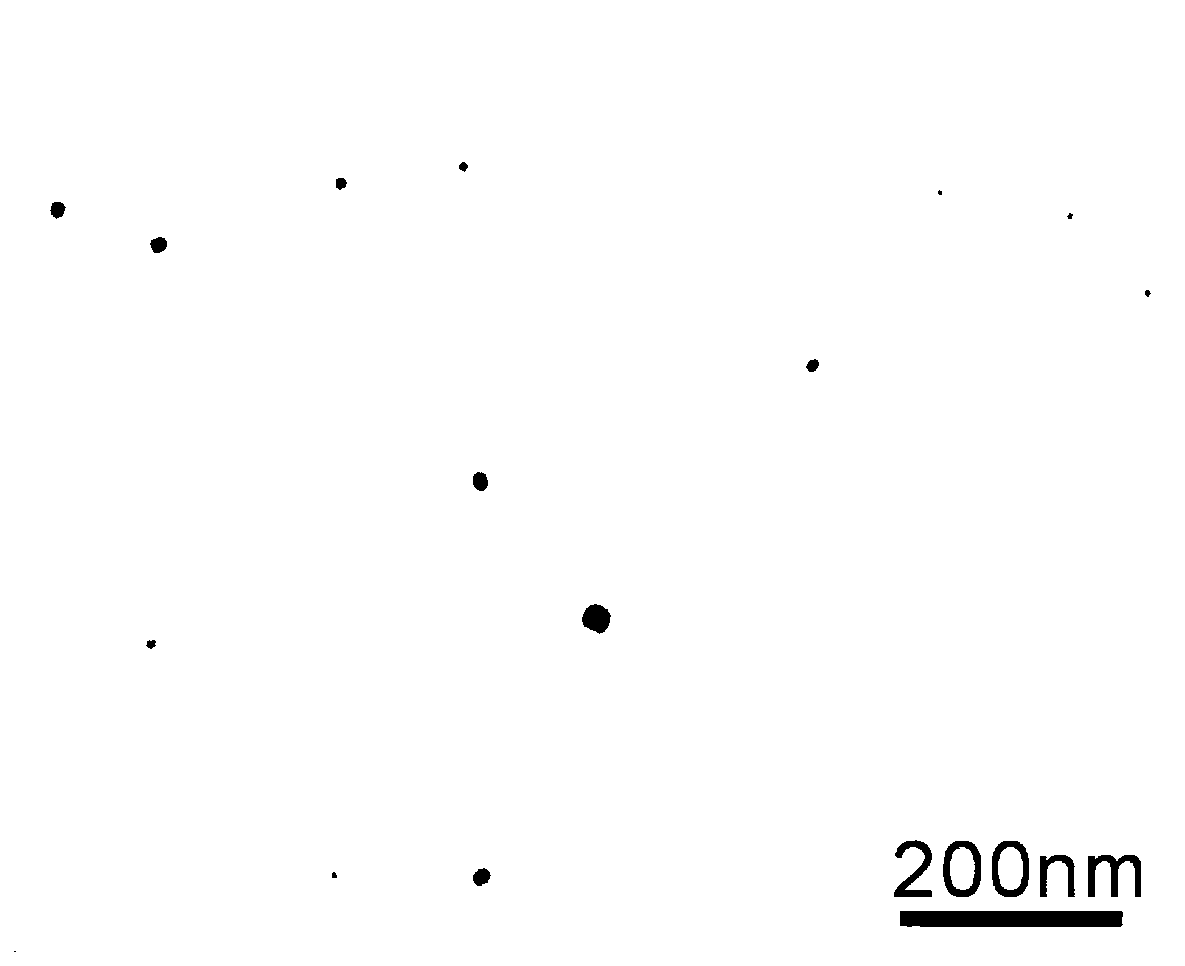
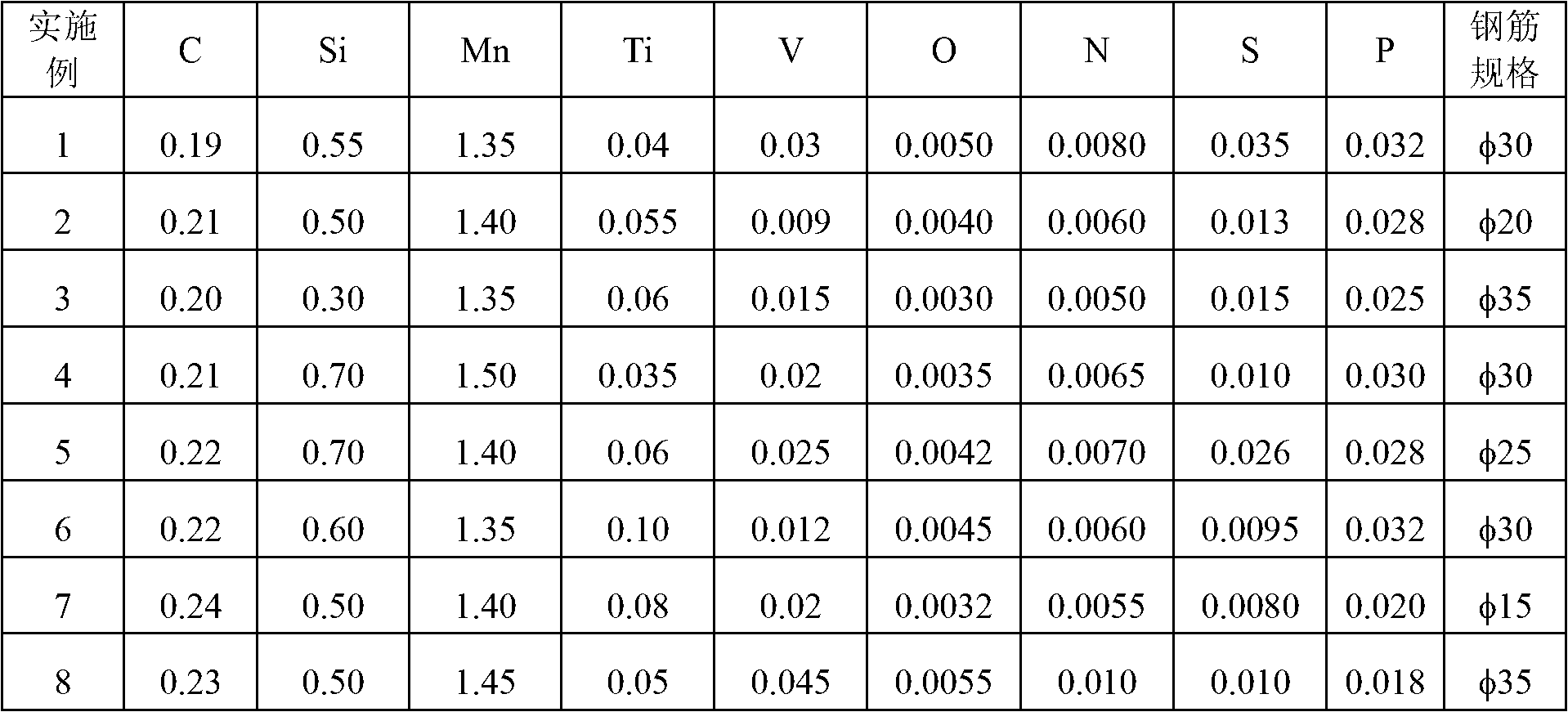
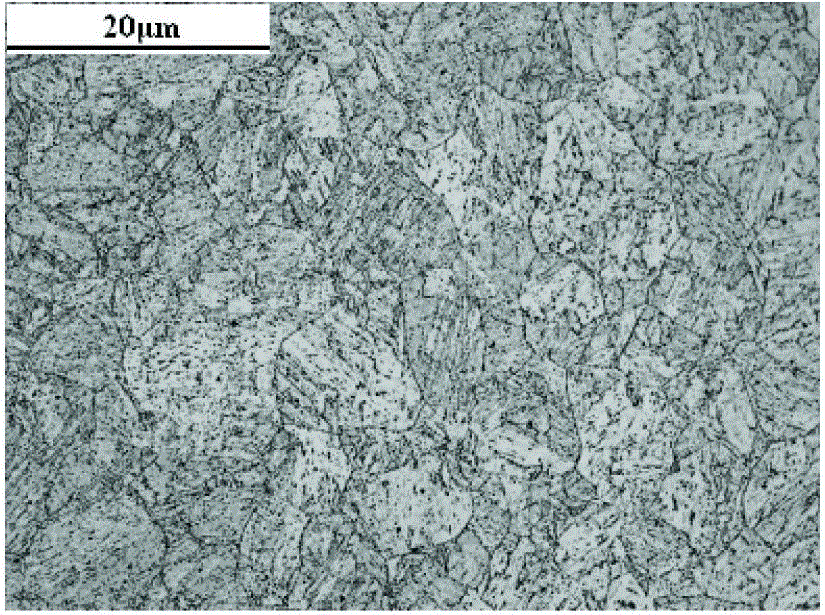
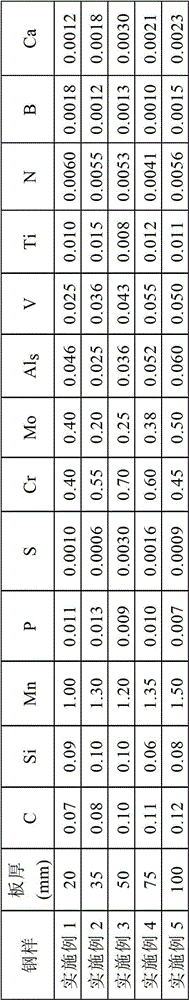
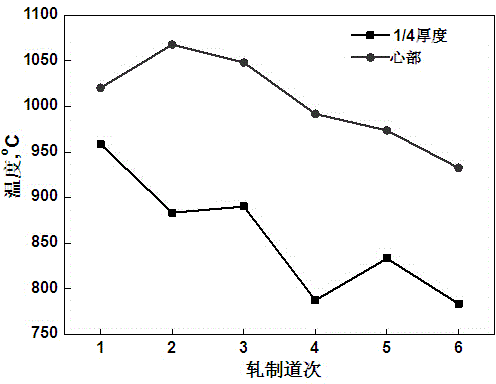
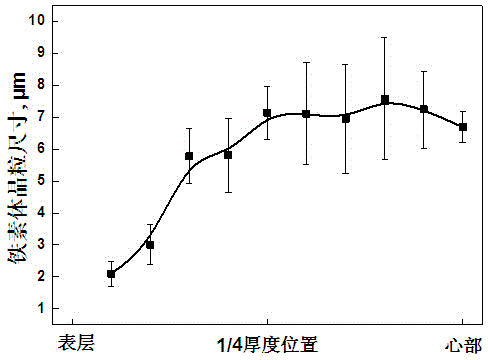
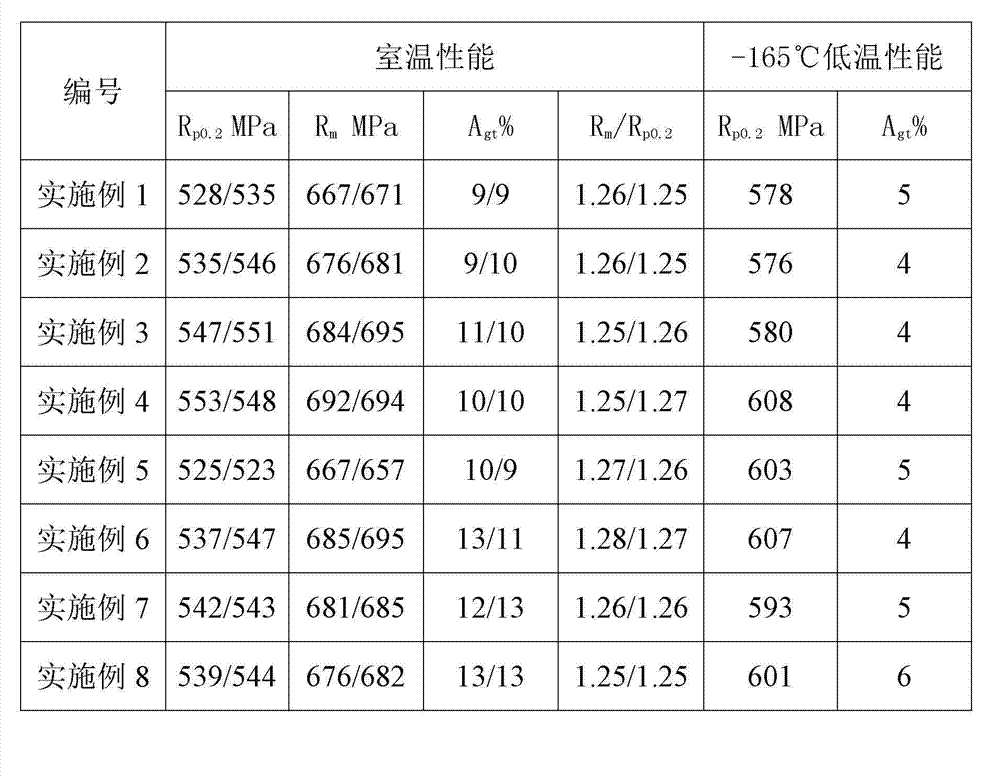
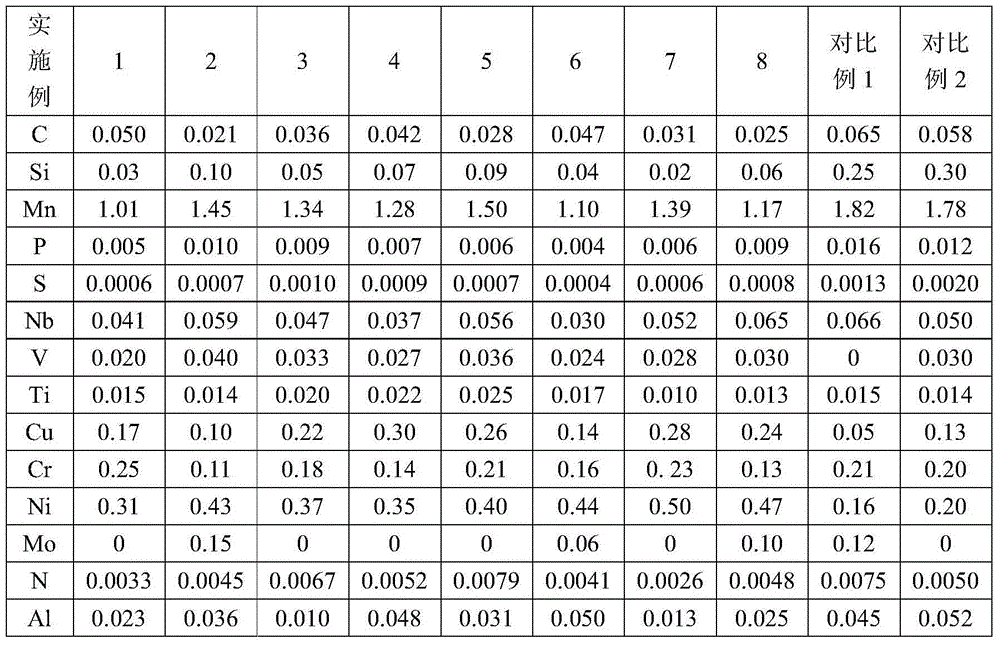
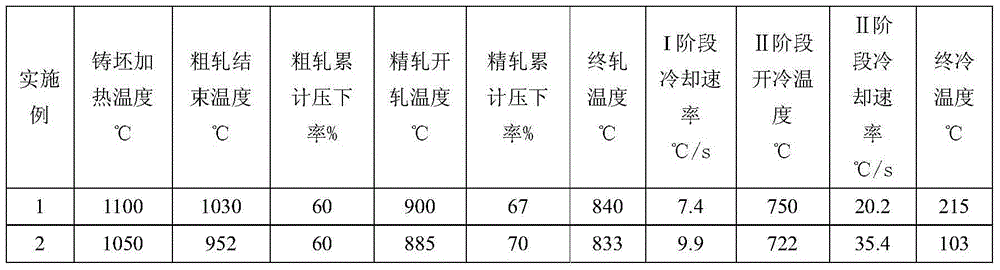
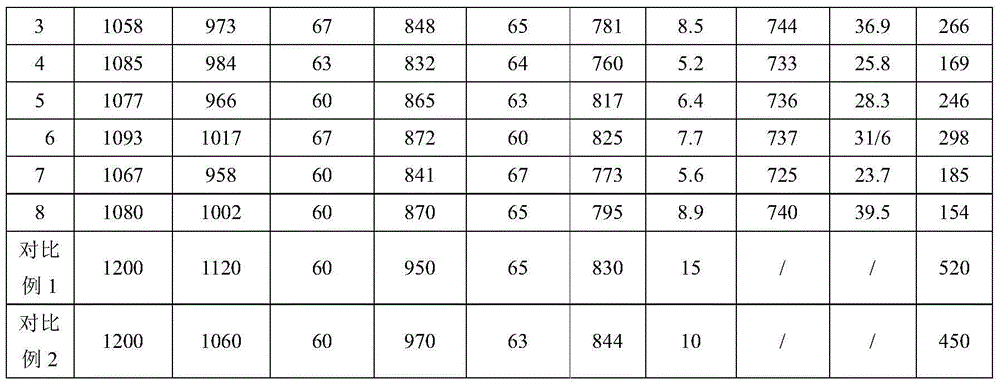
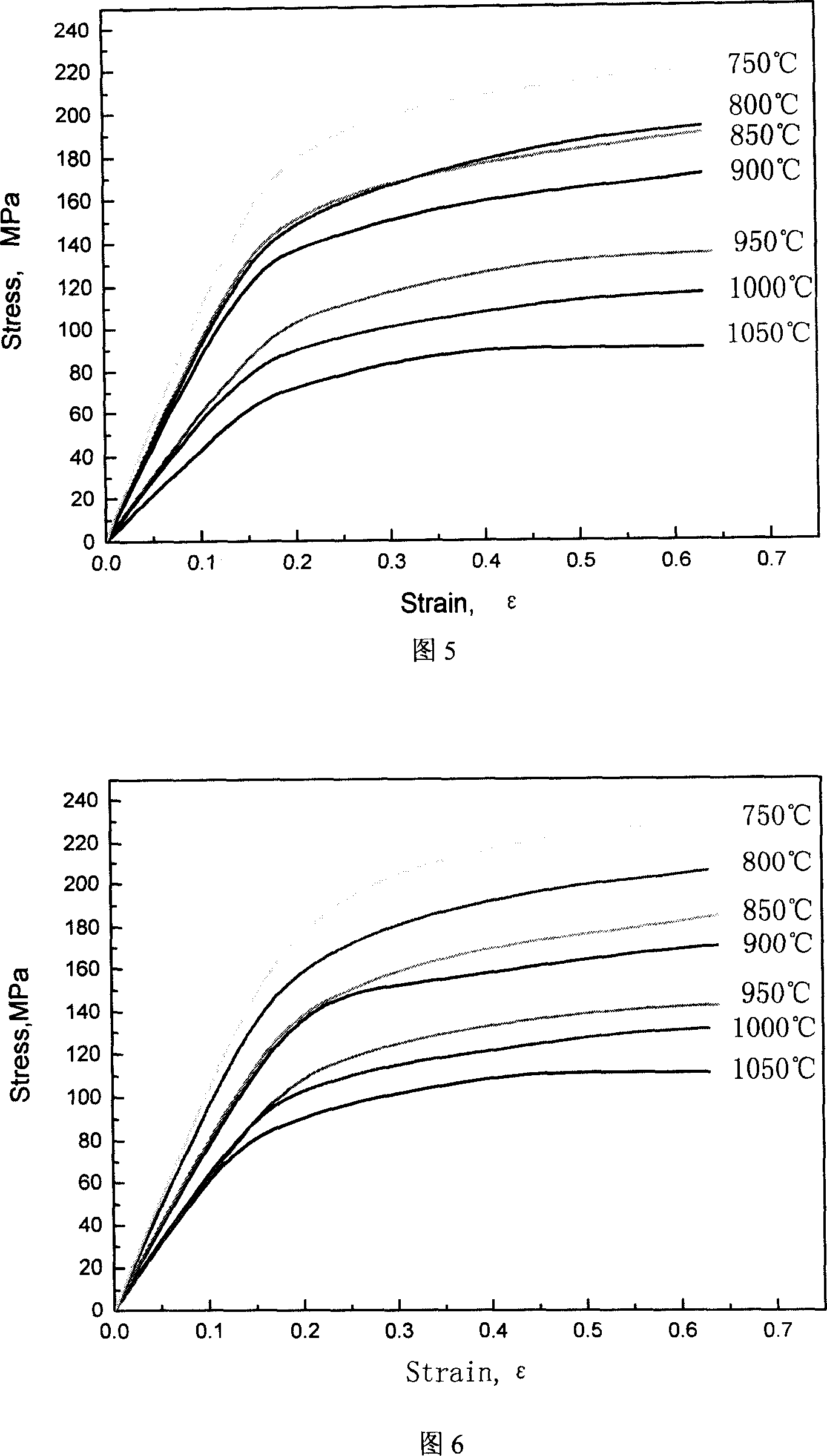
Patents
Literature
403 results about "Microalloyed steel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microalloyed steel is a type of alloy steel that contains small amounts of alloying elements (0.05 to 0.15%), including niobium, vanadium, titanium, molybdenum, zirconium, boron, and rare-earth metals. They are used to refine the grain microstructure or facilitate precipitation hardening.
Steel for microalloying lorry axle and technique for producing the same
InactiveCN101497968AHigh strengthHigh resistance to crack susceptibilityManufacturing convertersCrack resistanceMetallurgy
The invention discloses microalloyed steel used for an axle of a railway freight car, wherein the microalloyed steel contains the following chemical components by weight: 0.50-0.57 percent of C, 0.17-0.40 percent of Si, 0.60-1.00 percent of Mn, 0.20-0.35 percent of Cr, 0.18-0.40 percent of Ni, 0.08-0.18 percent of Mo, 0.02-0.06 percent of Al, 0.020-0.060 percent of Ti, 0.030-0.10 percent of V, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.020 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of B, less than or equal to 0. 20 percent of Cu, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of Sb, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of Sn, less than or equal to 0.04 percent of As, less than or equal to 0.0015 percent of [O] and less than or equal to 0.0060 percent of [N], and the rest is Fe. The invention has high strength, good plasticity, good low-temperature impact property and good crack-resistance sensitivity.
Owner:JIANGSU SHAGANG GROUP HUAIGANG SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
Technology of producing Ti micro alloyed high weather resistant steel plate using thin plate blank continuous casting continuous milling process
InactiveCN1785543AGood weather resistanceGood welding performanceMetal rolling arrangementsSheet steelHigh intensity
A conticasting and tandem rolling technology for manufacturing the high-strength and-weatherability Ti-microalloyed steel plate includes such steps as smelting, refining, conticasting, solidifying, heating, hot rolling, laminar flow cooling and coiling. Its advantages are high strength, high shaping performance, high weatherability and high weldability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PEARL RIVER STEEL & IRON
High ductility steel strip for J55 petroleum sleeve and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101210299AImprove toughnessReduce contentManufacturing convertersMetal rolling arrangementsThin slabHigh pressure water
A steel strip for J55 petroleum casing with high strength and high toughness petroleum casing and a manufacture method thereof belong to the field of micro-alloyed steel production technology. The method comprises converter smelting, LF refining, medium-thin slab continuous slab, heating, high-pressure water descaling, hot rolling and laminar cooling, and reeling, wherein the chemical components of steel comprise (wt%) C 0.15 to 0.20, Si 0.15-0.30, Mn 1.00 to 1.45, P not larger than 0.020, S not larger than 0.010, Nb 0.020 to 0.040, Ti 0.015 to 0.040, Al 0.020 to 0.050, and allowance Fe and other in inevitable impurities. A J55 petroleum casing with a yield strength of 420 MPa can be produced by combining Nb and Ti, micro-alloying and reasonable production process, and the product has the advantages of high strength, high toughness and good solderability.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Low-cost large-heat-input-weldable high-toughness steel plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103320719AIncrease contentUniform and excellent mechanical propertiesOil productionMechanical property
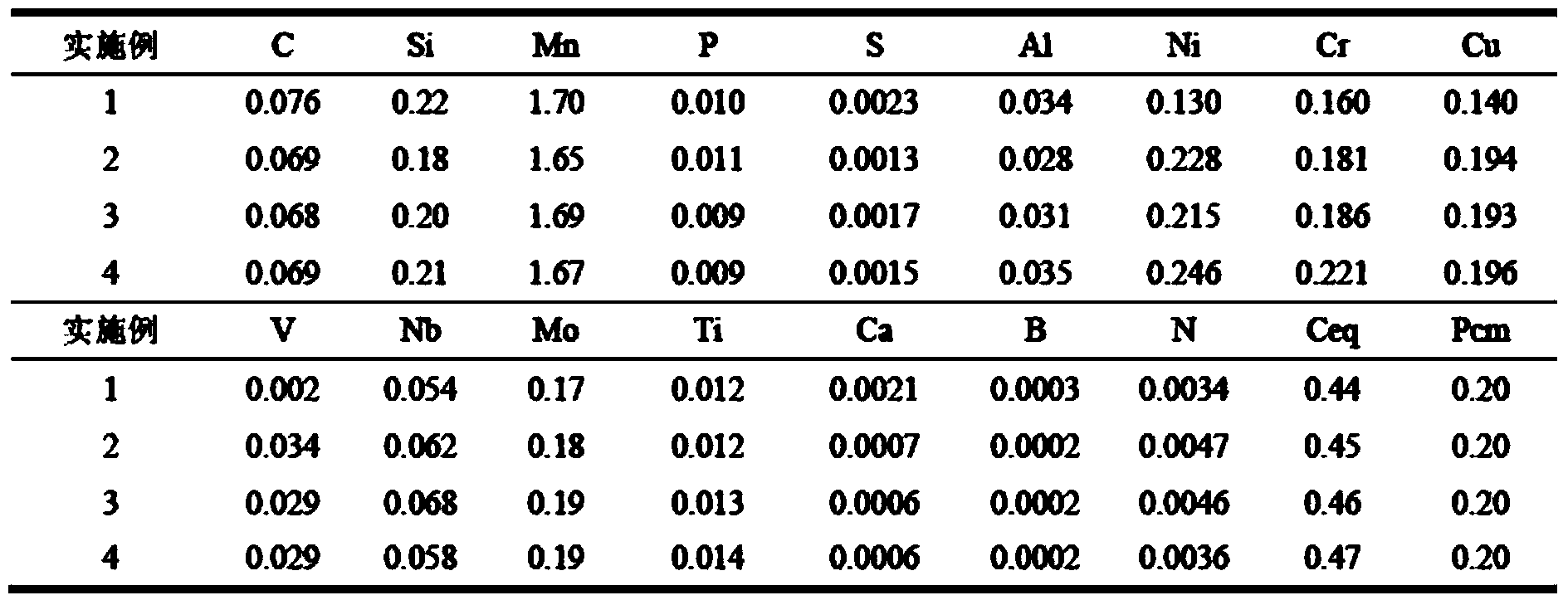
The invention discloses a low-cost large-heat-input-weldable high-toughness steel plate and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the low cost large-heat-input-weldable high-toughness steel plate and the manufacturing method thereof, metallurgical technical means of taking a component system of micro-alloyed steel with low C and high Mn-(Nb+Ti) as a basis, controlling the cold cracking welding sensitive index Pcm to be not higher than 0.22%, appropriately increasing the content of acid-dissolved Als, controlling the ratio of Mn / C to be 25-55, carrying out Ni+high Cr alloying, controlling [(%C)+(%Mn) / 6]*(%Si) to be not greater than 0.035, controlling (%Mn equivalent)*(%Cr equivalent) to be not smaller than 2.7, carrying out Ca treatment, controlling Ca / S to be 0.80-3.00, controlling Ti / N to be 1.5-3.0 and the like are adopted, and a TMCP (Thermo-Mechanical Control Process) and a tempering process are optimized, so that the microstructure of a finished steel plate is of fine bainite, the average crystal group size is smaller than 15 microns, the steel plate can bear large-heat-input welding while uniform and excellent mechanical properties are obtained and the toughness and the plasticity are matched, and then, the low-cost large-heat-input-weldable high-toughness steel plate is particularly applicable to engineering machinery, bridge structures, offshore oil production platforms, oil storage tanks and the like.