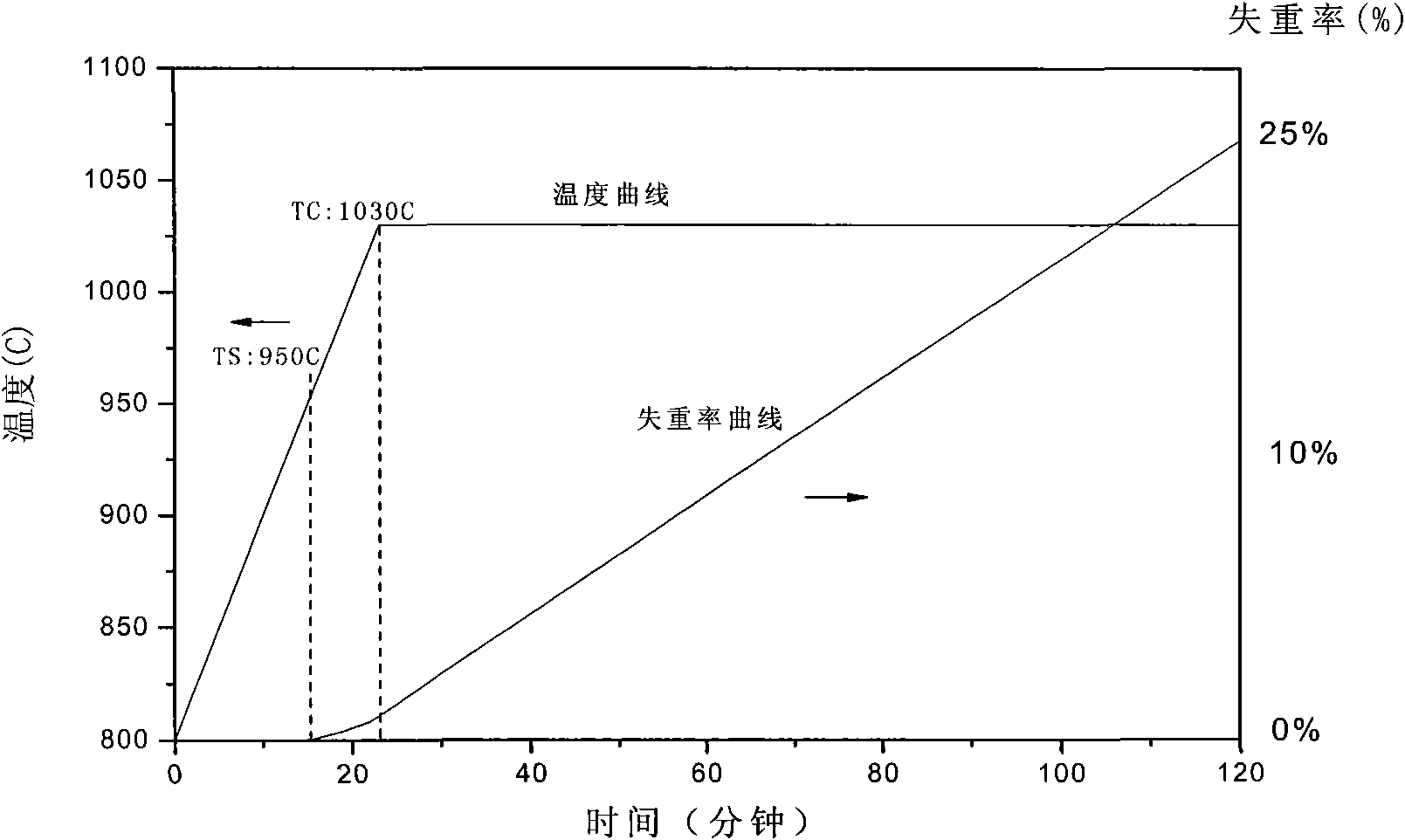
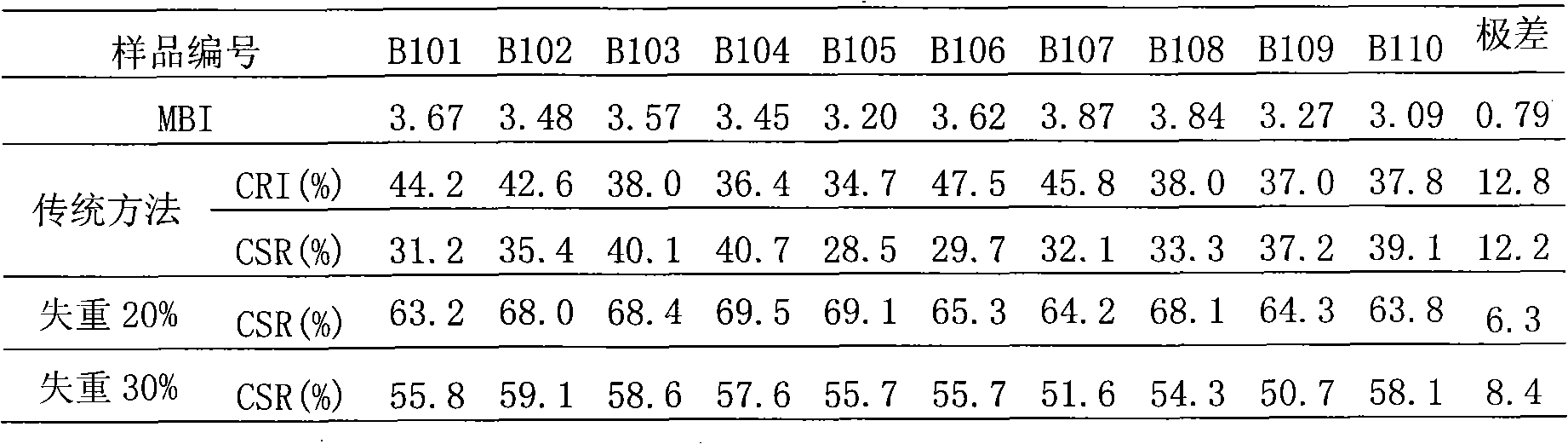
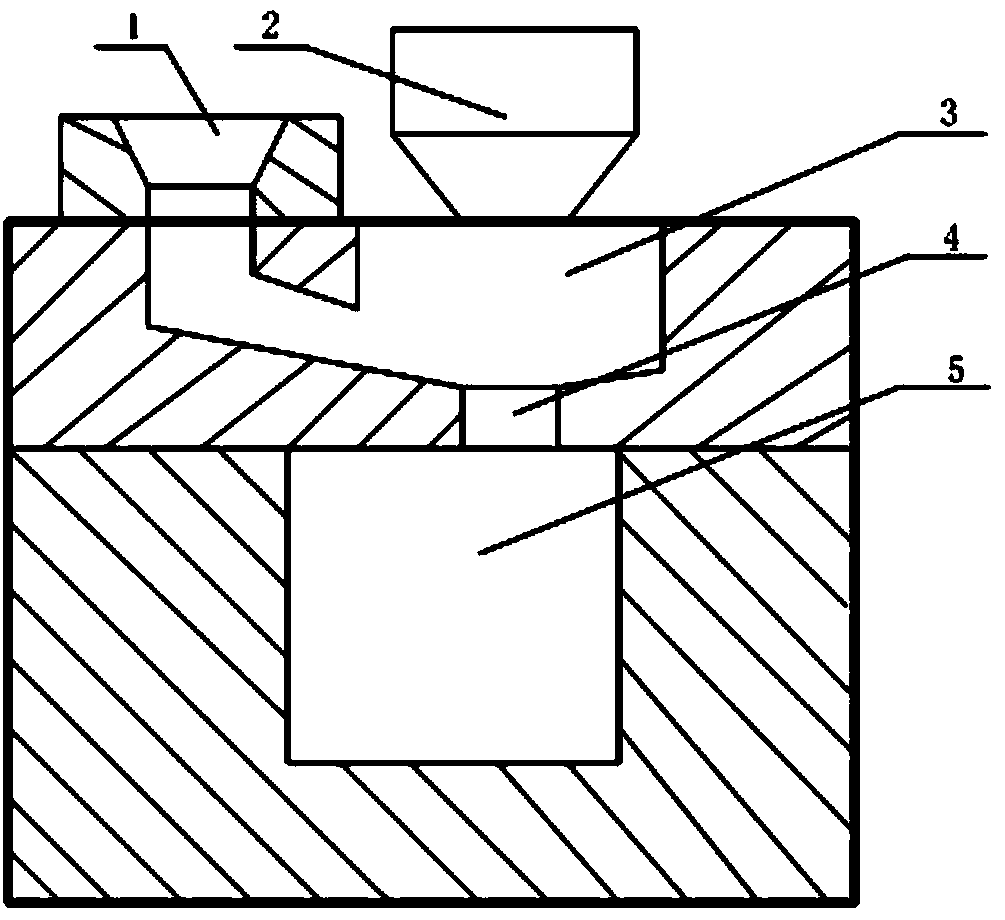
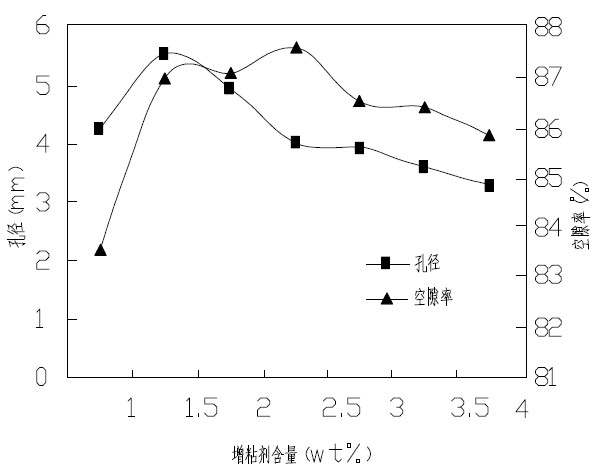
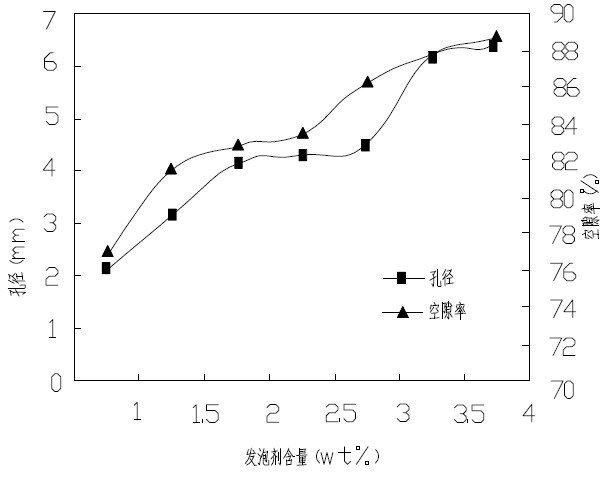
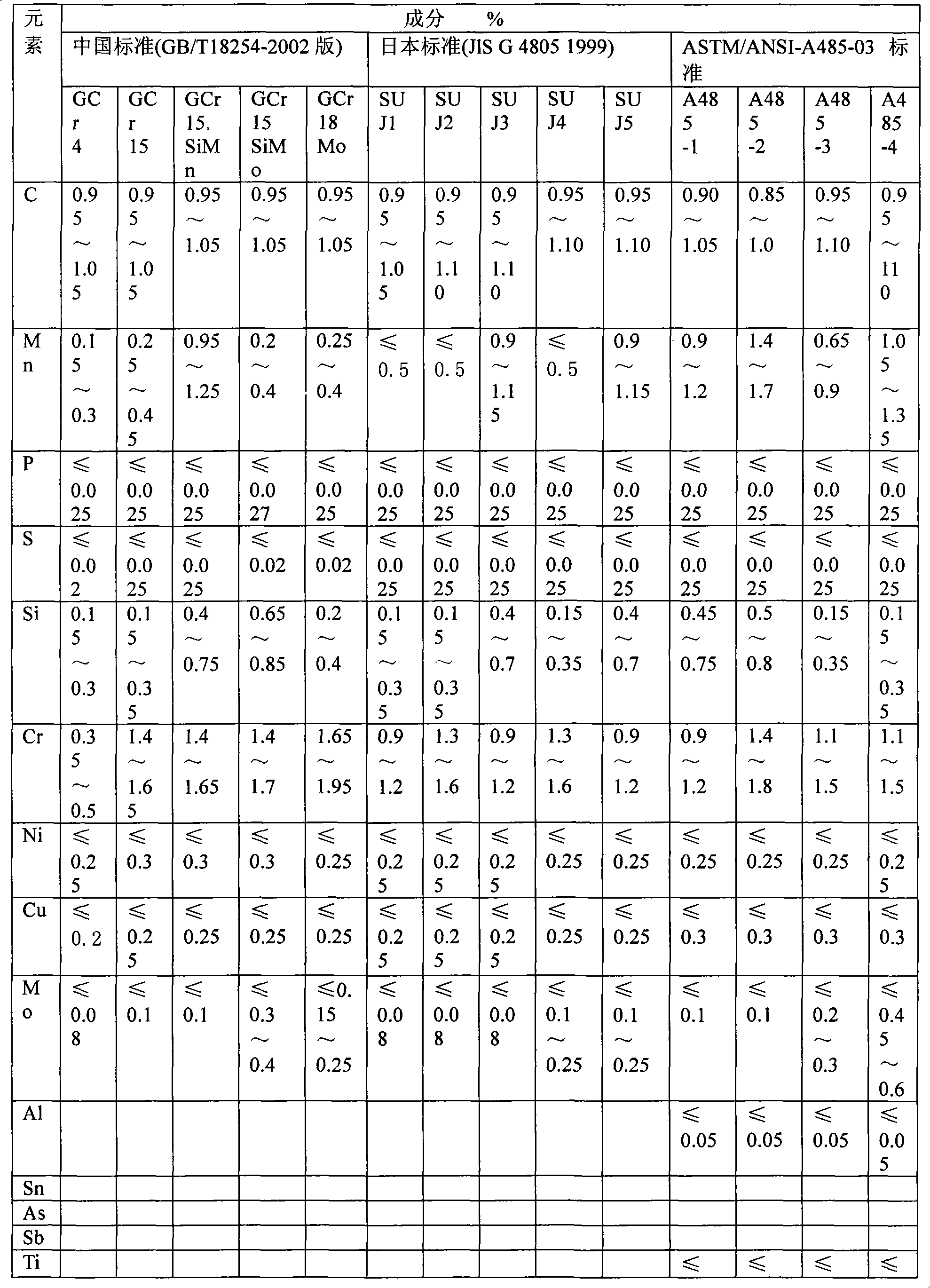
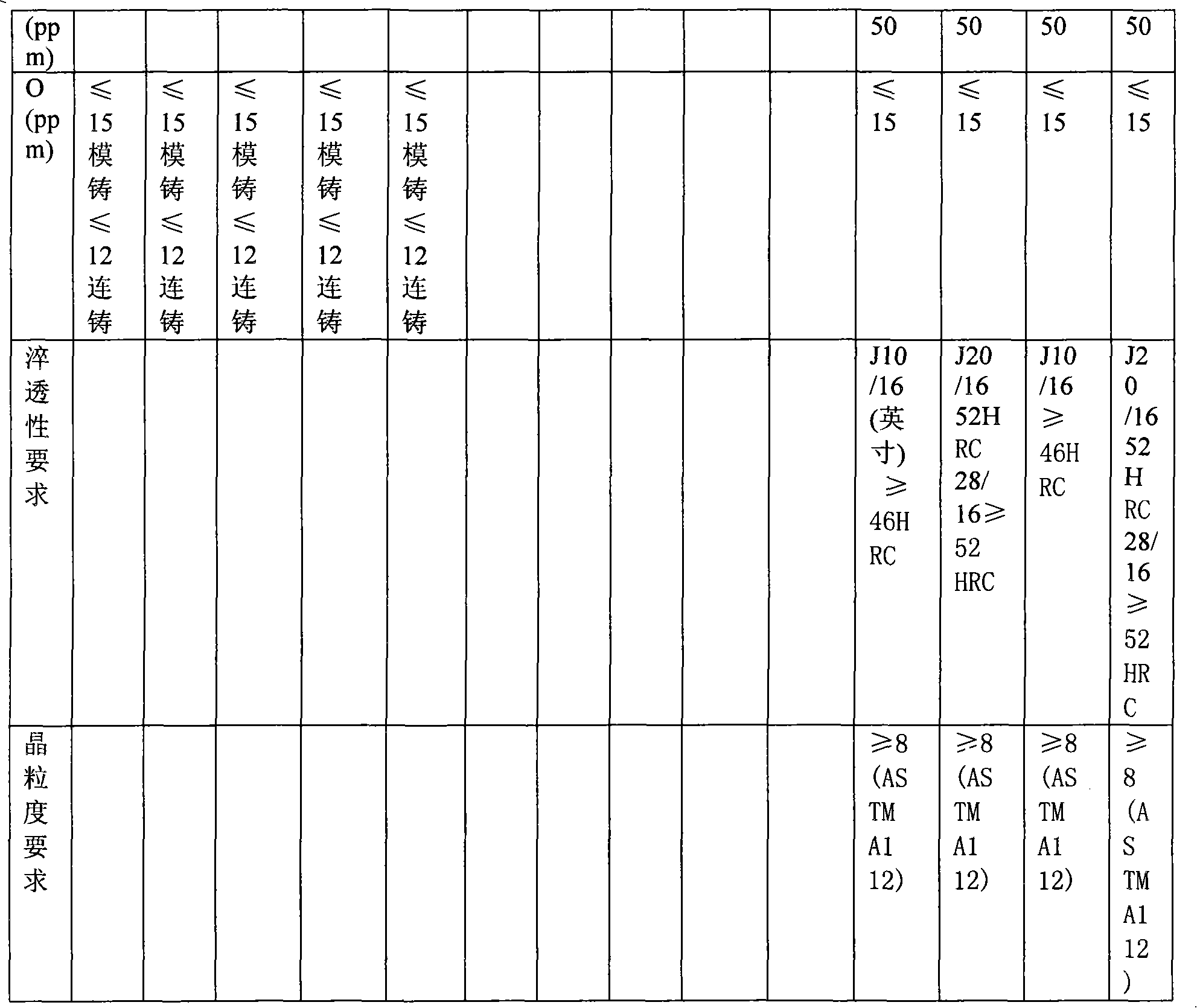
Patents
Literature
3135 results about "Electric furnaces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of direct iron-making / steel-making via gas or coal-based direct reduction and apparatus
The invention is a method and apparatus for iron-making / steel-making using a modified rotary hearth furnace, that is a finisher-hearth-melter (FHM) furnace. In the method the refractory surface of the hearth is coated with carbonaceous hearth conditioners and refractory compounds, where onto said hearth is charged with pre-reduced metallized iron. The pre-reduced metallized iron is leveled, then heated until molten, and then reacted with the carbon and reducing gas burner gases until any residual iron oxide is converted to iron having a low sulfur content. Nascent slag separates from the molted iron forming carburized iron nuggets. The nuggets are cooled, and then the iron nuggets and the hearth conditioners, including the refractory compounds, are discharged onto a screen, which separate the iron nuggets from the hearth conditioner. The hearth conditioner is recycled, and the iron nuggets are either prepared for sale or for additional treatment, such as alloying, in a final melter, where the final melter is preferably an electric furnace. Exhaust gases from the FHM furnace are recovered for calcining coal into fuel gases and coke.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
CrMnTi narrow hardenability strip pinion steels and method of manufacture
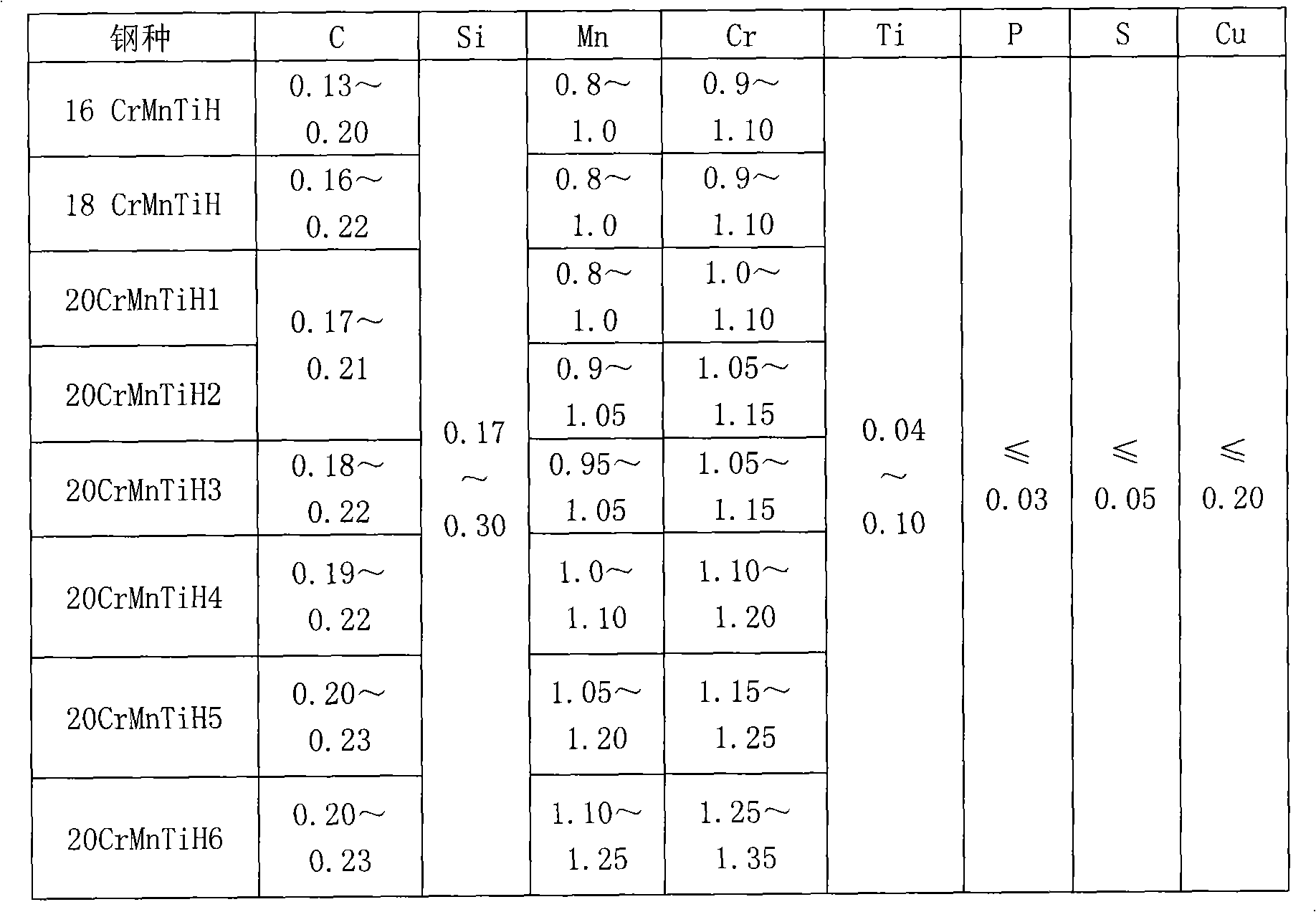
InactiveCN101289731AGuaranteed narrow hardenability band requirementsTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionPinion
The invention relates to CrMnTi narrow-hardenability gear steel and a method for manufacturing the same, belonging to the gear steel material and the production process thereof technical field. The chemical composition in percentage by weight of the gear steel is: 0.13-0.23 percent of C, 0.17-0.30 percent of Si, 0.80-1.25 percent of Mn, 0.04-0.10 percent of Ti, 0.90-1.35 percent of Cr, less than or