Patents
Literature
95 results about "Deposition pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
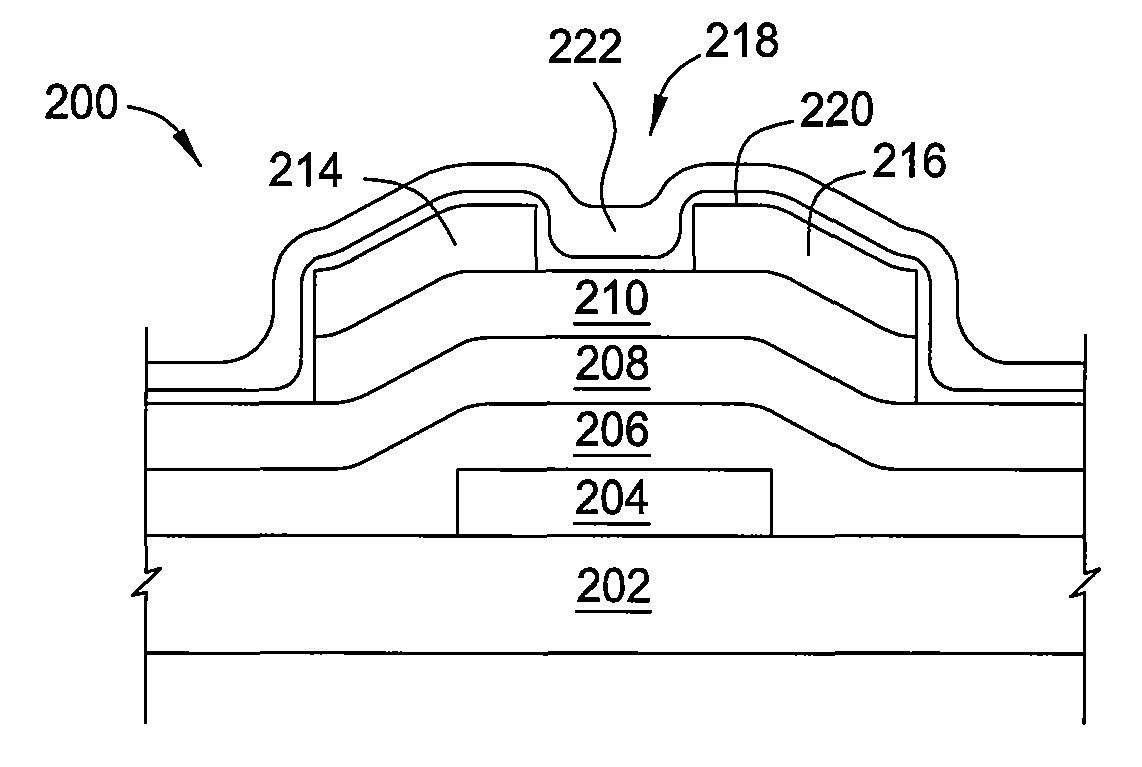
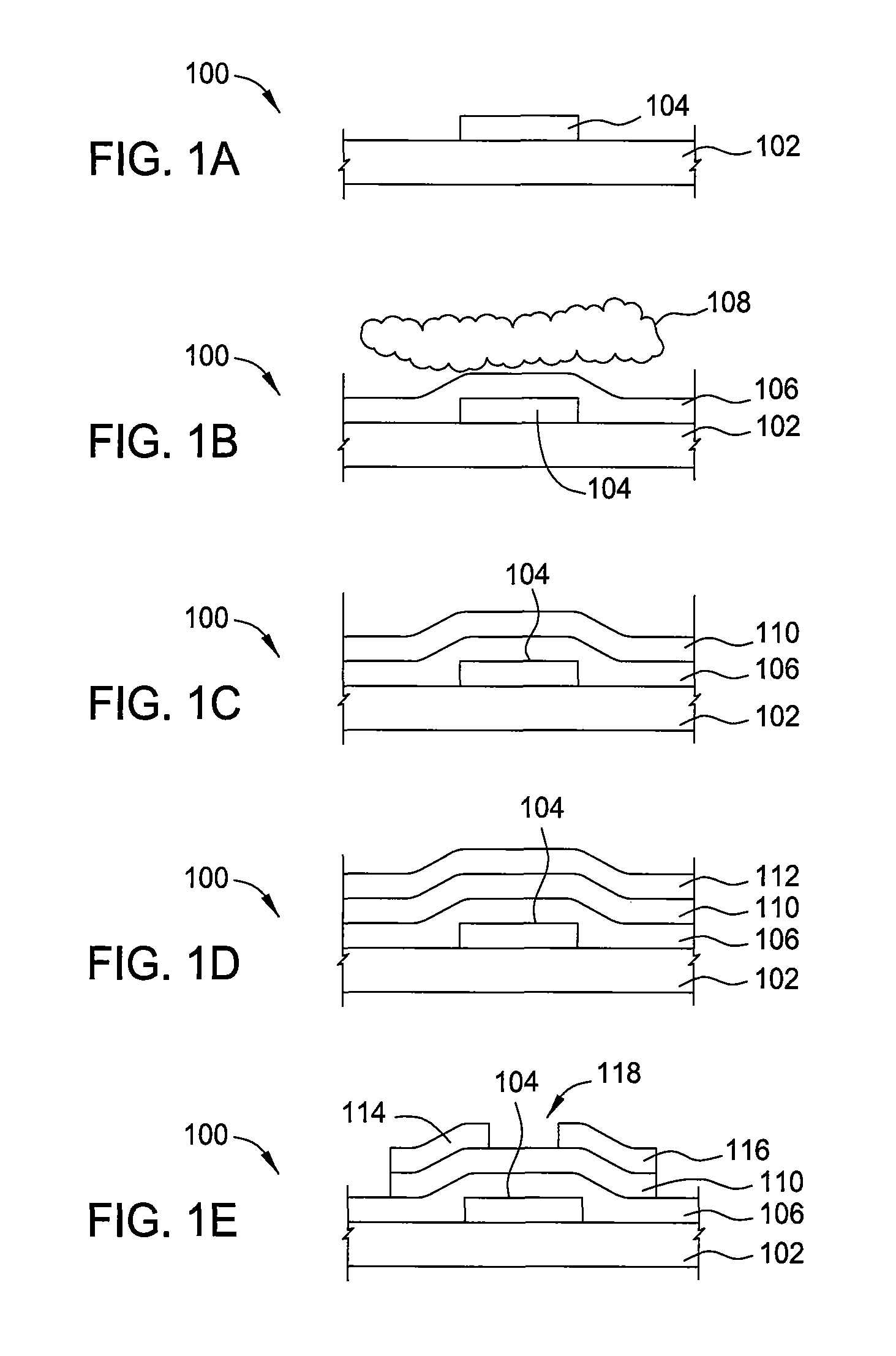
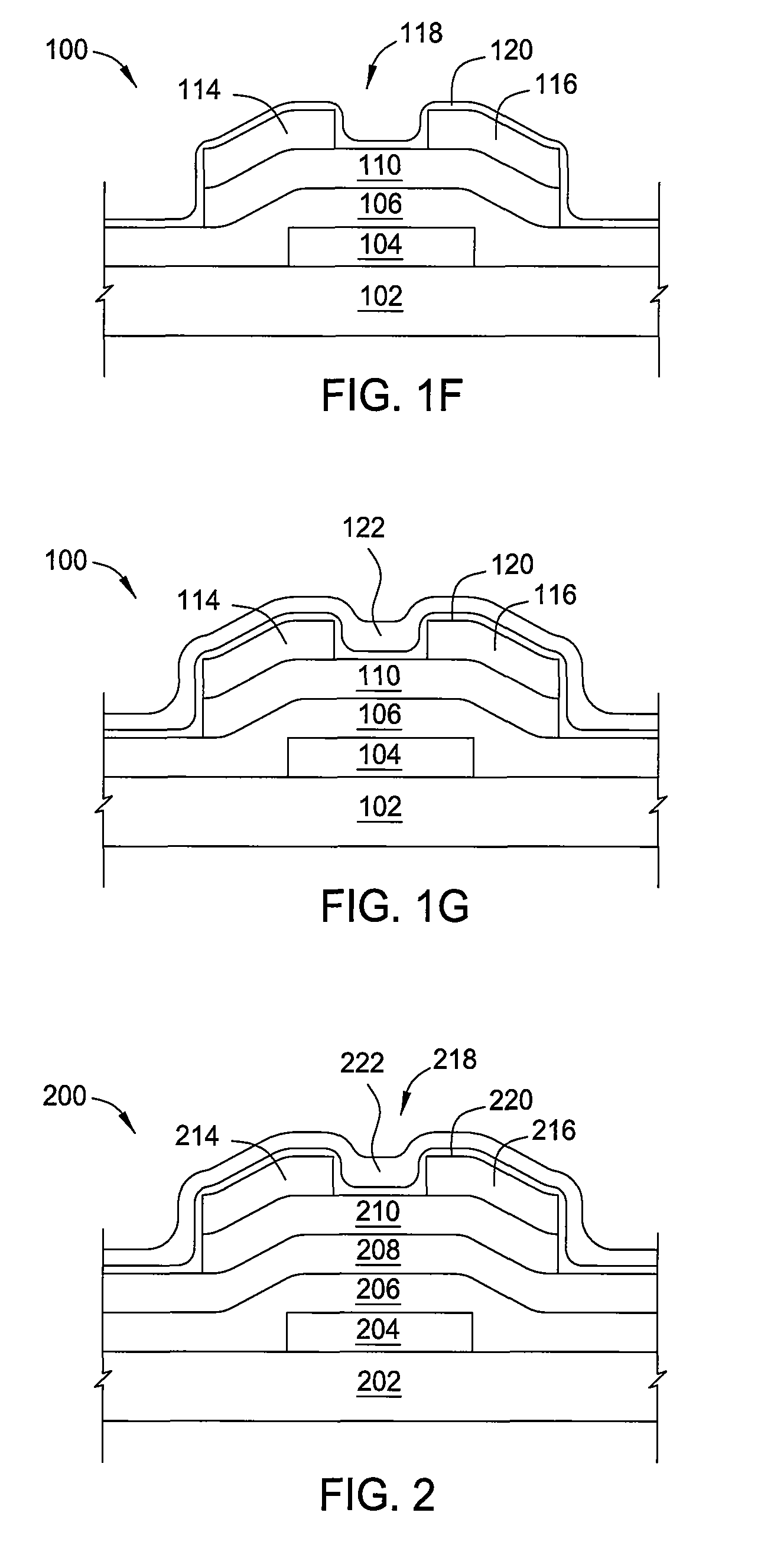
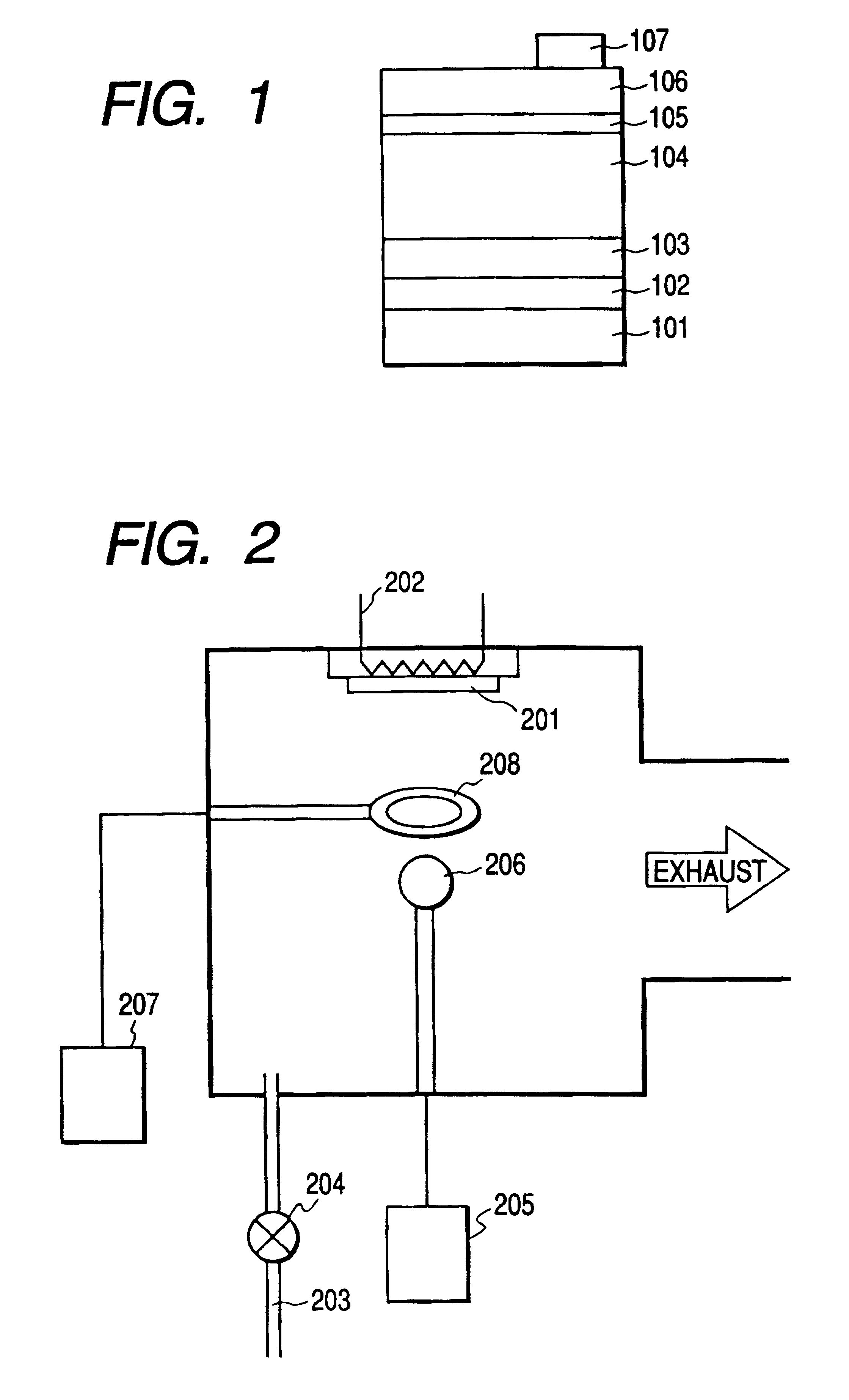
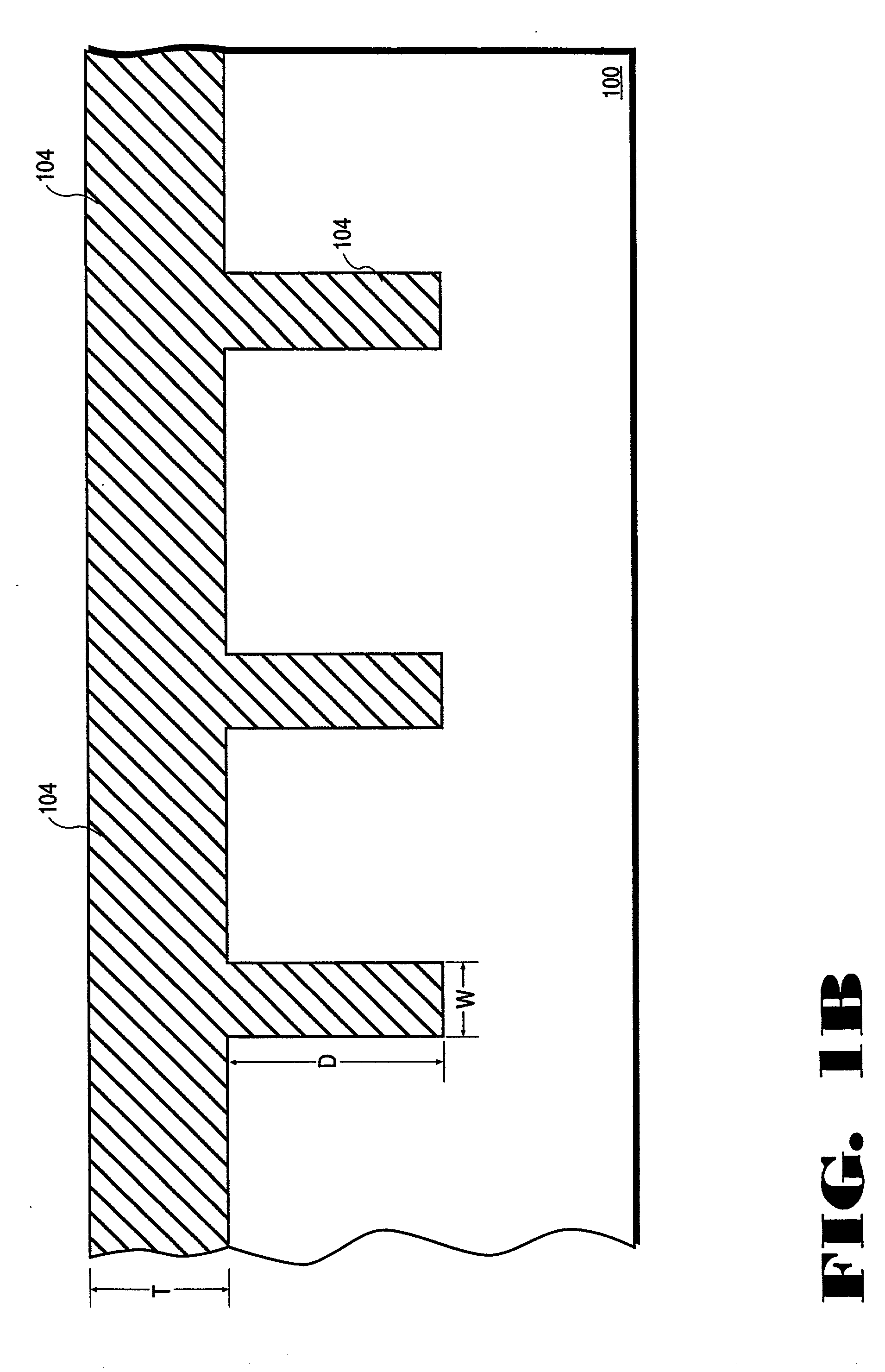
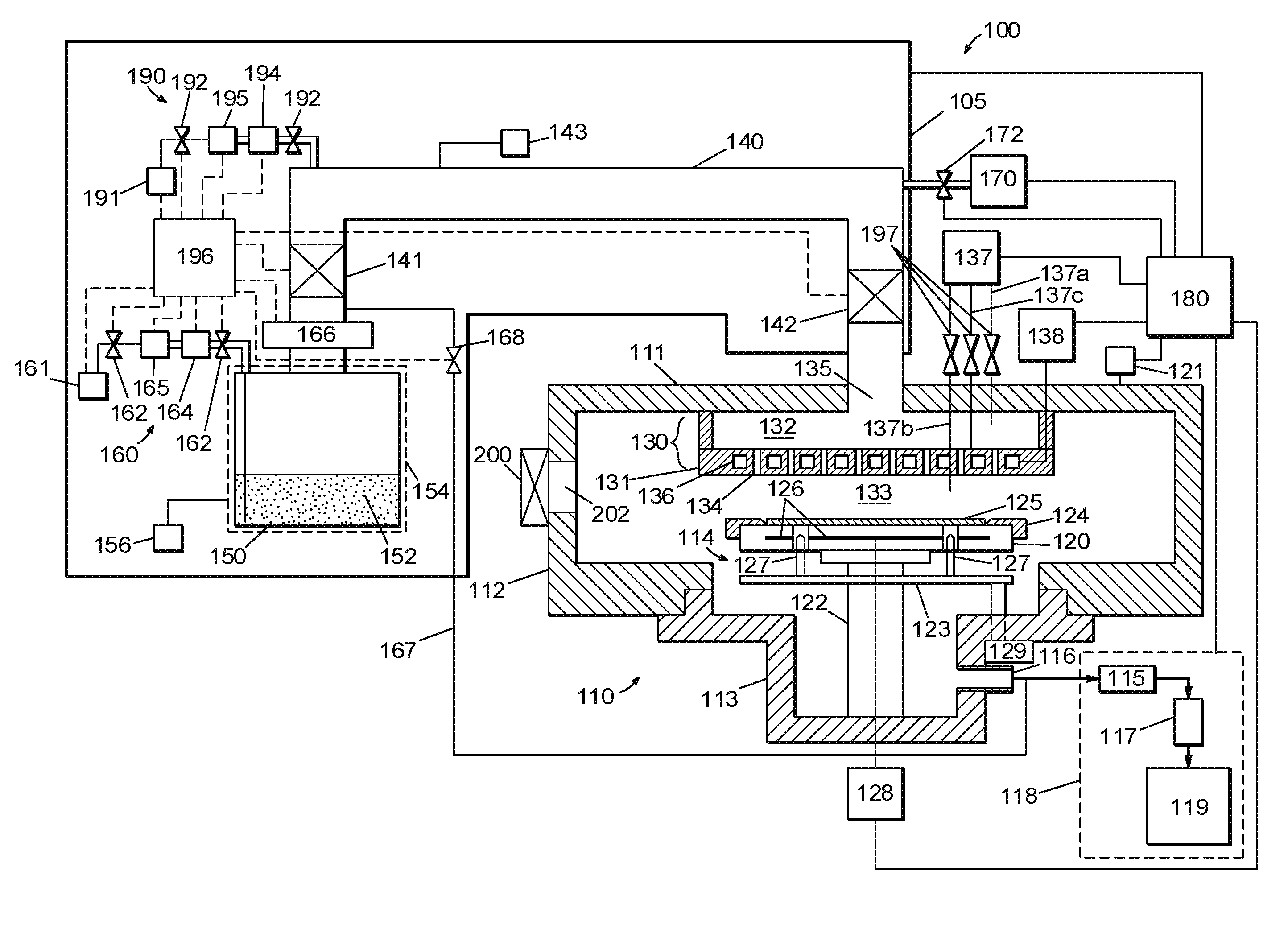
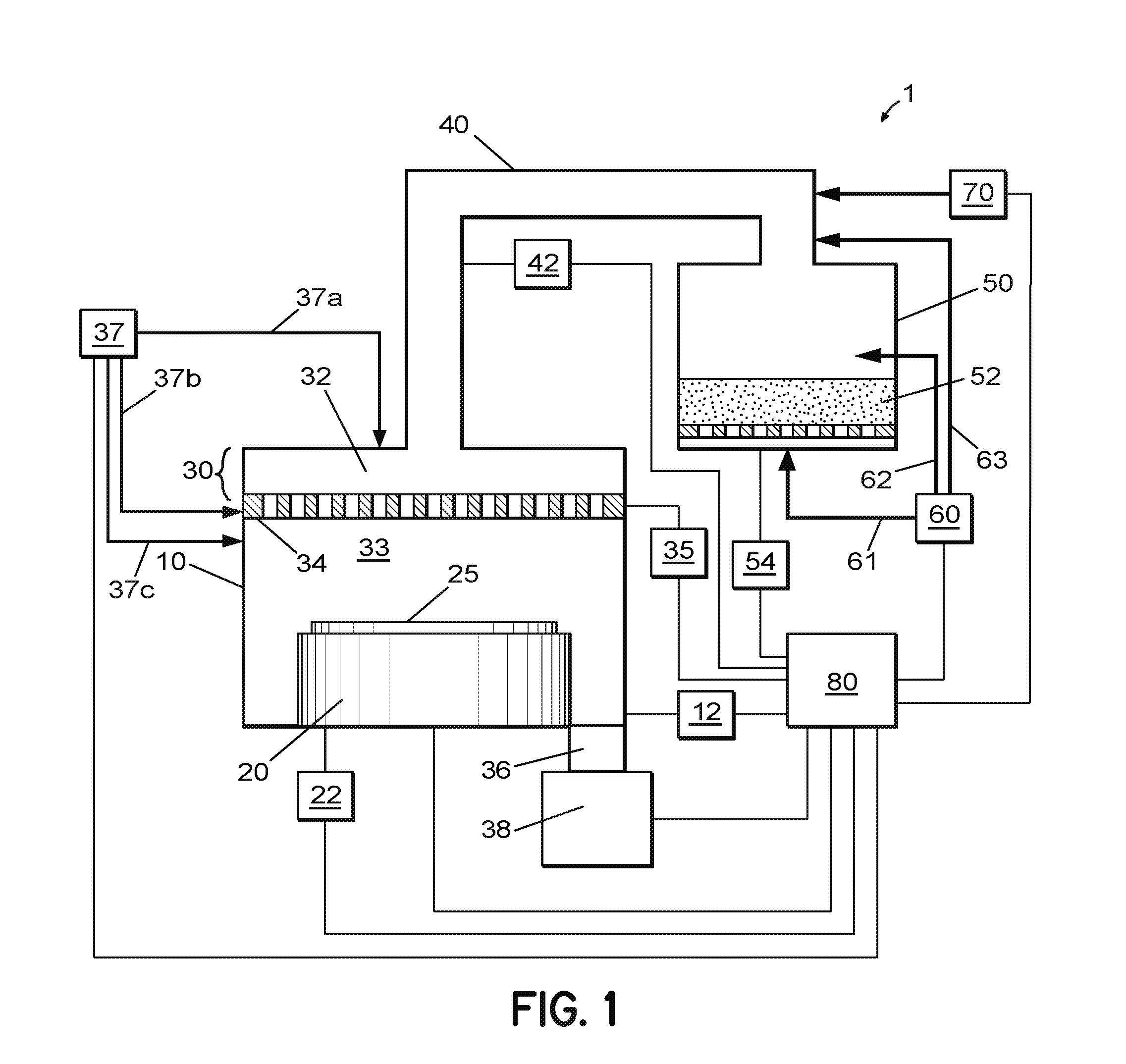
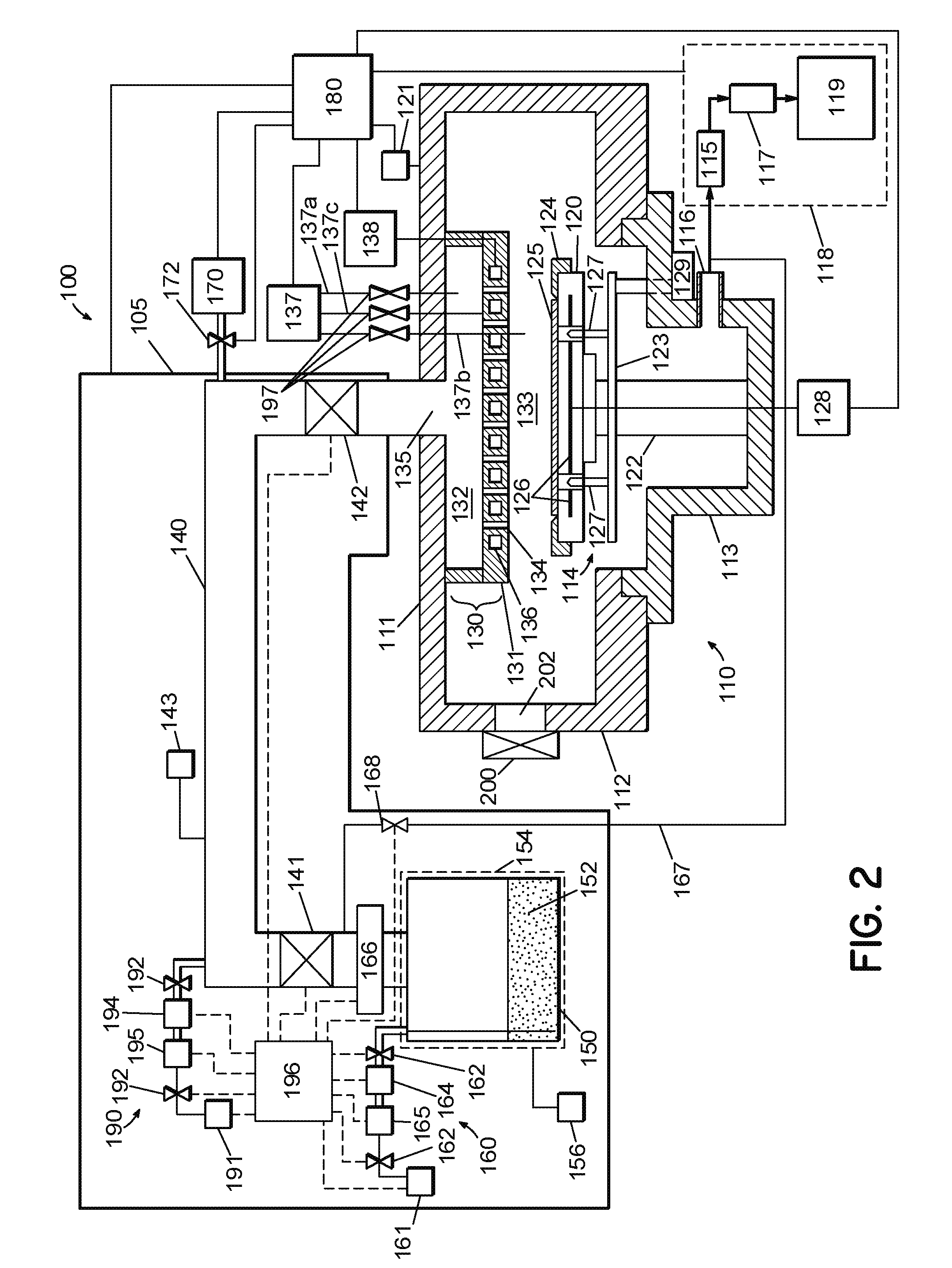
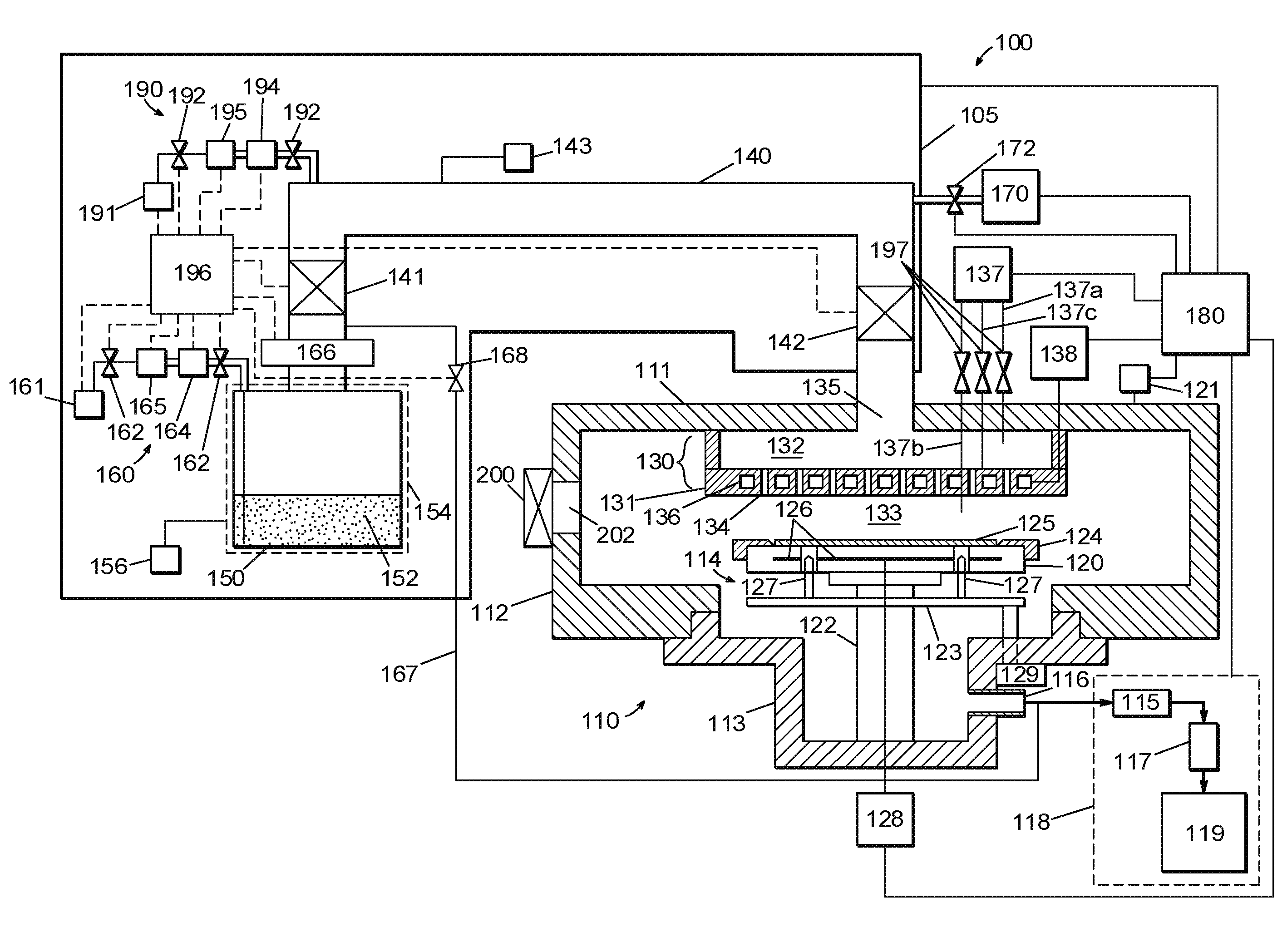
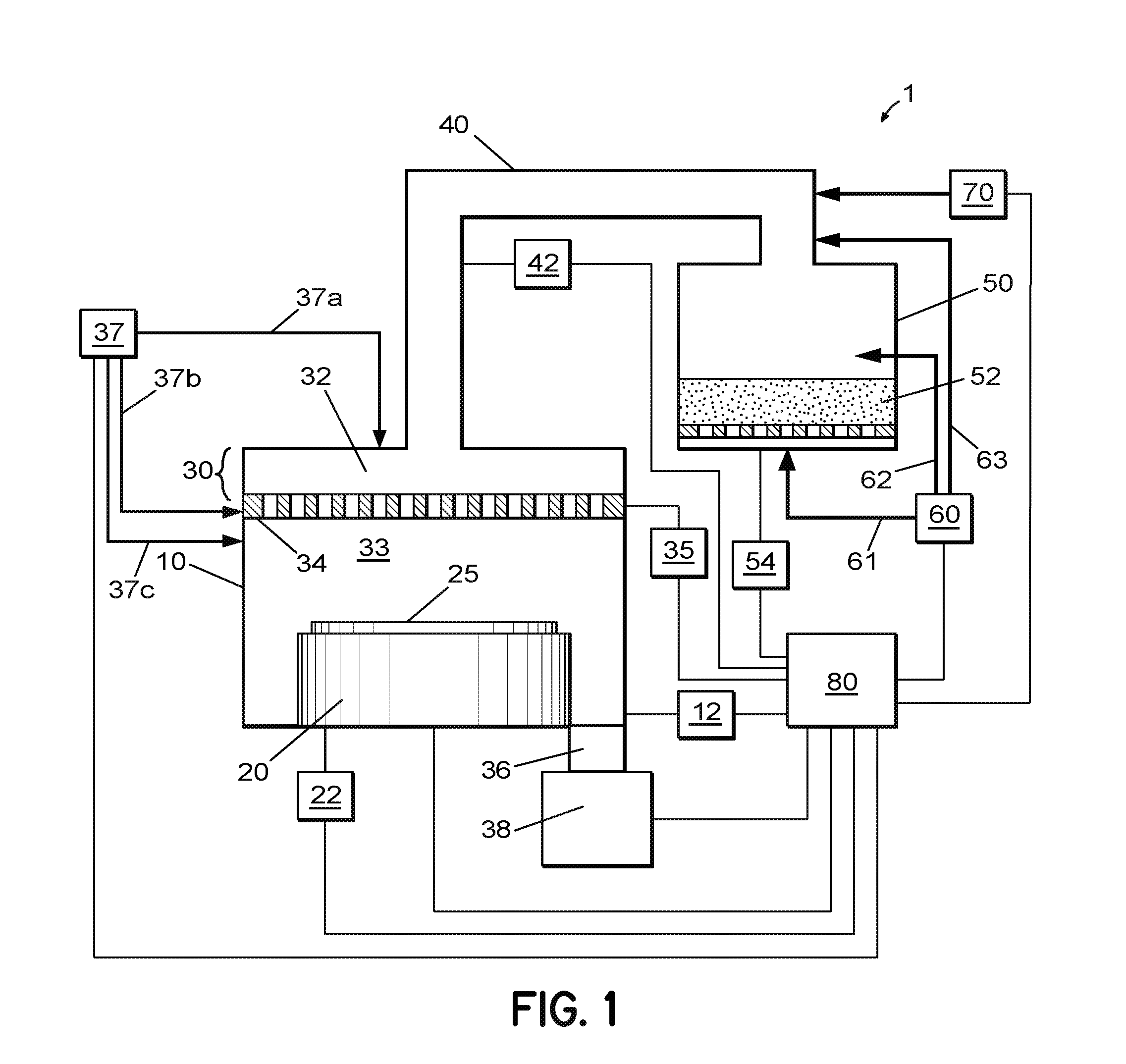
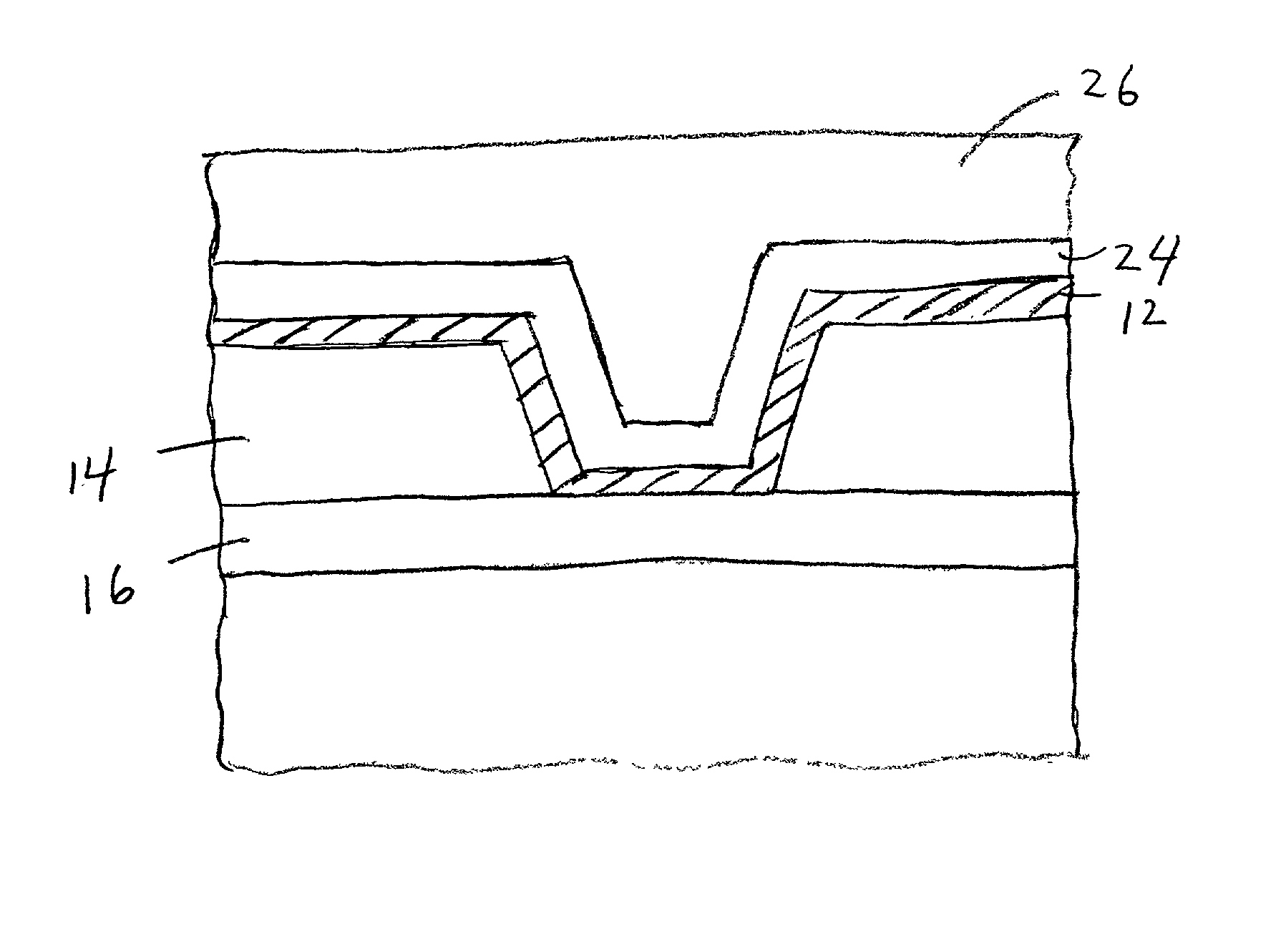
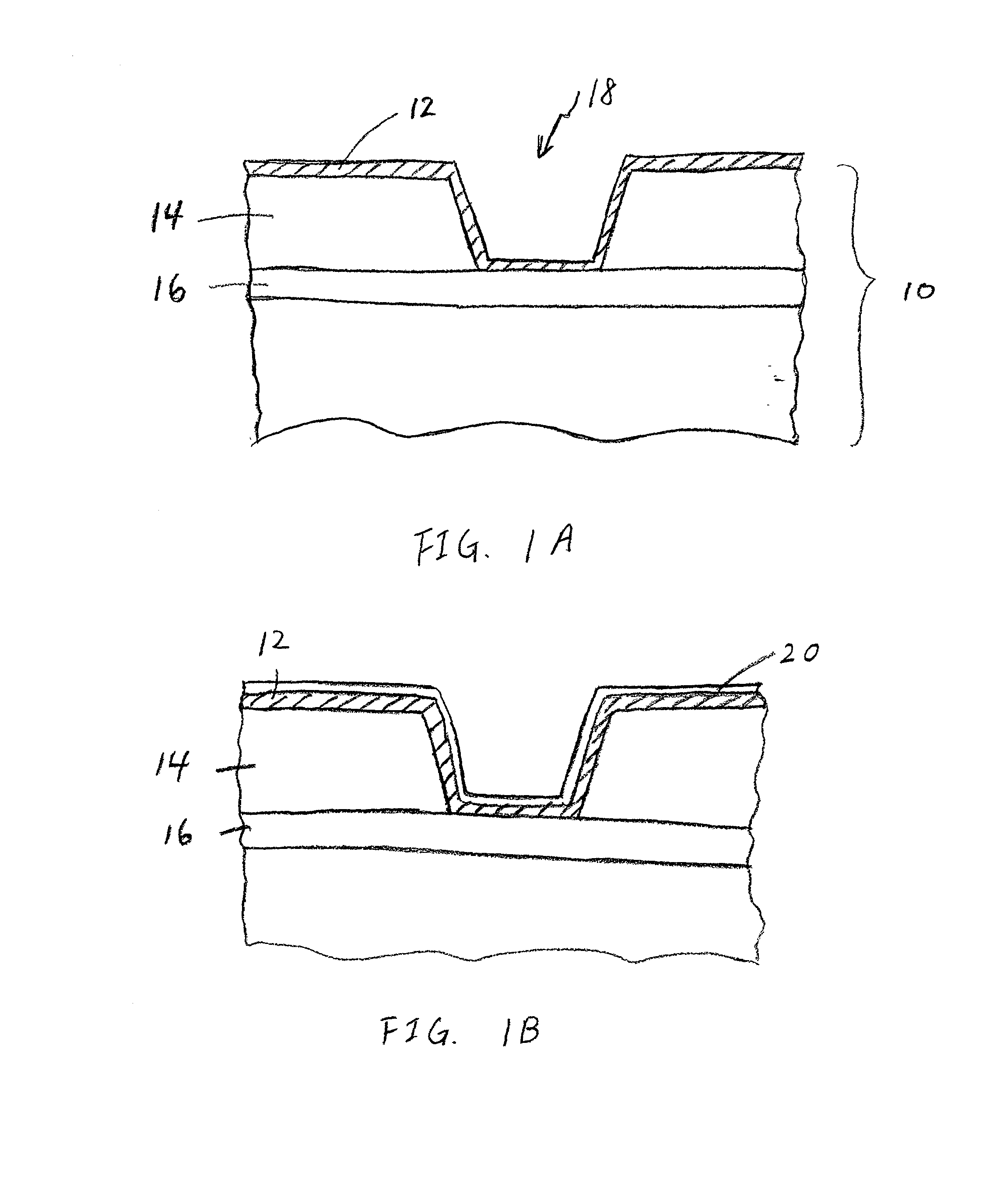
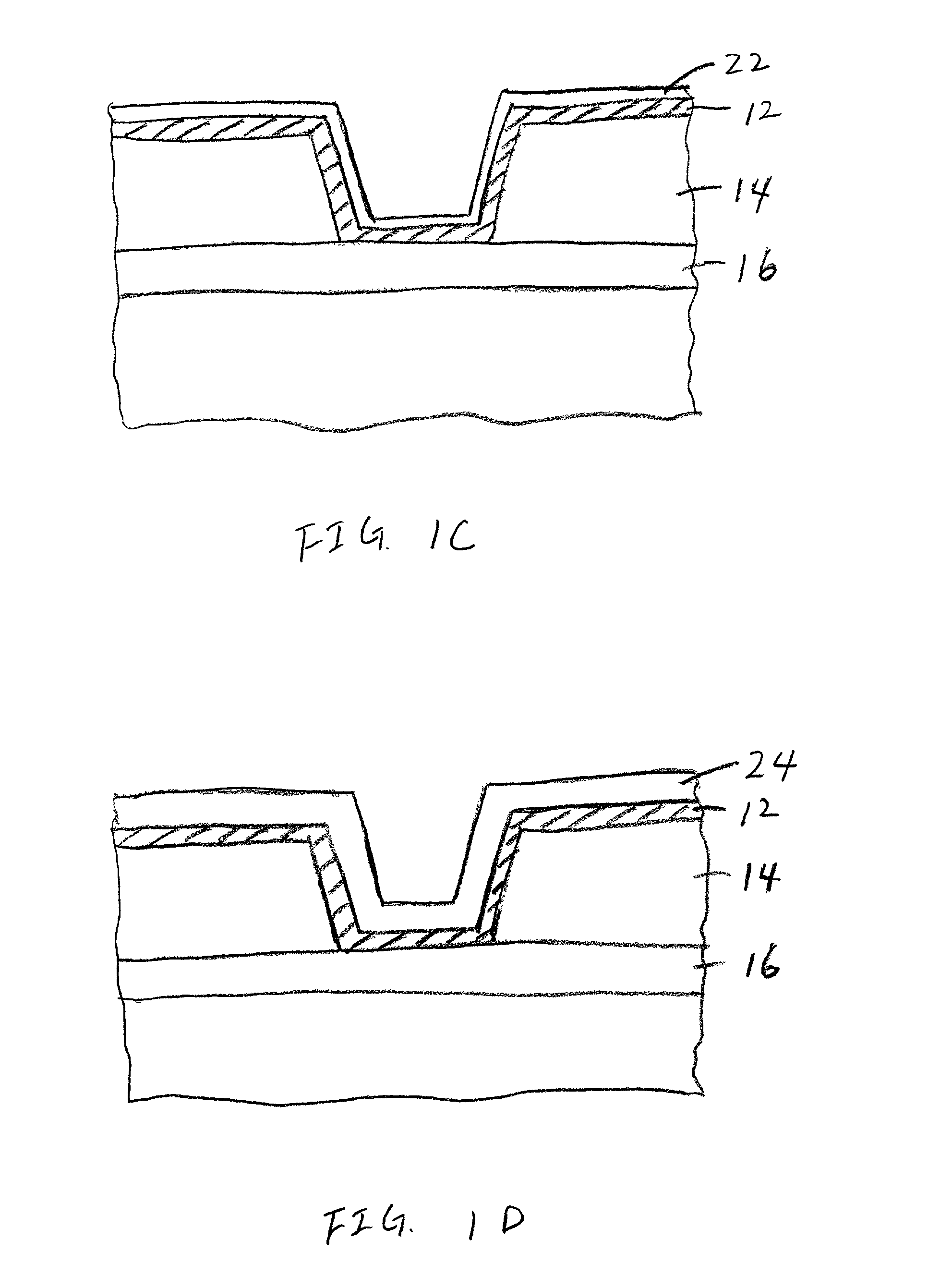
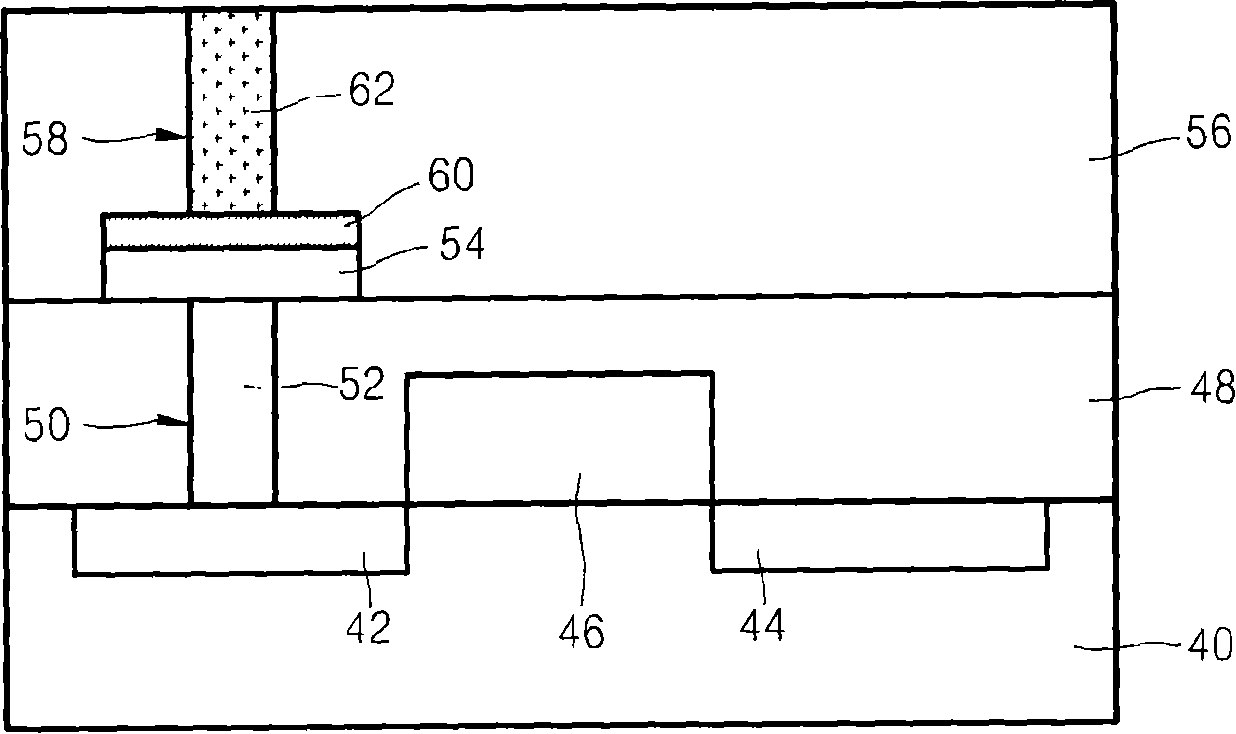
Method of fabrication of an infrared radiation detector and infrared detector device
InactiveUS6194722B1Noise minimizationLow costDecorative surface effectsFinal product manufactureOptoelectronicsInfrared detector
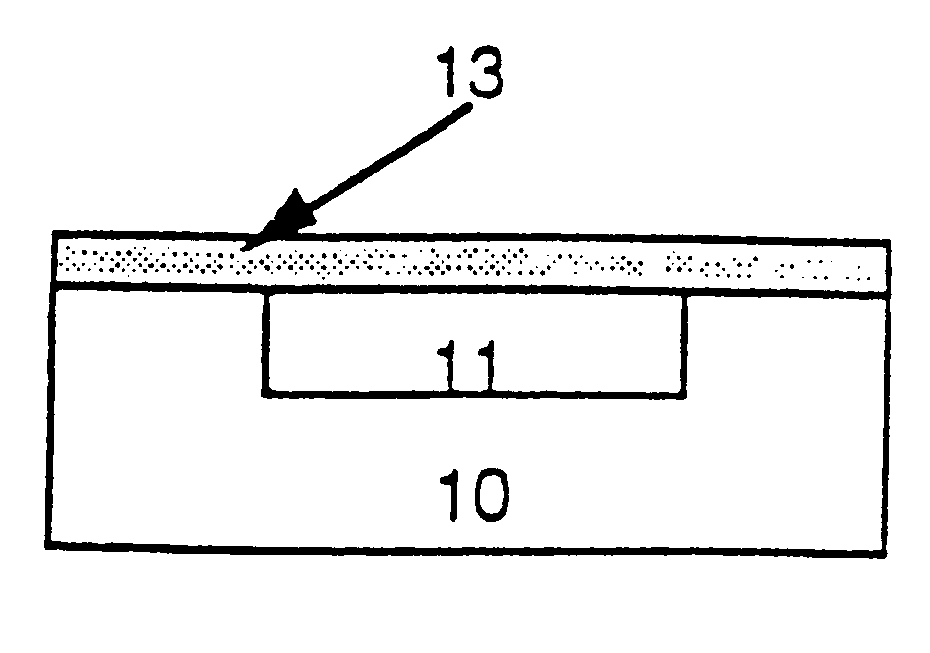
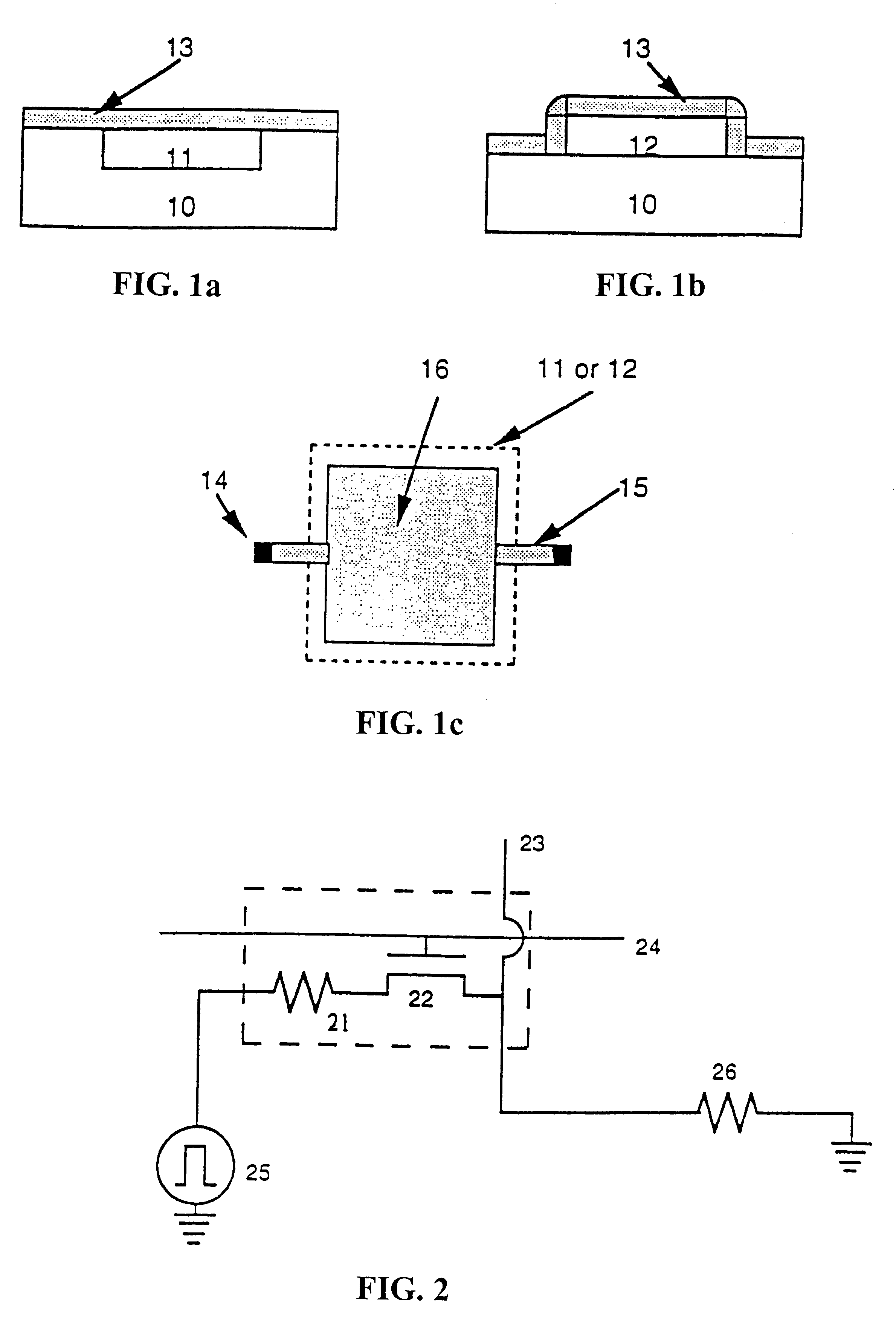
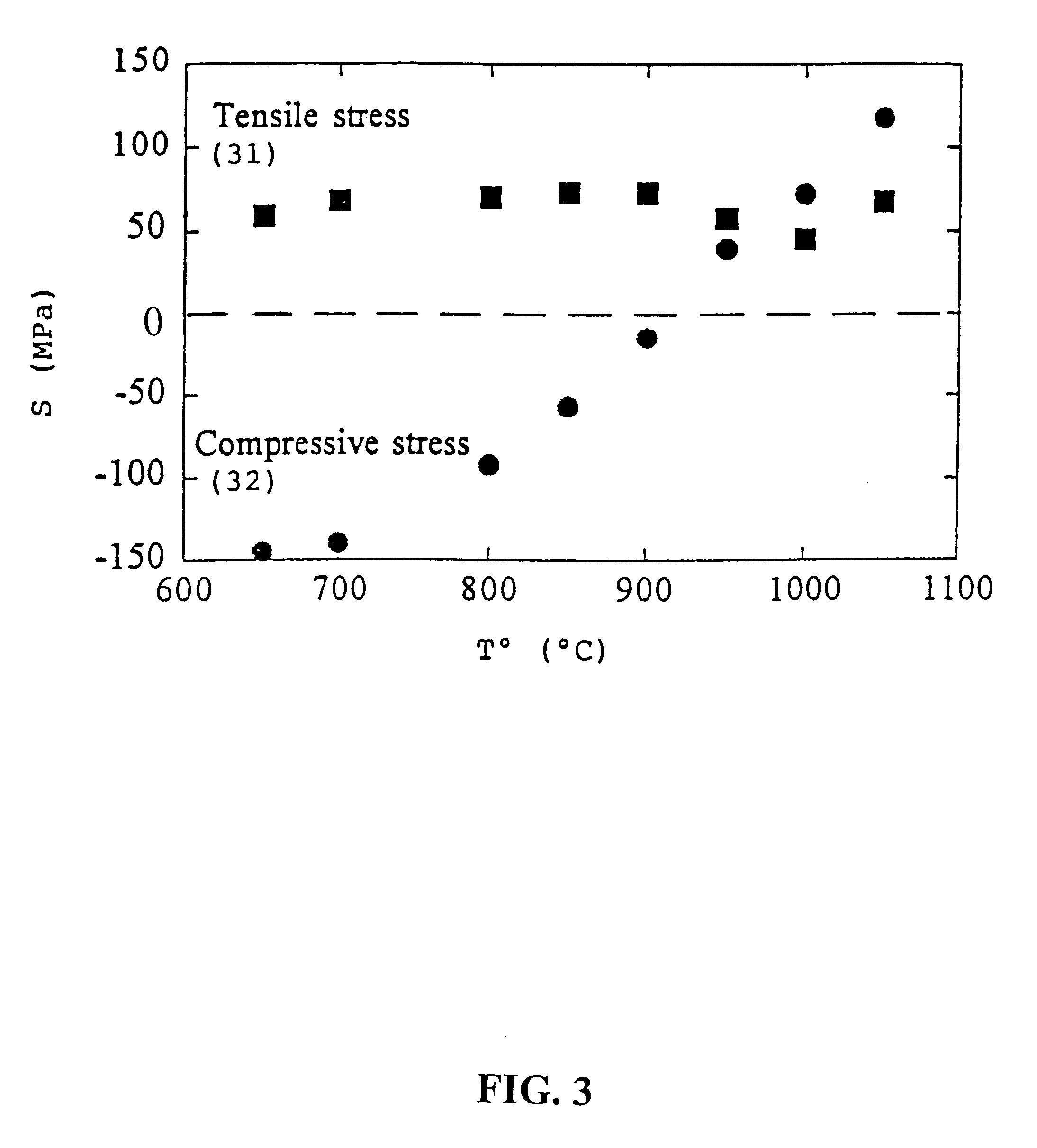
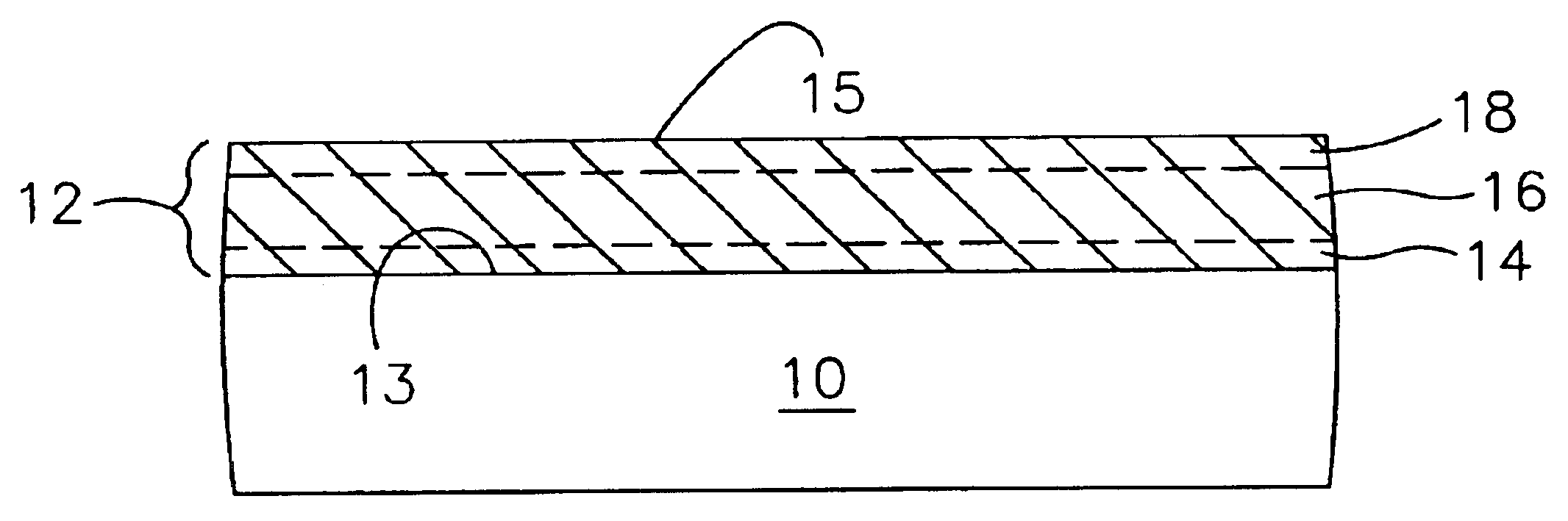
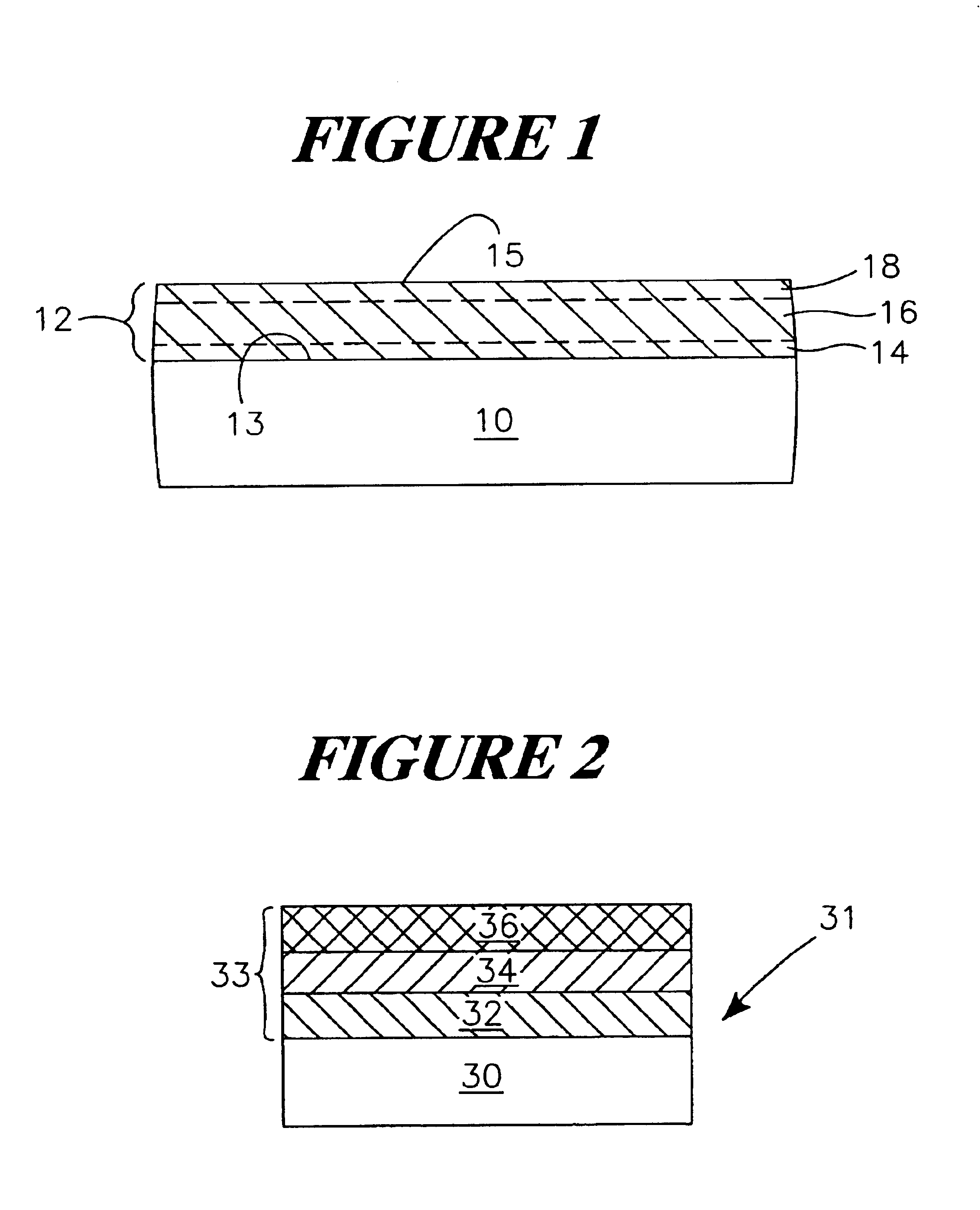
A method of fabricating an infrared detector, a method of controlling the stress in a polycrystalline SiGE layer and an infrared detector device is disclosed. The method of fabricating includes the steps of forming a sacrificial layer on a substrate; patterning said sacrificial layer; establishing a layer consisting essentially of polycrystalline SiGe on said sacrificial layer; depositing an infrared absorber on said polycrystalline SiGe layer; and thereafter removing the sacrificial layer. The method of controlling the stress in a polycrystalline SiGe layer deposited on a substrate is based on varying the deposition pressure. The infrared detector device comprises an active area and an infrared absorber, wherein the active area comprises a polycrystalline SiGe layer, and is suspended above a substrate.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
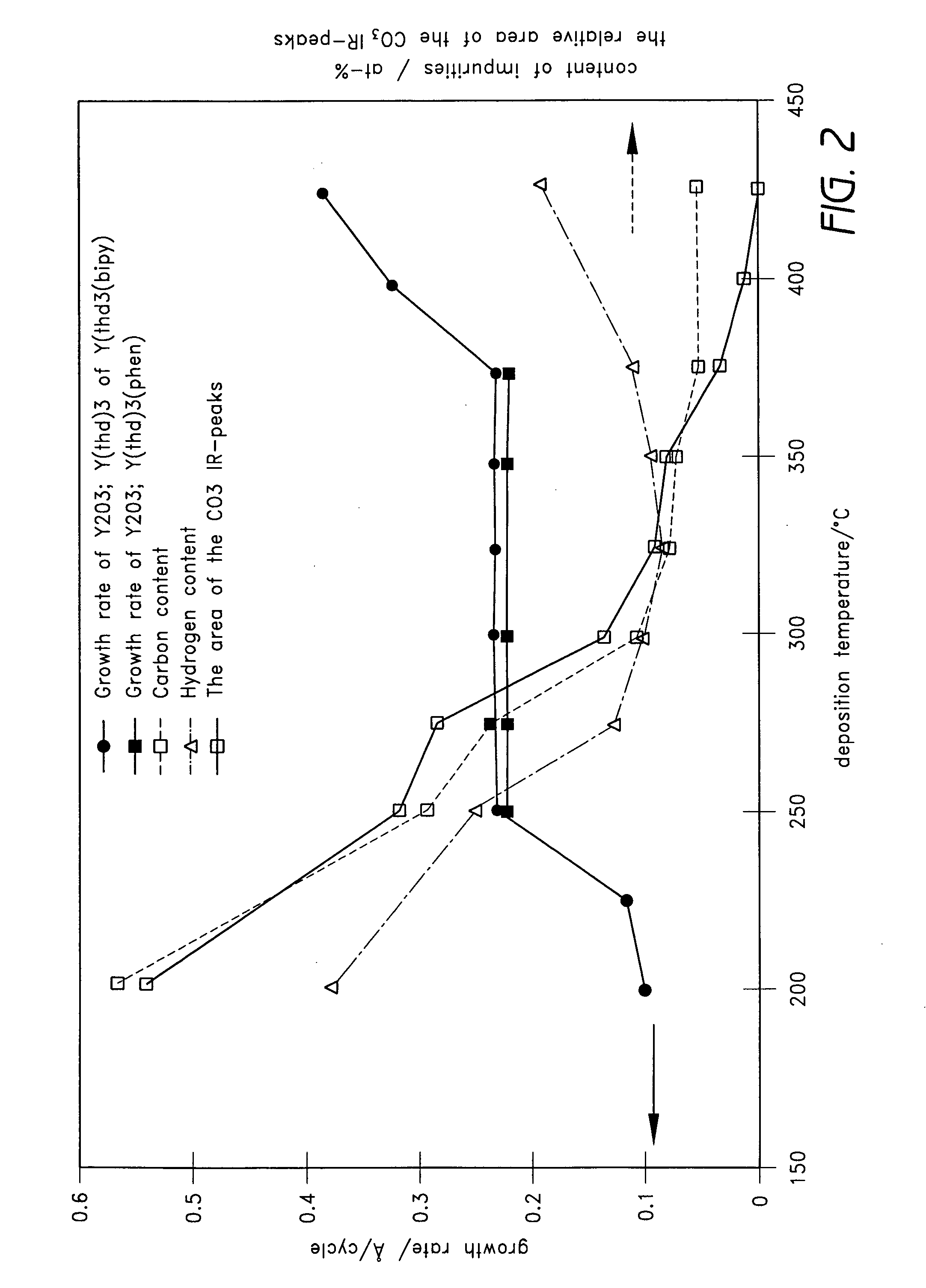
Method of depositing rare earth oxide thin films
InactiveUS6858546B2Increase probabilityIncrease ratingsPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperatureGadolinium
The present invention concerns a process for depositing rare earth oxide thin films, especially yttrium, lanthanum and gadolinium oxide thin films by an ALD process, according to which invention the source chemicals are cyclopentadienyl compounds of rare earth metals, especially those of yttrium, lanthanum and gadolinium. Suitable deposition temperatures for yttrium oxide are between 200 and 400° C. when the deposition pressure is between 1 and 50 mbar. Most suitable deposition temperatures for lanthanum oxide are between 160 and 165° C. when the deposition pressure is between 1 and 50 mbar.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
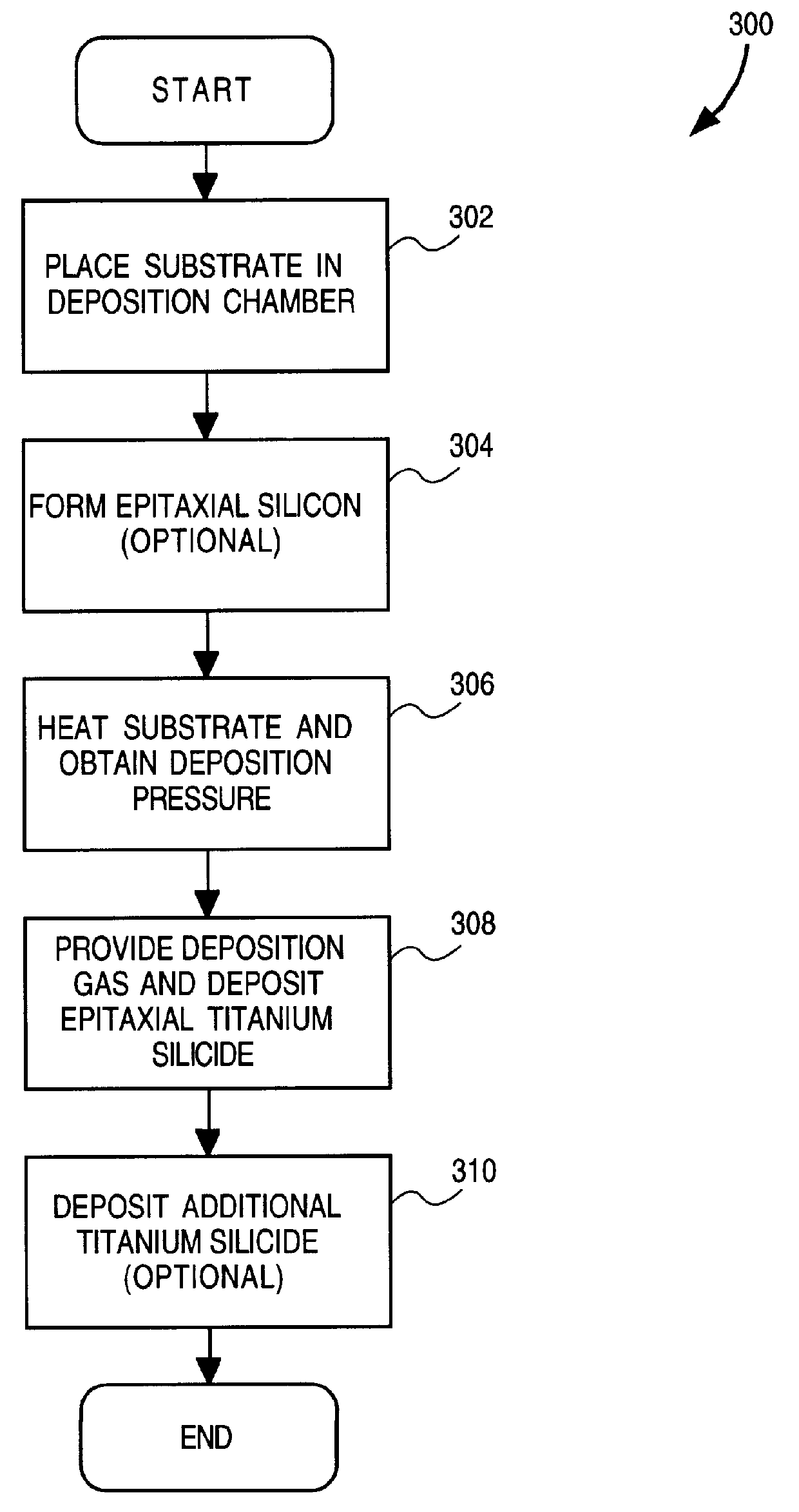
Method and apparatus for forming an epitaxial titanium silicide film by low pressure chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6019839APolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor depositionTitanium tetrachloride
