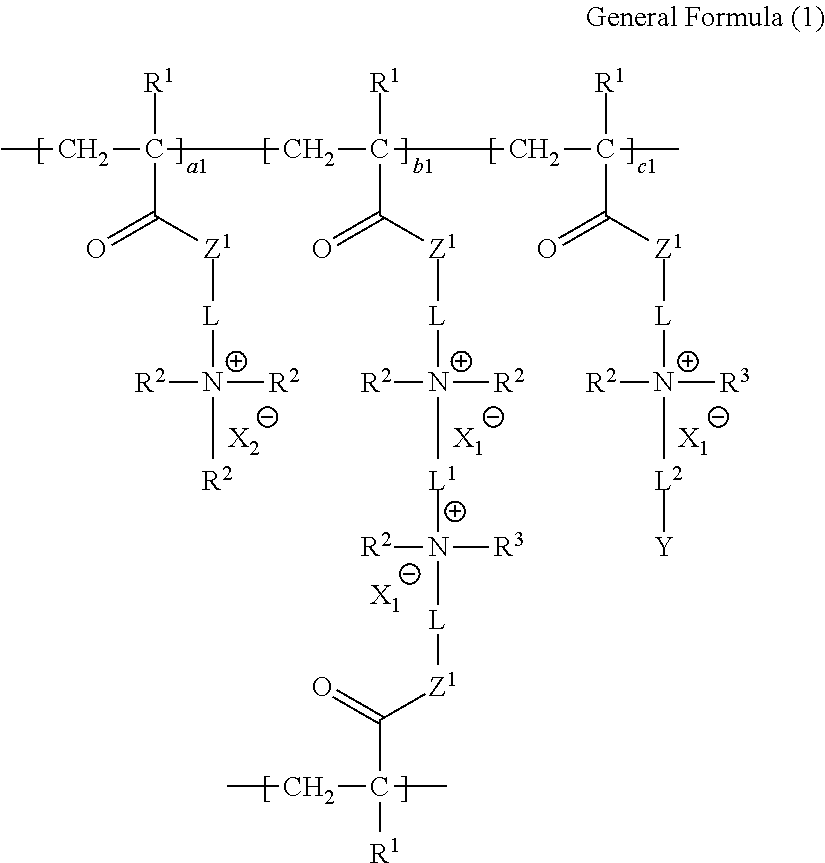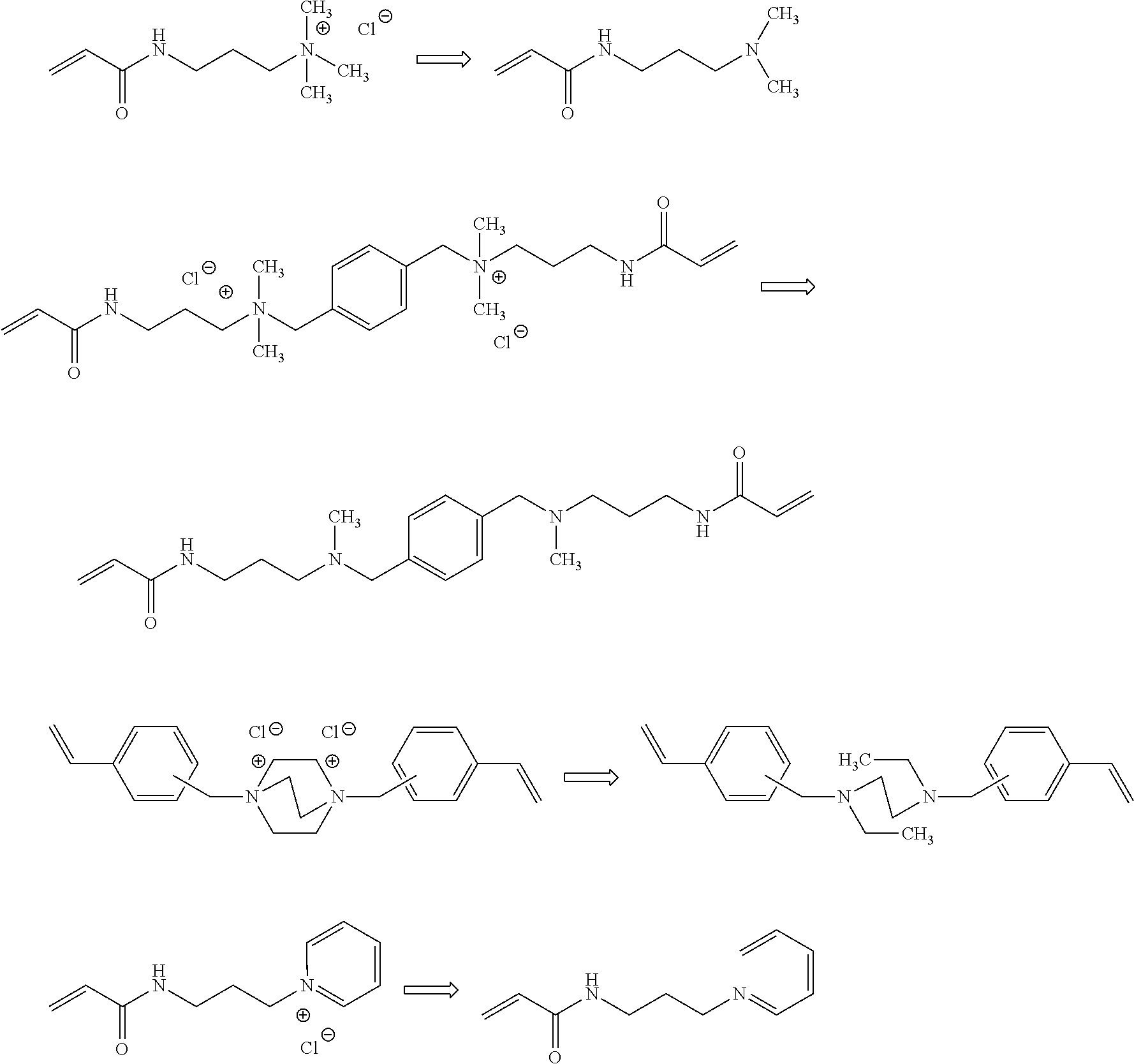Patents
Literature
386results about How to "Reduce water permeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
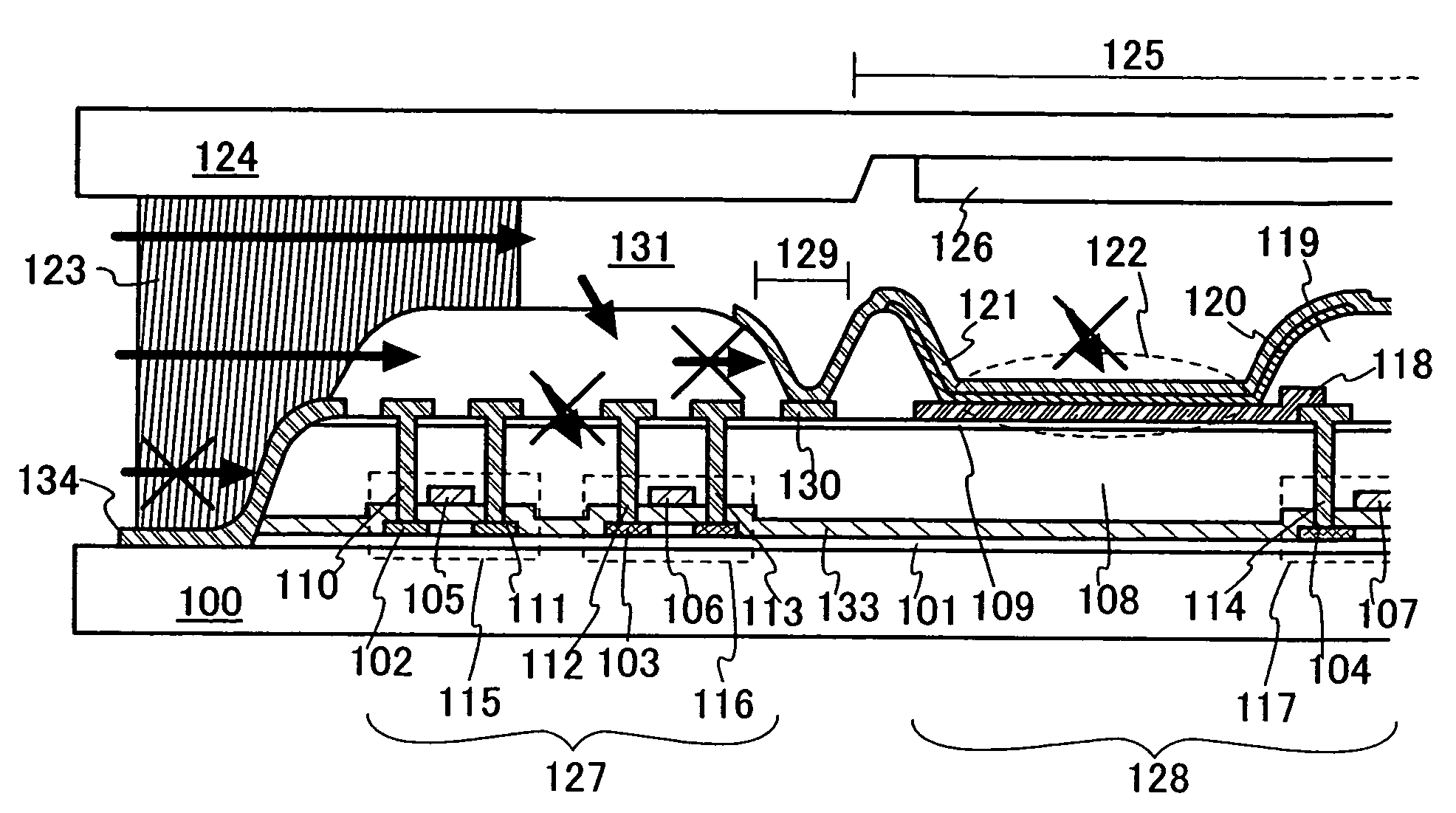
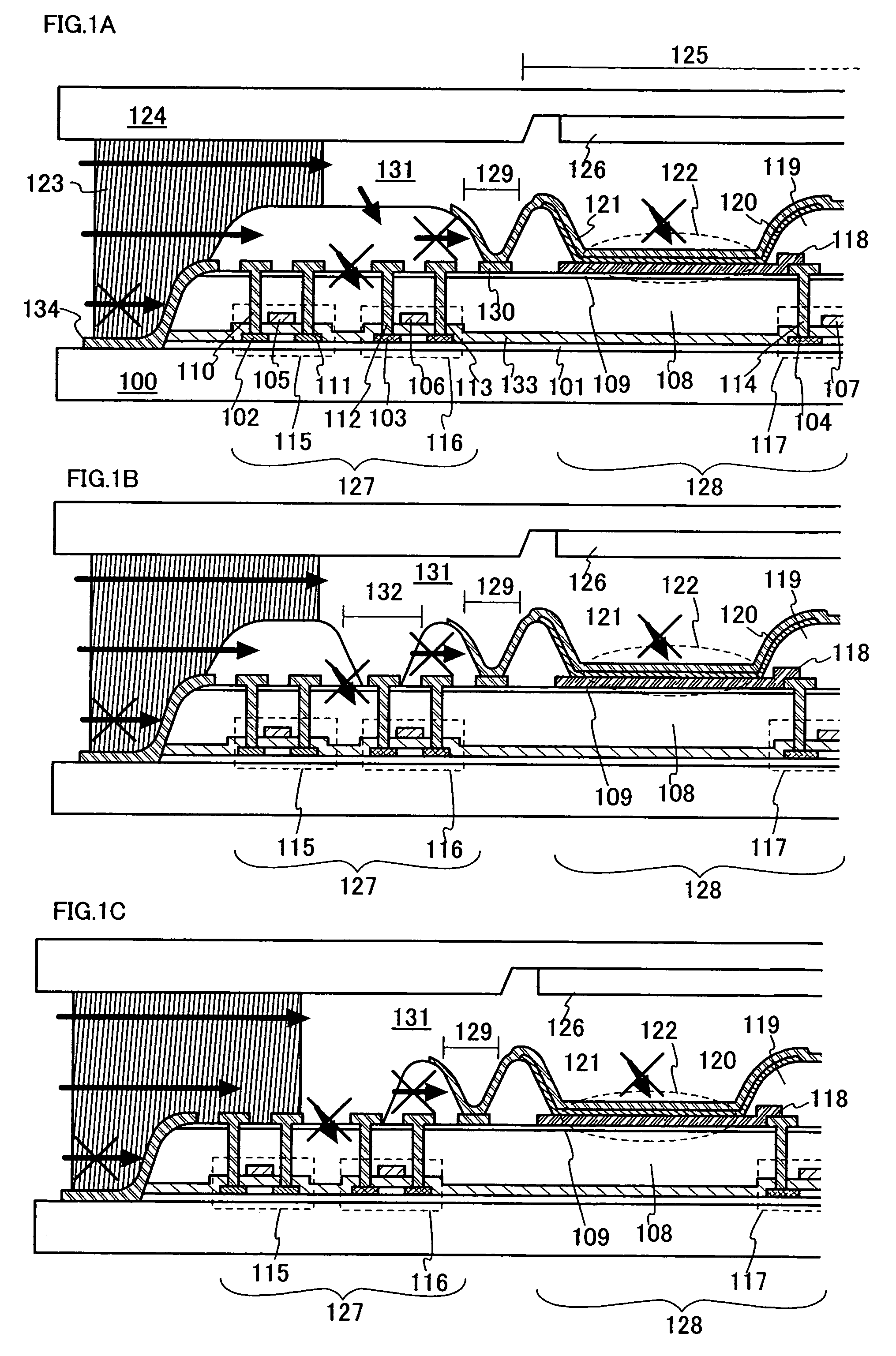
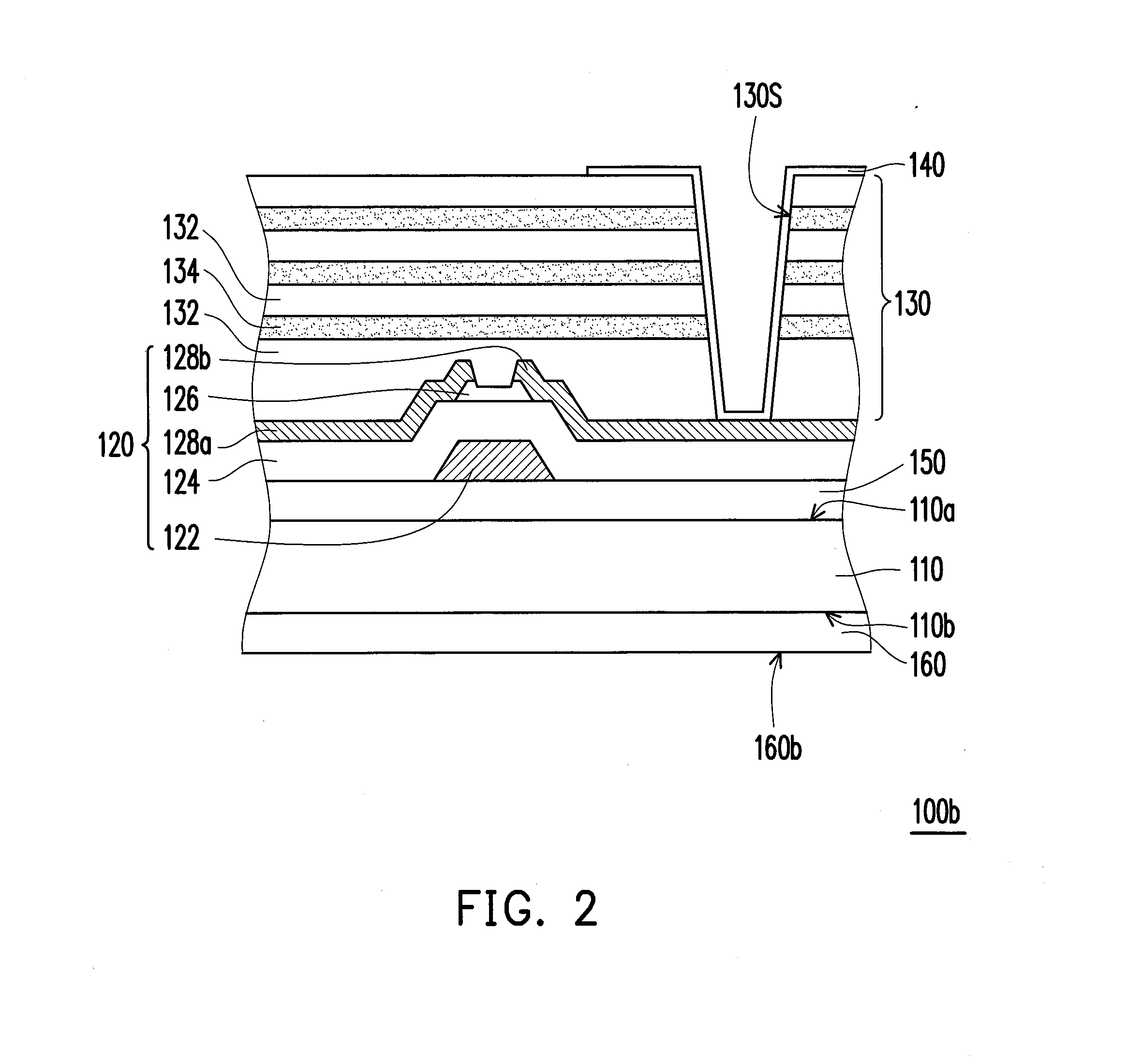
Display device
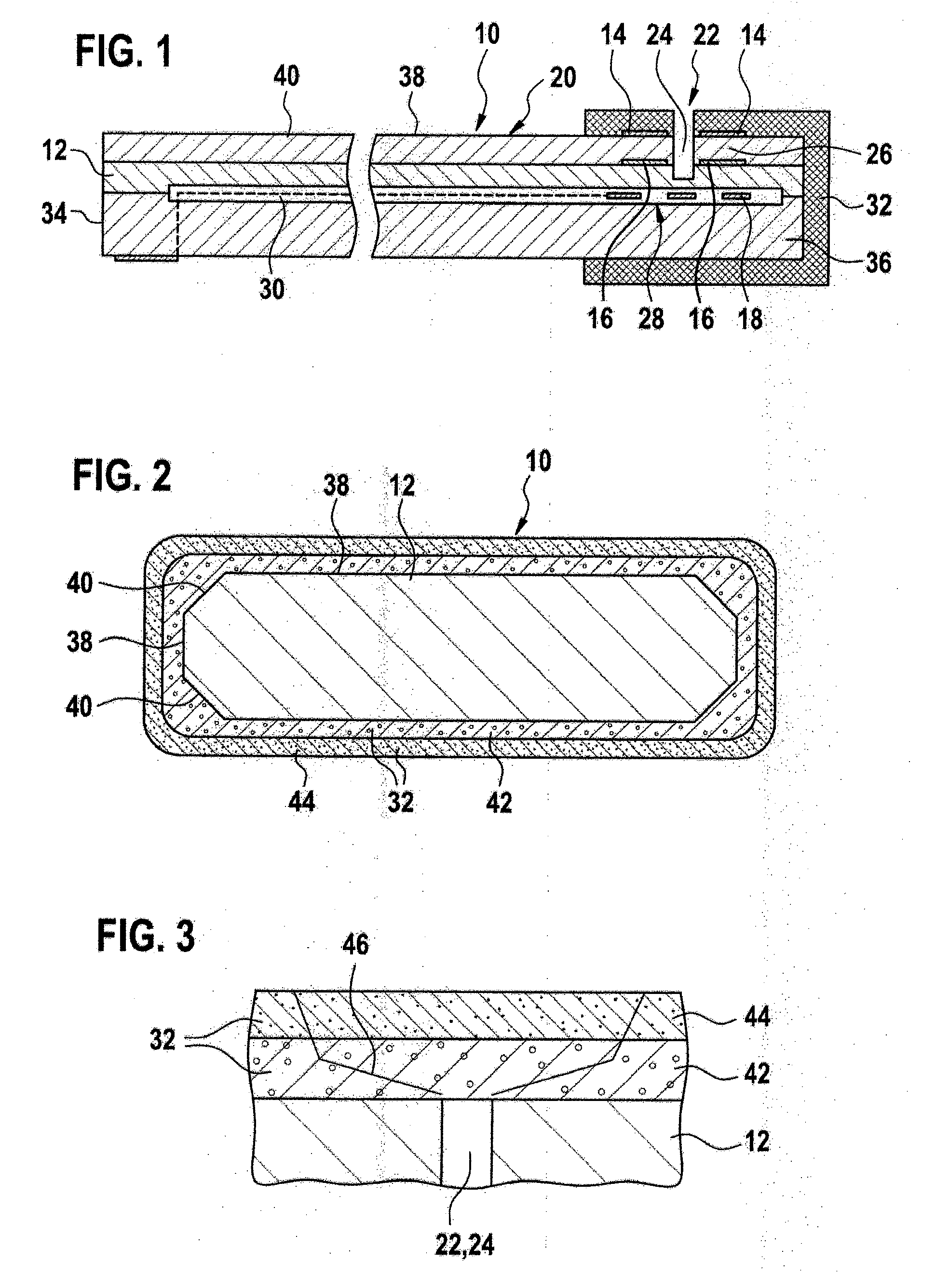
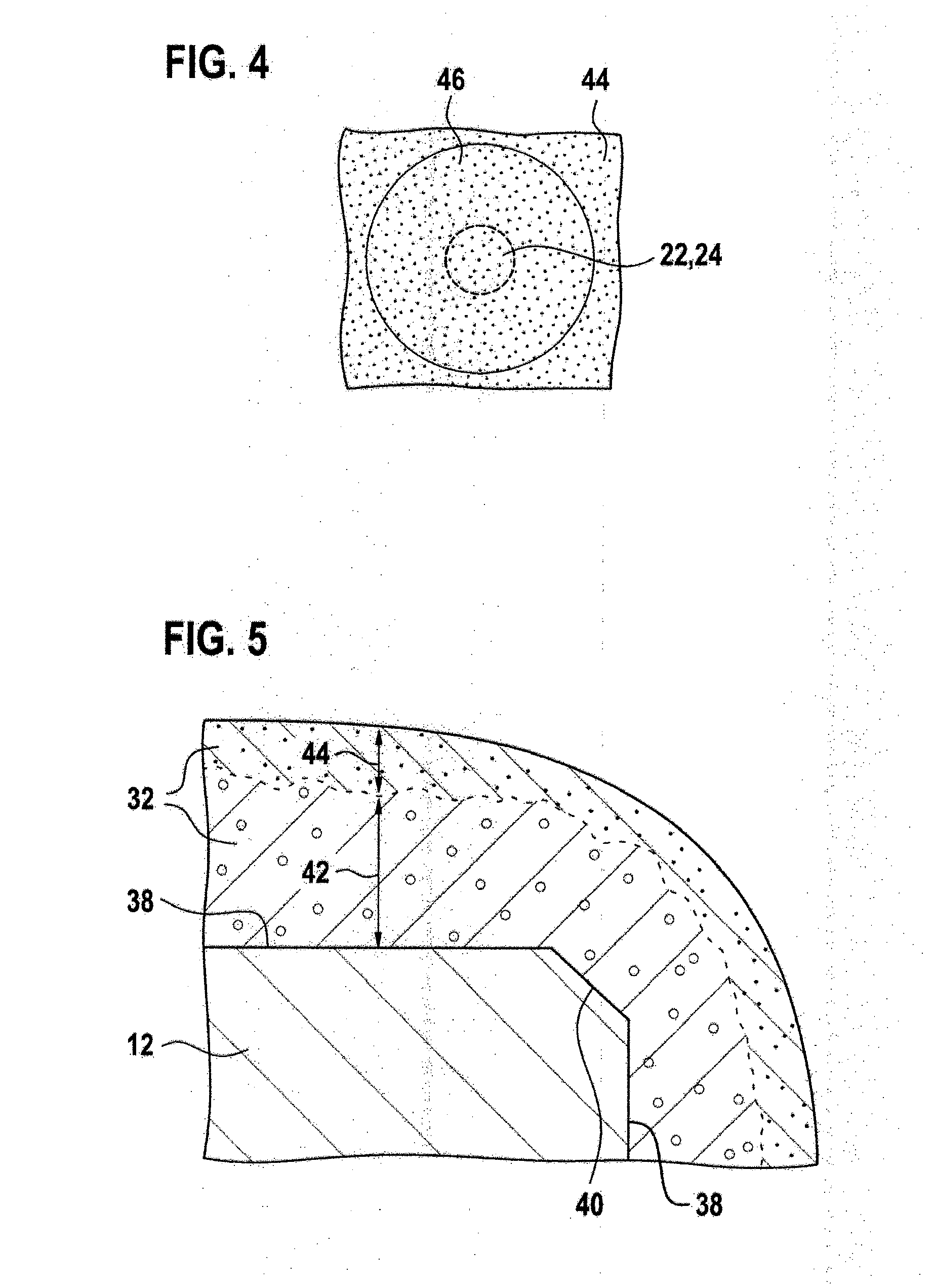
ActiveUS20050218396A1Reduce water permeabilityReducing light emissionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight emitting device
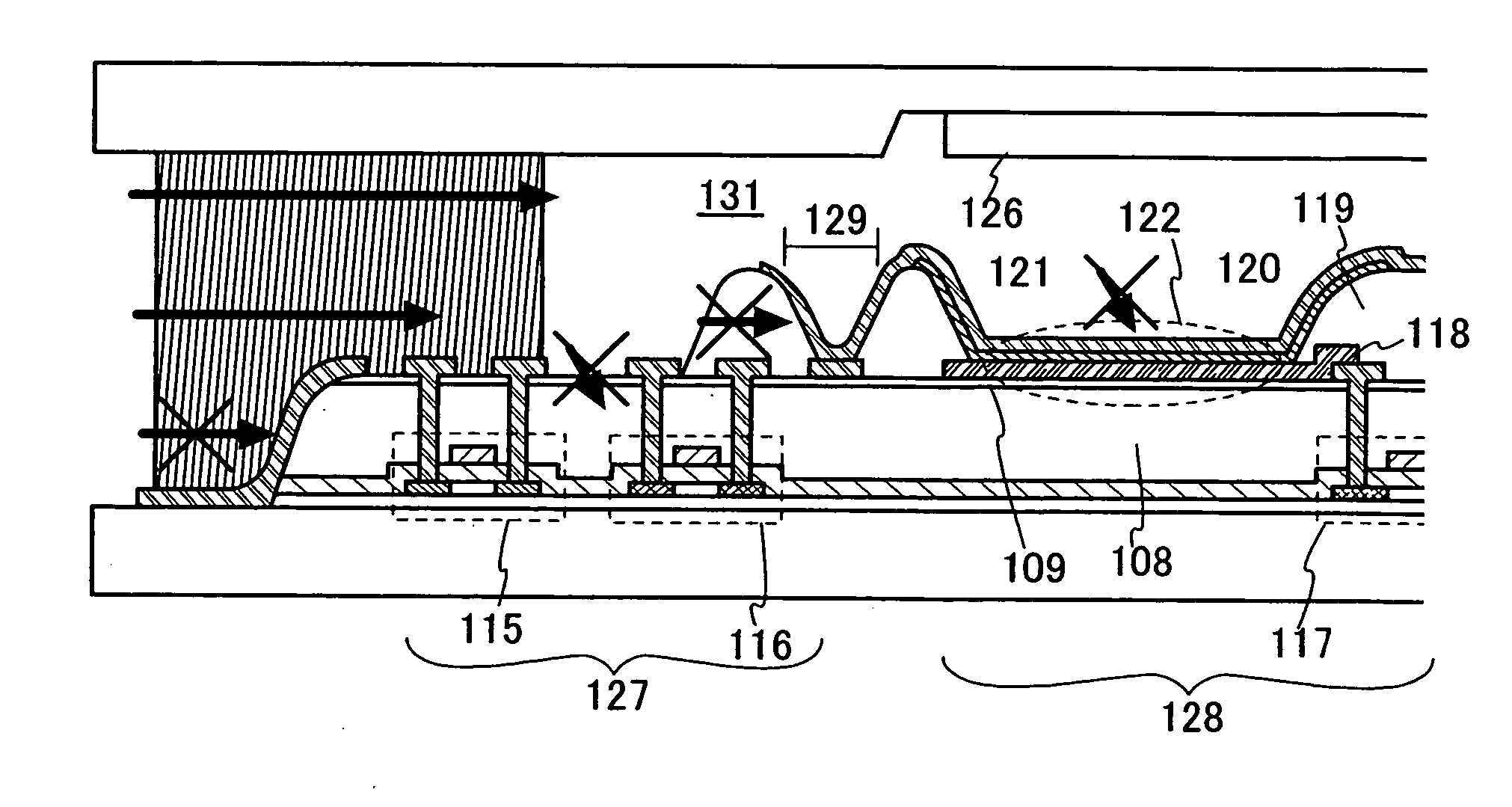
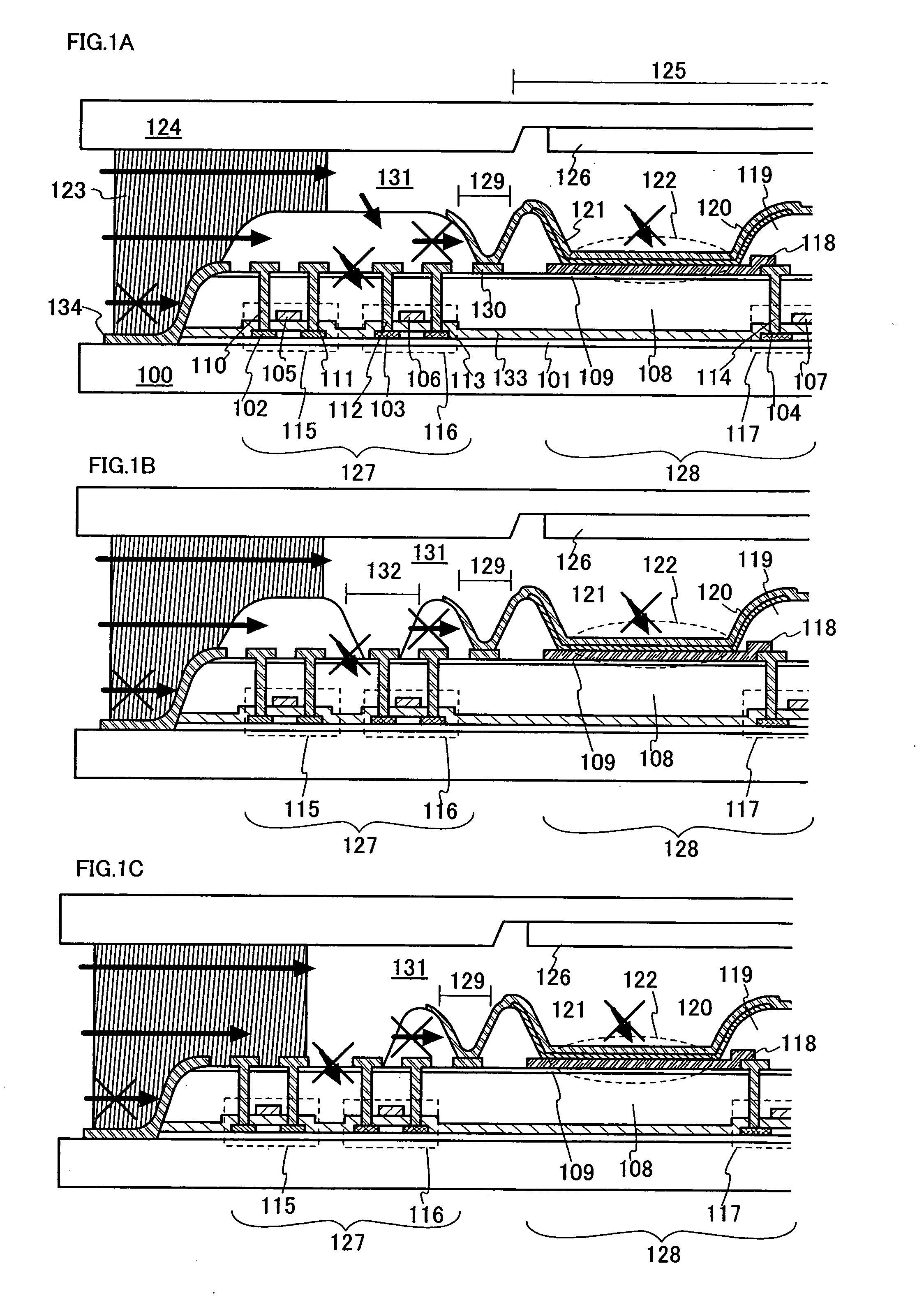
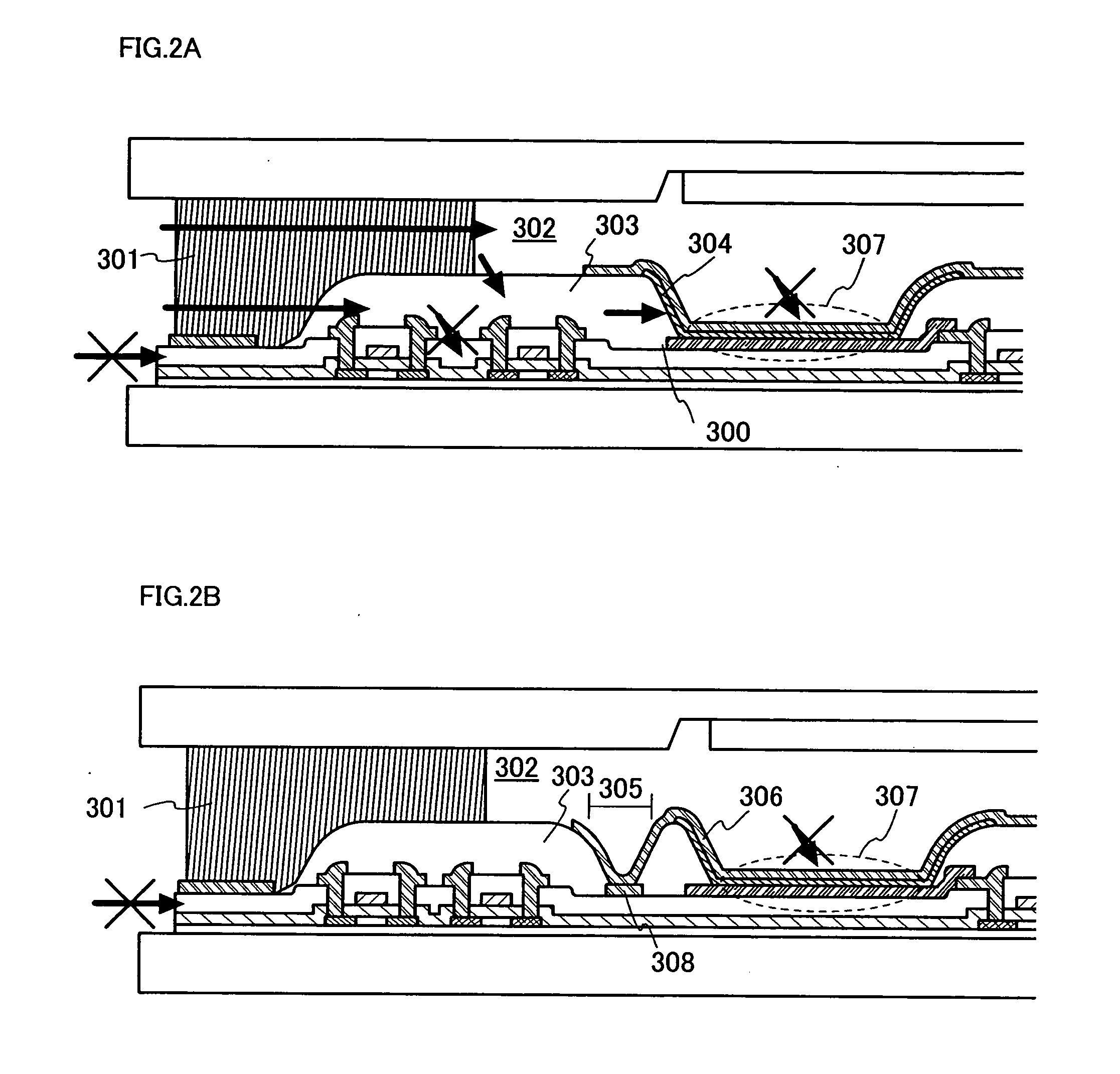
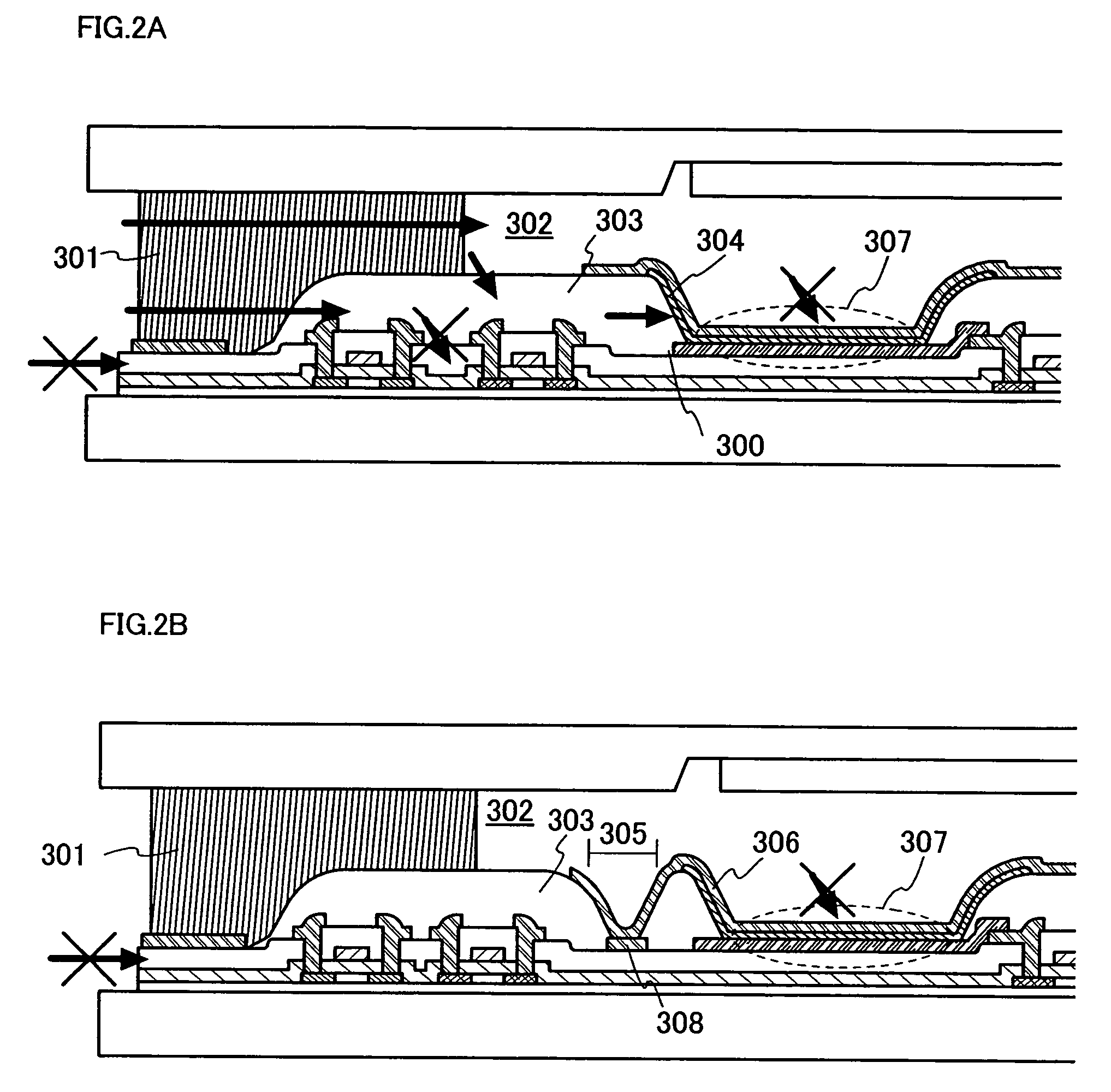
In a light emitting device using a light emitting element, the invention provides a sealing structure capable of preventing ingress of moisture from the outside and obtaining adequate reliability. The light emitting device has a light emitting element comprising a light emitting layer formed between a first electrode and a second electrode and a pixel portion comprising the light emitting element. The entire surface of the pixel portion is covered with the second electrode. An impermeable insulating film is formed in contact with the first electrode of the light emitting element. The edge of the first