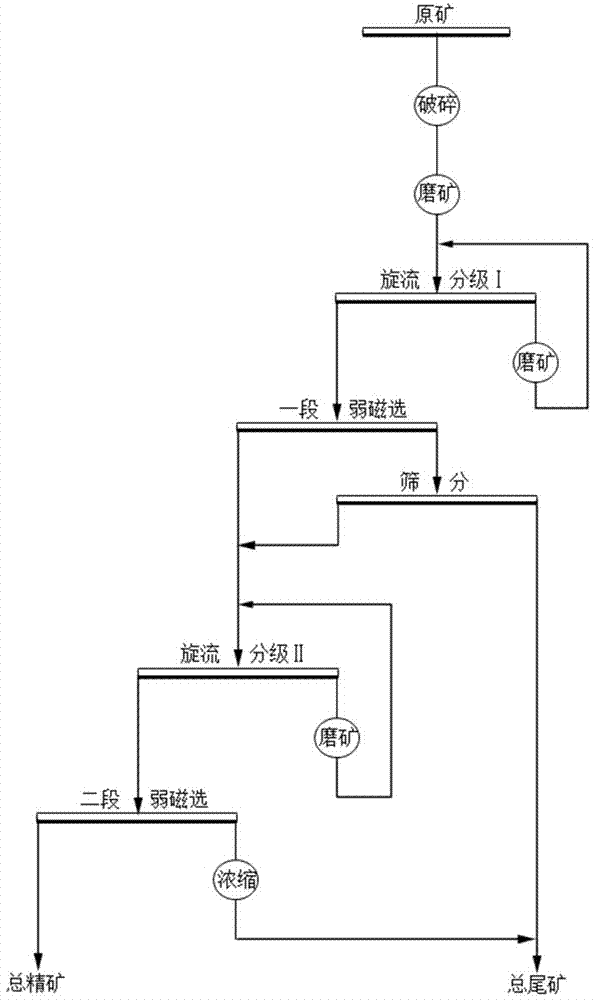
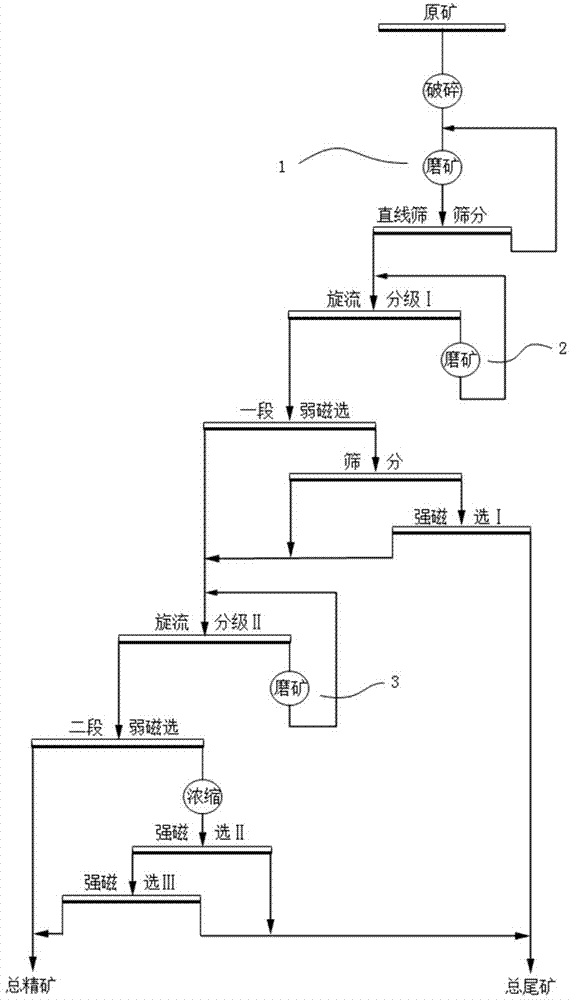
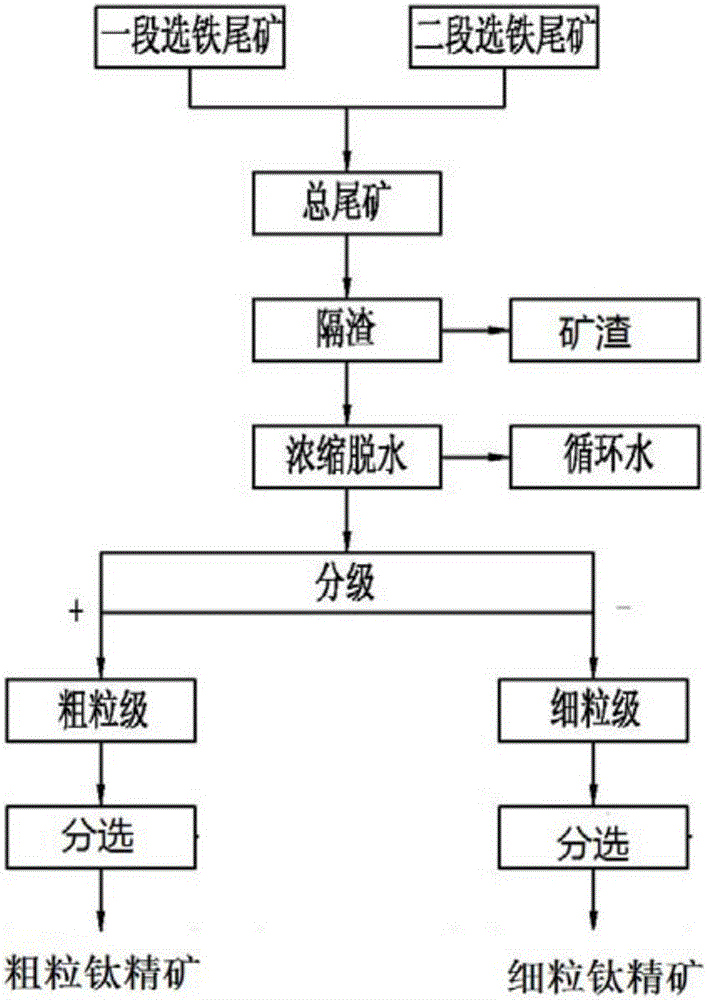
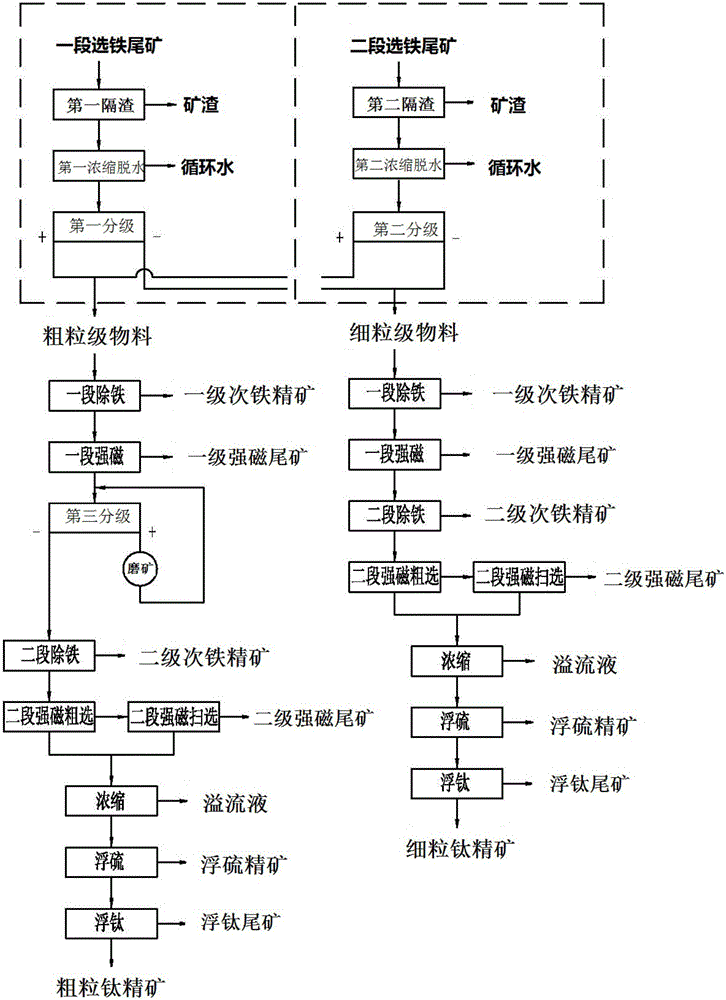
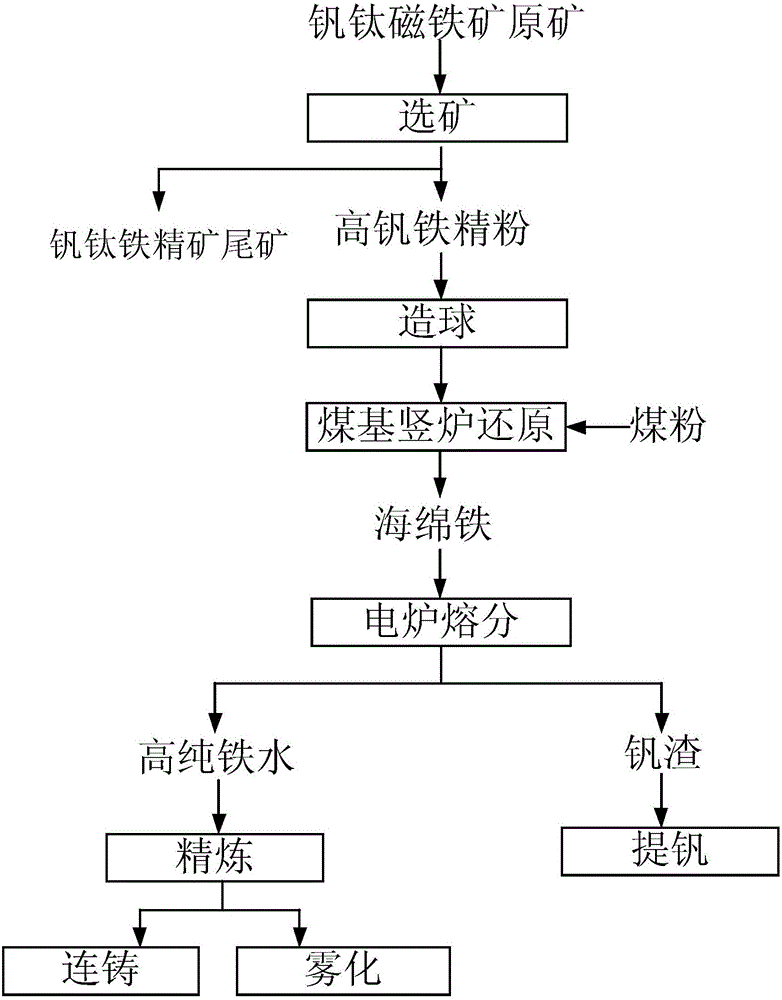
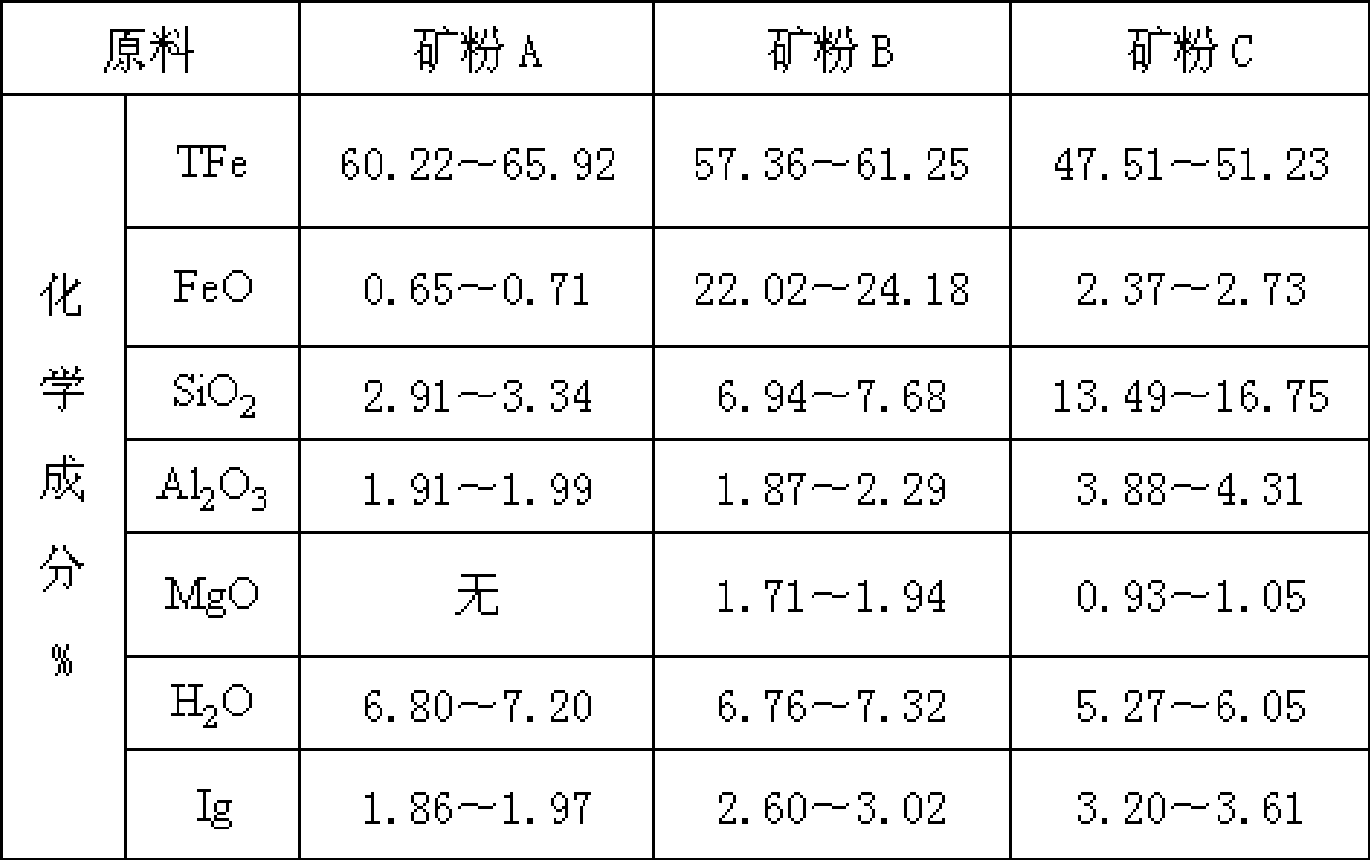
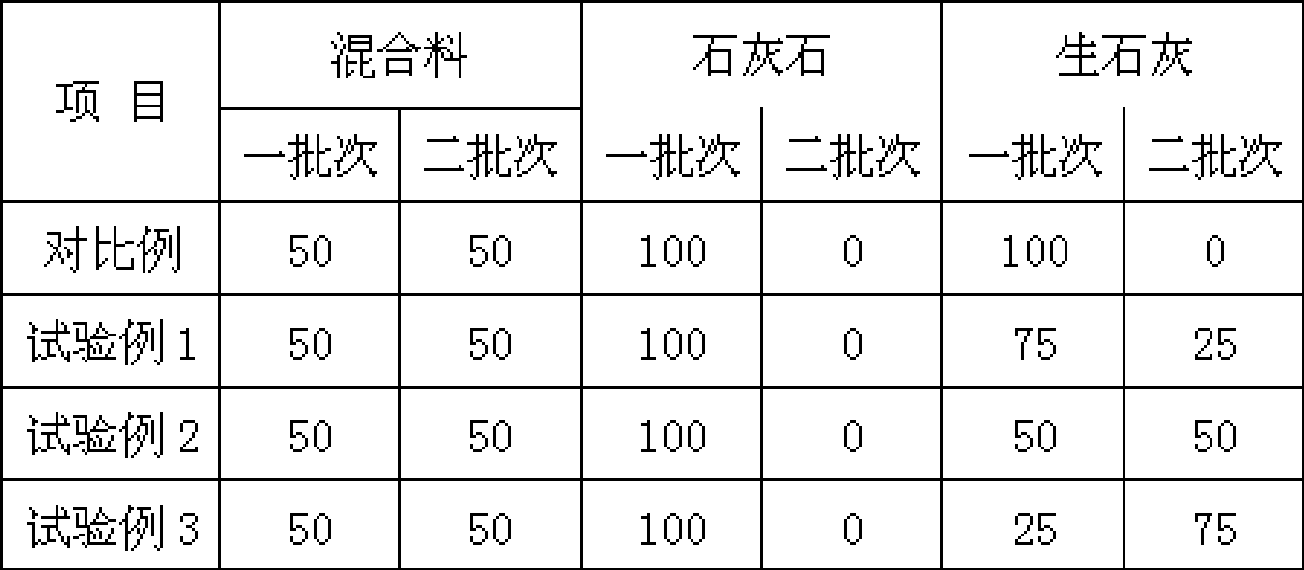
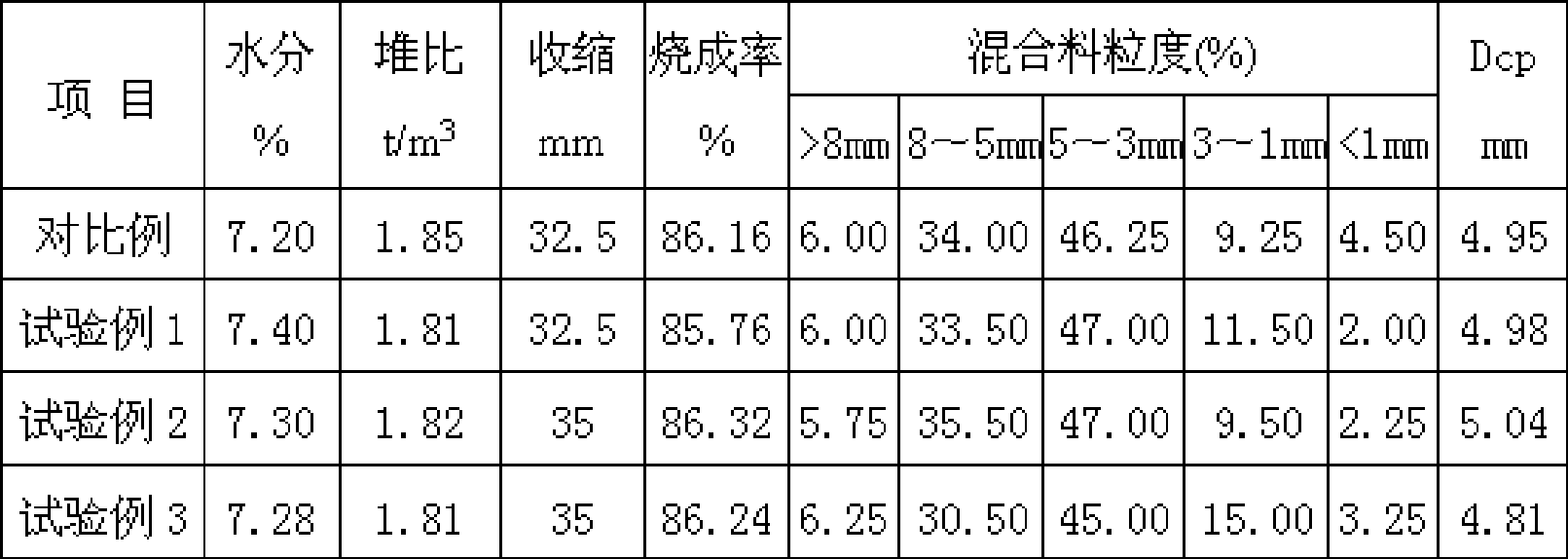
Patents
Literature
297 results about "Titanomagnetite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Titanomagnetite is a mineral containing oxides of titanium and iron, with the formula Fe²⁺(Fe³⁺,Ti)₂O₄. It is also known as titaniferous magnetite. It is part of the spinel group of minerals. The Curie temperature for titanomagnetite has been found to have a wide range of 200 to 580°C.
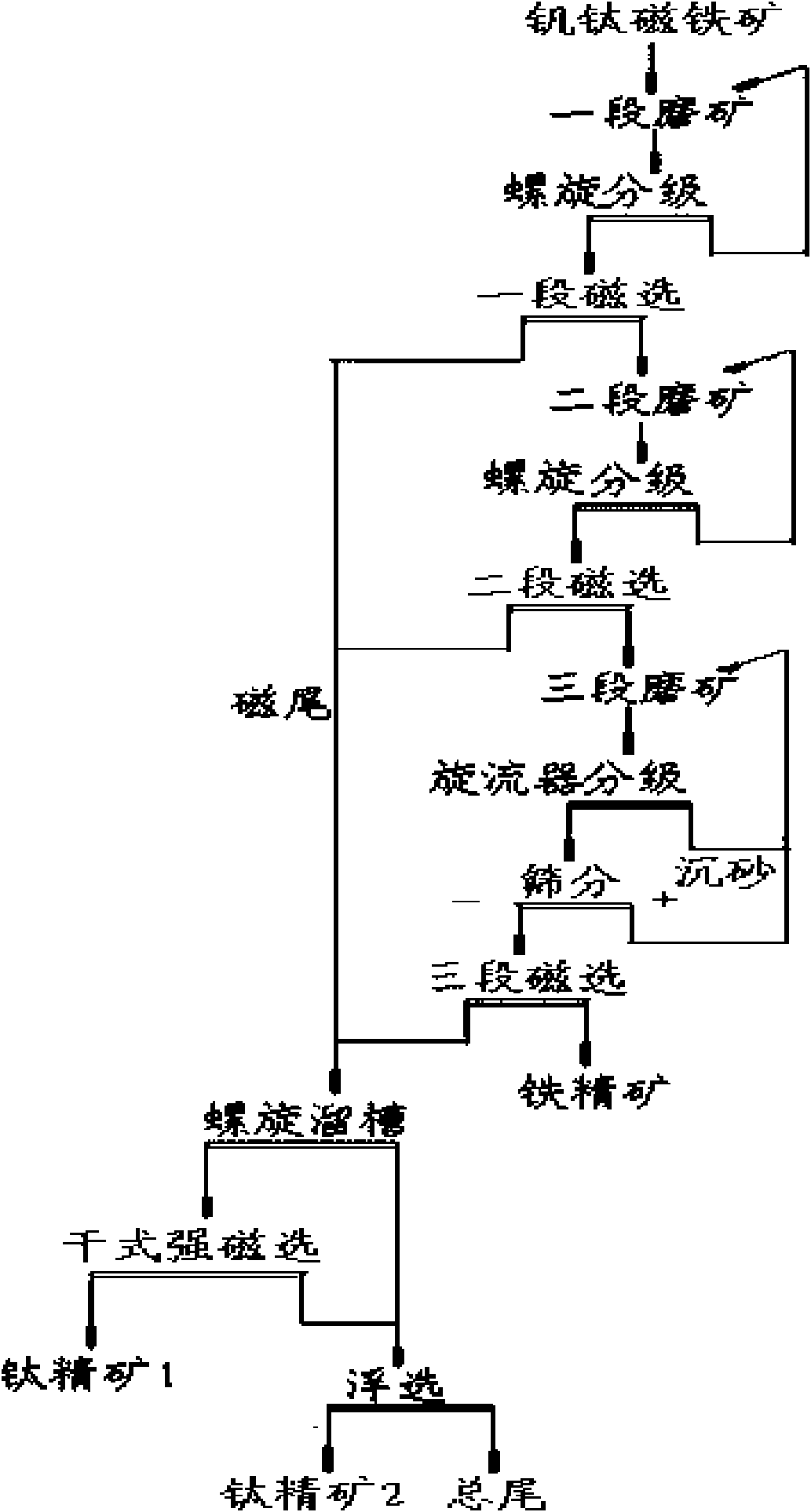
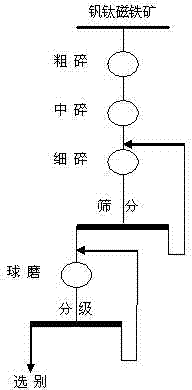
Vanadium titano-magnetite screen method
ActiveCN101564707AQuality improvementHigh recovery rateFlotationMagnetic separationMagnetiteMaterials science
The invention relates to a screen method for vanadium titano-magnetite with high quality, belonging to the ore screen field. The method adopts three stage-grinding and stage-concentration process for magnetic separation, wherein the field intensity of one-stage magnetic separation is 3000-4000 Gs; the field intensity of two-stage magnetic separation is 1800-2200 Gs; and the field intensity of three-stage magnetic separation is 1300-1700 Gs. The recovery rate of the screened iron ore concentrate and the titanium ore concentrate is high and the screened cost of the screened iron ore concentrate and the titanium ore concentrate is low, thus providing a new selection for the low grade vanadium titano-magnetite resource and having a broad application prospect.