A method and apparatus for forming an epitaxial titanium silicide film is described. According to the present invention, a monocrystalline silicon substrate is placed in a deposition chamber and heated to a temperature between 710-770 DEG C. A silicon source gas and titanium tetrachloride are then provided into the deposition chamber. The deposition pressure is maintained between 5-10 torr. An epitaxial titanium silicide film is then formed on the substrate from the silicon source gas and the titanium tetrachloride.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of depositing rare earth oxide thin films
InactiveUS20090035949A1Eliminate the problemIncrease probabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperatureMischmetal
The present invention concerns a process for depositing rare earth oxide thin films, especially yttrium, lanthanum and gadolinium oxide thin films by an ALD process, according to which invention the source chemicals are cyclopentadienyl compounds or rare earth metals, especially those of yttrium, lanthanum and gadolinium. Suitable deposition temperatures for yttrium oxide are between 200 and 400° C. when the deposition pressure is between 1 and 50 mbar. Most suitable deposition temperatures for lanthanum oxide are between 160 and 165° C. when the deposition pressure is between 1 and 50 mbar.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Capping layers for metal oxynitride TFTS
ActiveUS8012794B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrogenSub threshold
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming microcrystalline silicon film, method of fabricating photovoltaic cell using said method, and photovoltaic device fabricated thereby
InactiveUS6488995B1Improve featuresIncrease deposition rateFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingProduct gasMicrocrystalline silicon
Disclosed herein is a method of forming a microcrystalline silicon film by using a raw gas containing at least a silicon compound by a high-frequency plasma CVD method, wherein the formation of the film is conducted in such a manner that the residence time, tau (ms) of the raw gas in a film deposition chamber, which is defined as tau (ms)=78.9xVxP / M, in which V is a volume (cm3) of the deposition chamber, P is a deposition pressure (Torr), and M is a total flow rate (sccm) of the raw gas, satisfies tau<40. The method permits the formation of a good-quality microcrystalline silicon film at low cost.
Owner:CANON KK
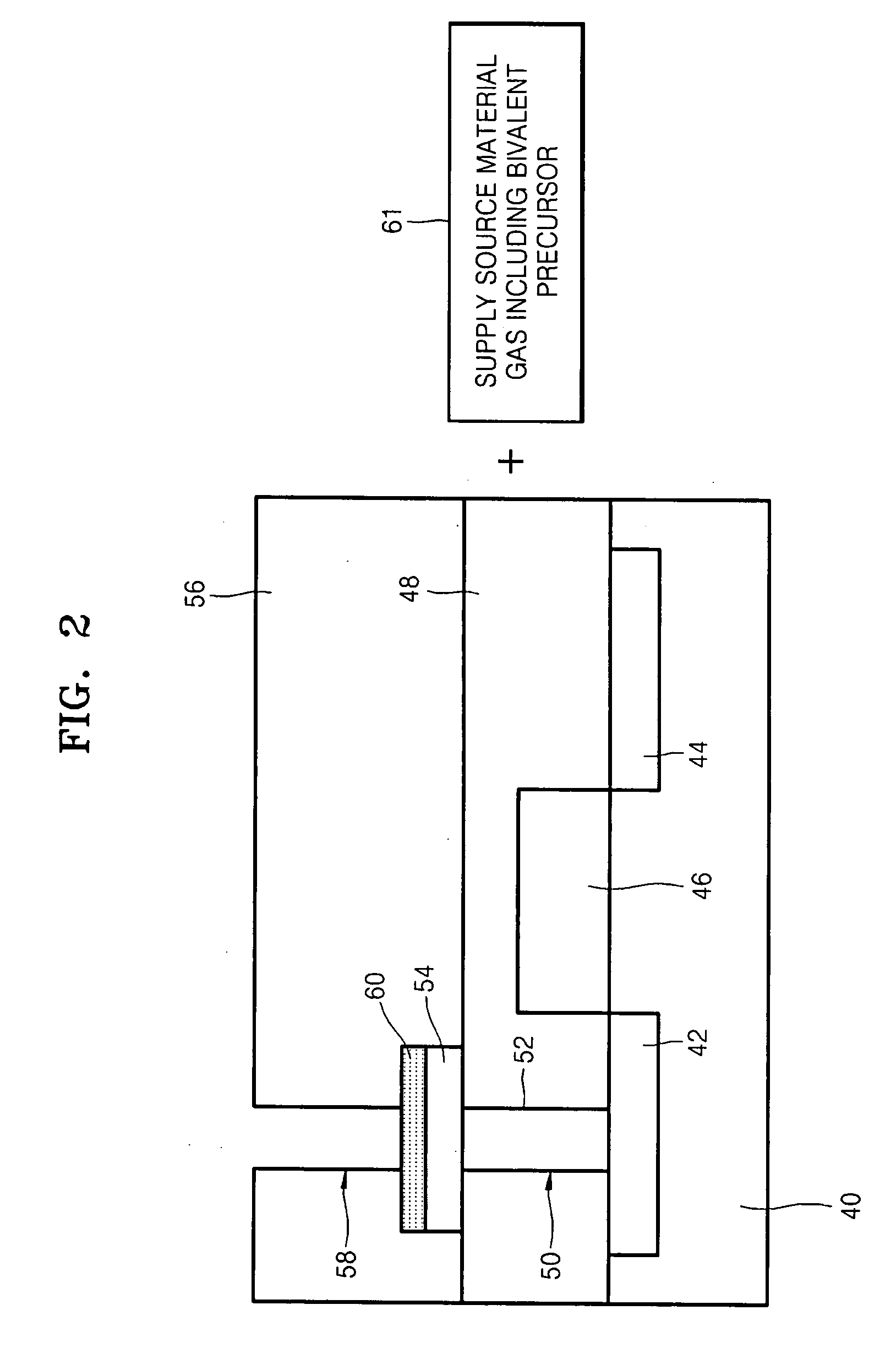
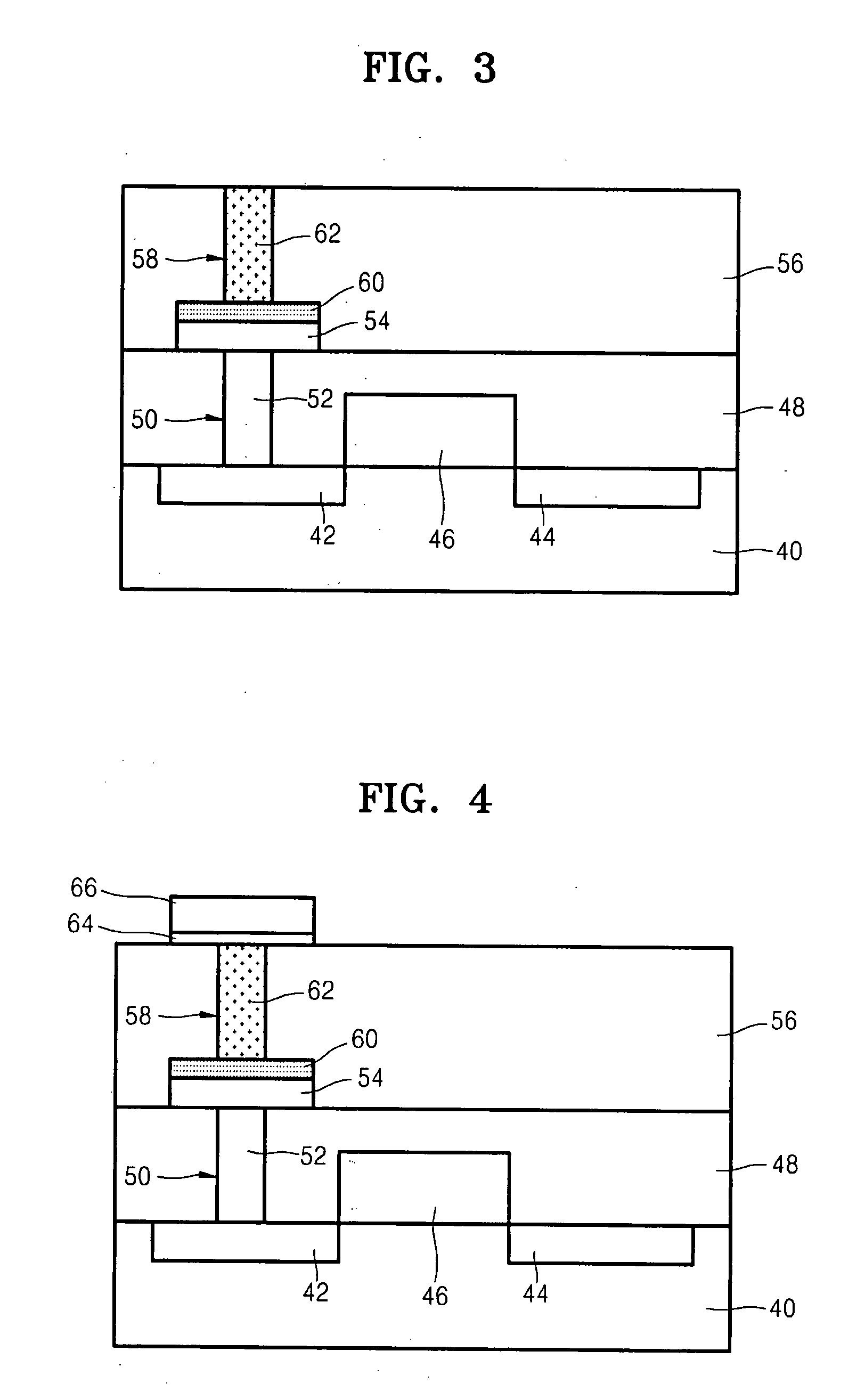
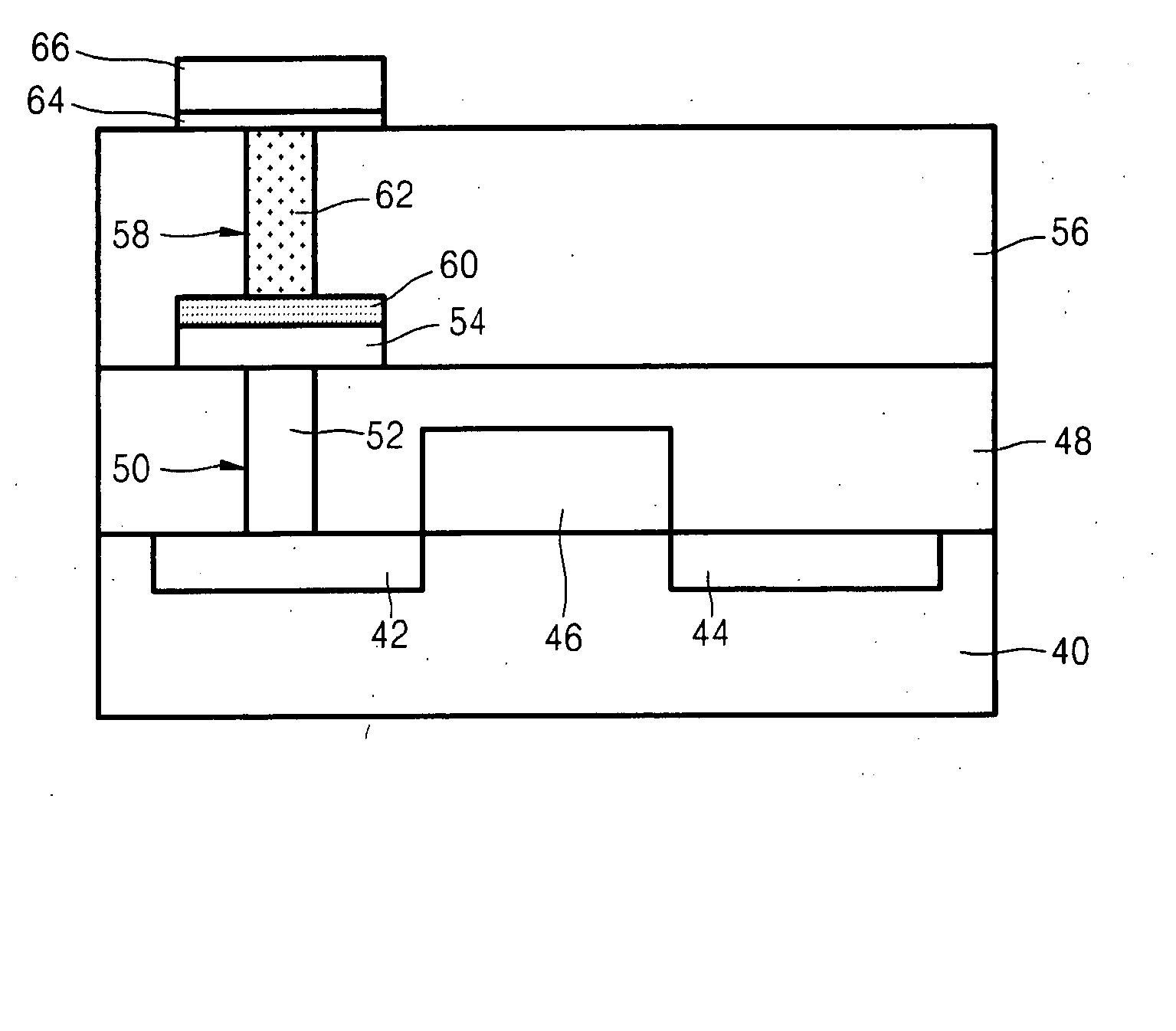
Method of forming phase change layer using a germanium precursor and method of manufacturing phase change memory device using the same
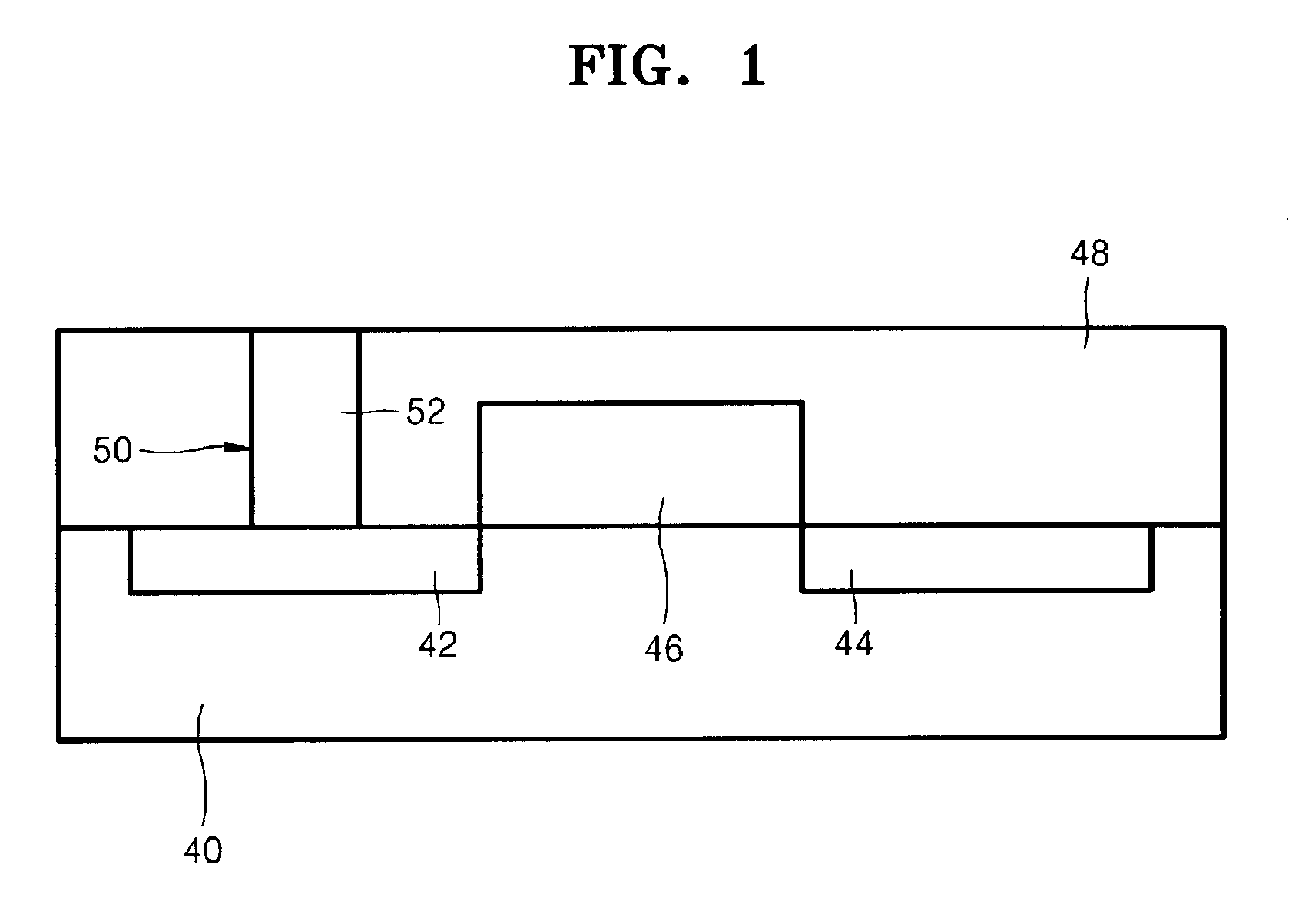
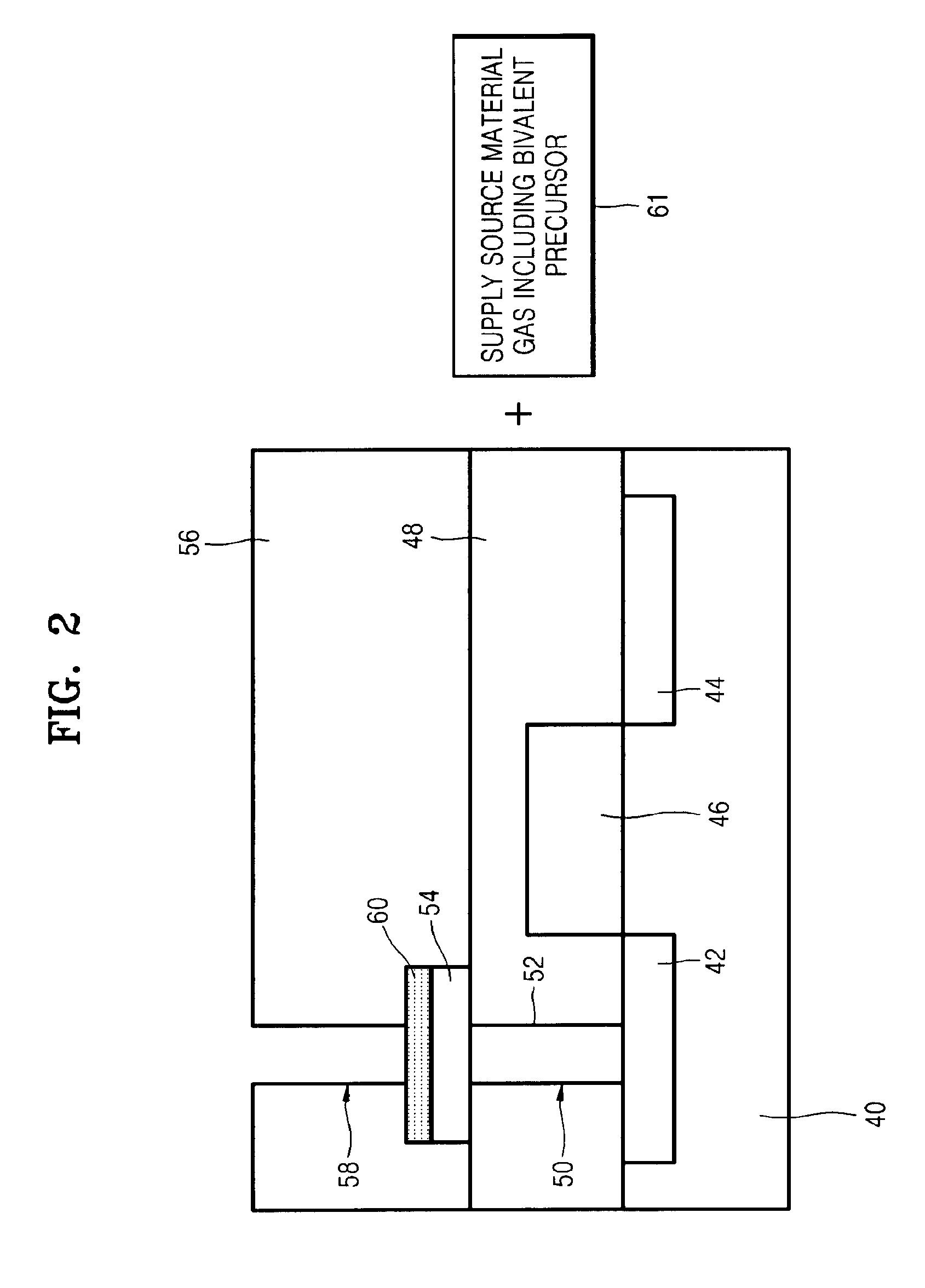
