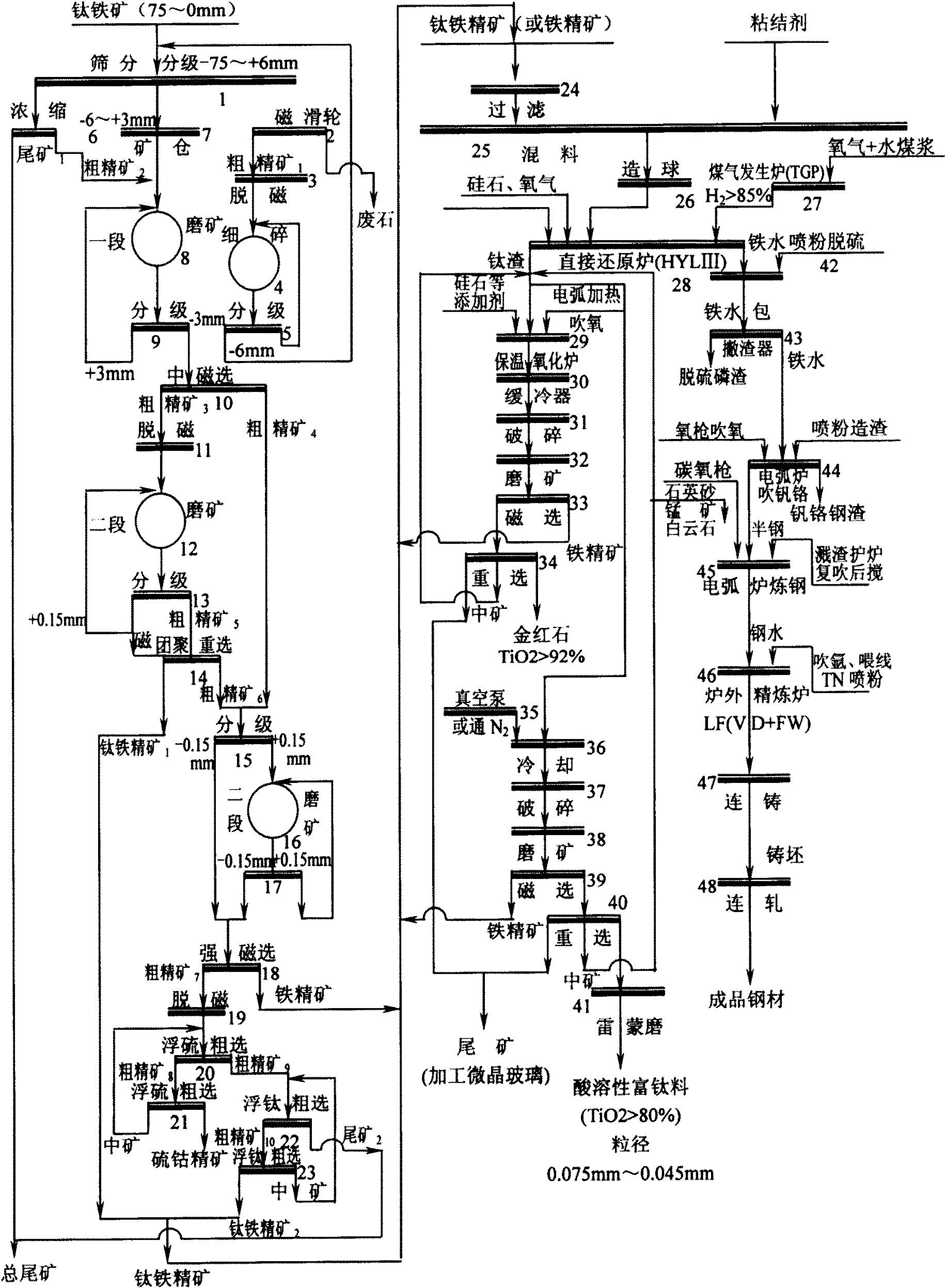
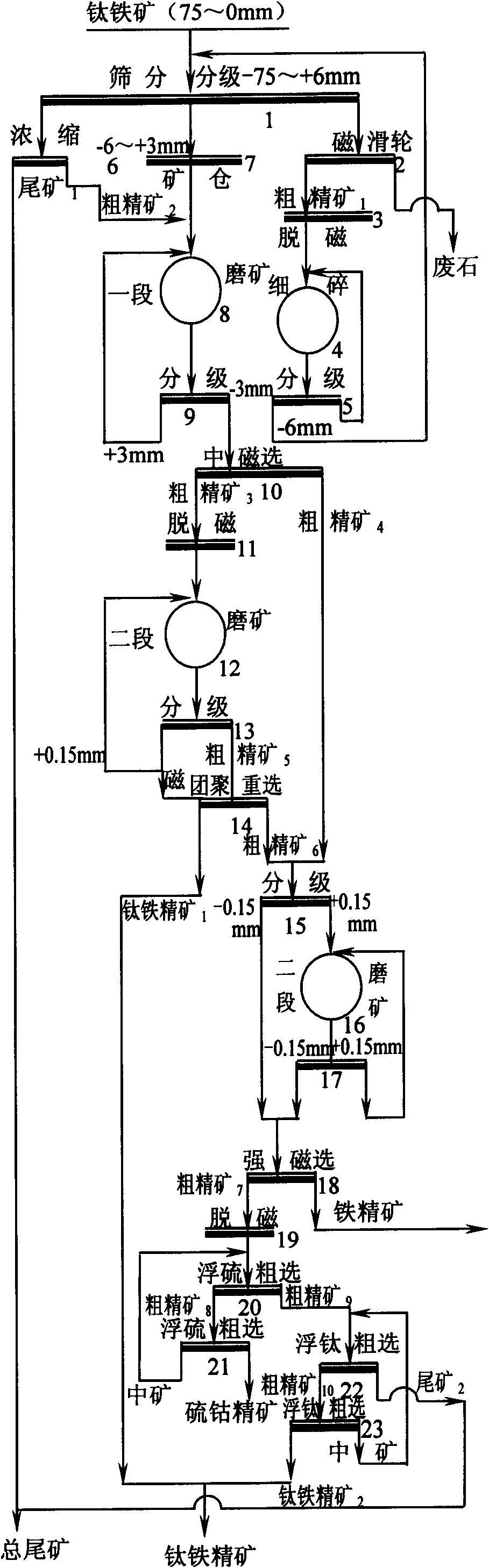
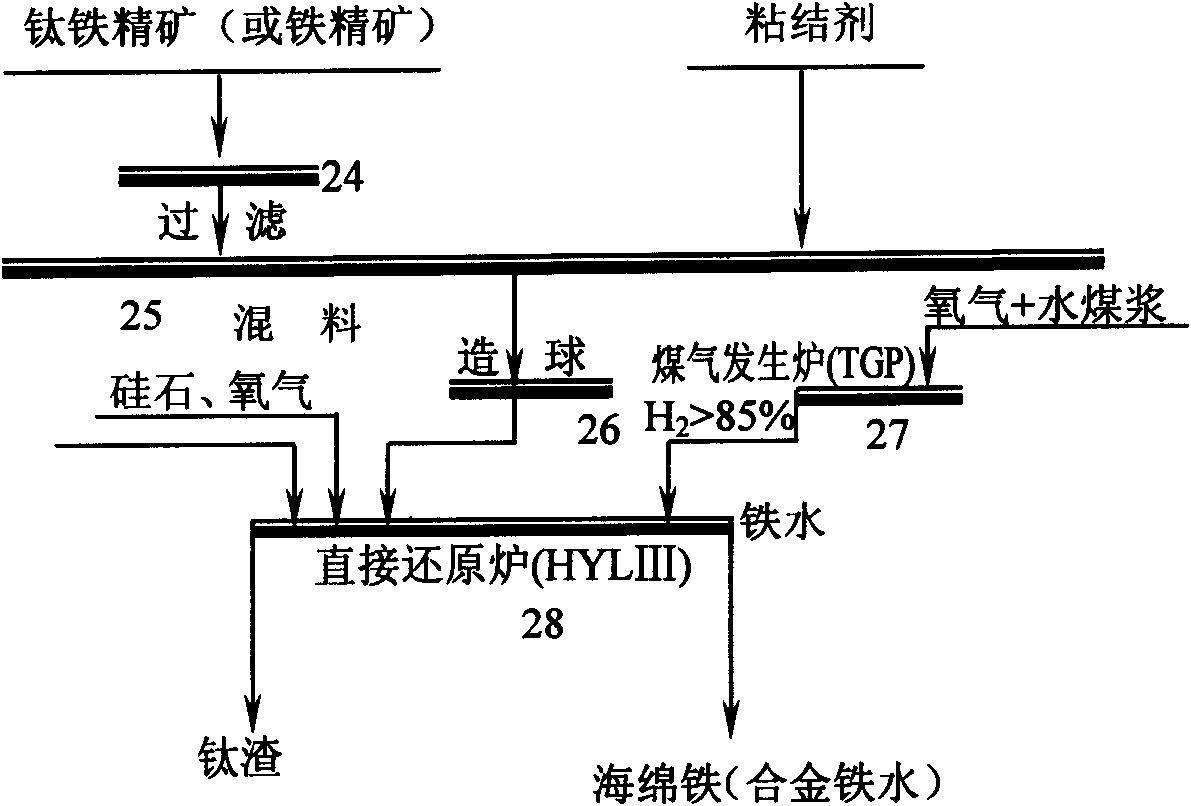
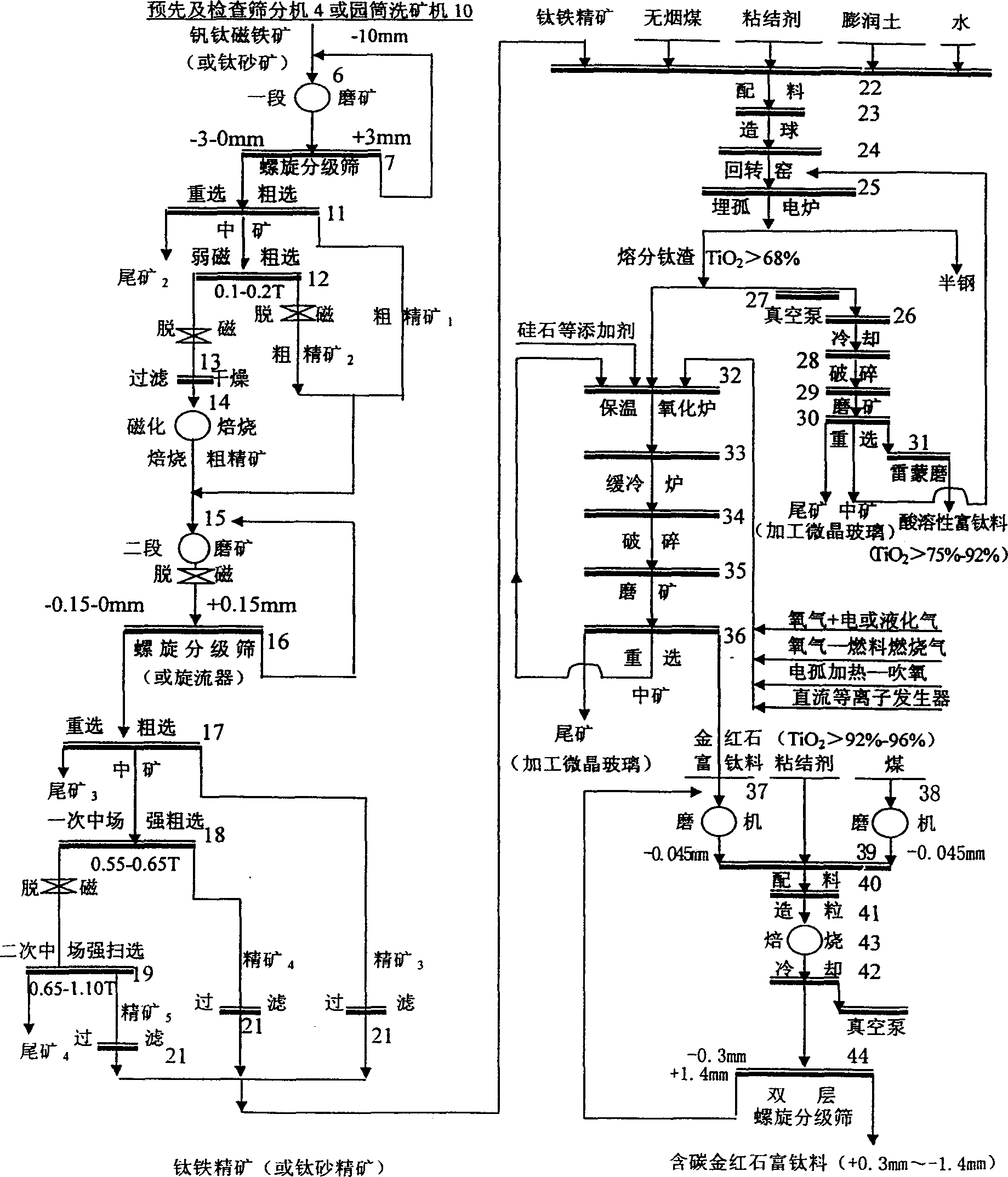
Patents
Literature
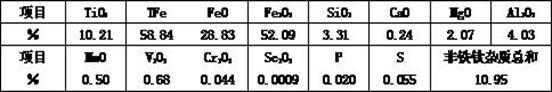
839 results about "Titanium slag" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
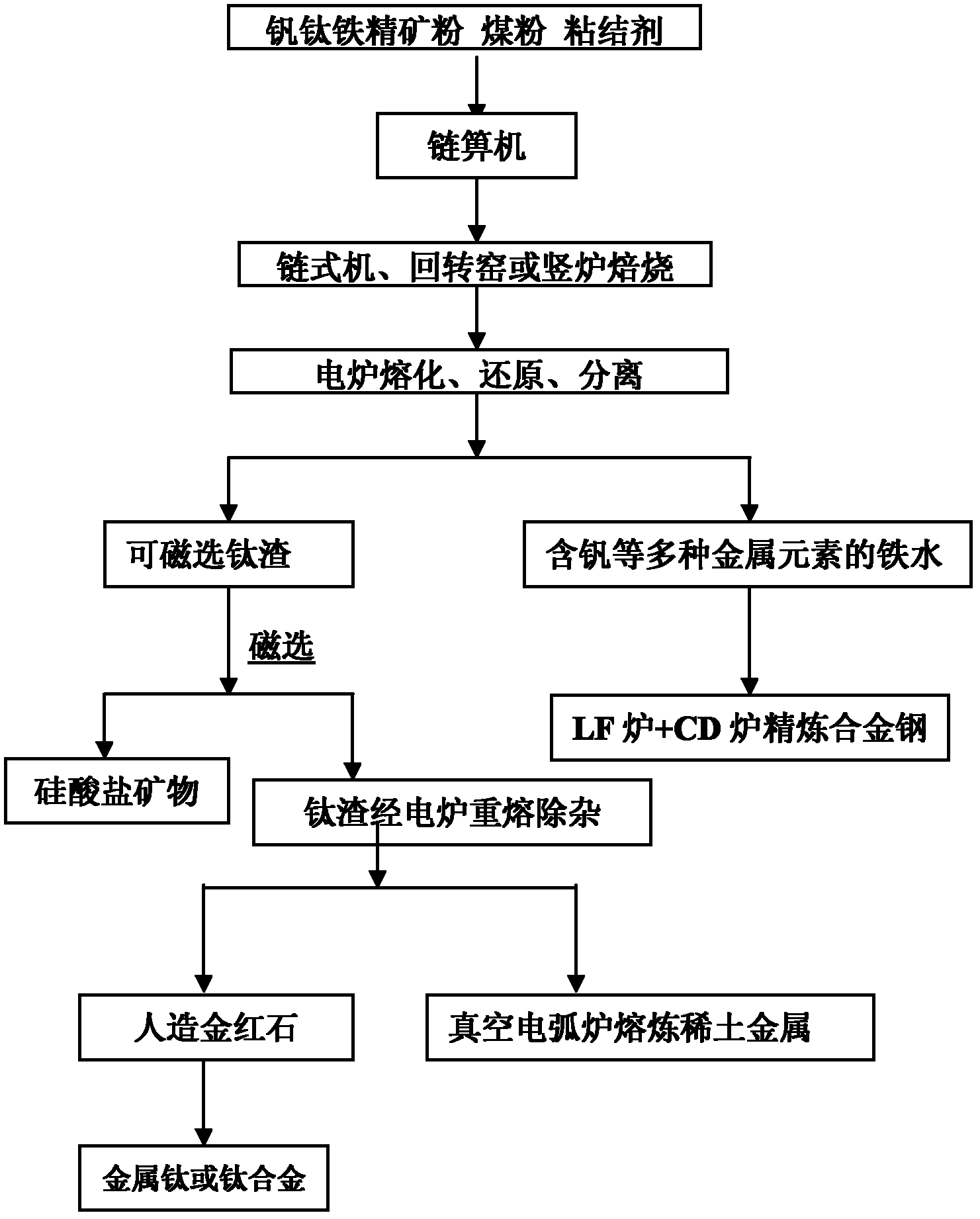
Method for producing titanium and steel products by utilizing titanium and iron ores
InactiveCN101613825AIncrease profitHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceRutileContinuous rolling
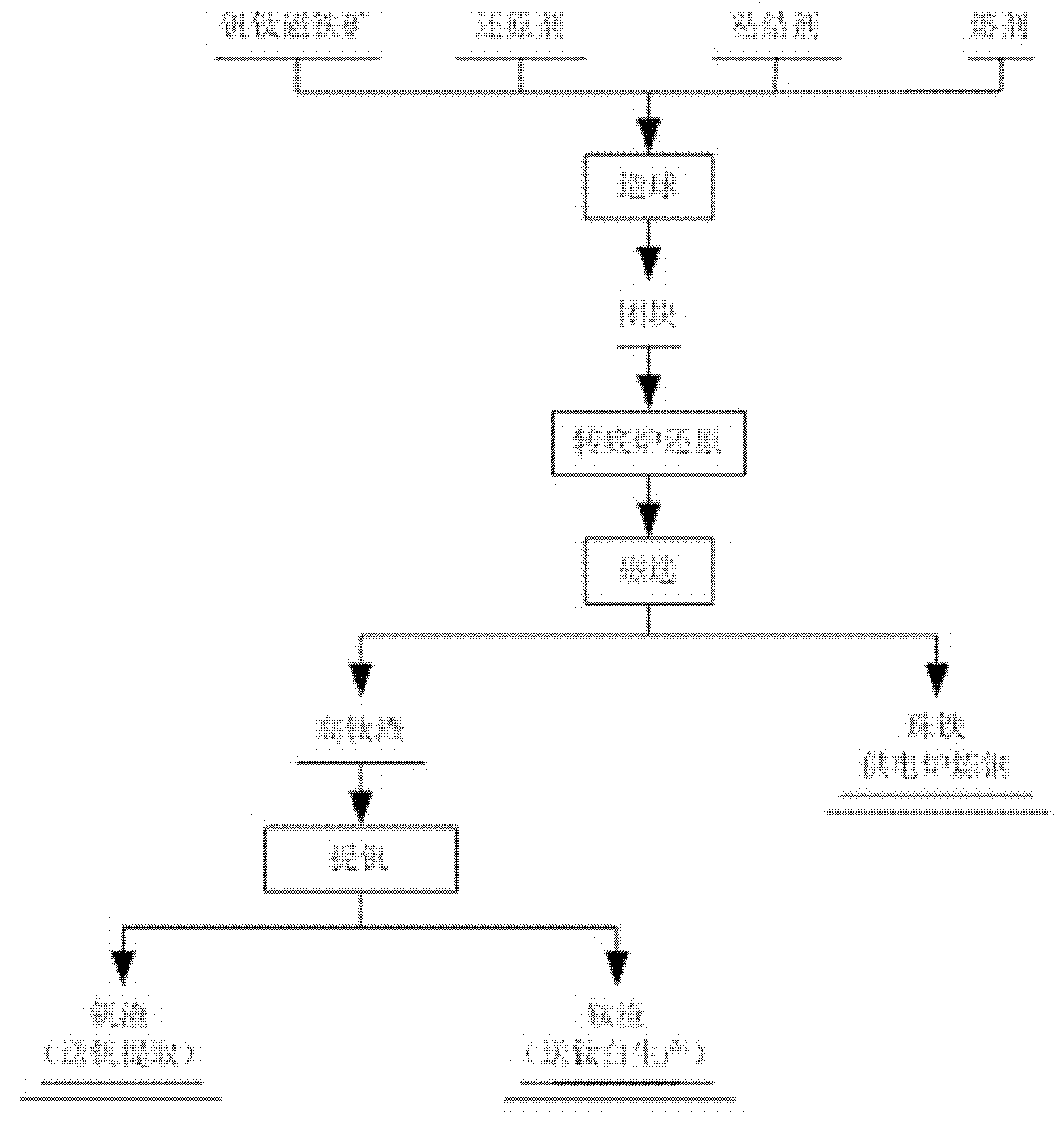
The invention discloses a method for producing titanium and steel products by utilizing titanium and iron ores, which belongs to the field of technical innovation of mining, dressing and smelting full process flow of the titanium and iron ores. Ordinary blast furnaces are not suitable for the smelting of high-titanium and medium-titanium schreyerite; and schreyerite mining, dressing and smelting enterprises in Panxi region extract rich parts and discard poor parts, and discard weathered ore of submarginal ore which accounts for over 95 percent of that of raw ore and is taken as mining mullock. The method comprises the following step: directly reducing titaniferous iron concentrate dressed from the mining mullock (TiO2 is over 5 percent, and TFe is over 13 percent) of the schreyerite, electric furnace melt producing titanium slag and molten water with electric furnace melt components, and producing a titanium-rich material and rutile with the titanium slag through mineral dressing by a fire method; producing alloy molten iron with the molten iron through electric smelting and vanadium-chrome steel slag blowing; and producing various alloy steel products the alloy molten iron in a continuous casting and continuous rolling mode through the electric smelting. The recovery rates of titanium, iron and vanadium are improved to 80 percent from 3.86 percent, improved to 70 percent from 34.5 percent and improved to 70 percent from 20.90 percent respectively.
Owner:PANZHIHUA JINTAI HI TECH
Method of producing titanium enriched material using titanium mineral
InactiveCN1429919AEfficient recyclingImprove resource utilization efficiencyMagnetic separationAdhesiveMagnetite
A process for preparing Ti-enriched material from V-Ti magnetite through preseparating to obtain Ti-Fe ore concentrate, proportionally mixing it with V-Ti-Fe core concentrate, adhesive and carbon reducer, smelting to obtain high-Ti slag and semi-steel, blowing V-Cr to melten alloy iron to obtain V-Cr contained steel slag, separating V and Cr, fire metallurge of high-Ti slag to obtain artificial rutile and microcrystal glass, ball grinding of artificial rutile and coal while adding adhesive to obtain C-contained Ti particles, calcining, cooling and classifying.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Method for separating vanadium-titanium magnetite to extract iron, vanadium and titanium
InactiveCN102179292AHigh technical difficultyIncrease processing costWet separationSmelting processMagnetite
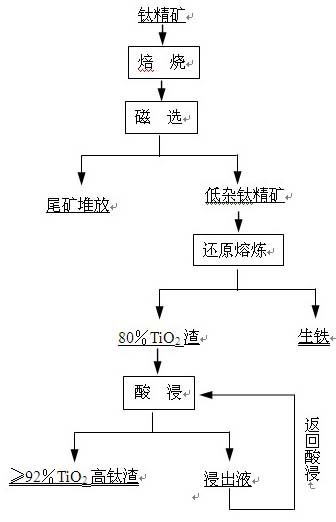
