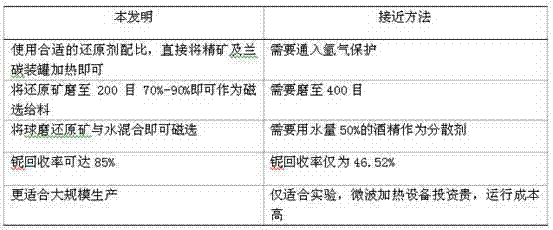
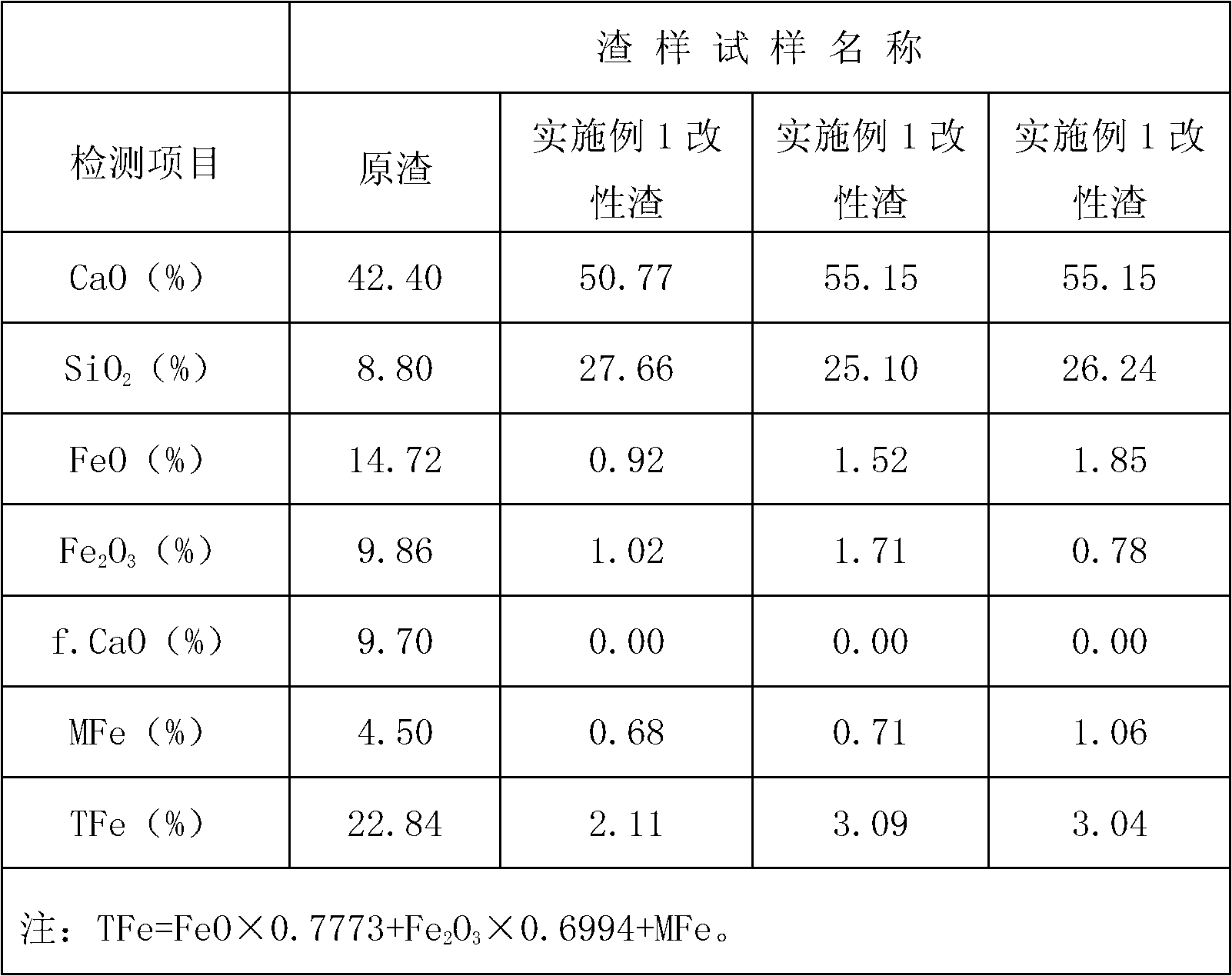
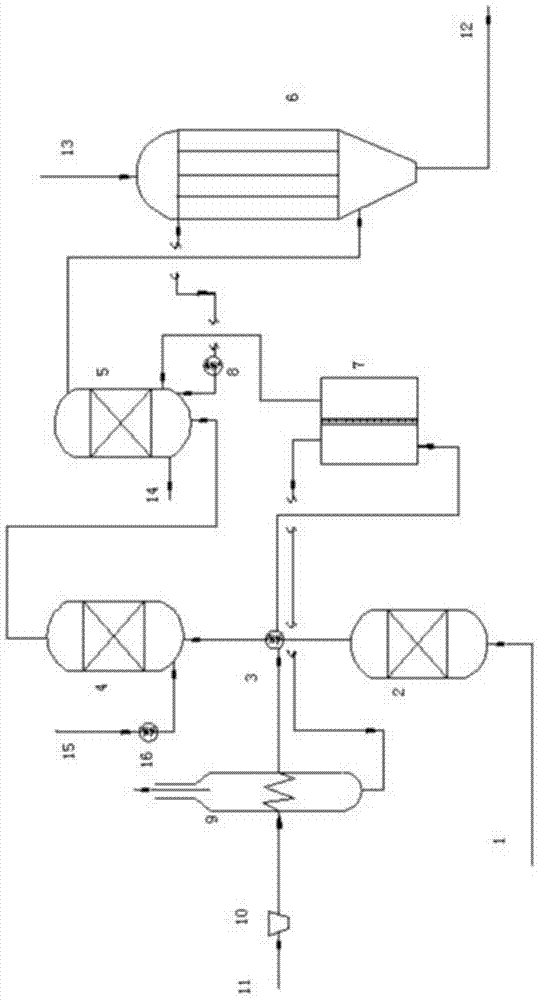
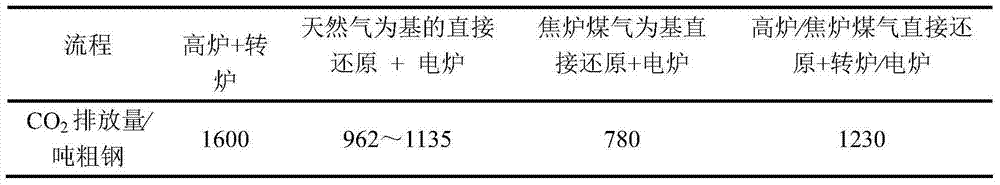
Patents
Literature
272 results about "Iron reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
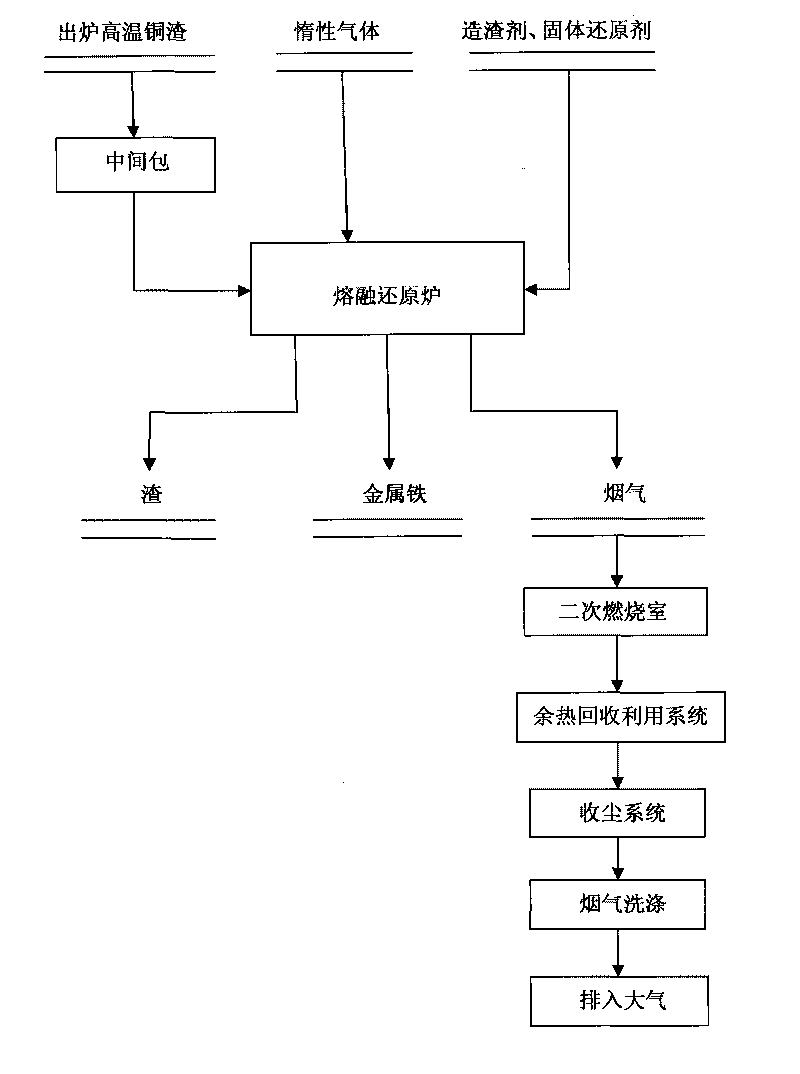
Method for fusing and reducing iron from copper residue by blowing inert gas
InactiveCN101736112AMeet the requirements of energy saving and emission reductionEmission reductionFluidised-bed furnacesMelting tankCombustion
The invention discloses a method for fusing and reducing iron from copper residue by blowing inert gas which comprises the steps of: transferring a high-temperature copper residue from a pouring packet to a high-temperature reduction furnace, adding reducing agent and slagging agent which are crushed into the reduction furnace, performing high-temperature iron reduction reaction, stirring inert gases and blowing into a furnace hearth during the reaction, spraying the inert gases and stirring the fused residue, performing high-temperature smoke secondary combustion, collecting dust and washing after recycling the waste heat, injecting into the atmosphere after emptying, and discharging high-temperature molten iron and slag from an iron outlet and a slag outlet after finishing the reaction. The invention takes full advantages of high-temperature waste heat of the discharged copper residue in order to save energy and reduce emission. The process flow is short; the discharge of contaminant is less, the recovering ratio is high; the applicability is wide; the process flow for recycling iron from copper residue is shortened; the operation in each process flow is simple; and the maintenance cost for furnace is lower.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
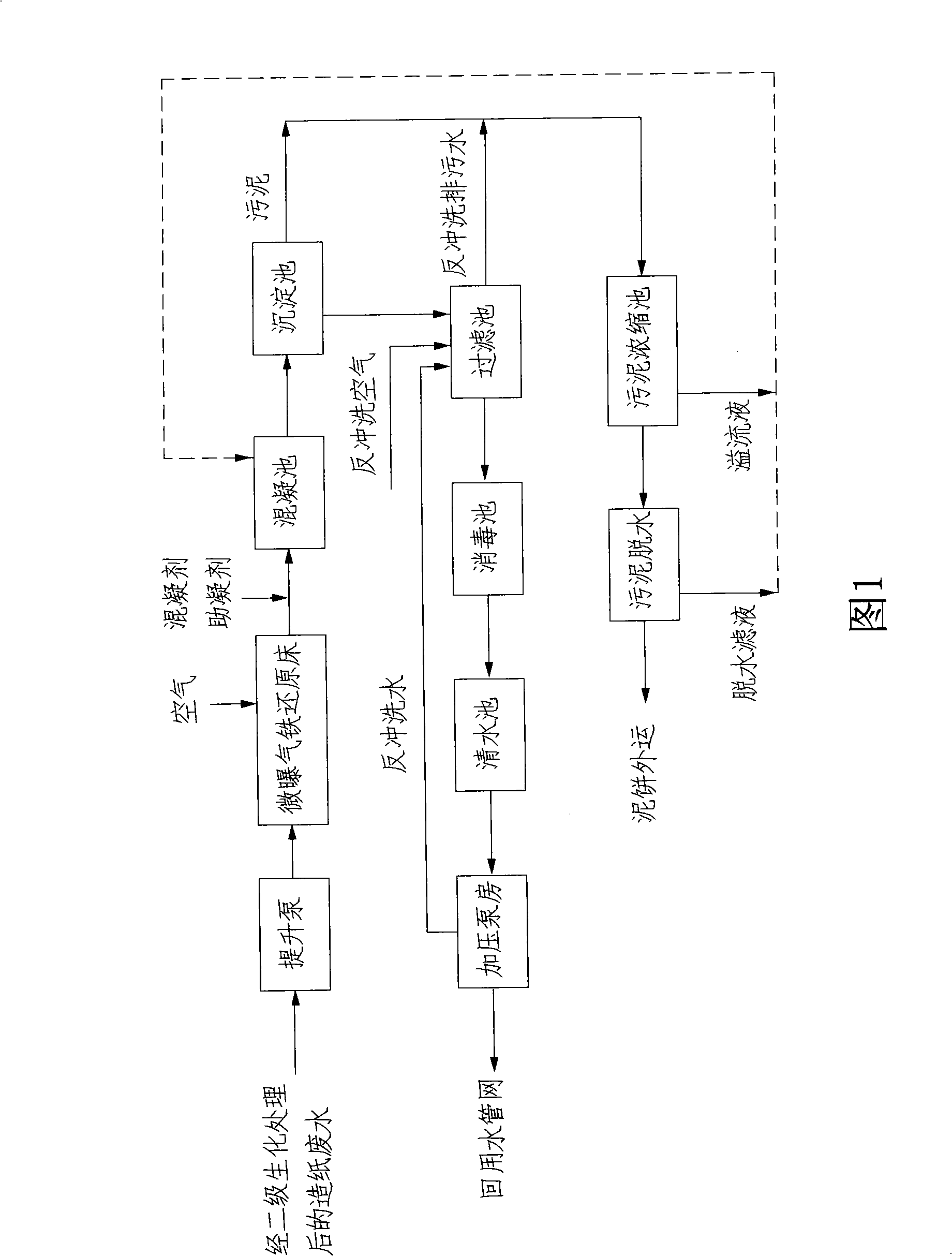
Advanced treatment process for paper-making waste water
ActiveCN101337752AHigh salt contentImprove conductivitySludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningMultistage water/sewage treatmentIron reductionWater pipe
The invention discloses an advanced treatment process of paper-making wastewater. The process comprises the following steps: introducing the paper-making wastewater after being subjected to secondary biochemical treatment into a micro-aeration iron reduction bed, backfilling iron chips in the micro-aeration iron reduction bed, and carrying out reducing reaction to the paper-making wastewater in the micro-aeration iron reduction bed; introducing effluent water after being processed according to step one into a coagulation basin, and adding a coagulating agent and a coagulant aid to the coagulation basin, so as to promote grains in the water to be agglomerated; introducing effluent water after being processed according to step two to a sedimentation tank for sludge separation; introducing the effluent water in the sedimentation tank into a filter basin for being filtered; introducing the effluent water filtered after being sterilized and disinfected into a reusing water pipe network; introducing sludge in the sedimentation tank and back washing blow-off water in the filter basin into a sewage thicker, and outwardly transporting the sludge and the back washing blow-off water after being dehydrated for disposal; and meanwhile, introducing dehydrate filtrate solution and overflowing liquid in the sewage thicker into the coagulation basin for re-treatment. The process has the advantages of simple process, good decoloration effect and cheap cost.
