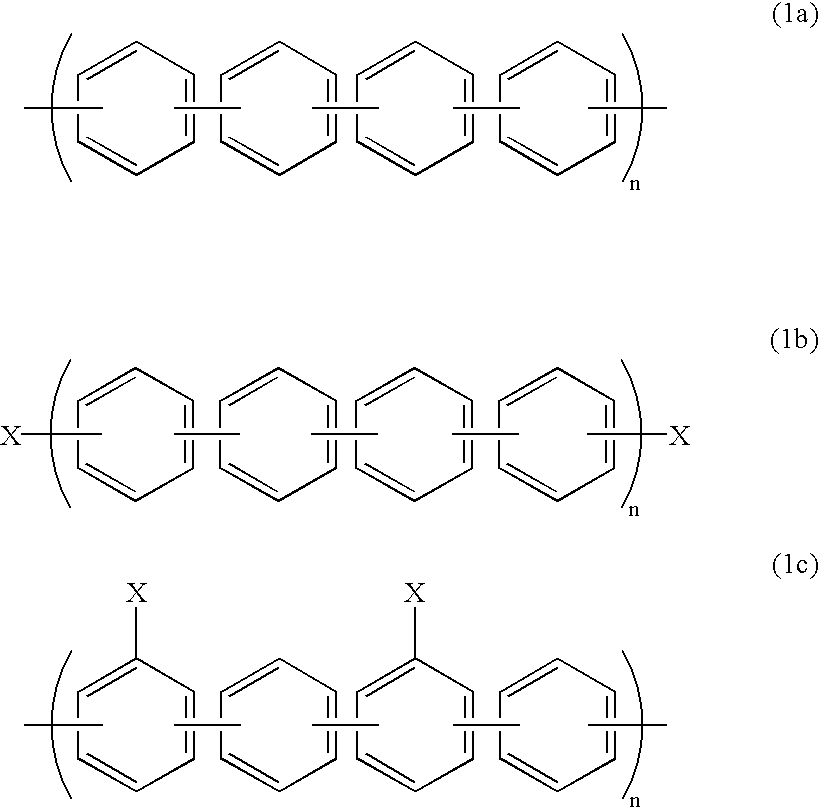
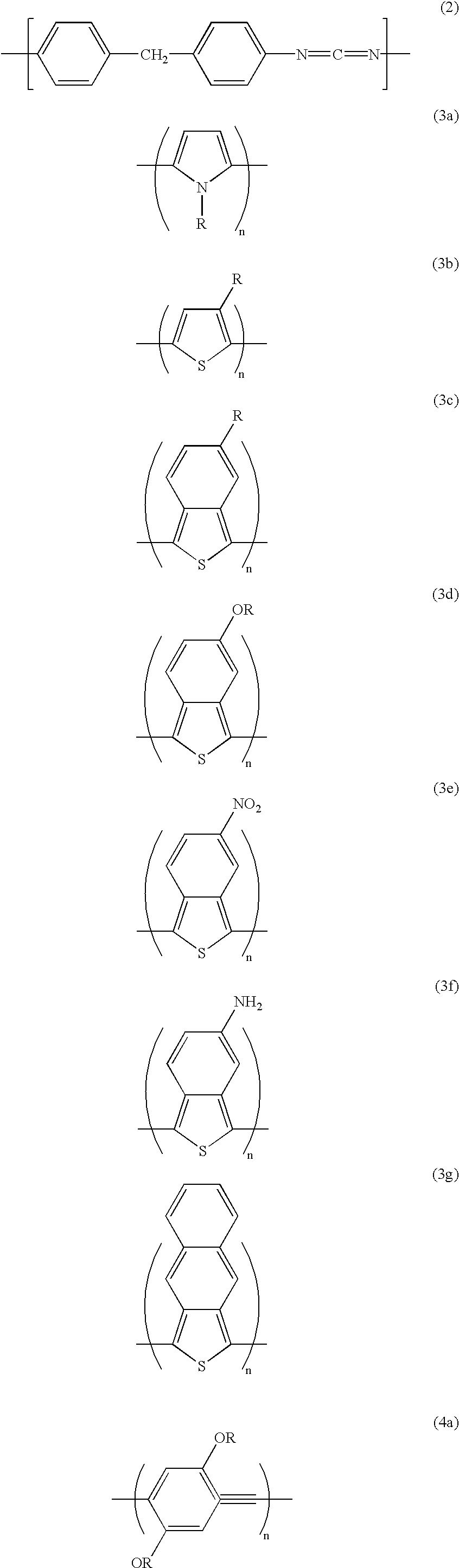
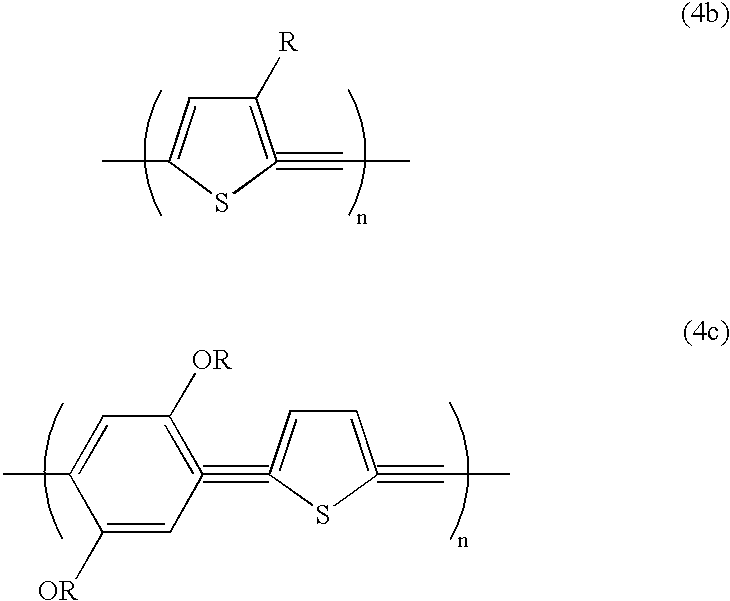
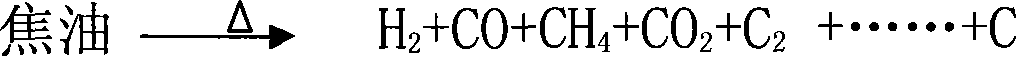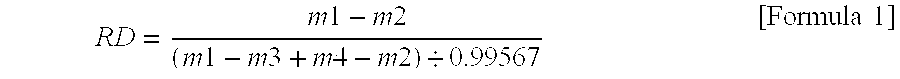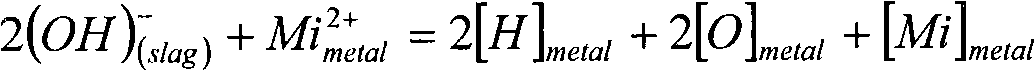Patents
Literature
1792 results about "Hydrogen content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
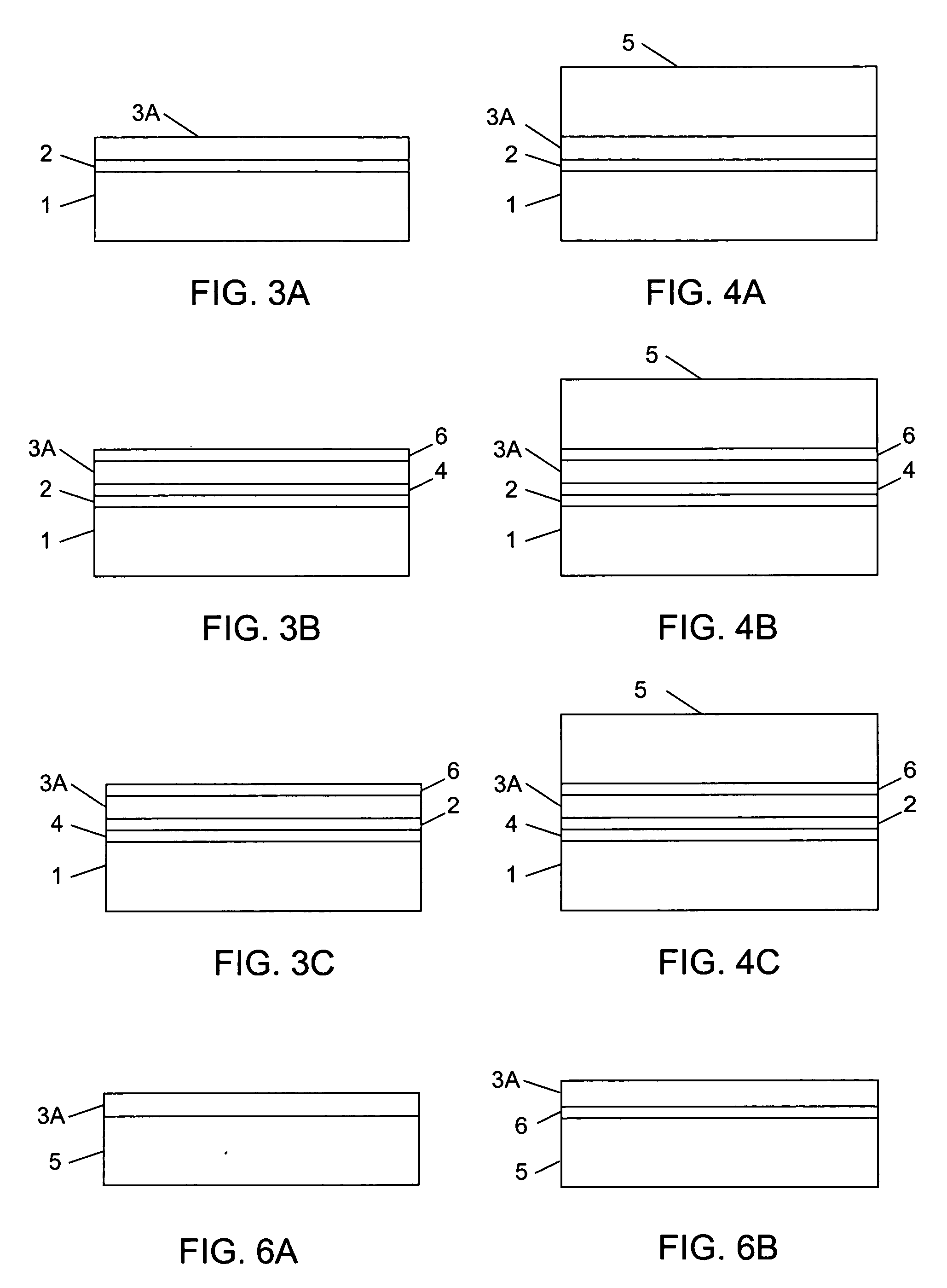
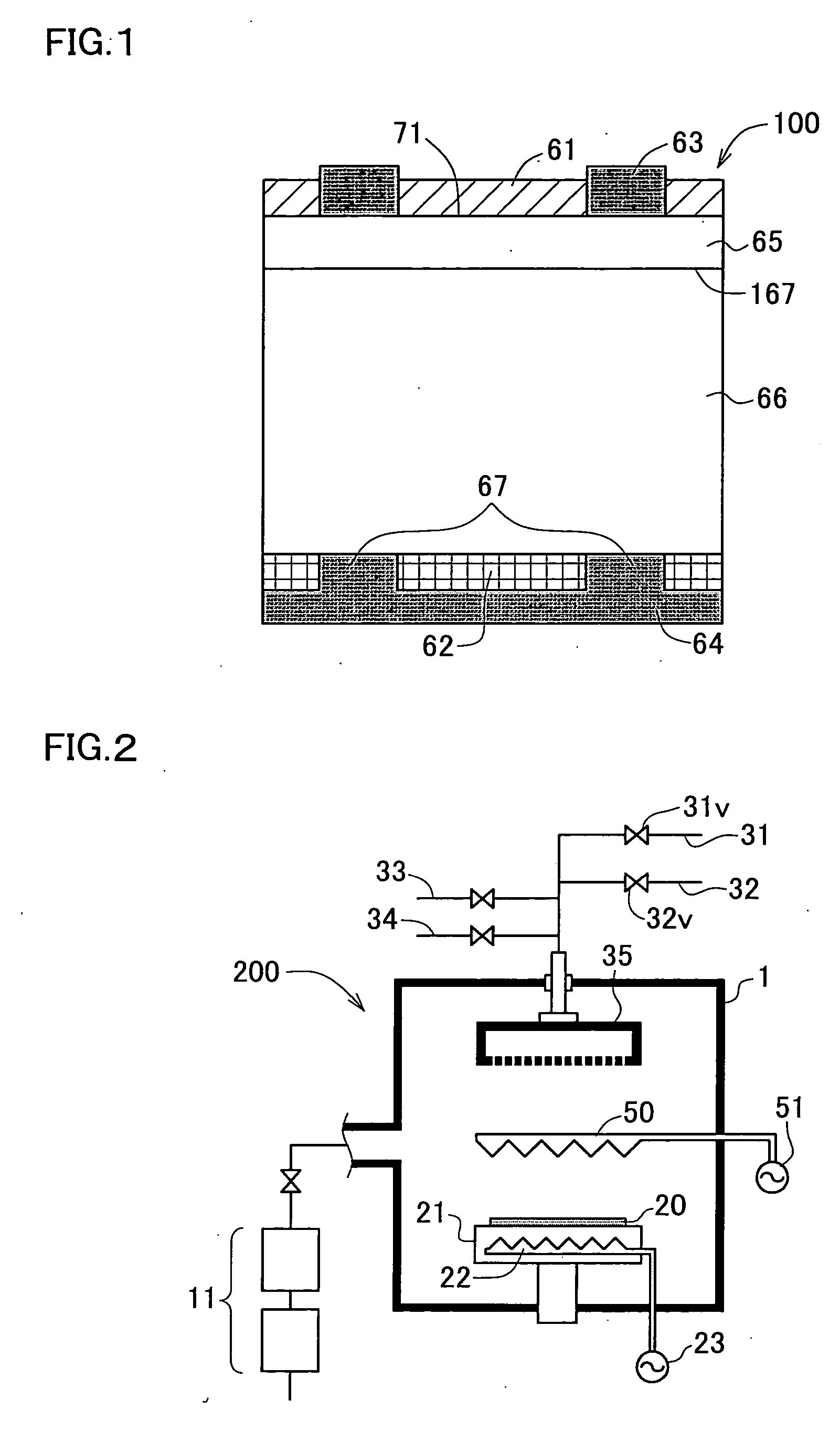
Barrier materials for display devices
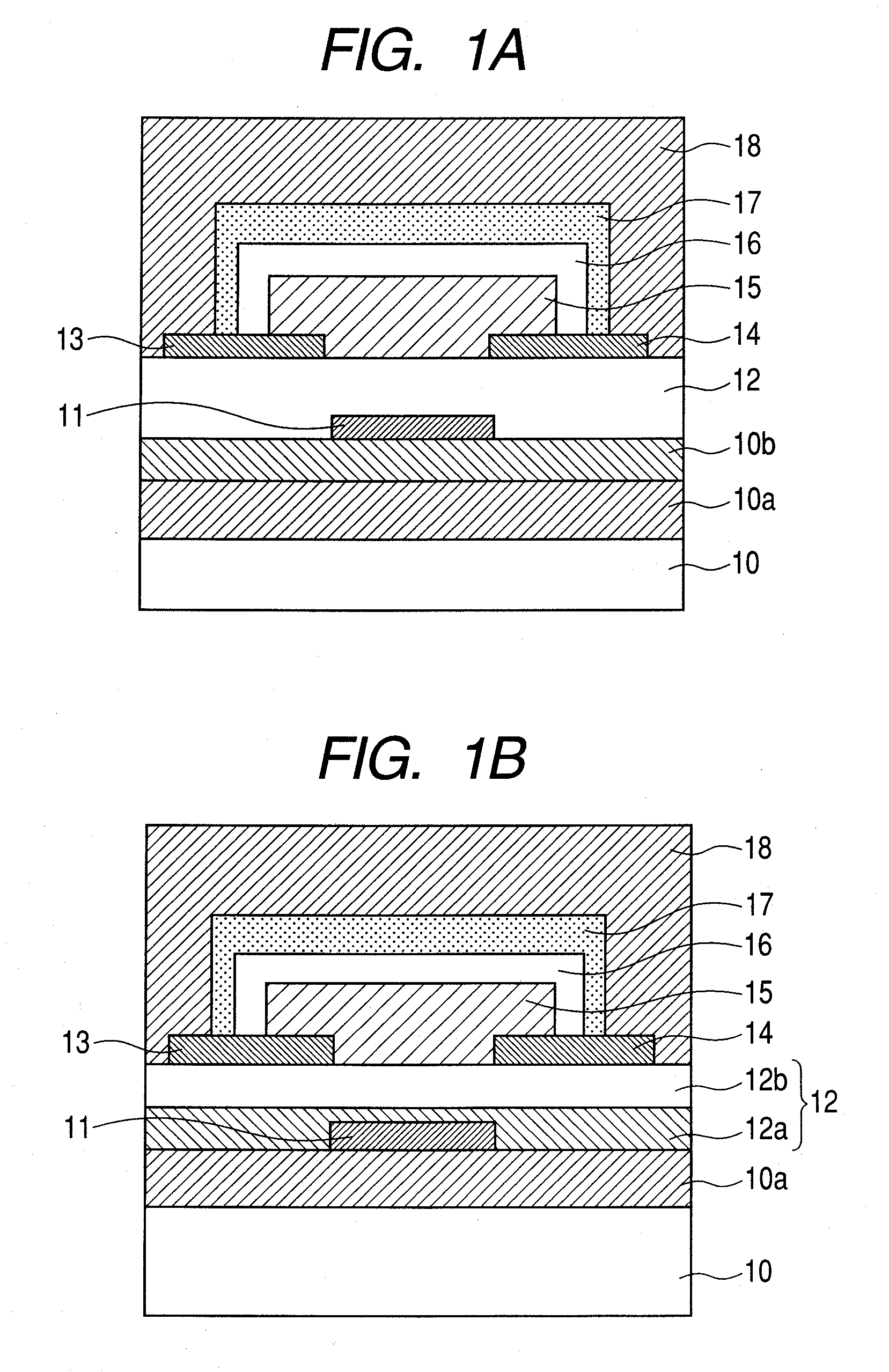
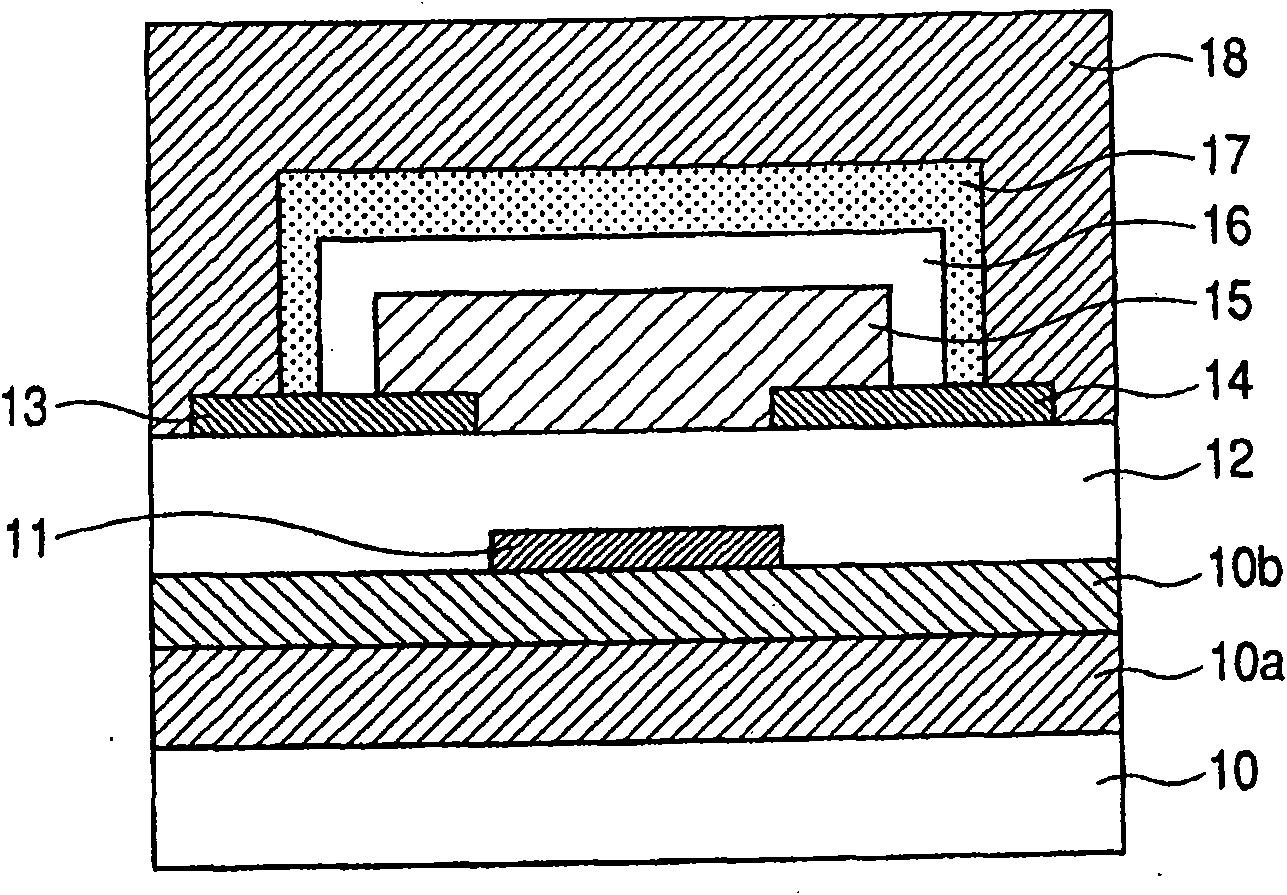
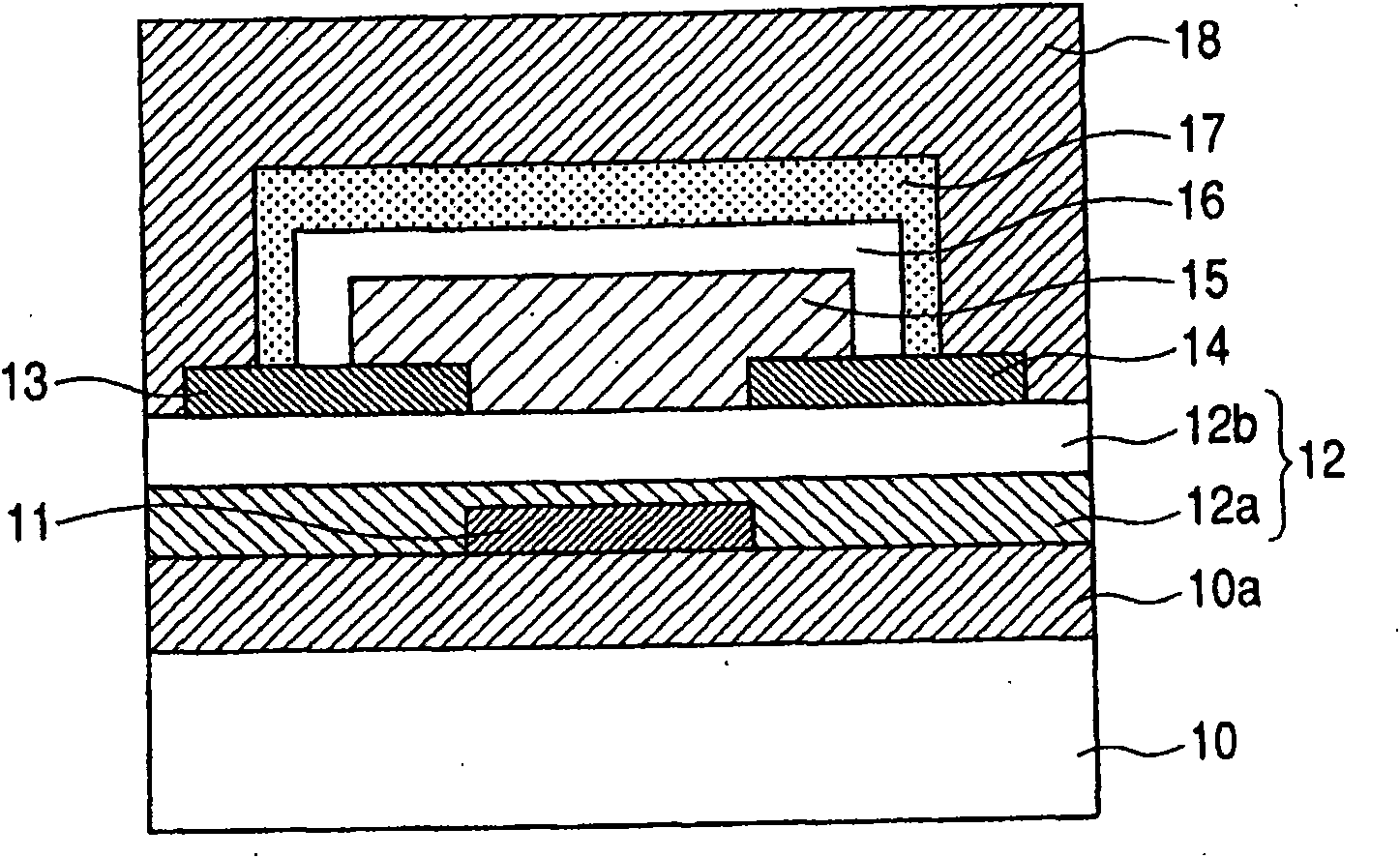
ActiveUS20150021599A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen contentDisplay device
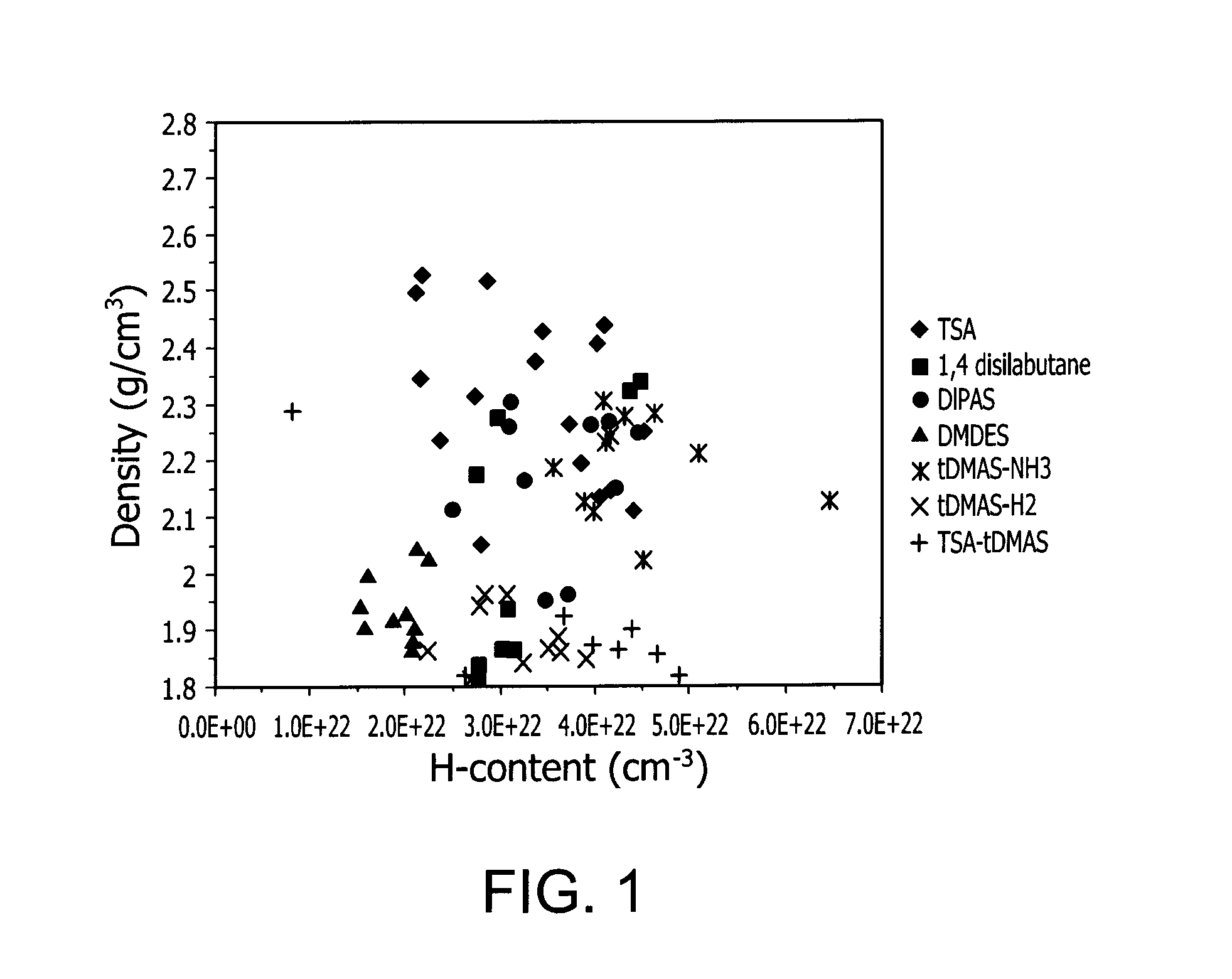
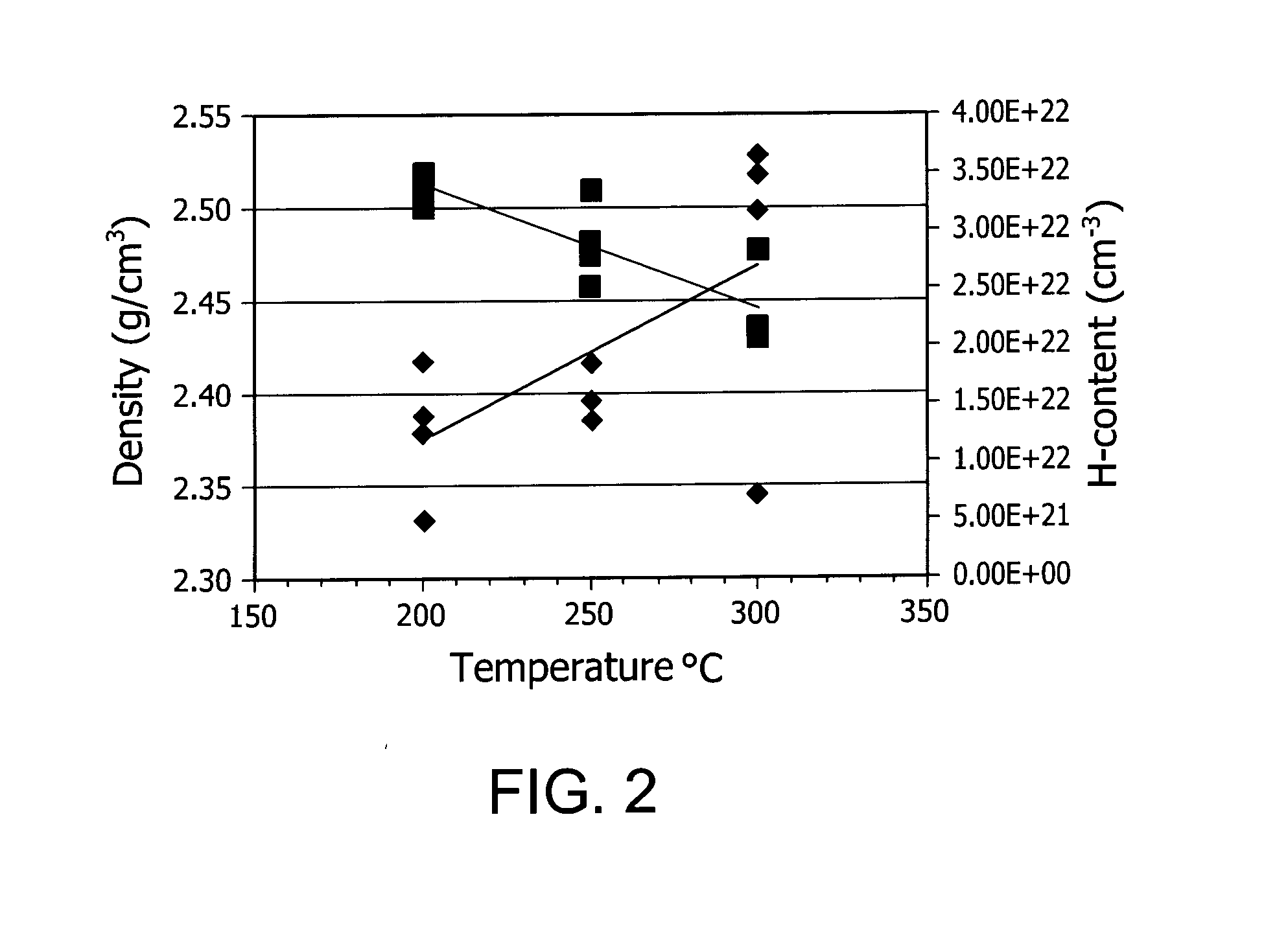
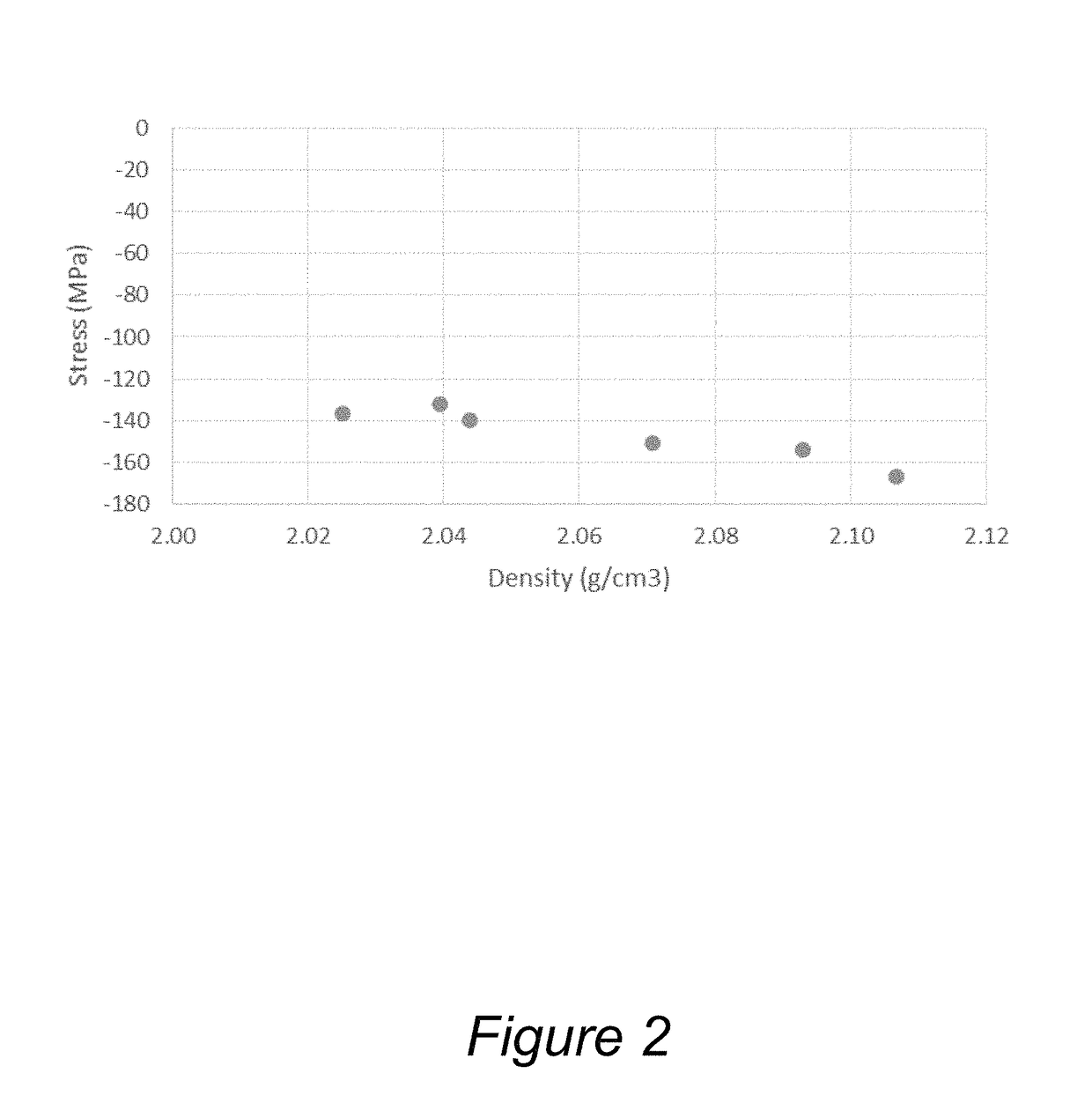
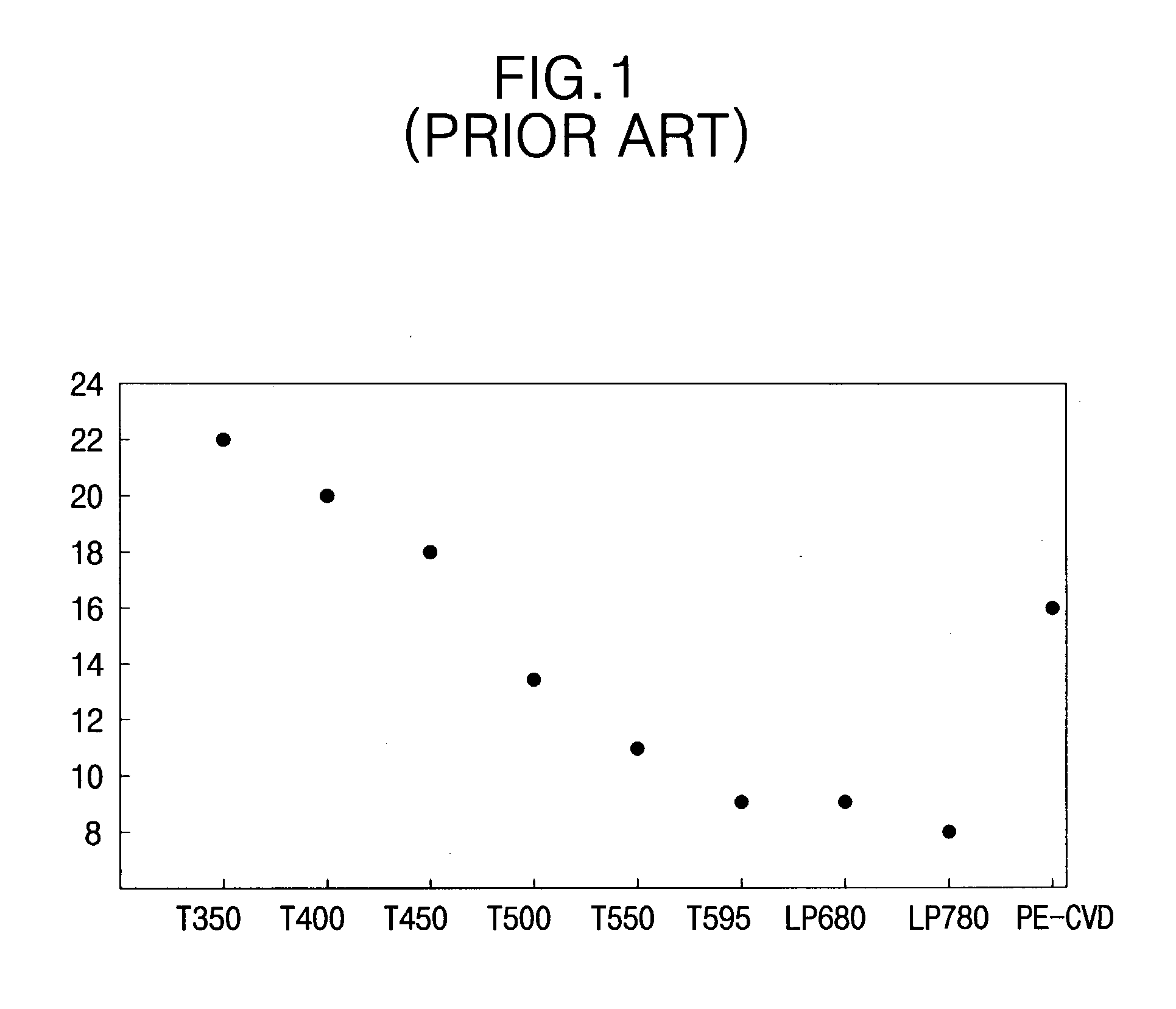
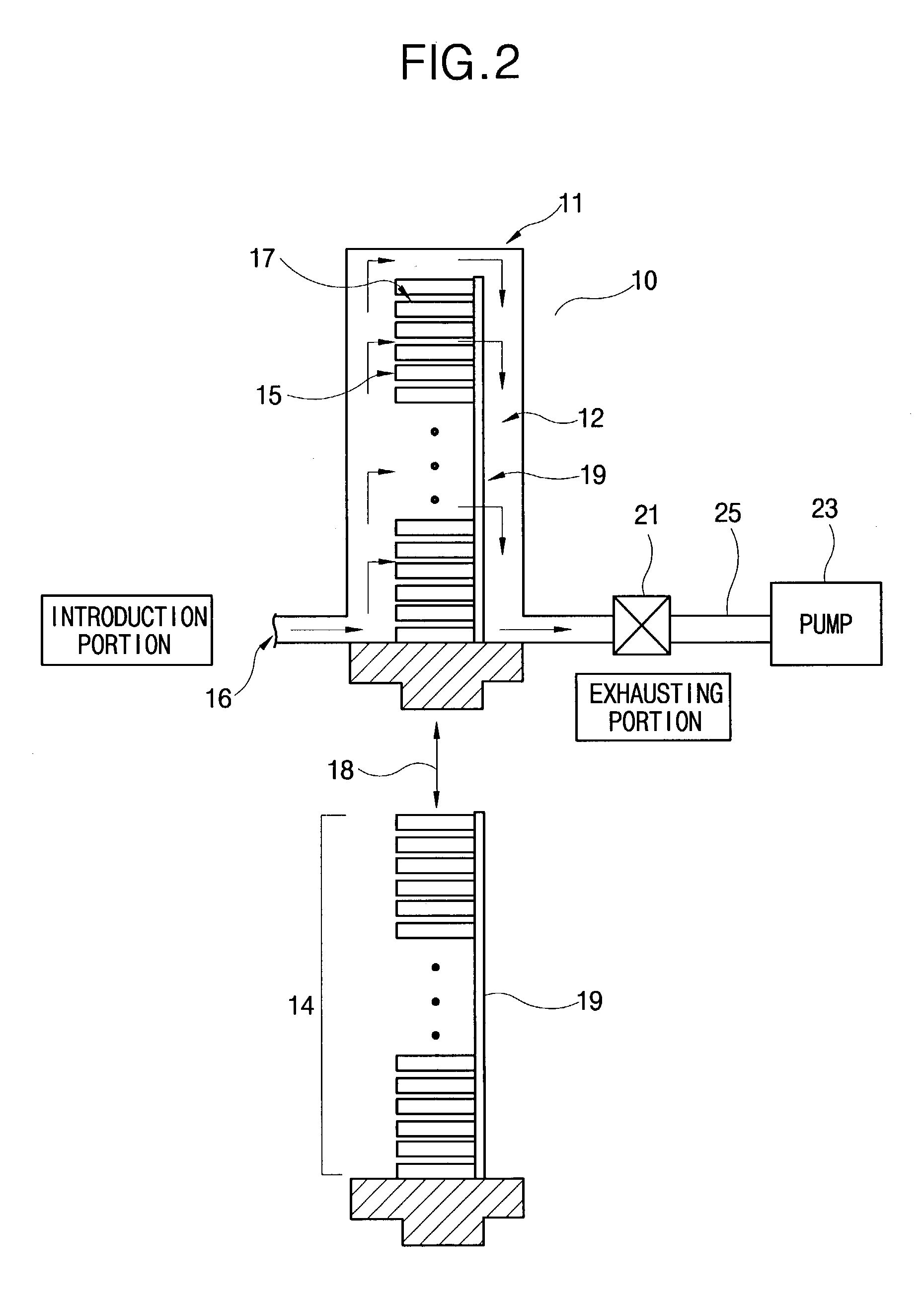
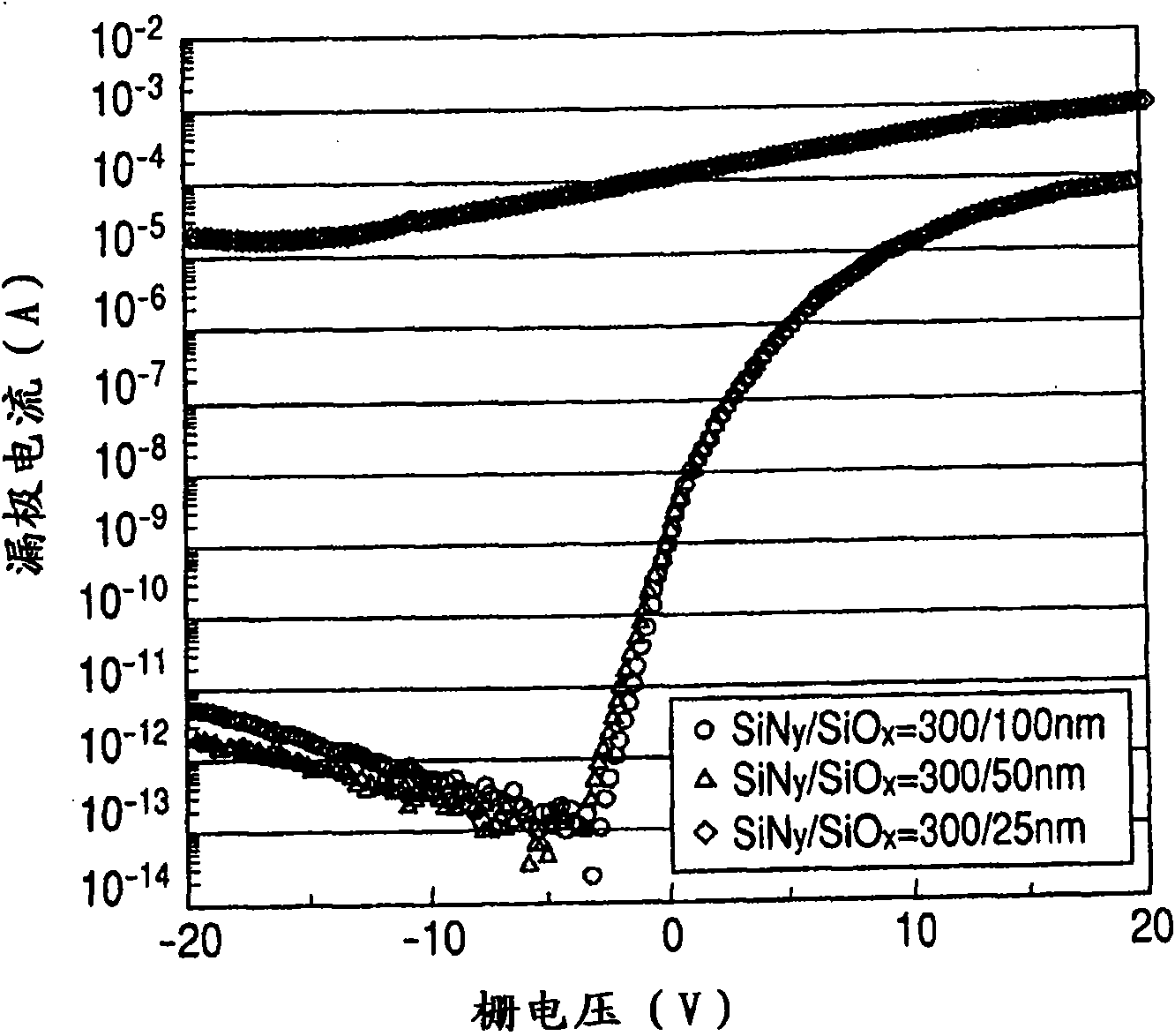
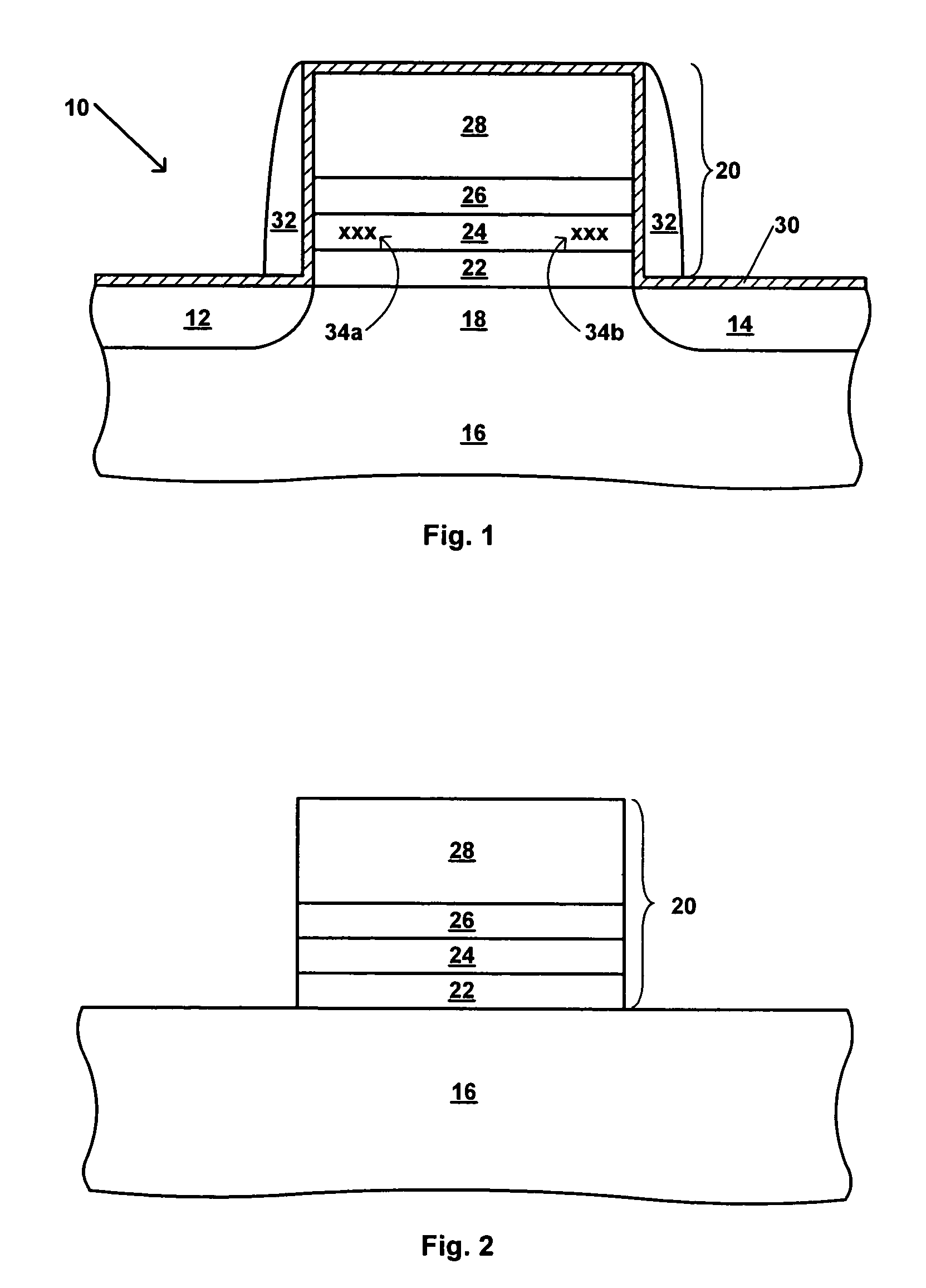
Described herein are apparatus comprising one or more silicon-containing layers and a metal oxide layer. Also described herein are methods for forming one or more silicon-containing layers to be used, for example, as passivation layers in a display device. In one particular aspect, the apparatus comprises a transparent metal oxide layer, a silicon oxide layer and a silicon nitride layer. In this or other aspects, the apparatus is deposited at a temperature of 350° C. or below. The silicon-containing layers