The invention discloses a method for separating vanadium-titanium magnetite to extract iron, vanadium and titanium, comprising the following steps of: magnetically selecting raw magnetite, that is, acquiring iron-vanadium concentrate and tail magnetite after performing magnetic selection on the vanadium-titanium magnetite; sorting titanium concentrate from the tail magnetite, that is, acquiring the titanium concentrate after performing floating selection on the obtained tail magnetite; roasting and magnetically selecting the titanium concentrate, that is, performing enriched-titanium impurity-removing magnetic selection after roasting the titanium concentrate; finely selecting the iron-vanadium concentrate, that is, performing the magnetic selection and fine section again on the iron-vanadium concentrate obtained from magnetic selection; reducing and smelting, that is, mixing the titanium concentrate obtained from the impurity-removing process with the iron concentrate according to the beneficiation yield, adding in a reducer and soda ash to perform reduced iron and vanadium smelting process; purifying vanadium slag, that is, removing the impurity of the vanadium slag obtained by reducing and smelting by using the acidic dipping to obtain the high-quality titanium slag product with the content of TiO2 larger than 92%; and extracting vanadium from pig iron, that is, performing vanadium extraction by converter blowing on the vanadium-containing pig iron obtained by reducing and smelting to obtain the semi-steel and vanadium slag. The method not only improves the utilization ratio of titanium, iron and vanadium but also obtains the high-titanium slag product with the content of TiO2 larger than 92% so as to widen the application field of titanium.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
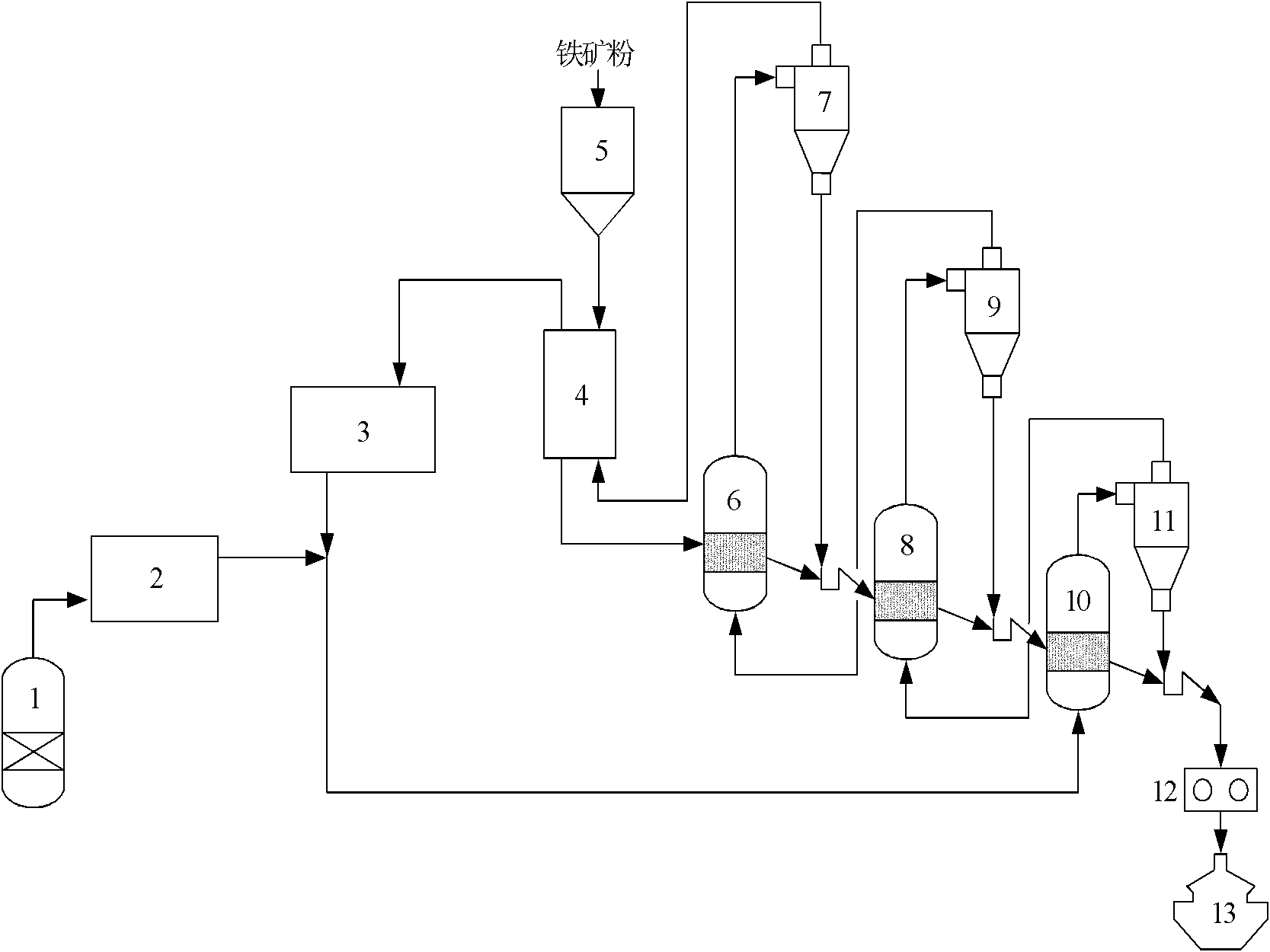
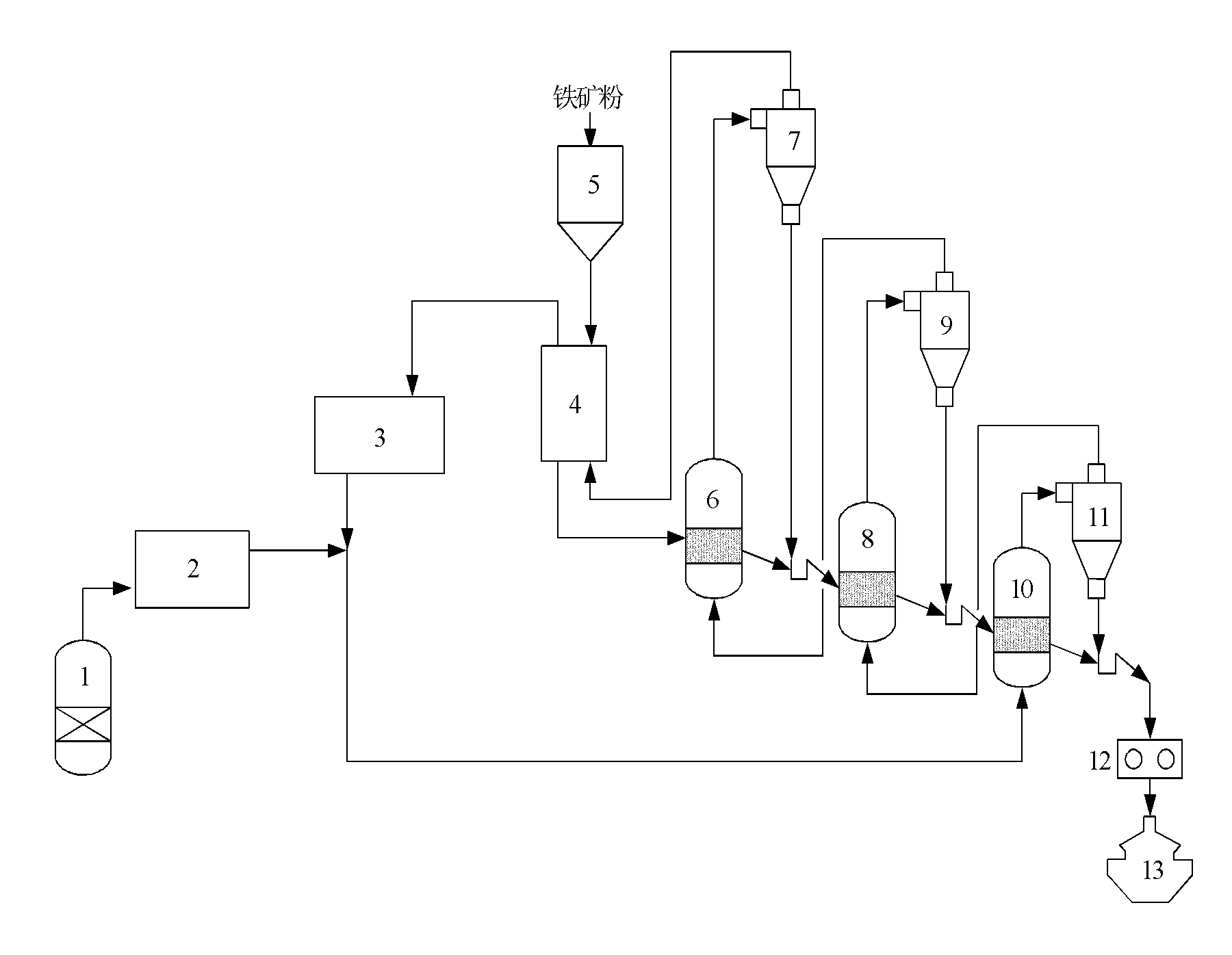
Method for reducing vanadium-titanium magnetite powder by coal reducing gas and fluidized beds
ActiveCN102127611AShort recovery timeHigh production heat efficiencyFluidised-bed furnacesProcess moduleMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for reducing vanadium-titanium magnetite powder by coal reducing gas and fluidized beds. High temperature coal gas produced by a coal reducing gas system is mixed with gas of a reducing exhaust gas purification system to form reducing gas, and the reducing gas enters third-stage, second-stage and first-stage reduction fluidized beds in turn; the preheated vanadium-titanium magnetite powder enters the first-stage, second-stage and third-stage reduction fluidized beds in turn and is fluidized and subjected to reduction reaction under the action of the reversely upward reducing gas; and the obtained directly reduced iron is briquetted, titanium slag is removed, vanadium slag is extracted, and the qualified molten steel is produced. The invention integrates process modules such as coal reducing gas, iron ore powder preheating, fluidized bed reducing, briquetting, electric furnace melting separation and the like, and has the advantages of high production thermal efficiency, low cost of preparing the reducing gas, short time of reducing the iron ore powder and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