A method of forming a phase change layer using a Ge compound and a method of manufacturing a phase change memory device using the same are provided. The method of manufacturing a phase change memory device included supplying a first precursor on a lower layer on which the phase change layer is to be formed, wherein the first precursor is a bivalent precursor including germanium (Ge) and having a cyclic structure. The first precursor may be a cyclic germylenes Ge-based compound or a macrocyclic germylenes Ge-based, having a Ge—N bond. The phase change layer may be formed using a MOCVD method, cyclic-CVD method or an ALD method. The composition of the phase change layer may be controlled by a deposition pressure in a range of 0.001 torr-10 torr, a deposition temperature in a range of 150° C. to 350° C. and / or a flow rate of a reaction gas in the range of 0-1 slm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of forming a phase change layer and method of manufacturing a storage node having the phase change layer
InactiveUS20080108175A1Good step coverageHighly integratedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperatureTe element
A method of forming a phase change layer may include providing a bivalent first precursor having germanium (Ge), a second precursor having antimony (Sb), and a third precursor having tellurium (Te) onto a surface on which the phase change layer is to be formed. The phase change layer may be formed by CVD (e.g., MOCVD, cyclic-CVD) or ALD. The composition of the phase change layer may be varied by modifying the deposition pressure, deposition temperature, and / or supply rate of reaction gas. The deposition pressure may range from about 0.001-10 torr, the deposition temperature may range from about 150-350° C., and the supply rate of the reaction gas may range from about 0-1 slm. Additionally, the above phase change layer may be provided in a via hole and bounded by top and bottom electrodes to form a storage node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Capping Layers for Metal Oxynitride TFTS
ActiveUS20100001274A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringNitrogen gas
A capping layer may be deposited over the active channel of a thin film transistor (TFT) in order to protect the active channel from contamination. The capping layer may affect the performance of the TFT. If the capping layer contains too much hydrogen, nitrogen, or oxygen, the threshold voltage, sub threshold slope, and mobility of the TFT may be negatively impacted. By controlling the ratio of the flow rates of the nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen containing gases, the performance of the TFT may be optimized. Additionally, the power density, capping layer deposition pressure, and the temperature may also be controlled to optimize the TFT performance.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming a phase change layer and method of manufacturing a storage node having the phase change layer
InactiveUS7902048B2Highly integratedGood step coverageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperatureTe element
A method of forming a phase change layer may include providing a bivalent first precursor having germanium (Ge), a second precursor having antimony (Sb), and a third precursor having tellurium (Te) onto a surface on which the phase change layer is to be formed. The phase change layer may be formed by CVD (e.g., MOCVD, cyclic-CVD) or ALD. The composition of the phase change layer may be varied by modifying the deposition pressure, deposition temperature, and / or supply rate of reaction gas. The deposition pressure may range from about 0.001-10 torr, the deposition temperature may range from about 150-350° C., and the supply rate of the reaction gas may range from about 0-1 slm. Additionally, the above phase change layer may be provided in a via hole and bounded by top and bottom electrodes to form a storage node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preparing slow-release type skeleton-type TiN/Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film
