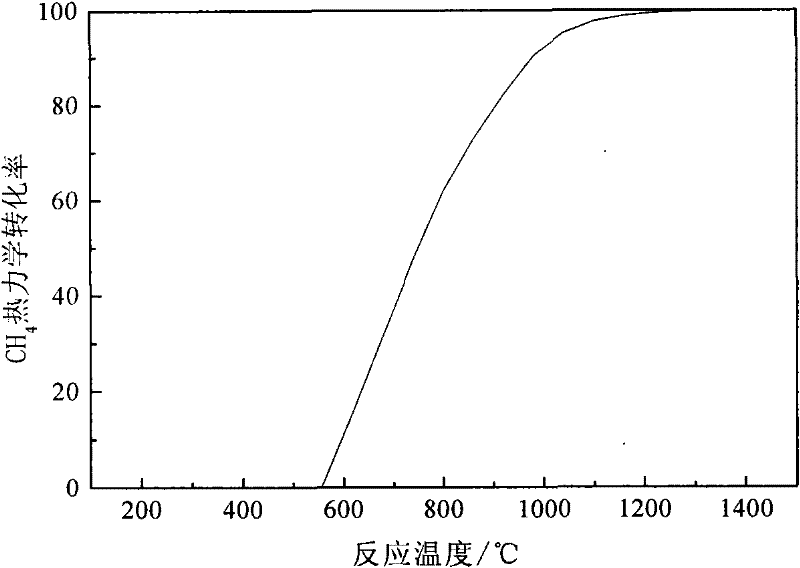
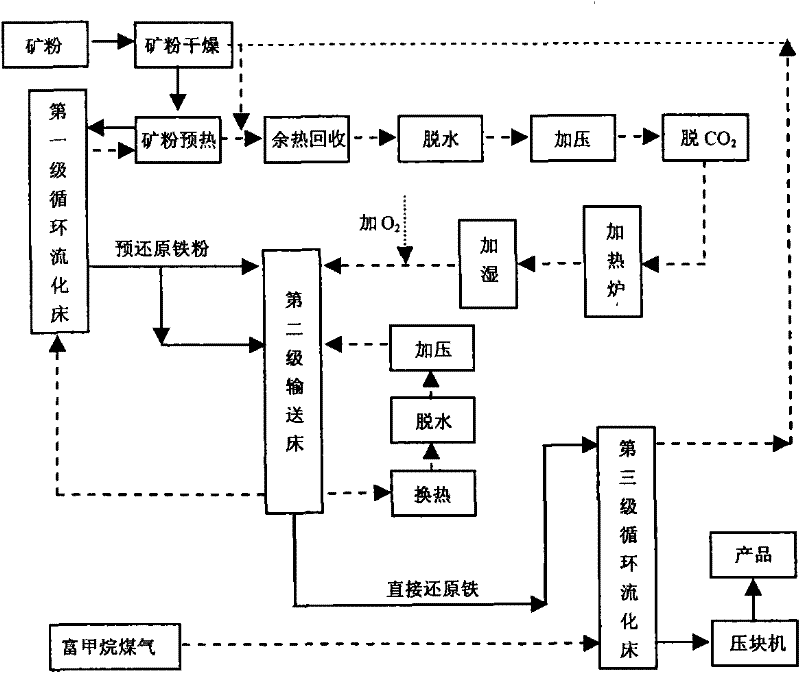
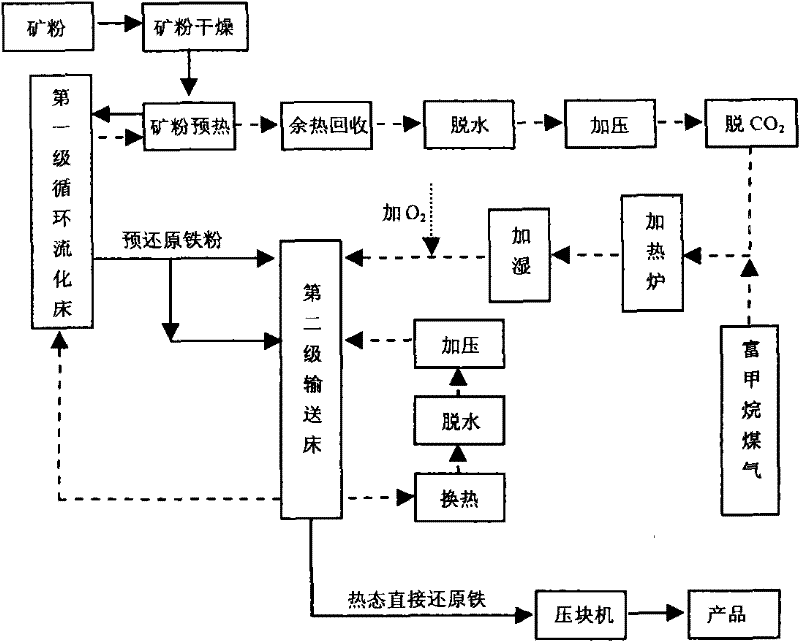
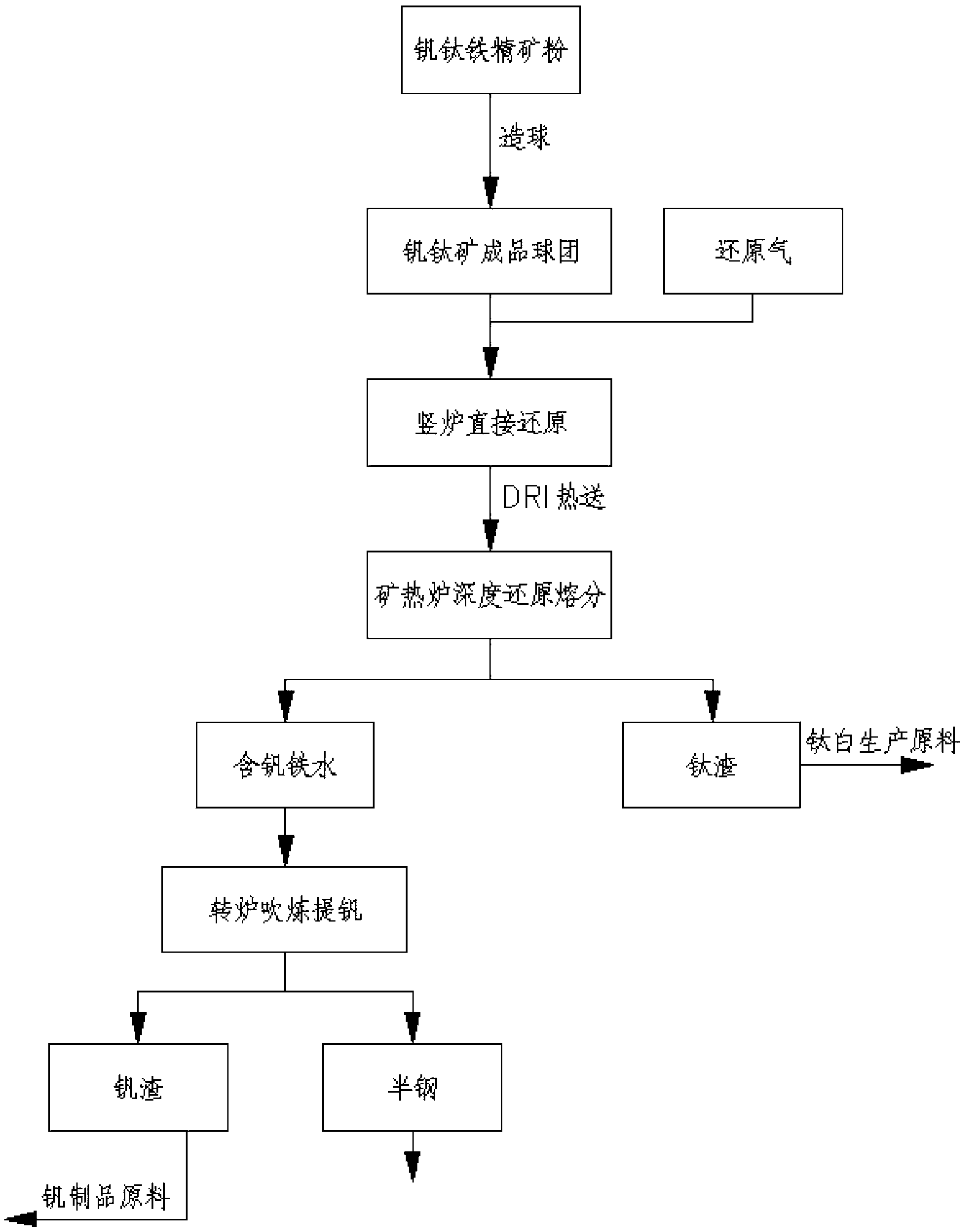
Patents
Literature
535 results about "Direct reduced iron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Direct reduced iron (DRI), also called sponge iron, is produced from the direct reduction of iron ore (in the form of lumps, pellets, or fines) to iron by a reducing gas or elemental carbon produced from natural gas or coal. Many ores are suitable for direct reduction.
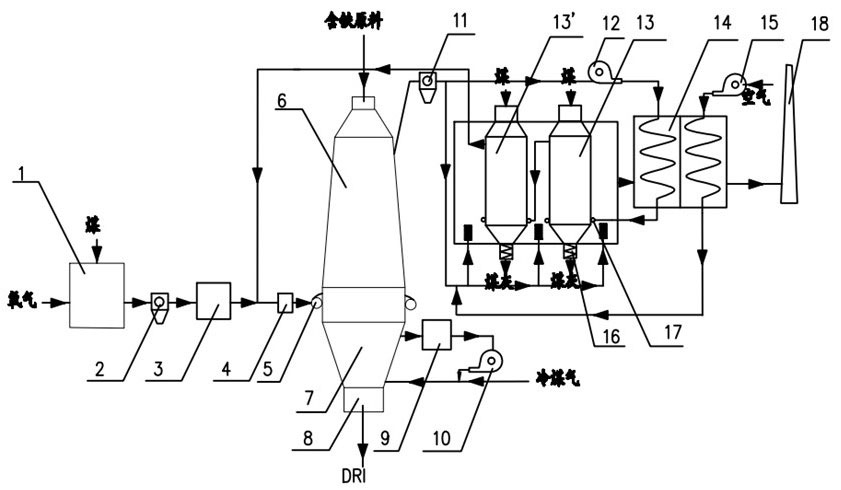
Method and device for producing direct reduced iron by using gas-based reduction shaft furnace
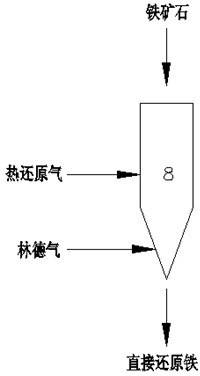
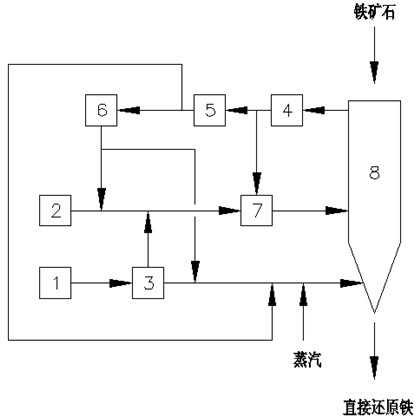
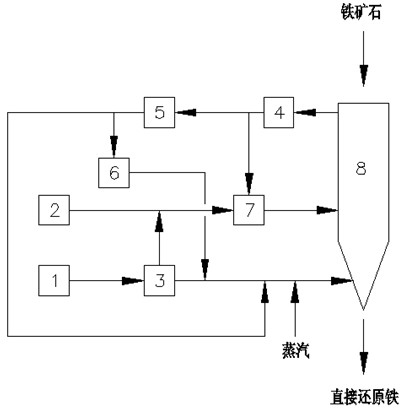
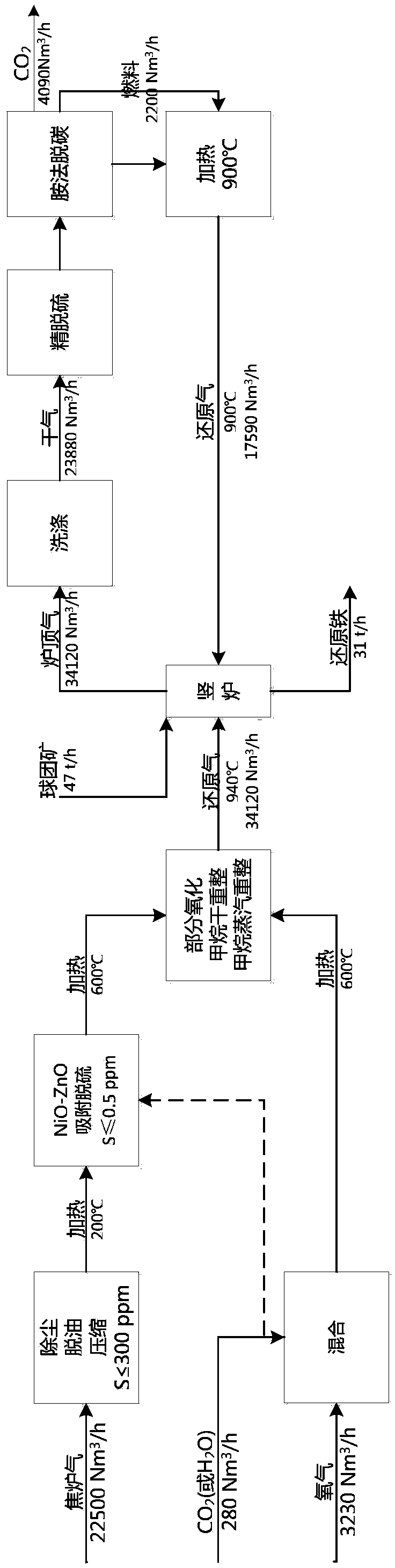
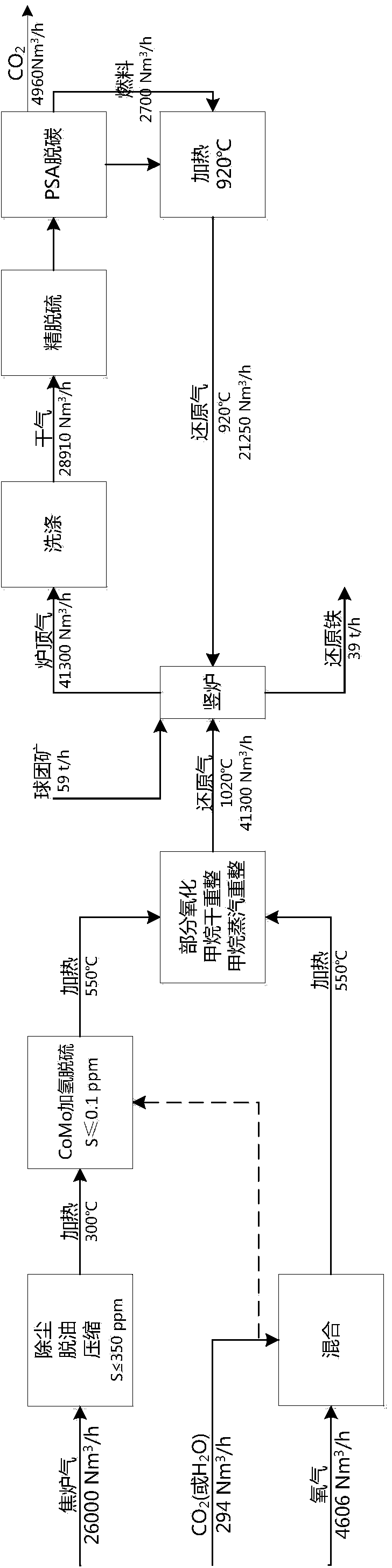
The invention discloses a method and device for producing direct reduced iron by using a gas-based reduction shaft furnace. Coal reducing gas and coke oven gas are mixed and supplied to a shaft furnace so as to produce direct reduced iron. The method comprises the following steps: separating the coke oven gas into hydrogen gas and linde gas, mixing the hydrogen gas with the coal reducing gas and using as reducing gas to reduce iron ores, and using the linde gas as cooling gas to cool direct reduced iron. The device for realizing the method comprises a shaft furnace, a coke oven gas source, a coal gasification device, a coke oven gas hydrogen-extracting device and a gas heating device. In the invention, coal gasification devices of different sizes can be flexibly used with a coke oven gas supply device, thereby reducing the size of the coal gasification device and effectively using the coke oven gas. Meanwhile, the invention cancels the minor cycle of a cooling section of a common shaft furnace, saves the equipment and investment, and brings the heat of direct reduced iron to a reducing section, thereby saving the heating load of the system reducing gas.