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Carbon-manganese composite microalloyed steel for engineering machinery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101654761AHigh hardenability and stabilityEasy to controlTemperature control deviceElectric furnaceMechanical componentsChemical composition
The invention relates to a carbon-manganese composite microalloyed steel for engineering machinery and a preparation method thereof. The steel comprises the following chemical compositions by weight percent: 0.32-0.37% of C, 0.15-0.30% of Si, 1.20-1.40% of Mn, 0.030% or less of P, 0.030% or less of S, 0.0005-0.0030% of B, 0.10-0.60% of Cr, 0.01-0.07% of Al and the balance Fe and trace impurities,wherein the content of available boron in the steel is not less than 95%. The invention also provides a preparation method of the composite microalloyed steel and the method controls the ratio of Ti to N to be 3-6 and the acid soluble aluminium content to be 0.030-0.050% so as to ensure that boron in the steel is almost available boron. The preparation method of the invention controls the contentof trace element boron and ensures the hardenability of steel so that the steel is suitable to be used for the preparation of important mechanical parts.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Super-thick quenched-tempered steel plate with 60kg-grade tensile strength and production method of the super-thick quenched-tempered steel plate
The invention discloses a super-thick quenched-tempered steel plate with 60kg-grade tensile strength and a production method of the super-thick quenched-tempered steel plate. The production method includes the means as follows: adopting a component system of low C-Mn-(Ti plus Nb plus V plus B) micro-alloy steel as base, appropriately improving the content of acid solution Als which is greater than or equal to (Mn equivalent / C) * (Ntotal minus 0.0292Ti); controlling (Mn equivalent) / C to be greater than or equal to 15, alloying (Cu plus Ni plus Mo plus Cr); controlling Ni equivalent to be greater than or equal to 0.90%, Mo equivalent to be greater than or equal to 0.25%, and Nb / Ti to be between 1.0 and 2.5; conducting Ca treatment, and controlling the ratio of Ca / S to be between 0.80 and 3.00, (Ca)*(S)0.18 to be less than or equal to 2.5*10 minus 3, and F*DI index to be greater than or equal to 0.65* thickness of a finished steel plate. Optimization control rolling plus an off-line special quenching-tempering technology enable the microstructural of the finished steel plate to be tiny tempering bainite plus tempered martensite, the average colony size is below 25 Mum, excellent matching of strong toughness / strong plasticity is obtained and the mechanical property along the direction of the thickness of the plate is uniform; the super-thick quenched-tempered steel plate with 60kg-grade tensile strength is specially applicable to large-sized steel structures and equipment such as water-electricity penstocks, volutes, ocean platforms, large-sized engineering machinery and can realize low-cost industrial production in stable batches.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Vanadium and titanium compound microalloyed steel bar and production method thereof
The invention discloses a vanadium and titanium compound microalloyed steel bar and a production method thereof. The steel in the steel bar comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.16 to 0.25 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.80 percent of Si, 1.20 to 1.50 percent of Mn, 0.001 to 0.12 percent of Ti, 0.001 to 0.10 percent of V, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of N, less than or equal to 0.045 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.045 percent of P, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The production method for the steel bar comprises the following steps of: a, smelting crude molten steel, tapping, deoxidizing and alloying; b, refining, trimming the components to make the components meet the component requirement of the steel bar, and casting; and c, performing hot rolling, wherein alloying vanadium and titanium after deoxidizing in the process of tapping, or in the process of refining. According to the vanadium and titanium compound microalloyed steel bar, the yield strength and the tensile strength of the steel are improved under the condition of not changing the ductility of the steel, and the performance requirements of the steel bars in 400 MPa or 500 MPa of grades are met.