InactiveCN101705468AGood dissolution effectDissolution rate is stableBiocideVacuum evaporation coatingSputter cleaningNitrogen gas
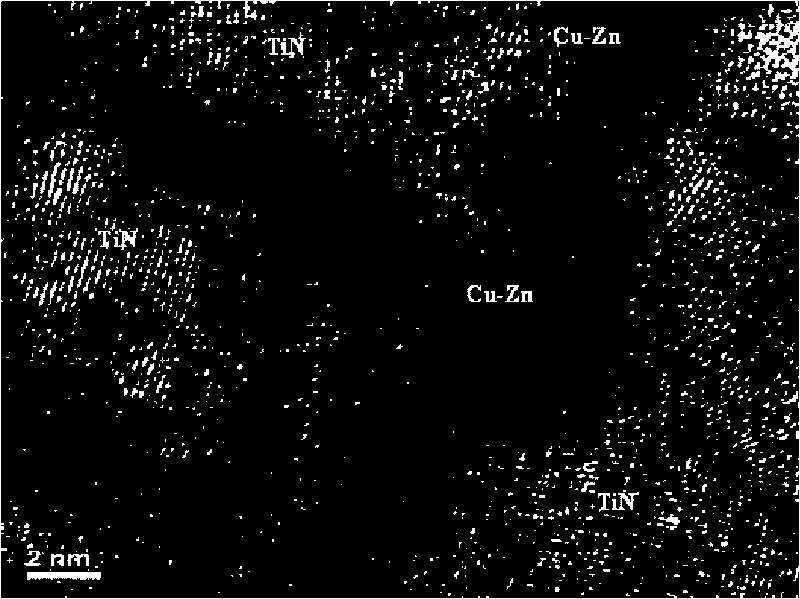
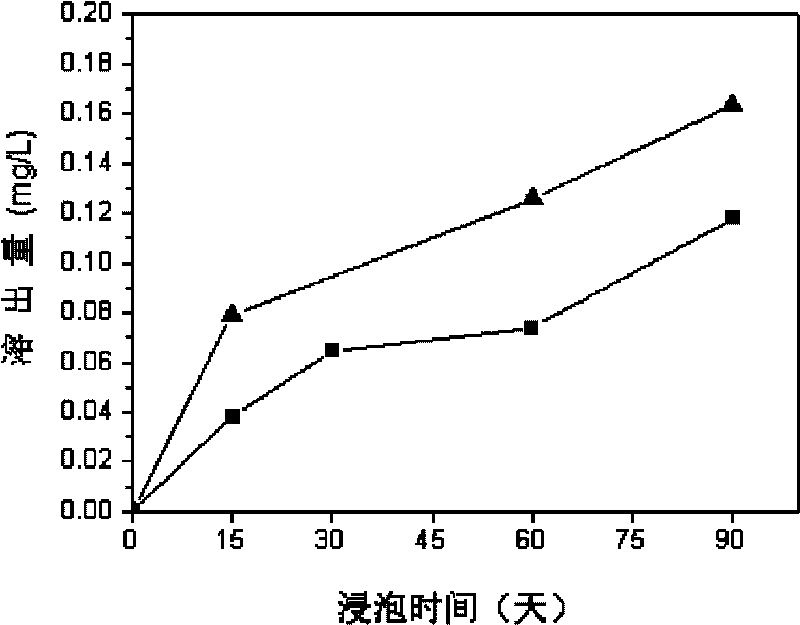
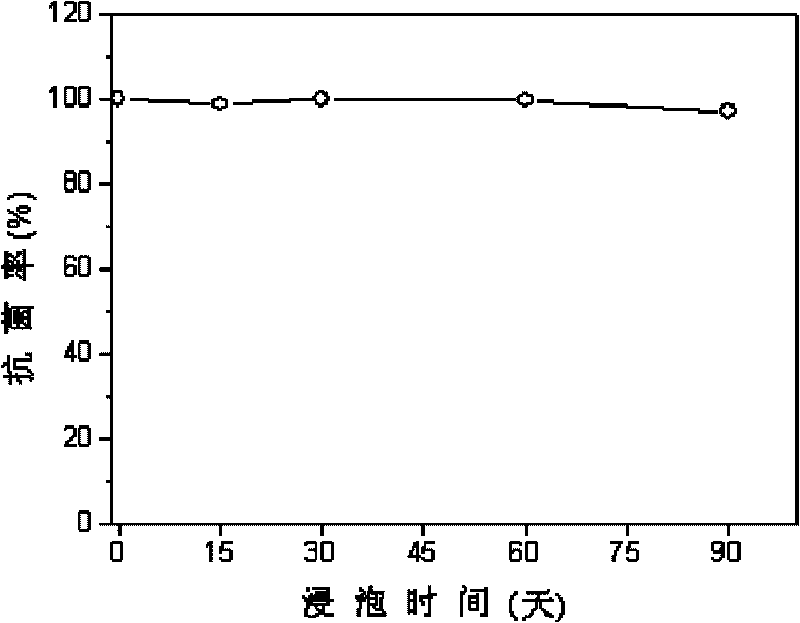
The invention discloses a method for preparing a slow-release type skeleton-type TiN / Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film and relates to a preparation method of an antibacterial film, which solves the problem that an antibacterial film prepared by the conventional method has poor durability of antibacterial effect. The method has the following steps of: 1. putting a matrix on a target platform of a vacuum room; and then heating to 200 DEG C and sputter cleaning for 20 min; 2. rotating the target platform of the vacuum room under the condition that argon flow is 6sccm, nitrogen flow is 2sccm, deposition pressure is 0.56Pa, and the deposition bias of the matrix is compound bias; and alternately depositing TiN layers and metal layers on the surface of the matrix till the total thickness of film layers is 0.1 micrometer-10 micrometers to obtain the slow-release type skeleton-type TiN / Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film. After the slow-release type skeleton-type TiN / Cu-Zu metal layer antibacterial film is soaked for three months, the ion dissolving speed is not reduced, and the antibiosis rate against colibacillus can still reach above 97%.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of preparing carbon-carbon composite material surface silicon carbide nano wire
InactiveCN1834287AEffective control of morphologyEffective control of purityChemical vapor deposition coatingFiberCarbon composites
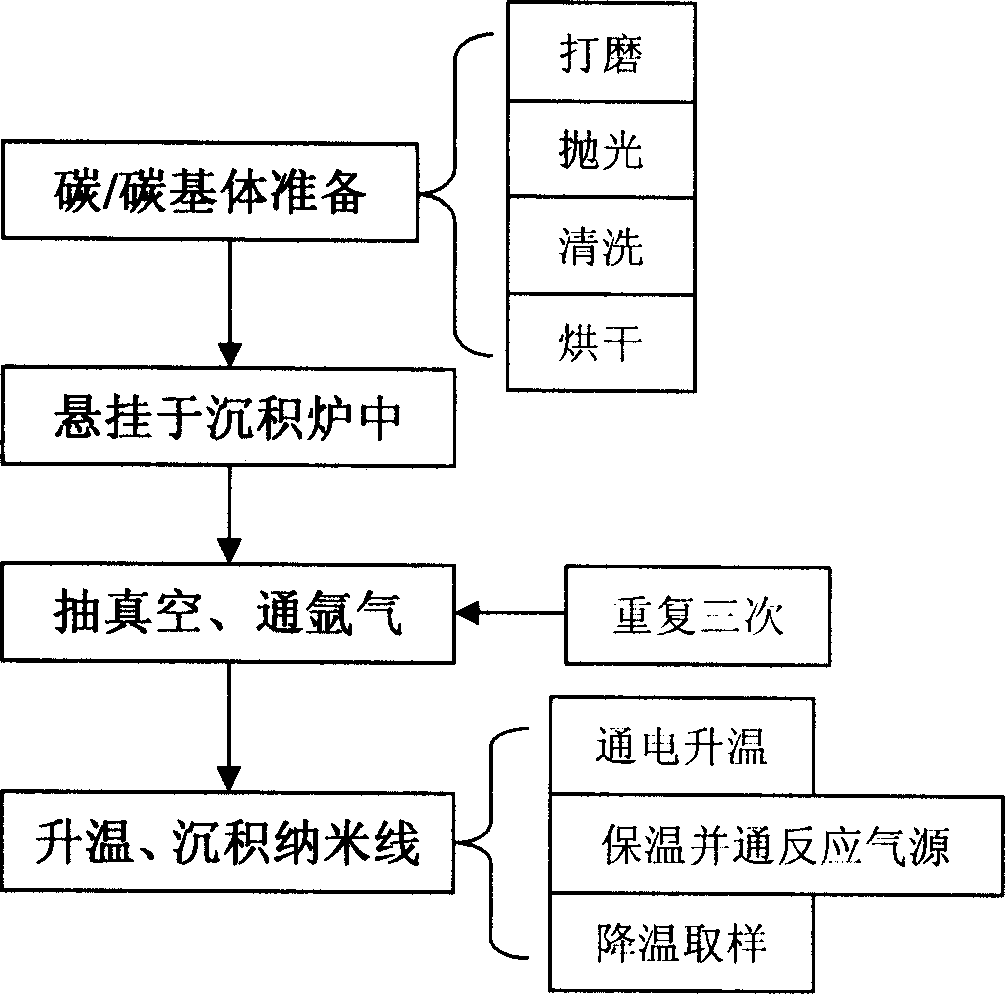
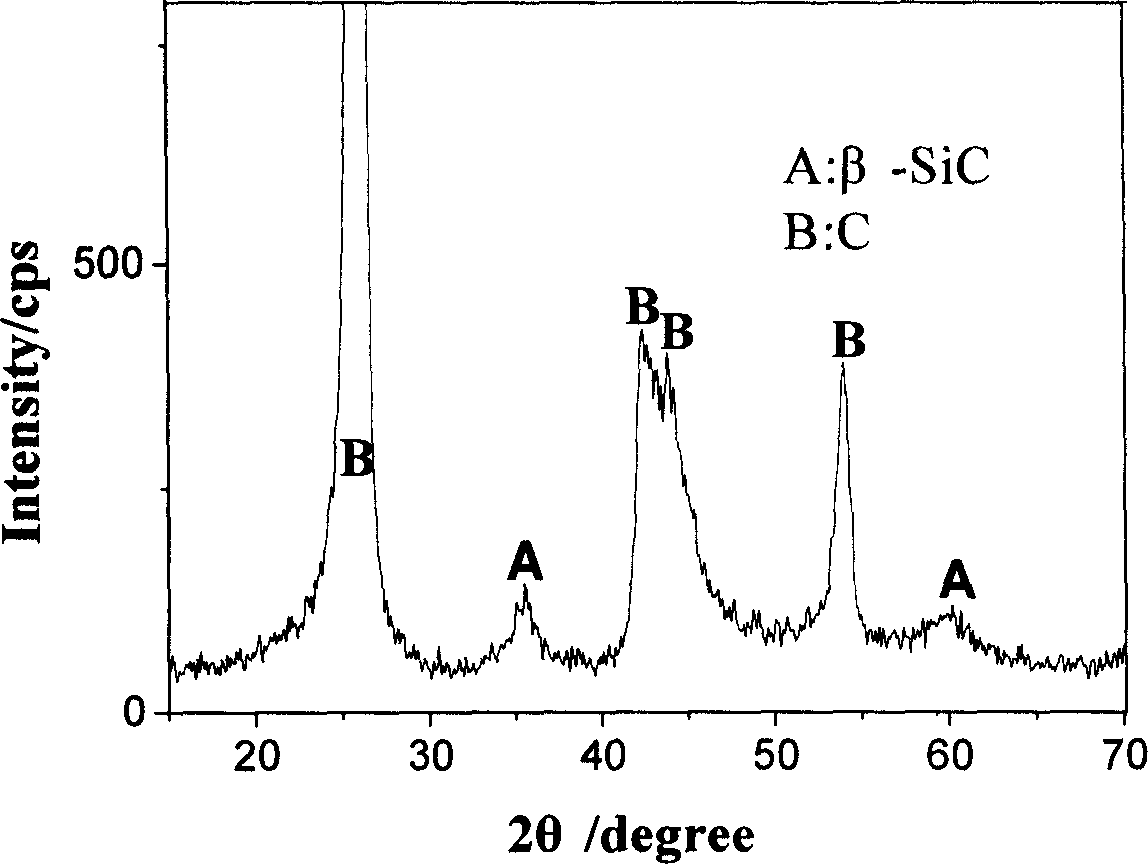
This invention relates to a method for manufacturing SiC nanowires on the surface of C / C composite, which comprises the steps of: (1) polishing the C / C composite, washing with distilled water, and drying; (2) binding the treated C / C composite with carbon fibers, and suspending in a vertical chemical vapor deposition furnace; (3) evacuating the furnace, pumping Ar into the furnace to normal pressure, and repeating for three times; (4) applying electricity, heating, and pumping H2 for pretreatment; (5) adjusting the flow rates of Ar, H2 and methyl trichlorosilane when the furnace temperature reaches the predetermined deposition temperature, keeping the temperature for deposition, the turning off the power and cooling naturally to obtain a layer of SiC nanowires on the surface of the material. The method has such advantages as simple process, no additive, low deposition pressure and temperature. The morphology and purity of the synthesized SiC nanowires can be effectively controlled by adjusting the deposition factors.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for controlling deposition of dielectric films
