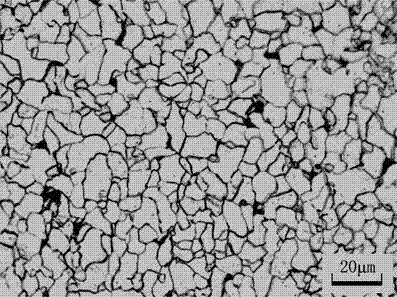
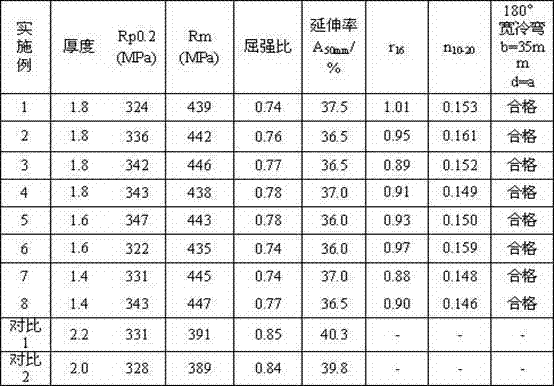
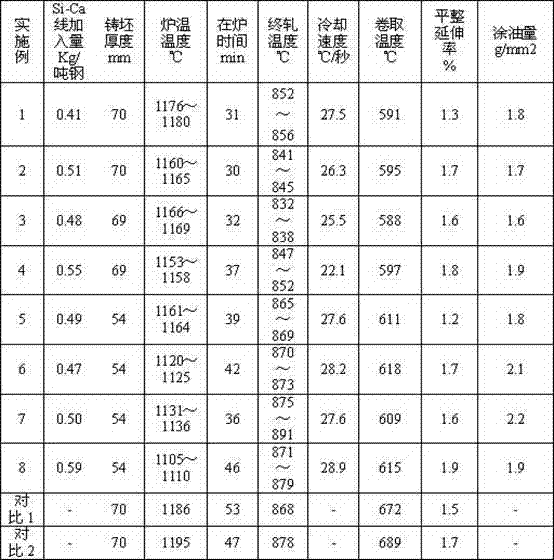
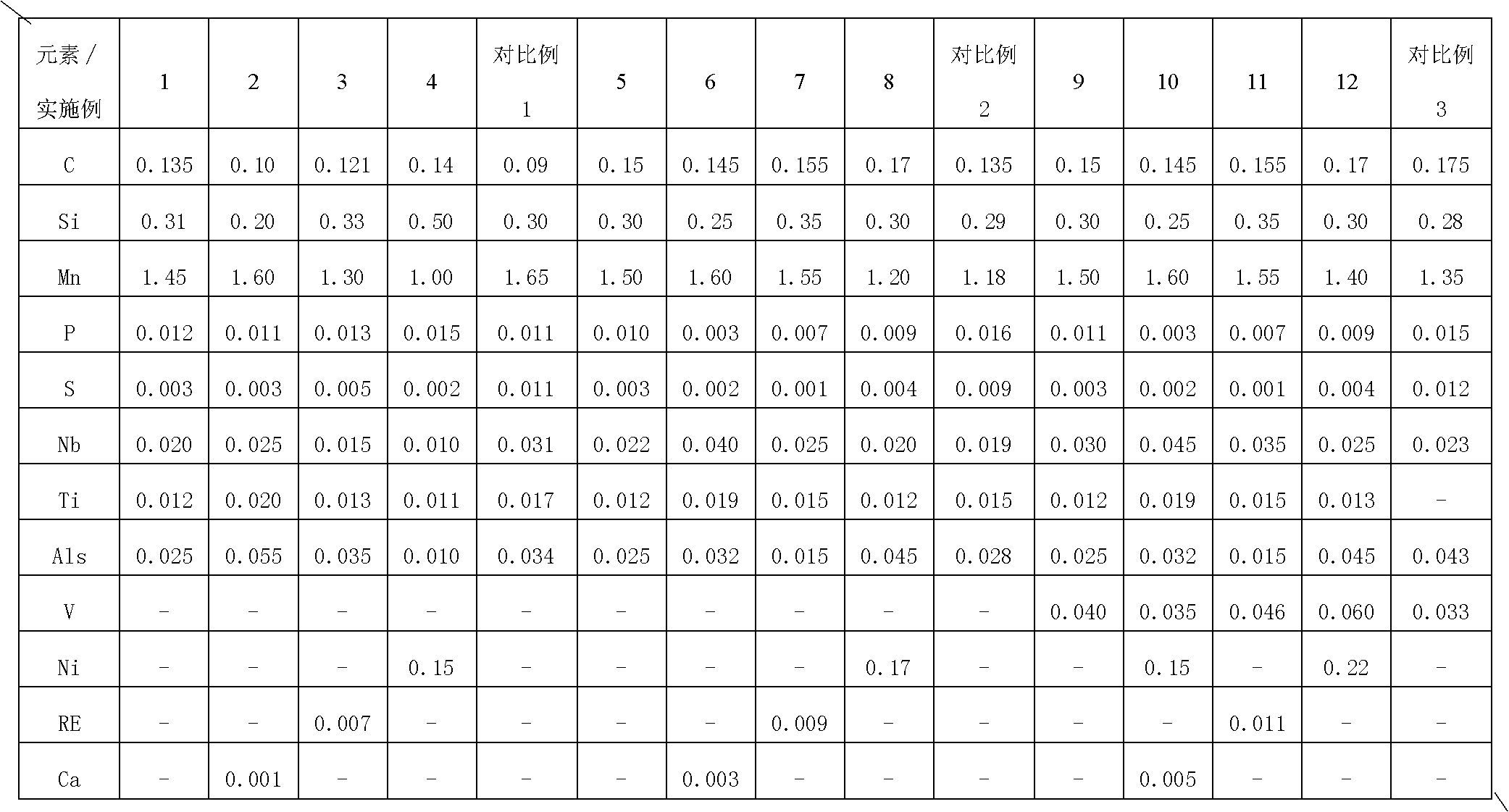
Patents
Literature
996 results about "Ladle furnace" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The ladle furnace is normally used to heat up, to hold and to finish all kinds of metal melts. Heating can be done either by graphite electrodes, plasma torches or by induction coils.