electrode and the impermeable insulating film are covered with a partition wall. An opening is formed along the circumference of the pixel portion in the partition wall. The opening passes through the partition wall in the thickness direction, and the side wall and the bottom face thereof are covered with the second electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
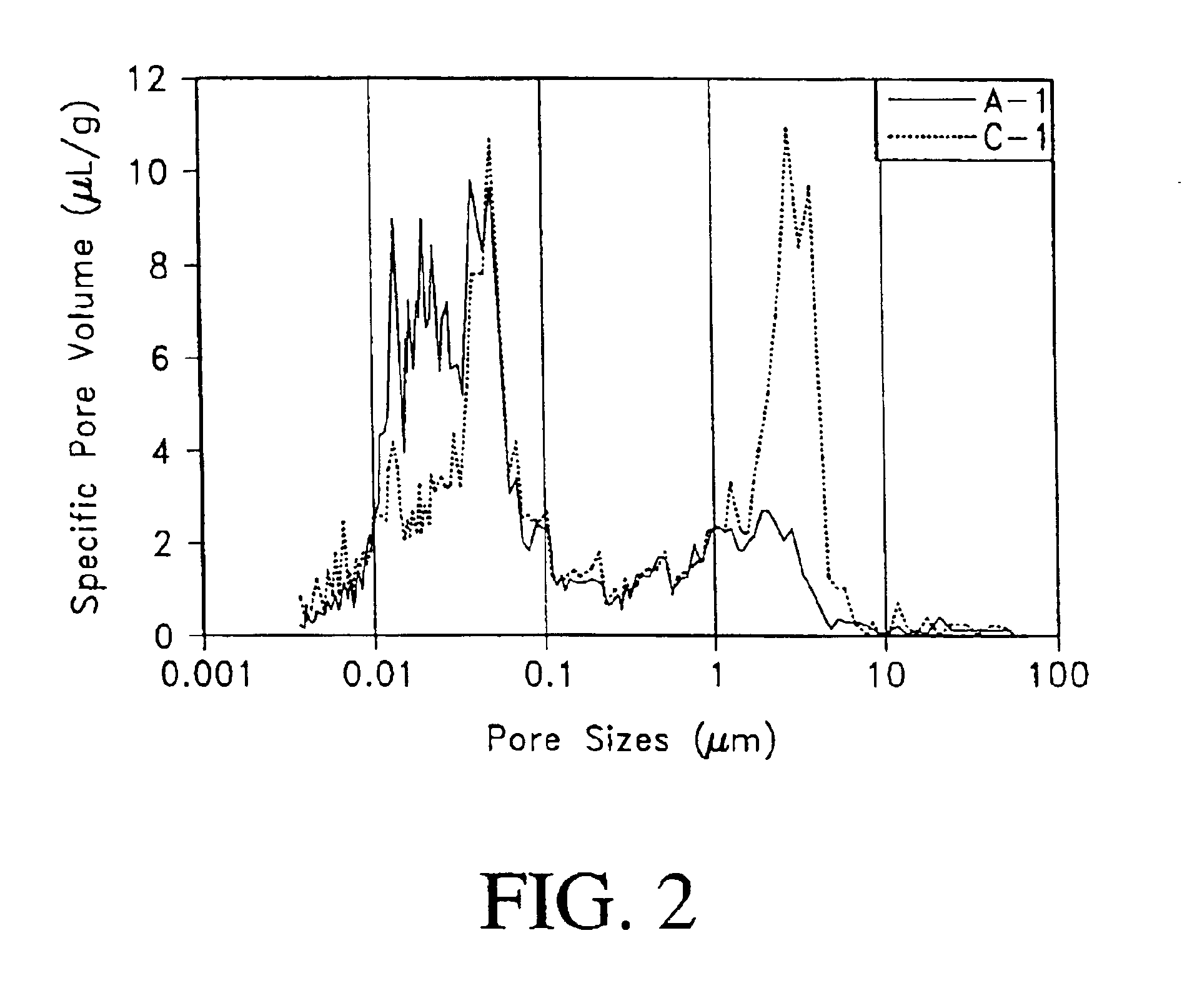
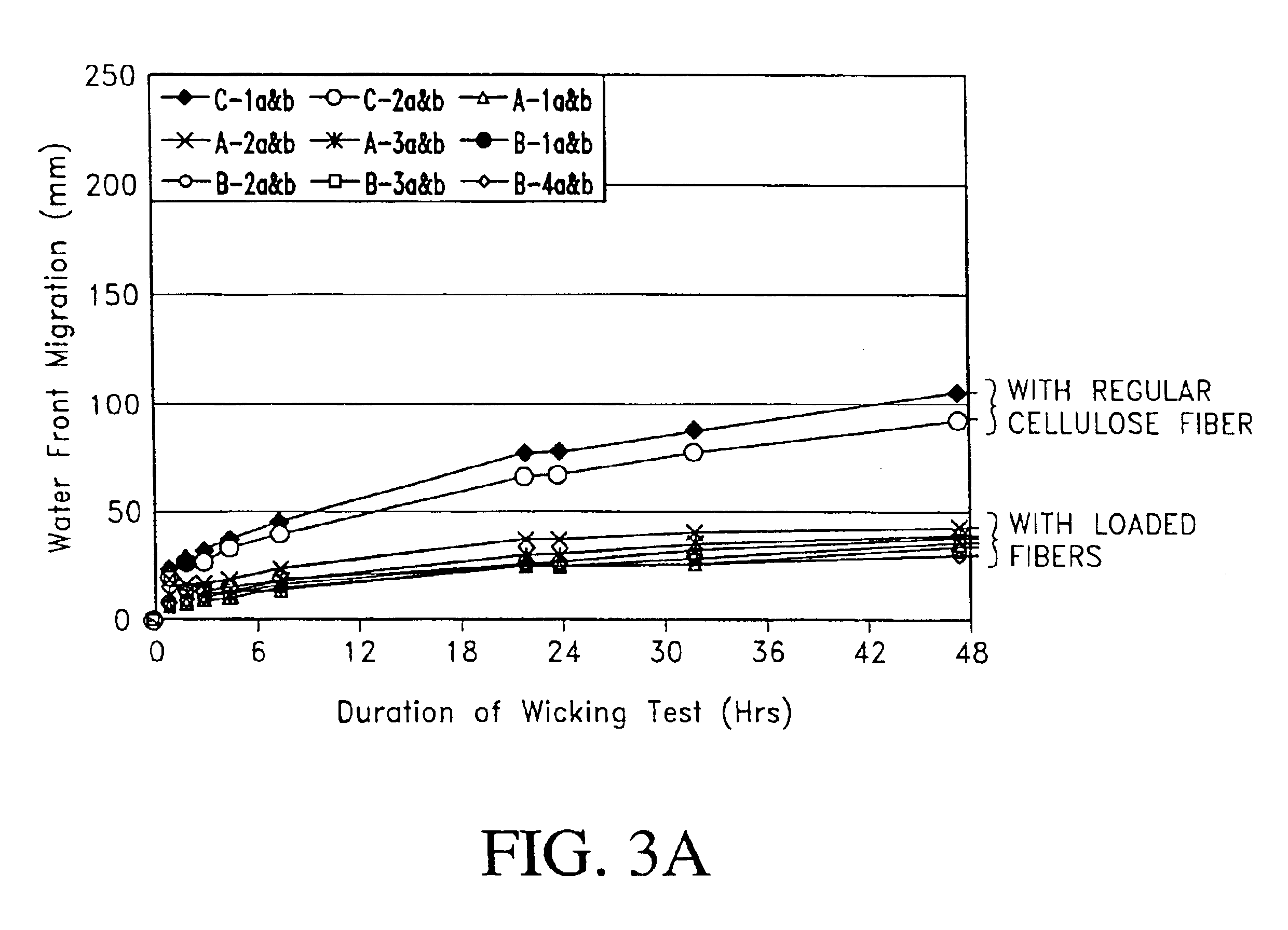
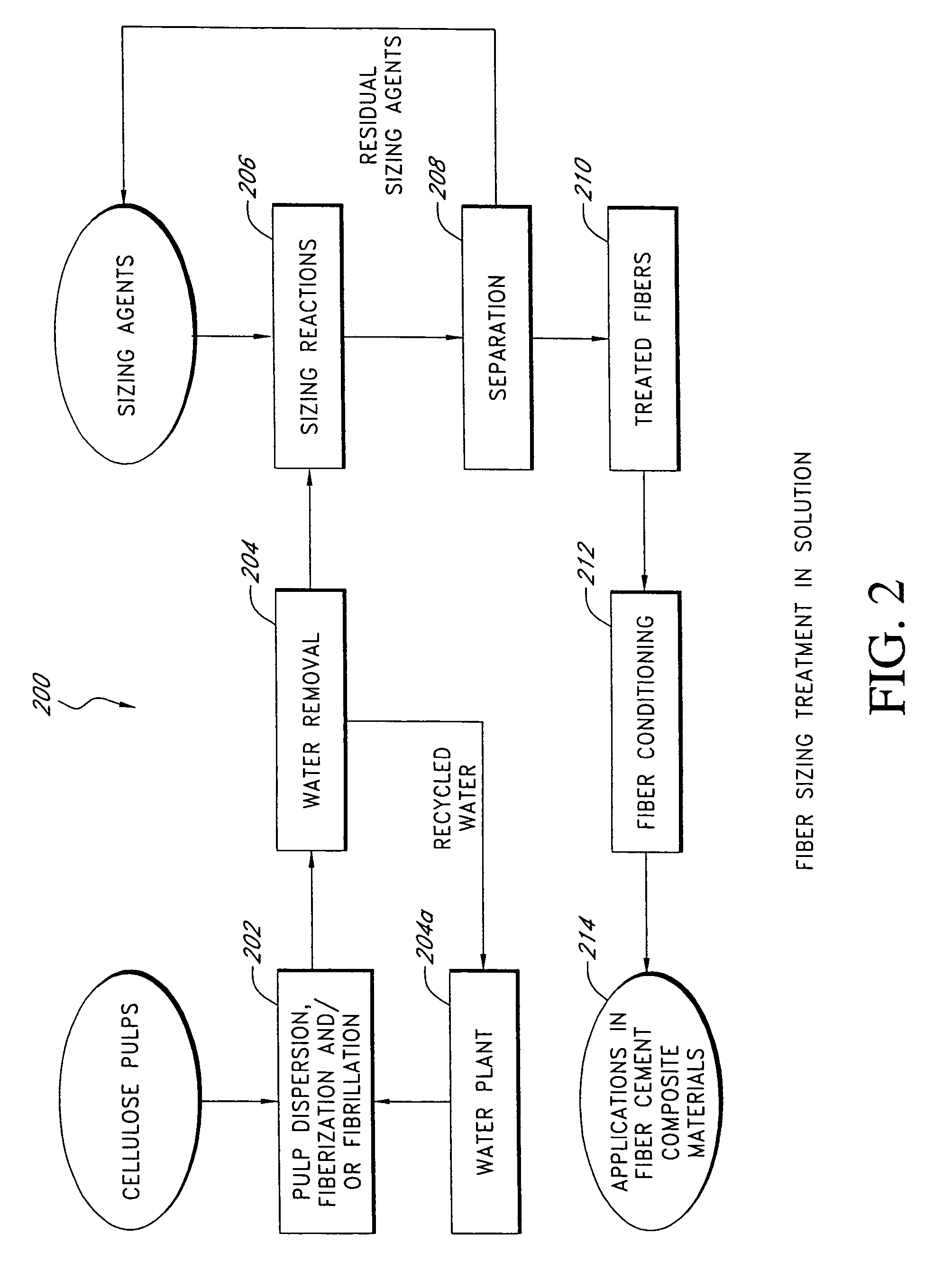
Fiber cement composite materials using cellulose fibers loaded with inorganic and/or organic substances
InactiveUS6872246B2Reduction of it pore volumeIncrease toughnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFreeze thaw resistanceChemical dissolution
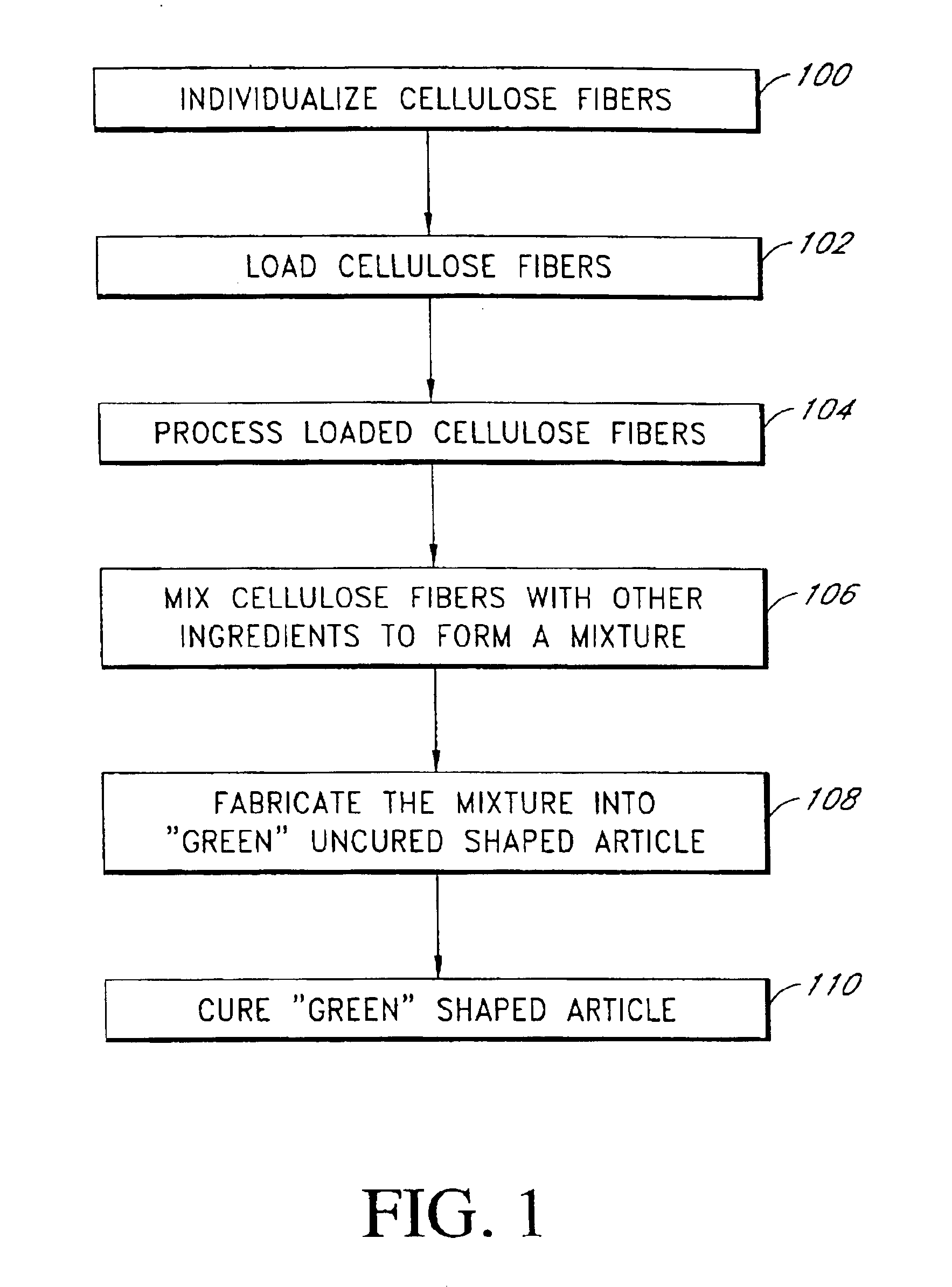
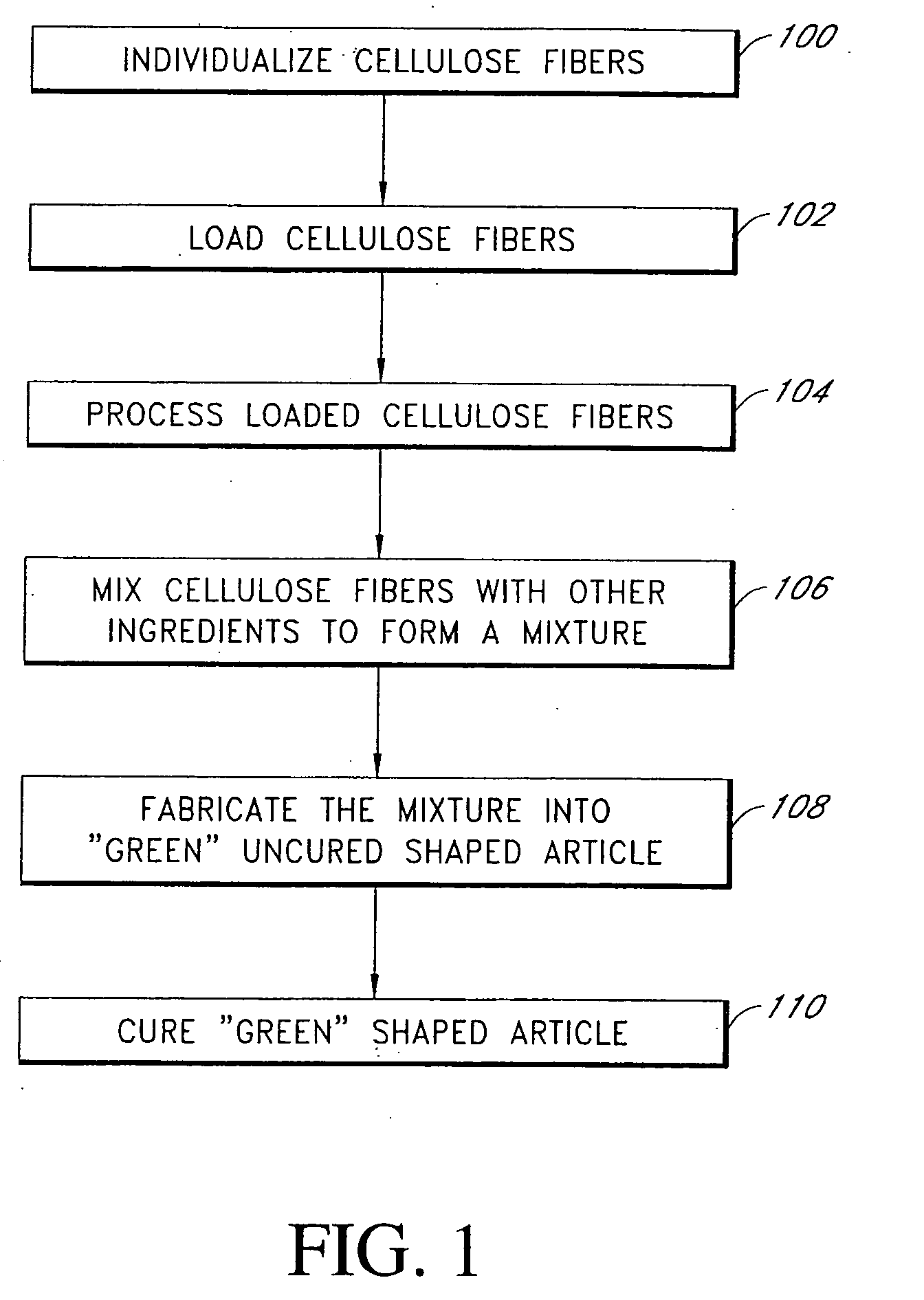
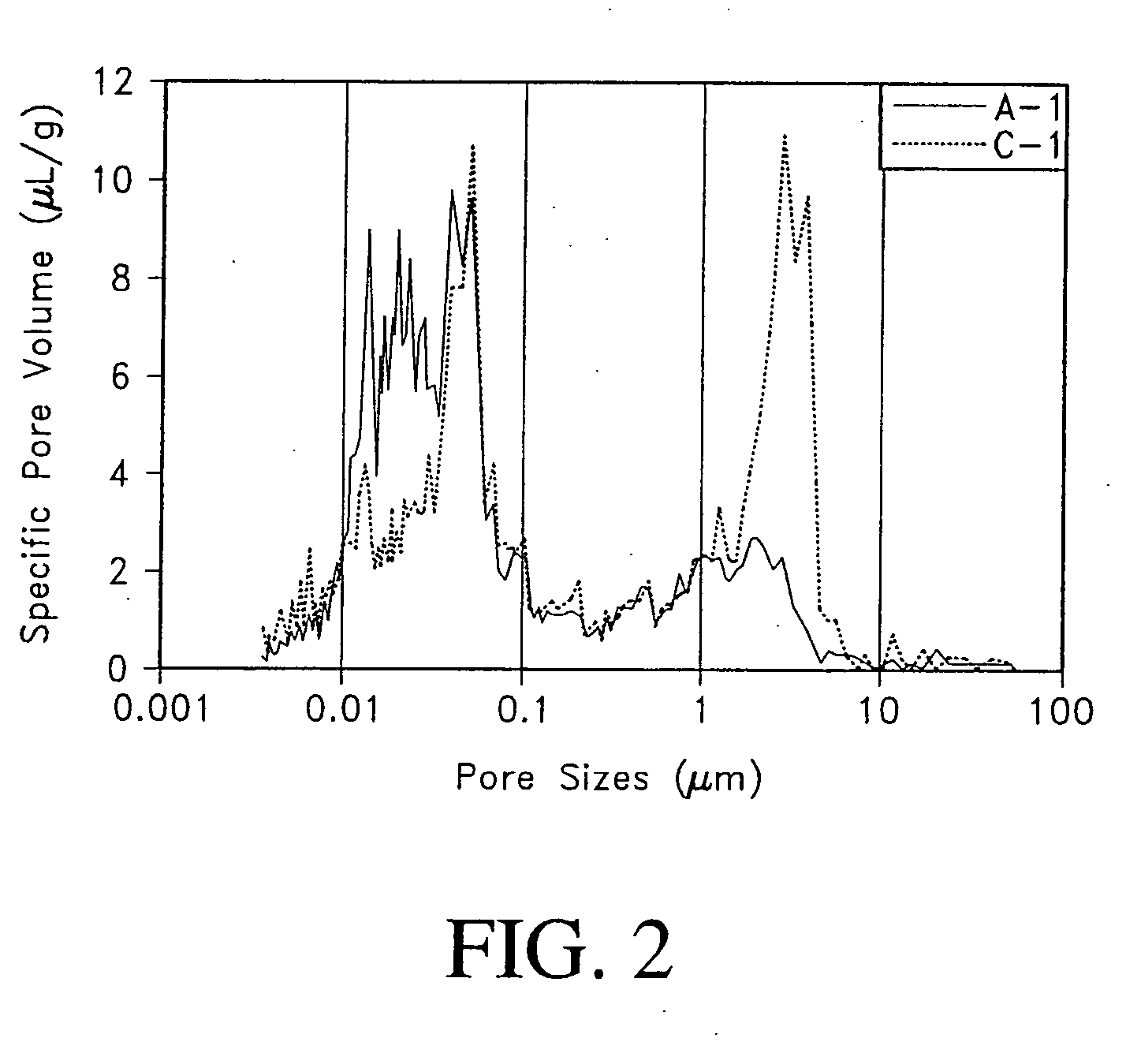
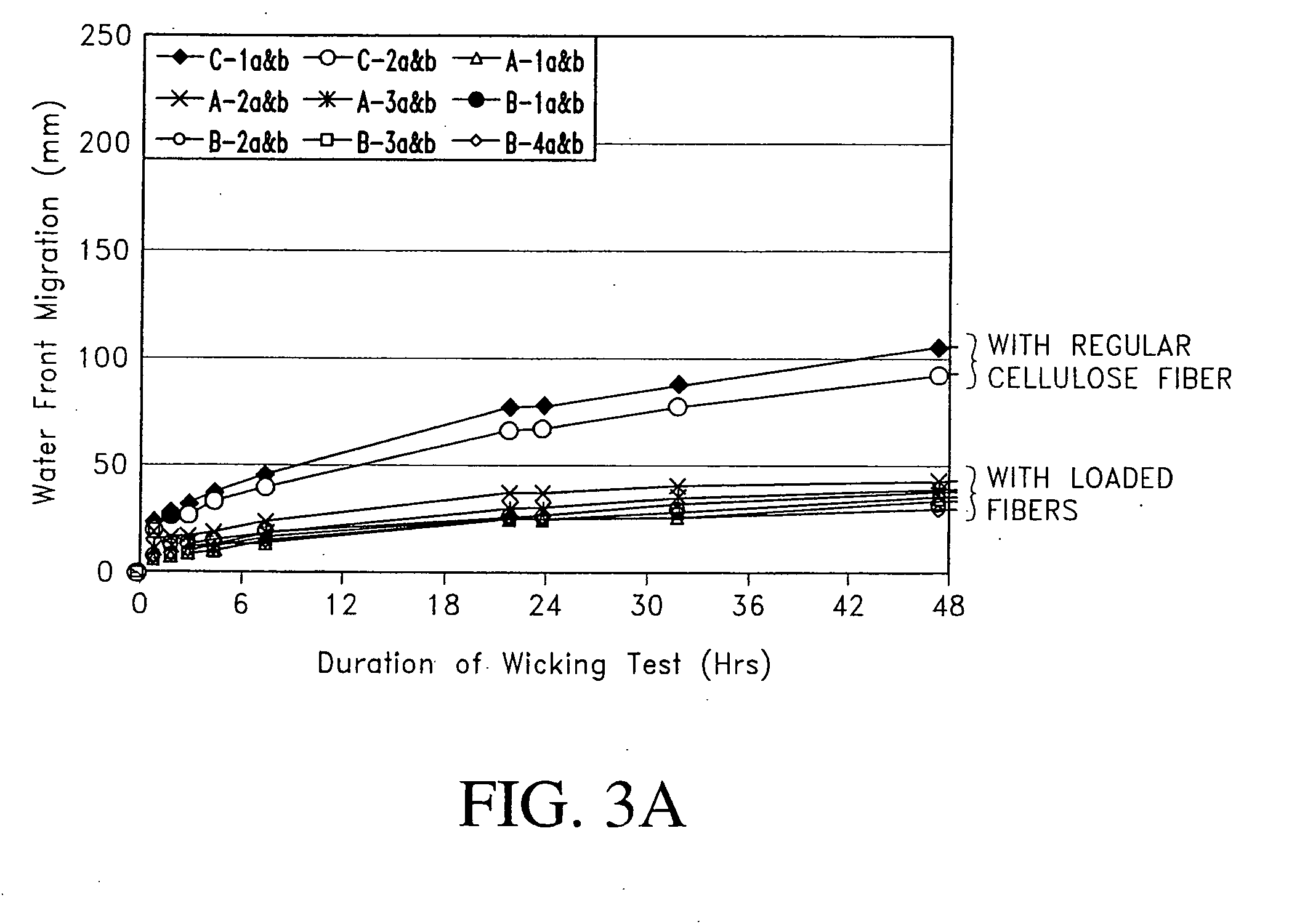
This invention discloses a new technology related to cellulose fiber reinforced cement composite materials using the loaded cellulose fibers. This invention discloses four aspects of the technology: fiber treatment, formulation, method and final product. This technology advantageously provides fiber cement building materials with the desirable characteristics of reduced water absorption, reduced rate of water