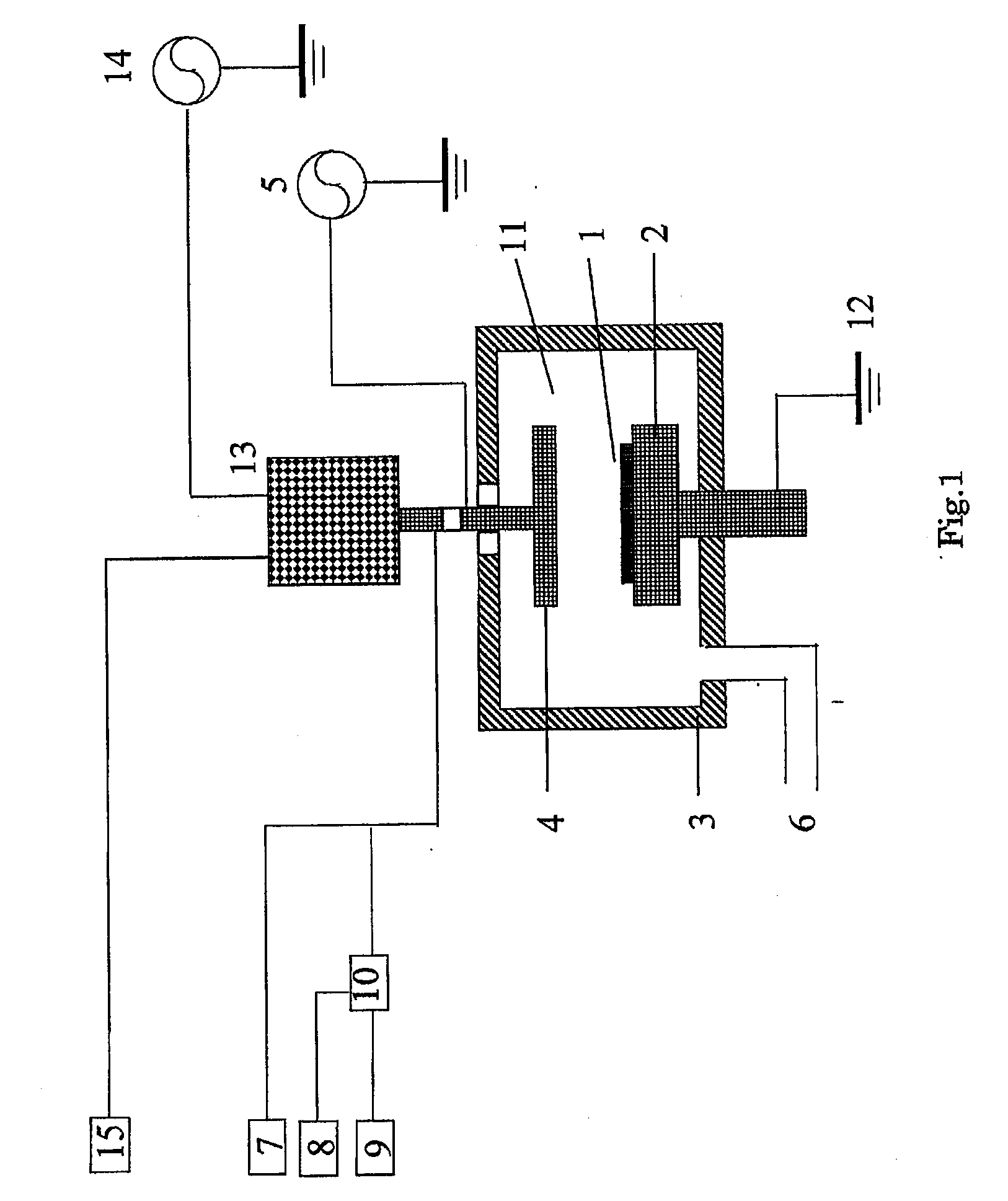
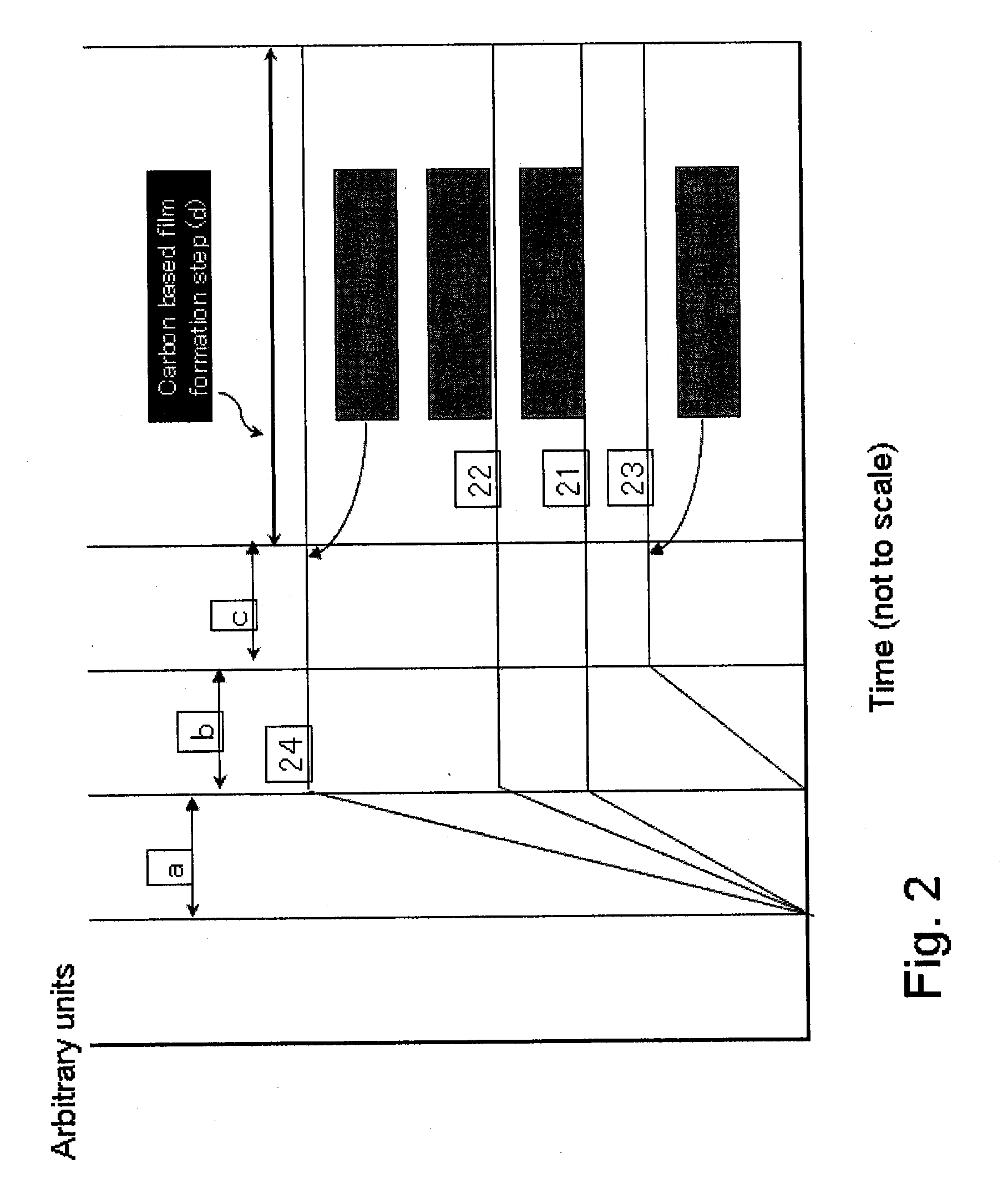
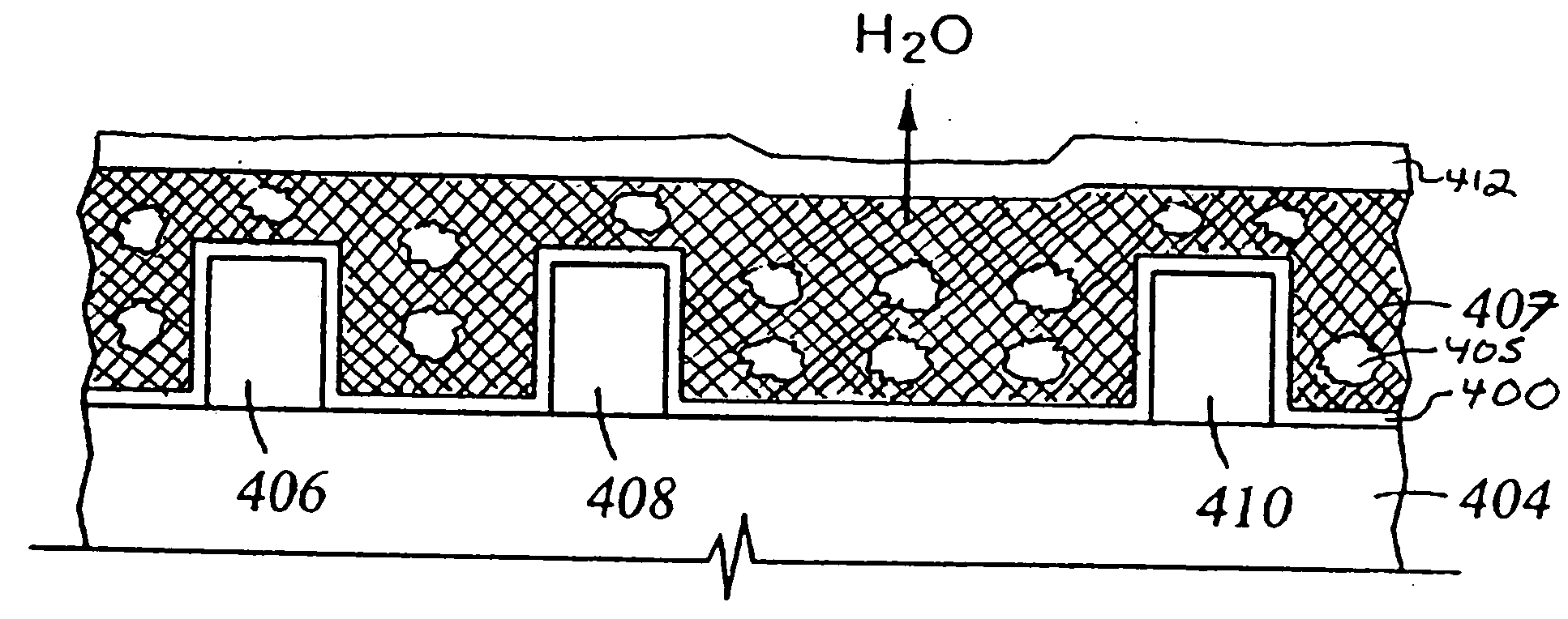
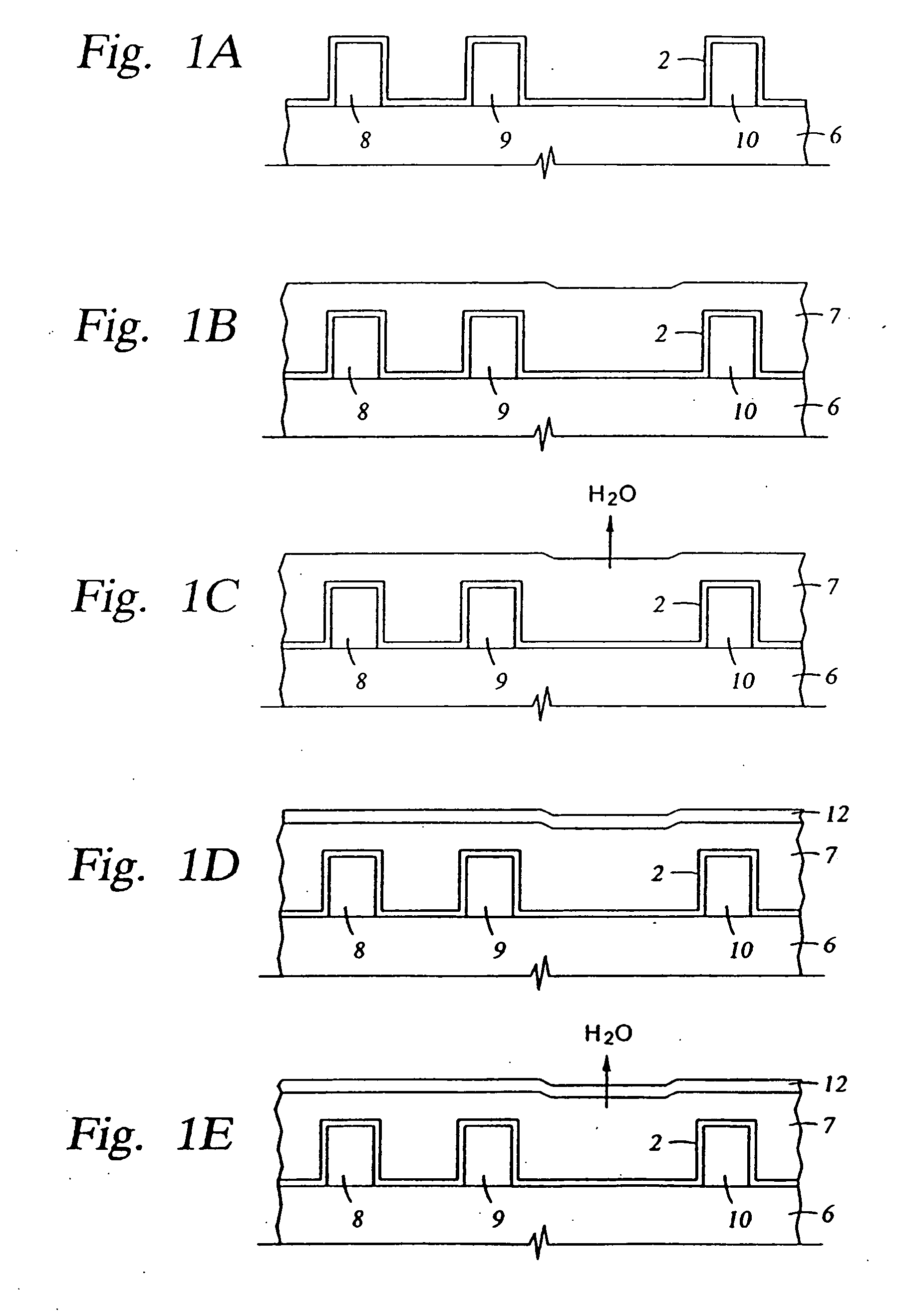
Patents
Literature
50results about How to "Reduce film stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
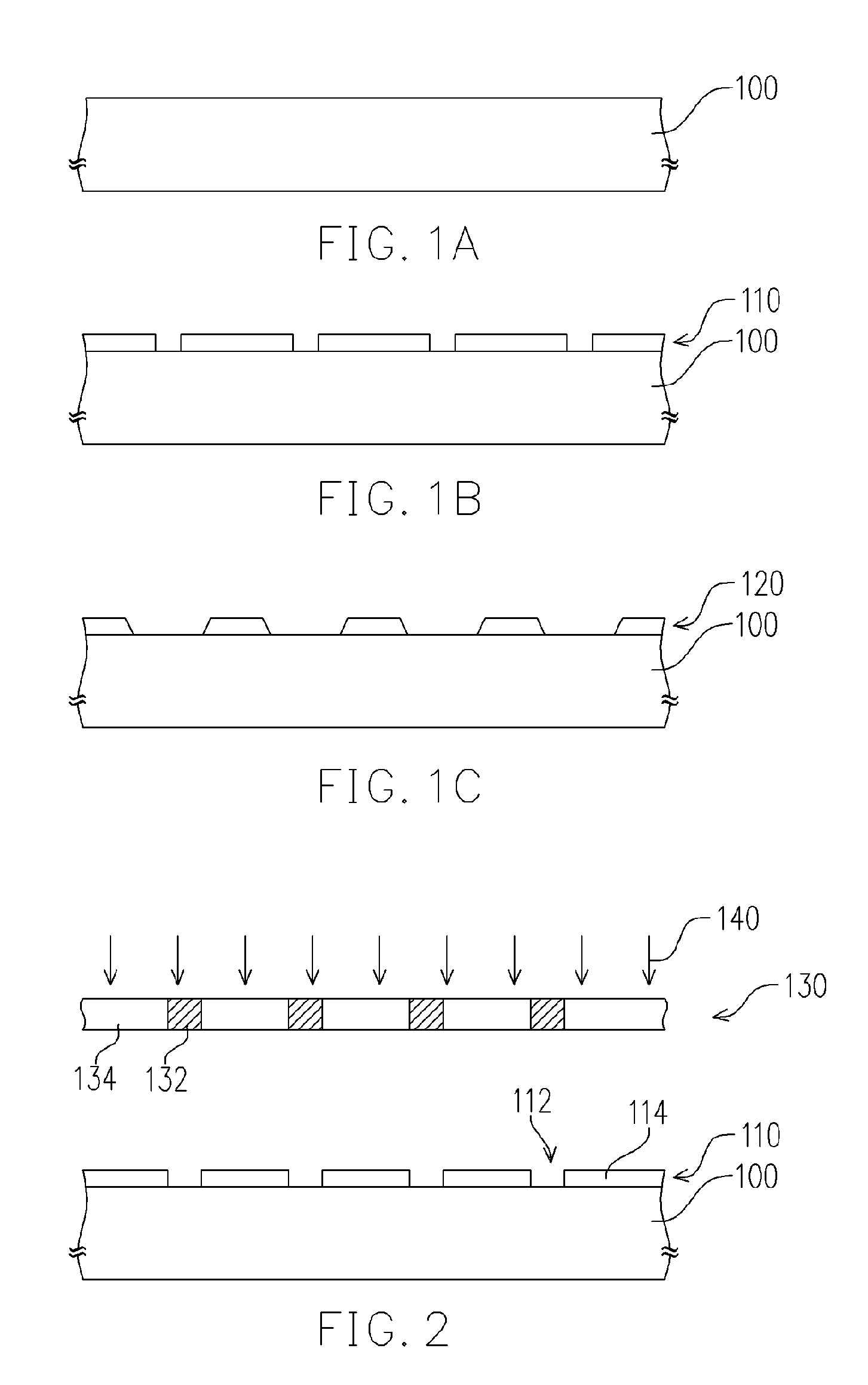
Low temperature formation of high quality silicon oxide films in semiconductor device manufacturing
ActiveUS9847221B1Relieve pressureReduce film stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricDevice material
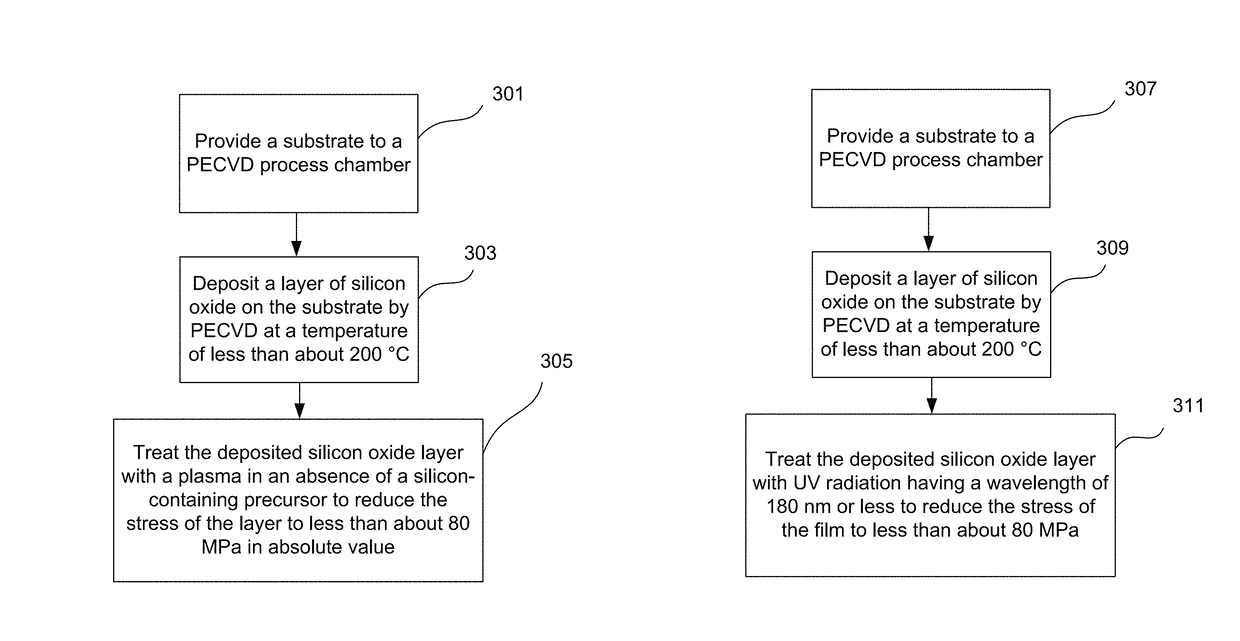
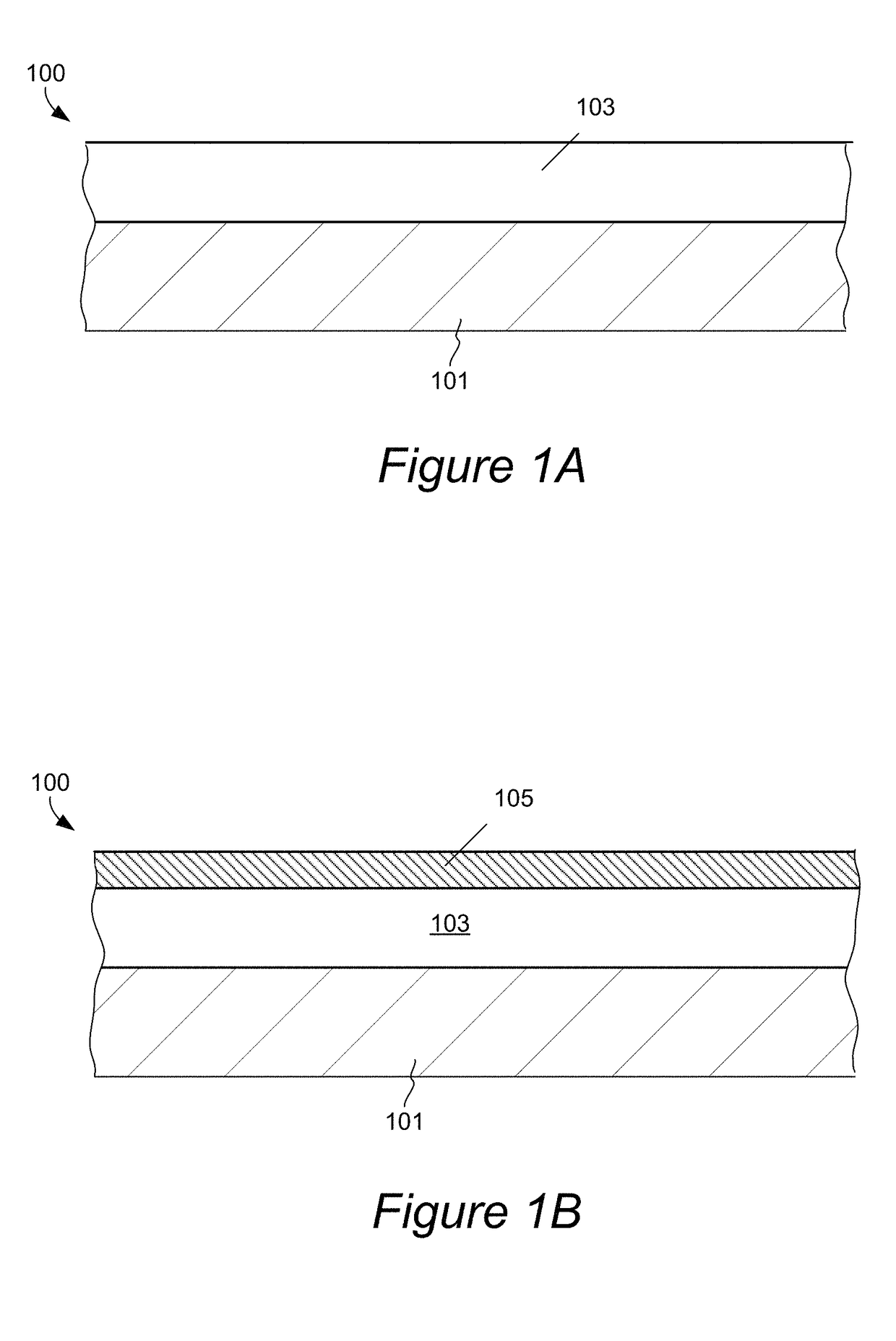
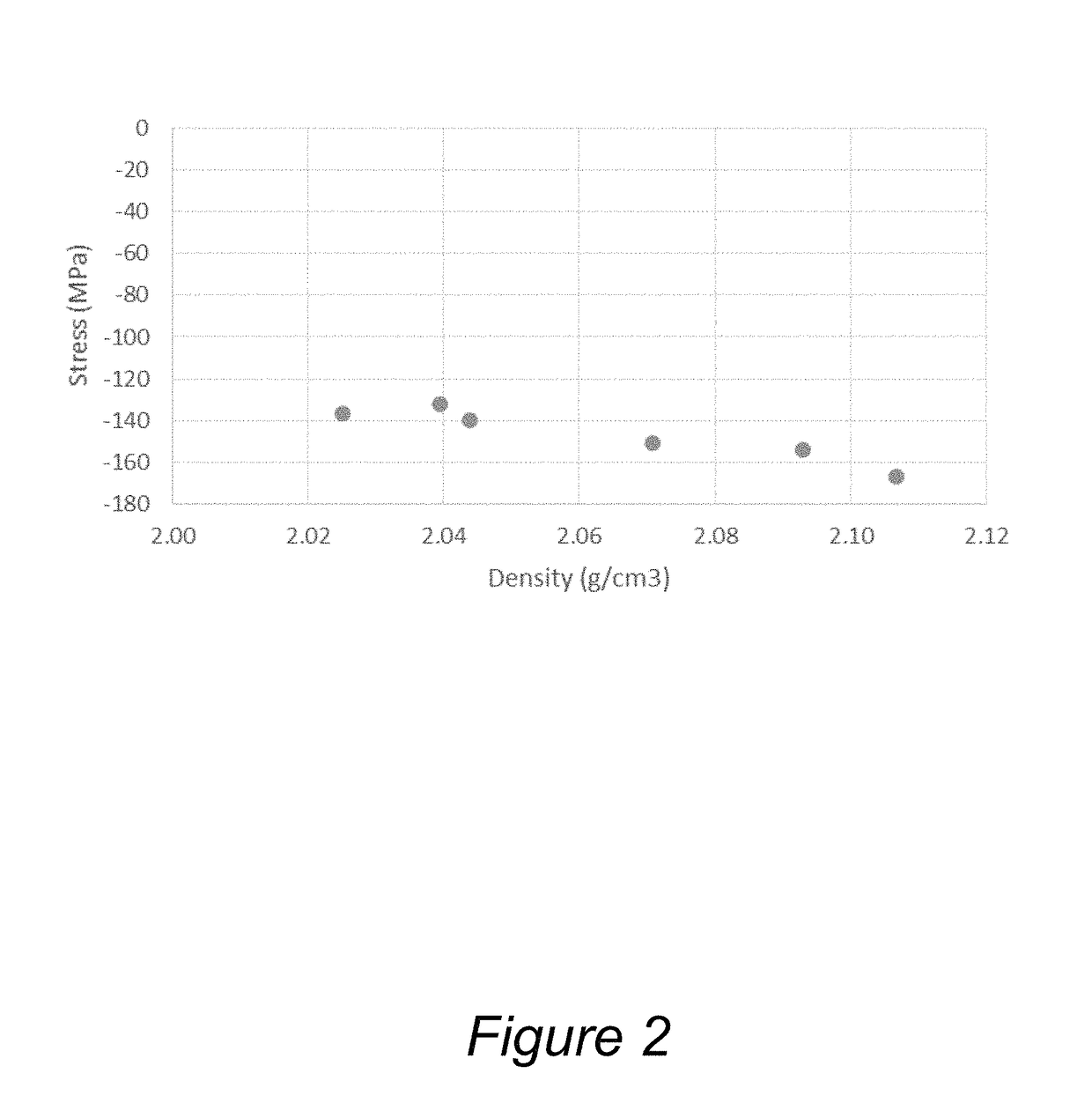
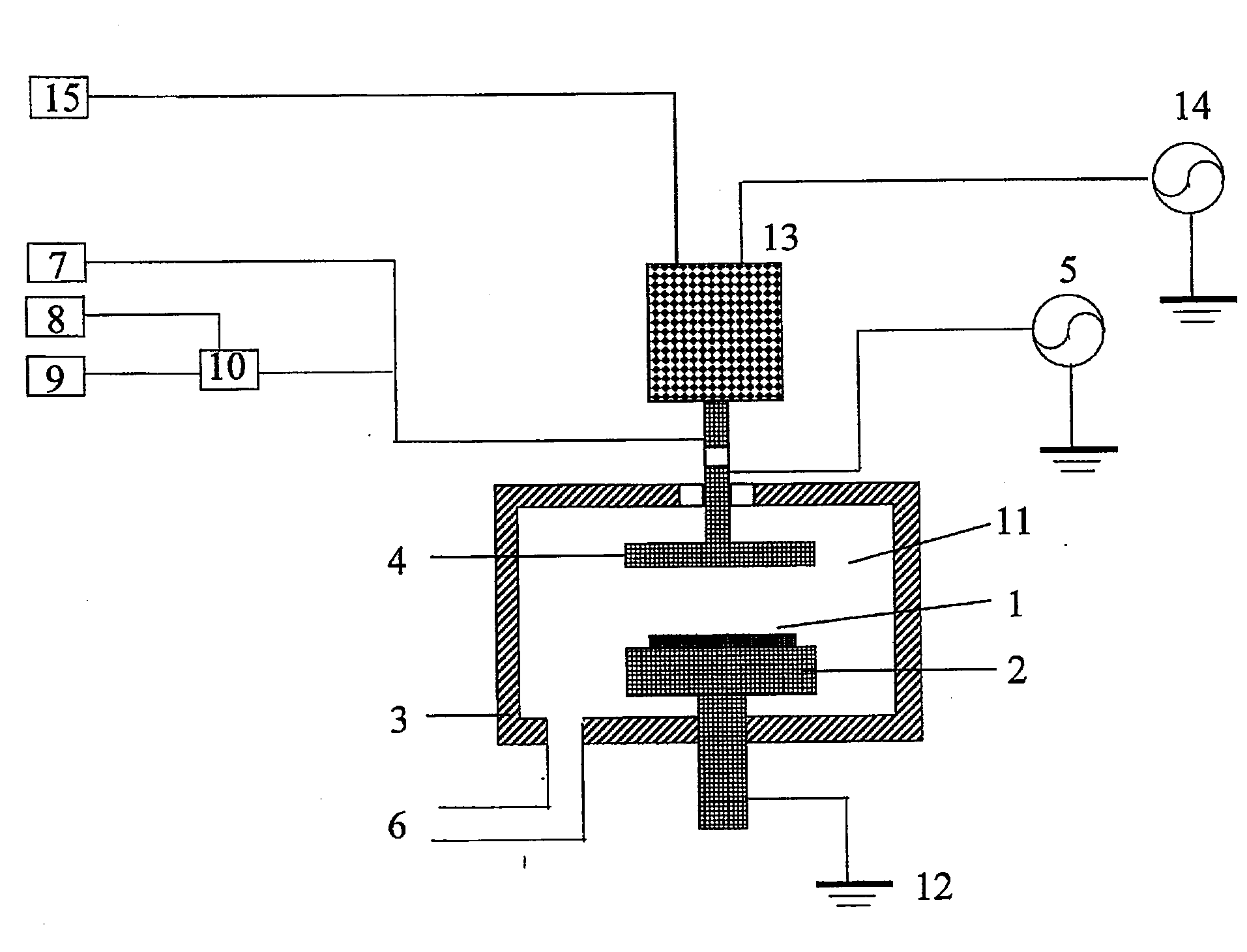
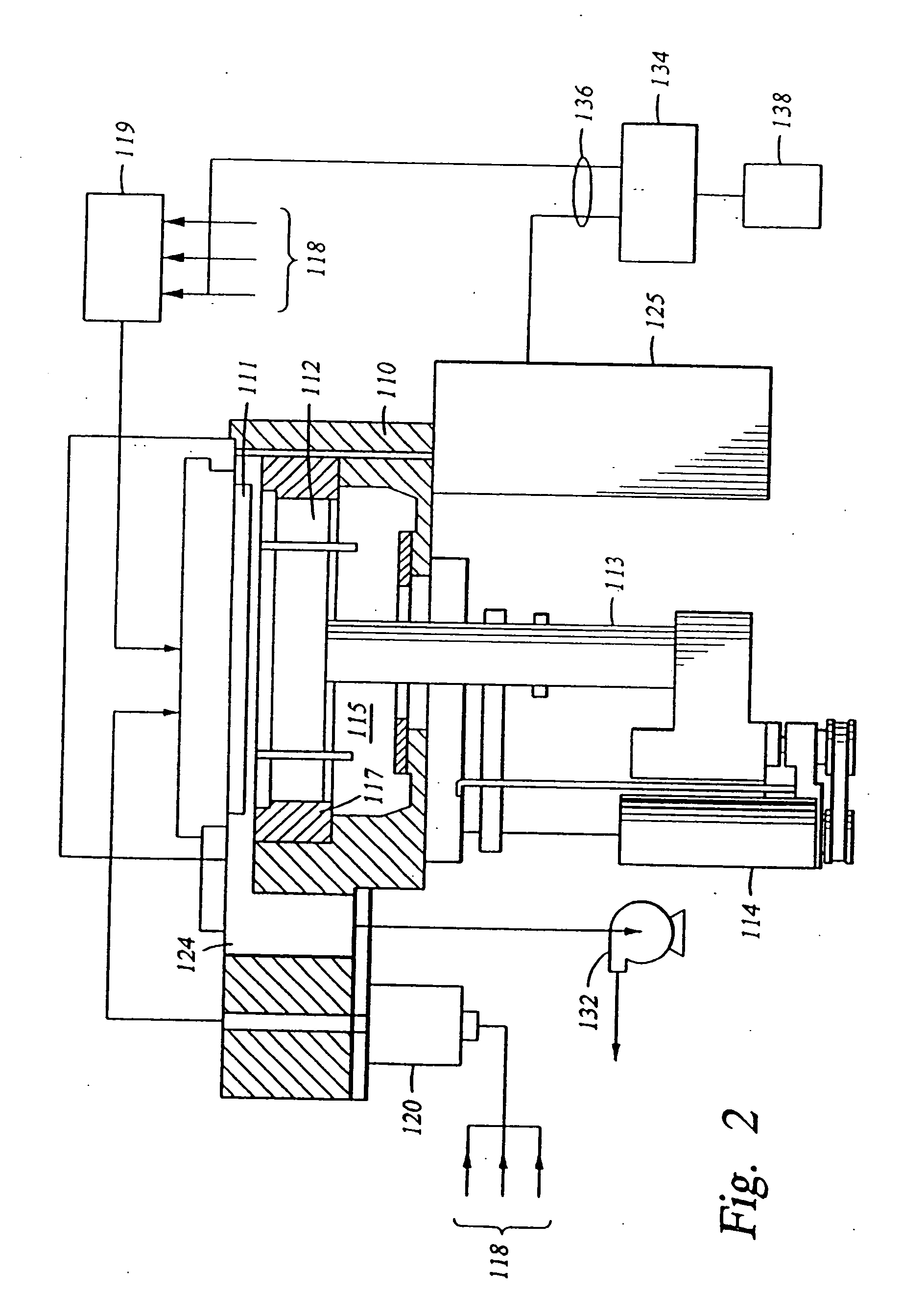
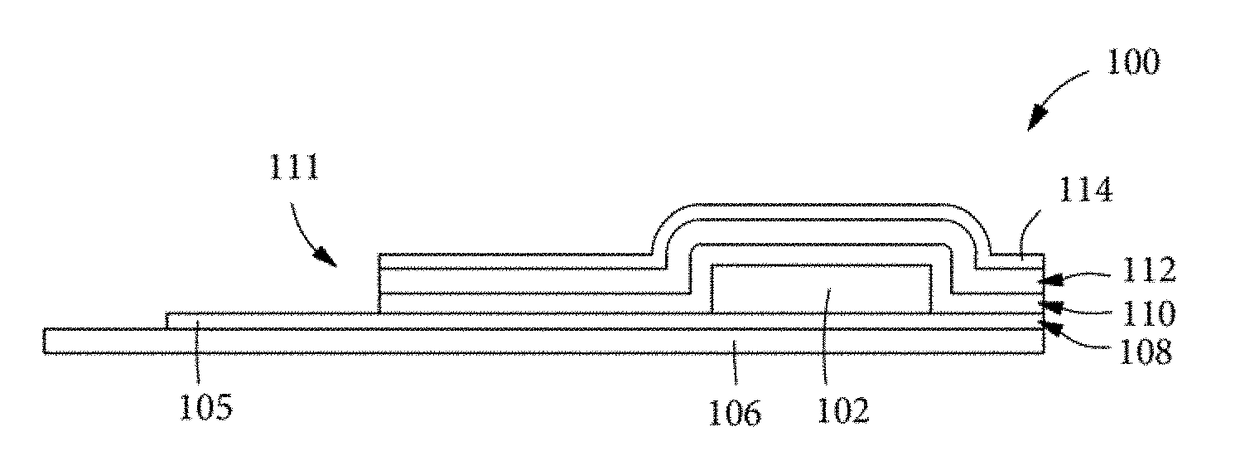
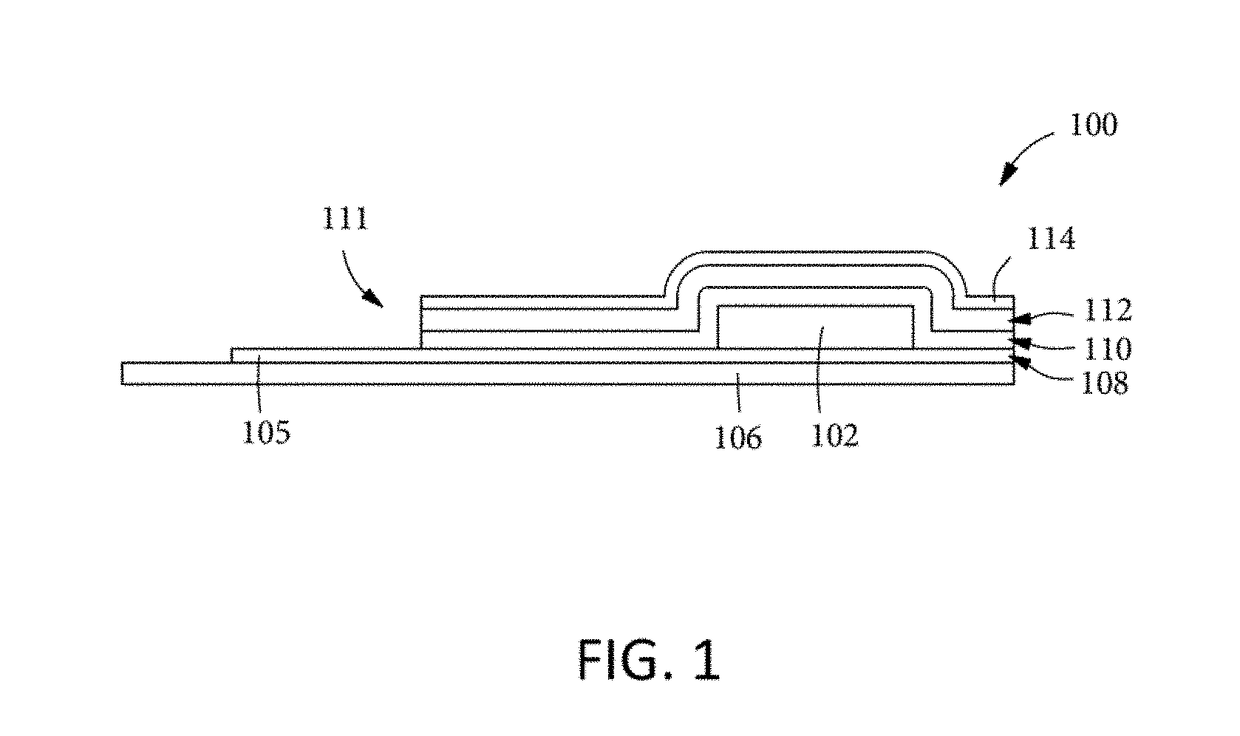
Silicon oxide layer is deposited on a semiconductor substrate by PECVD at a temperature of less than about 200° C. and is treated with helium plasma to reduce stress of the deposited layer to an absolute value of less than about 80 MPa. Plasma treatment reduces hydrogen content in the silicon oxide layer, and leads to low stress films that can also have high density and low roughness. In some embodiments, the film is deposited on a semiconductor substrate that contains one or more temperature-sensitive layers, such as layers of organic material or spin-on dielectric that cannot withstand temperatures of greater than 250° C. In some embodiments the silicon oxide film is deposited to a thickness of between about 100-200 Å, and is used as a hardmask layer during etching of other layers on a semiconductor substrate.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Method of forming hardmask by plasma CVD
InactiveUS20100189923A1Excellent mechanical and optical characteristicFunction increaseLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesCompound (substance)Plasma formation
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Low temperature process to produce low-K dielectrics with low stress by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD)
InactiveUS20060043591A1Reduce film stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseSilicon oxide
