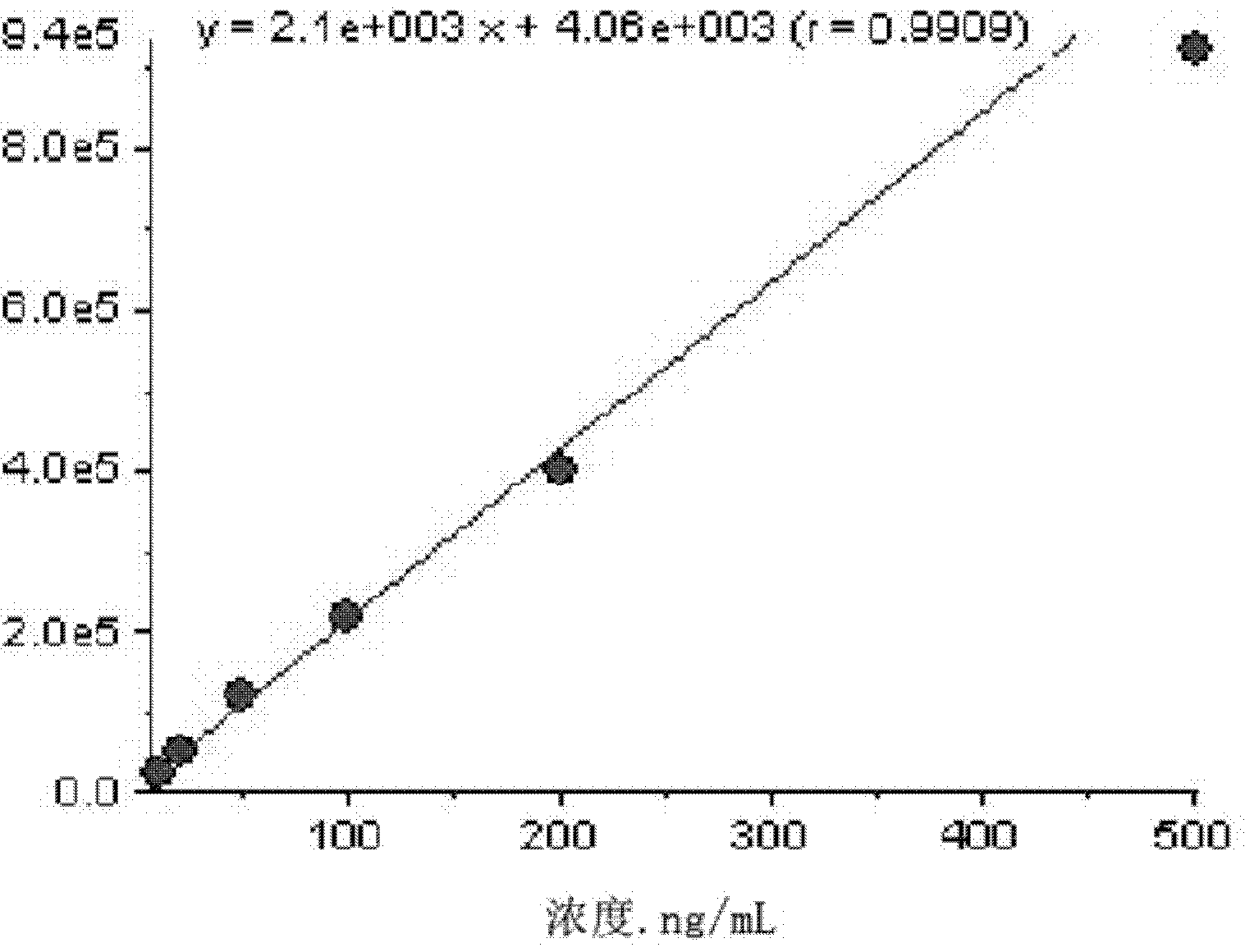
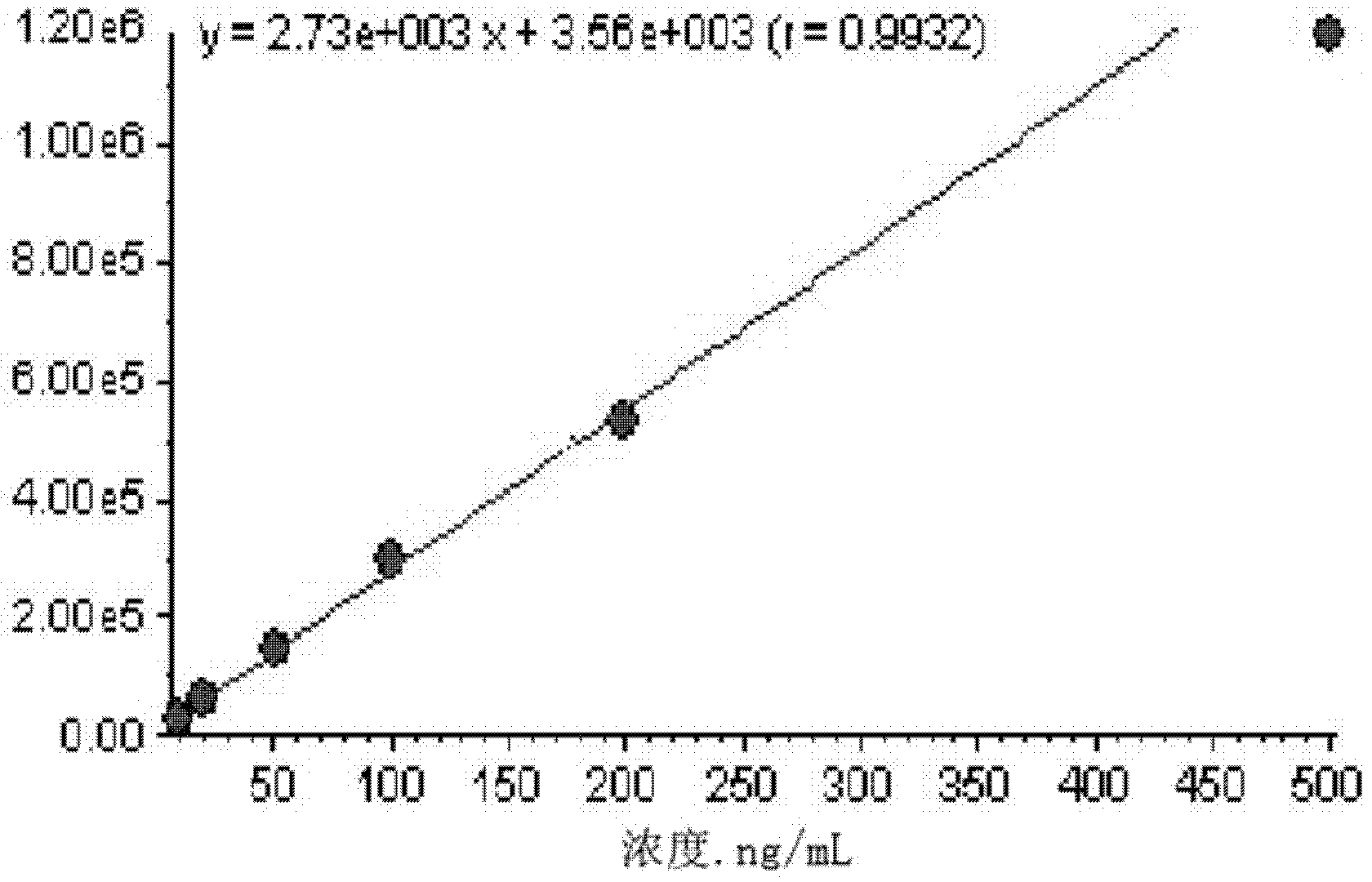
Patents
Literature
476 results about "Nitrogen flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
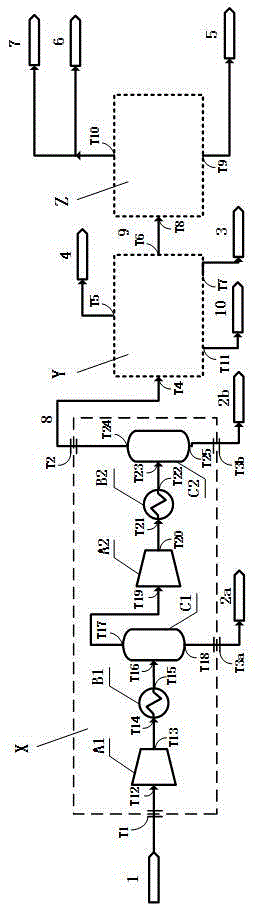
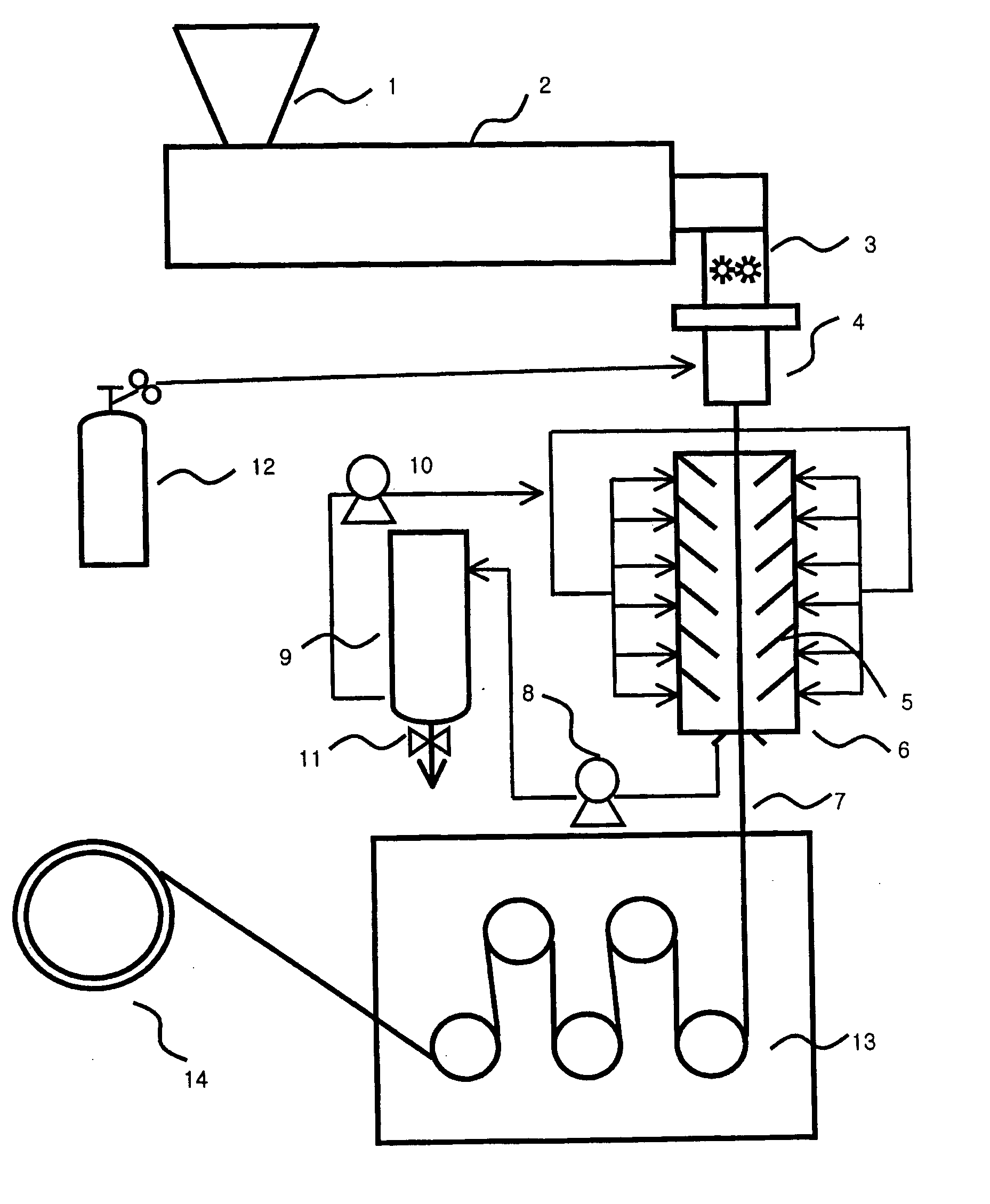
Nitrogen flow is confirmed by the flow indicator tube. If the ball does not rise up in the tube, then there is static pressure and the oxygen is not being displaced.
Method for starting operation of catalyst for hydrocracking in oxidation state
InactiveCN101003749AStrong resistance to sulfur poisoningImprove hydrogenation performanceHydrotreatment operations starting-upOxidation stateNitrogen gas
This invention relates to a start-up method for oxidation-state hydrocracking catalyst used in oil refinery process. The method comprises: loading the oxidation-state hydrocracking catalyst into a reactor, introducing nitrogen to replace air in the reactor and pipelines, pressurizing to meet the pressure requirement of hydrocracking, switching to hydrogen after nitrogen flow is stable, raising the temperature of the catalyst bed to meet the temperature requirement of catalyst reduction after hydrogen flow is stable, keeping the temperature, adjusting the temperature of the catalyst bed to meet the temperature requirement of hydrocracking, adjusting hydrogen flux to meet the flux requirement of hydrocracking, and introducing hydrocarbon reactants. The method does not need pre-sulfurization of the catalyst with additional sulfurization agent, thus can avoid the problems caused by pre-sulfurization, and partially reduced catalyst has higher hydrocracking activity.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparing polyimide/ silicon dioxide hollow micro-sphere composite film
The invention discloses a method for preparing polyimide / silicon dioxide hollow microballoon laminated film which has low dielectric constant and keeps thermal property, and steps of reaction are that: silicon dioxide hollow microballoon is put into ethanol solution, amino-containing silane coupling agent is added after ultra sonic dispersion, stirred for reaction, separated centrifugally, washed and dried; then under the protection of nitrogen flow, the dianhydride and the diamine with a mole-ratio 1:1 are added into the high boiling polarity aprotic solvent to prepare solvent containing 10 percent (wt / wt) of solid-content; the silicon dioxide hollow microballoon modified by silane coupling agent is put into the solvent, and the weight of the silicon dioxide hollow microballoon modified by the silane coupling agent is 2-50 percent of the weight of laminated film, the polyamide acid viscous fluid is prepared upon ultra sonic dispersion and a reaction of twenty-four hours at room temperature; the polyamide acid viscous fluid is taken and poured into the glass plate mould; finally the mould is put in vacuum to dry, the temperature is heated up continuously after the solvent is removed for cyclic reaction. Thus, the polyimide / silicon dioxide hollow microballoon laminated film is prepared..