absorption, lower water migration, and lower water permeability. This invention also impart the final products improved freeze-thaw resistance, reduced efflorescence, reduced chemical dissolution and re-deposition, and improved rot and fire resistances, compared to conventional fiber cement products. These improved attributes are gained without loss in dimensional stability, strength, strain or toughness.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH
Display device
ActiveUS7619258B2Extra level of reliabilityReduce water permeabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDisplay deviceMoisture
In a light emitting device using a light emitting element, the invention provides a sealing structure capable of preventing ingress of moisture from the outside and obtaining adequate reliability. The light emitting device has a light emitting element comprising a light emitting layer formed between a first electrode and a second electrode and a pixel portion comprising the light emitting element. The entire surface of the pixel portion is covered with the second electrode. An impermeable insulating film is formed in contact with the first electrode of the light emitting element. The edge of the first electrode and the impermeable insulating film are covered with a partition wall. An opening is formed along the circumference of the pixel portion in the partition wall. The opening passes through the partition wall in the thickness direction, and the side wall and the bottom face thereof are covered with the second electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Fiber cement composite materials using cellulose fibers loaded with inorganic and/or organic substances
InactiveUS20050235883A1Low water absorptionLow water migrationConstruction materialWater-repelling agents additionCement compositesCellulose fiber
This invention discloses a new technology related to cellulose fiber reinforced cement composite materials using the loaded cellulose fibers. This invention discloses four aspects of the technology: fiber treatment, formulation, method and final product. This technology advantageously provides fiber cement building materials with the desirable characteristics of reduced water absorption, reduced rate of water absorption, lower water migration, and lower water permeability. This invention also impart the final products improved freeze-thaw resistance, reduced efflorescence, reduced chemical dissolution and re-deposition, and improved rot and fire resistances, compared to conventional fiber cement products. These improved attributes are gained without loss in dimensional stability, strength, strain or toughness.