described herein comprise one or more of the following properties: a density of about 1.9 g / cm3 or greater; a hydrogen content of about 4×1022 cm−3 or less, and a transparency of about 90% or greater at 400-700 nm as measured by a UV-visible light spectrometer.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
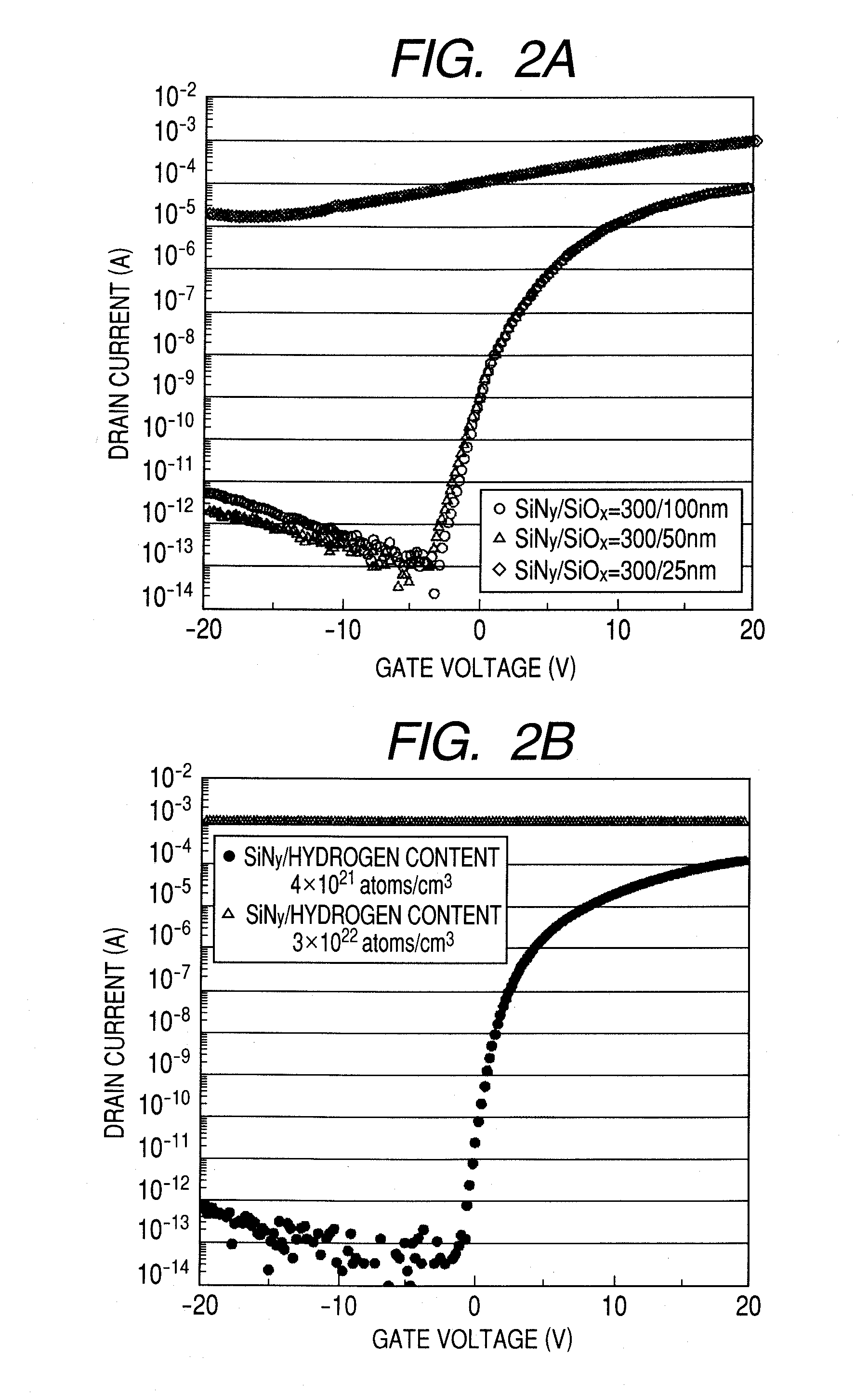
Oxide semiconductor device including insulating layer and display apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20100283049A1Lowering of the resistance of the semiconductor layerImprove productivityTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogen contentNitride
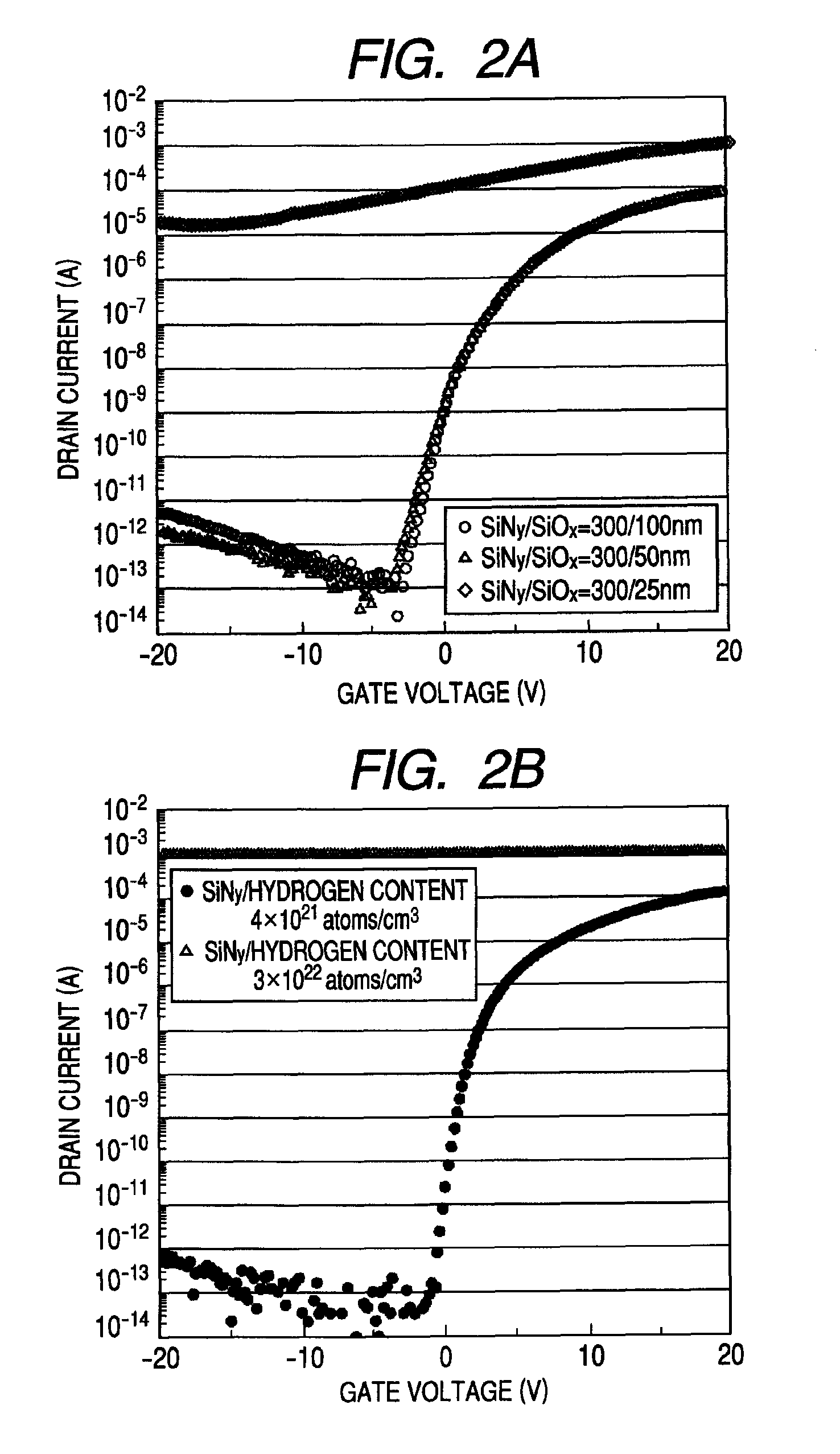
Provided is an oxide semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor layer and an insulating layer coming into contact with the oxide semiconductor layer in which the insulating layer includes: a first insulating layer coming into contact with an oxide semiconductor, having a thickness of 50 nm or more, and including an oxide containing Si and O; a second insulating layer coming into contact with the first insulating layer, having a thickness of 50 nm or more, and including a nitride containing Si and N; and a third insulating layer coming into contact with the second insulating layer, the first insulating layer and the second insulating layer having hydrogen contents of 4×1021 atoms / cm3 or less, and the third insulating layer having a hydrogen content of more than 4×1021 atoms / cm3.