Owner:HUATIAN ENG & TECH CORP MCC
Paracoccus denitrifican with denitrification and iron reduction functions and culturing method and application thereof
InactiveCN102676430AEffective recoveryReduce energy consumptionBacteriaWater contaminantsNitriteSulfur
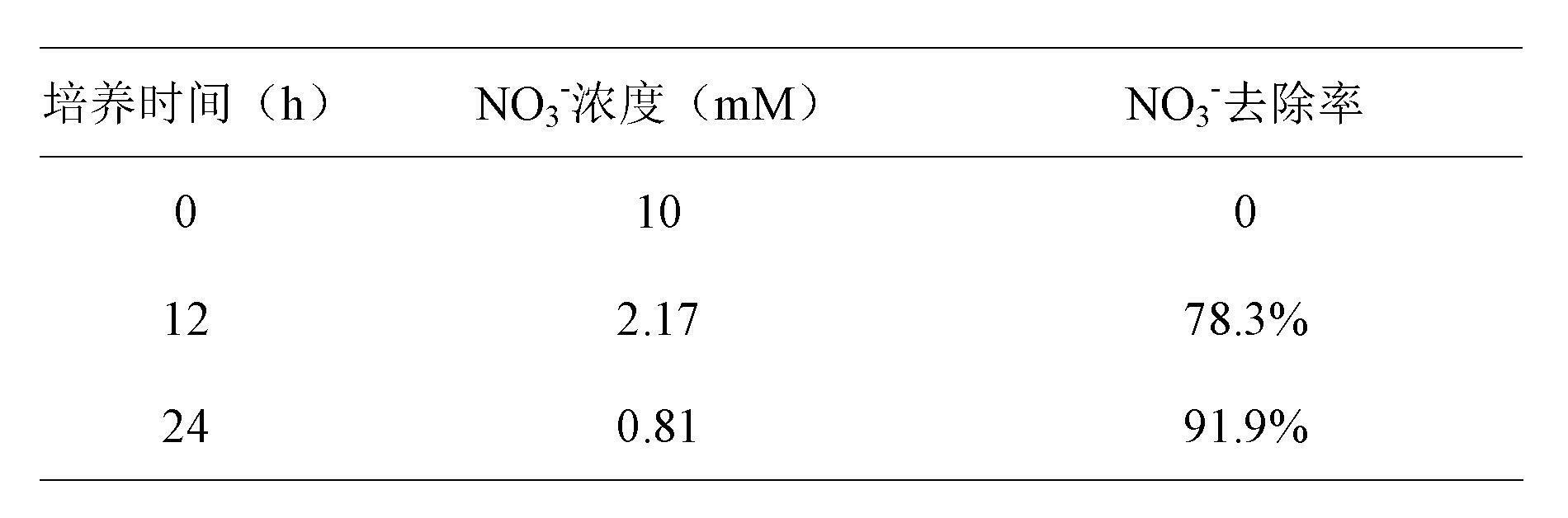
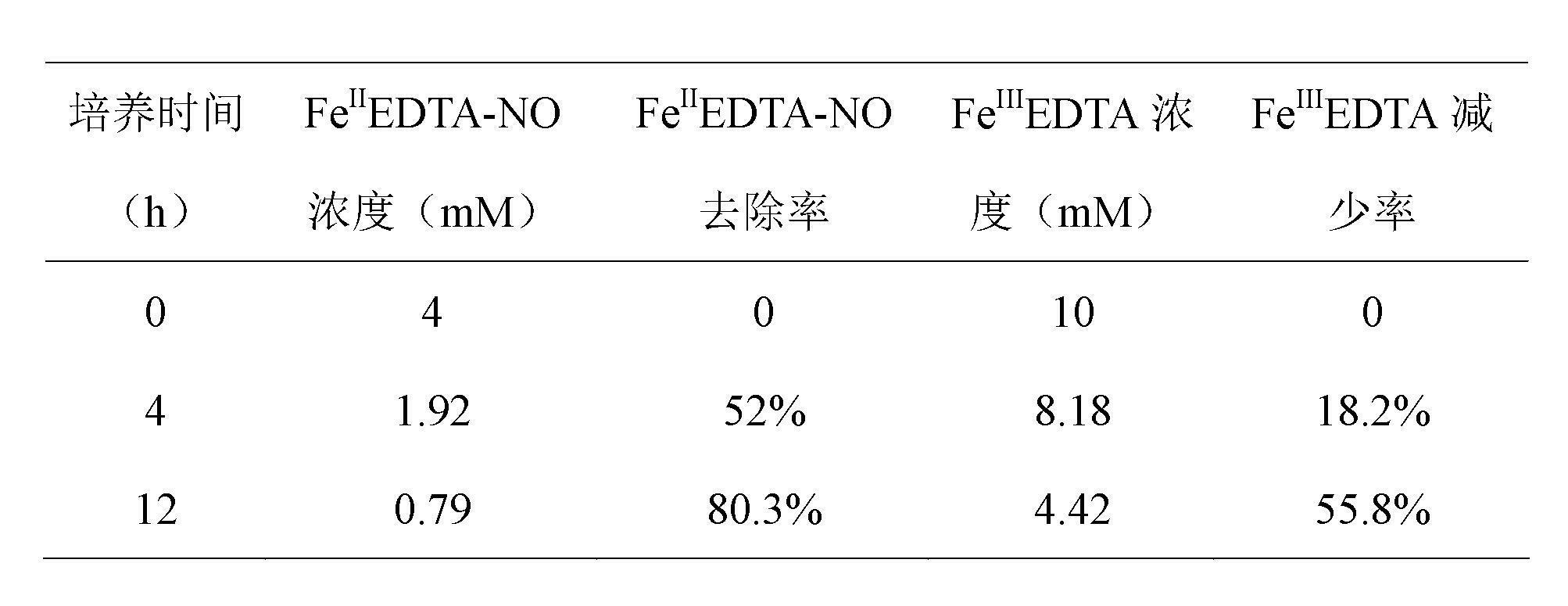
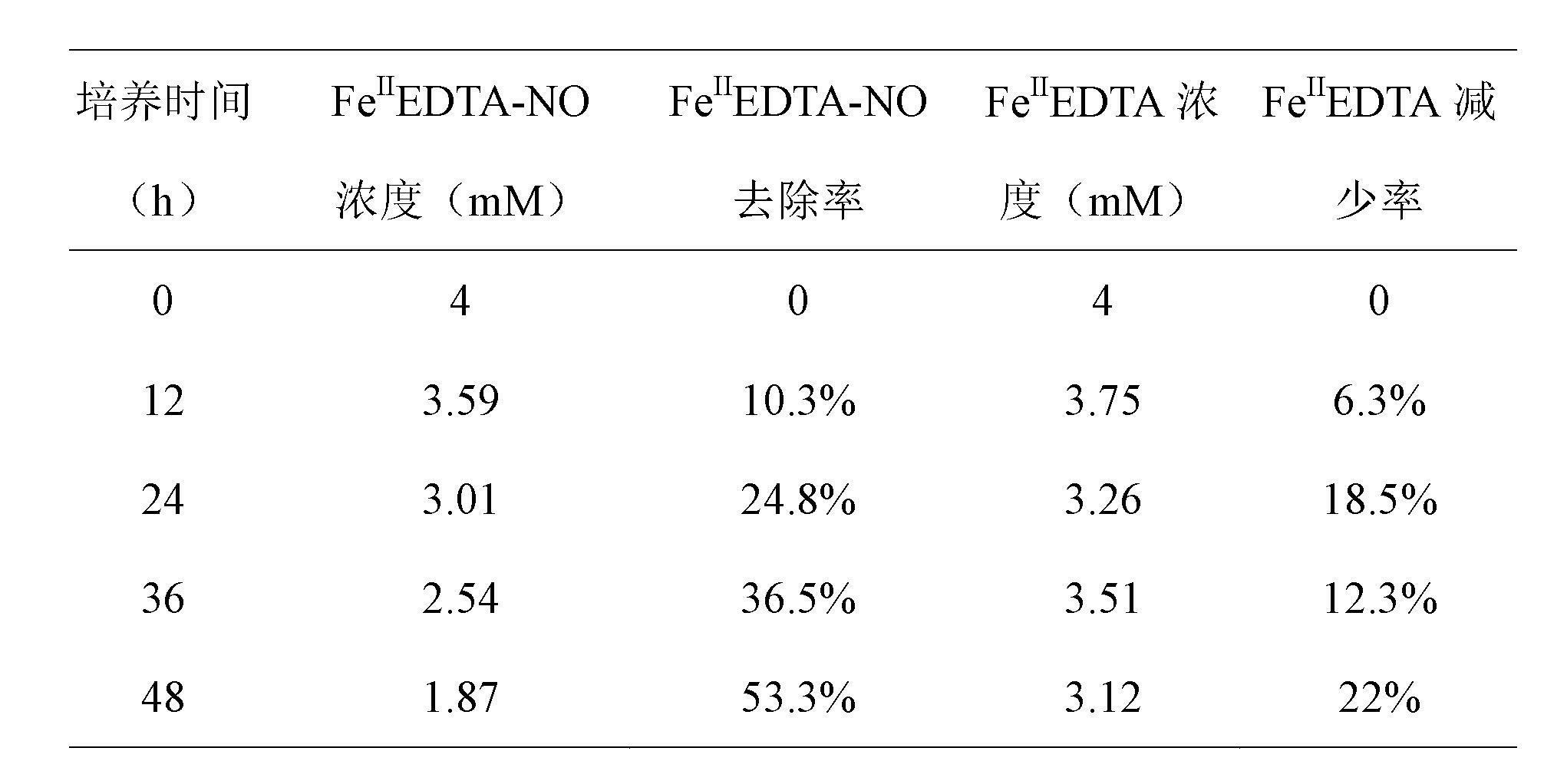
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental organisms, and relates to paracoccus denitrifican with heterotrophic denitrification, autotrophic denitrification and iron reduction functions and a culturing method and an application thereof. The bacterium is paracoccus denitrifican ZGL1 with the collection number CCTCC M2012158, and can be used for completing heterotrophic denitrification and autotrophic denitrification processes (including sulfur autotrophic denitrification and iron autotrophic denitrification) and effectively reducing ferric iron. During waste gas treatment, reduction of Fe(II)EDTA-NO and regeneration of Fe(II)EDTA are realized simultaneously for the same strain in a BioDeNOX denitration process, the aim of continuously denitrating is fulfilled, and low energy consumption, small investment and low running cost are realized. During waste water treatment, the strain can be used for removing nitrate and nitrite from waste water in a heterotrophic denitrification process, can be applied to waste water denitrification through sulfur autotrophic denitrification and iron autotrophic denitrification processes, is low in cost, and has a simple process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Direct iron-reduction by iron-ore briquet self-production reproduced gas
InactiveCN1896286AReduce consumptionRelatively small investmentShaft furnaceReducing atmosphereProduct gas
The present invention relates to a method of producing direct reduction iron with self-produced reduction gas of iron ore-coal pellet. With the coal in the iron ore-coal pellet as the whole reducing agent, the gas generated by self-pyrolysis of the coal in the iron ore-coal pellet as the self-produced reduction gas and the low heat value gas as the fuel heating the reduction gas, the self-produced reduction gas is recycled and reduces the iron ore into direct reduction iron in reducing atmosphere at high temperature. The present invention replaces the external reduction gas with the self-produced reduction gas facilitating zero release of greenhouse gases in the production of direct reduction iron and the realization of clean production.
Owner:苏亚杰
Method for producing direct iron-reduction by iron-ore briquet self-production reproduced gas
InactiveCN1896286BReduce consumptionRelatively small investmentShaft furnaceReducing atmosphereProduct gas
Owner:苏亚杰
Pretreatment method of copper-containing organic waste water