Owner:MERKLEY DONALD J +1
Waterproof moisture permeation polyurethane paint used for textiles and preparation method
The invention relates to waterproof moisture permeation polyurethane paint used for textiles and a preparation method. The waterproof moisture permeation polyurethane paint is prepared from methyl diphenylene diisocyanate, toluene di-isocyanate, polyether glycol (with the molecular weight of 2000), linear dihydroxylated alkylsiloxane (with the molecular weight of 1000), polyester dihydric alcohol (with the molecular weight of 2000), trimethylolpropane, chain extending agents, sealing compounds, dibutyl tin laurate and solvents through the processes of pre-polymerization reaction, chain extension reaction and sealing reaction. The production process is simple, and the products have the advantages of self-crosslinking effect, soft hand feeling, good cold resistance performance, high moisture permeation performance, high water pressure resistance and little reduction after water pressure resistance washing.
Owner:郯城丰润粮机配件有限公司
Nano spray plating technique for silver mirror
InactiveCN101469427AAvoid processing powerAvoid environmental problemsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperimposed coating processSurface layerWeather resistance
The invention provides nanometer spray plating for a silver mirror, namely obtain a high glaze metal mirror face by adopting coating technique, which is similar to the brand new decorative effect of plating. The whole technique consists of a paint bottom layer, a metal reflecting layer (spray plating layer) and a paint surface layer. The coating has excellent adhesive attraction, shock resistance, corrosion resistance, weather resistance and marresistance, has rich colors and is bright like a mirror. The nanometer spray plating can be used to various materials such as metal, resin, ABS, PC, PP+PS carbon element resin, plastic, glass, pottery and porcelain, acrylic, wood, plastic wood and calcium plastic.
Owner:汪正红
Method of Treating Underground Formations or Cavities by Microgels
ActiveUS20080096774A1Reduce water permeabilityReduce sediment showOther chemical processesSedimentation separationSoil scienceLiquid composition
The present invention relates to a method of treating porous and permeable underground formations or cavities of reservoir rock or sand foundation type. The method consists in injecting a liquid composition comprising microgels into the formations in order to reduce the production of water, gas or sands, and / or for zone abandonment.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
Waterproof primer for buildings
InactiveCN102127344AImprove permeabilityReduce strong alkalinityAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesEmulsionAdhesive
The invention provides a waterproof primer for buildings, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 40-60% of cationic emulsion, 0.5-1.0% of organosilicon adhesive force accelerator, 0.1-0.5% of defoaming agent, 0.01-0.3% of bactericide, 1-5% of film-forming assistant, 0.5-5% of thickening agent and the balance of water. By selecting the proper cationic emulsion, the alkali-curing substrate-sealed waterproof primer for buildings has the advantages of high alkali resistance, high sealing performance, high binding strength, excellent functional characteristics and strong adaptability to the substrate, and is easy and convenient for construction.
Owner:ASIA PAINT SHANGHAI +1
Double-layer baking-free permeable brick and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101956357ASolve pollutionGuaranteed water permeabilitySolid waste managementSingle unit pavingsBrickAdhesive
The invention discloses a double-layer baking-free permeable brick and a manufacturing method thereof. The permeable brick consists of a face layer and a base layer, wherein the face layer mainly comprises 3 to 5 weight parts of mountain flour and 2.2 to 4.4 weight parts of adhesive; the base layer mainly comprises 2 to 4 weight parts of sand stone and 1.2 to 2.4 weight parts of adhesive; the sand stone are small stones made of natural sand and crushed scraps from stone processing; and the thickness ratio of the face layer to the base layer is 1:10-20. The manufacturing method comprises that: the face layer is prepared by mixing and stirring the mountain flour, cement, polymerizer, water and paint in a ratio, filling the mixture in a forming mold, and compacting by vibration; the base layer is prepared by mixing and stirring the sand stone, cement, polymerizer and water in a ratio, uniformly filling the prepared base layer material in the mold after the face layer material is solidified initially and compacting by vibration; and removing the mold after the face layer and the base layer are solidified, maintaining at normal temperature for 10 to 20 days, and obtaining the double-layer baking-free permeable brick.
Owner:建德市新世纪装饰材料有限公司
Water-permeable agent for water-permeable bricks or water permeable concrete and application of water-permeable agent
The invention discloses a water-permeable agent for water-permeable bricks or water permeable concrete and application of the water-permeable agent. The water-permeable agent comprises, by weight, 75-110 parts of water reducing agent, 150-300 parts of retarder, 100-150 parts of binder, 55-70 parts of air entraining agent and 55-100 parts of water. The water-permeable agent has the advantages that the water-permeable agent can increase the workability of a water-permeable layer, increase water permeability and increase the durability and later strength of the water-permeable bricks and is low in adding amount and low in cost. The water-permeable bricks have the advatnages that the bricks use haycite and regenerated porous coarse aggregate as the aggregate of the water-permeable layer and use the water-permeable agent, the features of porosity, good water absorption performance and high strength of the aggregate and the good performance of the water-permeable agent are utilized to increase the strength and water permeability of the water-permeable bricks, and the bricks are lightweight and convenient to carry.
Owner:SHANDONG JINYI GARDEN SHARES CO LTD
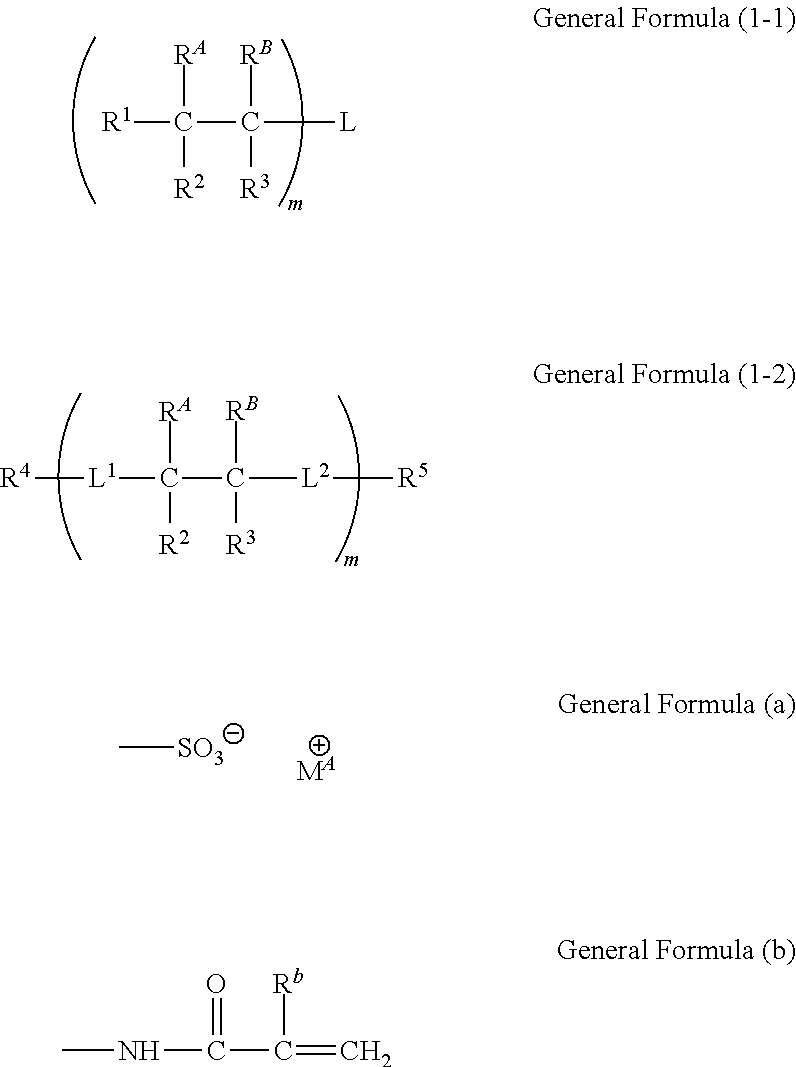
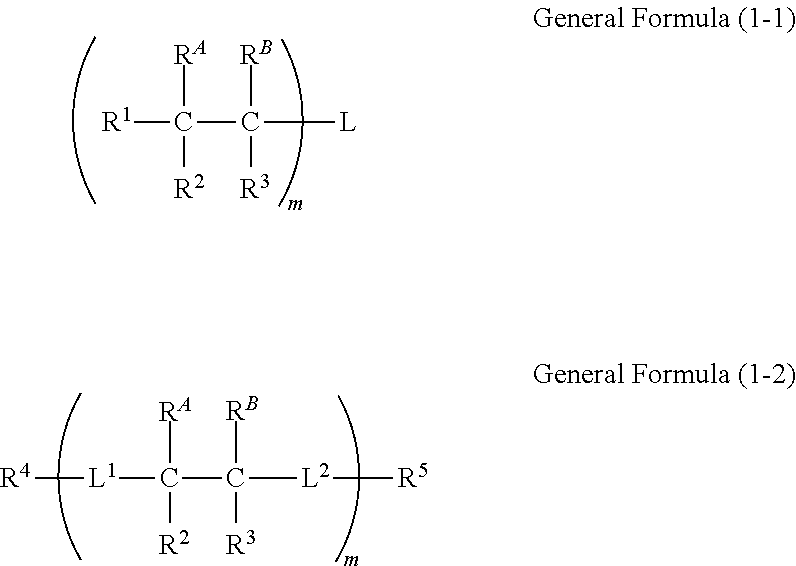
Curable composition, polymer functional cured product, water-soluble acrylamide compound, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20160369017A1Reduce water permeabilityLower resistanceMembranesCation exchanger materialsPolymer scienceAqueous solubility
There is provided a curable composition including a water-soluble acrylamide monomer represented by the following General Formula (1-1) or (1-2), a polymer functional cured product, a water-soluble acrylamide compound, and a method for manufacturing the same.In General Formulas (1-1) and (1-2), m represents an integer of 2 or greater, and L represents an m-valent group or a single bond. Here, in a case where L is a single bond, m is 2. L1 and L2 each represent a single bond or a divalent linking group. R1 to R5 each represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, and may be bonded to each other to form a ring, and may be bonded to L, L1, or L2 to form a ring. Either one of RA and RB represents a group represented by General Formula (a), and the other represents a group represented by General Formula (b).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for preparing high-strength solid buoyancy material
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-strength solid buoyancy material. The method comprises the steps as follows: a coupling agent in a mass ratio of (0.2:100) with hollow microspheres is adopted to perform pretreatment on 1-20 parts of hollow microspheres; 100 parts of resin, 0-60 parts of a curing agent, 0-15 parts of a toughening agent, 0-5 parts of a dispersing agent and 0-10 parts of a diluent are stirred and mixed to obtain a resin system material, the pretreated hollow microspheres and 1-30 parts of small fiber balls are gradually added into the resin system material step by step, the mixture is slow stirred and uniformly mixed, and original slurry is obtained; and the original slurry enters an injection molding process and is subjected to demolding so as to obtain the high-strength solid buoyancy material. Compared with a traditional solid buoyancy material, the high-strength solid buoyancy material has higher compressive strength, lower density and water permeability and good processability simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI COMPOSITES SCI & TECH CO LTD
Ion-exchange polymer and production method therefor, electrolyte membrane and production method therefor, and composition for producing ion-exchange polymer
ActiveUS20160367980A1Reduce membrane resistanceReduce water permeabilityIon-exchange process apparatusSolid electrolytesHydrogen atomHalogen
There are provided an ion-exchange polymer including a structure represented by the following General Formula (1) and a production method therefor, an electrolyte membrane and a production method therefor, and a composition for producing an ion-exchange polymer.In a case where the sum of a1, b1, and c1 is 1.000, a1 is 0.000 to 0.750, b1 is 0.240 to 0.990, and c1 is 0.001 to 0.100. L represents an alkylene group, L1 and L2 each represent a divalent linking group, R1 is a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group, R2 and R3 each represent an alkyl group or an allyl group, X1− and X2− each represent an inorganic or organic anion, and Y represents a halogen atom. Z1 represents —O— or —NRa—, and Ra represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and composition for recovering hydrocarbon fluids from a subterranean reservoir
InactiveUS20050065036A1Reduce the amount of waterImprove productivityOther chemical processesFluid removalHydrogenHydrogen atom
A method of modifying the permeability to water of a subterranean formation comprising injecting into the subterranean formation an aqueous composition comprising from about 0.005 percent to about 2 percent, by weight, of an alkyl or an alkylene oxide branched polyhydroxyetheramine or a salt thereof, wherein the fatty alkyl or alkylene oxide branched polyhydroxyetheramine is prepared by reacting a diepoxide with a) one or more fatty alkyl or alkylene oxide functionalized amines or a mixture of one or more alkylene oxide functionalized amines and b) one or more amines having two reactive hydrogen atoms and c) optionally reacting the resulting polyhydroxyetheramine with an acid or alkylating agent to form the salt.
