Process for comprehensively utilizing vanadium-titanium magnetite
A vanadium-titanium magnetite and process technology, applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of vanadium-titanium magnetite, to achieve the effects of low production cost, low energy consumption and high grade
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
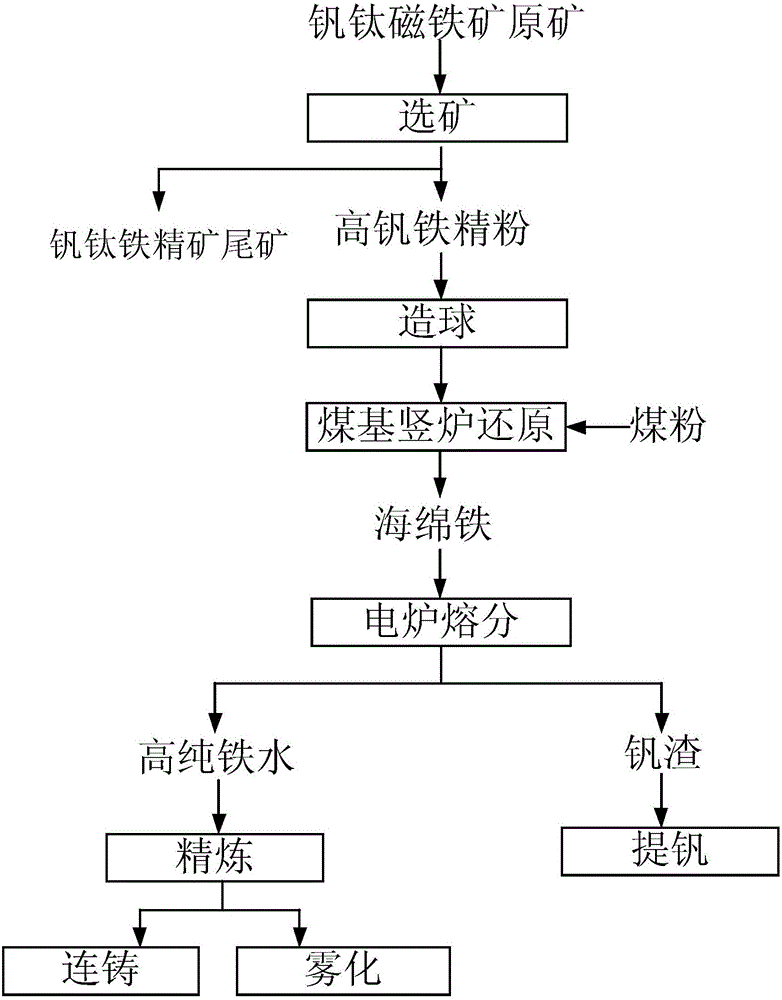
[0022] Embodiment one: the method that high added value utilizes vanadium-titanium magnetite, its steps are:
[0023] (1) The raw ore of vanadium-titanium magnetite is crushed, tailed, finely ground, weak magnetic separation, strong magnetic separation, shaking table separation to obtain high vanadium iron concentrate;
[0024] (2) Add 2.0% binder (starch and cellulose mixed at a ratio of 0.7:0.3) to the high-vanadium iron concentrate powder, mix and make pellets, air-dry, and add high-vanadium iron concentrate to the outside 40% of the powder weight is mixed with coal powder (3) the mixed material is reduced in a coal-based shaft furnace through cloth to obtain sponge iron, the reduction temperature is 880 ° C, the reduction time is 18 hours, and the metallization rate of the reduction product is 90%;
[0025] (4) The obtained sponge iron is heated at 1000°C for 0.5h in a power frequency electric furnace with a weak reducing atmosphere, and then heated to above 1500°C for mel...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment two: the method that high added value utilizes vanadium-titanium magnetite, its steps are:
[0028] (1) The vanadium-titanium magnetite raw ore is crushed, tailed, finely ground, weak magnetic separation, strong magnetic separation, shaking table separation to obtain high vanadium iron concentrate;
[0029] (2) Add 1.5% binder (starch and cellulose mixed at a ratio of 0.5:0.5) to the high-vanadium iron fine powder and mix it into pellets, air-dry, and add high-vanadium iron fine powder Mix 30% coal powder of powder weight;
[0030] (3) Reducing the mixed material through cloth in a coal-based shaft furnace to obtain sponge iron, the reduction temperature is 1000°C, the reduction time is 15 hours, and the metallization rate of the reduction product is 91.3%;
[0031] (4) The obtained sponge iron is heated at 1000°C for 40 minutes in an intermediate frequency electric furnace with a weak reducing atmosphere, and then heated to above 1500°C for melting, and van...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment three: high added value utilizes the method for vanadium-titanium magnetite, and its steps are:
[0034] (1) The vanadium-titanium magnetite raw ore is crushed, tailed, finely ground, weak magnetic separation, strong magnetic separation, shaking table separation to obtain high vanadium iron concentrate;
[0035] (2) Add 3.0% binder (starch and cellulose mixed at a ratio of 0.8:0.2) to the high-vanadium iron fine powder and mix it into pellets, air-dry, and add high-vanadium iron fine powder 55% pulverized coal by powder weight;
[0036] (3) Reducing the mixed material through cloth in a coal-based shaft furnace to obtain sponge iron, the reduction temperature is 1060° C., the reduction time is 13 hours, and the metallization rate of the reduction product is 92%;
[0037] (4) The obtained sponge iron is heated in an intermediate frequency electric furnace with a weak reducing atmosphere at 1050°C for 30 minutes and then heated to above 1500°C for melting and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com