InactiveUS6838293B2Increase pressureIncrease deposition rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricDeposition temperature
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and apparatus for forming insitu boron doped polycrystalline and amorphous silicon films
InactiveUS6410090B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperatureDecreased pressure
A method and apparatus for depositing a boron insitu doped amorphous or polycrystalline silicon film on a substrate. According to the present invention, a substrate is placed into deposition chamber. A reactant gas mix comprising a silicon source gas, boron source gas, and a carrier gas is fed into the deposition chamber. The carrier gas is fed into the deposition chamber at a rate so that the residence of the carrier gas in the deposition chamber is less then or equal to 3 seconds or alternatively has a velocity of at least 4 inches / sec. In another embodiment of forming a boron doped amorphous for polycrystalline silicon film a substrate is placed into a deposition chamber. The substrate is heated to a deposition temperature between 580-750° C. and the chamber pressure reduced to a deposition pressure of less than or equal to 50 torr. A silicon source gas is fed into the deposition at a rate to provide a silicon source gas partial pressure of between 1-5 torr. Additionally, a boron source gas is fed into the deposition chamber at a rate to provide a boron gas partial pressure of between 0.005-0.05 torr.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Silicon-based thin-film photoelectric conversion device, and method and apparatus for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100147379A1Quality improvementHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPresent methodEngineering
A present method of manufacturing a silicon-based thin-film photoelectric conversion device is characterized in that a double pin structure stack body is formed by successively forming, in an identical plasma CVD film deposition chamber, a first p-type semiconductor layer, an i-type amorphous silicon-based photoelectric conversion layer, a first n-type semiconductor layer, a second p-type semiconductor layer, an i-type microcrystalline silicon-based photoelectric conversion layer, and a second n-type semiconductor layer on a transparent conductive film formed on a substrate, and the first p-type semiconductor layer, the i-type amorphous silicon-based photoelectric conversion layer and the first n-type semiconductor layer are formed under such conditions that a film deposition pressure in the plasma CVD film deposition chamber is not lower than 200 Pa and not higher than 3000 Pa and power density per unit electrode area is not lower than 0.01 W / cm2 and not higher than 0.3 W / cm2. Thus, the silicon-based thin-film photoelectric conversion device attaining excellent quality and high photoelectric conversion efficiency can be manufactured at low cost and high efficiency using a simplified manufacturing apparatus.