A method for comprehensive utilization of vanadium-titanium magnetite
InactiveCN102277462AReasonable useLess investmentMagnetic separationProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingFurnace temperature
The invention relates to a method for comprehensive utilization of vanadium-titanium magnetite, which belongs to the field of new technology of direct reduction ironmaking in the metallurgical industry. In order to solve the problems of low utilization of iron, vanadium and titanium in vanadium-titanium magnetite, at the same time, due to the sintering process of traditional technology, the comprehensive energy consumption of the overall smelting process is relatively high, and the environmental pollution is serious. The invention provides a method of agglomerating vanadium-titanium magnetite and producing high-titanium slag and pearl iron by high-temperature reduction and melting in a rotary hearth furnace. The technical solution includes pelletizing of vanadium-titanium magnetite, high-temperature reduction in rotary hearth furnace, magnetic separation, and high-temperature reduction in rotary hearth furnace to directly produce high-titanium slag and pearl iron. Applying this method to process vanadium-titanium magnetite can not only effectively solve the problem of recovery of titanium and vanadium resources, but also obtain qualified iron pearls for steelmaking in electric furnaces, making full use of the iron, vanadium, and Valuable elements such as titanium.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
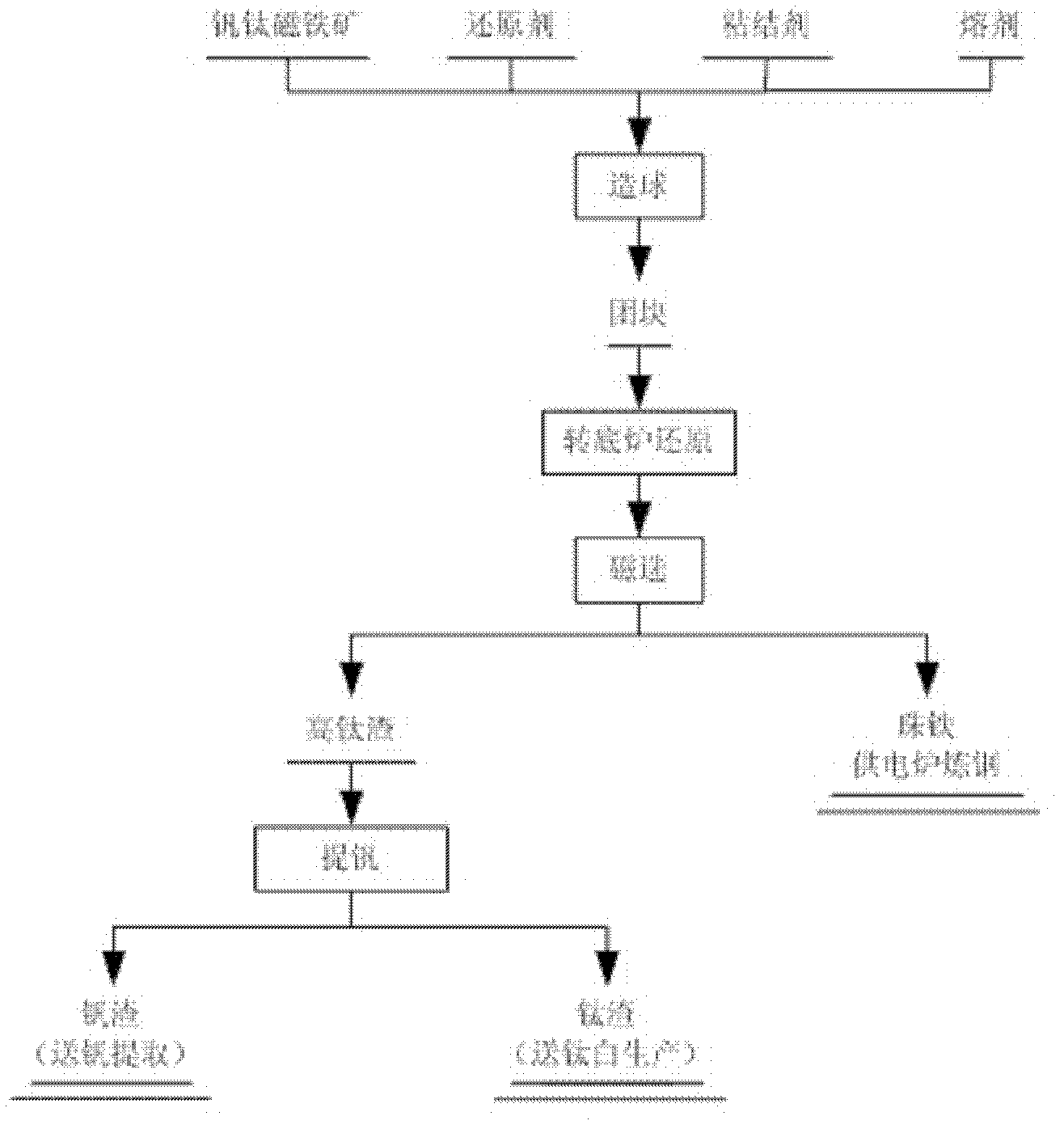
Titanium slag smelting method
The invention provides a titanium slag smelting method which comprises the following steps: preparing a mixture of titanium concentrates, a bonding agent and a carbonaceous reducing agent into pellets or briquettes; drying the pellets or briquettes; prereducing the pellets or briquettes by utilizing an annular furnace or a rotary hearth furnace, thereby preparing metallized pellets or metallized briquettes; and loading the metallized pellets or metallized briquettes into an electric furnace so as to melt and separate the metallized pellets or metallized briquettes, thus obtaining semisteel and titanium slag, wherein the smoke generated by prereducing the pellets or briquettes is used for providing heat for drying the pellets or briquettes, and the smoke generated in the melting and separating process is used for providing heat for prereducing the pellets or briquettes.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +1
Method for preparing rutile titanium dioxide from new process titanium slag
ActiveCN101898791AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costSolid waste disposalTitanium dioxideAluminium agentsRutile
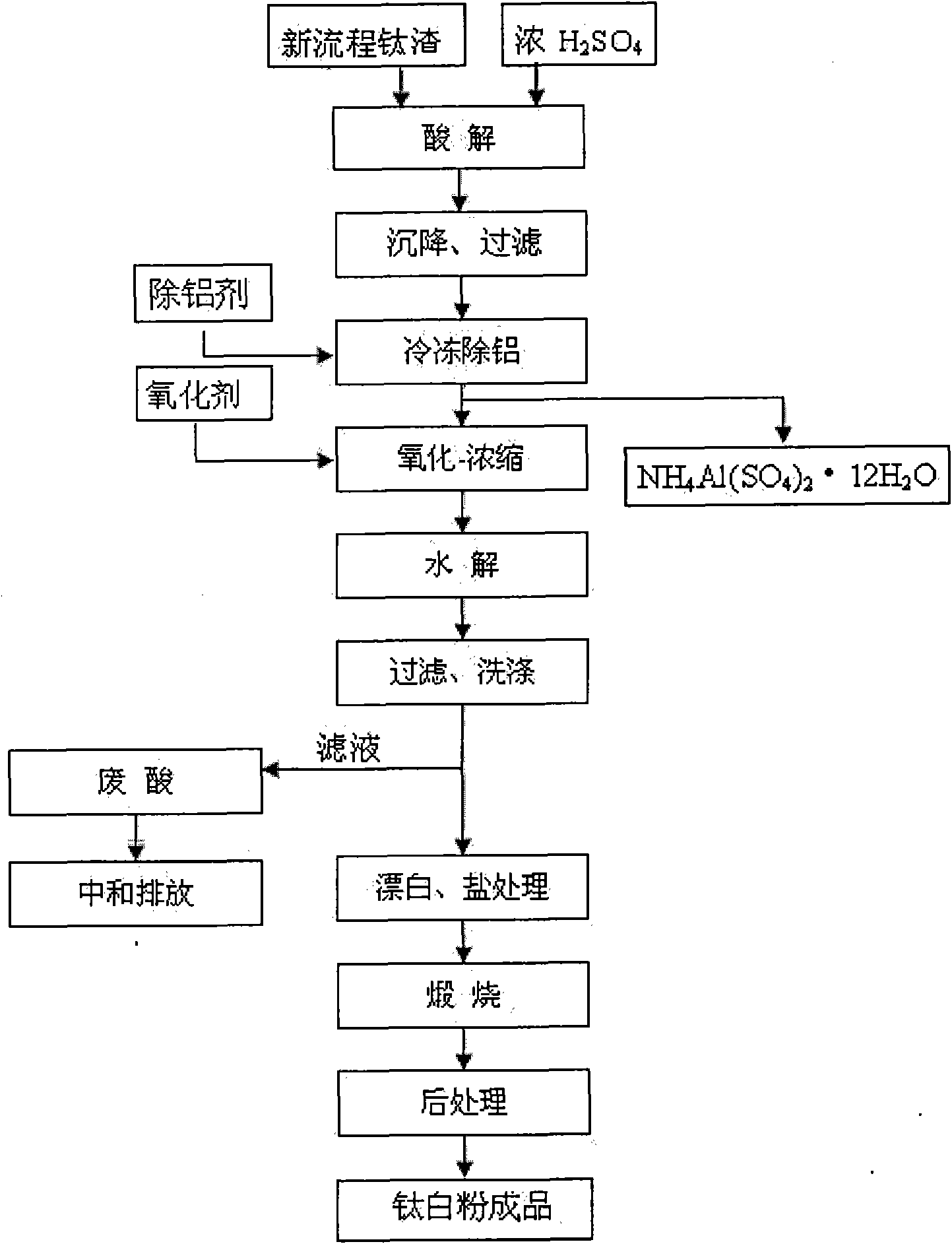
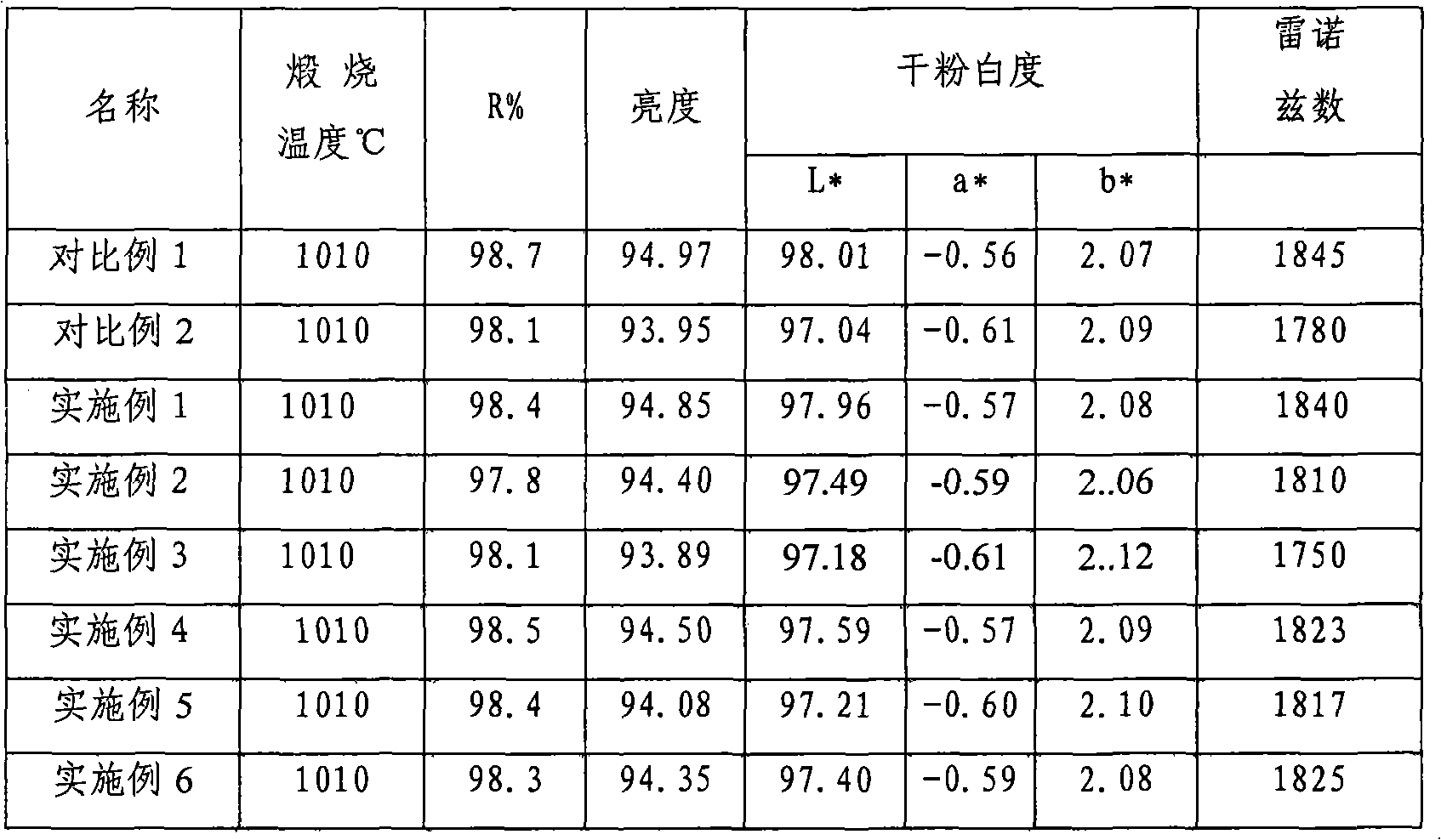
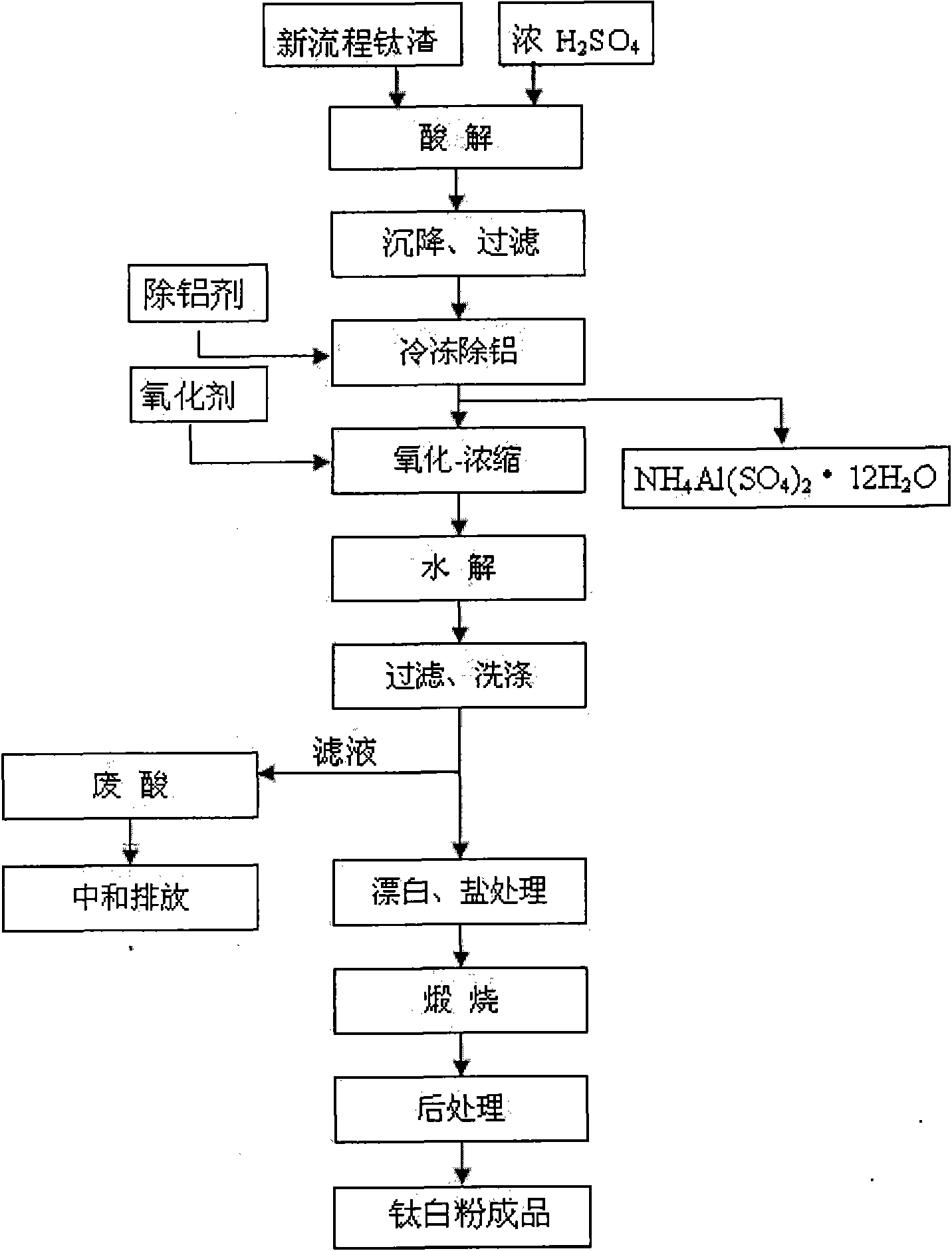