Owner:CISDI SHANGHAI ENG CO LTD +1
Direct reduced iron discharge system and method
InactiveUS6214086B1No loss in metallizationWide range of sizesMolten spray coatingNuclear energy generationEngineeringDirect reduced iron
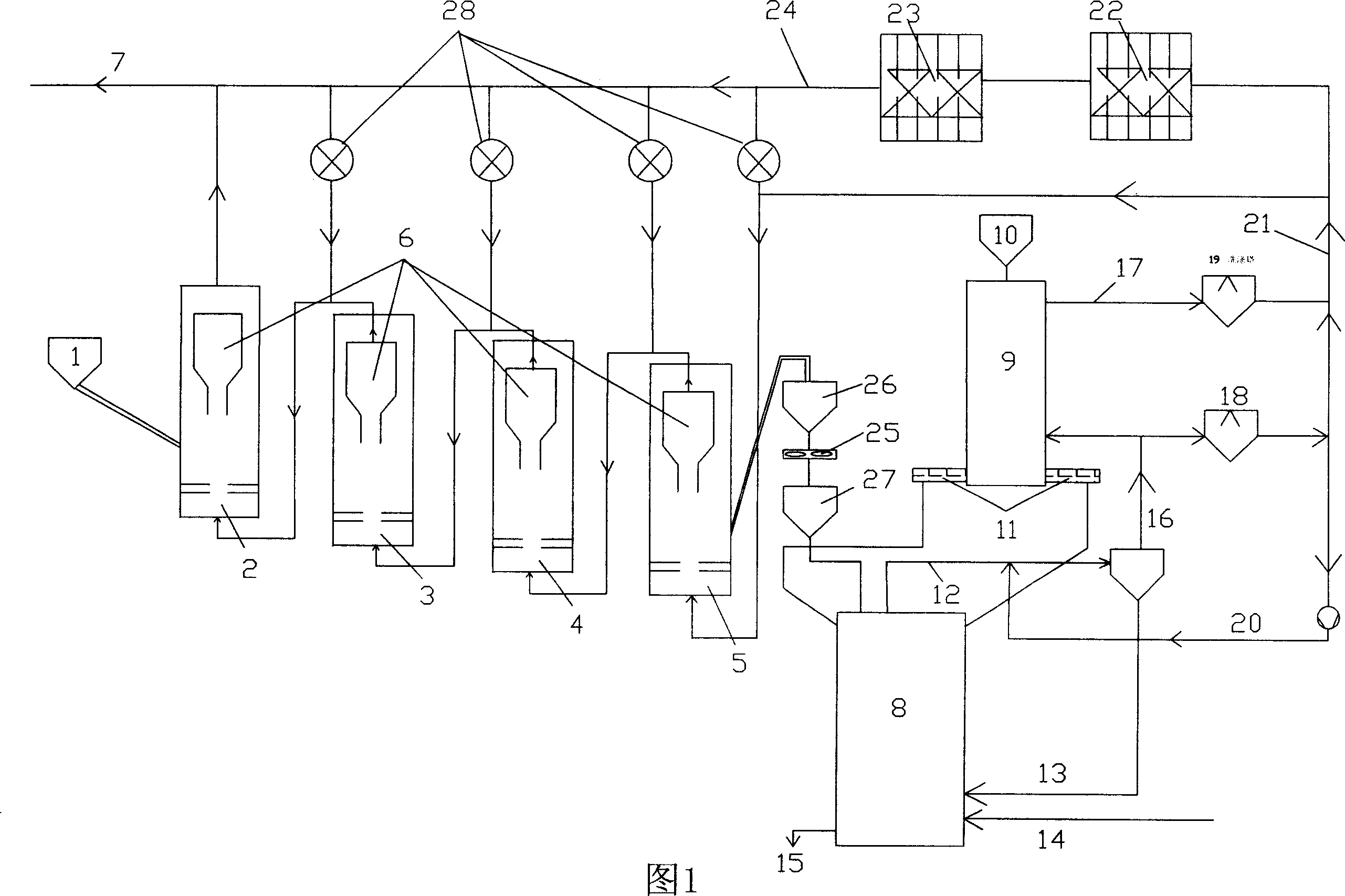
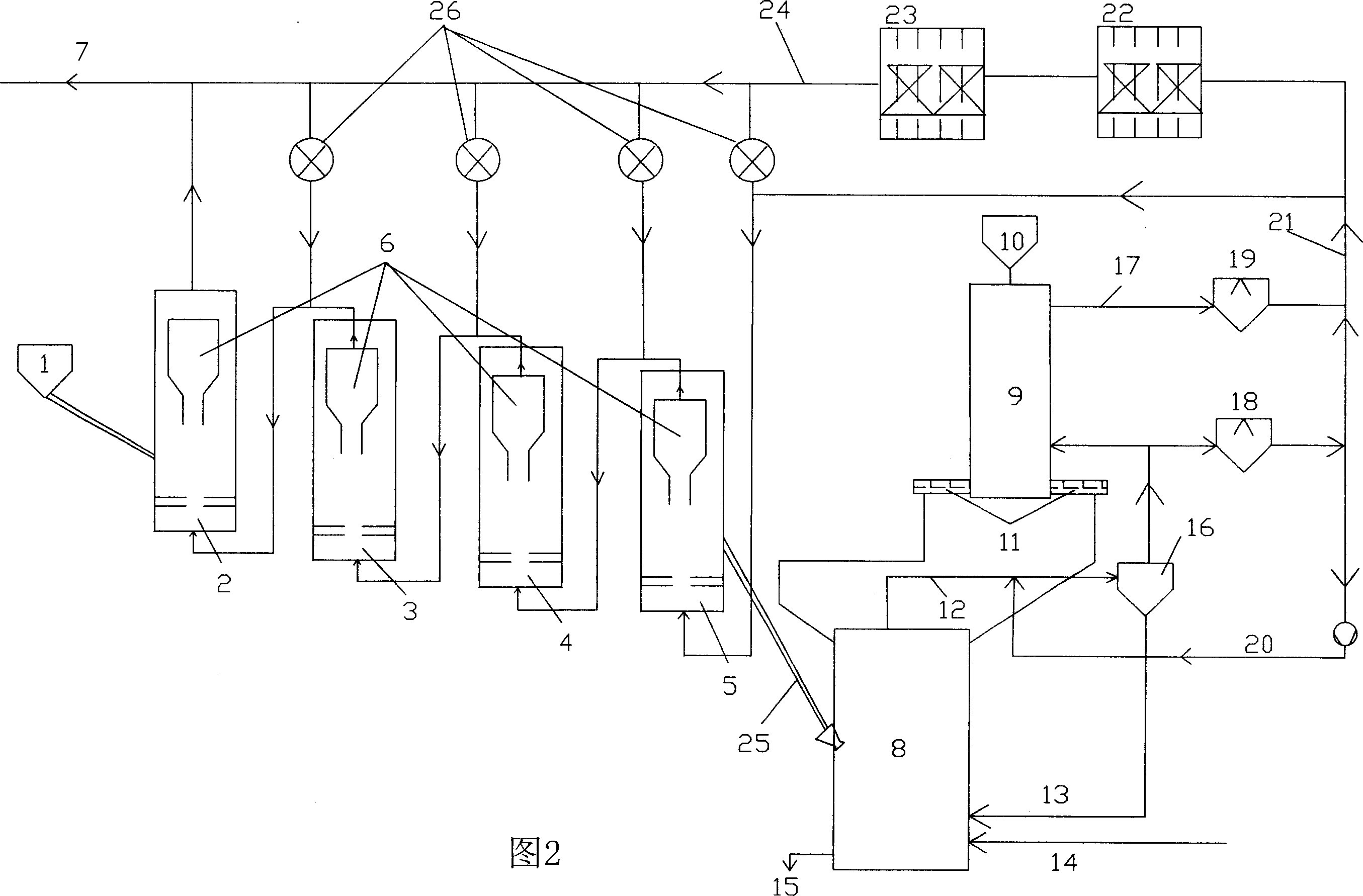
A method and apparatus for simultaneously supplying varying proportions of hot and cold direct reduced iron(DRI) material from a source of hot DRI for melting, storage, briquetting, or transport. The system uses gravity to transport hot DRI material from a reduction furnace to a furnace discharge section, which transports desired amounts to a cooling receptacle and to a hot DRI vessel. The cooling section of the apparatus is connected to the furnace discharge section through a dynamic seal leg. The hot section is also connected to the furnace discharge section through separate a dynamic sealing leg and can feed a surge vessel, a briquetter, a storage vessel or a melting furnace. The method of operation is also disclosed.
Owner:IDREX INT BV ROTTERDAM ZURICH BRANCH
Method for reducing vanadium-titanium magnetite powder by coal reducing gas and fluidized beds
ActiveCN102127611AShort recovery timeHigh production heat efficiencyFluidised-bed furnacesProcess moduleMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for reducing vanadium-titanium magnetite powder by coal reducing gas and fluidized beds. High temperature coal gas produced by a coal reducing gas system is mixed with gas of a reducing exhaust gas purification system to form reducing gas, and the reducing gas enters third-stage, second-stage and first-stage reduction fluidized beds in turn; the preheated vanadium-titanium magnetite powder enters the first-stage, second-stage and third-stage reduction fluidized beds in turn and is fluidized and subjected to reduction reaction under the action of the reversely upward reducing gas; and the obtained directly reduced iron is briquetted, titanium slag is removed, vanadium slag is extracted, and the qualified molten steel is produced. The invention integrates process modules such as coal reducing gas, iron ore powder preheating, fluidized bed reducing, briquetting, electric furnace melting separation and the like, and has the advantages of high production thermal efficiency, low cost of preparing the reducing gas, short time of reducing the iron ore powder and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Method for high-efficiency separation and comprehensive utilization of iron, aluminum and sodium in high-iron red mud
ActiveCN102851425AWon't breakReasonable useCombustible gas chemical modificationProcess efficiency improvementRed mudSlag
The invention provides a method for high-efficiency separation and comprehensive utilization of iron, aluminum and sodium in high-iron red mud. The method comprises the following steps of adding iron ore concentrate and coke powder into high-iron red mud as a raw material, pressing the mixture into red mud pellets, drying, pre-heating, directly reducing metallic oxides of iron and sodium by a rotary hearth furnace, feeding the reduced metalized pellets into an iron bath-type oxy-coal smelting reduction furnace, carrying out high-temperature melting separation, using separated iron for steel-making, recovering alumina from the modified high-aluminum slag, recovering the metallic oxide of sodium from smoke dust carried by exhaust gas, improving quality of mixed gas produced by the iron bath-type oxy-coal smelting reduction furnace, and feeding back the treated mixed gas to the rotary hearth furnace for use. The method provided by the invention can effectively realize high efficiency recovery and large-scale industrial comprehensive utilization of a red mud resource.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for recovering zinc oxide in Zn-containing dust treatment by rotary hearth furnace