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Flexible Template-Directed Microporous Partially Pyrolyzed Polymeric Membranes
InactiveUS20070209506A1High selectivityGood anti-plasticizing performanceMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCyclodextrinSolvent
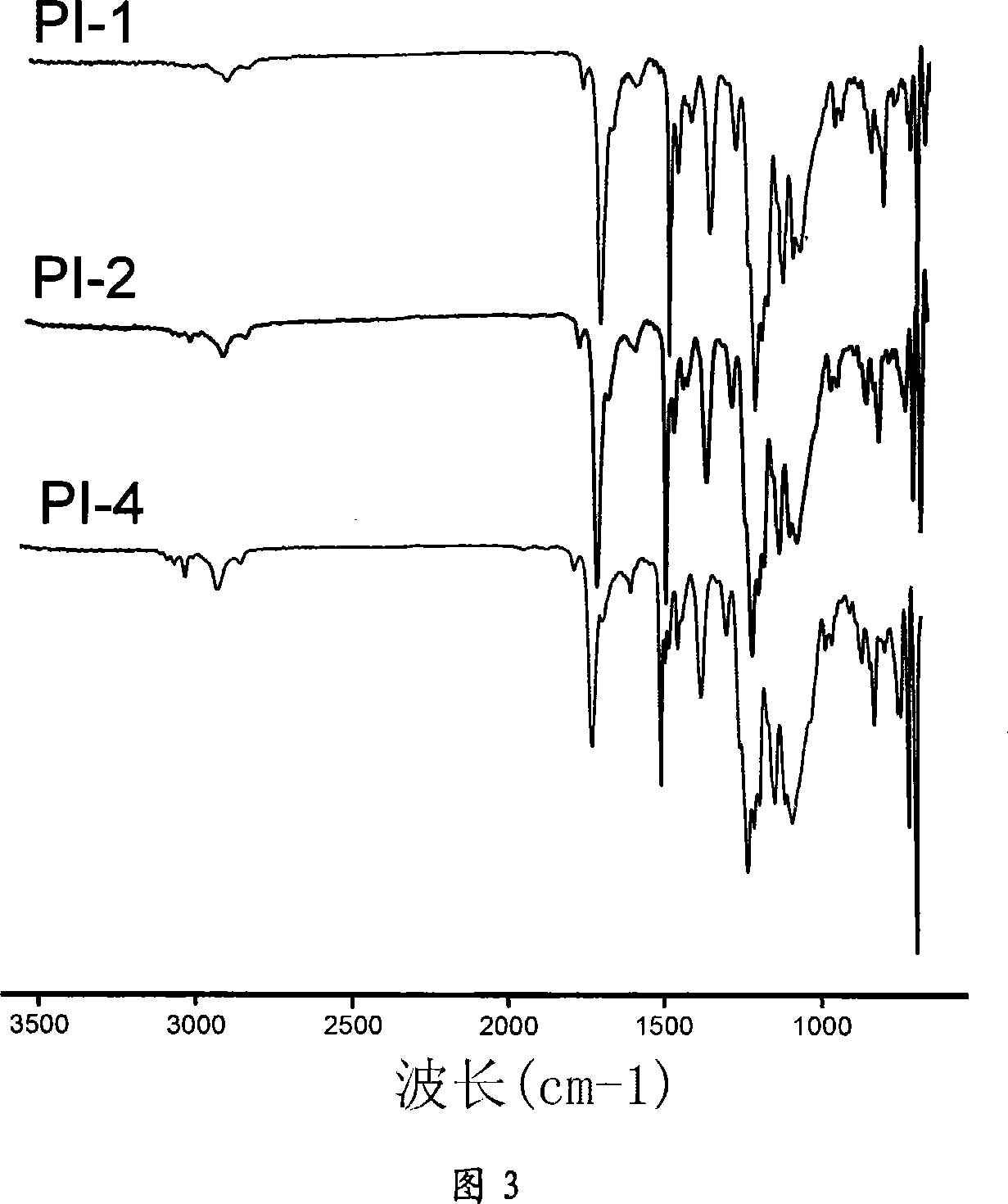
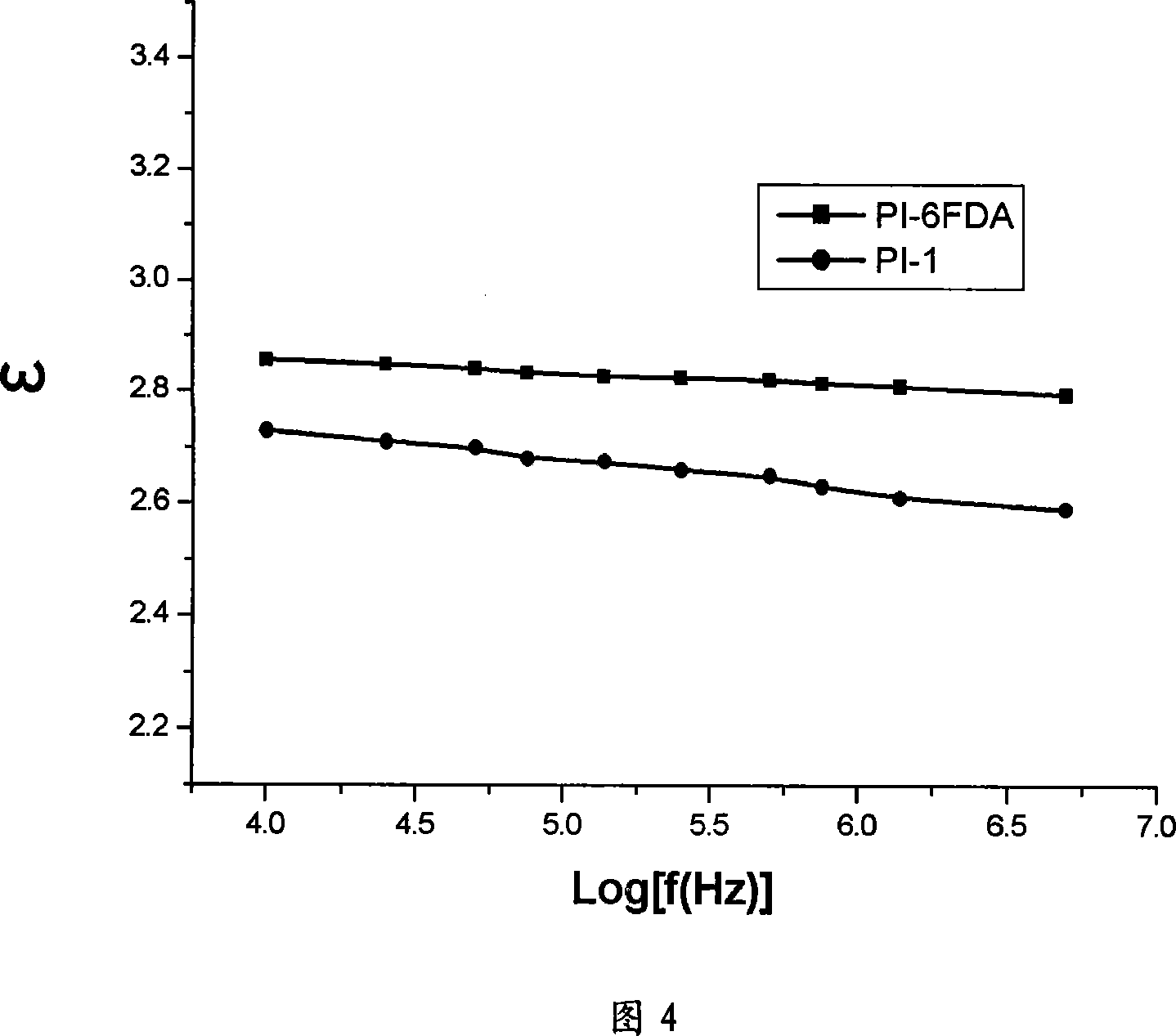
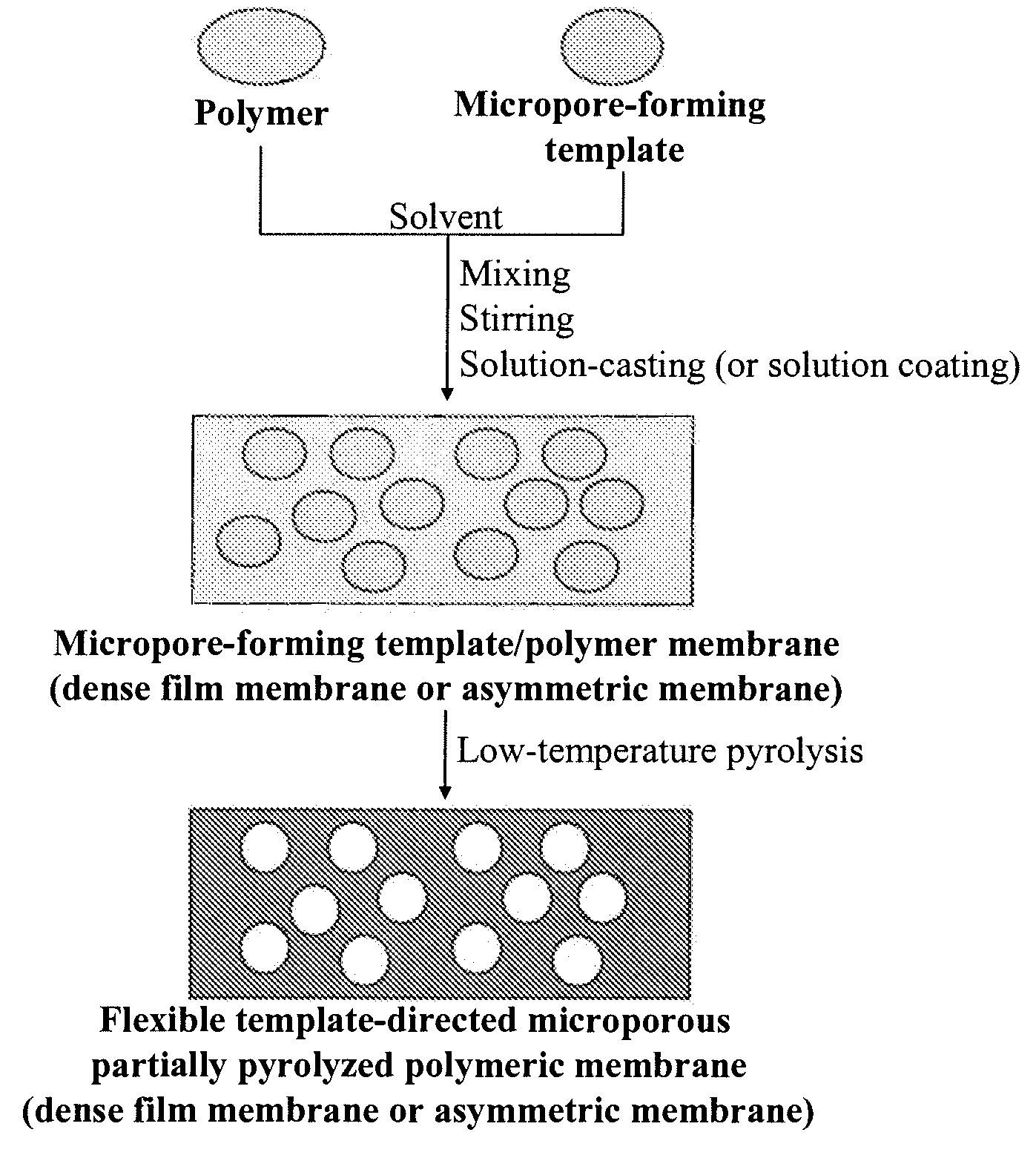
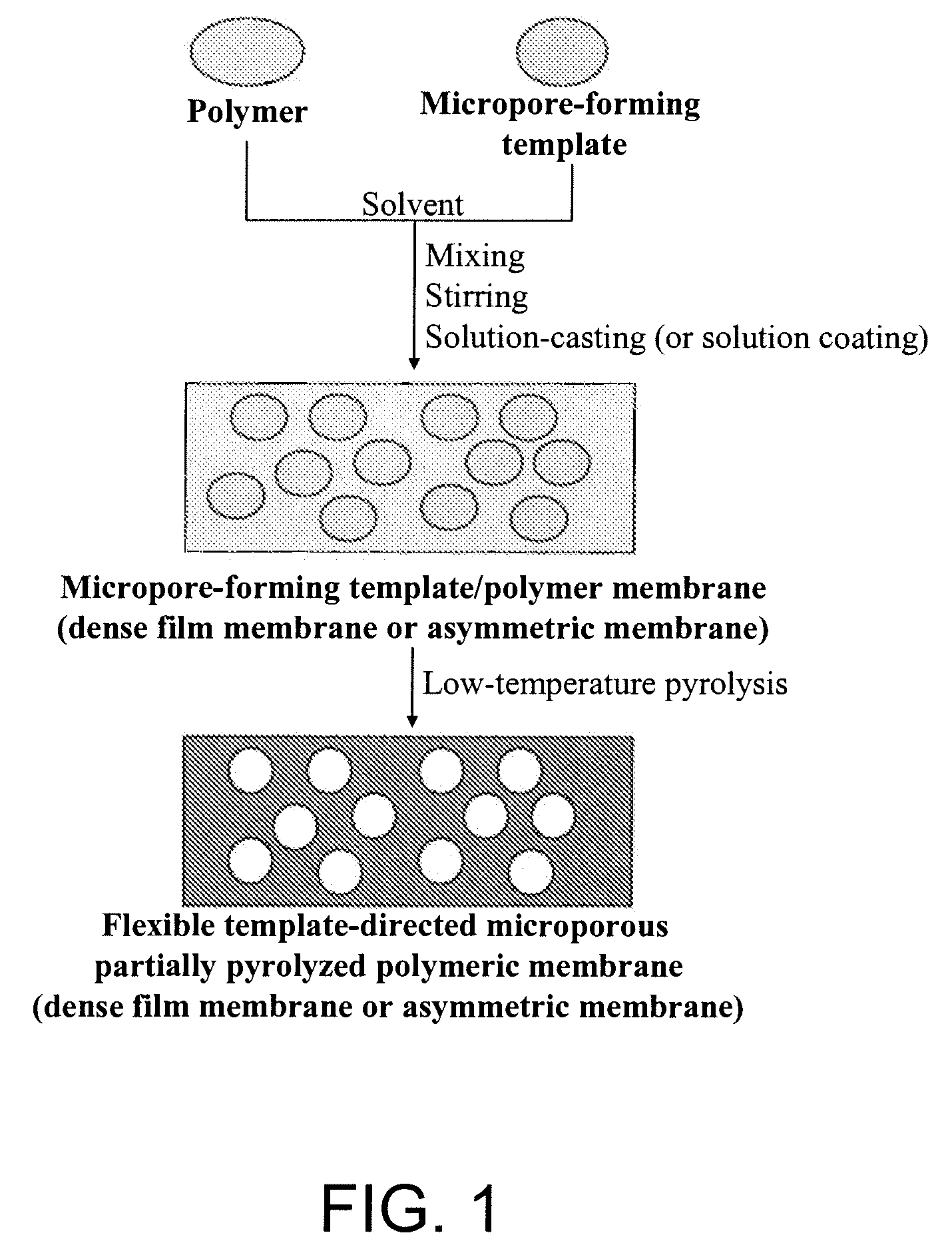
This invention describes a new concept of flexible template-directed microporous partially pyrolyzed polymeric membranes which have greatly improved performance in separation of gas pairs compared to their precursor polymeric membranes. Organic hosts, such as crown ethers, cyclodextrins (CDs), calixarenes (CXs), and spherands, or polymeric additives, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) were used as the micropore-forming templates. Micropore-forming template / polymer blend membranes comprising organic micropore-forming templates embedded in a polymer matrix were prepared by dissolving the organic micropore-forming templates in the polymer solution followed by solution-casting and solvent evaporation or solvent exchange. Low-temperature selectively pyrolyzing micropore-forming templates in the micropore-forming template / polymer blend membranes at a nitrogen flow resulted in the formation of flexible microporous partially pyrolyzed polymeric membranes.