The invention discloses a method for preparing titanium dioxide from new process titanium slag, and belongs to the technical field of titanium dioxide production. The method comprises the following steps of: performing acidolysis reaction on the new process titanium slag and concentrated sulfuric acid under certain conditions; leaching, precipitating and filtering the mixture to obtain clear titanium liquid; adding an aluminum removing agent into the clear titanium liquid to recover aluminum by freezing crystallization; adding oxidized trivalent titanium serving as an oxidant into the clear titanium liquid and concentrating the mixture; hydrolyzing, filtering and washing the concentrate by using a process for adding crystal seeds; and bleaching, salting, calcining and post-processing the filter cake to prepare the rutile titanium dioxide which meets the application requirement. The method has the most noticeable characteristic that the rutile titanium dioxide which meets the application requirement is prepared from the new process titanium slag which has the disadvantages of various impurities and difficult acidolysis; and thus a new raw material for producing the titanium dioxide by a sulfuric acid method is developed, various valuable elements are recovered as much as possible, the utilization ratio of the resource is improved and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN LOMON TITANIUM IND CO LTD
Method for comprehensive utilization of V-Ti-bearing iron ore concentrate by using tunnel kiln reduction-grinding - separation
InactiveCN101113488AAvoid defects such as loopsHigh yieldProcess efficiency improvementTunnel kilnResource utilization
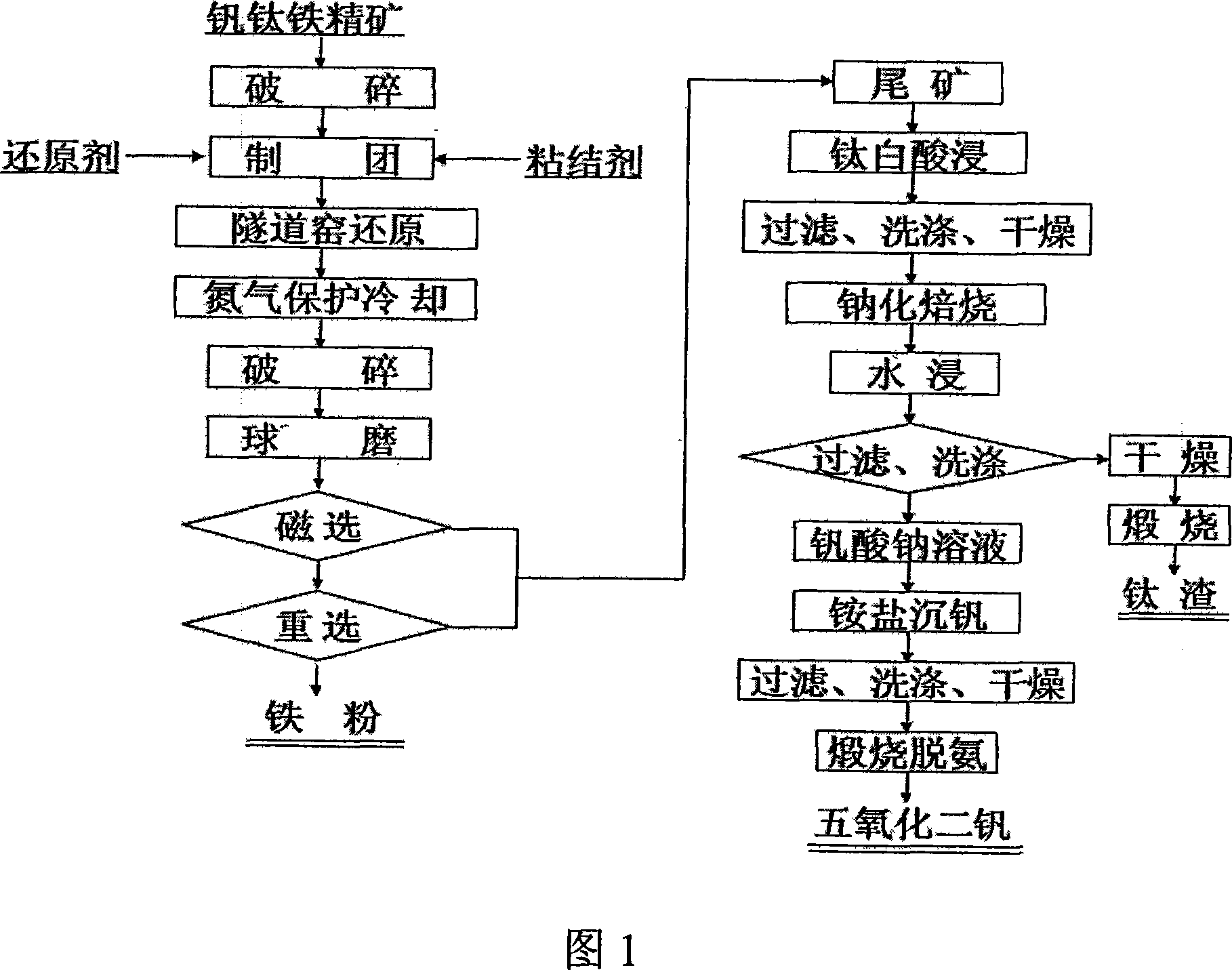
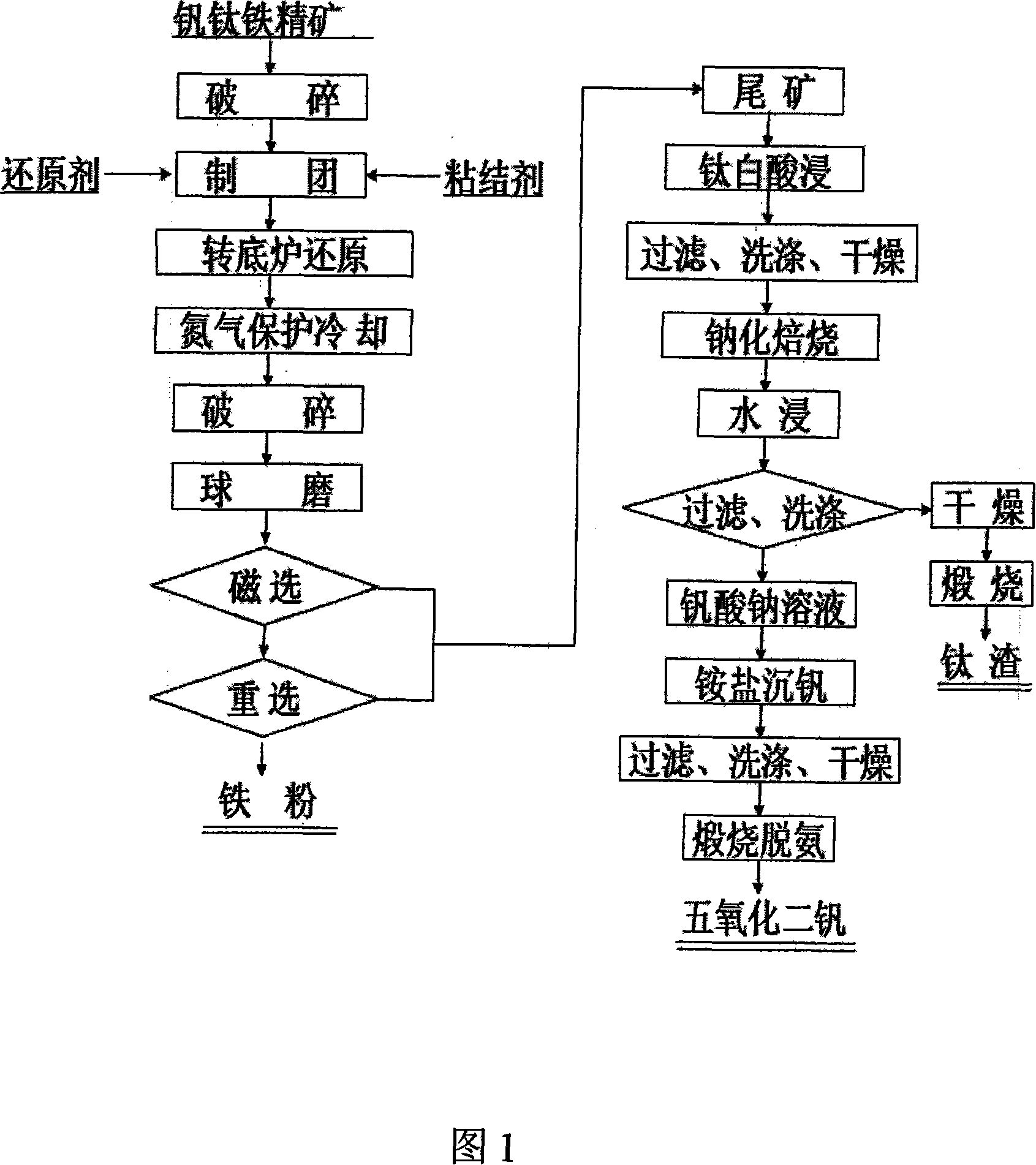
The invention relates to an iron powder production method by using a tunnel kiln to reduce concentrate pellets containing carbon vanadium ferrotitanium with titanium slag and vanadium pentoxide as combined products. Concentrate pellets are made from vanadium-titanium iron concentrate through crashing and damp milling. The iron powder and tailings are obtained by putting the concentrate pellets into the tunnel kiln to be reduced, crashing, wet-grinding, magnetic separation and gravity separation. The tailings are soaked with titania waste acid to eliminate remnants magnesium and iron. Then the tailings are filtrated and dried to obtain a new material. And then the new material is added with sodium salt to do salt roast and then to be soaked by water, then titanium slag and sodium vanadate are obtained respectively after the water soaking. At last, the vanadium pentoxide is obtained by ammonium vanadate precipitating and calcination deaminase to the sodium vanadate liquid. The invention eliminates the disadvantage of high energy consumption by electric furnace smelting and bad separating effect of vanadium and titanium, difficult control of vanadium and titanium trend and low yield rate of extracting vanadium and titanium through converter blowing iron molten, etc. The invention has the advantages of high yield rate of vanadium, titanium and iron and high resources utilization rate and explores a novel practical way for comprehensive utilization of vanadium, titanium and iron concentrate ore.