Owner:PANZHIHUA GANGCHENG GROUP
Nickel-free high-toughness 80kg-grade high-strength steel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102719757ASimple welding processHigh strengthHeat treatment process controlNickel freeToughness
The invention relates to nickel-free high-toughness 80kg-grade high-strength steel and a manufacturing method thereof. A component system of ultralow C, ultralow Si, medium Mn and Ti, V and B microalloy steel is used as a basis; the acid-soluble Als content in steel is properly improved, the Als is not less than 10*[(%Ntotal)-0.292(%Ti)], Mn / C is not less than 12, (%C)*(%Si) is not more than 0.01, and [(%Cr)+1.3(%Mo)]*[(%V)+(%C)] is not less than 0.087; Ca treatment is carried out, the Ca / S ratio is 1.00-3.00, and (%Ca)*(%S)<0.18> is not more than 2.5*10<-3>; F*DI index number * zeta is not less than 2.0* finished steel plate thickness, wherein zeta is on-line DQ (direct quenching) hardenability contribution factor, and F is B element hardenability contribution factor; DQ (thermo mechanical control process: TMCP) and off-line tempering process (T) are optimized; the microscopic structure of the steel plate is fine low-carbon tempered martensite and tempered lower bainite; the steel has the average colony size below 20 mu m, has excellent strength and plasticity and strong toughness, and is particularly suitable for hydroelectric pressure water pipes, steel branch pipes, scrolls, ocean platforms, large-sized engineering machines and other large-sized steel structures and equipment.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Vanadium-nitrogen additive for smelting microalloyed steel and method for preparing same
The invention discloses a vanadium-nitrogen additive for smelting microalloyed steel and a method for preparing same. The vanadium-nitrogen additive and the method are characterized in that the vanadium-nitrogen additive is uniformly mixed by vanadium-contained alloy powder, nitrogen increasing agent powder, and adhesive, wherein the mass ratio of the adhesive is 5-12%, the total mass ratio of the vanadium-contained alloy powder and the nitrogen increasing agent powder is 88-95%, and the ratio of V / N is controlled within 0.1-4. The method for preparing the vanadium-nitrogen additive used for smelting microalloyed steel comprises the following steps: mixing the vanadium-contained alloy powder and the nitrogen increasing agent powder by the weight percentage, mechanically and uniformly blending the mixed powders, subsequently adding 5-12% of the adhesive and uniformly mixing the powders again, finally mechanically forming blocks of spherule shapes or other shapes, and preparing the vanadium-nitrogen additive by drying the blocks. The ratio of V / N of molten steel can be controlled within 3.0-5.0 by the vanadium-nitrogen additive, the enhancement effect of the vanadium can be sufficiently played by utilizing the cheap nitrogen element, and the amount of the vanadium is reduced obviously.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
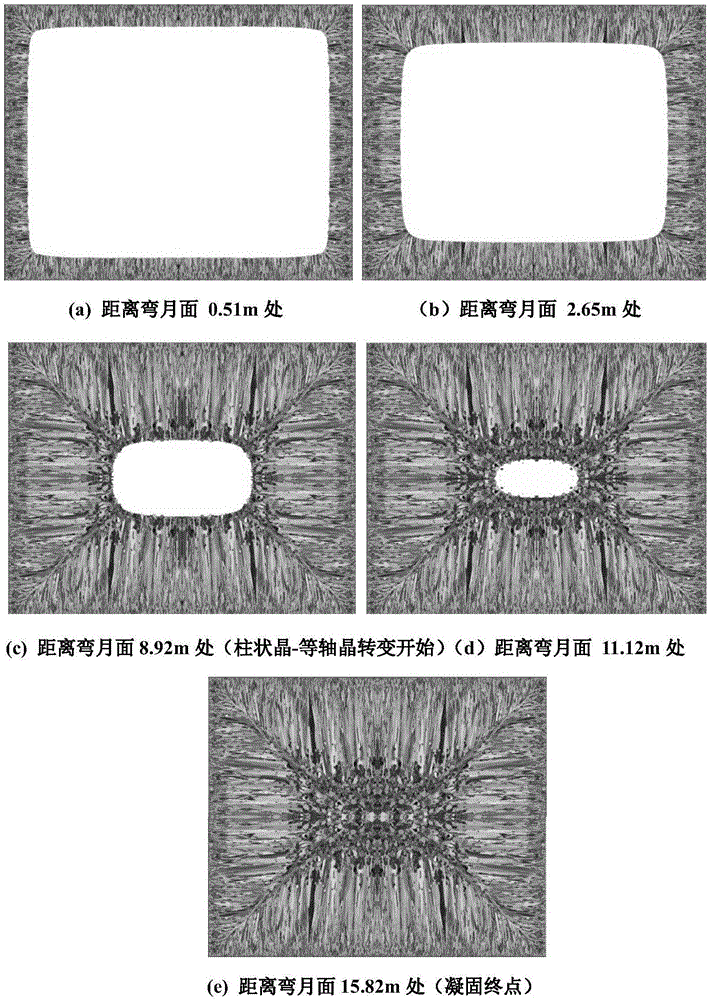
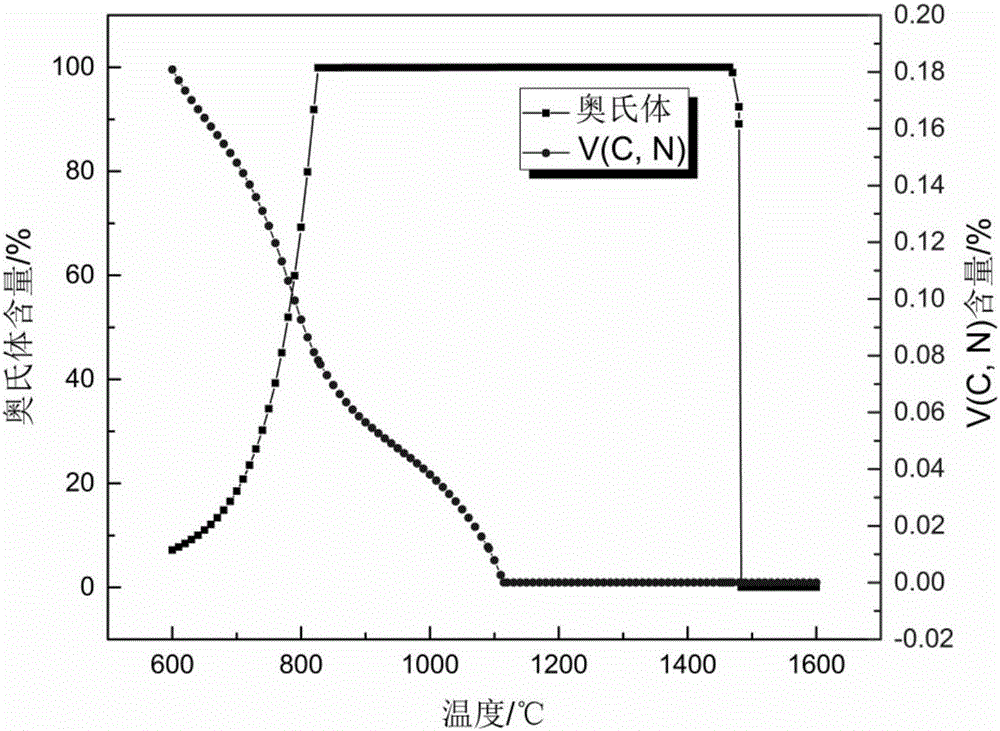
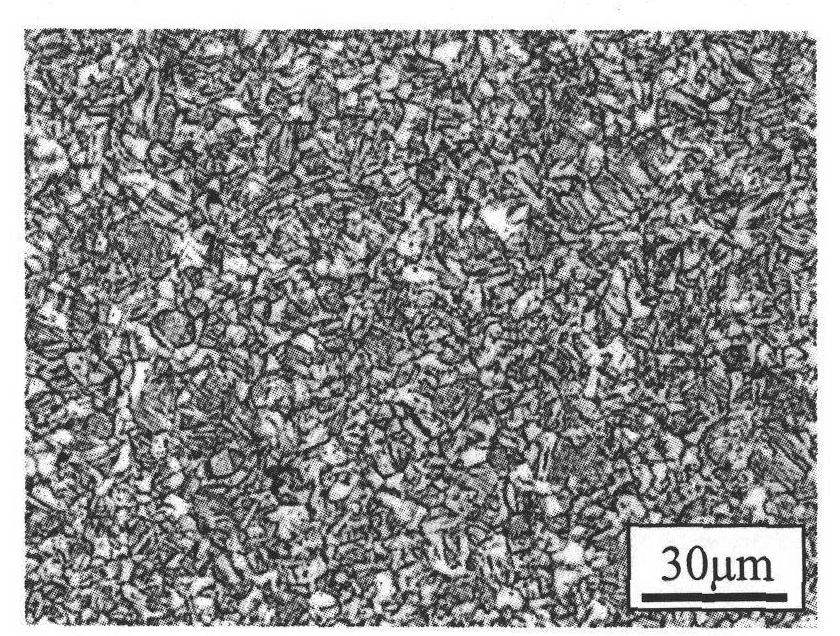
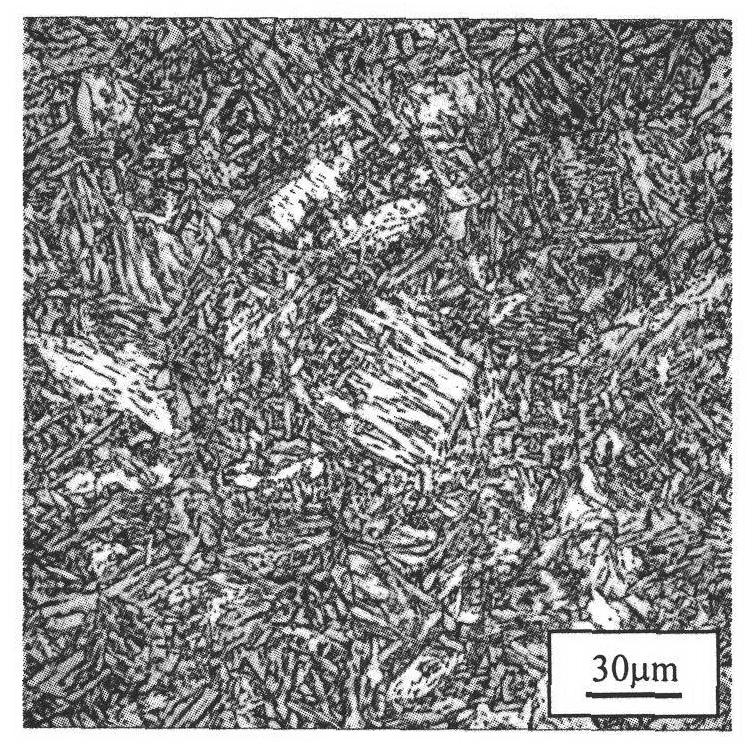
Microalloyed steel continuous casting cooling control method based on steel grade solidification characteristic and evolution of microstructures
The invention relates to a microalloyed steel continuous casting cooling control method based on the steel grade solidification characteristic and evolution of microstructures. The critical technical contents of the microalloyed steel continuous casting cooling control method comprise steel grade solidification characteristic experimental analysis, continuous cast blank solidification structure numerical simulation, continuous casting cooling process water amount regulation and control and the like. Change rules of the thermoplasticity and a third brittle temperature range of a target steel grade at different cooling rates are determined through experiments at first, then the influences of the cooling rates on austenite / ferrite transformation and the microalloy element second-phase particle precipitation law are comprehensively analyzed with te combination with the experiments, and finally, the microalloyed steel square blank continuous casting cooling precise control strategy of "low superheat pouring, low cooling of a third secondary cooling zone and high cooling of a fourth secondary cooling zone" is provided, relevant regulation and control schemes, that is, the superheating temperature is 23 DEG C (the original value is 37 DEG C), the water amount of the third secondary cooling zone is 2.6 L / min (the original value is 51.5 L / min), and the water amount of the fourth secondary cooling zone is 165.6 L / min (the original value is 18.4 L / min) are made a new continuous casting secondary cooling regulation and control mechanism based on the microalloyed steel characteristic is built, a cast blank solidification structure is optimized, and the strength of a surface microstructure of the solidification structure is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Easy-welding low-carbon bainitic steel and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101787489ASimple production processProduction applicableTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionBoron
The invention discloses an easy-welding low-carbon bainitic steel and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of microalloy steel. The steel comprises the chemical components by weight percent: 0.02-0.08% of C, 1.20-1.80% of Mn, 0.10-0.50% of Si, less than or equal to 0.010% of S, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, 0.10-0.30% of Mo, 0.020-0.050% of Nb, 0.03-0.10% of V, 0.005-0.030% of Ti, 0.0050-0.010% of N, 0.0005-0.0020% of B, less than or equal to 0.035% of Al and balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The proportion between the boron content and the nitrogen content in the steel simultaneously meets the conditions that 3N-10B is more than or equal to 0.005 and less than or equal to 0.015, and Ti+V+10B is more than or equal to 8.525N. The production process of smelting by an electric furnace or a converter, external refining, continuous casting and controlled rolling and cooling is adopted. The invention has the advantages that the yield strength of the steel is more than or equal to 550MPa, the tensile strength is more than or equal to 670MPa, the elongation is more than or equal to 20%, and the charpy impact energy under -40 DEG C is more than or equal to 200J; the charpy impact energy under -40 DEG C in a near weld zone is more than or equal to 100J when the weld heat input is 20-100Kj / cm; and the production process is simple and convenient.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Control device and technology for corner cracks of microalloy steel sheet billet