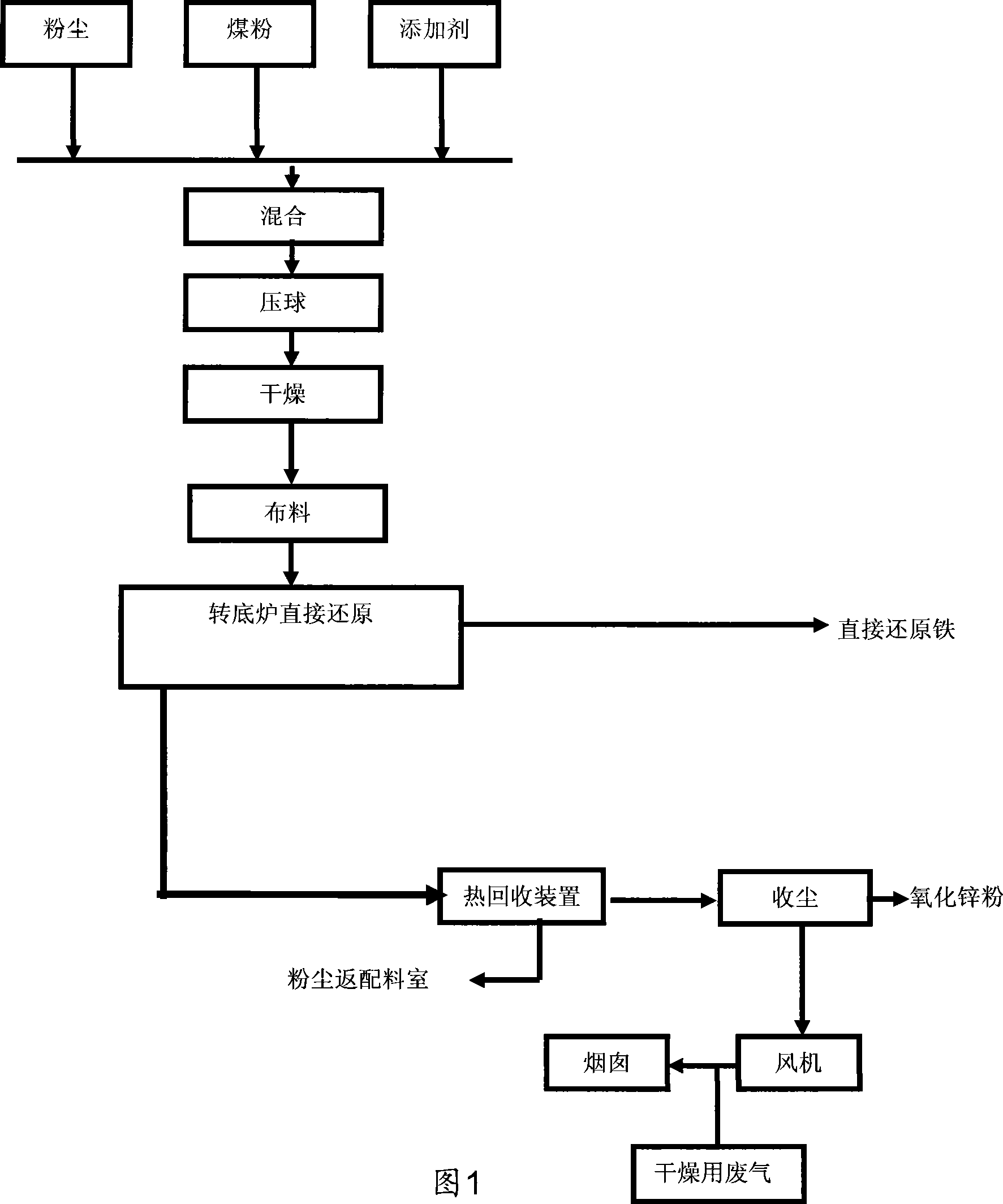
The invention discloses a method for reclaiming zinc oxide in treating zincky powder dust in a rotary hearth furnace. The zincky powder dust, coal and flux are mixed, then are subjected to briquetting and drying, are transported to the rotary hearth furnace and are subjected to direct reduction; zinc in the powder dust is reclaimed from exhaust gas; and a feed block of which zinc is removed is directly reduced through the rotary hearth furnace and is subjected to cooling or briquetting for use. The method has wide applicability to zincky materials, can farthest utilize resource reasonably, has low requirement on the thermal value of fuels, high temperature of flue gas and high zinc extraction rate; and the treated powder dust is changed into direct reduced iron for comprehensive utilization.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
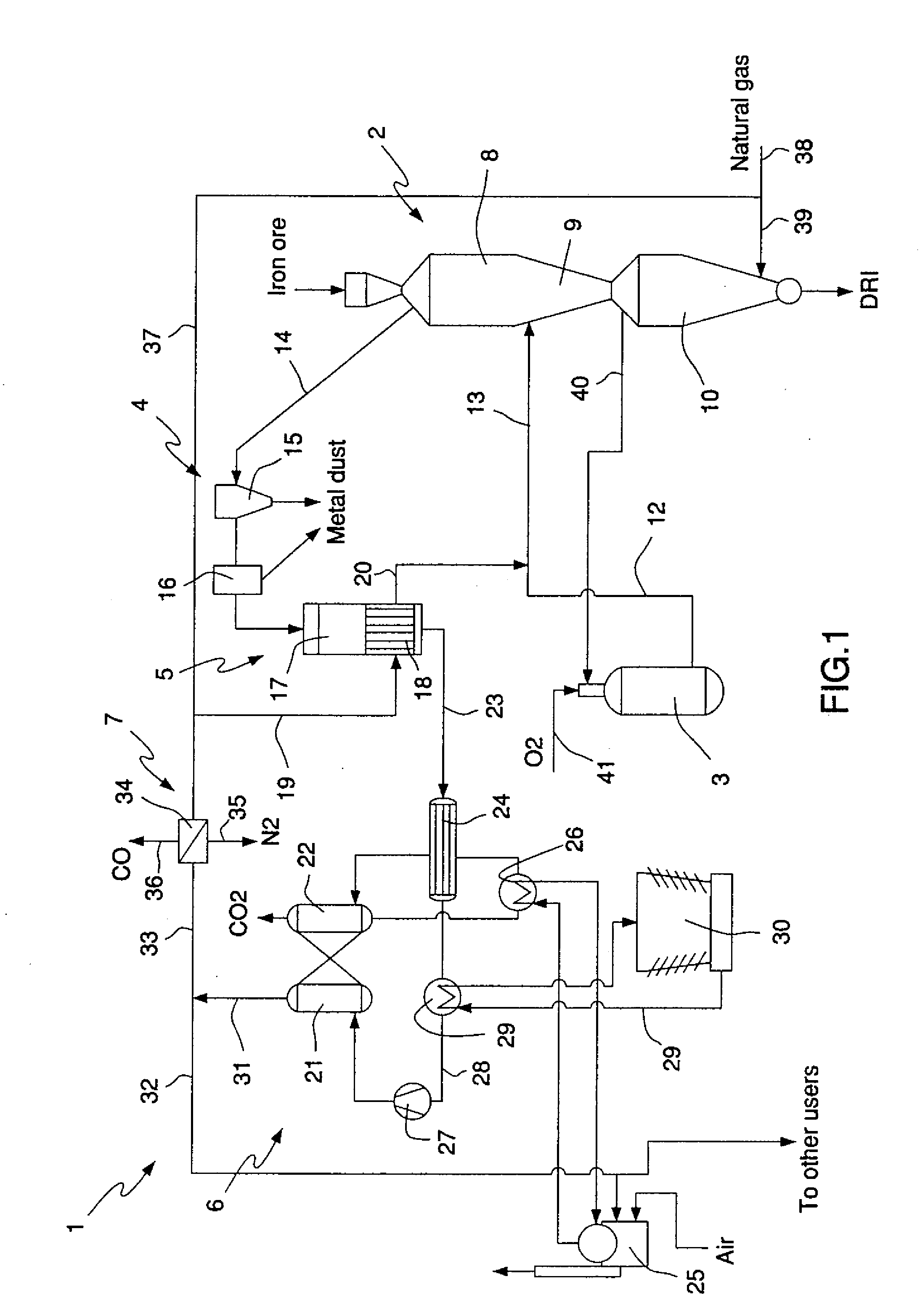
Method and apparatus for improved use of primary energy sources in integrated steel plants
ActiveUS6986800B2Increase productionReduction of fossil fuel specific consumptionBlast furnace detailsManufacturing convertersChemical agentFossil fuel
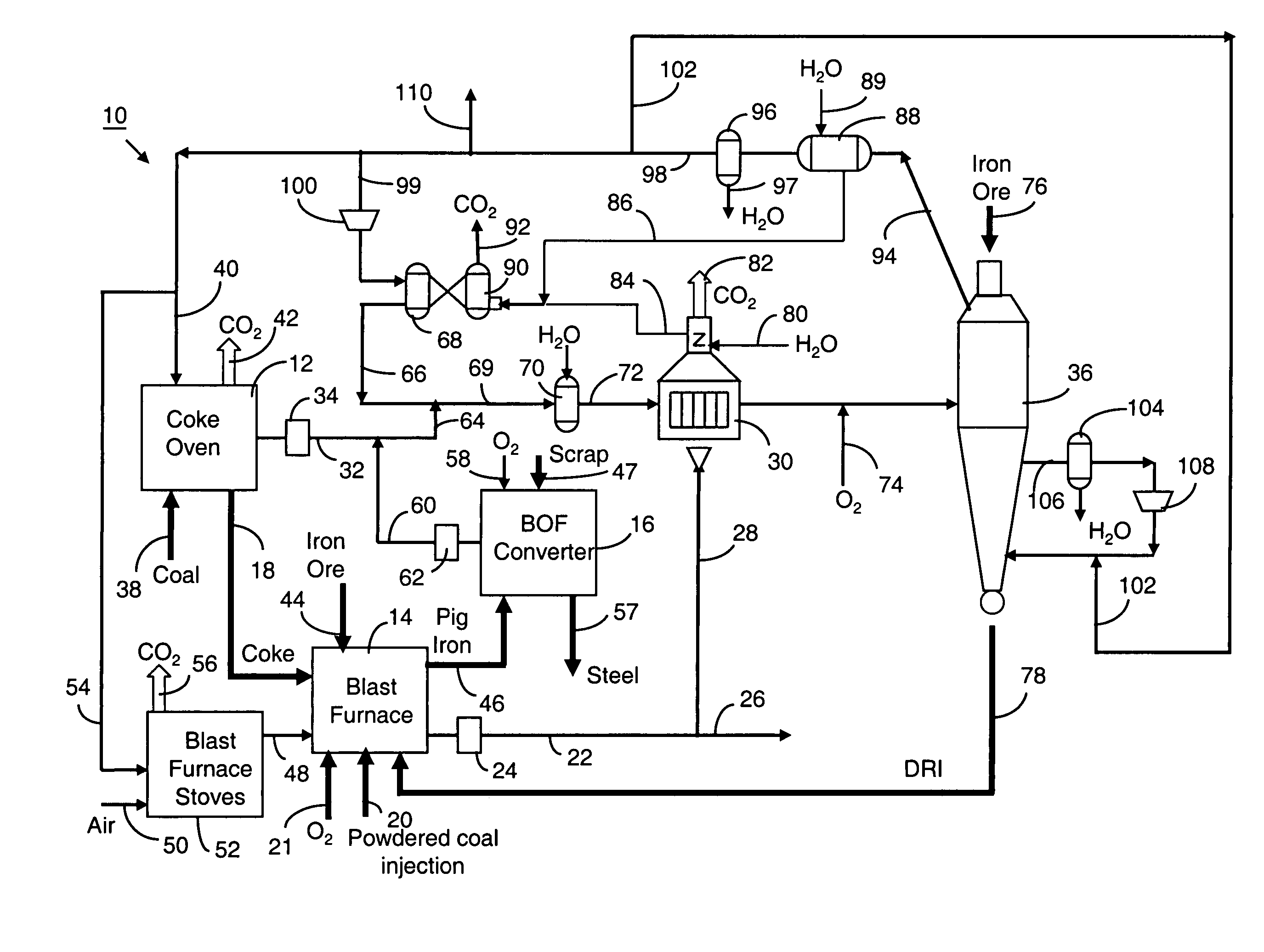
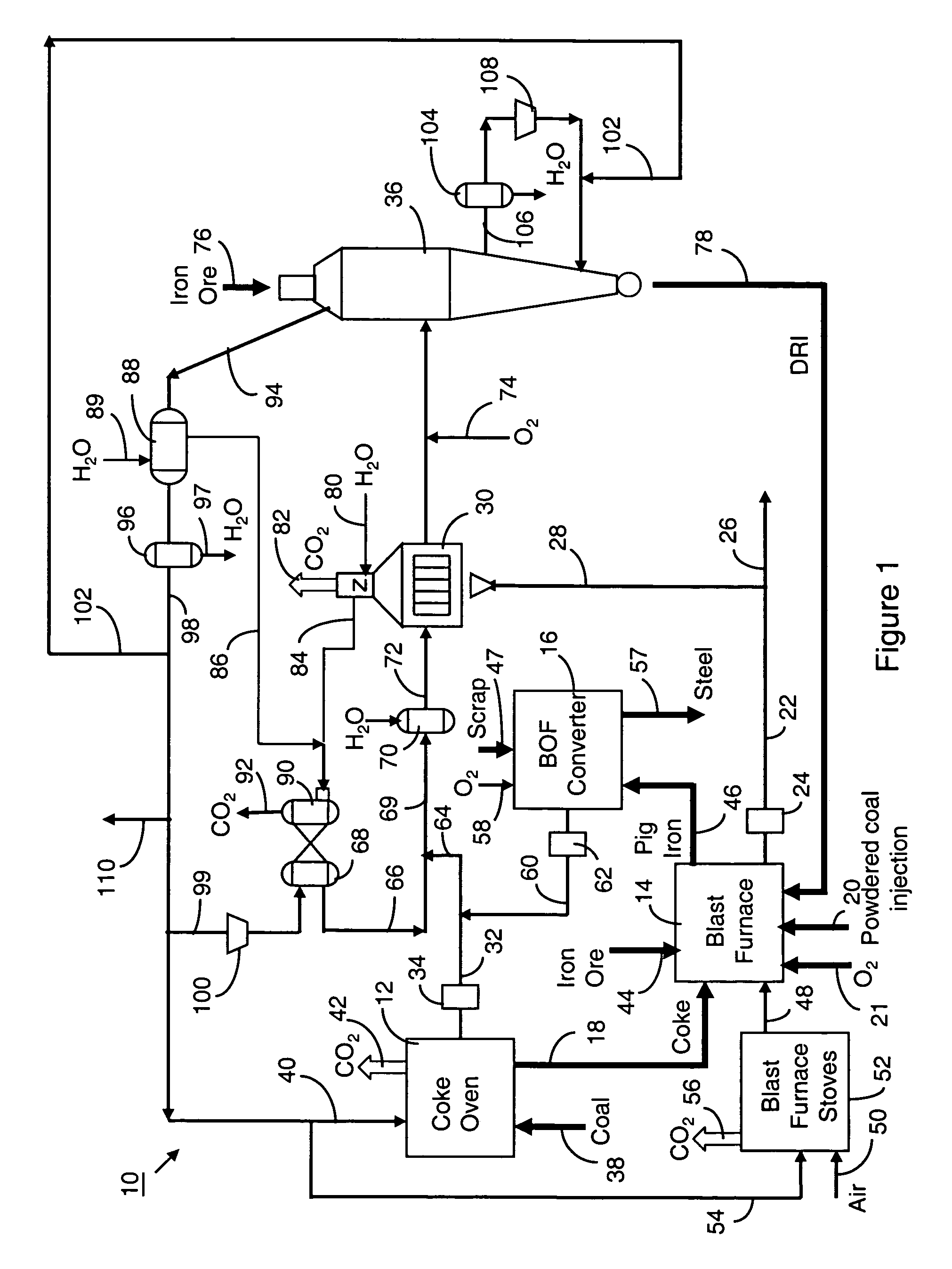
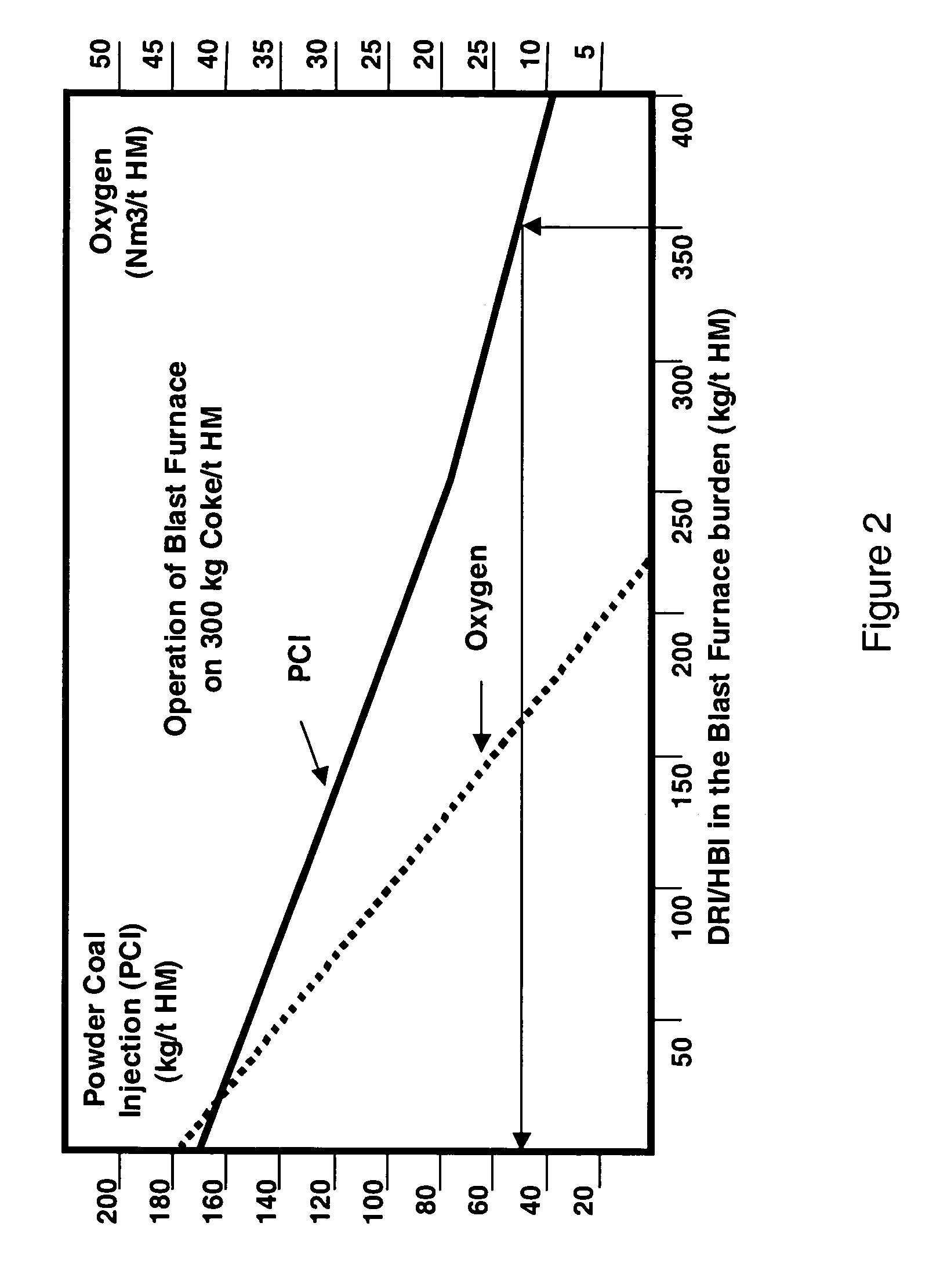
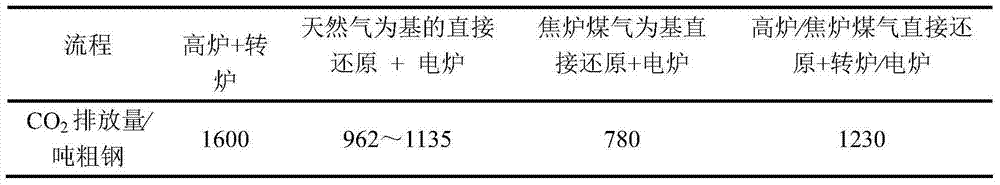
A method and an integrated steel plant wherein, instead of using coke oven gases, converter gases and blast furnace top gases available as fuel for power generation or other heating purposes, these gases are more efficiently utilized as chemical agents for direct reduction of iron ores producing DRI.DRI is charged to blast furnaces increasing production of crude steel without increasing the capacities of the coke oven plant and blast furnaces and without changes in the quality of the crude steel, or, if production rate is maintained, the fossil fuels specific consumption is significantly reduced.Utilisation of primary fossil energy according to the invention also reduces the specific CO2 emissions per ton of crude steel. The specific CO2 emission in conventional integrated mills is about 1.6 tons of CO2 per ton of crude steel.
Owner:HYLSA SA DE CV
Air-base direct reduction iron-making method for reducing iron concentrate powder by self-reforming of gas rich in methane
ActiveCN102206723ARealize self-reorganizationEliminate the effects ofGas emission reductionIron powderFluidized bed
An air-base direct reduction iron-making method for reducing iron concentrate powder by self-reforming of gas rich in methane. The method provided by the invention belongs to the field of iron-making technology. The method is characterized in that through a technology combining a circulating fluidized bed and a two-section high temperature conveying bed, iron ore powder is dried and preheated andthen is fed into a circulating fluidized bed for pre-reduction; the pre-reduced iron ore powder is fed into a high temperature fast conveying bed for a deep and rapid reduction in the presence of reducing gas at a reaction temperature of 940 to 1000 DEG C and methane is cracked by a effect of direct reduction of iron simultaneously; in a cooling zone of the high temperature fast conveying bed, the reduced iron ore powder is mixed with reducing gas from a cooling circuit and is fast cooled to a temperature of 700 to 800 DEG C; and the reduced iron ore powder can be utilized for producing hot pressed blocks and cold pressed blocks produced through a cooling treatment of a third stage circulating fluidized bed. The air-base direct reduction iron-making method realizes self-reforming of gas rich in methane in a reducing furnace and has the advantages of high utilization rate, high efficiency, environmental protection, etc.