equal to 0.20 percent of Cu, less than or equal to 0.050 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.030 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.05 percent of Mo, less than or equal to 0.25 percent of Ni, [O] less than or equal to 20x10<-6>, [H] less than or equal to 2.5x10<-6>, and the balance being Fe and inevitable impurities. The manufacturing method comprises the following process steps of smelting, continuous casting, rolling and hot rolling, wherein in the step of continuous casting, the superheat degree of a tundish is controlled between 10 and 30 DEG C, and the casting speed is between 0.50 and 0.85 m / min; in the step of rolling, the heating temperature is between 1130 and 1280 DEG C, the start rolling temperature is more than or equal to 1100 DEG C, and the finish rolling temperature is between 850 and 980 DEG C. The gear steel and round steel in the specification between phi 30 and 160 mm can be produced by adopting the manufacturing method. By adopting narrow-composition steel grade design, electric furnace burden structure optimization, electric furnace end point control, grain-refining and banded structure control and other reasonable technological measures, the method effectively realizes hardenability narrowing and other objectives.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High boron wear-resisting casting steel and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN100999803ASufficient sourceReduce manufacturing costFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlFerromanganeseAluminium
The present invention discloses one kind of antiwear high-boron cast steel and its preparation process. The antiwear high-boron cast steel has the chemical components including C 0.10-0.50 wt%, B 0.8-5.0 wt%, Cu 0.3-0.6 wt%, Mn 0.8-2.0 wt%, Cr 1.0-2.5 wt%, Si less than 1.5 wt%, Ti 0.08-0.20 wt%, Ce 0.04-0.12 wt%, Mg 0.02-0.18 wt%, N 0.06-0.18 wt%, S less than 0.05 wt%, P less than 0.05 wt%, and Fe and inevitable impurity for the rest. Its preparation process includes smelting in an electric furnace while adding ferromanganese, frrroboron and Al to deoxidize, composite modification of molten steel, fast cooling, and low temperature tempering to eliminate stress. The present invention has simple production process, low production cost and other advantages.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Leveler roll and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveCN101153377AReduce contentChange sizeIncreasing energy efficiencyFurnace typesStrip steelMachining