Owner:CANON KK
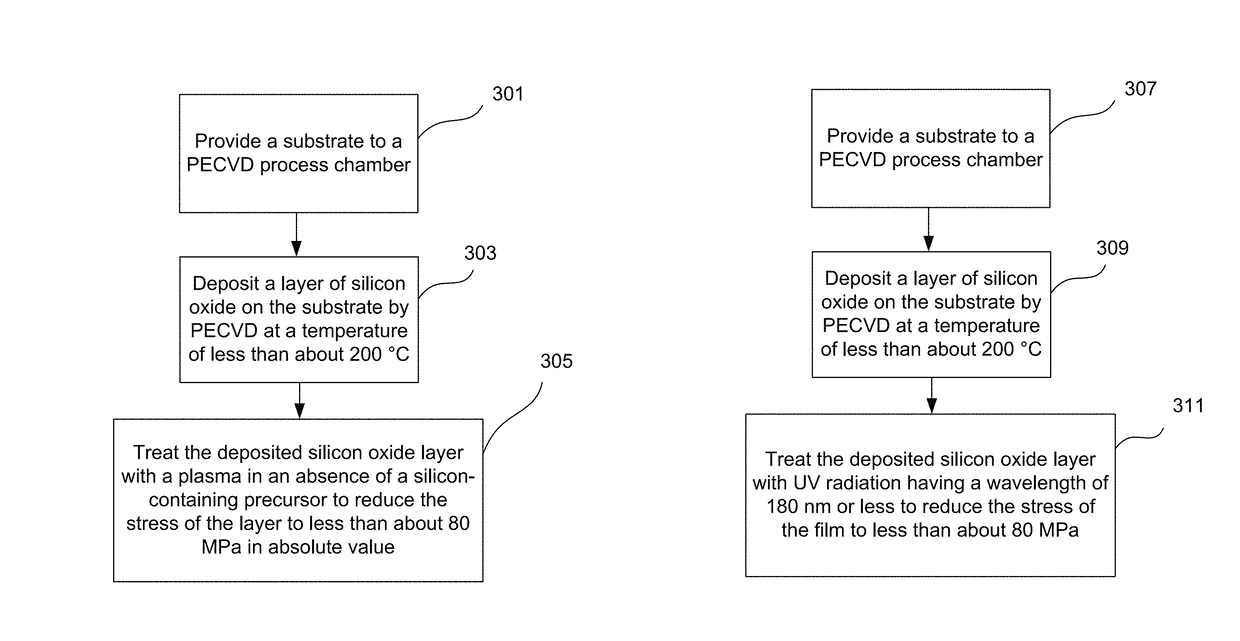
Low temperature formation of high quality silicon oxide films in semiconductor device manufacturing
ActiveUS9847221B1Relieve pressureReduce film stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricDevice material
Silicon oxide layer is deposited on a semiconductor substrate by PECVD at a temperature of less than about 200° C. and is treated with helium plasma to reduce stress of the deposited layer to an absolute value of less than about 80 MPa. Plasma treatment reduces hydrogen content in the silicon oxide layer, and leads to low stress films that can also have high density and low roughness. In some embodiments, the film is deposited on a semiconductor substrate that contains one or more temperature-sensitive layers, such as layers of organic material or spin-on dielectric that cannot withstand temperatures of greater than 250° C. In some embodiments the silicon oxide film is deposited to a thickness of between about 100-200 Å, and is used as a hardmask layer during etching of other layers on a semiconductor substrate.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Oxide semiconductor device including insulating layer and display apparatus using the same
ActiveUS8502217B2Lowering of the resistance of the semiconductor layerImprove productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHydrogen contentNitride
Owner:CANON KK
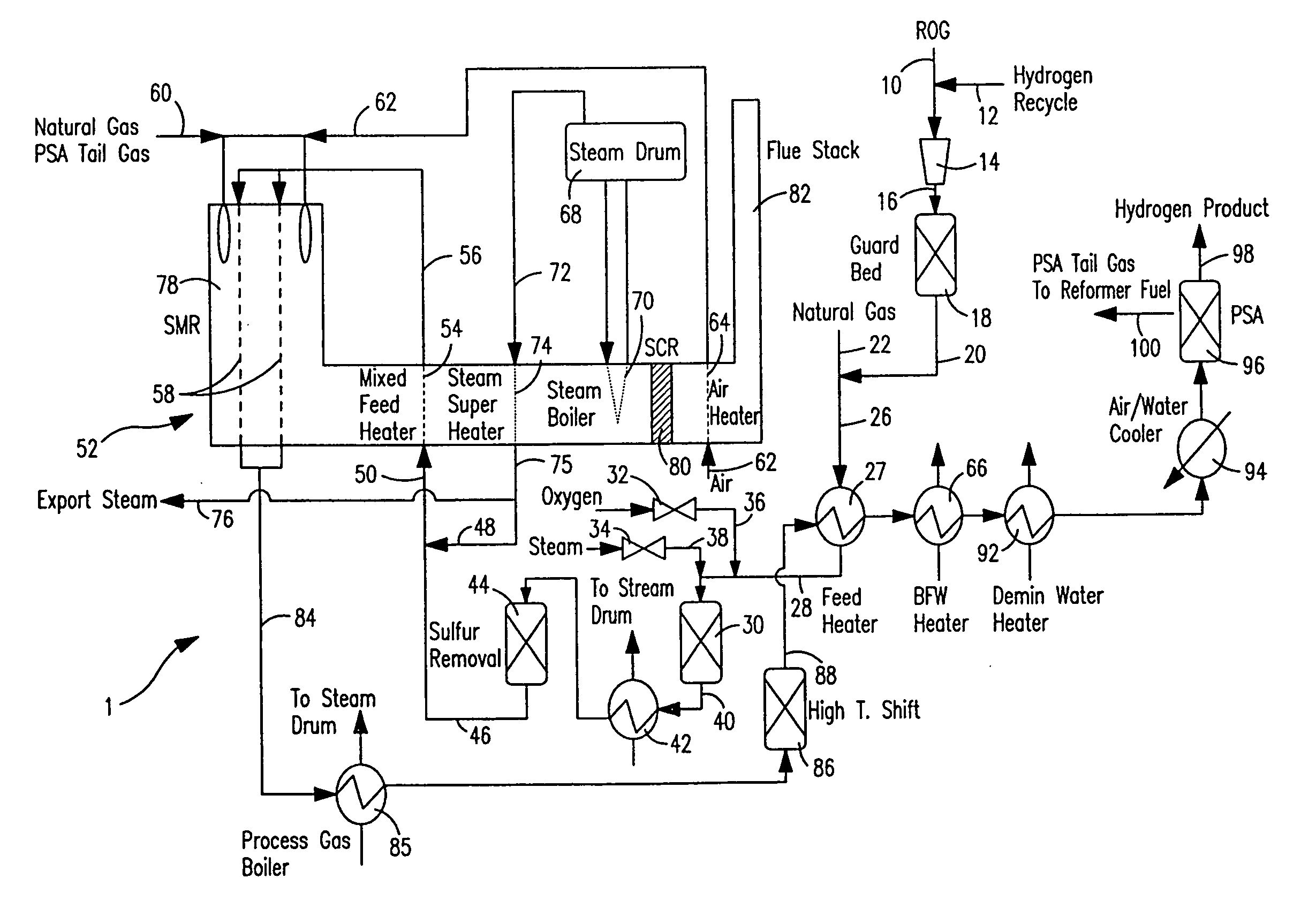
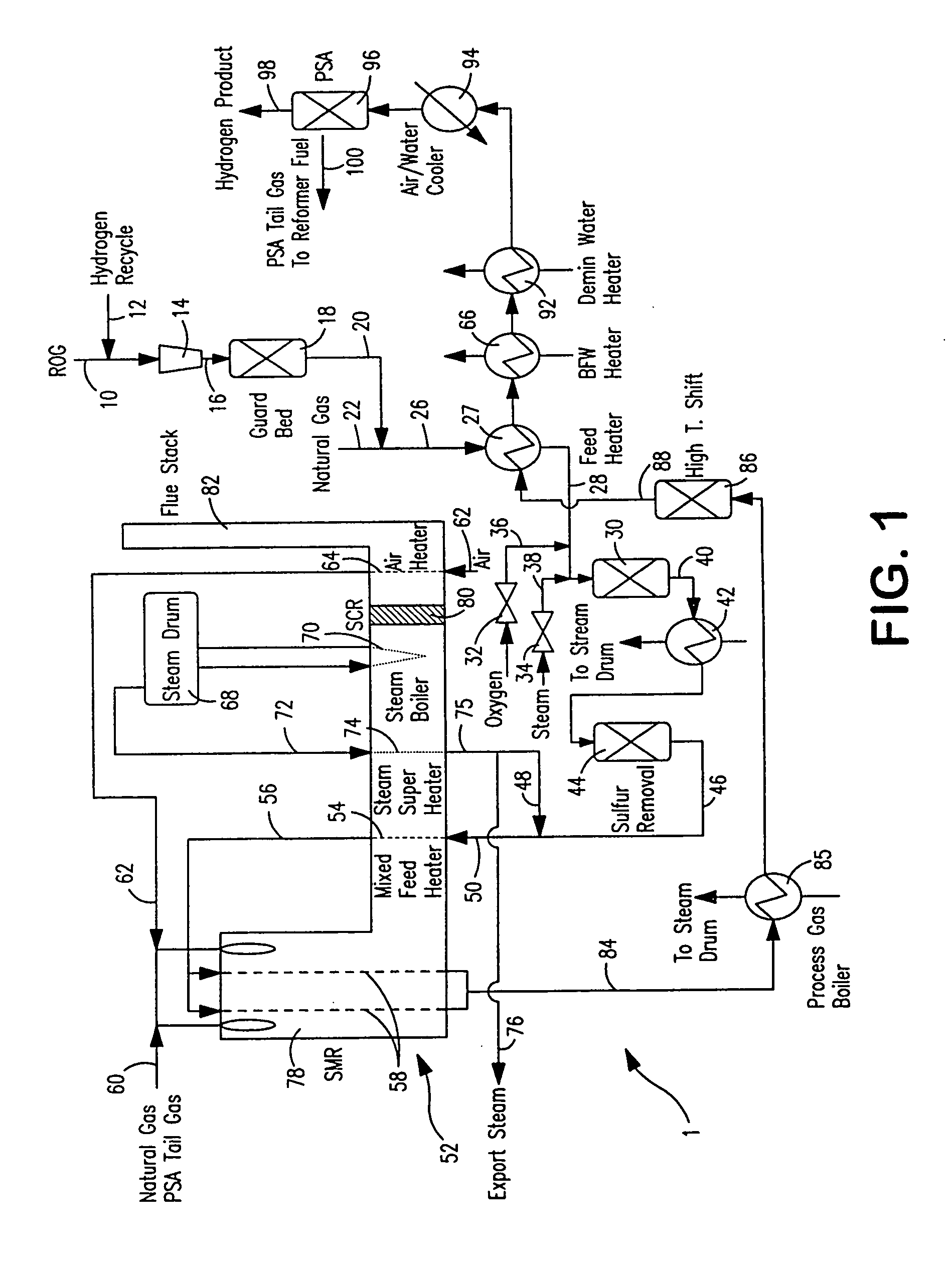
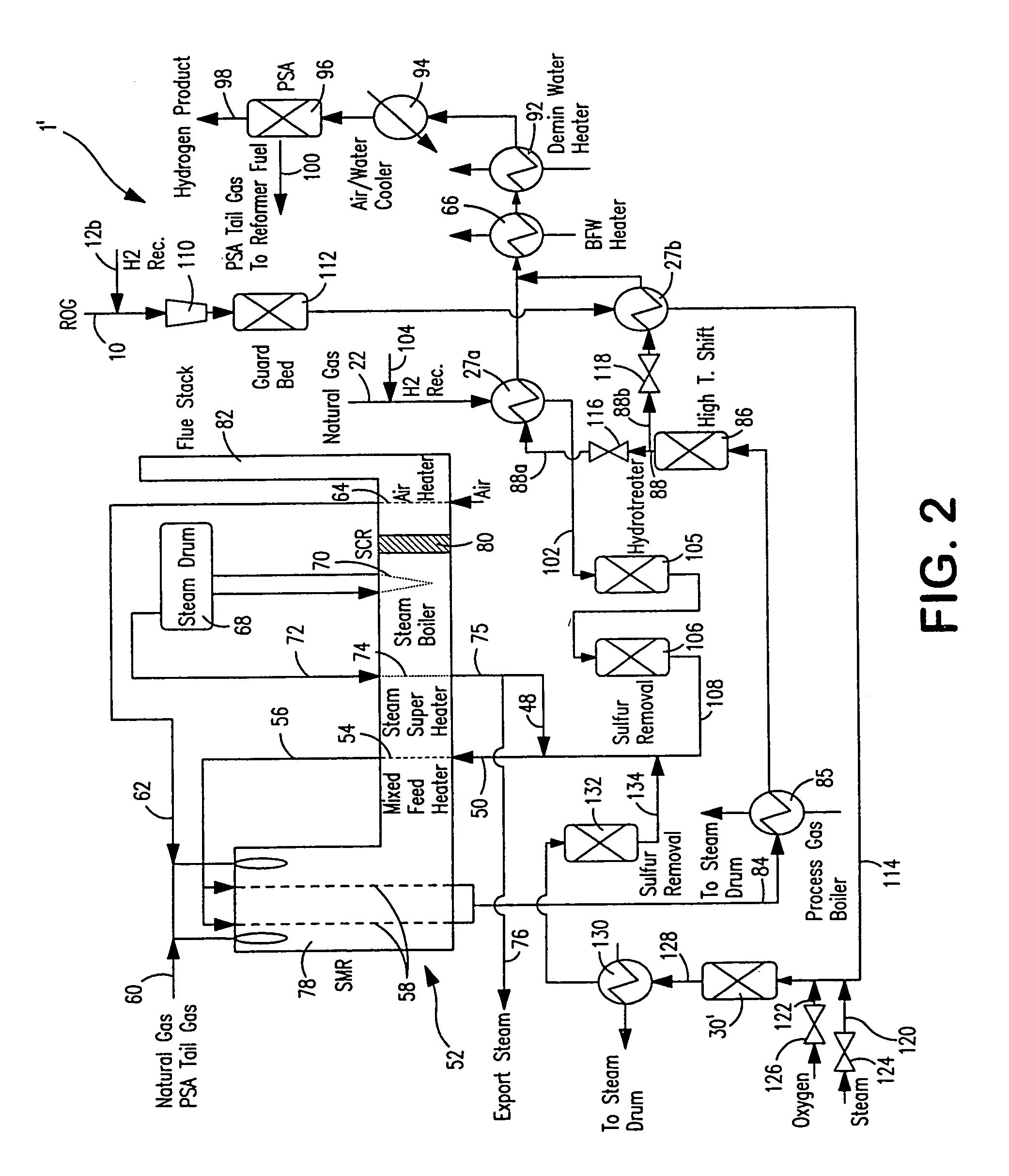
Steam methane reforming method
ActiveUS7037485B1Reduce fuel usageReduce firing rateHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesHydrogen separation using solid contactMethane reformerAlkane
A steam methane reforming method in which a feed stream is treated in a reactor containing a catalyst that is capable of promoting both hydrogenation and partial oxidation reactions. The reactor is either operated in a catalytic hydrogenation mode to convert olefins into saturated hydrocarbons and / or to chemically reduce sulfur species to hydrogen sulfide or a catalytic oxidative mode utilizing oxygen and steam to prereform the feed and thus, increase the hydrogen content of a synthesis gas produced by a steam methane reformer. The method is applicable to the treatment of feed streams containing at least 15% by volume of hydrocarbons with two or more carbon atoms and / or 3% by volume of olefins, such as a refinery off-gas. In such case, the catalytic oxidative mode is conducted with a steam to carbon ratio of less than 0.5, an oxygen to carbon ratio of less than 0.25 and a reaction temperature of between about 500° C. and about 860° C. to limit the feed to the steam methane reformer to volumetric dry concentrations of less than about 0.5% for the olefins and less than about 10% for alkanes with two or more carbon atoms.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
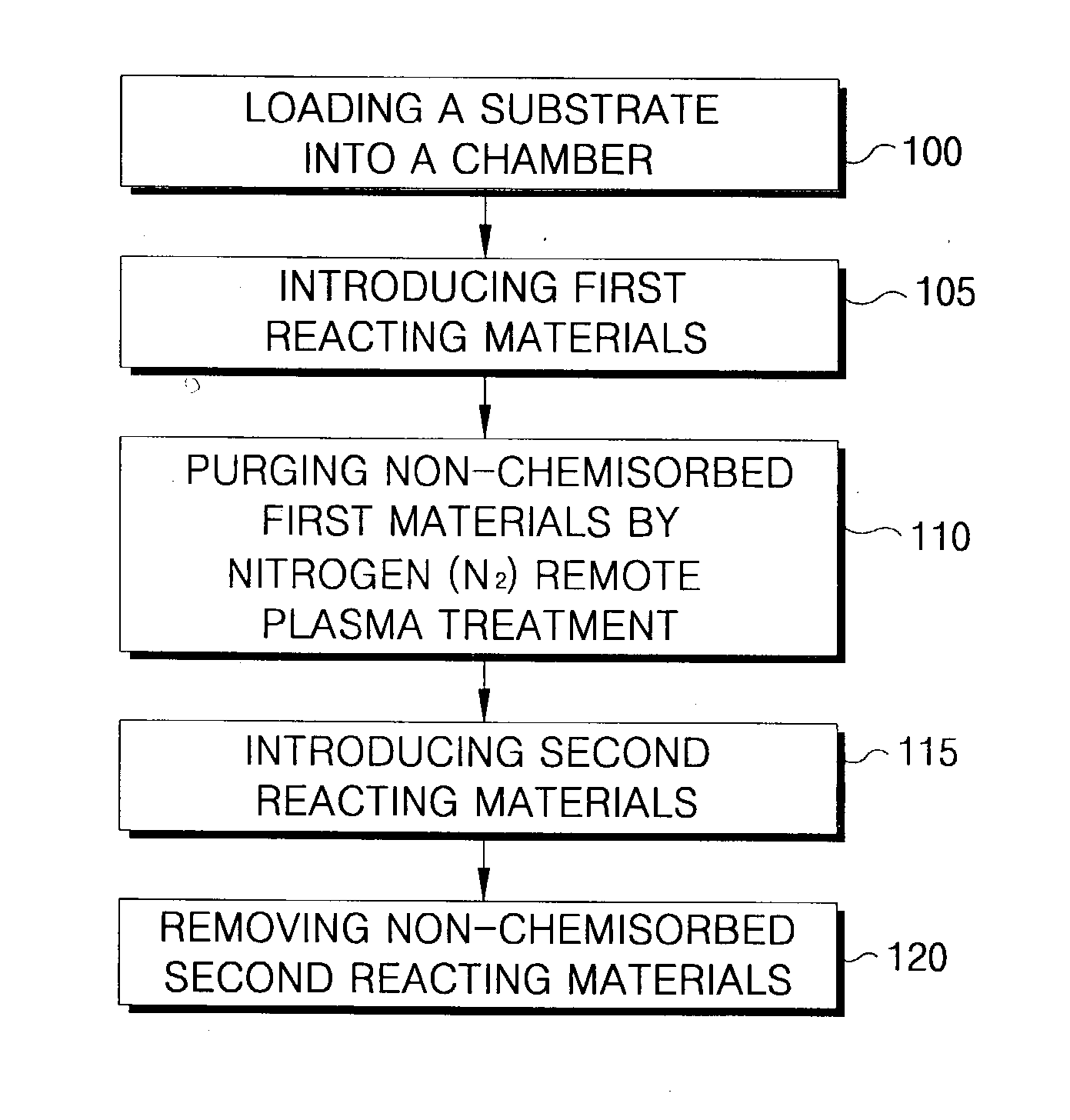
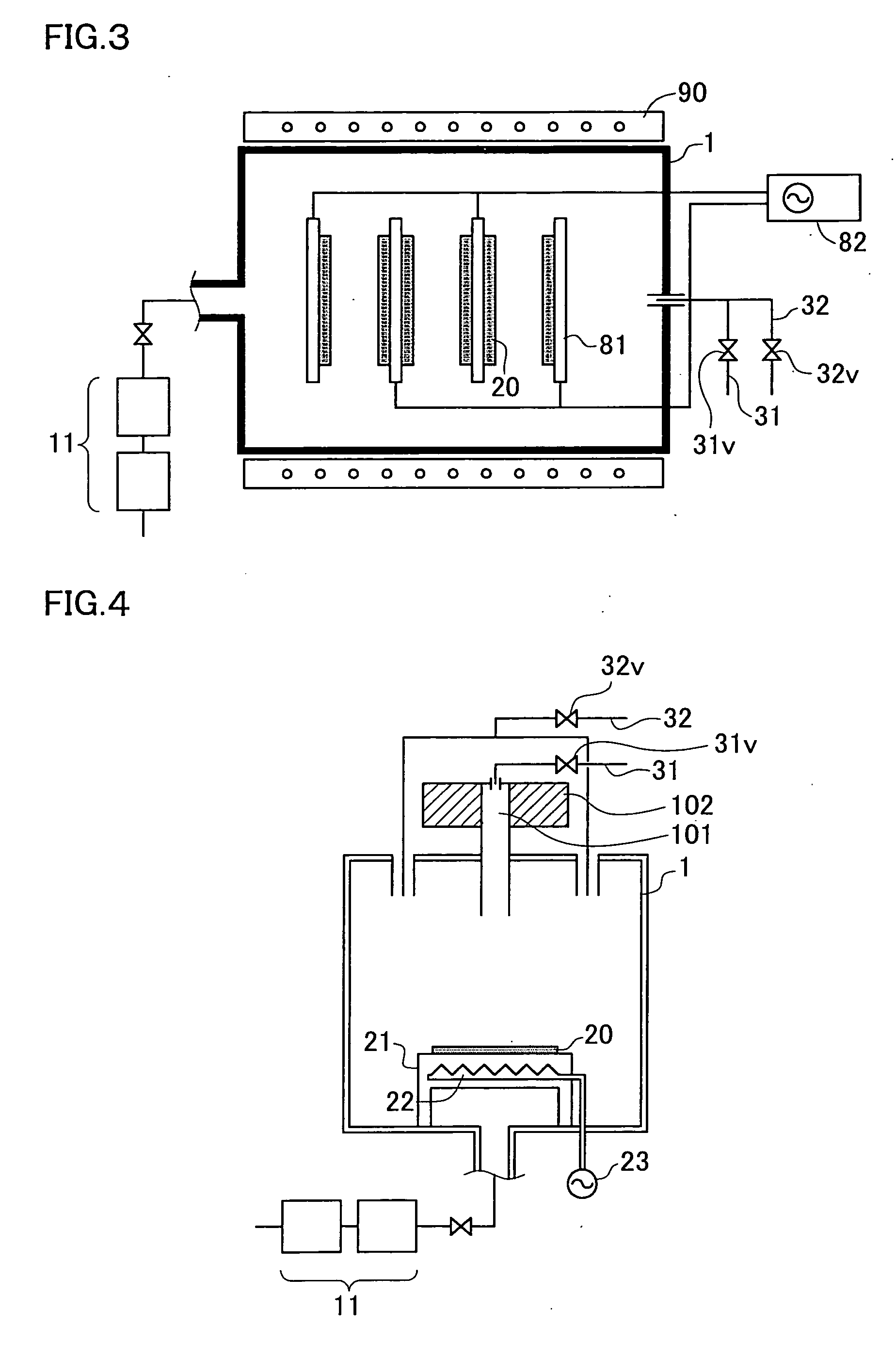
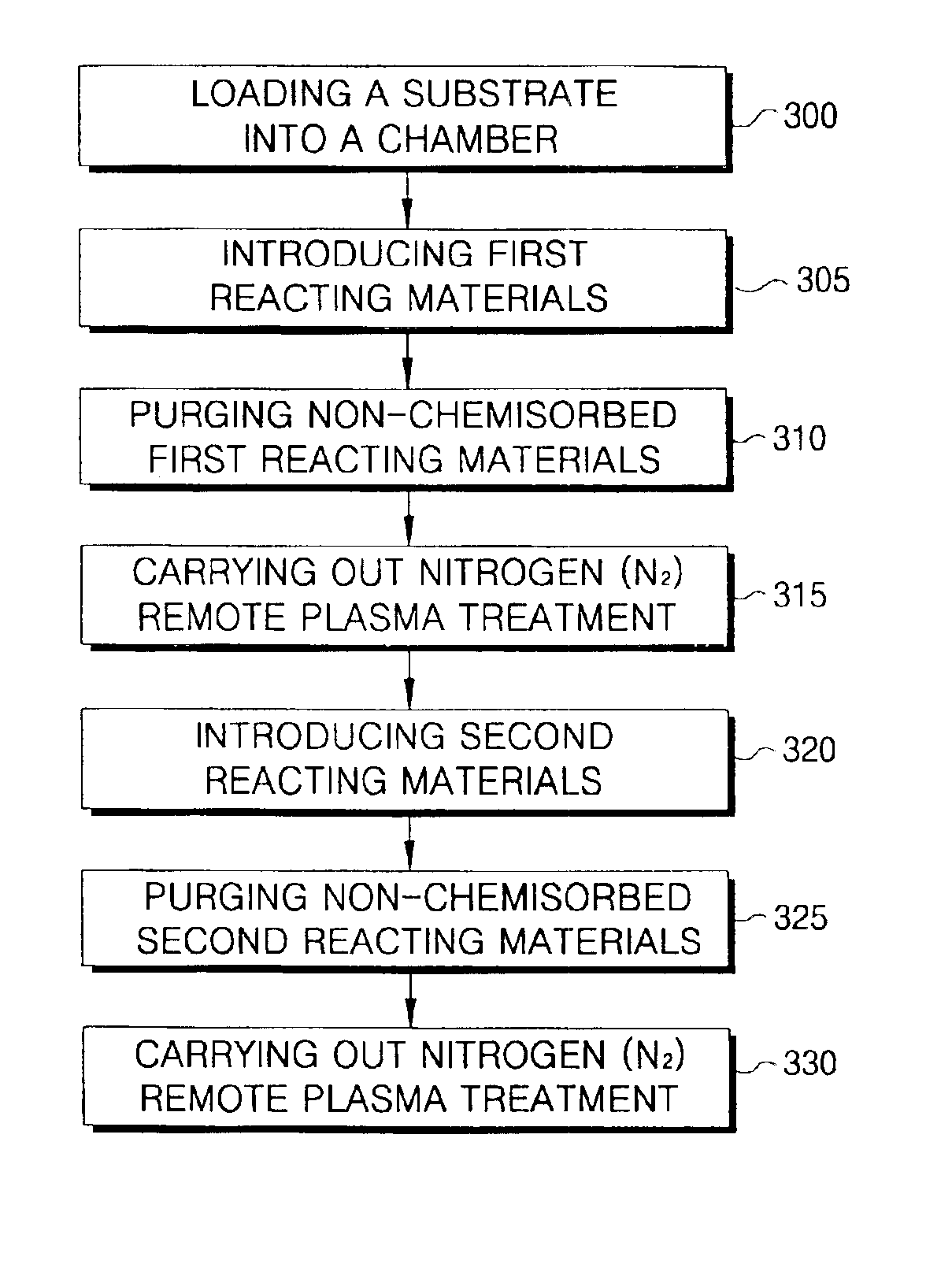
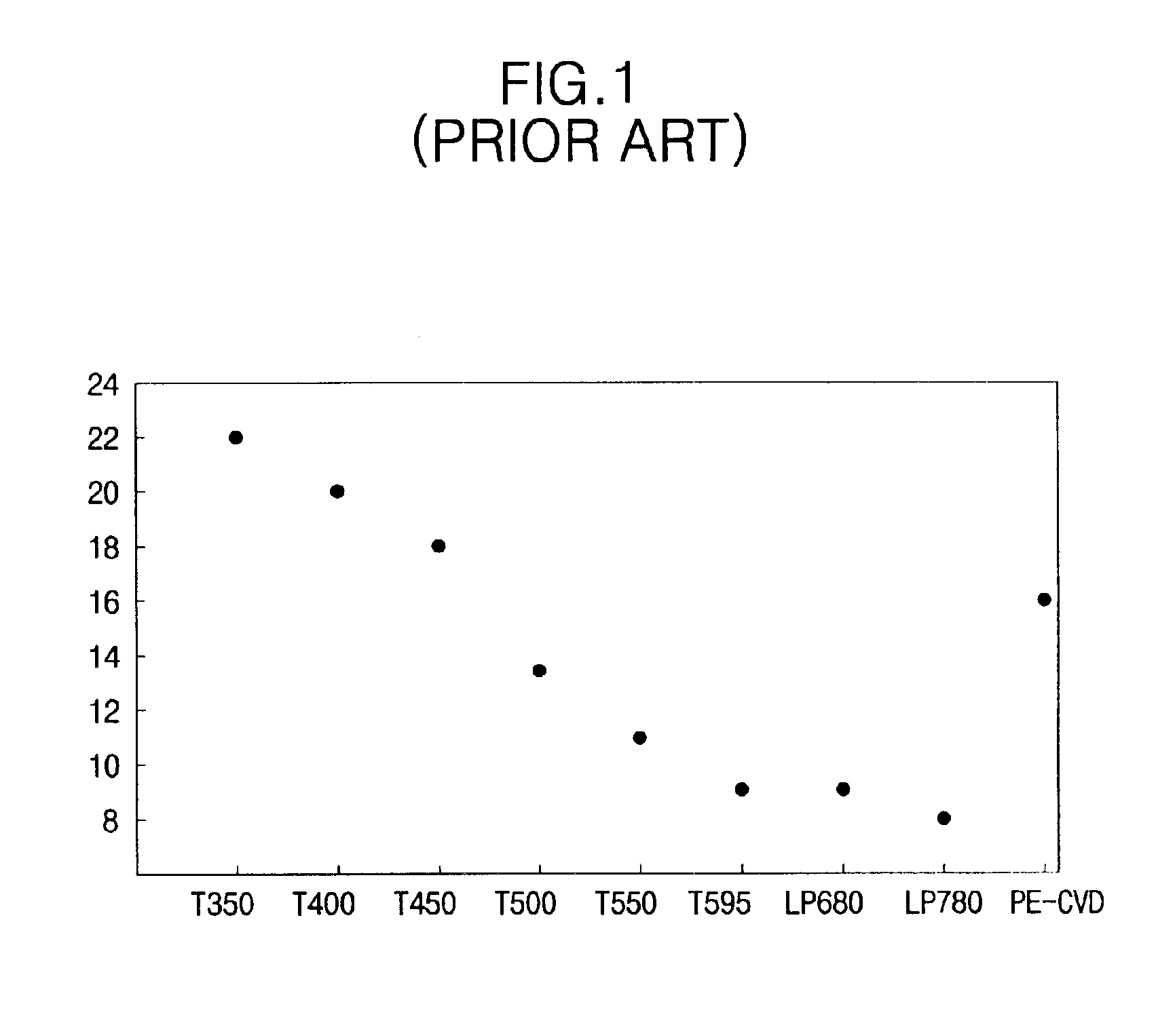
Method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen content on a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20030228770A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaDevice material
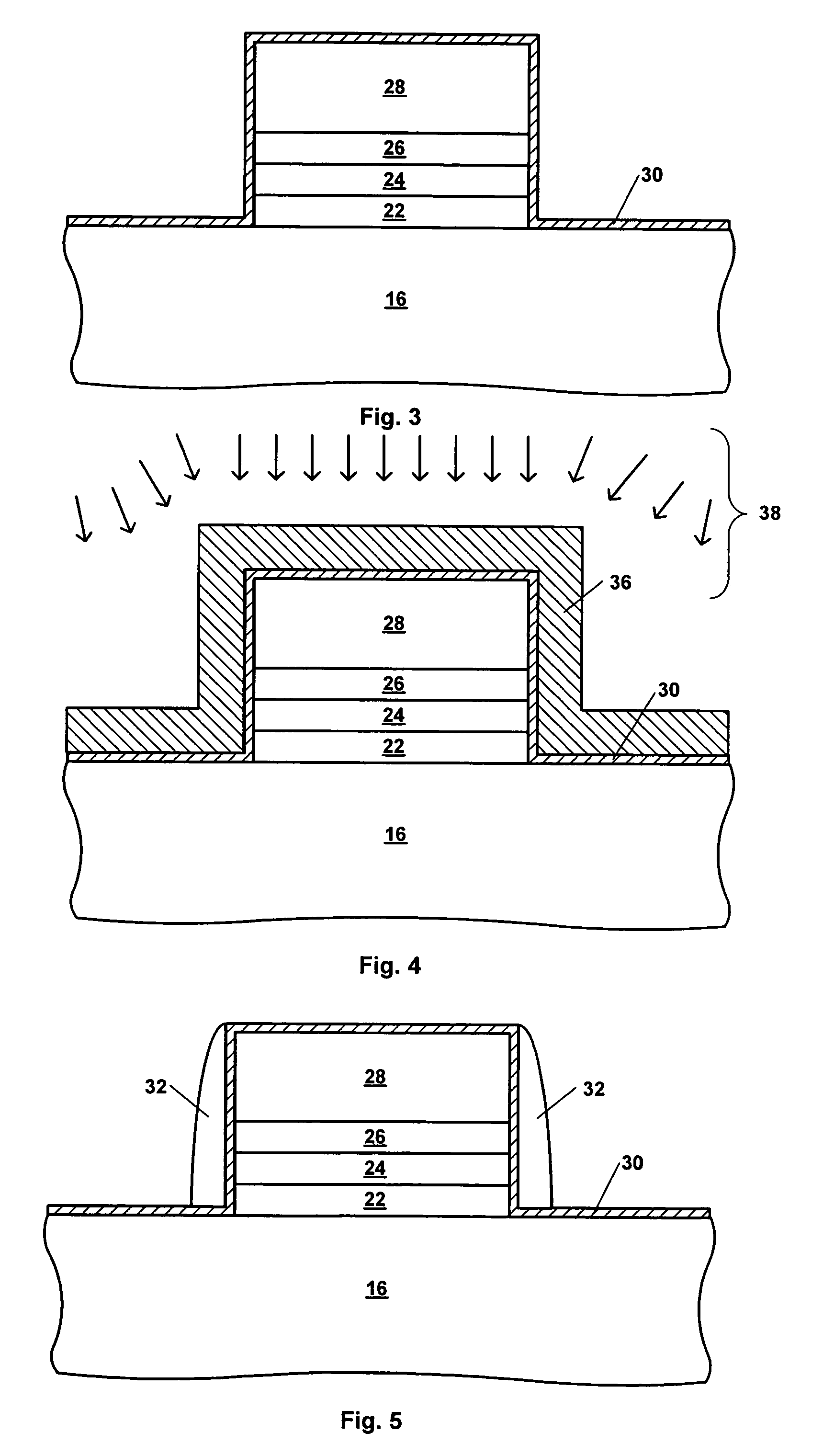
A method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen contents is provided by positioning a substrate inside a processing chamber, and supplying reacting materials into the chamber, chemisorbing a portion of the reacting materials onto the substrate. Then, a nitrogen (N2) remote plasma treatment is performed to reduce the hydrogen content of thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials on the substrate. Accordingly, a thin film is formed having a low hydrogen content, since the hydrogen bonds in the thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials are removed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of detachable direct bonding at low temperatures