ActiveCN108356242AIncrease cooling rateImprove tissue plasticityDistribution systemDistribution control
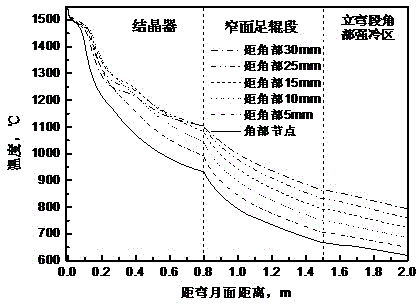
The invention provides a control device and technology for corner cracks of a microalloy steel sheet billet, and relates to the technical field of continuous casting and continuous rolling of steel sheet billets. The control device comprises a secondary cooling water distribution system, a corner efficient heat transfer narrow surface Gauss concave curved surface crystallizer and a crystallizer narrow surface foot roll zone new strengthened spraying system, wherein the new strengthened spraying system comprises a new water supply pipeline, a new strengthened spraying rack and a water distribution control system. In the control technology, dynamic water distribution is achieved through synergism of the corner efficient heat transfer narrow surface Gauss concave curved surface crystallizer,an integral strengthened cooling technology and a water distribution technology of the crystallizer narrow surface foot roll zone new strengthened spraying system and a wide surface integral slow cooling water distribution technology. According to the control device and the control technology, dispersion precipitation of microalloy carbonitride of corner structures of the cast billet can be stablyachieved, the corner structures of the cast billet are strengthened, narrow surface metals flow to side arcs during the large deformation pressing process of a liquid core of the cast billet, stressof the corner parts of the cast billet is reduced, and generation of the corner cracks of the microalloy steel sheet billet is radically controlled.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
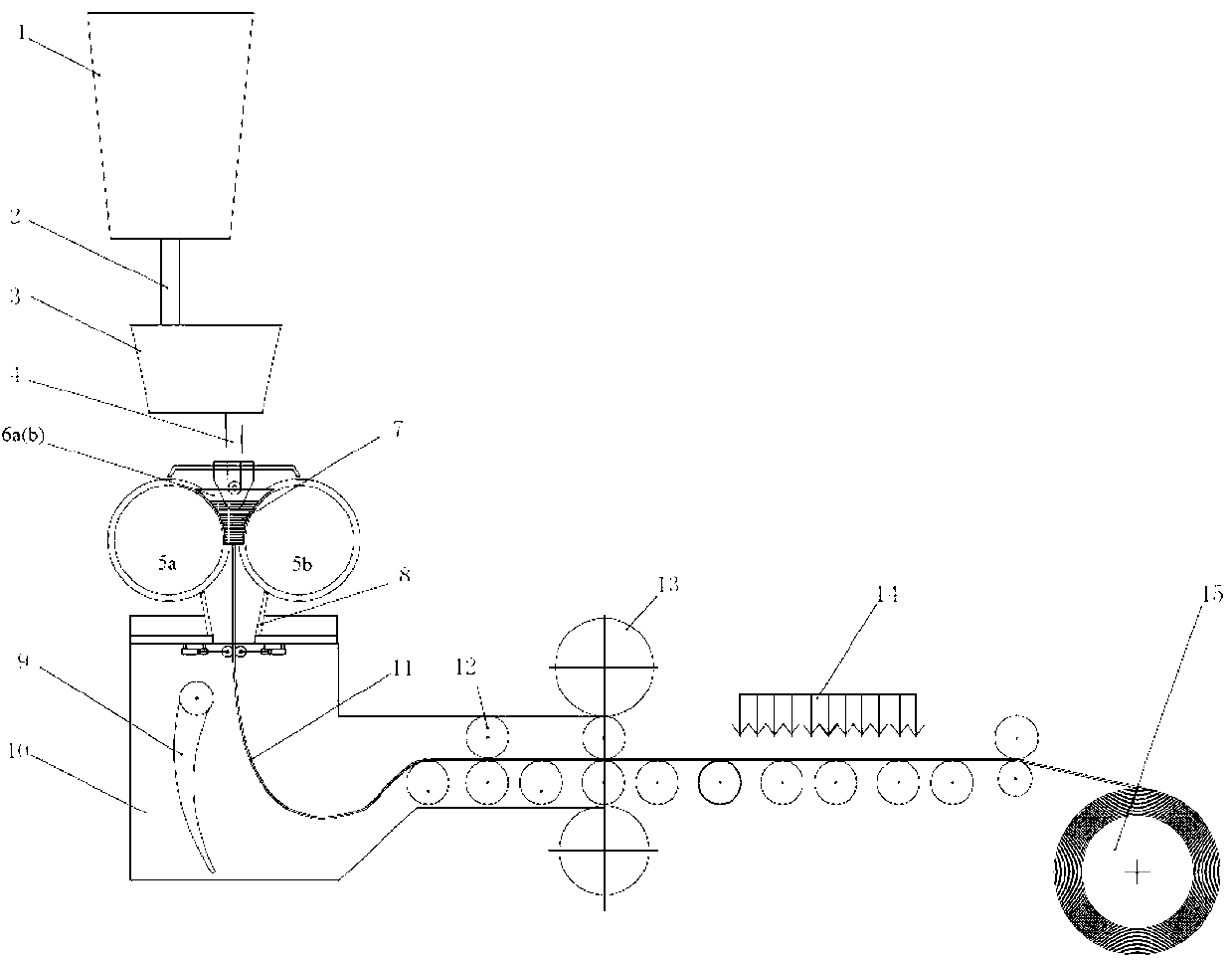
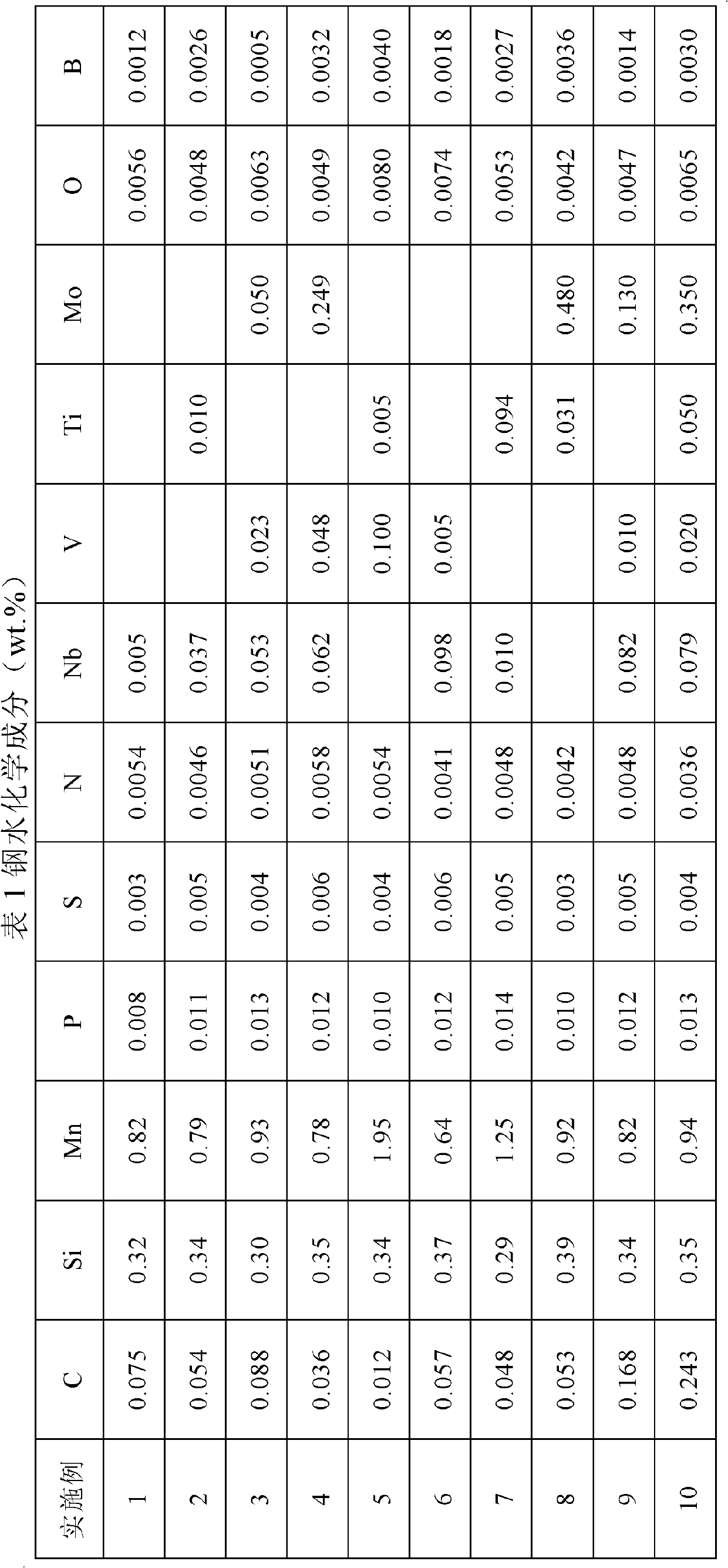
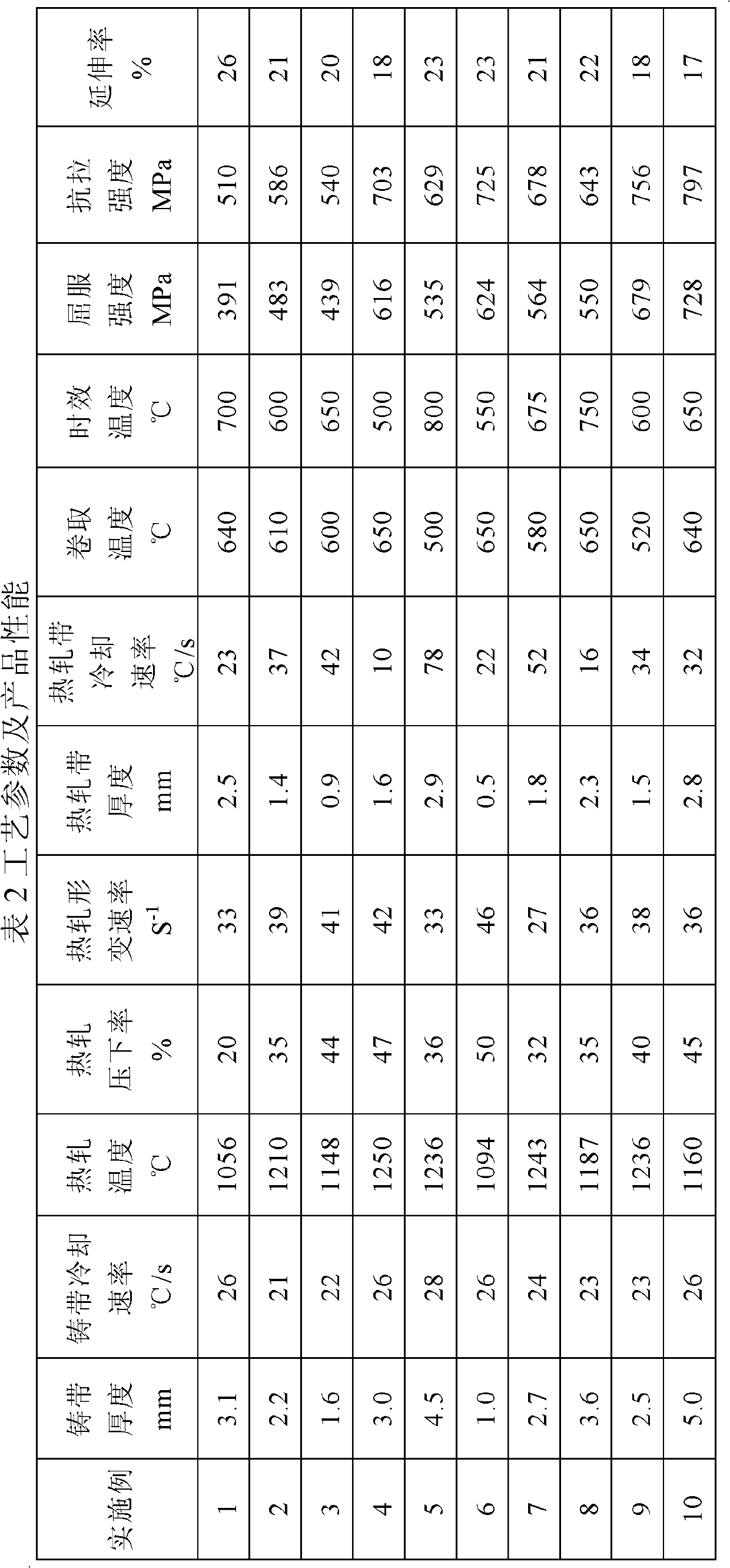
Manufacturing method of age-hardened thin-strip casting low-carbon microalloyed steel strip
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of age-hardened thin-strip casting low-carbon microalloyed steel strip. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) smelting, and continuously casting a thin strip, wherein the weight percents of the components are as follows: 0.01-0.25% of C, not more than 0.4% of Si, 0.6-2.0% of Mn, not more than 0.015% of P, not more than 0.01% of S, not more than 0.006% of N, not more than 0.008% of O, 0.0005-0.004% of B, 0.005-0.1% of Nb, 0.005-0.1% of V, 0.005-0.1% of Ti, and 0.05-0.5% of Mo, and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities, and the casting thickness in the dual-roller continuous casting machine is 1-5mm; 2) cooling the cast strip, wherein the cooling rate is more than 20DEG C / s; 3) hot-rolling at 1050-1250 DEG C, wherein the reduction rate is 20-50%, and the deformation rate is more than 20s-1; 4) cooling, wherein the cooling rate is 10-80DEG C / s; 5) reeling at 550-700 DEG C; 6) performing age-hardening treatment, wherein the age-hardening temperature is 500-800 DEG C, and the heating time is 0.1-30 minutes. The austenite online recrystallization of the cast strip after hot-rolling is realized, the obtained steel strip is provided with uniformly distributed bainite and acicular ferrite, the structure comprises nanoscale precipitation such niobium carbonitride, and a product has high strength and extensibility.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Hot rolling flat steel for high toughness X80 elbow and production method thereof
The invention relates to hot rolling flat steel for a high toughness X80 elbow and a production method thereof and belongs to the technical field of low carbon microalloyed steel. The hot rolling flat steel for the high toughness X80 elbow comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.060-0.085% of C, 0.10-0.35% of Si, 1.40-1.80% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, less than or equal to 0.003% of S, 0.04-0.07% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.06% of V, 0.010-0.020% of Ti, 0.15-0.50% of Ni, less than or equal to 0.20% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.50% of Mo, 0.010-0.040% of Al, less than or equal to 0.50% of Ceq, less than or equal to 0.23% of Pcm and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. A production process comprises the following steps: preparing molten iron in a blast furnace, pre-desulphurizing the molten iron, smelting in a converter, refining under LF and RH conditions, continuously casting slab, heating slab, rolling by adopting a 4300 rolling mill, rapidly cooling by virtue of ACC (activated calcium carbonate), cooling in heap, sampling and testing as well as warehousing and despatching. The hot rolling flat steel for the high toughness X80 elbow has the advantages that mechanical performance indexes of a steel plate are stable, plasticity and toughness are high, and excellent toughness is still maintained after high temperature baking, moulding and heat treatment are carried out.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO SHOUQIN METAL MATERIAL +1
Multi-cycle quenching-partitioning-tempering (M Q-P-T) technique
ActiveCN102337385AAvoid crackingHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlCooling curveTempering
The invention discloses a multi-cycle quenching-partitioning-tempering (M Q-P-T) technique, belonging to the field of thermal processing technologies. The technique disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: dividing a workpiece with a large section into a plurality of regions from the surface to the centre part along the section, and making an MQ-P-T technique for the workpiecein combination with an isothermal cooling transformation curve of the workpiece; through alternately cooling the workpiece in a medium capable of quickly cooling and a medium capable of slowly cooling for many times, realizing a Q-P-T technique process in each alternate cooling of quick cooling and slow cooling; and gradually finishing martensitic transformation and carbon-rich retained austenitegeneration from the surface layer to the internal layer in the technique. The technique can be used for quenching and cooling processes of various types of mechanical structure members, thick plates directly quenched after rolling and various types of large-size profile steels which are made of microalloyed steels or alloy steels containing various types of components. According to the application of the technique disclosed by the invention, the purpose of obviously improving strength and toughness of large-size workpieces is achieved on the premise of avoiding cracking.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Ferro-silicon nitride alloy core-spun wire and production method thereof