Owner:UOP LLC
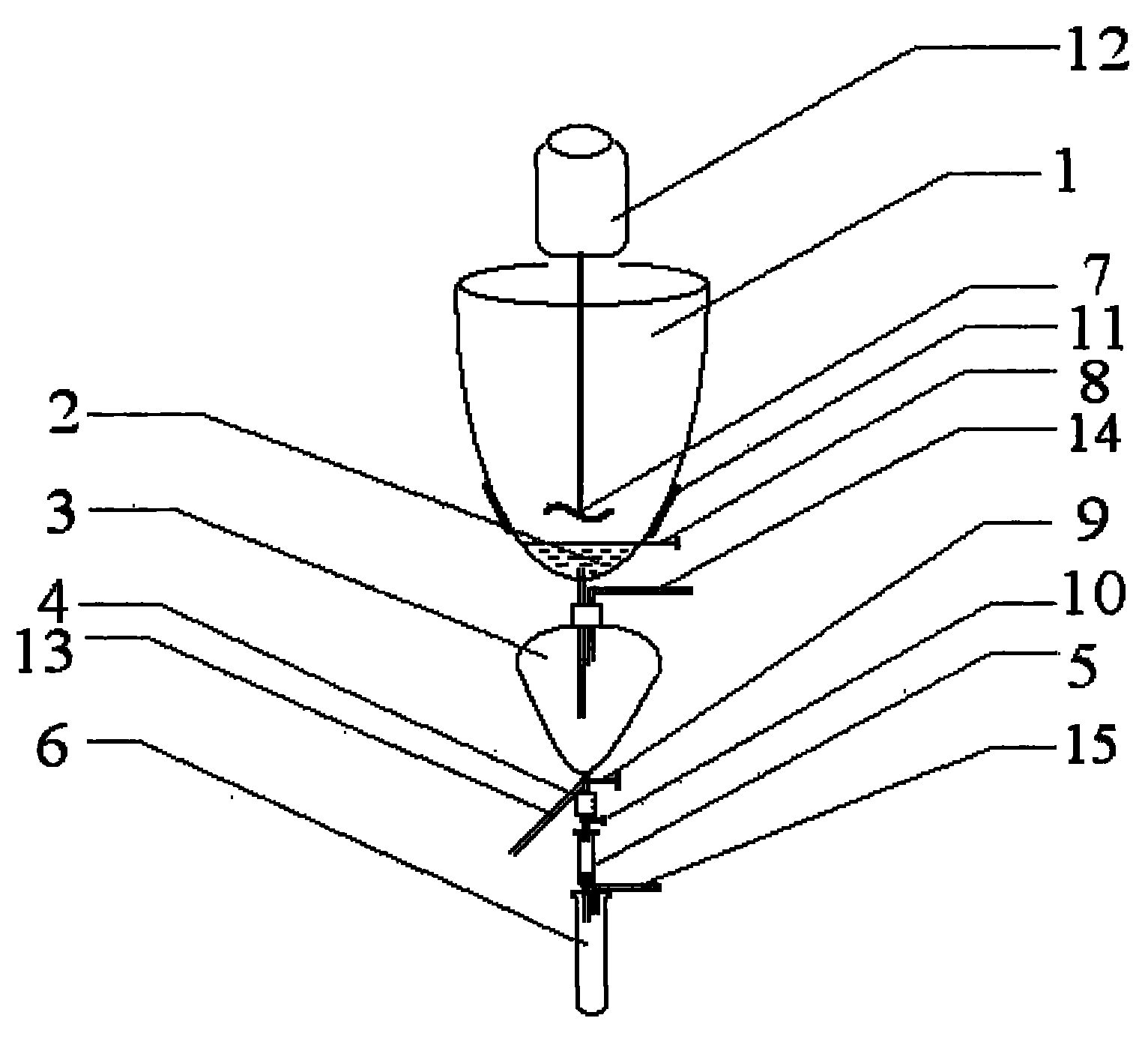
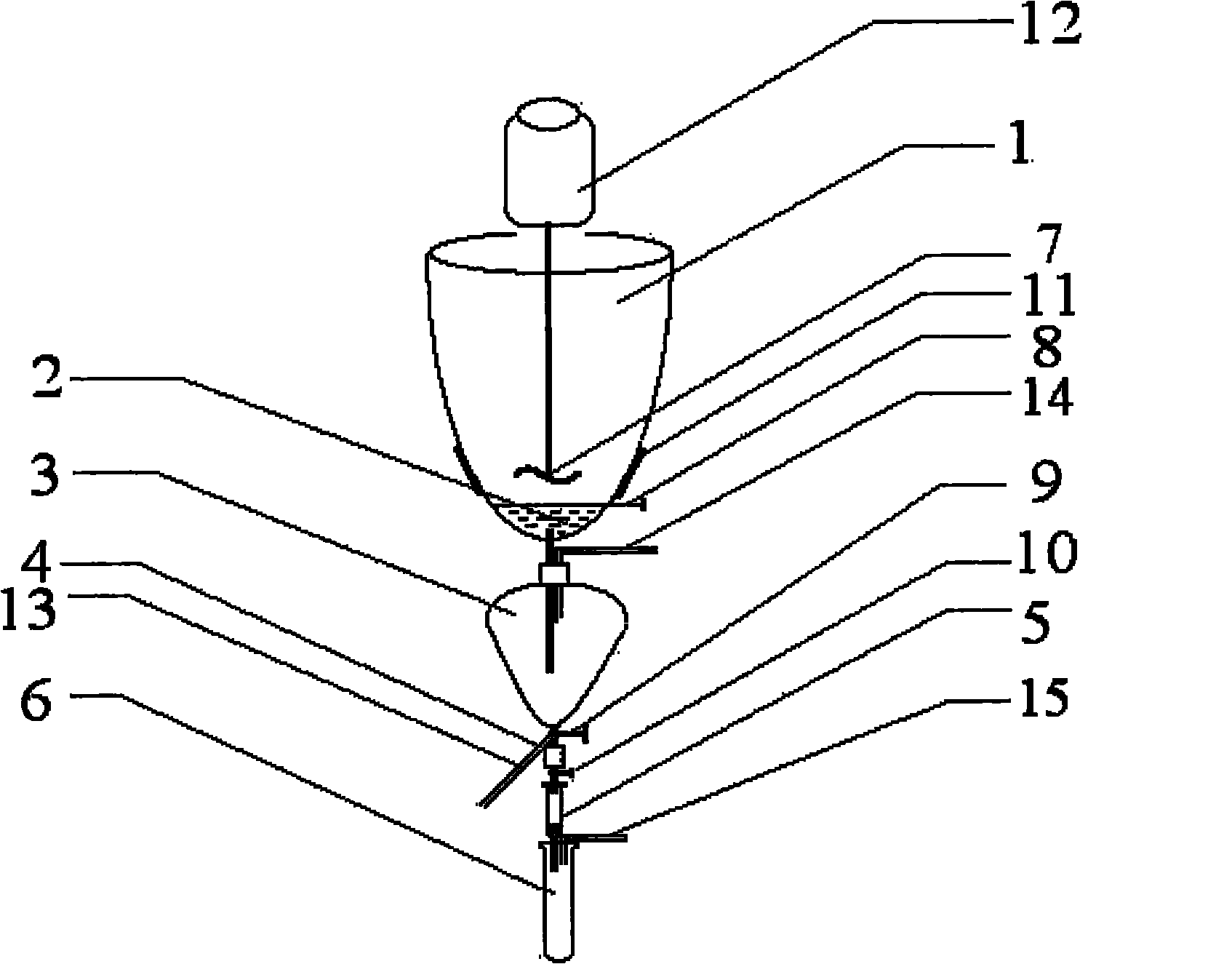
Integrated pesticide residue detection pretreatment device and pretreatment method
InactiveCN101813582AQuick checkQuick preprocessingPreparing sample for investigationPretreatment methodFiltration
The invention provides an integrated pesticide residue detection pretreatment device and a pretreatment method. The device comprises a cup body, a filter, a liquid divider, a jigger, a solid phase extraction column and a test tube, wherein a crushing homogenizer is arranged in the cup body, and the bottom of the cup body is connected with the filter; the liquid divider is arranged on the bottom of the filter to be used for carrying out standing stratification on filter liquid flowing out of the filter, and the bottom of the liquid divider is connected with a three-way valve; the jigger is connected with one opening of the three-way valve to be used for quantitatively collecting a target compound, and the bottom end of the jigger is provided with a second graduating valve; the solid phase extraction column is connected on the bottom of the jigger to be used for eluting the target compound; and the test tube is used for collecting eluent and is also connected with a nitrogen flow system used for concentrating the eluent. The device and the method integrate the processes of crushing, homogenizing, ultrasonic vibrating, suction filtration, liquid-liquid extraction, solid phase extraction, concentrating constant volume and the like; the treatment method is simple and has high efficiency, and the treatment device is convenient and simple, practical and portable and can be used for on-site operation.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
NMR CryoMAS Probe for High-field Wide-bore Magnets
InactiveUS20060176056A1Reduce riskImprovement factorElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonancePartial solutionNitrogen gas
An MAS probe is disclosed for obtaining a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high-field magnets where the magnet's RT shim bore is greater than 60 mm. All critical circuit components, including the sample coils, are located along with the spinner assembly in a thermally insulated cold zone pressurized with helium gas. The spinner assembly attaches to a sealed, curved, rotor-loading tube to permit automatic sample change, and it is surrounded by a partially insulated jacket cooled with a cryogenic fluid, generally nitrogen gas. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, variable temperature operation, field locking, and commonly available closed-cycle cold fingers. One major challenge in implementing CryoMAS is solving the problem of gas leakage from the spinner bearing, drive, and exhaust nitrogen into the cold zone, as some components will necessarily be ceramic, some plastic, and some metal. It is not desirable to use helium for the spinner bearing and drive gases for cost reasons and to prevent risk of degradation of o-ring-sealed magnet cryostats. A pressurized helium atmosphere in the cold zone may be utilized to prevent nitrogen flow from the spinner exhaust streams or atmosphere into the cold zone. The drawback to a pressurized cold zone is that the heat transfer coefficient in dense helium at low temperatures is very high, making it challenging to cool the sample coils and all the large, critical, circuit components in a practical manner. Part of the solution here is to use a first-stage cooling-jacket around the major heat leaks near the spinner exhaust flows. The critical components may be insulated with fine glass wool or teflon foam and conduction cooled without cooling much of the cold zone below the temperature of the first-stage cooling. The use of coaxial sapphire capacitors allows the noise contributions from the most critical capacitors to be reduced to a minor fraction of the total.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Ladle furnace use nitrogen gas nitrogen alloying process
The invention relates to a ladle furnace use nitrogen gas nitrogen alloying process. The process comprises the following steps: a) smelting nitrogen-contained stainless steel, controlling the components of the molten steel except the nitrogen to the targeted components, and controlling a nitrogen flush initial temperature at 30 to 50 DEG C above a refining treatment out-station temperature; b) during the nitrogen bottom blowing for the smelting of the nitrogen-contained stainless steel in the LF furnace, adding 1 to 20 ppm of nitrogen to each standard cube of nitrogen; c) during the nitrogen bottom blowing for the micro-alloying treatment, controlling the nitrogen flow at 6 to 120m<3> / h and the nitrogen flush pressure at 0.60 to 0.80 MPa; and d) when the nitrogen bottom blowing is finished, carrying out the argon bottom blowing for 4 to 6 minutes with the argon flow of 2 to 20 m<3> / h so as to average the stainless steel components and temperature. The process adds the nitrogen alloying function through the nitrogen bottom flowing to the ladle furnace (LF) in the prior stainless steel production process so as to replace a nitro alloy, make the nitrogen-contained stainless steel carry out continuous and stable nitrogen alloying in the ladle furnace, improve the purity of the molten steel, and consequently improve the molten steel quality and reduce the production cost.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Method for preparing slow-release type skeleton-type TiN/Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film
InactiveCN101705468AGood dissolution effectDissolution rate is stableBiocideVacuum evaporation coatingSputter cleaningNitrogen gas
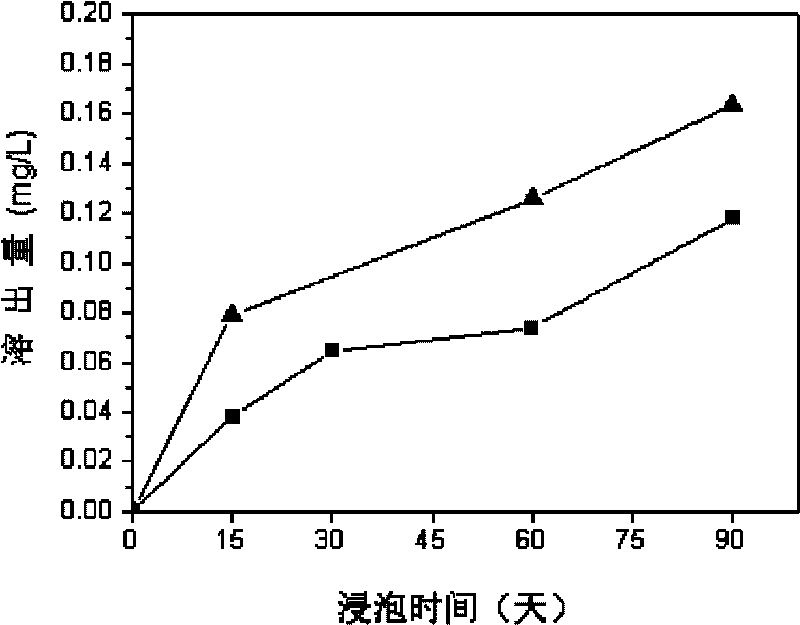
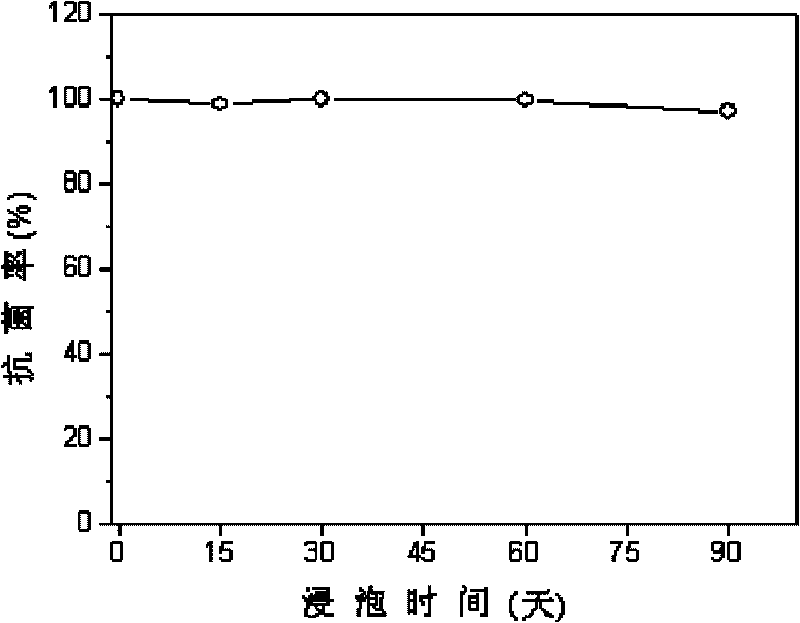