ActiveUS20060264004A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconHydrogen content
A method for detachable bonding that forms an amorphous silicon layer, or a silicon oxide layer with a high hydrogen content, on an element such as a carrier substrate. A second element, such as a substrate, is bonded to the amorphous silicon layer or silicon oxide layer, and the second element may then have a portion removed. A third element, such as a host or carrier substrate, is bonded to the second element or to the remaining portion of the second element to form a bonded structure. The bonded structure is then heated to cause the first element to detach from the bonded structure.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
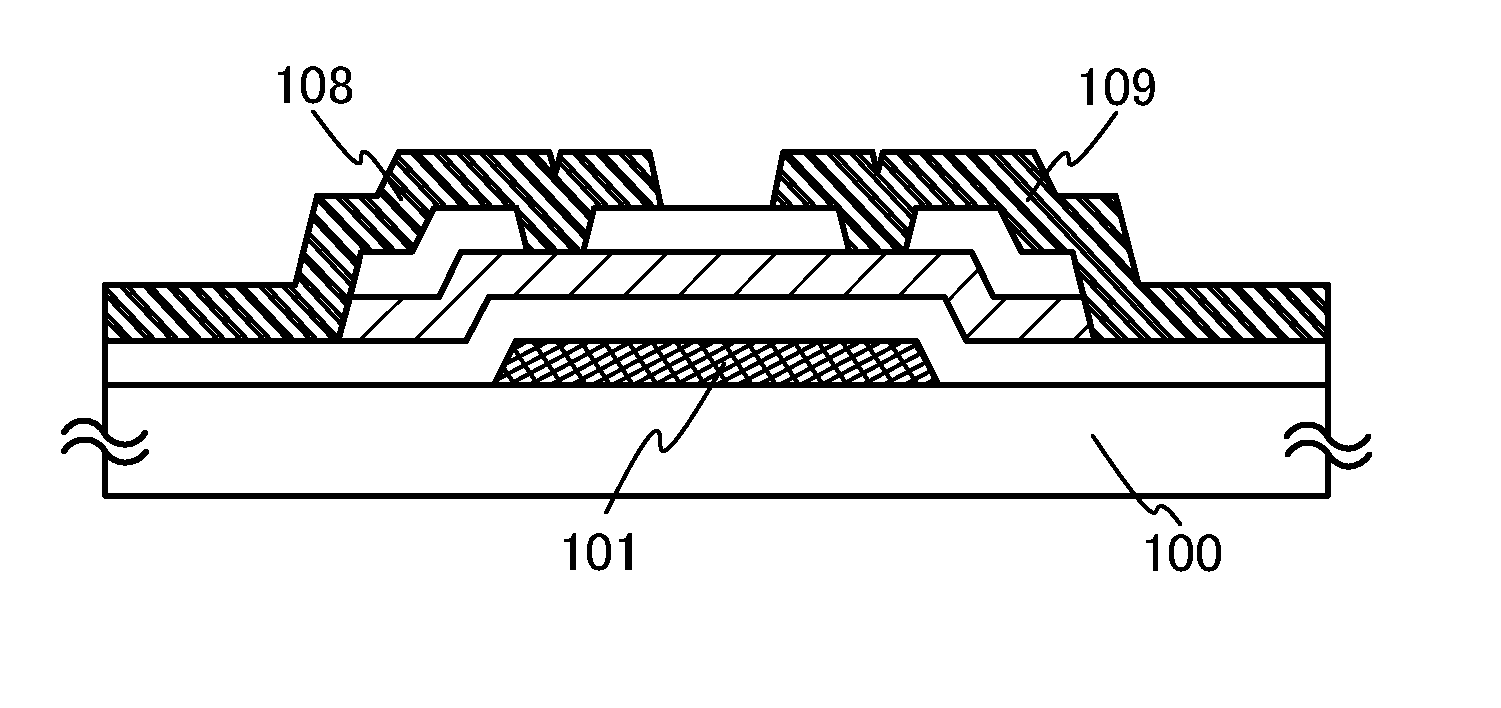
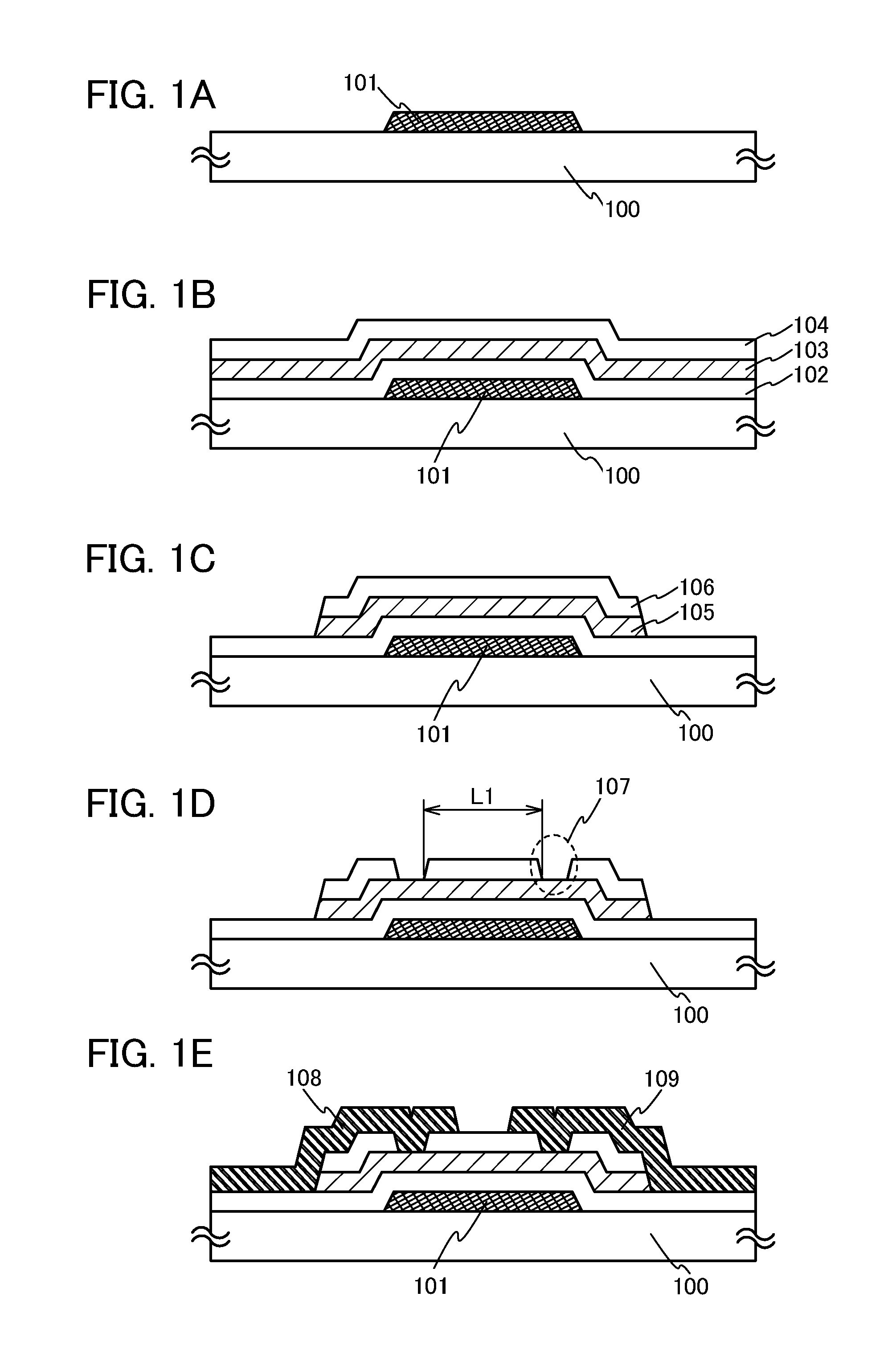
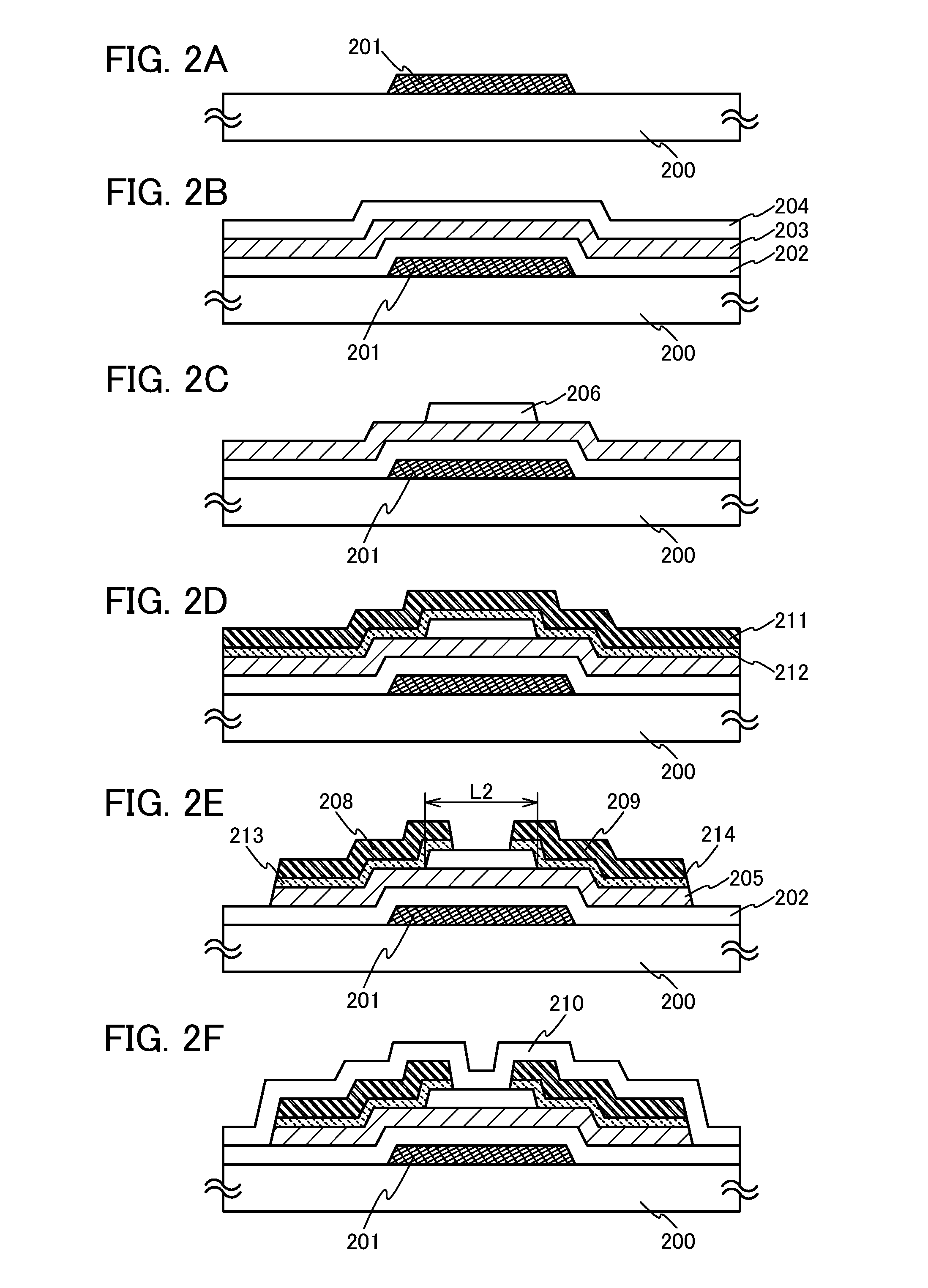
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
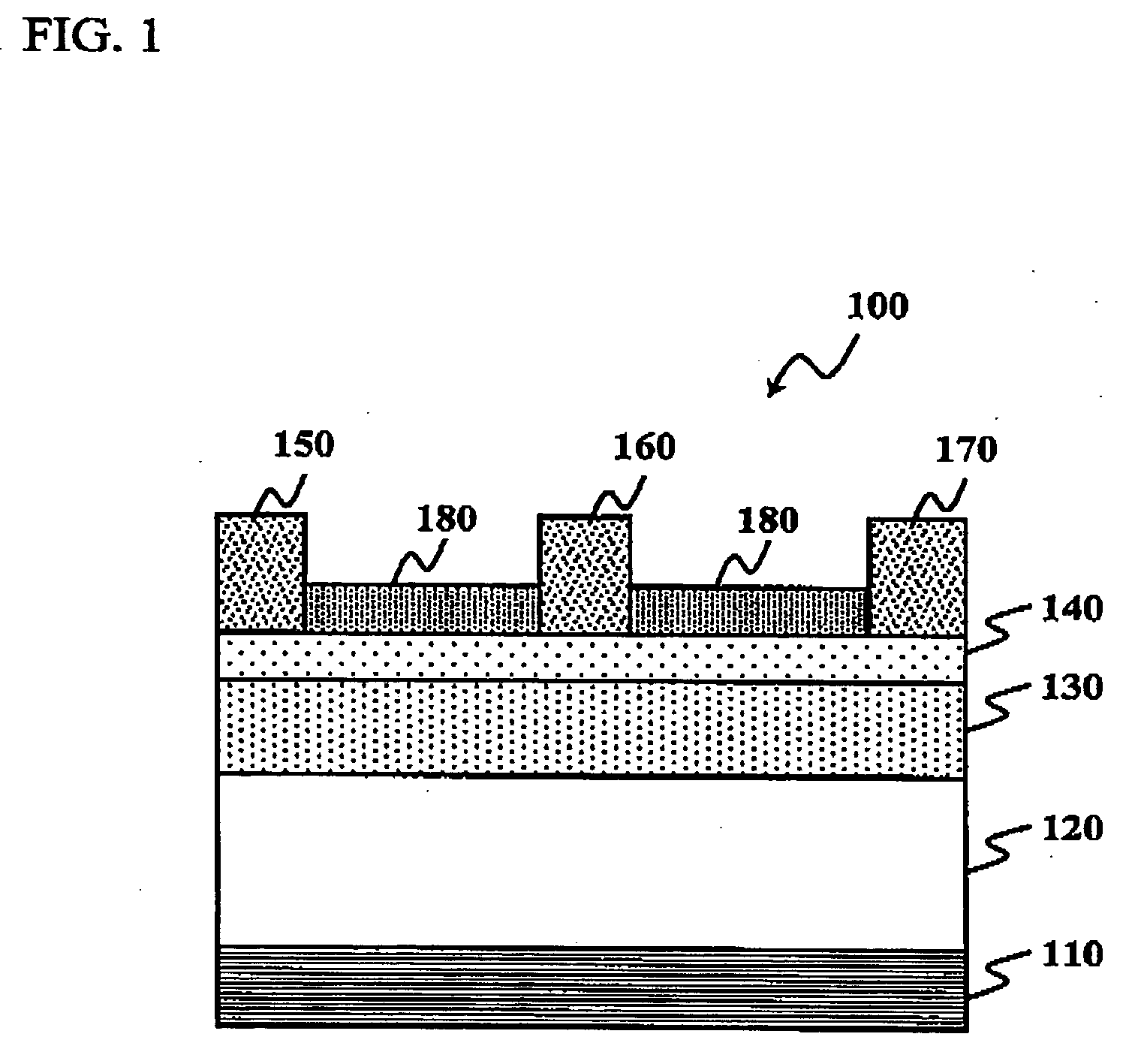
Homogeneity and stability of electric characteristics of a thin film transistor included in a circuit are critical for the performance of a display device including said circuit. An object of the invention is to provide an oxide semiconductor film with low hydrogen content and which is used in an inverted staggered thin film transistor having well defined electric characteristics. In order to achieve the object, a gate insulating film, an oxide semiconductor layer, and a channel protective film are successively formed with a sputtering method without being exposed to air. The oxide semiconductor layer is formed so as to limit hydrogen contamination, in an atmosphere including a proportion of oxygen. In addition, layers provided over and under a channel formation region of the oxide semiconductor layer are formed using compounds of silicon, oxygen and / or nitrogen.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device using a polymer film pattern
InactiveUS6465290B1Good pn junction characteristicImprove featuresTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen contentPolymer thin films
Claimed and disclosed is a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, the method comprising the steps of forming a dummy gate on a semiconductor substrate, forming a source-drain diffusion region by introducing an impurity into the semiconductor substrate having the dummy gate as a mask, removing the dummy gate to form an opening, and forming a gate electrode within the opening with a gate insulating film formed below the gate electrode. The dummy gate is further formed by coating the semiconductor substrate with a polymer having a higher carbon content than hydrogen content so as to form a polymer film, forming a photoresist pattern on the polymer film, and transferring the pattern shape of the photoresist pattern onto the polymer film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Solar cell and method of fabricating the same
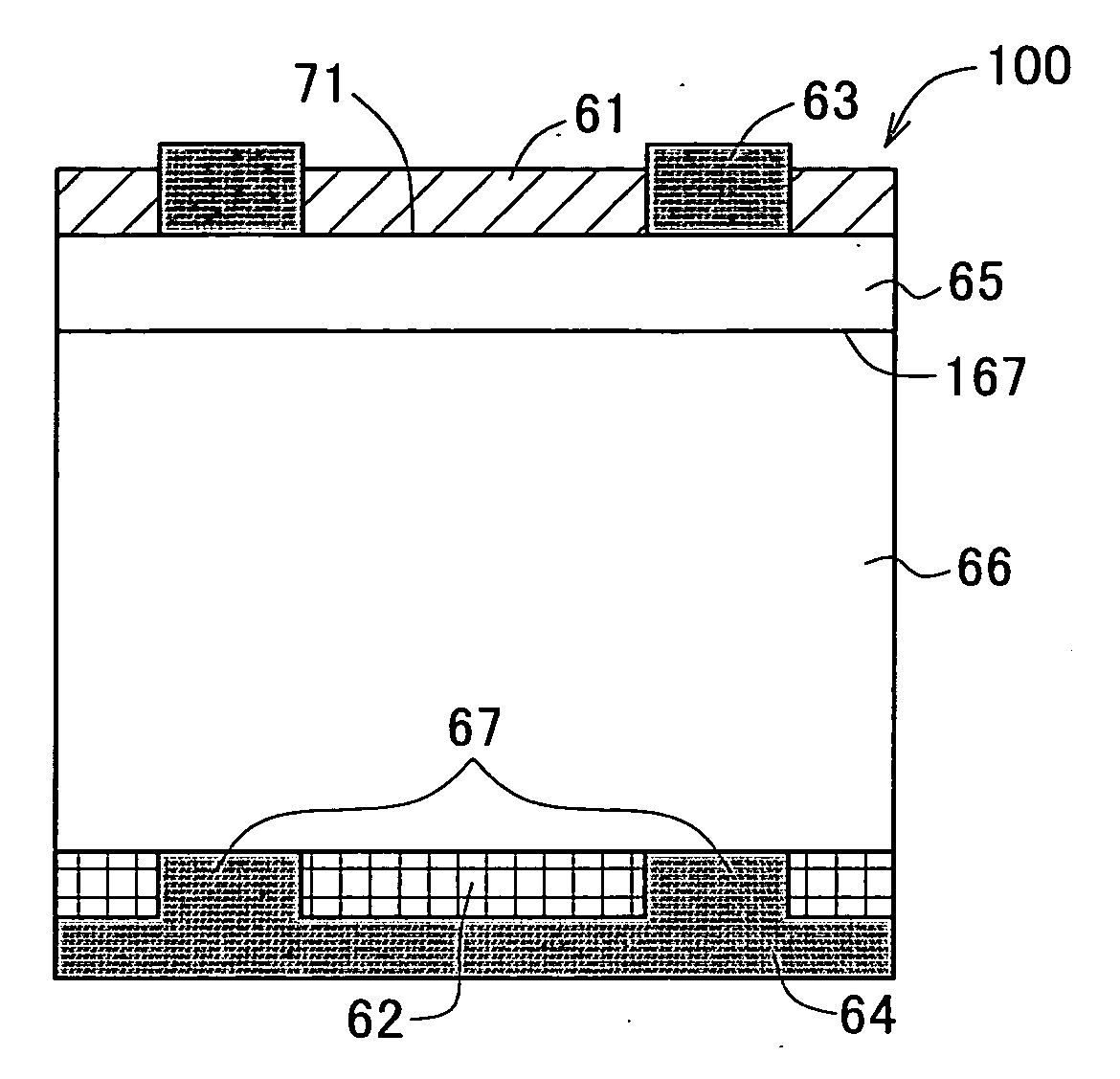
InactiveUS20070186970A1Temperature of substrate is reducedPromote passivationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen contentSolar cell