Owner:四川安宁铁钛股份有限公司
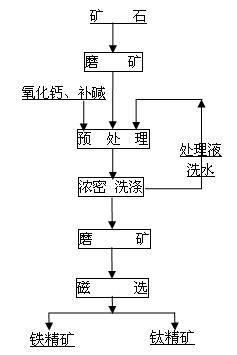
Beneficiating method for ilmenite
ActiveCN102181626AIncrease alkali concentrationHigh in ironBlast furnace detailsProcess efficiency improvementMagnetiteIlmenite
The invention discloses a beneficiating method for ilmenite, relating to a method for preparing titanium concentrate and iron concentrate by beneficiating crude ilmenite. The method is characterized in that: a beneficiating process of the method orderly comprises the following steps of: (1) grinding the crude ilmenite; (2) performing alkaline leaching pretreatment under the conditions of heating, oxygenating and pressurizing; (3) filtering pulp which is subjected to the alkaline leaching pretreatment; (4) washing filter residue and grinding; and (5) performing magnetic separation to obtain the titanium concentrate and the iron concentrate. In the method provided by the invention, the characteristic of iron and titanium compact symbiosis and the isomorphism occurrence characteristic of vanadium are damaged from the source of vanadium titano-magnetite by adopting the pretreatment process, so that mineral transformation of the vanadium titano-magnetite is realized, dissociation on lattice layers of titanium and iron is realized, high-quality iron concentrate and titanium concentrate with lower iron content are obtained through grinding and the magnetic separation process, an alkaline medium used in the pretreatment can be recycled, and the process has a small influence on environment and a bright application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
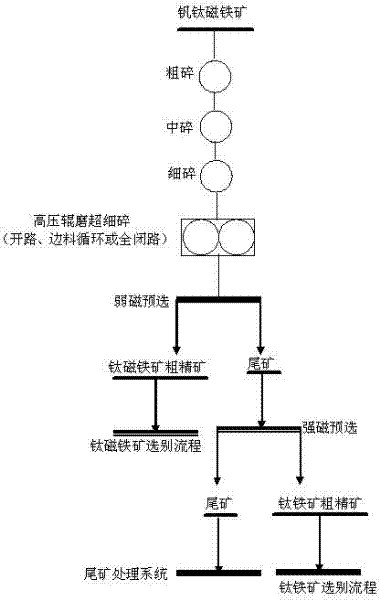
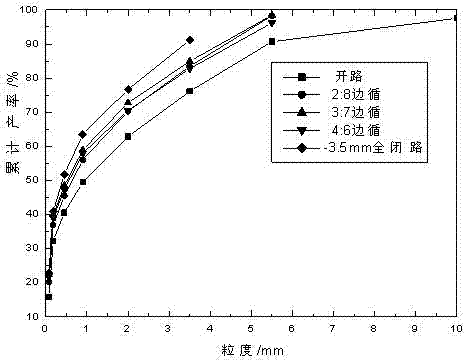
High-pressure roller milling-preselection processing method for vanadic titanomagnetite
InactiveCN102172556AHigh tail yieldRaise the gradeMagnetic separationGrain treatmentsMagnetiteEngineering
The invention discloses a high-pressure roller milling-preselection processing method for vanadic titanomagnetite. The raw ore is subjected to coarse crushing, secondary crushing, fine crushing and high-pressure roller milling superfine crushing, an open circuit crushing, scrap circulation crushing or fully-closed circuit crushing method is adopted, and low-intensity magnetism and high-intensity magnetism preselection is performed. The method disclosed by the invention reduces the energy consumption of crushing and ore milling and improves the ore selection efficiency in comparison with the conventional process; and the low-intensity magnetism and high-intensity magnetism preselection can separately select the main target ores-titanomagnetite and ilmenite in the vanadic titanomagnetite with higher pertinence, and the ore selection flow is simpler. By adopting a high-pressure roller mill as the superfine crushing apparatus after fine crushing, the particle size of the final crushed product can be reduced, and meanwhile, the preselection tailing discarding before milling is realized, the milling grade is improved and the energy consumption of ore milling is reduced. Compared with the traditional process, the particle size of the product is small, the equipment operation rate is high, and the unit crushing energy consumption is low. Meanwhile, the superfine crushed product can besubjected to preselection tailing discarding so as to improve the milling grade, reduce the energy consumption of ore milling, lighten the burden on subsequent selection process and improve the production efficiency.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
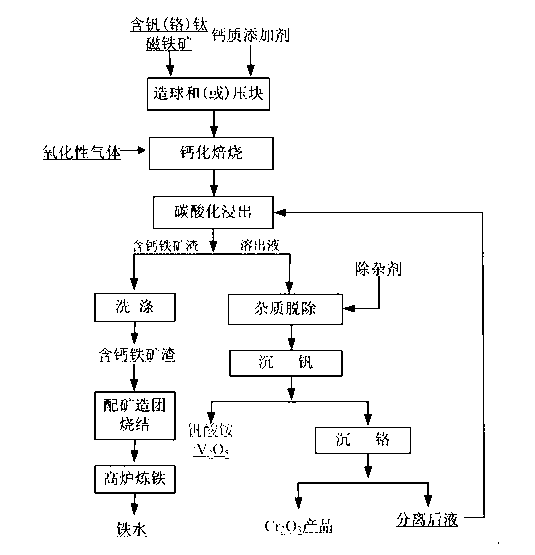
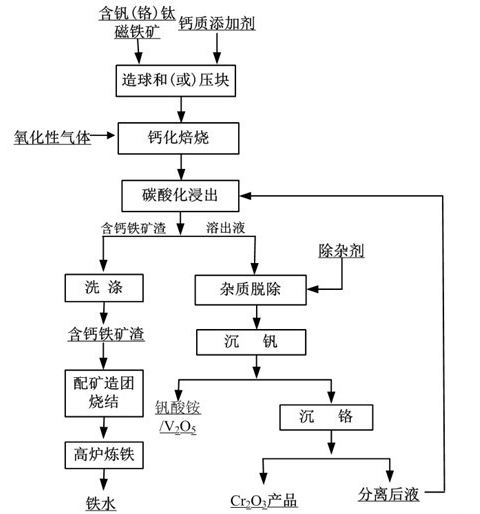
Method for recovering vanadium in vanadium-titanium magnetite ore
ActiveCN102703688ARealize comprehensive utilizationAvoid recyclingProcess efficiency improvementAdhesiveMagnetite
The invention discloses a method for recovering vanadium in vanadium-titanium magnetite ore. The method comprises the process steps of: (1) mixing, pelletizing or briquetting, vanadium-titanium magnetite ore, a calcium additive and an adhesive, drying and oxidizing roasting to obtain roasting clinker; (2) performing carbonation leaching on the roasting clinker by utilizing leaching solution containing CO3<2->, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain calcium-contained iron ore slag and chrome-vanadium-contained dissolving solution; and (3) adding a reagent with NH4+ into the dissolving solution for ammonia settlement, so as to obtain ammonia vanadate, or adding acid liquor into the dissolving solution, and directly acidifying to obtain V2O5. By adopting calcified roasting-carbonation leaching, the vanadium in the vanadium-titanium magnetite ore is recovered, obtained sintered pellets containing the calcium-contained iron ore slag can be directly applied to blast furnace smelting; and therefore, the problem of recovering the vanadium in the vanadium-titanium magnetite ore is effectively solved, and subsequent blast furnace smelting is not influenced. After the vanadium is recovered by using the method, chromium can be recovered from obtained crystallizing mother solution; and therefore, the vanadium-titanium magnetite ore is effectively and comprehensively utilized.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
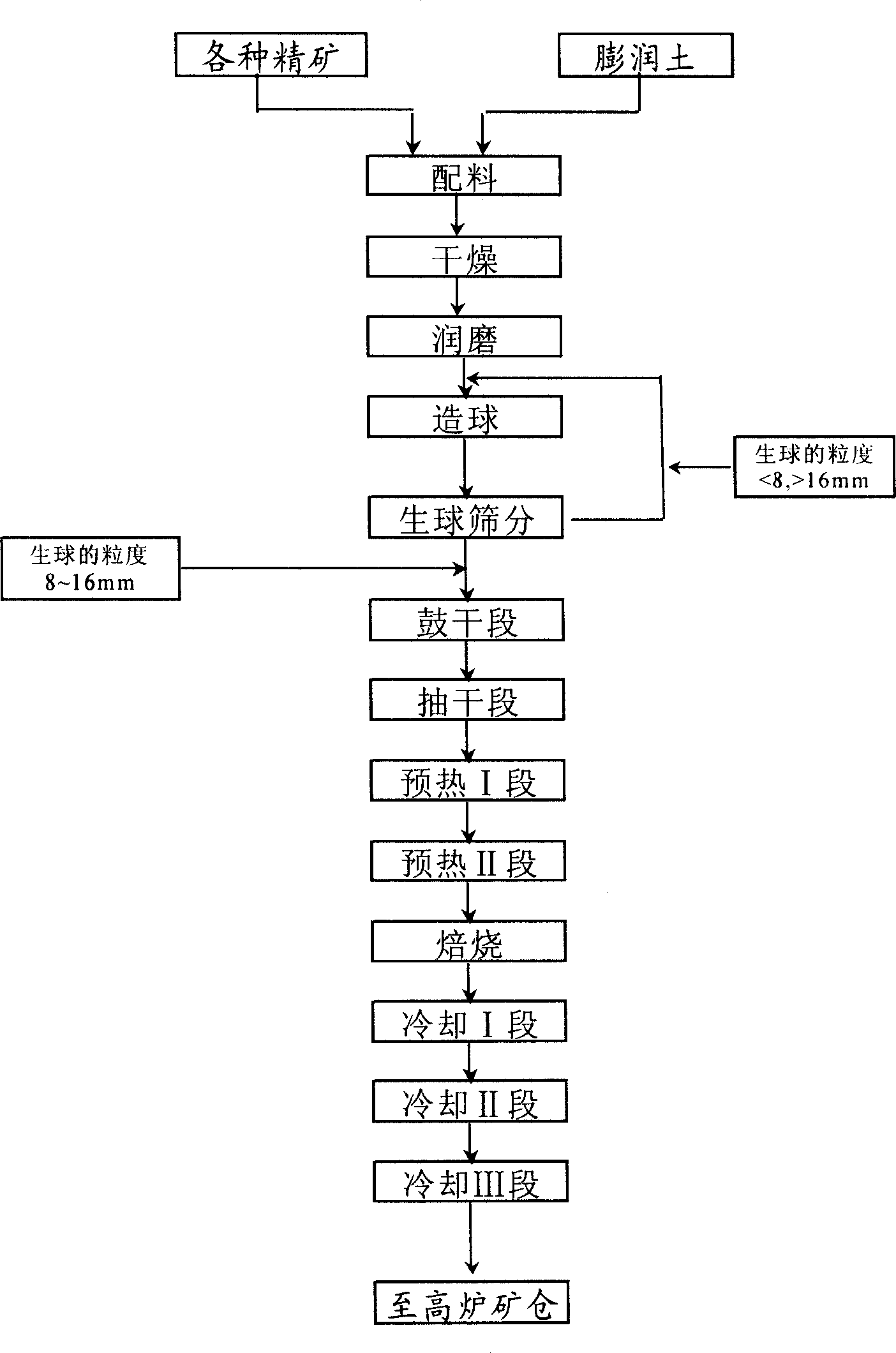
Method for producing high titanium type acid pellet vanadium titanium by chain grate - rotary kiln
This invention discloses a method for producing Ti-rich V-Ti oxidized pellets by chain grate and rotary kiln. The method comprises: mixing vanadic titanomagnetite concentrate with common magnetite concentrate at a weight ratio of 7:3, adding 2.0 wt. % of bentonite, palletizing to obtain 8-16 mm pellets by a disc pelletizer, drying (50-350 deg.C) and pre-heating (500-1000 deg.C) by a chain grate for 12 min, sending dried pellets into a rotary kiln, torrefying at 1150-1300 deg.C and 1.0 r / min for 30-35 min, and cooling torrefied pellets. The obtained Ti-rich V-Ti oxidized pellets have compression strength higher than 1800 N, and TiO2 content of 7.0%, thus can meet the requirement of blast furnace smelting.