Owner:BEIJING SHOUGANG INT ENG TECH
Gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction-electric furnace smelting separation process of vanadium titano-magnetite
InactiveCN103255255ARealize comprehensive utilizationEffective clean separationProcess efficiency improvementMagnetiteShaft furnace
The invention discloses a gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction-electric furnace smelting separation process of vanadium titano-magnetite. The process comprises the following steps of: a, forming finished product pellets; b, putting the finished product schreyerite pellets as raw materials into a direct-reduction shaft furnace and introducing a reducing gas to the shaft furnace to reduce the pellet ore, thus obtaining thermal-state direct reduced iron; c, feeding the thermal-state direct reduced iron to a smelting-separation electric furnace for reduction and smelting separation, thus separating out titanium slag and obtaining vanadium-containing iron liquid; and d, transferring the vanadium-containing iron liquid to a converter for blowing so as to separate out vanadium slag and semisteel. According to the gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction-electric furnace smelting separation process of vanadium titano-magnetite, the shortcomings of the existing process are improved, effective and clean separation of titanium, vanadium and iron is realized, the recovery and utilization rate of vanadium and titanium metal elements is improved and energy consumption and equipment one-time investment are reduced; and therefore, the process is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:CISDI ENG CO LTD
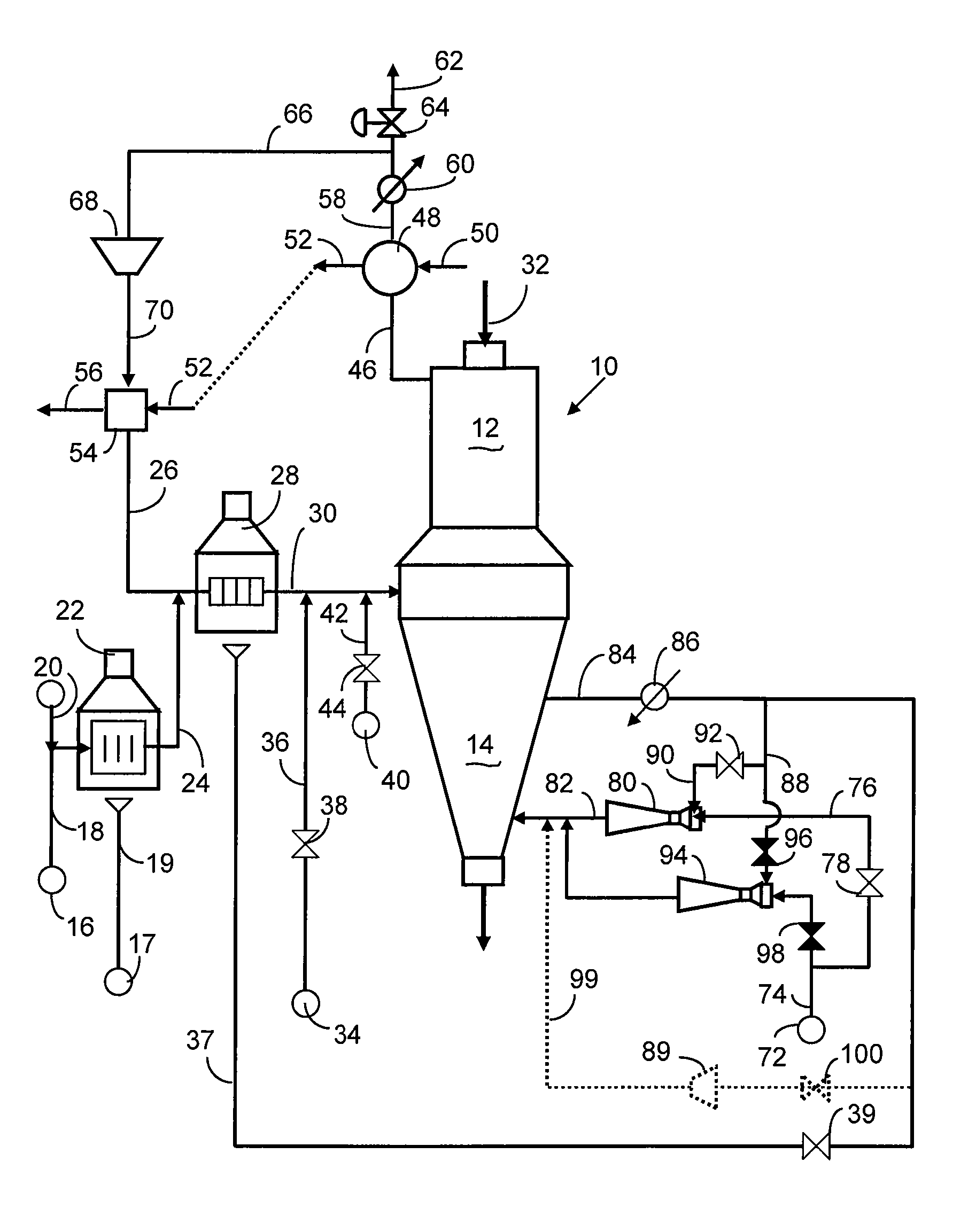
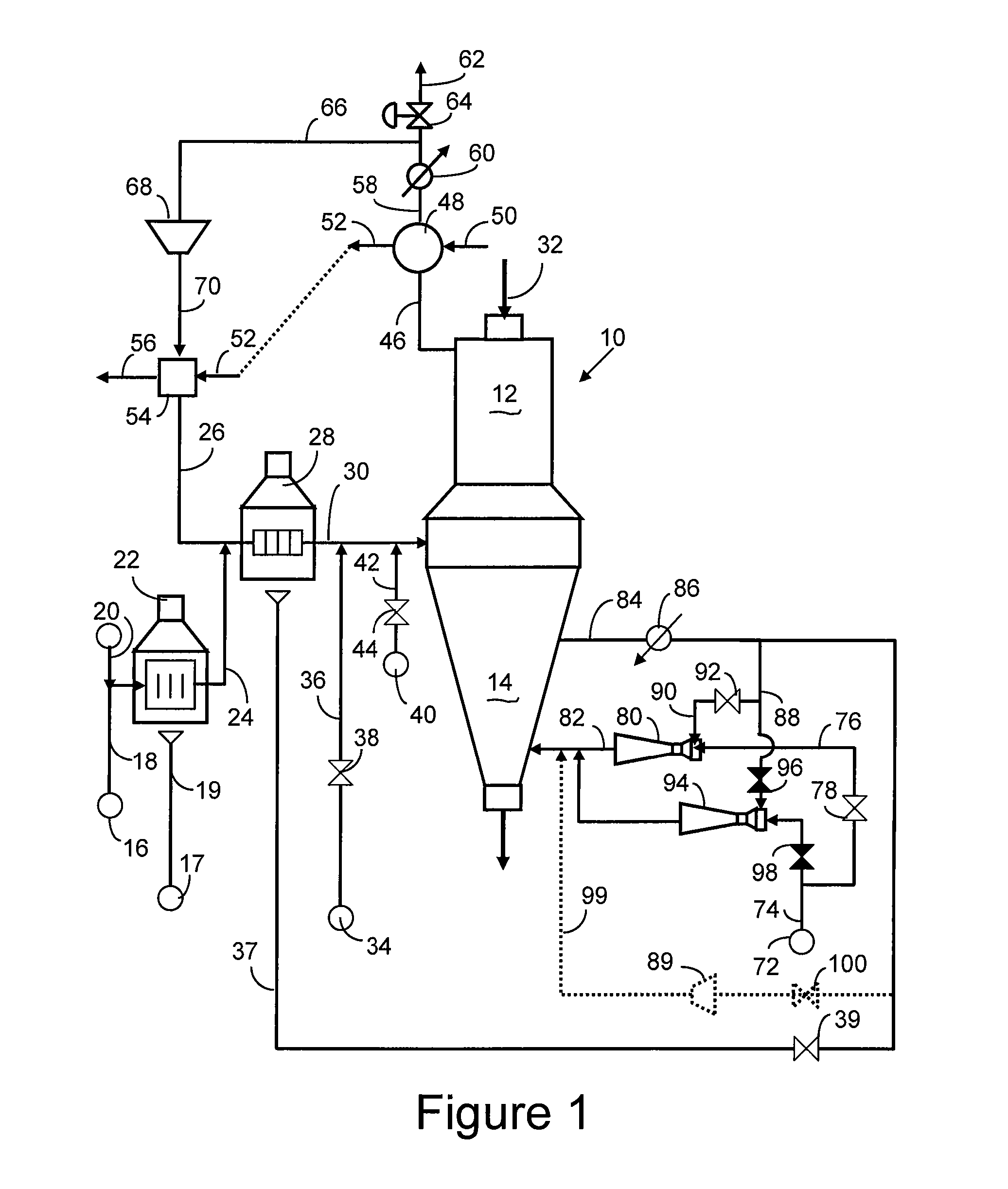
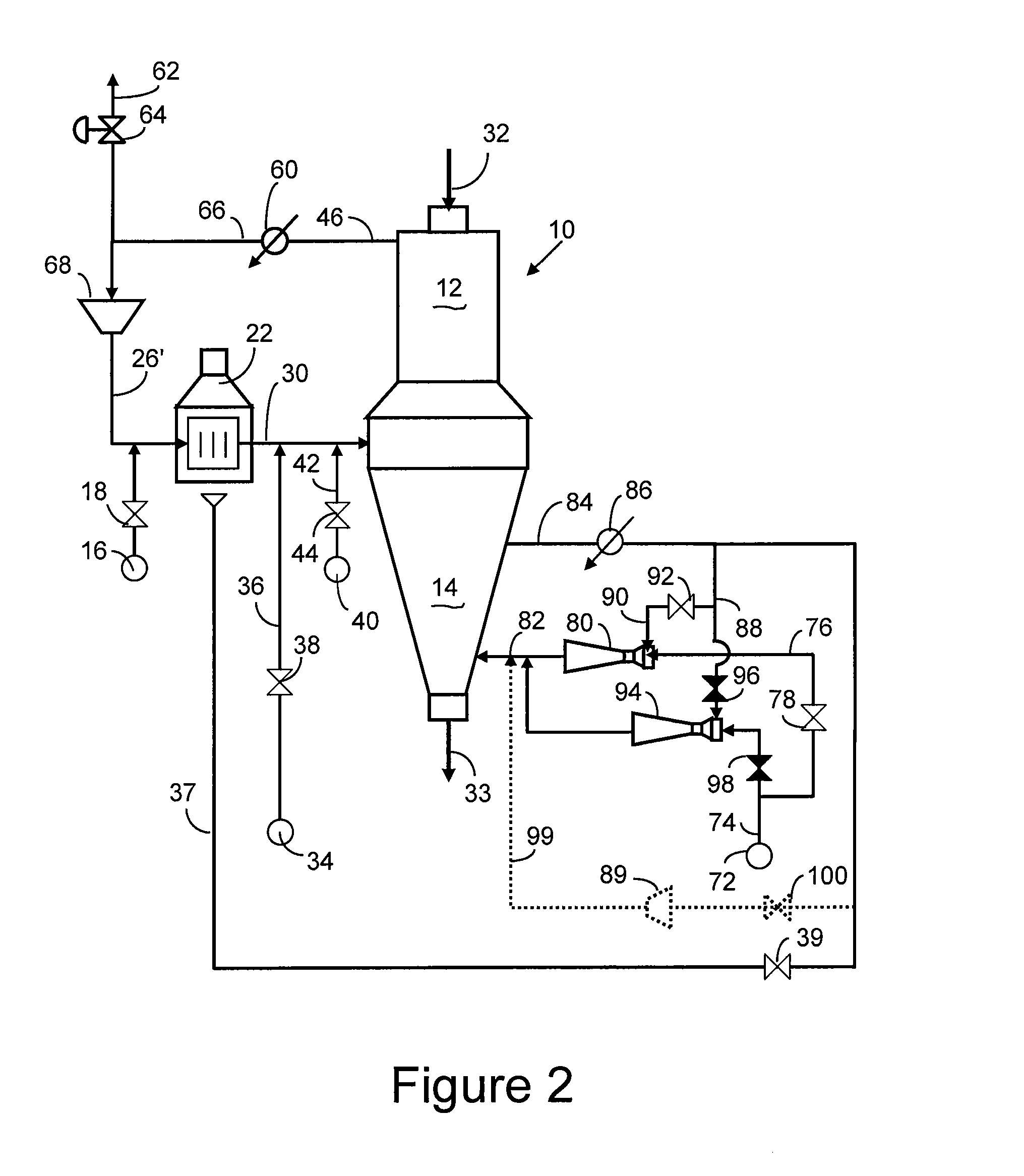
Method and Apparatus for Producing Direct Reduced Iron
ActiveUS20070245855A1Cutting costsLess-expensive equipmentBlast furnace detailsManufacturing convertersElectricityGas cooler
A direct reduction process for producing direct reduced iron (DRI) in a reduction reactor having a reduction zone for reducing iron-oxides-containing particles, such as iron ore pellets, to DRI by reaction of said iron oxides with a high temperature reducing gas, and a cooling zone for lowering the temperature of the DRI produced in said reduction zone, wherein a stream of cooling gas, usually natural gas, is circulated through said cooling zone, a portion of said cooling gas is withdrawn from the cooling zone, cooled and cleaned in a gas cooler and a portion of the cooled gas is recycled to said reduction zone by means of an ejector utilizing the high-pressure natural gas make-up feed as the ejector's motive fluid. Using an ejector for recycling the cooling gas instead of using a mechanical compressor provides significant savings in electricity and in capital, operational and maintenance costs. A direct reduction plant having a DRI cooling zone which uses at least one ejector in recycling at least a portion of cooling gas to the cooling zone.
Owner:HYL TECH SA DE CV
Process for production of direct reduced iron
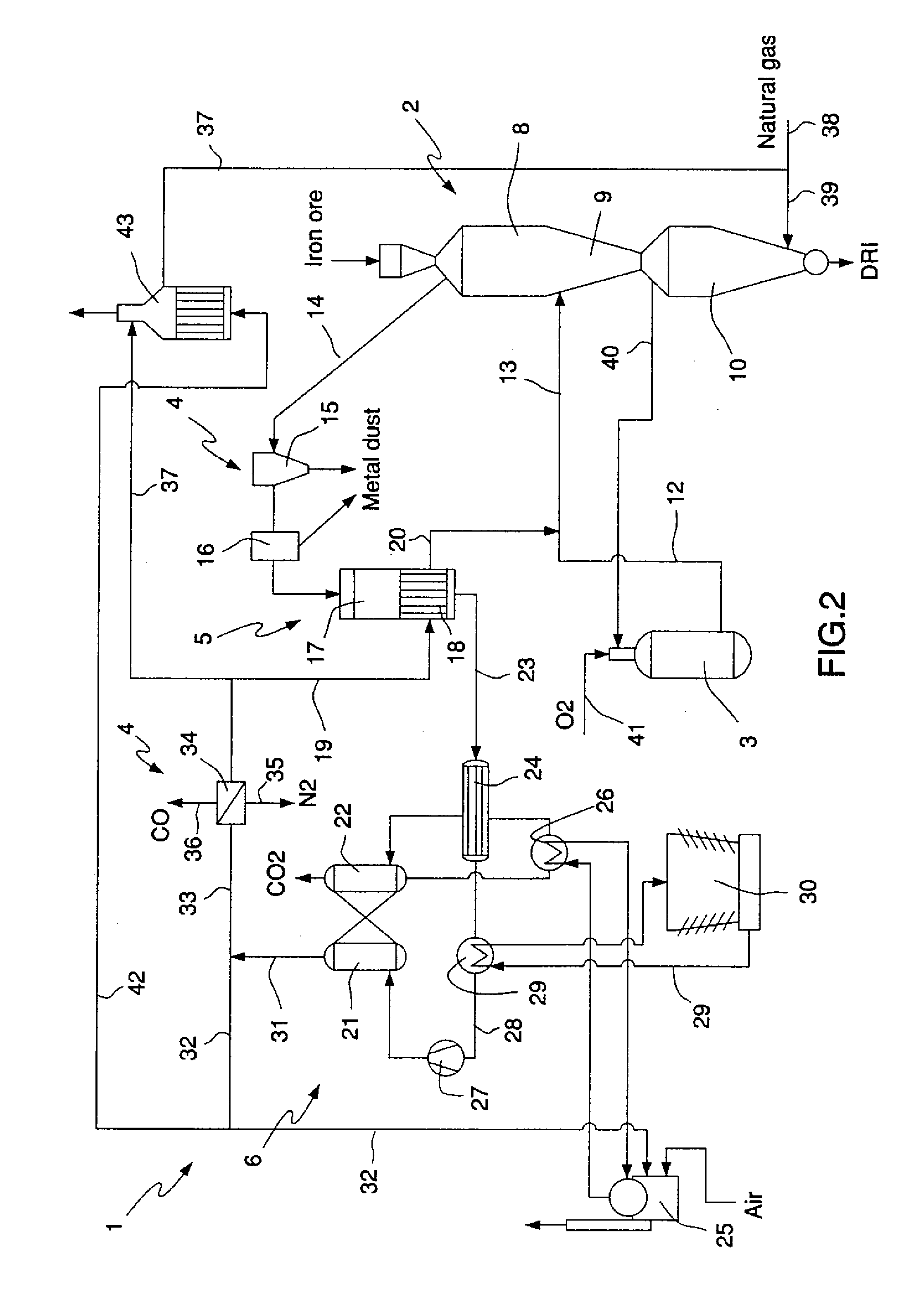
InactiveUS20110247457A1High strengthLow levelGas treatmentExhaust gas handlingNitrogen gasMaterials science
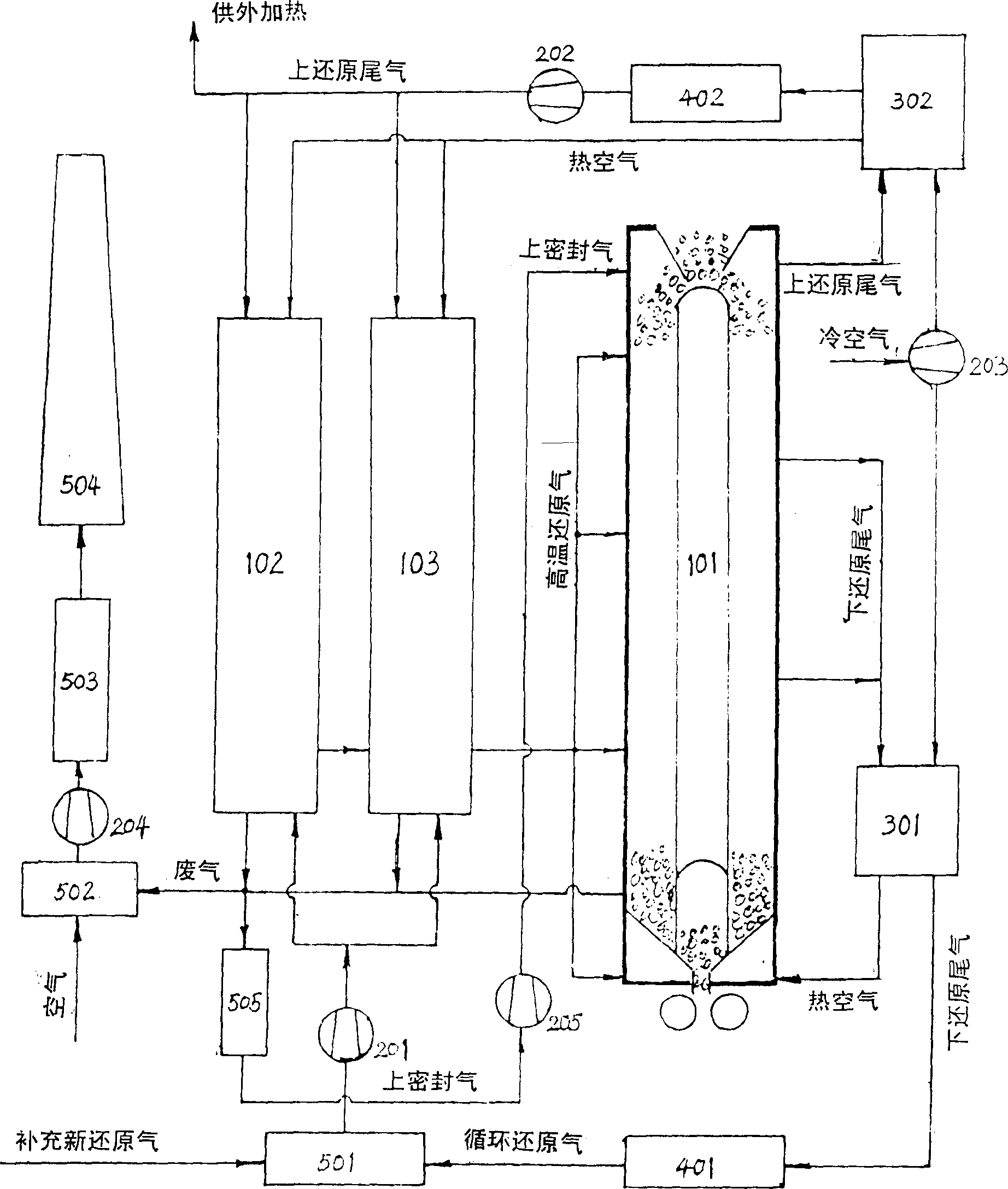
The present invention relates to a process for the direct reduction of iron ore performed by means of a plant comprising a gravitational furnace (2) having at least one iron ore reduction zone (8) in the upper part thereof, and at least one carbon deposition zone (9) and one reduced metal product cooling zone (10) in the lower part thereof, and means for feeding a reducing gas mixture into the reactor in correspondence to the with the reduction zone, means for recycle exhaust or reactor off gas from the reactor to syngas and mixing the recycled gas with natural gas to form a reducing gas mixture. According to the invention a in first reformation step (5) unreacted carbon monoxide CO and steam present in the reactor off gas is reformed to carbon dioxide and hydrogen following the water gas shift reaction CO+H20=CO2+H2, in a secondary reformation step the de-watered reactor off gas comprising mainly of carbon dioxide and hydrogen is processed to remove carbon dioxide, and in a third reformation step physical separation of both nitrogen and carbon oxide CO from the reducing syngas is carried out to bring down the levels of CO and any existing other gases in the recycled gas to as low level as possible such that recycled reducing gas is as close to pure hydrogen H2 as possible.
