Duplex stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of duplex stainless steel and its manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of economical duplex stainless steel and its manufacturing, can solve the problems of high cost and reduced material weldability, and achieve the effects of good weldability, excellent impact toughness, and excellent corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
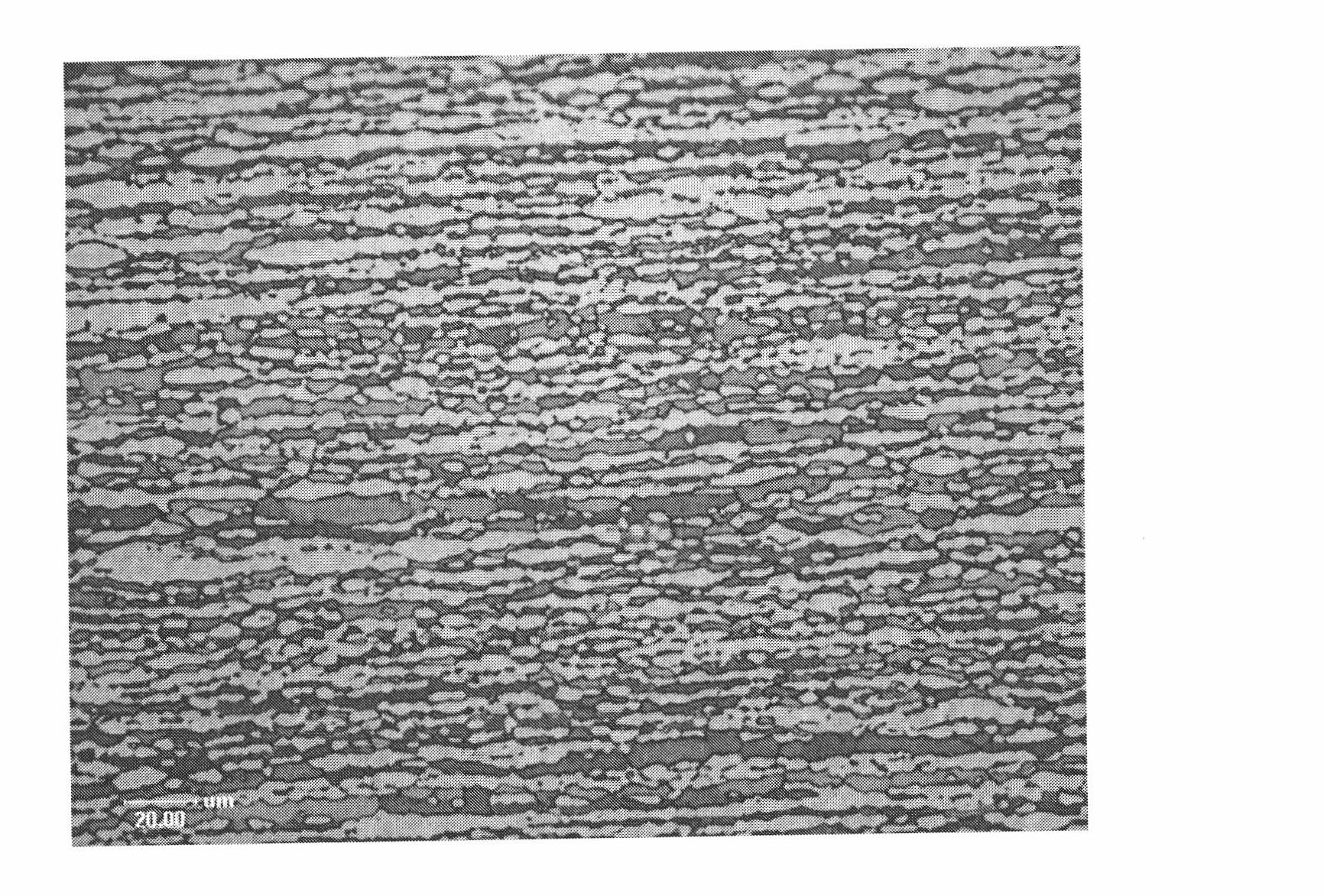
[0075] Experimental example 1: Metallographic structure of alloy
[0076] After grinding and polishing the sample, electrolytic corrosion is carried out. The corrosive agent is 40gKOH+100mlH 2 O, the corrosion current is 0.3-0.8A / cm 2 Finally, the austenite ratio is analyzed by quantitative metallography under a metallographic microscope. The metallographic structure of Example 1 alloy is as figure 1 As shown in the figure, the black structure is ferrite, the white structure is austenite, and the austenite phase accounts for about 53%.