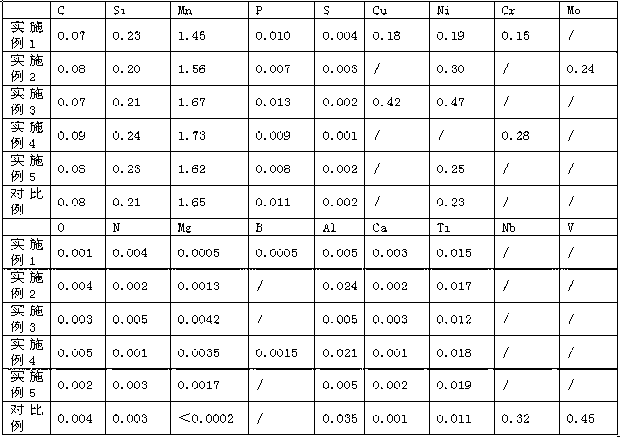
Rare-earth-containing ultrahigh strength collapse-resistant petroleum casing and production method thereof
InactiveCN102251180ALow elemental contentReduce residual stressDrilling rodsProcess efficiency improvementRare earthFlame cutting
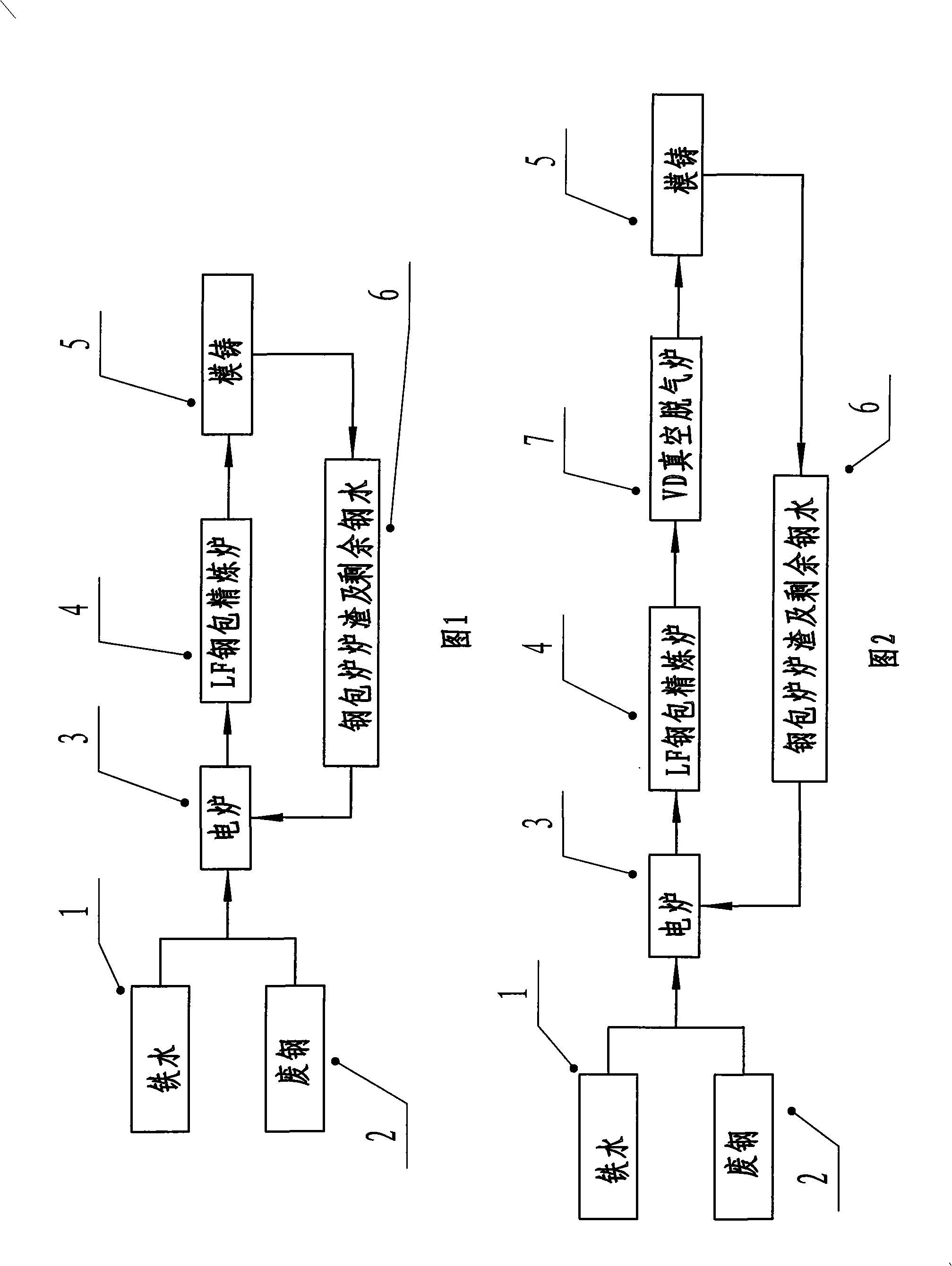
A rare-earth-containing ultrahigh strength collapse-resistant petroleum casing and a production method thereof belong to the technical fields of ferrous metal smelting and metal press working. The petroleum casing comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 90% of blast furnace molten iron and 10% of high quality steel scrap. The casing blank comprises the following chemical components by weight percent: 0.18-0.35% of C, 0.10-0.35% of Si, 0.55-1.10% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.025% of P, less than or equal to 0.020% of S, 0.60-1.10% of Cr, 0.15-0.50% of Mo, 0.01-0.03% of Al, 0.0005-0.0100% of RE ( RE is the mixed rare earth metals of Ce and La and the weight percents of Ce and La are 67% and 33% respectively), less than 0.10% of Cu, less than 0.10% of Ni and the balance of Fe and trace elements. The process flow of the production method is as follows: pretreating molten iron, smelting in a top-bottom blowing converter, refining in a ladle furnace (LF), performing VD vacuum treatment, performing continuous casting of round billets, performing flame cutting, heating the casing blanks, boring, performing continuous rolling, performing sizing and diameter reducing, cooling, performing saw cutting, performing heat treatment, straightening, performing flaw inspection and lathing screw threads. The mechanical properties of the petroleum casing are as follows: the strength is no less than 140000PSI, the residual stress is no more than 80MPa, the impact power is no less than 80J and the grain size is no less than the grade 8. The product is characterized in that the residual stress is low, the content of harmful elements is low, the impact toughness is high, the grains are small, and the product resists extrusion and is difficult to damage.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Production method for reducing and fining the high-carbon chromium bearing steel D-type impurity
ActiveCN1621538AGood workmanshipMeet production needsProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceAlkalinityHigh carbon
The production process with reduced and fined type-D inclusion in high-carbon chromium bearing steel features the four-step metallurgical process including initial smelting of steel liquid in electric furnace, refining in bottom blowing Ar LF ladle furnace, deairing in VD vacuum furnace, and die casting or continuous casting. By means of the comprehensive deoxidation process including pre-deoxidation of aluminum deposition of the steel from electric furnace, deoxidation with Fe-Si powder diffusion slag in LF site and vacuum carbon deoxidation in VD site; and the new refining process including high alkalinity slag desulfurization in LF site, adoption of low alkalinity slag in the VD site and reducing free CaO inside slag, the present invention reaches the aims of reducing and fining type-D inclusion.
