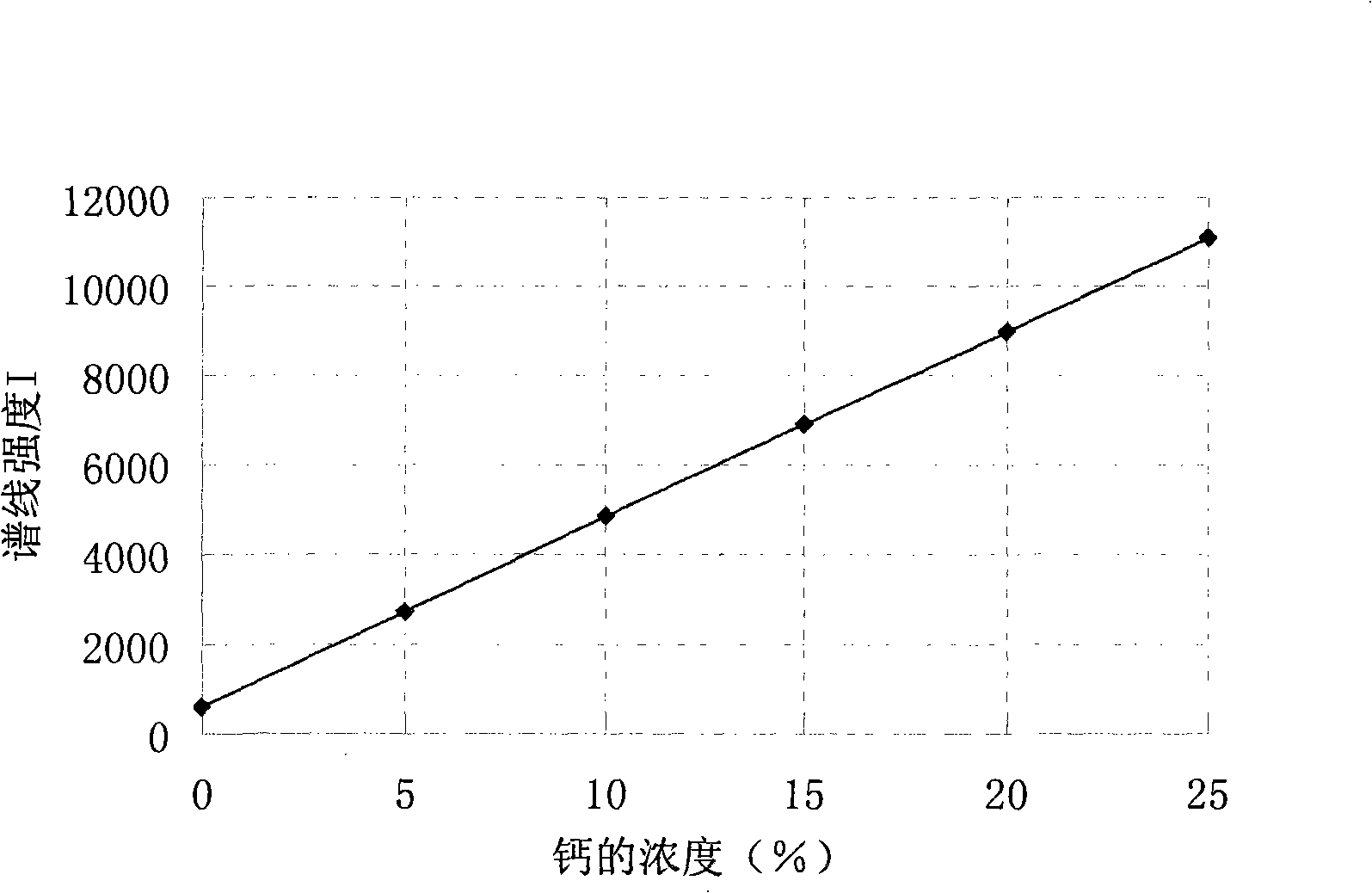
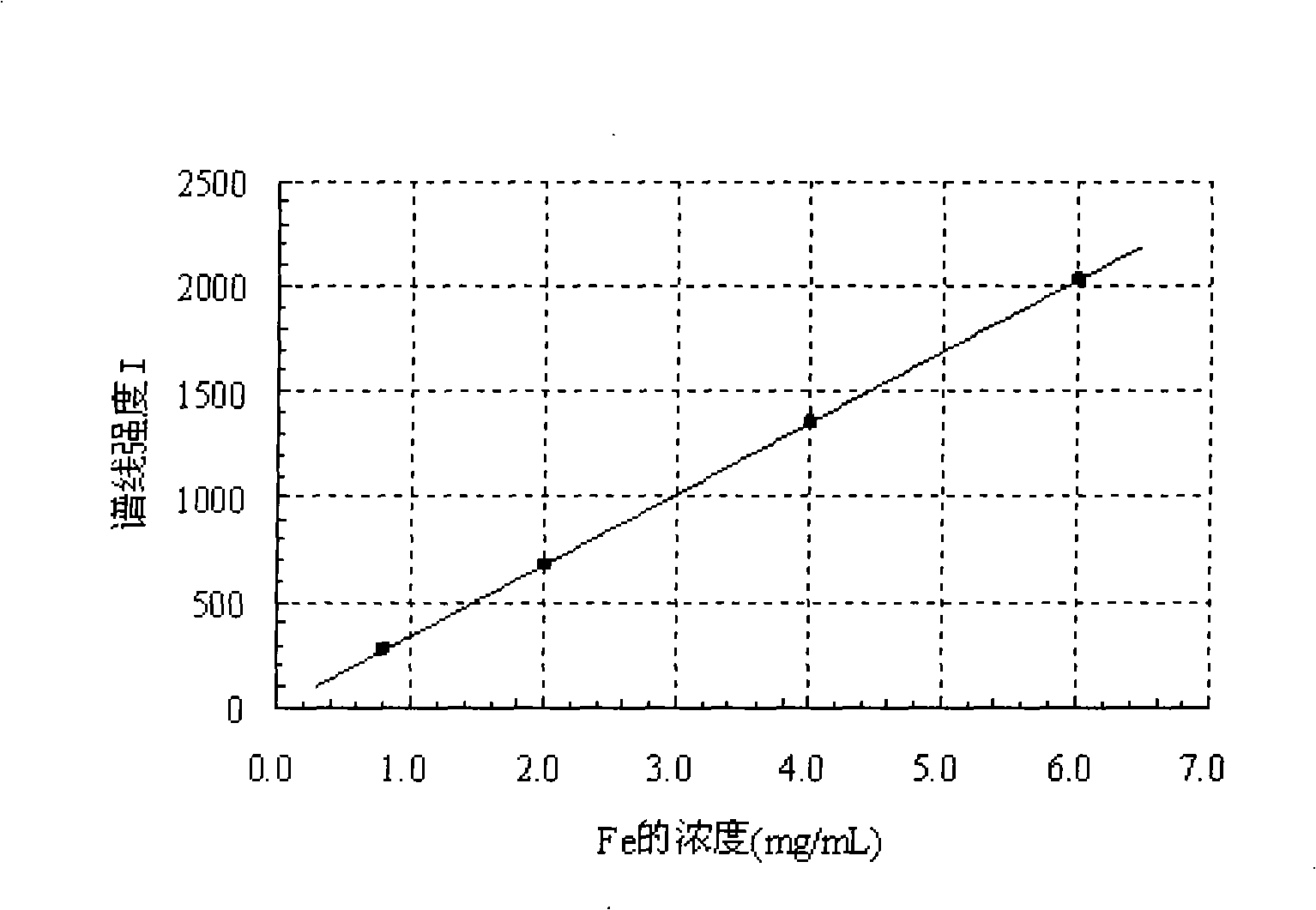
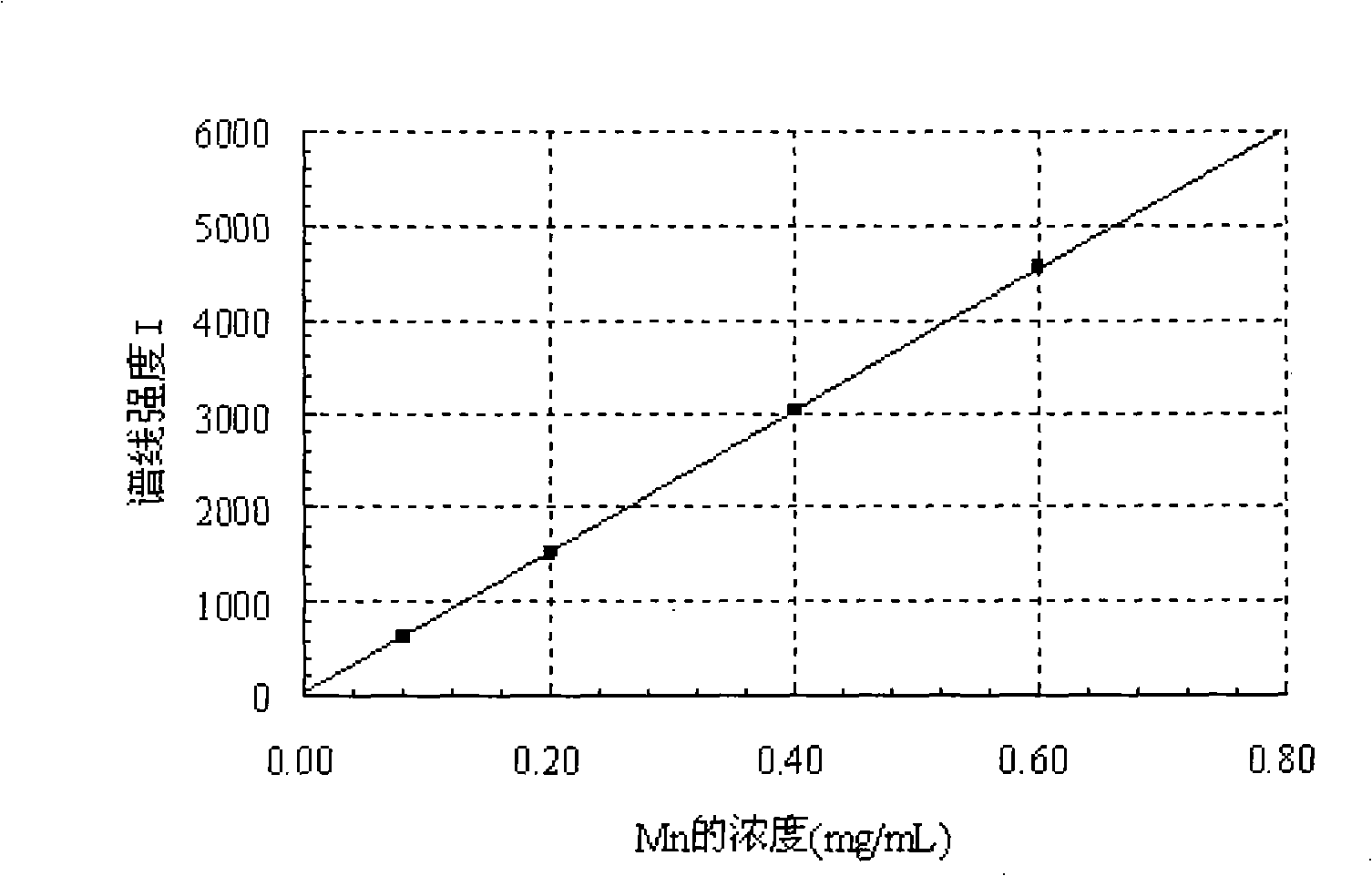
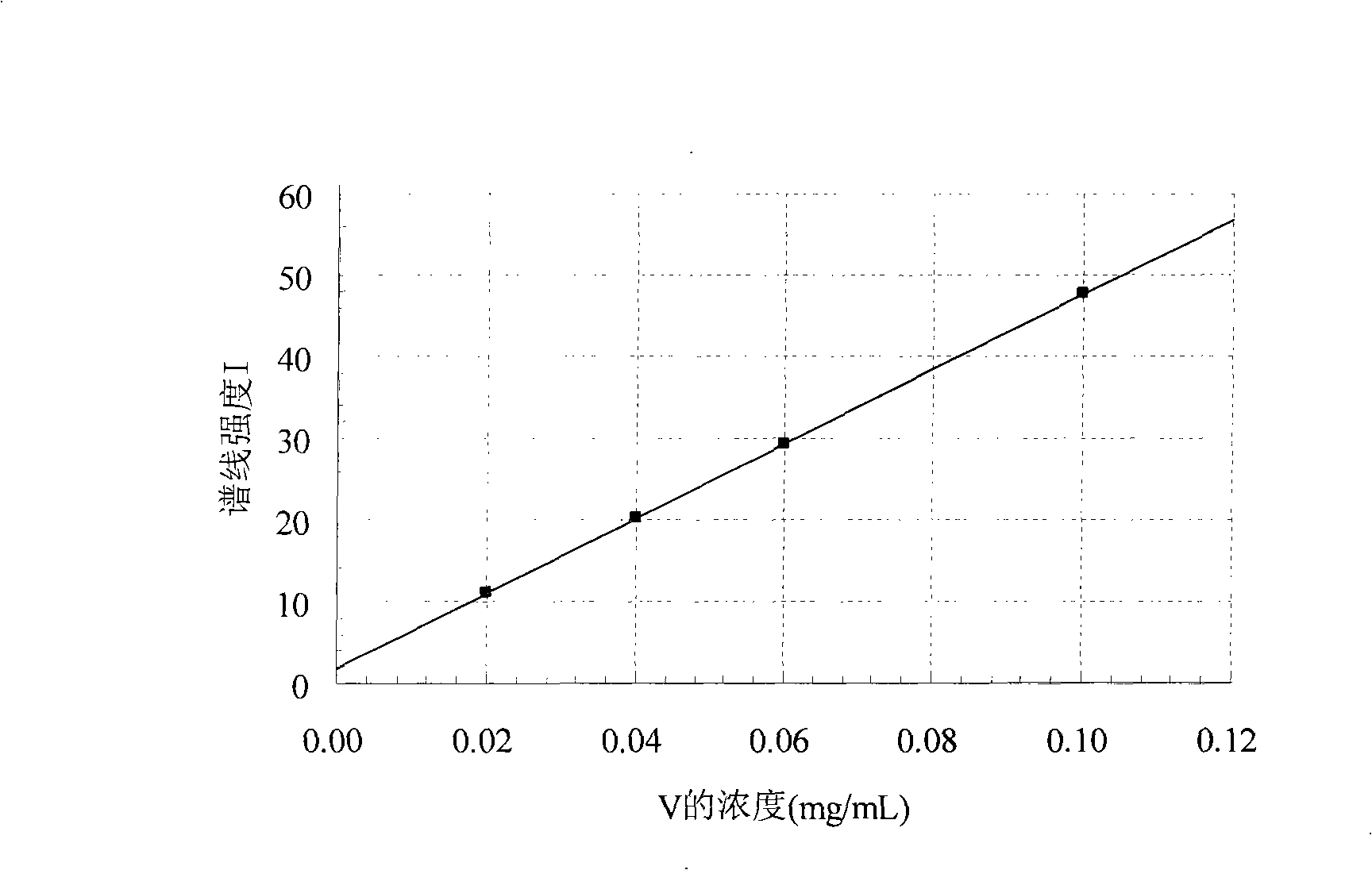
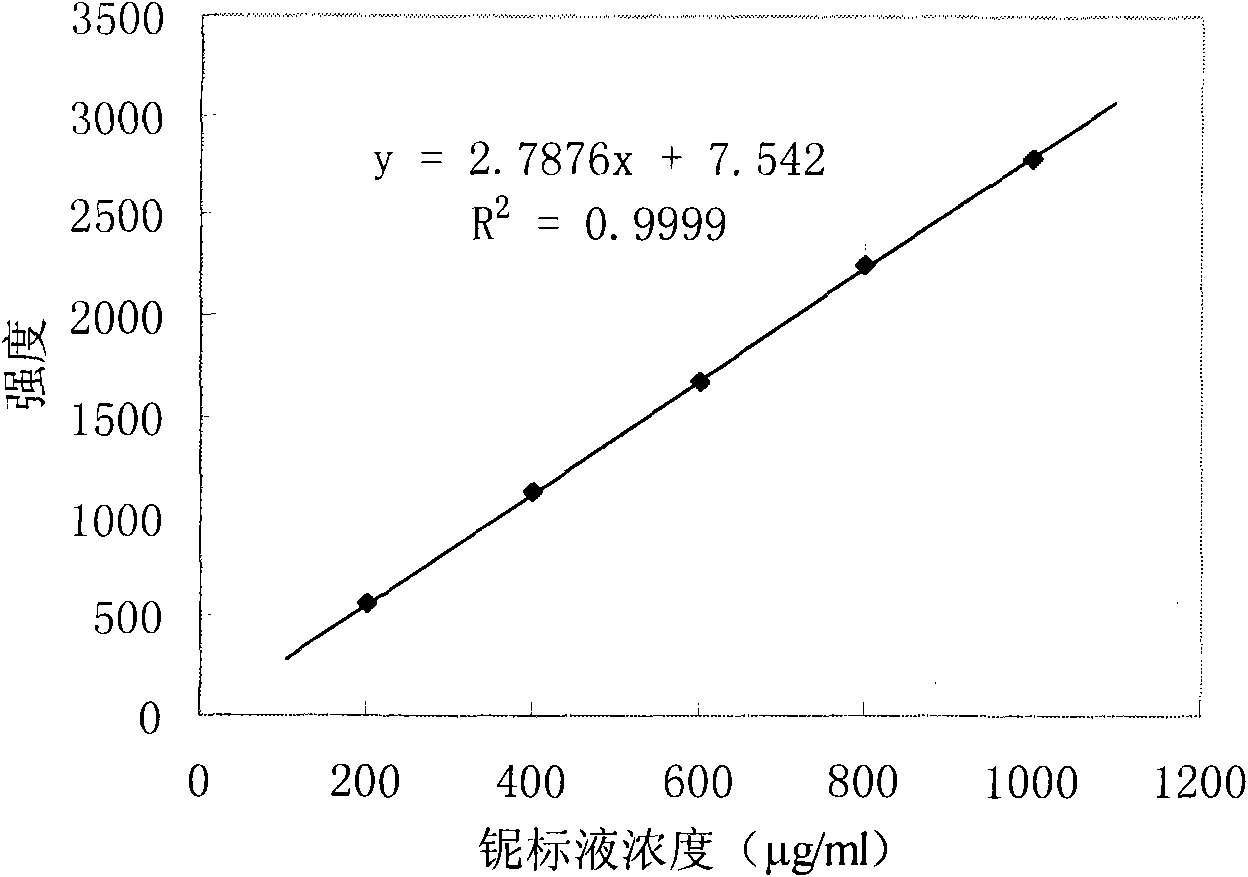
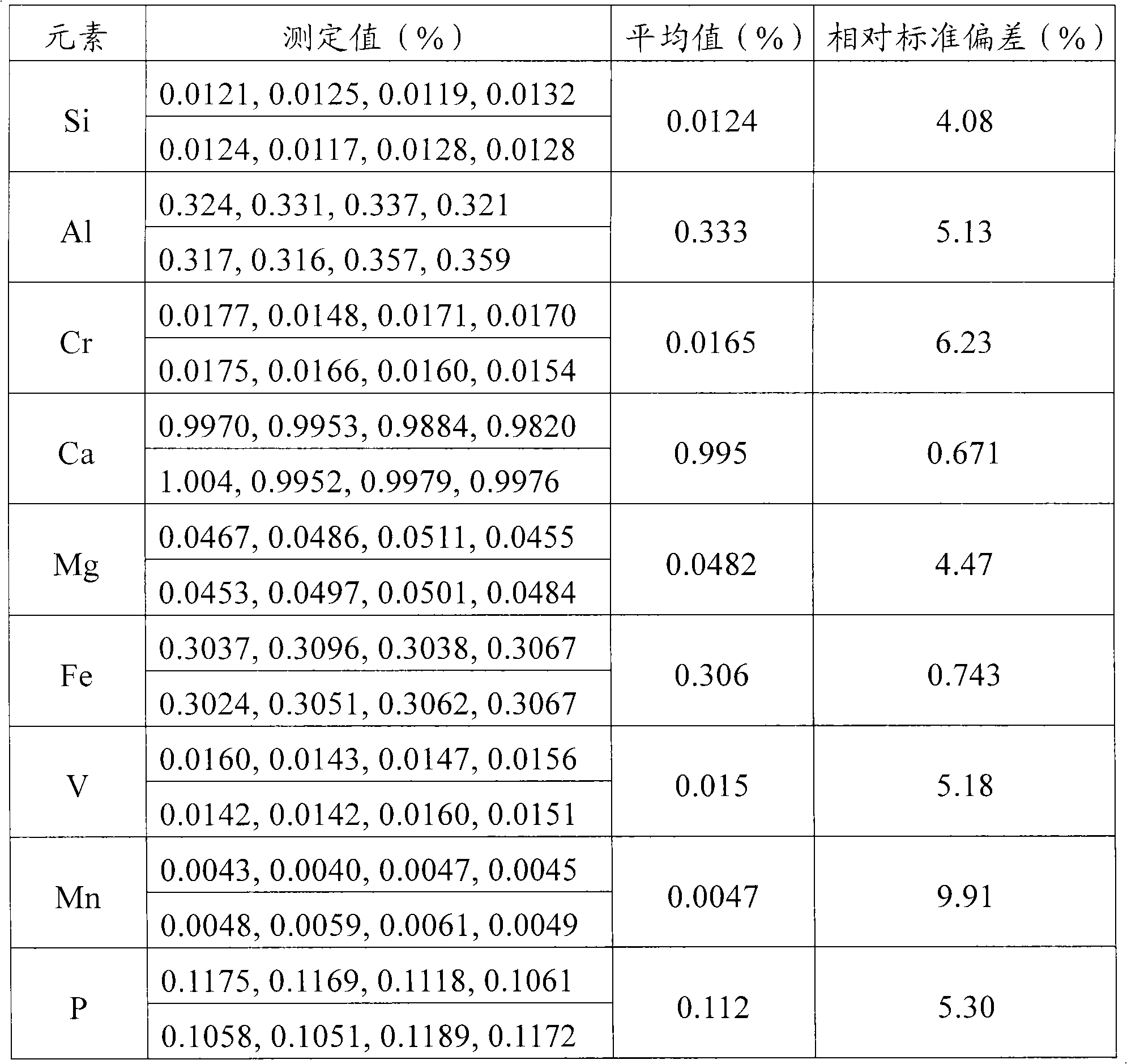
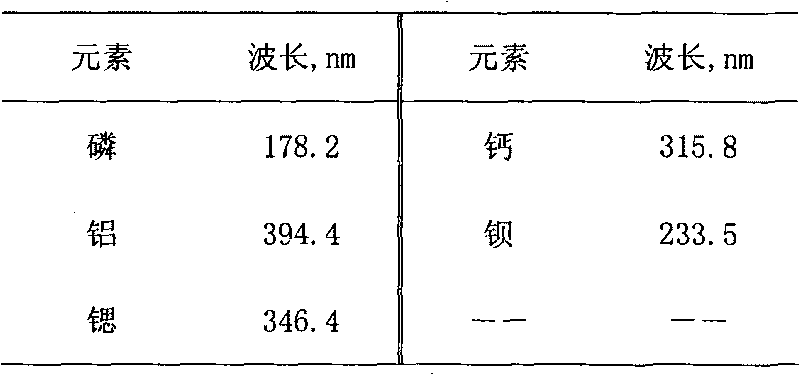
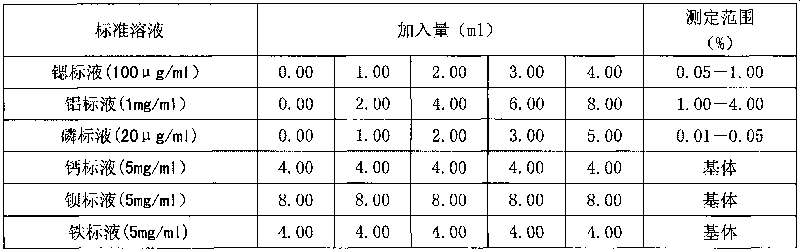
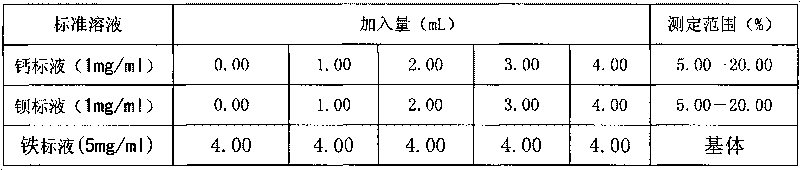
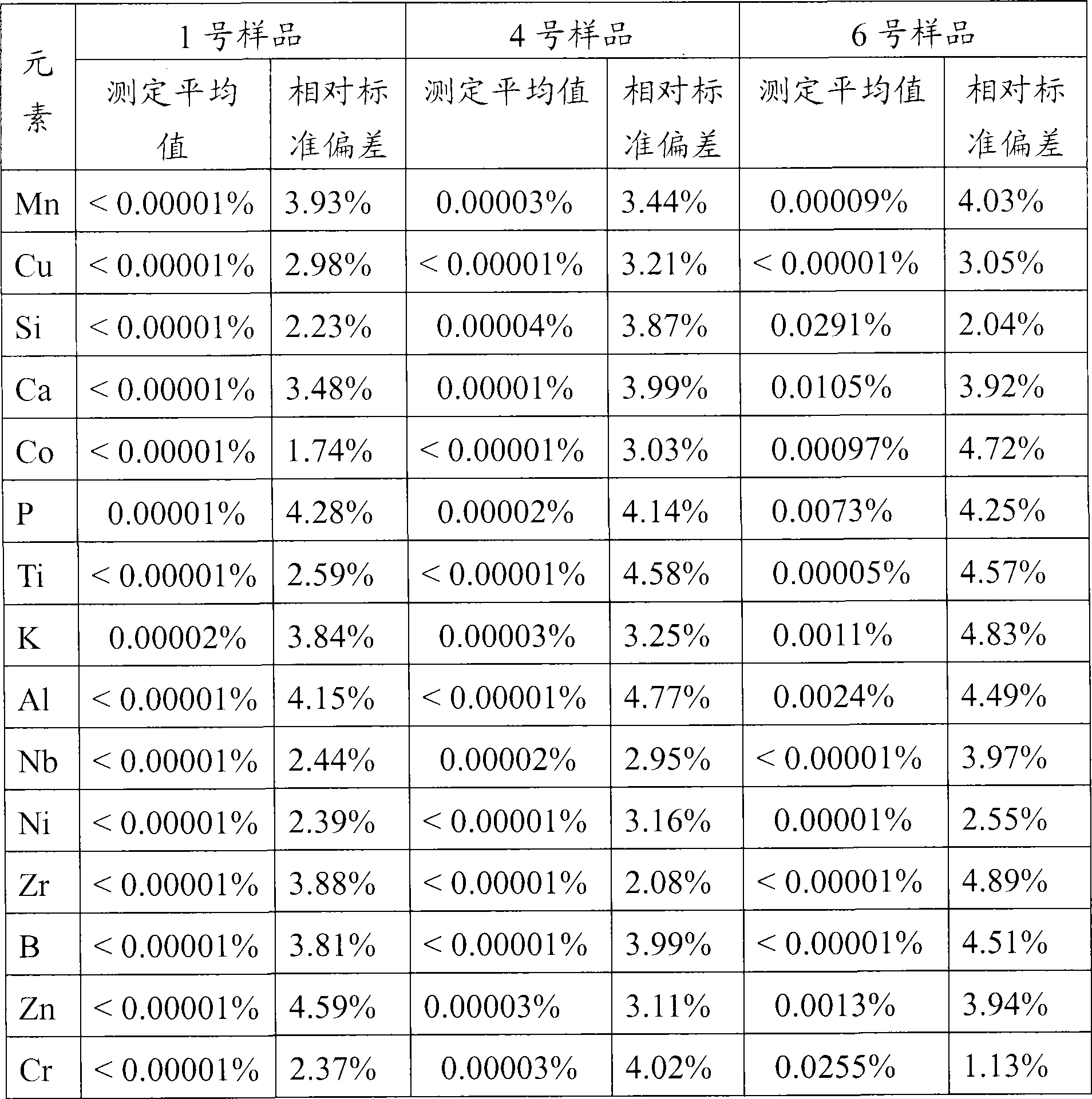
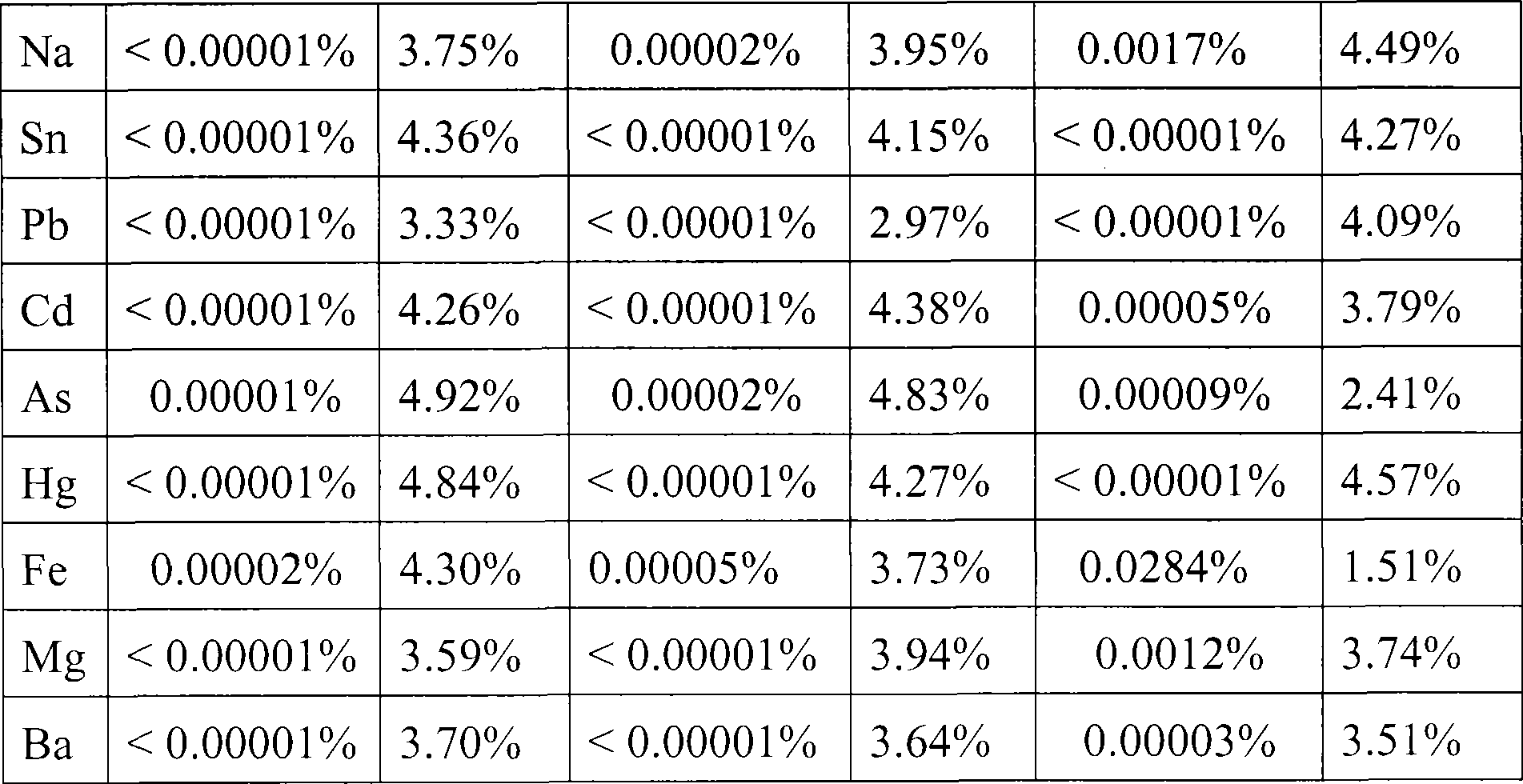
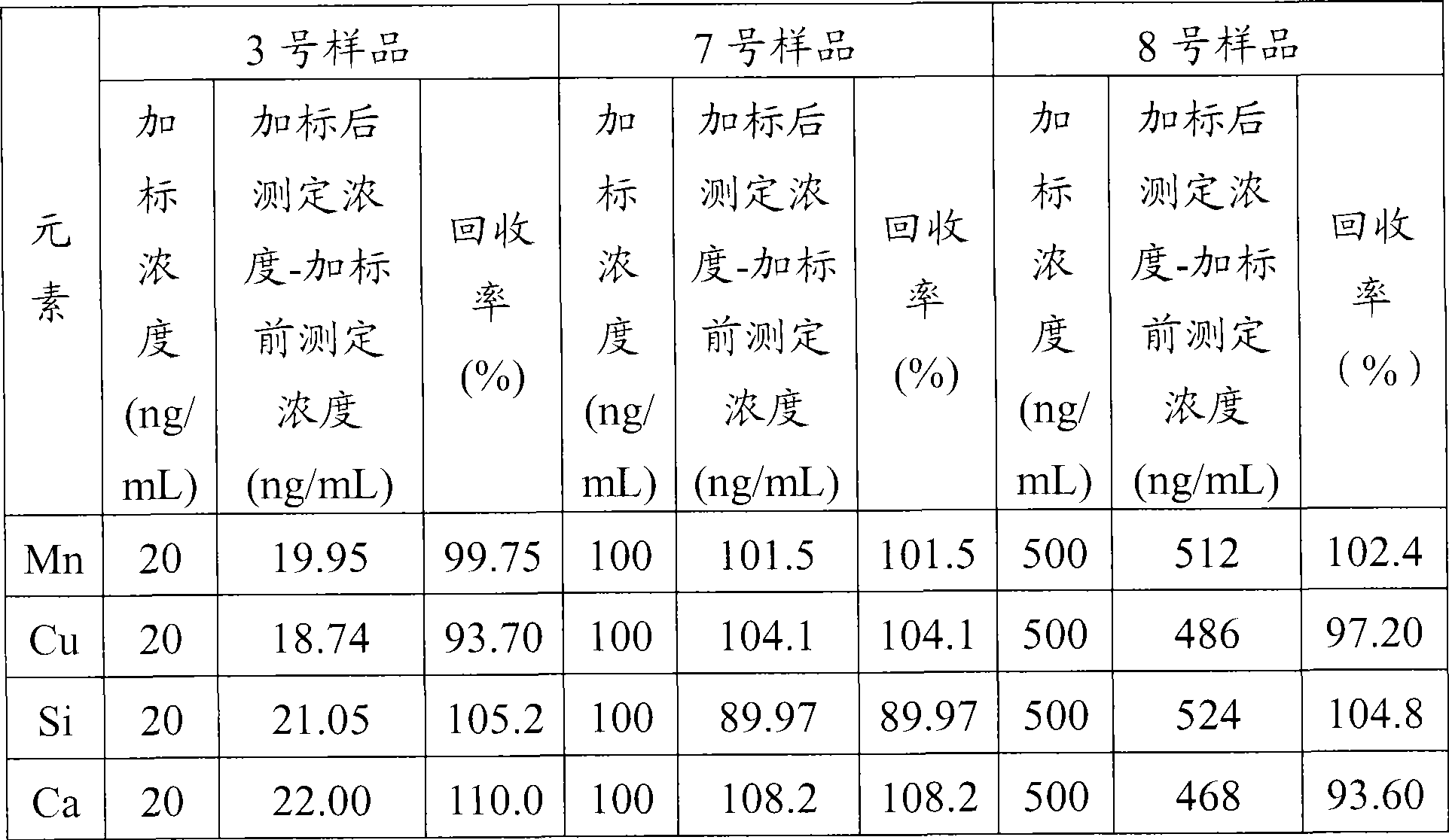
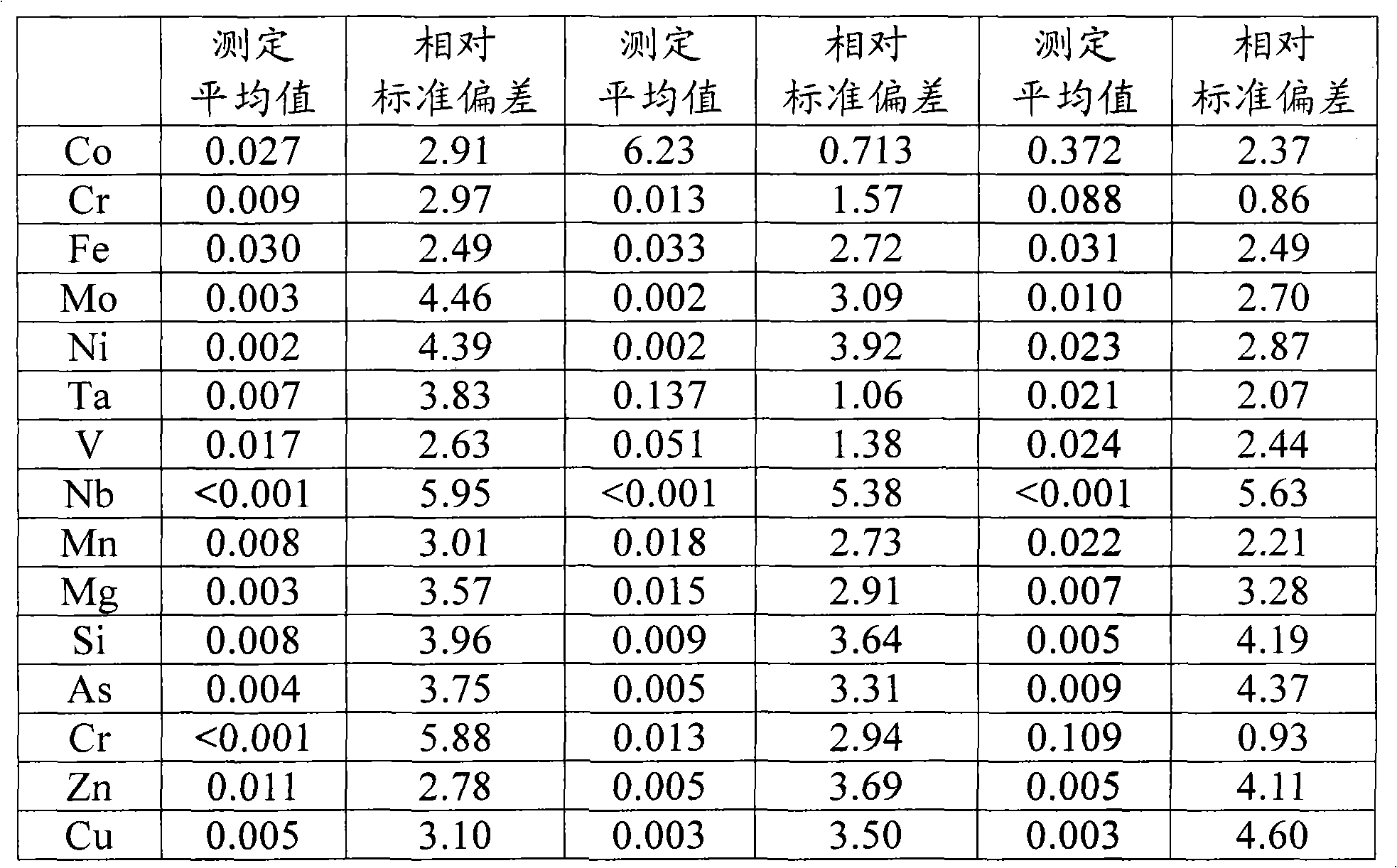
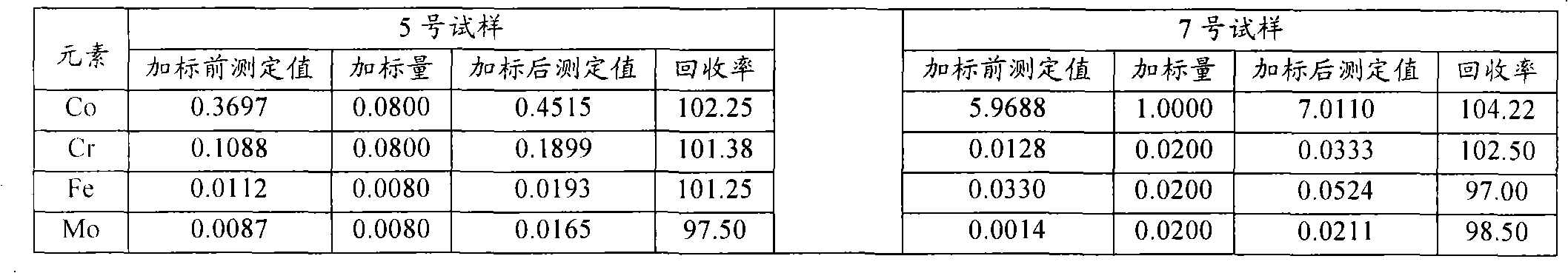
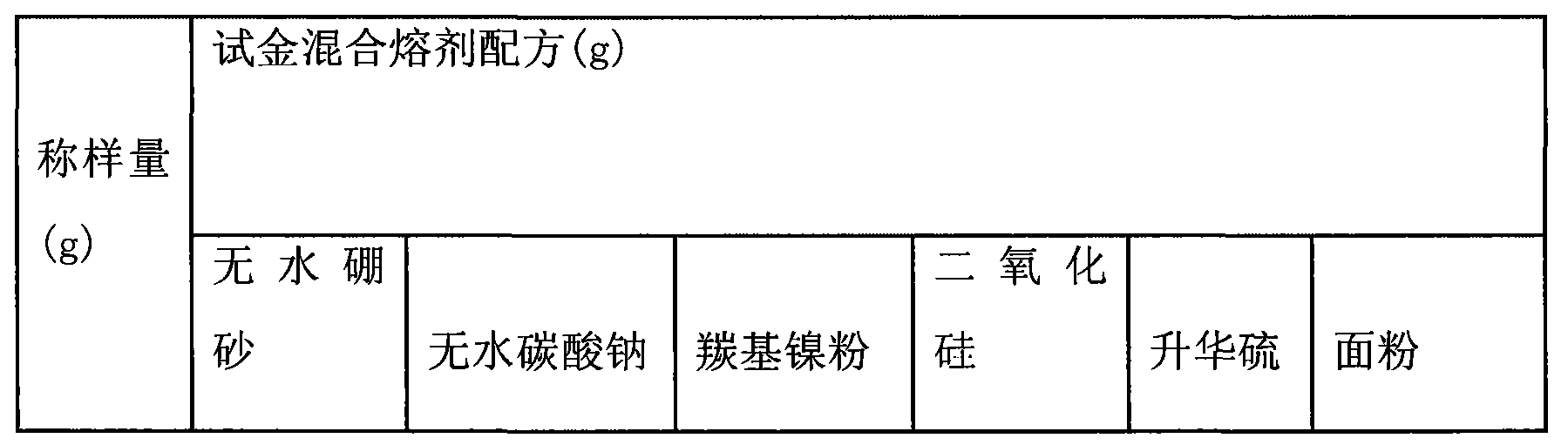
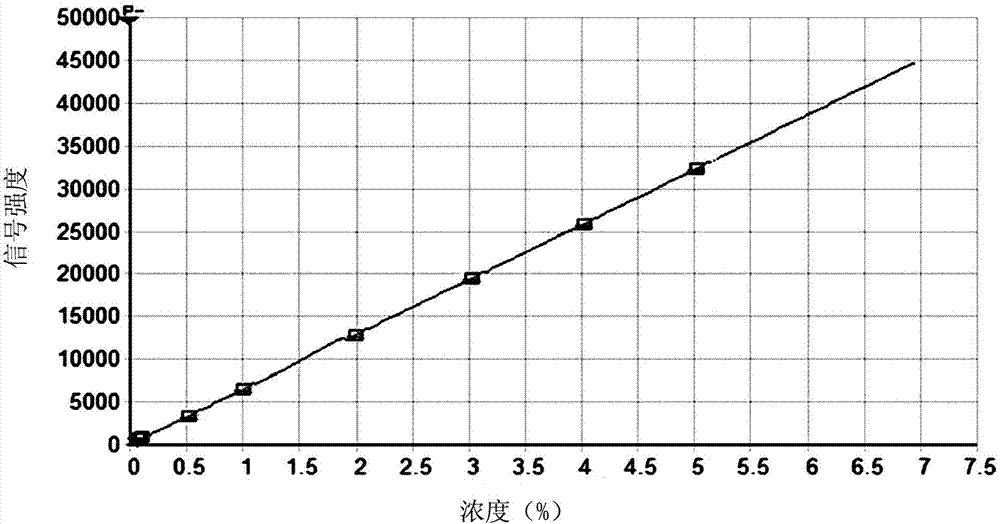
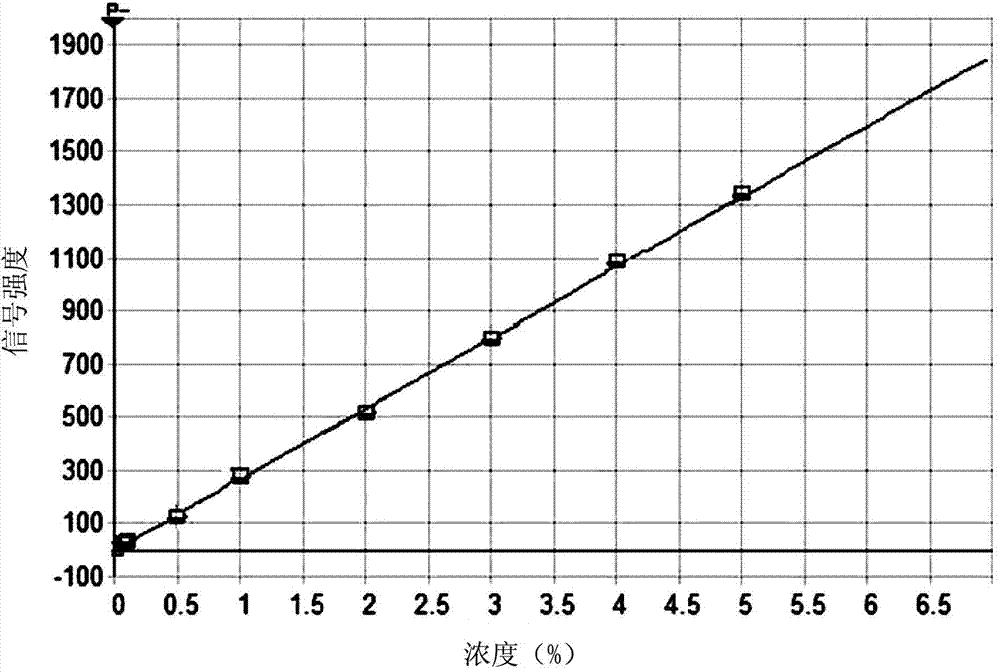
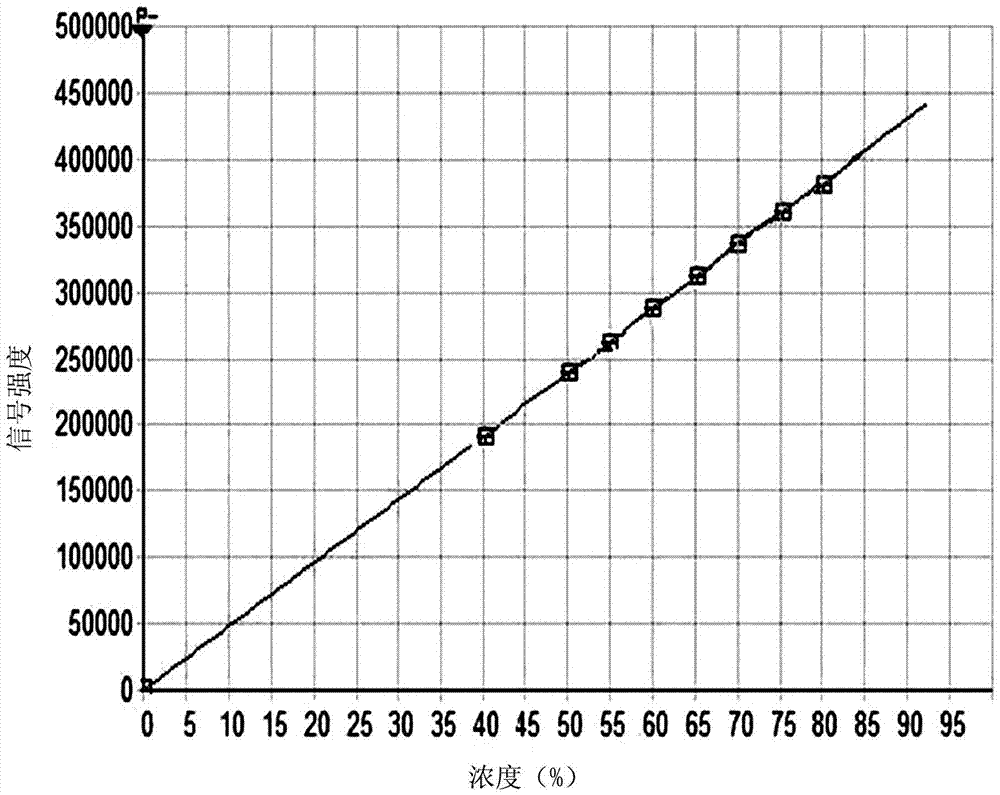
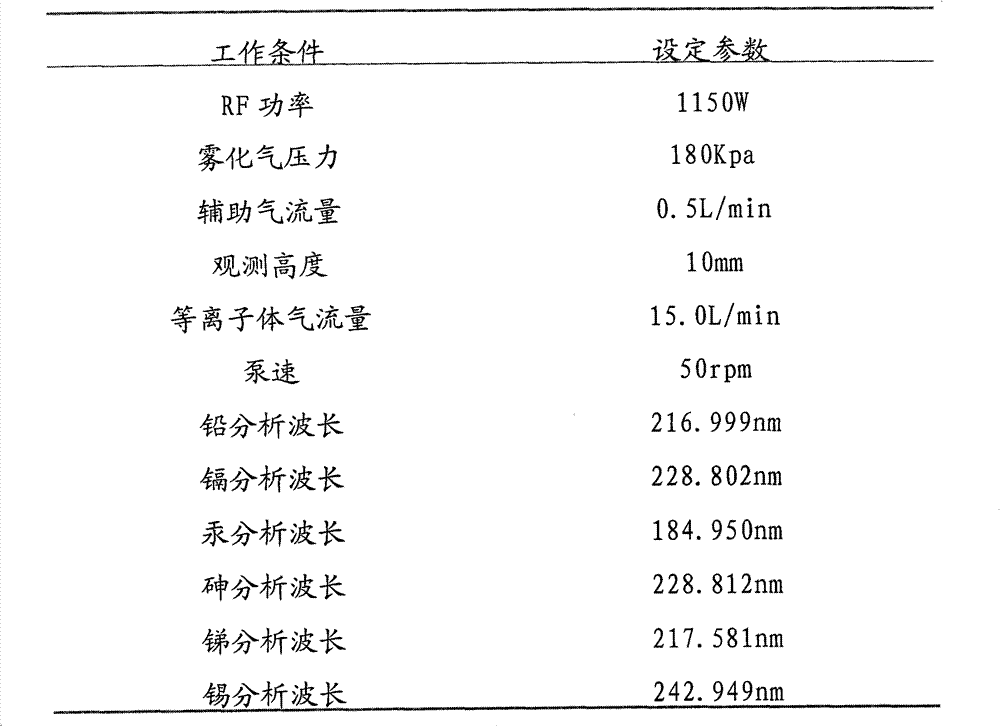
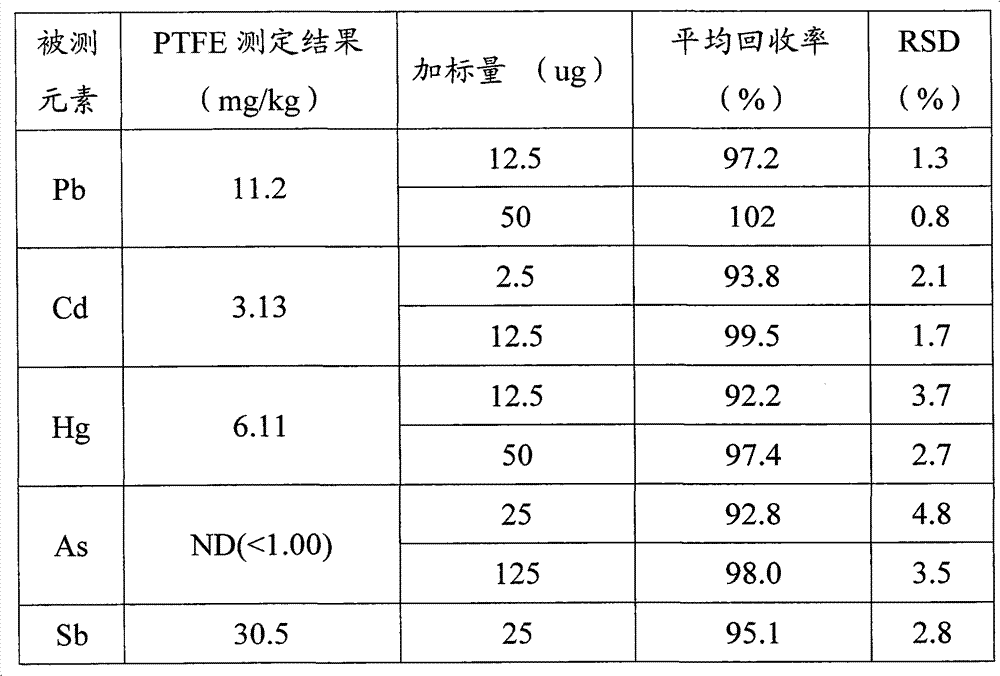
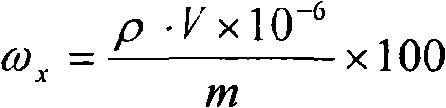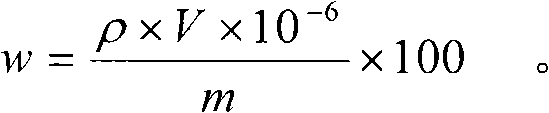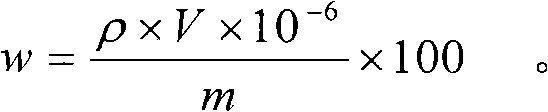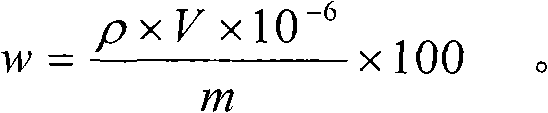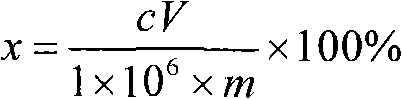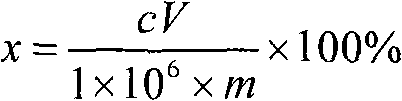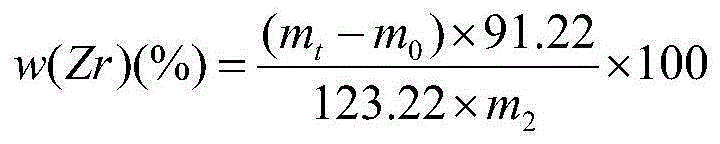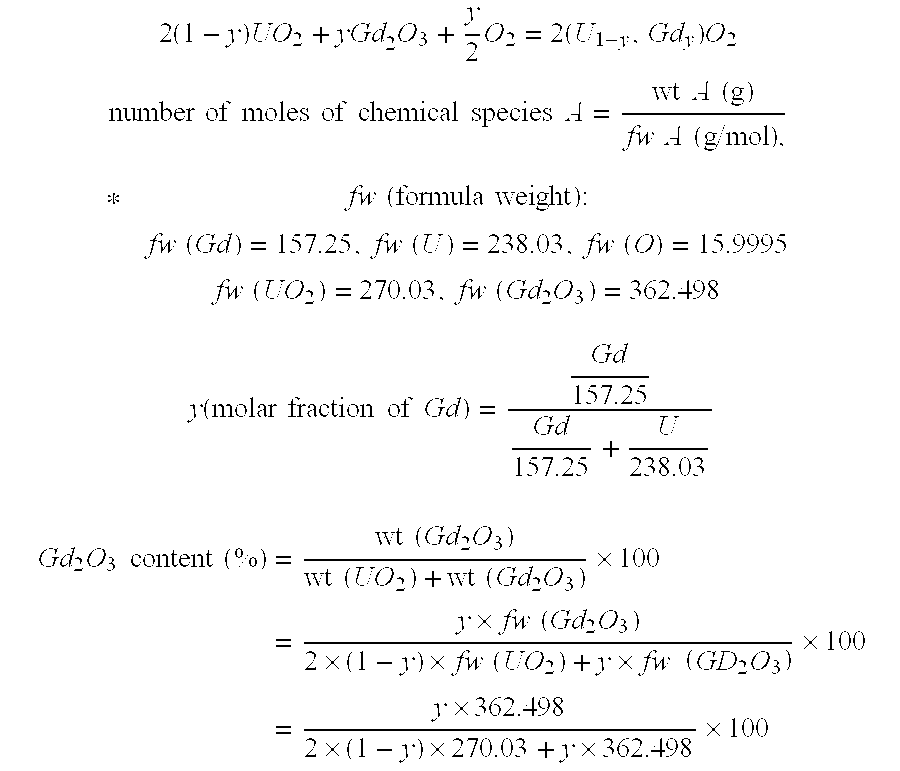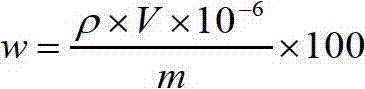Patents
Literature
237 results about "Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), also referred to as inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), is an analytical technique used for the detection of chemical elements. It is a type of emission spectroscopy that uses the inductively coupled plasma to produce excited atoms and ions that emit electromagnetic radiation at wavelengths characteristic of a particular element. It is a flame technique with a flame temperature in a range from 6000 to 10,000 K. The intensity of this emission is indicative of the concentration of the element within the sample.