The invention discloses a method for preparing a slow-release type skeleton-type TiN / Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film and relates to a preparation method of an antibacterial film, which solves the problem that an antibacterial film prepared by the conventional method has poor durability of antibacterial effect. The method has the following steps of: 1. putting a matrix on a target platform of a vacuum room; and then heating to 200 DEG C and sputter cleaning for 20 min; 2. rotating the target platform of the vacuum room under the condition that argon flow is 6sccm, nitrogen flow is 2sccm, deposition pressure is 0.56Pa, and the deposition bias of the matrix is compound bias; and alternately depositing TiN layers and metal layers on the surface of the matrix till the total thickness of film layers is 0.1 micrometer-10 micrometers to obtain the slow-release type skeleton-type TiN / Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film. After the slow-release type skeleton-type TiN / Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film is soaked for three months, the ion dissolving speed is not reduced, and the antibiosis rate against colibacillus can still reach above 97%.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Plasma enhanced ALD of tantalum nitride and bilayer
InactiveUS20050095443A1Producing a copper diffusion barrierReliably producedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNitrogen plasmaBi layer
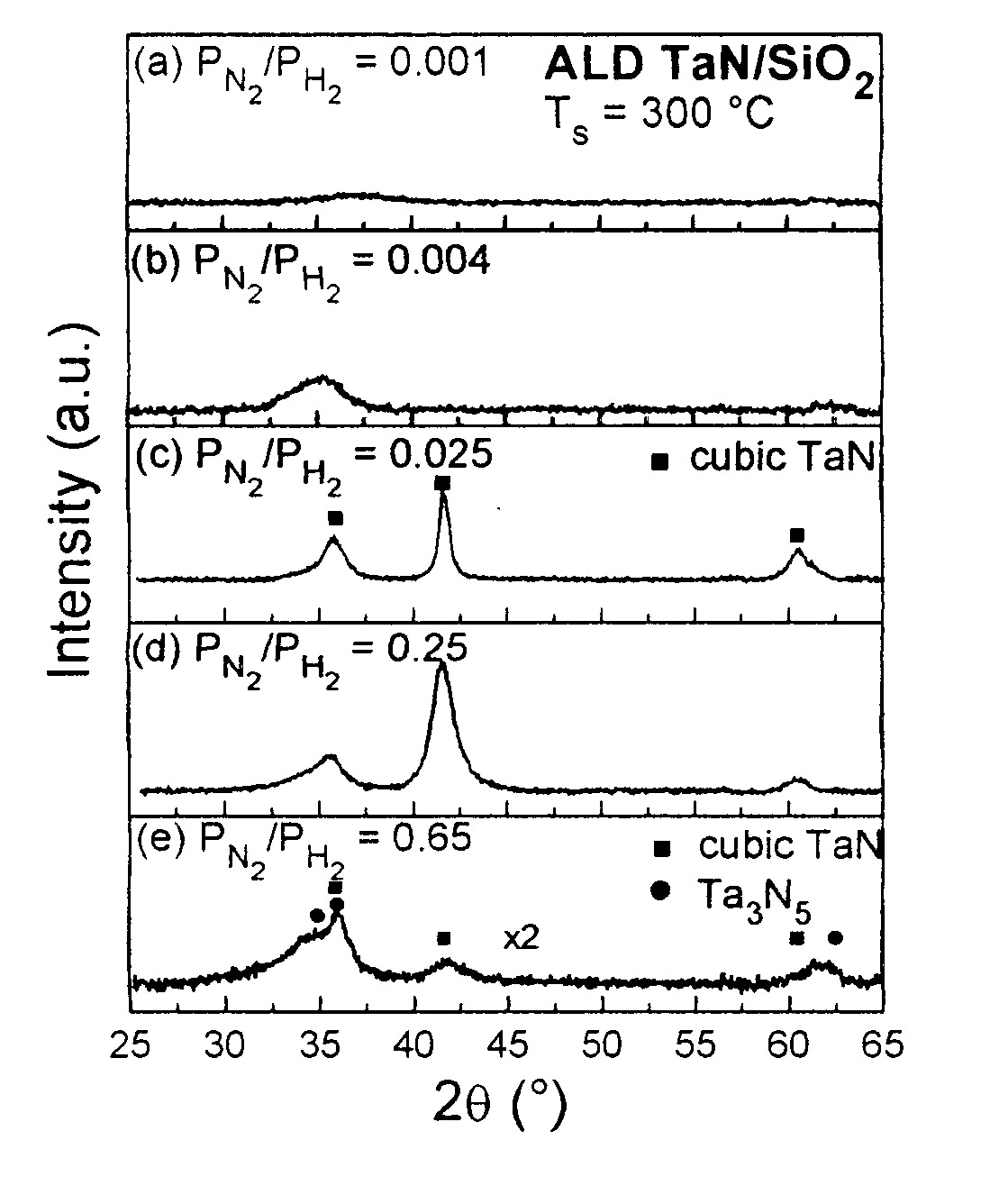
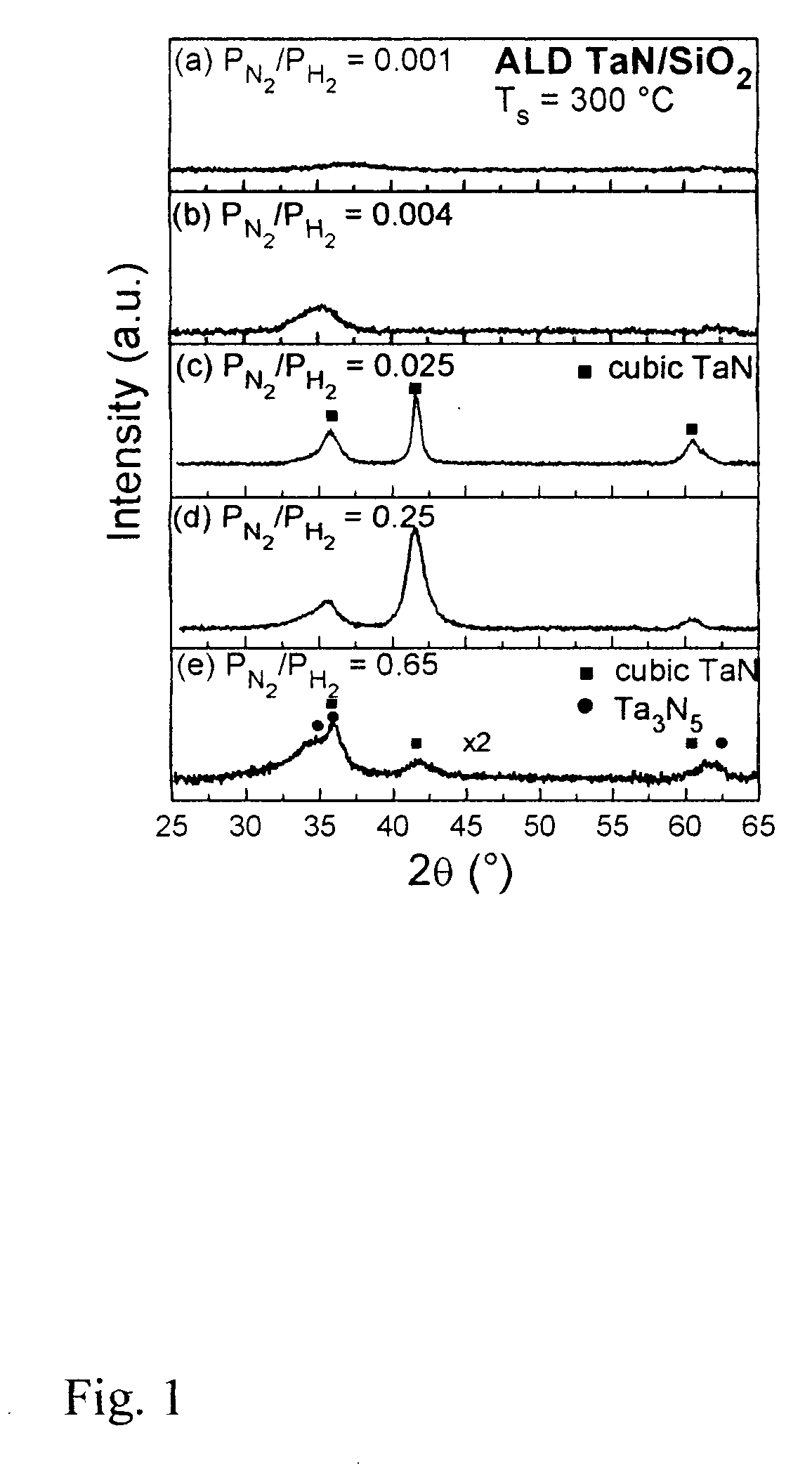
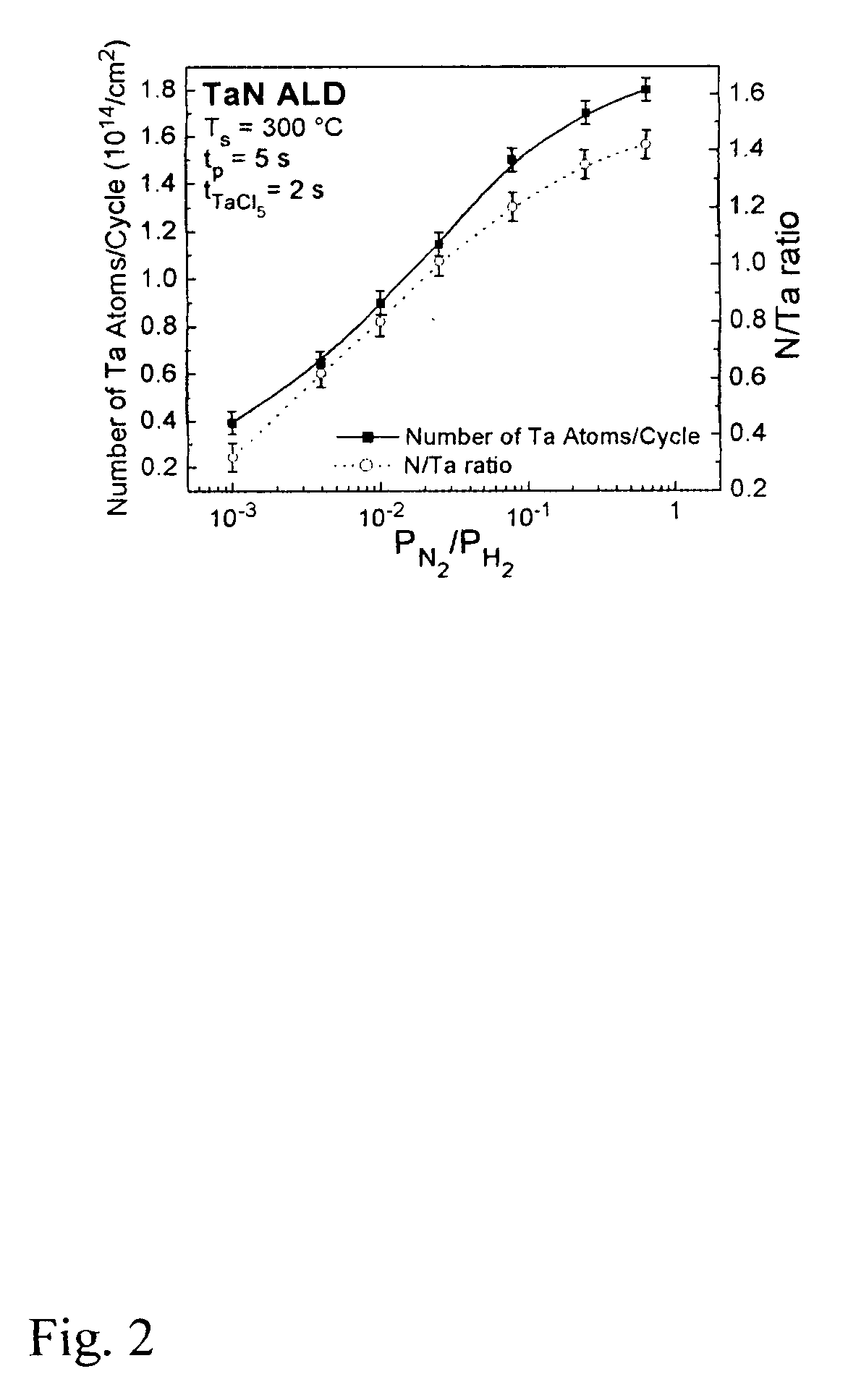
A method to deposit TaN by plasma enhanced layer with various nitrogen content. Using a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen plasma, the nitrogen content in the film can be controlled from 0 to N / Ta=1.7. By turning off the nitrogen flow during deposition of TaN, a TaN / Ta bilayer is easily grown, which has copper diffusion barrier properties superior to those of a single Ta layer or a single TaN layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dual-frequency silicon nitride for spacer application
InactiveUS20050287823A1Good shape retentionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDual frequencyHigh frequency power
A silicon nitride spacer material for use in forming a PFET device and a method for making the spacer includes the use of a dual-frequency plasma enhanced CVD process wherein the temperature is in the range depositing a silicon nitride layer by means of a low-temperature dual-frequency plasma enhanced CVD process, at a temperature in the range 400° C. to 550° C. The process pressure is in the range 2 Torr to 5 Torr. The low frequency power is in the range 0 W to 50 W, and the high frequency power is in the range 90 W to 110 W. The precursor gases of silane, ammonia and nitrogen flow at flow rates in the ratio 240:3200:4000 sccm. The use of the silicon nitride spacer of the invention to form a PFET device having a dual spacer results in a 10%-15% performance improvement compared to a similar PFET device having a silicon nitride spacer formed by a RTCVD process.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for preparing p-type zinc oxide film
InactiveCN1461044AConcentration control is convenientThe principle is simpleFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingAtmospheric airNitrogen gas
The method for preparing p-type zinc oxide film by using magnetron sputtering process is characterized by that it uses metal zinc as target for magnetron sputtering, and introduces nitrogen gas or nitrogen gas and oxygen gas into working gas argon gas as reactant gas, makes the pressure of magnetron sputtering vacuum chamber be 10(-1)Pa-10(o)Pa, the ratio of nitrogen flow and argon flow be in the range of 1:10-1:1, and the ratio of oxygen flow anjd argon flow be in the range of 0:1-1:1, then makes the obtained nitrogen-oxygen-zinc film undergo the process of heat treatment in atmosphere or oxygen atmosphere, its heat treatment temp. is 300-500 deg.c and treatment time is 0.5-5 hr. so as to obtain the invented product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Desorption and regeneration method for organic matter adsorbent
InactiveCN103447015AReduce dosageReduce separation loadCombustible gas purificationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesDesorptionWater vapor
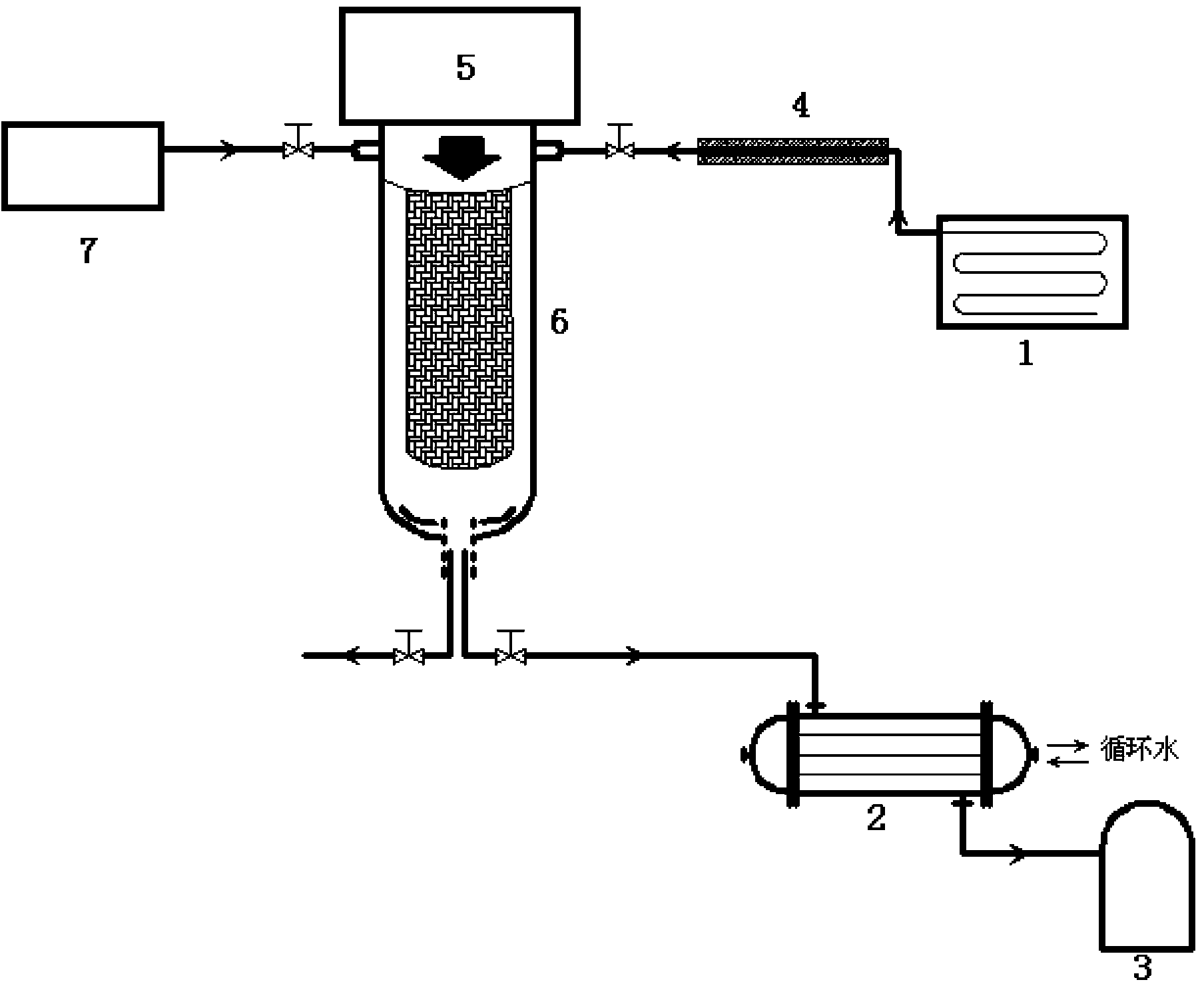
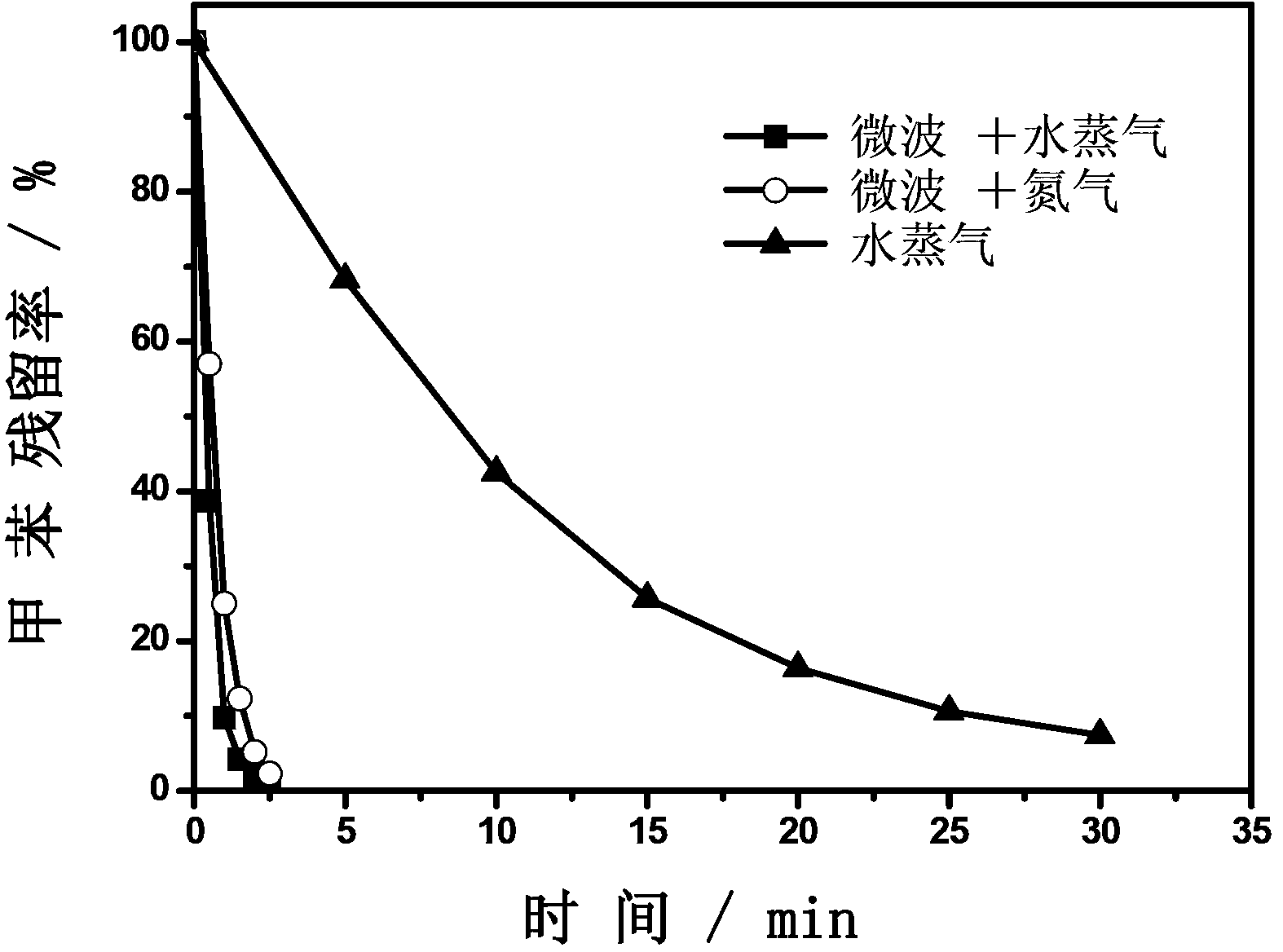
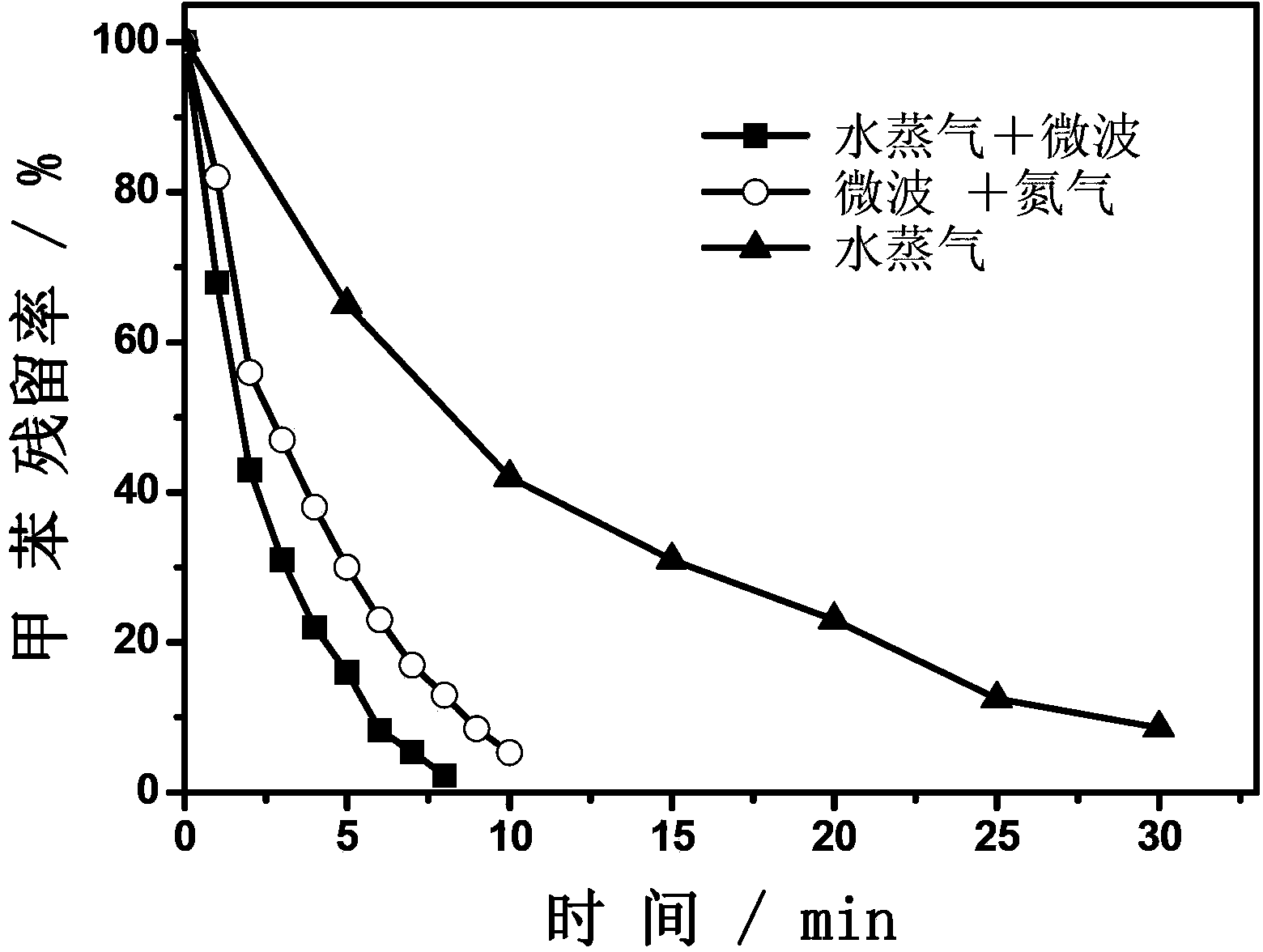
The invention discloses a desorption and regeneration method for an organic matter adsorbent. The method is characterized in that an organic matter adsorbent desorption and regeneration device of a microwave generator is arranged in a desorption tower; the to-be-desorbed adsorbent with organic matters is put in the desorption tower; steam is aerated from the top of the desorption tower; the microwave generator is started, wherein the microwave power is 500-10000W; desorption is carried out for 2-30 minutes; the desorbed organic matters and steam flow out from a steam outlet at the bottom of the desorption tower and enter a condenser for condensation; then the steam is cut off, nitrogen is aerated from the top of the desorption tower, and the nitrogen flows out from the bottom, wherein the microwave power is 200-2000W; drying treatment is carried out for 2-20 minutes; the microwave generator is turned off, and the nitrogen is cut off; the desorbed adsorbent is obtained. According to the method, the desorption rate is improved by a large margin by combining steam and the microwave technology, and less desorption residue is left.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Liquid nitrogen spay frozen granulation vacuum drying device and working method