Owner:LOUSSAVAARA KIIRUNAVAORA AB
Process and apparatus for the direct reduction of iron oxides in an electrothermal fluidized bed and resultant product
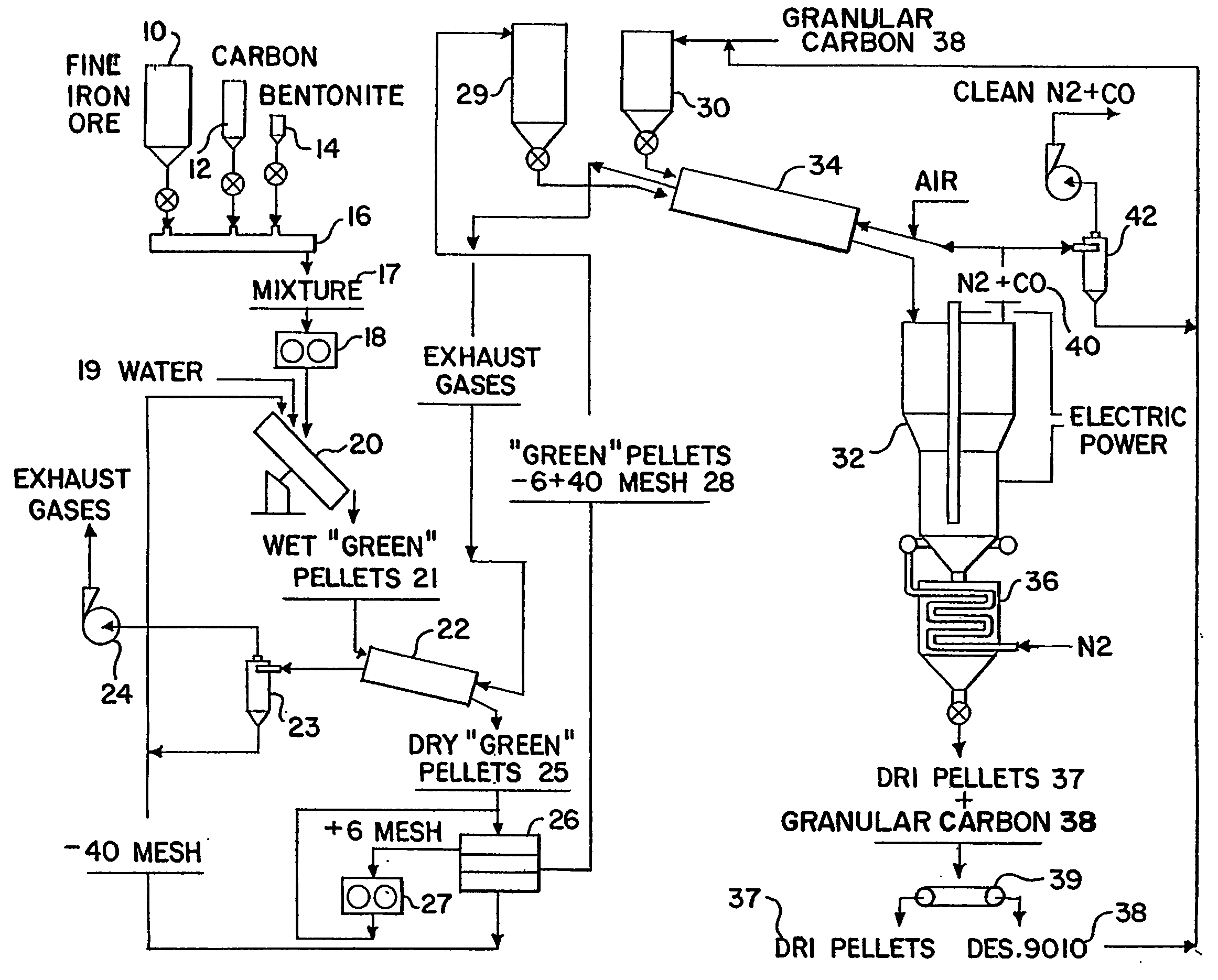
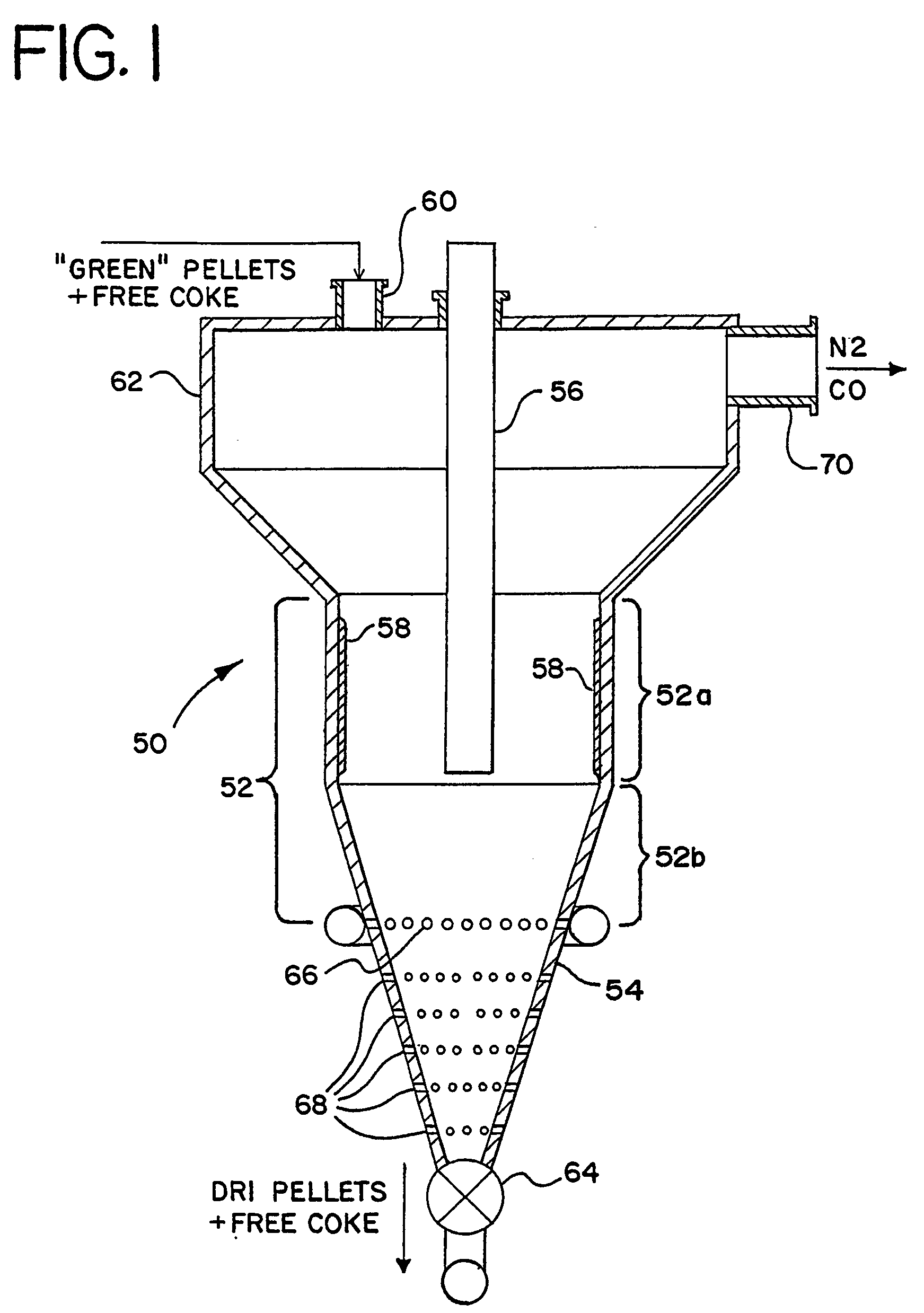
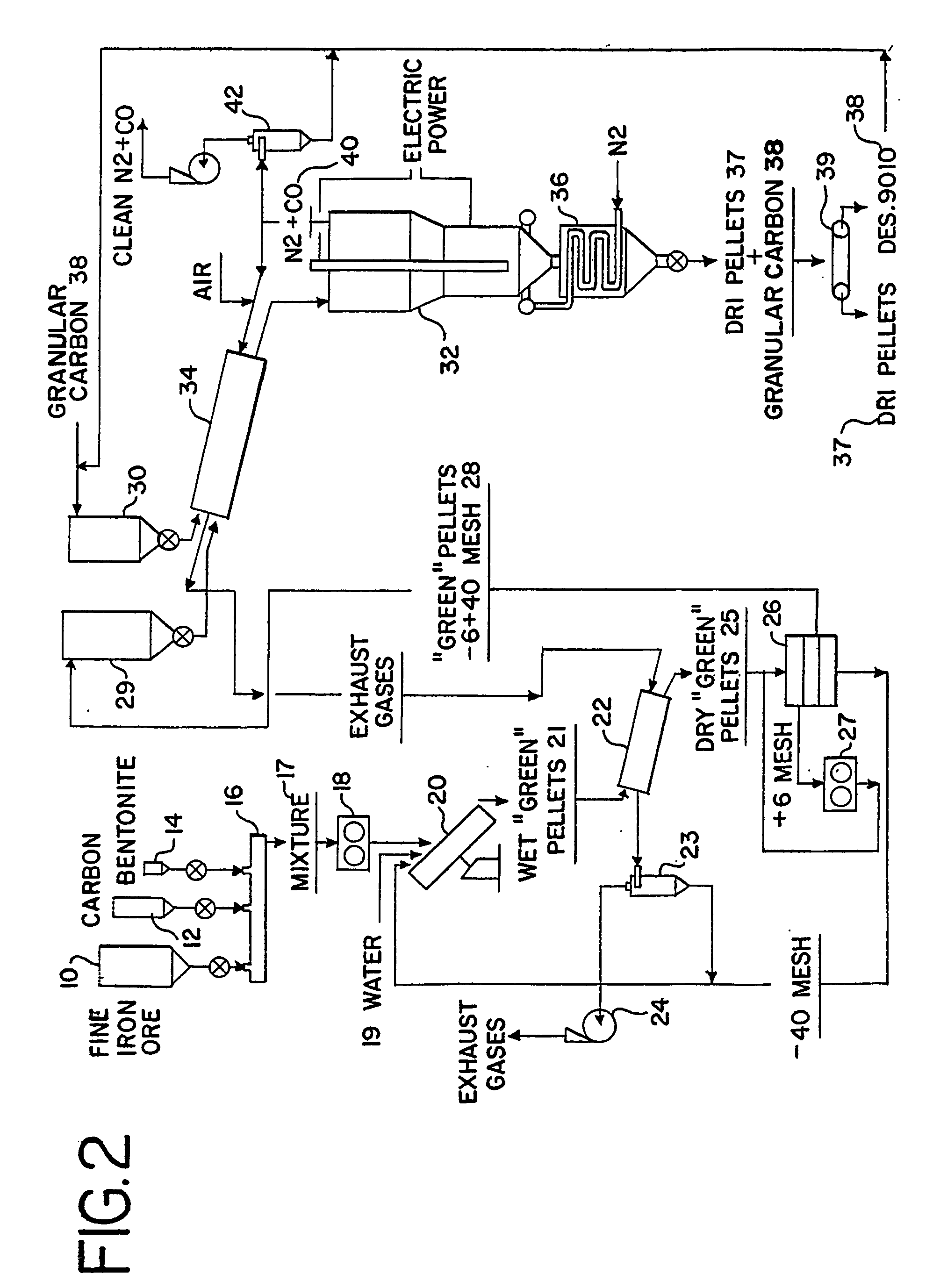
InactiveUS20050092130A1Avoid particle agglomerationInhibits the formation of depositsMaintainance of heating chambersCharge manipulationVolatilesFluidized bed
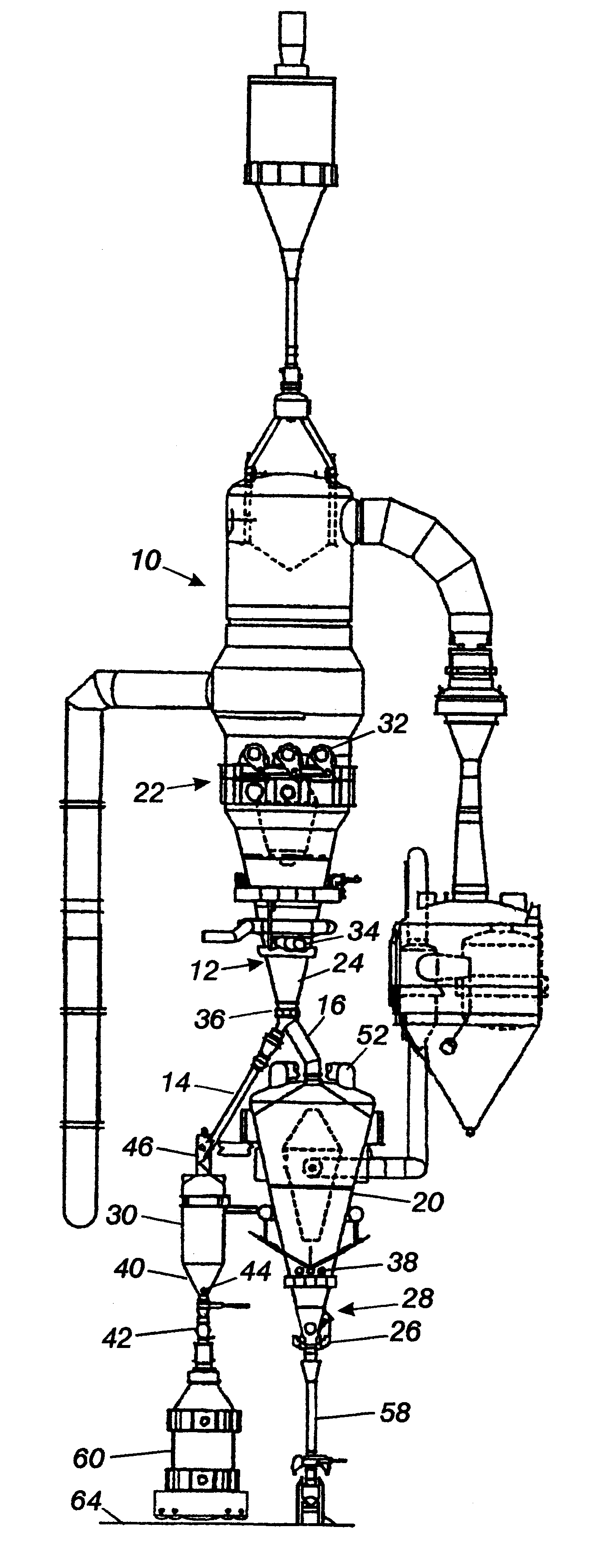
A method and an apparatus (50) for producing direct reduced iron (37) from dry pellets (25) composed of iron oxide and carbonaceous material. A mixture of pellets (25) and free coke particles (38) with weight relation from 3:1 to 5:1 is fed into the top of an electrothermal fluidized bed (32) that is fluidized by nitrogen. By exposing pellets (25) in the electrothermal fluidized bed (32) to temperatures of between approximately 850-1,100° C. for an average period of between approximately 15-60 minutes, the volatiles are removed and the pellets (25) metallized. Reduced pellets (37) mixed with free coke (38) are discharged from the bottom of fluidized bed (32) and cooled. The reduced iron pellets (37) are physically separated from any free coke (38) and the free coke (38) is recycled back into the fluidized bed (32).