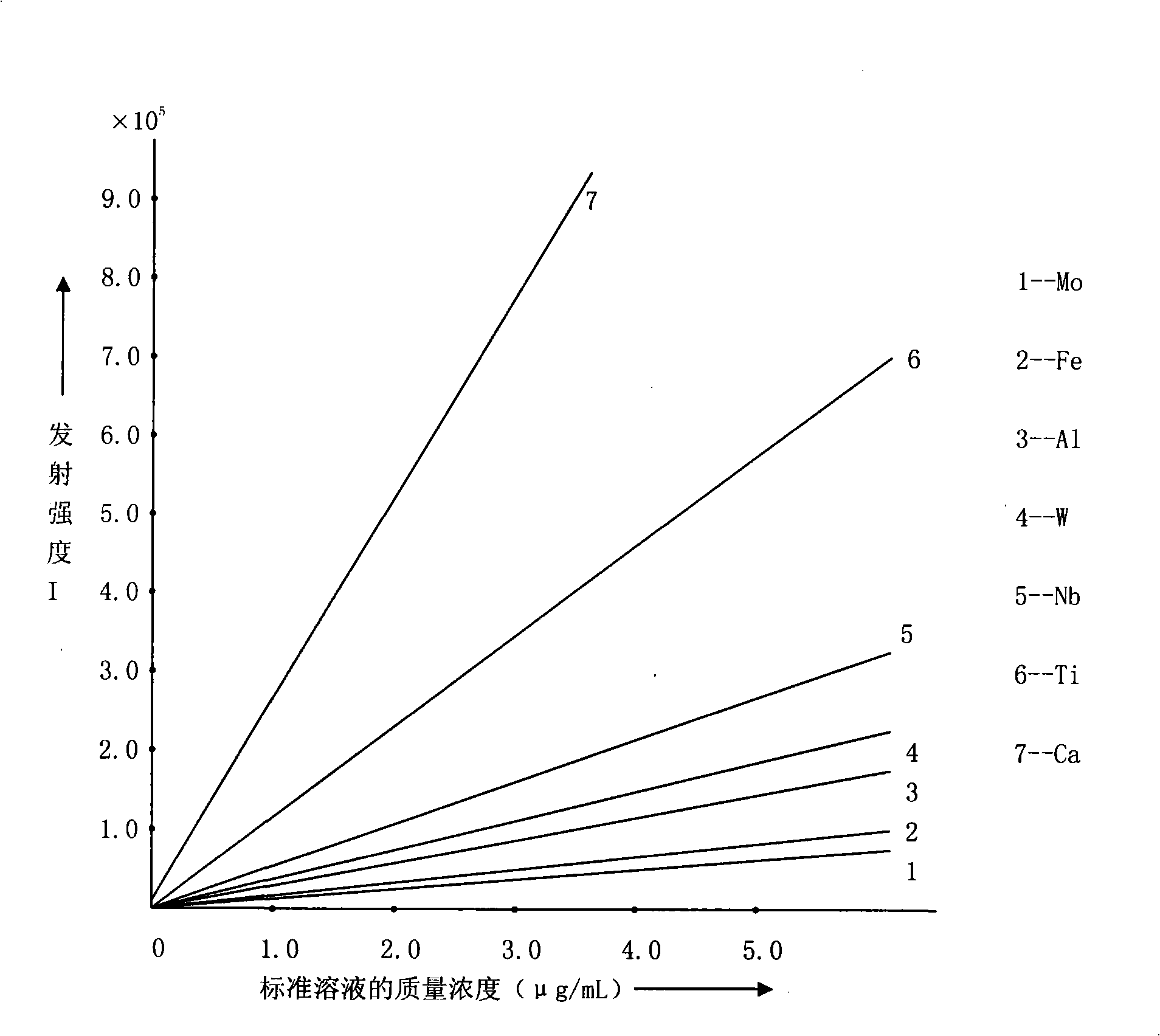
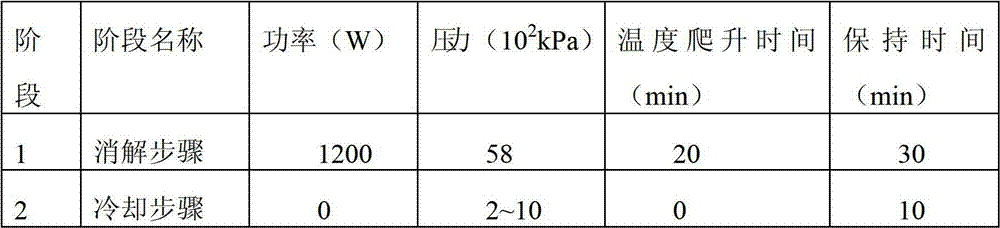
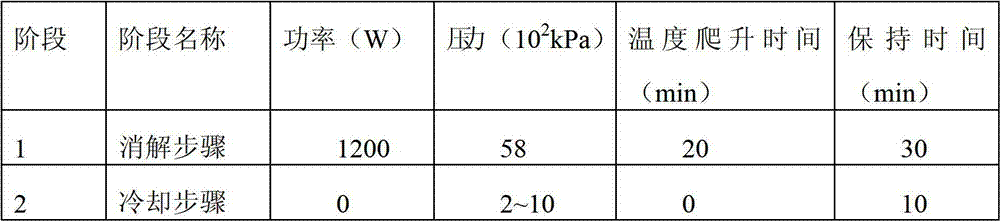
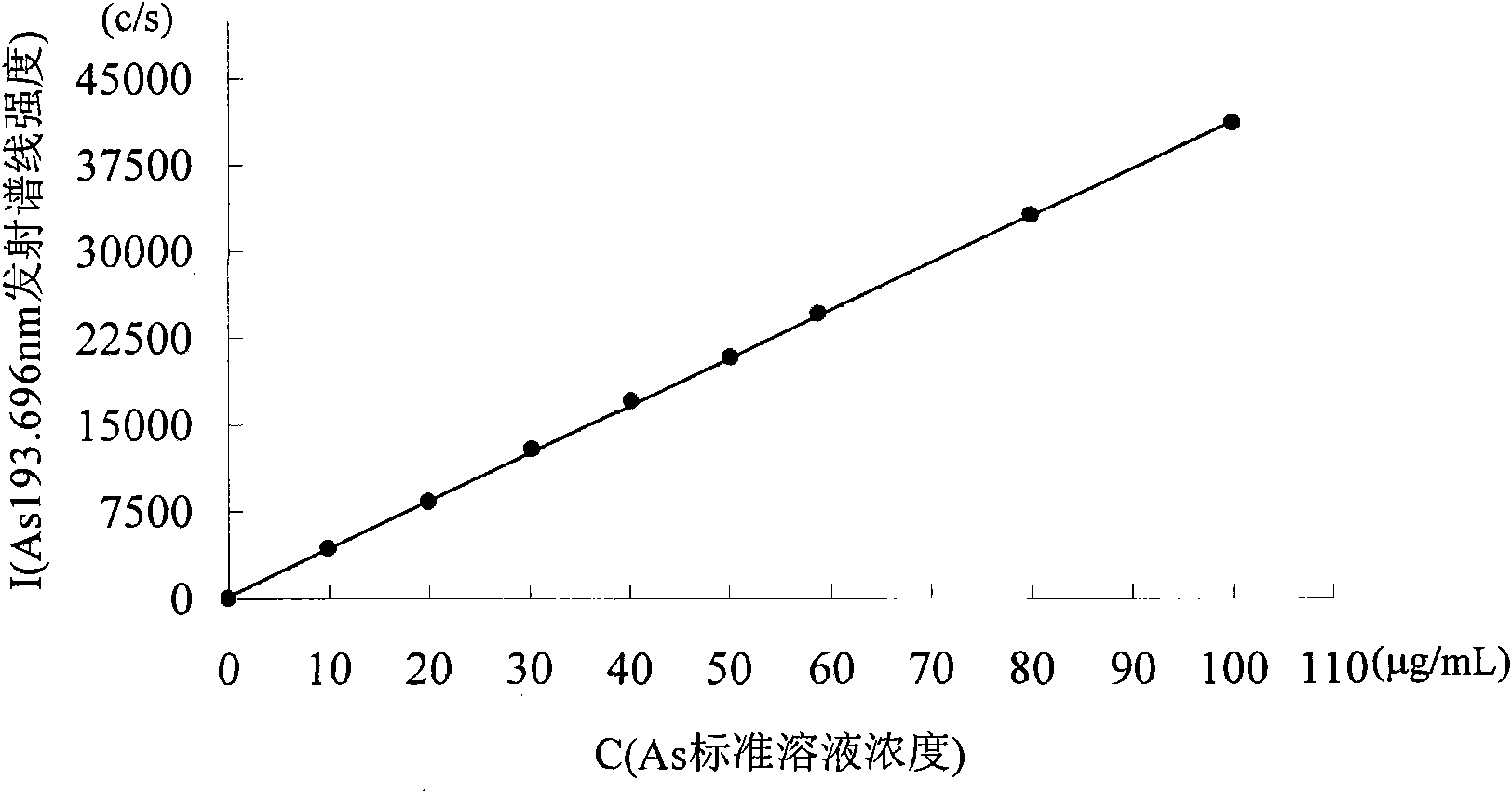
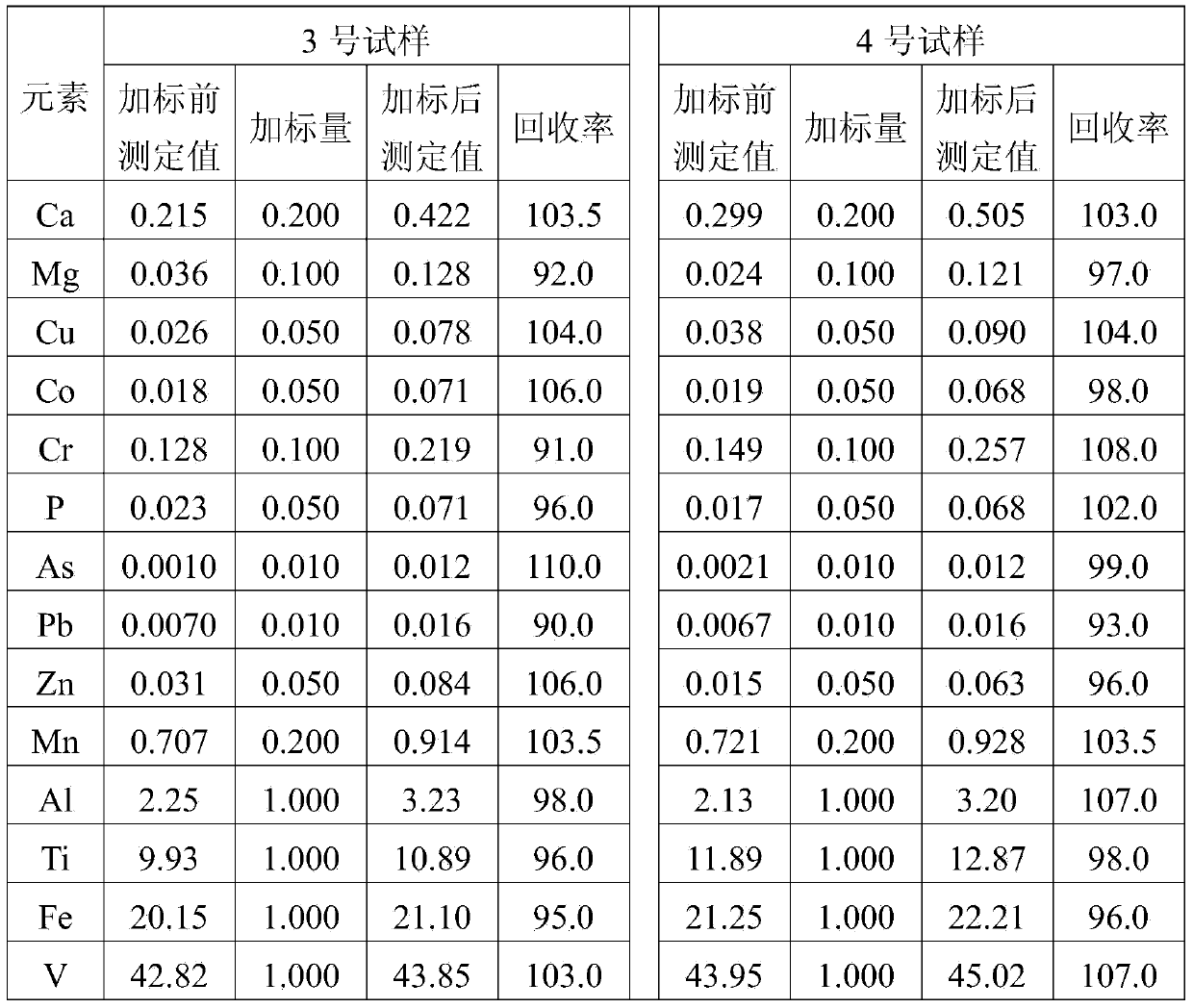
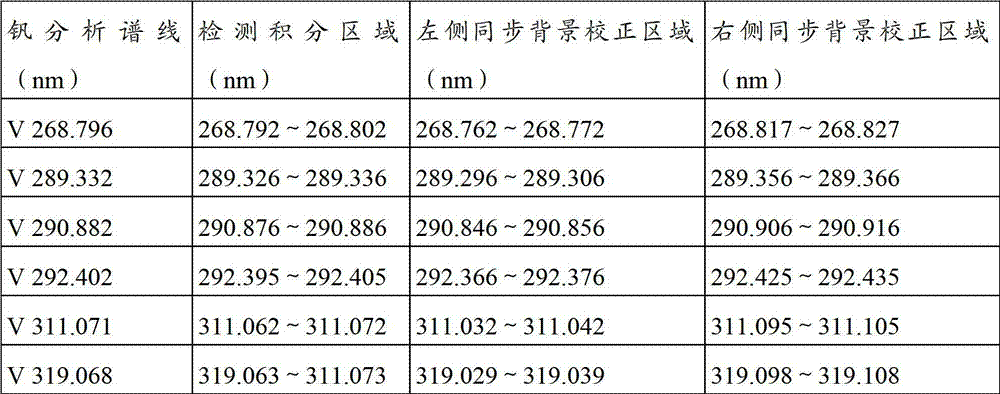
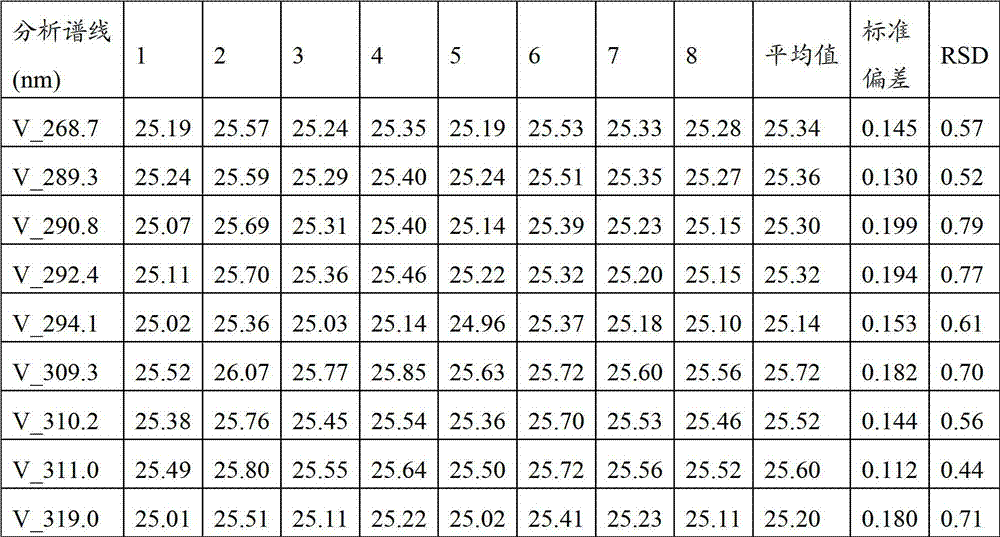
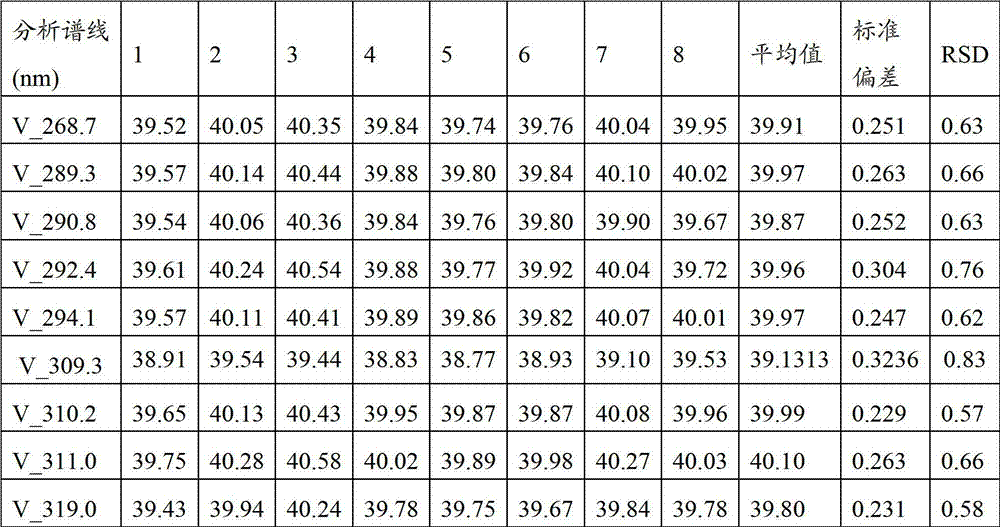
Analyses testing method of aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten impurity elements in chromium carbide
ActiveCN101303307ASolve difficult technical problemsImprove measurement accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationNiobiumDecomposition
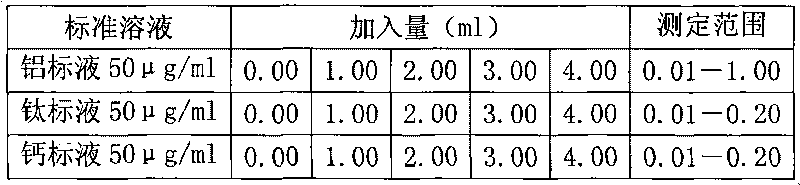
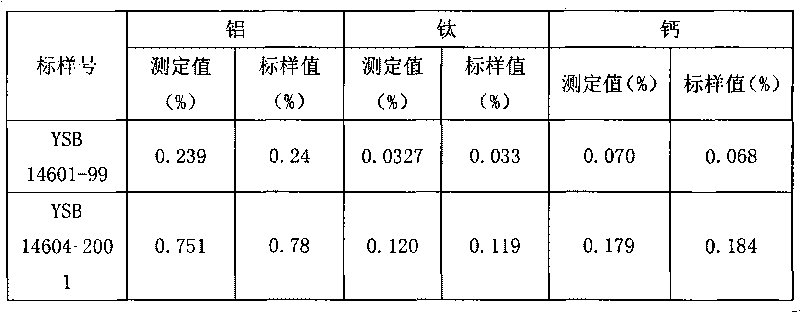
The invention discloses an analysis and detection method for impurity elements such as aluminum, calcium, ion, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten and the like in chromium carbide. The method comprises adding a chromium carbide sample into a dissolving cup, adding hydrofluoric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid sequentially, stirring, charging into a sealed high-pressure jar; putting the sealed high-pressure jar into a microwave extinguishing instrument for two times of microwave extinguishment; taking the high-pressure jar out of the microwave extinguishing instrument for cooling, transferring the dissolved chromium carbide liquid sample into a volumeric flask, diluting to a predetermined index, stirring; preparing a chromium substrate matched mixed standard solution series of aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium and tungsten; measuring element emission power of aluminum, calcium, iron, molybdenum, niobium, titanium, tungsten or the like in a blank liquid sample, a