The invention relates to a straightening roll and the manufacturing process thereof, wherein, the composition of the roll includes 0.60wt percent to 1.10wt percent of C, 0.20wt percent to 1.0wt percent of Si, 0.20wt percent to 0.60wt percent of Mn, 0.20wt percent to 1.00wt percent of Ni, 4.00wt percent to 6.00wt percent of Cr, 0.20wt percent to 1.00wt percent of Mo, 0.10wt percent to 0.50wt percent of V, less than or equal to 0.02wt percent of P, less than or equal to 0.02wt percent of S and the rest, Fe and other inevitable impurities; the manufacturing process of the roll includes: electric furnace smelting to secondary refining to ingot casing to electrode rolling to electrode rough machining to electroslag remelting to ingot casing to hydrogen diffusion annealing to forging to conditioning treatment to ultrasonic flaw detection and microscopic and macroscopic test to rough machining to quenching and tempering heat treatment to semifinishing to final heat treatment to finish machining to finished product. The invention increases the service life of the straightening roll and the surface quality of strip steel and eliminates the bottleneck in straightening high strength plate during production.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Needle ferrichrome-X70 pipeline steel with high crack-arresting toughenss and its production
The invention is about the X70 needle ferrite in-line steel, which has the toughness of crack arrest. The percentage composition is C 0.020-0.060,Mn 1.45-1.75,Si 0.100-0.500,S¿Q0.0020,P0.004-0.012,Nb0.050-0.080,Ti0.005-0.025,V0.010-0.060,Mo0.10-0.30,Cu¿Q0.30,Ni¿Q0.30,Ca0.0015-0.0040,N¿Q0.0080,Altotal0.015-0.045. The process is: a. refining by coverter or electric furnace; b. refined outside of the furnace, vacuum degass by RH, desulfurating by LF, Ca treatment; c. continuous metal cast process; d. hot rolling, the terminal temperature of the coarse crushing is 950-1000 Deg C.,the terminal temperature of finish rolling is 780-880 Deg C., the compression ratio of the non-recrystallized region is above 70%; e. batching, temperature is 480-580 Deg C..