Owner:ONDEO NALCO ENERGY SERVICES
Ion exchange membrane and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20160362526A1Lower resistanceReduce water permeabilityIon-exchange process apparatusAnion exchangersIon-exchange membranesIon-exchange resin
An ion exchange membrane obtained by using an ionic monomer having at least two or more polymerizable functional groups, in which a hydrophobicity index H obtained by an expression below from a monomer for forming an ion exchange resin and a material fixed to the resin in the ion exchange membrane is 1.6 or greater, and a manufacturing method therefor. Hydrophobicity index H=Σ{(log P of each component)×(molar ratio of each material in resin)}
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Water-based white sealed primer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a water-based white sealed primer and a preparation method thereof. The water-based white sealed primer comprises the following components in part by weight: 350 to 600 parts of water-based resin and 50 to 100 parts of modified barium metaborate. The water-based white sealed primer provided by the invention has performance of sealing wood tannic acid and has a durable and good sealing effect after construction on the base material containing the tannic acid, nicotine blot and water-based pigment. Water-based white wood coating is coated on the primer, so the water-based white wood coating is not polluted by the pollutants and is not discolored, and the primer has high rubbing property, covering power and corrosion resistance and can prevent wood from being rotten and deteriorated.
Owner:BEIJING ZHANCHEN CHEM +2
Method for manufacturing a solid electrolyte sensor element for detecting at least one property of a measuring gas in a measuring gas chamber, containing two porous ceramic layers
InactiveUS20160061767A1Increasing thermal massImprove robustnessWave amplification devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMetallurgyGas chamber
A method for manufacturing a sensor element is provided for detecting at least one property of a measuring gas in a measuring gas chamber, in particular for detecting a proportion of a gas component in the measuring gas or a temperature of the measuring gas. The method includes the following steps: providing at least one solid electrolyte which includes at least one functional element; applying, at least in sections, at least one first layer made of a ceramic material to the solid electrolyte, the first layer having a first porosity after the application; and applying, at least in sections, at least one second layer made of a ceramic material, the second layer having a second porosity after the application, and the first layer differing from the second layer with respect to at least one material property. Moreover, a sensor element which is manufacturable according to this method is provided.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Foam concrete
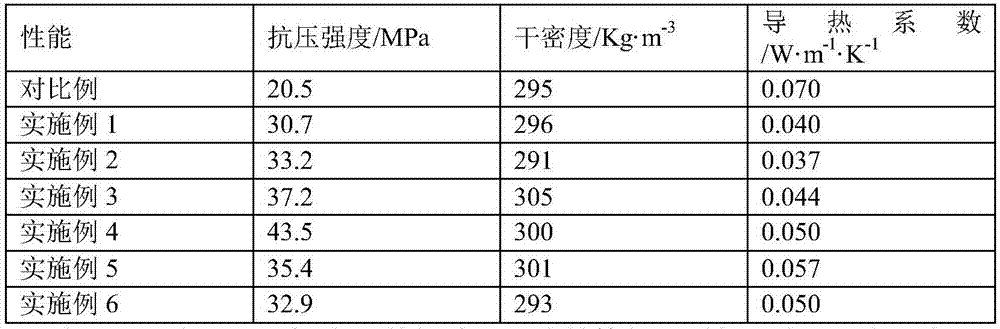
The invention discloses foam concrete. The foam concrete comprises following raw materials in parts by mass according to a formula: 210-300 parts of cement, 1.0-1.5 parts of a water reducing agent, 5.1-5.5 parts of an early strength agent, 2.1-2.9 parts of a coagulant, 1.7-3.4 parts of fibers, 12-20 parts of a chemical foaming agent, 0-90 parts of superfine slag powder and 100-160 parts of water, wherein the superfine slag powder is formed by aluminosilicate glass particles smaller than 15 mu m, and the specific surface area is 450-500 m<2>*kg<-1>. The compressive strength of the foam concrete is improved on the premise that the foam concrete keeps low density.
Owner:BEIJING MINJIA NEW BUILDING MATERIALS CO LTD
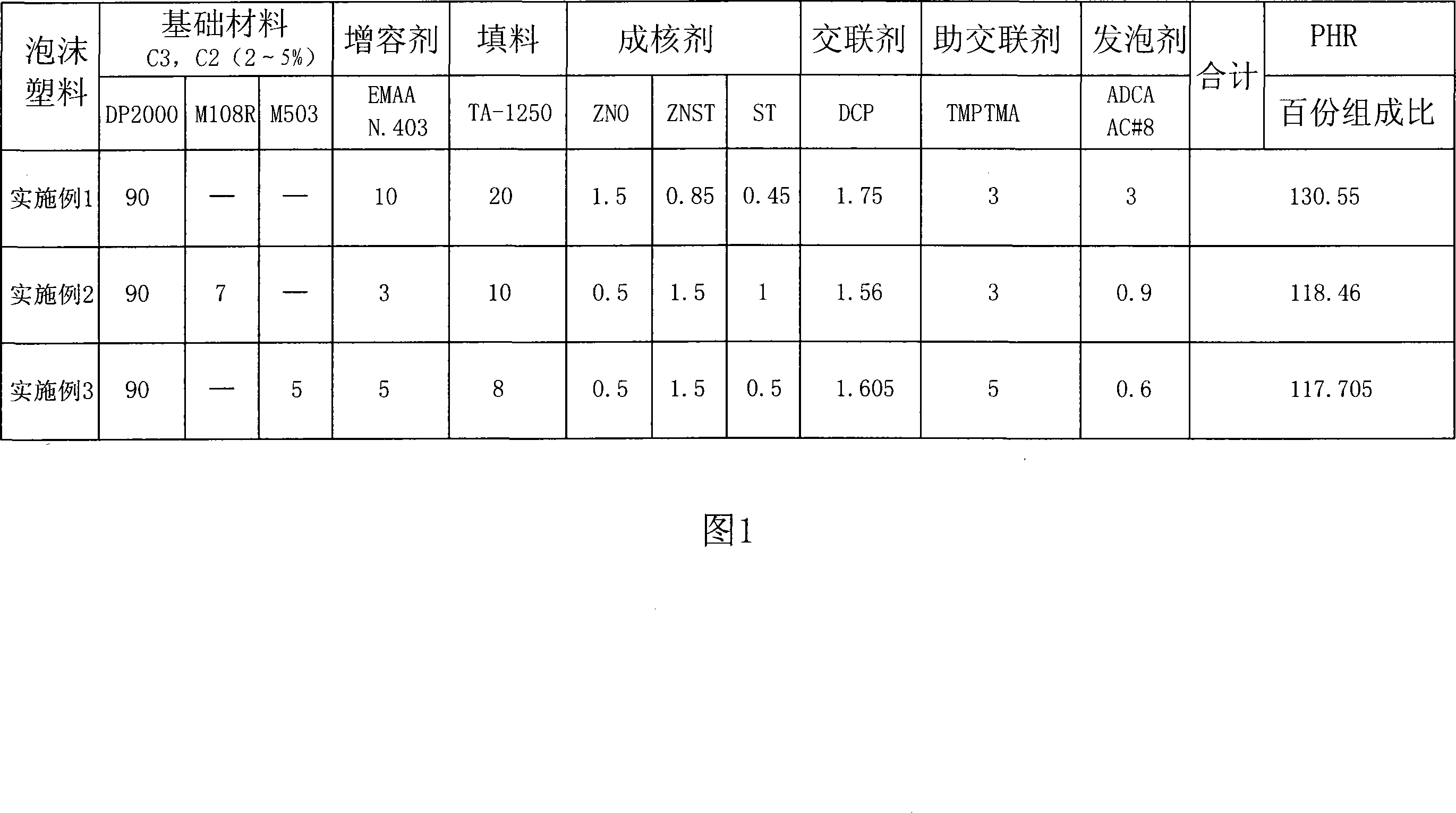
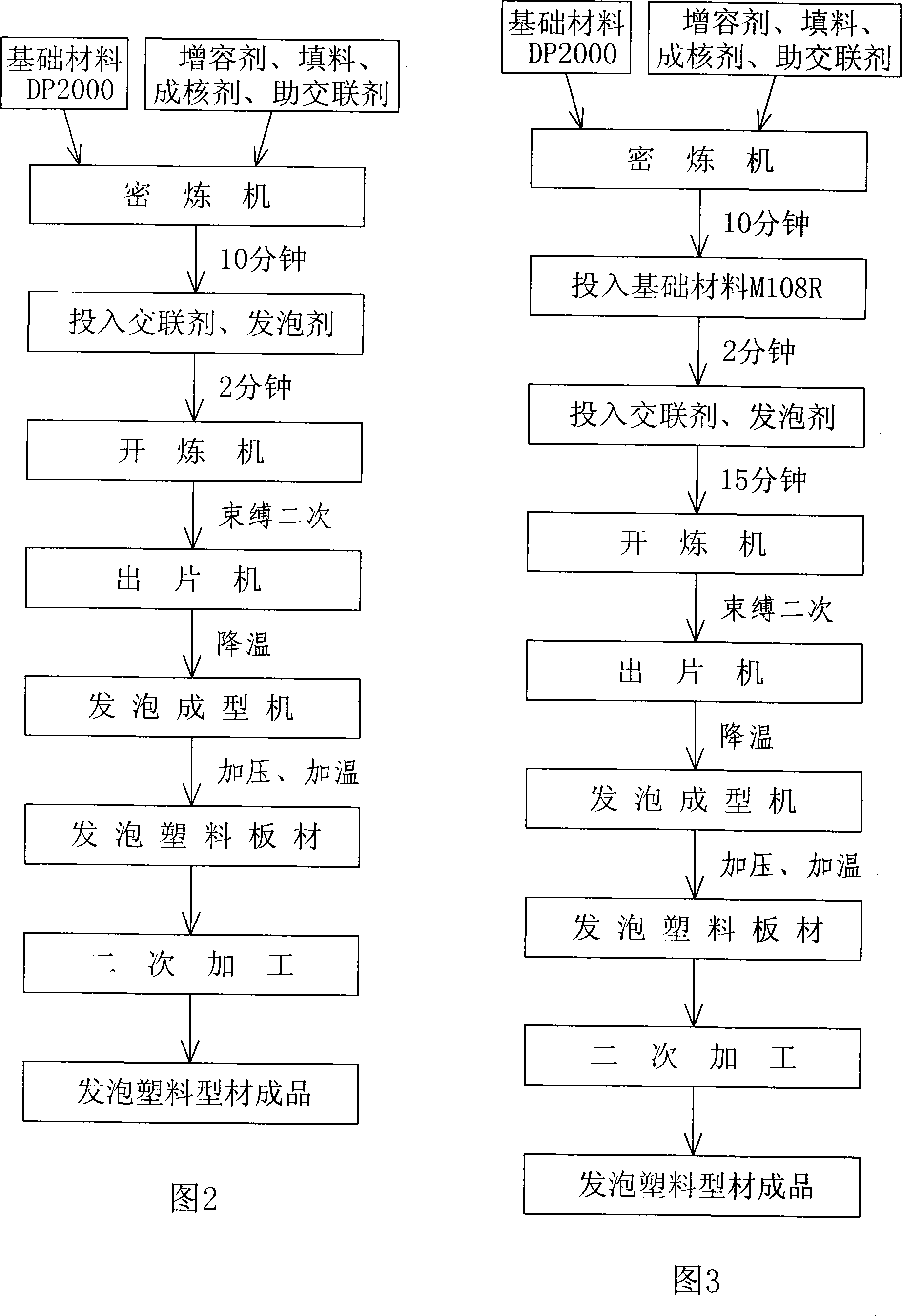
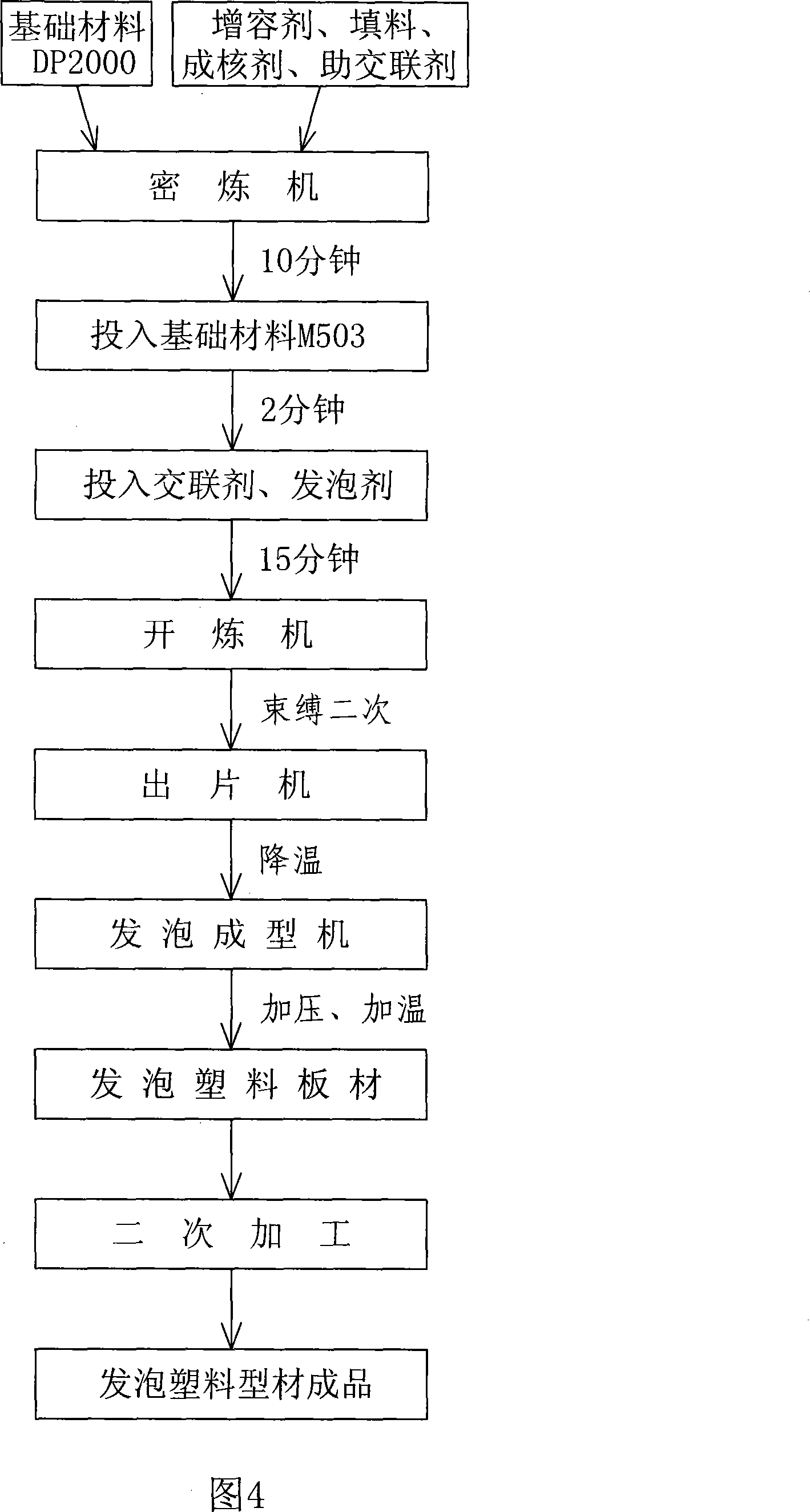
Degradable environment-friendly type polypropylene(PP) foam plastic and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an environment-friendly-type polypropylene (pp) aerated plastics and a process for preparation, and the aerated plastics utilizes plastic projectile body to be basis material, a third monomer is led in to be auxiliary crosslinking agent to crosslink and control degradation products, aerated plastics section products are made by processing graft copolymerization and cross-linking reaction to polypropylene, and closely welding, openly welding, tabletting, and foaming to shape with compatibilizer, filling material, nucleating agent, cross linking agent and inflating agent. The invention modifies the shortcomings that the traditional homopolymerized polypropylene can not get higher breakpoint extension force, high melt intensity and viscosity to foam and shape in the process of thermal foaming and shaping. The polypropylene (pp) aerated plastics products which are provided by the invention have excellent fire-resisting property and little heat distortion degree, and the softening point is between 100 DEG C and 130 DEG C. The invention can be used for long term in the temperature scope, and the application area is wide, wastes can be recycled, and can be automatically degraded, and the invention has no pollution to environment.