Owner:宝武特种冶金有限公司
Method for producing ultra-low-carbon steel
A method for producing ultra-low-carbon steel belongs to steel-making technology field. The process route is: molten iron desulfuration preprocess -converter smelting -RH vacuum process -slab continuous casting. The iron desulfuration preprocess applies blowing magnesium granules for desulfuration; the converter smelting terminal carbon content and oxygen activity of molten steel; applying slag dam operation when tapping without deoxidation; the ladle furnace proceeds operation of top slag modification and temperature controlling; RH vacuum processing to control the maximum vacuum; applying Al for deoxidation when the decarburization is finished, and alloying if the deoxidation is finished and assuring the deep vacuum processing time after the deoxidation; calming the molten steel when the vacuum is finished; applying non-carbon covering agent and non-carbon protection slag in the slab casting process; the continuous casting process uses full protection casting, and the casting process controls a reasonable pulling speed according to slab section. The advantages are: the invention resolves problem of nozzle clogging and improves castability of the ultra-low-carbon steel and implements multi-furnace continuous casting, and the components of carbon, phosphorus, sulphur and nitrogen of the completed product conforms smelting request of the ultra-low-carbon steel.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Low-cost high-purity medium carbon bearing steel for automobile hub and manufacturing method thereof
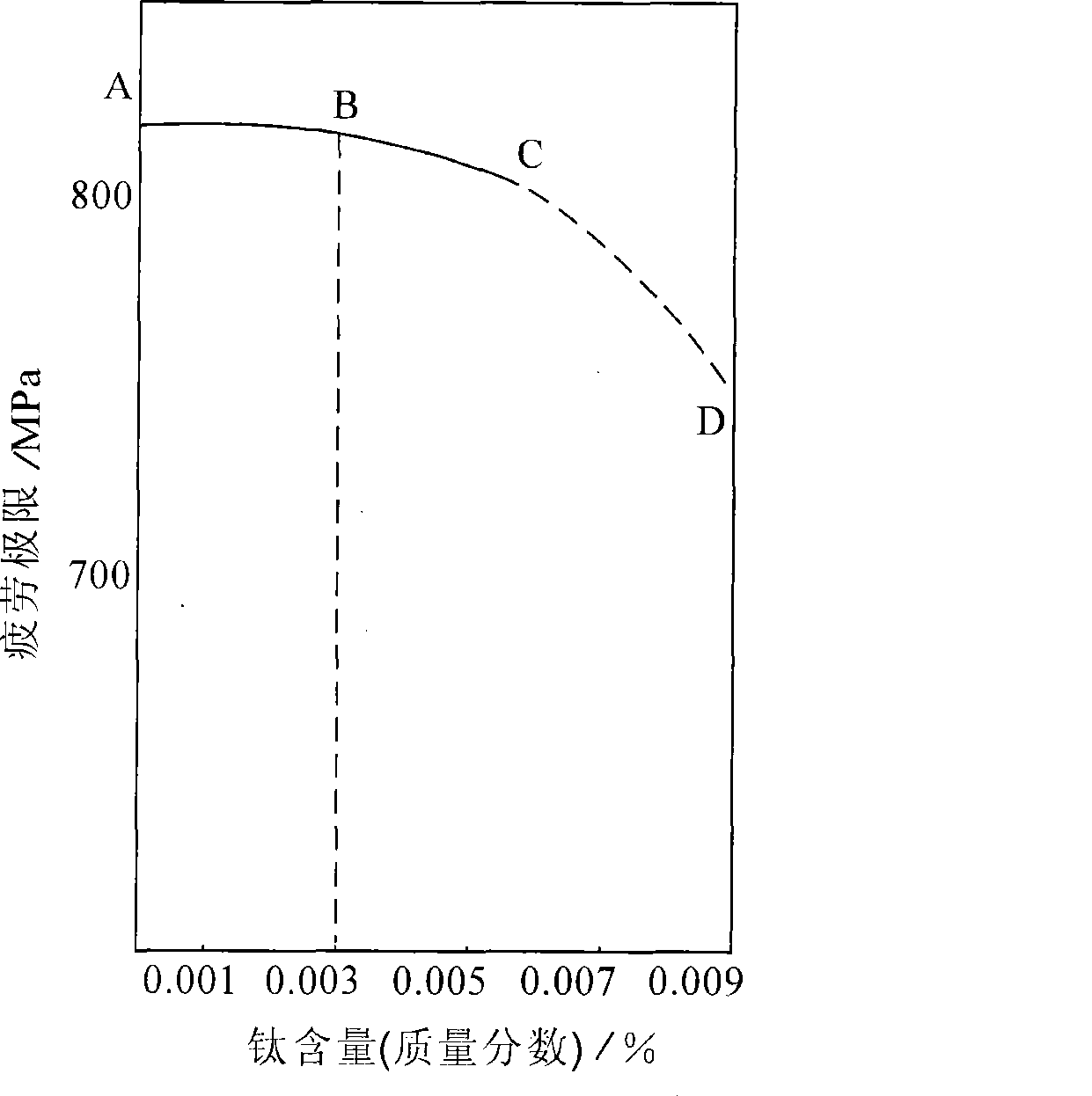
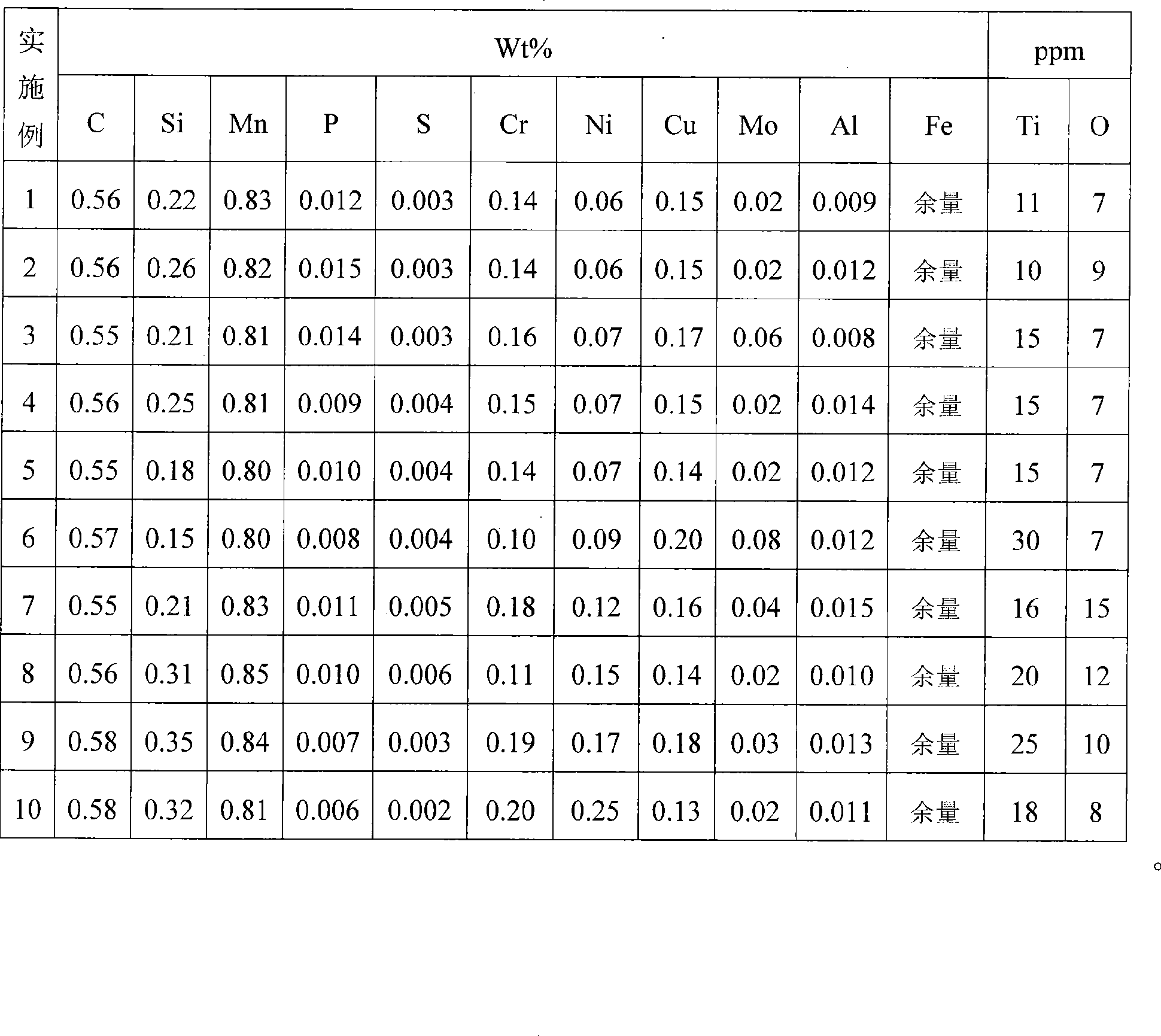
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of low-cost and high-purity medium-carbon bearing steel used for automobile hubs; the manufacturing method comprises the following steps: (a) the mass percentage of the components of the bearing steel is as follows: C: 0.55 percent to 0.58 percent, Si: 0.15 percent to 0.35 percent, Mn: 0.80 percent to 0.85 percent, P: less than or equal to 0.030 percent, S: less than or equal to 0.015 percent, Cr: 0.10 percent to 0.20 percent, Ni: less than or equal to 0.25 percent, Cu: less than or equal to 0.20 percent, Mo: less than or equal to 0.08 percent, Al: 0.008 percent to 0.015 percent, Ti: less than or equal to 30ppm, O: less than or equal to 15ppm, and the rest are Fe and inevitable impurities; (b) smelting, electric furnace initial melting+ ladle furnace refined melting+ vacuum degassing; (c) continuous casting into steel billet; (d) rolling. Compared with the prior art, the technological process has obviously shorter process and lower production cost; the impact resistance, torsion resistance, wear resistance and fatigue endurance of the produced automobile hub bearing are good.