Owner:GOLBERGER WILLIAM M +1
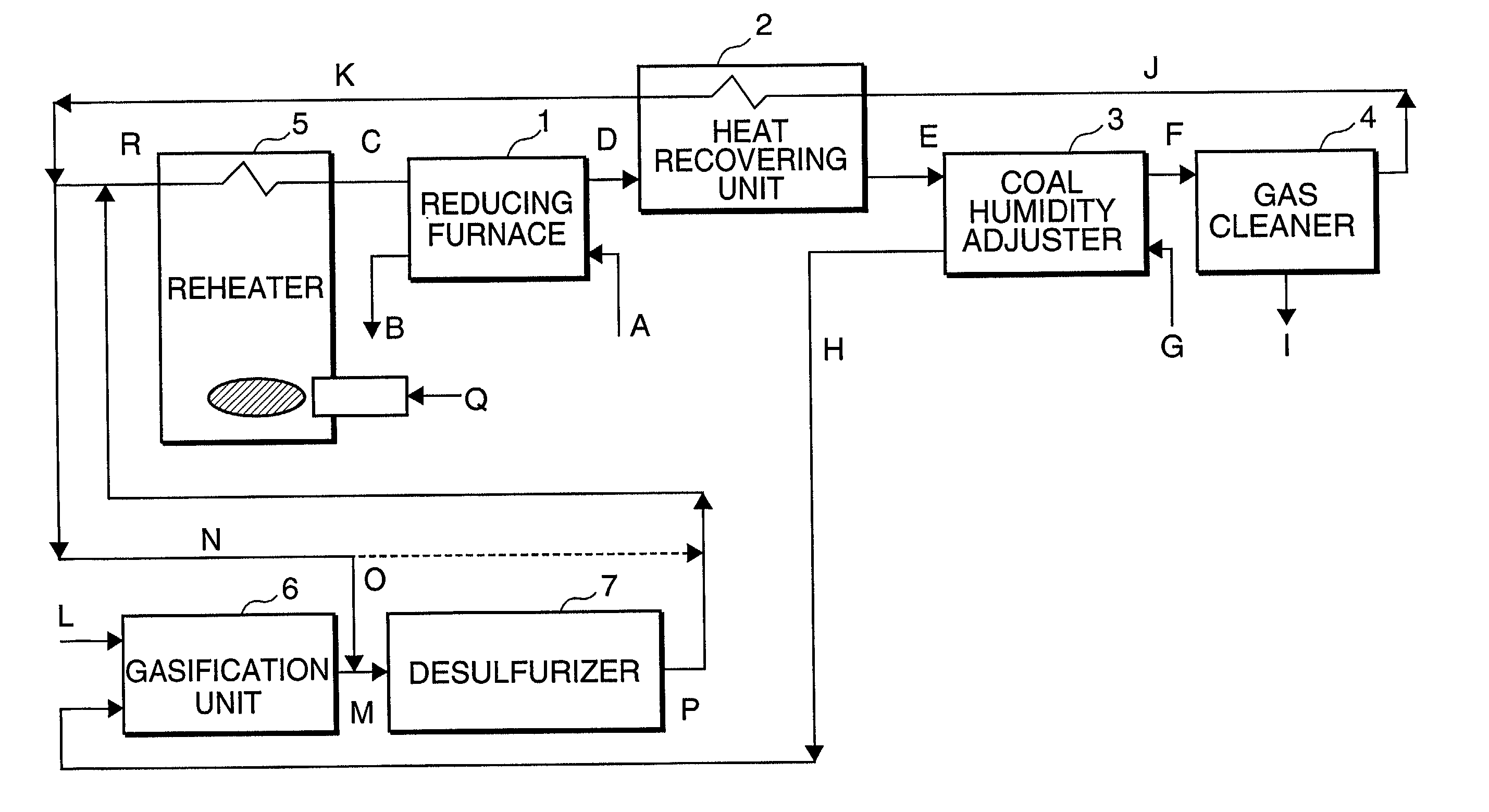
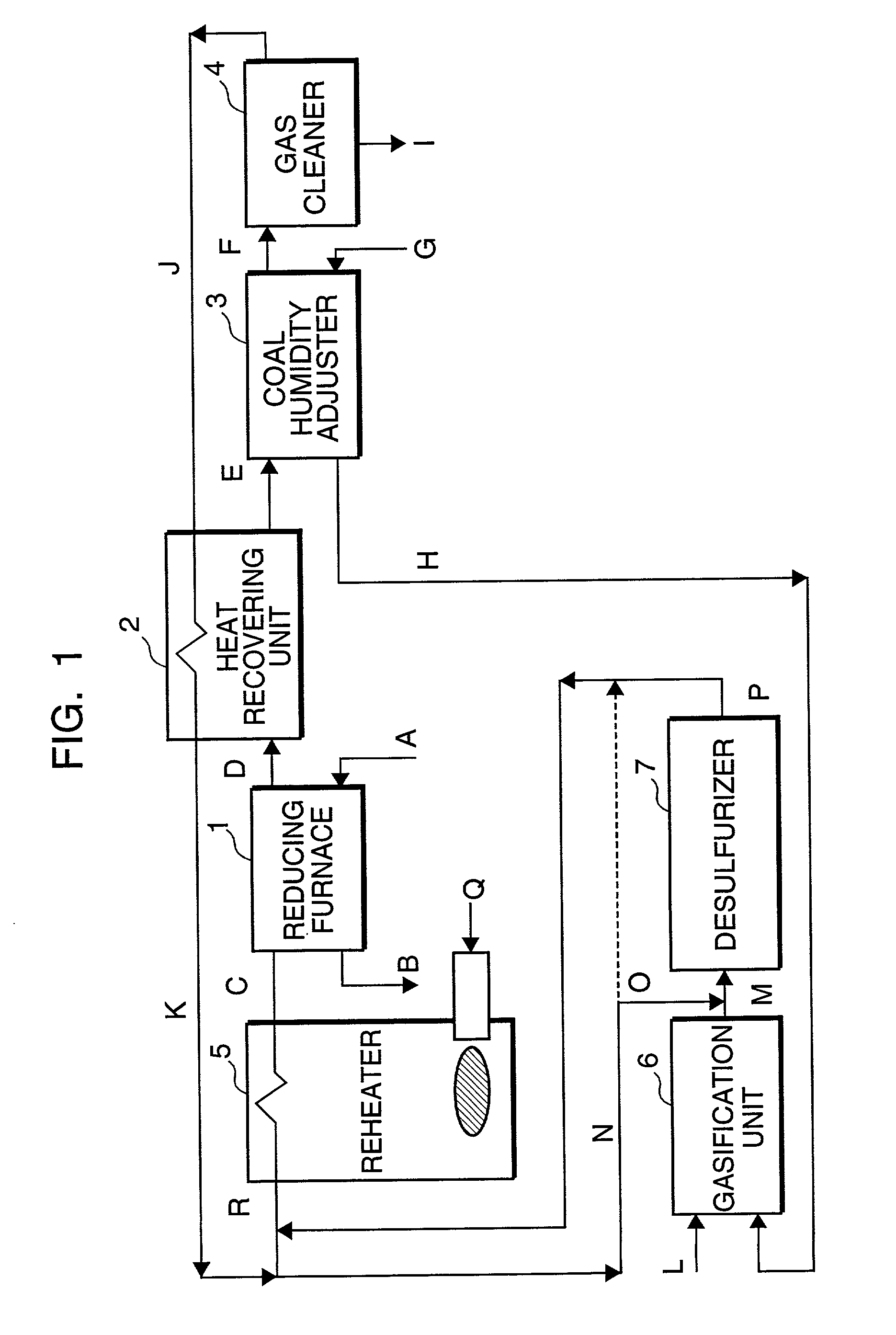
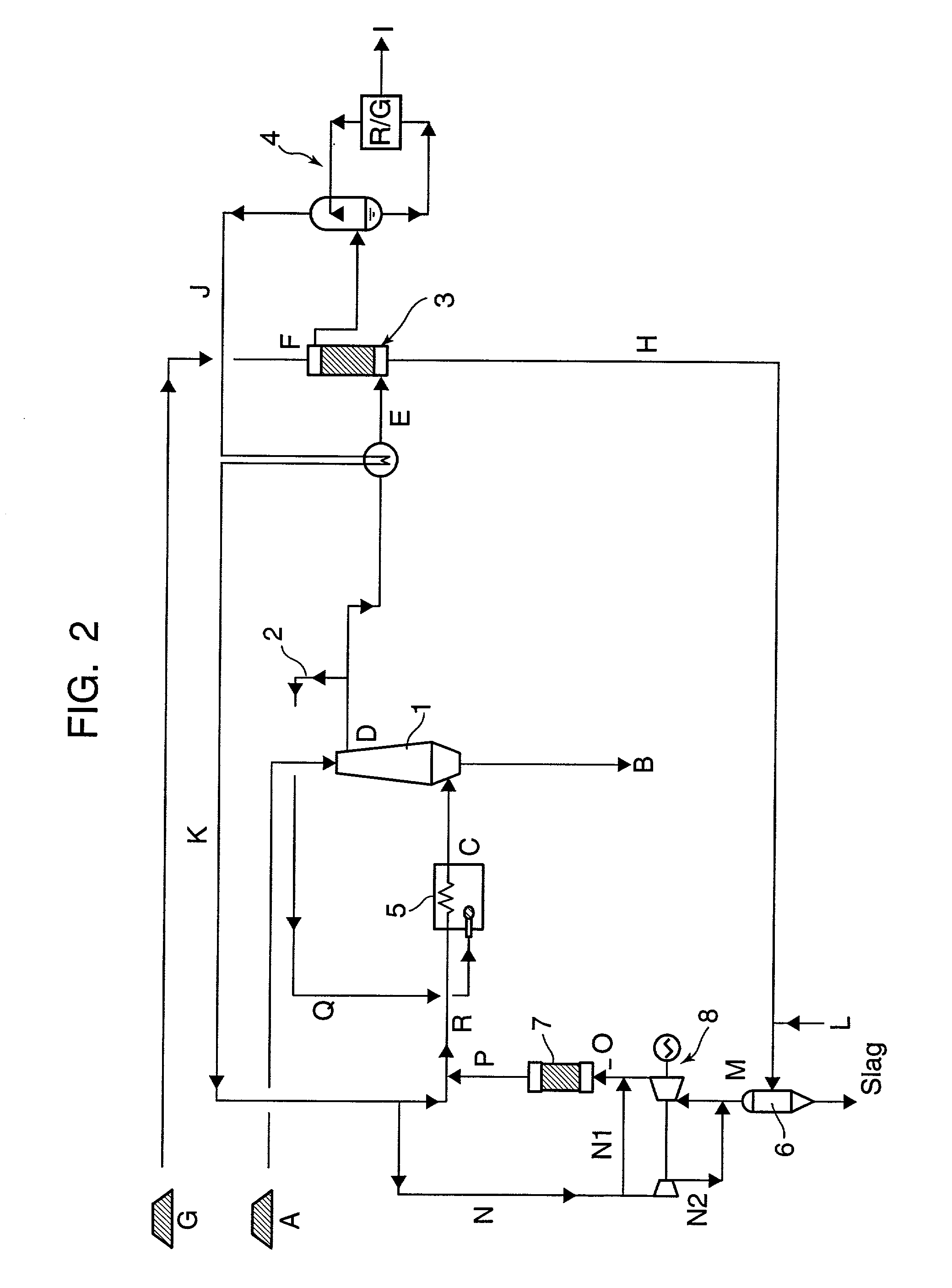
Method of producing direct reduced iron with use of coal-derived gas
InactiveUS20020078795A1Efficient use ofLow degreeTuyeresBell-and-hopper arrangementProduct gasCoal gasifier
In a method of producing direct reduced iron with use of a coal-derived gas, coal is heated to lower the moisture thereof, and the moisture-lowered coal is gasified in a coal gasification furnace to produce a coal-derived gas containing a reducing gas. The reducing gas is then utilized to reduce iron ore in an iron ore reducing furnace. With use of an exhaust gas from the iron ore reducing furnace, the coal is heated in the step of heating coal.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD +1
Controllable atmosphere rotary hearth furnace process for producing direct reduction iron
InactiveCN102994680AMeet temperature uniformity requirementsAvoid secondary oxidationHearth type furnacesSteelmakingShielding gas
The invention relates to a controllable atmosphere rotary hearth furnace process for producing direct reduction iron, comprising the steps of: pressing iron ore concentrate powder into pellets with the diameter of 30-40mm or directly using lump ores with the granularity of 5-25mm; preheating to 700-1000 DEGC at first; then mixing with a reducing agent; adding the mixture into a controllable atmosphere rotary hearth furnace; laying materials with the thickness of 30-70mm, wherein during laying materials, if the common iron ore powder pellets are used 5-10mm of reducing agent is paved at the bottom of the furnace in advance, and 5-10mm of reducing agent is scattered to the mixture at last, and the step of scattering the reducing agent is not needed if internally arranged carbon pellets are used; enabling all materials to operate in the controllable atmosphere rotary hearth furnace for 3-8h at 1200-1400 DEG C; discharging the materials out of the furnace by a water-cooled spiral discharging machine introduced with protective gas; and carrying out magnetic separation on the discharged materials to obtain sponge iron pellets. The materials are preheated at first and then reduced by the controllable atmosphere rotary hearth furnace, and the controllable atmosphere rotary hearth furnace process is suitable for various kinds of materials; and the temperature in a furnace hearth is uniform, the automation degree of equipment is high, workers operate simply and conveniently, and sponge iron meeting the demand of steel-making can be produced.
Owner:武汉桂坤科技有限公司
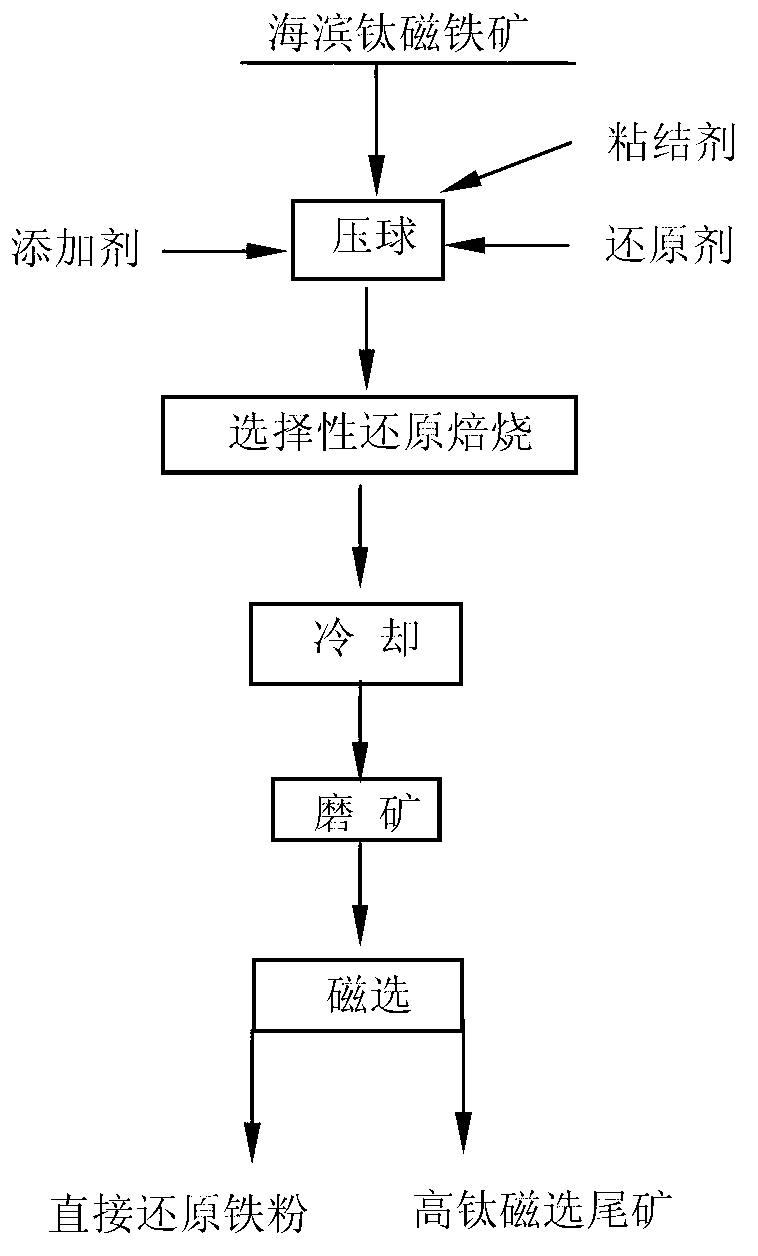
A process of separating iron and titanium in seaside titanomagnetite via direct reduction roasting by using coal
The invention provides a process of separating iron and titanium in seaside titanomagnetite via direct reduction roasting by using coal. According to the process, seaside titanomagnetite is employed as a raw material, a reducing agent, a binder, and an additive are added for briquetting, and then a selective direct reduction roasting - magnetic separation method is employed for respectively recovering iron and titanium. The process of the invention is simpler compared with other methods, wherein cost-effective coal is directly used as the reducing agent, additives added in the process is a mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium borate, and by adding the reducing agent and the additive, and controlling roasting temperature and time, selective reduction of iron and separation of iron and titanium can be achieved, ensuring the grade and recovery rate of direct reduced iron while reducing the titanium content in the direct reduced iron. The finally obtained direct reduction iron powder has a grade above 93%, the recovery rate of iron is generally greater than 85%, the titanium dioxide content is less than 0.5%, while the titanium dioxide content in obtained high titanium magnetic separation tailings is higher than 20%, and the recovery rate of titanium is greater than 90%.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +2
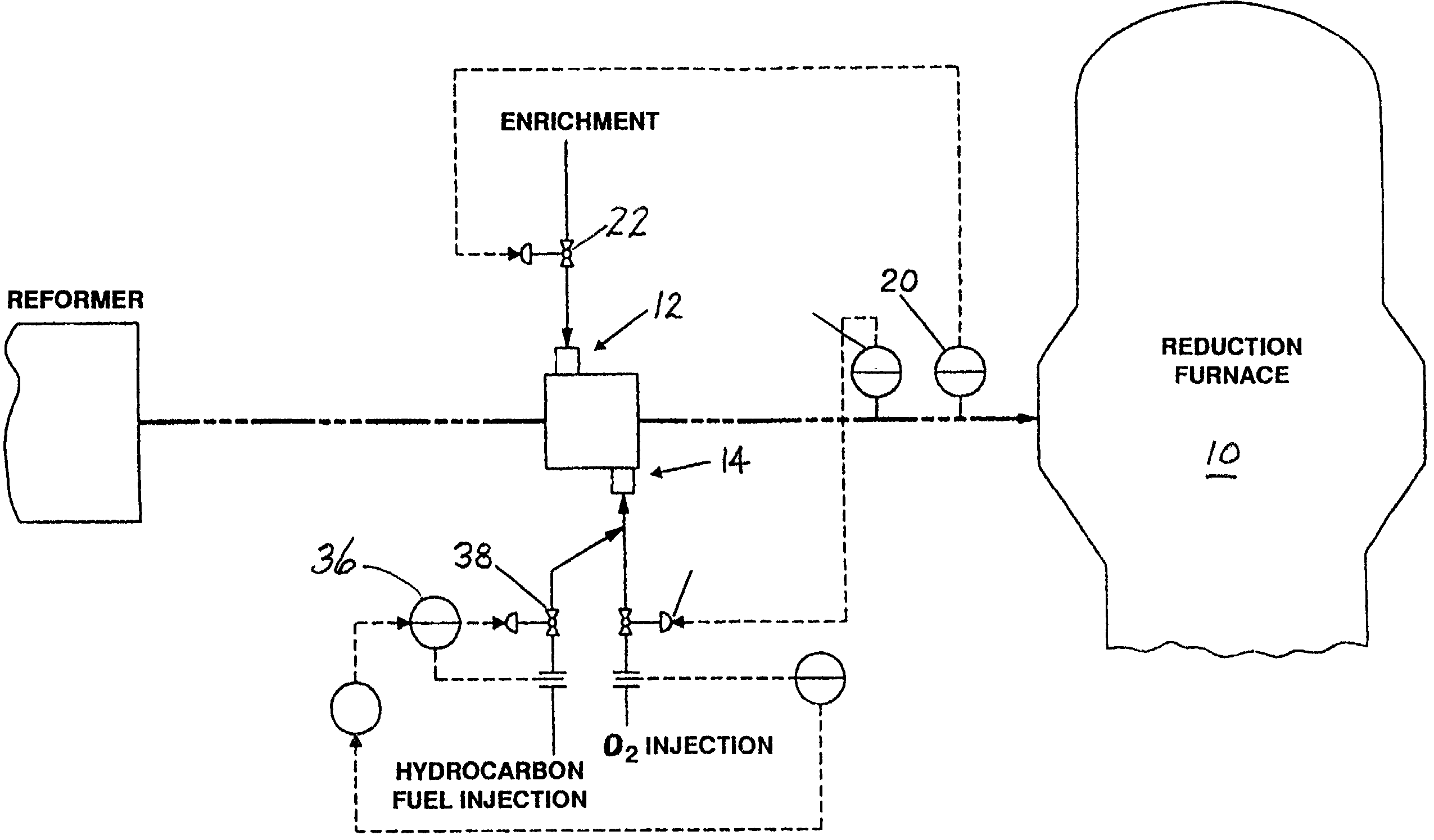
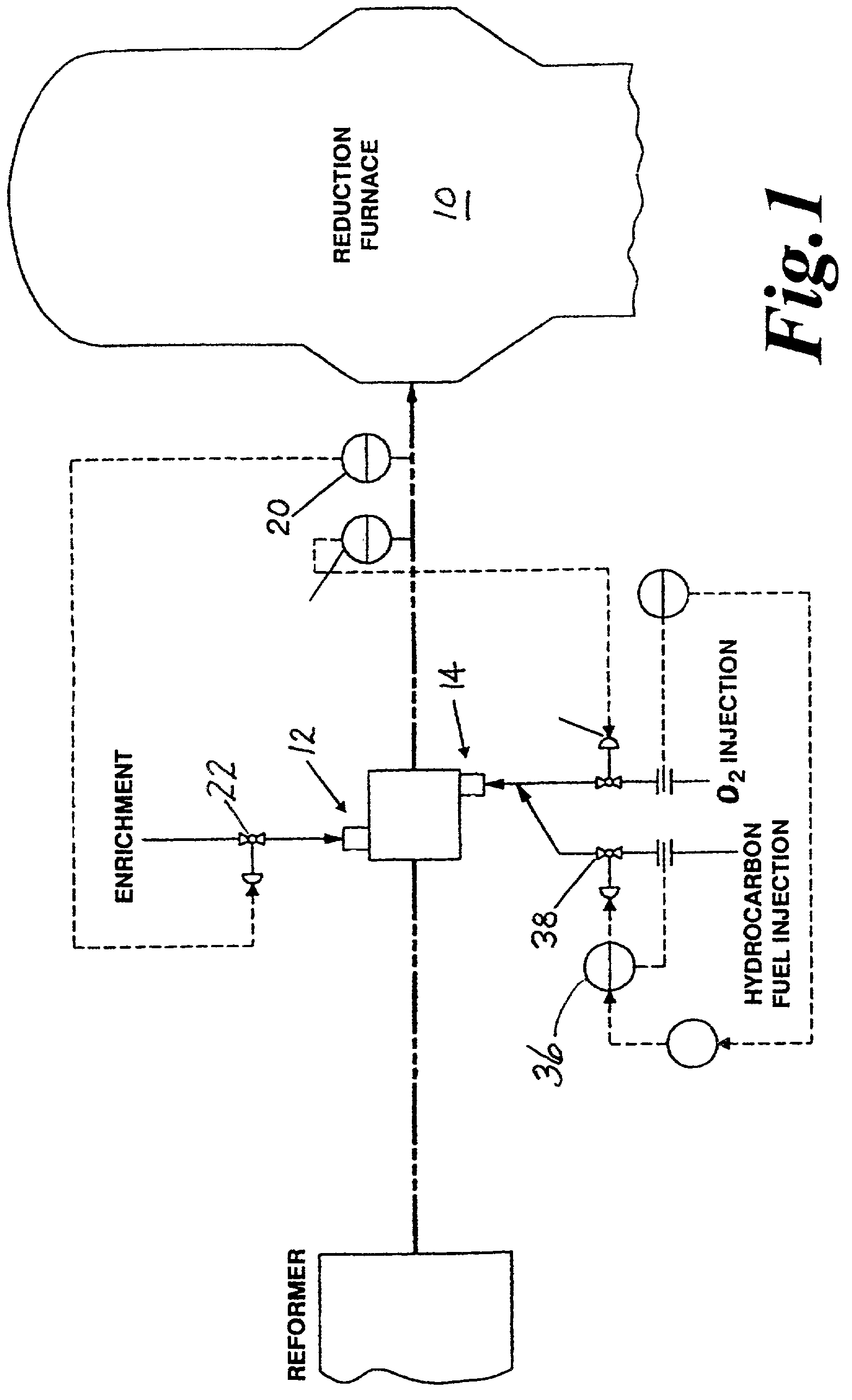
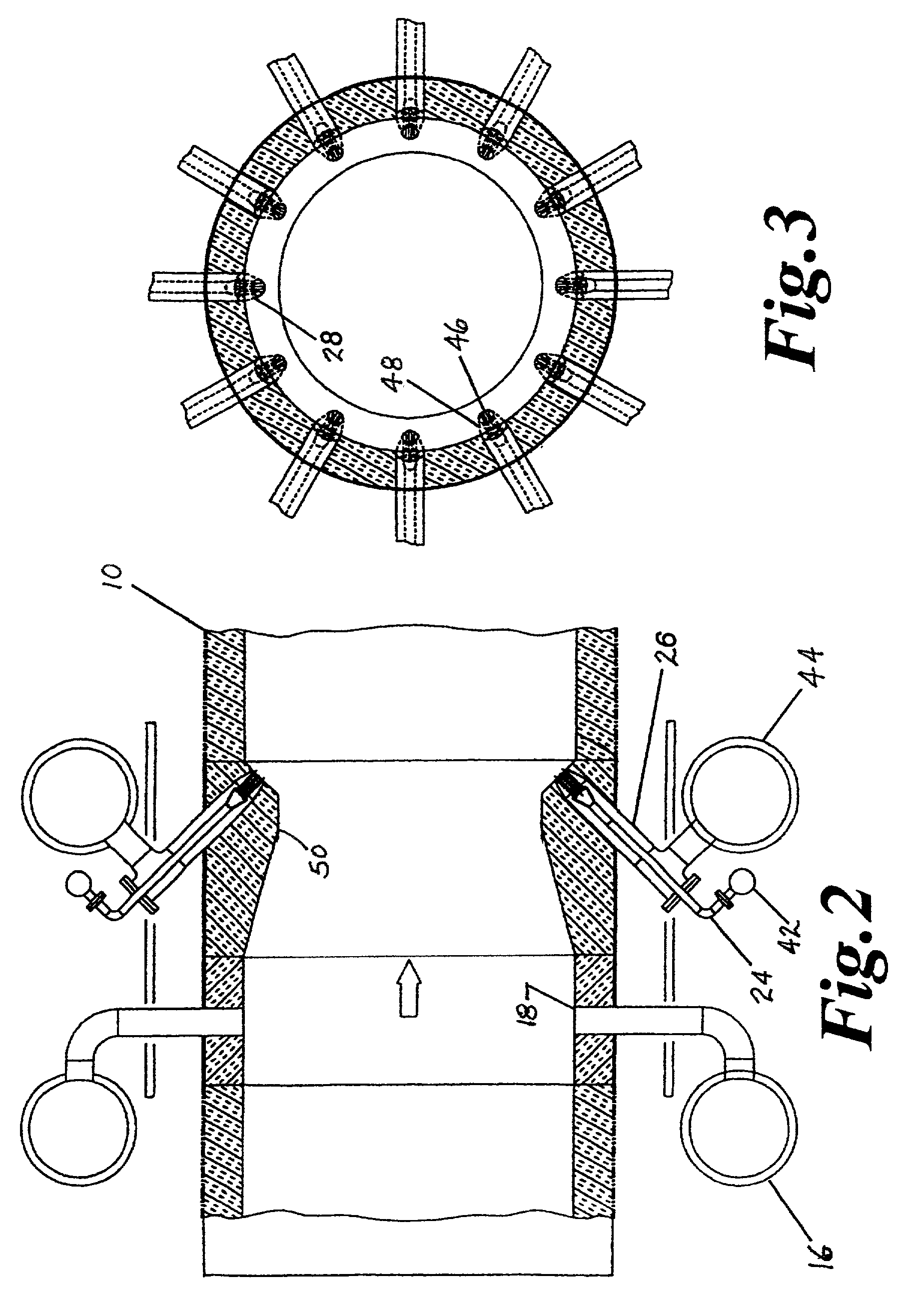
Apparatus and method for optimizing the use of oxygen in the direct reduction of iron
InactiveUS20020007699A1Increase volumeQuality improvementHydrogenChemical industryHydrogen contentProcess engineering
An apparatus and method for adjusting the parameters of a reducing gas stream prior to introduction into a direct reduction furnace, such parameters including temperature of the gas stream, and amount of hydrocarbon, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen contained in the reducing gas. The apparatus is placed in-line with the reducing gas recycle loop of a direct reduction furnace, which has an enrichment section which introduces hydrocarbon components to the main stream, and an oxygen / fuel injection system, located downstream from the enrichment section, which injects a shrouded stream of oxygen and hydrocarbon gas into the reducing gas stream. Temperature, carbon monoxide content, and hydrogen content of the reducing gas are adjusted by controlling the flow of oxygen and the ratio of hydrocarbon to oxygen injected in the oxygen / fuel injection system. Hydrocarbon content of the reducing gas is adjusted primarily by controlling the flow rate of the enrichment section.
Owner:MIDREX TECH INC
Direct iron-reduction by iron-ore briquet self-production reproduced gas
InactiveCN1896286AReduce consumptionRelatively small investmentShaft furnaceReducing atmosphereProduct gas