The invention discloses a ferro-silicon nitride alloy core-spun wire and a production method thereof, belonging to the technical field of core-spun wires. The ferro-silicon nitride alloy core-spun wire is formed by coating core powder with a steel belt, wherein the core powder comprises the following components in parts by mass: 70-95 parts of ferro-silicon nitride alloy, 4.9-29.7 parts of nitrogen-fixation alloy element ferric alloy, and 0.1-0.3 part of silicon-based rare earth alloy powder. The production method of the ferro-silicon nitride alloy core-spun wire comprises the following steps: preparing the ferro-silicon nitride alloy; preparing nitrogen-fixation alloy element ferric alloy; preparing silicon-based rare earth alloy powder; preparing the core powder; coating the core powder with the steel belt, namely coating the core powder by adopting the steel belt with the thickness of 0.34-0.45mm to obtain the core-spun wire with the diameter of 9-13mm. According to the ferro-silicon nitride alloy core-spun wire and the production method thereof, the nitrogen fixation effect and action can be obviously improved, the yield of nitrogen element in molten steel can be greatly increased, and the deficiency existing when the core-spun wire made of nitrogen-containing materials in the prior art serves as a nitrogen enhancement fortifier during production of microalloy steel can be overcome.
Owner:MAANSHAN XINGDA METALLURGICAL NEW MATERIAL
Corrosion-resistant microalloyed steel and steel rail and preparation method of corrosion-resistant microalloyed steel and steel rail
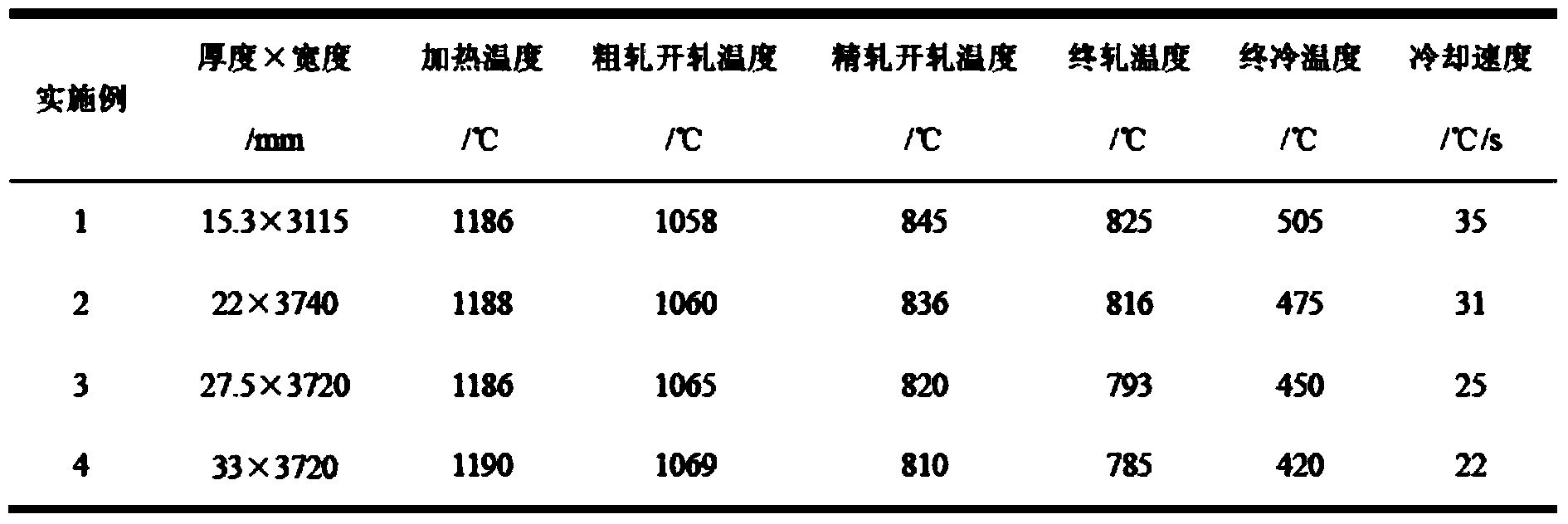
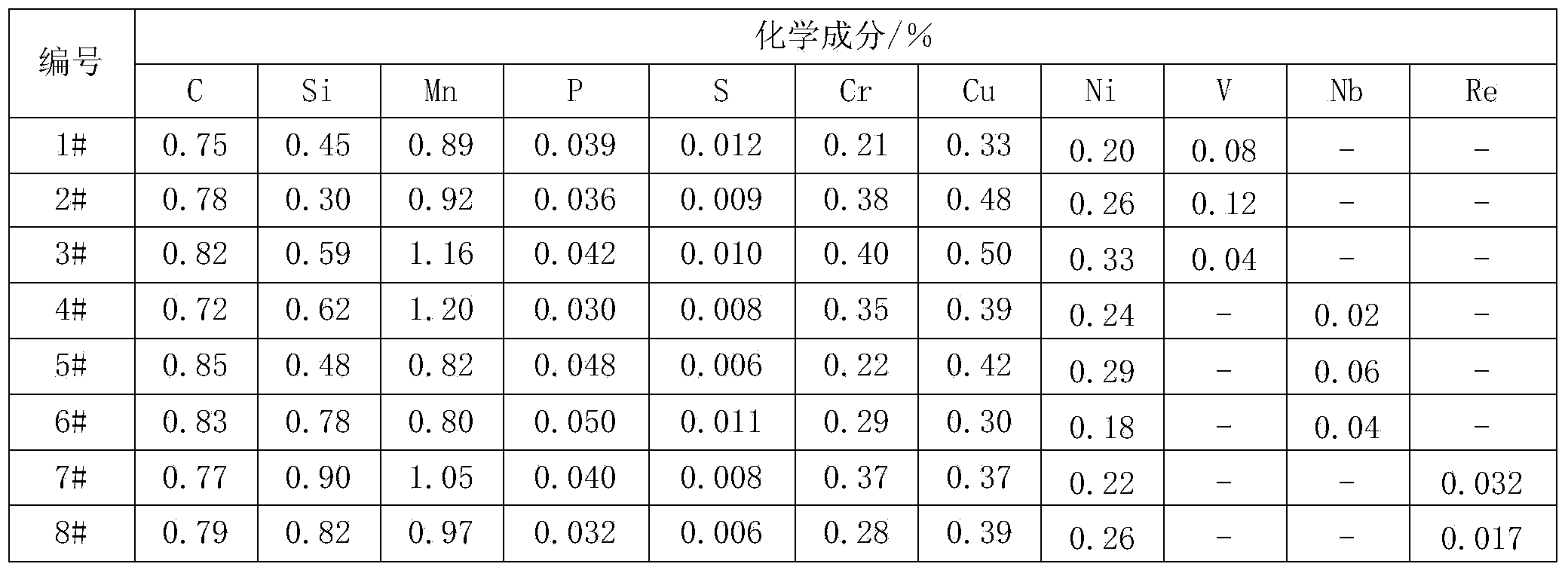
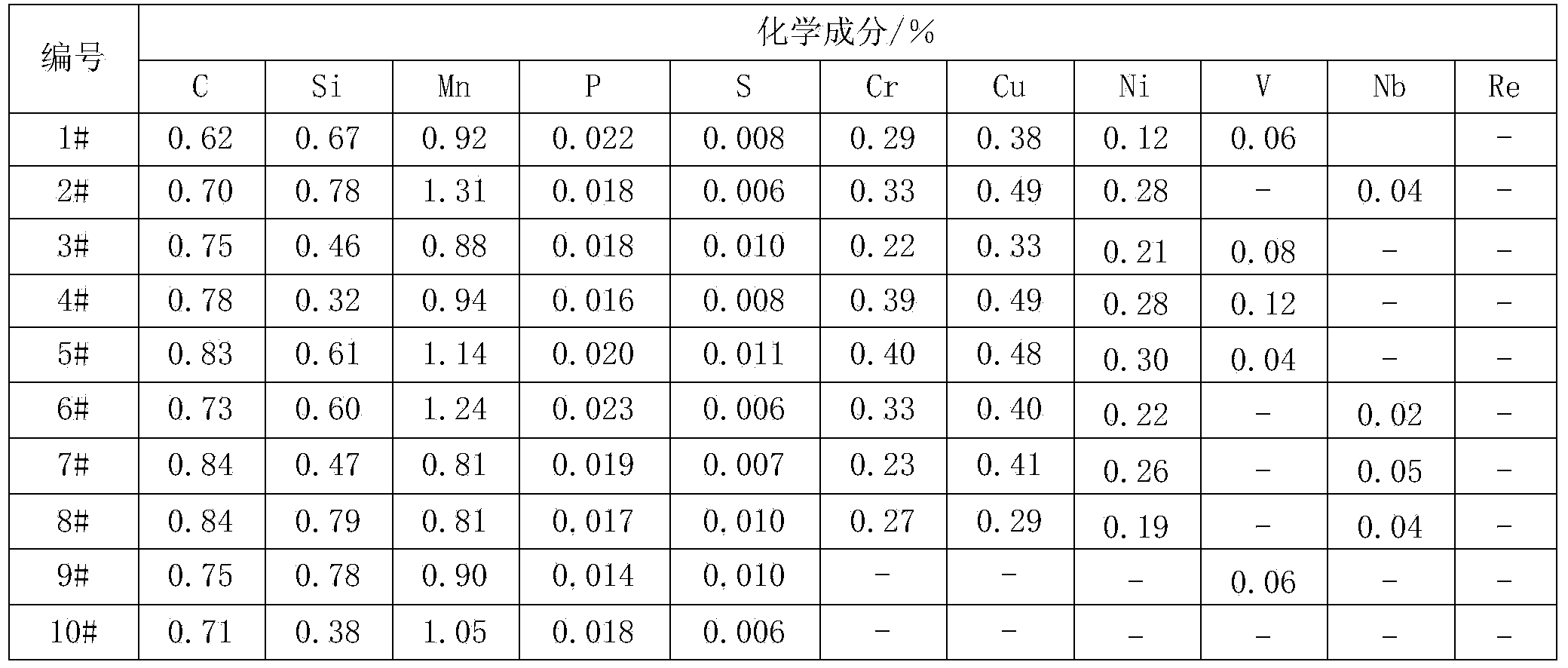
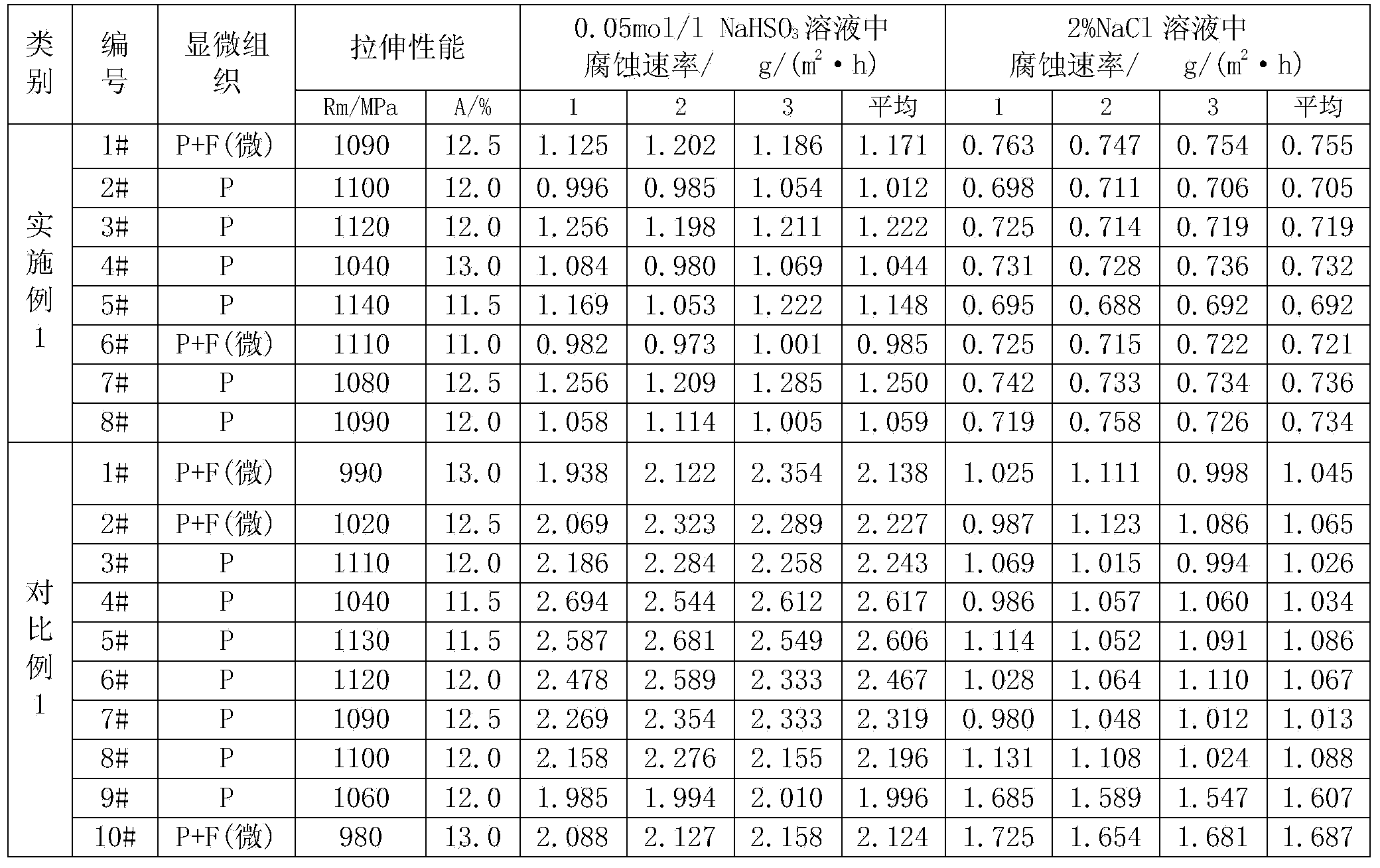
The invention relates to a steel rail material, in particular relates to a corrosion-resistant microalloyed steel, and aims to solve the technical problem that the corrosion-resistant microalloyed steel is not provided. The corrosion-resistant microalloyed steel is prepared from the following components by weight percent: 0.73% to 0.85% of C, 0.30% to 0.90% of Si, 0.80% to 1.20% of Mn, 0.20% to 0.40% of Cr, 0.30% to 0.50% of Cu, Ni accounting for one half to two thirds of the content of the Cu, 0.03% to 0.05% of P, less than or equal to 0.025% of S, at least one element from 0.04% to 0.12% of V, 0.02% to 0.06% of Nb or 0.005% to 0.05% of Re, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The microscopic structure of a steel rail product is formed by pearlite and a trace quantity of ferrites, wherein the tensile strength of the steel rail product is greater than or equal to 1000MPa, so that the steel rail product is good in marine environment corrosion resistance and atmospheric environment corrosion resistance. Thus, the steel rail product is suitable for coastal regions and tunnels with a high relative humidity.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Thick steel plate with excellent rack arrest property and preparation method of thick steel plate
The invention belongs to the field of preparing steels and in particular relates to a thick steel plate with excellent rack arrest property and a preparation method of the thick steel plate. The thick steel plate is prepared from the following chemical components including a plain carbon steel or a microalloy steel. The preparation method comprises the following steps: water cooling while carrying out rolling deformation on a billet after being discharged out of a furnace, ensuring the temperature of the surface of the billet to be cooled to 400-800 DEG C during each rolling, ultra rapid cooling to 600-700 DEG C with the cooling speed to be larger than or equal to 15 DEG C / s after rolling is finished, and finally, air cooling to room temperature. According to the thick steel plate and the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the tissue of the thick steel plate takes ferrite as a parent phase and a second phase as a pearlite, the upper and lower surface layers of the thick steel plate are both an ultra-fine grain layer, the thickness of a single-sided ultra-fine grain layer is larger than or equal to 0.1 times of the thickness of the thick steel plate, the ferrite average grain size of each ultra-fine grain layer is smaller than or equal to 3 microns, and the grain boundary density of a large angle boundary is larger than or equal to 0.676 microns<-1>. The thick steel plate is excellent in rack arrest property and improved in core toughness and can be used for shipbuilding, in particular to structure materials of large container ships, offshore platforms, crude oil, natural gas conveying pipelines and the like.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Niobium microalloyed steel for low-temperature reinforcing steel bar and rolling process of steel
ActiveCN103243264AGuaranteed performanceImprove low temperature resistanceTemperature control deviceChemical compositionElectric arc furnace
The invention discloses niobium microalloyed steel for a low-temperature reinforcing steel bar and a rolling process of the steel. The steel for the low-temperature reinforcing steel bar comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.05 to 0.15 percent of C, 0.15 to 0.40 percent of Si, 1.40 to 1.60 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of S, 0.50 to 2.00 percent of Ni, 0.10 to 0.80 percent of Cu, 0.015 to 0.050 percent of Nb and the balance of Fe and impurity elements. The rolling process of the steel for the low-temperature reinforcing steel bar comprises the following steps of: smelting steel in a converter, an electric-arc furnace or other smelting furnaces; performing external refining; performing continuous casting; rolling and forming on a continuous bar mill, wherein the parameters of the rolling process are as follows: steel billets are heated to 1,180 to 1,250 DEG C, the initial rolling temperature is 950 to 1,050 DEG C, and the finishing rolling temperature is 950 to 1,100 DEG C; and performing water passing and cooling after rolling, wherein the cooling bed feeding temperature is 500 to 650 DEG C. According to the steel for the low-temperature reinforcing steel bar and the low-temperature reinforcing steel bar products produced by the rolling process of the steel, low-temperature building engineering reinforced concrete structures such as LNG and the like can resist the low temperature of -165 DEG C, and the steel for the low-temperature reinforcing steel bar has good low-temperature resistance and is safe and reliable.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Technological process for molten steel secondary refining dephosphorization to produce ultra-low phosphorus steel