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
Bridge structural steel and production method thereof
ActiveCN102199725ATemperature control deviceProcess efficiency improvementThick plateChemical composition
The invention discloses bridge structure steel and a production method thereof. The production method comprises: pretreating molten iron; smelting in a top and bottom combined blown converter; refining in a ladle furnace (LF); performing Ruhrstahl Heraeus (RH) refining; continuously casting plate blanks; rolling wide and thick plates; and performing normalizing heat treatment. The produced bridge structural steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.11 to 0.16 percent of C, 0.10 to 0.45 percent of Si, 1.35 to 1.70 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.020 percent of P, 0.025 to 0.060 percent of Nb, 0.008 to 0.030 percent of Ti, 0.025 to 0.080 percent of V, 0.10 to 0.50 percent of Ni, 0.015 to 0.060 percent of Als, less than or equal to 40*10<-6> of N, less than or equal to 40*10<-6> of O, less than or equal to 2*10<-6> of H and the balance of iron and inevitable impurities, wherein Als represents Alsol. The lower yield strength of the steel plates produced by the method is not less than 370MPa, the tensile strength of the steel plates is not less than 510MPa, the yield to strength ratio of the steel plates is not more than 0.75, the percentage elongation after fracture of the steel plates is not less than 30 percent, the longitudinal AKv of the steel plates at -40 DEG C is not less than 240J, and the steel plates meet the requirements for manufacturing high-speed multi-track railway bridges and can be promoted to be used in engineering structures such as building, transport and ocean platforms.
Owner:LAIWU STEEL YINSHAN SECTION CO LTD
High-toughness medium-carbon quenched and tempered round steel of grade 120 KSI and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses high-toughness medium-carbon quenched and tempered round steel of the grade 120 KSI. The high-toughness medium-carbon quenched and tempered round steel of the grade 120 KSI comprises, by mass, 0.35%-0.50% of C, 0.15%-0.40% of Si, 0.60%-1.30% of Mn, equal to or less than 0.015% of P, equal to or less than 0.040% of S, 0.75%-1.30% of Cr, 0.15%-0.35% of Mo, equal to or less than 0.25% of Ni, equal to or less than 0.25% of Cu, 0.015%-0.040% of Alt, equal to or less than 0.10% of V, equal to or less than 0.10% of Nb, equal to or less than 0.05% of Ti, equal to or less than 0.008% of N, equal to or less than 0.0010% of B and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurity elements, wherein the content of V, the content of Nb and the content of Ti are not equal to or less than 0.010% at the same time. The round steel with the maximum specification reaching 260 mm is manufactured through Kanbara reactor (KR) pretreatment, basic oxygen furnace (BOF) smelting, ladle furnace (LF) refining, Ruhrstahl Heraeus (RH) vacuum degassing, continuous casting, heating, continuous rolling, and hardening and tempering, so that the requirements for high specifications and toughness are met.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Production of clean high carbon chromic bearing steel
A method for manufacturing high-cleaning and high carbon complex bearing steel includes: 1) choosing charging mixture 2) first steel making molten steel by is greater than or equal to 30ton electric furnace a. smelting furnace burden b. running out foaming slag and adding lime c. alloying when steel tapping with 92% tap and >90% level 3) refining molten steel by steel ladle furnace a. cleaning steel ladle and furnace cleaning b. through bottom blowing argon mixing with 60 min, earlier stage argon blowing intensity 0.4Mpa and later stage 0.3Mpa, material adding amount is less than or equal to 8Kg / ton steel c. precipitating and deoxidizing by two-stage aluminum feeding method, adding crystallized silicon powder, fluorite(content of calcium is greater than or equal to 98%) into slag face, and dispersing deoxidizing 4) vacuum furnace treating a. bottom blowing argon 0.3Mpa, 25min, vacuum content is less than or equal to 140Pa b. bottom blowing argon mixing 15min, 0.1Mpa without materials after treating 5) molten steel mould casting under inactive gas a. ingot moulding temperature 70deg.C, runner brick coating b. pouring speed 5.1ton steel / min of ingot body and mouth. It achieves high yield.
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
800 MPa-grade low-yield-ratio structural steel plate and production method thereof
ActiveCN102011068AGood welding performanceGood low temperature impact propertiesYield ratioHeat treated
The method relates to an 800 MPa-grade low-yield-ratio structural steel plate and a production method thereof. The steel comprises the chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.045 to 0.075 percent of C, 0.30 to 0.55 percent of Si, 1.55 to 1.95 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.0025 percent of S, 0.012 to 0.035 percent of Al, 0.15 to 0.25 percent of Cr, 0.15 to 0.3 percent of Mo, 0.2 to 0.4 percent of Cu, 0.2 to 0.4 percent of Ni, 0.008 to 0.04 percent of Nb, 0.008 to 0.04 percent of V, 0.008 to 0.03 percent of Ti, 0.0008 to 0.0015 percent of B, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The steel is subjected to RH vacuum treatment, ladle furnace (LF) external refining, full protection casting, a thermo mechanical control process (TMCP), and tempering heat treatment to form the steel plate with low yield ratio, high strength and high work hardening rate. The steel plate has the thickness specification of between 10 and 40 mm, the yield strength of more than or equal to 550MPa, the tensile strength of more than or equal to 800 MPa and the yield ratio of less than 0.70, and has excellent low temperature compact performance, cold forming performance and welding performance.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Hardening and tempering high-strength steel plate for wood based panel equipment and production method of tempering high-strength steel plate
The invention relates to a hardening and tempering high-strength steel plate for wood based panel equipment and a production method of the steel plate, and belongs to the field of manufacturing low-alloy high-strength structural steel. The steel plate consists of the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.18 to 0.24 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.50 percent of Si, 0.80 to 1.20 percent of Mn, more than or equal to 0.02 percent of P, more than or equal to 0.01 percent of S, 0.20 to 0.50 percent of Mo, 0.20 to 0.50 percent of Ni, 0.70 to 1.00 percent of Cr, more than or equal to 0.003percent of B, 0.017 to 0.030 percent of Nb, 0.040 to 0.050 percent of V, 0.017 to 0.026 percent of Ti, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The production method of the steel plate comprises the following steps of: electric furnace smelting, vacuum decarburization / vacuum arc decarburization (VD / VOD) furnace vacuum decarburization, ladle furnace (LF) furnace refining, continuous casting (die casting), billet steel (ingot) clearing, heating, plate rolling, hardening and tempering, steel plate checking and polishing, tempering, sampling inspection, and warehousing. The hardening andtempering high-strength steel plate for the wood based panel equipment adopts Cr-Ni-Mo-B system micro-alloy elements for composite strengthening, and acquires good obdurability matching through a reasonable heat treatment process, and simultaneously the welding performance of a thick plate is not reduced.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL +1
550Mpa yield-strength low-carbon bainitic steel for engineering machinery and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a low-carbon bainitic steel for engineering machinery, which is prepared from the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.05-0.10% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 1.50-1.80% of Mn, at most 0.010% of S, at most 0.018% of P, at most 0.10% of Nb, at most 0.10% of Mo, 0.010-0.040% of Ti, 0.0010-0.0030% of B, 0.20-0.50% of Cr, 0.015-0.050% of Al and the balance of Fe and trace impurity. The existing equipment is utilized; molten iron pretreatment, reblowing converter smelting, LF (ladle furnace) refining, RH refining, and plate blank continuous casting are carried out; and the contents of part of elements are adjusted, microalloying treatment, TMCP (thermomechanical rolling process) production, controlled rolling and water cooling are carried out, and no heat treatment is required, thereby obtaining the bainitic steel for engineering machinery, which has the advantages of high strength and favorable low-temperature toughness. The bainitic steel for engineering machinery is widely used in the fields of engineering machinery manufacturing and the like, such as large-size load-bearing steel structures, large-size earth mover, autocranes, excavators, mining machines, hydraulic supports, electric wheel dump trucks, mine cars and the like.