The present invention relates to a method of producing direct reduction iron with self-produced reduction gas of iron ore-coal pellet. With the coal in the iron ore-coal pellet as the whole reducing agent, the gas generated by self-pyrolysis of the coal in the iron ore-coal pellet as the self-produced reduction gas and the low heat value gas as the fuel heating the reduction gas, the self-produced reduction gas is recycled and reduces the iron ore into direct reduction iron in reducing atmosphere at high temperature. The present invention replaces the external reduction gas with the self-produced reduction gas facilitating zero release of greenhouse gases in the production of direct reduction iron and the realization of clean production.
Owner:苏亚杰
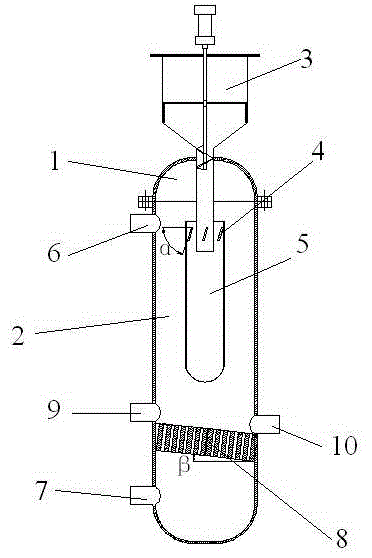
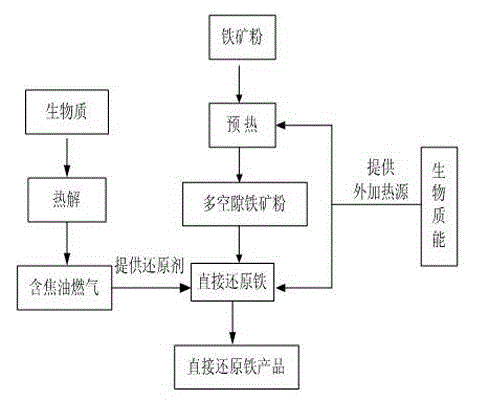
Device and method for direct reduction and iron making of pyrolyzing tar based on biomass
InactiveCN103146865AGet rid of dependenceLess investmentGas emission reductionElectrical resistance and conductanceIron powder
The invention provides a device and method for direct reduction and iron making of pyrolyzing tar based on biomass. The device is composed of a biomass pyrolysis area and an iron ore reduction area, wherein a biomass feeder is arranged on the top of the biomass pyrolysis area; the baiting pipe of the biomass feeder is connected with a pyrolysis basket through a baffle board; the iron ore area is provided with a gas inlet, a gas outlet, a ceramic screen, an iron powder feed port and an iron powder discharging port; and a resistance wire is arranged on outer side surface of the iron ore reduction area. The method comprises the following steps: pre-heating, dehydrating and pore-forming of the iron ore powder, deposition of gaseous biomass tar on the surface of porous iron ore powder surface, tar cracking and iron ore reduction. The direct reduction and iron marking is performed by pyrolyzing tar based on biomass in replacement of the coal and natural gas, so the investment is less, the cost is low, the production efficiency is high, and the obtained product is high in quality, the dependence of the iron-making industry to the fossil energy is cast off, the harm to the environment is reduced while directly improving the quality of the directly reduced iron product, and the technical and equipment problem in the environment-friendly iron-making industry is fundamentally solved.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing direct iron-reduction by iron-ore briquet self-production reproduced gas
InactiveCN1896286BReduce consumptionRelatively small investmentShaft furnaceReducing atmosphereProduct gas
Owner:苏亚杰
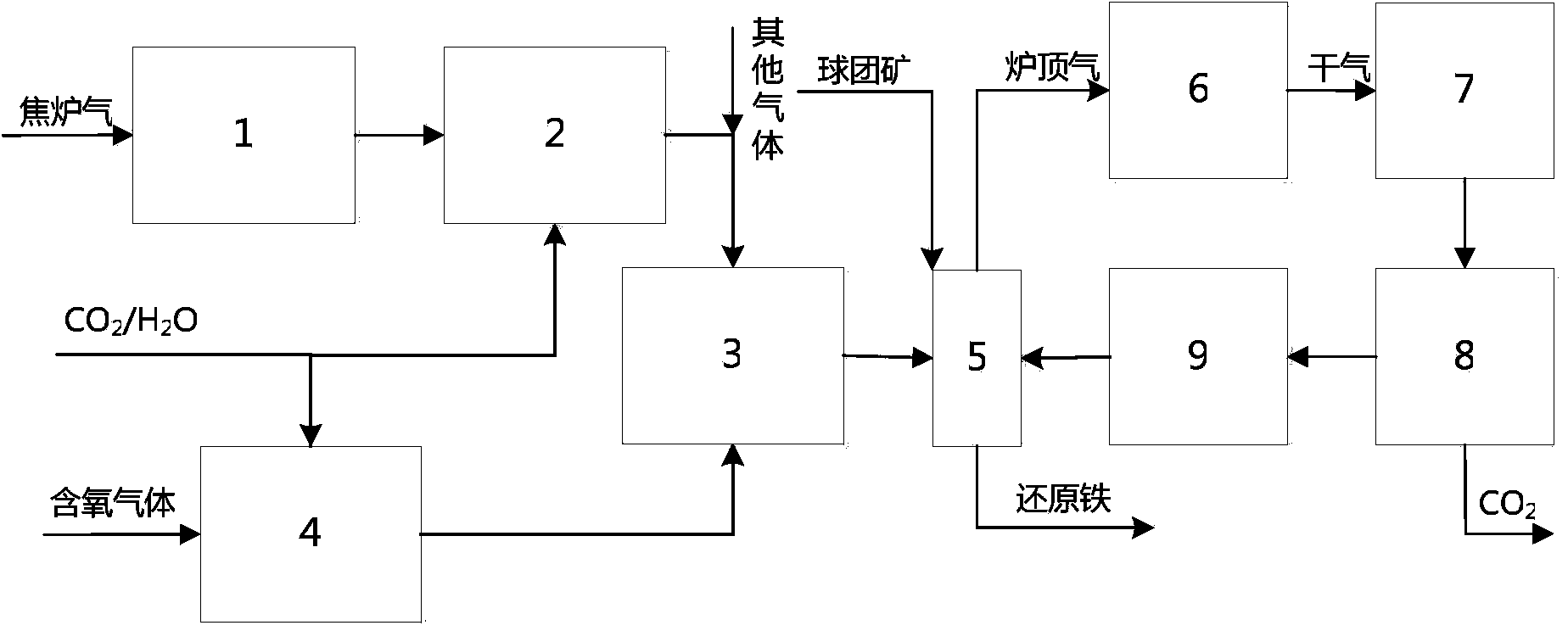
Method for producing gas-based directly reduced iron by utilizing non-catalytic conversion of coke-oven gas, and system thereof
ActiveCN103525965AAvoid inactivationGuaranteed uptimeShaft furnaceProcess efficiency improvementWater vaporEngineering
The invention relates to a method for producing gas-based directly reduced iron by utilizing the non-catalytic conversion of a coke-oven gas, and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the coke-oven gas obtained after routine purification and fine desulfurization treatment with a mixed gas comprising one or above two of a converter gas, a blast furnace gas and a purified tail gas to form a raw material gas mixture, and partially combusting the raw material gas mixture and an oxygen-containing gas at a converter burner outlet at a controlled flame temperature of 1100-2300DEG C for the conversion of hydrocarbons in the coke-oven gas and carbon dioxide or water vapor to generate a synthetic gas containing H2 and CO; and allowing the synthetic gas containing H2 and CO to enter a shaft furnace and reduce iron oxide in order to produce reduced iron, and cooling, washing, decarburizing, desulphurizing and purifying a reduced tail gas discharged from a shaft furnace to obtain a purified tail gas. The invention also provides a system for producing the gas-based directly reduced iron by utilizing the non-catalytic conversion of the coke-oven gas.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
Technique for reverting ironmaking by comprehensive utilization of fusion of coal gas and small ore
ActiveCN101153349AImprove utilization efficiencyPrevent carbon evolution reactionShaft furnaceGas emission reductionFluidized bedShaft furnace
A melting reduction iron making technology with comprehensive utilization of gas and fine ore, and the technological procedures are as follows: firstly the oxygen delivered into the melting gasification final reduction furnace undergoes the gasification reaction with the gas filled into the melting gasification furnace, to generate the reductive gas, secondly the gas yielded by the melting gasification final reduction furnace is delivered into a shaft furnace to reduce the block ore, thirdly the residue gas yielded by the melting gasification final reduction furnace is mixed with the gas output by the shaft furnace, then CO2 is eliminated through water / gas conversion and pressure-variation absorption to obtain the mixed gas containing hydrogen for treatment of the raw material of fine core by a multi-stage fluidized bed reactor and, fourthly the directly reduced power iron produced in the form of thermal pressed block after being processed by the multi-stage fluidized bed reactor, and the directly reduce iron sprayed into the melting gasification furnace or produced by the shaft furnace are reduced finally into the melted iron in the melting gasification final reduction furnace. The present invention combines the advantages of both the shaft furnace and the fluidized bed reactor, uses the shaft furnace and the fluidized bed reactor as the reduction reactor at the same time, improves the comprehensive capability in the pre-reduction process of the melting reduction techniques, and accomplishes the comprehensive utilization of the resource of fine ore and the block ore.