Owner:攀枝花钢城集团有限公司球团厂
Method for selecting and smelting titanium from vanadium titanomagnetite at low temperature
InactiveCN102352423AQuick restoreIncrease magnetic susceptibilityProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceDc arc furnaceTitanium metal
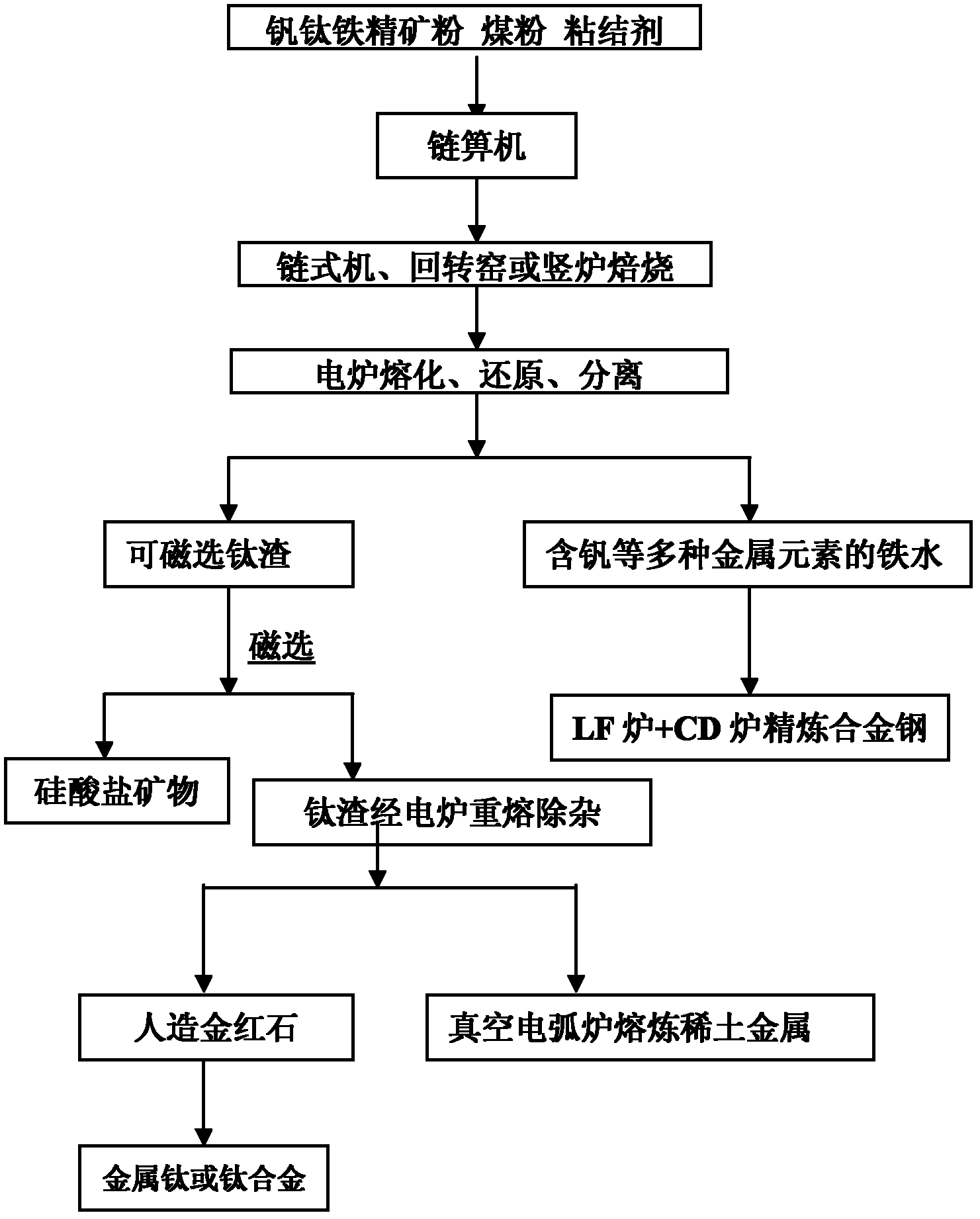
The invention relates to a method for selecting and smelting titanium from vanadium titanomagnetite at low temperature, belonging to the technical field of metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: 1) roasting at the low temperature of 500-1100 DEG C; 2) adding a solid reductant to the roasted product, carrying out reduction smelting at 1100-1300 DEG C, and separating slag and iron torespectively obtain molten iron and titanium slag; carrying out magnetic separation on the titanium slag to remove impurities, thereby obtaining the titanium-rich material; and 4) adding required metal oxide concentrate into a direct-current arc furnace, and directly alloying the molten iron to obtain alloy steel. The smelting method provided by the invention is a brand new smelting method, and changes the existing iron ore selection into titanium ore selection; the pellet is molten and reduced by roasting at low temperature, and the separated molten iron facilitates the addition of ores withdeficient metal elements so as to directly smelt the alloy steel; the titanium slag is subjected to magnetic separation to obtain the titanium-rich material, and the titanium-rich material is furthersmelted to obtain the titanium alloy or titanium metal; and the smelting slag can be used as the raw material for smelting rare earth metals so as to sufficiently and respectively utilize the elements in the ores in one step.
Owner:攀枝花慧泰金属新材料有限公司
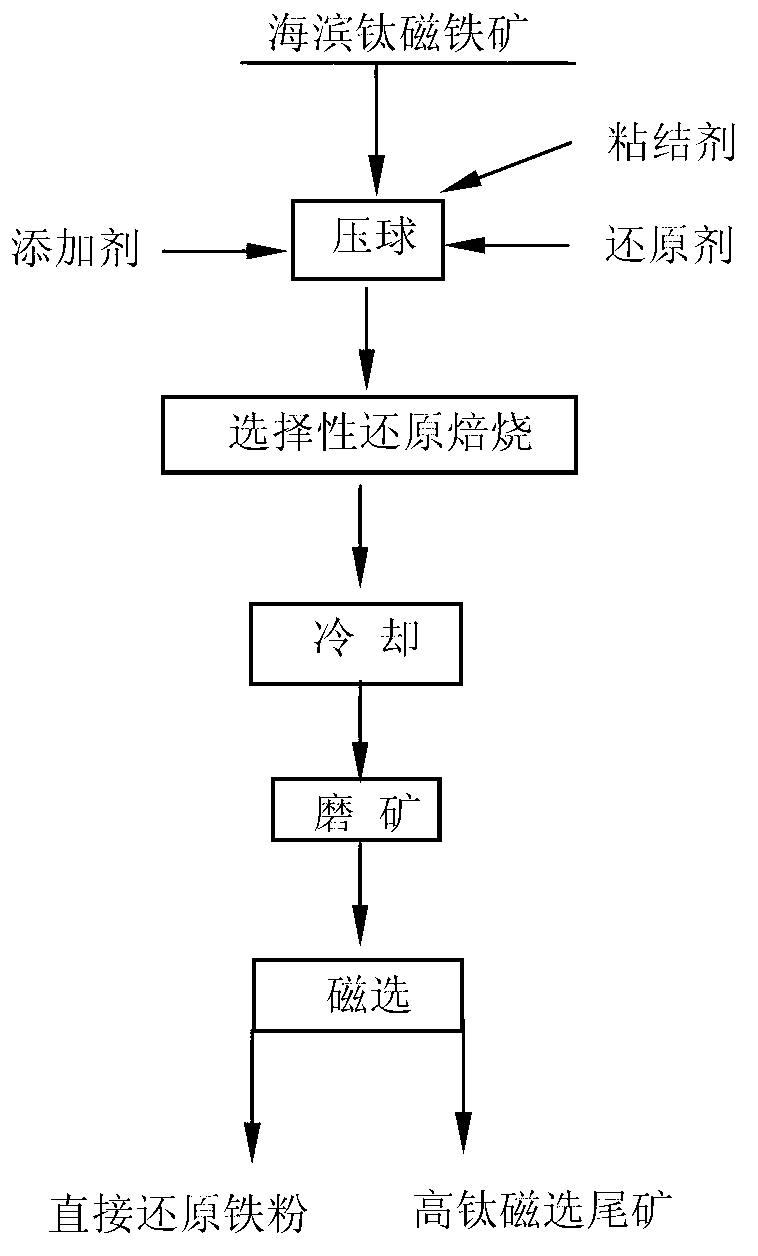
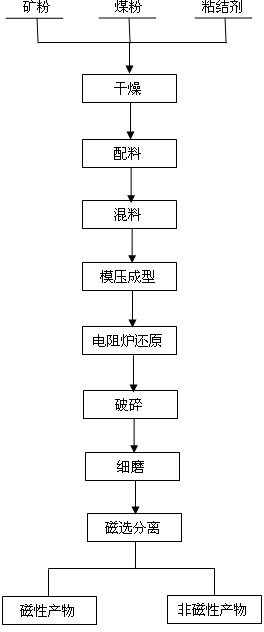
A process of separating iron and titanium in seaside titanomagnetite via direct reduction roasting by using coal
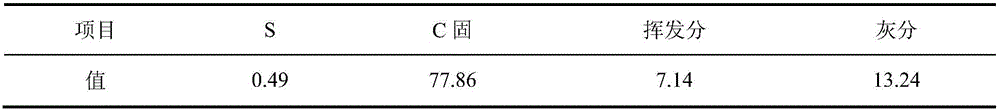
The invention provides a process of separating iron and titanium in seaside titanomagnetite via direct reduction roasting by using coal. According to the process, seaside titanomagnetite is employed as a raw material, a reducing agent, a binder, and an additive are added for briquetting, and then a selective direct reduction roasting - magnetic separation method is employed for respectively recovering iron and titanium. The process of the invention is simpler compared with other methods, wherein cost-effective coal is directly used as the reducing agent, additives added in the process is a mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium borate, and by adding the reducing agent and the additive, and controlling roasting temperature and time, selective reduction of iron and separation of iron and titanium can be achieved, ensuring the grade and recovery rate of direct reduced iron while reducing the titanium content in the direct reduced iron. The finally obtained direct reduction iron powder has a grade above 93%, the recovery rate of iron is generally greater than 85%, the titanium dioxide content is less than 0.5%, while the titanium dioxide content in obtained high titanium magnetic separation tailings is higher than 20%, and the recovery rate of titanium is greater than 90%.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +2
Mineral processing technology for comprehensively recycling iron phosphate from low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite
InactiveCN102728477AEfficient use ofIncrease the economic benefits of the dressing plantFlotationMagnetic separationPhosphateMagnetite
The invention discloses a mineral processing technology for comprehensively recycling iron phosphorus from low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite. The low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite is subjected to stage grinding and low intensity magnetic separation processes to obtain iron ore concentrate and magnetic separation tailings; the magnetic separation tailings uses low temperature flotation to recycle phosphorus after concentration, wherein the low temperature flotation is as follow: adding a slurry pH adjusting agent, an inhibitor and a collecting agent to the slurry of magnetic separation tailings, adjusting the pH of the slurry to 9-10, and performing flotation under 15-20 DEG C. The technology provided by the invention puts forward a mineral processing technology for comprehensively recycling iron phosphorus aiming at the low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite, which firstly adopts the low intensity magnetic separation method to recycle iron from ores and then adopts the low temperature flotation method to recycle phosphorus from tailings, thus realizing efficient utilization of such kind of mineral resources and increasing the economic benefits of concentrators. The low temperature flotation of the technology can reduce the subsequent costs of processing phosphate ores, improve the benefit of the comprehensive utilization of resources, reduce the production cost and achieve low cost and efficient recycling of phosphorus.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Microcrystal glass made from titanium-containing magnetic iron are tailings
This invention provides a glass ceramic produced by debris of magnetite that contains titanium. it takes titanium-containing debris as the main raw material, plus quartz sand that SiO2 purity greater than 96% and content of 18% ~ 30%; With further increase feldspar that content of 2% to 5% as additives; the weight percentage of above glass ceramic composition: SiO2: 55 ~ 65, Al2O3: 4 to 10, CaO: 10 ~ 20, MgO: 3-7, TiO2: 4 to 7, Fe2O3: 4.0 ~ 9.5, ZrO2: 0 ~ 1.5 , K2O - Na2O: 4 to 9. This invention can comprehensive utilize of titanium containing vanadium and titanium magnetite debris, can effectively solve the problem of environmental and safety issues caused by the long-term accumulation of debris, and reduce production costs.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for recovering ilmenite from dense difficult to dissociate vanadium titano-magnetite
InactiveCN103495502ASimple stepsImprove recycling effectMagnetic separationWet separationMagnetitePollution
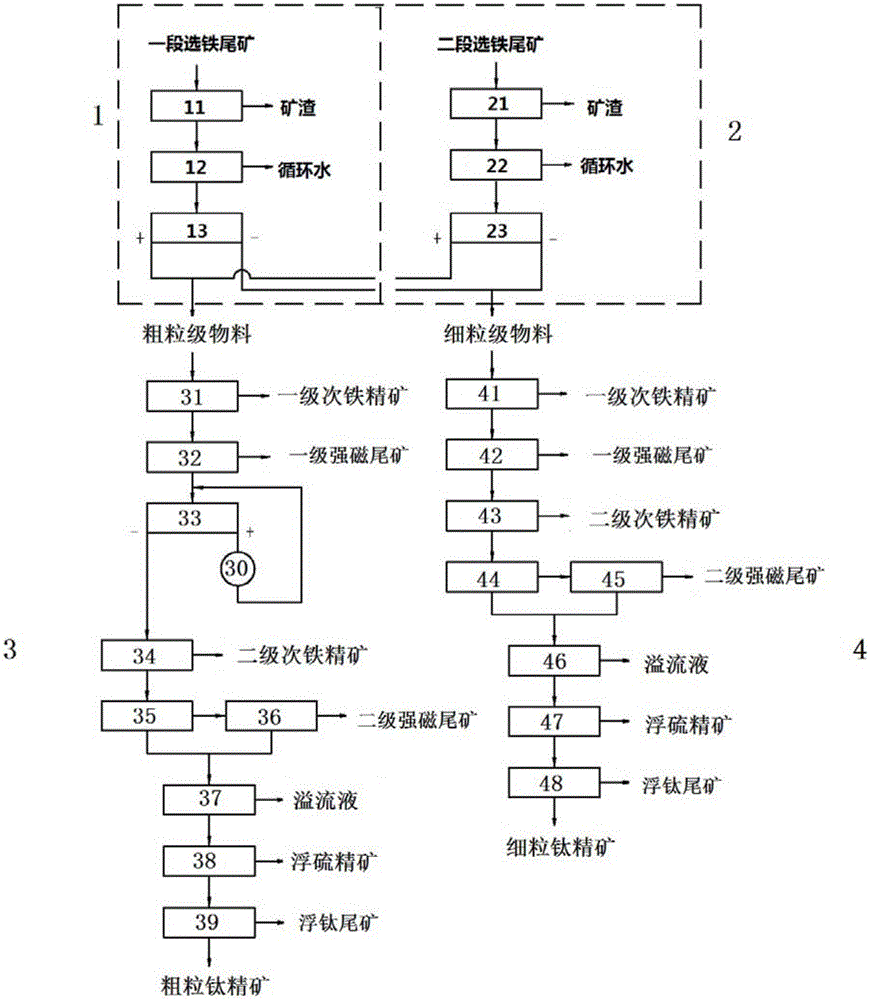
The invention discloses a method for recovering ilmenite from dense difficultly to dissociate vanadium titano-magnetite. According to the method, by ways of two-stage ore grinding, two-stage magnetic separation, and demagnetizing after one-stage magnetic separation, the fineness and proportion of ores in each step are controlled, so that the wastage of dressing devices can be reduced, the service lives of devices can be prolonged, and the investment of dressing plants can be saved; on the premise that iron ore concentrates are required to be subjected to fine grinding, through staged ore grinding, magnetic separation and demagnetizing, a problem that the finenesses of recovered iron and titanium have less possibility of being concurrently considered is solved, the recovery rates of iron and titanium are improved, and considerable economic benefits are created for mining enterprises; finally, according to the method, in the process of ilmenite recovery, the requirements of magnetic separation and flotation on the particle size of ores are avoided, and multiple devices are directly adopted for gravity concentration, so that an effect of environmental friendliness, cleanness and no pollution is achieved in the process of production, and a foundation is laid for the building of green mines.