ActiveCN105347552AImprove operational flexibilityImprove biodegradabilityWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsPretreatment methodFenton reagent
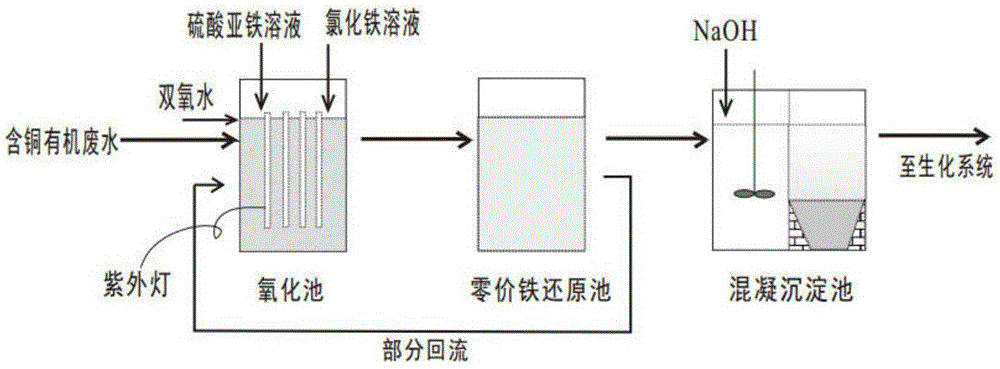
The invention discloses a pretreatment method of copper-containing organic waste water. The copper-containing organic waste water contains copper ions, the copper-containing organic waste water is added with hydrogen peroxide and ferrous iron and ferric iron solutions, the mixed solution forms Fenton and Fenton-type reagents under the UV irradiation and the Fenton and Fenton-type reagents can realize catalytic degradation of organic pollutants and release of complex copper ions. The oxidized waste water goes through a zero-valent iron reduction system, the copper ions are displaced by the zero-valent iron and the ferric ions are reduced to form ferrous ions. A part of product water containing the ferrous ions is returned into an oxidation tank for Fenton / Fenton-type oxidation reaction and undergoes an oxidation degradation reaction. The product water is subjected to pH adjustment, pollutants are further removed by flocculation deposition and the deposited product water directly enters into a biochemical system. The zero-valent iron reduction system has a simple and easy replacement method. The pretreatment method fully utilizes copper ions in the system, effectively degrades organic pollutants and effectively recovers copper ions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV YANCHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH & ENG RES INST
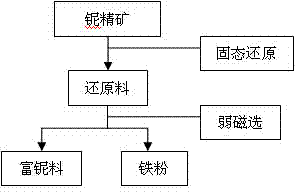
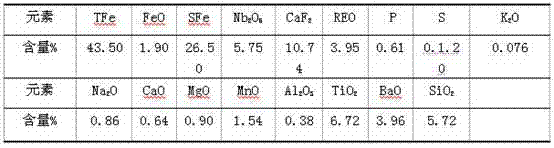
Method for enriching niobium by high-temperature roasting and low-intensity magnetic separation
InactiveCN104498737AAchieve separationIncrease productivityMagnetic separationIron reductionRoasting
The invention relates to a method for enriching niobium by high-temperature roasting and low-intensity magnetic separation and belongs to the technical field of mineral extraction metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: performing solid-state reduction of a niobium ore concentrate to obtain a reduced ore containing the niobium and metal iron; ball-milling the reduced ore containing the niobium and the metal iron and then performing low-intensity magnetic separation to obtain a niobium-rich material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, iron oxide in the niobium ore concentration is selectively reduced in a solid state, so that the metal transformation rate is above 90%; by reduction of the iron oxide, a mineral structure of niobium-iron rutile in the original ore is damaged; subsequently niobium oxide can be separated from the metal iron by low-intensity magnetic separation; finally the content of iron in the obtained niobium-rich material is lower than 8%; compared with the original 'solid-state iron reduction-high-temperature melt separation-smelting' method, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the niobium-rich material of which the iron content is basically the same and also has the advantages of saving power consumption, reducing emission and improving the efficiency.
