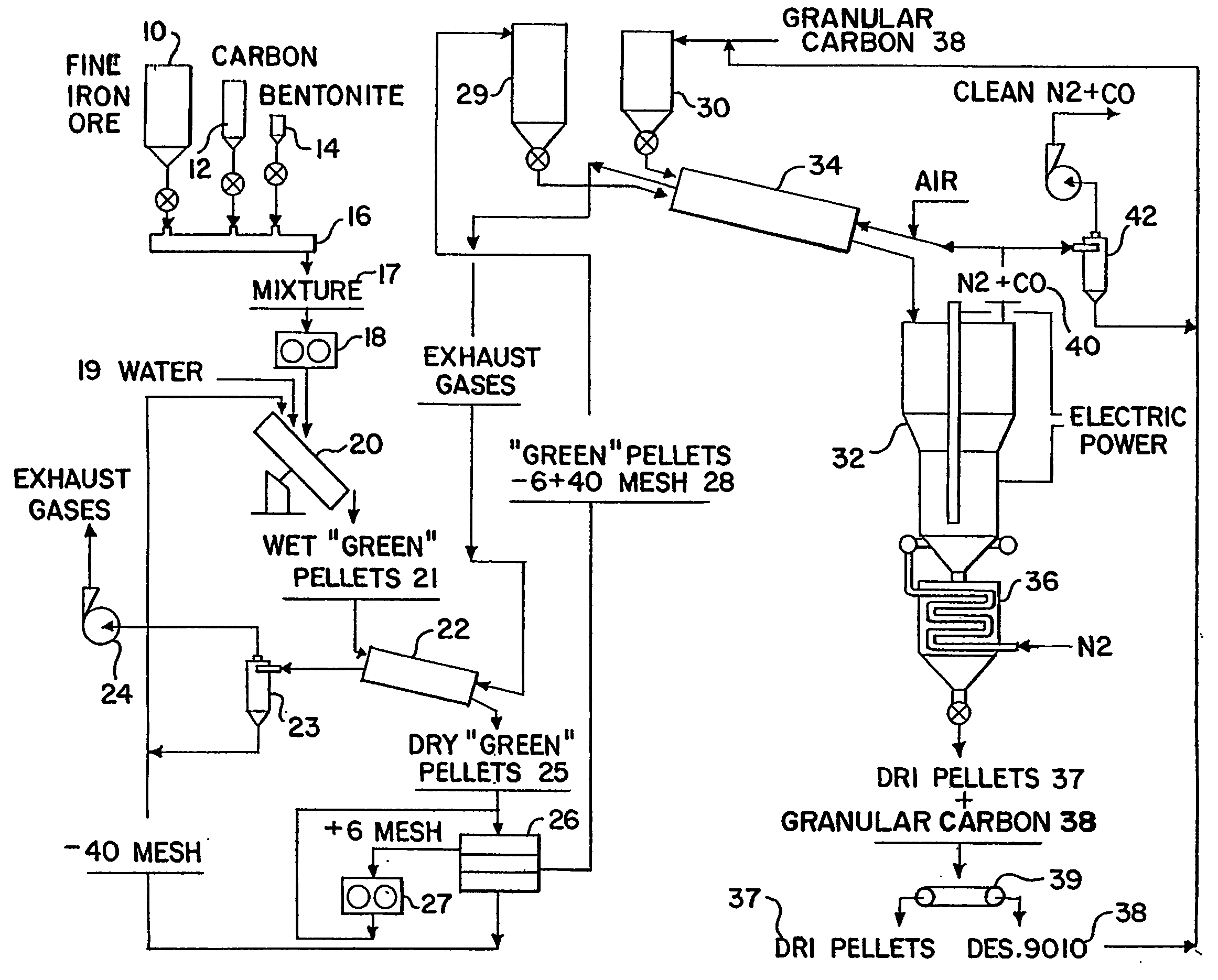
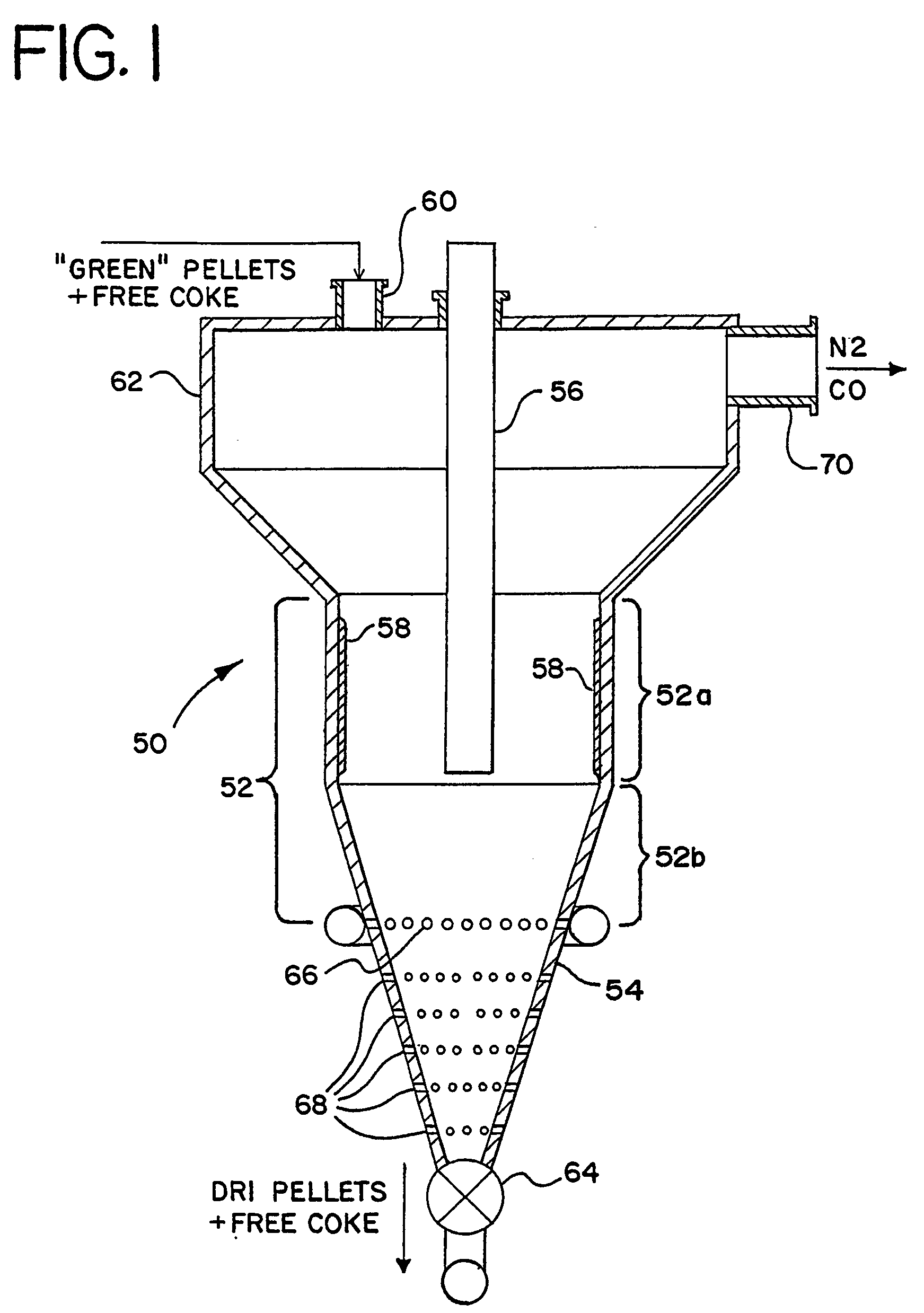
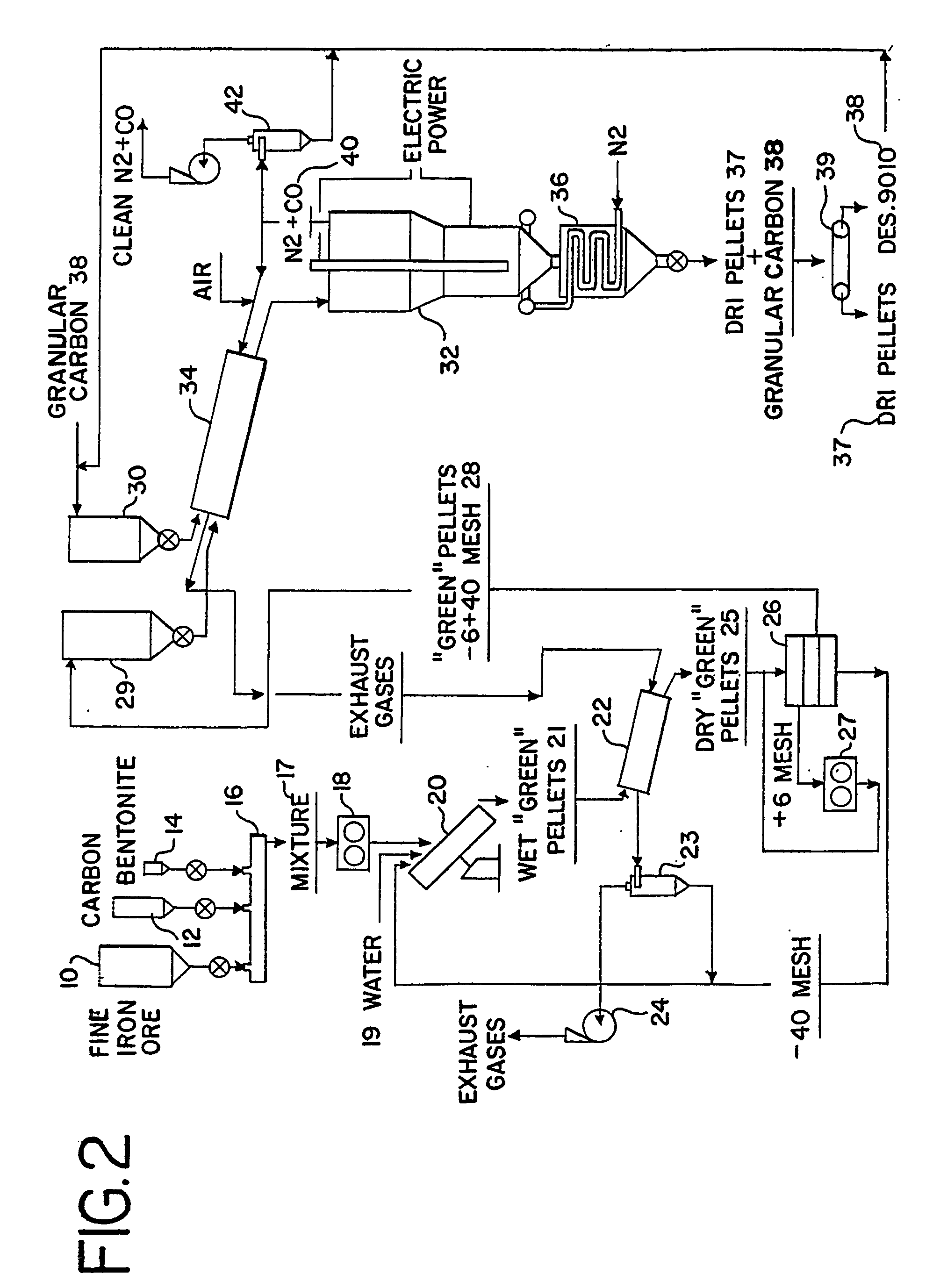
Process and apparatus for the direct reduction of iron oxides in an electrothermal fluidized bed and resultant product
a technology of electrothermal fluidized bed and process apparatus, which is applied in lighting and heating apparatus, furnaces, charge manipulation, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrolled agglomeration of iron onto the surface of electrodes and other internal surfaces, and achieve the effect of preventing particle agglomeration and deposition formation and reducing cross-sectional area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
DRI
[0044] The production of DRI pellets was conducted at the following operation parameters in a pilot EFB furnace having an inside FB diameter of 61 cm (24 in.). (In this example, as well as Examples 2 and 3, infra., Flexi coke brand of petroleum coke and Desulco 9010 brand of granular carbon were used for expediency.)