Low K dielectric films exhibiting low mechanical stress may be formed utilizing various techniques in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, carbon-containing silicon oxide films are formed by plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition at low temperatures (300° C. or less). In accordance with another embodiment, as-deposited carbon containing silicon oxide films incorporate a porogen whose subsequent liberation reduces film stress.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Capacitor and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20090273882A1Reduce film stressThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor electrodesDielectric layerCapacitor
A capacitor includes a first electrode, a dielectric layer, and a second electrode. The capacitor also includes a buffer layer formed over at least one of an interface between the first electrode and the dielectric layer and an interface between the dielectric layer and the second electrode, wherein the buffer layer includes a compound of a metal element from electrode materials of one of the first and second electrodes and a metal element from materials included in the dielectric layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Low temperature process to produce low-K dielectrics with low stress by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD)
InactiveUS7422776B2Reduce film stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseSilicon oxide
Low K dielectric films exhibiting low mechanical stress may be formed utilizing various techniques in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, carbon-containing silicon oxide films are formed by plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition at low temperatures (300° C. or less). In accordance with another embodiment, as-deposited carbon containing silicon oxide films incorporate a porogen whose subsequent liberation reduces film stress.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Preparation of photomask blank and photomask
ActiveUS20050260505A1Improve chemical resistanceSuppress changesCellsVacuum evaporation coatingFlash-lampResist