Owner:FUJIAN ZHENGYI IND
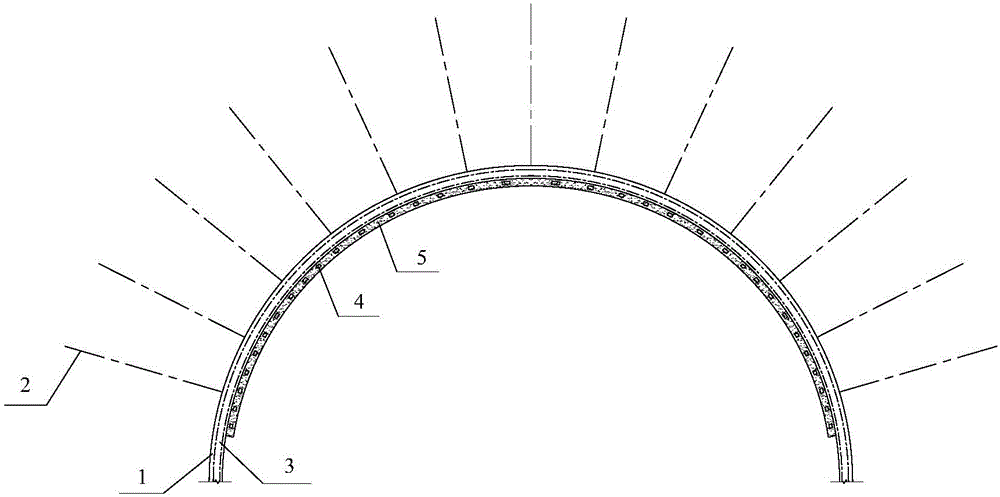
Tunnel lining rapid repair structure based on carbon fiber woven mesh and repair method thereof
ActiveCN104895581AImprove bearing capacityReduce external water pressureUnderground chambersTunnel liningFiberJoist
The invention relates to a tunnel lining rapid repair structure based on a carbon fiber woven mesh and a repair method thereof. The tunnel lining rapid repair structure based on the carbon fiber woven mesh comprises self-propelled hollow grouting anchors, joist steel, the carbon fiber woven mesh, U-shaped hooks and a composite mortar layer. The joist steel is arranged on a tunnel lining to be repaired, one end of each self-propelled hollow grouting anchor stretches into the tunnel lining to be repaired in the radial direction of the tunnel lining to be repaired, the other end of each self-propelled hollow grouting anchor is connected with joist steel, the carbon fiber woven mesh is laid on the inner wall of the tunnel lining to be repaired and connected with the joist steel through the U-shaped hooks, and the composite mortar layer is sprayed on the inner surface of the carbon fiber woven mesh. The tunnel lining rapid repair structure based on the carbon fiber woven mesh and the repair method thereof aims to solve the problems existing in the existing tunnel lining reinforcing technology, the structure is reasonable in design, the mechanical property is good the steps of the method is simple, the operability is high, and the project cost is low.
Owner:SHANXI PROVINCIAL RES INST OF COMM +1
Very early setting ultra-high strength cement
Clinkered materials containing high concentrations of {(C,K,N,M)4(A,F,Mn,P,T,S)3(cl,{overscore (S)})} (crystal X), and {(C2S)3(C{overscore (S)})3 Ca(f,cl) 2} or {(C2S)3(C{overscore (S)})3Ca(f,cl)2} (crystal Y), and / or {C5S2{overscore (S)}) (crystal Z) directly from the kiln, rapidly hardening ultra-high early strength cement including these clinkered materials, methods for forming and using said compositions and the cements so produced are claimed. The methods include the steps of forming a mixture of raw material containing CaO, MgO, Al2O3, Fe2O3, TiO2, Mn2O3, SiO2, SO3, Na2O, K2O, P2O5 and F, respectively designated C, M, A, F, T, Mn, S, {overscore (S)}, N, K, P and f, and heating said mixture to an elevated temperature between 900° C. and 1,200° C.; before determining average amount of crystals X, Y, and Z. Final mixtures comprising these clinkers and hydraulic or portland type cement are made to produce cement compositions having crystal X concentrations of approximately 5% to 35% by weight, crystal Y concentrations of approximately 5% to 40% by weight, and / or crystal Z concentrations of approximately 5% to 40% by weight, with the remainder being hydraulic or portland type cement. The cements so produced are rapid hardening and exhibit high strengths ranging from 2,000 psi to 7,000 psi in one hour, 6,000 to 8,000 psi in one day and 9,000 to 12,000 psi in 28 days. They are sulfate and sea-water attack resistant and have low heats of hydration, minimal shrinkage, and high water impermeability. The methods claimed also results in significant reduction in gaseous emissions including SOx, NOx and COx.
Owner:ULTIMAX CORP
Preparation technology and product of high-performance EVA photovoltaic packaging adhesive film
ActiveCN104592907AMeet the requirements of anti-PIDMeet anti-PID requirementsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesChemistryAdhesive
The invention relates to a preparation technology and a product of a high-performance EVA photovoltaic packaging adhesive film. The product comprises the following raw material components in parts by weight percentage: 94.5-98% of EVA resin, wherein the content of VA in the EVA resin is 24-28% and the melt flow speed of the EVA resin is 15g / 10min-35g / 10min; 0.3-3% of multifunctional group cage-type polysilsesquioxane, 0.2-1% of crosslinking initiator, and / or 0.2-1% of coupling initiator, 0.1-0.5% of anti-ultraviolet anti-aging additive, and liquid or solid with a melting point of less than 90 DEG C; the method includes the steps of mixing, granulating, melting, extruding into a film shape from a die head, pressing the film through a press roller, cooling and sizing, rolling to obtain the EVA adhesive film product. By means of adding a functional POSS, the POSS molecule contains a plurality of ethylene and / or coupling groups of glass / backboard as additives so that many functions of the EVA photovoltaic packaging adhesive film can be improved and the high-performance EVA photovoltaic packaging adhesive film can be prepared.
Owner:浙江利昌科技有限公司
Composite curing agent for restoring soil polluted by heavy metals and application method thereof
InactiveCN106701088ASimple preparation processLow costSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSlagPhosphate
The invention relates to the field of soil restoration, in particular to a composite curing agent for restoring soil polluted by heavy metals and an application method thereof. The composite curing agent is composed of curing agent powder and curing agent liquid. The curing agent powder comprises, by weight parts, 2-5 parts of cement, 1-2 parts of activated steel slag powder, 2-4 parts of quicklime and 1-2 parts of phosphate, and the curing agent liquid is water glass. By adoption of the composite curing agent for restoring soil polluted by the heavy metals, heavy metal pollutants in the soil can be solidified and stabilized durably and effectively, and the composite curing agent has the advantages of being good in restoration effect and high in stability. The content of effective state heavy metals in the restored soil is lower than the national standard, and the soil has the advantages of being not subjected to cracking easily and secondary argillization.
Owner:东莞中科土壤科技开发有限公司
Flexible active device array substrate and organic electroluminescent device having the same
InactiveUS20130126915A1Improve reliabilityReduce water permeabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic electroluminescenceInorganic materials
A flexible active device array substrate including a flexible substrate, an active device array layer, a barrier layer, and a plurality of pixel electrodes is provided. The active device array layer is disposed on the flexible substrate. The barrier layer covers the active device array layer. The barrier layer includes a plurality of organic material layers and a plurality of inorganic material layers. The organic material layers and the inorganic material layers are alternately stacked on the active device array layer. The pixel electrodes are disposed on the barrier layer, and each of the pixel electrodes is electrically connected to the active device array layer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
High-water-resistance backboard for solar battery assembly
ActiveCN104966754AGood weather resistanceReduce water permeabilityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPolyesterPotential induced degradation
The invention discloses a high-water-resistance backboard for a solar battery assembly, which comprises an olefin copolymer layer, a bonding layer, a polyester base layer and a fluorine-containing weather resistant layer. According to the invention, the backboard is enabled to have excellent moisture blocking performance through adding super absorbent resin (SAP) to the olefin copolymer layer, thereby being capable of effectively reducing occurrence of a PID (Potential Induced Degradation) phenomenon in the assembly. The high-water-resistance backboard provided by the invention for the solar battery assembly has the advantages of good weather resistance, high bonding strength, good water blocking performance, low cost and the like, and can be widely applied to packaging of the solar battery assembly.
Owner:HANGZHOU FIRST APPLIED MATERIAL CO LTD
Fiber cement composite materials using sized cellulose fibers
InactiveUS7815841B2Low water absorptionImprove freeze-thaw resistanceConstruction materialWater-repelling agents additionChemical treatmentCement composites
This invention discloses a new technology related to cellulose fiber reinforced cement composite materials using cellulose fibers that are treated with inorganic and / or organic resins to make the fibers more hydrophobic, as well as other chemical treatments. This invention discloses four aspects of the technology: fiber treatment, formulations, methods and the final product. This technology advantageously provides fiber cement building materials with the desirable characteristics of reduced water absorption, reduced rate of water absorption, lower water migration, and lower water permeability. This invention also impart the final products improved freeze-thaw resistance, reduced efflorescence, and improved rot and UV resistances, compared to conventional fiber cement products. These improved attributes are gained without loss in dimensional stability, strength, strain or toughness. In some cases the physical and mechanical properties are improved. This invention also discloses the method of treating cellulose fibers with various chemicals to impart the fiber hydrophobicity for applications in the fiber reinforced cement composite materials.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH LTD
Anti-corrosion additive for compositions in contact with iron-based substrates
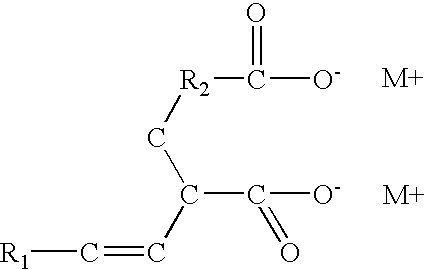
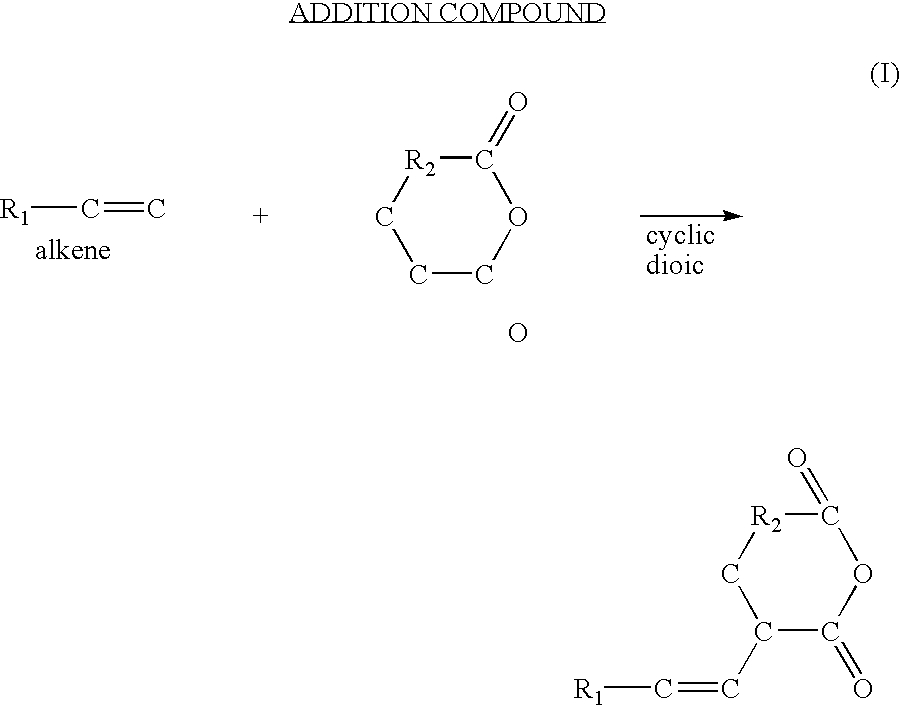
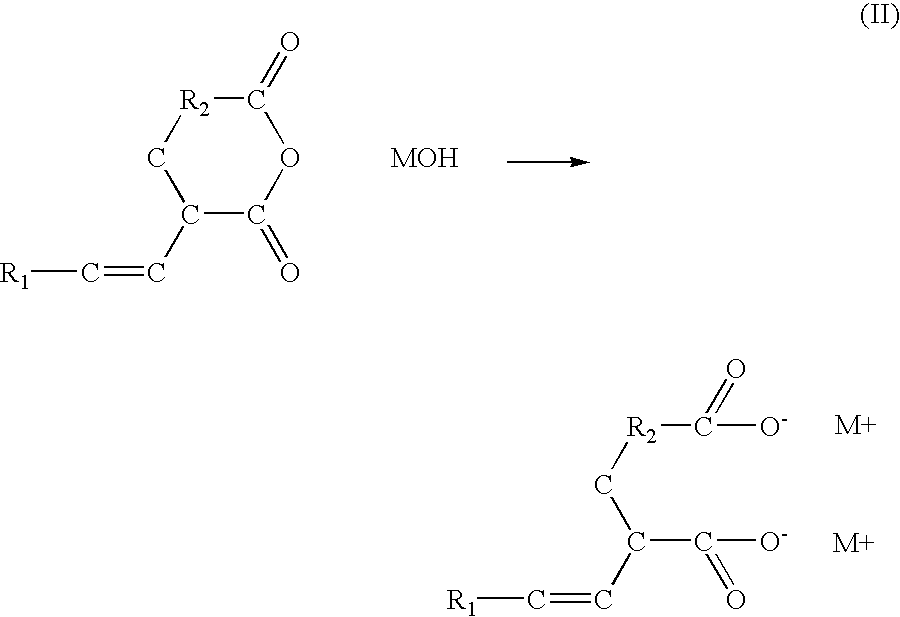
InactiveUS20040237834A1Reduce water permeabilityAvoid corrosionOther chemical processesSalt solutionFerric
There is described a dialkali based salt solution of dioic acid as an anti-corrosive additive alone or in admixture in an effective amount with another composition such as concrete.
