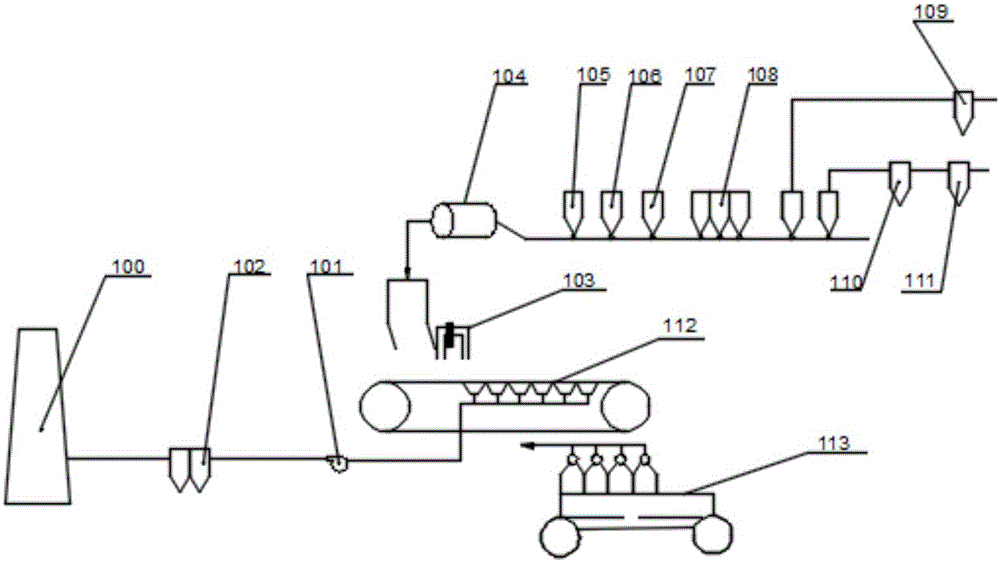
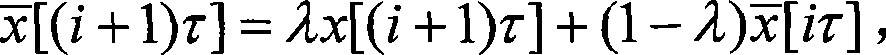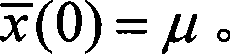Patents
Literature
700 results about "Blast furnace smelting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blast-furnace smelting method for vanadium titano-magnetite
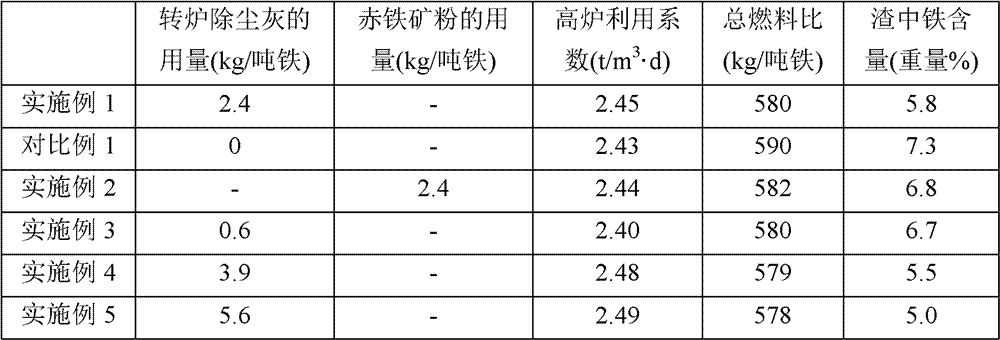
InactiveCN101775451ARaise the gradeReduce tons of iron slagBlast furnace detailsMagnetiteBlast furnace smelting
The invention discloses a blast-furnace smelting method for vanadium titano-magnetite. The method is realized in a way that: vanadium titano-magnetite accounts for 30-60% of ferrous burden which is fed into a blast furnace, and the burden comprises 40-65% of agglomerate, 30-50% of pellet and 5-10% of lump ore; the diacidic basicities CaO / SiO2 of agglomerate, pellet and blast-furnace slag are respectively controlled at 1.6-2.5, 0.6-1.0 and 1.05-1.20; the content of MgO in blast-furnace slag is controlled at 7.5-9.0%; by adding two batches of ore and three batches of coke and using the charging operation of the development center, manganese oxide ore or sintered manganese ore powder, and fluorite are incorporated into injection coal and injected into the blast furnace along with the coal