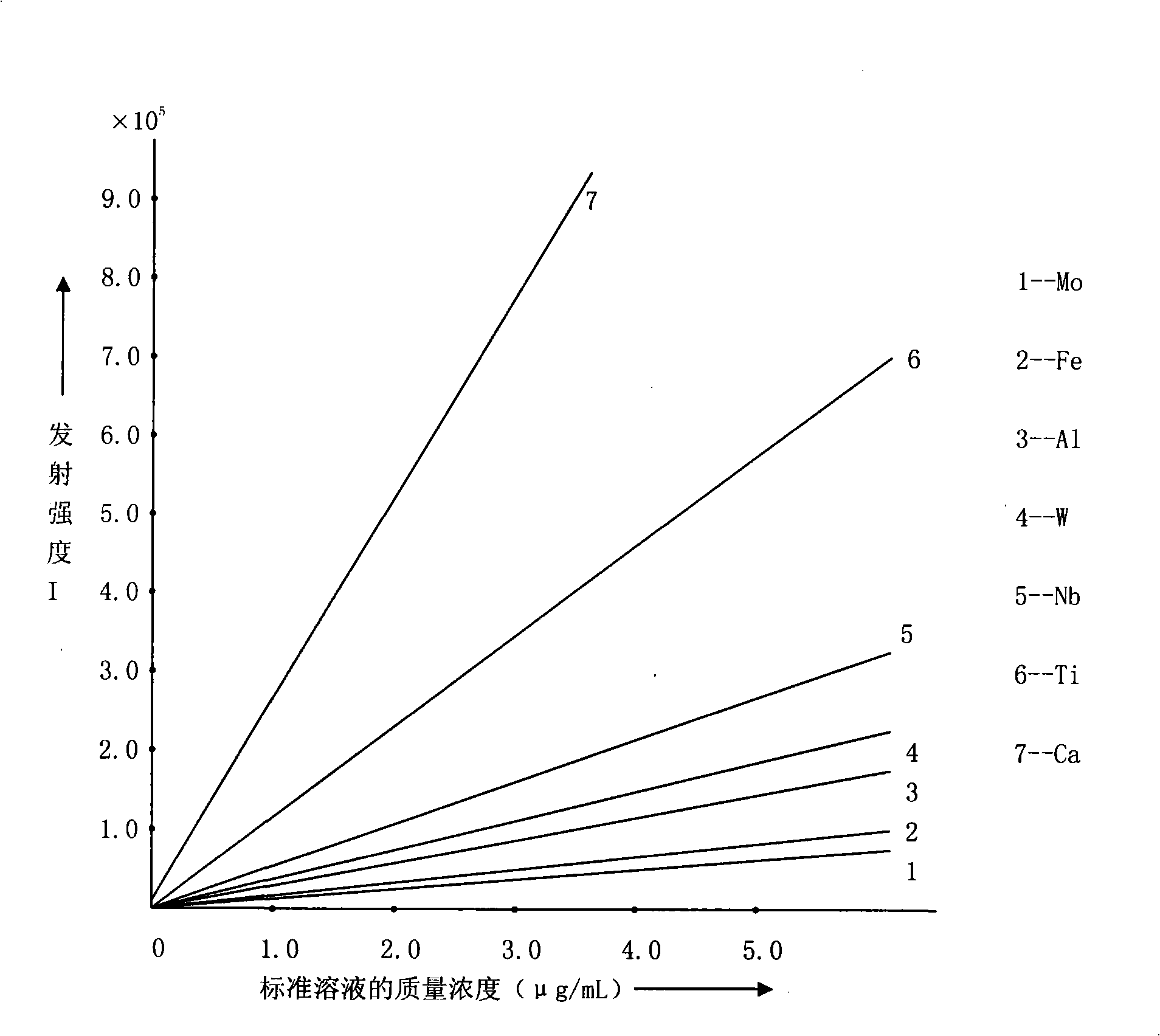
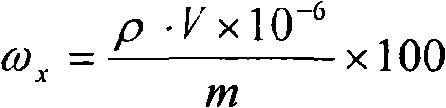Analyses testing method of aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten impurity elements in chromium carbide
A technology for aluminum and impurity elements in chromium carbide, applied in thermal excitation analysis, material excitation analysis, preparation of samples for testing, etc. High accuracy and precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1: Determination of elements such as aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten in chromium carbide (sample S-1)
[0041] Take 0.1000 g of chromium carbide sample and place it in a polytetrafluoroethylene sample dissolving cup, first use 1 to 2 mL of deionized water to rinse the cup wall, then add in turn the purity to be high-purity (MOS grade, the same as in the following examples), mass concentration It is 1.0mL of hydrofluoric acid of 1.14g / mL, and the purity is high-grade pure, and the mass concentration is 1.5mL of sulfuric acid 1.84g / mL, and the purity is high purity (MOS level, the following examples are the same), and the mass concentration is 1.42g / 0.8 mL of nitric acid, mix well, cover the cup, put the sample dissolving cup into the high-pressure tank, and seal the high-pressure tank. Place the high-pressure tank in the microwave digestion apparatus, and perform the first microwave digestion according to the working condition...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2: Determination of elements such as aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten in chromium carbide (sample S-2)
[0049] Take 0.1000 g of chromium carbide sample and place it in a polytetrafluoroethylene sample dissolving cup, first rinse the cup wall with 1-2 mL of deionized water, and then add high-purity hydrofluoric acid with a mass concentration of 1.14 g / mL in sequence 1.5mL, 2.0mL of sulfuric acid with a purity of 1.84g / mL, 0.8mL of high-purity nitric acid with a mass concentration of 1.42g / mL, mix well, cover the cup, and dissolve the sample The cup is put into the high-pressure tank, and the high-pressure tank is sealed. Place the high-pressure tank in the microwave digestion apparatus, and carry out the first microwave digestion according to the working conditions shown in Table 1 above. After the first microwave digestion is completed, remove the high-pressure tank from the microwave digestion device. After the high-pressure ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: Determination of elements such as aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten in chromium carbide (sample S-3)
[0055] Take 0.1000 g of chromium carbide sample and place it in a polytetrafluoroethylene sample dissolving cup, first rinse the cup wall with 1-2 mL of deionized water, and then add high-purity hydrofluoric acid with a mass concentration of 1.14 g / mL in sequence 2.0mL, 2.0mL of sulfuric acid with a purity of 1.84g / mL, 0.8mL of high-purity nitric acid with a concentration of 1.42g / mL, mix well, cover the cup, and dissolve the sample The cup is put into the high-pressure tank, and the high-pressure tank is sealed. Place the high-pressure tank in the microwave digestion apparatus, and carry out the first microwave digestion according to the working conditions shown in Table 4. After the first microwave digestion is completed, remove the high-pressure tank from the microwave digestion device, and wait for the high-pressure tank...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com