Owner:包钢集团矿山研究院(有限责任公司)
Method for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil by combination of biochar and iron-reducing bacteria agent
ActiveCN103752604AMaintain and improve physical and chemical propertiesAccelerates the bioremediation processContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismIn situ remediation
The invention discloses a method for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil by combination of biochar and an iron-reducing bacteria agent. Adsorption of the biochar and oxidation-reduction of iron-reducing bacteria are fully exerted, and the bioremediation process of the heavy metal contaminated soil is greatly accelerated by the synergistic effect. An organic waste for preparing the biochar disclosed by the invention is wide in source, and low in cost; the iron-reducing bacteria agent is simple in preparation method, aeration facilities do not need to be added in the soil repairing process by the anaerobic metabolism ability, and operation is facilitated. The method for repairing the heavy metal contaminated soil by combination of the biochar and the iron-reducing bacteria agent has the advantages of a bioremediation technology, is outstanding in heavy metal fixing, passivating and ageing effects, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Method for preparing 2,3-dichlorin fluorobenzene
InactiveCN101337862ATake advantage ofImprove responseHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationNitrobenzeneIron reduction
The invention discloses the preparation method of 2,6-dichlorofluorobenzene, which comprises the following steps: preparing 3,5-dichloro-4-fluoroaniline from 3,5-dichloro-4-fluorobenzonitrile by iron reduction or catalytic hydrogenation; and replacing diazo group in 3,5-dichloro-4-fluoroaniline by hydrogen in the presence of a reducing agent to obtain 2,6-dichlorofluorobenzene. The method can prepare 2,6-dichlorofluorobenzene by a reasonable process, and has the advantages of simple and easy reaction process and high yield of the product. Additionally, 3,5-dichloro-4-fluoroaniline can be selected from (1) 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene rectification residues from combined production or byproduct of 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene; (2) rectification tailings of 2,3,4-trifluoronitrobenzene; and (3) rectification residues of 3-chloro-4-fluoronitrobenzene. Accordingly, the materials can be easily obtained to fully utilize the resources and reduce the production cost.
Owner:常山新星高科化工技术有限公司
Modification technology of iron reduction and component reconstruction for molten slag
InactiveCN102796833AEfficient use ofIncrease added valueManufacturing convertersRecycling and recovery technologiesMolten saltIron reduction
The invention relates to the field of metallurgy waste residue treatment, particularly relates to a modification technology of iron reduction and component reconstruction for molten slag, comprising the following steps: adding a modified material in molten slag, wherein the modified material comprises coke and SiO2, the weight ratio of coke to SiO2 to the molten slag is 0.08-0.12:0.10-0.12:1; heating up the molten slag after mixing to 1500-1700 DEG C; after fully reaction of the modified material and the molten slag, separating molten iron from the molten slag, and then discharging the molten iron. The technology has simple process, is a short flow technology of modification and regeneration of resources, has no need for new devices, can be used directly in on line production, is a supplement for existing steel smelting technology, and only needs auxiliary production technologies.
Owner:SHANGHAI MCC ENVIRONMENTAL ENG TECH CO LTD +1
System device and method for modifying coke oven gas to directly reduce iron ore
ActiveCN103898265AEmission reductionSuitable for energy resource characteristicsGas emission reductionEngineeringShaft furnace
The invention relates to a system device and method for modifying coke oven gas to directly reduce iron ore, and belongs to the technical field of non-blast furnace iron-making process. The invention provides a new process, the coke oven gas produced in the coking process is modified and reformed as hydrogen-enriched reducing gas (H2 and CO), and the hydrogen-enriched reducing gas is introduced into a shaft furnace to directly reduce the iron ore. The large quantity of hydrogen-enriched reducing gas required for direct iron reduction technology is provided by the invention, the obtained hydrogen-enriched reducing gas obtained by modifying is used for the direct reduction of the iron ore so as to effectively reduce the emission of carbon dioxide in the iron ore reduction process, the direct reduction is completely different from the path of directly reducing iron from the natural gas and suitable for the energy resource feature of China.
Owner:丰镇市新太新材料科技有限公司
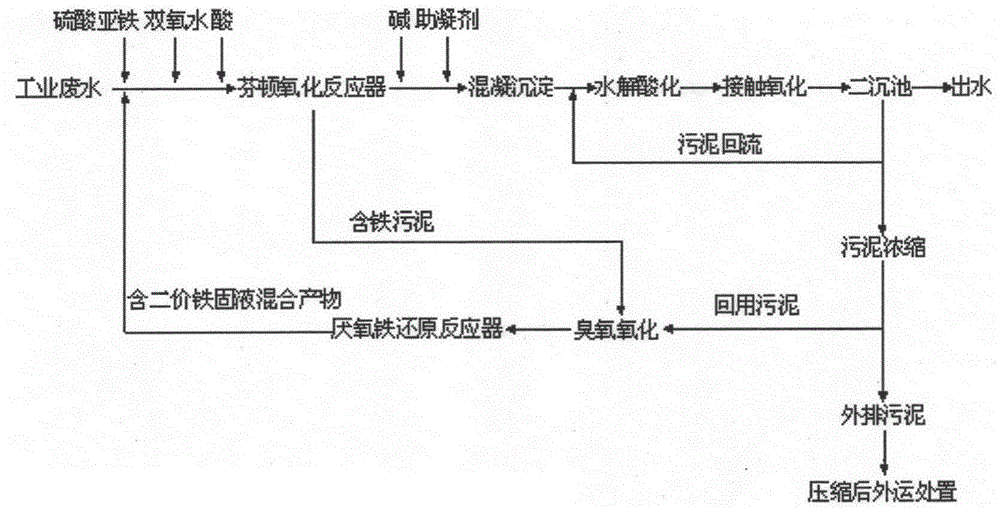
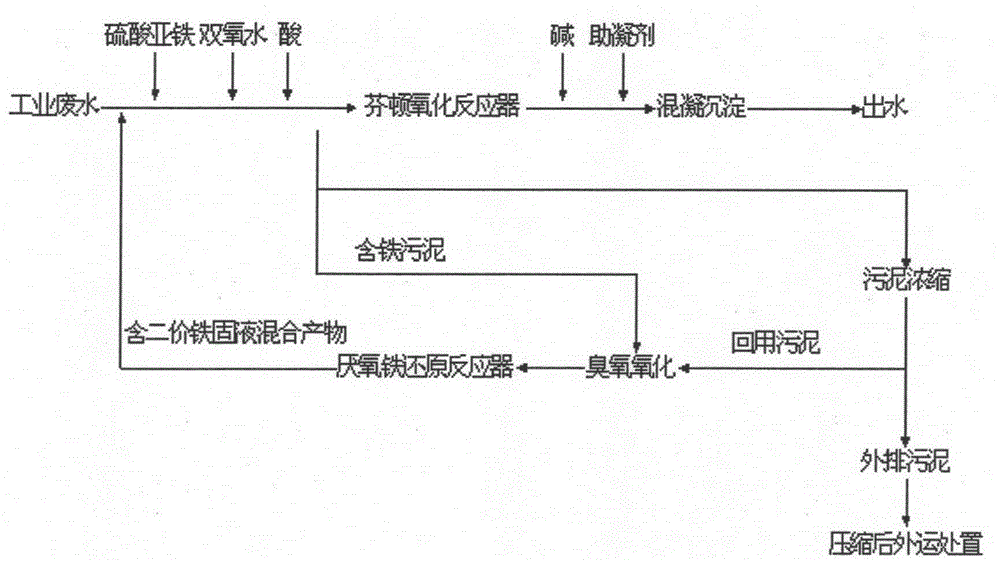
Fenton oxidation-biological combination treatment technology capable of achieving ozone-anaerobic iron reduction and sludge reduction
InactiveCN105417869APromote degradationAchieve reductionTreatment using aerobic processesSludge treatment by oxidationBiological cellLysis
The invention discloses a Fenton oxidation-biological combination treatment technology capable of achieving ozone-anaerobic iron reduction and sludge reduction. The technology comprises the processes that after iron-containing sludge generated in Fenton oxidation is mixed with retained partial biological treatment sludge discharged by a secondary sedimentation tank, the mixed sludge firstly enters an ozone reaction tank, refractory organics in the iron-containing sludge are initially decomposed into micromolecular easily-degraded organics, lysis and wall breaking are performed on microbial cells of the retained biological treatment sludge, and then the mixed sludge enters an anaerobic iron reduction reactor; the degradability of organic components in the sludge is further improved in the anaerobic iron reduction reactor, and meanwhile the process of converting Fe<3+> in the Fenton iron-containing sludge into Fe<2+> is achieved under the action of an anaerobic iron reducing bacterium; a Fe<2+>-containing solid-liquid product generated through a reaction is completely reused in the front step of a Fenton oxidation technology to partially replace Fe<2+> put in the Fenton oxidation technology, and meanwhile system sludge reduction is achieved to save engineering investment and operating cost.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Ternary composite organic pollution repairing agent containing iron oxide, humus and reducing bacteria thereof, and preparation method of repairing agent
ActiveCN102443400APromote degradationIn situ repair effect is goodAgriculture tools and machinesSludge processingCompound organicHumin