Owner:攀枝花锐龙冶化材料开发有限公司
Comprehensive utilization method for red mud
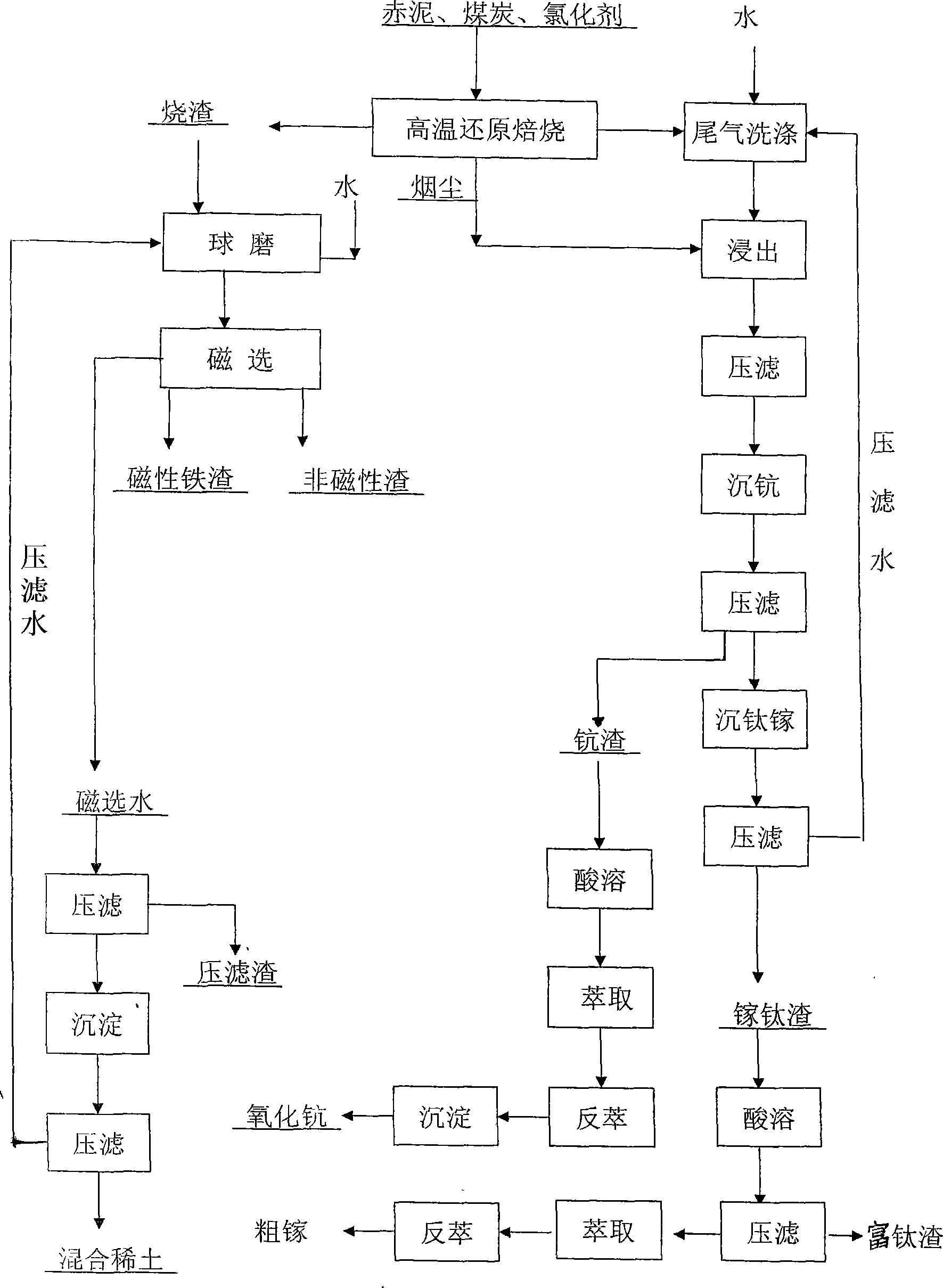
InactiveCN101463426APromote environmental protectionGood benefitSolid waste managementProcess efficiency improvementWash waterRed mud
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively utilizing red mud, comprising the following steps: chloridizing roasting, namely roasting the mixture of the red mud, coal and calcium chloride; cinder treatment, namely obtaining magnetic iron slag and non-magnetic slag after magnetic separation is carried out to levigated cinder, and then separating the magnetic iron slag and non-magnetic slag; adding calcined soda or oxalic acid after levigation liquid and wash water are rich in mischmetal due to cyclic use, and then precipitating mischmetal slag; treatment of dry dust and circulation liquid, namely, after dry powder for roasting dust collection is collected, mixing the dry powder with scouring water which is used for tail gas circulation and then leaching soluble ScCl3 and GaCl3; after filter pressing, precipitating scandium by adding oxalic acid crystal in filtrate; carrying out filter pressing again, precipitating gallium and Ti(OH)4 by adding ammonia into the filtrate, dissolving obtained gallium-titanium slag with acid and then using P2O4 extractant to extract the gallium; and using extractant to extract the scandium after scandium precipitate is dissolved by acid, carrying out precipitation again by adopting back-extraction acid dissolving, and obtaining Sc2O3 by means of roasting. The method can realize recovery of valuable metals from the red mud, and secondary residual slag is totally used for building material production; and the method has environment protection effects and economic benefits, plays an important role in the development of recycling economy and is applicable to enterprises generating red mud.
Owner:张钦
Method for preparing titanium-enriched material from high-impurity-content ilmenite concentrate
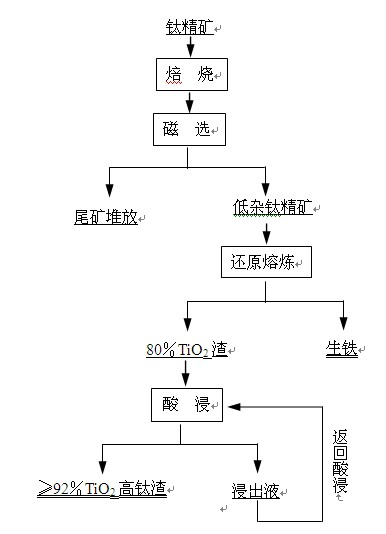
The invention discloses a method for preparing a titanium-enriched material from high-impurity-content ilmenite concentrate, which relates to the technical field of a preparation method of a titanium-enriched material. The technical route is as follows: raw ore, magnetic separation, iron concentrate, tailings, floatation, ilmenite concentrate, roasting, magnetic separation, reduction smelting, titanium slag, purification and titanium-enriched material. The invention integrates the advantages of an electric-furnace smelting method and an acid leaching method, and overcomes the defects of the two methods; and thus, the method provided by the invention can be used for treating high-impurity-content rock-type ilmenite concentrate, and can also be used for producing a high-quality titanium slag product.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Method for comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanium and iron ore concentrate by using rotary hearth furnace reduction-grinding - separation
The present invention relates to a method of using a rotary hearth furnace to deoxidize the ore concentrate pellets containing carbon and vanadium and titanium and iron for producing iron powder and joint titanium slag and vanadic oxide. The vanadium and titanium and iron ore concentrate is made into pellets positioned in the rotary hearth furnace for deoxidizing and then crashing, after the wetmilling, the crashed pellets are dressed by the magnetic separation and reelected to get the iron powder and the mine tailing, which is lixiviated by titanium dioxide waste acid to remove the titanium slag and the sodium vanadate solution, at last, the sodium vanadate solution is added with sodium salt to sink vanadium, and calcinations to remove ammonia, thereby getting the vanadic oxide product. The present invention eliminates the shortcomings that the fusion energy consumption of the electric furnace is high, the separation effect of vanadium and titanium is bad, the run of vanadium and titanium is difficult to control, and the yield of extracting vanadium and titanium from the molten iron blown in the rotary hearth furnace is low. The present invention has the advantages of high yield of vanadium and titanium and iron and high utilization rate of resources, and develops a doable new route for the comprehensive utilization of the vanadium and titanium and iron ore concentrate.
Owner:攀枝花锐龙冶化材料开发有限公司
Method for wet-process vanadium extraction by using vanadium- and titanium-containing converter slag
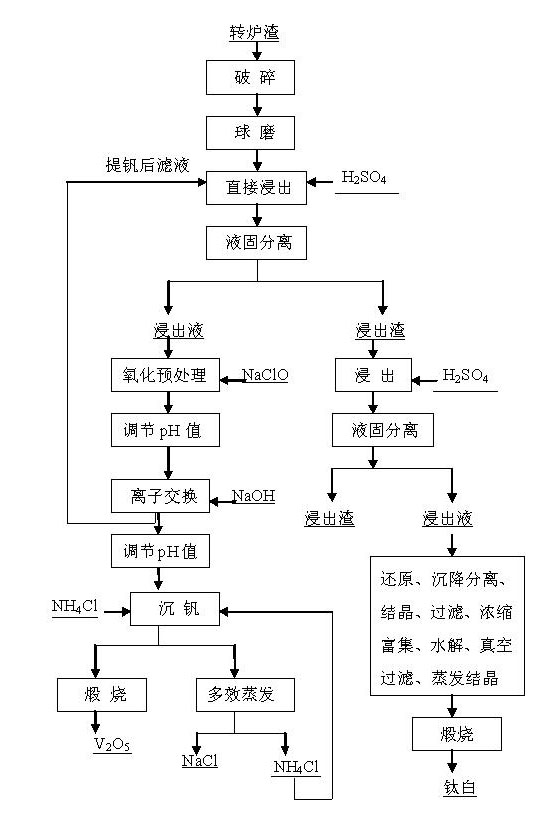
ActiveCN101967563AShort processReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementIon exchangeAmmonium metavanadate
The invention discloses a method for wet-process vanadium extraction by using vanadium- and titanium-containing converter slag, which comprises: performing acid leaching directly by using 5 to 30 mass percent sulfuric acid; adding NaClO into the leachate to perform oxidization treatment, performing ion exchange purification and separation by using alkalescent anion exchange resin which is transformed by sulfuric acid, and desorbing by using NaOH; adding ammonium chloride into stripping liquid to precipitate vanadium, filtering and calcining ammonium metavanadate filter cake to obtain powdered vanadium pentoxide; and processing titanium-enriched leaching residue to obtain titanium dioxide. In the invention, the direct leaching of converter vanadium-titanium slag is realized, process flow in shortened, the pollution caused by adding oxidant is avoided, and due to the use of the low-concentration sulfuric acid, the material consumption and the requirements on the corrosion resistance of equipment are reduced at the same time. The method realizes the comprehensive recovery and utilization of all valuable elements, belongs to a novel all wet-process smelting technique, and avoids waste discharge in a whole process.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
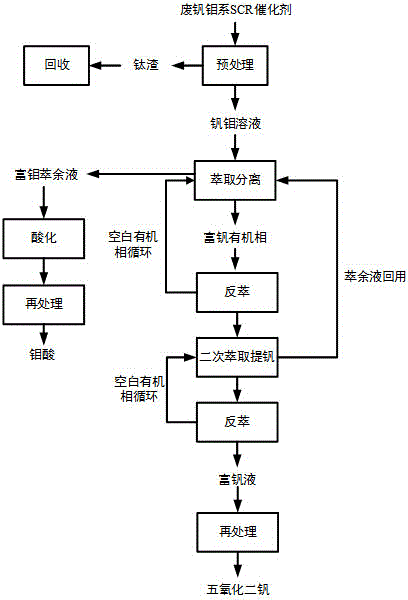
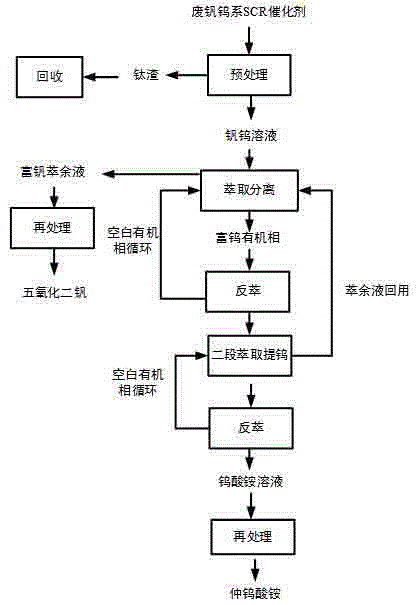
Method for separating and purifying vanadium and molybdenum of waste vanadium-molybdenum SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst
ActiveCN104831075ARealize separation and recoveryReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying vanadium and molybdenum of a waste vanadium-molybdenum SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out pretreatment on a catalyst to obtain a titanium slag and a vanadium-molybdenum solution; extracting and separating the vanadium-molybdenum solution, acidifying the obtained molybdenum-rich raffinate, and reprocessing to prepare a molybdenic acid product; carrying out reverse extraction on the obtained molybdenum-rich organic phase, then carrying out a two-stage extraction and vanadium purification process, and carrying out reverse extraction again to obtain a vanadium-rich solution; and reprocessing the vanadium-rich solution to prepare vanadium pentoxide. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problem of difficult vanadium and molybdenum separation, recovery and purification of the waste vanadium-molybdenum SCR catalyst in industry is thoroughly solved; in addition, the recovery rates of vanadium and molybdenum exceed 95%; a high-purity (greater than 99%) molybdenic acid product and a vanadium pentoxide product of which the purity exceeds 99.5% can be respectively obtained; recycling of resources is really realized; and the method has good environmental and economic benefits, and is suitable for industrial popularization and application.