A photomask blank is prepared by forming a light-absorbing film on a transparent substrate, and irradiating the light-absorbing film with light from a flash lamp at an energy density of 3 to 40 J / cm2. A photomask is prepared by forming a resist pattern on the photomask blank by photolithography, etching away those portions of the light-absorbing film which are not covered with the resist pattern, and removing the resist.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
LOW k POROUS SiCOH DIELECTRIC AND INTEGRATION WITH POST FILM FORMATION TREATMENT
ActiveUS20120329287A1Reduce and minimize stress changeMinimize impactElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricUnsaturated hydrocarbon
A porous SiCOH dielectric film in which the stress change caused by increased tetrahedral strain is minimized by post treatment in unsaturated Hydrocarbon ambient. The p-SiCOH dielectric film has more —(CHx) and less Si—O—H and Si—H bonding moieties. Moreover, a stable pSiOCH dielectric film is provided in which the amount of Si—OH (silanol) and Si—H groups at least within the pores has been reduced by about 90% or less by the post treatment. A p-SiCOH dielectric film is produced that is flexible since the pores include stabilized crosslinking —(CHx)— chains wherein x is 1, 2 or 3 therein. The dielectric film is produced utilizing an annealing step subsequent deposition that includes a gaseous ambient that includes at least one C—C double bond and / or at least one C—C triple bond.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
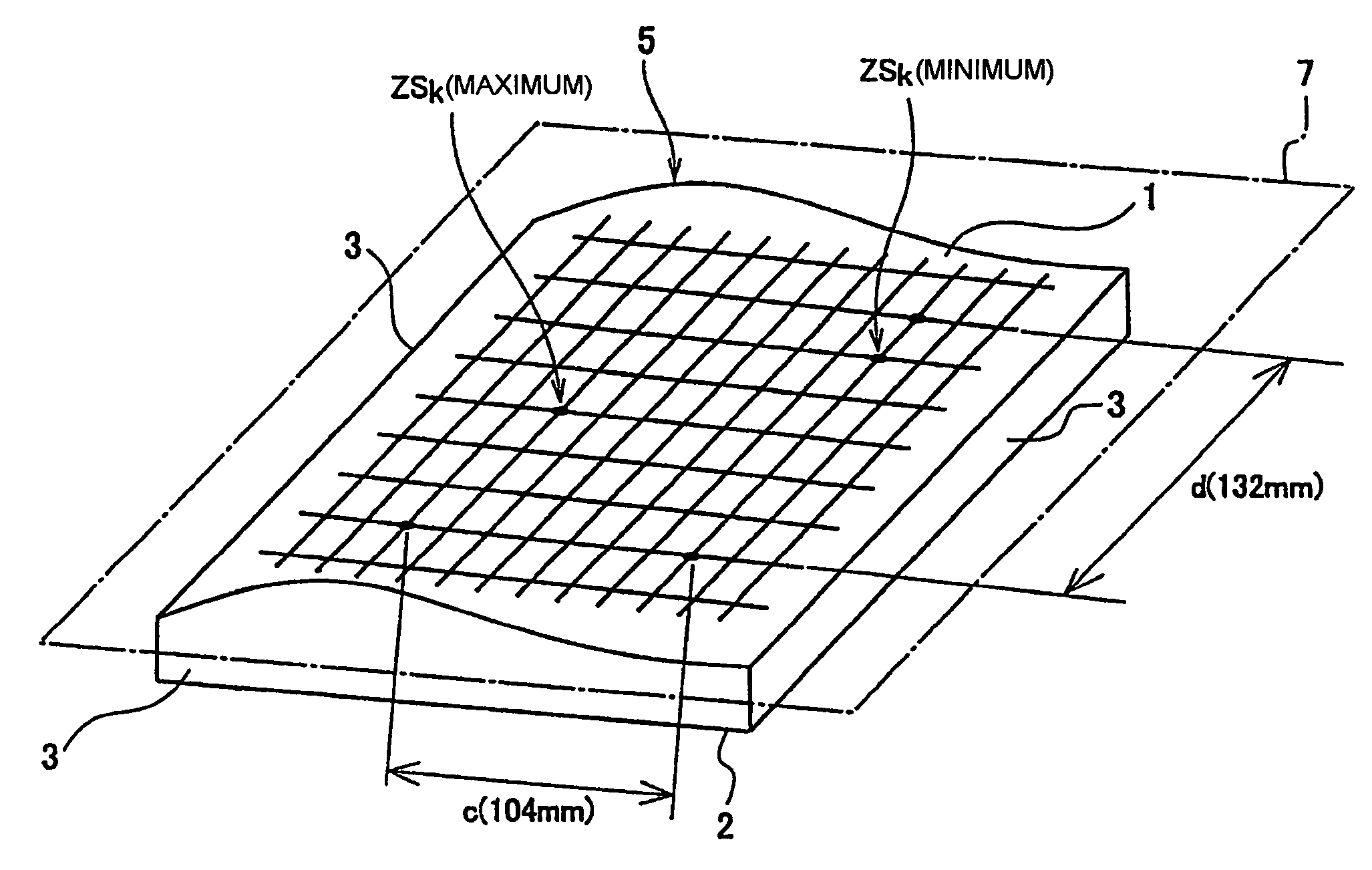
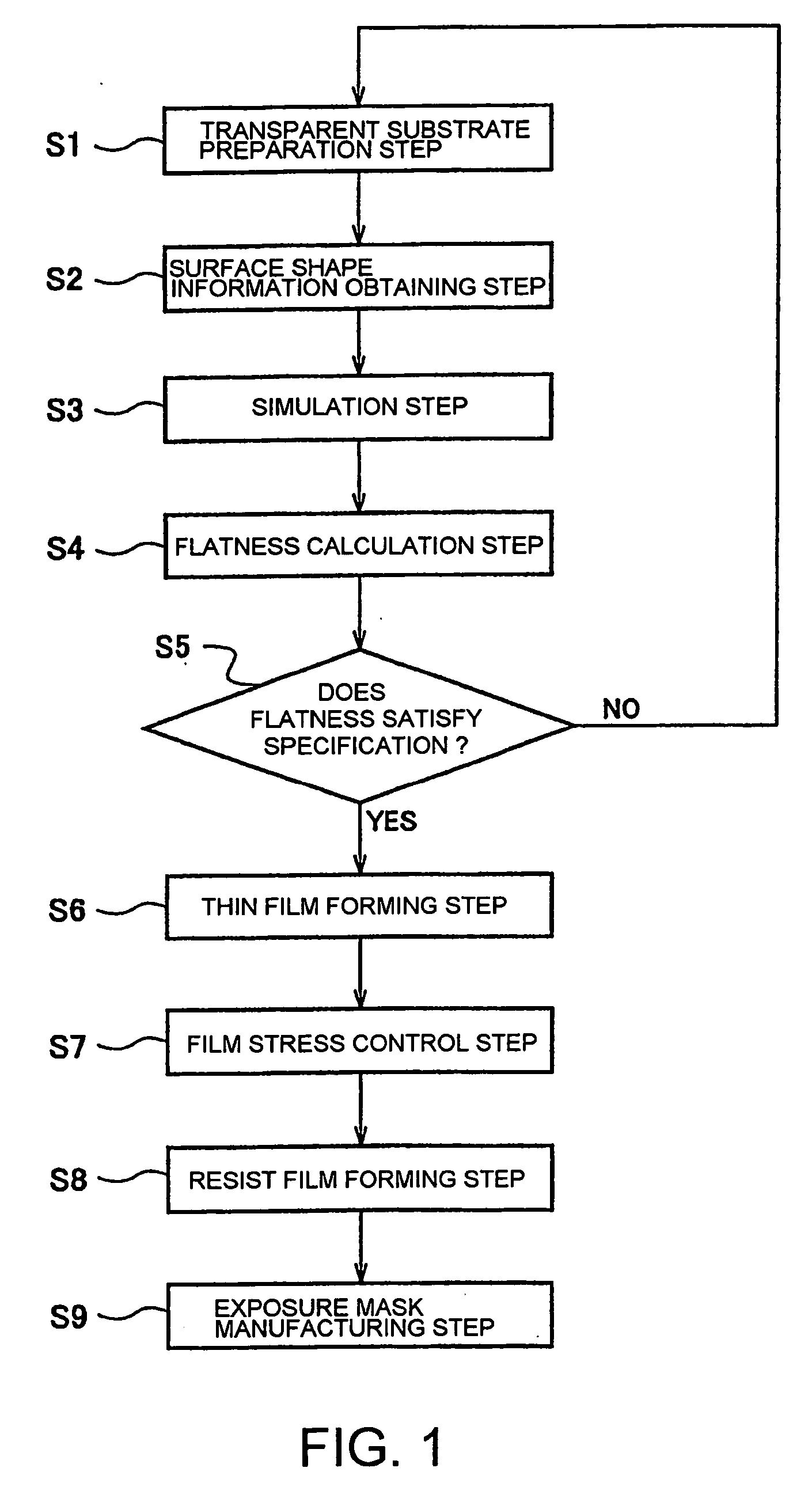
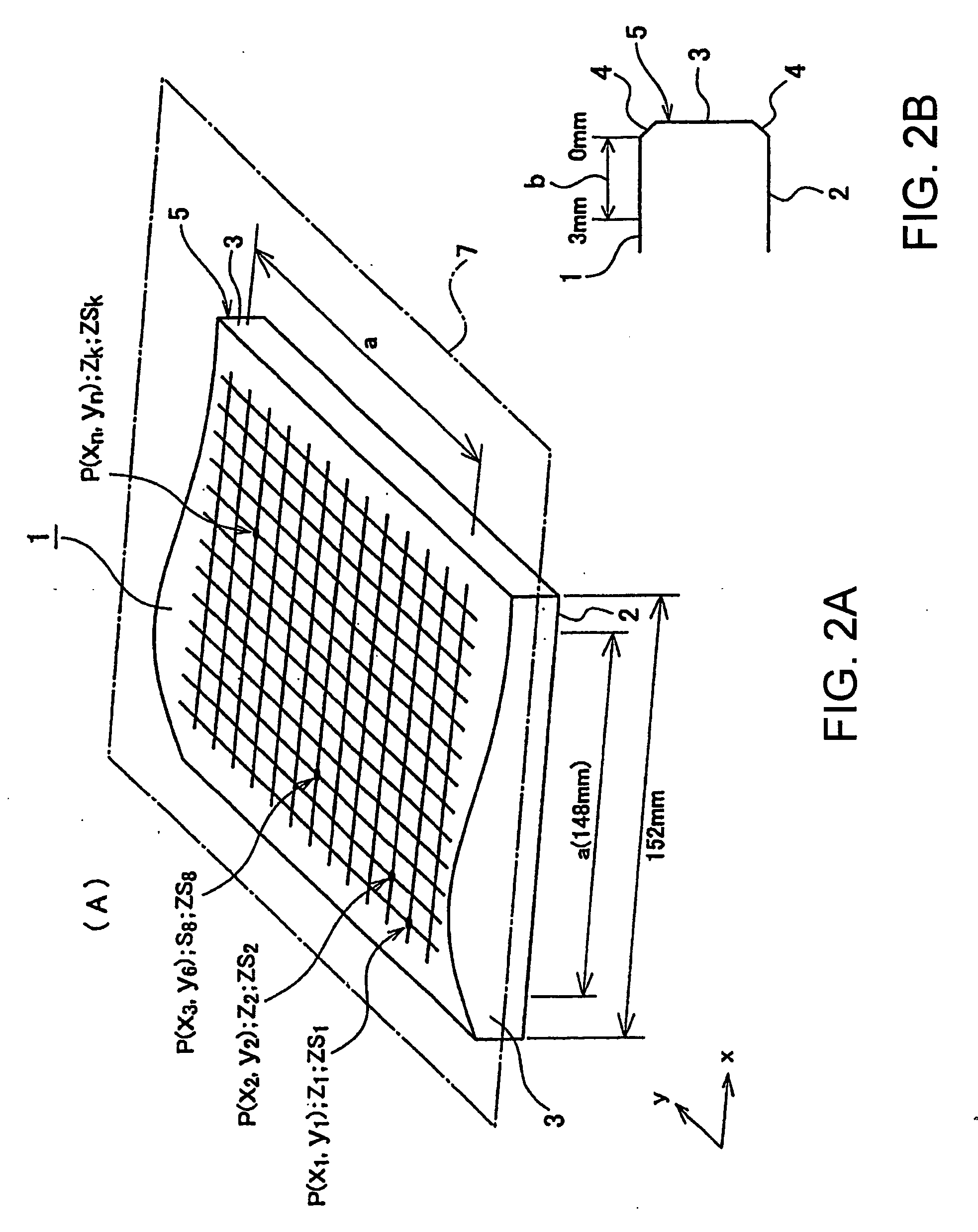
Mask blank transparent substrate manufacturing method, mask blank manufacturing method, and exposure mask manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060194126A1Inhibition of defect generationImprove accuracyPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMeasurement pointEngineering
A method includes a preparation step of preparing a transparent substrate having a precision-polished main surface, a surface shape information obtaining step of obtaining, as surface shape information, height information at a plurality of measurement points on the main surface of the transparent substrate that contacts a mask stage of an exposure apparatus, a simulation step of obtaining, based on the surface shape information and shape information