chromium carbide liquid sample and the prepared series mixed standard solution by an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer in the same time, obtaining the analysis result by checking a standard working curve or by linear equation calculation. The invention adopts two times of microwave extinguishment using the mixed acid, solves the problem of hardness in chromium carbide decomposition, having a measurement range from 0.010% to 1.00%, which is high in accuracy, and good in precision.
Owner:ZHUZHOU HARD ALLOY GRP CO LTD
Method for measuring contents of aluminum, titanium, manganese, nickel, tungsten and iron in cobalt-base alloy
ActiveCN101718689AEasy to handlePromote precipitationPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsManganeseMaterials science
The invention belongs to a technique for analyzing elements of an alloy, and relates to a method for measuring the contents of aluminum, titanium, manganese, nickel, tungsten and iron in a cobalt-base alloy. The method adopts an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer and is different according to different measured elements and different tungsten contents; when high-content tungsten is dissolved, the volume of test solution needs to be maintained between 20 and 40 mL, or the tungsten is easy to be separated out; by performing interference experiments and spectrogram analyses, the method finds the optimal analytical line, overcomes the interferences caused by a plurality of elements such as major elements of cobalt, chromium, tungsten and the like in the cobalt-base alloy, and improves the measuring accuracy; the sample dissolving speed is accelerated, and the sample dissolving time is shortened to 2 hours from about two or three days; and the method has wide measuring ranges including: 0.05 to 0.30 percent of the aluminum, 0.05 to 0.30 percent of the titanium, 0.05 to 1.00 percent of the manganese, 0.05 to 24.00 percent of the nickel, 0.05 to 20.00 percent of the tungsten, and 0.05 to 3.00 percent of the iron.