The invention discloses a ternary composite repairing agent, containing iron oxide, humus and reducing bacteria thereof, for in-situ remediation of organic pollution in soil and sediment. The repairing agent of the invention is prepared by carrying out fermentation enlarge culture on ferric reducing microorganism and mixing with iron oxide and humus uniformly. The microbial repairing agent of the invention can accelerate degradation of organic pollutants under an anaerobic condition and has good in-situ remediation effect on organic pollution soil and black and stink sediment. Raw materials are all natural substances and environment-friendly, and cause no secondary pollution. The microbial repairing agent of the invention is simply applied without excavating or disturbing original environment or oxygen, requires low work amount and small cost, and is apt to large-scale usage. The preparation method of the repairing agent of the invention can obtain a microbial repairing agent product simply and fast.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
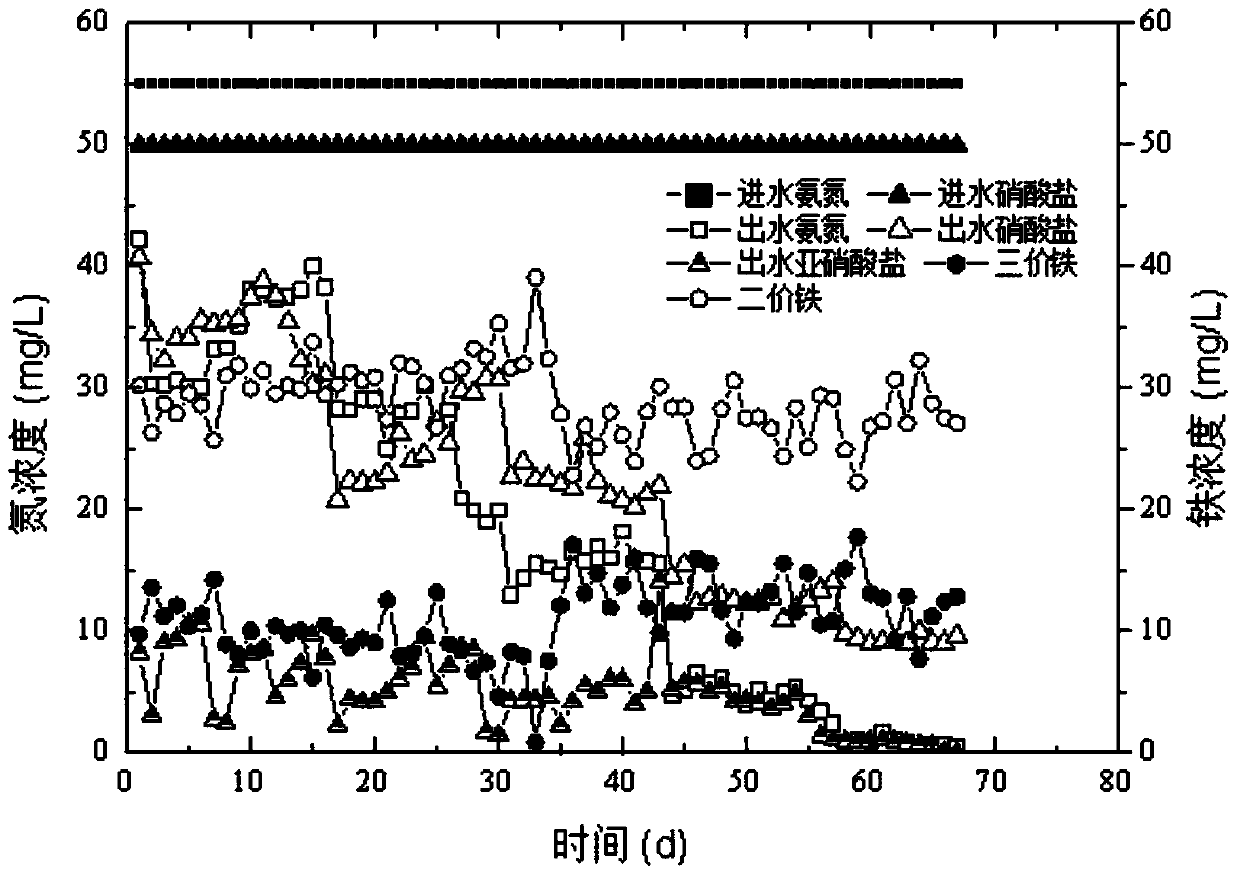
A method for simultaneously removing ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen from a water body
ActiveCN107555616ASynchronization removal implementationNo generationWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesNitrationNitrogen gas
A method for simultaneously removing ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen from a water body is disclosed. The method includes subjecting the water body containing ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen to oxidation-reduction treatment by adopting an iron catalyst under functions of anaerobic ammoxidation microbes, iron autotrophic denitrification microbes and iron-reduction ammoxidation microbes.The iron catalyst includes one or a plurality of elementary iron, a ferrous compound and a ferric compound. The catalytic treatment is performed in an anaerobic environment. The anaerobic ammoxidationmicrobes, iron autotrophic denitrification microbes and iron-reduction ammoxidation microbes provide reaction functional microbes for anaerobic ammoxidation, iron autotrophic denitrification and iron-reduction ammoxidation, allow oxidation-reduction treatment of the ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen to be performed stably and continuously under the premise of not continuously adding the catalyst, and can completely convert the ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen into nitrogen without a byproduct. The method is free of secondary pollution.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
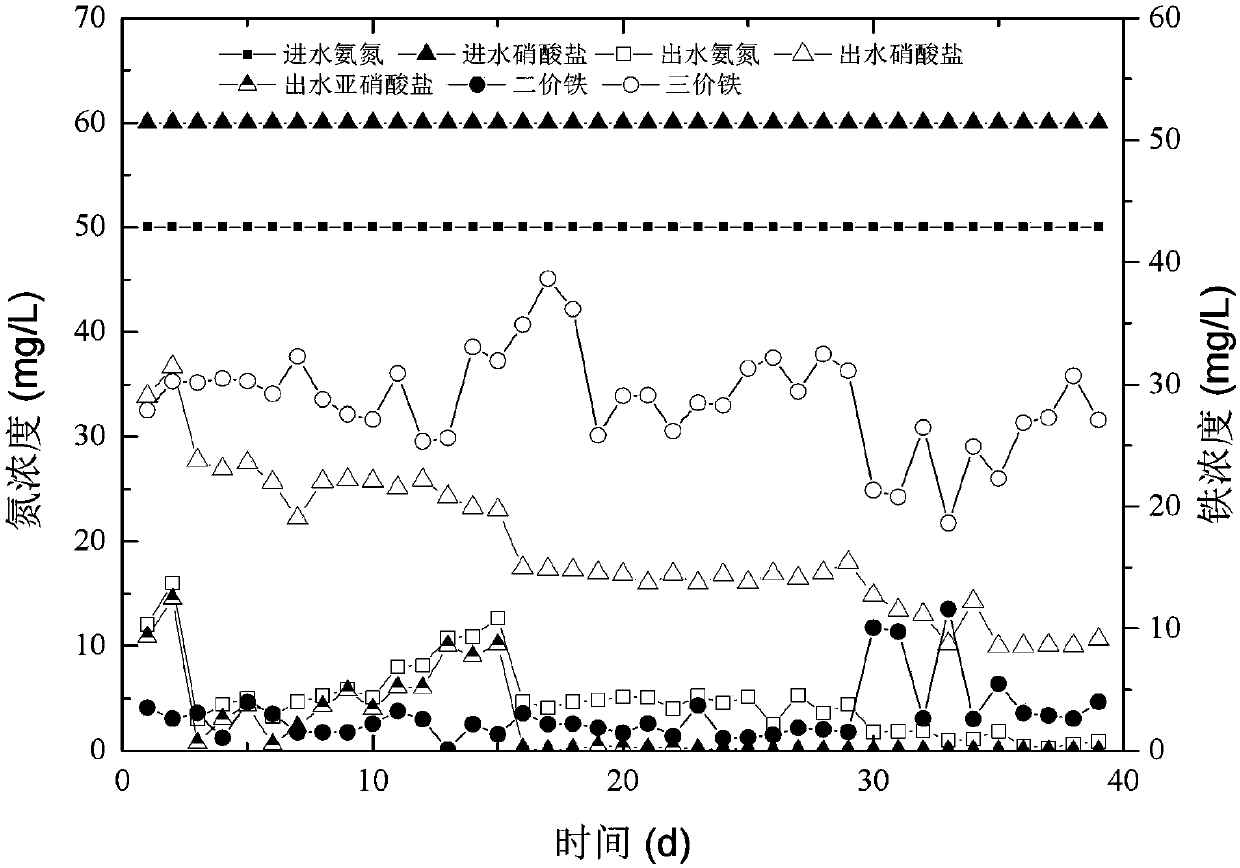
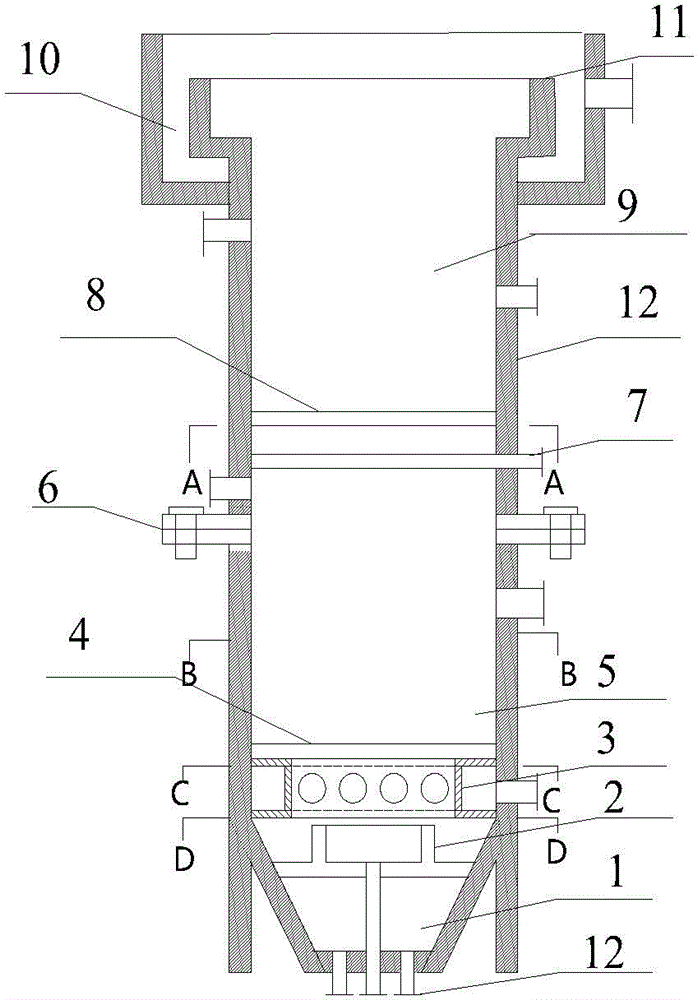
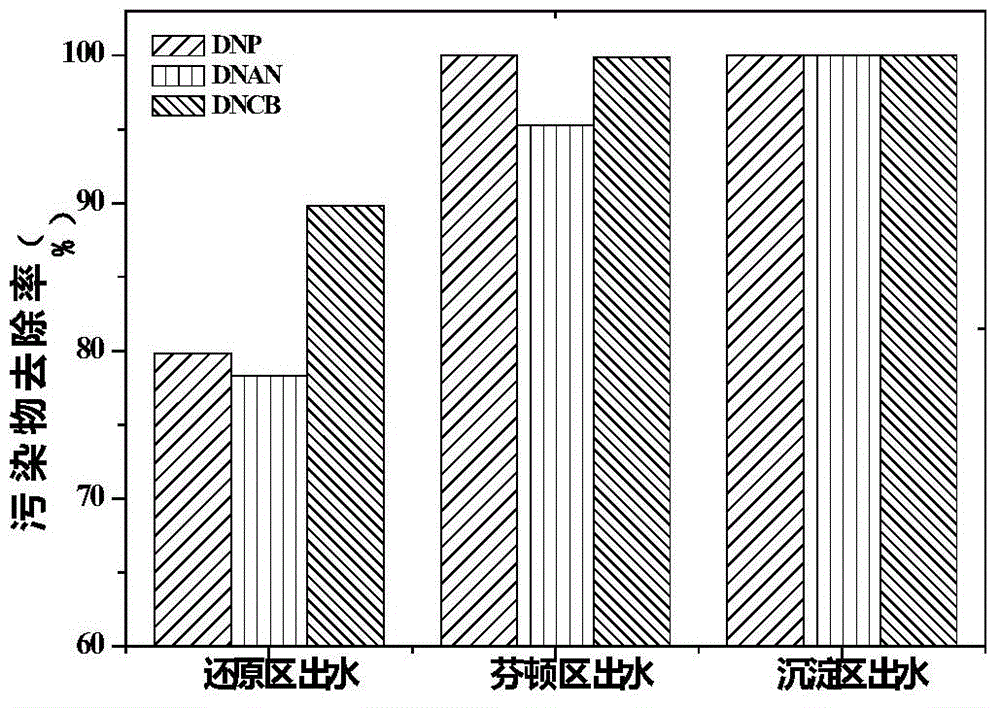
Zero-valent iron reduction-Fenton oxidation integrated reaction device and method for treating nitroaromatic compound wastewater by using zero-valent iron reduction-Fenton oxidation integrated reaction device
ActiveCN104591426ASimple process flowLow running costWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentEngineeringIron reduction
The invention discloses a zero-valent iron reduction-Fenton oxidation integrated reaction device. The reaction device comprises a reactor body with a hollow cylindrical structure, wherein the inner part of the reactor body is divided into four reaction areas, namely an iron mud collecting area, a zero-valent iron reduction area, a zero-valent iron Fenton oxidation area and a sedimentation area from bottom to top; the four reaction areas are communicated with one another, and iron scraps fills up the zero-valent iron reduction area and the zero-valent iron Fenton oxidation area. According to the zero-valent iron reduction-Fenton oxidation integrated reaction device disclosed by the invention, a zero-valent iron reduction technology and a zero-valent iron Fenton oxidation technology are combined to ensure that the effective space of a reactor can be used to a greatest extent, the technological process of wastewater treatment can be simplified, and the running cost can be reduced; and according to the zero-valent iron reduction-Fenton oxidation integrated reaction device, the zero-valent iron reduction technology and the Fenton oxidation technology are coupled, iron ions produced by a zero-valent iron reduction working section can be fully used in a Fenton oxidation working section as catalysts, and thus the treatment efficiency of the Fenton oxidation working section can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for treating cobalt intermediate product
The invention discloses a method for treating a cobalt intermediate product. The method for treating the cobalt intermediate product comprises the steps that S1, acid dissolution leaching is carried out, specifically, water is added to the cobalt intermediate product to prepare pulp, and sulfuric acid is added to the pulp during stirring for leaching, the cobalt intermediate product contains the following components: 26.90% of cobalt, 1.58% of copper, 3.99% of manganese, 1.62% of calcium, 4.09% of manganese and 5.09% of iron; S2, reduction leaching is carried out, specifically, hydrogen peroxide is added as a reducing agent for further leaching, and then filtering is carried out to obtain leaching liquid and leaching residue; and S3, iron removal is carried out, specifically, carbonate isadded to the leaching liquid to adjust the pulp, and then solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain iron removal slag and iron removal liquid. The method for treating the cobalt intermediate product is simple in process and is realized through three steps of acid dissolution leaching, reduction leaching and iron removal. The hydrogen peroxide is adopted to reduce Co3+ which is difficult toleach in the leaching process, and the leaching of cobalt and the removal of iron can be quickly and effectively achieved without any environmental pollution, and the method for treating the cobalt intermediate product belongs to clean production. Compared with other commonly used reducing agents, the reagent cost of the hydrogen peroxide is lower in price, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:浙江格派钴业新材料有限公司
Method for producing stainless steel master liquid
ActiveCN102719726AProcess production time shortenedShorten production timeProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceElectric arc furnaceFerrosilicon
g stainless steel master liquid, which adopts two electric arc furnaces for smelting. The method includes the following steps in sequence: (I) 4 to 6 tons of carbon steel scrap are loaded into the electric arc furnace A and spread on the floor, 130 to 162 tons of high-phosphorus chromium-nickel cast iron are loaded in the middle of the electric arc furnace A, 4 to 6 tons of carbon steel scrap are loaded in the upper layer of the electric arc furnace A, and arc is started; (II) electric melting, desiliconization and dephosphorization are carried out, and treatment is carried out in the electric arc furnace A for 100 to 140 minutes until P is less than or equal to 0.020 percent; and molten iron is poured into a ladle, and is poured into the electric arc furnace B in one step or two steps equally; (III) after the molten iron is poured into the electric arc furnace B in two steps, 48 plus or minus 3 tons of high-carbon ferrochromium and 45 plus or minus 3 tons of high-phosphorus chromium-nickel cast iron are added into the electric arc furnace B, or after the molten iron is poured into the electric arc furnace B in one step, 48 plus or minus 3 tons of high-carbon ferrochromium is added into the electric arc furnace B; (IV) after electricity is supplied for no less than 8 minutes, oxygen is blown to assist melting, 8 plus or minus 2 tons of lime is added, and after 60 plus or minus5 minutes, the burden in the furnace is completely molten down. 300kg to 500kg of ferrosilicon is added for reduction, and after 8 plus or minus 3 minutes of reduction, the stainless steel master liquid is tapped. In the method for producing the stainless steel master liquid, the high-phosphorus chromium-nickel cast iron accounts for 66 to 74 percent per ton of steel.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Reduction kiln equipment and method for directly reducing iron