Owner:BOTREE CYCLING SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing high-titanium iron by step-by-step metal thermal reduction
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-titanium iron by step-by-step metal thermal reduction, which comprises an aluminum thermal reduction smelting step and a reinforced reduction refining step, wherein the raw materials include rutile or high-titanium slag, aluminum powder, iron ore concentrate, slag forming agent and KClO3 in a mass ratio of 1.0: 0.37-0.50: 0.05-0.10: 0.15-0.25: 0.20-0.25, and the smelting temperature is 1,900 to 2,200 DEG C; the reinforced reduction refining time in the second step is 10 to 30 minutes, and after the refining is finished, a high-titanium iron alloy is obtained by cooling, ingot formation and impurity removal; and the composite reducing agent is calcium-magnesium alloy. The method has the advantages of wide raw material source and low production cost; the step-by-step reduction operations are adopted in the method, the reduction smelting of the first step is performed under the condition that the aluminum is insufficient, and the calcium-magnesium alloy composite reducing agent is adopted in the deoxidization refining of the second step, so the Al residue in the high-titanium iron alloy is remarkably reduced, and oxygen is effectively removed; and the transfer of high-temperature melt is realized by casting, and the metal slag separation process is reinforced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for preparing microcrystalline glass by utilization of red mud-fly ash-titanium slag
The invention discloses a method for preparing microcrystalline glass by the utilization of red mud-fly ash-titanium slag, comprising the following steps: burdening 25-70 wt% of red mud, 23-70 wt% of fly ash, 1-10 wt% of titanium slag and 0-10 wt% of a cosolvent, mixing, melting, moulding, carrying out nucleation amd crystallization, and carrying out cold working. Main components of the product contain, by weight, 12-39.8% of Al2O3, 13.6-50% of SiO2, 0.8-5.2% of TiO2, 6.5-19% of CaO, 0.5-7.1% of Fe2O3, 0.64-2% of MgO and 1.5-8.2% of Na2O+K2O. the technology is simple; utilization rate of waste residues is high, and amount of admixture reaches more than 90%; costs of raw materials are effectively reduced; and performance of the product reaches the microcrystalline glass architectural decoration quality standard ''JCT872-2000'', and the product can be used in preparation of various tubes and sheet materials.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
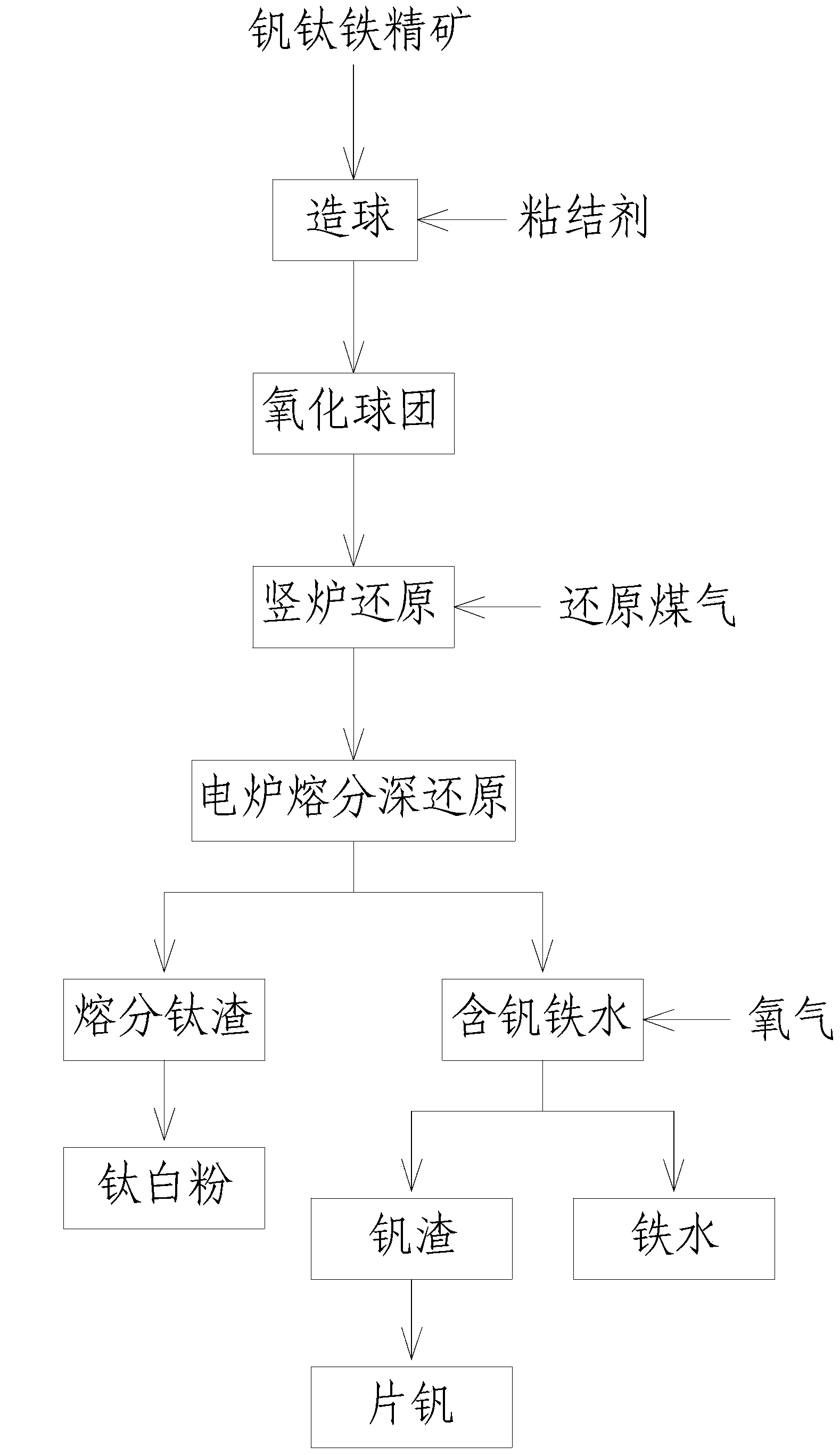
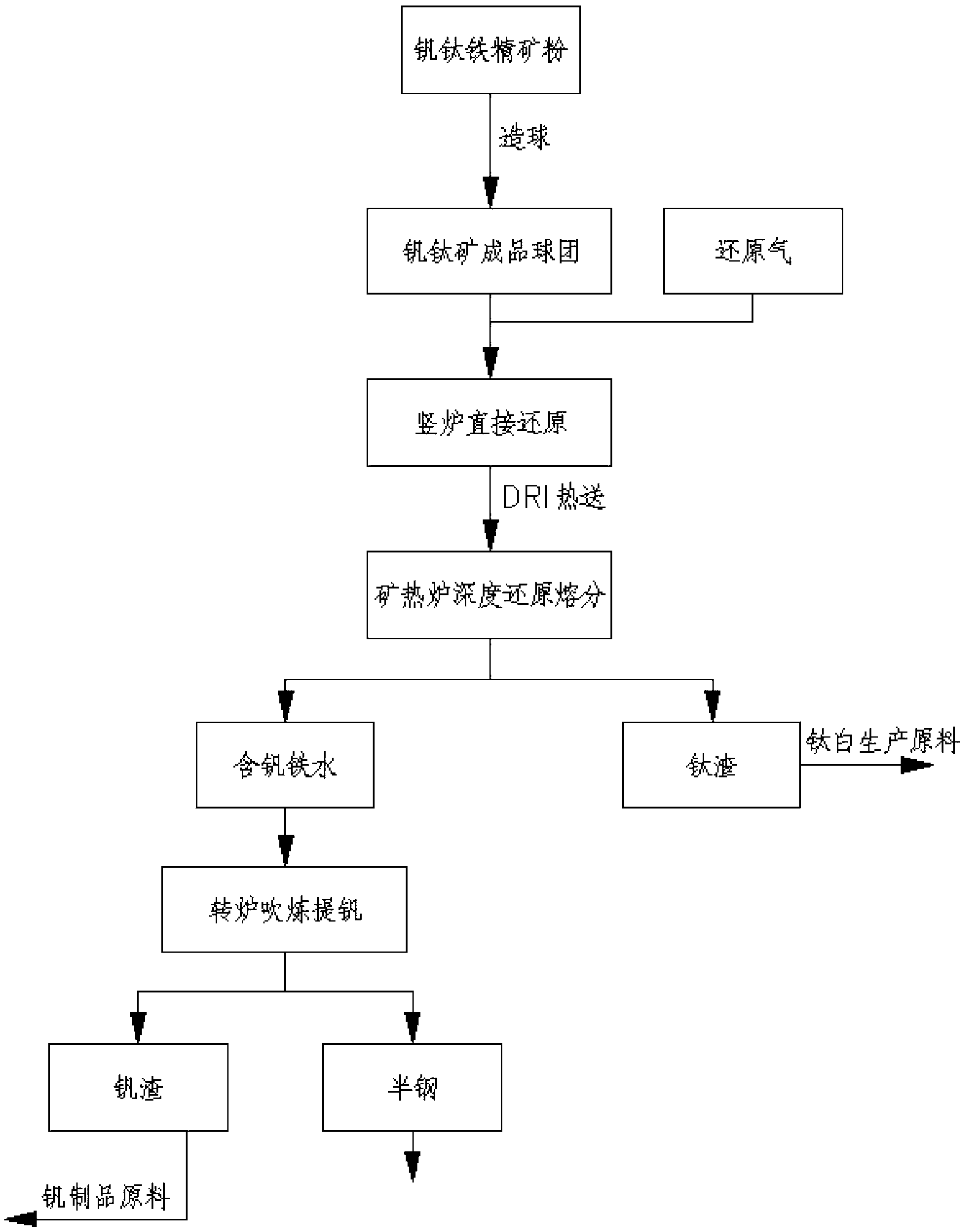
Method for recovering iron, vanadium and titanium from schreyerite through shaft furnace reduction and electric furnace smelting and separating deep reduction
ActiveCN103451419AHigh recovery rateReduce dependenceShaft furnaceGas emission reductionLand resourcesMagnetite
The invention discloses a method for recovering iron, vanadium and titanium from schreyerite through shaft furnace reduction and electric furnace smelting and separating deep reduction. The method comprises the following steps of: producing a vanadium-titanium oxidized pellet; directly reducing the vanadium-titanium oxidized pellet; smelting and separating a metalized pellet through an electric furnace; extracting vanadium from molten vanadium-containing iron; smelting and separating titanium slag to manufacture titanium dioxide; smelting and separating vanadium slag to manufacture V2O5. According to the method, coal gas, converted coke oven gas or natural gas is used as a reducing agent to reduce original vanadium titanium magnetite, so that the dependency of the traditional blast furnace process to coking coal can be greatly reduced, and diversification of metallurgical energy is realized; by adopting the process, the vanadium titanium magnetite can be smelted completely; mixed smelting of common iron ore and vanadium titanium magnetite is not needed, so that the smelting efficiency is higher; titanium dioxide in the smelted and separated titanium slag produced in smelting accounts for more than 50%, therefore, the slag can be directly used as the raw material for preparing titanium dioxide, and as a result, the recovery rate of vanadium, titanium and iron can be raised; simultaneously, the smelted and separated titanium slag and vanadium slag can be directly utilized, thus the environmental pollution and land resource occupation caused by piling and storing the slag can be avoided.