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
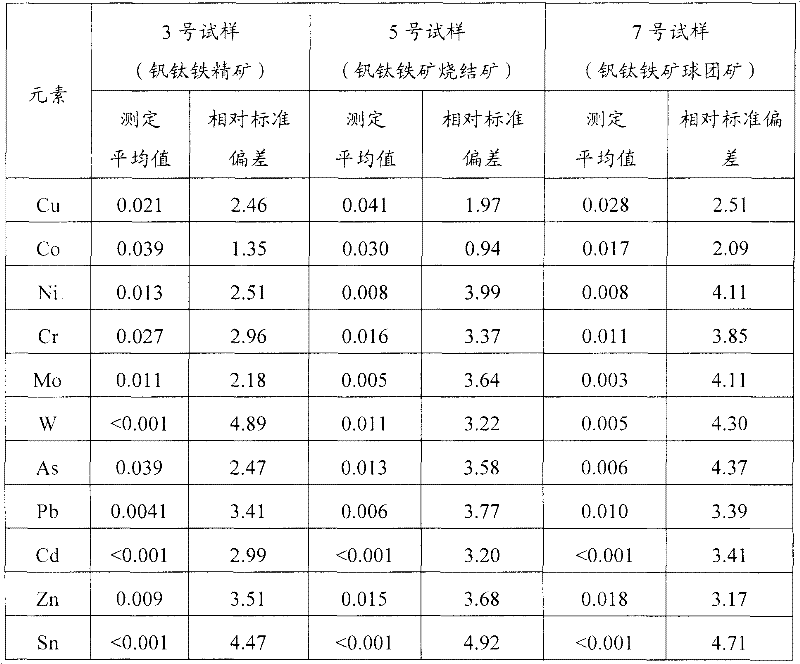
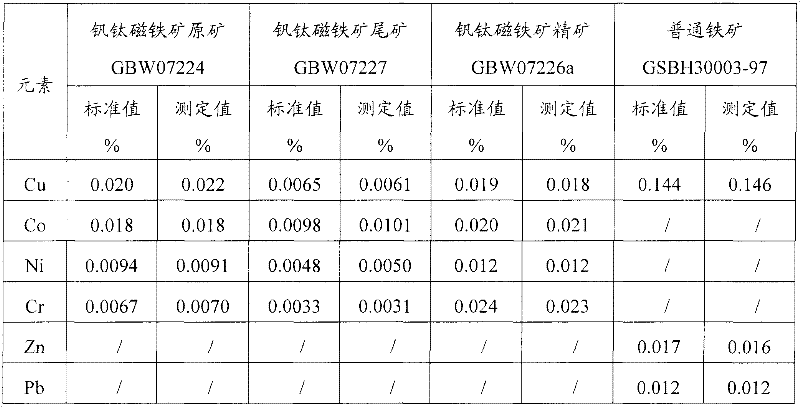
Digestion method and detection method for iron ore
InactiveCN101839828AAvoid influenceImprove detection accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsDigestionHigh pressure
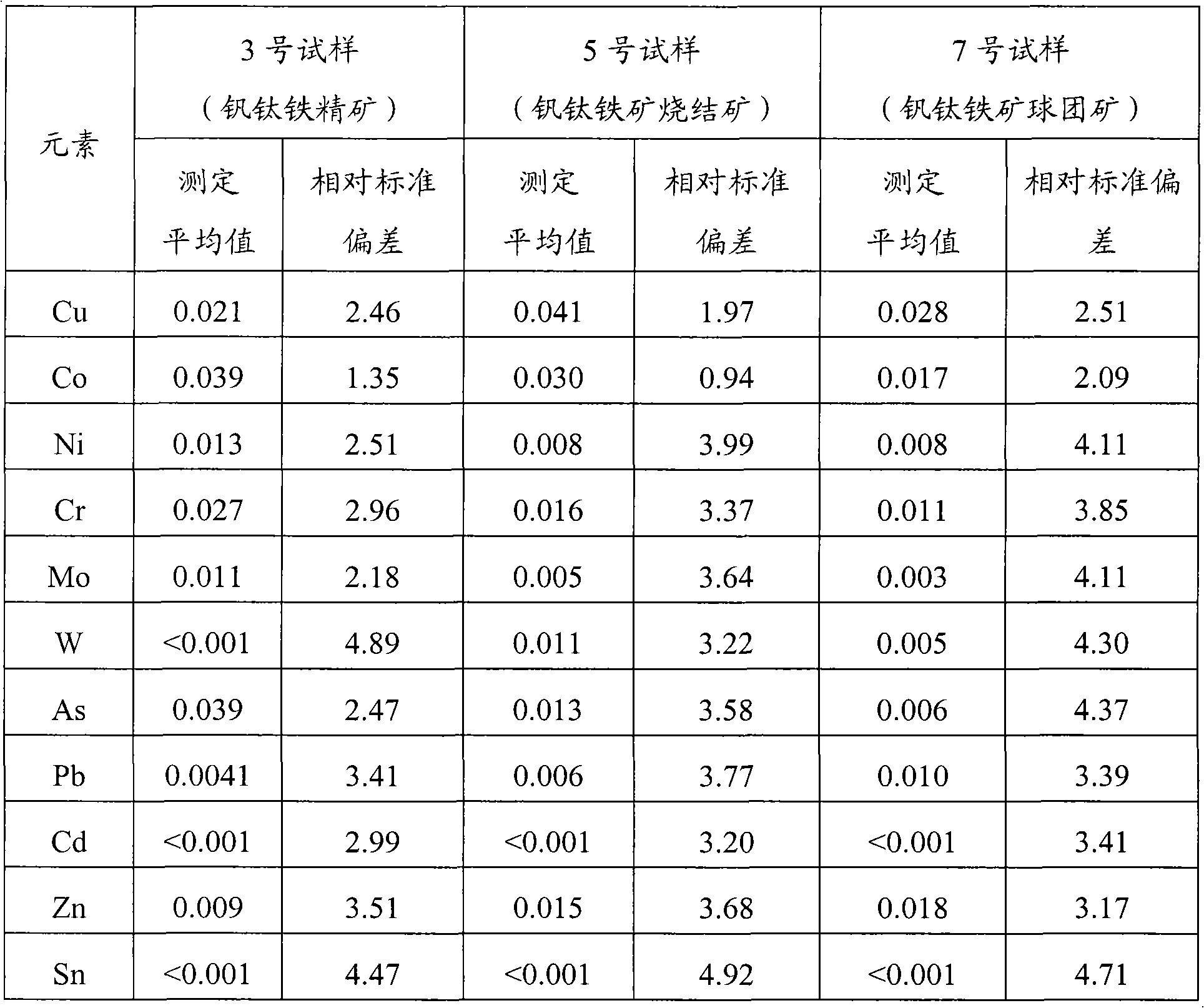
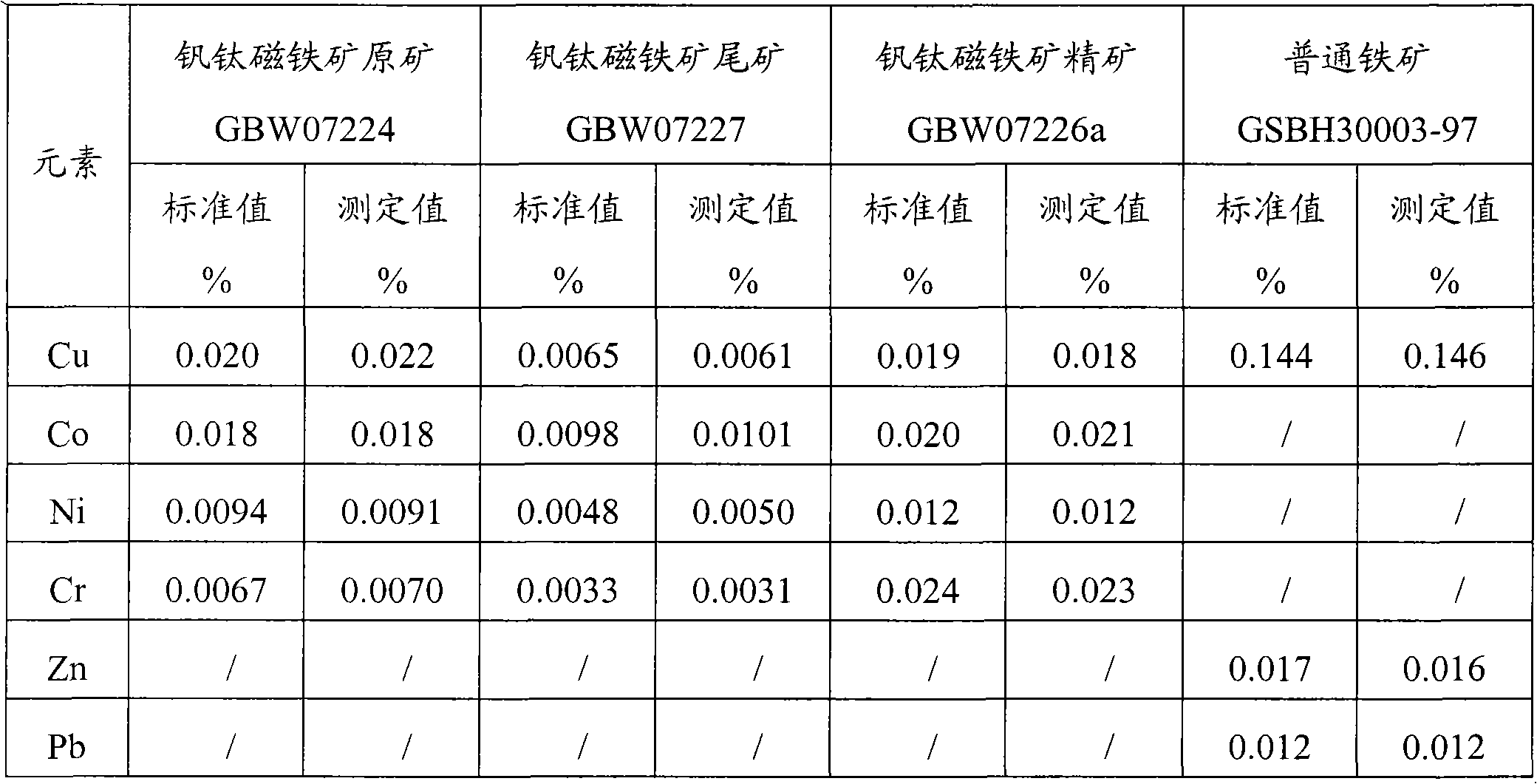
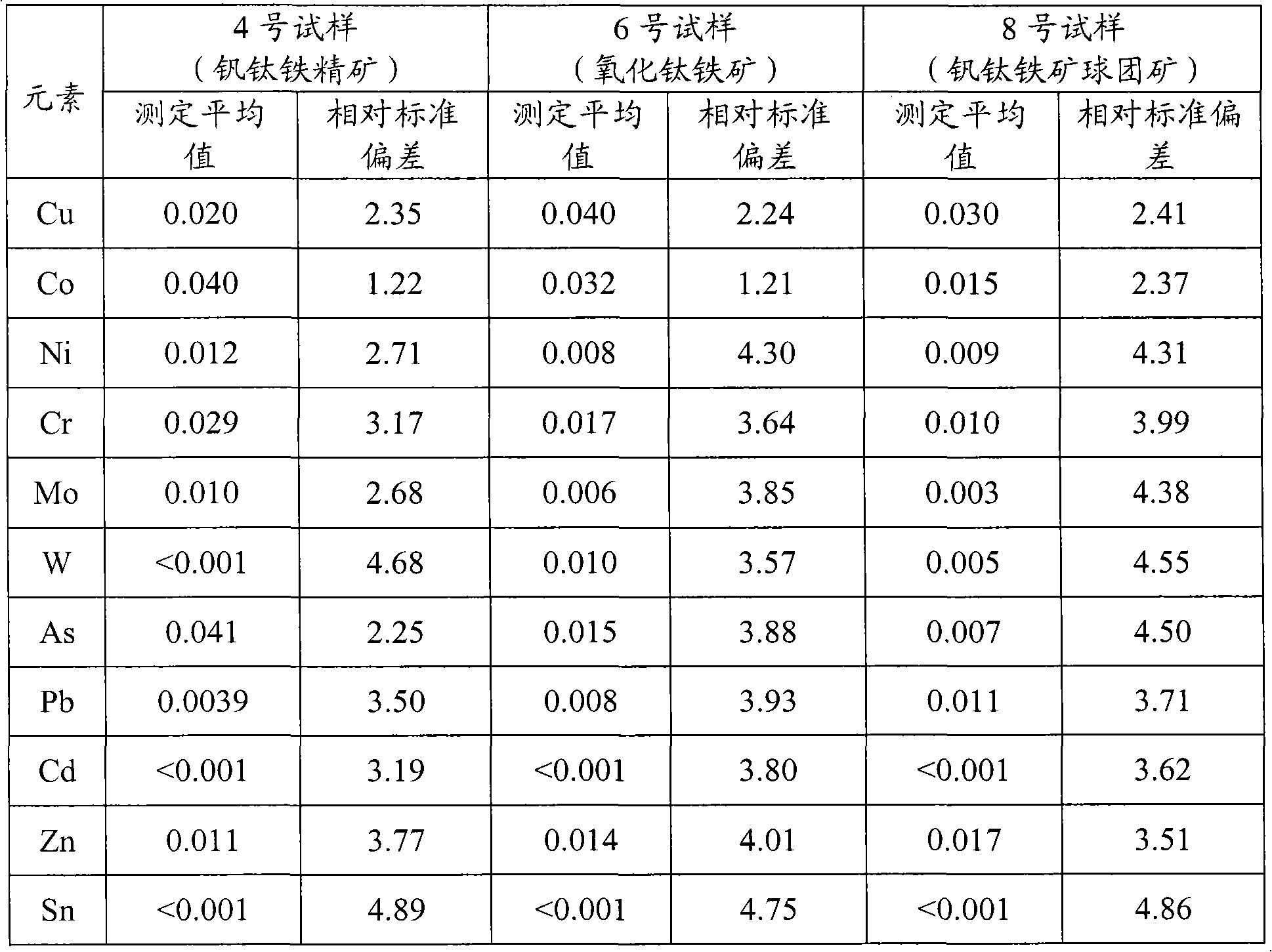
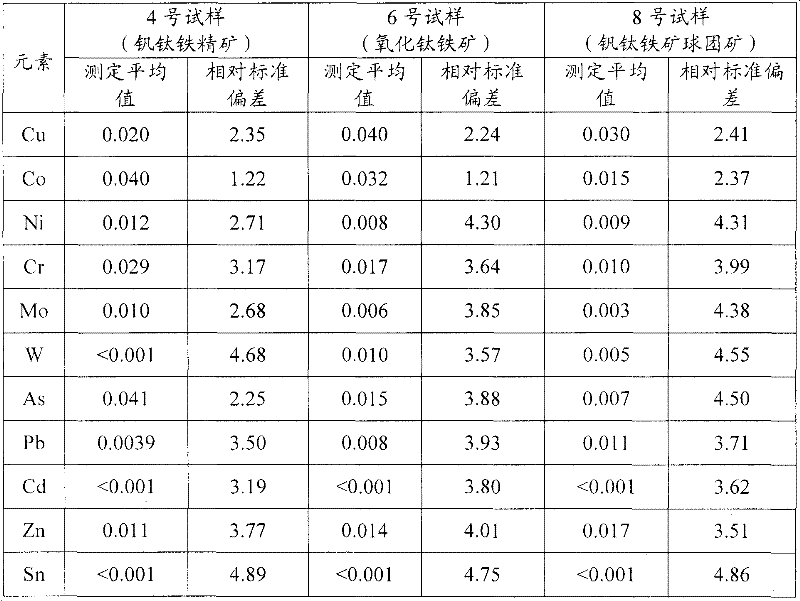
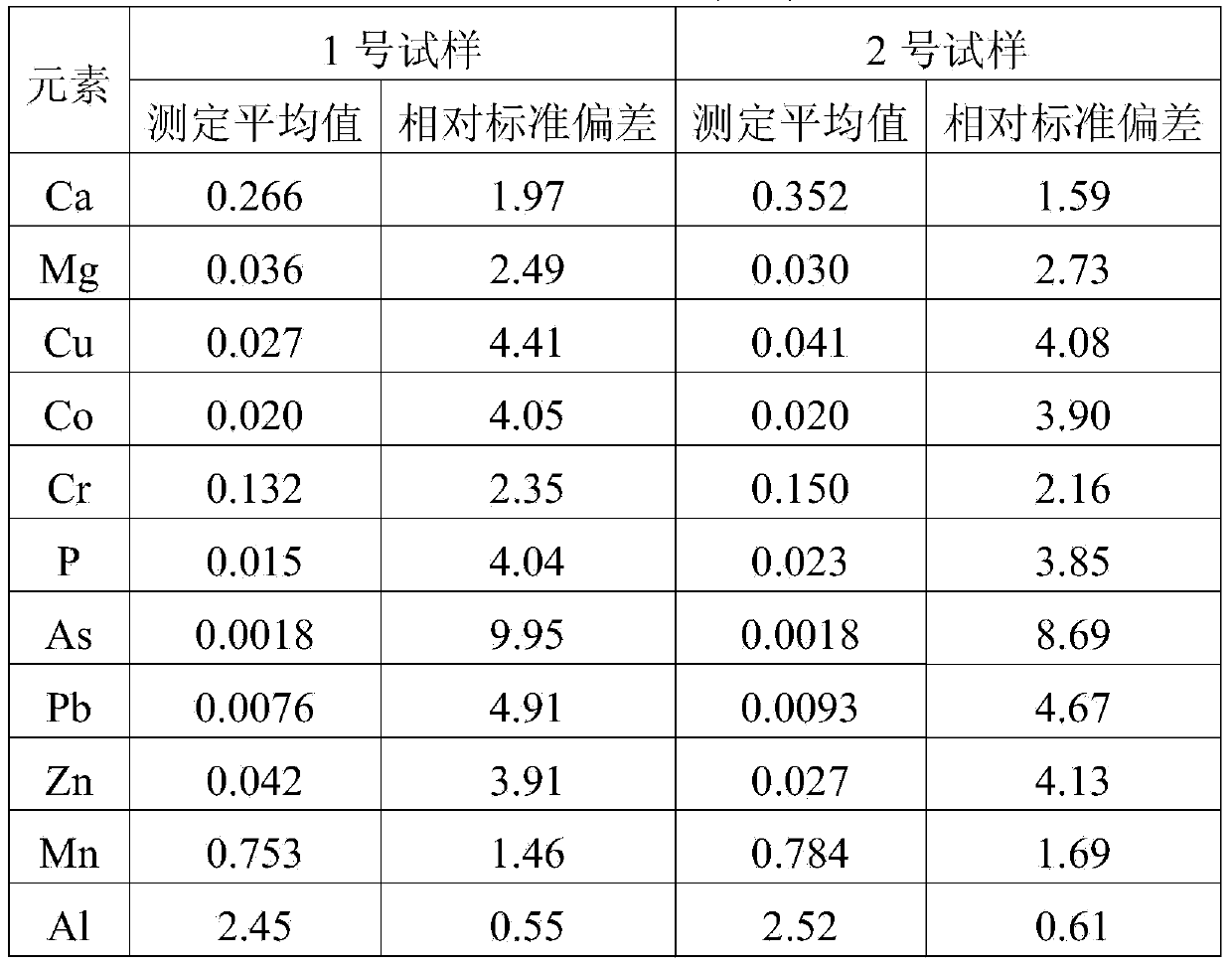
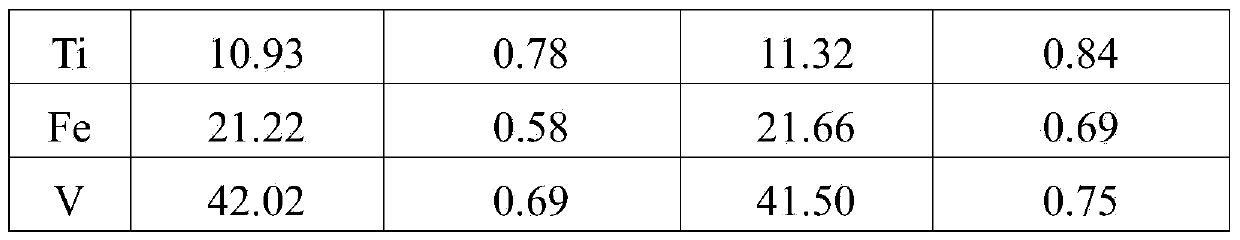
The invention provides a digestion method and a detection method for iron ore. The digestion method comprises the following steps: adding an iron ore sample in which hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid (or sulfuric acid) are mixed, then carrying out high-pressure closed microwave digestion to obtain a suspension; and heating the suspension in an unclosed system to secure the second digestion with residual nitric acid (or residual sulfuric acid) and added perchloric acid and hydrogen peroxide, thereby obtaining a solution which is digested fully. The detection method comprises the following steps: preparing a solution with the digested solution, and detecting the prepared solution by inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry, thereby obtaining content of each element of the iron ore sample. The invention has the advantages of high efficiency, high accuracy, and simple and fast process. Especially, the invention realizes accurate detection of key element content in iron ore, such as As, Pb, Zn, W, Sn, Ca, Mg, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr and Mo which affect product quality of iron and steel smelting and vanadium / titanium extraction.