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-speed steel roll ring and its production
A high-speed steel roller ring for rolling wire or rod material contains C, W, Mo, V, Cr, Al, Ni, Co, Nb, Ti, Ce, Na, Mg, Si, Mn, S, P and Fe proportionally. It is prepared through smelting in electric furnace, centrifugal casting, and annealing, high-temp quenching and tempering twice. Its advantages are high hardness, tension strength and toughness for breaking, smooth surface and high size stability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Electric locomotive pantograph copper-soaking carbon contact strip producing method
ActiveCN104774012AImprove conductivityHigh mechanical strengthPower current collectorsShock resistanceNitrogen gas
The invention discloses an electric locomotive pantograph copper-impregnated carbon contact strip producing method. The method comprises the steps that 1, pitch coke powder, graphite powder, siliconized graphite powder and high temperature pitch are mixed according to the proportion to be ground into powder; the mixed powder is prepressed into a stage stock column, and then the stage stock column is solidified and squeezed to be molded and roasted, so that a composite carbon contact strip is obtained; 2, the composite carbon contact strip is cleaned and dried, then is cooled and placed into a graphite crucible, and is placed in an electric furnace at temperature of 1300-1400 DEG C to be preheated; copper liquid is poured into the crucible to soak the composite carbon contact strip, then the crucible is placed in an oil press cover, nitrogen is led in, heat preservation is kept for 3-5 min under the specific intensity of pressure, and finally cooling is carried after pressure releasing. According to the electric locomotive pantograph copper-impregnated carbon contact strip producing method, the electroconductibility of the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is improved, the electrical resistivity is lowered, the mechanical strength of the carbon contact strip and copper impregnated angle can be increased, then the carbon contact strip abrasive resistance and self-lubrication are improved, the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is more resistant to abrasion, main line damage and block dropping are avoided, the shock resistance is high, and the service life of the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is prolonged.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Strength determination method and device for reacted blast furnace coke
ActiveCN101936979ASolving thermal property evaluationSolve the situationFuel testingChemical methods analysisNitrogen gasInsertion reaction
The invention discloses a strength determination method for reacted blast furnace coke, which comprises the following steps of: (1) placing a coke sample in a reactor; (2) putting the reactor in an electric heating furnace; (3) inserting a temperature thermocouple into the coke in the reactor;(4) putting an electronic balance on a lifting table and connecting the electronic balance and the reactor through a chain; (5) regulating the electric furnace to heat through a temperature controller and introducing nitrogen when the temperature in the center of a material layer reaches 400 DEG C; (6) introducing carbon dioxide gas when the temperature in the center of the material layer reaches 780 DEG C; (7) cutting the nitrogen and introducing prepared mixed gas when the temperature in the centerof the material layer reaches a certain value, maintaining the temperature of the heating furnace, and when the loss ratio of the coke samples reaches the required value continuously introducing the carbon dioxide gas or the mixed gas, introducing the nitrogen and cooling after the carbon dioxide gas or the mixed gas reaches the specified dissolve loss quantity; and (8) stopping introducing the nitrogen and cooling naturally when below 100 DEG C. The invention more truly reflects the actual conditions of the coke in a blast furnace, and the prediction of the thermal properties of the coke is more accurate.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Preparation method of wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron
The invention discloses a preparation method of wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron and belongs to the technical field of metal materials. According to the preparation method, common scrap steel, carburant, ferrochromium, ferromolybdenum, copper plates, ferrochromium nitride, ferrosilicon, ferromanganese, ferroboron and aluminum are smelted in an electric furnace so as to form the wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron. The molten wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 3.0-3.5% of C, 18-25% of Cr, 0.3-0.5% of Mn, 0.3-0.5% of Si, 0.18-0.25% of N, 0.5-0.8% of Mo, 0.2-0.4% of B, 0.08-0.12% of Al, 0.5-1.0% of Cu, less than 0.05% of S, less than 0.05% P and the balance of Fe. Molten iron is treated with an inoculator when taken out from the electric furnace, and is treated with a suspending agent when poured, so as to obtain fine solidification structures. Therefore, the wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron has excellent properties.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Direction reduction and electric furnace smelting-separation preparation process of vanadium-titanium magnetite cold bound pellet
The cooled agglomerated carbon-contained pellet prepared with vanadium titano magnetite concentrate and opposite direct reduction with former pellet comprises: mixing the concentrate, reducer and bonding agent, drying, grinding, and pelletizing to obtain the cooled agglomerated carbon-contained pellet drying and sieving into the reduction furnace with reducer for reduction atmosphere; loading the reduced pellet into electric furnace to melt and separate the iron liquid, V, Ti and Cr. This invention is fit to the pellet on wide application temperature and low energy consumption, has well efficiency and low running cost, and can also extract V, Ti Fe and Cr from electric furnace with high yield and obvious environmental protection.
Owner:鲜帆 +2
Technology of producing Ti micro alloyed high weather resistant steel plate using thin plate blank continuous casting continuous milling process
InactiveCN1785543AGood weather resistanceGood welding performanceMetal rolling arrangementsSheet steelHigh intensity
A conticasting and tandem rolling technology for manufacturing the high-strength and-weatherability Ti-microalloyed steel plate includes such steps as smelting, refining, conticasting, solidifying, heating, hot rolling, laminar flow cooling and coiling. Its advantages are high strength, high shaping performance, high weatherability and high weldability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PEARL RIVER STEEL & IRON
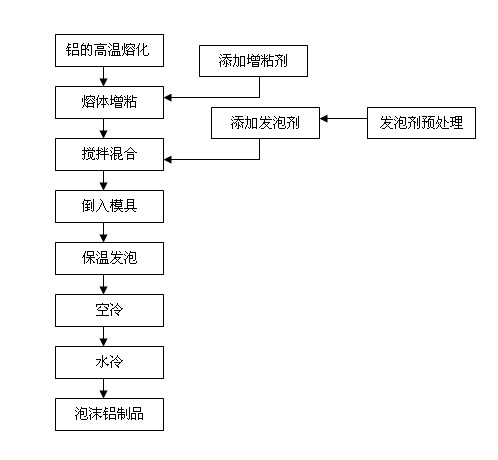
Method for preparing foamed aluminum by foaming melt