powder; and thus, the content of MnO in the slag and the content of CaF2 in the slag are respectively controlled at 1.0-4.5% and 0.50-2.0%, and the oxygen-enrichment percentage of the blast furnace is controlled at 2.0-4.0%. Compared with the smelting blast furnace using the same quality and structure of the burden, the comprehensive coke ratio of the invention is reduced by 20-50kg per ton of iron, the content of TFe in the slag is reduced by 50%, and the comprehensive cost per ton of iron is reduced by 30-50 yuan. The invention has wide prospects for popularization and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Blast furnace molten iron silicon content feature analysis and prediction method
InactiveCN101211383AImprove forecast hit rateEliminate dependenciesGenetic modelsChecking devicesFeature extractionFiltration
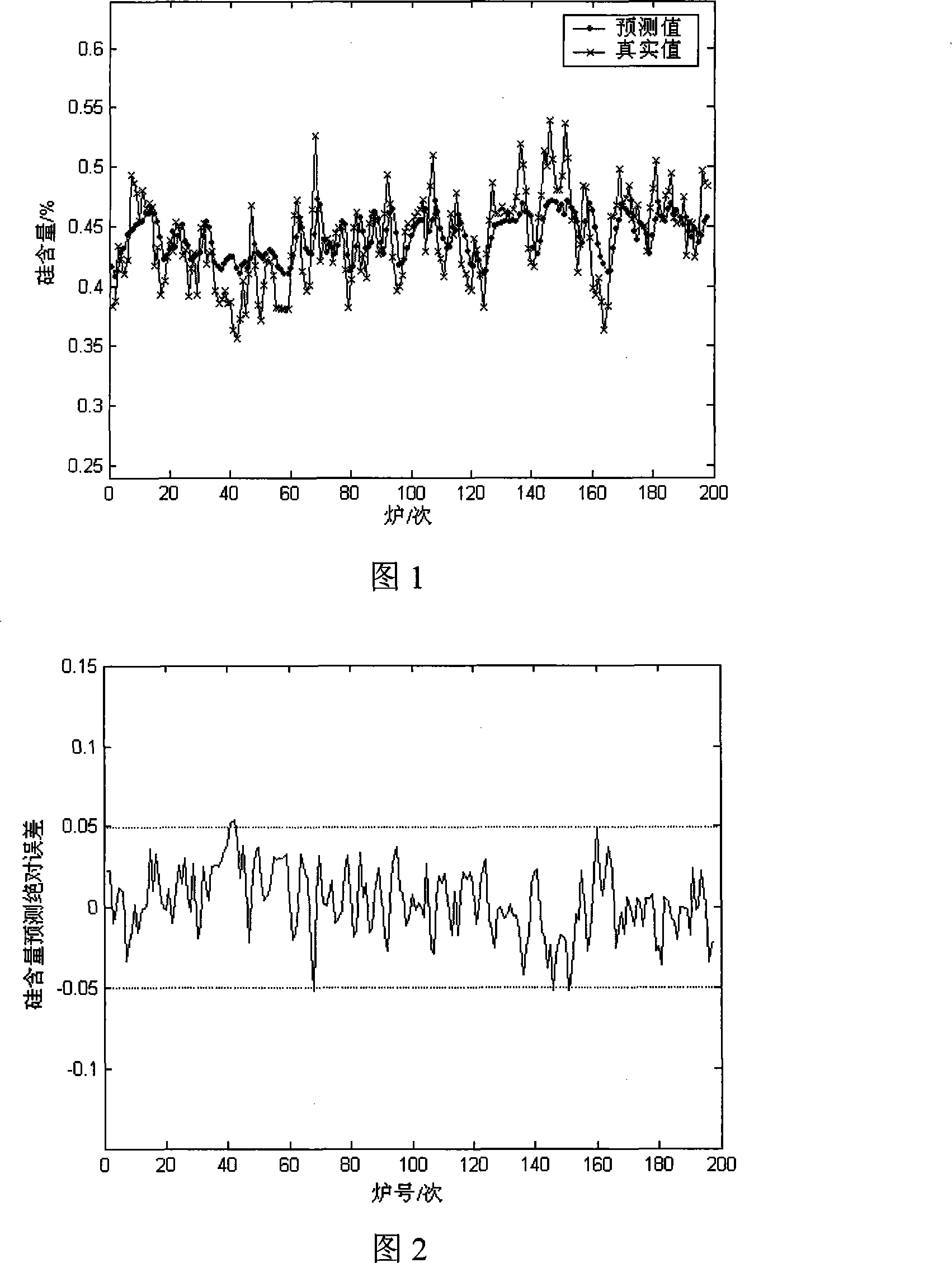
The invention discloses a characteristics analysis and forecast method for blast furnace molten iron silicon content. Blast furnace technological parameters in a forecast module for blast furnace molten iron silicon content are deemed as input variables; after exponential weight mobile average filtration and normalized pre-process for sample data of the input variables, the