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +2
Detection method for simultaneously measuring migrated masses of lead, cadmium, chromium, arsenic, antimony and germanium in plastic packaging container for foods by ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry) method
InactiveCN102023155AEfficient determinationEasy to measurePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical emission spectrometryRadio frequency
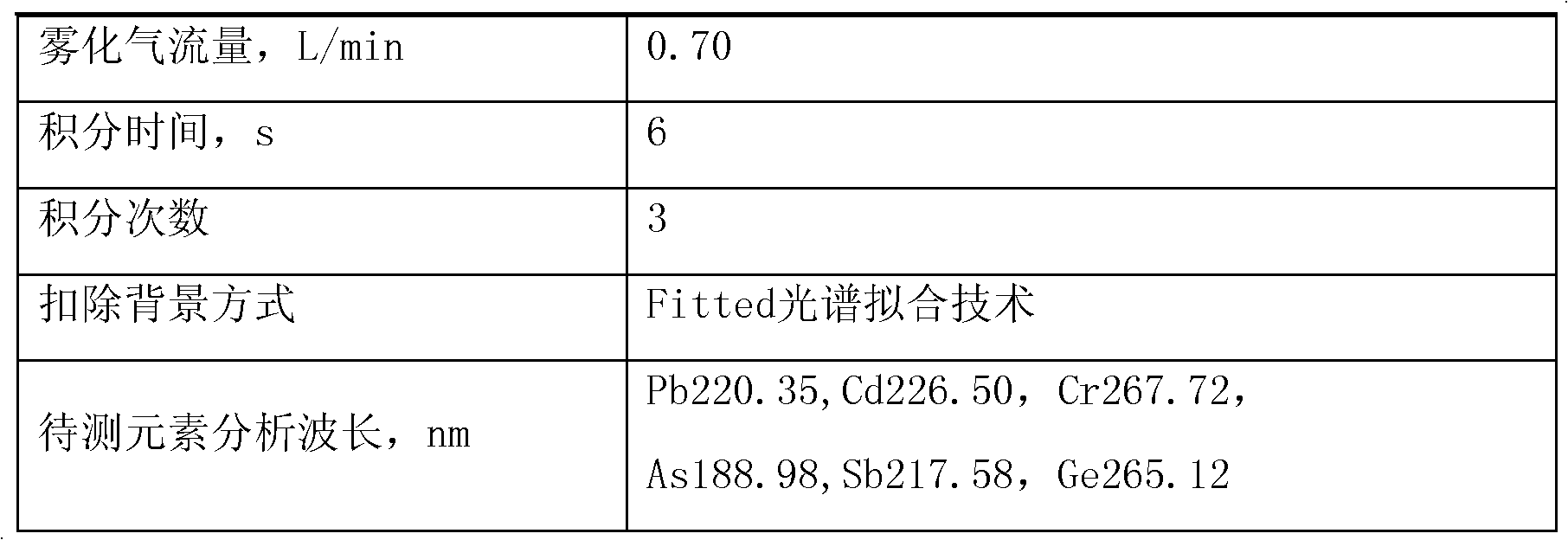
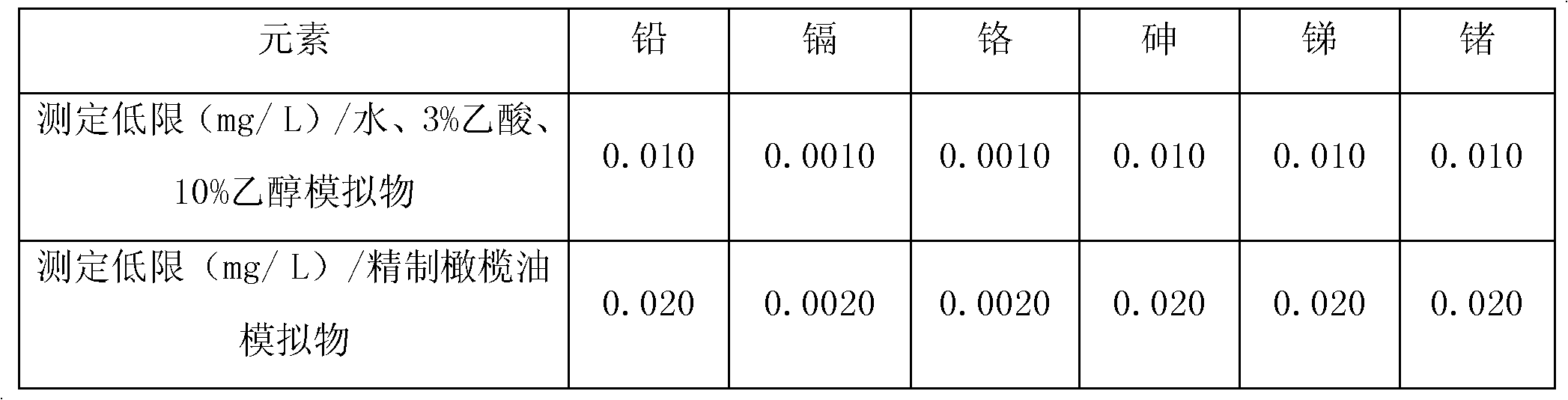
The invention relates to a detection method of harmful element migrated masses in a plastic packaging container for foods, in particular to a detection method for simultaneously measuring migrated masses of lead, cadmium, chromium, arsenic, antimony and germanium in a plastic packaging container for foods by an ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry) method. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out a migration test; 2, carrying out a blank test; and 3, carrying out measurement by an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. The ways of RF (radio frequency) power amplification (for a 3% acetic acid simulacrum test solution), ethanol removal (for a 10% ethanol simulacrum test solution) and microwave digestion (for a delicate olive oil test solution) are used to efficiently, simply and quickly measure the migrated masses of various harmful elements in four simulacrums in the plastic packaging container for the foods simultaneously.