of the mask stage, height information at the plurality of measurement points by simulating the state where the transparent substrate is set in the exposure apparatus, a flatness calculation step of calculating, based on the height information obtained through the simulation, a flatness of the transparent substrate when it is set in the exposure apparatus, a judging step of judging whether or not the calculated flatness satisfies a specification, and a thin film forming step of forming a thin film as serving as a mask pattern, on the main surface of the transparent substrate whose flatness satisfies the specification.
Owner:HOYA CORP
3D printed chamber components configured for lower film stress and lower operating temperature
ActiveUS20160233060A1Reduce film stressAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge tubesOperating temperature3d printed
A chamber component for a processing chamber is disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a chamber component for a processing chamber includes a component part body having unitary monolithic construction. The component part body has a textured surface. The textured surface includes a plurality of independent engineered macro features integrally formed with the component part body. The engineered macro features include a macro feature body extending from the textured surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Nanolaminate thin films and method for forming the same using atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20060216548A1High quality nanolaminate thin film have been substantially reduced or eliminatedImprove dielectric breakdown strengthLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsSilicon dioxide
A nanolaminate thin film and a method for forming the same using atomic layer deposition are disclosed. The method includes forming an aluminum oxide layer having a first thickness on at least a portion of a substrate surface by sequentially pulsing a first precursor and a first reactant into an enclosure containing the substrate. A layer of silicon dioxide is formed on at least a portion of the aluminum oxide layer by sequentially pulsing a second precursor and a second reactant into the enclosure to form a nanolaminate thin film.