[0045]“Green” DRI Pellets
Composition:Fine iron oxide (99.3% Fe2O3, 100% −75%Flexi coke (˜6% of volatile components,−23.5%100% Bentonite (100% −1.5%Pellet size:−8 + 40 mesh−2.35 + 0.425 mmSpecific density:2.2-2.5 g / cc
[0046] Feeding:
Mixture of “Green” DRI pellets and heat treated coke“Desulco 9010”Composition: “Green” DRI pellets:Desulco 901070:30“Desulco 9010” particle sizes:−4 + 30 mesh4.75 + 0.6 mm
[0047] Process Parameters
Feeding rate:105-115 lb / hrAverage power applied120-125 kWNitrogen rate:38-45 scf / minInlet N2 pressure30-45 in. H2OOperation FB temperature:1020-1050° C.Average retention time of DRI pellets in FB:˜1 hrDischarge rate of mixture “DRI” pelle...
example 2
Direct Reduction of Iron Oxide Fines in Electrothermal FB without Preliminary Preparation
[0050] The direct reduction of iron oxide fines without any preliminary preparation (i.e., pelletizing) was conducted at the following operation parameters in a pilot EFB furnace with inside FB diameter of 61 cm (24 in.).
Fine iron oxide:99.3% Fe2O3,100% Flexi coke:volatile components−2.7%free carbon −94%sulfur-0.9% 0.9%100% “Desulco 9010” particle sizes:−4 + 30 mesh4.75 + 0.6 mm
[0051] Feeding:
Mixture of Iron oxide fines + Flexi coke + “Desulco 9010”Composition:Iron oxide fines50%, wFlexi coke15%, w“Desulco 9010”35%, w
[0052] Process Parameters:
Feeding rate:85-90 lb / hrAverage applied power:95-105 kWNitrogen rate:18-25 scf / minInlet N2 pressure:20-35 in. H2OOperation FB temperature:920-960° C.Average retention time of DRI pellets in FB:˜1 hrDischarge rate of mixture “DRI” pellets and48-50 lb / hrDesulco 9010:
[0053] Discharge Composition:
Magnetic fraction (reduced DRI pellets):40-42%Desulco 90...
example 3
Production of Iron-Bearing Carbon Pellets
[0055] In this example, production of iron-bearing carbon (IBC) pellets was conducted at the following operational parameters in a pilot EFB furnace with an inside FB diameter of 61 cm (24 in.).
IBC pellets
[0056] Composition:
Fine iron oxide (99.3% Fe2O3, 100% 50-60%Flexi coke (˜6% of volatile components,−38-48%100% Bentonite (100% −2%Pellet size:−8 + 40 mesh−2.35 + 0.425 mmSpecific bulk density:1.05-1.55 g / cc
Feeding:
[0057] Mixture of “Green” IBC pellets and heat treated coke Desulco 9010”Composition:
“Green” IBC pellets (50 / 48): Desulco 901075:25“Green” IBC pellets (60 / 38): Desulco 901070:30“Desulco 9010” particle sizes:−4 + 30 mesh4.75 + 0.6 mm
[0058] Process Parameters:
Feeding rate:120-130 lb / hrAverage applied power:78-85 kWNitrogen rate:“Green” IBC pellets (50 / 48): Desulco 901020-21 scf / min“Green” IBC pellets (60 / 38): Desulco 901024-25 scf / minInlet N2 pressure:20-30 in. H2OOperation FB temperature:915-950° C.Average retention tim...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle sizes | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com