Owner:THE INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT ZHEJIANG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for simultaneously measuring elements of silicon, aluminum, calcium and barium
InactiveCN101344487AAccurate measurementReduce pollutionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationRelative standard deviationAcid dissolution
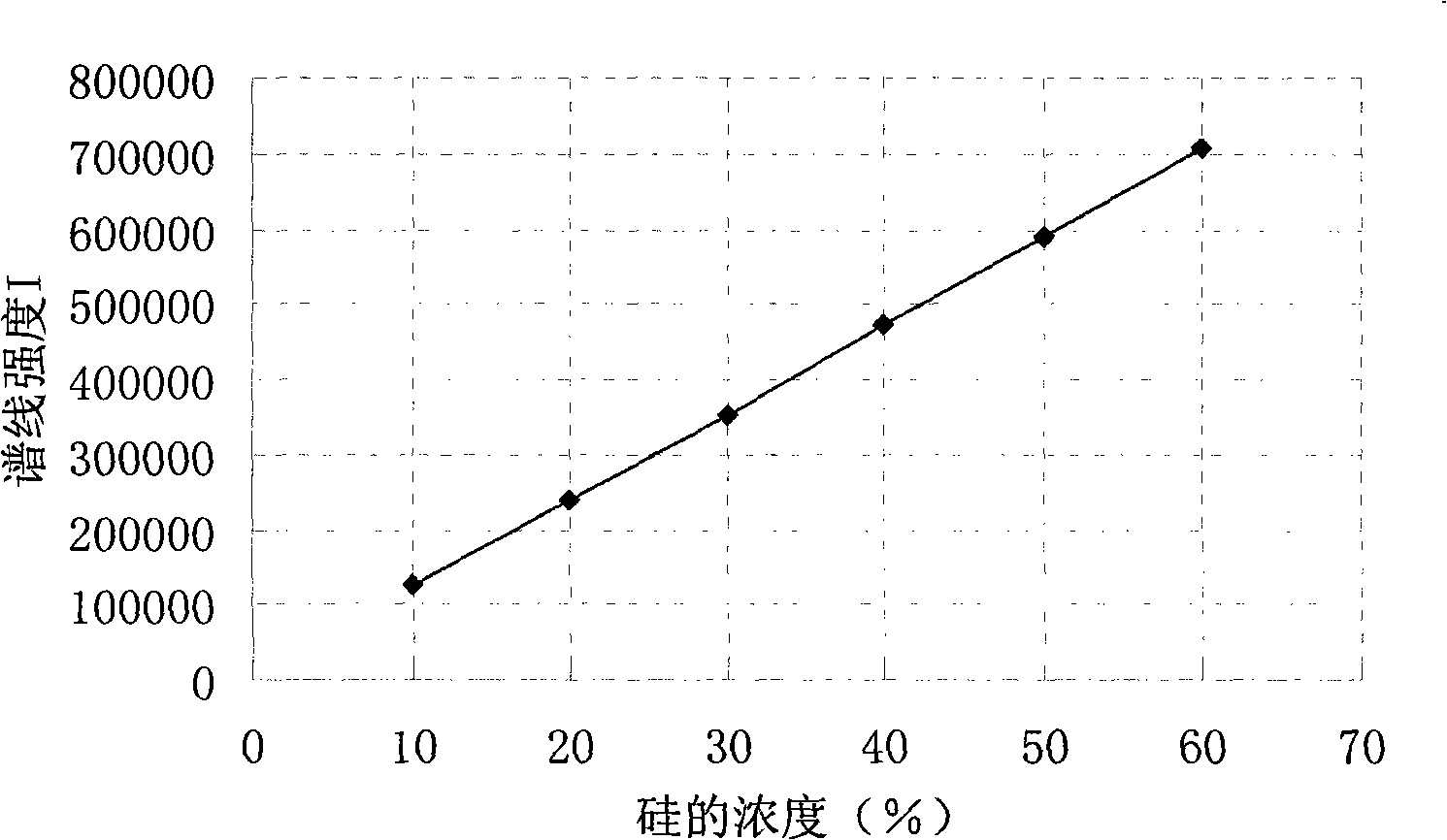
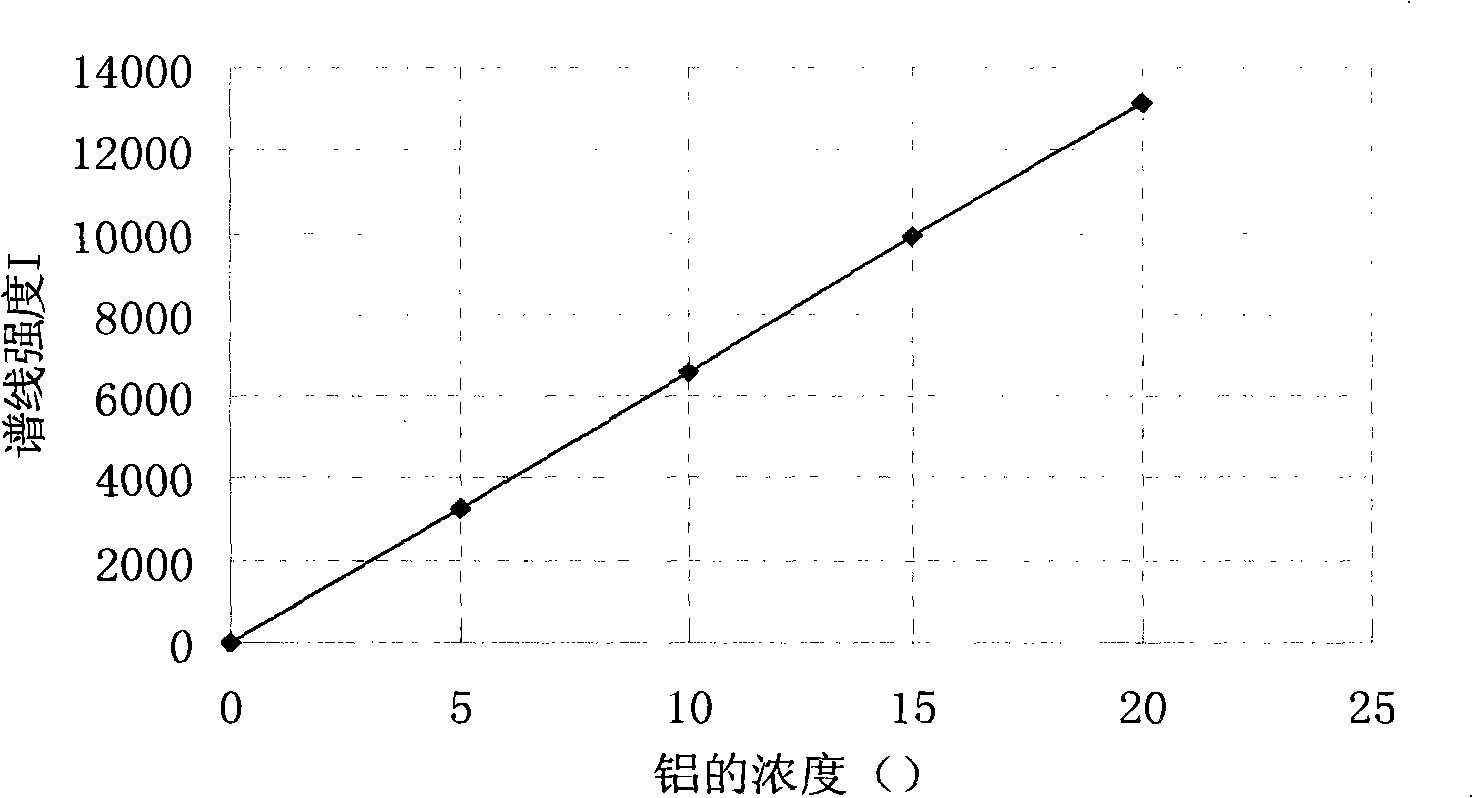
The invention discloses a method that can simultaneously analyze various elements, aims at solving the defects that currently the analysis of various elements cannot be finished at one time, and consequently the analysis time is long and the reagent usage is large, and discloses a method that can simultaneously measure the elements of silicon, aluminum, calcium and barium and comprises the following steps: a test sample is preprocessed through the acid dissolution method, microwave-digested, naturally cooled, and then placed into a volumetric flask with scales, diluted and shaken until well distributed, a solution with a standard working curve is prepared, an atomic emission spectrograph of inductance coupled plasmas is started and led to reach the measurement requirement, a plasma torch is lighted, the relative standard deviation of the plasma torch is led to be less than 5 percent, wavelength of each element is chosen, the working curves are plotted, and the content of each element is computed. The method combines the microwave digesting sample dissolution technique with the atomic emission spectrograph of inductance coupled plasmas, can simultaneously analyze nine elements including silicon, etc., is accurate and quick, has greatly reduced reagent usage, and reduces the environmental pollution that is caused by chemical reagents.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Method for measuring trace elements in high titanium high boiler slag
InactiveCN101349648ABreak down completelyShort processing timeAnalysis by thermal excitationTrace elementBoiler slag
The invention relates to a method for measuring microelements in high titanium blast furnace slag, which comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting an alkali fusion method to pre-process samples, and leading the samples to be totally conversed into soluble salt, and preparing into sample solution, secondly, preparing standard solution of iron, manganese, vanadium and phosphor with different concentrations, thirdly, respectively measuring the spectral line strength of calcium in the standard solution of iron, manganese, vanadium and phosphor with different concentrations, utilizing the concentration of elements to be the abscissa and the spectral line strength to be the longitudinal coordinate to draw a working curve, fourthly, measuring the intensity of the spectral lines of iron, manganese, vanadium and phosphor in sample solution under the condition which is the same to the step three, and calculating and assuring the content of the four elements in each sample solution according to the working curve. The invention has the advantages that the method is simple and fast, which has little dosage of agents and samples, and can simultaneously measure a plurality of elements. The method shortens analysis time, and lowers test cost.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Method for determining niobium element content in ferroniobium
InactiveCN101609048AAvoid hydrolysisBreak down completelyAnalysis by thermal excitationPretreatment methodNiobium
The invention relates to a method for determining niobium element content in ferroniobium, which comprises the following steps: a sample is weighted and put in a polytetrafluoroethylene beaker and deionized water is added for humidifying the sample; hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid are added into the sample, and then are heated so that the sample is slowly dissolved; after the sample is completely dissolved, the breaker is taken down and cooled; after the sample is cooled to room temperature, the volume is metered; reagent blank without the sample is adopted, and then standard solution of niobium element with different volumes is added, and finally deionized water is added and the volume is metered; spectral line strength of niobium element in standard solution is determined under the working condition of a setting inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer and a working curve is drawn; the spectral line strength of niobium element in ferroniobium sample solution to be determined is determined, and then a computer automatically determines the concentration of niobium element in sample solution according to the working curve. The method mainly solves problems of long operational process, narrow measuring range and the like, determines appropriate sample processing methods and analytic conditions of instruments, and realizes effectively, rapidly and accurately measuring niobium element in ferroniobium.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Digestion method and detection method of titanium-rich material
InactiveCN101315316AEfficient and fast digestionReduce salt concentrationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationHydrofluoric acidMicrowave
The invention provides a method for digesting a rich titanium product and a method for detecting the rich titanium product. The method comprises the following steps: placing a sample of the rich titanium product in a container; adding nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid into the container; sealing the container; conducting digestion with microwave to obtain a digestion solution. The method comprises the step of adopting an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer to detect the digestion solution prepared through the above steps. According to the digesting method and the detecting method, a plurality of key impurities with the content ranging from 15% to 0.001%, which determine the quality of the rich titanium product, can be simultaneously detected. Furthermore, the accuracy, the precision and the working efficiency of detection data are greatly improved.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +2
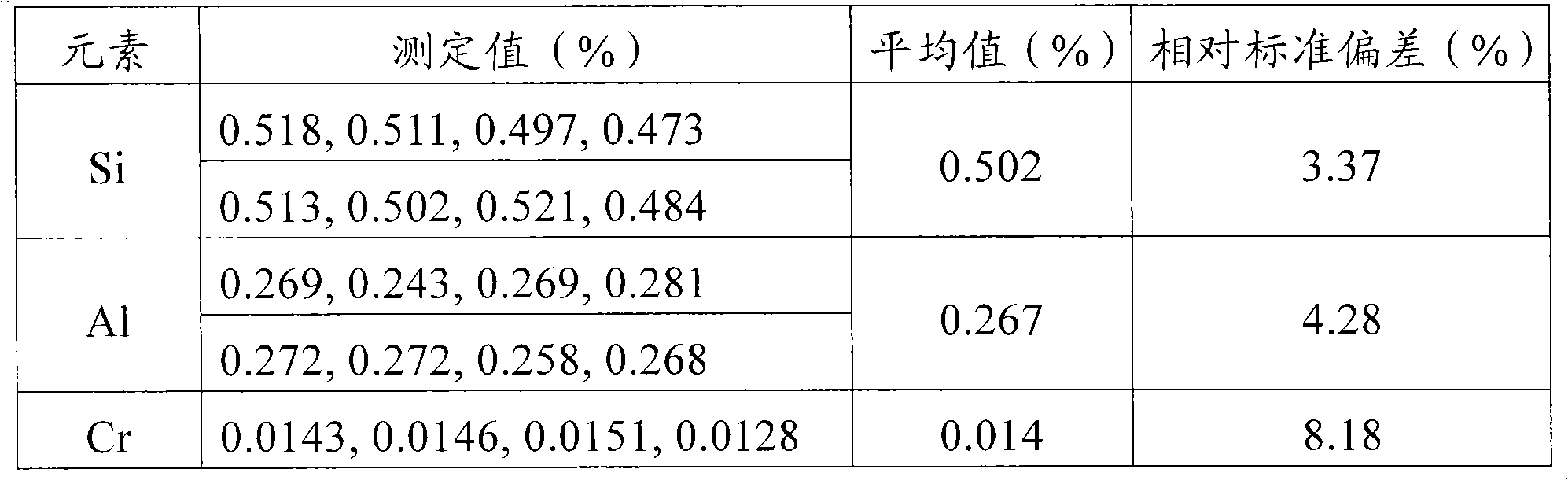
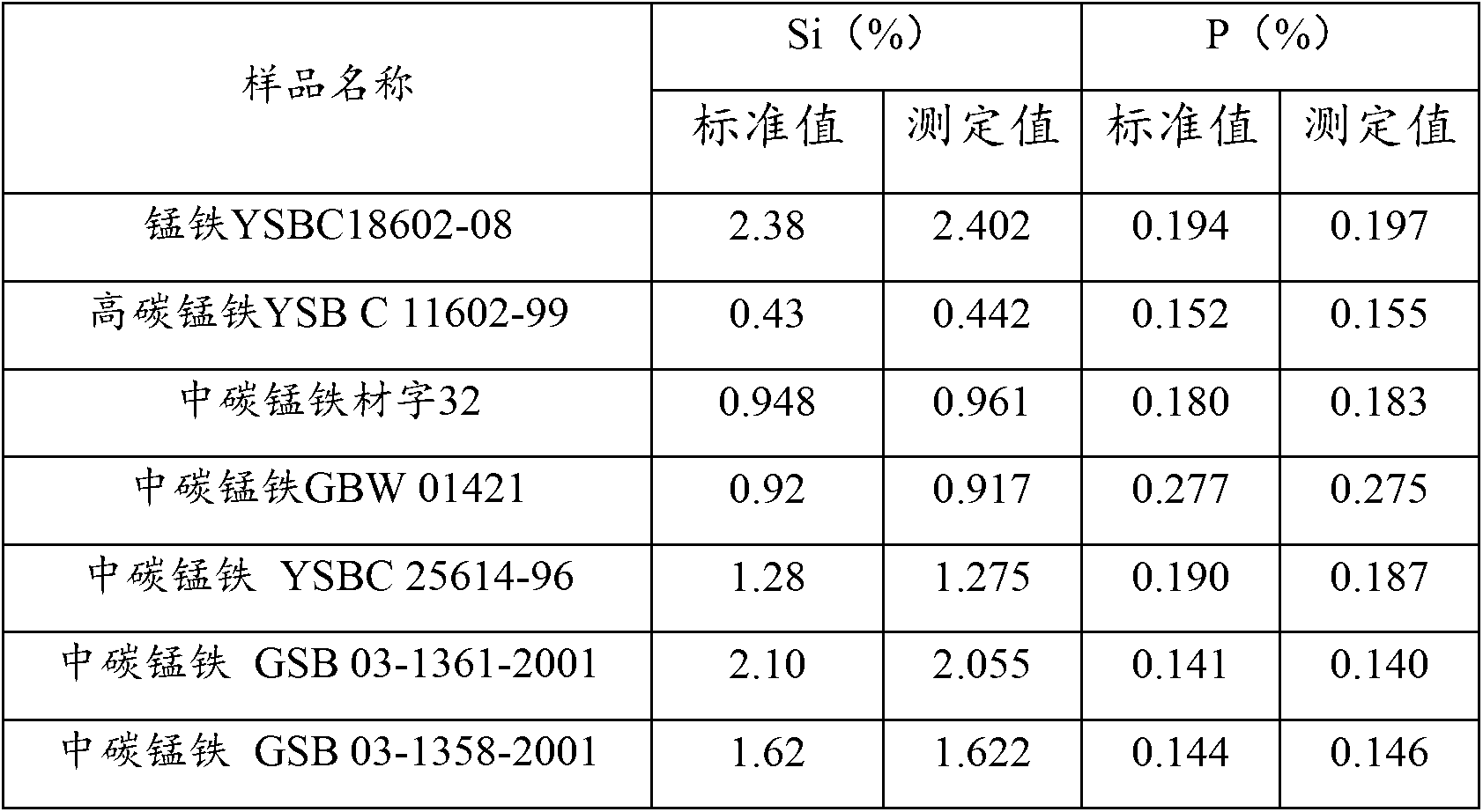
Method for measuring content of silicon and phosphorus in ferromanganese iron by inductively coupled plasma spectrum emission instrument
ActiveCN103175824AImprove accuracyRapid determinationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationUltimate tensile strengthInductance
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of silicon and phosphorus in ferromanganese iron by an inductively coupled plasma spectrum emission instrument. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing an atomized solution of a ferromanganese iron sample and standard solutions comprising a manganese standard solution, a phosphorus standard solution and a silicon standard solution; and introducing the atomized solution into an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, and measuring the spectral line intensity of an element to be measured, thus obtaining the content of silicon and phosphorus in the ferromanganese iron sample according to the spectral line intensity measured via the standard solutions with given concentrations. Due to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the content of silicon and phosphorus in ferromanganese iron can be rapidly and accurately measured.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Digestion method and detection method of iron ore
InactiveCN102252880AAvoid influenceImprove detection accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationDigestionHigh pressure
The invention provides a digestion method and a detection method of iron ore. The digestion method comprises the following steps of: performing closed-vessel microwave-assisted digestion on iron ore samples mixed with hydrofluoric acid and sulfuric acid to form suspension; and heating the suspension in an opened system to perform digestion for the second time by using the residual sulfuric acid so as to obtain completely digested solution. The detection method comprises the step of detecting solution to be tested, which is prepared from the digested solution by a detection method such as inductive coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy so as to obtain the content of each element of the iron ore. The digestion method and the detection method have the characteristics of high efficiency, simpleness, quickness and accuracy; and particularly, the key elements, such as As, Pb, Zn, W, Sn, Ca, Mg, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr, Mo and the like, of the iron ore can be detected accurately, wherein the key elements can influence the quality of products prepared by the processes such as iron and steel smelting, vanadium extraction, titanium extraction and the like.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +2
Method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples and detection method for tungsten-based samples
ActiveCN102230861APreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectrophotometryInductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy
The invention discloses a method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples and a detection method for tungsten-based samples. The method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples comprises the following steps: putting a tungsten-based sample in a container, adding water and nitric acid into the container, keeping the container airtight, carrying out microwavedigestion and settlement-separation on the sample under gradient temperatures, and restarting microwave for rinsing and deposition after the temperature of the solution decreases and is close to the boiling point of water so as to obtain a sample solution for detection and precipitates of tungstic acid. The detection method for tungsten-based samples in the invention is to analyze the digested sample solution with at least one analytical method selected from the group consisting of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry, graphite oven atomic absorption spectrometry and spectrophotometry so as to obtain the content of elements in the tungsten-based sample.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +1
Method for measuring contents of aluminum, calcium, barium, strontium, and phosphorus in silicon-calcium-barium alloy by ICP (inductively coupled plasma)
The invention relates to the technical field of ferrous metallurgical analysis, in particular to a method for measuring contents of aluminum, calcium, barium, strontium, and phosphorus in silicon-calcium-barium alloy by ICP (inductively coupled plasma). The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving a sample with nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, fuming with sulfuric acid, diluting to a certain volume, and introducing an atomized solution into an inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometer to measure the intensity of a spectral line to be measured; and solving the concentration of elements corresponding to substances to be measured based on the measured spectral line intensity of known concentration standard substances. The method has the advantages of no pollution and capability of analyzing and determining the content of the calcium, the barium, the aluminum, the phosphorus and the strontium in the silicon-calcium-barium alloy and meanwhile, separating the barium and the strontium which can not be separated by a chemical analytical method.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Method for clearing and detecting vanadic oxide
InactiveCN101532929AAvoid volatile lossAvoid pollutionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMulti methodPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for clearing and detecting vanadic oxide which includes steps as follows: taking vanadic oxide to a container, adding nitric acid to the container, processing pre-action under the normal temperature, then closing the container, processing microwave clearing. The detecting method includes steps as follows: using one or many methods of an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, a flame atomic absorption spectrometry and a graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for analyzing the cleared vanadic oxide, accordingly, obtaining elementary content of vanadic oxide sample.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
Digestion method and detection method of Tungsten-base class sample
InactiveCN102213657AMeet the requirements of technical indicatorsMeet the test requirementsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicrowavePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a digestion method of a Tungsten-base class sample, wherein the digestion method comprises the following steps: weighting and putting the tungsten-base class sample in a container, rinsing the wall of the container with a right amount of water; adding nitric acid and phosphoric acid, and then carrying out sample digestion and complex reaction by virtue of microwaves withinthe closed container; and after microwave processing is finished, cooling and diluting until an appropriate volume is achieved, thereby obtaining a sample solution used for detection. In addition, inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrum method and other detection methods are chosen to determine elements.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +1
Method for determining zirconium content in silicon-zirconium alloy
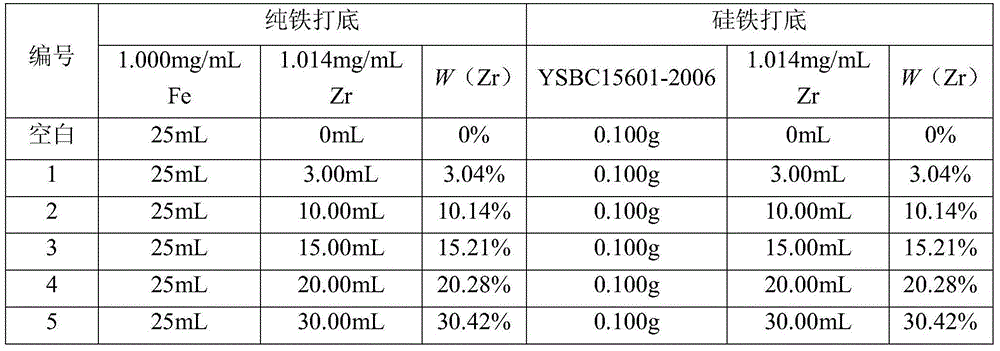
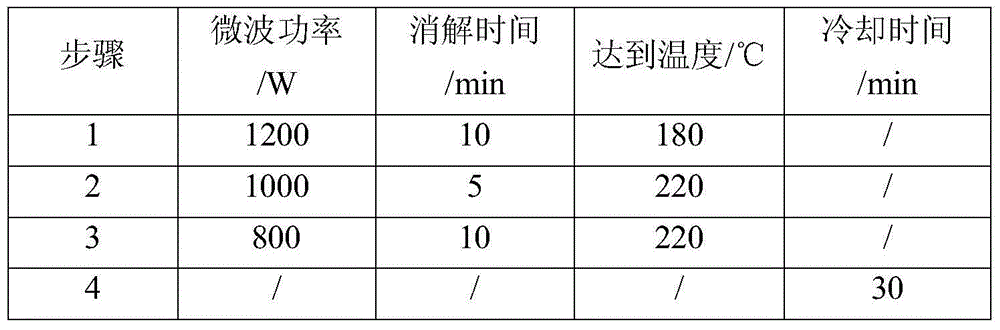
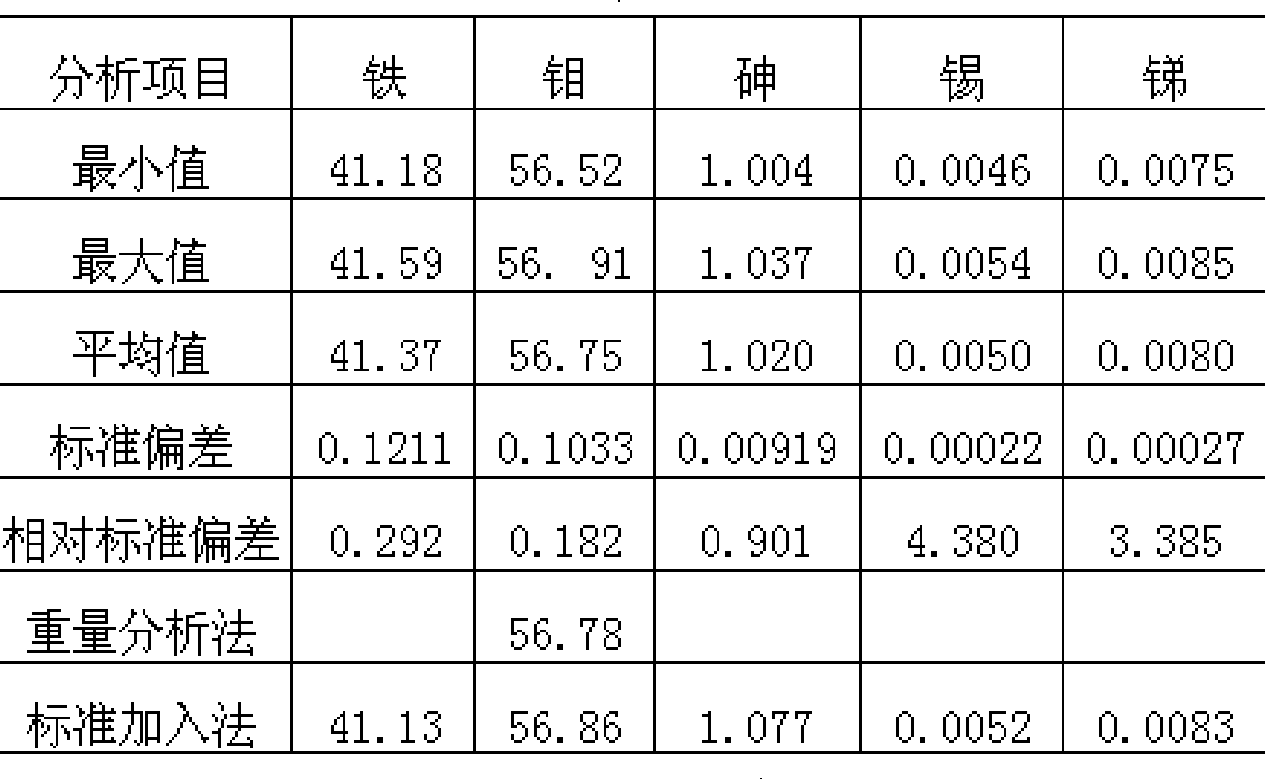
InactiveCN104597037ASolve the problem of cumbersome analysis operation and slow analysis speedReduce dosageAnalysis by thermal excitationFerrosiliconZirconium alloy
The invention relates to a method for rapidly determining zirconium content in silicon-zirconium alloy, belonging to the technical field of chemical analysis tests. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving pure iron or silicon iron as matrix, adding standard solutions with different amounts of zirconium to prepare a standard solution; determining the standard solution by virtue of an ICP-OES to prepare a standard curve; dissolving a sample with one or more of nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid and perchloric acid, and diluting with water to achieve a certain volume; introducing the solution into the ICP-OES to determine to-be-determined spectral line intensity; determining the concentration of a to-be-determined element on a calibration curve. The zirconium content range in the silicon-zirconium alloy can be determined to be 0-30%; the standard solution prepared by the method is similar to sample solution matrix; the matrix effect is removed; the problems of fussy chemical analysis operation and slow analysis speed are solved by virtue of a high-precision analysis instrument; and the method has the advantages of being simple, fast, high in accuracy and precision and the like.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
Method for measuring impurity elements arsenic, tin antimony in ferromolybdenum
ActiveCN101435775AEasy pretreatmentSuitable for mass production inspectionAnalysis by thermal excitationImpurityAntimony
The invention provides a method for determining arsenic, tin and antimony in ferromolybdenum, which belongs to the field of quantitative analysis in analytical chemistry. The method for determining arsenic, tin and antimony in ferromolybdenum comprises the steps of dissolving a ferromolybdenum specimen in mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, using standard serial solutions to draw a working curve on an inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer, deducting interference among elements and background interference through a computer program correction mode and determining arsenic, tin and antimony which are trace detrimental impurity element in a specimen solution. The method does not need to perform separation, enrichment and other fussy operation during specimen pretreatment and only needs to suck the ferromolybdenum specimen solution into an instrument for determination, and the percentage content of trace arsenic, tin and antimony in the specimen can be simultaneously displayed after tens of seconds. The content range that can be directly determined by the method is as follows: 0.005 to 1.00 percent of arsenic, 0.001 to 0.20 percent of tin and 0.001 to 0.10 percent of antimony.