Owner:VEECO INSTR +1
LOW k POROUS SiCOH DIELECTRIC AND INTEGRATION WITH POST FILM FORMATION TREATMENT
InactiveUS20090061649A1LessIncrease strainElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricUnsaturated hydrocarbon
A porous SiCOH (e.g., p-SiCOH) dielectric film in which the stress change caused by increased tetrahedral strain is minimized by post treatment in unsaturated Hydrocarbon ambient. The inventive p-SiCOH dielectric film has more —(CHx) and less Si—O—H and Si—H bondings as compared to prior art p-SiCOH dielectric films. Moreover, a stable pSiOCH dielectric film is provided in which the amount of Si—OH (silanol) and Si—H groups at least within the pores has been reduced by about 90% or less by the post treatment. Hence, the inventive p-SiCOH dielectric film has hydrophobicity improvement as compared with prior art p-SiCOH dielectric films. In the present invention, a p-SiCOH dielectric film is produced that is flexible since the pores of the inventive film include stabilized crosslinking —(CHx)— chains wherein x is 1, 2 or 3 therein. The dielectric film is produced utilizing an annealing step subsequent deposition that includes a gaseous ambient that includes at least one C—C double bond and / or at least one C—C triple bond.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
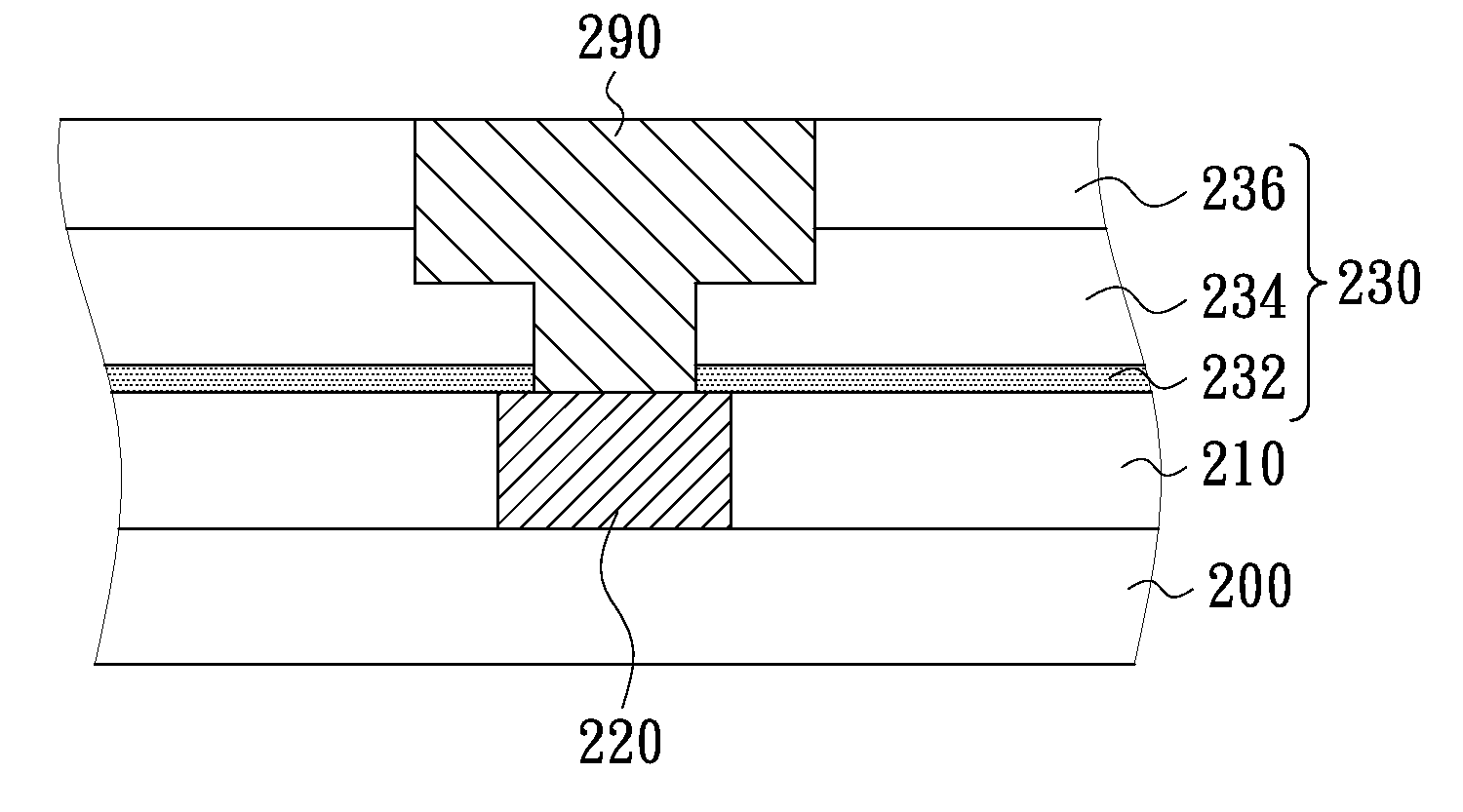
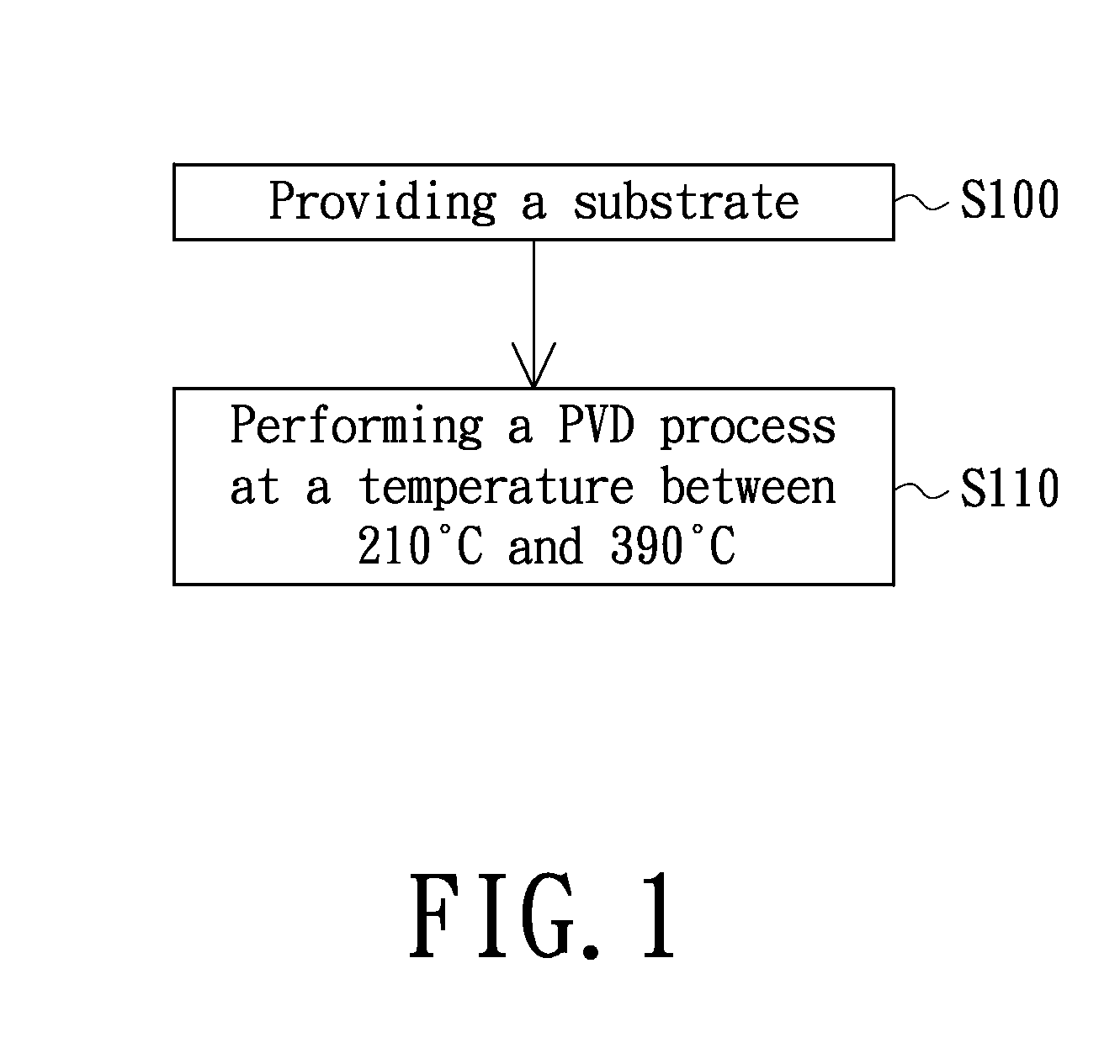
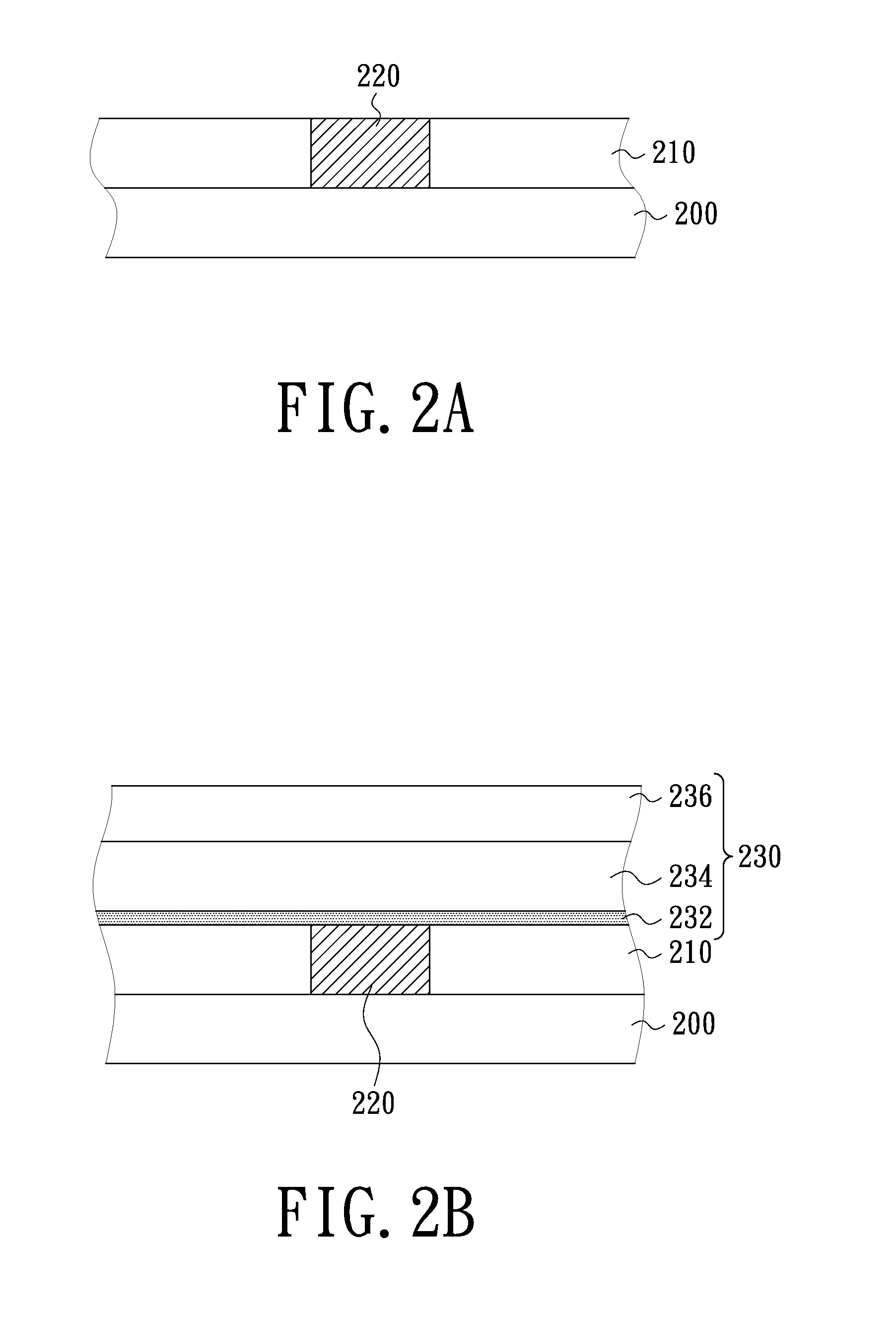
Method for manufacturing interconnection structure and of metal nitride layer thereof
InactiveUS20120270389A1Reduce film stressAvoid distortionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGas phaseInterconnection
A method for manufacturing a metal nitride layer including the following steps is provided. Firstly, a substrate is provided. Then, a physical vapor deposition process is performed at a temperature between 210° C. and 390° C. to form a metal nitride layer on the substrate. Also, the physical vapor deposition process can be performed on a pressure between 21 mTorr and 91 mTorr. The method can be used in the manufacturing process of an interconnection structure for decreasing the film stress of the metal nitride layer. Therefore, the interconnection structure can be prevented from line distortion and film collapse.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Multilayer ceramic electronic component
ActiveUS20090268374A1Low film stressHigh effective volume fractionFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricMetallurgyElectron
A multilayer ceramic electronic component includes a laminate including a stack of a plurality of ceramic layers and a plurality of internal electrodes extending along interfaces between the ceramic layers, and a plurality of external electrodes electrically connecting the internal electrodes exposed at surfaces of the laminate. Each external electrode includes a plating layer at least at the portion directly connected to the internal electrodes. The plating layer has a compressive film stress of about 100 MPa or less or a tensile film stress of about 100 MPa or less.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method of, and apparatus for, forming hard mask
ActiveUS20150228496A1Little film stressIncrease film densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTitanium nitrideOxygen
A method of forming a hard mask includes depositing step for depositing a titanium nitride film on a surface of a to-be-processed object; adsorbing step for adsorbing oxygen-containing molecules onto a surface of the titanium nitride film; and heating step for heating the titanium nitride film to a predetermined temperature.
Owner:ULVAC INC
Preparation of photomask blank and photomask
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for forming patterns and thin film transistors
InactiveUS20070105393A1Reduce film stressImprove yieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsPellicle membrane
A method for forming a pattern is provided. First, a substrate is provided. Then, a discontinuous film is formed on the substrate so as to reduce the stress of the film. After that, the discontinuous film is patterned to form a pattern. Besides, a method for manufacturing a thin film transistor (TFT) is also provided. First, a substrate is provided. Then, a poly silicon island is formed on the substrate. After that, a gate insulating layer is formed to cover the poly silicon island. Then, a gate is formed on the gate insulating layer. After that, a source / drain is formed in the poly silicon island below one side and the other side of the gate respectively, and a channel layer is formed between the source / drain. At least one of the poly silicon island and the gate is formed according to the above mentioned method for forming the pattern.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Method for treating surface of magnesium or magnesium alloy
InactiveUS20060237326A1High film forming rateLow dissolution rateAnodisationAnodizingVolumetric Mass Density
A method for surface treatment is disclosed. The method is achieved by forming a MgO film on a metal surface through anode processing of Mg or Mg alloy in an alkaline solution. The alkaline solution includes a hydroxide, a thickening agent, and a film adjusting agent. As the method is performed, the target object is immersed in the alkaline solution, and the target object is connected to an anode with an average electric current density of 1˜5 A / dm, at a temperature of 0˜30° C., and within a time period of 10˜120 minutes to form a film of 5˜25 μm. The forming rate of the film of the method of the present invention is fast, and the formed film is of little stress.