Owner:LAIWU STEEL YINSHAN SECTION CO LTD
Method for smelting ultra-low-carbon steel
InactiveCN101215618ARealize continuous pouringRealize multi-furnace continuous pouringManufacturing convertersSlagSulfur
The invention relates to a process for smelting ultra-low-carbon steel, which comprises melted iron pretreatment desulfuration, converter smelt, LF furnace refining, RH vacuum process and continuous casting procedure in turn. Converter smelt tapping adopts non deoxidization tapping, steel which is tapped off is refined by LF ladle furnace before carried out melt iron vacuum decarburization processing, wherein refining is mainly used to proceed modifying property processing and further desulfuration and heating for top slag of melted iron, and the melted iron is reinforced with positive oxygen blowing decarburization after shifted into a RH vacuum container. The process can control carbon, nitrogen and sulfur in steel to preset objects which are required, and has excellent castability when a casting machine casted, thereby realizing casting by several furnaces.
Owner:BENGANG STEEL PLATES
Sheet-billet produced hot-rolled pickled steel with thickness of 1.8mm or lower for automobile and production method thereof
InactiveCN102787273ALow yield ratioImprove surface qualityWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsCar manufacturingHigh pressure water
The invention relates to a sheet-billet produced hot-rolled pickled steel with thickness of 1.8mm or lower for an automobile, which comprises the following chemical components by weight: 0.04-0.07% of C, 0.10-0.30% of Si, 0.60-1.30% of Mn, 0.025% of P or less, 0.012% of S, 0.02-0.04% of Ti and 0.010-0.030% of Als. The preparation method of the sheet-billet produced hot-rolled pickled steel with thickness of 1.8mm or lower comprises the following steps: desulphurizing molten iron, smelting by a converter, alloying, treating by a ladle furnace, casting and rolling continuously, dephosphorizing high-pressure water by controlling the pressure at 25-35Mpa, controlling rolling, cooling by laminar flow, curling, pickling by acid, levelling by controlling the extension rate at 2% or lower, and finishing by adopting static oil removal. The produced thin hot-rolled pickled steel for the automobile, which has the tensile strength of 400MPa or higher and the thickness of 1.8 mm or lower, has the characteristics of low yield ratio, high surface quality, short production cycle and low cost, achieve the match of high strength and good stamping performance and can replace the cold-rolled high-strength steel to manufacture the automobile.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Quake-proof construction steel with lamellar tearing resistance and excellent performance and production method thereof
InactiveCN101994058AGood welding performanceSimplify welding production processProof constructionSheet steel
The invention relates to quake-proof construction steel with lamellar tearing resistance and excellent performance and a production method thereof. The steel is suitable for steel plates of which the thicknesses are between 20 and 100 millimeters and comprises the following chemical components: less than or equal to 0.015 percent of C, less than or equal to 0.015 percent of Si, less than or equal to 0.015 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.015 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of S, 0.02 to 0.04 percent of Nb, 0.005 to 0.020 percent of Ti, 0.010 to 0.060 percent of Als and the balance of Fe. The method comprises the following steps of: performing the pretreatment of molten iron; performing desulfuration treatment; controlling target components of a smelting terminal point, wherein the target components comprise 0.05 to 0.07 percent of [C] and less than or equal to 0.015 percent of [P]; refining through a ladle furnace, and feeding aluminum wires and blasting argon; performing relative humidity (RH) vacuum treatment, and introducing the argon before the treatment; adding SiCa wires; casting continuously and performing the pouring of full-process protection; heating casting blanks; performing rough rolling; performing precision rolling; and cooling. The steel of the invention has the excellent quake-proof performance (ReH / Rm is less than or equal to 0.77); and the contractibility rate of a cross section in the full-thickness direction is between 40 and 70 percent, so the steel meets the requirements of key stressed points of major constructions such as steel structure work and the like fully.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Control method for surface decarburization and ferrite distribution of steel disc bar of spring
ActiveCN103045935AReduce manufacturing costReduce intensityManufacturing convertersWire rodSpring steel
The invention relates to a control method for surface decarburization and ferrite distribution of a steel disc bar of a spring. The method comprises the steps of raw material preparation,smelting in a converter, LF (Ladle Furnace), VD (Vacuum Degassing) treatment, continuously casting, flaw detection and coping, heating, rolling, spinning, wind cooling by stelmor, intensively coiling, detecting and putting in a storeroom, rolling wire rods to be 8-18 mm in diameter, ensuring that the tensile strength (ob) is 950-1100MPa and the percentage reduction of area (Z) is 30-50 percent after aging treatment, and organizationally adding a small amount of dispersedly distributed into sorbite. Compare with other processes, the strength is decreased to a certain extent, the reduction of area is improved to a certain extent, the variation range of the strength and reduction of area is smaller, the performance is more stable, pulling and reeding operation is facilitated, the production cost of spring steel is lowered, and the service life of the spring steel is prolonged.
Owner:TIANJIN IRON & STEEL GRP
A non-modulated production process of plastic mold steel thick plate
The invention discloses a production technology of a non-modulated plastic die steel thick plate. The production technology comprises the following steps: converter smelting and ladle furnace (LF) and Ruhrstahl Heraeus (RH) refining are adopted to pour a continuous cast billet; the heating temperature is 1150-1200 DEG C, the precision rolling temperature is 900-950 DEG C, the finish rolling temperature is 860-900 DEG C; the cooling control of the steel plate is performed after the steel plate is rolled, the phase transformation strengthening and the precipitation strengthening of the microalloyed carbon nitride are utilized to ensure that when the section of the steel plate is not modulated, the structure and performance are uniform along the section, the plastic die steel of which section hardness is 300-340 is obtained; the rolled steel plate is tempered to eliminate the stress and avoid sawing crack, the hardness of the steel plate is uniform after tempering, and the section has granular bainite structure. In the production technology, the alloy component is controlled, Ni is not added, a small amount of Mo, B and V are added and the Cr content is increased properly, thus the steel plate has higher hardenability; and the cooling control of the rolled steel plate is performed to ensure that the large-section steel plate has bainite structure. The production technology is suitable for the production of the non-modulated plastic die steel thick plate, which is prepared from the 320mm continuous cast billet and of which thickness is less than 120mm.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Duplex stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to duplex stainless steel. The duplex stainless steel comprises the following chemical components in percent by weight: 0.01-0.08% of C, 0.2-1.0% of Si, 1.5-3.5% of Mn, 19.0-21.0% of Cr, 1.2-2.8% of Ni, 0.08-0.18% of N, less than or equal to 0.5% of Mo, less than or equal to 1.0% of W, less than or equal to 1.0% of Cu and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities; PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number) is 20-24, the martensitic temperature Md formed by strain induction is 60-130 DEG C. A manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: selecting vacuum induction smelting in an electric furnace, argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) or electric furnace, argon oxygen decarburization (AOD), external refining and LF (Ladle Furnace) smelting; carrying out die casting or continuous casting on molten steel, controlling the superheat degree to be 20-50 DEG C in die casting, matching with fast cooling, preventing nitrogen from escaping, and controlling the overheat degree to be 20-50 DEG C and the plate blank casting speed to be 0.8-2m / min; and putting a die-casting blank or a continuous casting blank into a heating furnace for heating to 1100-1250 DEG C, preserving the heat for 0.5-1.5 hours, processing the die-casting blank or the continuous casting blank on a forging production line or a hot-rolling mill group to the needed thickness, then carrying out annealing at the speed of 0.5-2.5min / mm and the temperature of 1030-1150 DEG C. The obtained duplex stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and TRIP effect.