ActiveCN106268503AIncreased sublimation surface areaEnough to migrateGranulation by liquid drop formationHigh energyFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a liquid nitrogen spray frozen granulation vacuum drying device and a working method. The device solves the problem that in the biotechnology field, when liquid materials are frozen and dried directly, due to the fact that the water sublimation surface is small and air current channels among particles are not smooth, the speed is low, and the efficiency is low. The device sprays the liquid materials into continuously sprayed ultralow-temperature liquid nitrogen mist through nitrogen pressure, material liquid drops are rapidly frozen to be amorphous spherical particles, the amorphous particles are in a non-balanced high-energy state, and drying is easy. Particle materials made through co-spray are stacked on screens which can be folded in a spray chamber and have a heating function, and the larger sublimation surface of the particle materials and through moisture migration and overflowing channels formed by particle voids and the porous screens are beneficial for rapid drying of the materials. In addition, when co-spray granulation is conducted, low-temperature nitrogen flow flows through made material particles and condenser pipes from top to bottom, and the material particles can keep low temperature and fully utilize residual cool.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Method for preparing microbial fuel cell anode electrodes from agricultural wastes
InactiveCN105762372ALarge specific surface areaIncrease capacitanceCell electrodesCapacitancePorous carbon
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial fuel cells, in particular to a method for preparing microbial fuel cell anode electrodes from agricultural wastes.The method includes drying a sample, increasing the temperature to 400 DEG C at a temperature increase rate of 10 DEG C / min in an atmosphere of nitrogen, reacting at 400 DEG C for 30 minutes, carbonizing the sample by controlling nitrogen flow speed at 600 Ml / min, taking the carbonized sample out, grinding the carbonized sample to be in 60-mesh size, soaking the ground carbonized sample for 6 hours by 5wt% HCl, and washing the soaked ground carbonized sample to be neutral; soaking the neutral sample for 6 hours by 3wt% HF, washing the soaked sample to be neutral and drying; mixing the dried sample with KOH, grinding a mixture to be in a 100-mesh size, and transferring the ground mixture to a nickel crucible to activate at 700-900 DEG C in an atmosphere of nitrogen for 1-2 hours, wherein the ratio of the sample to the KOH is 1:2-1:6.The method for preparing the microbial fuel cell anode electrodes from the agricultural wastes has the advantages that the high-quality biomass porous carbon electrodes, prepared from agricultural wastes-bean dregs, are high in specific surface area and capacitance and have good microbial biomass enrichment effect; the method, which is capable of achieving waste resource utilization, is high in raw material use efficiency, powerful in functionality, capable of achieving environment friendliness of the electrodes and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing glyceride carbonate by using loop reaction device
ActiveCN103030622AImprove mass transfer efficiencyTo achieve the purpose of closed collectionOrganic chemistryChemical industryGas phaseCirculator pump
A method for preparing glyceride carbonate by using a loop reaction device comprises the following steps: adding glycerin, dimethyl carbonate and an alkali catalyst into a loop reactor, starting a loop circulating pump, pumping out the materials from the bottom of the loop reactor into an outer circulating heat exchanger so as to raise the temperature of the materials, ejecting the materials into the loop reactor by using an ejector so as to circulate the materials, and reacting the materials; emitting methanol steam and dimethyl carbonate steam which are generated in the reaction together with nitrogen from the upper part of the loop reactor into a separating tower, wherein the dimethyl carbonate is condensed, and reflows from the bottom of the separating tower into the loop reactor, the methanol and the nitrogen flow out from the top of the separating tower into a methanol gas phase condenser so as to condense the methanol, and a small amount of uncondensed methanol, dimethyl carbonate and nitrogen is pumped into the loop reactor by the ejector of the loop reactor for further reaction; and after the reaction, evaporating out excessive dimethyl carbonate gas from the upper part of the loop reactor, enabling the dimethyl carbonate gas to enter a dimethyl carbonate gas phase condenser to be condensed and collected, and obtaining the glyceride carbonate from the loop reactor. The method has the advantages of no pollution and high mass and heat transfer efficiency.
Owner:CHINA RES INST OF DAILY CHEM IND
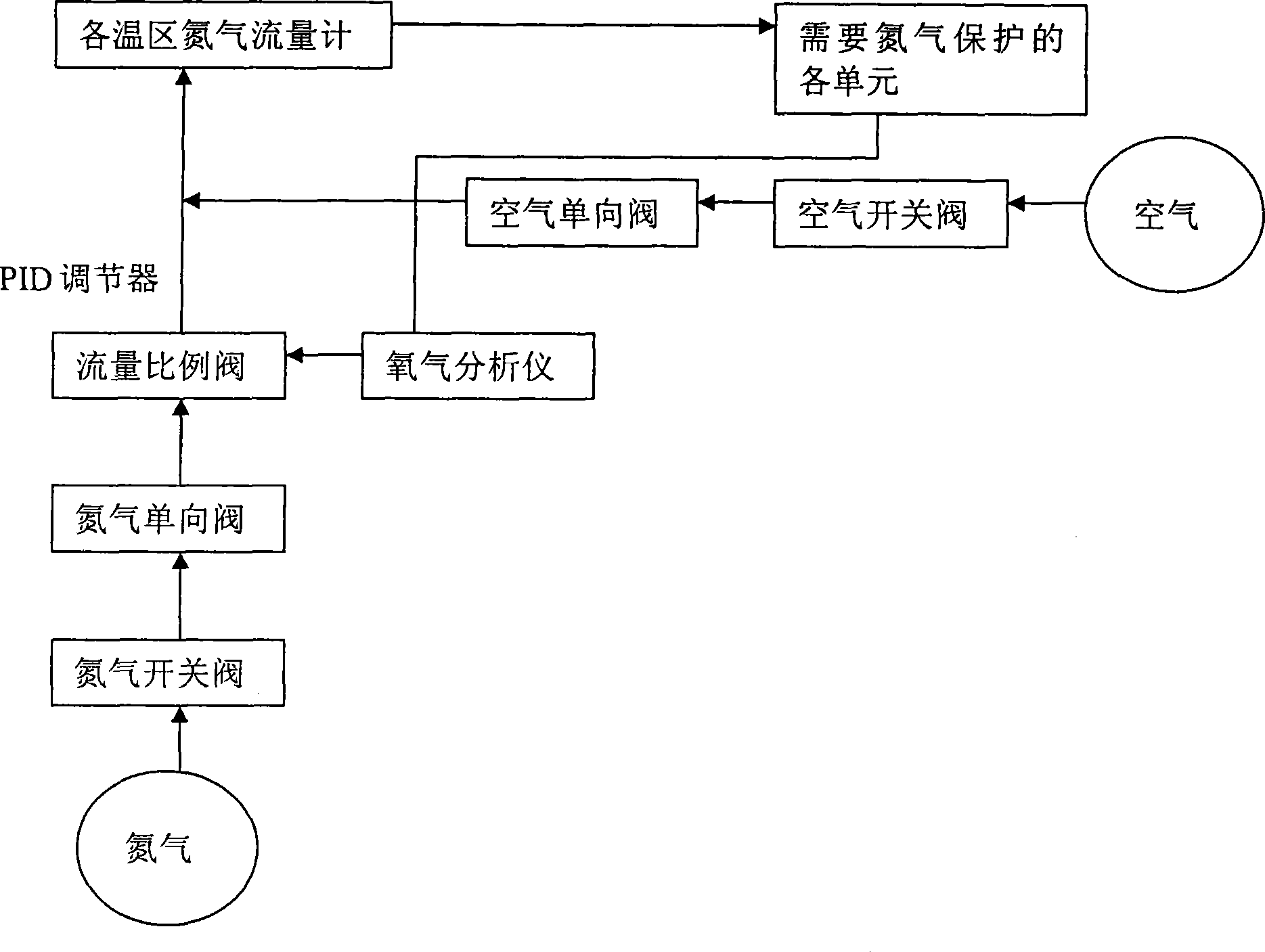
Nitrogen closed-loop control method and system
InactiveCN101364115AAdjust oxygen concentration in real timeGuaranteed normal consumptionControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsSoldering apparatusProportional controlLoop control
The invention provides a nitrogen gas closed-loop control method and a system which are used for adjusting the oxygen concentration in the hot zone of each unit requiring nitrogen protection in a reflow soldering furnace. An oxygen content analyzer is used for the on-line detection of the oxygen content of the gas inside the reflow soldering furnace; and a PID adjustor periodically adjusts the opening degree of a proportional control valve based on the closed-loop feedback, thereby controlling the nitrogen flow. The control method and the system can automatically detect the gas environmental conditions inside the reflow soldering furnace, automatically control the oxygen concentration in each hot zone inside the reflow soldering furnace, ensure that the oxygen concentration reaches the desired preset value as quickly as possible, and maintain the oxygen concentration at the preset value. The control method and system have the advantages of stable soldering environment, high soldering quality, low nitrogen consumption and low production cost.