Owner:XINJIANG BAYI IRON & STEEL
Biomass-based direct-reduction ironmaking device and method
InactiveCN102392093AIncrease volumeReduce manufacturing costGas emission reductionSyngasCombustion chamber
The invention provides a biomass-based direct-reduction ironmaking device and a method thereof. The device provided by the invention comprises a blower fan, an air / pulverized coal premix pipe, a biomass feeder and a combustion chamber, wherein the biomass feeder is connected with the air / pulverized coal premix pipe; one end of the air / pulverized coal premix pipe is connected with the blower fan and the other end is connected with the combustion chamber; the bottom of the combustion chamber is provided with a slag removal outlet, the top is equipped with a flue gas outlet, and the intermediate part is provided with a reactor for direct-reduction ironmaking. The direct-reduction ironmaking method comprises green pellet preparation, preheating and direct reduction. The heat source needed for the preheating and reduction is provided by biomass combustion. Synthetic gas prepared by biomass catalysis and gasification is used as a reducing agent needed during the reduction process. According to the invention, coal and natural gas are replaced with biomass for direct-reduction ironmaking, thus reducing the dependence on fossil energy in the ironmaking industry, improving the quality of direct-reduction iron products, minimizing the harm to the environment, and fundamentally solving technological and equipment problems in the green ironmaking industry.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Apparatus for manufacturing molten irons by hot compacting fine direct reduced irons and calcined additives and method using the same
ActiveUS20060162499A1Reduce the amount requiredCharge manipulationFluidised-bed furnacesProduction rateFluidized bed
A method for manufacturing molten iron including the steps of producing reducing material of mixed hot fine direct reduced iron and calcined additives, the reducing material being produced from multiple fluidized beds; charging the reducing material to at least one pair of roller presses; roll pressing the reducing material through the one pair of roller presses to produce continuous compacted material having protrusions formed on pressed surfaces; crushing the compacted material; charging the crushed compacted material to a coal packed bed; and supplying oxygen to the coal packed bed to manufacture molten iron, wherein in the producing compacted material, the compacted material is formed such that acute and obtuse angles are formed between a center line formed along a length of a cross section that is cut along a lengthwise direction perpendicular to an axial direction of the roller presses and connecting lines that connect grooves closest to each other across the cross sectional area. An apparatus for manufacturing molten iron performs the inventive method for manufacturing molten iron. The processes involved in manufacturing molten iron using the invention are convenient, efficient, improve productivity, and allow for more flexibility with respect to equipment operation during the manufacture of compacted material.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
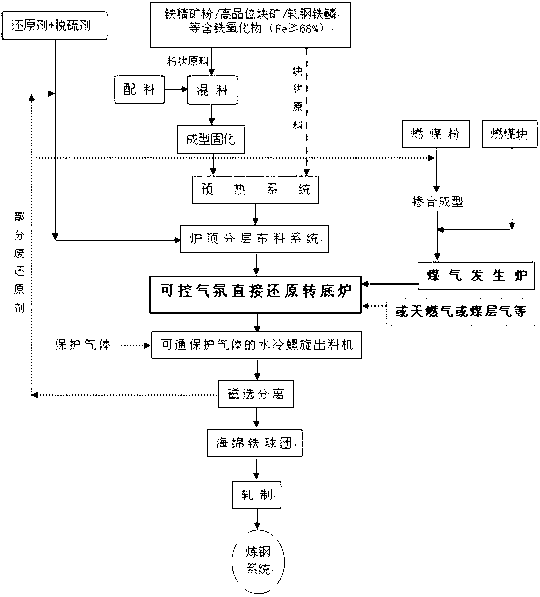
Method for producing directly reduced iron from coal
ActiveCN102010924ATake advantage ofMeet the requirements of reducing gasShaft furnaceHydrogenDirect reduced iron
The invention discloses a method for producing directly reduced iron from coal. A technical process that CO is taken as main reducing gas for producing the directly reduced iron is adopted. The reducing gas is led into a reducing vertical furnace to carry out the reducing reaction with iron-containing raw materials to generate the directly reduced iron, much CO2 in the furnace top gas discharged from the reducing vertical furnace is modified into CO by adopting the reducing reaction, the CO is mixed with the reducing gas, and then, the mixed gas enters the reducing vertical furnace for reacting. In the invention, a carbon-based packed bed is used for modifying the top gas of the reducing vertical furnace, the modified gas component can meet the requirements of the reducing vertical furnace for the reducing gas, the fuel of the process route is coal, the CO2 gas is discharged by the system, and the coal energy can be fully used, thereby achieving a theoretical minimum value of unit consumption. Moreover, by using the carbon-based packed bed for modifying the gas, hydrogen can be enriched in the reducing gas by a method of adding steam, thereby improving the production efficiency.
Owner:CISDI SHANGHAI ENG CO LTD +1
Process of coal-gas one-step production of direct-reduction iron and production apparatus
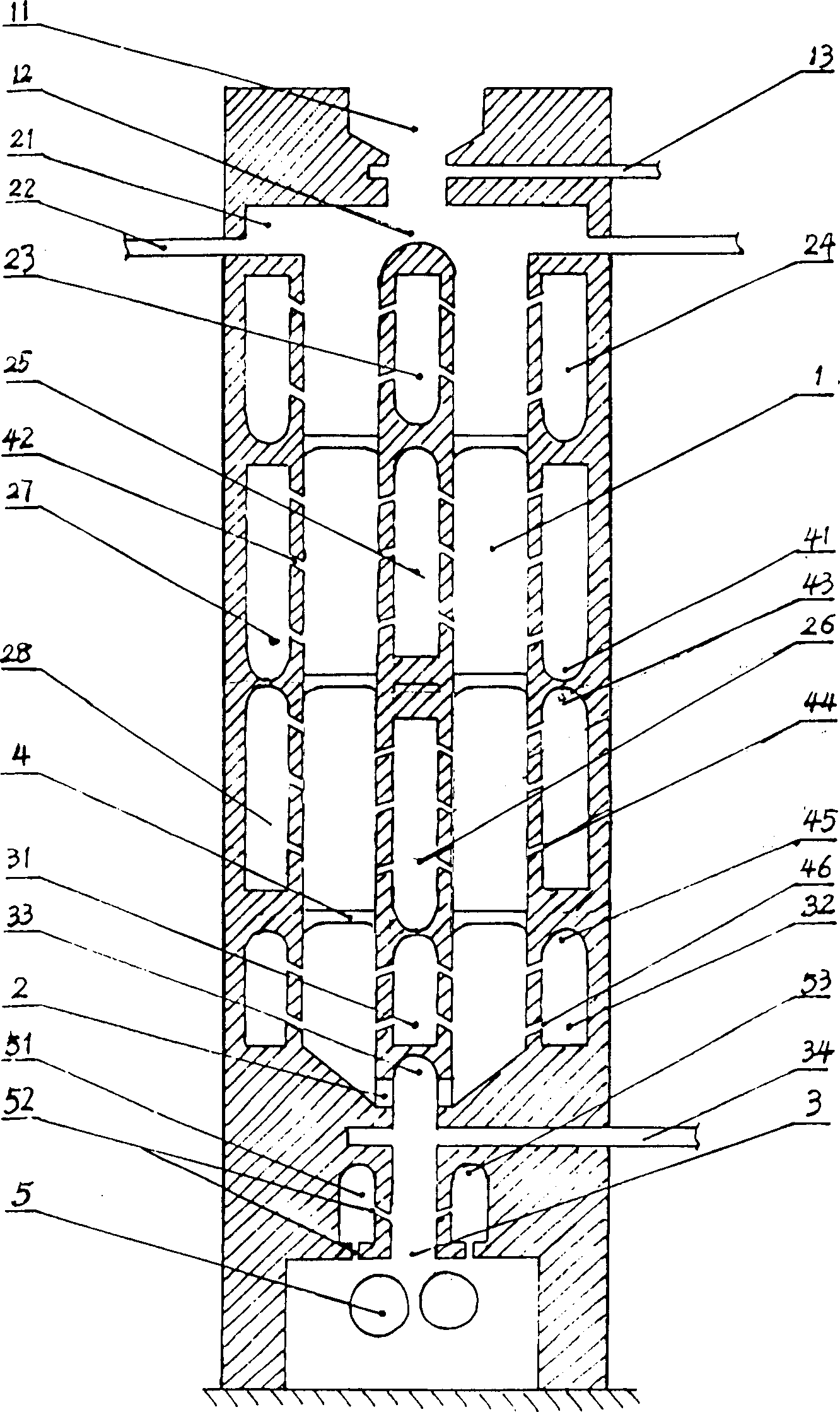
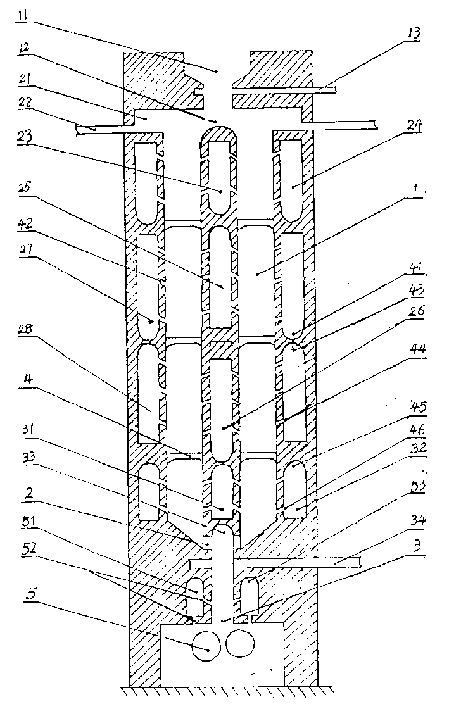
The invention is a craft method and the producing device for using coal gas one-step to produce direct reduced iron, the materials which contains carbon iron mineral are added into reducer of reducing straight stove and fall down freely, the high temperature reducing gas is ejected into reducer from the gas room at two sides of reducer, the gas penetrates the materials sidelong, after the reducing to materials, the tail gas is collected by the collecting room which is at two sides of the reducer and is in staggered arrangement with reducing gas room, in order to realize the direct reducing to materials. Thereof, the tail gas in lower reducing part is supplied by the new reducing gas and circulates.
Owner:苏亚杰
Reduced iron powder production process
InactiveCN103042223AIncrease production capacityReduce pollutionFluidised-bed furnacesTunnel kilnIron powder
The invention relates to a reduced iron powder production process which is characterized by including the steps: (1) distributing and weighing powdered iron, reduced pulverized coal and lime powder according to the weight ratio of 75-85:12-18:3-7, adding the powdered iron, the reduced pulverized coal and the lime powder into a damp mill for mixing and grinding after distribution to form wet materials by stirring; (2) conveying the wet materials to a ball press for pressing the wet materials into balls; (3) conveying finished balls into a grate for drying and transforming green balls into direct reduced iron-metalized pellets in a rotary hearth furnace; (4) enabling the pellets to directly enter a quenching tank or a quenching bath for rapid cooling after discharge, grinding the pellets into powder and then removing impurities in the powder to obtain primary iron powder; and (5) drying the primary iron powder in a dryer and then conveying the primary iron powder into a secondary reduction furnace for secondary fine reduction. In the novel process, direct reduced iron prepared by the rotary hearth furnace is used as the primary iron powder, primary iron powder produced by a tunnel kiln can be replaced, and accordingly, the problems in production of a current tunnel kiln are solved.
Owner:NINGXIA ZHONGLEIXIN TECH IND
Method for producing direct reduced iron
ActiveCN101597662AReduce manufacturing costEfficient use ofFluidised-bed furnacesHigh activityMaterials science
The invention relates to a method for producing direct reduced iron. Refined iron ore powder is taken as raw material, the material and reducing agent are mixed in proportion of 1:0.5-5.0, binding material is added to prepare a preform, and the preform is placed in a reducing furnace to produce direct reduced iron at 700-1600 DEG C by reduction. The reducing agent is straw and fruit of crops, or dry fruit shell, or branch, leaf and wooden meal of trees, or the mixture thereof. The straw and fruit of crops, or dry fruit shell, or branch, leaf and wooden meal of trees, or the mixture thereof is dried and dehydrated at 50-300 DEG C to be made into powder, or is treated by insulating from air at 400-1200 DEG C to be made into powder. The characteristic of the powder after high temperature treatment is close to that of activated carbon, and the powder, being used as the reducing agent of reduced iron, has high activity, fast reducing speed, good reducing effect and good product quality; by applying the invention, use of non-renewable energy resource can be reduced, thus being beneficial to environmental protection, and the production cost is low.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG XINHUA IND FURNACE CO LTD
Method for recovering iron, vanadium and chromium in vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate
ActiveCN102041377AImplement synchronous recyclingHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementIron sulphateMagnetite
The invention provides a method for recovering iron, vanadium and chromium in vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate, which comprises the following steps: milling the vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate, carrying out magnetic separation, directly reducing iron, milling, carrying out magnetic separation to obtain an iron powder product and tailings, and treating the tailings by the following steps: pelletizing, roasting, leaching while stirring, boiling the leaching liquor, simultaneously adding sulfates, cooling to crystallize and precipitate to obtain polyvanadates and liquor containing chromium, adding ferric sulfate into the liquor containing chromium to reduce chromium, and adding Ca(OH)2 to generate Cr(OH)3 precipitate. The method can be used for synchronously and effectively recovering multiple valuable metals, such as iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium, in the vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate so as to produce products with high added value, such as high-quality reduced iron powder, red vanadium, chromium, titanium and the like, thereby sufficiently and effectively utilizing the limited ore resources in a reasonable way. The metal recovery rate of the method is high, wherein the recovery rate of iron is higher than 90%, the recovery rate of vanadium is higher than 80%, the recovery rate of chromium is higher than 78%, and the recovery rate of titanium is higher than 90%. The method is not involved with the use of coke, and has the advantages of low power consumption and no environment pollution.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
System device and method for modifying coke oven gas to directly reduce iron ore
ActiveCN103898265AEmission reductionSuitable for energy resource characteristicsGas emission reductionEngineeringShaft furnace
The invention relates to a system device and method for modifying coke oven gas to directly reduce iron ore, and belongs to the technical field of non-blast furnace iron-making process. The invention provides a new process, the coke oven gas produced in the coking process is modified and reformed as hydrogen-enriched reducing gas (H2 and CO), and the hydrogen-enriched reducing gas is introduced into a shaft furnace to directly reduce the iron ore. The large quantity of hydrogen-enriched reducing gas required for direct iron reduction technology is provided by the invention, the obtained hydrogen-enriched reducing gas obtained by modifying is used for the direct reduction of the iron ore so as to effectively reduce the emission of carbon dioxide in the iron ore reduction process, the direct reduction is completely different from the path of directly reducing iron from the natural gas and suitable for the energy resource feature of China.
Owner:丰镇市新太新材料科技有限公司
System and method for preparing reducing gas for gas-based shaft furnace
ActiveCN107337179AGas composition is flexible and adjustableLow costHydrogenChemical industrySyngasProcess engineering
The invention provides a system and a method for preparing reducing gas for a gas-based shaft furnace. The system comprises a gas-based shaft furnace top gas scrubber, a top gas decarbonization device, a coke oven gas purification device, a coke oven gas desulfurization device, a reformer, a heat recovery unit, a syngas dust removal device, a syngas desulfurization and decarbonization device and a mixer. According to the system and the method, coke oven gas and syngas from a gasifier are combined, and effective gas components in the coke oven gas and high-temperature characteristics of the syngas are sufficiently used for producing the reducing gas for direct reduction iron; the system has the advantages of flexible and adjustable gas components, high thermal efficiency, low cost, good product gas quality and the like.
Owner:CERI ENERGY & AIR PROTECTION TECH CO LTD +1
Determination method of phosphorus content in direct reduced iron
ActiveCN102262009AImprove accuracyEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsTest sampleDirect reduced iron
The invention provides a method for measuring phosphorus content of directly reduced iron. A reagent is added into a directly reduced iron test sample for certain treatment so as to prepare test sample solution to be measured; and after color development, the phosphorus content of the directly reduced iron can be measured directly by spectrophotometry in the prior art. The method is convenient tooperate; furthermore, the accuracy rate of the measured phosphorus content is high, so a measurement result of the phosphorus content has high stability, reproducibility and accuracy. The experiment shows that the method is reliable and practical, and can meet the daily requirement of measuring the phosphorus content of the directly reduced iron.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com