The invention relates to a process for controlling phosphor in producing an ultra-low phosphorus steel by a microalloy steel, a high carbon steel and a special steel, in particular to a process method for producing the ultra-low phosphorus steel by refining and dephosphorization outside a molten steel furnace. The method comprises: (1) a step of tapping in a converter, during which, a tapping temperature is between 1550 and 1660 DEG C; a phosphor content is lower than 0.02 percent in tapping; and steel is tapped by adopting the treatment of non-deoxidization and slag stopping; (2) a step of primary dephosphorization, during which, a dephosphorization fusing agent is added into a steel ladle along the steel flow when the steel is tapped in the converter; and an adding amount of the dephosphorization fusing agent is between 5 and 20 kg / t; (3) a step of deep dephosphorization, during which, cored wire is fed to a steel liquid by adopting a wire feeding process; (4) a step of slag skimming: firstly, slag is skimmed; and secondly, a steel ladle covering agent is added; (5) a step of heating and stirring, during which, the steel liquid is heated and stirred in a refining furnace, and a heating temperature of the steel liquid is controlled to be between 1, 580 and 1, 620 DEG C; (6) the steel liquid is subjected to the treatment of deoxidization and alloying refining; and (7) a step of continuous casting: the continuous casting adopts whole-process protection, casting and rephosphoration control. The process method has high and stable dephosphorization efficiency and short dephosphorization time till the phosphor content is lower than 0.0030 percent.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Microalloying steel for ultra-high-strength sucker rod
InactiveCN101307413AImprove strong plasticityImprove organizationChemical compositionMicroalloyed steel
The invention relates to a Nb microalloyed steel for an ultrahigh strength sucker rod. The sucker rod made of steel is suitable for a heavy oil well, a deep well, a large pump strong exploitation well, etc, and is a special type oil rod urgently needed for oil fields in China. The steel comprises the following chemical compositions in percentage by weight: 0.12 to 0.20 percent of C, 0.50 to 1.60 percent of Si, 0.90 to 1.60 percent of Mn, 0.90 to 2.00 percent of Cr, less than or equal to 0.20 percent of Mo, less than or equal to 0.20 percent of Ni, 0.035 to 0.055 percent of Nb, 0.010 to 0.030 percent of Ti, less than or equal to 0.050 percent of V, 0.0010 to 0.0020 percent of B, less than or equal to 0.025 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.020 percent of S and the balance being Fe. The tensile strength of rolled steel is high than 965 MPa; the minification of a plastic surface is higher than 50 percent; and the specific elongation delta200 of the plastic surface is more than 10 percent. The Nb microalloyed steel is suitable for manufacturing the sucker rod for an overweight loaded oil pumping field and has good fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance and economy.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Extremely-thick high-strength high-toughness seabed pipeline steel for ultra-deep sea and manufacturing method of extremely-thick high-strength high-toughness seabed pipeline steel
The invention discloses extremely-thick high-strength high-toughness seabed pipeline steel for ultra-deep sea. The extremely-thick high-strength high-toughness seabed pipeline steel for ultra-deep sea is prepared from the following components: 0.020-0.050% of C, not greater than 0.10% of Si, 1.00-1.50% of Mn, not greater than 0.010% of P, not greater than 0.0010% of S, 0.10-0.30% of Cu, 0.10-0.25% of Cr, 0.31-0.50% of Ni, not greater than 0.15% of Mo, 0.030-0.065% of Nb, 0.015-0.040% of V, 0.010-0.025% of Ti, 0.010-0.050% of Al, not greater than 0.008% of N, and the balance of Fe. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the extremely-thick high-strength high-toughness seabed pipeline steel for ultra-deep sea. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: 1) casting blank; 2) roughly rolling; 3) finely rolling; 4) cooling; and 5) relaxing. The extremely-thick high-strength high-toughness seabed pipeline steel for ultra-deep sea disclosed by the invention has characteristics of high strength and excellent low-temperature toughness, and can be widely applied to the microalloyed steel manufacturing field.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Wide and thick superfine-grain hot-rolled plate and method for producing same
InactiveCN1952197AIncrease temperatureIncrease spray coolingRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsUltra fineCooling capacity
The invention discloses a generous specification ultra-fine grain hot rolling plate and its production methods. Its chemical composition (by weight percentage) is: C:0.12-0.18%,Si:0.12-0.25%,Mn: 0.70-1.30%,P:<=0.02%,S:<=0.015%, and Fe as the rest and inevitable impurities, plate thickness 8~14mm. In the invention through raising appropriately the mill inlet temperature, increasing the cooling capacity of the finishing mill , allocating the deflection of each finishing mill pass, to make it process in the non-recrystallization area of the austenite; rapid cooling after rolling and reeling at a low temperature, to obtain ultra-fined ferrite and multiphase of bainite, ferrite grain size3-6 mum, the mechanical properties of yield strength up to 400Mpa, over 520Mpa tensile strength, specific elongation over 28%. The invention can save alloy sources and bring great economic and social benefits for enterprises as there are no special steel alloy elements in the steel to substitute micro-alloyed steel with the same grade.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Method for producing titanium-microalloyed steel based on completely endless thin-slab continuous casting and continuous rolling process
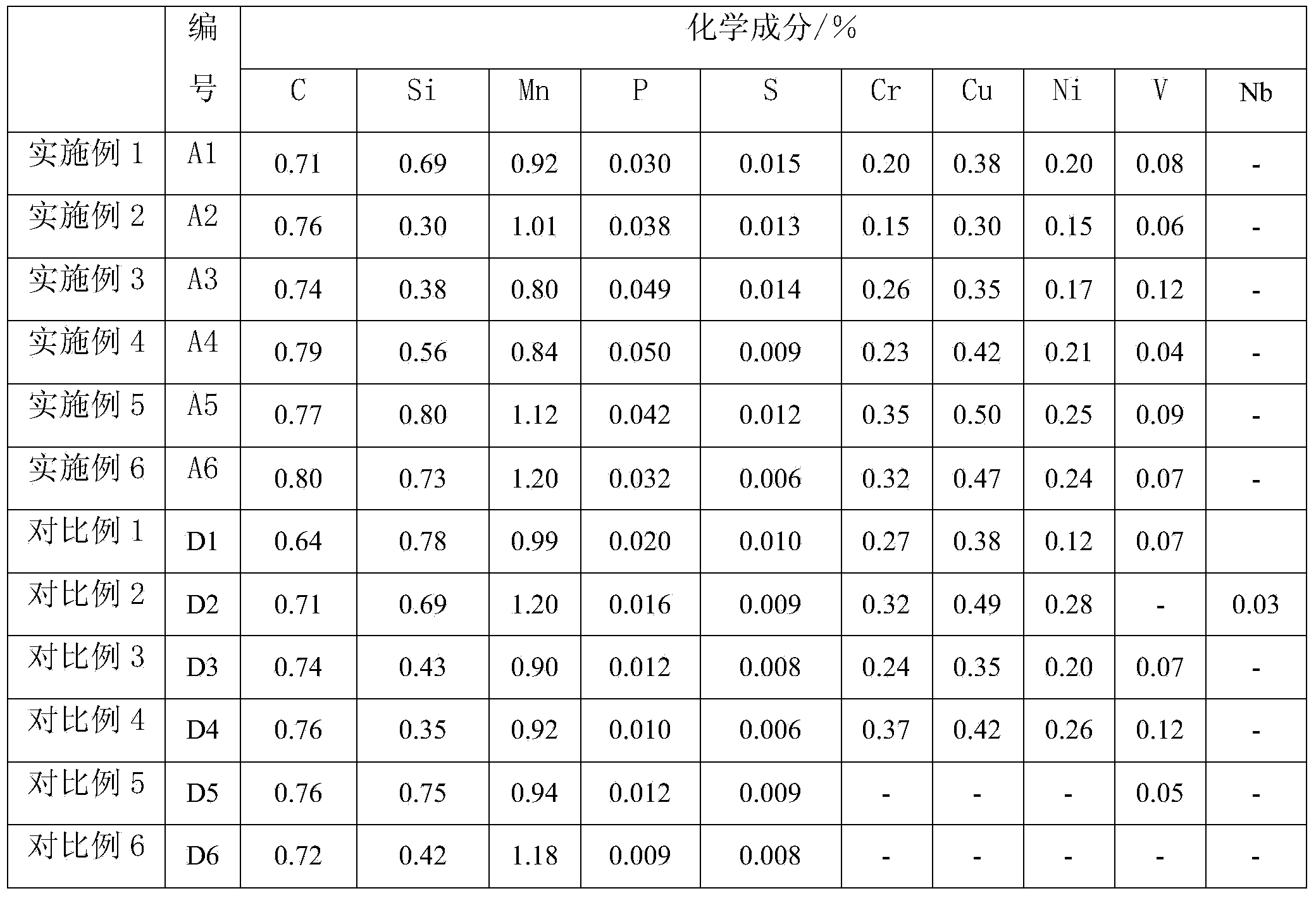
The invention provides a method for producing titanium-microalloyed steel based on completely endless thin-slab continuous casting and continuous rolling process. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting raw materials which comprise 0.04-0.10% of C, 0.10-0.50% of Si, 0.60-1.20% of Mn, 0.020-0.040% of Al, 0.010-0.040% of Ti, less than or equal to 0.01% of S, less than or equal to 0.025% of P, less than or equal to 0.005% of N and the balance being an iron element according to the mass percentage; carrying out converter smelting and LF (ladle furnace) smelting on the raw materials in sequence; and carrying out completely endless thin-slab continuous casting and continuous rolling on molten steel formed through LF smelting to produce hot rolled strip steel with different thicknesses, wherein in the completely endless thin-slab continuous casting and continuous rolling production line, the inlet temperature of rough rolling is greater than or equal to 900 DEG C, the outlet temperature of an induction heating furnace is 1100-1180 DEG C, the outlet temperature of finish rolling is 830 DEG C-900 DEG C, and the rolling temperature is 580-640 DEG C. The method solves the problems of high cost, high energy consumption and the like existing in a traditional technological method for producing the titanium-microalloyed steel and achieves the purposes of energy conservation, environmental protection and cost reduction.