experiment example 2
[0077] Experimental example 2: X-ray diffraction analysis
[0078] The tensile test specimens are manufactured according to JIS-13B standard and stretched to break according to GB / T228-2002 on the MTS-810 tensile machine. 1# is the sample near the fracture, 2# is the sample at the middle of the clamping part and the fracture, and 3# is the sample before stretching. Such as image 3 Shown are the X-ray diffraction analysis of different parts of the material after stretching of the alloy of Example 3. It can be seen from the figure that the austenite peak is higher before stretching, and the closer to the fracture, the austenite peak weakens. This shows that in the process of tensile deformation, part of the austenite undergoes phase transformation and deformed martensite is formed, which makes the amount of austenite less and weakens the diffraction peak of austenite.
experiment example 3
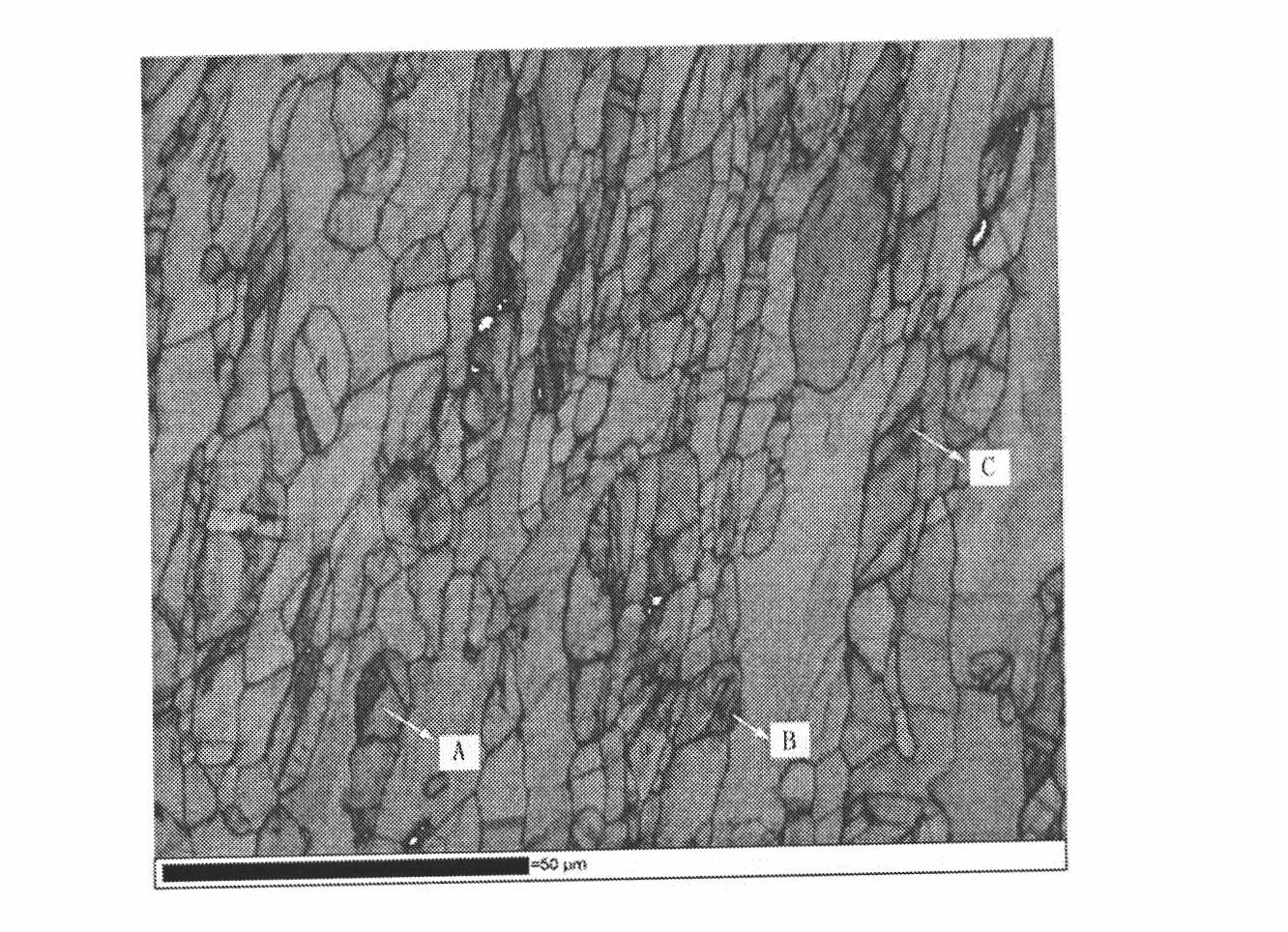
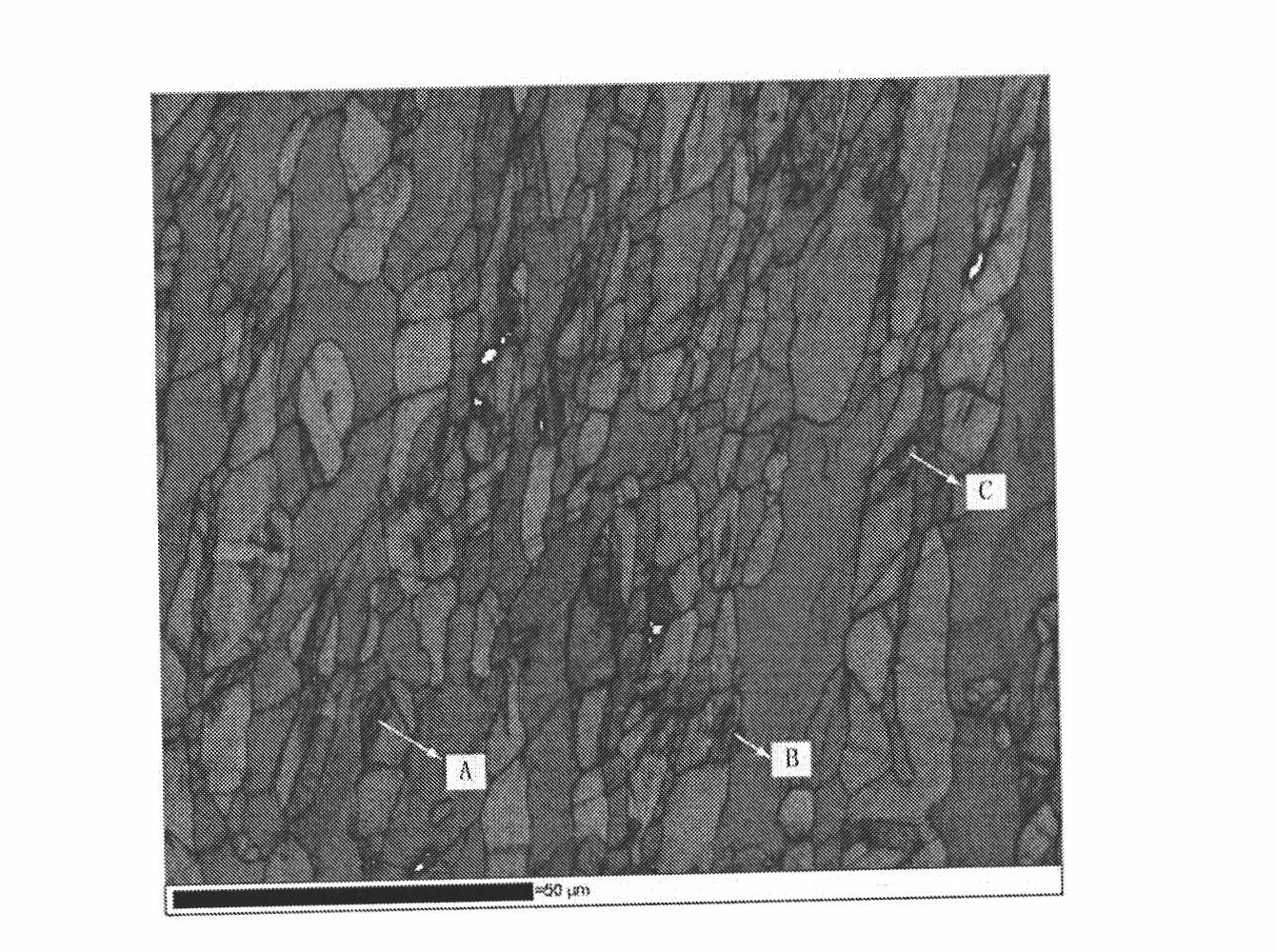
[0079] Experimental example 3: EBSD (electron backscatter diffraction) analysis
[0080] After the alloy was cold deformed by 10%, it was ground, polished and analyzed by EBSD (electron backscatter diffraction). The results of Example 2 are as follows Figure 2a with 2b Shown. among them Figure 2a The image quality (ImageQuality) map. Because the imaging quality reflects the stress distribution and lattice distortion in the tissue, the position with poor imaging quality, that is, the position with darker color, has greater lattice distortion and residual stress. 2b is a phase image (Phase Image), and different colors represent different phases. The blue in the figure is the austenite phase; and because the crystal structure is close to the lattice constant, it is difficult to distinguish between ferrite and martensite, so the red in the figure is ferrite or martensite. Examining the positions A, B, and C in the figure, on the one hand, there are large lattice distortion and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| corrosion potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com