A solar cell (100) comprising a semiconductor solar cell substrate (66) having a light receiving surface formed on the first major surface and generating photovoltaic power based on the light impinging on the light receiving surface, wherein the light receiving surface of the semiconductor solar cell substrate (66) is coated with a light receiving surface side insulating film (61) composed of an inorganic insulating material where the cationic component principally comprising silicon, and the light receiving surface side insulating film (61) is a low hydrogen content inorganic insulating film containing less than 10 atm % of hydrogen. A solar cell having an insulating film exhibiting excellent passivation effect insusceptible to aging can thereby be provided.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen content on a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6933245B2Reduce hydrogen contentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaChemisorption
A method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen contents is provided by positioning a substrate inside a processing chamber, and supplying reacting materials into the chamber, chemisorbing a portion of the reacting materials onto the substrate. Then, a nitrogen (N2) remote plasma treatment is performed to reduce the hydrogen content of thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials on the substrate. Accordingly, a thin film is formed having a low hydrogen content, since the hydrogen bonds in the thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials are removed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
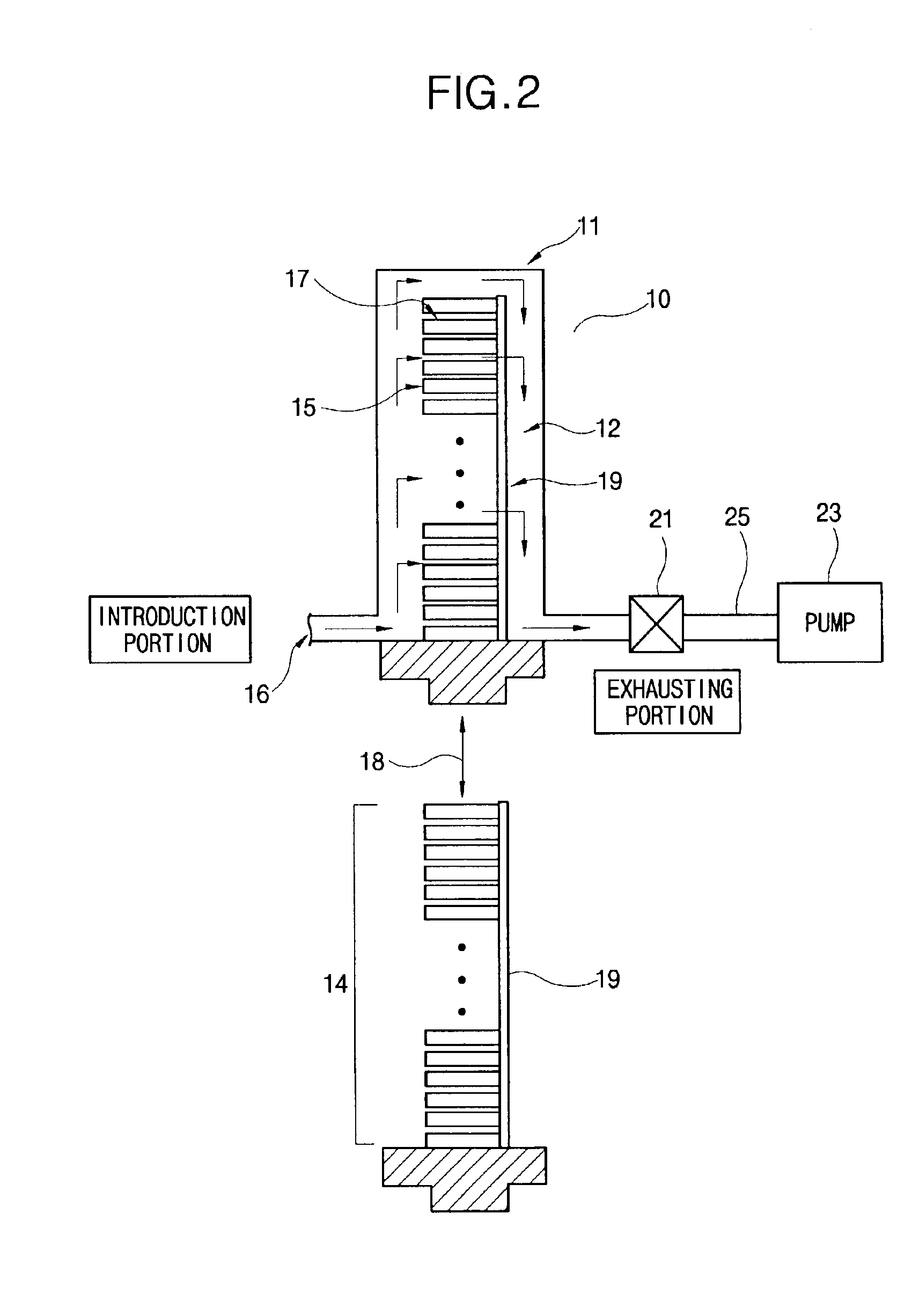
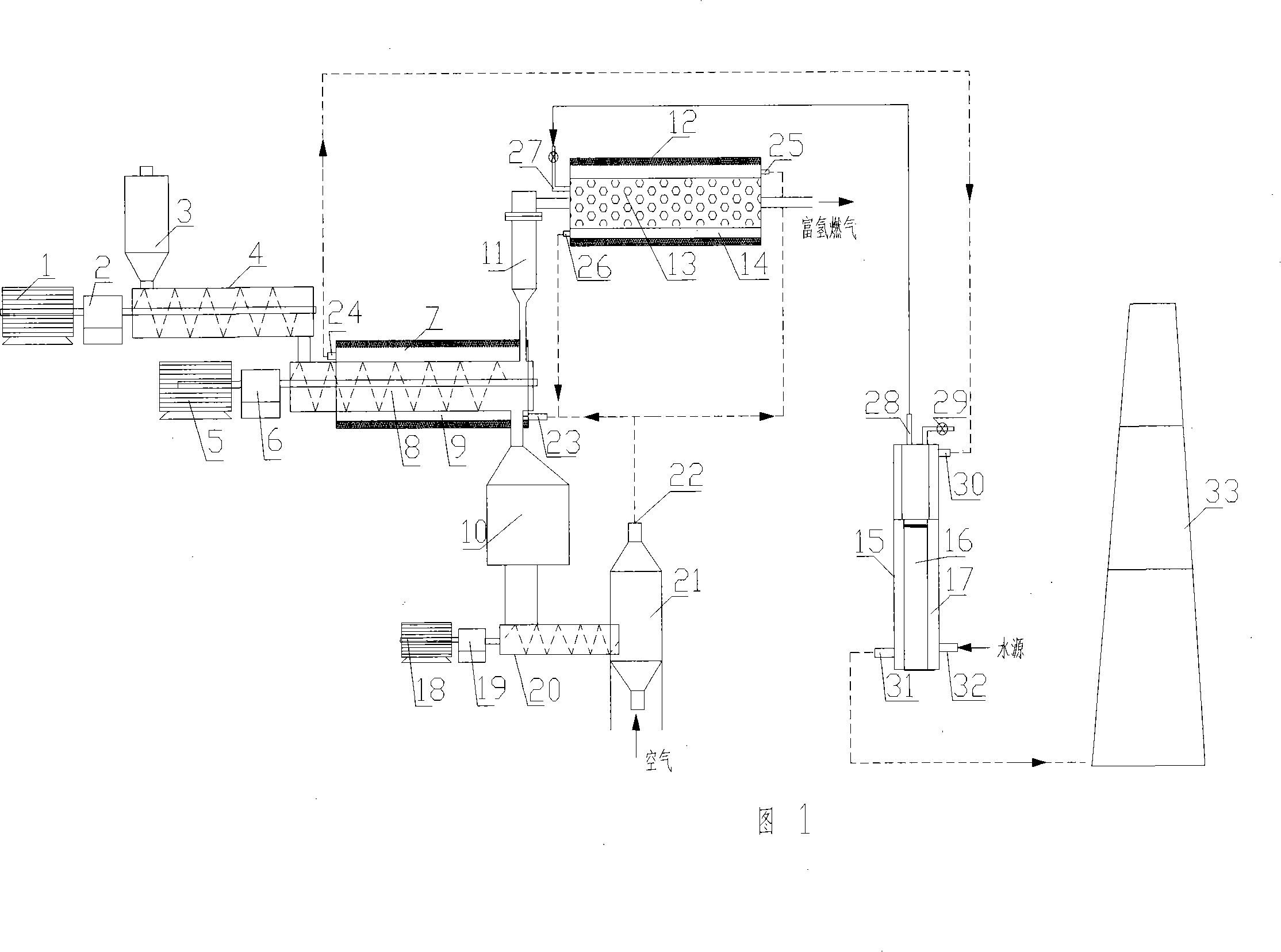
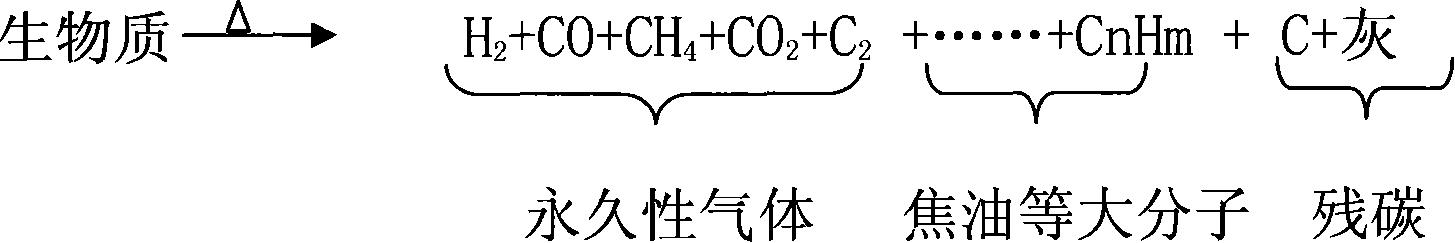
Method and device for preparing biomass hydrogen-rich combustion gas
InactiveCN101100621AReduce material requirementsReduce control requirementsHydrogenGaseous fuelsWater vaporGas phase
Production of biomass hydrogen-enriching fuel gas is carried out by thermal cracking for biomass raw materials at 550-650 deg. C under isolated air, converting it into gas-phase product and residual carbon, separating residual carbon from gas-phase product, transferring out of reacting system, burning to obtain heat energy, cracking at 800-950 deg. C and reforming into hydrogen, methane and other light hydrocarbons. It combines bitter spar catalyst and steam; it can eliminate tar, decrease methane content and increase hydrogen content. Hydrogen content reaches to 30%-55 wt%.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Raw material carbon composition for carbon material for electrode in electric double layer capacitor
ActiveUS7582902B2Improve the level ofGood reproducibilityTransistorCarbon compoundsMetallurgyHydrogen content
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
Formation evaluation combination system for petrophysical well log analysis
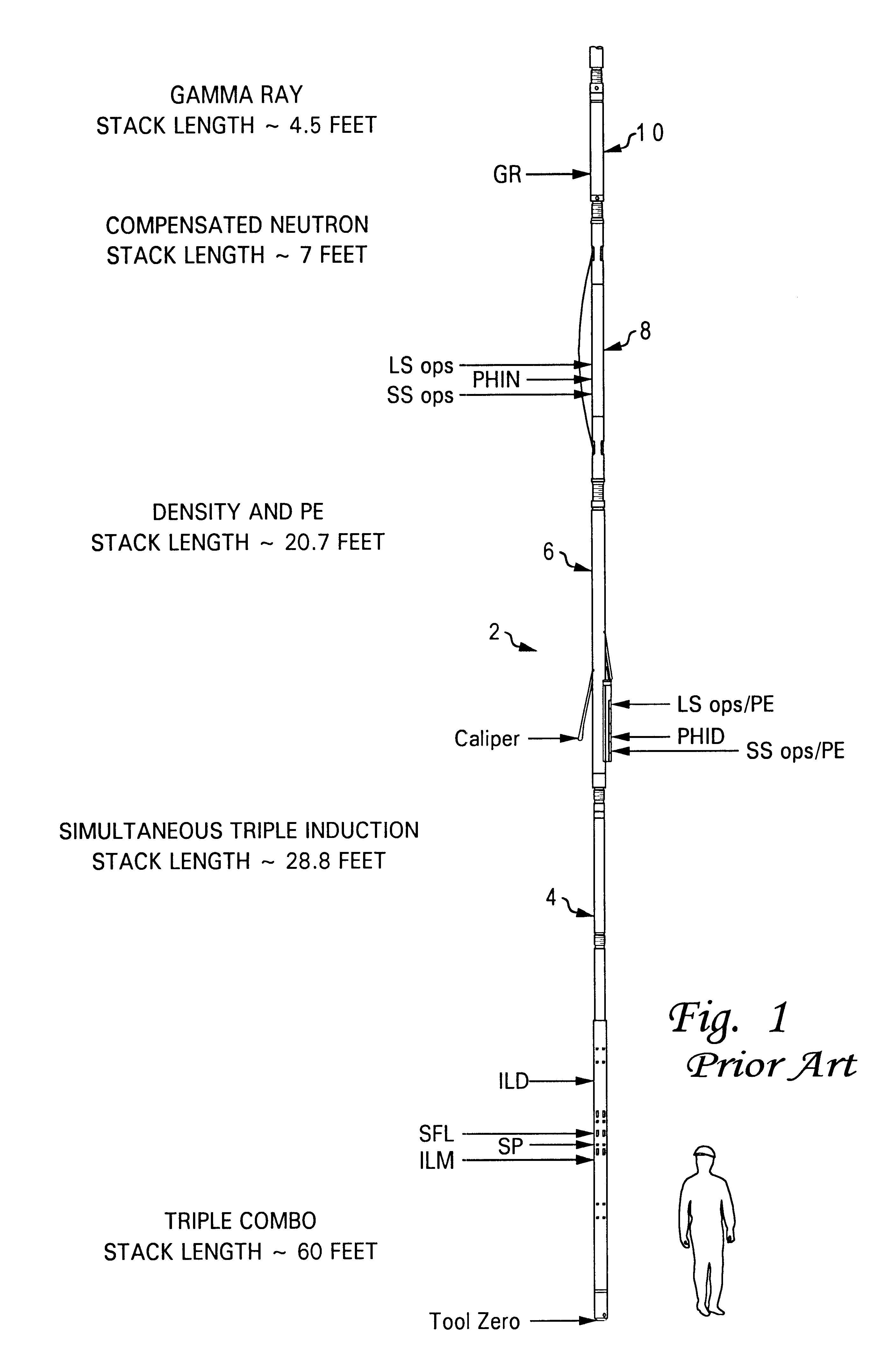
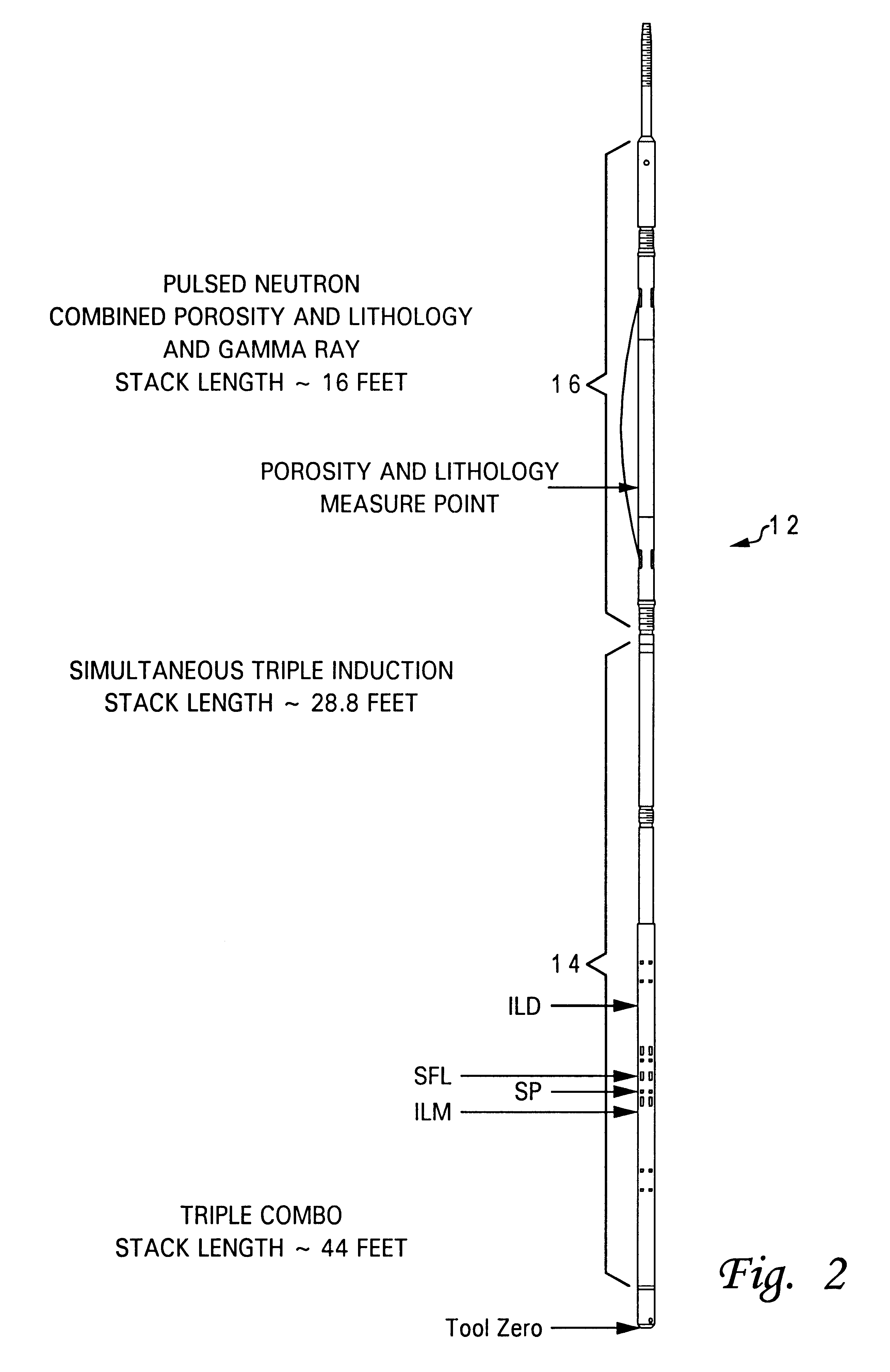
InactiveUS6376838B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationGamma ray detectionNeutron porosity
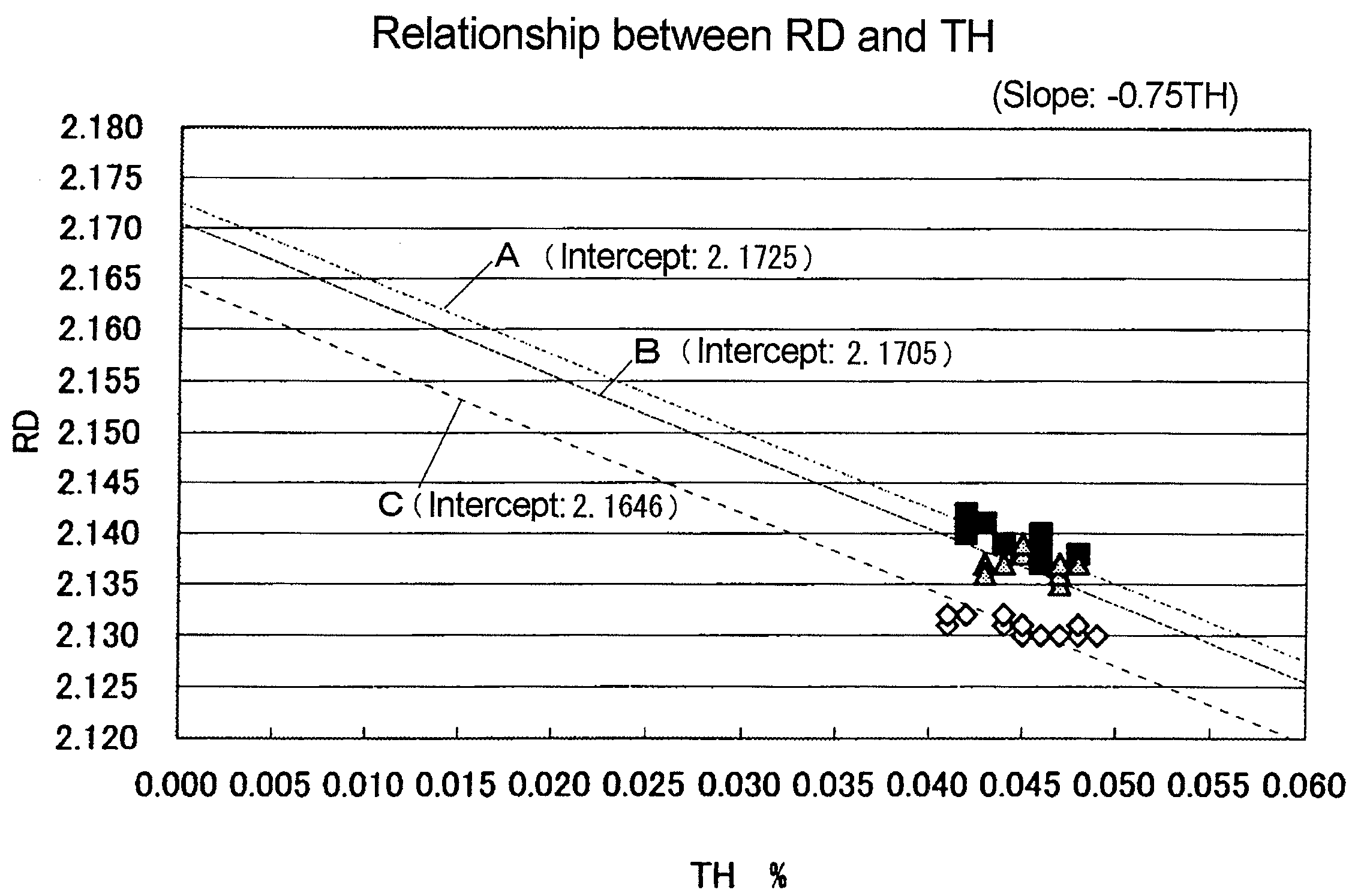
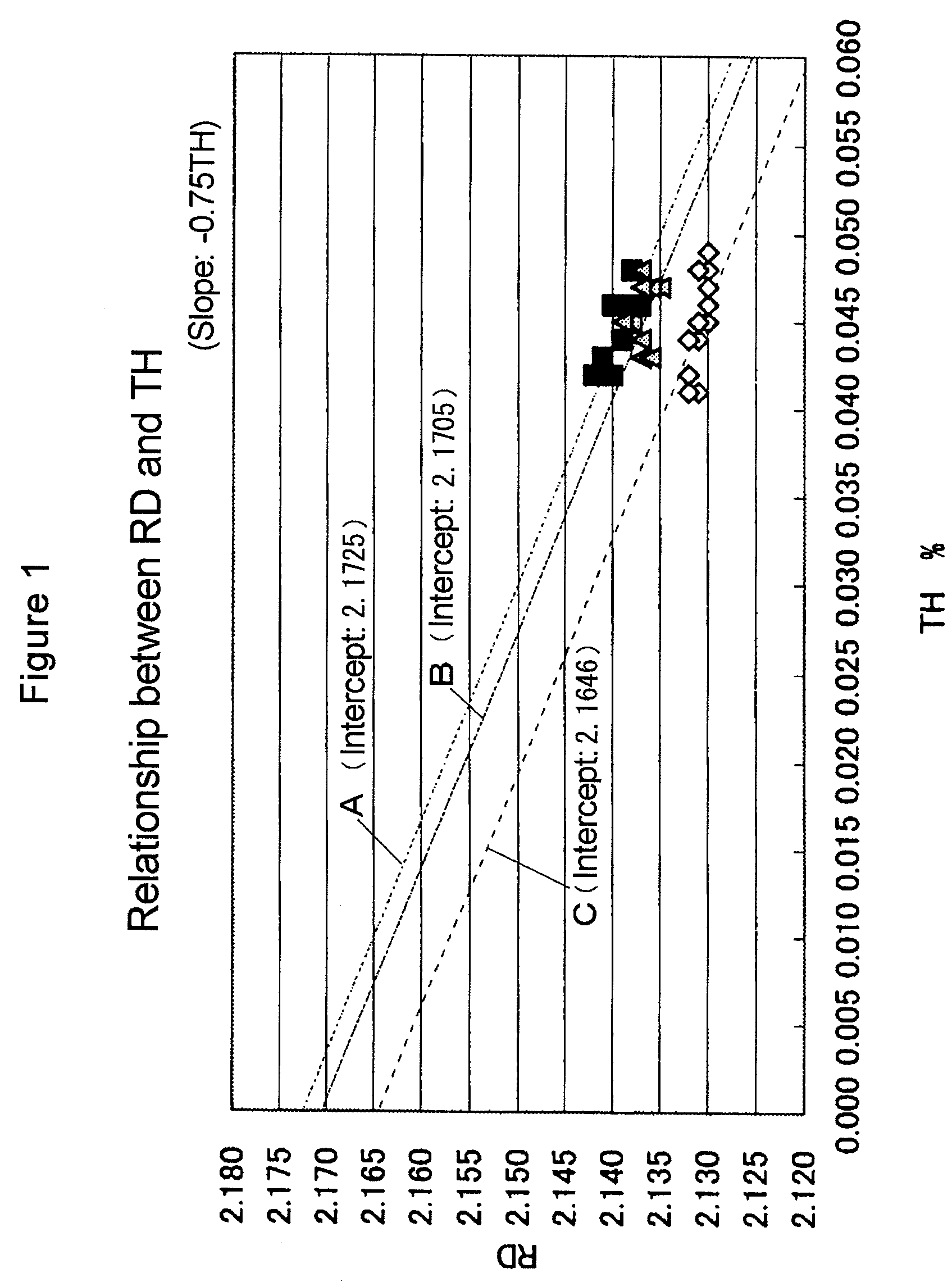
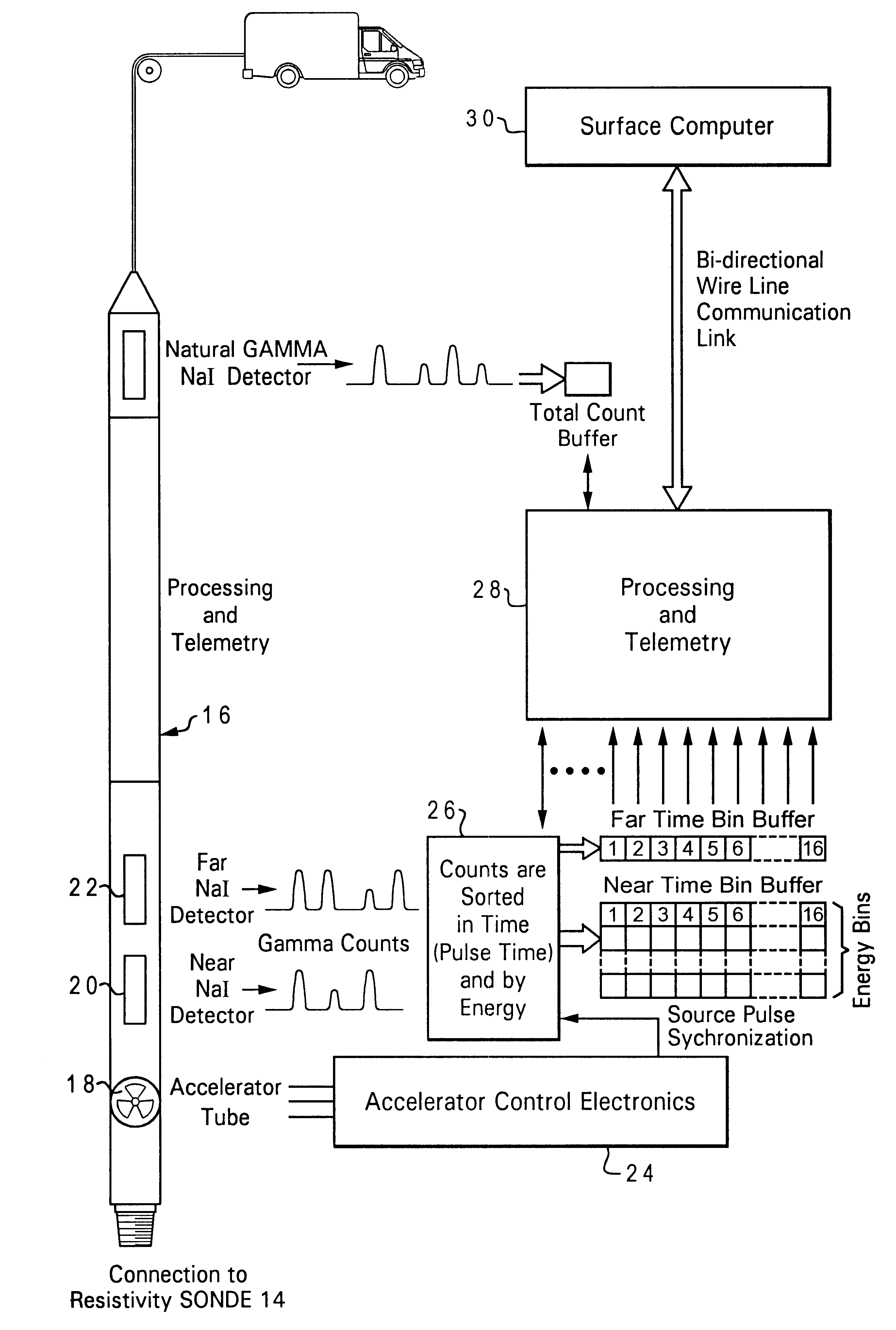
A method of measuring characteristics of a geologic formation, using the time, energy and spatial spectra of gamma rays induced by an accelerator, which allows (i) the measurement of the photoelectric absorption (Pe) factor of the formation using a gamma-ray spectrum detected from gamma rays induced in the formation, (ii) the calculation of a neutron porosity of the formation using the gamma-ray spectrum, and (iii) the determination of a bulk density of the formation using the spectroscopic measurements. The Pe factor may be inferred by directly mapping the spectroscopic measurements. The porosity may be calculated by relating the gamma-ray spectrum to a hydrogen content of the formation. The density may be determined by computing a gamma diffusion length of the formation based on the gamma-ray spectrum. In addition to these measurements, the resistivity of the formation and its spontaneous potential may also be measured using an electromagnetic induction system.