Owner:PANDA ELECTRONICS GROUP +1
Device of boiling chlorination furnace for continuous slagging and slagging method
ActiveCN102774880AContinuous slaggingControlled slaggingTitanium halidesVertical tubeAutomatic control
The invention relates to a device of a boiling chlorination furnace for continuous slagging and a slagging method. The device is formed by a slagging pipe, a slagging valve, a water cooling spiral deslagging machine and a slagging tank that are sequentially connected through pipelines, the slagging valve comprises a vertical tube and a material discharge chamber that are in parallel, the material discharge chamber is communicated with the vertical tube through a hole at the bottom of the material discharge chamber, a material discharge opening is arranged at the upper part of the material discharge chamber, and the vertical tube and the bottom of the material discharge chamber are respectively provided with an air inlet. Slag forms stock columns in the vertical tube so that the device automatically seals, therefore, gas in the boiling chlorination furnace is prevented from leaking, slagging discharge rate is controlled through nitrogen flow regulation, and regulation and control of chlorination slagging rate are realized. According to the device, the boiling chlorination furnace realizes continuous slagging through a sealing and controllable manner without using a mechanical valve, therefore, the chlorination furnace is effectively prevented from leaking gas in the slagging process. The device has the advantages of being good in sealing performance, simple in operation, safe and reliable, easy to realize automatic control and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
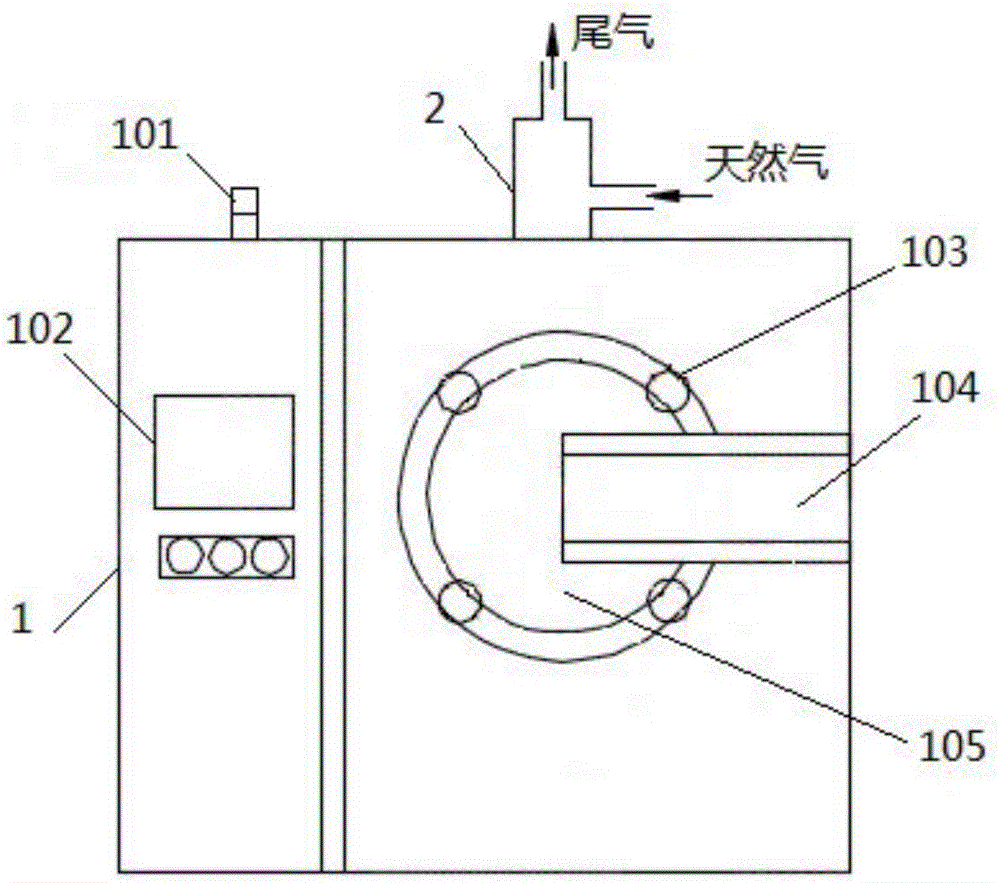
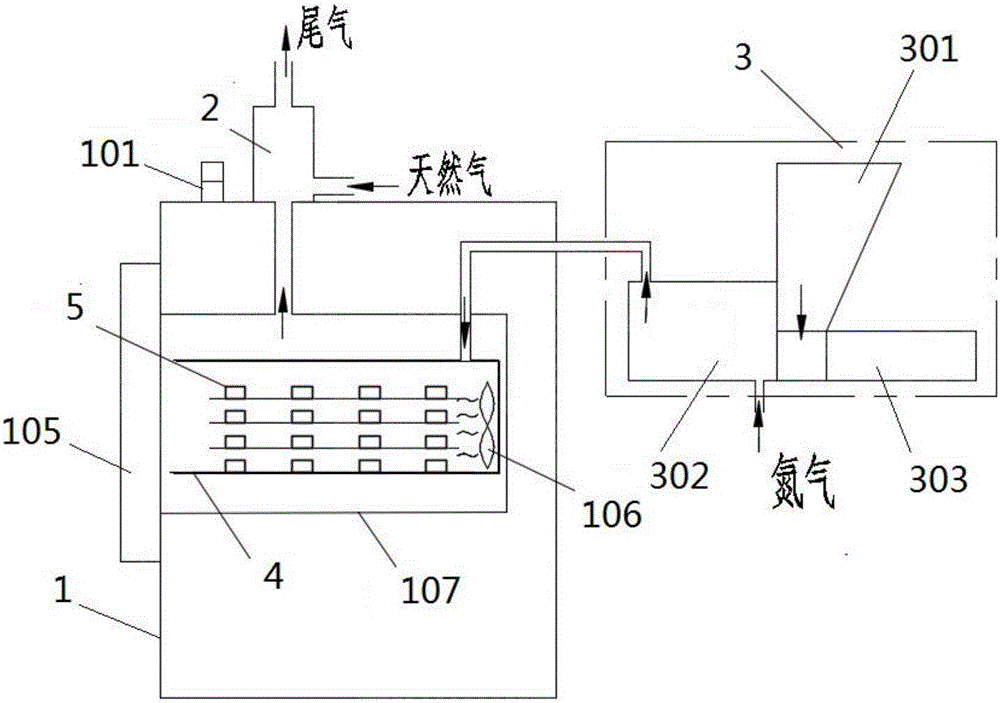
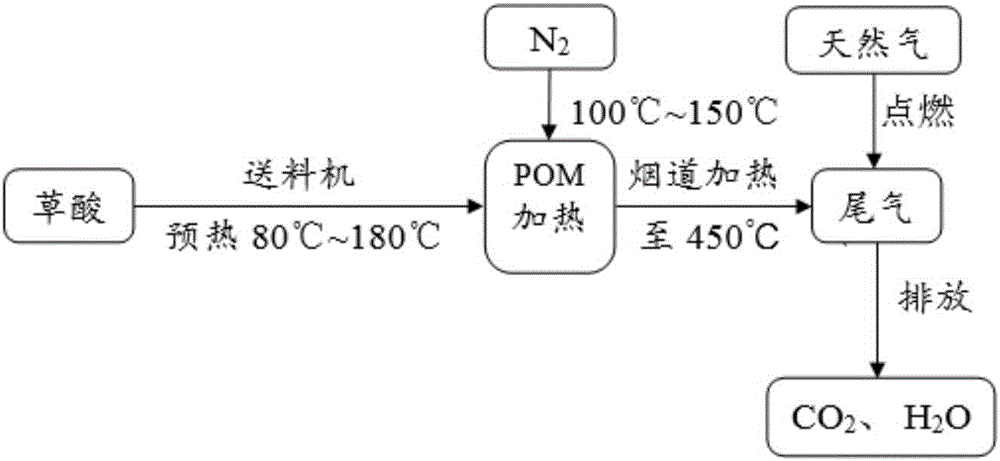
Catalytic debinding furnace taking oxalic acid as catalyst and catalytic debinding method
Disclosed are a catalytic debinding furnace taking oxalic acid as a catalyst and a catalytic debinding method. The catalytic debinding furnace comprises a furnace body and a feeding machine for conveying the oxalic acid into the furnace body. A debinding furnace pipe for holding materials is located inside the furnace body. The debinding furnace pipe is connected with the feeding machine through a heat-resisting pipeline. A heating tank for introducing nitrogen and a storage tank for holding the oxalic acid are arranged inside the feeding machine. The heating tank is used for heating the oxalic acid so that the oxalic acid can be gasified. The gasified oxalic acid and the nitrogen flow into the debinding furnace pipe together to participate in a catalytic reaction. The debinding furnace pipe is connected with a combustion chamber located above the furnace body through an exhaust pipeline, the combustion chamber is provided with a gas inlet and a gas exhaust port, natural gas is introduced into the combustion chamber through the gas inlet so that decomposition products of the oxalic acid can be combusted, and water vapor, carbon dioxide and waste gas in the furnace body are exhausted through the gas exhaust port. Through the catalytic debinding furnace taking the oxalic acid as the catalyst and the catalytic debinding method, the product yield can be increased; and besides, tail gas only contains CO2 and H2O, and thus the standard of environment-friendly emission is reached.
Owner:SHENZHEN SINTERZONE TECH CO LTD
Olefin polymer effluent gas recycling device and method in production
ActiveCN104792117AEfficient recyclingHigh recovery rateSolidificationLiquefactionOligomerOlefin polymerization
The invention discloses an olefin polymer effluent gas recycling device and method in production. The device comprises a compressing mechanism, a pre-dissociation mechanism and a cryogenic mechanism. The compressing mechanism is used for receiving effluent gas of olefin polymer in the production, the pressure of gas components in the effluent gas is compressed in the same grade, and recycled C4+ high-carbon hydrocarbon flow and residue effluent air flow are output. The pre-dissociation mechanism is used for receiving the residue effluent air flow from the compressing mechanism, and outputting recycled oligomerization physical flow and the residue effluent air flow. The cryogenic mechanism is used for receiving the residue effluent air flow from the pre-dissociation mechanism, and recycling C2+low carbon hydrocarbon flow and nitrogen flow in the residue effluent air flow. By cooperative working of the compressing mechanism, the pre-dissociation mechanism and the cryogenic mechanism, hydrocarbon substances in the effluent gas can be effectively recycled, it is achieved that the low polymer is recycled in low energy consumption, and meanwhile the hydrocarbon and the nitrogen with high recycling rates can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation of asymmetric polyethylene hollow fiber membrane
ActiveUS20070045175A1Reduce water permeabilitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiberHollow fibre membrane
A porous polyethylene hollow fiber membrane having a pore-size gradient across the inner and outer surfaces thereof is prepared by introducing, during the cooling step of a melt-spun polyethylene hollow fiber, a nitrogen flow and a solvent having a boiling point in the range of 30 to 80° C. to the inner and outer surfaces of the melt-spun hollow fiber, respectively.
Owner:C M S COSTRUZIONE MACCHINE SPECIALI
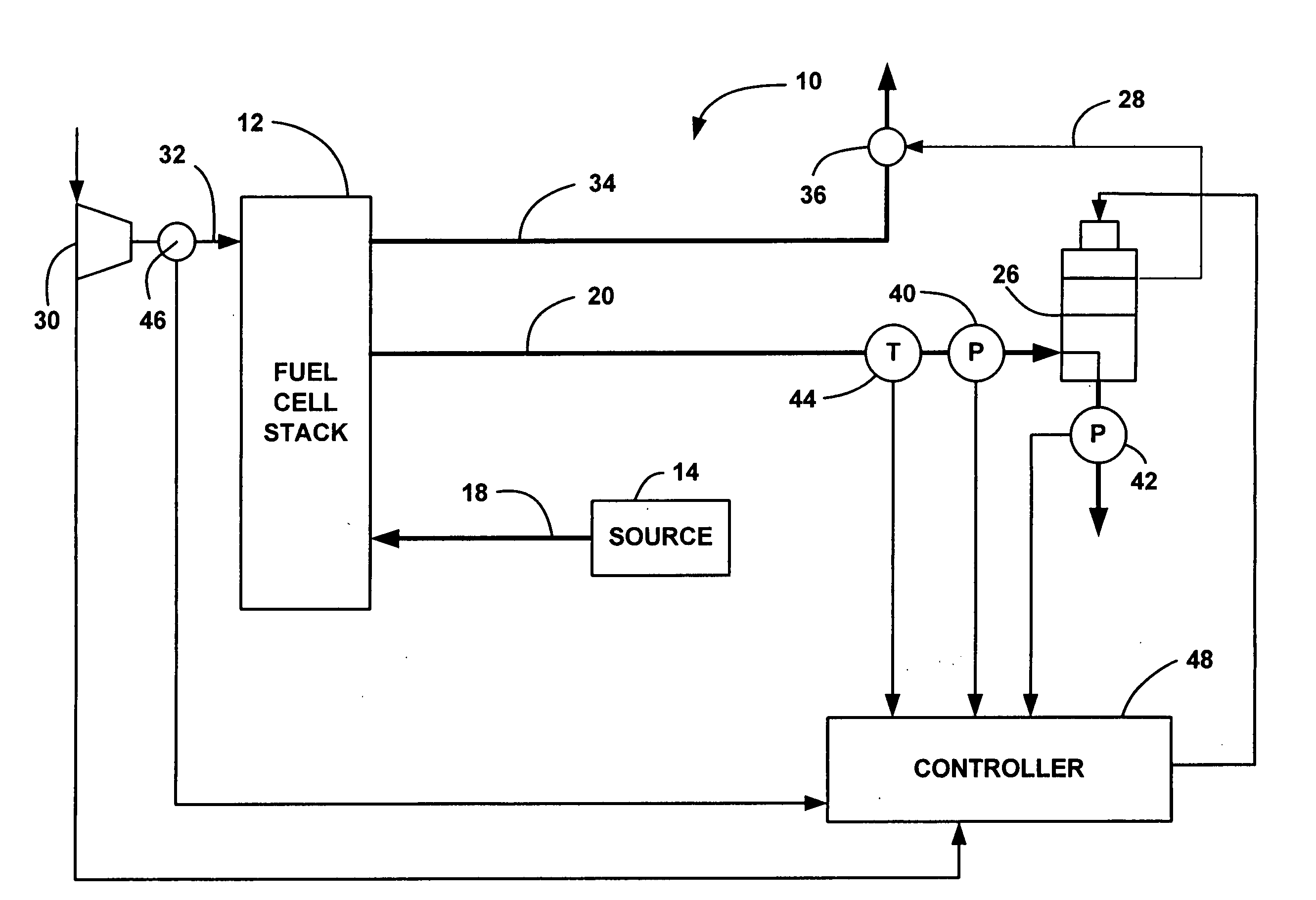
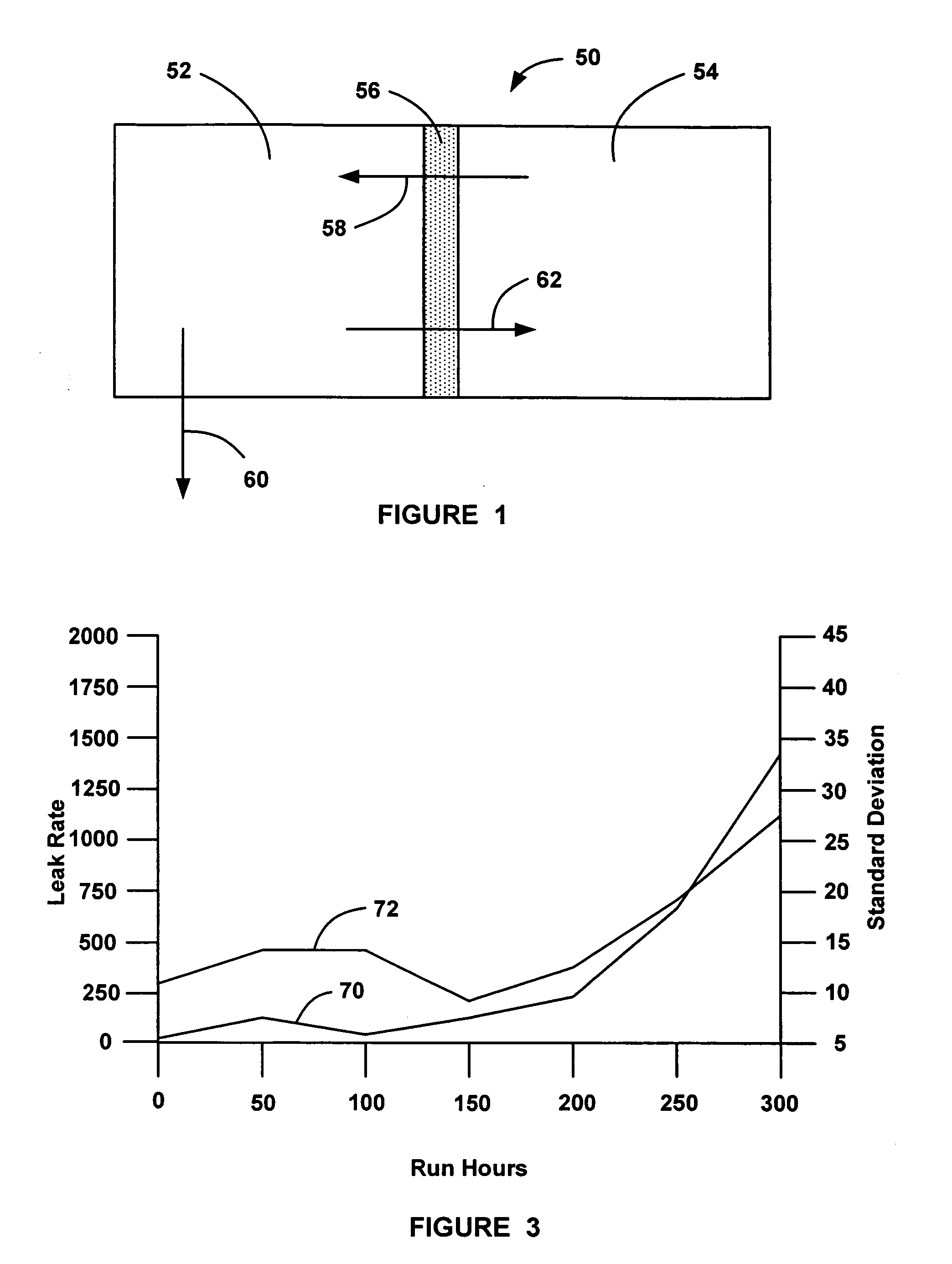
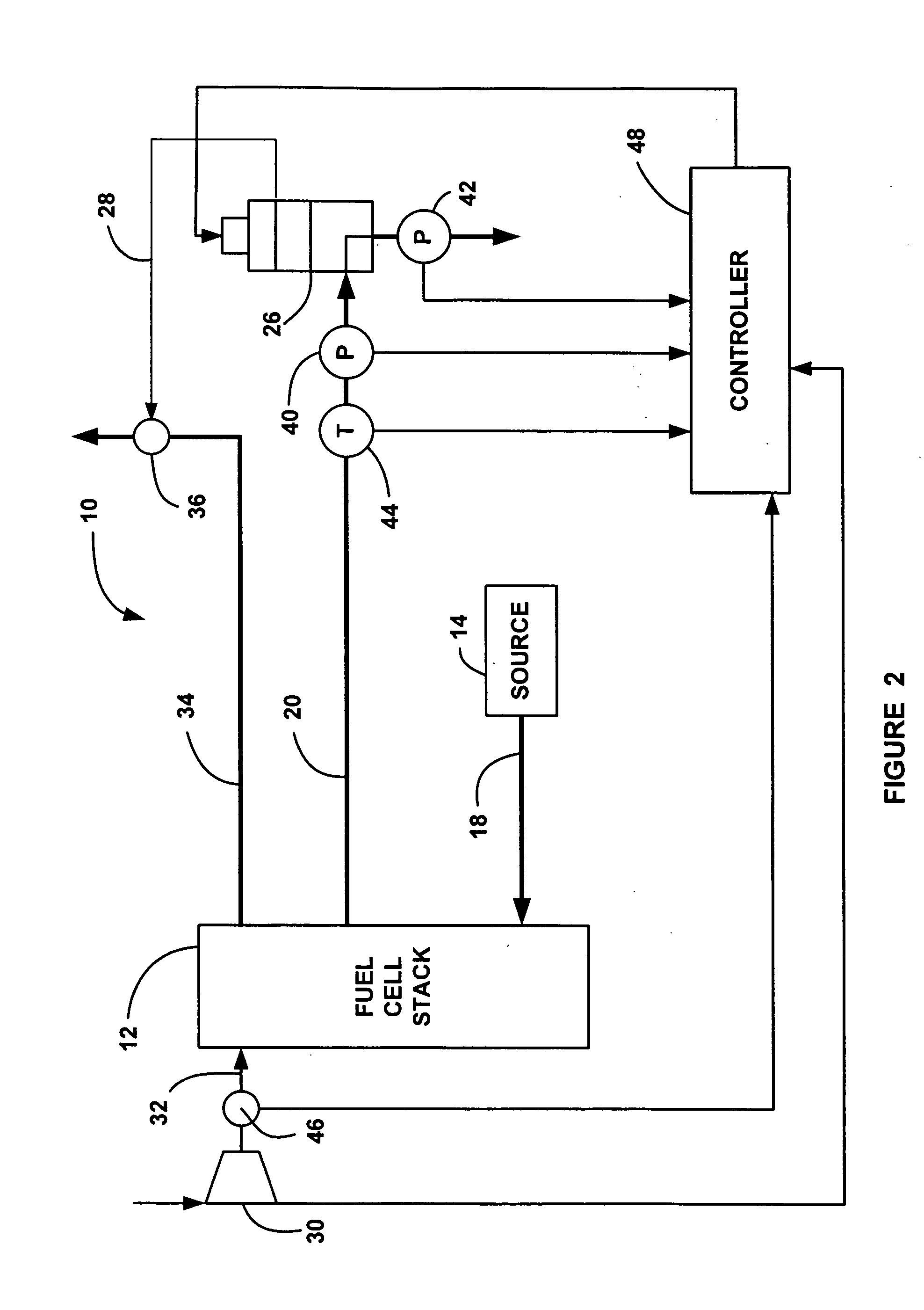
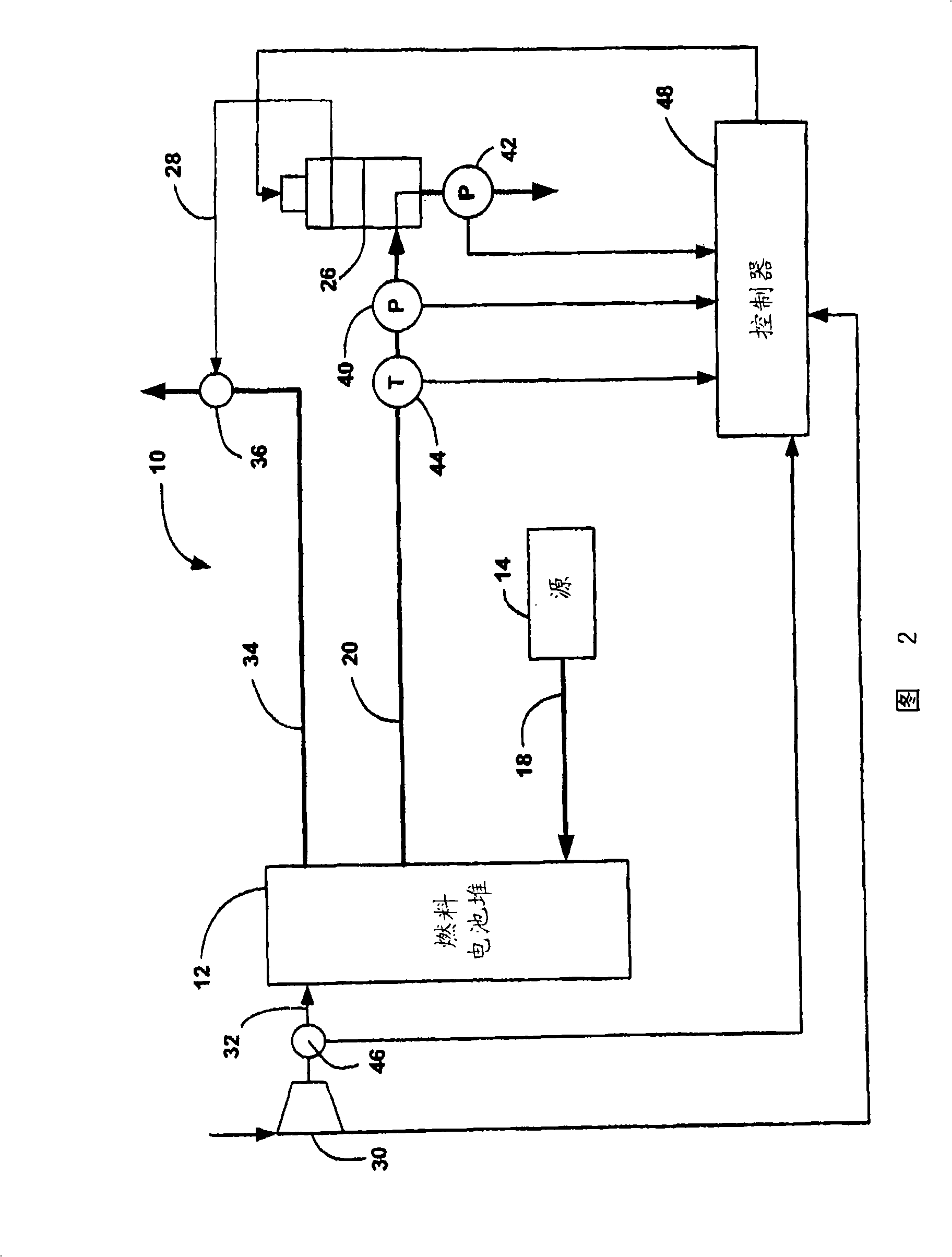
Online detection of stack crossover rate for adaptive hydrogen bleed strategy
A system and method for determining when to provide an anode exhaust gas bleed from a fuel cell stack as the fuel cell stack ages. The method determines the amount of nitrogen flowing from a cathode side to an anode side of the fuel cell stack. The method also determines the amount of nitrogen flowing from the anode side to the cathode side by determining a standard deviation of voltage outputs of the fuel cells, and using the standard deviation as a model for determining the leak rate of nitrogen from the anode side to the cathode side. The method determines the concentration of nitrogen in the anode side based on the nitrogen flow between the cathode and anode side, and opens a bleed valve to bleed the anode exhaust gas if the concentration of nitrogen in the anode side goes above a predetermined value.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Porous carbon material and method for preparing same