Owner:SICHUAN JINGDA MINING TECH
Method for recycling micro-particle ilmenite through vanadium-titanium magnetite titanium beneficiation main tailings
ActiveCN110882826AIncrease profitAvoid wastingFlotationMagnetic separationMagnetiteMagnetic separator
The invention belongs to the technical field of mineral processing, and particularly relates to a method for recycling micro-particle ilmenite through vanadium-titanium magnetite titanium beneficiation main tailings. For the problems that in the prior art, the micro-particle yield of micro-particle-level ilmenite in vanadium-titanium magnetite titanium beneficiation main tailings is large, and themicro-particle-level TiO2 distribution rate is high, according to the technical scheme of the method, classifying equipment is adopted for classifying the vanadium-titanium magnetite titanium beneficiation main tailings, a ZCLA concentrating machine is adopted for enrichment for the coarse fraction, a ZH combined magnetic separator is adopted for enrichment for the fine fraction, and after concentrates of two devices enter a ball mill for ore grinding, the ZH combined magnetic separator is adopted for one roughening and one refining, ZH concentrates with the TiO2 grade larger than 18% are obtained, then preselection desulfuration and one-roughening, four-refining and one-sweeping refining are conducted, and titanium concentrates with the TiO2 grade larger than 47% are obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN LOMON MINING & METALLURGY +1
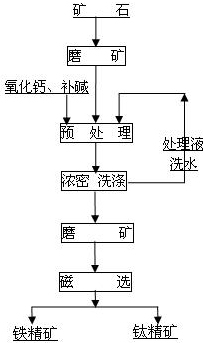
Beneficiation method of ilmenite
The invention discloses a beneficiation method of ilmenite and relates to the method for performing beneficiation on an ilmenite raw ore to prepare iron ore concentrate and ilmenite concentrate. The beneficiation method is characterized in that the beneficiation process comprises the following steps of (1) smashing the ilmenite raw ore; (2) grinding the ilmenite raw ore; (3) performing alkaline leaching pretreatment under conditions of water adding, temperature rising, oxygen adding and pressurization; (4) filtering ore pulp after the alkaline leaching pretreatment; (5) washing a filtered filter residue phase and performing ore grinding; (6) utilizing a washbox and performing magnetic separation to obtain the iron ore concentrate and the ilmenite concentrate. According to the method, dense symbiosis features of titanium and iron and isomorphism occurrence features of vanadium are damaged from the source of vanadium titanium magnetite ores by means of the treatment procedure, mineral transformation of the vanadium titanium magnetite is achieved, dissociation on lattice levels of titanium and iron is achieved, and the high-quality iron ore concentrate and the low-iron ilmenite concentrate can be obtained through a magnetic separation process and ore grinding. Alkali medium utilized by pretreatment can be recycled, therefore, influence of the process on the environment is small, and the beneficiation method has good application prospects.
Owner:GUANGXI KESHENGDA MACHINERY MFG
Efficient beneficiation method for low-grade titanic magnetite hard to select and smelt
ActiveCN107335535AHigh recovery rateWeakening of magnetic agglomerationWet separationMagnetiteRotational flow
The invention discloses an efficient beneficiation method for low-grade titanic magnetite hard to select and smelt. The method comprises the steps that in the crushing step, the low-grade titanic magnetite hard to select and smelt is crushed; in the first section ore grinding classification step, the titanic magnetite obtained after crushing is ground, first rotational flow classification is conducted, first fine particle overflow and first coarse grain pulp are obtained, and the first coarse grain pulp is subjected to first grinding again to return,; in the one-section low intensity magnetic separation step, the first fine particle overflow is subjected to first low intensity magnetic separation, and first iron concentrate pulp and first tailings pulp are obtained; in the screening classification step, the first iron concentrate pulp I is screened, and plus sieve coarse ore and minus sieve fine pulp are obtained; and in the second-section ore grinding classification step, the first iron concentrate pulp and the plus sieve coarse ore are combined and subjected to second rotational flow classification, second fine particle overflow and second coarse grain pulp II are obtained, and the second coarse particle pulp is subjected to second grinding to return to second rotational flow classification. For the low-grade titanic magnetite hard to select and smelt, the iron and titanium recycling rate is increased in combination of rotational flow classification and low intensity magnetic separation, and the method has the beneficial effects of being simple in technology, easy to operate and high in beneficiation efficiency.
Owner:YUXI DAHONGSHAN MINING
Titanium concentration method and device for vanadium titano-magnetite
ActiveCN106391295AImprove sorting efficiencyHigh recovery rateMagnetic separationWet separationSlagMagnetite
The invention relates to the technical field of mineral concentration, and especially relates to a titanium concentration method and device for vanadium titano-magnetite. The titanium concentration method comprises that one-stage iron concentration tailings of the vanadium titano-magnetite is subjected to primary slag separation treatment, primary enriching and dehydration and first classification, to be divided into one-stage iron concentration tailings coarse materials and one-stage iron concentration tailings fine materials; two-stage iron concentration tailings of the vanadium titano-magnetite is subjected to secondary slag separation treatment, secondary enriching and dehydration and secondary classification, to be divided into two-stage iron concentration tailings coarse materials and two-stage iron concentration tailings fine materials; the one-stage iron concentration tailings coarse materials and the two-stage iron concentration tailings coarse materials are combined to form coarse-fraction materials, and the one-stage iron concentration tailings fine materials and the two-stage iron concentration tailings fine materials are combined to form fine-fraction materials; the coarse-fraction materials are subjected to separation, to obtain coarse titanium concentrate; and the fine-fraction materials are subjected to separation, to obtain fine titanium concentrate. The method and device can decrease the enriching amount of tailings, reduce the energy consumption of titanium concentration, and improve the titanium recovery rate.