The invention relates to a preparation method of foamed aluminum, in particular to a method for preparing the foamed aluminum by primarily foaming a melt, which can prepare a foamed aluminum product by primarily foaming aluminum. The method comprises the following steps of: starting a thermoelectric furnace for heating to 800 DEG C until the aluminum is fully molten; lowering the temperature to 680 DEG C, adding metal calcium into aluminum liquid and stirring so as to increase the surface viscosity of the melt; pretreating titanium hydride, adding pretreated titanium hydride into the melt and stirring to uniformly distribute the titanium hydride in the melt for full decomposing; and heating a mold, putting the melt into the thermally-treated mold, preserving heat and foaming at the temperature of 650 DEG C, taking a prefabricated member out, performing air cooling to shape the high-temperature foam melt in the mold and taking the prefabricated member out for water cooling so as to obtain the foamed aluminum product. When applied to a filling piece of a regular cavity, the method simplifies a process, greatly lowers production cost, is suitable for diversified development of industrial production and brings convenience to the research of specific technology.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH +4
Method for producing low carbon bainite high-strength steel based on sheet bar continuous casting and rolling process flow
ActiveCN101254527ASimple metallurgical compositionImprove toughnessProcess efficiency improvementMetal rolling arrangementsThin slabLaminar cooling
The invention discloses a method for producing high-strength low-carbon bainite steel based on thin slab continuous casting and rolling process. The method includes the following steps: melting by using a rotary furnace or an electric furnace, refining molten steel in an LF furnace after the component analysis, performing the composition adjustment, continuously casting thin slabs, directly heating the thin slabs at the temperature of 950-1100 DEG C in a roller-hearth heating (soaking) furnace at a temperature not less than 1150 DEG C, controlling the tapping temperature of heated thin slabs in a range from 1050 DEG C to1160 DEG C, rolling by using a continuous rolling mill to produce plates, finishing at a temperature of 840-860 DEG C, performing laminar cooling, and coiling with a down coiler at a temperature of 550-600 DEG C to produce the steel coil. The method can produce non-tempered high-strength steel based on thin slab continuous casting and rolling process, and has the advantages of simple metallurgical composition of steel, low cost of alloying production, and stability in high toughness and good forming and welding properties of the steel coil.
Owner:湖南华菱涟源钢铁有限公司 +1
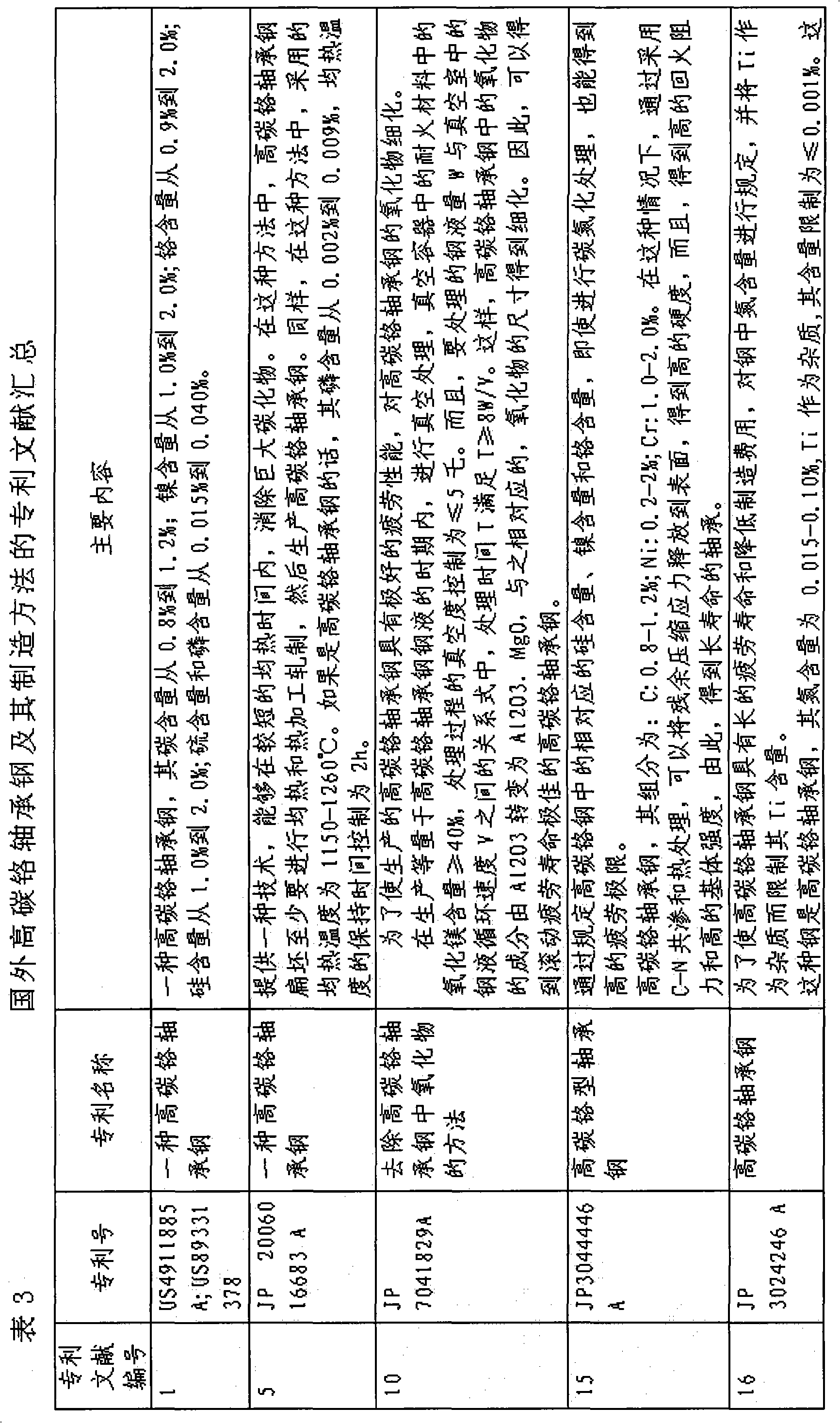
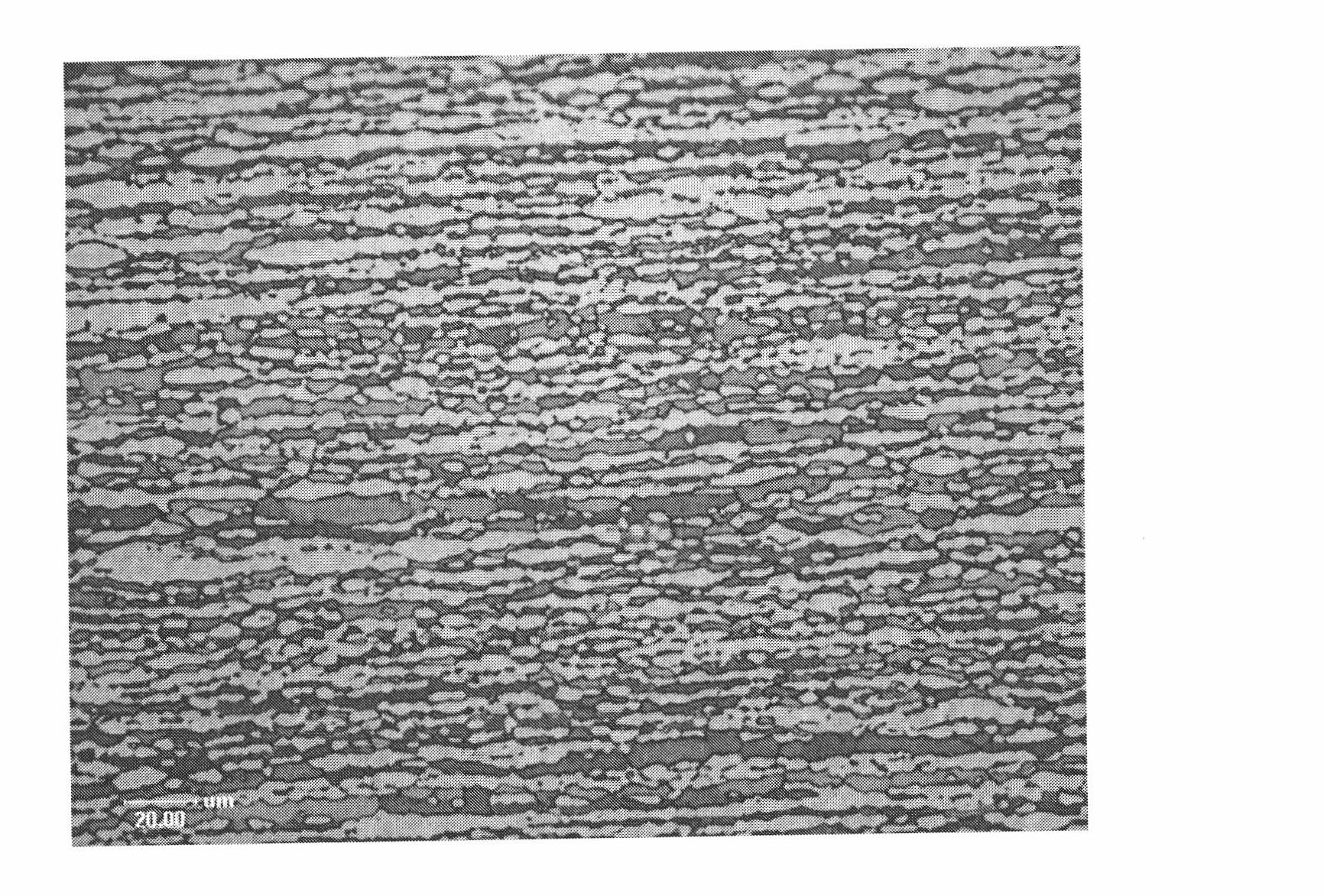
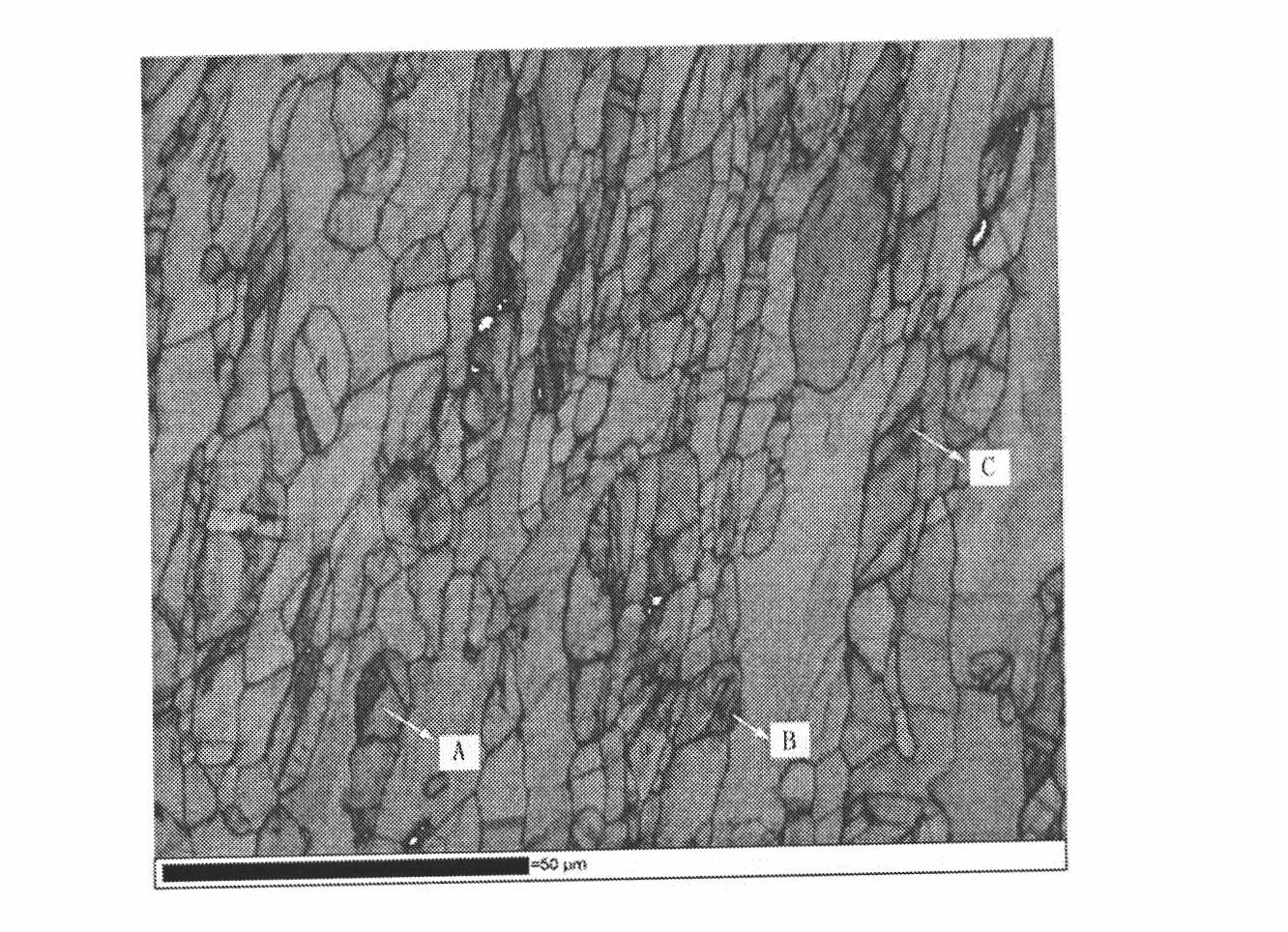
High-carbon-chromium bearing steel and manufacture method thereof
The invention discloses high-carbon-chromium bearing steel and a manufacture method thereof. The high-carbon-chromium bearing steel comprises the following chemical compositions by weight percentage: C: 0.90-1.05; Cr: 0.90-1.20; Mn: 0.90-1.25; Si: 0.45-0.75; Al: 0.02-0.04; oxygen is less than or equal to 0.0007; phosphorus is less than or equal to 0.010; sulfur is less than or equal to 0.005; titanium is less than or equal to 0.0025; copper is less than or equal to 0.15; nickel is less than or equal to 0.10; nitrogen is less than orequal to 0.0070; and the balance of unavoidable impurities and Fe. The manufacture method comprises the following steps: smelting in an electric furnace, refining in a ladle arc furnace, degassing in a vacuum furnace, pouring steel liquid into steel ingots, heating steel ingots in a heating furnace, rolling the steel ingots into square billets by a rolling mill, heating the steel ingots in a heating furnace and rolling the steel ingots into round steel by a rolling mill. Compared with the prior art, the invention has high hardenability, high crystal grain size of more than 8 grade, high commonality in technology and wide application.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Ultrahigh-strength and high-toughness welded cast steel
InactiveCN101074472AGood effectImprove hardenabilityHeat treatment process controlSmelting processUltimate tensile strength
A high-strength and high-toughness welding cast steel consists of C 0.12-0.17 wt%, Si 0.10-0.50 wt%, Mn 0.8-1.2 wt%, S+P<=0.025 wt%, Ni 4.00-4.50 wt%, Cr 0.7-1.2 wt%, Mo 0.40-0.50 wt%, V 0.04-0.08 wt%, Cu 0.20-0.40 wt% and iron residue. The process is carried out by selecting electric furnace + AOD duplex smelting process, pouring and heating to obtain final product. The yield strength reaches above 800 MPa, V-shaped notch impact reaches above 55J at -20 degree. It can be used for ship, ocean and petrochemical industries.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Wear-resisting white cast iron and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a wear-resisting white cast iron and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of wear-resisting materials. The liquid wear-resisting white cast iron is smelted in an electric furnace at first, and the liquid iron is composed of 2.9-3.3% of C, 4.5-5.5% of Mn, 6.0-7.2% of Cr, 0.45-0.70% of B, 0.50% of Si<, 0.05% of S<, 0.05% of P< and the balance of Fe by mass fraction. Modification treatment is performed on the wear-resisting white cast iron by adding a compound modificator to a casting ladle, wherein the addition amount of the compound modificator accounts for 1.8-3.0% of the mass fraction of the liquid iron in the casting ladle; besides, the wear-resisting white cast iron has excellent properties after being quenched by air cooling at a temperature ranging from 950 to 1000 DEG C and tempered at a temperature ranging from 280 to 320 DEG C.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Duplex stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to duplex stainless steel. The duplex stainless steel comprises the following chemical components in percent by weight: 0.01-0.08% of C, 0.2-1.0% of Si, 1.5-3.5% of Mn, 19.0-21.0% of Cr, 1.2-2.8% of Ni, 0.08-0.18% of N, less than or equal to 0.5% of Mo, less than or equal to 1.0% of W, less than or equal to 1.0% of Cu and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities; PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number) is 20-24, the martensitic temperature Md formed by strain induction is 60-130 DEG C. A manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: selecting vacuum induction smelting in an electric furnace, argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) or electric furnace, argon oxygen decarburization (AOD), external refining and LF (Ladle Furnace) smelting; carrying out die casting or continuous casting on molten steel, controlling the superheat degree to be 20-50 DEG C in die casting, matching with fast cooling, preventing nitrogen from escaping, and controlling the overheat degree to be 20-50 DEG C and the plate blank casting speed to be 0.8-2m / min; and putting a die-casting blank or a continuous casting blank into a heating furnace for heating to 1100-1250 DEG C, preserving the heat for 0.5-1.5 hours, processing the die-casting blank or the continuous casting blank on a forging production line or a hot-rolling mill group to the needed thickness, then carrying out annealing at the speed of 0.5-2.5min / mm and the temperature of 1030-1150 DEG C. The obtained duplex stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and TRIP effect.