Owner:CHUNG CHENG INST TECH
Reflective mask blank for EUV lithography, and reflective layer-coated substrate for EUV lithography
ActiveUS20140234756A1Improve reflectivityReduce film stressOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPhysicsLithography
To provide a mask blank for EUVL wherein the incident angle dependence of EUV reflectivity and the film stress in a Mo / Si multilayer reflective film are improved, and a reflective layer-equipped substrate for such a mask blank. The reflective layer-equipped substrate for EUV lithography (EUVL), comprises a substrate, and a reflective layer for reflecting EUV light, formed on the substrate, wherein the reflective layer comprises a second multilayer reflective film having a Mo layer and a Si layer alternately stacked plural times on the substrate, an adjustment layer stacked on the second multilayer reflective film, and a first multilayer reflective film having a Mo layer and a Si layer alternately stacked plural times on the adjustment layer.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Method for reducing the intrinsic stress of high density plasma films
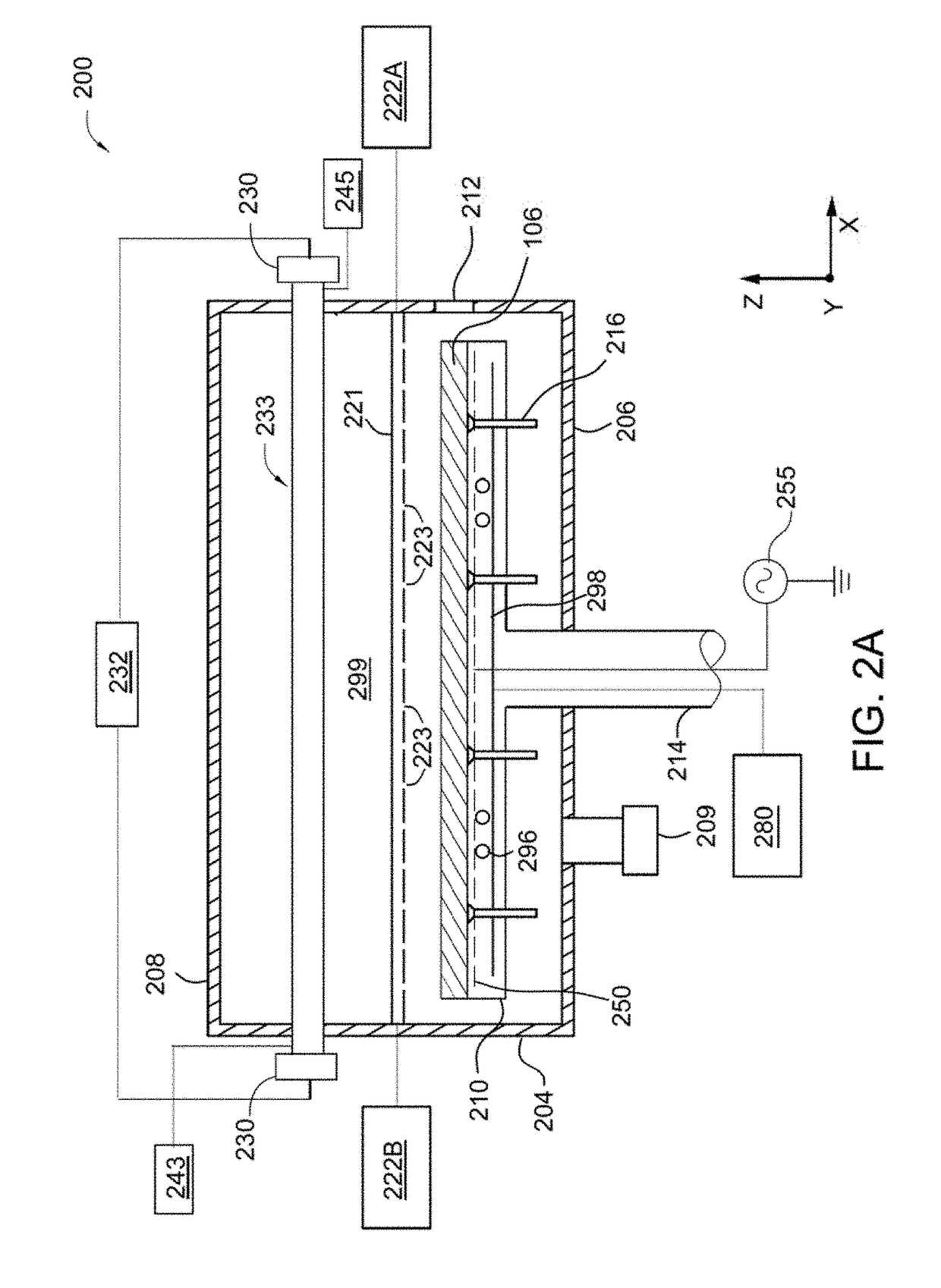
InactiveUS7294205B1Extended processing timeReduce film stressLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceHigh density
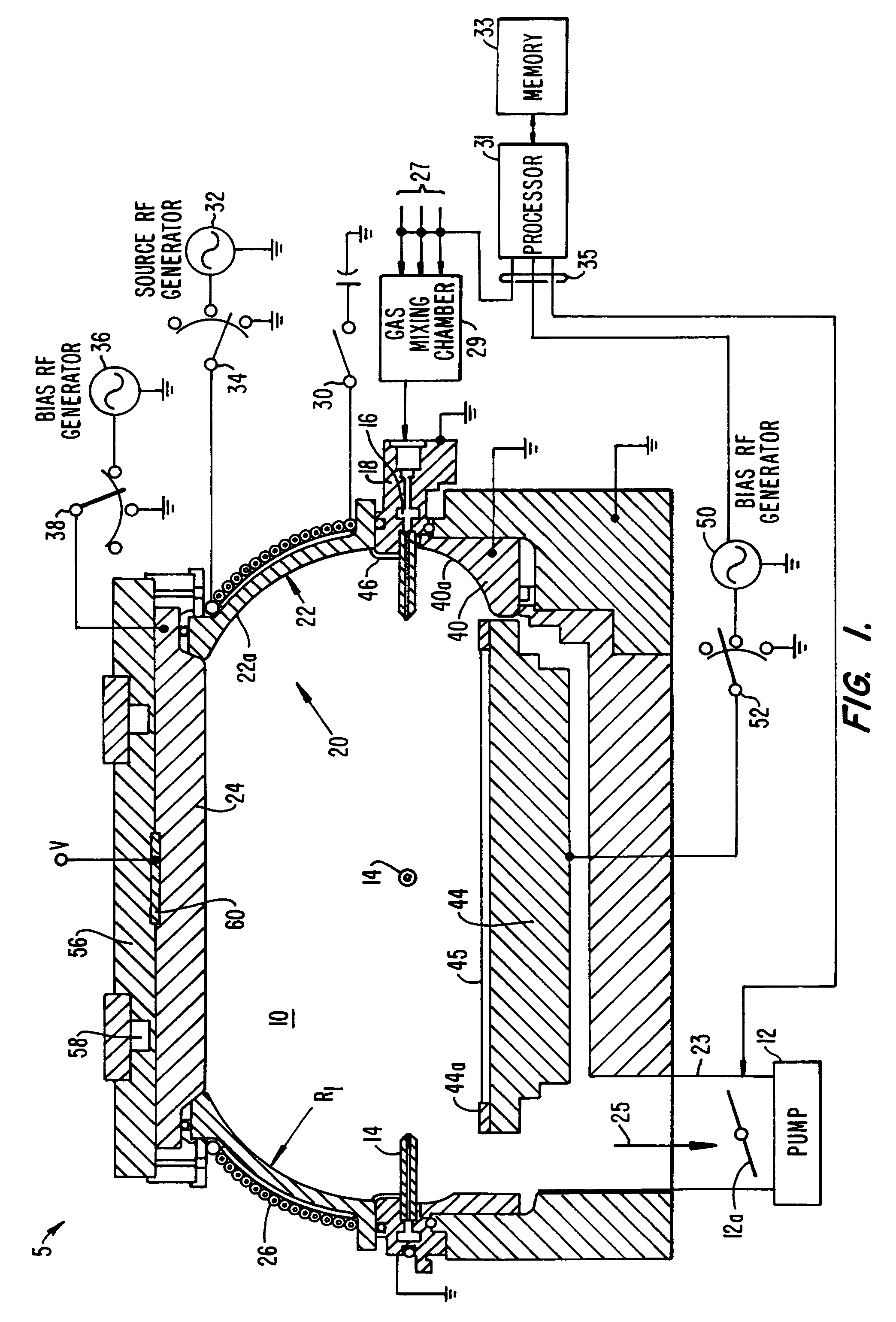
A layer of reduced stress is formed on a substrate using an HDP-CVD system by delaying or interrupting the application of capacitively coupled RF energy. The layer is formed by introducing a process gas into the HDP system chamber and forming a plasma from the process gas by the application of RF power to an inductive coil. After a selected period, a second layer of the film is deposited by maintaining the inductively-coupled plasma and biasing the plasma toward the substrate to enhance the sputtering effect of the plasma. In a preferred embodiment, the deposited film is a silicon oxide film, and biasing is performed by application of capacitively coupled RF power from RF generators to a ceiling plate electrode and wafer support electrode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Photonic- and Phononic-structured pixel for electromagnetic radiation and detection
InactiveUS20200191655A1Low thermal conductivityReduce film stressThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsNanowireSpectral response
A thermal pixel configured as an electromagnetic emitter and / or an electromagnetic detector operating within a limited bandwidth. The thermal pixel comprises a micro-platform thermally isolated from a surrounding off-platform region by phononic nanowires. In embodiments, the micro-platform is comprised of metamaterial and / or photonic crystal filters providing operation over a limited bandwidth. In other embodiments, the micro-platform is comprised of nanotube structure providing a broadband emission / absorption spectral response. Structural configurations for the pixel take advantage of the Kirchhoff law of thermal radiation which states that a good thermal emitter is also a good absorber. In a preferred embodiment the pixel is fabricated using a silicon SOI starting wafer.
Owner:CARR WILLIAM N
Optical element for x-ray
InactiveUS20090148695A1Good optical performanceSuppress surface shapeRadiation/particle handlingLayered productsSoft x rayX-ray
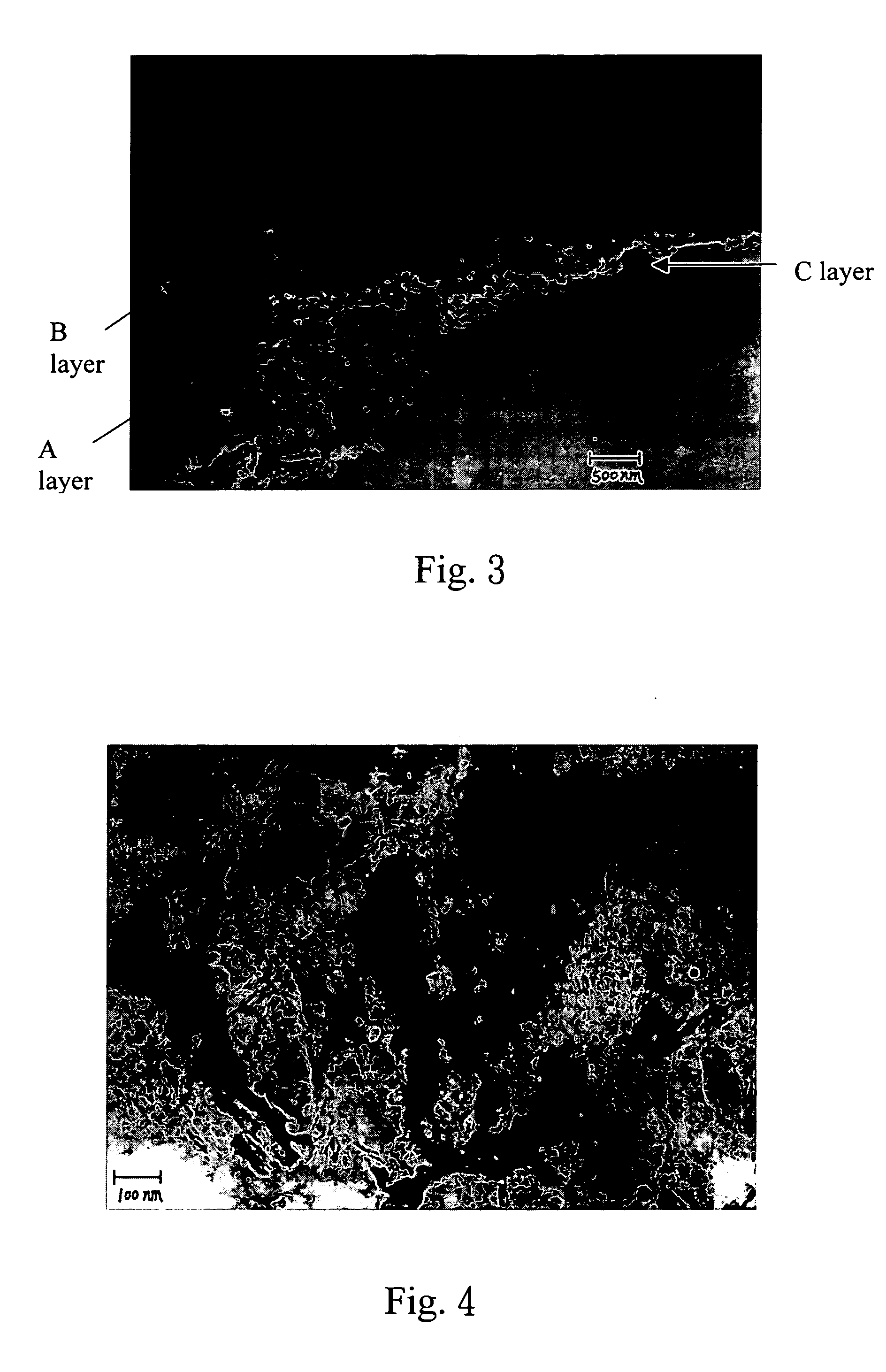
An optical element for X-ray includes a substrate, a first multilayer film having a reflection property with respect to light in a soft X-ray wavelength range, and a second multilayer film, disposed between the substrate and the first multilayer film, for reducing film stress of the first multilayer film. The second multilayer film has a periodic structure having a unit period film thickness which is 90% or more and less than 110% of a two or more integral multiple of 7 nm.