Owner:CHINA ERZHONG GRP DEYANG HEAVY IND
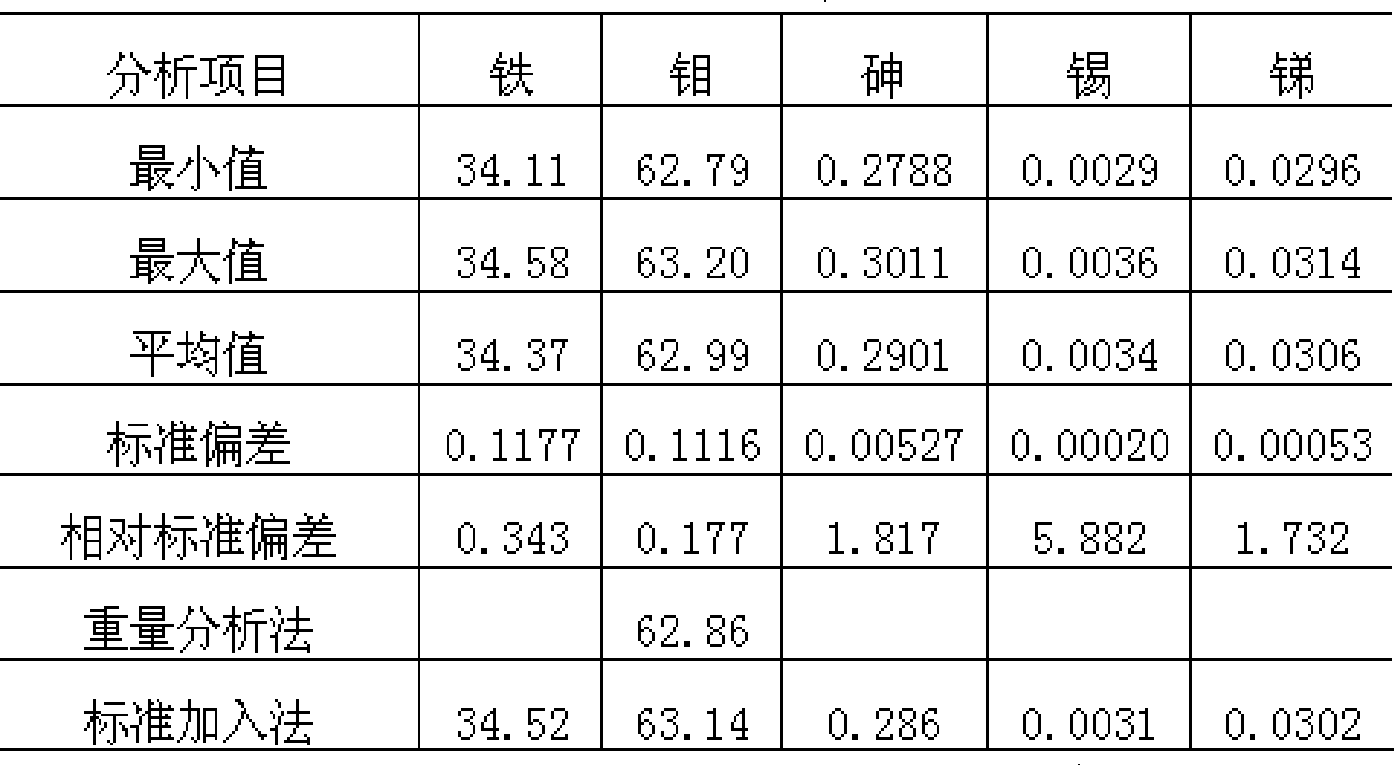
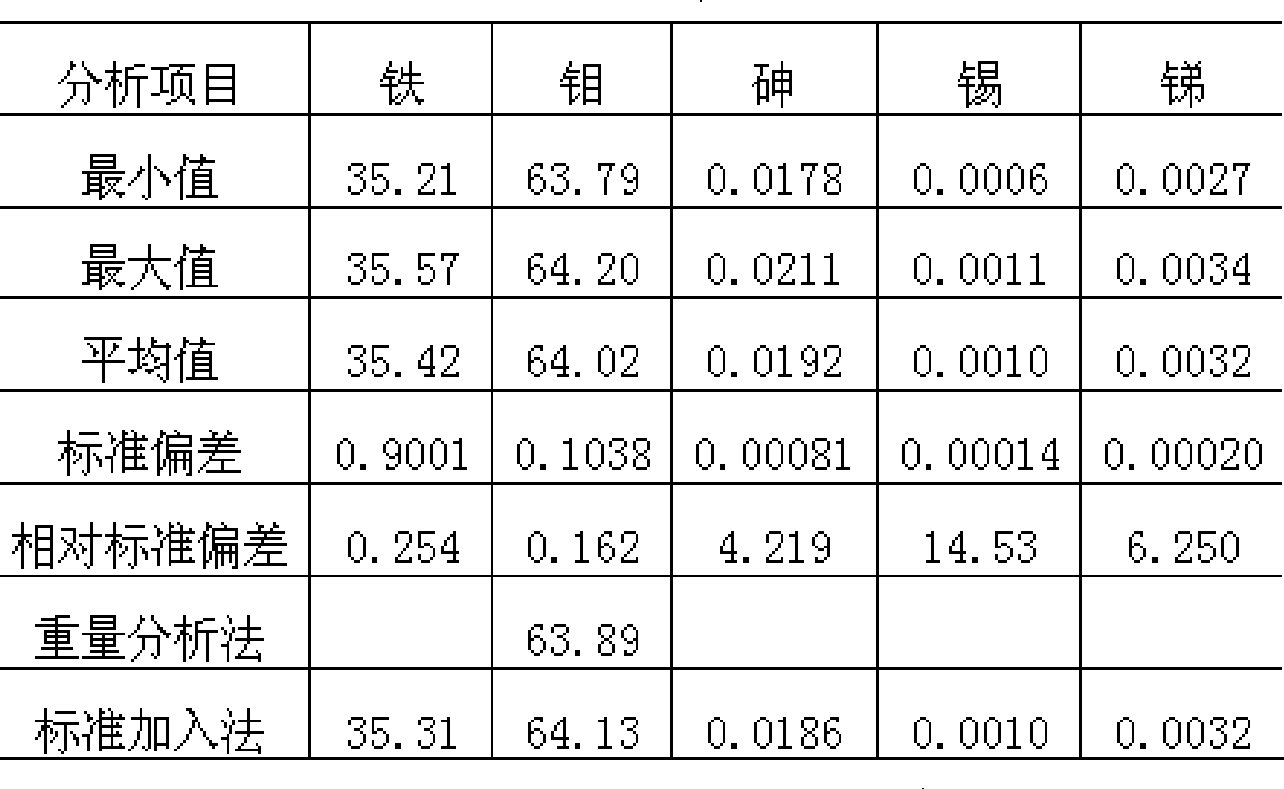
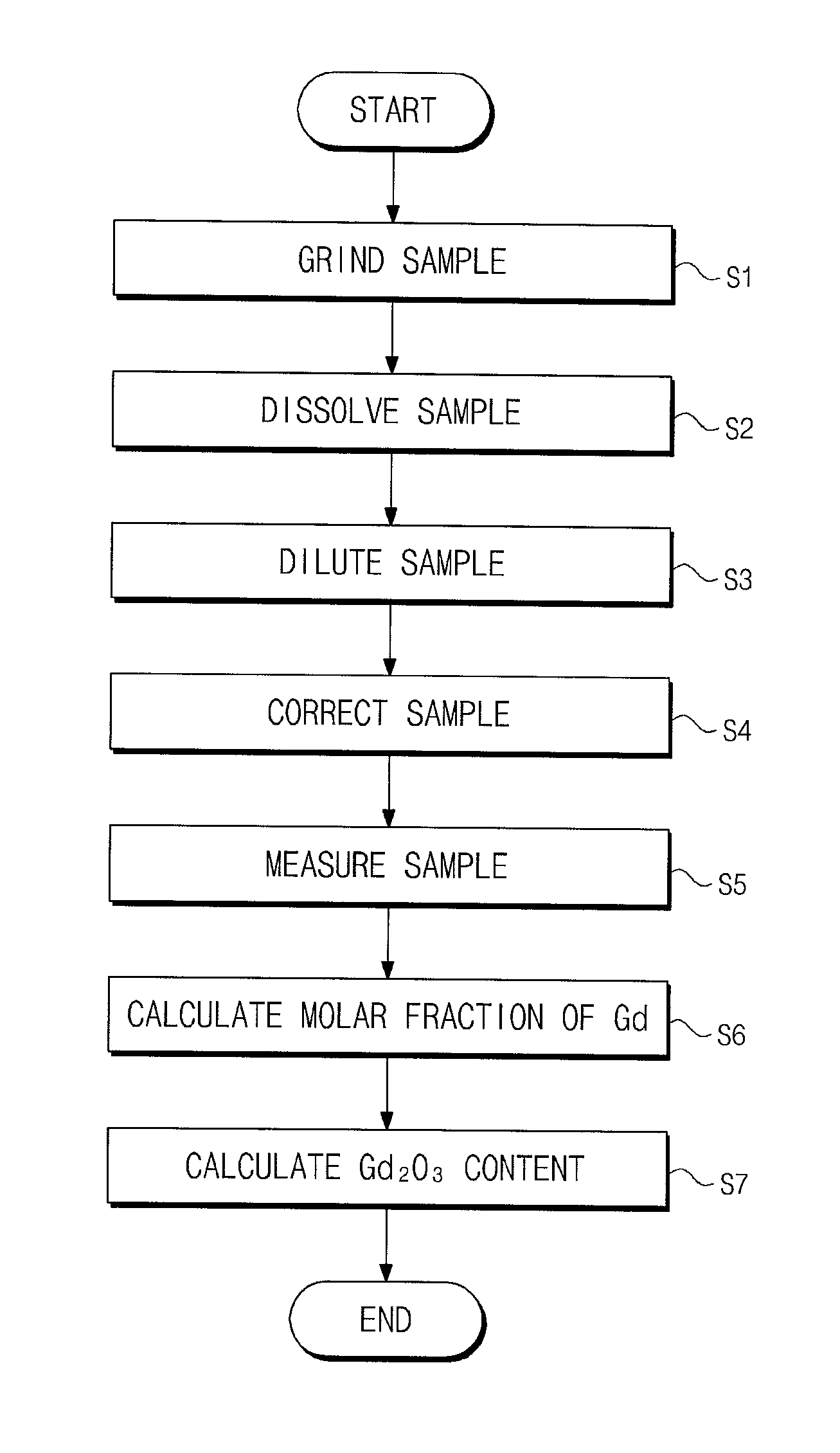
Method of measuring gadolinia content using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry
A method of measuring a gadolinia content using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry is provided. The method can include grinding sintered gadolinium using a percussion mortar to obtain a ground sample; warming the ground sample and then dissolving it with an acid solution to obtain dissolved gadolinia; diluting the dissolved gadolinia with distilled water to obtain a diluted gadolinia solution; measuring mass of each of a uranium element and a gadolinium element in the diluted gadolinia solution by a unit of ppm using the inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry; and calculating a molar fraction of gadolinium from the diluted gadolinia solution and then calculating the gadolinia content using the molar fraction of gadolinium.
Owner:KEPCO NUCLEAR FUEL CO LTD
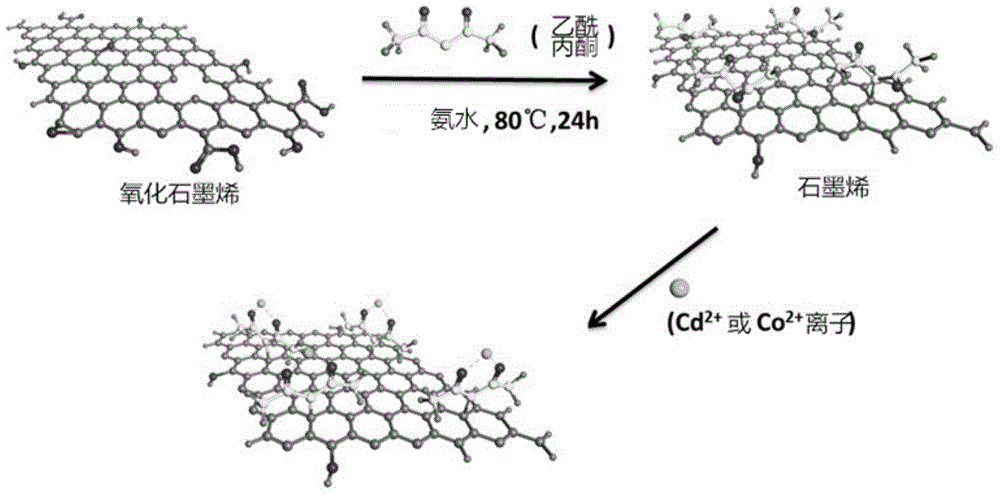
Method for adsorbing heavy metal ions via graphene
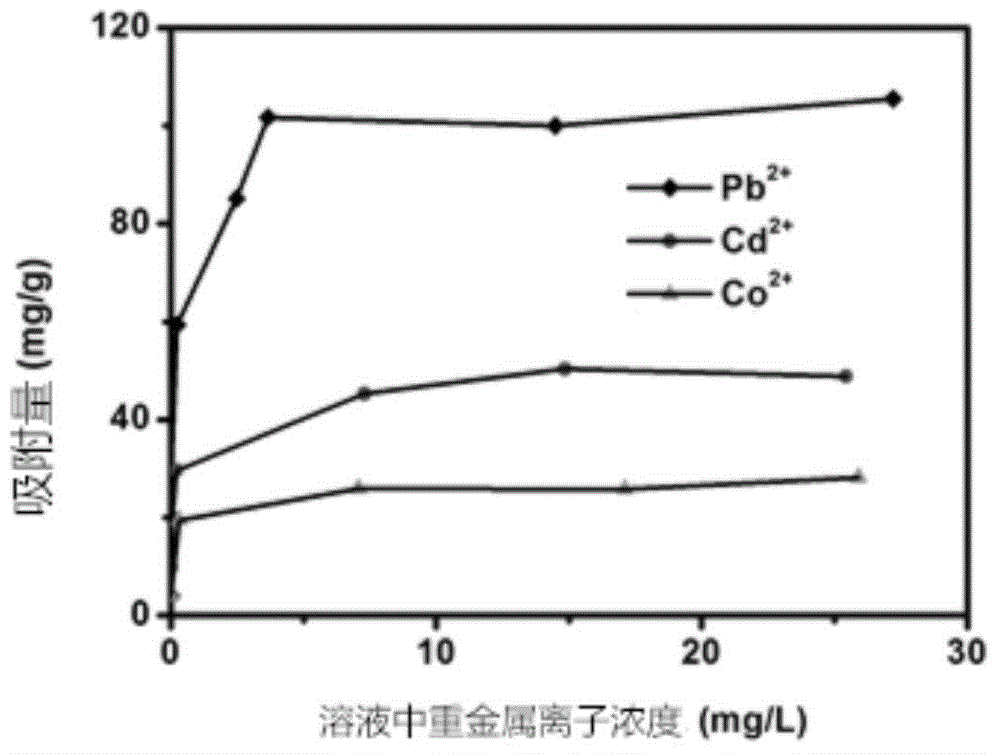
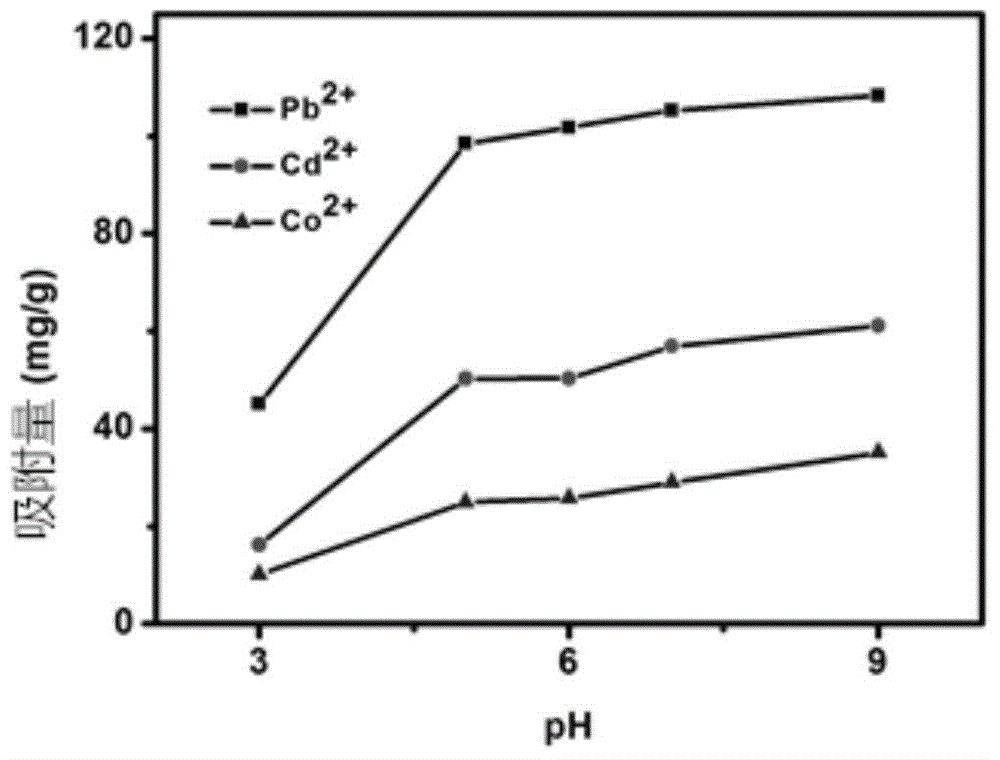
InactiveCN104016438AHas a complexing effectLarge specific surface areaWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSorbentCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a method for adsorbing heavy metal ions via graphene. The method comprises the following steps: adding the graphene taken as an adsorbent prepared by reduction of diacetone into an aqueous solution of heavy metal ions Pb2<+>, Cd2<+> and Co2<+>, regulating pH (Potential Of Hydrogen), stirring and filtering so as to obtain filtrate; and measuring the concentration of the ions in the filtrate via an inductive-coupling plasma atom emission spectrum, stabilizing the concentrations of the Pb2<+>, the Cd2<+> and the Co2<+> and the quality of the graphene and changing the pH so as to determine the optimal pH. According to the method, the maximum adsorption quantity of the prepared graphene to the Pb2<+> is 105.4mg / g; the maximum adsorption quantity of the prepared graphene to the Cd2<+> is 49.28mg / g; the maximum adsorption quantity of the prepared graphene to the Co2<+> is 27.78mg / g, wherein the maximum adsorption quantity of the prepared graphene to the Cd2<+> is 4.5 times greater than the maximum adsorption quantity of an acidified multi-walled carbon nanotube to the Cd2<+>. Thus, the method has a good application prospect in the treatment of sewage.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for determining chromium content and aluminum content in nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite
ActiveCN102735678ALarge amount of solutionSolve solubilityPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationElement analysisMaterial resources
The invention belongs to a nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite element analysis technology, and relates to a method for determining chromium content and aluminum content in nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite, wherein microwave sample digestion and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy are adopted to determine the chromium content and the aluminum content in the nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite. According to the method, 5-10 mL of hydrochloric acid, 1-5 mL of nitric acid and 5-10 drops of hydrofluoric acid are adopted to treat (metal-inorganic non-metal powder) nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite, such that problems of large use amounts of reagents for dissolving the sample, difficult dissolving of the sample, incomplete dissolving of the sample, and the like in the prior art are solved. With the present invention, spectrum analysis is performed to find the best analysis line so as to overcome interference of the major element nickel in the nickel-chrome-aluminum coated diatomite and improve measurement accuracy; the study results show that the established method for determining the chromium content and the aluminum content in the nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite is accurate and reliable, and can meet requirements of research and production; and the method of the present invention has characteristics of rapidness, easy operation, manpower saving and material resource saving.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
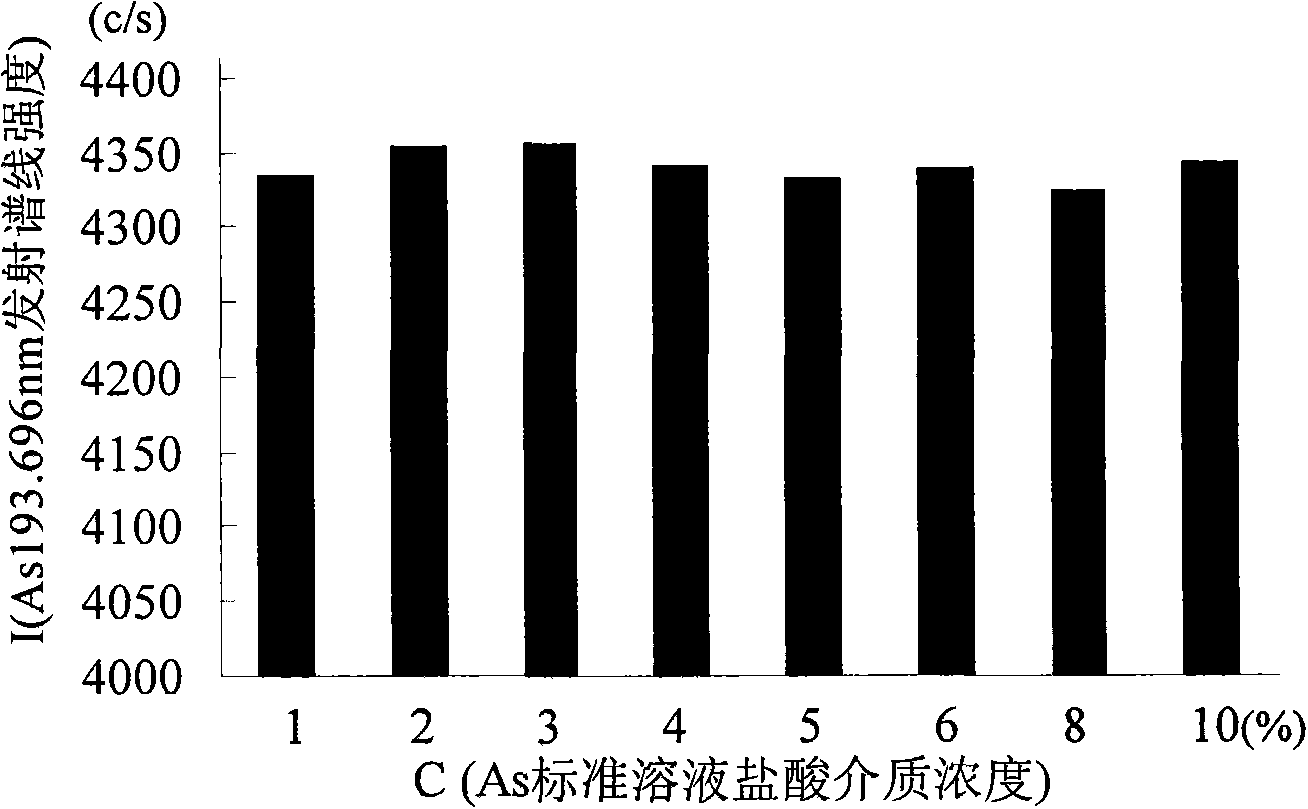
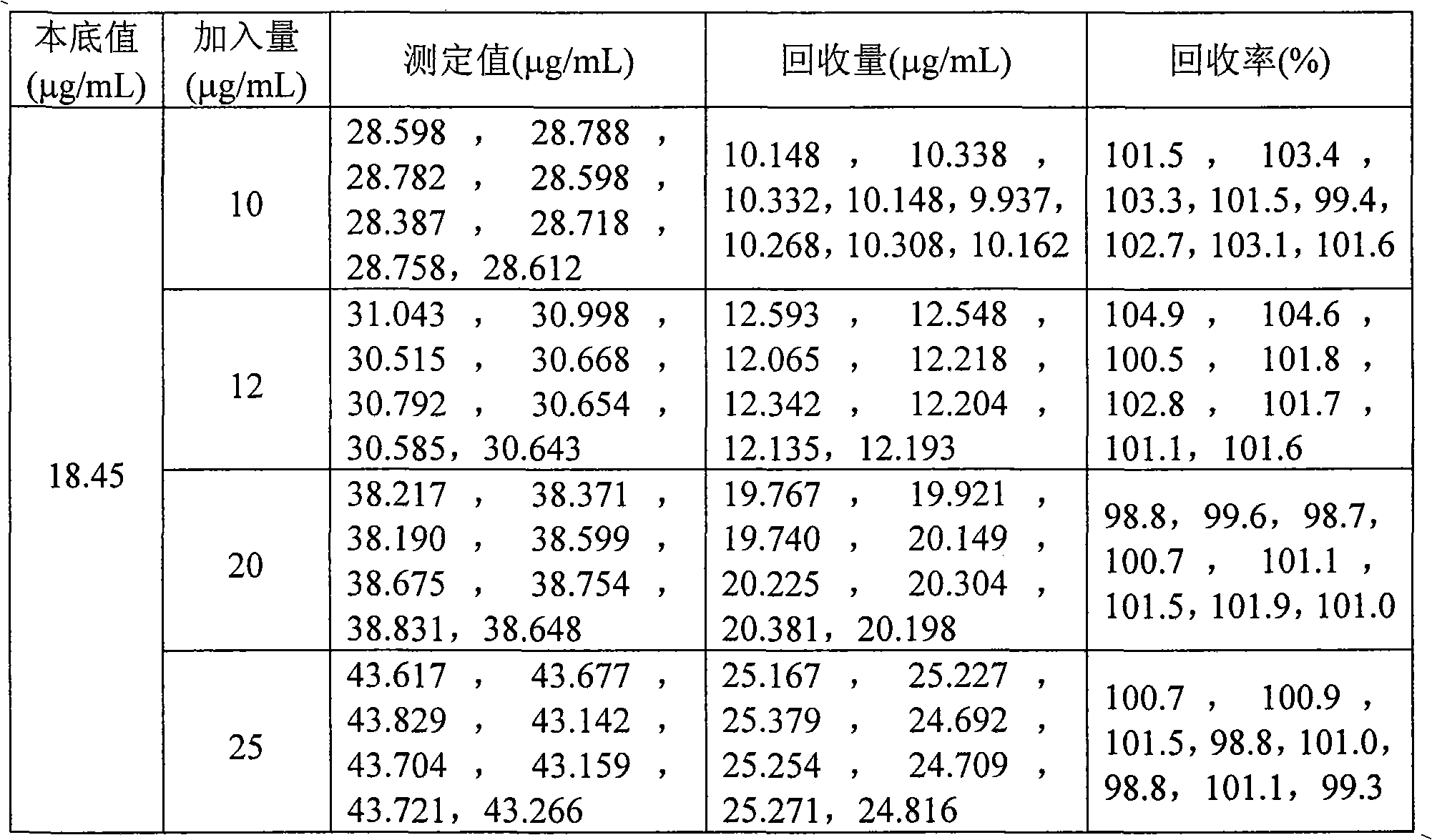
Method for analyzing arsenic content in glass refining agent
InactiveCN101620186AAvoid volatile lossSimplify the analysis processAnalysis by thermal excitationOperabilityDigestion
The invention discloses a method for analyzing arsenic content in a glass refining agent, which comprises the following steps: processing samples by a potassium permanganate preoxidation-hydrofluoric acid wet digestion method to obtain a sample digestion solution; measuring the content of arsenic in the digestion solution by an inductance coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry. By using potassium permanganate as a pre-oxidizing agent to carry out routine wet acid digestion on glass refining agent samples, the method can effectively avoid volatilizable loss of low-valent arsenic components in the preliminary processing of the samples, therefore, a routine inductance coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometer can be used to directly measure the content of the effective content-arsenic in the glass refining agent without allocating a hydride generator or an atomic fluorescence spectrometer. The method has the advantages of high operability, high analysis speed, high accuracy and favorable sensitivity and repetitiveness.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for determining precious metal in platinum-palladium ores
InactiveCN103940805AObserve spectral lines in real timeReal-time observation of measurement resultsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWater bathsOptical Emission Spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for determining precious metal in platinum-group metal ores. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a nickel-sulfonium button from a nickel-sulfonium fire assay enriching sample; (2) grinding the nickel-sulfonium button with a grinder; (3) adding the ground nickel-sulfonium button in a hydrochloric acid solution and heating for dissolving to remove base metal and sulfonium from the nickel-sulfonium button; (4) adding a reductant and a coprecipitator to the solution obtained from the step (3) to recover a small quantity of precious metal lost in the solution; (5) performing suction filtration at negative pressure to obtain a precious metal precipitate; (6) dissolving the precipitate in the step (5) together with a filtering membrane with aqua regia in a water bath and diluting with pure water to a fixed volume; (7) drawing calibration curves of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium by an ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) and determining the intensity of spectral lines of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium in the sample solution; (8) automatically calculating the content of to-be-detected elements by a computer according to the calibration curves and a sample information table. The method has good stability and high result accuracy degree. According to the method, six precious metal elements can be determined simultaneously just by one-time sample weighing and pretreatment, the working efficiency is increased greatly and the detection cost is lowered.
Owner:WANBAO MINING
Method for determination of silicon content in ferro-aluminum manganese
InactiveCN102565026AAnalytical data is reliableFew kindsAnalysis by thermal excitationLinear correlationManganese
The invention provides a method for determination of silicon content in ferro-aluminum manganese, comprising the following steps: dissolving a sample to be tested with hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, introducing the solution into an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrograph, and automatically calculating and displaying the concentration of silicon in the sample of ferro-aluminum manganese according to the standard working curve for silicon stored in the spectrograph. The method of the invention implements the working curves comparison and automatic analysis and verification with the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrograph, so that the working process is greatly simplified with high analysis speed and high accuracy. The standard working curve for calibration of silicon solution is automatically drawn by an analysis software, and the linear correlation coefficient between the sample of ferro-aluminum manganese and the standard working curve is greater than 99.9% so as to provide reliable analytical data for manufacturing plants in a fast and accurate manner; moreover the reagents are less used in terms of category and dosage so as to relatively reduce the environmental pollution.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
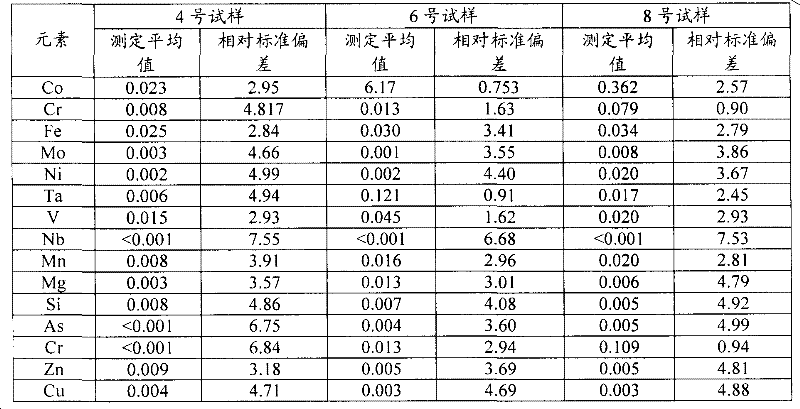
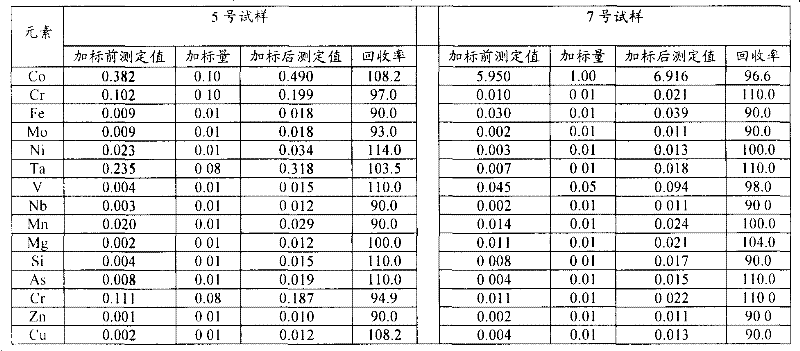
Combined method for measuring content of impurity elements and matrix element niobium in niobium-iron alloy
ActiveCN103926236AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityAnalysis by thermal excitationNiobiumCombined method
The invention provides a combined method for measuring the content of impurity elements and a matrix element niobium in a niobium-iron alloy. The method comprises the following steps: digesting a sample at room temperature by concentrated hydrofluoric acid, concentrated nitric acid and concentrated hydrogen peroxide, thereby forming a to-be-measured solution; and respectively preparing series standard solutions comprising impurity elements and a niobium element, detecting the standard solutions by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, drawing an impurity element calibration curve and a niobium element calibration curve, measuring the to-be-measured solution by the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, and combining the measurement result with the calibration curves to obtain the content of the impurity elements and the niobium element in the niobium-iron alloy sample. The method has the advantages that the content of the impurity elements such as silicon, tantalum, tungsten, titanium, aluminum, copper, phosphorus, manganese, lead, tin and vanadium and the content of the matrix element niobium in the niobium-iron alloy can be simultaneously measured; the method is high in accuracy and reliability and has the characteristics of convenience in operation, rapidness, environment friendliness, low cost and the like.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for measuring content of Al, Ti and Ca in low-carbon silicon iron