InactiveCN102643942AImprove thermal conductivityFacilitate conductionFluidised-bed furnacesCombustion chamberEngineering
Owner:辽宁博联特冶金科技有限公司
Method for synchronously separating iron, vanadium and manganese in vanadium extracting tailings
ActiveCN105018734AHigh recovery rateEfficient use ofProcess efficiency improvementResource utilizationManganese
The invention discloses a method for synchronously separating iron, vanadium and manganese in vanadium extracting tailings. According to the method, the vanadium can be converted into soluble vanadate in the iron reduction process by adding sodium salt, and in other words, vanadium conversion and iron reduction are performed at the same time. Calcined ore is processed through water quenching, not only can heat of the calcined ore be fully utilized to reach needed leaching temperature, but also crushing and ore grinding loads can be reduced, and electric consumption is reduced. Then, the vanium enters a solution through ore grinding leaching; the iron and the manganese are separated through weak magnetic separation according to magnetic differences, and therefore the iron, the vanadium and the manganese can be synchronously separated. The method has the beneficial effects of being simple in technology, low in energy consumption and high in metal recovery rate; the vanadium extracting tailings can be efficiently utilized; and the method plays an important role in increasing the resource utilization rate of vanadium titano-magnetite.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for pretreatment on industrial wastewater by nascent state ferrous iron reduction
ActiveCN102627360ARaise the pHSolve processing problemsMultistage water/sewage treatmentIndustrial waste waterPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection and especially relates to a method for pretreatment on industrial wastewater by nascent state ferrous iron reduction. The method is characterized in that acidic wastewater and zero-valent iron undergo a reaction in the presence of a catalyst to produce a large amount of high-activity nascent state ferrous iron and the acidity of the acidic wastewater is eliminated and a pH value of the acidic wastewater is improved; the high-activity nascent state ferrous iron and alkaline wastewater are mixed according to a certain ratio so that nascent state ferrous iron ions form a high-activity structural-state ferrous complex under alkaline conditions; through negative and positive ions and the catalyst in the wastewater, reduction performances of structural-state ferrous iron are improved; and through addition of a trace amount of an oxidizing agent, catalytic oxidation effects of residual ferrous iron are performed so that a ferrous iron structural form is changed and coagulating precipitation effects of ferrous iron are improved. The method realizes preparation of nascent state ferrous iron from acidic waste water, utilizes reduction effects of zero-valent iron and ferrous iron, realizes synchronous treatment on acidic wastewater and alkaline wastewater, realizes treatment of wastes with processes of wastes against one another and saves a treatment cost.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
High-concentration nitrobenzene wastewater pretreatment device and treatment method
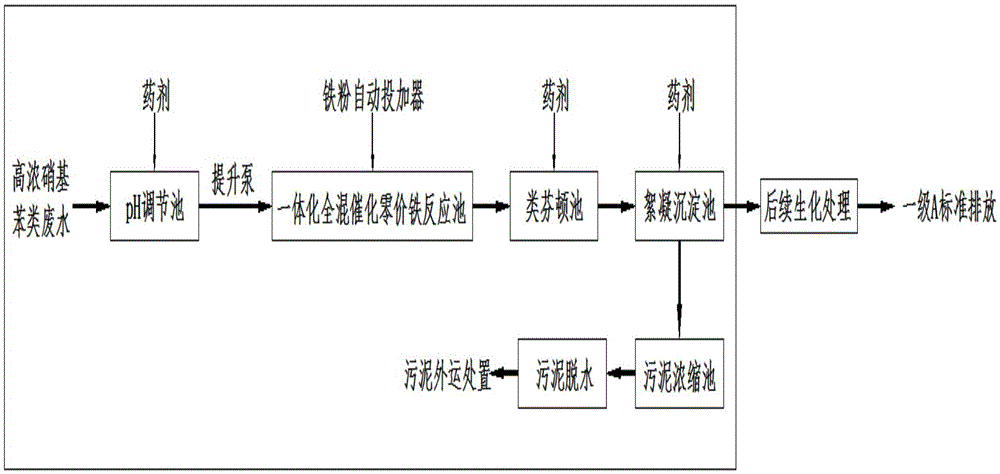
ActiveCN105645633AReduce consumptionLow running costWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsHigh concentrationPretreatment method
The invention discloses a high-concentration nitrobenzene wastewater pretreatment device and treatment method, belonging to the field of organic chemical industry wastewater treatment. The device and method solve the problems of high pretreatment difficulty, low treatment efficiency, high treatment cost, complex operation and the like in the existing high-concentration nitrobenzene wastewater treatment method. The pretreatment device is sequentially composed of a pH regulating tank, an integrated complete-mixing zero-valent iron reaction tank, a Fenton-like reaction tank and a flocculating settling tank. The integrated complete-mixing zero-valent iron reaction tank has high reduction treatment capacity for nondegradable organic matters, can not harden after long-term operation, and has the advantages of wide pH value range, low iron powder consumption, lower operating cost and simple operation. The Fenton-like reaction tank performs Fenton oxidation by utilizing Fe<2+> and H2O2 which are dissolved out by the integrated complete-mixing catalytic zero-valent iron reduction reaction, thereby lowering the pollutant concentration under economical conditions. Thus, the high-concentration nitrobenzene wastewater pretreatment method has the advantages of favorable treatment effect and lower operating cost, is simple to operate, and can stably satisfy the subsequent biochemical treatment requirements.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Gas-based DRI (direct-reduced iron) device and rapid iron reduction method
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy and metallurgical equipment, and relates to a gas-based direct reduction iron method device and a method for rapidly reducing iron. The device of the present invention uses reducing gases such as H2, water gas, and coke oven gas as reducing agents for 140-325-mesh powdered iron ore to perform deep reduction deoxidation, decarburization, and desulfurization to realize gas-based reduction of iron. The invention can be used for deoxidation, decarburization, desulfurization and other treatments of copper powder, cobalt powder, nickel powder, tungsten powder, molybdenum powder and other metal powder materials. In addition to the deep reduction of ordinary iron ore powder, the device and method can also directly reduce ultra-pure iron concentrate powder or iron oxide scale into secondary reduced iron powder for powder metallurgy without the need for secondary reduction. The hot powder metallurgy powder after reduction is directly hot loaded and sent to the hydraulic press mold, and various mechanical parts and components are produced by hot rolling. This device is also suitable for coal-based direct reduction of DRI products.