Owner:TAIHE IRON MINE CHONGQING IRON & STEEL GROUP MINING +1
Method for extracting scandium oxide from titanium slag chloride waste
InactiveCN102796876ATo achieve the purpose of preliminary enrichment of scandiumImprove product qualityProcess efficiency improvementSodium hydroxideMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for extracting scandium oxide from titanium slag chloride waste, belonging to the field of comprehensive utilization of vanadium titano-magnetite resources. The method comprises the following steps: a, adding water to titanium slag chloride waste, and leaching; b, adding a reducer to the supernate obtained in the step a, then adding humic acid, regulating the pH value, and filtering to obtain precipitate; c, adding a hydrochloric acid solution to perform acidolysis reaction, and then filtering to obtain a coarse scandium solution; d, respectively performing extraction, washing and back extraction on the coarse scandium solution by taking (2-ethylhexyl)-2-ethylhexyl phosphonate as an extractant, the hydrochloric acid solution as a washing agent and a sodium hydroxide solution as a back extractant, thus obtaining a pure scandium solution; and e, adding oxalic acid to perform scandium precipitation, and calcining to obtain scandium oxide, wherein the grade of the obtained scandium oxide is about 95%. The method disclosed by the invention is high in product quality and simple in process, reasonably utilizes scandium resources in the titanium slag chloride waste, and has favorable economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:PANZHIHUA UNIV
Method for synthetically reclaiming iron, vanadium and titanium from vanadium titanium magnet concentrate
InactiveCN101168802ATake advantage ofCannot be efficiently recycledRotary drum furnacesTitanium dioxideRecovery methodMagnetite
The invention relates to a comprehensive recovery method of iron, vanadium and titanium for vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ores, in particular to the comprehensive recovery and utilization of the vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ore of which the vanadium content is higher. In particular, the invention is vanadium extraction through water immersion after the vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ore is performed with sodium activation and sintered, the vanadium product is made from leach solution, the remaining slag is performed with reduction quickly through a rotary furnace after carbon is added, the reduction product is melted through the electric furnace, to segregate the melted iron and the titanium slag, the melted iron is used to make steel, and the titanium slag is used to produce white titanium pigment through a sulfuric acid method titanium white technology. The method of the invention is applied to the refining technology of the vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ore, to ensure that the recovery rate of the vanadium and titanium is greatly enhanced, the recovery rate of the total vanadium in the iron concentrated ore can reach more than 80 percent, titanium is fully recovered, and the production of massive blast furnace slag is avoided.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
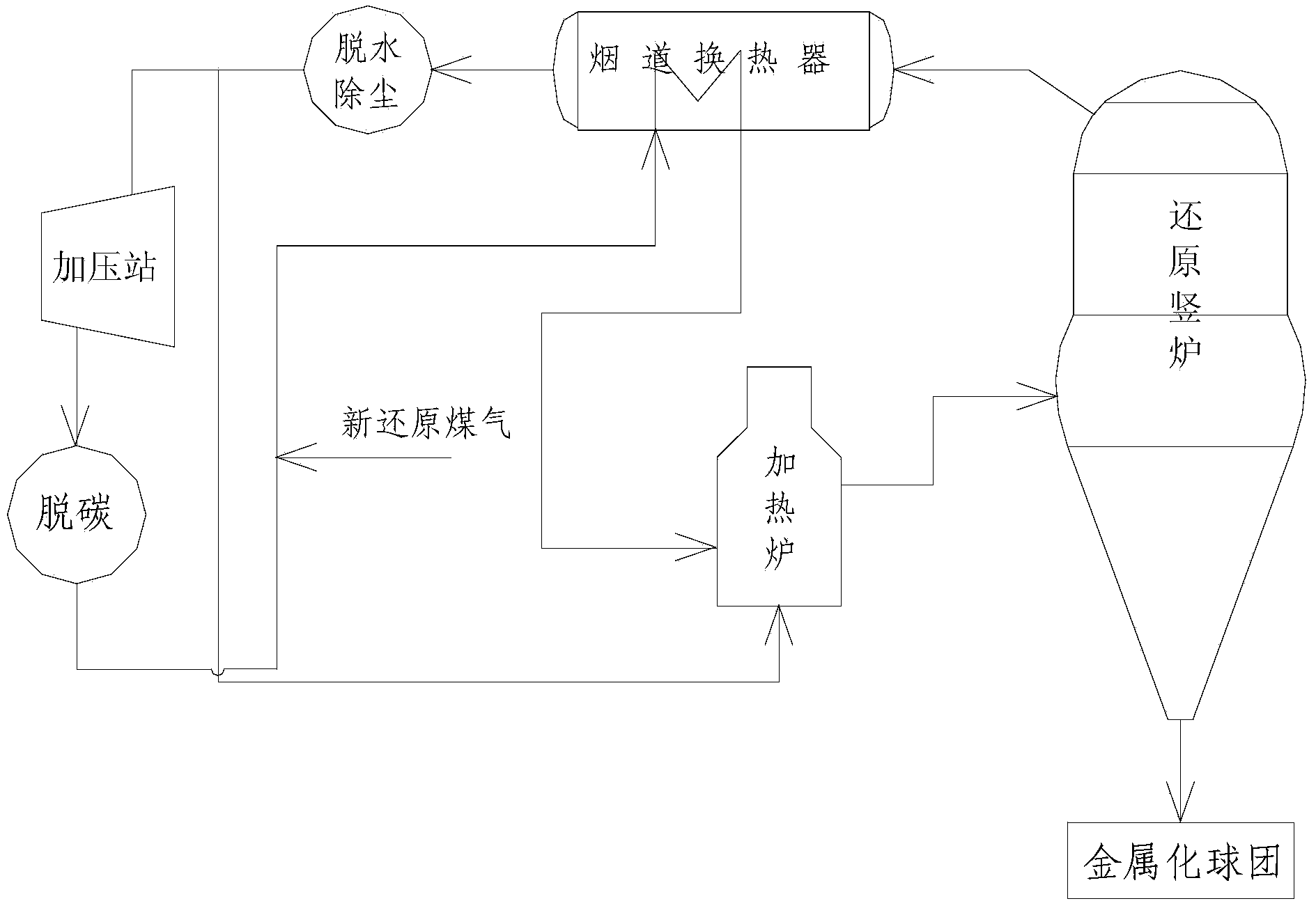
Gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction-electric furnace smelting separation process of vanadium titano-magnetite
InactiveCN103255255ARealize comprehensive utilizationEffective clean separationProcess efficiency improvementMagnetiteShaft furnace
The invention discloses a gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction-electric furnace smelting separation process of vanadium titano-magnetite. The process comprises the following steps of: a, forming finished product pellets; b, putting the finished product schreyerite pellets as raw materials into a direct-reduction shaft furnace and introducing a reducing gas to the shaft furnace to reduce the pellet ore, thus obtaining thermal-state direct reduced iron; c, feeding the thermal-state direct reduced iron to a smelting-separation electric furnace for reduction and smelting separation, thus separating out titanium slag and obtaining vanadium-containing iron liquid; and d, transferring the vanadium-containing iron liquid to a converter for blowing so as to separate out vanadium slag and semisteel. According to the gas-based shaft furnace direct reduction-electric furnace smelting separation process of vanadium titano-magnetite, the shortcomings of the existing process are improved, effective and clean separation of titanium, vanadium and iron is realized, the recovery and utilization rate of vanadium and titanium metal elements is improved and energy consumption and equipment one-time investment are reduced; and therefore, the process is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:CISDI ENG CO LTD
Fluidized bed combustion ash and high titanium slag compounded stable pavement base material
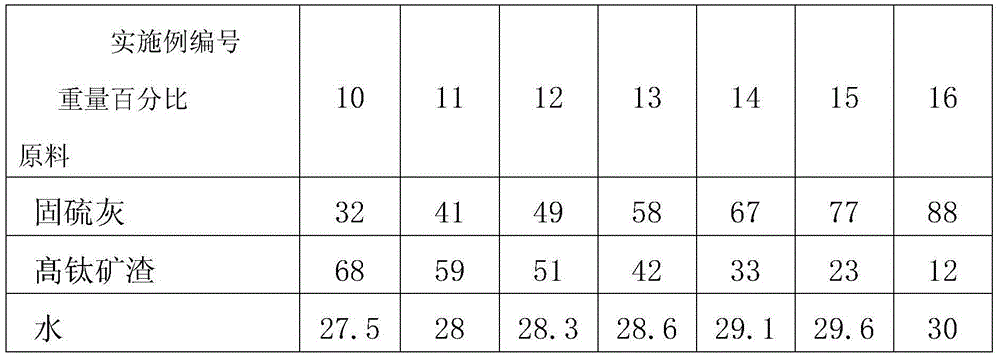
ActiveCN104003638AElicit activityHigh strengthSolid waste managementNatural resourceRoad engineering
The invention discloses a fluidized bed combustion ash and high titanium slag compounded stable pavement base material. The fluidized bed combustion ash and high titanium slag compounded stable pavement base material is formed by mixing 30-90wt% of fluidized bed combustion ash with 10-70wt% of high titanium slag. The fluidized bed combustion ash, the high titanium slag and water are stirred and mixed, and the obtained mixture is molded and maintained to make a fluidized bed combustion ash and high titanium slag compounded stable pavement base. The compounded stable pavement base material completely utilizes difficult-treatment and high-discharge-amount industrial wastes comprising the fluidized bed combustion ash and the high titanium slag, contains no lime or fly ash, and has better performances than traditional lime-fly ash stable pavement base material; and the compounded stable pavement base material has the advantages of low cost, no consumption of natural resources, simple and easy preparation method, suitableness for being used in areas short of traditional road engineering materials, substantial economic benefit, wide market prospect and strong practicality.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
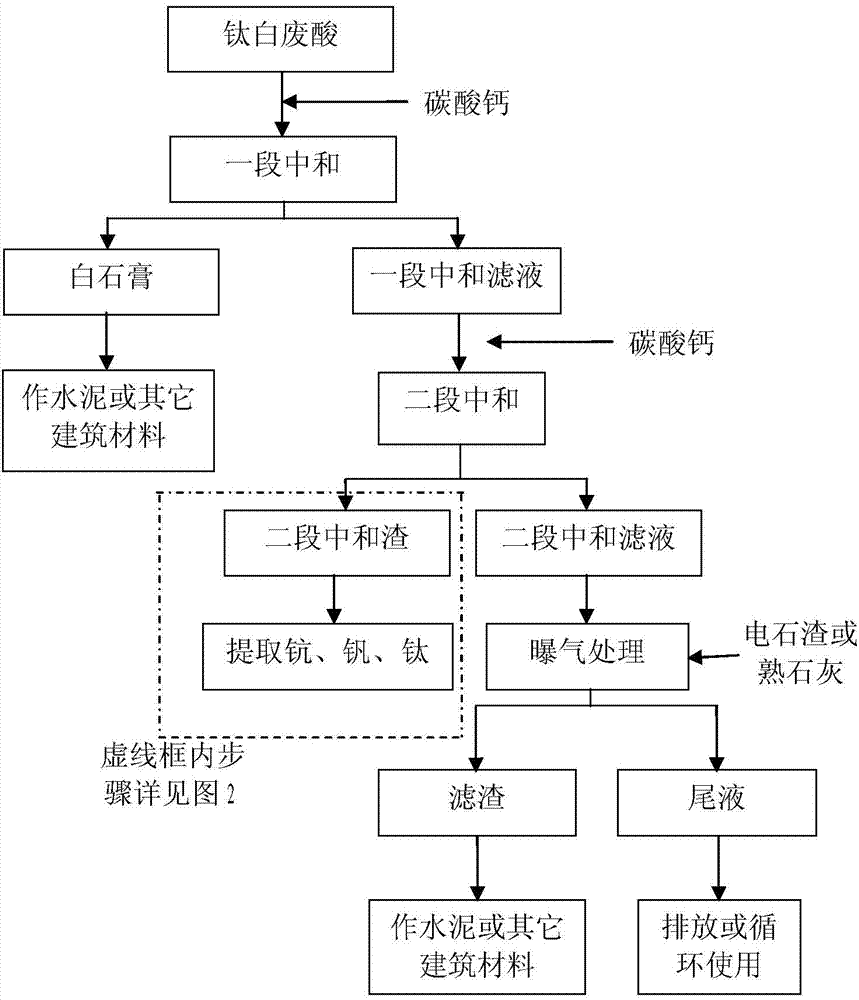
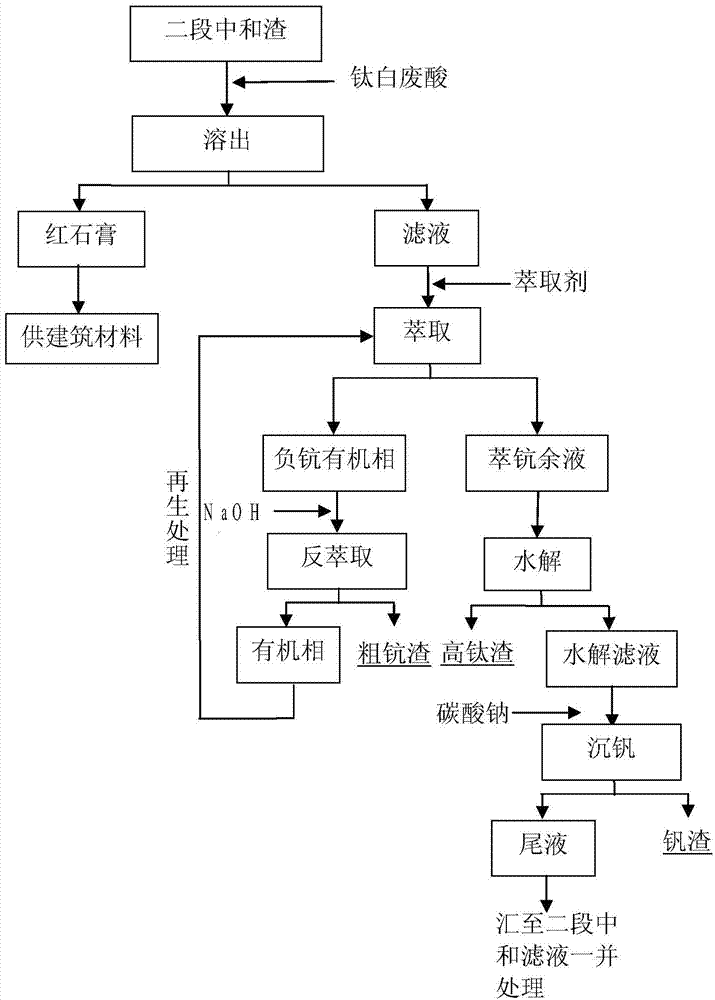
Method for enriching scandium, titanium and vanadium from sulfuric acid method titanium dioxide waste acid, and for treating waste acid
InactiveCN103540752ARealize environmental protectionReduce extraction costsNature of treatment waterWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationDissolutionHydrolysis
The invention relates to a method for enriching scandium, titanium and vanadium from sulfuric acid method titanium dioxide waste acid, and for treating waste acid. The method comprises the steps that: titanium dioxide waste acid is subjected to two-stage neutralization by using calcium carbonate, such that white gypsum is obtained, and two-stage neutralization slag with enriched scandium, titanium and vanadium are obtained; the two-stage neutralization slag is dissolved by using titanium dioxide waste acid; the dissolution liquid is subjected to scandium extraction and stripping, such that crude scandium slag is obtained; scandium extraction residue liquid is subjected to titanium hydrolysis, such that high-titanium slag is obtained; the hydrolysis filtrate is subjected to neutralization vanadium precipitation by using sodium carbonate, such that vanadium slag is obtained; the liquid after vanadium precipitation is subjected to aeration and further neutralization with the two-stage neutralization filtrate, and can reach a discharge standard and can be discharged. With the method provided by the invention, scandium, titanium and vanadium can be effectively enriched from titanium dioxide waste acid, and the treated waste acid tail liquid can reach a discharge standard and can be discharged.