Owner:SHARP KK
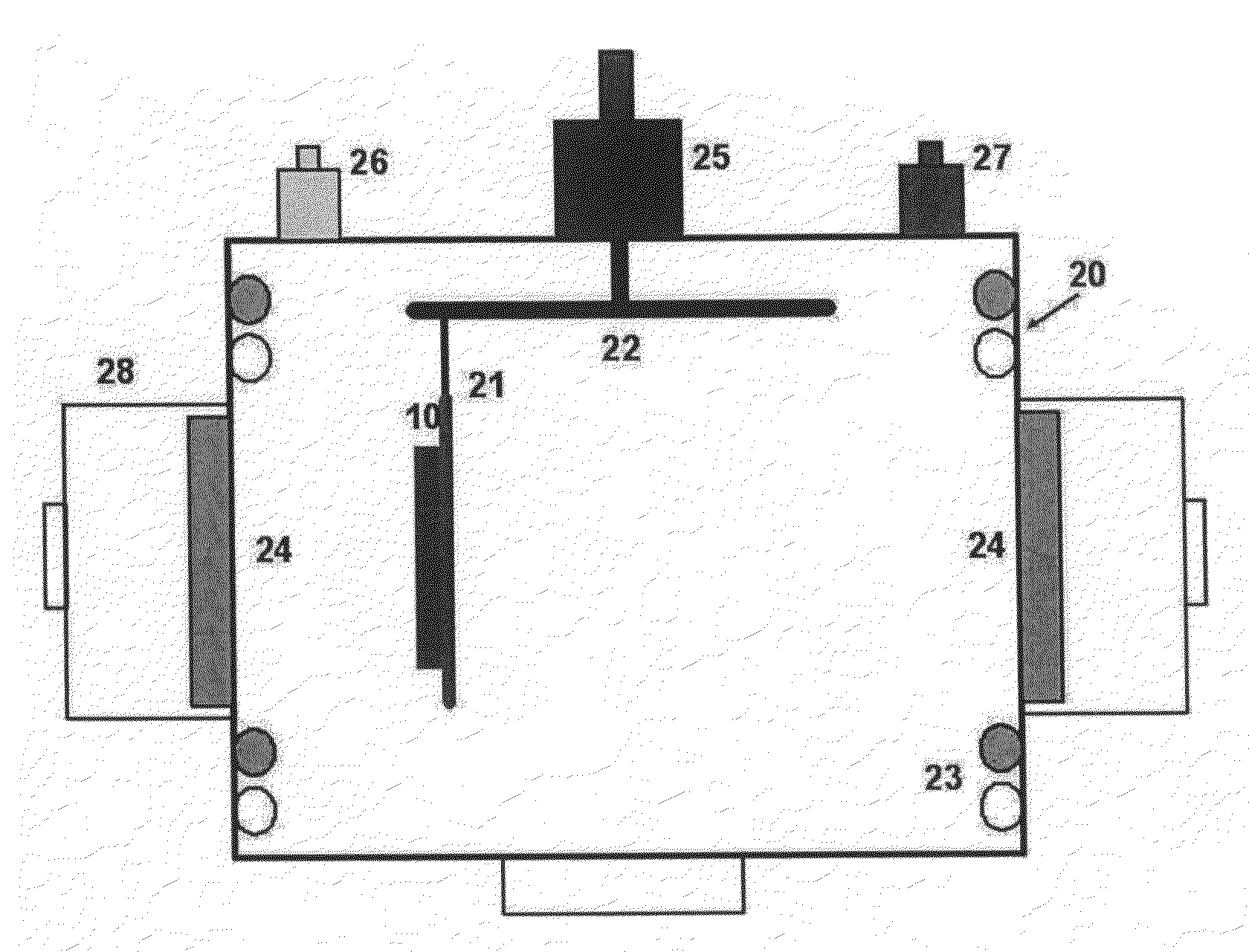
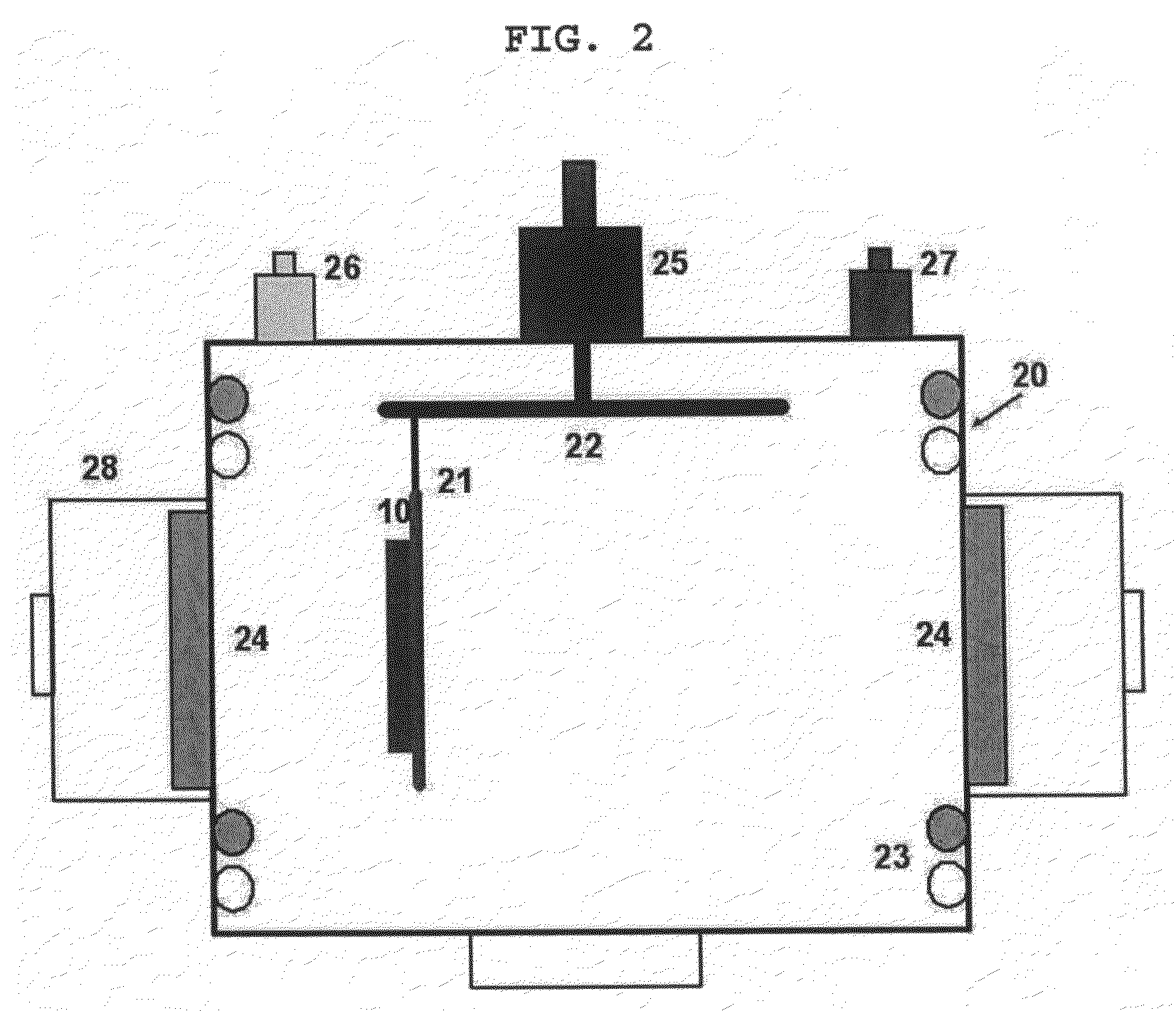
Method of manufacturing film bulk acoustic resonator using internal stress of metallic film and resonator manufactured thereby
ActiveUS7671427B2Impedence networksSolid-state devicesThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorInternal stress
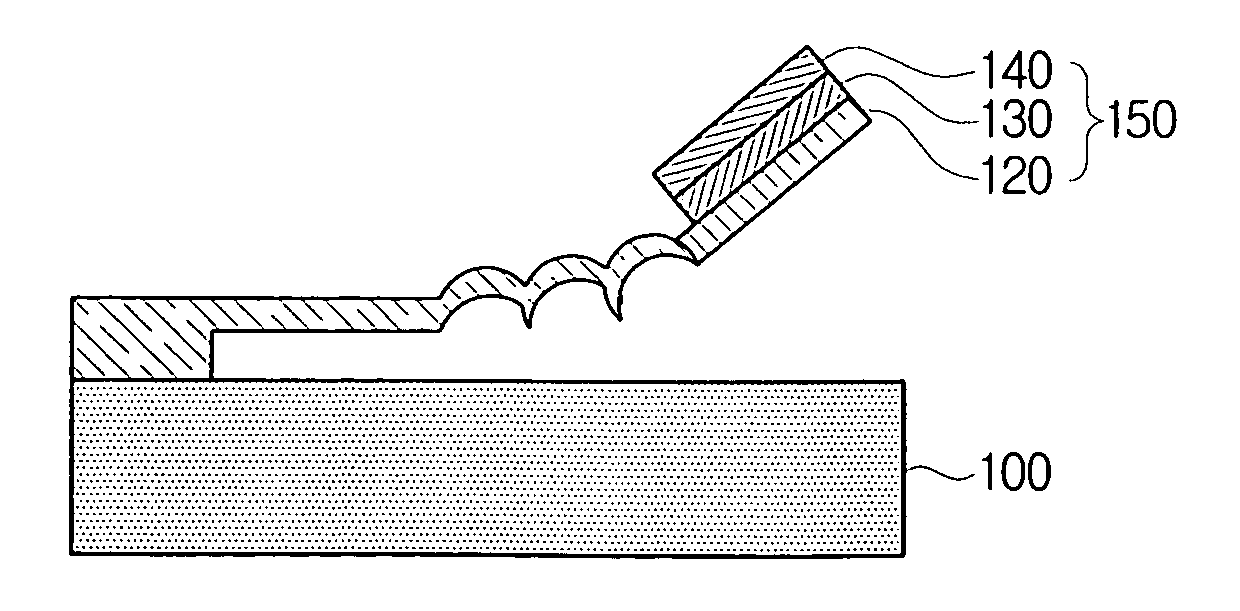
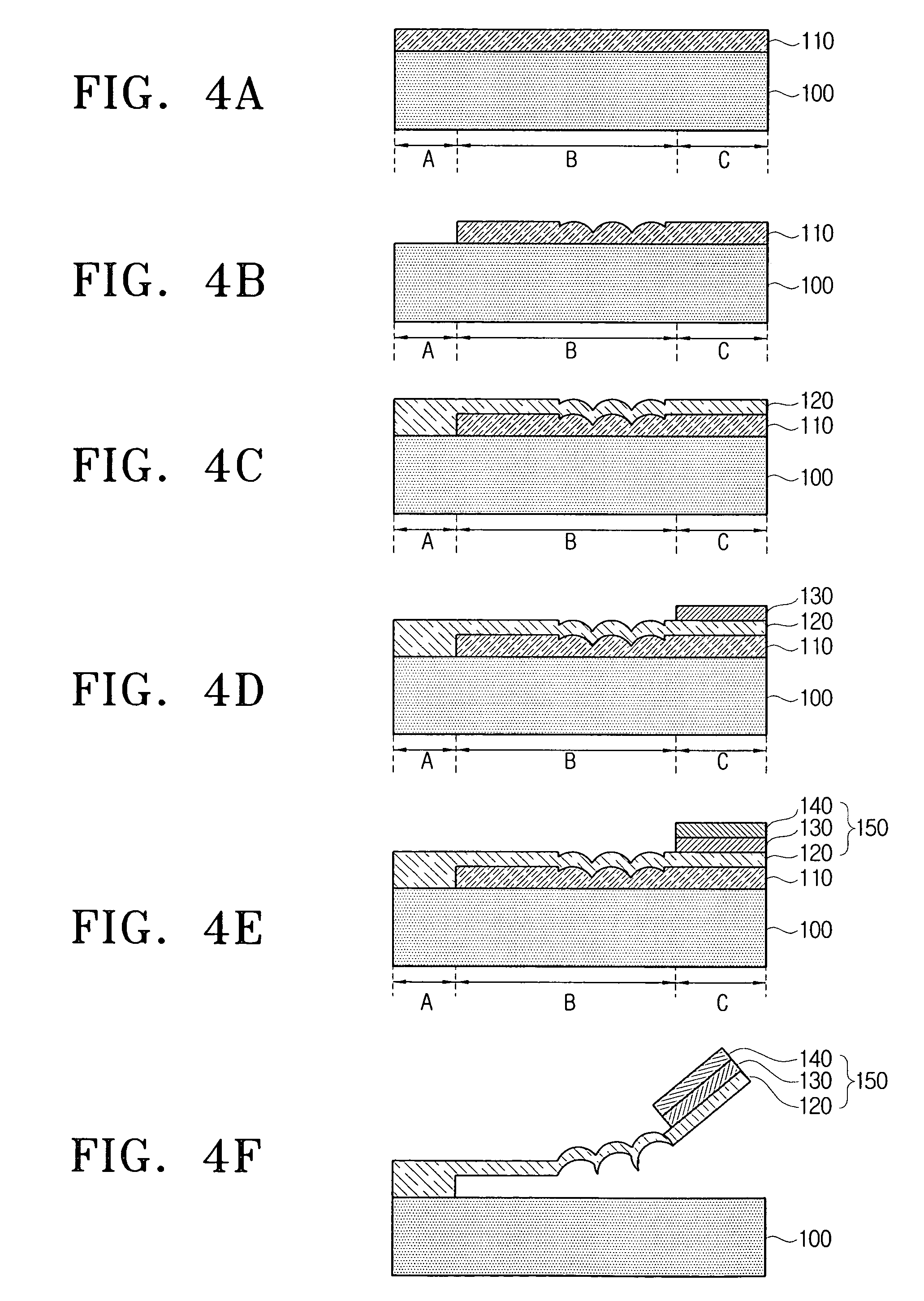
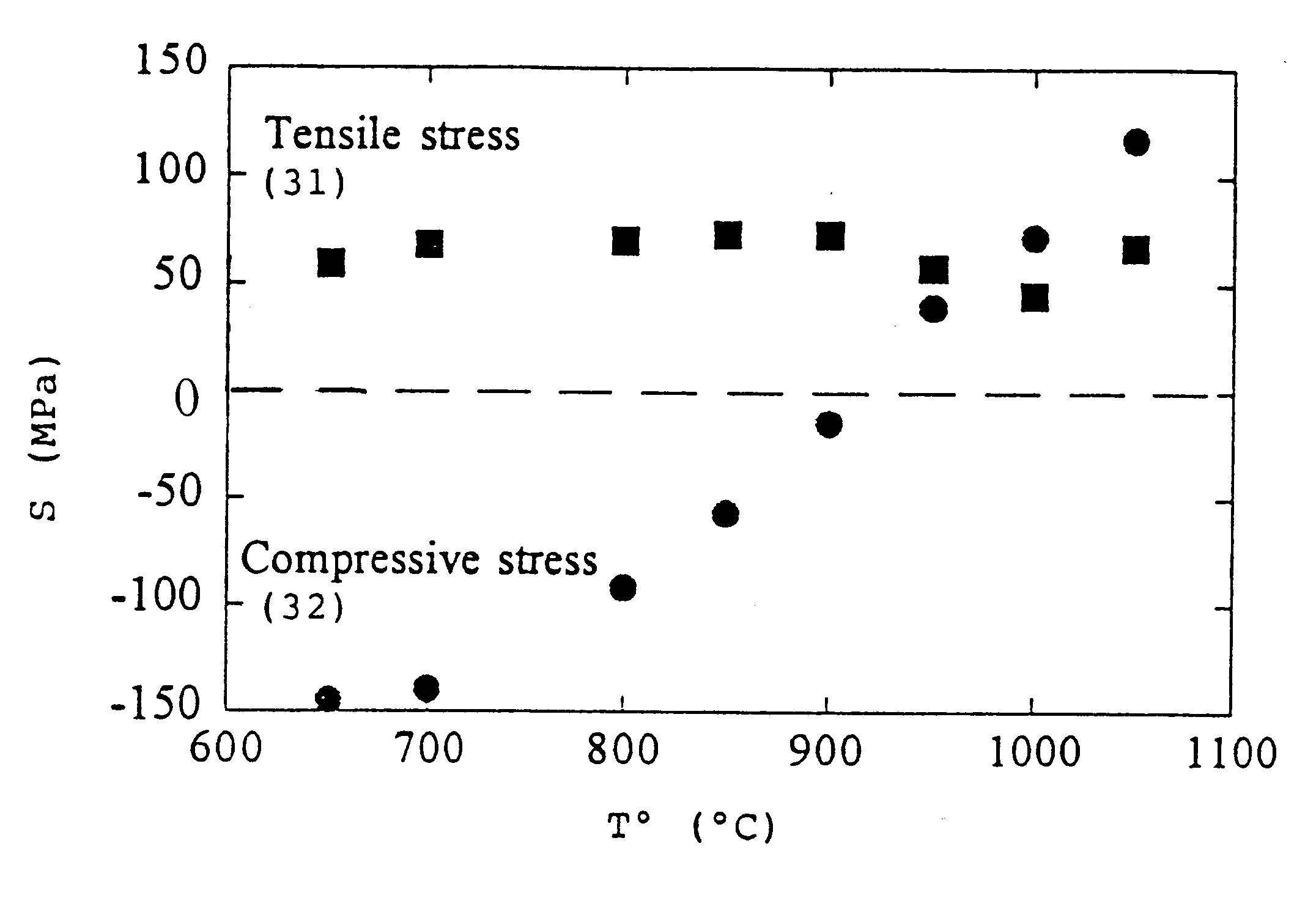
A method of manufacturing a film bulk acoustic resonator and the resonator manufactured thereby. The method includes the laminating a sacrificial layer on a semiconductor substrate, removing a predetermined area from the sacrificial layer to realize electric contact between a signal line of the semiconductor substrate and a lower electrode, forming the lower electrode by depositing metal film for lower electrode on the sacrificial layer, by patterning based on a shape of the sacrificial layer, forming a piezoelectric layer by depositing a piezoelectric material on the lower electrode and by patterning based on a shape of the lower electrode, and forming an upper electrode by depositing metal film on the piezoelectric layer and by patterning based on a shape of the piezoelectric layer, wherein at least one of a deposition pressure and a deposition power is controlled to generate upward stress when depositing the metal film for the lower electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
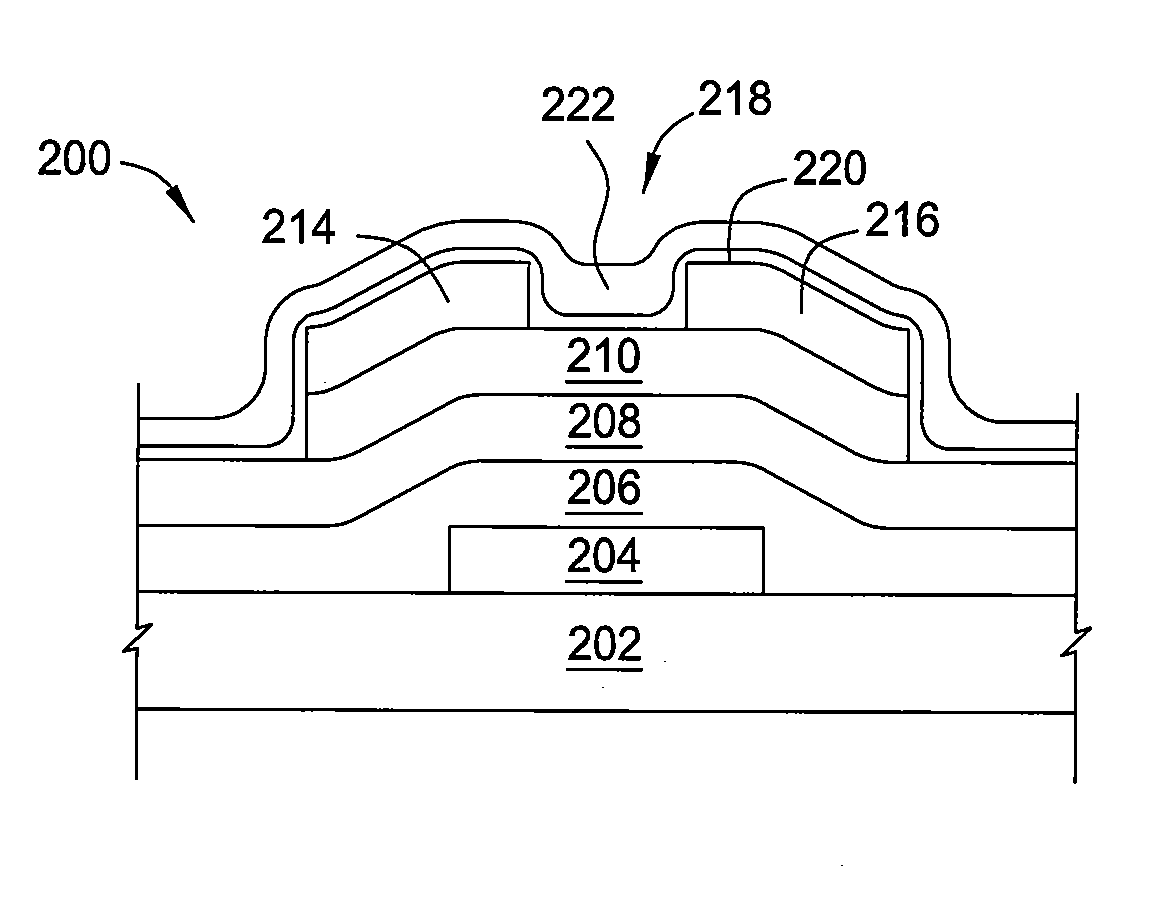
Method of fabrication of an infrared radiation detector and infrared detector device
InactiveUS6274462B1Noise minimizationLow costFinal product manufactureDecorative surface effectsOptoelectronicsInfrared detector
A method of fabricating an infrared detector, a method of controlling the stress in a polycrystalline SiGE layer and an infrared detector device is disclosed. The method of fabricating includes the steps of forming a sacrificial layer on a substrate; patterning said sacrificial layer; establishing a layer consisting essentially of polycrystalline SiGe on said sacrificial layer; depositing an infrared absorber on said polycrystalline SiGe layer; and thereafter removing the sacrificial layer. The method of controlling the stress in a polycrystalline SiGe layer deposited on a substrate is based on varying the deposition pressure. The infrared detector device comprises an active area and an infrared absorber, wherein the active area comprises a polycrystalline SiGe layer, and is suspended above a substrate.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Semi-solid deposition pressure welding device for dissimilar metals
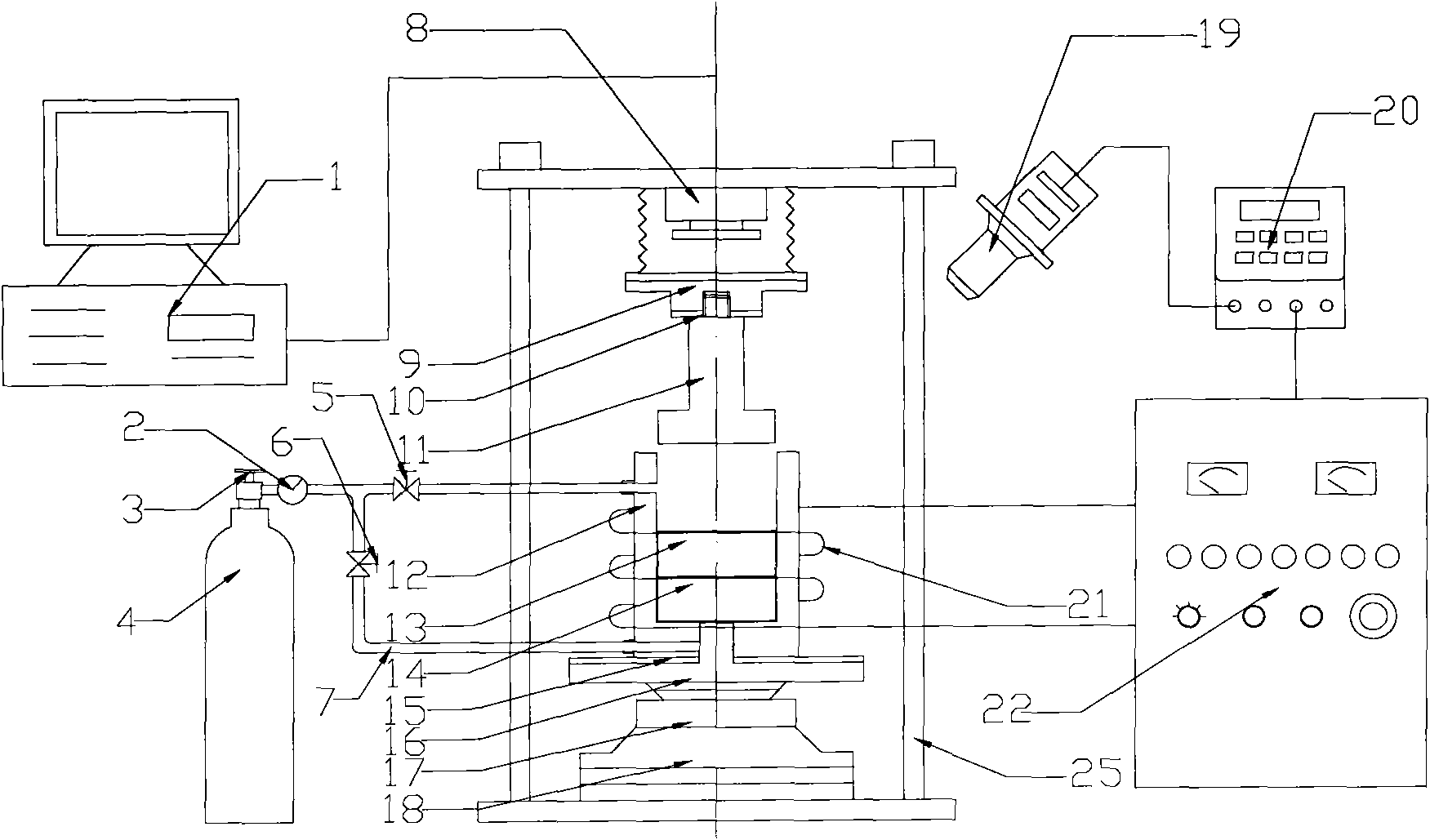
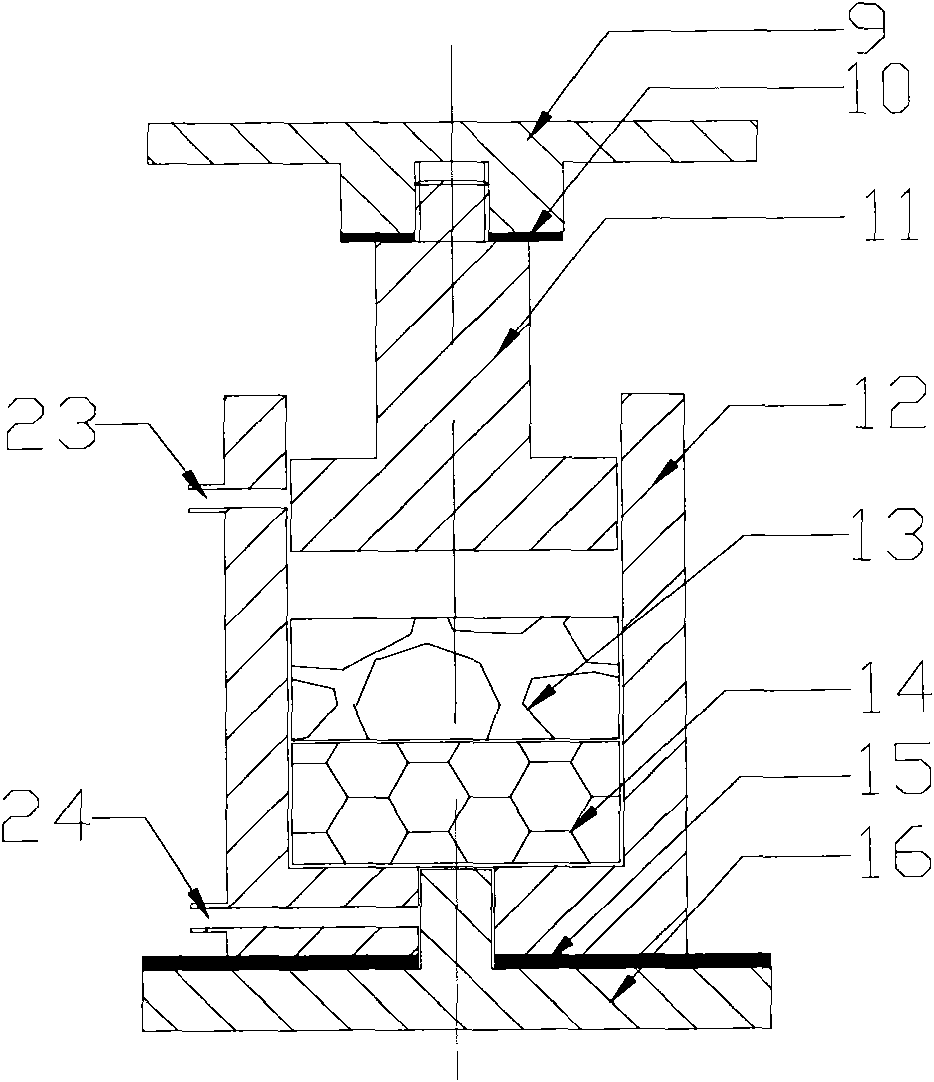
ActiveCN102079011APrevent oxidationFlexible temperature adjustmentNon-electric welding apparatusShielding gasInduction heating