Owner:PANGANG GRP MINING
A method of using biomass fuel to strengthen the sintering of refractory iron ore
ActiveCN102296177AMeet the requirements of fast burningMeet caloric requirementsPorosityTitanomagnetite
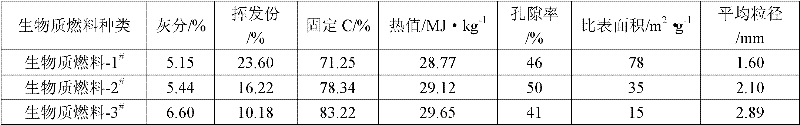
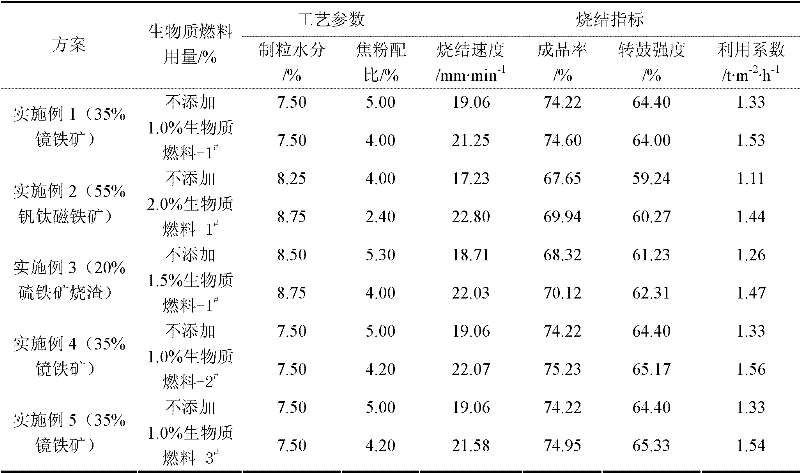
The invention relates to a method for reinforcing the sintering of iron ores (vanadic titanomagnetite, specularite, secondary iron-containing resources and the like) difficult to pelletize by biomass fuel. By applying the biomass fuel with high burning velocity to the sintering of the iron ores difficult to pelletize, the sintering speed and the utilization coefficient can be improved. The reinforcing method comprises the following steps of: adding 1 to 4 percent of biomass fuel into a sinter mixture containing the iron ores difficult to pelletize, wherein the biomass fuel is required to have 65 to 85 percent of content of fixed carbon, 10 to 25 percent of volatile matter, more than 24 to 30MJ / kg of calorific value, 40 to 60 percent of porosity, 10 to 100m2 / g of specific surface area and 1 to 4mm of average particle size; after weighing the iron ores difficult to pelletize, a flux, sintering return fines and the biomass fuel according to the weight ratio, sufficiently mixing the raw materials and pelletizing; distributing the mixture, igniting and sintering to obtain agglomerates. After the biomass fuel is adopted to reinforce the sintering of the iron ores difficult to pelletize, the sintering speed can be improved by 2 to 5mm / min, the utilization coefficient can be improved by 0.2 to 0.4t / (m2.h) and meanwhile, low intensity variation of an agglomerate revolving drum is ensured.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
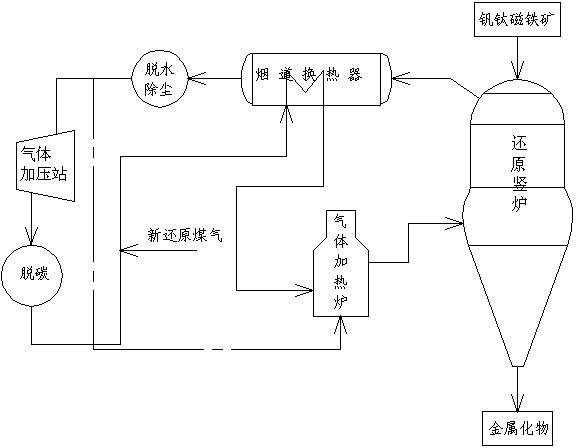
Non-blast-furnace iron making process for directly reducing vanadium titanomagnetite through gas-based shaft furnace
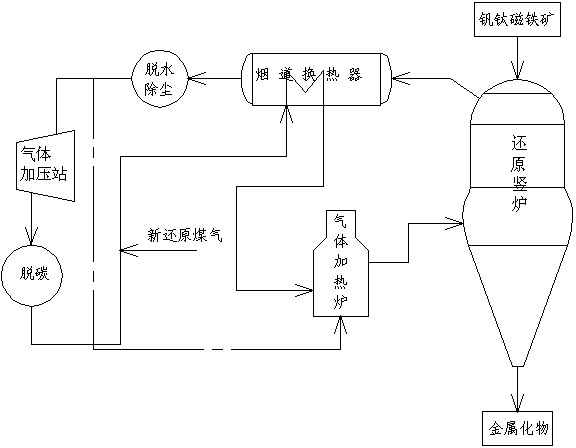
ActiveCN102424876AReduce dependenceAchieve diversificationShaft furnaceLand resourcesResource utilization
The invention discloses a non-blast-furnace iron making process for directly reducing vanadium titanomagnetite through a gas-based shaft furnace. The non-blast-furnace iron making process comprises the following steps of: (a) charging vanadium titanomagnetite oxidized pellet materials into the shaft furnace; (b) introducing reducing gas at the temperature of between 900 and 1,100DEG C and the pressure of between 0.35 and 0.65MPa through the bottom of the shaft furnace, and performing reduction reaction with the vanadium titanomagnetite; and (c) discharging metalized materials generated in thereaction through the lower part of the shaft furnace. In the process, gas prepared from noncoking coal is used as a reducer to reduce the vanadium titanomagnetite, the dependence of the traditional flow to coking coal is greatly reduced, and smelting energy is diversified; and compared with the traditional process, the process has the advantages that: three metals, namely vanadium, titanium and iron are comprehensively recovered, the recovery rate of the titanium element is particularly improved, full vanadium titanomagnetite is charged into the furnace to be melted, the titanium dioxide content of slag in the subsequent smelting process of the reduced sponge iron is over 47 percent, the slag can directly serve as a raw material for preparing titanium white, the resource utilization rate is improved, and the pollution to the environment and the occupation of land resources caused by slag stacking are avoided.
Owner:TAIHE IRON MINE CHONGQING IRON & STEEL GROUP MINING +1
Floating agglomeration electromagnetic concentrating equipment
InactiveCN104815753AEfficient removalAvoid the phenomenon of running blackMagnetic separationEngineeringNon magnetic
The invention provides floating agglomeration electromagnetic concentrating equipment. The lower end of a cylinder is provided with a concentrate discharging port or connected with a concentrate discharging pipe, a discharging port of a feeding pipe extends into the cylinder and is positioned on the middle upper portion in the cylinder, an output port of a micronano bubble generating device is communicated with an inner cavity of the cylinder tangentially and corresponds to the discharging port of the feeding pipe in position, an alternating magnetic field generator is positioned on the periphery of the cylinder and provides a nonuniform alternating magnetic field, and an overflow tank is positioned above the cylinder and communicated with the upper end of the cylinder. The equipment can generate a lot of micronano bubbles, especially nano bubbles, and the micronano bubbles and the alternating pulse electromagnetic field jointly act to enable magnetic or strongly-magnetic minerals and nonmagnetic or weakly-magnetic gangue minerals in material ore pulp to be in dispersion, agglomeration, re-dispersion and selective agglomeration respectively so as to enable the nonmagnetic or weakly-magnetic gangue minerals to thoroughly break away from a magnetic chain finally, so that escape of tailings is avoided effectively, and high-grade magnetic iron concentrate or titanomagnetite concentrate is obtained finally.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Process for comprehensively utilizing vanadium-titanium magnetite
The invention relates to a process for treating and comprehensively utilizing a vanadium-titanium magnetite. The process is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) treating a raw vanadium-titanium magnetite by crushing, tailings discarding, fine grinding, low-intensity magnetic separating, high-intensity magnetic separating, and separating by a shaking table, so as to obtain a titanium concentrate and a high-vanadium-ferrum concentrate; (2) adding an adhesive to the high-vanadium-ferrum concentrate; uniformly mixing and pelletizing; drying; uniformly mixing with pulverized coal or coke powder; distributing; performing controlled reduction that V is not reduced through a coal based shaft furnace so as to obtain sponge iron, wherein the amount of used reducing agents such as the pulverized coal is 30 to 70% of the weight of high-vanadium-ferrum concentrate powder, and the reduction is performed for 10 to 18 hours at the temperature of 850 to 1060 DEG C; (3) heating the obtained sponge iron for 0.5 to 1.0 hour at the temperature less than 1050 DEG C through an intermediate frequency / main frequency furnace under a weak reduction atmosphere; then heating until the temperature is more than 1500 DEG C; performing melt separation to enable vanadium to enter slag, thus obtaining high-grade vanadium slag and high-purity molten iron. With the adoption of the process, a plurality of valuable elements in the vanadium-titanium magnetite can be effectively separated and utilized with high additional value.
Owner:WUHAN COSRED SCI & TECH LTD
Process of extracting Cr-V oxide from high Cr, V and magnetite ore
ActiveCN101020970ADoes not affect the production processDoes not affect productivityProcess efficiency improvementSlagMagnetite
The process of extracting Cr2O3 and V2O5 from high-chromium vanadium titanium magnetite includes the following steps: 1. smelting molten iron containing V 0.28- 0.50 wt% and Cr 0.5-2.5 wt% with high-chromium vanadium titanium magnetite in a blast furnace or an electric furnace; 2. air refining the molten iron to obtain V-Cr slag with V2O5 not less than 6 wt% and Cr2O3 not less than 15 wt%, and semisteel; and 3. separating V2O5 from the V-Cr slag through crushing, roasting, leaching and purifying; adding ammonium salt into separated liquid and regulating pH value to 2-10, so as to prepare Cr2O3. The present invention recovers and utilizes valuable metal from molten iron without affecting iron and steel production.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL
Method for preparing sintering ore of vanadium-titanium magnetite ore
InactiveCN101381809AAl <sub>2</sub> o <sub>3</sub> Low contentReduce the water content of crystallizationSurface layerMagnetite
The invention relates to a method for preparing sinters of vanadium titano-magnetite, which belongs to the technical field of vanadium melting. The method for preparing the sinters has high sintering speed and high barrate strength, and particularly comprises the following steps: a. 51 to 57 portions of concentrated vanadium titano-magnetite, 15 to 19 portions of mineral powder A, 4 to 6 portions of mineral powder B, 6 to 8 portions of mineral powder C and 4.5 to 6 portions of coke breeze are prepared into mixture; b. 4 to 6 portions of limestone, 1.5 to 5.5 portions of quicklime and 50 weight percent of the mixture in step a are uniformly mixed for pellet fabrication; c. 1.5 to 5.5 portions of the quicklime and 50 weight percent of the mixture in step a are uniformly mixed, and pellets prepared in step b are placed into the mixture and rolled for pellet fabrication; and d. the pellets prepared in step c are sintered, and the sinters of the vanadium titano-magnetite are obtained after natural cooling of the pellets. The quality of the sinters prepared is obviously improved; and the surface layer fuel speed of pelletized particles can be quickened and the solid fuel consumption can be reduced under the condition of melting in a blast furnace.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES
Direct reduction roasting-magnetic separation red mud comprehensive using method based on rotary kiln
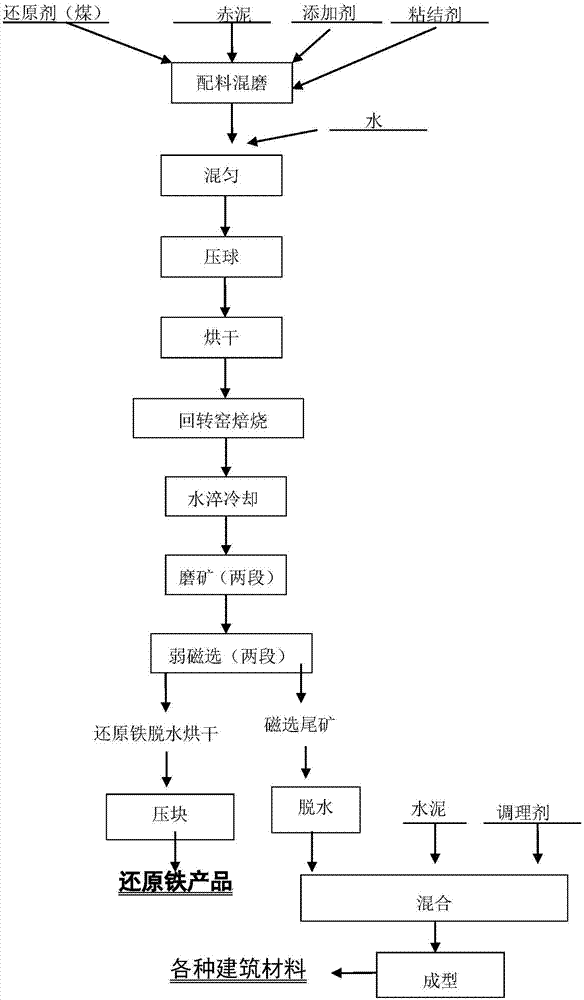
ActiveCN107254583ANo pollution in the processPromote reductionSolid waste managementRotary drum furnacesSteelmakingRed mud
The invention provides a direct reduction roasting-magnetic separation red mud comprehensive using method based on a rotary kiln, and belongs to the technical field of resource comprehensive using. According to the method, red mud serves as a raw material, coal powder is a reducing agent, titanomagnetite is an addition agent, starch and bentonite are binder for conducting ball pressing, iron is recovered by adopting a direct reduction roasting-magnetic separation technology, amendment is added into tailings after the iron is recovered for adjusting ingredients, and then, after cement is added, different kinds of building materials are produced. The method has the advantages that the red mud can be fully used, after the red mud and titanomagnetite are mixed, reduction roasting is conducted, the titanomagnetite can improve conducting of the reducing process, meanwhile, the low-cost coal is used as the reducing agent, after the tailings obtained from magnetic separation are conditioned, the building materials can be produced, finally, direct reduction iron blocks with iron grade of more than 92% are obtained, the recovery rate of the iron is normally higher than 85%, and other ingredients meet the requirements of direct steelmaking.