The invention relates to a porous carbon material and a method for preparing the same. The method for preparing the porous carbon material comprises the following steps of: using porous organic framework material poly-tetraphenylmethane as a raw material, taking alkali metal hydroxide such as KOH, NaOH or CsOH as an activating agent, and mixing the raw material and the alkali metal hydroxide in a certain proportion; under the condition of nitrogen flow, slowly programmable heating up to the activation temperature from the room temperature; and maintaining the nitrogen flow, controlling the temperature to be the activation temperature, and carrying out activation for at least 30 minutes to obtain the porous carbon material. The preparation method of the porous carbon material is simple in technology; and the porous carbon material prepared by the method is high in specific surface area and heat stability and uniform in pore size distribution, and has good gas storage property.
Owner:ZHUHAI PAINTER TECH
Device and method for carrying out microwave thermal desorption on oil-containing drilling cuttings
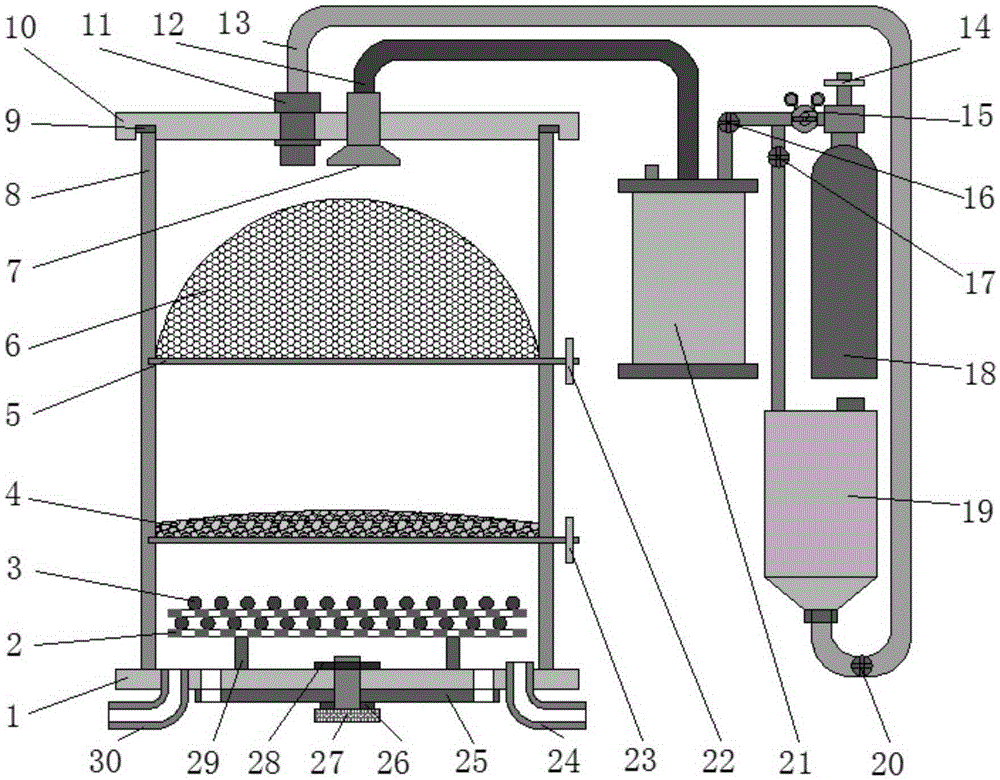
InactiveCN104141465AImprove uneven distributionGood performance of entrainment and entrainmentConstructionsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMicrowaveThermodynamics
The invention discloses a device for carrying out microwave thermal desorption on oil-containing drilling cuttings. The device comprises a microwave generation and conduction unit, a reaction unit, a nitrogen purging unit and a condensation and separation unit; the microwave generation and conduction unit is used for generating micro waves and conducting the generated micro waves to a reaction unit; (ii) the reaction unit is used for receiving the micro waves from the microwave generation and conduction unit and enabling the micro waves to act on the oil-containing drilling cuttings; (iii) the nitrogen purging unit comprises a nitrogen source, a flow controller and at least two nitrogen pipelines, is used for inputting at least two bunches of nitrogen flow into the reaction unit so as to remove air together with oil gas generated by reaction and is capable of controlling the flow velocity of the nitrogen flow; (iv) the condensation and separation unit is used for cooling the oil gas which is generated by the reaction and condensing the oil gas into liquid phase. The invention also discloses a method for carrying out the microwave thermal desorption on the oil-containing drilling cuttings by using the device.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Method for preparing 3C-SiC nanoparticles 2nm in grain size through laser ablation process
InactiveCN103754879AStrong and stable emissionStrong and stable light emissionMaterial nanotechnologySilicon carbideLaser lightGreen-light
The invention discloses a method for preparing 3C-SiC nanoparticles 2nm in grain size through a laser ablation process. The method comprises the steps of sequentially ultrasonically cleaning a 6H-SiC polycrystalline ceramic chip in de-ionized water, absolute ethyl alcohol and acetone for 5-10min, and drying through an electric hair drier or nitrogen flow; ultrasonically processing in de-ionized water for 3-5min, and cleaning residual organic matters; adding the cleaned 6H-SiC polycrystalline ceramic chip in a beaker, and adding de-ionized water which is 4-5mm above the upper surface of the 6H-SiC polycrystalline ceramic chip; placing the beaker on a three-dimensional controllable platform, and repeatedly moving the platform slowly in a horizontal direction; radiating laser on the polycrystalline ceramic chip which is soaked in the de-ionized water for 45-60min by taking an excimer pulse laser as a laser light source at wavelength 248nm and an intensity of 300-350mJ / Pulse after being reflected and focused, thus obtaining 3C-SiC nanoparticles suspending in the de-ionized water. The prepared 3C-SiC nanoparticles disclosed by the invention are about 2nm in grain size and free from an agglomeration phenomenon, and the sample has relatively strong light emission within a purple-blue-blue green light range at wavelength 415-495nm.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
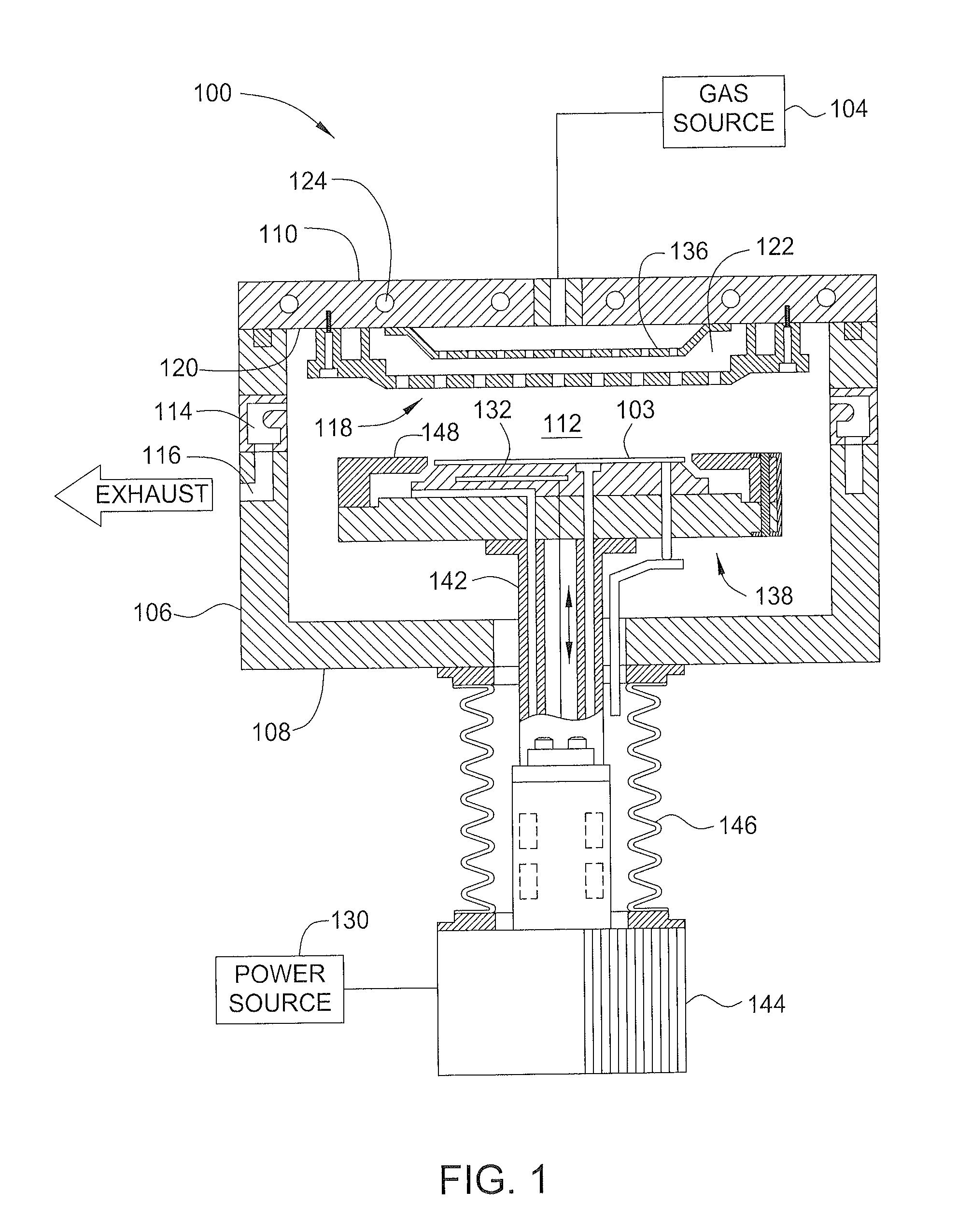
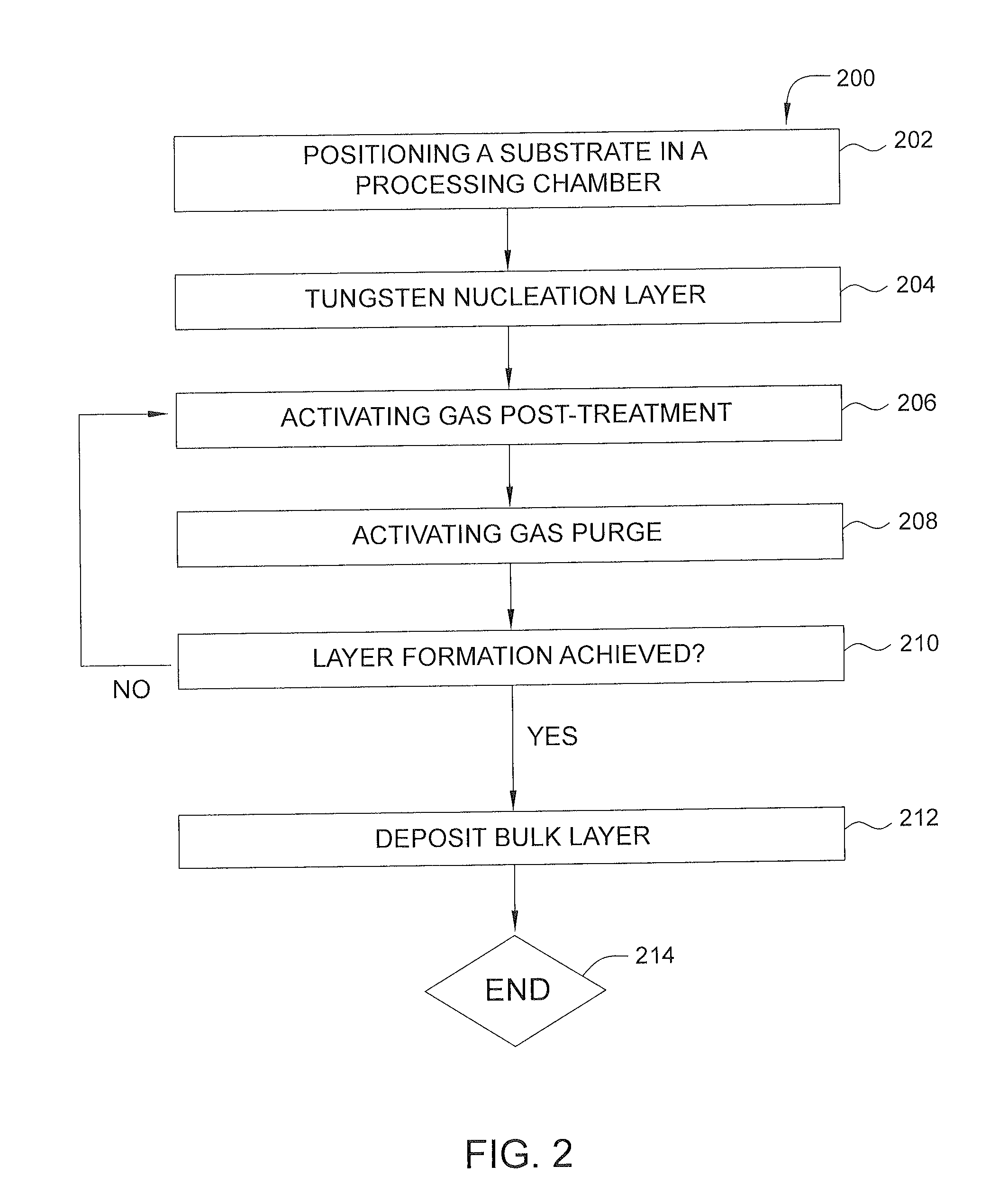
Method of reducing tungsten film roughness and resistivity
InactiveUS20140147589A1Low resistivityReduce roughnessChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperatureNucleation
Methods for controlling crystal size in bulk tungsten layers are disclosed herein. Methods for depositing a bulk tungsten metal layer can include positioning a substrate with a barrier layer in a processing chamber, forming a tungsten nucleation layer, post-treating the nucleation layer with one or more treatment gas cycles including an activating gas and a purging gas, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature, and depositing a bulk tungsten layer with alternating nitrogen flow on the nucleation layer. The post-treatment cycling can be applied optionally to the bulk metal deposition with alternating nitrogen flow.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Nano-stack TiN gradient film and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101298655AHigh bonding strengthSuppress generationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSuperalloyNitrogen gas
The invention relates to an ion plating technique, in particular to a nano laminated TiN gradient film and a preparation method thereof, which solves the problems that superficial wear resistance and corrosion resistance of parts such as automobile engine valves and plane blades that work at the temperature lower than 600 DEG C and are composed of high-temperature alloys, as well as the problem that plating layers of normal TiN ion plating films are easy to crack. The invention utilizes the ion plating technique for depositing the nano laminated TiN gradient film on the surface of the high-temperature alloy. The preparation method of the nano laminated TiN gradient film comprises following steps: firstly, oil stains on the surface of the alloy are removed and the alloy is ultrasonically cleaned in an organic solvent; secondly, a model that is cleaned is loaded and clamped on a clamping fixture and placed into a vacuum chamber of an ion plating device, and after the vacuum chamber is vacuumized into a required vacuum degree and heated to a certain temperature, argon is let into the vacuum chamber so as to implement ion bombardment cleaning; finally, by adjusting the changes of beam current of an evaporator source, negative bias voltage and nitrogen flow rate in a plating process, the nano laminated TiN gradient film with good inhibiting performance of plating layer cracks is obtained, the thickness of each layer of the nano laminated TiN gradient film is 50 to 100 nanometers, and the total thickness of the plating film can be adjusted in a range between 1.5 to 3.6 micrometers.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for growth of germanium nitrogen codoped silicon carbide single crystal material