The invention relates to a semi-solid deposition pressure welding device for dissimilar metals. The device comprises a pressure control device, a temperature control device, a gas protection device and a die assembly, wherein the pressure control device is connected with the die assembly and transfers pressure to the die assembly; a heating coil in the temperature control device is arranged outside the die assembly; a temperature control signal is used for regulating and inducing the magnitude and on / off of the current of the heating coil so as to control the heating process of the die assembly; and the gas protection device is connected with the die assembly and inputs protection gas into the die device. The semi-solid deposition pressure welding device for dissimilar metals provided by the invention is easy to operate and has the advantages of simple structure, excellent welding effect and good market prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Anti-deposition pressure atomization nozzle
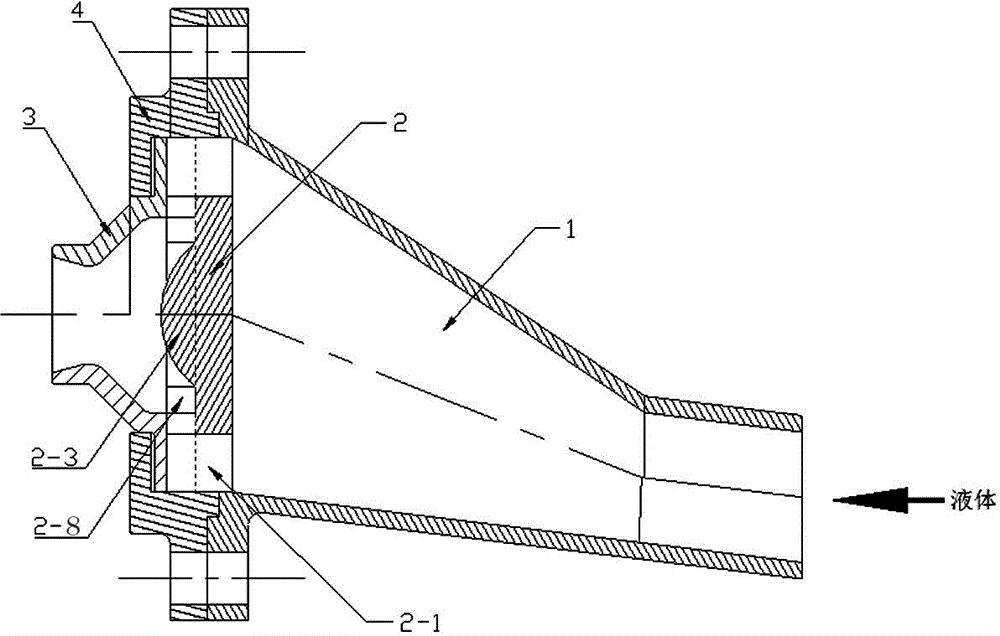
ActiveCN103817027AAvoid depositionSimple structureMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesCycloneEngineering
An anti-deposition pressure atomization nozzle is characterized in that a nozzle inner cavity is separated into a water inlet chamber and a cyclone atomization chamber through a cyclone piece. The water inlet chamber is connected with the a water inlet pipe. The cyclone atomization chamber is provided with a atomization nozzle body. The bottom of the water inlet chamber is oblique. The horizontal height of inlet of the water inlet chamber is lower than the height of the outlet of the water inlet chamber. A plurality of liquid distribution holes or grooves which are evenly distributed are formed in the cyclone piece. The water inlet chamber is communicated with the cyclone atomization chamber through the liquid distribution holes or grooves. The lowest point of each liquid distribution hole or groove is not lower than the highest point of the bottom of the water inlet chamber. One side, facing the cyclone atomization chamber, of the cyclone piece is provided with a tangential slot which is communicated with the distribution holes or grooves. The anti-deposition pressure atomization nozzle has the advantages that pressurized liquid enters the tangential slot of the cyclone piece from the water inlet chamber through the liquid distribution holes or grooves, the liquid is fed into the cyclone atomization chamber in a high-speed tangential manner, and the liquid rotating at high speed leaves the nozzle and then dispersed to form droplet groups of certain particle size; the anti-deposition pressure atomization nozzle is simple in structure, less prone to deposition and blocking, convenient to machine and manufacture, good in atomizing effect, and low in energy loss.