Owner:RIZHAO STEEL HLDG GROUP
Marine environment corrosion-resistant steel rail
ActiveCN104060065AGood mechanical propertiesReduce corrosion rateTransportation capacityRoom temperature
The invention relates to a steel rail material, and in particular relates to a marine environment corrosion-resistant steel rail. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a marine environment corrosion-resistant steel rail. The marine environment corrosion-resistant steel rail is prepared by adopting a heat treatment method comprising the following steps: performing accelerated cooling on the steel rail which is subjected to hot rolling and is positioned in an austenitic phase area at a cooling speed of 2-5 DEG C / s; stopping accelerated cooling until the temperature of a rail head tread is reduced to be less than 480 DEG C, and air-cooling to room temperature to obtain a steel rail finished product, wherein a microscopic structure of the steel rail finished product is a pearlite consisting of lamellar ferrites and cementite alternately distributed among the lamellar ferrites; the separation distance among pearlite sheets is not more than 120nm; the tensile strength of the steel rail finished product is more than or equal to 1200MPa, and the elongation percentage of the steel rail finished product is more than or equal to 10%. The steel rail disclosed by the invention is capable of resisting marine environment corrosion, has a corrosion rate of less than 1 / 2 of that of carbon and ordinary microalloyed steel rails under equal conditions in a marine environment, and is suitable for application in heavy haul railways with high transportation capacity and high axle load in coastal regions.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Production method of microalloyed steel for high heat input welding
The invention discloses a production method of microalloyed steel for high heat input welding and belongs to the technical field of production of microalloyed steel. The production method of the microalloyed steel for high heat input welding comprises the steps of converter steelmaking, and ladle furnace (LF) or VD furnace refining and rolling, specifically, before molten steel is discharged after LF or VD furnace refining, oxygen is confirmed, the O in the molten steel is controlled to be 20-45 PPm, then AlMg alloy core-spun wires are injected, the wire injection value is controlled to be 0.10-1.65 m / t, the wire injection speed is controlled to be 2.5-3 m / s, argon stirring is conducted for 5-7 minutes in the wire injection process, and argon weak stirring is conducted for 1-2 minutes after the wires are injected. By adoption of the method, the low-temperature impact performance of a steel plate and a welding fusion line part can be effectively improved and enhanced, the content of precious alloy such as Ni, Nb and V in the microalloyed steel can be reduced, the production cost of the microalloyed steel can be reduced by 10-30 yuan per ton, and the economic benefits are remarkable.
Owner:MAANSHAN XINGDA METALLURGICAL NEW MATERIAL
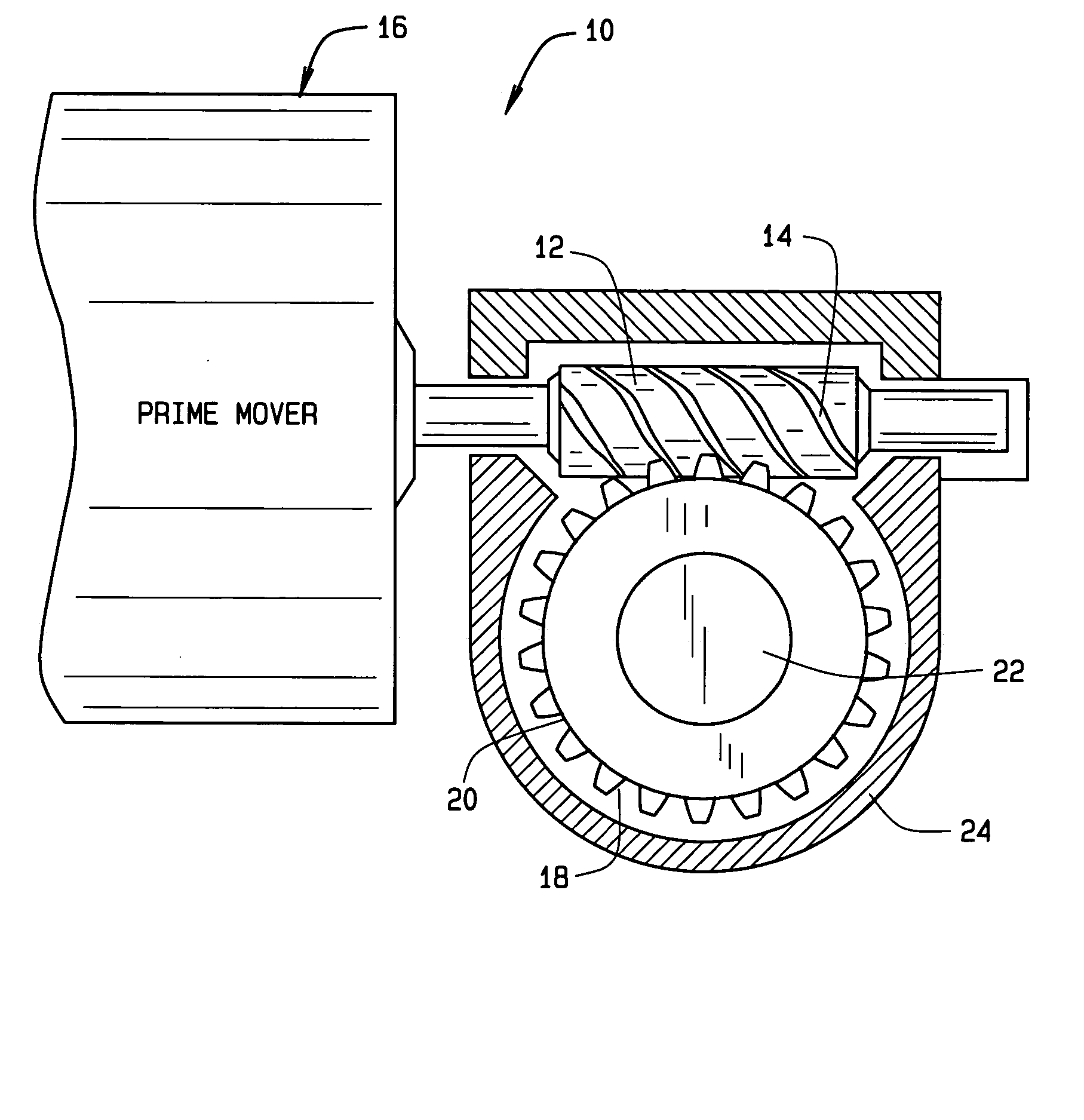
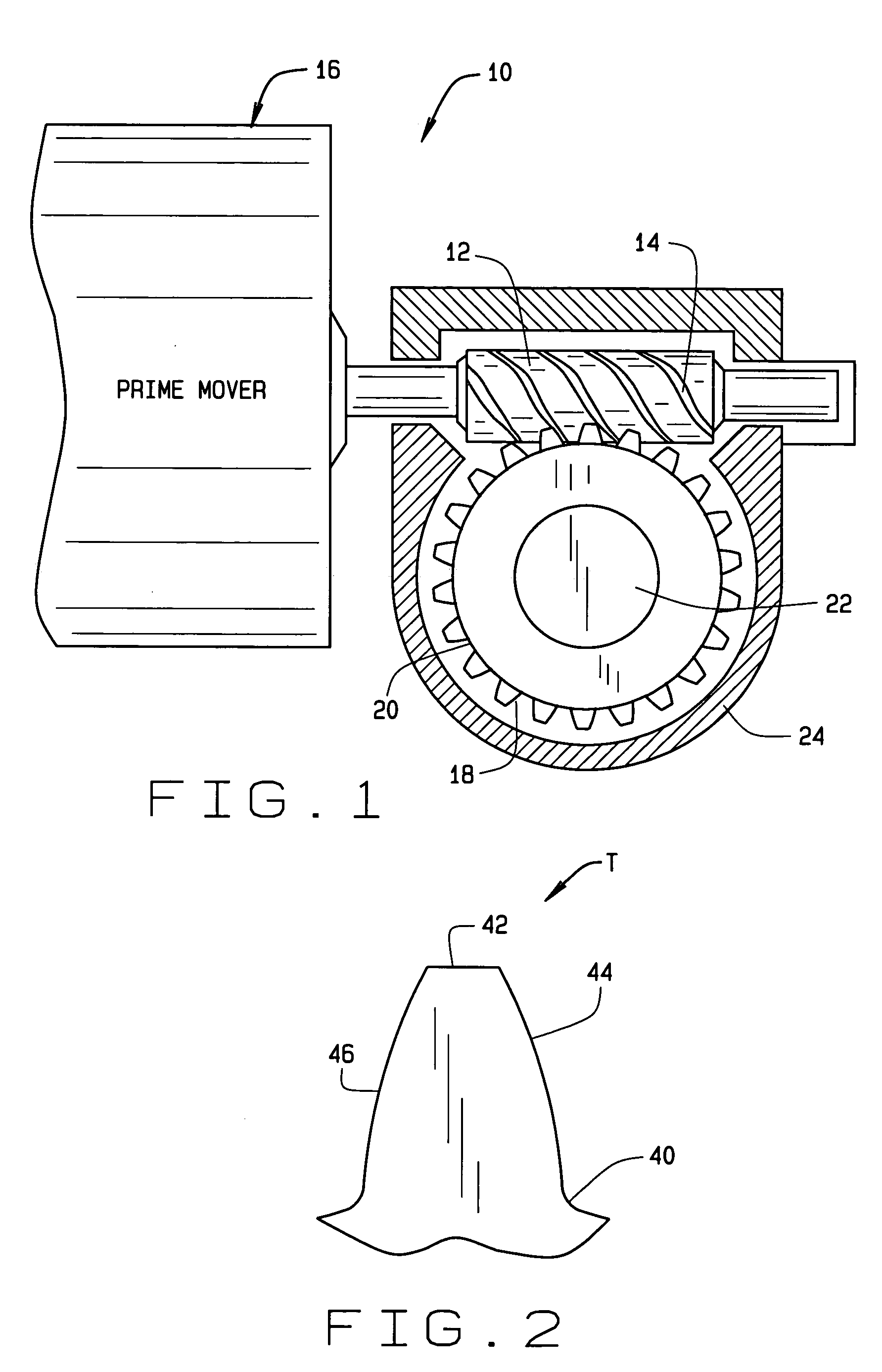
Worm gear assembly having improved physical properties and method of making same
InactiveUS20050274215A1Improve propertiesHigh levelToothed gearingsSolid state diffusion coatingSilicon matrixPhysical property
The ability of a worm assembly to resist adhesive and / or abrasive wear, hertzian contact fatigue, and bending fatigue are enhanced by selecting a worm shaft produced from a hardened steel which will maintain the tooth geometry of the worm tooth during service; selecting a worm gear made from a work-hardening metal (such as austenitic steel, a microalloyed steel, wrought steel, compacted metal powder, or cast iron); imparting a finish to the worm and / or worm gear and / or applying a tribological coating containing metal carbides dispersed in an amorphous hydrocarbon or silicon matrix to the worm and / or worm gear.