Owner:张建华
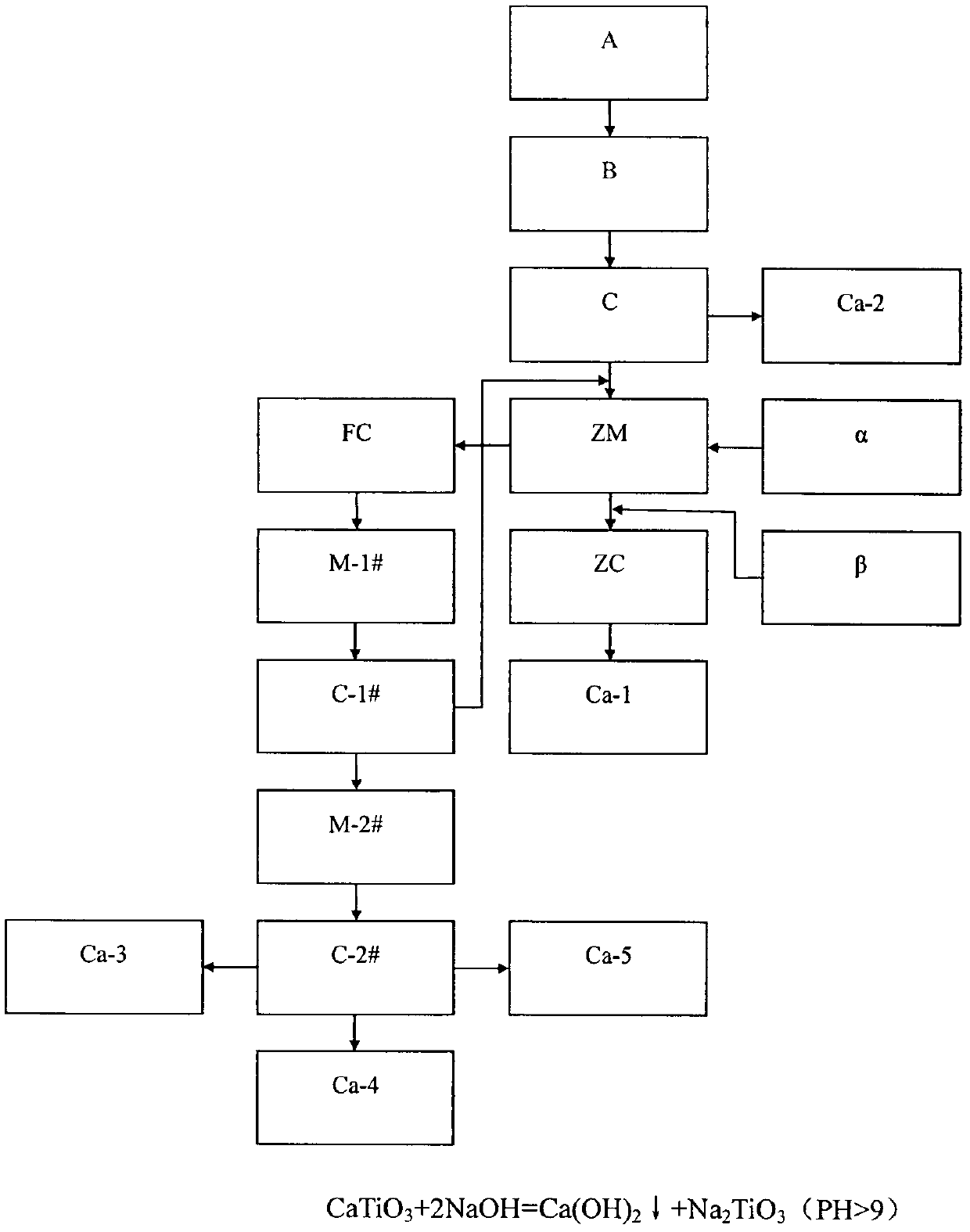
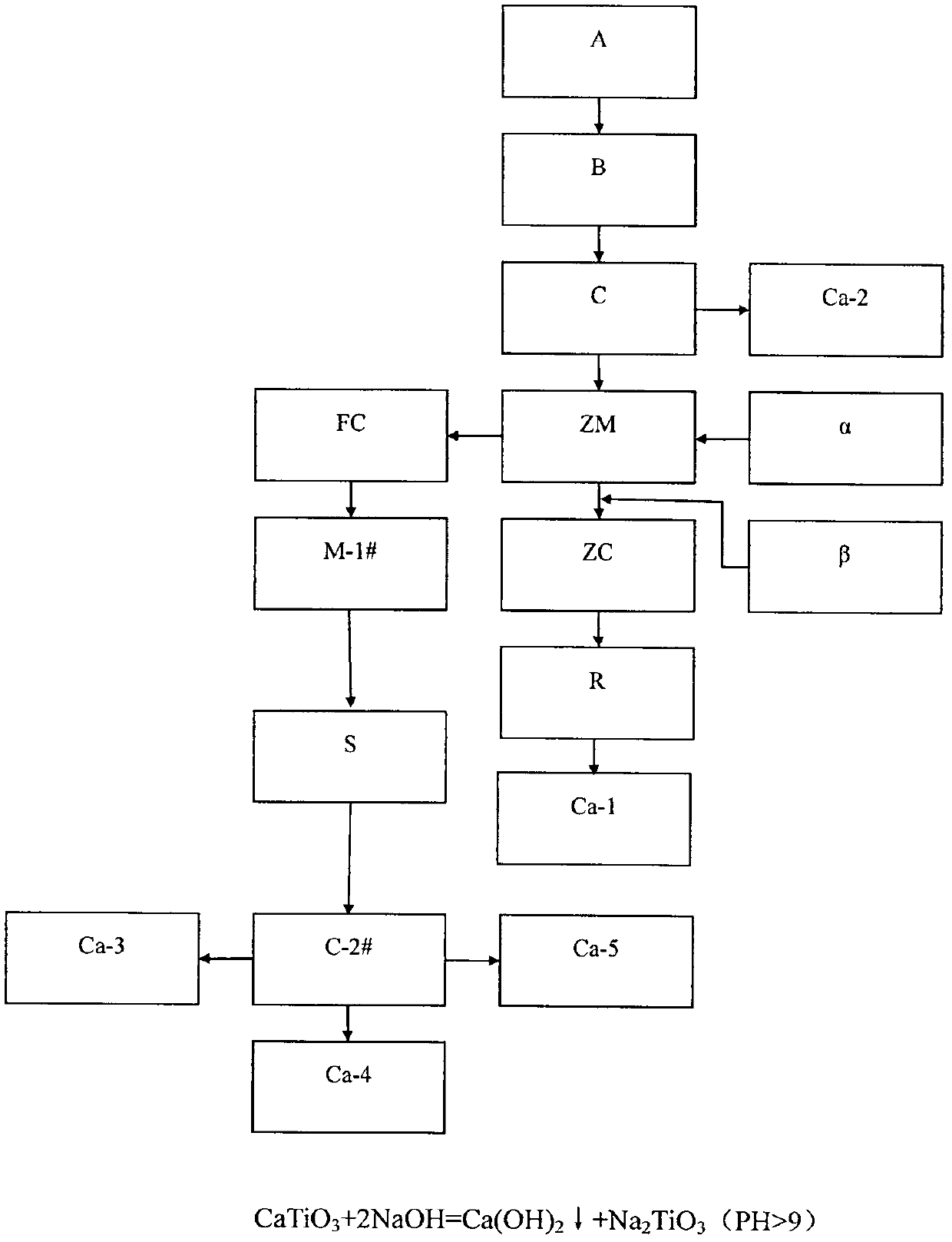
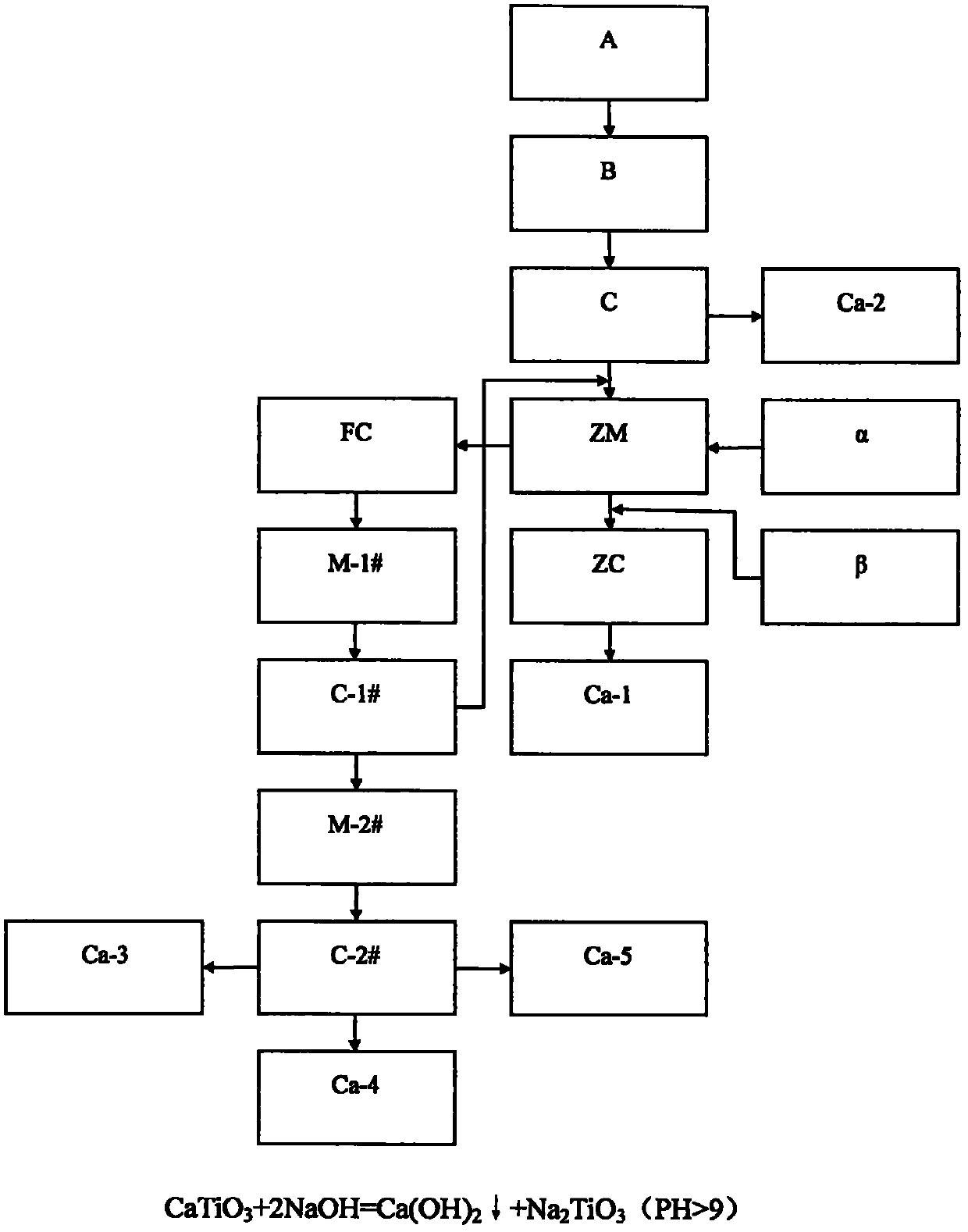
Method for separating iron, vanadium and titanium in vanadic titanomagnetite
The invention provides a method for separating iron, vanadium and titanium in vanadic titanomagnetite. According to the method, most of vanadium is left in slag by controlling a direct reduction temperature, iron enters a magnetically-separated substance, a by-product sodium sulphate obtained through fractional crystallization carried out through sodium-modification vanadium extraction wastewater, is added in vanadium-titanium slag after magnetic separation, and vanadium is extracted in a water-leaching manner after oxidation roasting, so as to obtain vanadium-containing solution and titanium-rich slag. According to the method, on one hand, the recovery rate of vanadium is increased, on the other hand, due to a small amount of the vanadium-titanium slag, lots of sodium salt has no need to be added, and moreover, the small amount of the added sodium salt is treated by virtue of the sodium-modification vanadium extraction wastewater to obtain the by-product, thus cost is saved, secondary resource recycling is realized, and economic benefits are improved; and in addition, the magnetically-separated substance obtained in a manner of carrying out magnetic separation at first, and then adding sodium salt in vanadium-titanium slag and carrying out oxidation roasting, is relative pure compared with the magnetically-separated substance obtained in a manner of adding sodium salt and carrying out oxidation roasting at first, and then carrying out magnetic separation, a sulphur content of the magnetically-separated substance is low, and the quality is guaranteed.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for recycling titanium, silicon, aluminum, calcium and magnesium from titaniferous blast furnace slag by multistage acid leaching
InactiveCN103952567ALow costQuality improvementRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementSlagManganese
The invention discloses a method for recycling titanium, silicon, aluminum, calcium and magnesium from titaniferous blast furnace slag by multistage acid leaching. The titaniferous blast furnace slag is especially titaniferous blast furnace slag obtained by carrying out iron making on vanadium titanomagnetite in Panzhihua regions. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out acid leaching (especially multistage acid leaching) on furnace slag to obtain an acid leaching solution and white carbon black; and carrying out an extraction technique on the acid leaching solution to obtain titanium, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, manganese, iron, chromium, vanadium and other useful metals. On the premise of recycling resources, the method implements cyclic utilization of waste (using waste of one technique as a raw material of another technique), eliminates waste discharge, obviously lowers the cost and enhances the recycling efficiency.