Owner:CANON KK
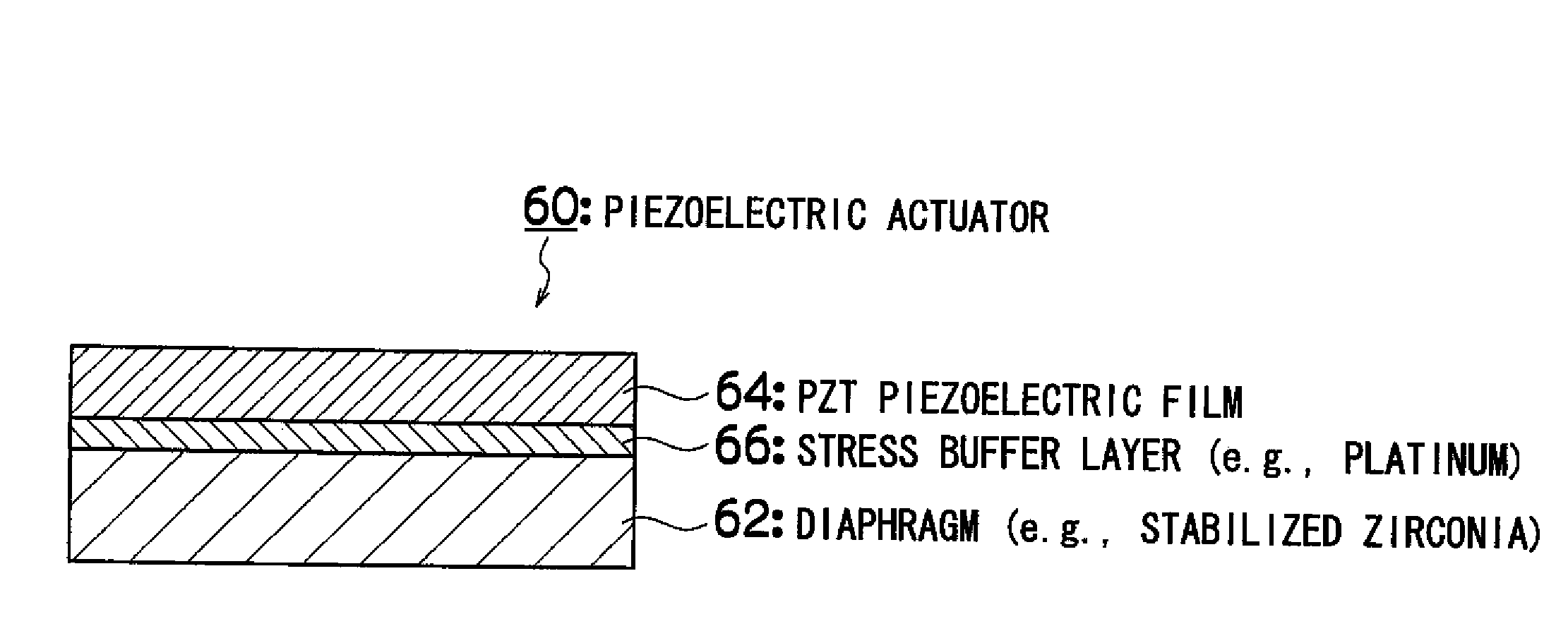
Piezoelectric actuator, method of manufacturing same, and liquid ejection head
InactiveUS20080238263A1Reduce film stressRelieve pressurePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric actuatorsRoom temperature
The piezoelectric actuator comprises: a supporting substrate; a thermal stress controlling layer which is formed on the supporting substrate; and a piezoelectric body which is formed as a film onto the thermal stress controlling layer on the supporting substrate at a higher temperature than room temperature, wherein the thermal stress controlling layer reduces a film stress induced by formation of the piezoelectric body.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Multilayer ceramic electronic component including external electrodes that include a plating layer having a low film stress
ActiveUS8154848B2Reduce film stressMeet high volumeFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricMetallurgyElectronic component
A multilayer ceramic electronic component includes a laminate including a stack of a plurality of ceramic layers and a plurality of internal electrodes extending along interfaces between the ceramic layers, and a plurality of external electrodes electrically connecting the internal electrodes exposed at surfaces of the laminate. Each external electrode includes a plating layer at least at the portion directly connected to the internal electrodes. The plating layer has a compressive film stress of about 100 MPa or less or a tensile film stress of about 100 MPa or less.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
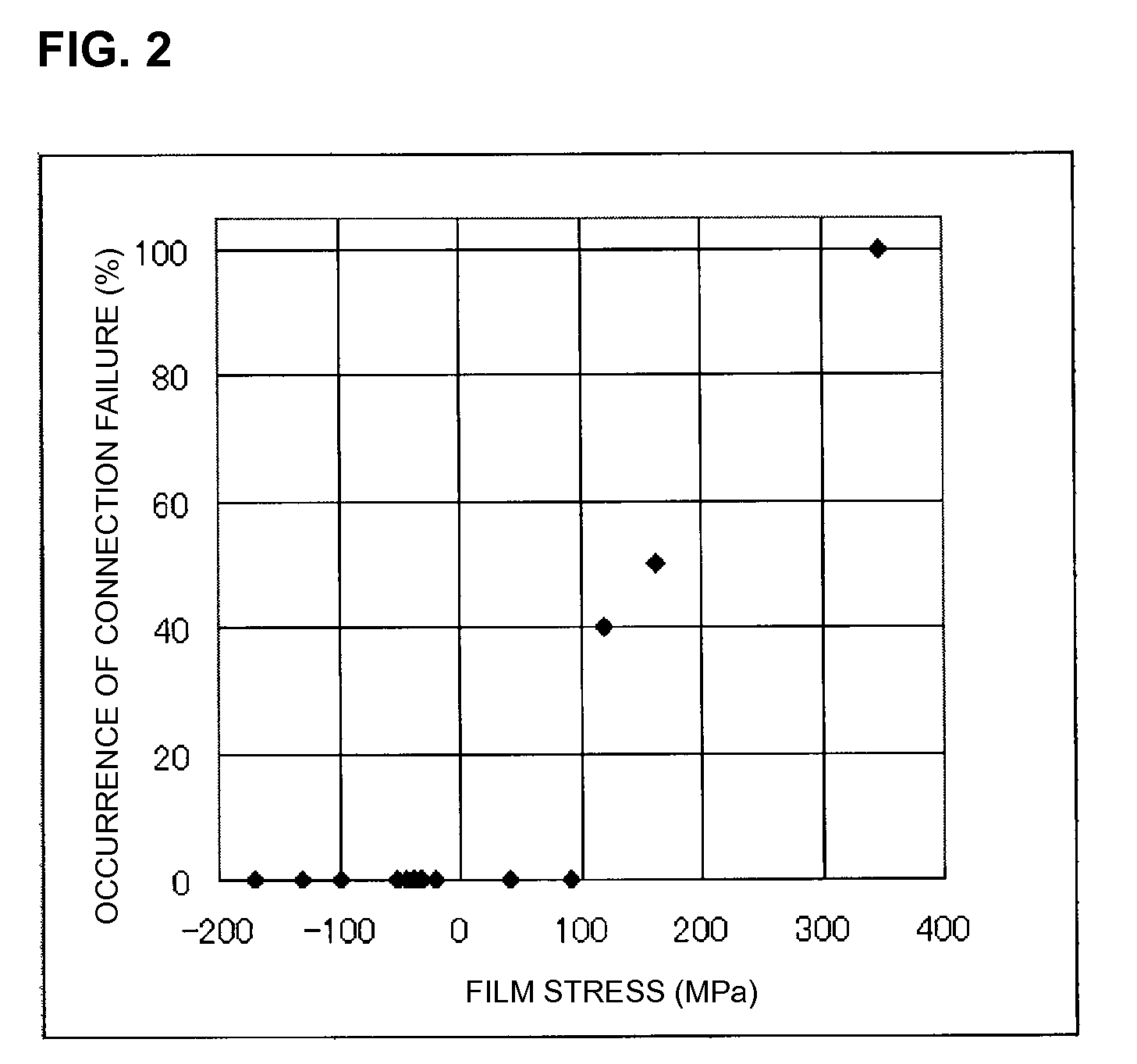
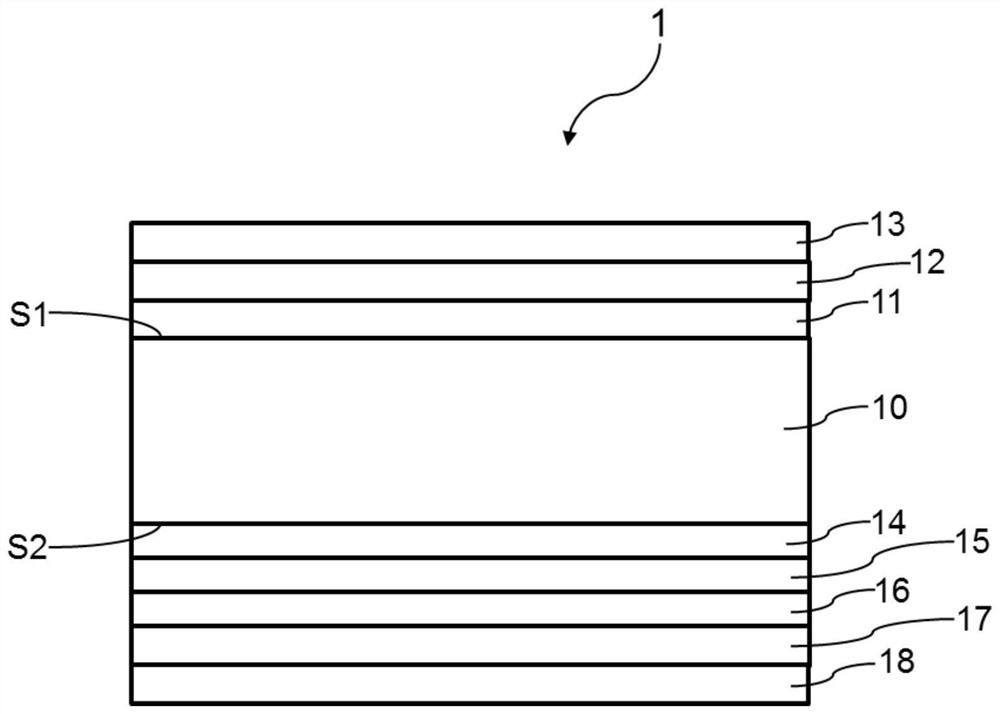
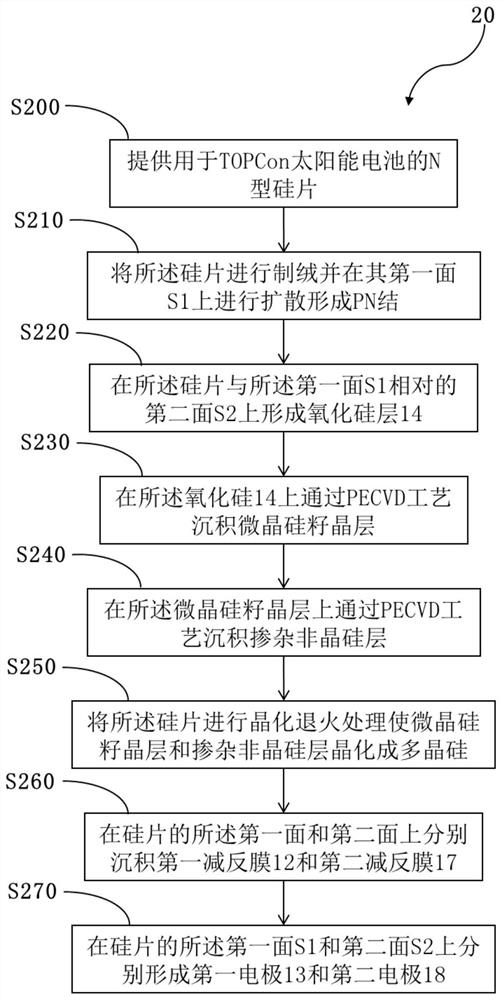
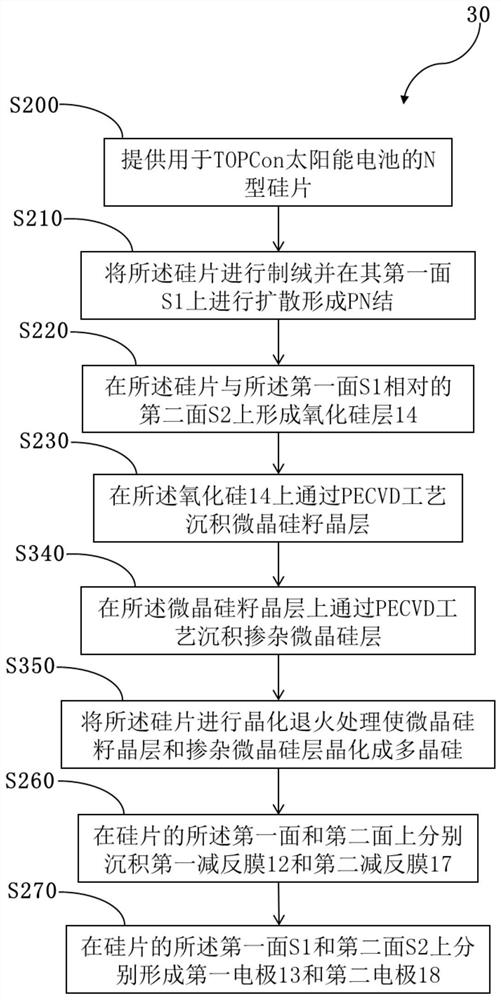
TOPCon solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN111987182AReduce film stressSolve the problem of bursting filmFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon oxideSolar battery
The invention provides a TOPCon solar cell and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: (a) providing an N-type silicon wafer for a TOPCon solar cell; (b) texturing the silicon wafer and diffusing on the first surface of the silicon wafer to form a PN junction; (c) sequentially forming a silicon oxide layer, a microcrystalline silicon seed crystal layer, a doped amorphous silicon layer or a doped microcrystalline silicon layer on a second surface, opposite to the first surface, of the silicon wafer; (d) carrying out crystallization annealing treatment on the silicon wafer to crystallize microcrystalline silicon and / or amorphous silicon into polycrystalline silicon; (e) respectively forming a first anti-reflection passivation film and a secondanti-reflection passivation film on the first surface and the second surface of the silicon wafer; and (f) respectively forming a first electrode and a second electrode on the first surface and the second surface of the silicon wafer. According to the invention, the problem of film explosion when the doped amorphous silicon layer or the doped microcrystalline silicon layer reaches a certain thickness can be effectively solved, the leakage current can be effectively reduced, and improvement of the open-circuit voltage, the filling factor and the conversion efficiency of the TOPCon cell can be facilitated.
Owner:IDEAL ENERGY (SHANGHAI) SUNFLOWER THIN FILM EQUIPMENT LTD
Photonic- and phononic-structured pixel for electromagnetic radiation and detection
ActiveUS20210381900A1Minimize electron scatteringSimilar effectOpticsNanoopticsNanowireSpectral response
A thermal pixel configured as an electromagnetic emitter and / or an electromagnetic detector. The thermal pixel comprises a micro-platform suspended with semiconductor nanowires from a surrounding support platform. The nanowires comprise phononic structure providing a decrease in thermal conductivity. In some embodiments, the pixel is structured for operation within a broad bandwidth or a limited bandwidth. Metamaterial and / or photonic crystal filters provide pixel operation over a limited bandwidth. In some other embodiments, the micro-platform comprises a nanotube structure providing a broadband emission / absorption spectral response.