Owner:广西冶金研究院有限公司
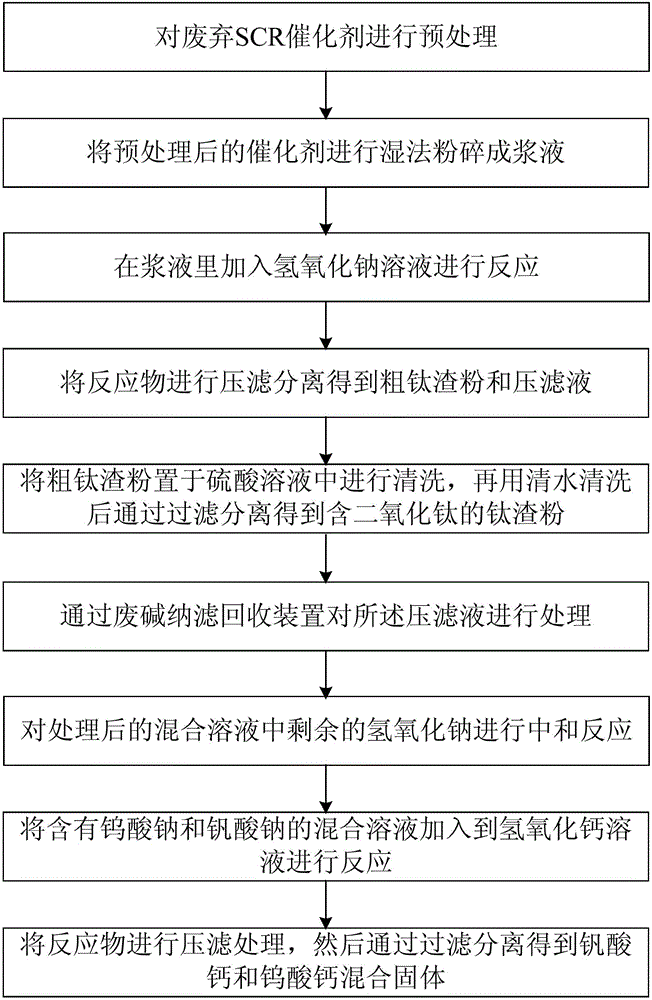
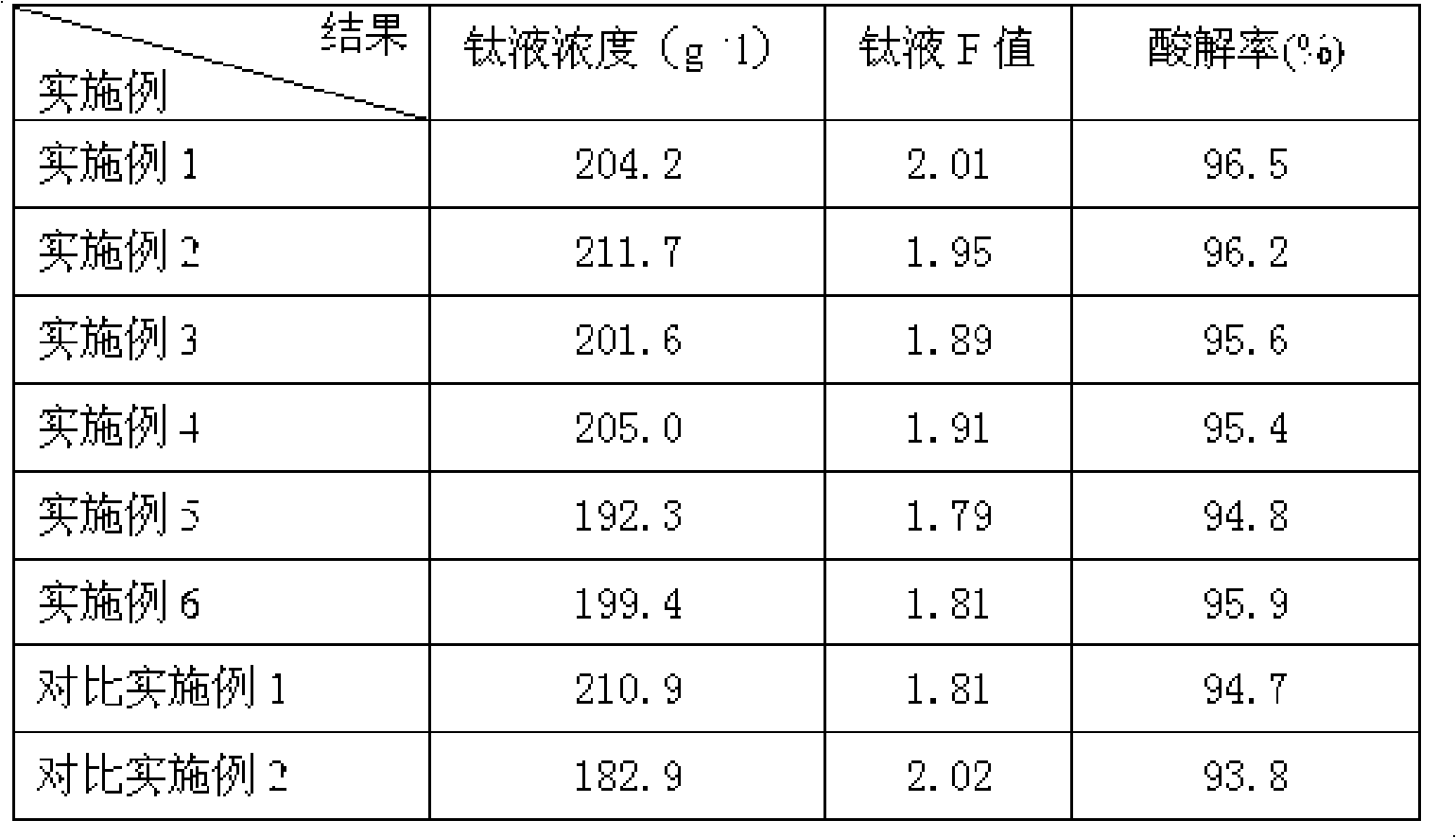
Method for extracting titanium slag, tungsten and vandic salt from waste SCR catalyst
ActiveCN106119544ASolve harmless disposalLow investment requirementProcess efficiency improvementSlurryCalcium tungstate
The invention provides a method for extracting titanium slag, tungsten and a vandic salt from a waste SCR catalyst. The method comprises the steps that the waste SCR catalyst is preprocessed and crushed into slurry by use of a wet method; a sodium hydroxide solution is added into the slurry for reaction; coarse titanium slag power and compression filtrate are obtained by filter-pressing and separating the slurry by use of a plate-and-frame filter press; the coarse titanium slag power is placed into a sulfuric acid solution for cleaning, cleaned with clear water, and then filtered and separated for obtaining titanium slag powder containing titanium dioxide; and the compression filtrate is treated through a waste alkali nanofiltration recovery device, the compression filtrate containing sodium tungstate and sodium vanadate is added into a saturated calcium hydroxide solution for reaction, products from the reaction are subjected to filter pressing, and then calcium vanadate and calcium tungstate mixed solid bodies are obtained through filtering and separating.
Owner:安徽思凯瑞环保科技有限公司
Method for comprehensively smelting sefstromite
ActiveCN101906498AHigh recovery rateImprove economyElectric furnaceTunnel kilnBlast furnace smelting
The invention provides a method for comprehensively smelting sefstromite. The method fundamentally solves the problem that the vanadium content in molten iron is difficult to increase so as not to finally extract vanadium, a valuable resource, because the conventional blast furnace smelting cannot utilize one hundred percent sefstromite by directly reducing the one hundred percent sefstromite into vanadium-titanium sponge iron by a tunnel kiln direct reduction method. The method comprises the following steps of: when the vanadium-titanium sponge iron is smelted in an electric furnace, first reducing V2O5 in slag and putting the V2O5 into steel by controlling a reducing atmosphere and then scratching away oxides of difficultly reduced elements such as Si, Al, Ti, Ca, Mg and the like along with the slag to obtain high titanium slag; and oxidizing the vanadium in the molten steel into the slag by oxidizing and blowing to improve the V2O5 content in the slag so as to provide guarantee for subsequent vanadium extraction from the slag and extremely improve the recovery rate and the recovery economic value of the vanadium. The method can also produce high-quality molten steel for developing steel grade with high added value, so the valuable resource, namely the sefstromite can be fully, effectively and rationally utilized.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
Method for selecting and smelting titanium from vanadium titanomagnetite at low temperature
InactiveCN102352423AQuick restoreIncrease magnetic susceptibilityProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceDc arc furnaceTitanium metal
The invention relates to a method for selecting and smelting titanium from vanadium titanomagnetite at low temperature, belonging to the technical field of metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: 1) roasting at the low temperature of 500-1100 DEG C; 2) adding a solid reductant to the roasted product, carrying out reduction smelting at 1100-1300 DEG C, and separating slag and iron torespectively obtain molten iron and titanium slag; carrying out magnetic separation on the titanium slag to remove impurities, thereby obtaining the titanium-rich material; and 4) adding required metal oxide concentrate into a direct-current arc furnace, and directly alloying the molten iron to obtain alloy steel. The smelting method provided by the invention is a brand new smelting method, and changes the existing iron ore selection into titanium ore selection; the pellet is molten and reduced by roasting at low temperature, and the separated molten iron facilitates the addition of ores withdeficient metal elements so as to directly smelt the alloy steel; the titanium slag is subjected to magnetic separation to obtain the titanium-rich material, and the titanium-rich material is furthersmelted to obtain the titanium alloy or titanium metal; and the smelting slag can be used as the raw material for smelting rare earth metals so as to sufficiently and respectively utilize the elements in the ores in one step.
Owner:攀枝花慧泰金属新材料有限公司
Aluminum thermal self-propagating-injection depth reduction based method for preparing metal titanium
ActiveCN104131178AShort processReduce energy consumptionIncreasing energy efficiencyRoom temperatureMedium frequency
An aluminum thermal self-propagating-injection depth reduction based method for preparing metal titanium belongs to the technical field of metal titanium smelting. The method is as below: using an aluminum thermal self-propagating reduction process to reduce rutile or high titanium slag to obtain a high temperature melt; then conducting insulation smelting separation on the high temperature melt in a medium frequency induction furnace to form a slag layer with alumina as an upper layer and a titanium melt layer as a lower layer; injecting CaF2-CaO pre-melted slag to the alumina based slag layer in a bottom blowing way; washing slag and refining; then injecting a high temperature calcium magnesium steam or a high-temperature steam to the high temperature titanium metal melt layer through inert carrier gas carrying in a bottom blowing mode, and conducting eccentric mechanical stirring and depth reduction refining; and finally, cooling the high temperature melt to room temperature to remove the upper metal smelting slag, so as to obtain the metal titanium. The method of the invention can realize low cost and short process preparation of metal titanium, and the prepared metal titanium has oxygen removed completely. The method has the advantages of short process, low energy consumption and simple operation, etc.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for determining impurity content in high-titanium slag
InactiveCN102253030AEasy to measureAccurate measurementPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationFritImpurity
The invention discloses a method for determining the impurity content in high-titanium slag, and belongs to the metallurgical chemical field. According to the method, a high-titanium slag sample is molten by a mixed flux; a frit is leached by a sulfuric acid solution to prepare a test solution; and the impurity component in the diluted high-titanium slag test solution is determined by an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer. With the invention, the content of the impurity component in high-titanium slag can be determined accurately, simply, and rapidly.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Method for acid hydrolysis of acid soluble titanium slag
ActiveCN101323465AImprove acid hydrolysis rateLow costTitanium dioxideAcid hydrolysisMaterials science
The invention belongs to the field of adopting the sulfuric acid process to prepare titanium dioxide, particularly relating to an acidolysis method for acid-soluble titanium slag and aiming at providing a novel acidolysis method for the acid-soluble titanium slag. The method has the advantages that the acidolysis rate can be enhanced and the manufacturing cost can be reduced and has the following steps: A. the acid-soluble titanium slag and sulfuric acid are mixed in an acidolysis reaction container, and compressed air of 0.1 to 0.35 MPa is injected into the container, and the mixture is stirred for 20 to 50 minutes; B. steam of 0.2 to 0.45 MPa is injected into the container and the material obtained from the step A is stirred while heating, and when the temperature of the material reaches 160 DEG C to 190 DEG C, the steam injection is stopped, and then the reaction generates a solidified material; C. the solidified material obtained from the step B is cured and extracted to obtain titanium solution which is then adopted to prepare titanium dioxide as the normal method. With the method, the acidolysis rate can be raised by 2 to 3 percent and simultaneously the manufacturing cost can be conserved due to that the low pressure compressed air and steam are adopted.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Method for preparing artificial rutile by microwave heating and oxidation sintering
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing artificial rutile, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy preparation. High titanium slag is used as a raw material, which is broken into pieces and heated by a microwave at the controlled temperature of 850-950 DEG C for 20-40 minutes, cooled to room temperature; thereby the artificial rutile is achieved of TiO2 with a grade of over 90 wt percent. Low-valent titanium in high tiranium slag is oxidized through oxidation calcination to realize the concentration of titanium components; thereby the rutile phase grows and roughens. Meanwhile, since the activity of the mineral surface of the high titanium slag can be enhanced by the microwave heating, the crystal transformation of TiO2 can be realized in relatively low temperature, and desulfuration and the decarburization can be realized.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Vanadium and tungsten separating and purifying method for spent vanadium and tungsten SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalysts
ActiveCN104862485ARealize separation and recoveryRealize recycling of resourcesProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystAmmonium paratungstate
The invention discloses a vanadium and tungsten separating and purifying method for spent vanadium and tungsten SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalysts. The method comprises the following steps: a spent catalyst is pretreated to obtain titanium slag and a vanadium and tungsten solution; the vanadium and tungsten solution is extracted for separation, and an obtained vanadium-rich raffinate is treated again to obtain vanadium pentoxide; a tungsten-rich organic phase obtained through separation is subjected to two-stage extraction for tungsten extraction after back extraction, a product is subjected to back extraction again to obtain an ammonium tungstate solution, and the ammonium tungstate solution is treated to prepare ammonium paratungstate. The blank of lack of a vanadium and tungsten separating, purifying and recovering technology for the spent vanadium and tungsten SCR catalysts in the denitration industry is filled up completely, the recovery rates of vanadium and tungsten both exceed 95%, the obtained vanadium pentoxide and ammonium paratungstate products all meet the high-purity standard, and the purity is higher than 99%.
Owner:BOTREE CYCLING SCI &TECH CO LTD
Method for clean production of titanium dioxide by using sodium hydroxide
ActiveCN101172648AObvious superiorityLow reaction temperaturePigmenting treatmentTitanium dioxideSeparation technologyTitanium nitride
The invention belongs to the preparation of inorganic metallic compound and the processing filed of mineral resource, in particular to a preparation method for titanium dioxide (titanium pigment) through high titanium slag and sodium hydroxide without pollution. The invention is characterized in that the high titanium slag is taken as the raw material; the high titanium slag and the sodium hydroxide having temperature range from 350 DEG C to 550DEG C are reacted to prepare a medium product; the medium product is then washed through water(or carbonatation), acid solubled, reduced, hydrolyzed and burned to prepare anatase or rutile titanium dioxide. The alkali circulation, the acid circulation and the separation technology of the invention greatly reduce the production energy consumption, simplify the production process, reduce the device investment, and increase the technology maneuverability, thereby providing an effective method for the comprehensive use of titanium resource and the preparation of titanium dioxide(titanium pigment).
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com