Owner:唐竹胜
Ozone-anaerobic iron reduction combined Fenton oxidation technology for sludge reduction
InactiveCN105366899AAchieve reductionPromote degradationSludge treatment by oxidationBiological sludge treatmentChemistryIron reduction
The invention discloses an ozone-anaerobic iron reduction combined Fenton oxidation technology for sludge reduction. The technology comprises the following steps: part of iron-containing sludge produced by Fenton oxidation firstly undergoes ozone oxidation treatment so as to preliminarily decompose refractory organic matter in the iron-containing sludge into small molecular easily biodegradable organic matter; then, the small molecular easily biodegradable organic matter enters an anaerobic iron reduction reactor; degradability of organic components in the sludge is further improved in the anaerobic iron reduction reactor, and simultaneously under the action of anaerobic iron-reducing bacteria, the process of converting Fe<3+> in the Fenton iron-containing sludge to Fe<2+> is completed; and finally, solid-liquid products containing Fe<2+> after the reaction all return to the front end of the Fenton oxidation process so as to partially replace Fe<2+> added in the Fenton oxidation process. Sludge reduction of the system is realized, so as to save construction investment and operating cost.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Iron-reduced tuftedmonas and its use
This invention opens a hair iron reduction Cong Aeromonas and its applications. After a lot of inventors experimental study, and selected a hair iron reduction Aeromonas Cong, a reduction of humus and iron reduction activity. This reduction of citric acid to iron, ferric hydroxide, water iron ore, goethite three-valent iron; can restore humus and humus model of AQDS (anthraquinone 2 ,6 - disulfonic acid). Iron reducing gross Cong Aeromonas facultative anaerobic, the electronic spectrum for the broader use of this bacterium in the anaerobic oxidation conditions to the electronic donor: glycerol, glucose and sucrose.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
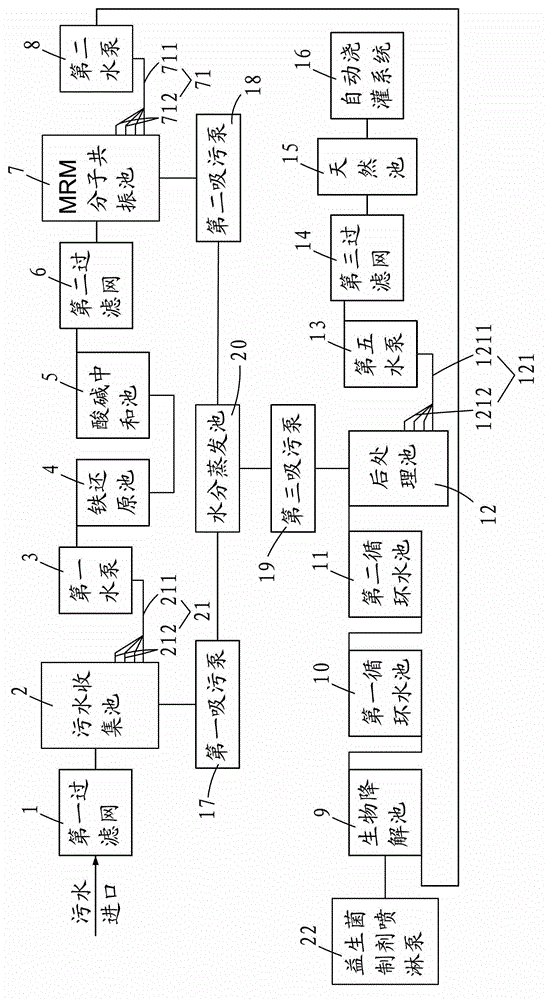
Sewage treatment method
ActiveCN102745862ACause secondary pollutionAvoid contamination damageWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsEnergy based wastewater treatmentIron reductionHeavy metals
The invention provides a sewage treatment method. The sewage treatment method comprises the following steps of filtering sewage by a first filter screen, reducing the filtered sewage by an iron reduction tank, carrying out acid-base neutralization by an acid-base neutralization tank, carrying out MRM molecular resonance, carrying out biodegradation purification, and standing for 24 hours in an after-treatment tank. The sewage treatment method realizes zero discharge of sewage. The sewage treatment method has a low cost, can be operated simply, does not adopt any chemical reagents in after-treatment, does not produce secondary pollution on the environment, and solves the problem that heavy metals and microbes in specialized laboratory sewage produced by the existing scientific research institutions and hospitals pollute and damage the environment.
Owner:张明荣
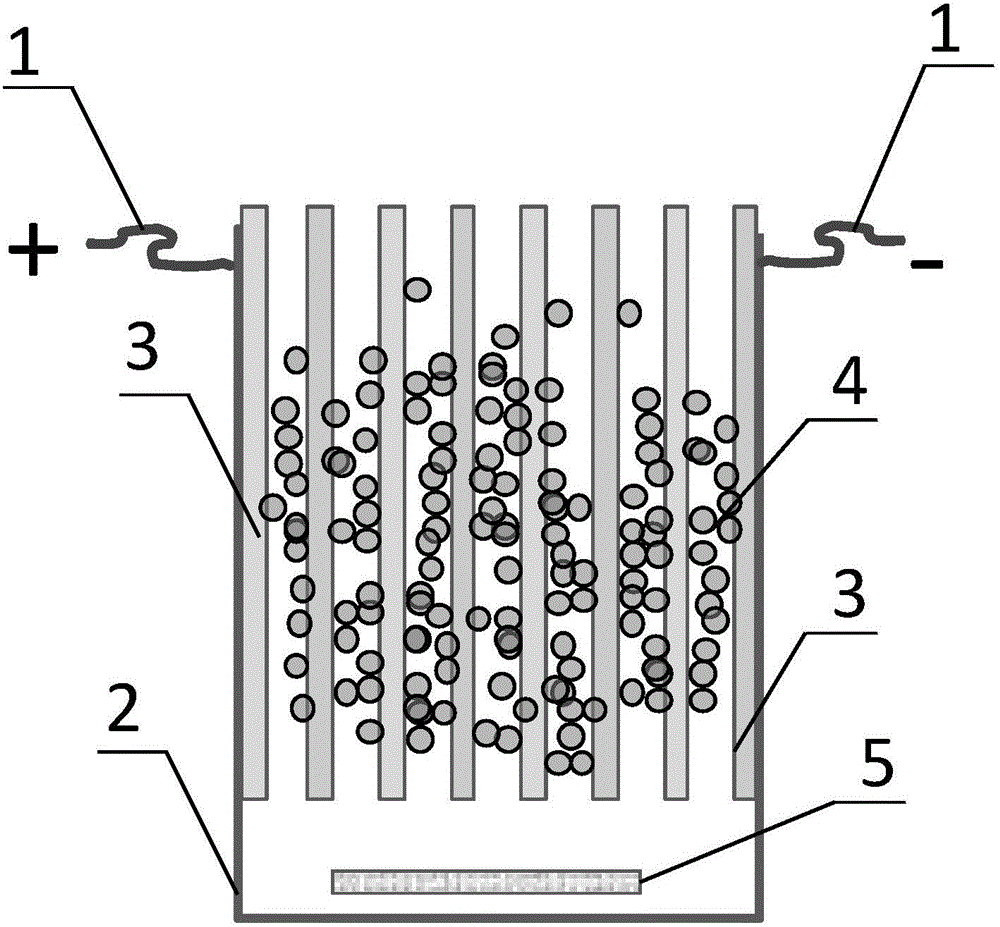
Zero-valent iron type water purifying method based on electric field intensification and reactor
InactiveCN106477689AAccelerated corrosionIncrease profitWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsEngineeringTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a method for intensifying zero-valent iron reduction to remove pollutants. The method includes that an electric field is formed by applying direct current at an anode end and a cathode end respectively, and the zero-valent iron is fed into a reactor and reacts with the pollutants in water under a sufficiently mixed hydraulic condition, so that water purification is achieved. The method has the advantages that water purifying effects are effectively improved through coupling between electrochemical action and the zero-valent iron action, so that the defects of activity declining and zero-valent iron packed bed hardening due to corrosion and passivation of traditional zero-valent iron surfaces are overcome, and zero-valent iron utilization efficiency is improved substantially; the technical principle includes that the zero-valent iron is disposed in the direct-current electric field, and on the basis of conventional chemical corrosion of the zero-valent iron, the electric field intensifies electrochemical corrosion effect of the zero-valent iron, so that the electron donating ability of the zero-valent iron is enhanced, and the problems of corrosion layer deposition and treatment effect declining are effectively avoided. The invention further provides the reactor for implementing the method.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extraction method of ferro-vanadium-titanium ore
InactiveCN102260786AGood for healthBeneficial protectionProcess efficiency improvementIron reductionHuman health
The extraction method of iron-vanadium-titanium ore, firstly, roasting is carried out to separate iron and titanium, titanium and vanadium are leached, iron is reduced and roasted, and the vanadium in the raw ore is extracted by adding industrial chemical additives, and processed into vanadium dioxide; , by adding industrial chemical additives, then extracting the titanium element, and processing it into titanium dioxide; finally, the raw materials are processed again, and chemical additives and reducing agents are added to increase the content of reduced iron powder to more than 95% (TFe). The beneficial effect of the present invention is that by adding industrial chemical additives and reducing agents, and then heating and processing, the grade of iron can be increased to more than 95% (TFe), which greatly improves economic benefits and reduces production energy consumption Cost, to achieve resource reuse, effective utilization, environmental protection and other technological leaps, greatly beneficial to human health and environmental protection.