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
Hot-rolled H-shaped steel for low temperature-resisting structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102021475AImprove low temperature resistanceTemperature control deviceChemical compositionHeating furnace
The invention relates to low temperature-resisting H-shaped steel and a preparation method thereof, wherein the steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.12-0.22 percent of C, 0.10-0.40 percent of Si, 1.1-1.50 percent of Mn, not more than 0.025 percent of P, not more than 0.025 percent of S, 0.02-0.05 percent of Nb and the balance of iron and trace impurities. The preparation method of the low temperature-resisting H-shaped steel comprises the following steps of: desulfurizing, smelting by using a 120-ton top and bottom combined blown converter, refining by using an LF (Ladle Furnace), continuously casting shaped blanks and rolling large H-shaped steel, wherein after the refinement outside the furnace, the oxygen content in molten steel is not more than 10ppm, and in the continuously-casting process, the superheat degree is controlled to be 20-30 DEG C, the specifications of casting blanks are 555*440*90, 750*370*90 and 1024*390*90, the soaking temperature of a heating furnace is 1200-1300DEG C, the initial rolling temperature at the outer side of a flange is 1100-1180 DEG C, the temperature at the center of a web plate is 1100-1170 DEG C, the final rolling temperature at the outer side of the flange is 850-960 DEG C, the temperature at the center of the web plate is 800-880 DEG C, and the H-shaped steel with the specification of H250-H900 isrolled.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Production method for low-alloy medium-thick steel plate
The invention discloses a production method for a low-alloy medium-thick steel plate. The process route comprises the following stages in turn: converter steelmaking, external refining, continuous casting, heating, rolling, and accelerated cooling. Steel comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.15-0.17% of C, 0.20-0.40% of Si, 0.55-0.65% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.020% of P, less than or equal to 0.020% of S, 0.020-0.040% of Al, 0.014-0.016% of Nb, and less than or equal to 0.30% of CEV. The (P+F) micro-structural feature of the traditional Q345D steel plate is maintained by the steel plate; according to the design of the components of the steel plate, the Mn is reduced by 0.9%, no Ni is added and 0.015% of Nb is increased, so that the cost per ton of steel alloy is reduced; the Nb micro-alloying treatment is supplemented with TMCP (Thermo Mechanical Control Process) technology, so that the demand on the performance of the steel plate is met, the percentage elongation is increased by 2%-3% and the impact toughness is increased by about 90J; the CEV of the steel plate is reduced to below 0.30% and the welding property of the steel plate is greatly improved; and the measures, such as, the great reduction of the alloy, the eliminating of ladle furnace process route, the Direct Hot Charging Rolling (DHCR) of hot casting blank, and the like, are taken, so that the production cost of the steel plate is greatly lowered.
Owner:HUNAN VALIN XIANGTAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
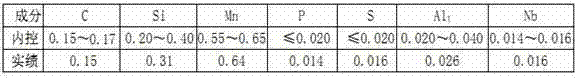
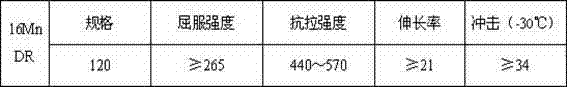
120mm low temperature pressure vessel 16mndr steel thick plate and production method thereof
Owner:NANYANG HANYE SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
Hot rolling ferrite/bainite high strength steel plate and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to hot rolling ferrite / bainite high strength steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The hot rolling ferrite / bainite high strength steel comprises the following main chemical components by mass percentage: 0.05-0.10% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 0.80-1.30% of Mn, 0.02-0.06% of Alt, 0.40-0.8% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.09% of P, less than or equal to 0.010% of S, less than or equal to 0.006% of N, and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The manufacturing method of the hot rolling ferrite / bainite high strength steel comprises the steps of molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, alloy fine adjustment and argon blowing, LF (ladle furnace) refining, a continuous casting heating technology, a rolling technology, a cooling technology and a rolling technology. According to the steel and the method, C and Mn contents are strictly controlled based on the composition of C-Mn steel, an Si content is reduced, Cr and P are added appropriately, Nb, V and Ti microalloy elements are not added, noble alloys such as Mo and Ni are not added, the cost is lowered greatly, the hot rolling ferrite / bainite dual phase steel with the tensile strength reaching 550-650MPa is obtained by adopting an appropriate rolling and cooling control technology, a hole expansion rate is high, and the forming property is excellent.
Owner:JIGANG GRP
Production method of wide and heavy steel plate with excellent ultra-low-temperature toughness used for offshore wind power
The invention discloses a production method of a wide and heavy steel plate with excellent ultra-low-temperature toughness used for offshore wind power, belonging to the technical field of rolling of the wide and heavy steel plate used for offshore wind power through a continuous coasting blank. The production process comprises the steps of: molten iron, converter smelting, LF (Ladle Furnace) refining, RH (Ruhstahl Hausen) vacuum degassing, continuous casting, steel blank check, heating, phosphorous removal, rough rolling, fine rolling, ACC (Activated Calcium Carbonate) water cooling, straightening, cooling in pile, shearing, shot blasting, normalizing, checking and storage. According to the European EN110225 standard, on the basis of the continuous casting blank, through adding micro-alloying elements, such as Nb, V, Ti and the like, and reasonably controlling rolling, a cooling process and a normalizing heat treatment method, the production yield strength is 355-410 MPa, the strength of extension is 470-550 MPa, the coefficient of elongation is 26-36%, the average value of the percentage of contraction of a section in a direction Z is 35-81%, the impact absorbing energy of a core part of the steel plate at ultra-low temperature of -60 DEG C is 100-240 J, and meanwhile, the wide and heavy steel plate has steel with good using performance as well as the thickness is 40-130 mm, and the specification is S355G8+N.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO SHOUQIN METAL MATERIAL +1
Method for smelting tire cord steel and method for continuously casting tire cord steel
ActiveCN103060513ARealize clean productionInclusion deformable strongManufacturing convertersIngotOxygen content
The invention discloses a method for smelting tire cord steel and a method for continuously casting tire cord steel; the methods comprise the following steps of: (1), carrying out primary smelting on molten iron or semi-steel by converter top-bottom blowing, and tapping into a steel ladle without deoxidization; (2), carrying out recarburization and pre-alloying on the molten steel in the tapping process, so on the basis of the total weight of the molten steel, the activity oxygen content in the molten steel is 0.004-0.008wt%, the C content is 0.64-0.68wt% and the Al content is less than 0.4wt%; (3), blowing argon to the molten steel in the steel ladle after tapping, and carrying out vacuum refining and alloy fine adjustment; and (4), carrying out ladle furnace refining on the molten steel which is subjected to the vacuum refining by using the manner of bottom blowing argon, adding refining slags batch by batch and adding deoxidizing agents batch by batch, so the total content of FeO and MnO in the steel ladle top slag is less than or equal to 10wt%. In the methods, the tire cord steel is produced by using the technological process consisting of converter primary smelting, vacuum refining and steel ladle furnace refining and cogged ingot continuous casting pouring, and thus the clean production of tire cord steels is achieved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Utilization method for steel scoria