Owner:PRECISION ENERGY SERVICES
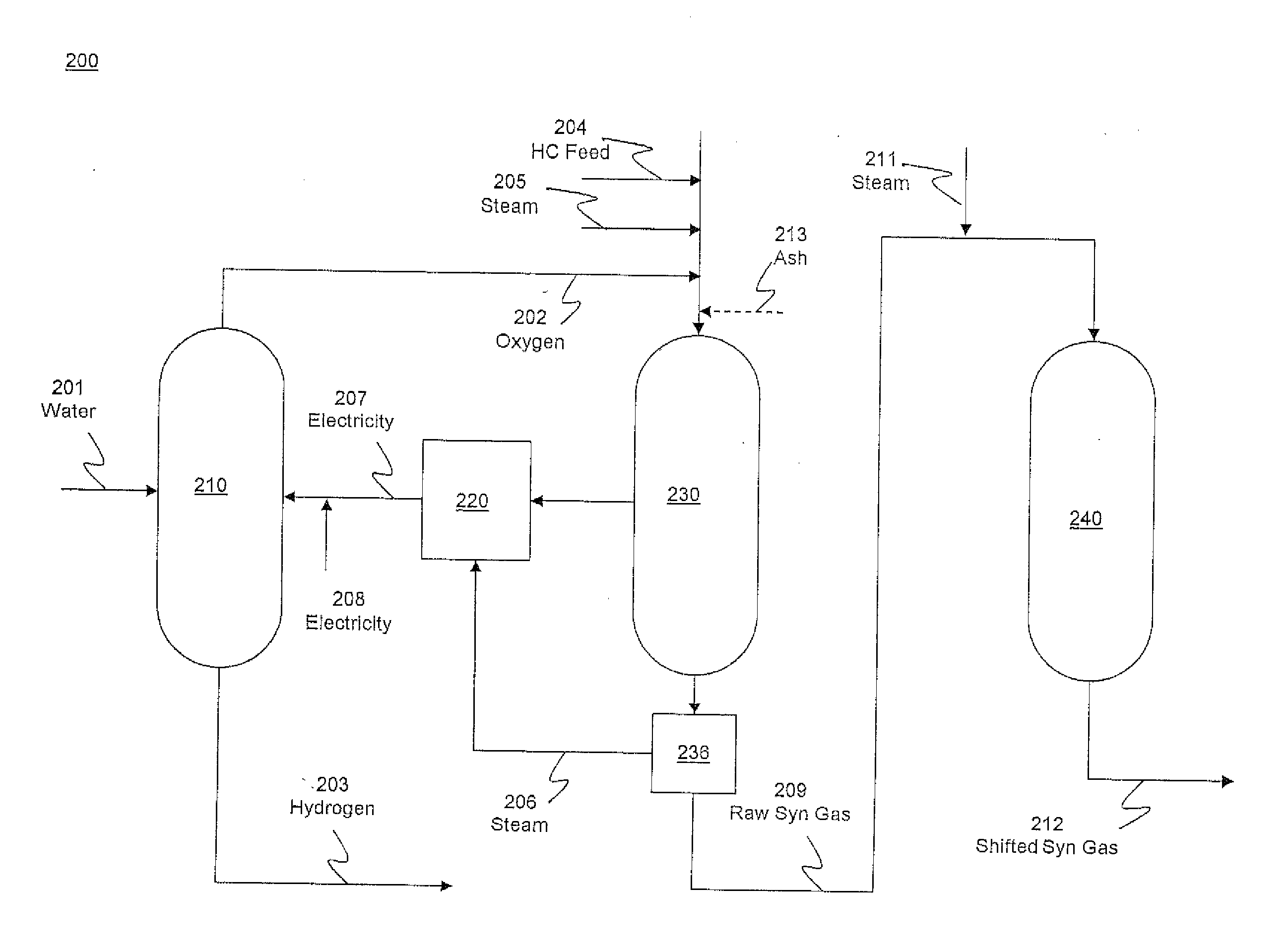
Hydrogen production from an integrated electrolysis cell and hydrocarbon gasification reactor
An integrated process for hydrogen gas production includes:a. operating a water electrolysis cell with an external source of electricity to produce oxygen and hydrogen;b. optionally operating an air separation unit to produce additional oxygen for the process;c. introducing a hydrocarbon feedstock into a membrane wall gasification reactor with an ash-forming material and steam, and oxygen from the electrolysis cell and, optionally, oxygen from the air separation unit to produce hot raw synthesis gas;d. passing the hot raw synthesis gas from the gasification reactor to a steam-generating heat exchanger to produce steam and a cooled raw synthesis gas;e. introducing the steam generated in the heat exchanger into a turbine to produce electricity to operate the electrolysis cell; andf. recovering the hydrogen gas from the water electrolysis cell and, optionally, subjecting the synthesis gas to a water-gas shift reaction to increase the hydrogen content and recovering the hydrogen.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Preparation method of organic silicon rubber for encapsulating LED being convenient for vacuum defoamation
InactiveCN101880396AReduce surface tensionReduce defective rateOther chemical processesAdhesivesRoom temperatureTransmittance
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
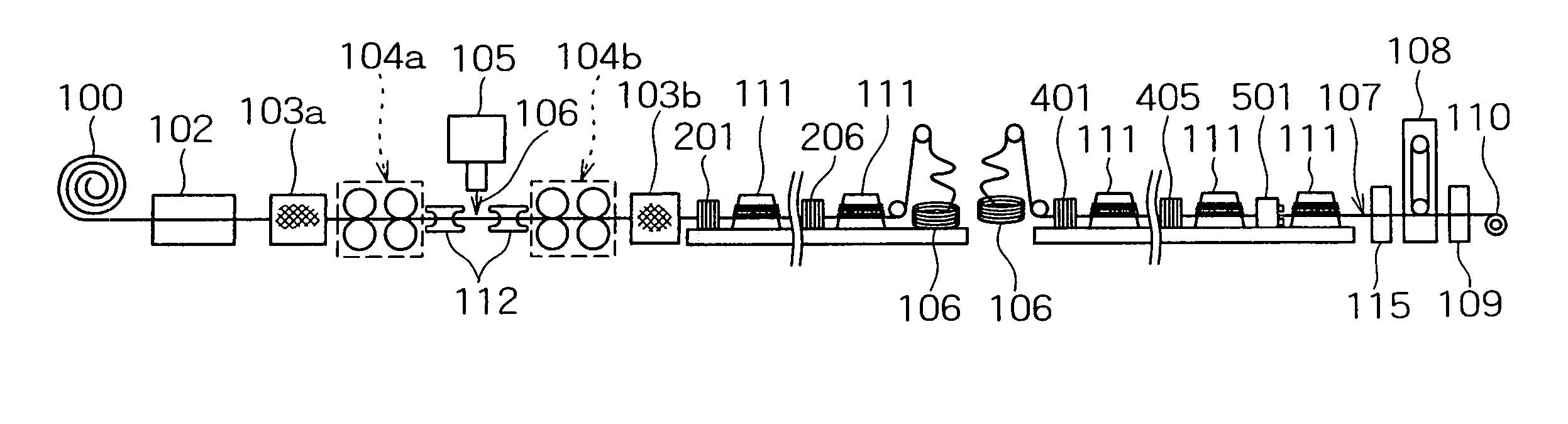
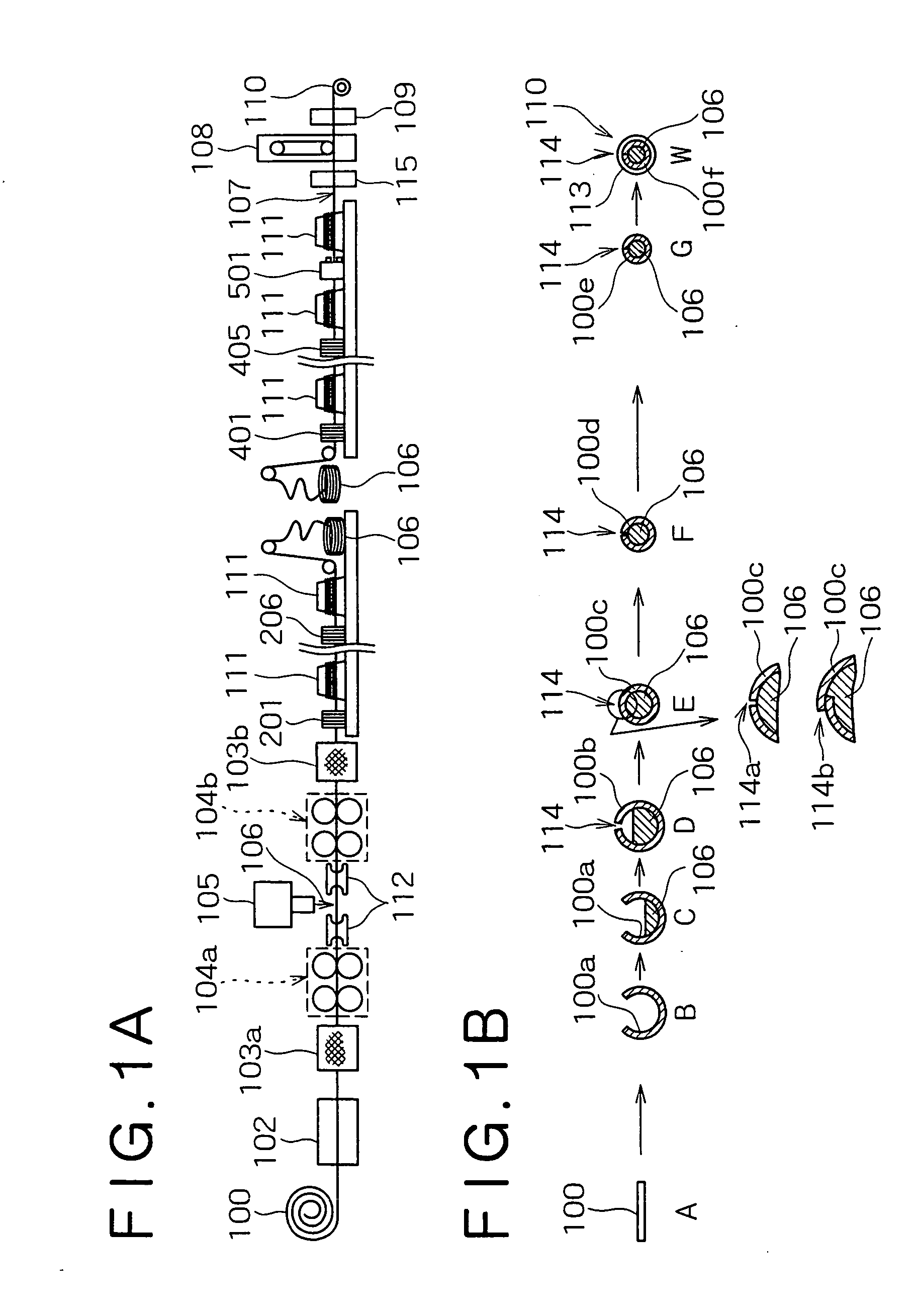
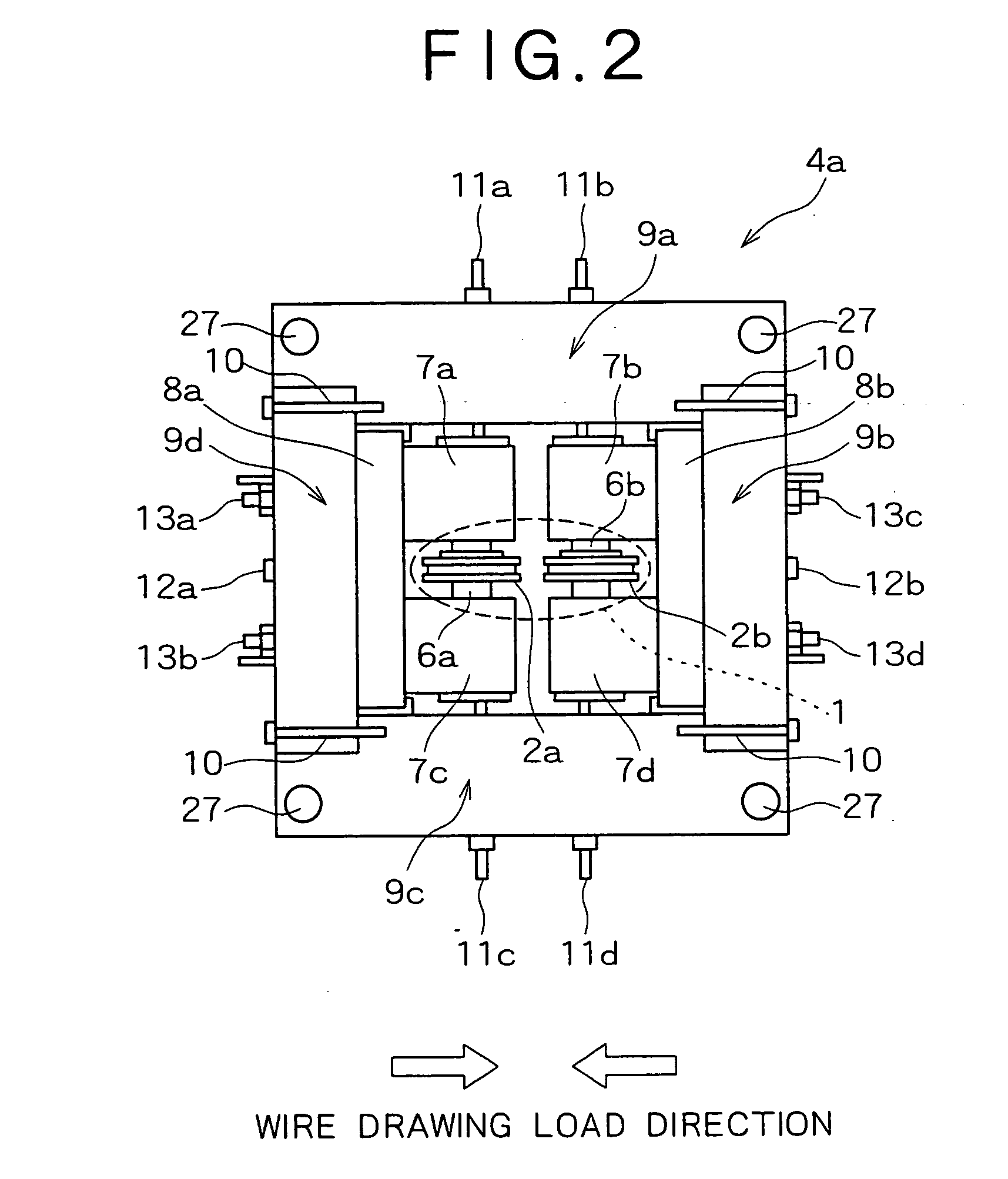
Method for manufacturing seamed flux-cored welding wire
ActiveUS20050044687A1Improve feeding effectReduce contentDrawing diesWelding/cutting media/materialsWire rodSulfur
Disclosed herein is a manufacturing method, excellent in wire drawability, of a seamed flux-cored welding wire having both favorable feedability and low hydrogen content characteristic. The method for manufacturing a seamed flux-cored wire, comprises the steps of: drawing a tube-like formed wire including a flux filled therein using a lubricant; removing the lubricant from the drawn wire by a physical means; and coating a lubricant (coating an oil) for wire feeding on the wire surface. The respective steps are carried out in an in-line manner. In the wire drawing step, a wire drawing lubricant containing a sulfur-bearing high-pressure lubricant is used, and the overall wire drawing from the tube-like formed wire to a roughly product-diameter wire is carried out by means of a roller die.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
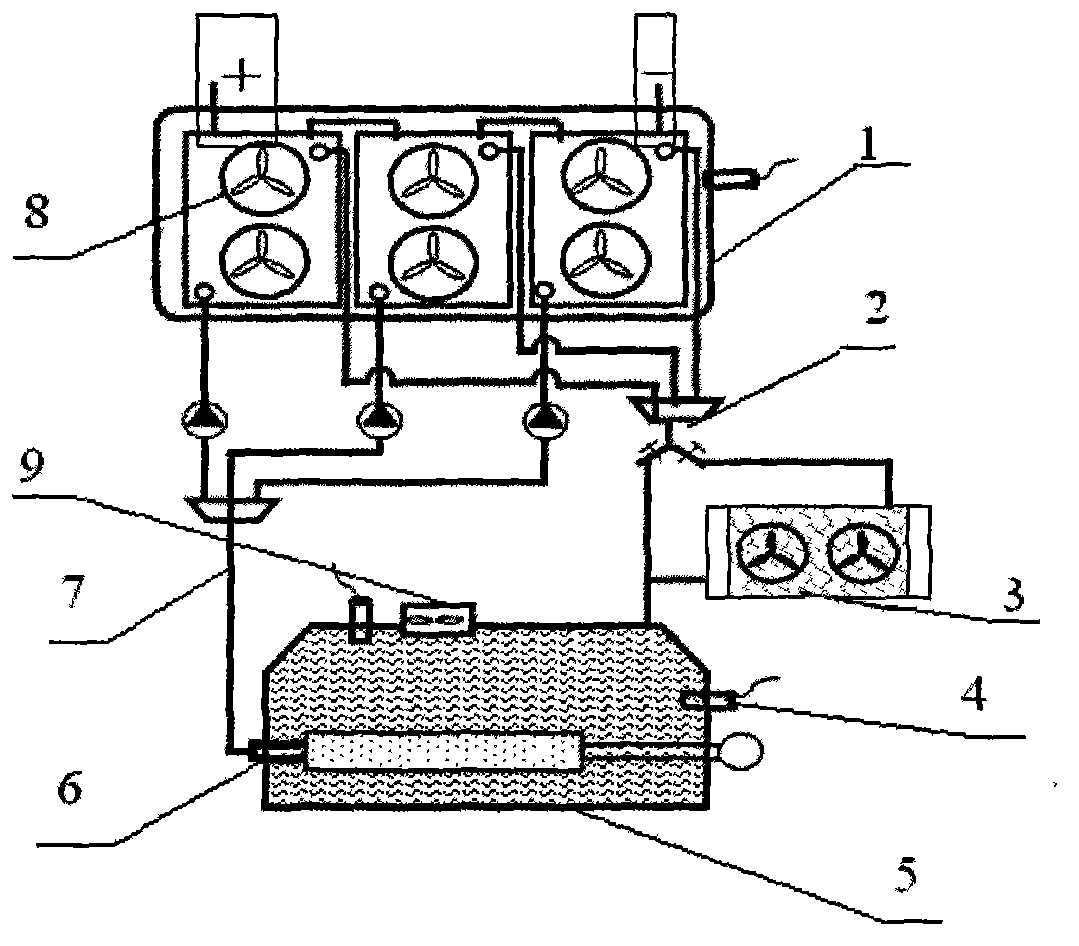
Aluminum air fuel cell system
InactiveCN103296338AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityFuel and primary cellsFinal product manufactureFiltrationElectric vehicle
The invention relates to an aluminum air fuel cell system, and particularly relates to the aluminum air fuel cell system with a temperature control system, a hydrogen discharging system and a filtration system and having a circulating electrolyte. The system includes an electrolyte tank, a cell stack and a ventilation system; also includes an electrolyte supplied system, an electrolyte return system, the hydrogen discharging system, a temperature measurement system, the filtration system and a heat dissipation system. The system can realize circulation of the electrolyte, effectively separates precipitation, controls a hydrogen content and an internal temperature of cells, meets requirements of high power output and long time running, and can be widely applied to the field of power cells for electric vehicles and large standby power supplies.