Owner:彭海洋
Slow-release composite repairing reagent for treating persistant halohydrocarbons in soil and preparation method of same
ActiveCN108690625AFriendlyHigh mechanical strengthContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersHalohydrocarbonLocust bean gum
The invention discloses a slow-release composite repairing reagent for treating persistant halohydrocarbons in soil and a preparation method of same. The preparation method includes steps of: 1) preparing microbial liquid saturated black charcoal; 2) preparing a colloidal solution A containing locust bean gum and an organic carbon source; 3) preparing a colloidal turbid liquid B containing the locust bean gum, organic carbon source, nano zero-valent metal, and the microbial liquid saturated black charcoal; 4) performing a crosslinking reaction for 2-6 h; 5) performing a delayed crosslinking reaction for 2-6 h to obtain the slow-release composite repairing reagent. By means of excellent adsorption performance of the black charcoal, high-effective chemical reduction effect of the nano zero-valent metal and dissimilatory iron reduction dehalogenation capability of functional microorganisms, the repairing reagent can achieve physical-chemical-biological synergistic reinforced repairing effect to the soil polluted by the persistant halohydrocarbons, and has advantages of long action period, stable structure, low cost and environment-friendly property.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES +2
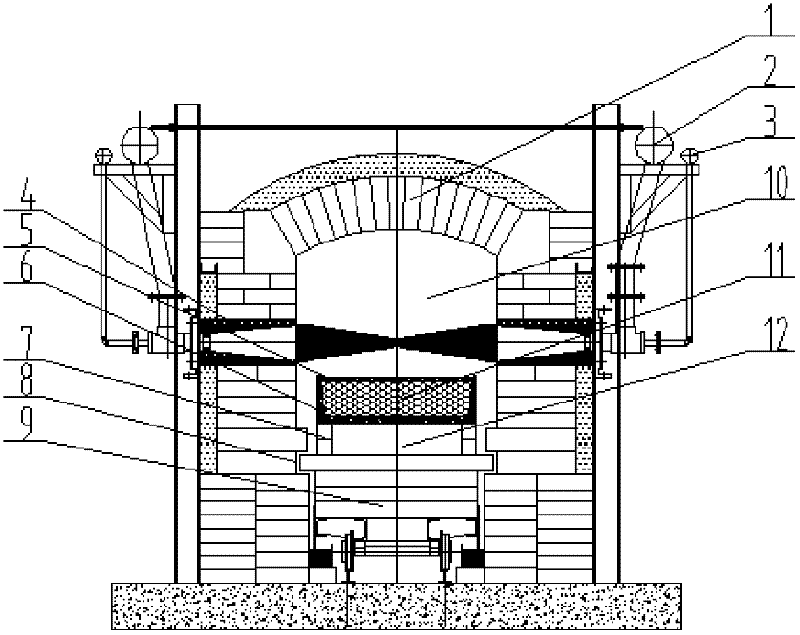
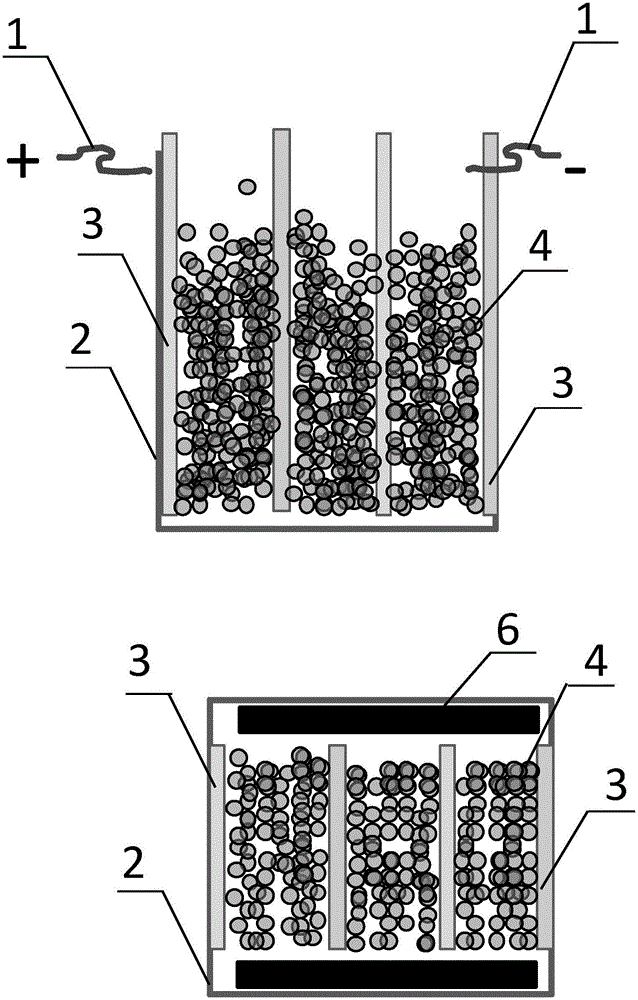
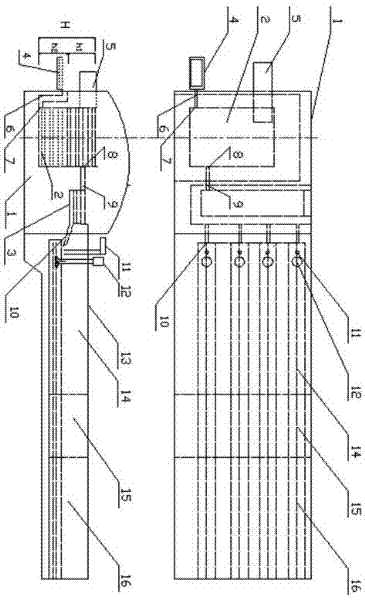
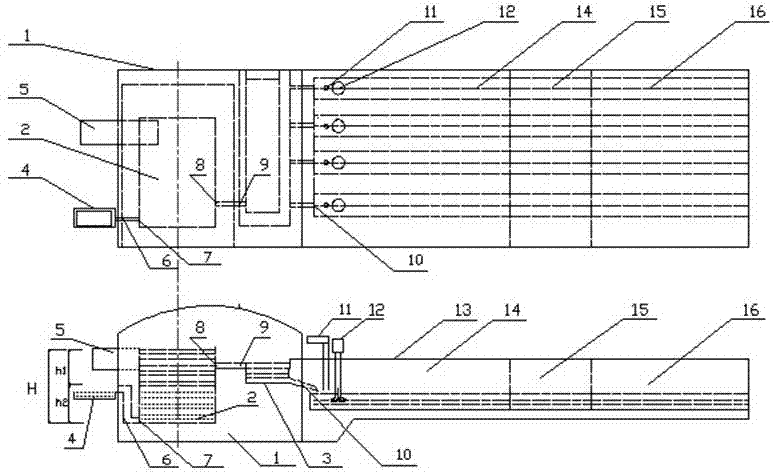
Preparation method of red mud iron reduction furnace slag light foamed ceramic and iron reduction furnace
The invention discloses a preparation method of red mud iron reduction furnace slag light foamed ceramic and an iron reduction furnace. A red mud iron reduction furnace is characterized by comprising an iron reduction furnace 1, a melting bath 2, a furnace slag melting bath 3, a molten iron melting bath 4, a feeding machine 5, a molten iron channel 6, a molten iron inlet 7, a furnace slag melt outlet 8, a furnace slag melt channel 9, a furnace slag melt feeding hole 10, a foaming agent inlet 11, a stirring machine 12, a float glass kiln body 13, a foaming section 14, a foam stabilizing section 15 and an annealing section 16; red mud is taken as a main material, and green coke precious stone, waste glass dust, quartz sand, coal gangue and titanium dioxide are added; and the ceramic consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 35-82.5 percent of red mud, 3-15 percent of green coke precious stone, 3-10 percent of waste glass dust, 1-15 percent of quartz sand, 10-20 percent of coal gangue and 0.5-5 percent of titanium dioxide. Industrial waste is taken as a major raw material, so that production cost is reduced, environmental pollution is lowered, and economic efficiency and environmental friendliness are realized; waste can be recycled; and a prepared red mud iron reduction furnace slag light foamed ceramic tile has high strength, high heat preserving property and high decorating characteristic.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for alleviating nano zero-valent iron passivation
InactiveCN106830267AEasy to operateReduce energy consumptionTransportation and packagingWater contaminantsReduction ActivityNanometre
The invention relates to the technical field of materials and discloses a method for alleviating nano zero-valent iron passivation. The method comprises the following steps: selecting at least one iron reduction microbe, culturing by selecting a proper culture medium, and ending culture while reaching the stable phase of the microbes; and adding the at least one iron reduction microbe screened in the step (1) into a reaction system of zero-valent iron reduced organic pollutants when the reduction activity of the nano zero-valent iron is less than or equal to 50% of the original activity. Compared with the existing method for alleviating zero-valent iron passivation, the method disclosed by the invention is environment-friendly, adopts ubiquitous iron reduction microbes in the environment and is simple in operation. In addition, the method disclosed by the invention is low in energy consumption, does not need extra energy and is capable of simultaneously achieving the effects of alleviating nano zero-valent iron passivation and promoting degradation of the pollutants.
Owner:SUZHOU INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY USTC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com