Owner:THE TIMKEN CO
Hot-rolled flat plate of large-wall thickness deep-sea pipe steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a hot-rolled flat plate of large-wall thickness deep-sea pipe steel and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of low-carbon microalloyed steel. The hot-rolled flat plate comprises, by weight, 0.025-0.045% of C, 0.10-0.35% of Si, 1.10-1.40% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, less than or equal to 0.003% of S, 0.04-0.07% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.06% of V, 0.010-0.020% of Ti, 0.15-0.40% of Ni, less than or equal to 0.20% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.08% of Mo, 0.010-0.040% of Al and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities, wherein a ratio of Al / N is greater than or equal to 2. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of blast furnace molten iron collection, pre-desulphurization of blast furnace molten iron, smelting by a converter, LF+RH refining, plate blank continuous casting, plate blank heating, rolling by 4300 rolling mill, ACC fast-cooling, stack cooling, sampling and examination, and warehousing and transportation. The hot-rolled flat plate has stable mechanical property indexes, good plasticity-toughness matching and excellent corrosion resistance. The hot-rolled flat plate subjected to UOE molding pipe-preparation has performances reaching to an X70 level.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO SHOUQIN METAL MATERIAL +1
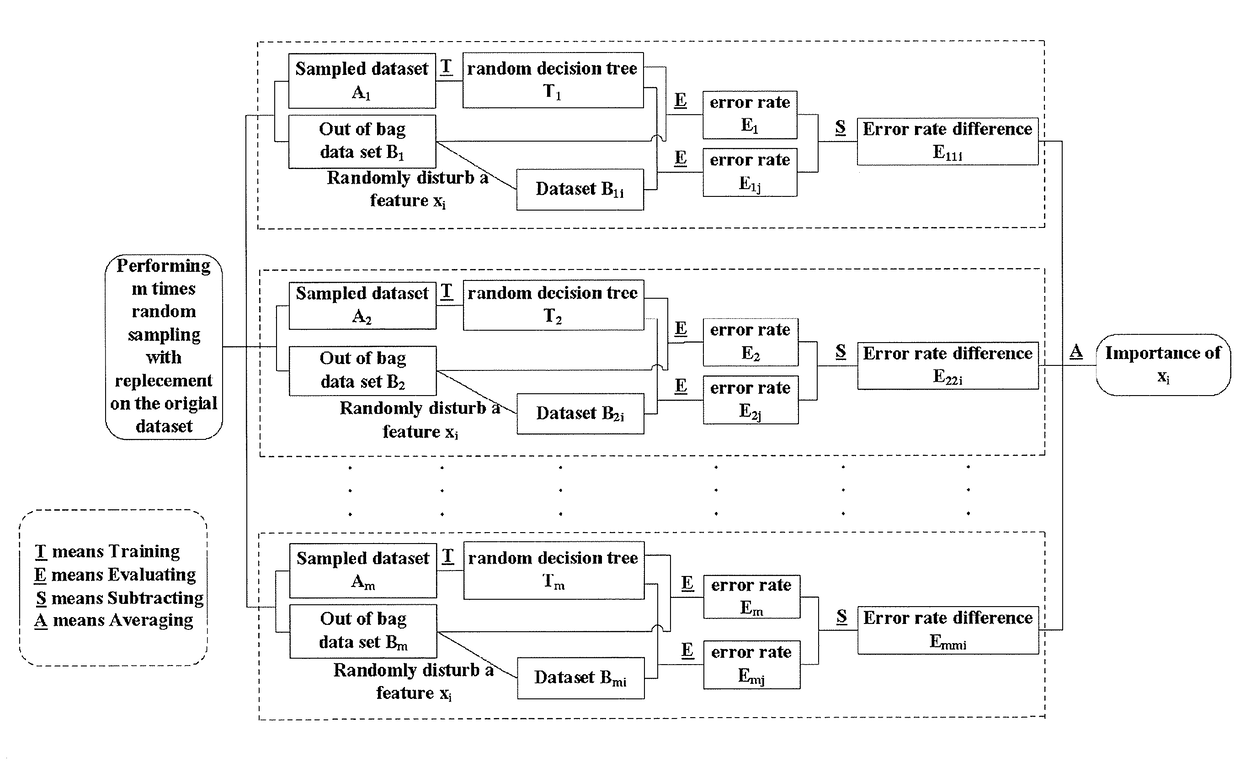
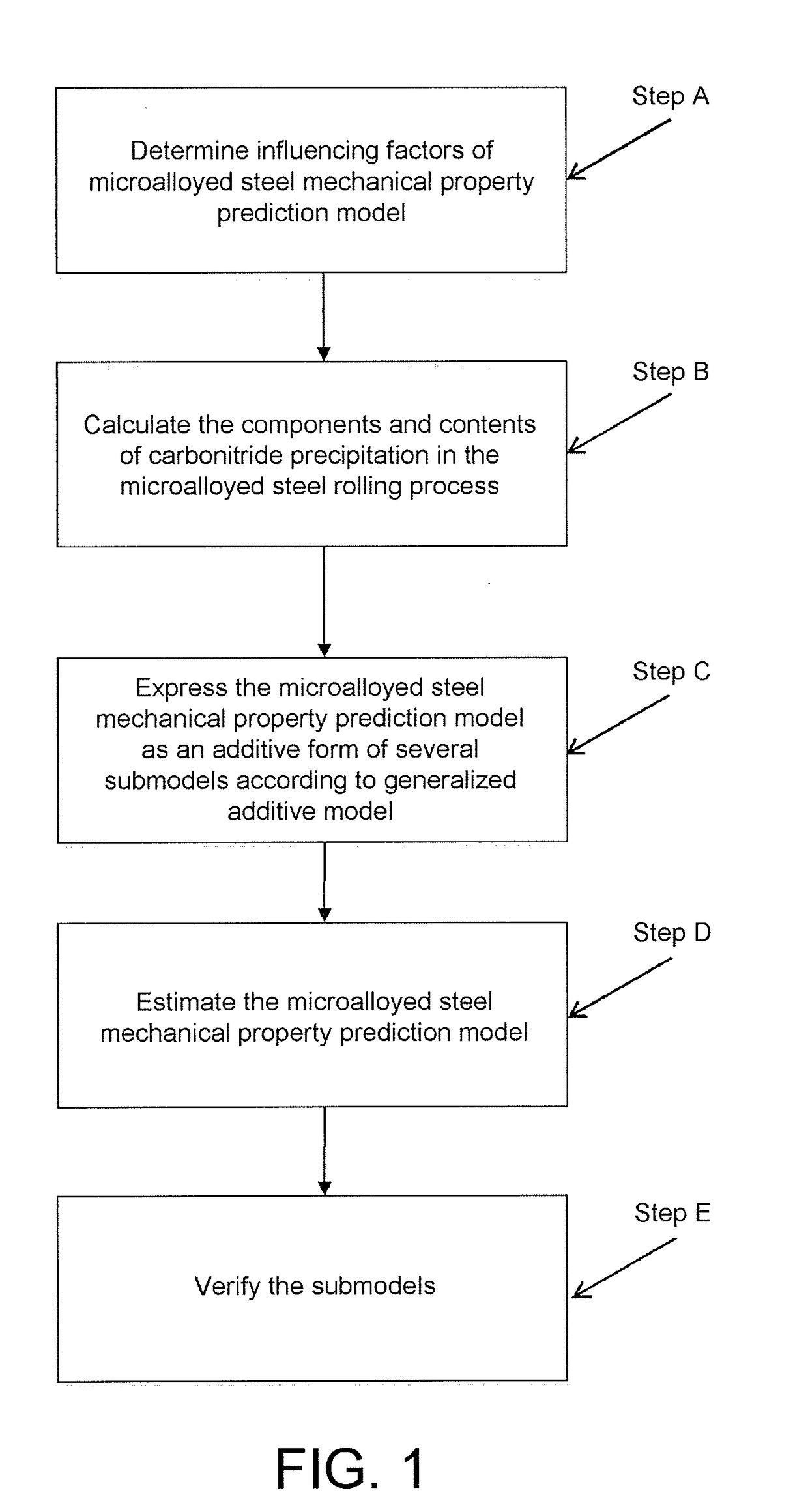
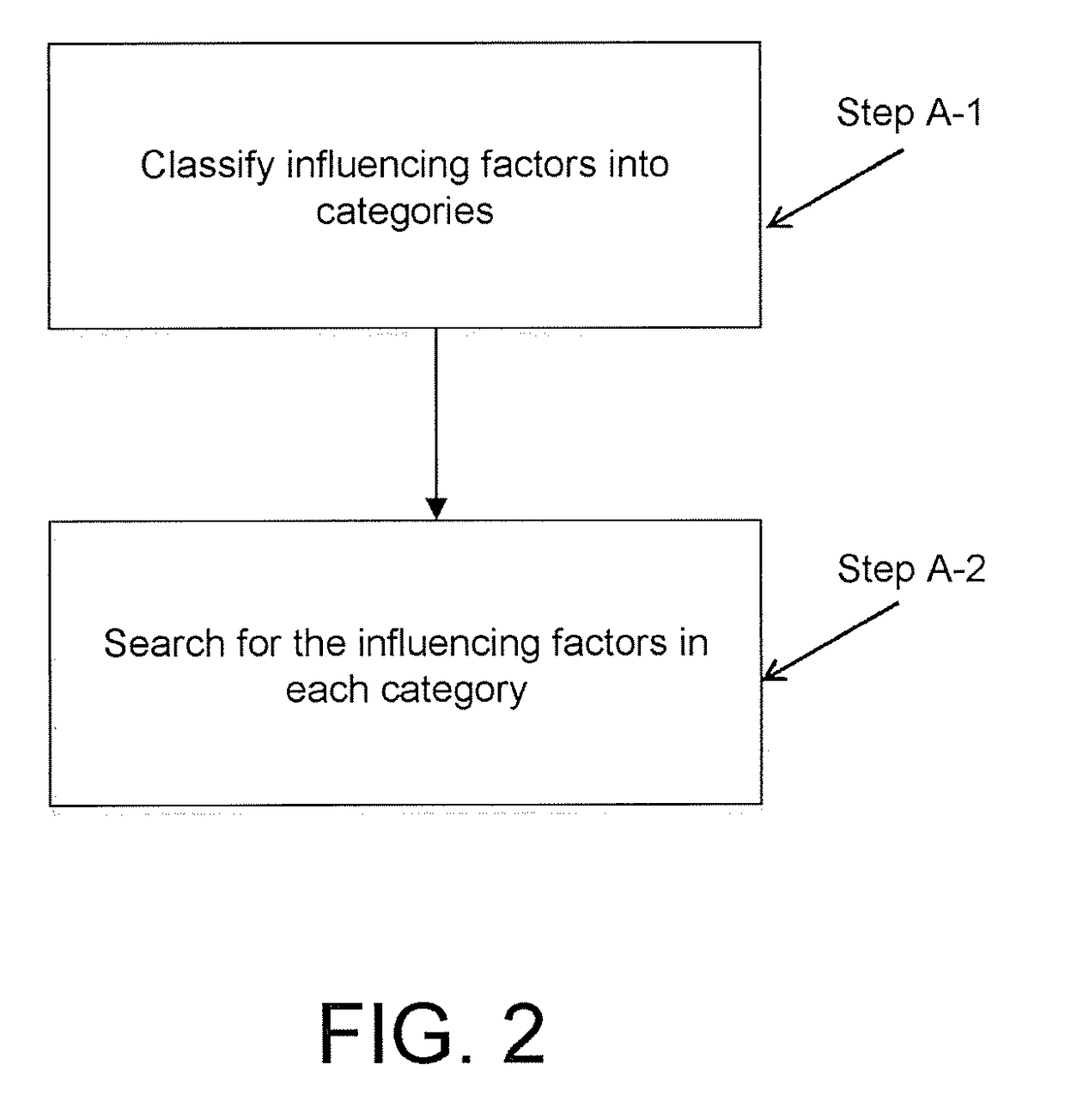
Microalloyed steel mechanical property prediction method based on globally additive model
ActiveUS20180260717A1Improve reliabilityStrong extensionMathematical modelsDesign optimisation/simulationAdditive modelGeneralized linear model
The present invention provides a microalloyed steel mechanical property prediction method based on globally additive model, including the following steps: determining some influencing factors of the microalloyed steel mechanical property prediction model; calculating the components and contents of carbonitride precipitation in a microalloyed steel rolling process; expressing the microalloyed steel mechanical property prediction model as an additive form of several submodels according to generalized additive model; estimating the microalloyed steel mechanical property prediction model; and verifying reliability of the submodels. The microalloyed steel property prediction models obtained in the foregoing solution have advantages such as high prediction precision and a wide adaptation range, and may be used for design of new products and steel grade component optimization, so as to reduce the quantity of physical tests, shorten the product research and development cycle, and reduce costs.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
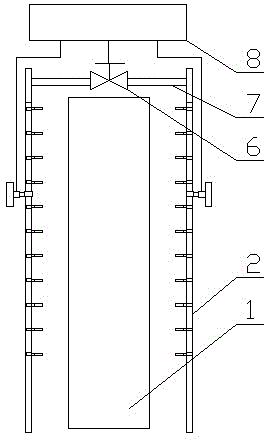
Intensive cooling control device and control method of microalloyed steel continuous casting slab corners in vertical bending segment
The present invention provides an intensive cooling control device and control method of microalloyed steel continuous casting slab corners in a vertical bending segment. The intensive cooling control device of the microalloyed steel continuous casting slab corners in the vertical bending segment comprises two sets of spraying racks installed at two sides of a continuous casting plate vertical bending segment, and is characterized in that each set of spraying racks comprise two spraying racks which are connected by connecting rods, each connecting rod is connected with a spraying rack horizontal driving device, a set of spraying pipes are installed on each spraying rack, the spraying pipes are connected with a water supply pipeline via an electromagnetic valve, and the electromagnetic valve and the horizontal driving devices are connected with a continuous casting machine control system. Intensive cooling of corners of continuous casting slabs of different microalloyed steel types and corresponding section dimensions thereof in the continuous casting machine vertical bending segment can be achieved, microalloy element carbonitride can be effectively suppressed for being precipitated from the casting blank structure grain boundary, and anti-crack capability of the casting blank is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com