Owner:CHONGQING WENNENG ENERGY SCI & TECH
Hydrogen-rich water and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102408147APrevent precipitationSimple and easy to prepareWater/sewage treatment by substance additionHydrogen contentNitrogen gas
The invention relates to hydrogen-rich water and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of food beverages. The hydrogen-rich water is prepared by the following steps: firstly introducing nitrogen into a closed pressure vessel, emptying the nitrogen, introducing hydrogen to 0.1-4 MPa, stirring for 10-30 minutes with the pressure being maintained at 0.1-4 MPa. After the hydrogen-rich water is filled, the hydrogen content within a shelf life of 12 months is 1.35-1.65 ppm; the redox potential is between -400 and -600 mV; and the elimination activity of active oxygen peroxide SOSA index is 7.0-9.0 units. The invention solves the problems that hydrogen is dissolved in water and does not precipitate; the prepared bottle-packed hydrogen-rich water finished product can be stored for a long time, is convenient for transportation and sale, can be drunk immediately when a bottle is opened; the preparation and filling methods of the hydrogen-rich water are simple and practical, do not consume a lot of equipment and energy, and has low cost.
Owner:CHENGDU LIST PHARMA
Quiescent transfer of melts
InactiveUS20080202644A1Easy to cleanBlast furnace detailsCharge manipulationHydrogen contentHandling system
A quiescent melt handling system includes a holding furnace (2, 120, 320-720) for a molten metal melt. The holding furnace has a relatively large surface area and a relatively shallow depth, having a width to depth ratio in the range of 4-100 to 1. Also provided is structure (650-680) in the holding furnace for separating inclusions from the melt in the holding furnace. A quiescent transfer casting method includes melting a metal to form a melt and transferring the melt into a holding furnace. A hydrogen content in the melt is passively equilibrated with a dry atmosphere maintained in the holding furnace. Subsequently, the melt is withdrawn from the holding furnace.
Owner:ALOTECH LTD
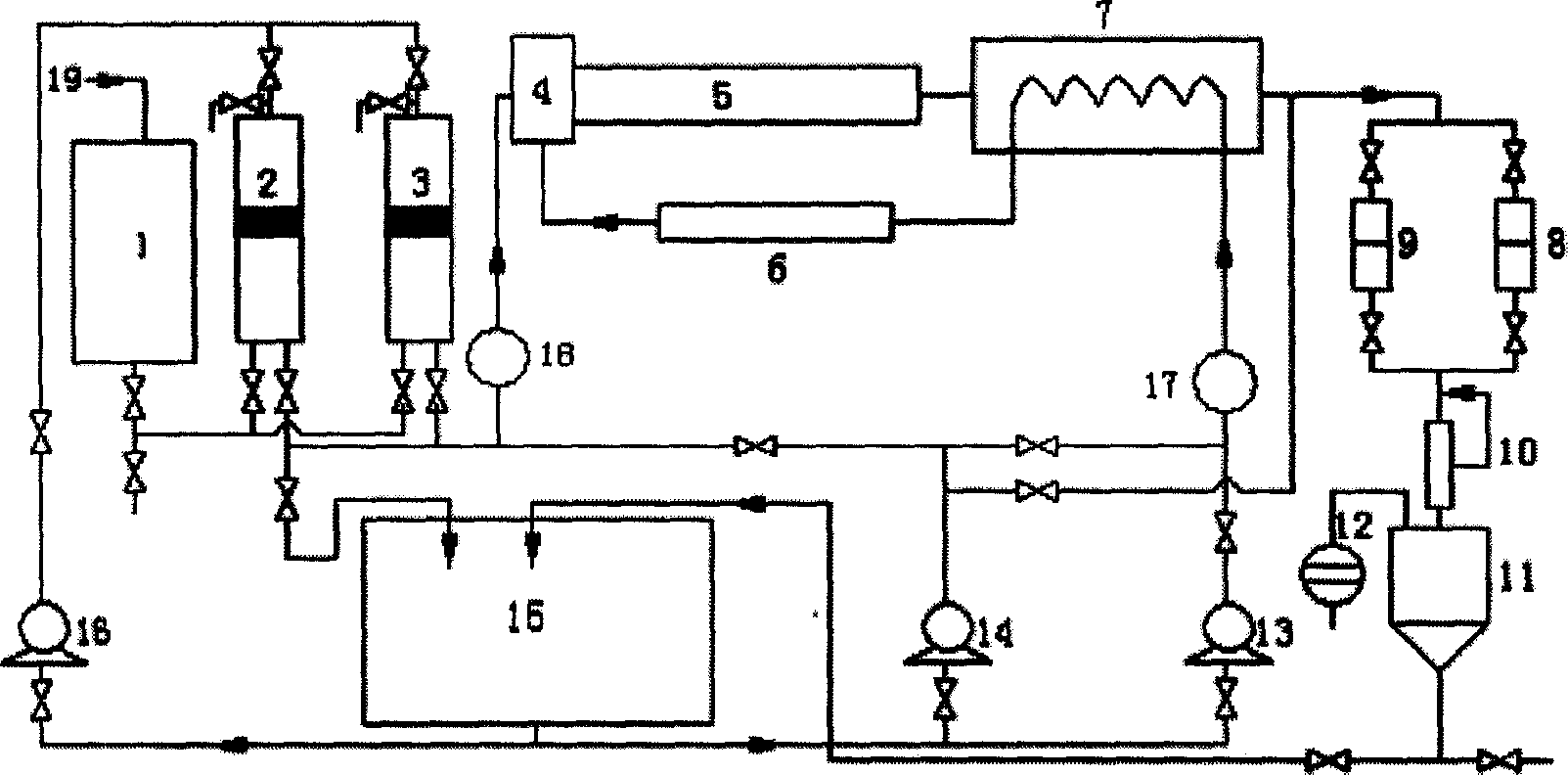
Coal-biomass co-overcritical water catalysis-gasification hydrogen production plant and method
ActiveCN1654313AMild reaction conditionsEasy to controlHydrogen productionBulk chemical productionCO2 contentHydrogen content
The present invention discloses one kind of supercritical water catalytic coal and biomass gasifying process and apparatus for producing hydrogen. The apparatus has material feeder with one inlet connected to the outlet of the material pump and the other inlet connected to the outlet of feeding tank, pre-heater with outlet connected to the preheated water inlet and inlet connected to the outlet of inner pipe outlet of the cooler, cooler with inlet connected to the inlet of water pump, water pump with outlet connected to the water tank, cooler jacket with outlet connected to the inlet of the first filter and the inlet of the second filter, and back pressure valve with inlet connected to the outlets of the first filter and the second filter. The present invention has special heating mode for fast heating of the reaction material, raised hydrogen content in the gas product, raised CO2 content in the gas product, and easy separation of CO2 and feeding of CO2 to the processing terminal. The present invention is simple, effective and feasible.
Owner:陕西中核交大超洁能源技术有限公司
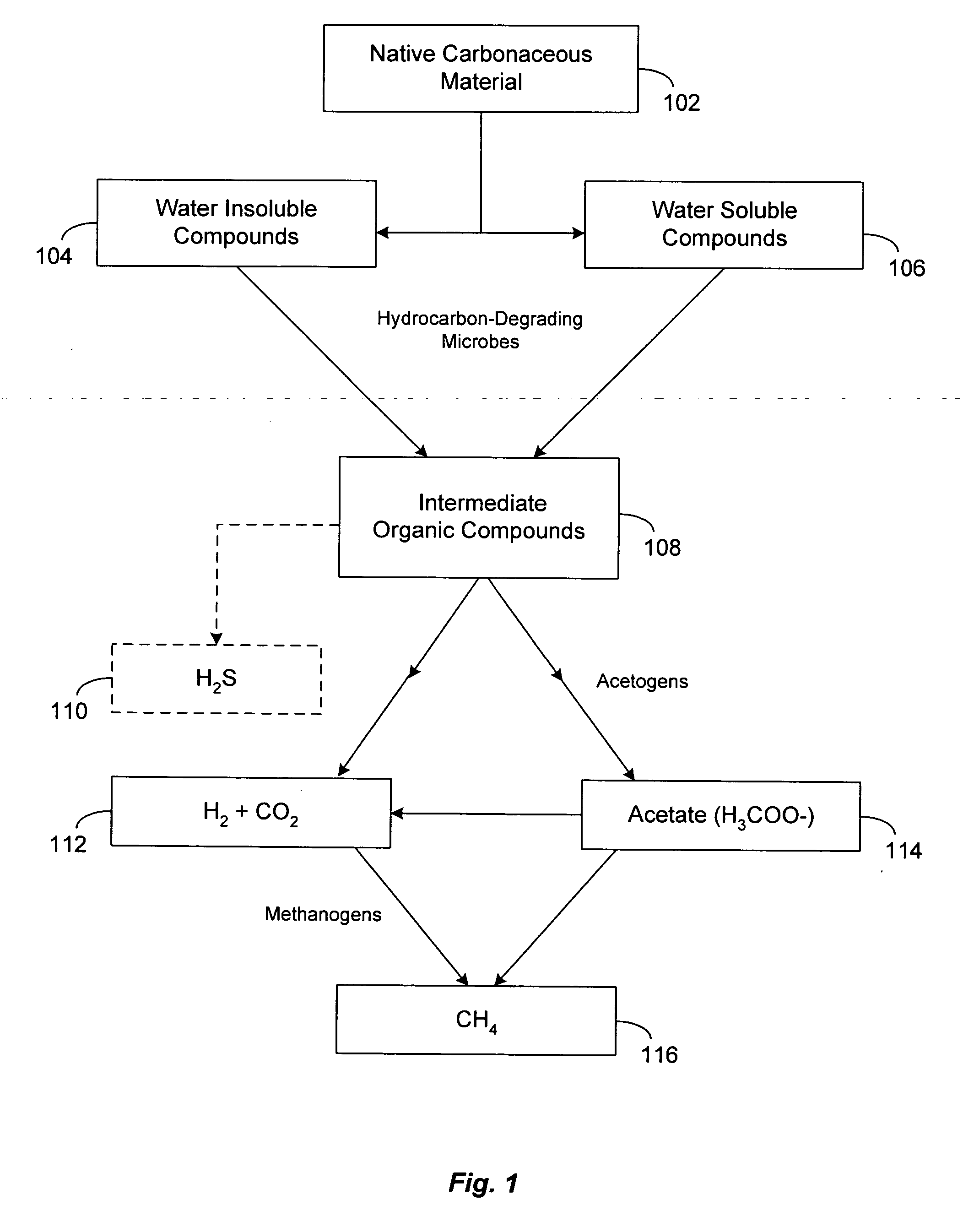
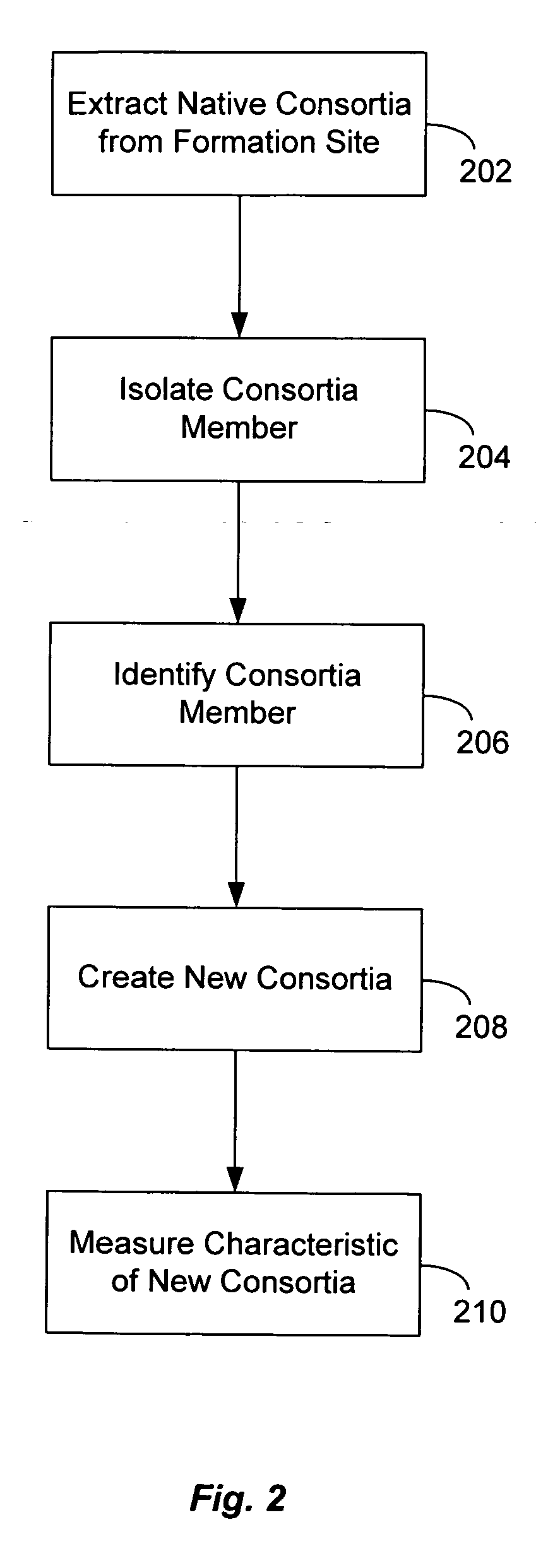
Generation of materials with enhanced hydrogen content from anaerobic microbial consortia
InactiveUS20060223153A1Easy extractionPromote recoveryBacteriaUnicellular algaeSource materialHydrogen content
A microbial consortia for biogenically increasing the hydrogen content of a carbonaceous source material, where the consortia includes a first microbial consortium to metabolize the carbonaceous source material into one or more first intermediate hydrocarbons, a second microbial consortium, which includes one or more species of Pseudomonas microorganisms, to convert the first intermediate hydrocarbons into one or more second intermediate hydrocarbons and oxidized carbon and a third microbial consortium to convert the second intermediate hydrocarbons into one or more smaller hydrocarbons and water, where the smaller hydrocarbons have a greater mol. % hydrogen than the carbonaceous source material.
Owner:LUCA TECH
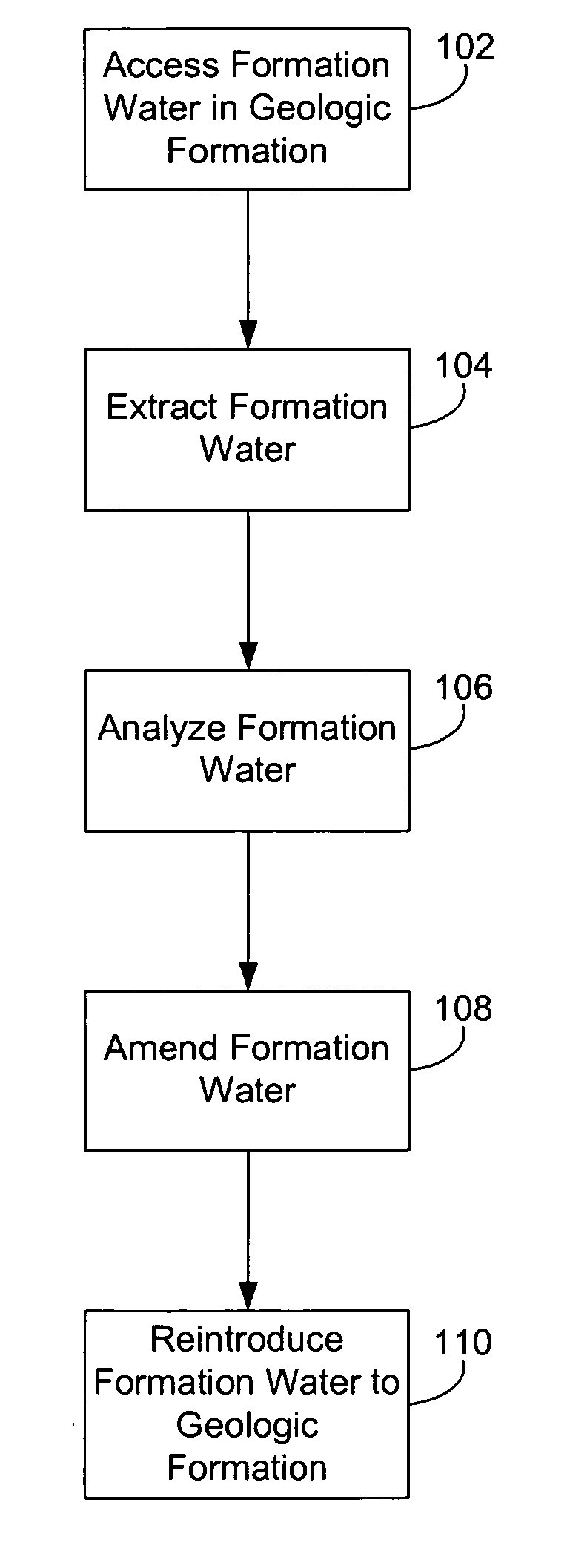
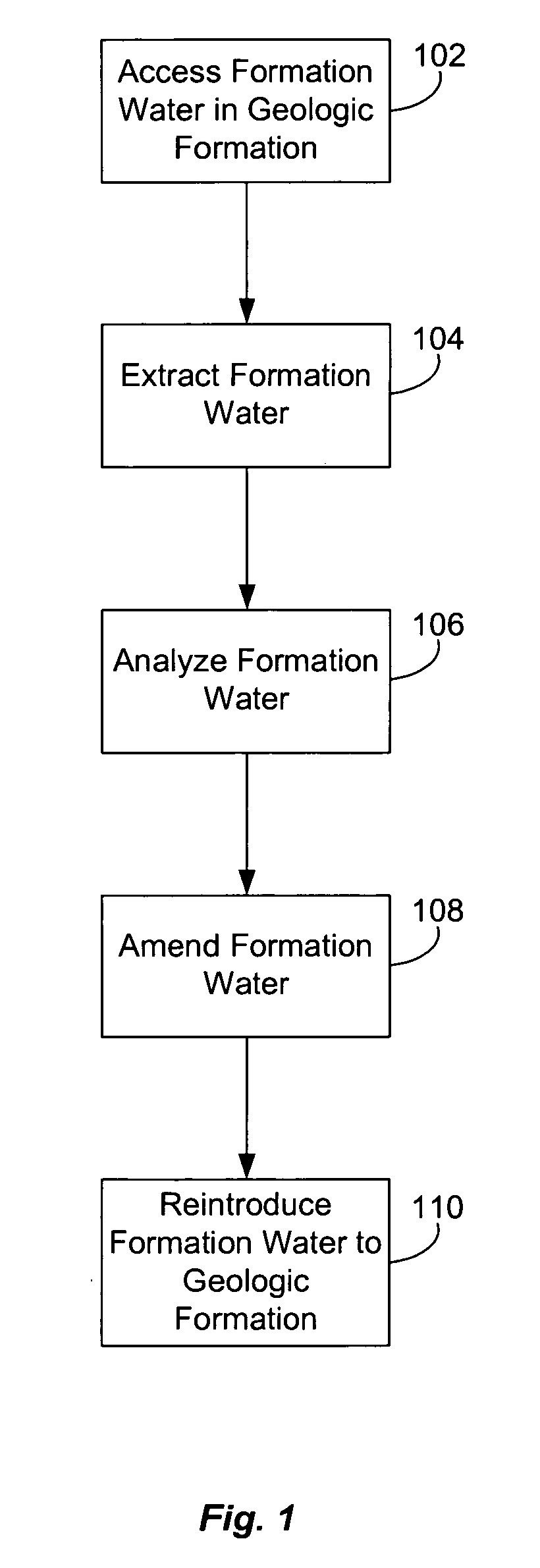
Biogenic fuel gas generation in geologic hydrocarbon deposits
ActiveUS20060254765A1High hydrogen contentReduce salinitySurveyMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteBiofuel
A method to stimulate the biogenic production of a metabolite with enhanced hydrogen content that includes forming an opening in a geologic formation to provide access to a consortium of microorganisms, and injecting water into the opening to disperse at least a portion of the consortium over a larger region of a hydrocarbon deposit. The method may also include measuring a change in the rate of production of the metabolite in the formation. Also, an method to stimulate biogenic production of a metabolite that includes measuring a salinity level of formation water in a geologic formation, and injecting water into the opening to reduce the salinity level of the formation water in the formation. The method may also include measuring a change in the rate of production of the metabolite in the formation.
Owner:TRANSWORLD TECH
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and process for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050020021A1Image degradationLess fluctuationTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialHydrogen content
In the manufacture of a semiconductor device having a high-performance and high-reliability, a silicon nitride film 17 for self alignment, which film is formed to cover the gate electrode of a MISFET, is formed at a substrate temperature of 400° C. or greater by plasma CVD using a raw material gas including monosilane and nitrogen. A silicon nitride film 44 constituting a passivation film is formed at a substrate temperature of about 350° C. by plasma CVD using a raw material gas including monosilane, ammonia and nitrogen. The hydrogen content contained in the silicon nitride film 17 is smaller than that contained in the silicon nitride film 44, making it possible to suppress hydrogen release from the silicon nitride film 17.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Oxide semiconductor device including insulating layer and display apparatus using the same
Provided is an oxide semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor layer and an insulating layer coming into contact with the oxide semiconductor layer in which the insulating layer includes: a first insulating layer coming into contact with an oxide semiconductor, having a thickness of 50 nm or more, and including an oxide containing Si and O; a second insulating layer coming into contact with the first insulating layer, having a thickness of 50 nm or more, and including a nitride containing Si and N; and a third insulating layer coming into contact with the second insulating layer, the first insulating layer and the second insulating layer having hydrogen contents of 4 x 1021 atoms / cm3 or less, and the third insulating layer having a hydrogen content of more than 4 x 1021 atoms / cm3.