ActiveCN106968018AAchieve dopingRealize germanium nitrogen co-dopingPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsHigh concentrationOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a method for growth of a germanium nitrogen codoped silicon carbide single crystal material. A PVT method is adopted according to the method; in the germanium-doped silicon carbide single crystal growth process, nitrogen at a certain proportion is led into a growth atmosphere, argon is led in to serve as a carrier gas with the pressure controlled to be 700-850 mbar, argon flow is 15-30 sccm, and the nitrogen flow is 0.5-2 sccm; and the germanium nitrogen codoped silicon carbide single crystal is obtained. On the one hand, high-concentration germanium element doping is implemented, and on the other hand, by adjusting specific doping concentration of germanium and nitrogen, the goal of increasing silicon carbide crystal lattice fitness degree, reducing crystal stress and improving crystal quality is achieved. Application of the silicon carbide crystal material to visible light and infrared light wave bands is expanded.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Online detection of stack crossover rate for adaptive hydrogen bleed strategy
The invention relates to online detection of stack crossover rate for adaptive hydrogen bleed strategy, in particularly, a system and method for determining when to provide an anode exhaust gas bleed from a fuel cell stack as the fuel cell stack ages. The method determines the amount of nitrogen flowing from a cathode side to an anode side of the fuel cell stack. The method also determines the amount of nitrogen flowing from the anode side to the cathode side by determining a standard deviation of voltage outputs of the fuel cells, and using the standard deviation as a model for determining the leak rate of nitrogen from the anode side to the cathode side. The method determines the concentration of nitrogen in the anode side based on the nitrogen flow between the cathode and anode side, and opens a bleed valve to bleed the anode exhaust gas if the concentration of nitrogen in the anode side goes above a predetermined value.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
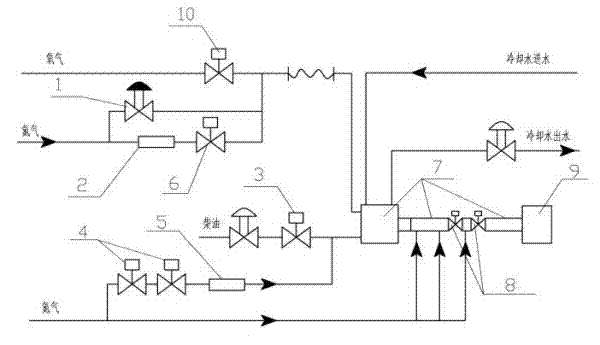
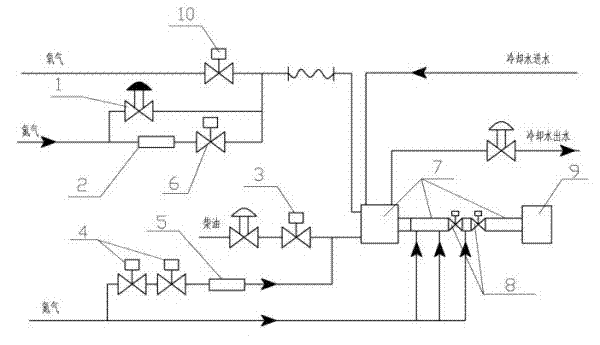
Igniting method for gasification furnace start-up burner
The invention relates to an igniting method for a gasification furnace start-up burner. The method comprises the following steps of: before ignition, putting a start-up burner into a hearth of a gasification furnace and purging the start-up burner with nitrogen; and in the ignition process, introducing pure oxygen and diesel into the start-up burner, adjusting nitrogen flow, wherein the pure oxygen flow is 1.15-1.40kg / s, the diesel flow is 0.3-0.45kg / s, and the nitrogen flow is 0.01-0.05kg / s. According to the invention, through introducing certain nitrogen in the ignition process and replacing pure oxygen combustion with oxygen enriched combustion, the phenomenon that the start-up burner is easy to damage because of partial overheating is avoided effectively, and the phenomenon that the start-up burner is damaged by the greater temperature fluctuation of the start-up burner caused by the frequent adjustment of the flow of the fuel diesel in the start-up burner is avoided simultaneously; the ignition success rate of the gasification furnace is improved, the labor intensity is reduced, the production cost is saved, and the maintaining expense is reduced.
Owner:HENAN LONGYU COAL CHEM
Method for simultaneously detecting five medicaments in water
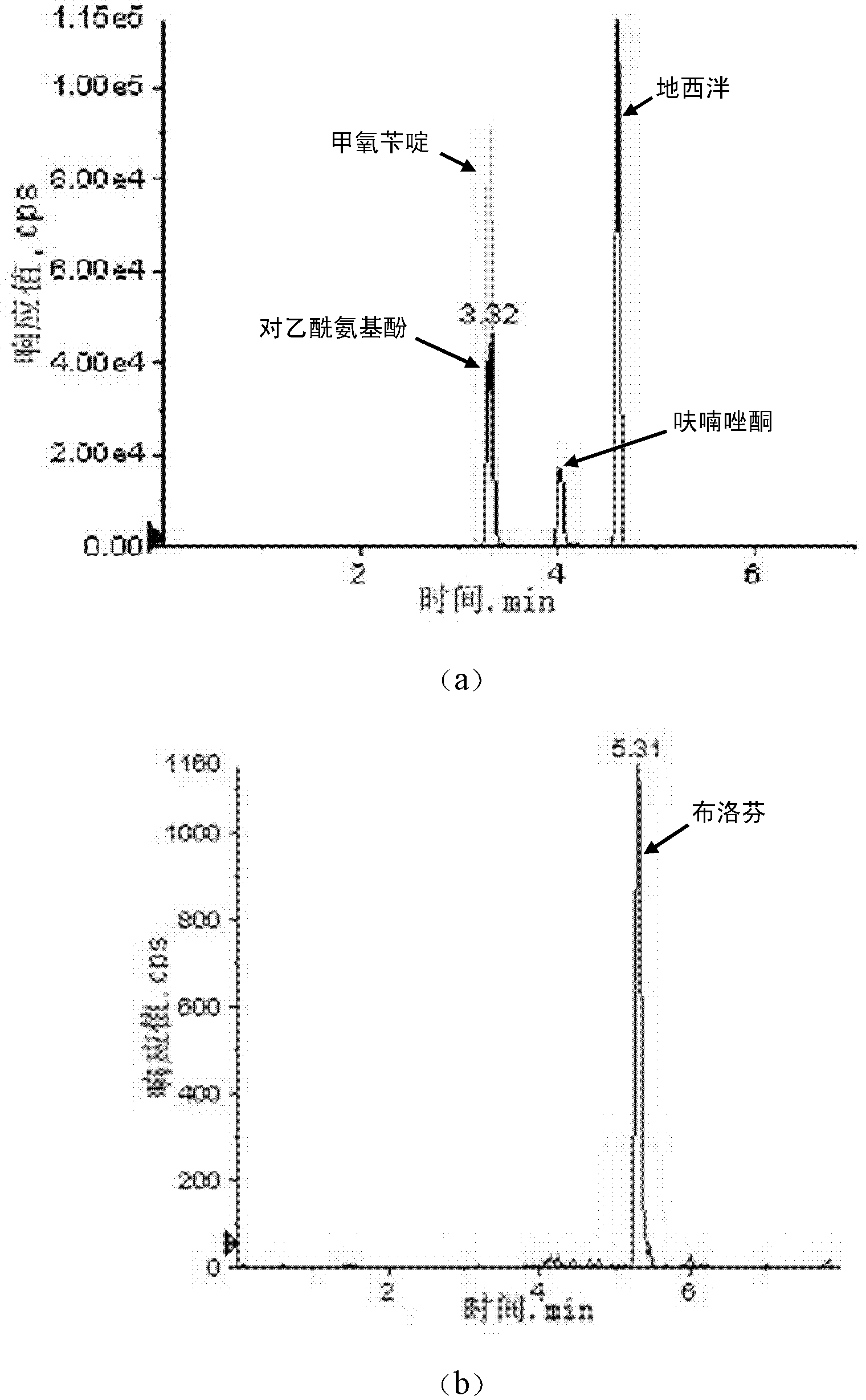
InactiveCN103323550AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityComponent separationTrimethoprimSolid phase extraction
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting the medicaments such as furazolidone, diazepam, trimethoprim, acetaminophen and ibuprofen in water. The method comprises the following steps of: filtering a water sample to remove suspended matter; adjusting the pH of the water sample to be 2 to 4; activating hydrophile-lipophile balance (HLB) solid phase extraction column by using acetone, methanol, ammonium acetate-containing formic acid aqueous solution and ultrapure water in sequence; after the enrichment is finished, drying the HLB solid phase extraction column under the protection of nitrogen and eluting the HLB solid phase extraction column; collecting eluant, and drying the eluant by blowing a nitrogen flow; adding acetonitrile to dissolve the residue; and quantitatively detecting the concentration of the five medicaments. By the method, the water sample pretreatment is environment-friendly, easy to operate, large in enrichment factor, and high in reproducibility; and the content of the five common medicaments in a water environment can be analyzed quickly and accurately.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for preparing TiB2-Co coating by supersonic-speed flame spraying
InactiveCN102363877AImprove wear resistanceGood mechanical propertiesMolten spray coatingPorosityWear resistant
The invention discloses a method for preparing a wear-resistant TiB2-Co coating by supersonic-speed flame spraying. Metal ceramic mixed TiB2-based and Co-based alloying powder is formed by performing ball-milling by mechanical alloying at room temperature at the rotation speed of 440 revolutions per minute for six hours; the surface of a piece to be sprayed which is obtained after sand blasting is uniform and coarse; a coating of which thickness is 150 to 200mu m is sprayed on the piece to be sprayed; supersonic-speed flame spraying process parameters are specifically that: oxygen pressure is 1.02Mpa, propane pressure is 0.4 to 0.6Mpa, nitrogen pressure is 0.65Mpa, oxygen flow is 10 to 12.5m<3>h, propane flow is 1,100 to 1,200L / min, nitrogen flow is 1,000 to 1,100L / miunm, vertical speed of a spraying area is 50mm / s, and horizontal speed of the spraying area is 170mm / s, and spraying distance is 185mm; and the invention has the advantages that the TiB2-Co coating which has high wear resistance can be obtained by performing supersonic-speed flame spraying of TiB2-Co composite metal ceramic powder. The TiB2-Co coating has a good mechanical property, and a compact layer structure, is low in porosity.
Owner:JIUJIANG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com