy to analyzeReduce economic costsEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySlagOptical emission spectrometry
A method and device are provided for analysis of a molten material using optical emission spectrometry. The molten material may be, for example, a molten metal, such as casting iron or steel, or slag, glass, or lava. A sensitive element is used having at least one emission spectrometer and at least one excitation device to effect the excitation of the molten material and to enable the partial or complete generation of a radiation to be analyzed by a spectrometer present in the sensitive element. The sensitive element is brought into contact with the molten material and transmits information, which contains analysis elements supplied by the spectrometer. An immersion sensor is also provided for carrying at least part of the device for performing the analysis method.
Owner:HERALUS ELECTRO NITE INT NV
Method for measuring impurity in high pure gold by plasma atomic emission spectrometer
ActiveCN101349646AAccurate measurementEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by electrical excitationAnalytical controlImpurity
The invention relates to a method for using a plasma atomic emission spectrometer to measure impurities in high-purity gold, which comprises the following steps: weighing one unit of sample in a bunsen beaker, adding aqua regia to dissolve, replenishing hydrochloric acid deionized water to do constant volume to a scale after dissolving, respectively getting sample solution in more than two colorimetric tubes, solution in each tube is 15ml, adding gold standard solution which is mixed by elements according to a multiple relation in turn, doing constant volume by deionized water, starting the plasma atomic emission spectrometer, starting a circulating water pump, opening analytic control software, entering a 'standard addition method' control procedure, choosing a spectral line for measuring in a spectral line base, setting the concentration value of curved lines, scanning a whole band, sucking sample solution in each colorimetric tube in an instrument in turn according to the sequence that the concentration is from low to high, clicking a feeler switch to get an initial curve point of the point after sucking in each time, assuring curved lines, and leading the linear coefficient to be more than 0.99, outputting the concentration value result of each determined element, and calculating the result of the percentage content of each determined element according to the calculating formula.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NONFERROUS METALS & RARE EARTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com