Owner:CANON KK
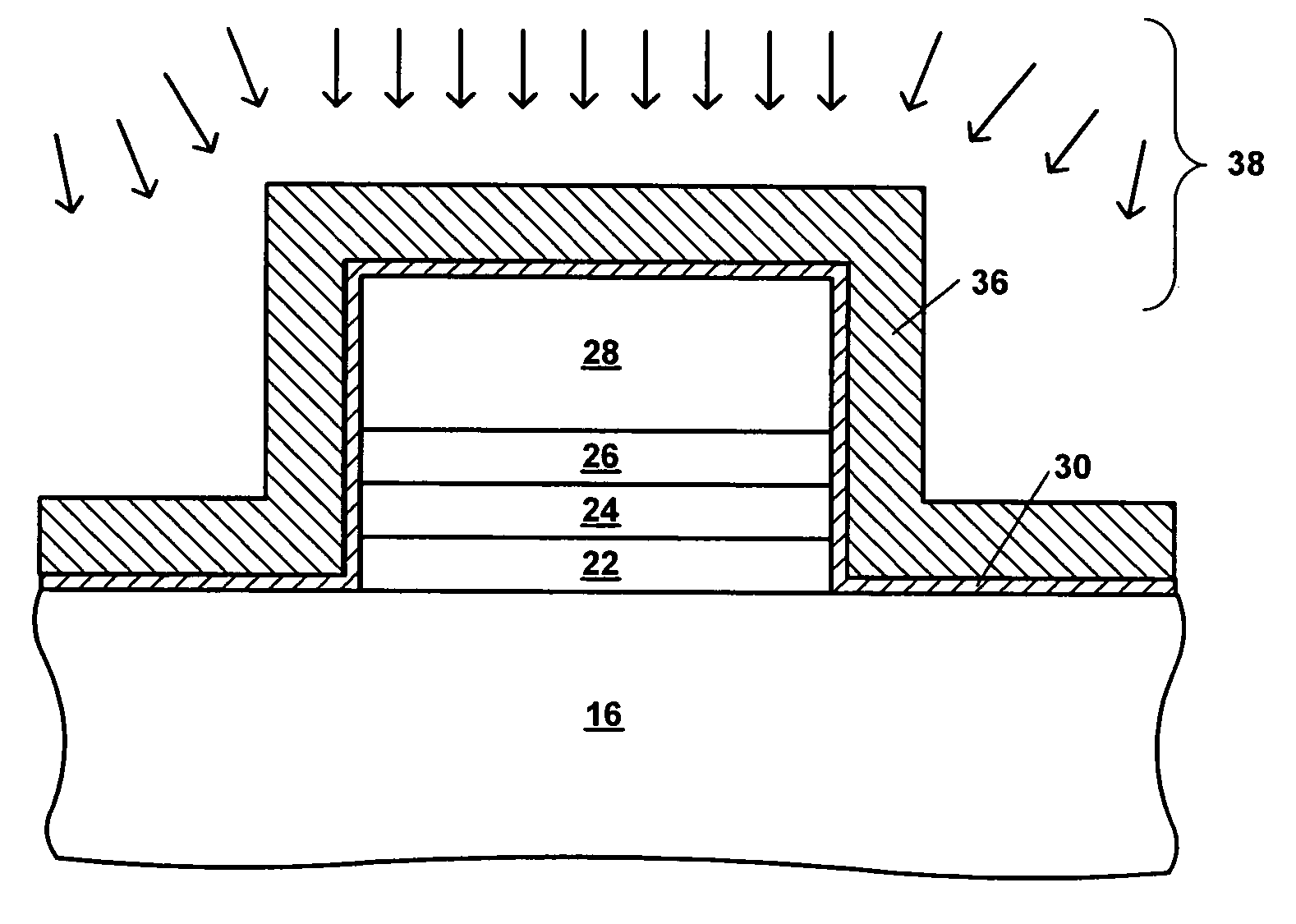
Process for fabrication of spacer layer with reduced hydrogen content in semiconductor device
ActiveUS6949481B1Reduce hydrogen contentRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen contentEngineering
Process for fabricating a semiconductor device including steps of providing a semiconductor substrate having formed thereon a semiconductor device; depositing over the semiconductor device a spacer layer, the spacer layer having a first hydrogen content; and applying a treatment to reduce the first hydrogen content to a second hydrogen content. The invention is particularly useful when applied to flash memory devices such as a charge trapping dielectric flash memory device.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
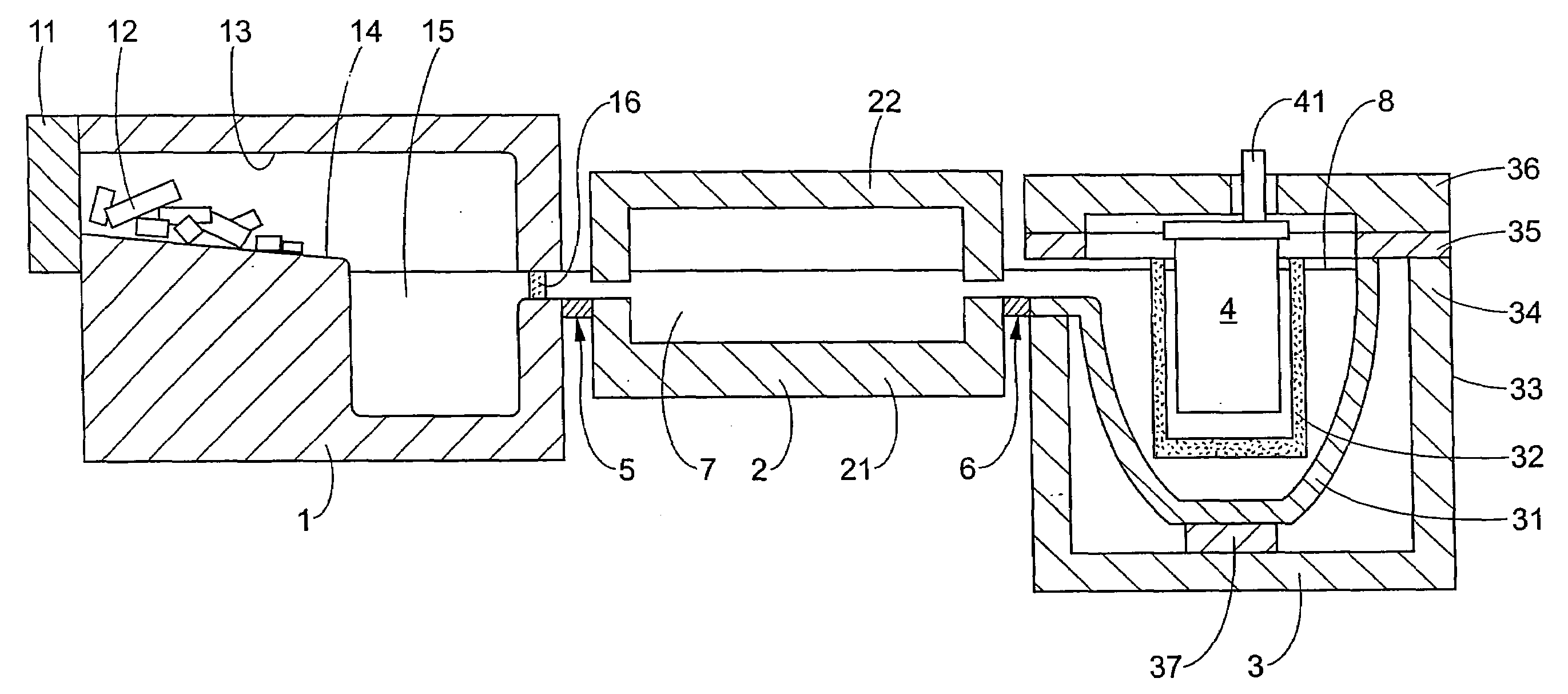
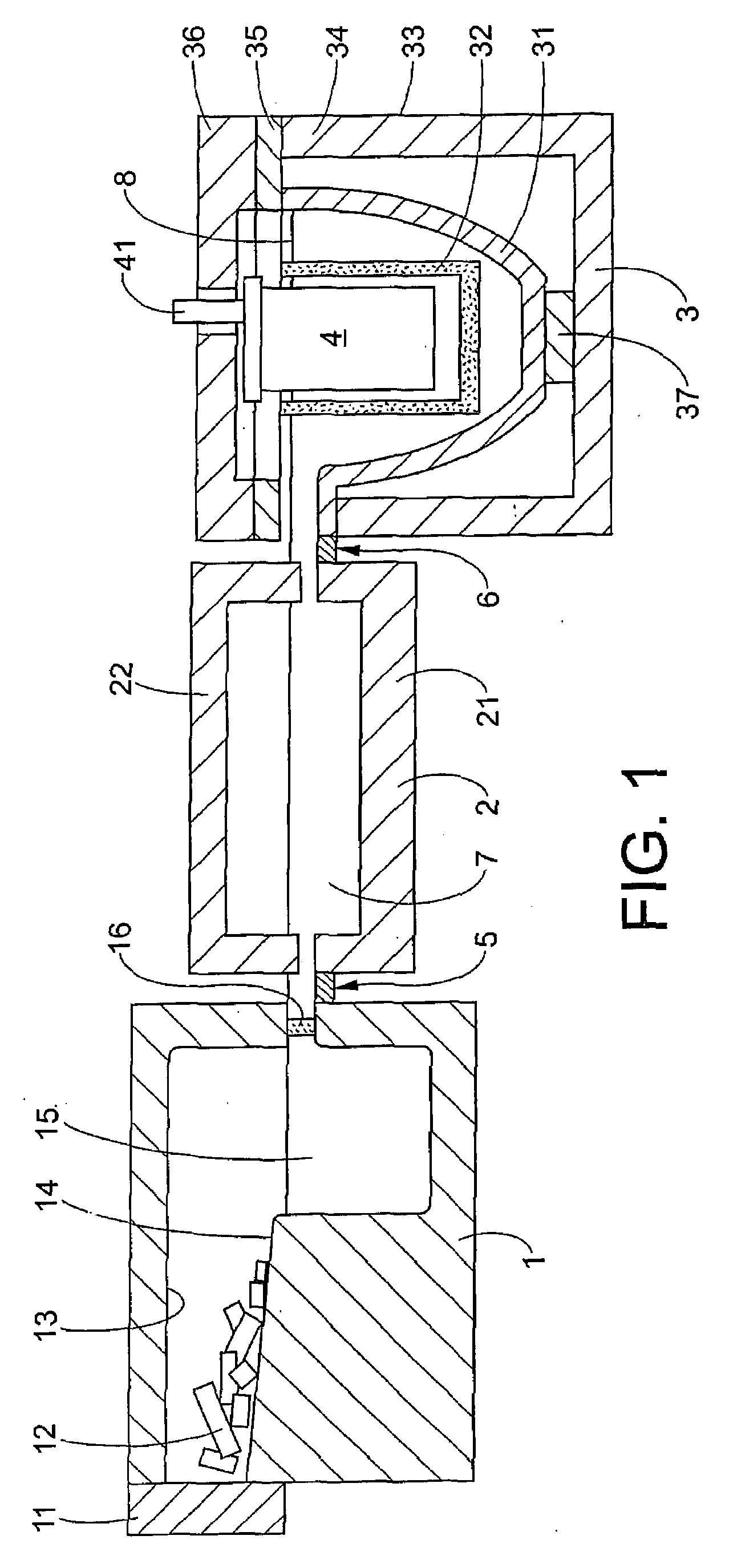
Method of detachable direct bonding at low temperatures
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
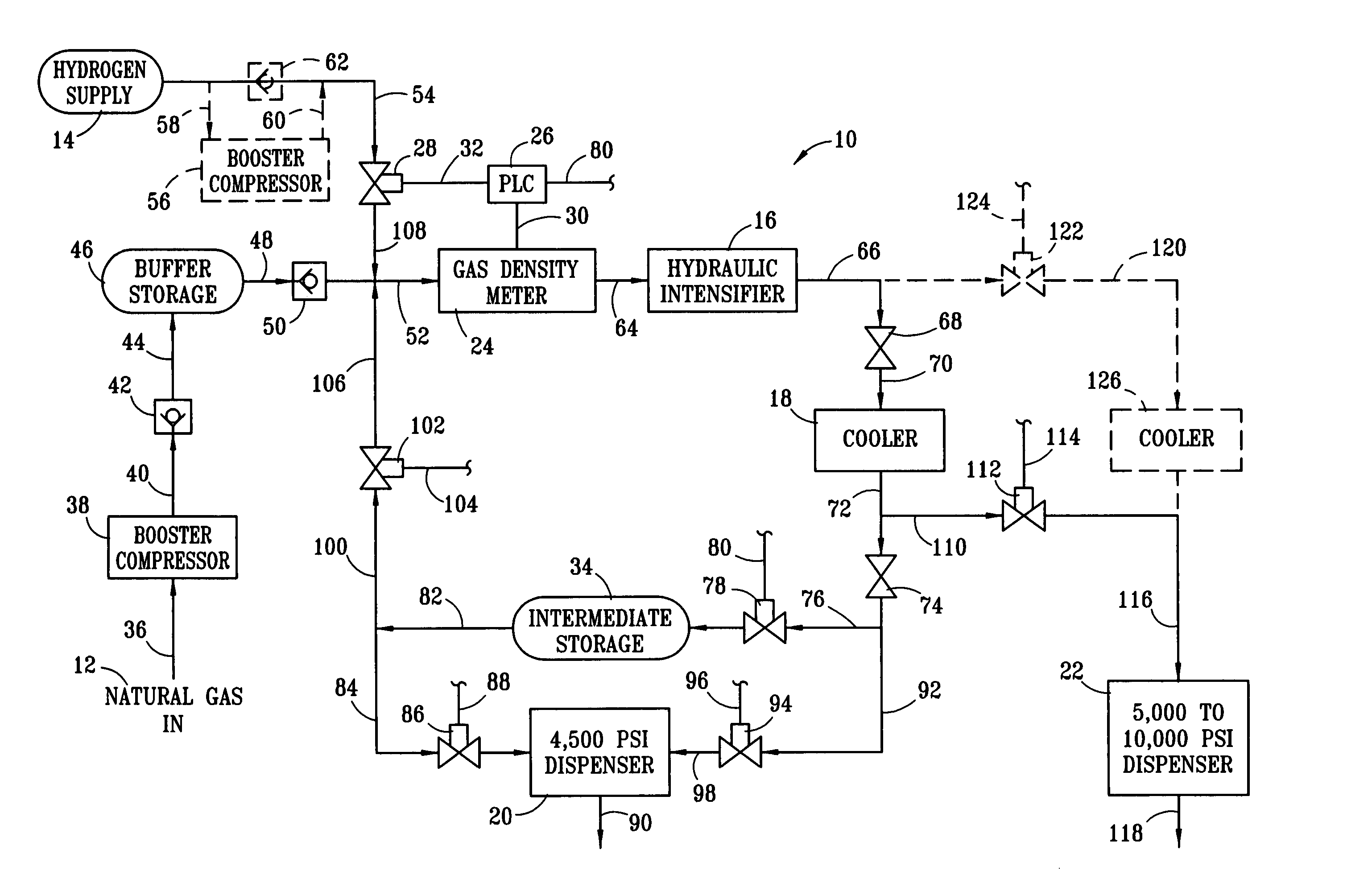
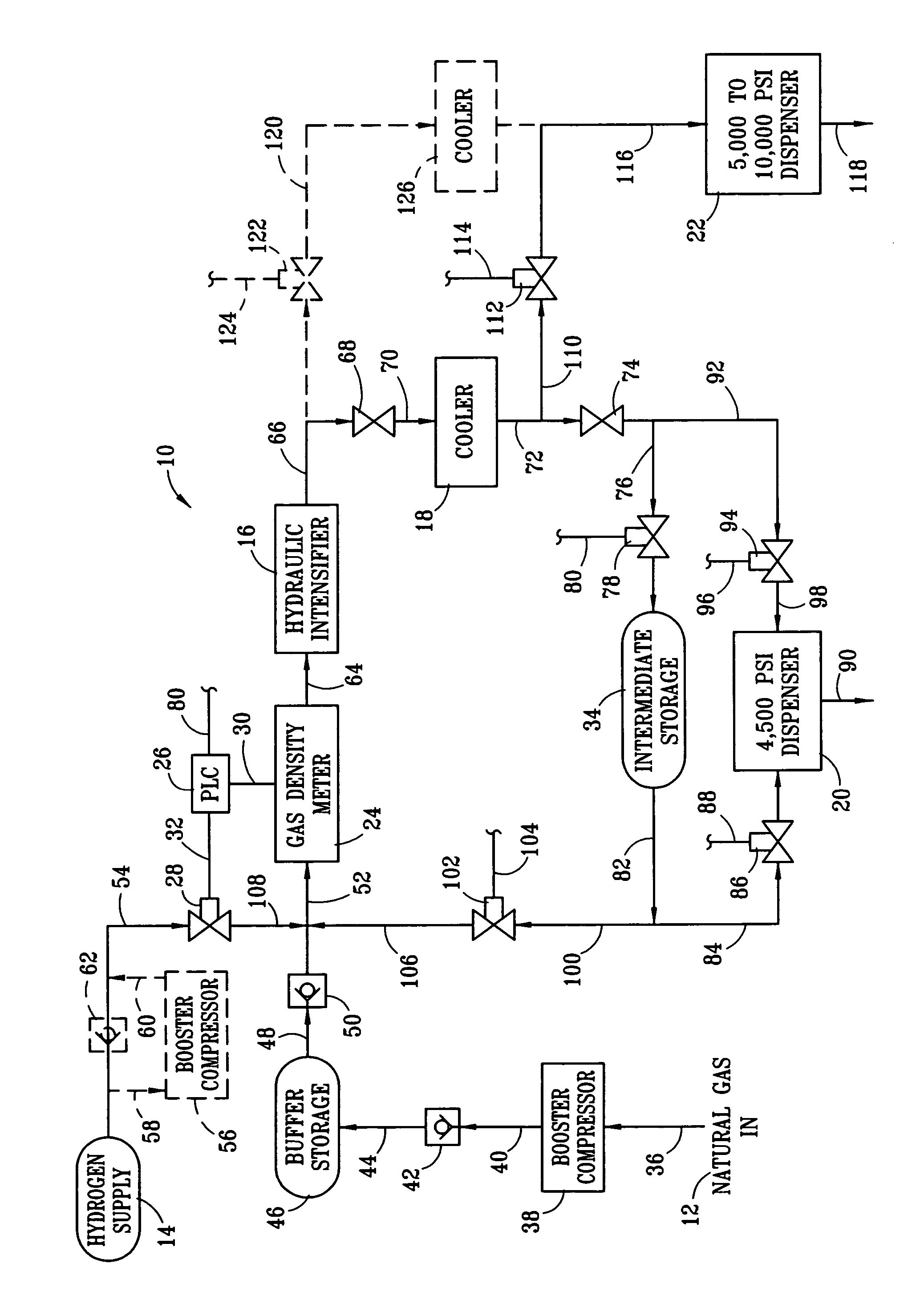
Dual-service system and method for compressing and dispensing natural gas and hydrogen
InactiveUS7168464B2Easy to switchFacilitate pressureLiquid fillingFrozen sweetsVolumetric Mass DensityGas cooler
A dual service system and method for selectively compressing and dispensing methane, hydrogen, and variable mixtures of methane and hydrogen for use as a gaseous fuel. The use of an in-line gas density meter, hydraulic intensifier, pressurized gas cooler, optional intermediate storage and multiple dispensers are disclosed. An inline gas density meter is used in combination with a programmable logic controller and a control valve on the hydrogen supply line to create a closed feedback loop for selectively controlling the hydrogen content of the resultant pressurized fuel gas.
Owner:INTEGRYS TRANSPORTATION FUELS
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
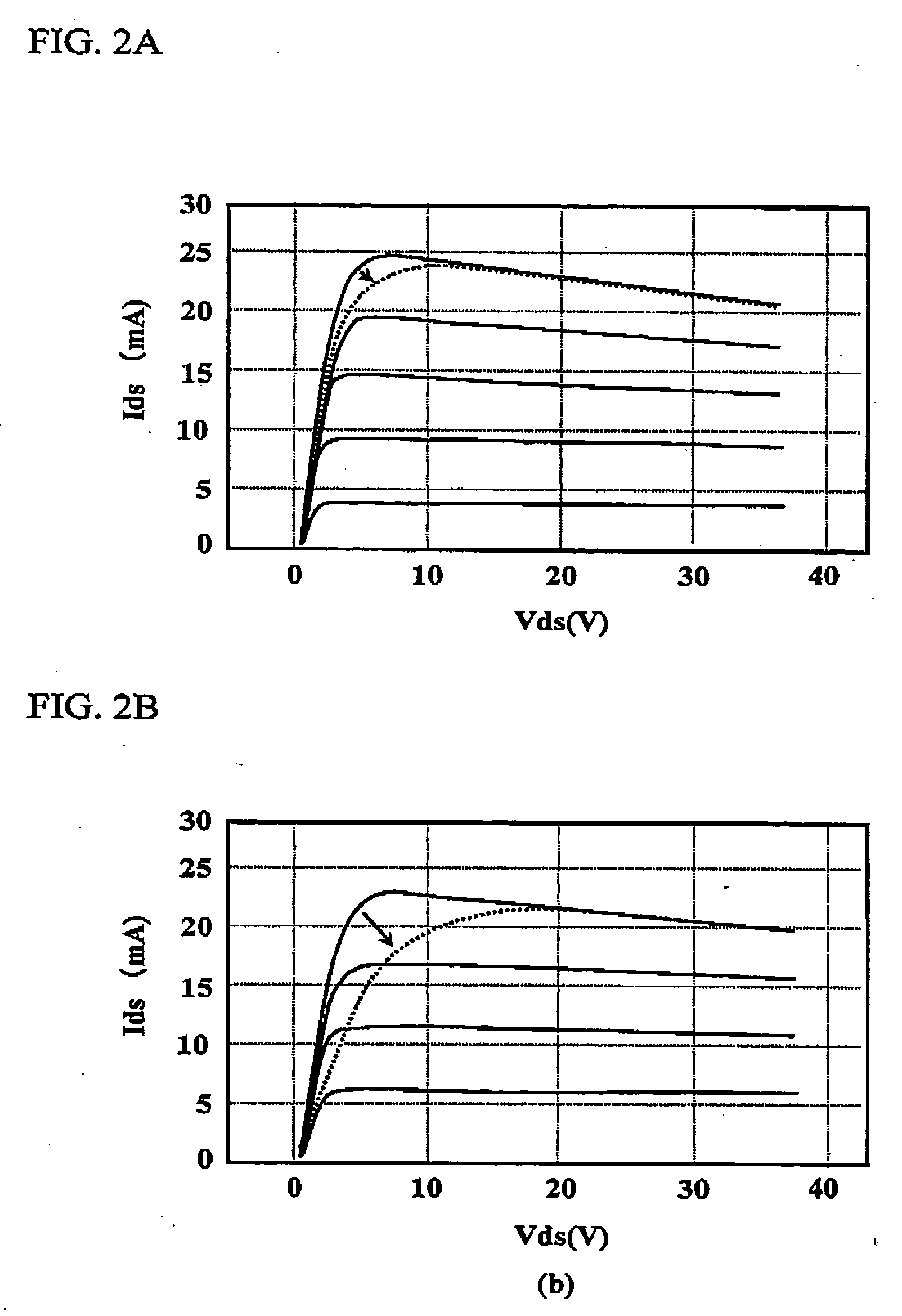
ActiveUS20050221628A1High characteristic requirementEnhanced Vapor DepositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrogen contentNitride semiconductors
A semiconductor device includes a silicon nitride (SiN) film provided on a crystal surface of a nitride semiconductor, the SiN film having a hydrogen content equal to or smaller than 15 percent.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC DEVICE INNOVATIONS
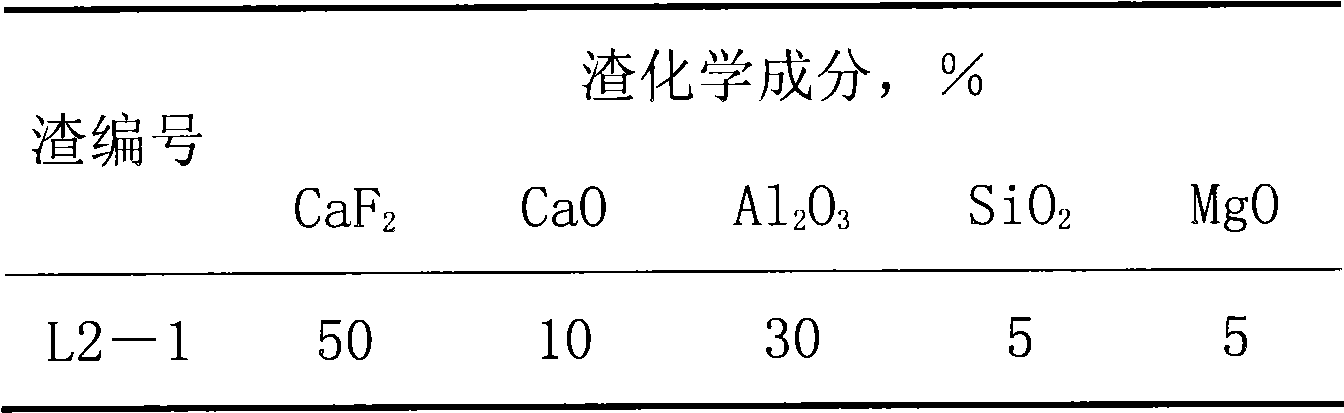
Electroslag remelting slag system with low hydrogen permeability, preparation method and using method thereof
The invention discloses an electroslag remelting slag system with low hydrogen permeability, and a preparation method and a using method thereof. The slag system is prepared from the following chemical compositions in percentage by weight: 45 to 50 percent of CaF2, 10 to 15 percent of CaO, 30 to 35 percent of Al2O3, 5 to 10 percent of SiO2, and 5 to 10 percent of MgO, wherein the MgO is adopted toreplace partial CaO. The preparation method is to crush the compositions into particles after melting, and bake the particles. The using method adopts pre-melting slag and argon protection to carry out electroslag remelting. Compared with the prior art, the slag system and the methods have the advantages that: the slag system has low hydrogen permeability, can effectively reduce the hydrogen content in steel in the remelting initial stage to ensure that the hydrogen content in the steel in the normal remelting stage is maintained at a lower level, and the hydrogen content in the remelted steel is less than 1.5ppm.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com