InactiveCN101403021ARealize hot recyclingReduce pollutionElectric furnaceElectric arc furnaceSmelting process
The invention relates to an utilization method of steel slag, which includes the following steps: slagging materials are added into an LF ladle refining furnace for slagging and refining and 20kg to 50kg / t of the slagging materials are added into each ton of molten steel; then in the moulding process, the slags of the ladle furnace and remanent molten steel after moulding are returned to an electric furnace for smelting; the slagging materials are added into the electric furnace and 50kg to 70kg / t of the slagging materials are added into one ton of the molten steel; in the smelting process of the electric furnace, the adding amount of the slagging material lime and the power supply volume of the electric furnace are decreased; as for steel grades which need to be deaerated, after the LF ladle refining furnace is refined and slags are made after the slagging materials are added, the molten steel is sent to a VD vacuum degassing furnace for deaeration; then moulding is carried out; and the slags of the ladle furnace and remanent molten steel after moulding are returned to the electric furnace for smelting. The utilization method of the steel slag is lower in cost and can avoid sulfur enrichment in the ladle refining process.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Smelting method of axle steel for high-speed motor car
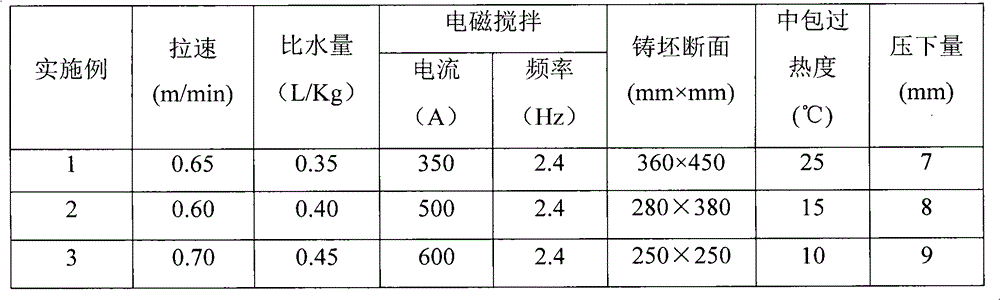
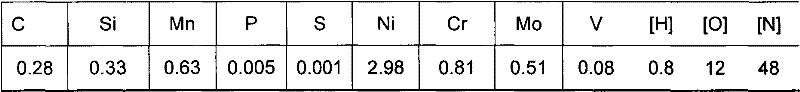
The invention relates to a smelting method of axle steel for a high-speed motor car, which comprises the following steps of: I. smelting in an electric furnace, firstly adding steel scraps into the electric furnace and adding pretreated molten iron, wherein the weight proportion of the pretreated molten iron is 80% to 95%, and in the steel scraps, P is less than or equal to 0.015% and S is less than or equal to 0.010%; blowing oxygen and adding lime, and tapping from the electric furnace after P is less than or equal to 0.008%; adding slagging materials, iron alloys and metals into steel ladles according to the types of steel; II. adopting slag systems with high alkalinity and high Al2O3 content for ladle furnace refining, controlling the alkalinity R of molten slag, wherein R is equal to 4.0 to 6.0; the molten steel comprises following components in percent by weight: 0.26 to 0.31% of C, 0.20 to 0.35% of Si, 0.55 to 0.70% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.005% of S, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, 0.75 to 0.90% of Cr, 2.90 to 3.30% of Ni, 0.45 to 0.55% of Mo and 0.08 to 0.13% of V; and III. feeding Si and Ca into the molten steel and blowing argon from the bottom after carrying out VD (Vacuum Distillation) and the vacuum refining. Inclusions of the steel rolled axle smelted by the smelting method of axle steel for the high-speed motor car meet the using requirements on the high-speed axle.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
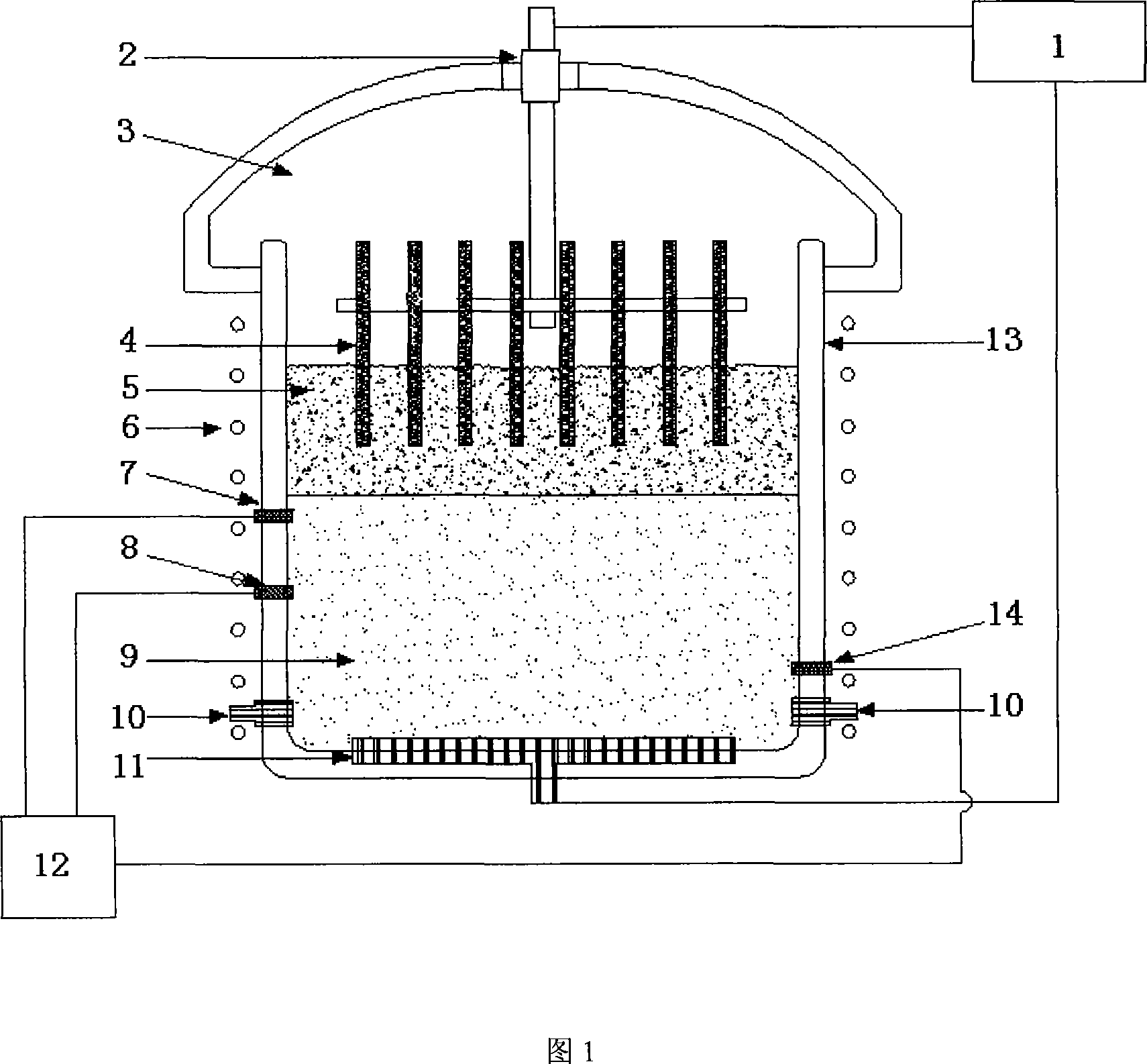
Impressed electric field pollution-free deoxygenation refining method and device for ladle furnace
The invention relates to a method for additionally adding an electric field in a ladle furnace to deoxidate and refine without pollution and a device of the method, which belong to the technical field of the refining technology. The method is characterized in that the method comprises: additionally adding the electric field between molten steel or molten metal and molten slag in the ladle furnace, taking the molten slag as a channel which transmits dissolved oxygen in the molten steel or the molten metal outwards, applying a direct current pulse electric field between the molten steel or the molten metal and the molten slag which is on the molten steel or the molten metal, controlling the transmitting direction and the speed of oxygen atoms from a system between the molten steel or the molten metal and the molten slag, simultaneously reinforcing the mass transfer process of the dissolved oxygen in the molten steel or the molten metal, and thereby realizing deoxidation of the molten steel or the molten metal without pollution. The invention has the advantages of simple technology, convenient operation, rapid and effective deoxidation and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Thin hot-rolled pickled steel with good formability and production method thereof
ActiveCN102787270AReduce the difficulty of productionImprove surface qualityMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionHigh pressure water
The invention relates to a thin hot-rolled pickled steel with good formability, which comprises the following chemical components by weight percent (wt%): 0.04-0.07% of C, 0.10-0.30% of Si, 0.41-0.60% of Mn, 0.025% of P or less, 0.012% of S and 0.010-0.030% of Als. The preparation method of the thin hot-rolled pickled steel with good formability comprises the following steps: desulphurizing molten iron, smelting by a converter, alloying, treating by a ladle furnace, casting and rolling continuously, dephosphorizing high-pressure water, controlling rolling, cooling by laminar flow, curling, pickling by acid levelling and finishing adopting static oil removal. The produced hot-rolled pickled steel which has the tensile strength of 370MPa or higher and the thickness of 1.8 mm or lower, is low production difficulty and good in surface quality and is convenient to weld, oil and paint. In addition, the thin hot-rolled pickled steel has the advantages of good punch formability, high forming size accuracy, short production cycle, high yield and low cost.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Steel plate smelting method for improving high heat input welding performance
ActiveCN103215507AAccurate Oxygen ContentMeet the requirements of steel plates for high heat input weldingSteelmakingHeat-affected zone
The invention discloses a steel plate smelting method for improving high heat input welding performance. The method comprises the following process flows of converter steel smelting, ladle furnace refining, vacuum furnace refining and continuous casting; and steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: at most 0.10% of C, 0.1-0.3% of Si, 1.3-1.7% of Mn, at most 0.015% of P, at most 0.005% of S, 0.01-0.12% of Ti, at most 0.5% of Ni, at most 0.5% of Cu, at most 0.3% of Cr, at most 0.3% of Mo, 0.0001-0.005% of Mg, 0.0005-0.002% of B, 0.005-0.025% of Al, 0.001-0.003% of Ca, at most 0.005% of N, at most 0.005% of O and the balance of Fe. A proper deoxidizing agent adding sequence is adopted, the oxygen content is precisely controlled, small and dispersed nano-level occluded foreign substances are formed in molten steel, and the growth of austenite crystals in a welding heat affected zone is effectively pinned, thus the requirements for steel plates for high heat input welding can be met.