Owner:衡阳市金铭环境科技有限公司
Method for smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite in blast furnace
ActiveCN102041331AImprove technical and economic indicatorsReduced stabilityBlast furnace detailsFurnace temperatureSlag
The invention provides a method for smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite in a blast furnace, which comprises the following steps of: controlling blast kinetic energy, air quantity and air speed of the blast furnace with different furnace volume in different ranges respectively, and forming an air inlet with the length of 450 to 480mm on the two sides of an iron notch of the blast furnace respectively; controlling the blast oxygen enrichment rate in the range of 2.6 to 3.0 percent; controlling the blast temperature in the range of 1,150 to 1,200 DEGC; and controlling the furnace temperature of the blast furnace in the range of 1,450 to 1,500 DEG C. By methods of adjusting the blast kinetic energy, blast volume and the blast temperature, controlling feeding rate, the reaction temperature of the blast furnace and slag basicity, and the like, the strengthened smelting of the vanadium-titanium magnetite in the blast furnace is realized, the utilization factor of the blast furnace is improved, and iron loss is reduced.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +1
Method for smelting vanadium titano-magnetite by HIsmelt fusion reduction process
The invention relates to the technical field of vanadium titano-magnetite smelting, and provides a method for smelting vanadium titano-magnetite with a HIsmel smelting reduction process. The preheatedand pre-reduced vanadium titano-magnetite is directly sprayed into a HIsmel smelting reduction furnace through a mine gun of the HIsmel smelting reduction furnace, the temperature of hot air, the oxygen content of the hot air, the blowing amount of mineral powder, the blowing amount of pulverized coal and the blowing quantity of flux are controlled, the percentage content of FeO in slag is controlled, the over-reduction reaction of TiO2 is restrained, and generation of TiC, TiN and TiCN in the slag and molten iron is reduced. High melting point solid particles TiC, TiN and TiCN are preventedfrom being produced in the molten iron and the slag, so that the objective of all vanadium-titanium ore smelting which is not achieved in the long process of current blast furnace ironmaking is achieved, vanadium titano-magnetite ore resources are used in large scale, and the technical problem that TiO2 in the blast furnace slag cannot be continuously utilized due to low grade is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Direct reduction-magnetic separation method of vanadium titanomagnetite
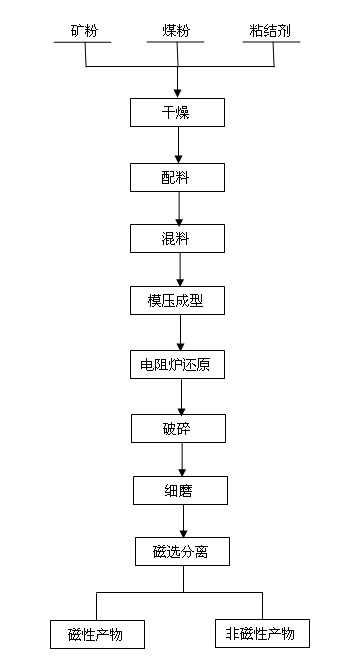
InactiveCN102430472AGuaranteed Metallization RateGuaranteed RecoveryMagnetic separationIron powderCrucible
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy and particularly relates to a direct reduction-magnetic separation method of vanadium titanomagnetite. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding iron ore concentrate powder and pulverized coal, evenly mixing and molding; putting a blank into an airtight lidded crucible, and burying the crucible in pulverized coal; directly reducing ferric oxide for 60-300 minutes at 1250-1350 DEG C on the condition that the molar ratio of C to O is 1.2-1.4 so that ferric oxide is deoxidized to generate metal iron, thus obtaining a reduzate of which the metallization rate is 85-94%; and crushing the cooled reduzate, and carrying out magnetic separation to obtain iron powder with a grade of 85-90% and titanium slag containing 60-70% of titanium. By utilizing the technical scheme of the invention, primary separation of iron, vanadium and titanium is realized; after magnetic separation, 60-70% of vanadium in raw materials enters into magnetic products and 60-70% of titanium is remained in non-magnetic products and the iron recovery rate can reach 90-95%.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Carbon-containing pellet for blast furnace
InactiveCN102978385AReduce manufacturing costImprove mechanical propertiesBlast furnace detailsProcess efficiency improvementSlagSludge
The invention discloses a carbon-containing pellet for a blast furnace, which belongs to the technical field of carbon-containing pellets. The carbon-containing pellet provided by the invention comprises, by mass, 11 to 13 parts of ash collected from the head of a sintering machine through electric precipitation, 38 to 42 parts of blast furnace sludge, 20 to 22 parts of fly ash collected from an ore groove at the front of a furnace, 17 to 19 parts of calcium-free chromium slag, 10 to 12 parts of vanadic titanomagnetite, 3 to 5 parts of zirconia, 1 to 2 parts of bentonite and 1 part of calcium hydroxide. According to the invention, the ash collected from the head of the sintering machine through electric precipitation, the blast furnace sludge, the fly ash collected from the ore groove at the front of the furnace and the calcium-free chromium slag are used as components of the pellet, so resource recycling of the above-mentioned wastes is realized, and production cost for the carbon-containing pellet is reduced; a prepared wet pellet has falling strength of more than 9.5 times / 0.5 m and compressive strength of more than 33.65 N / pellet, a prepared dry pellet has falling strength of more than 4.2 times / 0.5 m and compressive strength of more than 96.82 N / pellet, and the pellet has good mechanical properties.
Owner:TONGLING ZHAOLIN IND & TRADE CO LTD
Process for producing granulated iron by directly reducing low-grade complex difficultly-processed ore
InactiveCN102212635AImproving the Efficiency of the Grinding and Magnetic Separation ProcessImprove efficiencyFluidised-bed furnacesSlagOxidation state
The invention relates to a process for producing granulated iron by directly reducing low-grade complex difficultly-processed ore, in particular to a process for producing granulated iron by rapidly directly reducing clay nickel ore, oolitic hematite, antelope quarries, vanadium titanomagnetite, hematite, specularite, limonite, siderite and the like. The technical scheme is as follows: the low-grade complex difficultly-processed ore is sufficiently mixed with a reducing agent, a desulfurizing agent and a metal gathered agent; an alkalinity regulator is added; the basicity range of the material is controlled within 0.2-0.8; and the mixed carbon-containing material enters reducing equipment so as to be heated and reduced. The alkalinity regulator is added to the low-grade complex difficultly-processed ore so that non-iron oxides are rapidly gathered and quit metal elements so as to form slag. On the other hand, the metal gathered agent is added so that the metal elements in an oxidation state are gathered more rapidly and quit the slag so as to form fine particles when the metal elements are reduced from the oxidation state to a metal state. The efficiency of the subsequent ore-grinding magnetic separation process can be increased through the granulated material. The grade and the recovery rate of the product can be increased.
Owner:TANGSHAN OUTSTANDING SCI & TECH
Process method for preparing palletized blast-furnace titanium slag into active slag powder
The invention discloses a process method for preparing palletized blast-furnace titanium slag into active slag powder, belonging to the technical field of environmental protection. The process method is applied in a comprehensive utilization process of solid industrial waste slag after vanadium titanomagnetite is smelted. The product belongs to the professional field of new materials in a building material metallurgic industry. The process method comprises the following steps: a. evenly mixing materials according to the content of TiO2 in the materials; b. dehydrating the materials; c. grading, deironing and crushing to technological requirements and grinding; d. adding grinding additive according to the process requirements when grinding and separating out the slag powder and a mine returning material; e. mixing the slag powder in the step d and powder compound additive, placing into an intermediate bin, dissolving the soluble compound additive into water in regulation, adding into the slag powder on site to form active blending material-active titanium slag powder; and f. grinding the mine return material at one time, carrying out magnetic separation, returning the nonmagnetic materials into step d, carrying out secondary grinding and secondary separation on the magnetic materials and separating out tailing-primary fireproofing material, concentrate, a blast furnace protective agent and a metallurgical additive. The process method is short in flow, low in investment and low in energy consumption and is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:王开玺
Direct vanadium extracting method for vanadium-titanium magnetite
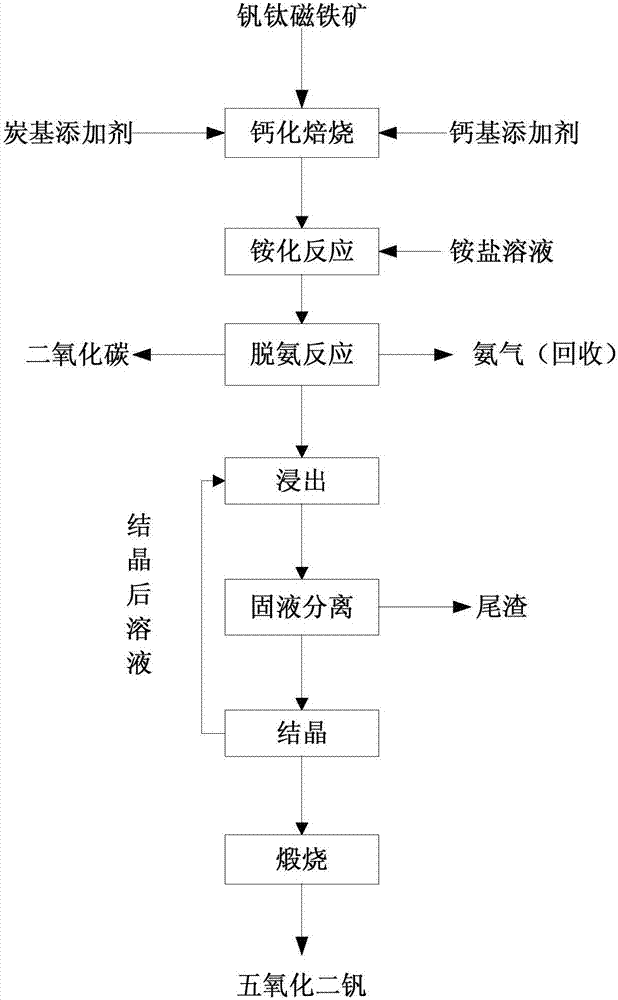
ActiveCN107090551AImprove leaching rateLow vanadium contentProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionCalcification
The invention provides a direct vanadium extracting method for vanadium-titanium magnetite. The method comprises the steps that calcification roasting is conducted by taking a mixture of the vanadium-titanium magnetite and a carbon-based additive as a raw material, a calcification roasting product is subjected to aftertreatment, and then vanadium-containing liquid is obtained. According to the method, the vanadium recycling rate is high; the impurity content of leachate is low, and a high-purity vanadium product can be prepared through simple impurity removal; no waste gas is generated, the operation technology is simple, the equipment requirement is low, and the technology cost is low; the vanadium extracting process does not influence iron making, tailings obtained after vanadium extracting do not contain sodium salt and can be directly subjected to ore blending for iron making, and then comprehensive utilization of vanadium-titanium magnetite resources is achieved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com