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
High-boron high-speed steel roller material and smelting process thereof
ActiveCN102994692AHigh yieldEasy to useProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceMetallic aluminumSilicon alloy
The invention provides a high-boron high-speed steel roller material and a smelting process thereof. The smelting process of the high-boron high-speed steel roller material comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting Q235 waste steel, ferrotungsten, ferromolybdenum, ferrovanadium, high carbon ferro-chrome, metal copper, metal aluminum, calcium-silicon alloy, rare earth ferrosilicon magnesium alloy, ferrocolumbium, ferroboron, ferrosilicon, vanadium-nitrogen alloy, zirconium ferrosilicon and ferrotitanium as materials for smelting low-alloy high-speed molten steel in an electric furnace; then, adding the ferrovanadium and part of ferroboron to carry out alloying in a discharging process; finally, adding part of ferroboron and composite modificator in a casting ladle, adding the vanadium-nitrogen alloy, the zirconium ferrosilicon, the ferrosilicon and part of ferroboron in the casting process. The obtained casting piece has a little alloy elements, excellent abrasive resistance and good thermal fatigue resistance. When the high-boron high-speed steel roller material is used as a roller, the service life is prolonged by more than six times relative to a high nickel-chrome infinite cast-iron roller, and prolonged by 20% relative to a high-vanadium high-speed steel roller. Moreover, the roller is safe to use and reliable.
Owner:YUNNAN HEAVY EQUIP MFG GRP
55Si2MnVNbN spring steel and production process thereof
InactiveCN101717893AHigh strengthHigh tensile strengthTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsWorking environmentSpring steel
The invention relates to spring steel and a production process thereof, in particular to 55Si2MnVNbN spring steel and a production process thereof. The 55Si2MnVNbN spring steel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.52 to 0.60 percent of C, 1.60 to 1.90 percent of Si, 0.60 to 0.80 percent of Mn, 0.15 to 0.35 percent of Cr, 0.06 to 0.12 percent of V, 0.015 to 0.025 percent of Nb, 0.80 to 1.50 percent of N, less than or equal to 0.0035 of P, less than or equal to 0.0035 percent of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The process comprises electric furnace electrosmelting, LF refining, VD furnace vacuum degassing, continuous casting and rolling. The spring steel can meet the requirements of springs on various severe working environments, high strength and long service life and has high tensile strength, high delayed fracture resistance, high corrosion resistance, high fatigue resistance and high elasticity attenuation resistance.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Hot-work die steel for extrusion wheel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102534391AImprove hardenabilityReduced temper softening resistanceMetal-working apparatusTemperingThermal fatigue
The invention relates to hot-work die steel for an extrusion wheel and a manufacturing method of the die steel. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the manufacturing method comprises the following steps: hot-forging after scrap steel or molten iron and scrap steel are smelted in an electric furnace and are subjected to electroslag remelting or vacuum induction melting and then carry out spheroidizing annealing at a temperature of 700-880 DEG C; quenching at a temperature of 1,020-1,120 DEG C and tempering at a temperature of 530-650 DEG C, wherein the hot-work die steel has a hardness of up to 40-52HRC and a tensile strength of up to 1,850-1,955MPa. The hot-work die steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.30-0.50wt% of C, 0.80-1.20wt% of Si, 0.2-0.5wt% of Mn, 3.00-5.00wt% of Cr, 1.00-1.50wt% of Mo, 0.70-1.20wt% of V, 0.005-0.03wt% of N and less than 0.030wt% of P, less than 0.030wt% of S and the balances of Fe and inevitable impurities. The steel has the characteristics of low cost, good thermal fatigue property, high heat stability and excellent comprehensive property and can be used for manufacturing the extrusion wheel of a continuously-extrusion-molded coating machine and other hot-work dies.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Easy-weld hardening high-strength steel plate and production method thereof
InactiveCN101096735AMeeting the demands of growing usageReduce manufacturing costRoll force/gap control deviceTemperature control deviceChemical compositionSheet steel
The invention relates to an easily welded, hardened and tempered high-intensity steel plate and its producing method, which comprises the following part: C<=0.15%, 0.15%-0.50% Si, 0.80%-1.80% Mn, P<=0.02%, S<=0.01%, Mn<=0.6%, Nb<=0.07%, B<=0.003%, Ni<=1.20%, Cr<=0.80%, Ti<=0.03%, V<=0.08%, the rest Fe and unavoidable impurity. The invention smelts with the electric furnace, which is provided with the low quantity P, S and the pure steel, gets the users' favor, has the low cost and the market competitive ability, solves the problem of big crystal grain and low dynamic ductility, and is fit for producing the high-intensity steel with low draught pressure rolling mill in the other steel factory. The invention also reduces the labor strength, which saves the time of the work, improves the availability ratio of the material, and reduces the leveling expense of making the steel plate.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL
Vanadium-containing high-boron high-chromium wear-resistant alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a vanadium-containing high-boron high-chromium wear-resistant alloy and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of wear-resistant materials. The alloy is characterized in that a strengthening phase is iron chromium boride and VC, the volume fraction of the strengthening phase is 15 to 40%, and chemical components of the alloy comprise, by weight, 0.10 to 0.80% of C, 0.5 to 1.5% of Si , 0.5 to 3.0% of Mn, 2.0 to 28.0% of Cr, 0.5 to 3.0% of Ni, 0.5 to 6.0% of B, 0.5 to 10.0% of V, 0.5 to 3.0% of Ti, less than 0.04% of P and less than 0.04% of S, with the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities. The alloy provided by the invention can be directly used after electric-furnace smelting, casting forming, polishing and cleaning and removal of stress at a temperature of 200 to 650 DEG C and has the advantages of simple preparation process, low energy consumption, good strength, hardness, toughness and wear resistance, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Non-molybdenum non-nickel middle chrome wear resistant steel casting and heat treatment method thereof
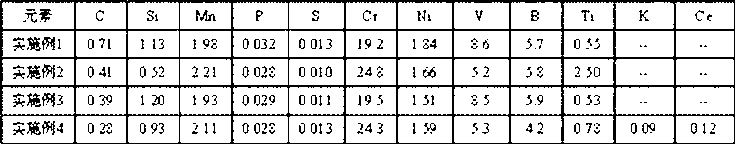
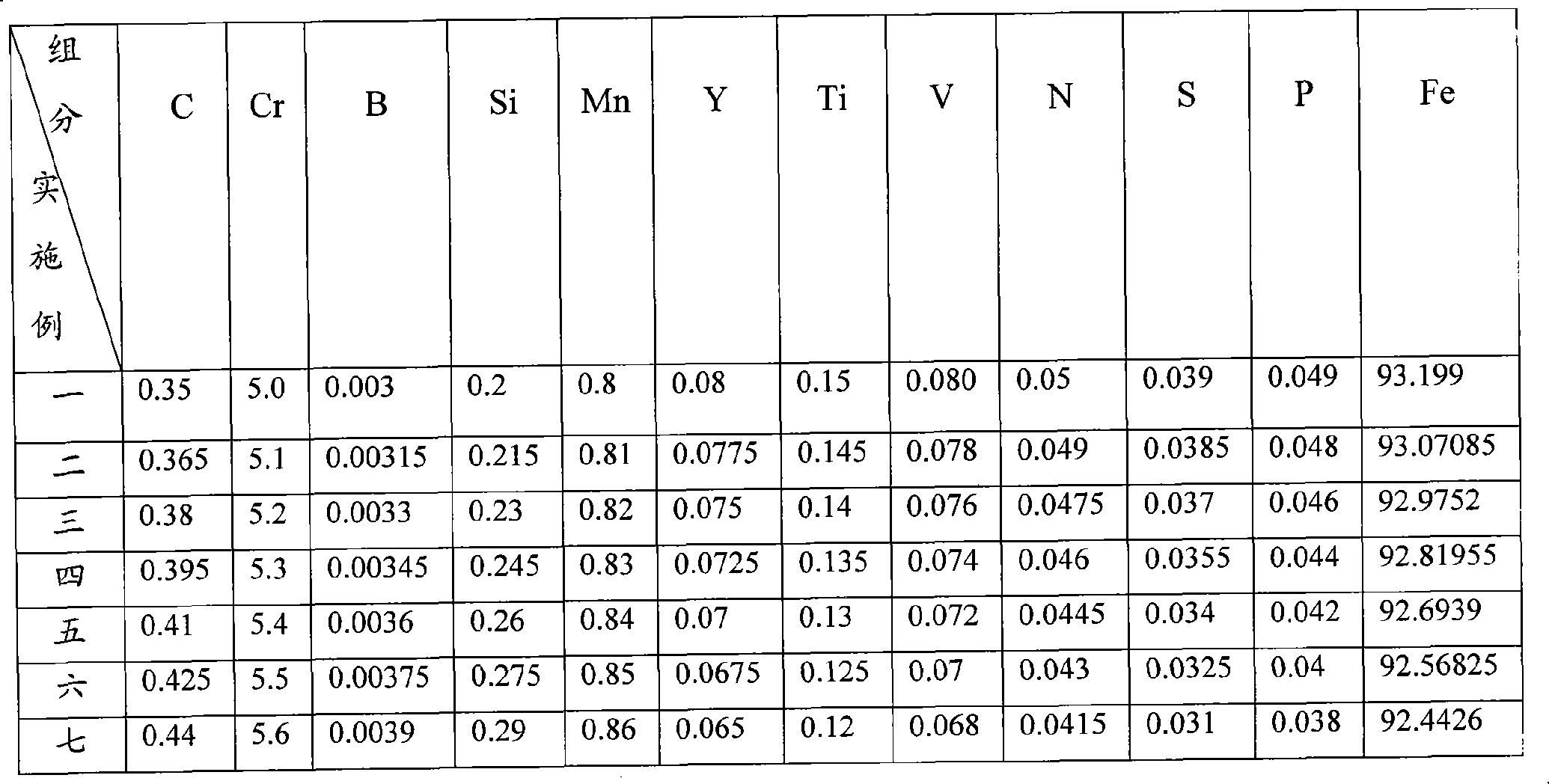
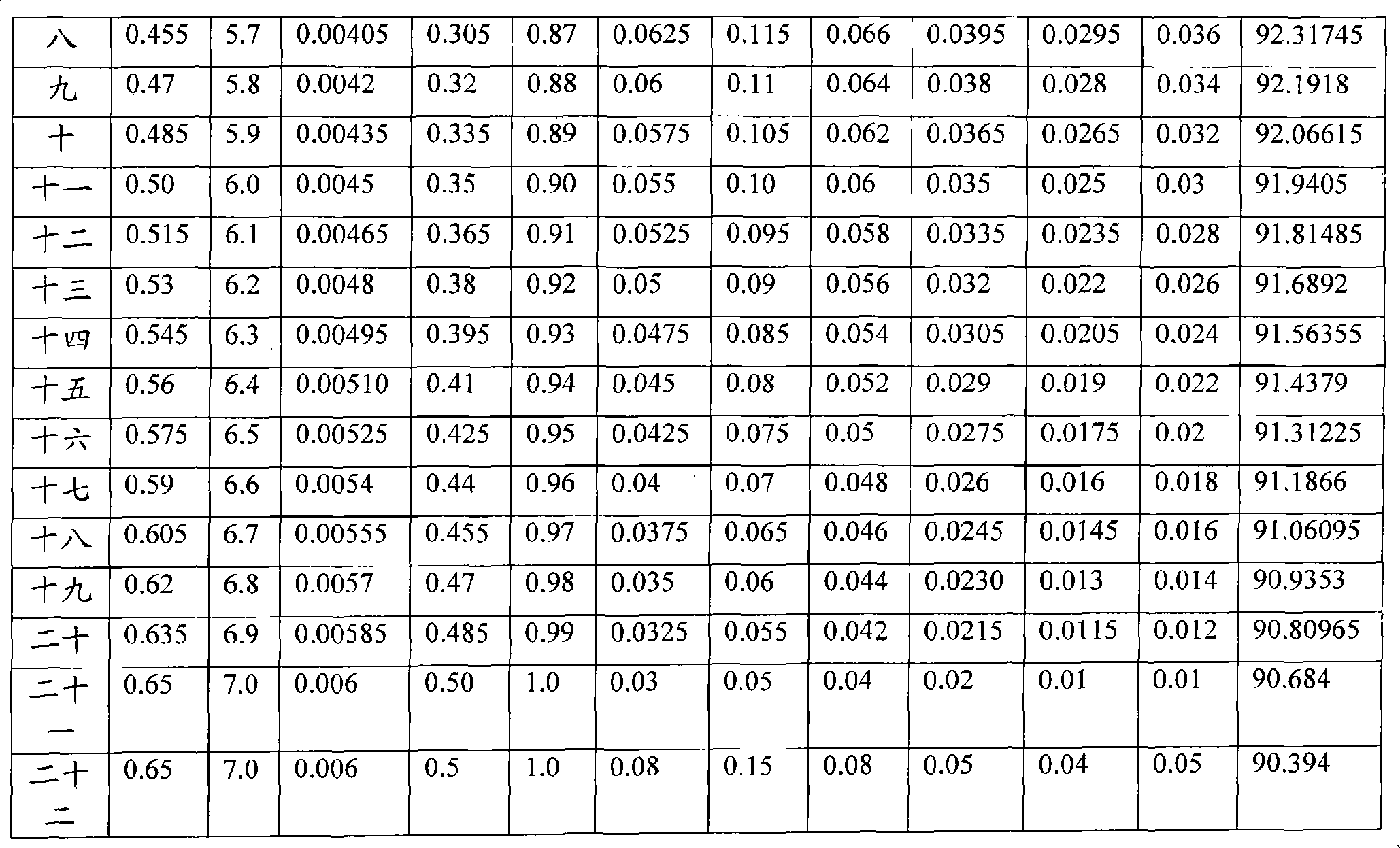
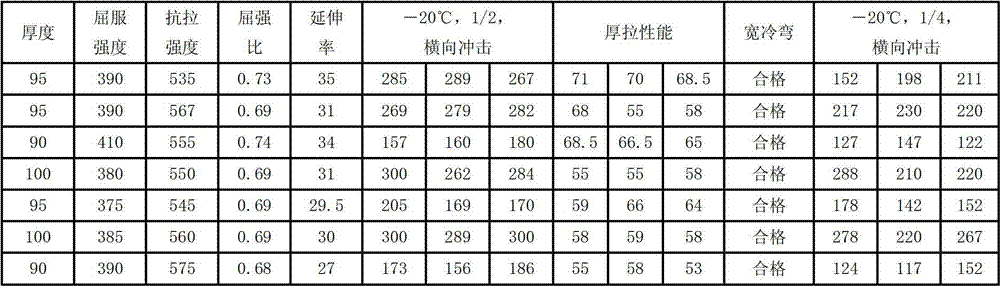
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal wear-resistant materials and particularly relates to a wear-resistant casting steel part which is free of molybdenum-nickel and medium-chromium and a heat treatment method thereof. The wear-resistant casting steel part which is free of molybdenum-nickel and medium-chromium comprises the components of the following mass percentages: 0.35 to 0.65 wt percent of C, 5.0 to 7.0 wt percent of Cr, 0.003 to 0.006 wt percent of B, 0.2 to 0.5 wt percent of Si, 0.8 to 1.0 wt percent of Mn, 0.03 to 0.08 wt percent of Y, 0.05 to 0.15 wt percent of Ti, 0.04 to 0.08 wt percent of V, 0.02 to 0.05 wt percent of N, less than 0.04 wt percent of S, less than 0.05 wt percent of P and the balance of ferrite. The wear-resistant casting steel part which is free of molybdenum-nickel and medium-chromium can be manufactured by an electric furnace using a sand casting. The invention carries out step quenching by using two types of quenching oils with different temperatures, thus leading to depth of more than 60mm of the quenching full hardening layer of the cast steel, high hardness, good uniformity of the hardness, and no cracks in the heat treatment. The casting steel is free of expensive alloying elements such as molybdenum or nickel, raw materials resource is rich, the manufacture cost is low and economic benefit is good.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
High-performance ocean platform steel and its production method
The invention provides high-performance ocean platform steel and its production method. When the thickness of a steel plate is 8-40mm, the steel plate is composed of the following chemical components, by weight, 0.11-0.13% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 1.45-1.55% of Mn, 0.012% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.035-0.045% of V, 0.025-0.030% of Nb, 0.050% or less of Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Al, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities; and when thickness of a steel plate is 40-100mm, the steel plate is composed of the following chemical components, by weight, 0.10-0.12% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 1.50-1.60% of Mn, 0.012% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.070-0.075% of V, 0.030-0.040% of Nb, 0.050% or less of Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Al, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The production method of the steel plate of the invention comprises the steps of electric furnace smelting, LF furnace refining, VD vacuum treatment, continuous casting (or die casting), heating, control rolling, cooling, stacking, and normalizing to prepare the steel plate. Through a reasonable component design and process optimization, the steel plate of the invention has excellent mechanical performances, welding performances and processing performances, and has strong market competitiveness.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL +1
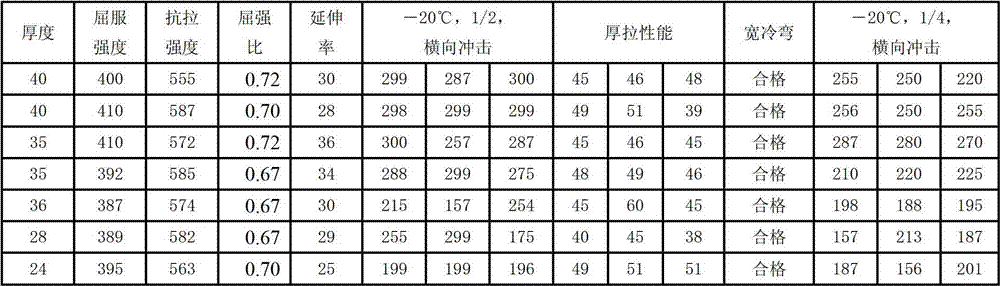
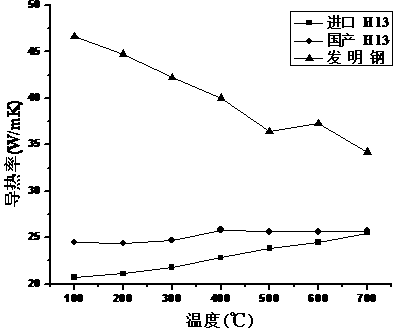
Ultrahigh thermal conductivity wear-resistant hot stamping die steel and manufacturing method thereof
Belonging to the technical field of alloy steel preparation processes, the invention relates to an ultrahigh thermal conductivity wear-resistant hot stamping die steel and a manufacturing method thereof. Current hot stamping die steel on the market is mainly various improved H13, H11 and other high alloy hot work die steel. The steel provided by the invention comprises the following components by mass percent: 0.33-0.40% of C; less than 0.30% of Si; less than 0.30% of Mn; 1.0-2.0% of W; 4.0-5.0% of Mo; less than 0.30% of Cr; 0.10-0.20% of V; and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. And in the impurity elements, S is smaller than or equal to 0.01%; P is smaller than or equal to 0.01%; and O is smaller than or equal to 30ppm. The steel is characterized in that: simple C, Mo and W are adopted as the main elements to coordinate the ratio of carbides; low Mn, low Cr and low Si content are maintained; after electric furnace smelting, electroslag remelting, annealing, high temperature homogenization, forging and annealing, the material has good machining properties; and after heat treatment, the material has excellent impact toughness, tempering stability and thermal fatigue performance. With ultrahigh thermal conductivity, the steel can be more suitable for hot stamping.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
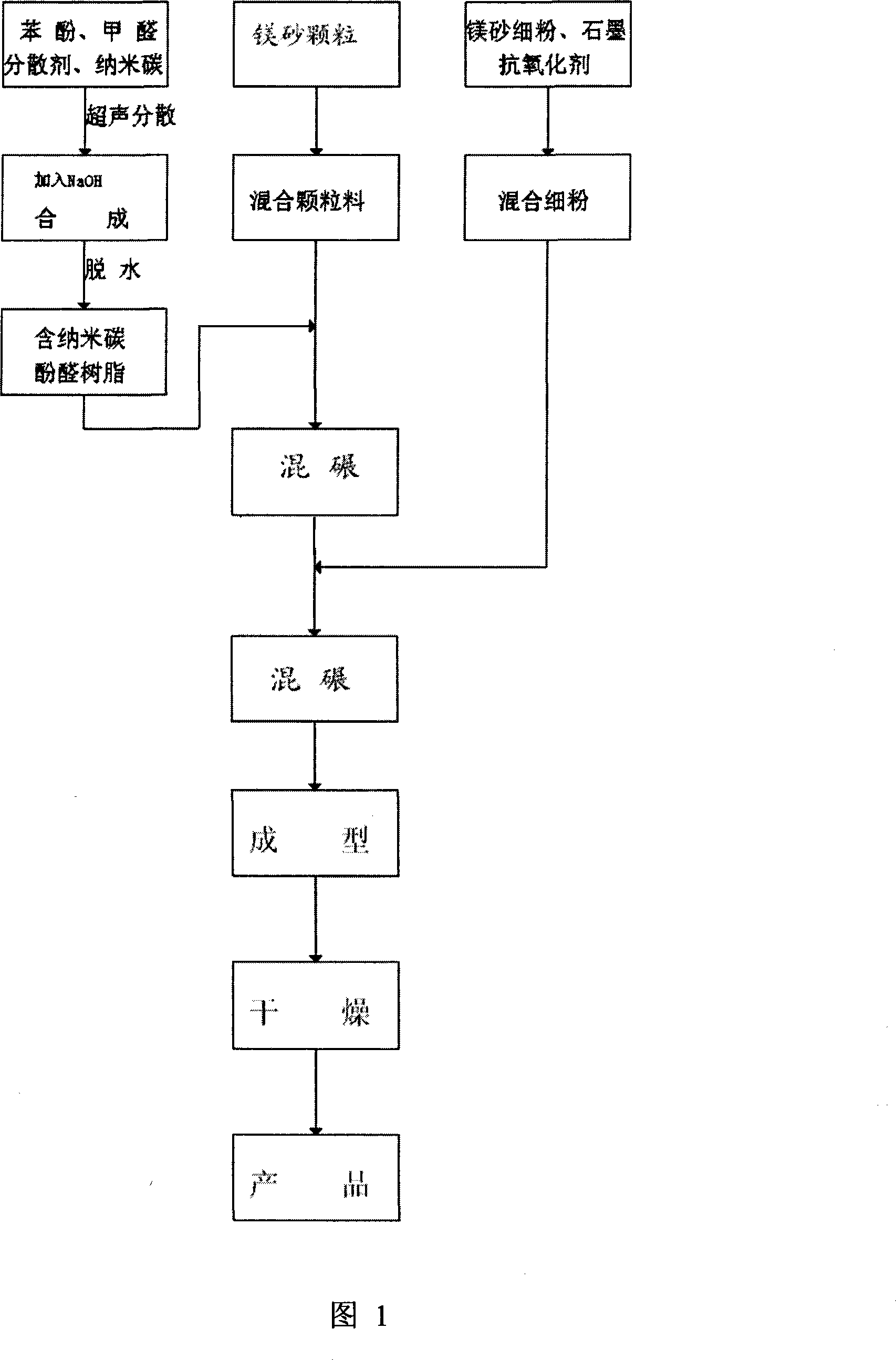
Phenolic resin containing nano-carbon powder, nano-carbon modified low carbon magnesium carbon brick and production method thereof