InactiveCN101750407AQuick analysisAccurate analysisAnalysis by thermal excitationPollutionInductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy
The invention relates to a method for measuring the content of Al, Ti and Ca in low-carbon silicon iron, which comprises the following steps: dissolving a sample through a nitric acid and a hydrofluoric acid, after fuming the sample through a perchloric acid, adding a proper amount of hydrochloric acid, and heating to dissolve a salt; diluting to a certain volume with water; introducing atomization solution into an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer; measuring the intensity of a spectral line to be tested; and calculating the concentration of a corresponding element of the substance to be tested according to the intensity of the spectral line which is measured by the standard substance at known concentration. The method has the advantages of capacity of quickly and accurately analyzing the content of Al, Ti and Ca in the low-carbon silicon iron and no pollution.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Digestion method and detection method for vanadium-nitrogen-titanium-iron mixed alloy conductor
ActiveCN103808558APromotes fast digestionStable storagePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationAlloyDigestion
The invention provides a digestion method and a detection method for a vanadium-nitrogen-titanium-iron mixed alloy cored wire. The digestion method comprises the following steps: putting a cored wire into a container, adding a concentrated nitric acid and a concentrated hydrochloric acid to the container; carrying out first time of pre-reaction under an open state; adding a concentrated sulfuric acid and carrying out second time of pre-treatment under the open state; carrying out digestion and complexation reaction by microwave in a closed state, so as to obtain a solution. The detection method comprises the following steps: cooling the solution, diluting and fixing volume to obtain a sample solution; determining the content of elementary compositions in one or more sample solutions by using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry, titration, spectrophotometry and an electrochemical process. The digestion method and the detection method have the advantages of being safe to operate, simple and rapid, efficient and complete, fewer in man-made factors, and easy to accurately control and repeatedly reappear, and technical indexes such as the accuracy, the precision and the like of an analysis result are improved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for determining content of vanadium
ActiveCN103048309AAccurate measurementAnalysis by thermal excitationSodium metavanadateAnalytical chemistry
The invention provides a method for determining content of vanadium. The method for determining content of vanadium comprises the following steps: digesting a vanadium-containing sample with hydrochloric acid to obtain a vanadium-containing solution, and determining the content of vanadium in the vanadium-containing solution using an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer. According to the method, the content of vanadium in sodium metavanadate can be determined fast and accurately.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for measuring content of heavy metal in polymer
InactiveCN102928400AReduce dosageEasy to implementAnalysis by thermal excitationCadmium CationAntimony
The invention relates to a method for measuring the content of a heavy metal in a polymer, and in particular relates to a method for synchronously testing the contents of lead, cadmium, mercury, arsenic, antimony, tin, copper and zinc in the polymer by processing the polymer using oxygen bomb combustion, concentrating absorption liquid, carrying out acid digestion and subsequently using a plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) method. The method for measuring the content of the heavy metal in a polymer material comprises the following steps of: firstly, combusting oxygen bomb, secondly, carrying out acid digestion, and thirdly, testing by using an inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry instrument. The polymer is sufficiently combusted under a rich oxygen condition by using an oxygen combustion method, the combustion product is absorbed by water, and the absorption liquid is concentrated and subjected to acid digestion; and with the adoption of the method, the treatment to the polymer is efficient, simple, convenient and rapid.
Owner:谱尼测试集团深圳有限公司
Method for determining content of manganese, phosphorus, arsenic, potassium, sodium and copper in direct reduced iron
InactiveCN102252883AImprove accuracyEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationPotassiumManganese
The invention provides a method for determining the content of manganese, phosphorus, arsenic, potassium, sodium and copper in direct reduced iron. The method comprises the following steps: using the conventional inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry to determine spectral line strength of test sample liquid and getting the corresponding content values of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper from standard working curves of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper according to the spectral line strength, and the method is characterized by sequentially adding mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid and perchloric acid into a test sample for dissolving, adding dilute hydrochloric acid for dissolving salts and filtering the dissolved liquid so as to prepare the test sample liquid. Not only is the operation convenient, but also the determined content of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper is high in accuracy and the determination result further has good stability, reproducibility and accuracy. Tests prove that the method in the invention is reliable and practical and can meet the daily need of determining the content of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper in the direct reduced iron.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
Method for measuring boric acid and borate in cosmetics by microwave digestion -ICP-OES
InactiveCN101846629ATest applicableNot easy to pollutePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationMicrowave digestionHydrogen peroxide
The invention relates to a method for detecting the content of boric acid and borate in cosmetics. A method for measuring boric acid and borate in cosmetics by microwave digestion -ICP-OES comprises the following steps of: performing microwave digestion on a cosmetic sample through nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide to decompose organic substances, guiding sample solution into an inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometer atomizer to form aerosol, loading the aerosol into high-temperature high-frequency plasma by argon to generate ionization and generate a characteristic spectral line, and measuring the spectral line intensity of a boron element and an internal standard yttrium element in the sample solution, wherein the intensity of the boron element is in direct proportion to the content of the boron element; and correcting a response value of the boron element according to the ratio of an actually measured yttrium internal standard response value to an expected internal standard response value, performing quantitative measurement by adopting a standard curve method, calculating the content of the boron element in the cosmetics, and obtaining the content of the boric acid and the borate through conversion coefficients. The method has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity and accurate result.
Owner:THE INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT ZHEJIANG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for testing niobium content in niobium-iron alloy
InactiveCN103115916AAccurate measurementAccurate calculationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationTitaniumUltimate tensile strength
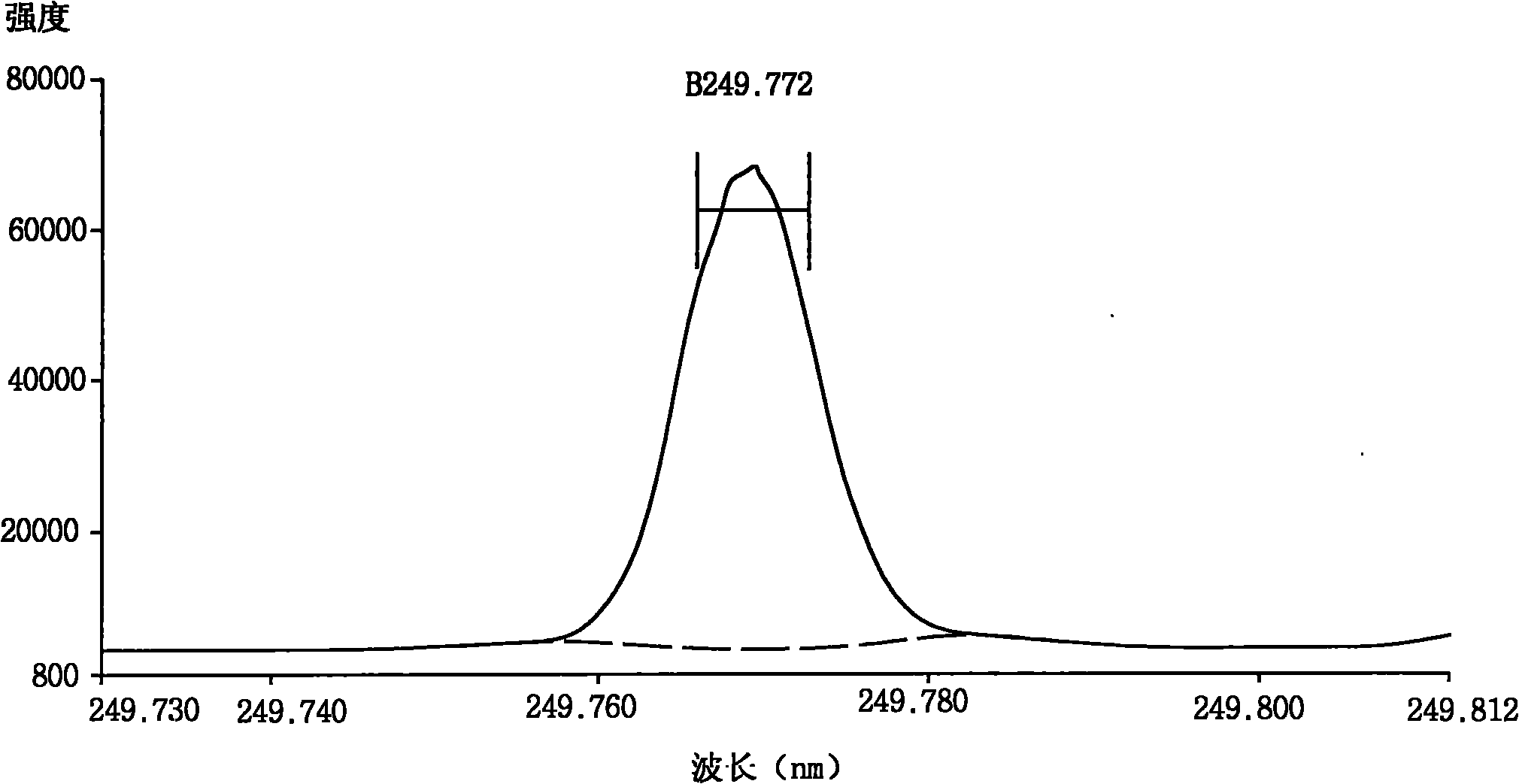
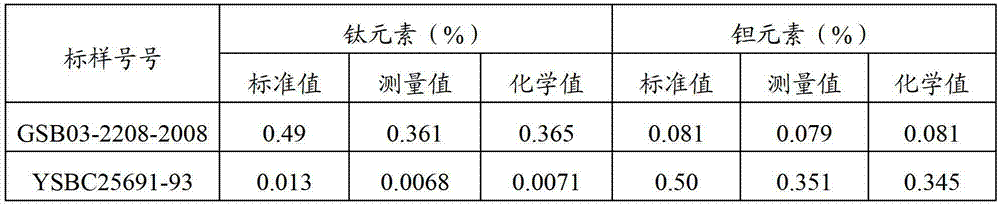
The invention discloses a method for testing niobium content in a niobium-iron alloy. The method comprises the steps of dissolving a niobium-iron alloy sample, depositing the niobium in the niobium-iron alloy in a niobium pentaoxide sediment mode, and weighing the mass of the niobium pentaoxide; preparing a niobium pentaoxide sediment solution, and preparing a standard solution, wherein the standard solution comprises a titanium standard solution and a tantalum standard solution; introducing the solution into which the niobium pentaoxide sediment is dissolved into an inductively coupled plasma atom emission spectrometer so as to test the spectral line intensity of the titanium and the tantalum, and obtaining the content of the titanium and the tantalum in the niobium pentaoxide sediment according to the spectral line intensity which is tested from the standard solution with known concentration; and subtracting the content of the titanium and the tantalum from the content of the niobium pentaoxide so as to obtain the content of the niobium in the niobium-iron alloy. By utilizing the technical scheme of the invention, the content of the titanium and the tantalum which are deposited together with the niobium in the niobium-iron alloy can be rapidly and accurately tested, thereby accomplishing the precise calculation on the niobium in the niobium-iron alloy.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com