Owner:CARR WILLIAM N
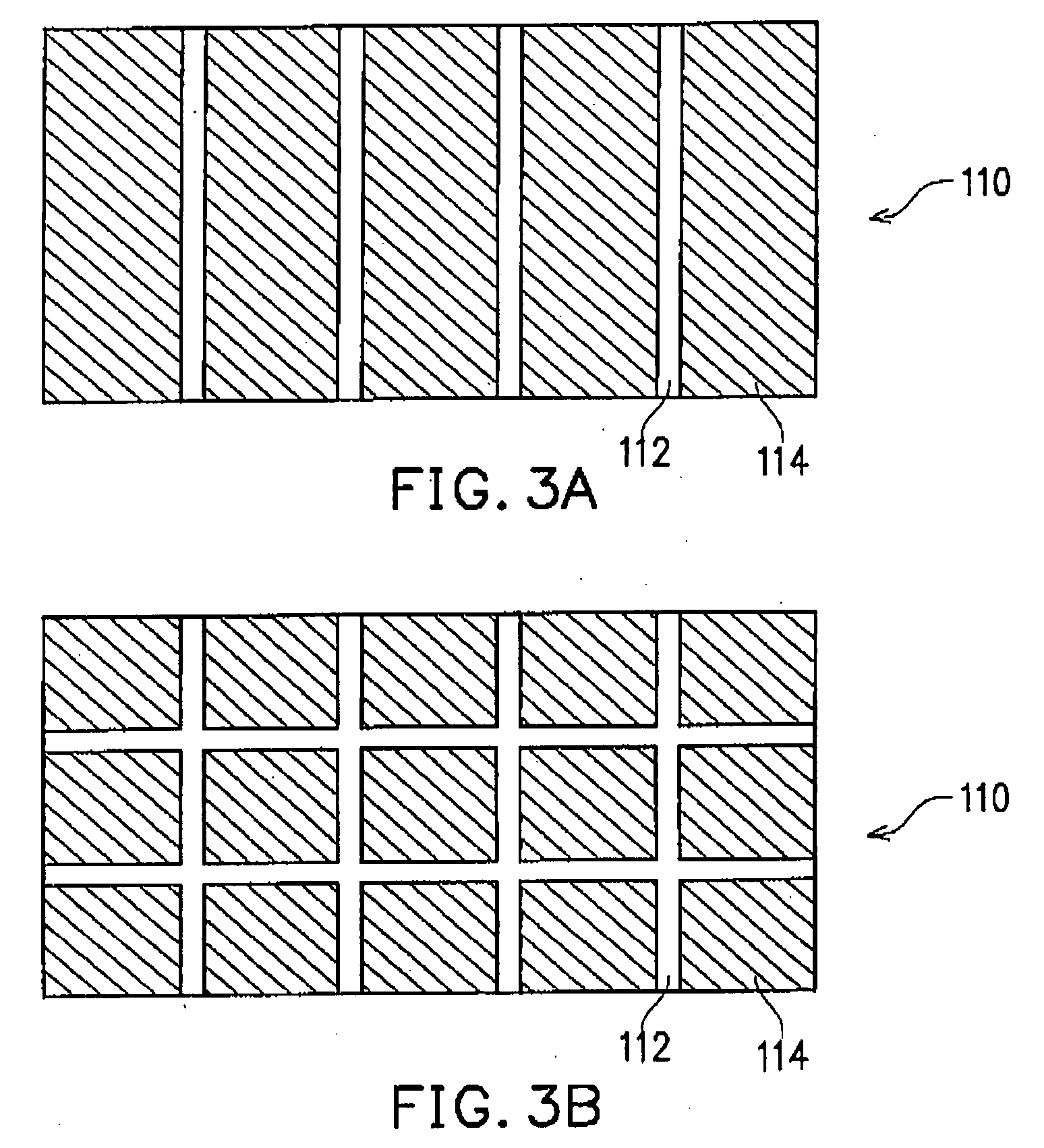
CVD thin film stress control method for display application
ActiveUS20180331328A1Reduce film stressSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityMetallurgy
Embodiments of the present disclosure generally describe a method for depositing a barrier layer of SiN using a high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP-CVD) process, and in particular, controlling a film stress of the deposited SiN layer by biasing the substrate during the deposition process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Super-long-span dome structure
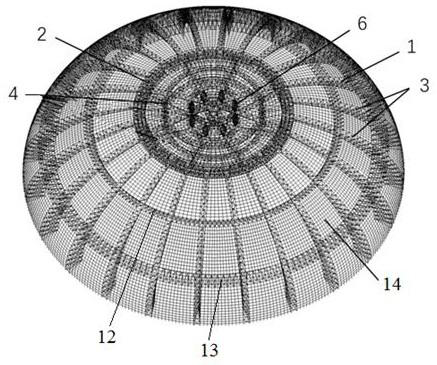
ActiveCN111379321AImprove mechanical performanceUniform structural stiffnessArched structuresVaulted structuresStructural rigidityLong span
The invention discloses a super-long-span dome structure. The super-long-span dome structure comprises multiple variable-cross-section midspan dual-limb cavity giant arches with a joint rotating shaft, upper limbs and lower limbs in the variable-cross-section midspan dual-limb cavity giant arches define cavity structures, two energy dissipating vibration reducing devices are symmetrically mountedin each cavity structure, the energy dissipating vibration reducing devices in the variable-cross-section midspan dual-limb cavity giant arches are located on the same circumference, branch limbs of the upper limbs and the lower limbs are fixedly connected with a first ring truss, at least two giant variable-cross-section space trusses are evenly mounted in an annular interval between the variable-cross-section midspan dual-limb cavity giant arches, the upper end of the giant variable-cross-section space trusses are fixedly connected with a first ring truss, the first ring truss is covered with a first dome surface single-layer net shell, each space is covered with a second dome surface single-layer net shell fixedly connected with the first ring truss, due to the dome structure, the stress property is greatly improved, the structure rigidity is uniform, joint configuration is relatively simple, and in the building process, large geometrically nonlinear deformation cannot be generated.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Method for forming thin film transistor
InactiveUS20070238230A1Reduce film stressRelieve pressureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPellicle membrane
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
CVD thin film stress control method for display application
ActiveUS10312475B2Reduce film stressSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityMetallurgy
Embodiments of the present disclosure generally describe a method for depositing a barrier layer of SiN using a high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP-CVD) process, and in particular, controlling a film stress of the deposited SiN layer by biasing the substrate during the deposition process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Coatings for multilayer insulation materials
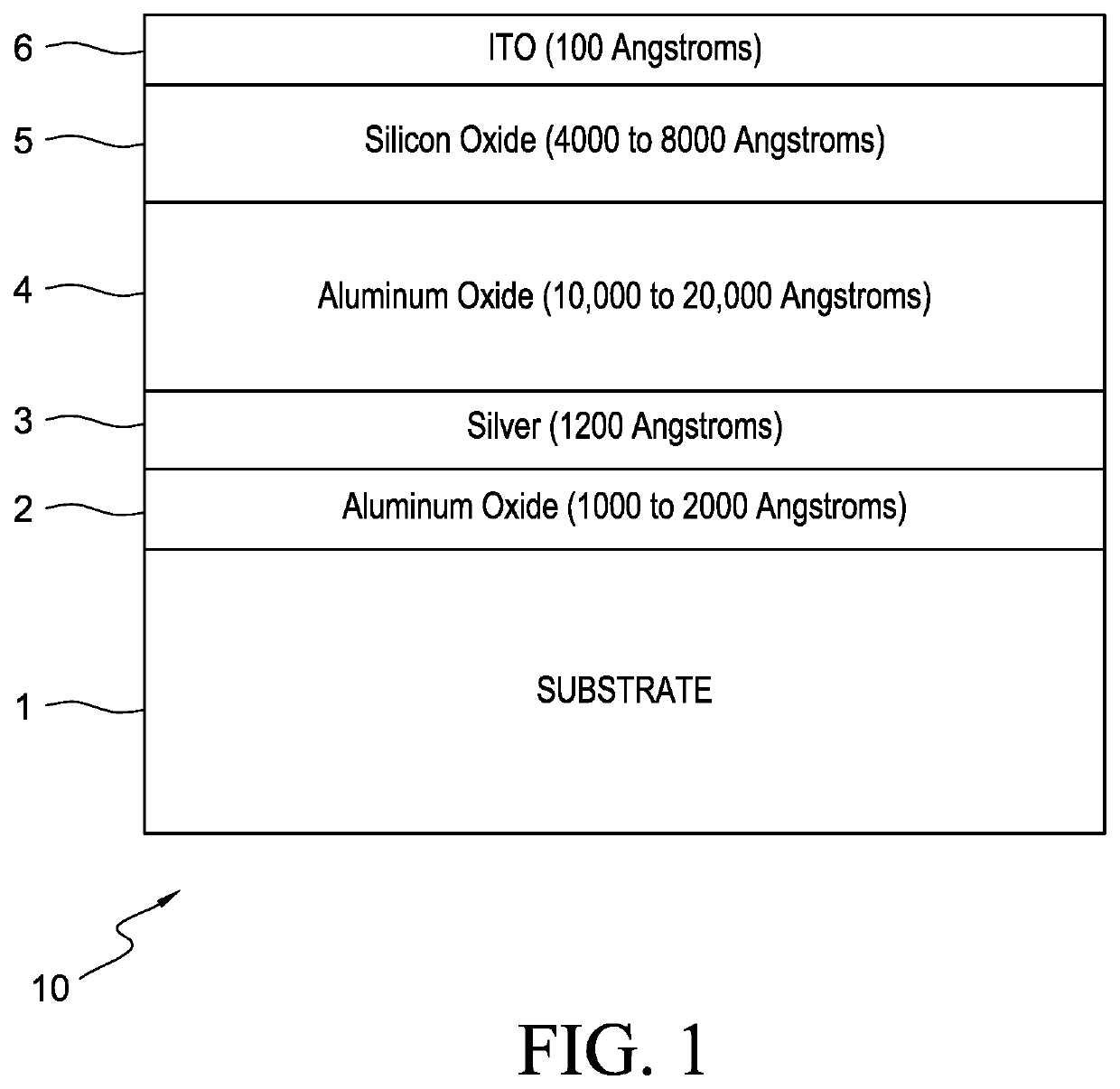
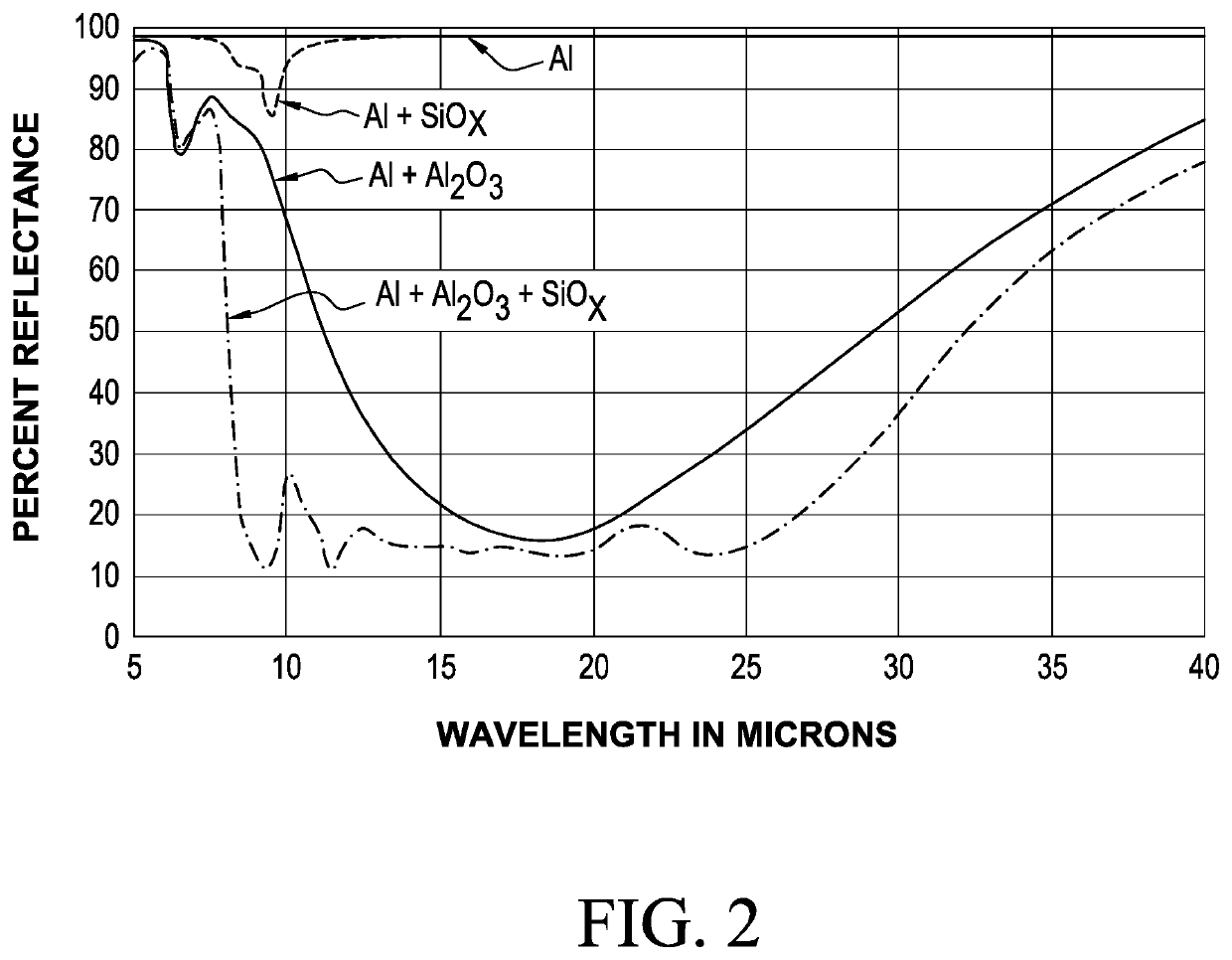
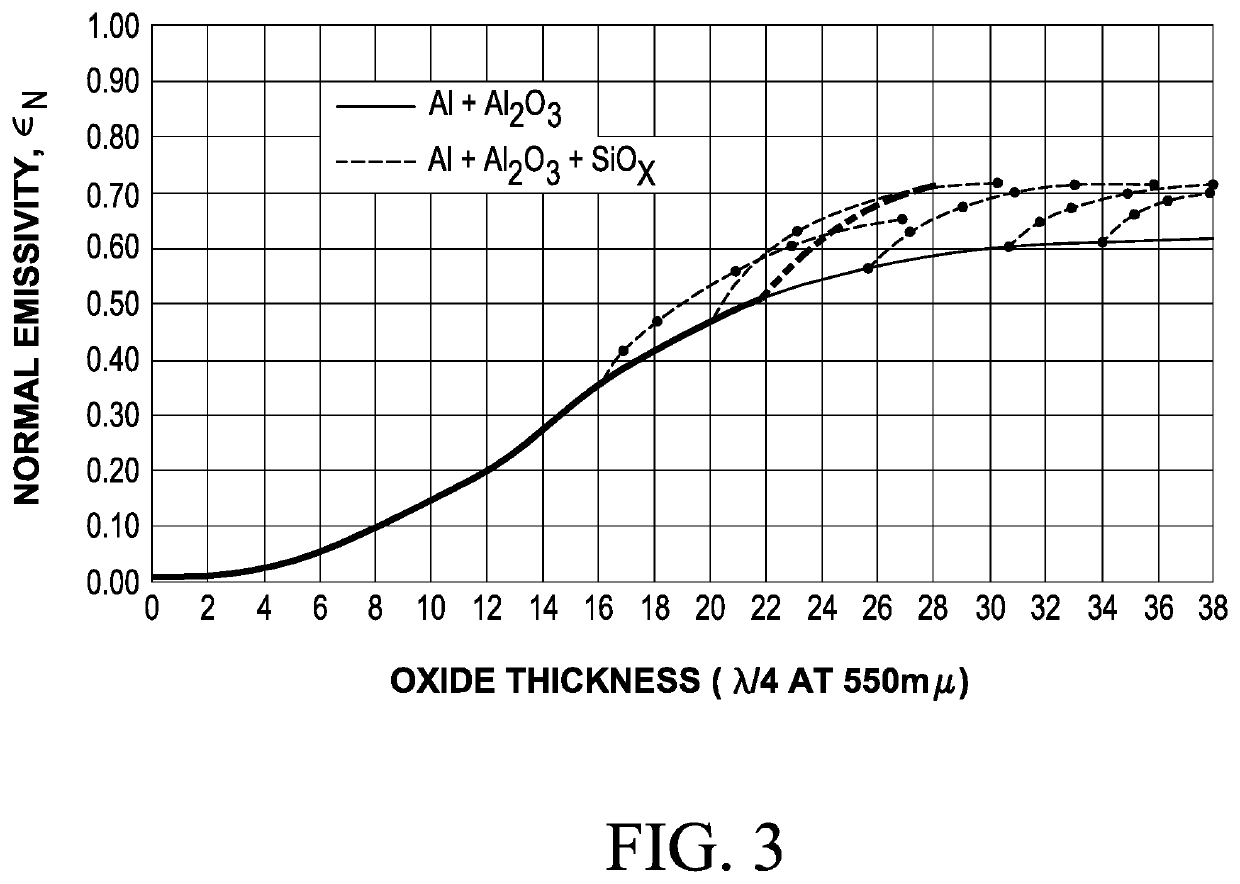
ActiveUS10815013B1Increase solar absorbanceDecrease solar absorbanceCosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic vehiclesAbsorptanceSolar absorptance
A laminate has a composite coating on a substrate. The substrate is a polymeric substrate with a surface resistivity of 4×102 to 1×108Ω / □; or a textured substrate with surface features which are 100 nm to 10 microns high. The composite coating comprising a tie layer of a nickel-chromium alloy; a layer of a reflective metal; a layer of aluminum oxide; a layer of silicon oxide; and optionally a layer of indium tin oxide. The laminate has a solar absorbance at a wavelength of 0.25 microns to 2.5 microns of between 0.07 and 0.7; and the laminate has an IR emittance of 0.1 to 0.8. Solar absorbance and IR emittance of the laminate may be independently to control the ratio of solar absorbance to IR emittance. Solar absorbance may be adjusted by changing the surface resistance or degree of texturing on the substrate. IR emittance may be adjusted by changing oxide film thickness.
Owner:NASA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com