The invention relates to a low-carbon MgO-C brick containing modified phenolic resin and nanocarbon which are produced by nano carbon powder and a preparation method thereof. Phenolic resin bonding agent containing nano carbon powder is produced by ohenol, formaldehyde, a dispersant and nano carbon powder; the low-carbon MgO-C brick is produced by adopting fused magnesite, graphite, phenolic resin and an antioxidant as raw materials. The ultrasonic dispersion method adopted by the invention replaces partial graphite with the nano carbon powder and leads the nano carbon powder into the low-carbon MgO-C brick, thus obviously improving the anti-erosion ability and the oxidation resistance of the MgO-C brick. The brick has comparatively low thermal expansion coefficient, low thermal conductivity, low oxidative mass loss and thinner decarburized layer; a slag resistance experiment under conditions of 1600 DEG C, 3h heat preservation and carbon sequestration shows that erosion and osmosis phenomenon of the brick are not obvious, thereby being applicable to sites of converters, electric furnaces and ladle working linings, external scouring of furnaces, key components for continuous castings and refractories for blast furnace ironmaking etc., thus having comparatively large application range.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
Martensite precipitation hardening stainless steel for structural member and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides a martensite precipitation hardening stainless steel for structural member and a manufacturing method thereof. The martensite precipitation hardening stainless steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.05 percent of C, 13.50 to 15.50 percent of Cr, 2.5 to 4.0 percent of Cu, 3.0 to 5.0 percent of Ni, 0.15 to 0.40 percent of Nb and Ta, 0.010 to 0.040 percent of N, 0.050 to 0.15 percent of V, less than or equal to 0.80 percent of Si, less than or equal to 1.00 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.025 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of S, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The stainless steel is smelted by combining an electric furnace, AOD refining and vacuum self-consuming technology, so the stainless steel has the characteristics of high strength, good plasticity, good corrosion resistance and the like, and can meet the requirements of high-strength components such as high-pressure values, oil drill, efficient heavy-duty machinery and the like on material performance.
Owner:宝武特种冶金有限公司
Preparation technology of TC17 titanium alloy wire
ActiveCN102451862ASolve the problem that cannot meet the current requirements of titanium alloy wire for aerospaceWire rodTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a preparation technology of a TC17 titanium alloy wire. The preparation technology is characterized by comprising the following steps of: rolling the TC17 titanium alloy into a disk with specification of (Phi)12mm; performing three times of grinding on the (Phi)12mm disk; after the grinding and when the total working rate reaches 30%, performing heat treatment and stress relief annealing in an electric furnace or a vacuum furnace; when the diameter of the wire is greater than or equal to (Phi)10mm, controlling the stretching temperature at 780+ / 20 DEG C; when the diameter of the wire is less than (Phi)10mm, controlling the stretching temperature at 730+ / -20 DEG C; repeatedly performing annealing-stretching-grinding-annealing of the wire after the heat treatment until the diameter of the wire is greater than or equal to (Phi)5.5mm, and performing vacuum heat treatment; before obtaining the finished product and after performing the vacuum heat treatment, removing the lubricant and scale impurity layer on the material surface by use of a round-blade mould with 0-5 degrees of internal and external taper angles according to the diameter of the finished product, stretching to obtain a bright wire with diameter of less than or equal to (Phi)5.0mm, and checking the finished product; and if the finished product is qualified, delivering as the finished product. The preparation technology disclosed by the invention makes up for the shortcoming that the TC17 titanium alloy wire cannot be produced domestically.
Owner:SHENYANG HANRUIDA TITANIUM
Multielement high-chromium wear-resisting cast-iron sieve-plate and production thereof
An antiwear multi-element screening plate made of high-Cr cast iron contains C (2.2-3.2 wt.%), Cr (18-28), Mn (0.6-1.5), Si (0.4-1.0), Mo (0.4-1.5), Ni (0.5-1.2), Nb (0.1-0.5), Ca (0.01-0.08), Zn (0.008-0.050), Mg (0.002-0.010), Ce (0.003-0.10), Ti (0.08-0.15) and Fe (rest). It is made up by electric furnace and cold hardened resin-sand mould. Its advantages are high bending strength, hardness, antiwear performance and impact toughness, and low cost.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Smelting process of Cr-Mn series spring steel
ActiveCN104745765AImprove liquiditySolve the problem of high alkalinity slag and difficult adsorption and inclusionElectric furnaceProcess efficiency improvementNon-metallic inclusionsSmelting process
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy and discloses a smelting process of Cr-Mn series spring steel. The smelting process of Cr-Mn series spring steel comprises the following steps: (1) by taking a low-sulfur molten iron and a high-quality steel scrap as the electric furnace smelting iron and steel materials, controlling the electric furnace end point carbon content to greater than 0.15%; (2) adding active lime and composite refining slag in the electric furnace tapping process, and adding calcium carbide to perform pre-deoxidation in the tapping process; (3) feeding an Al line in an argon station before LF refining; (4) producing high basicity white slag in the refining earlier stage and controlling the basicity of slag in the refining middle and later stages to 1.5-2.5; (5) controlling the ultimate vacuum front argon flow to 15-25 L / min and controlling the ultimate vacuum late argon flow to 30-45 L / min; (6) adding a granular alkaline covering agent and a carbonized rice hull to perform double protection by VD emptying; and (7) stabilizing the speed of continuous casting to 0.8-0.9 m / min, and controlling the degree of superheat to 20-30 DEG C. By adopting the process, the non-metallic inclusion content in the molten steel is reduced.
Owner:ZENITH STEEL GROUP CORP +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com