Owner:HYCRETE INC
Method for manufacturing a modular building block unit and construction therewith
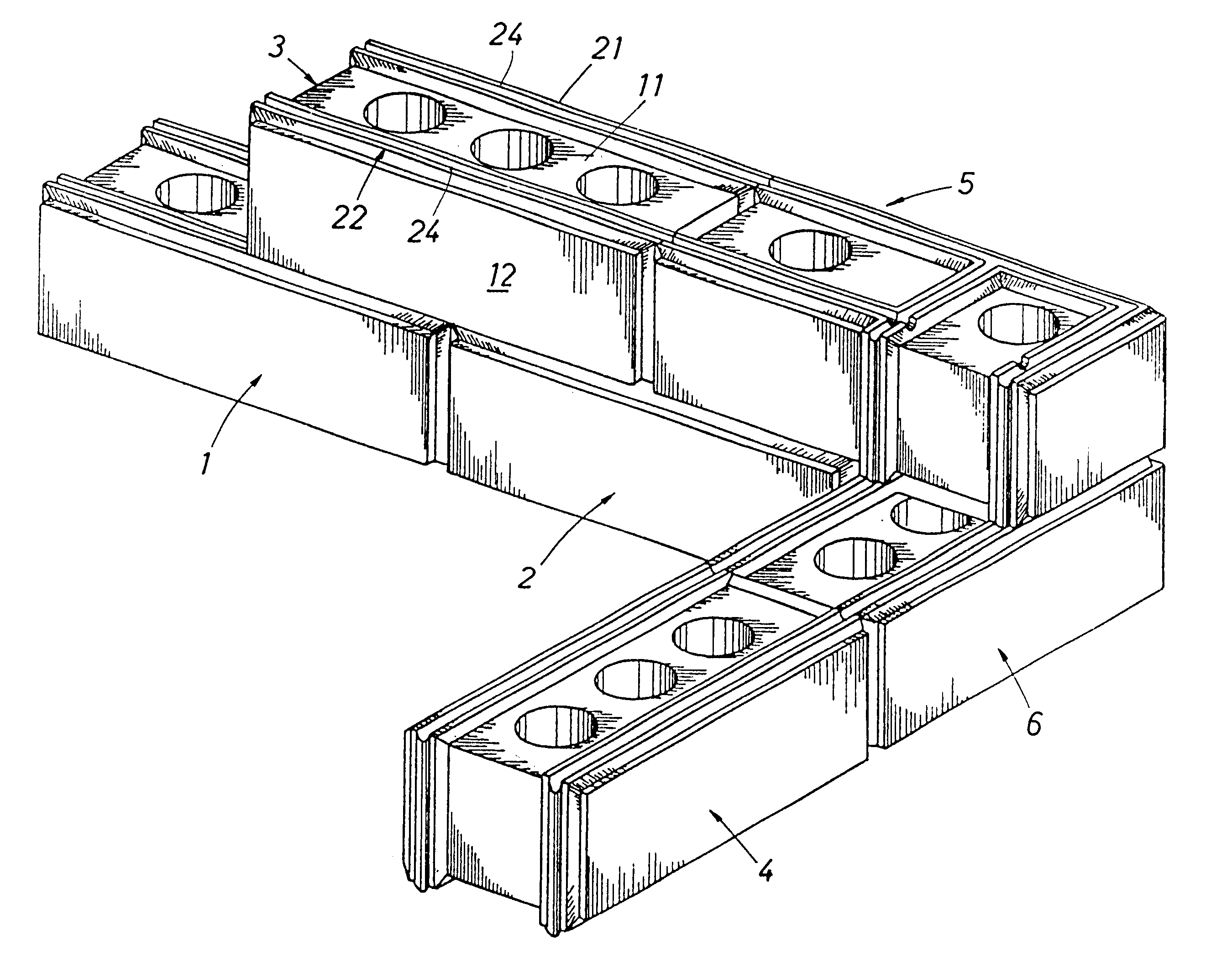
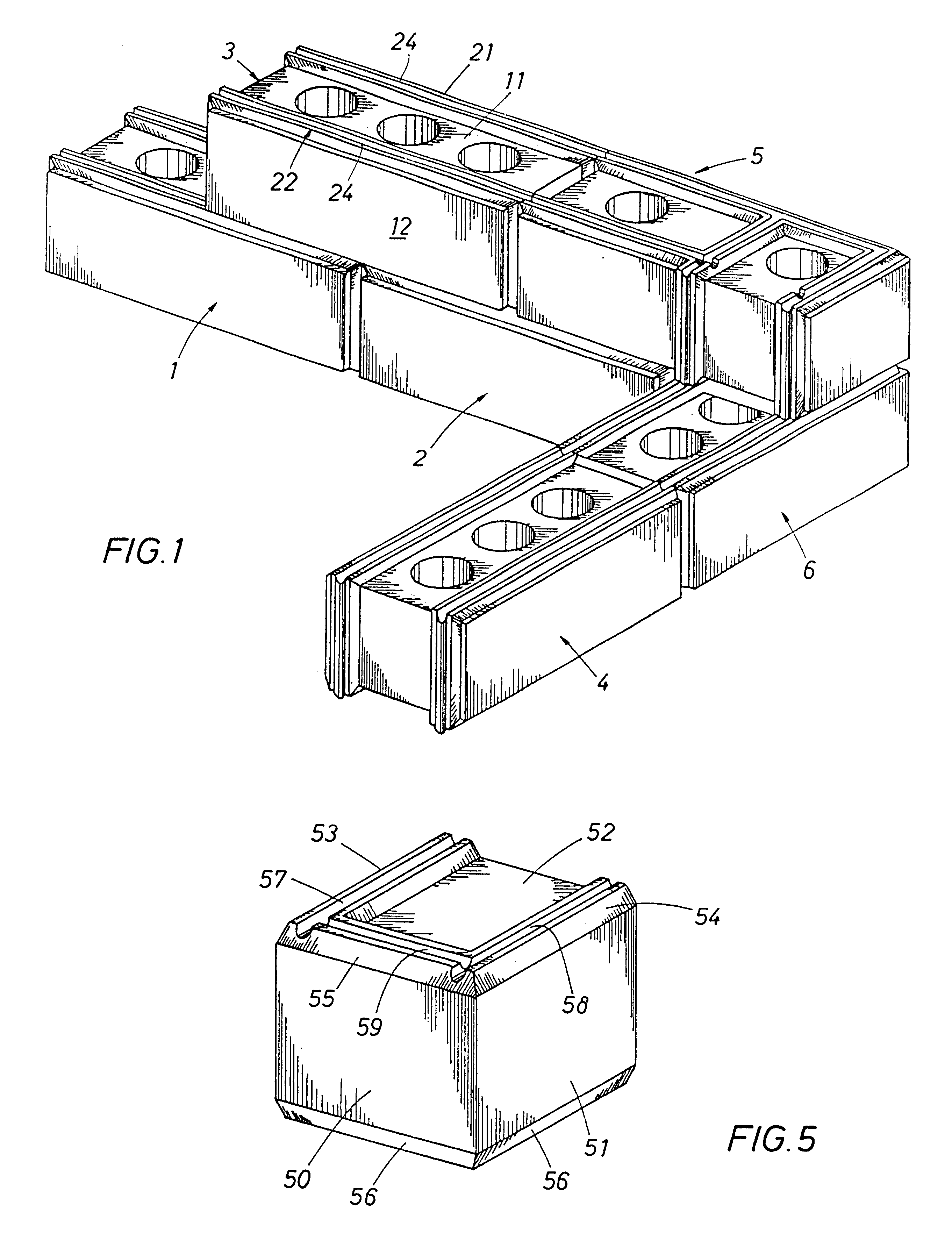
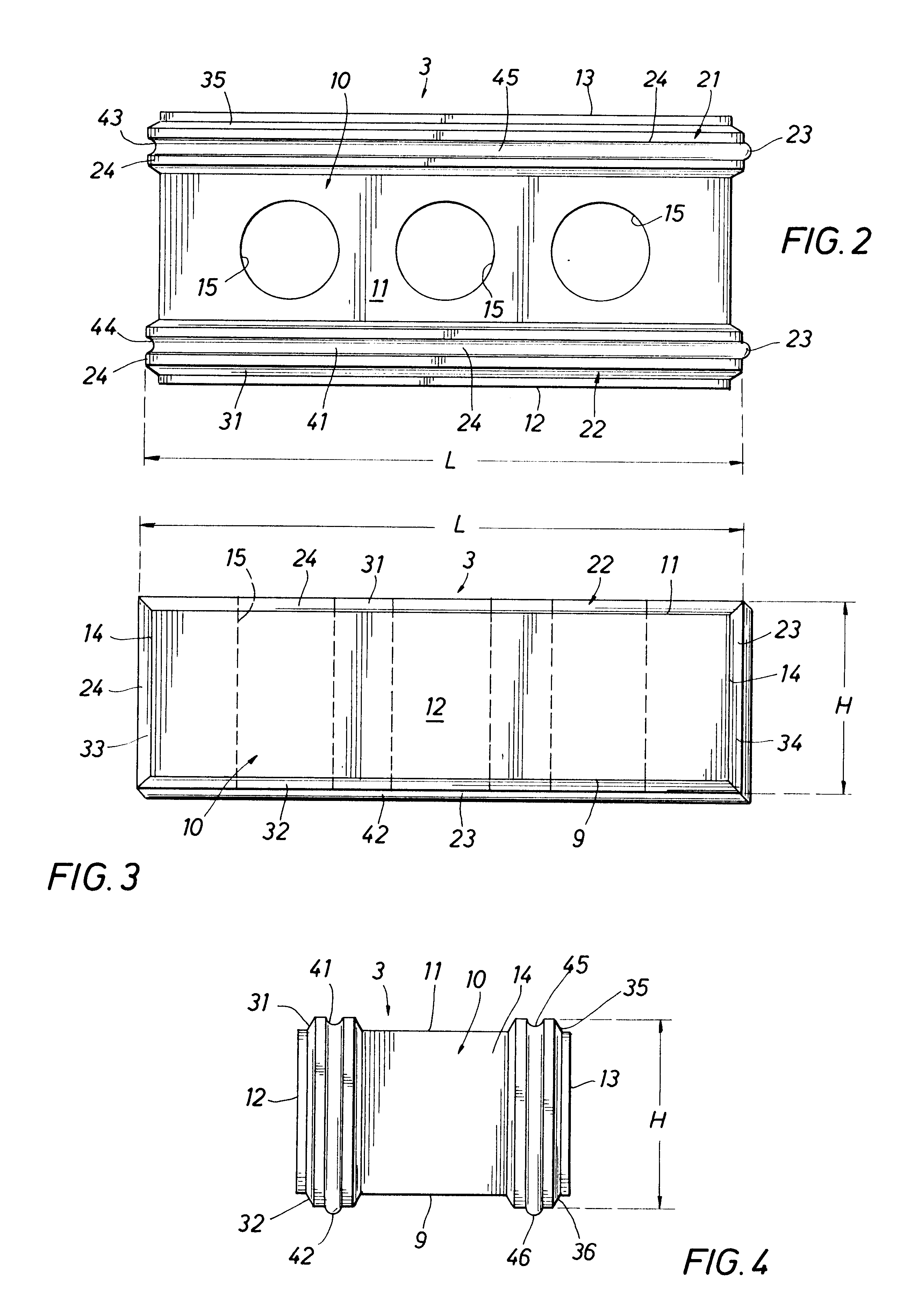
InactiveUS6298632B1Reduce water permeabilityUniform appearanceTailstocks/centresWallsBrickBuilding unit
A modular building unit (1-6, 1A) including a building block (10, 10A) having lower and upper faces (9, 9A, 11, 11A), side faces (12, 12A, 13, 13A) and end faces (14, 14A). At least the lower and upper faces are provided with mounting strips (21-24, 53A, 54A) interfit with mating mounting strips (21-24, 53A, 54A) on similar adjacent modular building units (1-6, 1A) to join the adjoining building block units (1-6, 1A) in predetermined dimensionally accurate relationships. A method of securing the mounting strips (21-24, 53A, 54A) to the building block or brick (10, 10A) and the method of interlocking and securing adjacent modular building units (1-6, 1A) to each other are disclosed. A preferred embodiment of mounting strips (53A, 54A) is shown in FIGS. 8-10. A mold (203) is shown in FIG. 12 for the preferred method of forming a building block or brick (200).
Owner:SHERWOOD DON T
Encapsulated Chlorine Dioxide Generator
InactiveUS20130017241A1Reduce water permeabilityEnhancing storage and shipping stabilityBiocidePretreated surfacesElectric generatorPolyvinyl alcohol
An encapsulated chlorine dioxide generator is provided. The encapsulated generator includes a core particle that includes a metal chlorite and a solid acid. The encapsulated generator also includes a protective layer that is disposed about at least a portion of the core particle. The protective layer includes a copolymer of polyvinyl alcohol and a polyalkylene glycol. The encapsulated generator is formed in a method including the steps of forming the core particle and disposing the protective layer about the core particle. The encapsulated generator is also used in a method of cleaning an environment. The method of cleaning the environment includes the steps of providing the encapsulated generator and forming chlorine dioxide from the encapsulated chlorine dioxide generator to clean the environment.
Owner:BASF SE
Novel PVA-based preserving and packaging coating material and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN101565482AImprove water resistanceImprove film formationFlexible coversWrappersStearic acidFood packaging
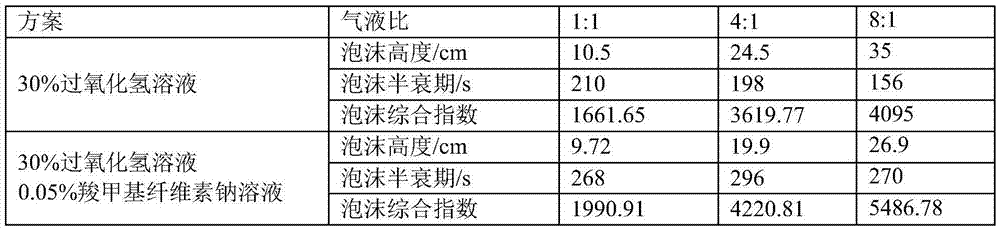
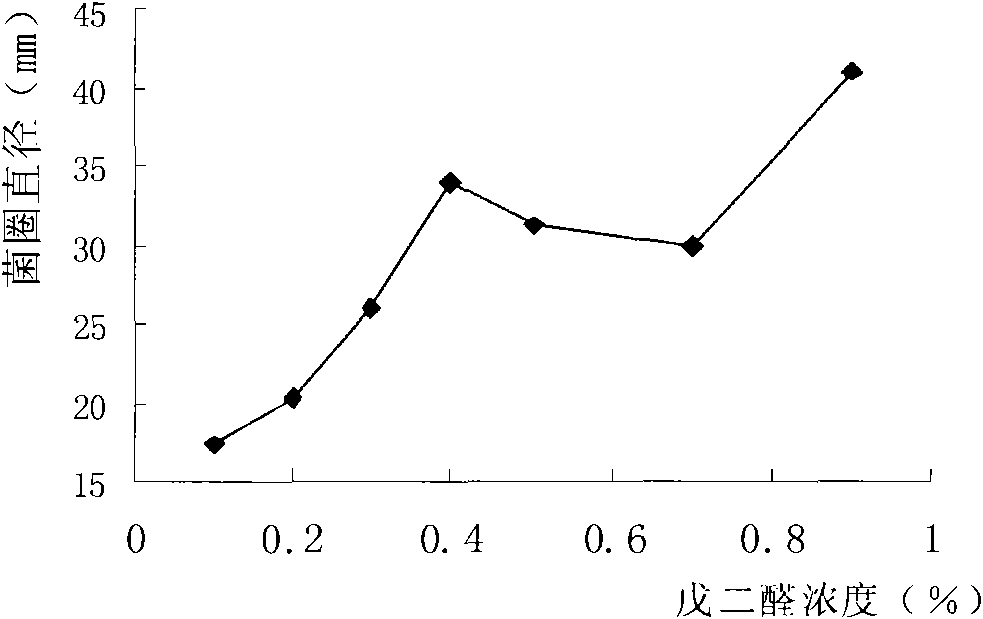
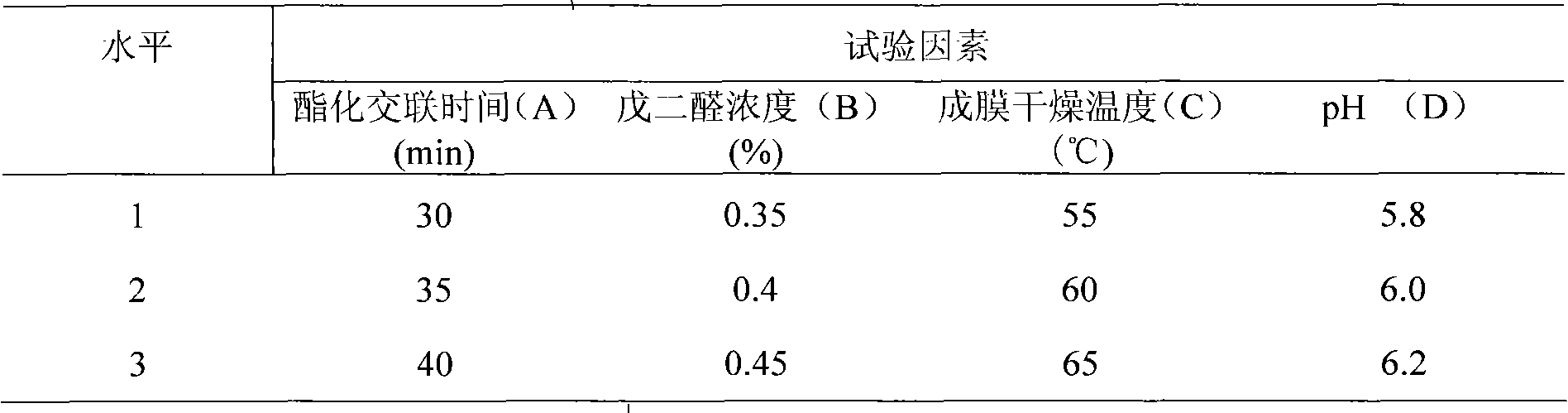
The invention relates to a process for preparing a novel PVA-based preserving and packaging coating material, and belongs to the field of food packaging materials. The process comprises the following steps: mixing the new materials according to the following concentration: 3 to 8 percent of PVA and water, 1 to 3 percent of stearic acid and water, and 0.35 to 0.45 percent of glutaric dialdehyde and water; soaking the PVA for 2 hours at a normal temperature, heating and dissolving the PVC; dissolving the stearic acid in 95 percent ethanol, heating and dissolving the stearic acid; when the temperature of the PVA and the stearic acid reaches over 85 DEG C, mixing and reacting the PVA and the stearic acid for 3 to 10 minutes; adding the glutaric dialdehyde into the mixture, and reacting the mixture and the glutaric dialdehyde for 30 to 50 minutes at the temperature of 85 DEG C; and adjusting the pH value of the obtained product to between 4 and 6.5, and preparing the PVA-based preserving composite coating material. The process adopts the glutaric dialdehyde as a crosslinking agent of the stearic acid and a PVA diatomic substrate, and the novel PVA-based preserving and packaging coating material obtained by crosslinking reaction can obviously reduce the water permeability of the PVA substrate after film-forming, improve the water resistance, and generate strong antibacterial property.
Owner:CHANGSHU YIHAO FOOD PACKAGING MATERIAL TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com