Owner:NANJING LANSHAN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Method for preparing carbon-silicon carbide composite material by using chemical gas-phase permeation method
InactiveCN102344294AMake up for mechanicsMake up for the shortcomings of easy layeringWater bathsSilanes
The invention provides a method for preparing a carbon-silicon carbide composite material by using a chemical gas-phase permeation method. The method is characterized in steps that: a carbon fiber weaved body is placed in a deposition chamber, and deposed carbon particles are adopted as a dividing surface, wherein methane is adopted as a reaction gas, argon is adopted as a diluting gas, a deposition pressure in the deposition chamber is 6 to 7kPa, a deposition temperature is 900 to 1000 DEG C, and a deposition time is 3 to 12 hours; then silicon carbide crystal whiskers are deposed, wherein methyl trichloro silane is adopted as a reaction gas, hydrogen is adopted as a carrier gas, methyl trichloro silane is positioned in a evaporation vessel for water bath heating, a water bath temperature is 35 to 40 DEG C, a pressure in the evaporation vessel is controlled at 0.2 to 0.3MPa, a total flow of hydrogen and methyl trichloro silane is controlled at 200 to 300ml / min, methyl trichloro silane is delivered into the deposition chamber by hydrogen through a bubbling method, argon is used as a diluting gas, a deposition pressure in the deposition chamber is 6 to 7kPa, a deposition temperature is 1100 to 1150 DEG C, and a deposition time is 1 to 7 days, such that the carbon-silicon carbide composite material is obtained. The composite material provided by the invention has good toughness and high anti-interlaminar shear strength.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for forming insitu boron doped polycrystalline and amorphous silicon films
InactiveUS20020162505A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDeposition temperatureDecreased pressure
A method and apparatus for depositing a boron insitu doped amorphous or polycrystalline silicon film on a substrate. According to the present invention, a substrate is placed into deposition chamber. A reactant gas mix comprising a silicon source gas, boron source gas, and a carrier gas is fed into the deposition chamber. The carrier gas is fed into the deposition chamber at a rate so that the residence of the carrier gas in the deposition chamber is less then or equal to 3 seconds or alternatively has a velocity of at least 4 inches / sec. In another embodiment of forming a boron doped amorphous for polycrystalline silicon film a substrate is placed into a deposition chamber. The substrate is heated to a deposition temperature between 580-750° C. and the chamber pressure reduced to a deposition pressure of less than or equal to 50 torr. A silicon source gas is fed into the deposition at a rate to provide a silicon source gas partial pressure of between 1-5 torr. Additionally, a boron source gas is fed into the deposition chamber at a rate to provide a boron gas partial pressure of between 0.005-0.05 torr.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of fabricating conductive carbon thin-film of high-hardness and application of the carbon thin-film as electrode for thin-film electro-luminescent device
InactiveUS20080053819A1Improve conductivityGood physical propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesThin film electrodeHardness
The present invention provides a method of fabricating a carbon thin-film having high conductivity and high hardness, comprising the steps of: supplying argon (Ar) to the chamber as sputtering gas; maintaining the initial vacuum of the chamber at about 10−6 Torr; forming deposition pressure of about 10−3 Torr so as to activate plasma; and applying negative DC bias to the substrate, and a method of fabricating a thin-film electroluminescent device comprising the steps of: providing a transparent TCO or ITO substrate; forming a phosphor layer on the top of the transparent substrate; forming an insulation layer on the top of the phosphor layer through vacuum deposition; and forming a carbon thin-film electrode through closed-field unbalanced magnetron sputtering.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
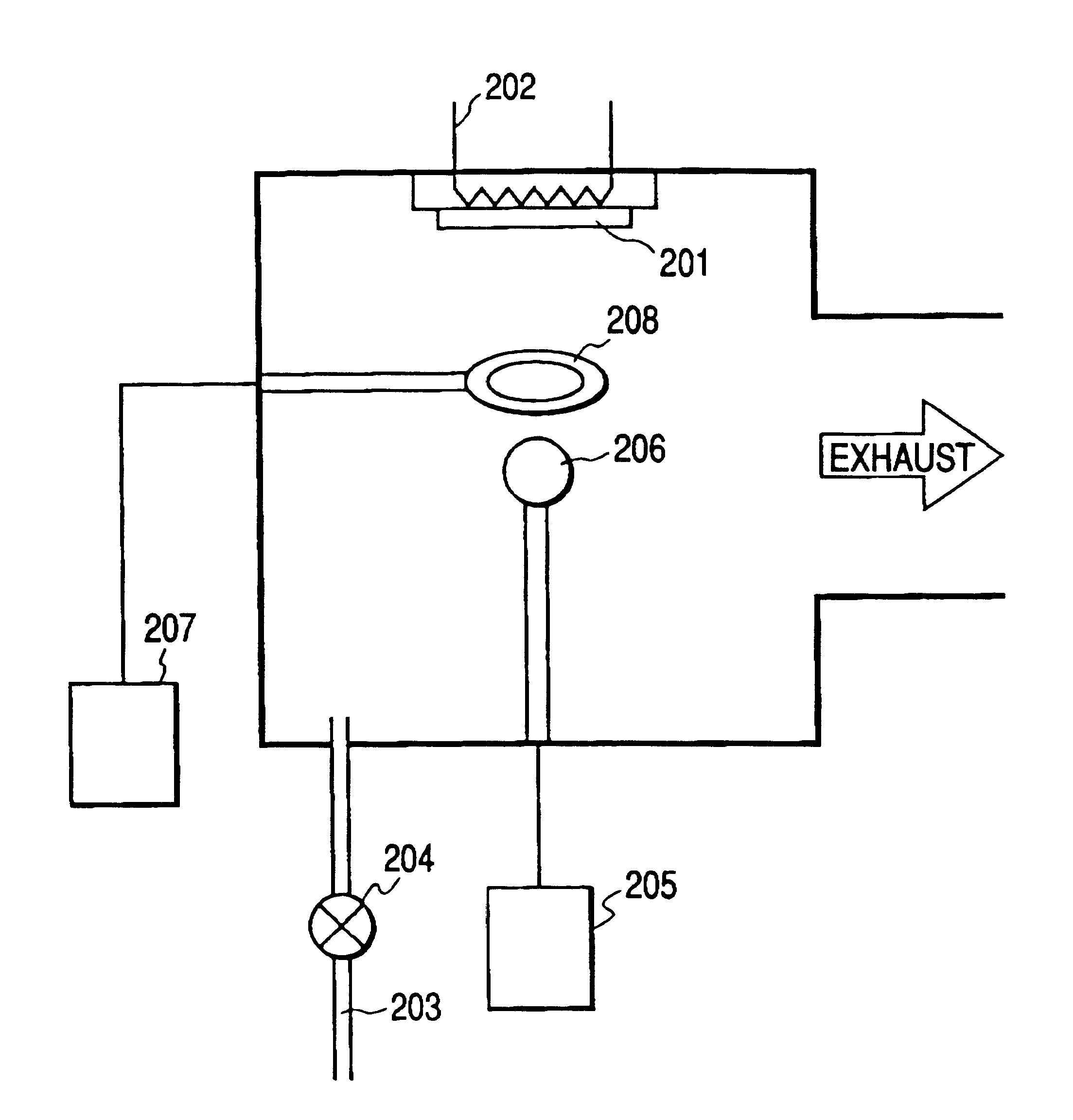
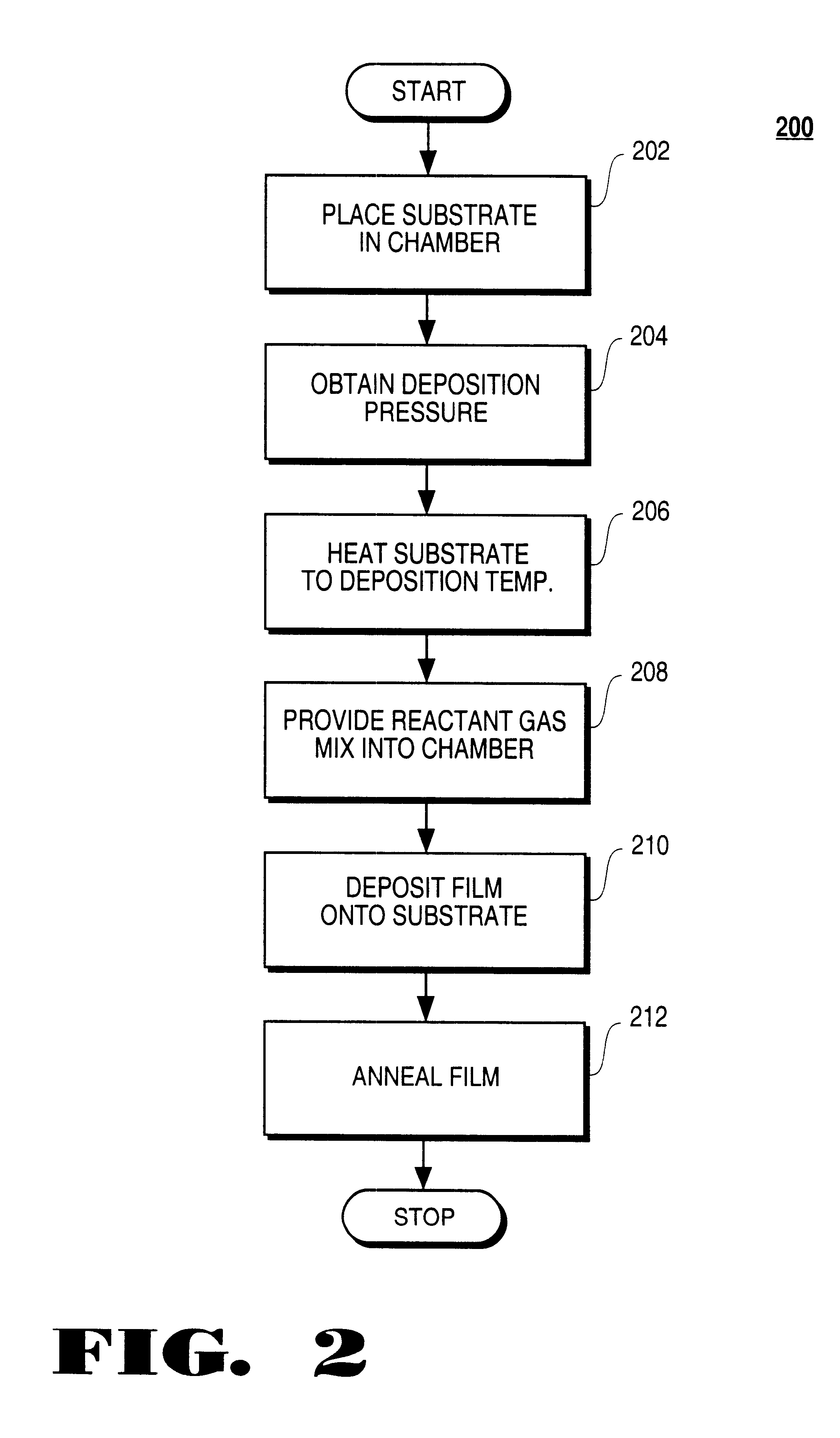
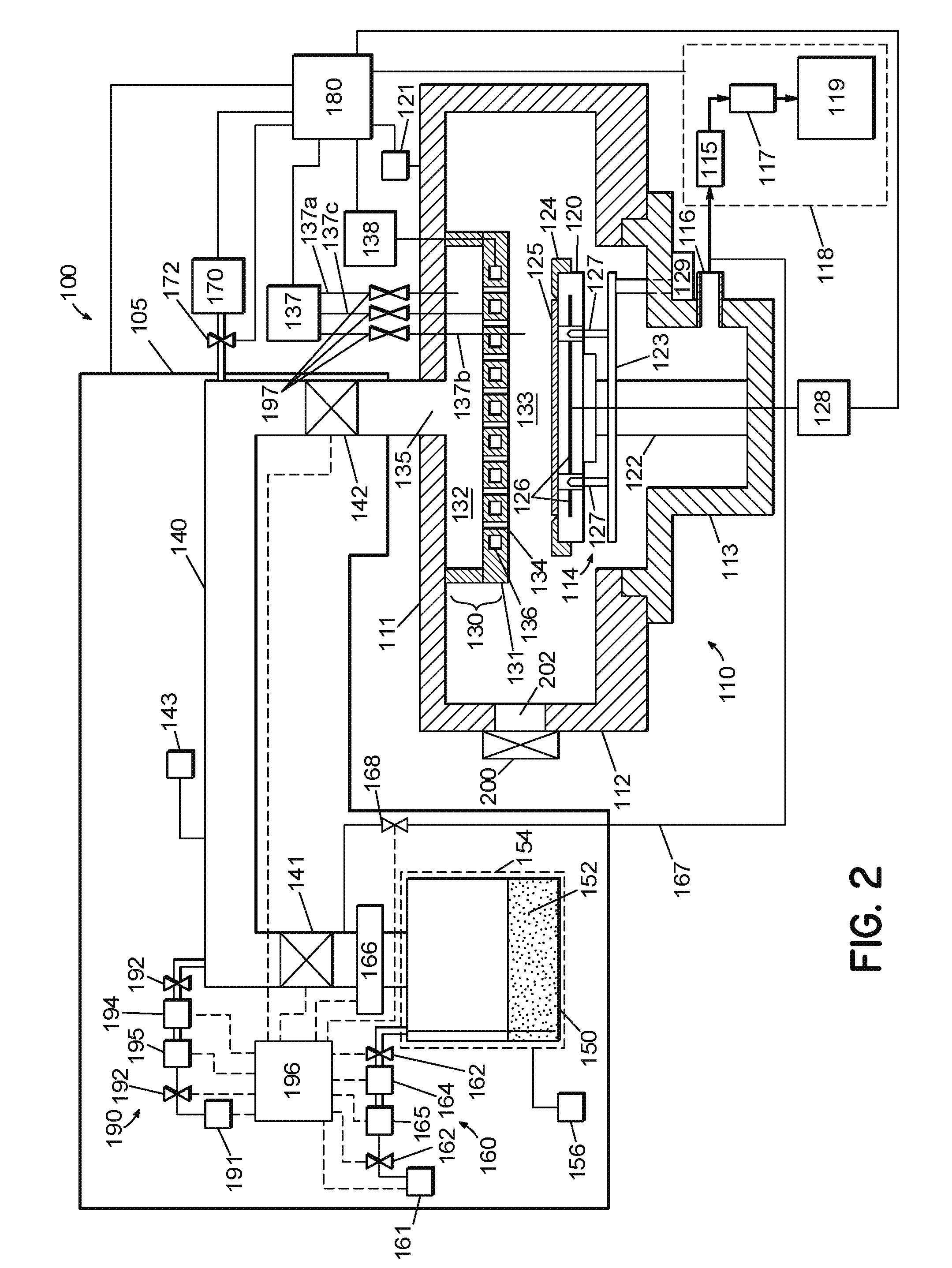
Method for heating a substrate prior to a vapor deposition process
A method for depositing a thin film on a substrate in a vapor deposition system is described. Prior to the deposition process, the substrate is provided within the vapor deposition system and coupled to an upper surface of a substrate holder within the vapor deposition system, whereby the substrate is heated to a deposition temperature in a first gaseous atmosphere. Thereafter, the first gaseous atmosphere is displaced by a second gaseous atmosphere, and the pressure is adjusted to a deposition pressure. The second gaseous atmosphere comprises a gaseous composition that is substantially the same as the carrier gas utilized to transport film precursor vapor to the substrate and the optional dilution gas utilized to dilute the carrier gas and film precursor vapor.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Double-layer silicon nitride antireflection film and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN103117310AImprove passivation effectPromote absorptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesDeposition temperatureSilanes
The invention discloses a double-layer silicon nitride antireflection film and a manufacture method thereof. The double-layer silicon nitride antireflection film is composed of an upper-layer silicon nitride film and a lower-layer silicon nitride film, wherein the thickness of the lower-layer silicon nitride film is 10nm-15nm, the refractive index of the lower-layer silicon nitride film is 2.2-2.5, the thickness of the upper-layer silicon nitride film is 70nm-75nm, and the refractive index of the upper-layer silicon nitride film is 2.0-2.05. In manufacture, a polished mono-crystalline silicon piece is obtained, deposition temperature, deposition pressure intensity and deposition power are consistent, and a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PEVCD) process is adopted to set two group of ammonia and silane gas flow ratio parameters ordered from small to big and deposition time in the advancing direction of silicon wafers so as to manufacture the double-layer silicon nitride antireflection film. Under the condition that existing resources and other devices and materials are not added, the antireflection film identical in texture layers and different in performance parameter is manufactured in the same device through two process steps, accordingly crystalline silicon surface passivation effect is improved, sunlight reflecting effect of the crystalline silicon surface is reduced, absorption on long waves and short waves of the silicon wafers is increased, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ALEX NEW ENERGY
Method for heating a substrate prior to a vapor deposition process
A method for depositing a thin film on a substrate in a vapor deposition system is described. Prior to the deposition process, the substrate is provided within the vapor deposition system and coupled to an upper surface of a substrate holder within the vapor deposition system, whereby the substrate is heated to a deposition temperature in a first gaseous atmosphere. Thereafter, the first gaseous atmosphere is displaced by a second gaseous atmosphere, and the pressure is adjusted to a deposition pressure. The second gaseous atmosphere comprises a gaseous composition that is substantially the same as the carrier gas utilized to transport film precursor vapor to the substrate and the optional dilution gas utilized to dilute the carrier gas and film precursor vapor.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
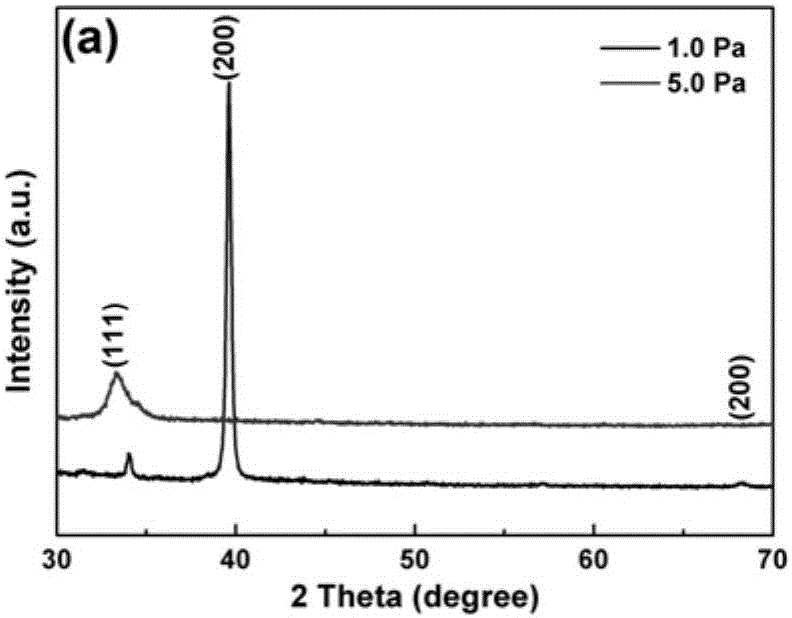
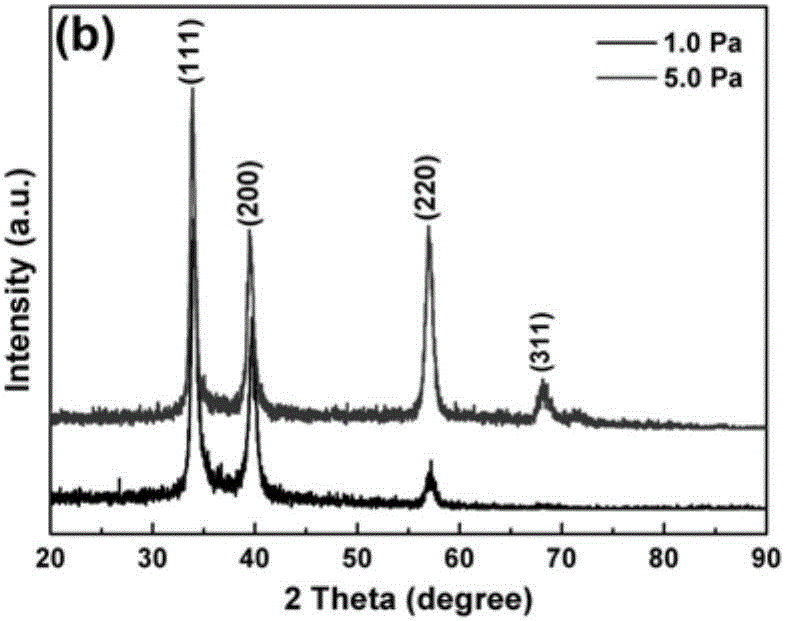
Preparation method for transition metal nitride super-capacitor coating material
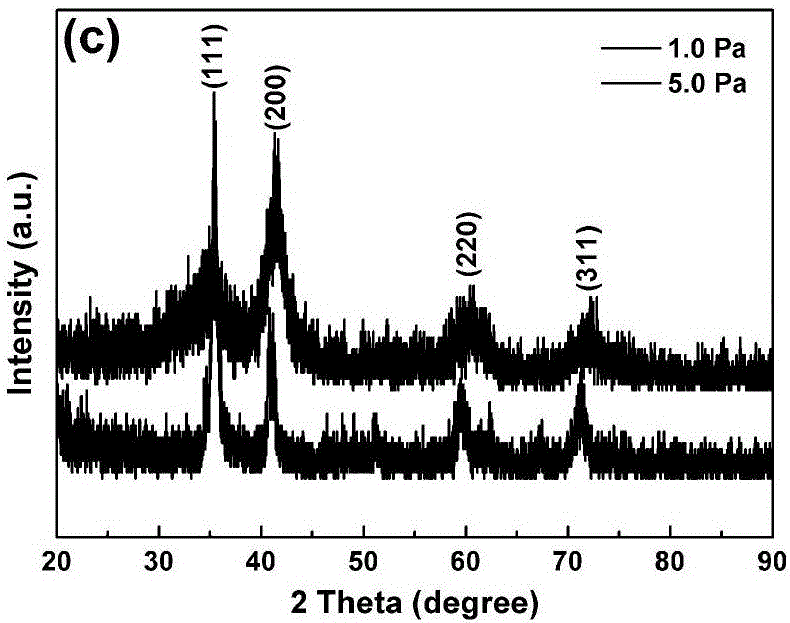
The invention discloses a preparation method for a transition metal nitride super-capacitor coating material, and relates to a super-capacitor. The transition metal nitride super-capacitor coating material is obtained by performing reactive magnetron sputtering at different deposition pressures. The different deposition pressures are between 1.0 and 5.0 Pa; the transition metal nitride is ZrN, HfN and NbN. By regulating and controlling the deposition pressure during a thin film depositing process, the maximum specific capacitance values of the transition metal nitrides can be respectively 12.0, 13.5, and 10.2 mF / cm<2>; after 20,000 times of recycling, the capacity retention rates are all up to 90 percent.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method of forming phase change layer using a germanium precursor and method of manufacturing phase change memory device using the same
A method of forming a phase change layer using a Ge compound and a method of manufacturing a phase change memory device using the same are provided. The method of manufacturing a phase change memory device included supplying a first precursor on a lower layer on which the phase change layer is to be formed, wherein the first precursor is a bivalent precursor including germanium (Ge) and having a cyclic structure. The first precursor may be a cyclic germylenes Ge-based compound or a macrocyclic germylenes Ge-based, having a Ge-N bond. The phase change layer may be formed using a MOCVD method, cyclic-CVD method or an ALD method. The composition of the phase change layer may be controlled by a deposition pressure in a range of 0.001 torr-10 torr, a deposition temperature in a range of 150 DEG C. to 350 DEG C. and / or a flow rate of a reaction gas in the range of 0-1 slm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High throughput process for the formation of a refractory metal nucleation layer
InactiveUS20030157797A1Efficient mixingEffective distributionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium nitrideHigh pressure
A method for the formation of a refractory metal nucleation layer (e.g., a tungsten nucleation layer) on a semiconductor device substrate that includes first depositing a metallic barrier layer (e.g., a titanium-nitride barrier layer) on the substrate. Next, the metallic barrier layer is exposed to a silicon-containing gas (e.g., monosilane) to form a layer of silicon (e.g., a monolayer of silicon) on the metallic barrier layer. The layer of silicon is then exposed to a refractory metal-containing gas (e.g., WF6) in a manner such that the refractory metal-containing gas undergoes a reduction reaction with the layer of silicon. The result of this reaction is the formation of a refractory metal layer (e.g., a tungsten metal layer) on the metallic barrier layer. Subsequently, an alternating exposure of the refractory metal layer to the silicon-containing gas and the refractory metal-containing gas is conducted. This alternating exposure deposits additional refractory metal on the refractory metal layer in order to form a refractory metal nucleation layer. Processes according to the present invention employ a relatively high pressure (i.e., between 40 and 300 Torr) during formation of the tungsten nucleation layer. The relatively high pressure facilitates fast reactions and temperature stabilization during formation of the refractory metal nucleation layer and, thus, a high throughput process. In addition, the process can be combined with a conventional tungsten core layer deposition conducted at a relatively high pressure without the need to expend process time cycling between two different deposition pressures, thus providing a high effective throughput.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High-throughput chemical vapor infiltration process based on parameter region control, application thereof and device adopting same
ActiveCN107058975ARapid uniform densificationDensification is efficientChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperatureRetention time
The invention discloses a high-throughput chemical vapor infiltration process based on parameter regional control, application thereof and a device adopting the same. The high-throughput chemical vapor infiltration process based on parameter region control comprises the following steps: folded carbon paper is utilized to divide a deposition area into deposition zones with different specific areas, fiber preforms of same types and dimensions are placed in each of the deposition zones at preset deposition temperature, deposition pressure and gas flow, so that region control within the retention time is realized, and high-throughput composite materials with different parameter systems are prepared in single experiment; the deposition rate and the microstructure of the carbon paper and the fiber preforms in the deposition zones are tested and characterized, quick and efficient parameter optimization of the retention time and the specific areas is realized, deposition parameters and deposition areas with better deposition characteristic and better densification characteristic are sought out, and a series of technological parameters are selected in an optimized manner. According to the high-throughput chemical vapor infiltration process based on parameter region control, application thereof and device adopting the same, optimized deposition parameters and deposition areas in combination with area movement of large-dimension fiber preforms are utilized, and finally rapid and uniform densification of large-dimension composite material components is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method of forming a phase change memory and method for forming phase change layer
InactiveCN101165934ALow deposition temperatureGood step coverageSolid-state devicesChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperaturePhase-change memory
A method for manufacturing phase change memory and a method for forming a phase change layer in the phase change memory are provided in the present invention. The method for manufacturing the phase change memory includes providing a bottom layer comprising a germanium (Ge) bivalent first precursor forming the phase change layer onto it. The phase change layer may be formed by one of MVCOD, cyclic-CVD or ALD. The composition of the phase change layer may be varied by modifying the deposition pressure, deposition temperature, and / or supply rate of reaction gas. The deposition pressure may range from about 0.001-10 torr, the deposition temperature may range from about 150-350 DEG C., and the supply rate of the reaction gas may range from about 0-1 slm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com