Non-blast-furnace iron making process for directly reducing vanadium titanomagnetite through gas-based shaft furnace
A technology of vanadium-titanium magnetite and gas-based shaft furnace, applied in the direction of shaft furnace, furnace, furnace type, etc., can solve the problems of economic waste, recycling, and non-renewable resources, so as to avoid environmental pollution and improve recycling , the effect of reducing dependence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
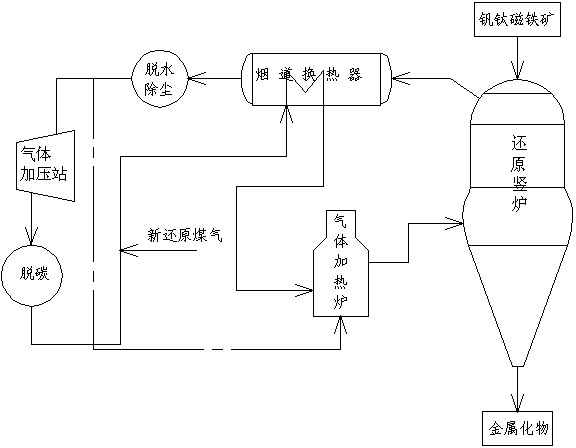
[0015] Embodiment 1: The gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite non-blast furnace ironmaking process in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0016] a, the vanadium-titanium magnetite raw material is loaded into the shaft furnace;
[0017] b. Pass reducing gas with a temperature of 1100°C and a pressure of 0.65 MPa into the shaft furnace from the lower part of the shaft furnace to carry out reduction reaction with the vanadium-titanium magnetite;
[0018] c. The metallized material generated by the reaction is discharged through the lower part of the shaft furnace. In the reduced gas, H in volume percentage 2 and CO content ≥ 85%, H 2 The volume ratio to CO is 5.4.
[0019] In this embodiment, the reduced gas reduces the vanadium-titanium magnetite in a circulating flow, and the circulation mode is: the reduced gas becomes the furnace top gas after the reduction reaction, and the high-temperature furnace top gas enters the flue hea...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Embodiment 2. The difference between the gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction of vanadium-titanium-magnetite non-blast furnace ironmaking process in this embodiment and the embodiment 1 is: the temperature of the reduced gas is 900 ° C, the pressure is 0.35 MPa, and the H in the reduced gas 2 The ratio to CO is 3.1.
[0023] In practice, this process is used to smelt vanadium-titanium magnetite. Vanadium-titanium magnetite is used as the smelting raw material without adding ordinary iron ore. The titanium dioxide content of the slag produced by reduction in the subsequent smelting process is above 47%. .
Embodiment 3
[0024] Embodiment 3: The difference between the gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite in this embodiment and the non-blast furnace ironmaking process in Embodiment 1 is: the temperature of the reduced gas is 1000°C, the pressure is 0.5 MPa, and the H in the reduced gas 2 The ratio to CO is 4.2.
[0025] In practice, this process is used to smelt vanadium-titanium magnetite. Vanadium-titanium magnetite is used as the smelting raw material without adding ordinary iron ore. The titanium dioxide content of the slag produced by reduction in the subsequent smelting process is above 47%. .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com