Owner:HUNAN VALIN XIANGTAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
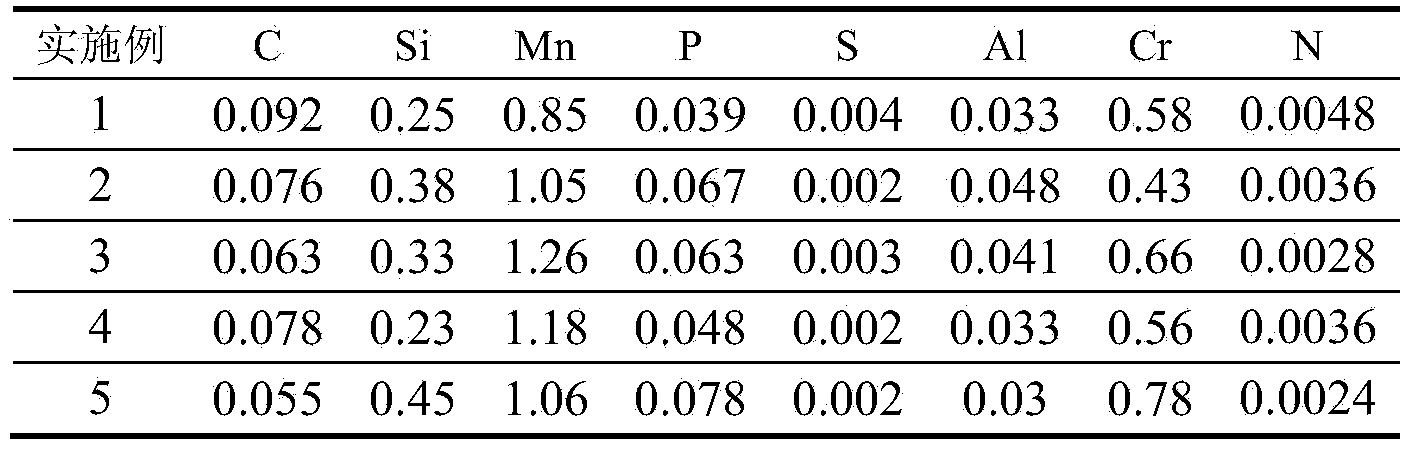
100-150mm alloy structural steel 4140 thick plate and production technique thereof
The invention discloses a 100-150mm alloy structural steel 4140 thick plate and a production technique thereof. The 100-150mm alloy structural steel 4140 thick plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.39-0.42% of C, 0.20-0.30% of Si, 0.85-0.95% of Mn, at most 0.010% of P, at most 0.003% of S, 0.020-0.040% of Als, 0.9-1.0% of Cr, 0.17-0.23% of Mo, and the balance of Fe and residual elements. KR molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, argon blowing, LF (ladle furnace) refining, VD (vacuum degasser) refining, die casting, steel ingot slow cooling, steel ingot conditioning, heating, controlled rolling, cooling in pile, heat treatment and slow cooling are utilized to strictly control the contents of P, S and other harmful elements capable of influencing the plasticity and toughness of the steel plate, thereby ensuring the minimized internal residual stress of the 4140-grade 100-150mm-thick steel plate; and the internal quality is acceptable, and various performance indexes satisfy the standard requirements. The reasonable quenching and tempering technique is utilized to ensure that various properties of the 4140 steel plate satisfy the requirements.
Owner:NANYANG HANYE SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
Ladle furnace use nitrogen gas nitrogen alloying process
The invention relates to a ladle furnace use nitrogen gas nitrogen alloying process. The process comprises the following steps: a) smelting nitrogen-contained stainless steel, controlling the components of the molten steel except the nitrogen to the targeted components, and controlling a nitrogen flush initial temperature at 30 to 50 DEG C above a refining treatment out-station temperature; b) during the nitrogen bottom blowing for the smelting of the nitrogen-contained stainless steel in the LF furnace, adding 1 to 20 ppm of nitrogen to each standard cube of nitrogen; c) during the nitrogen bottom blowing for the micro-alloying treatment, controlling the nitrogen flow at 6 to 120m<3> / h and the nitrogen flush pressure at 0.60 to 0.80 MPa; and d) when the nitrogen bottom blowing is finished, carrying out the argon bottom blowing for 4 to 6 minutes with the argon flow of 2 to 20 m<3> / h so as to average the stainless steel components and temperature. The process adds the nitrogen alloying function through the nitrogen bottom flowing to the ladle furnace (LF) in the prior stainless steel production process so as to replace a nitro alloy, make the nitrogen-contained stainless steel carry out continuous and stable nitrogen alloying in the ladle furnace, improve the purity of the molten steel, and consequently improve the molten steel quality and reduce the production cost.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Control method for nitrogen content of molten steel of wear-resistant steel
ActiveCN103627841AMeet performance requirementsFulfill customer's requestManufacturing convertersWear resistantNitrogen
The invention discloses a control method for nitrogen content of molten steel of wear-resistant steel. By virtue of optimization of a converter tapping technology, improvement of orders of deoxidizing slagging and alloying of an LF (Ladle Furnace), as well as rational control on ladle bottom argon blowing flow rate and pressure in different smelting stages, and complete protective casting of continuous casting process, the nitrogen content of the molten steel can be controlled within 0.0030% after converter tapping, nitrogen adding in molten steel during LF+RH (Ladle Furnace process +Ladle Furnace process) is steadily controlled within 0.0010%, nitrogen adding in molten steel in the continuous casting process is steadily controlled within 0.0005%, and finally, nitrogen content in a high alloy wear-resistant steel continuous casting billet is controlled within 0.0045%, therefore, internal quality and surface quality of the casting billet are improved greatly.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com