invention can use an improved dynamic separate composition analysis method for conducting characteristic extraction for the sample data of the input variables, so as to eliminate relevance between production technological parameters; a dynamic recurrence module for forecast of the blast furnace molten iron silicon content is established using the least square support vector machine arithmetic, so as to bring in a genetic arithmetic to optimize module parameters. The invention has common universality for molten iron silicon content forecast in blast furnace smelting process, so as to gain rather good forecast accuracy and improve the forecast hit ratio for blast furnace molten iron silicon content.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
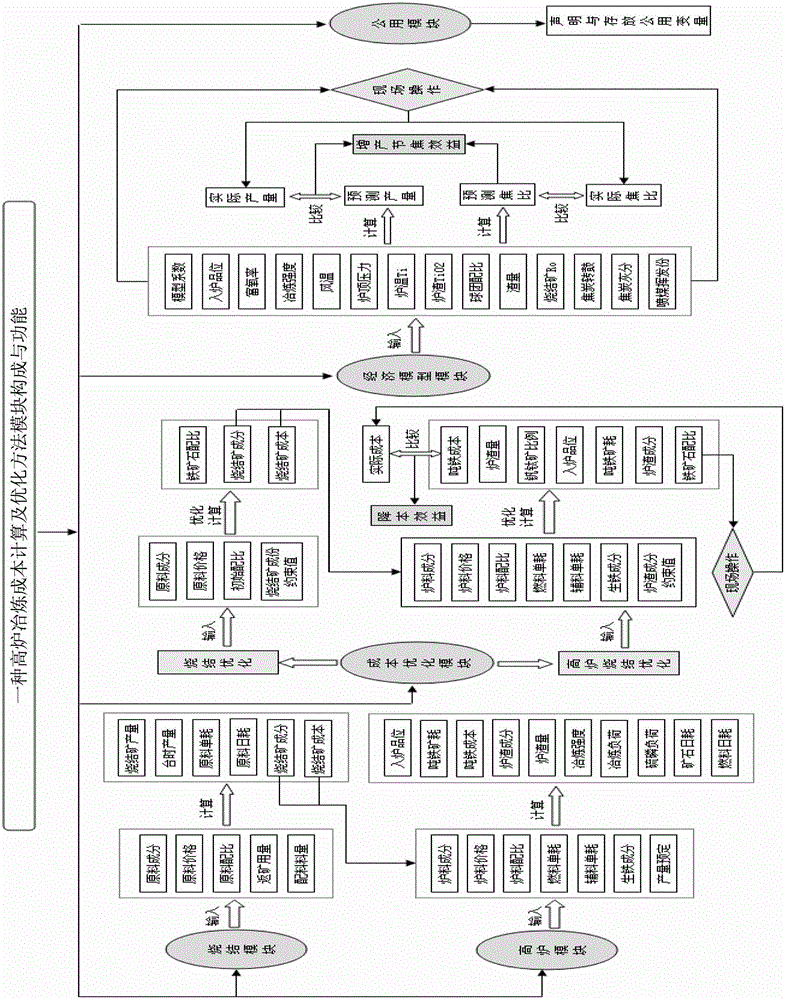
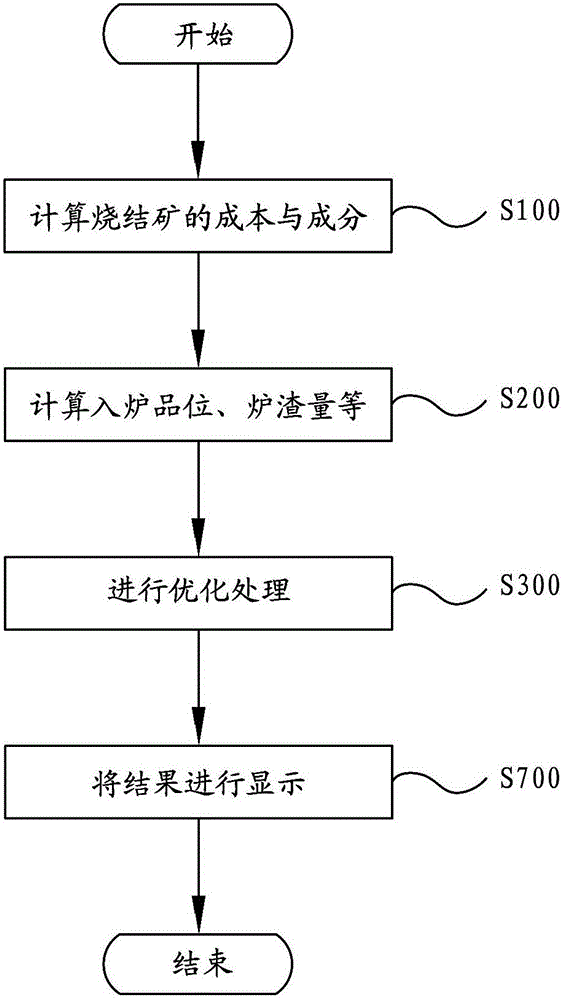
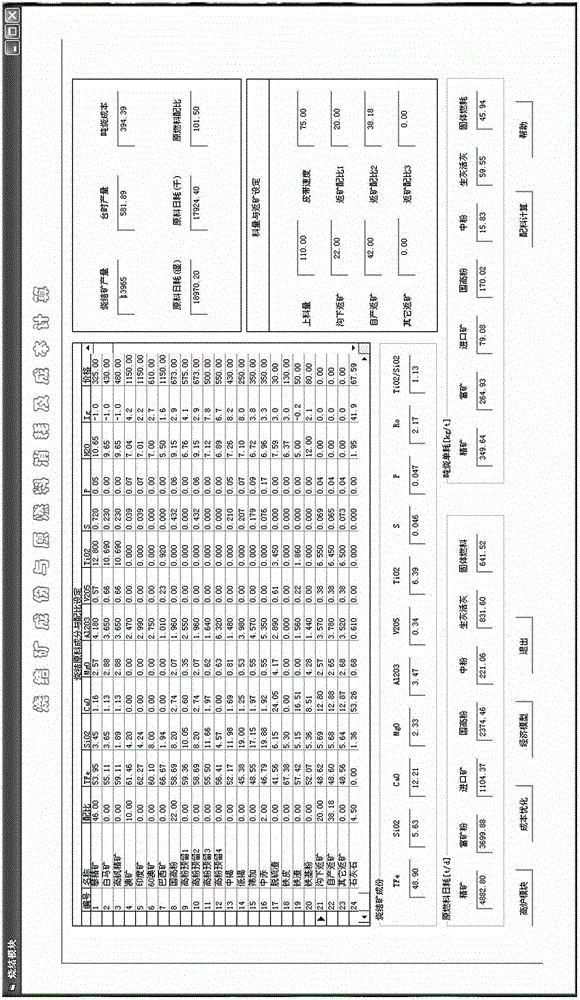
Blast furnace smelting cost calculating and optimizing method
InactiveCN102722652ARaise the ratioReduce smelting costBlast furnace detailsSpecial data processing applicationsAlkalinityBlast furnace smelting
The invention relates to the field of the pig iron smelting, and particularly relates to a blast furnace smelting cost calculating and optimizing method. The blast furnace smelting cost calculating and optimizing method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: calculating the component content, the alkalinity and the unit price of a sinter according to the ratio of sintering materials; calculating the furnace charging grade, the slag amount and the slag component content by using the component content and the unit price of the sinter according to the proportion of blast furnace burdens; and optimizing the component content, the alkalinity and the unit price of the sinter as well as the furnace charging grade, and the slag amount and the slag component content of the blast furnace. The above process is an inverse process of calculating components of the sinter or the slug components and the slug cost. The blast furnace smelting cost calculating and optimizing method provided by the invention can calculate the proportion of low cost iron ore in an inverse mode, and the blast furnace smelting cost calculating and optimizing method is used to guide the production. Moreover, the blast furnace smelting cost calculating and optimizing method can meet the production requirements of a blast furnace and achieve the favorable smelting cost.
Owner:PANGANG GRP PANZHIHUA STEEL & VANADIUM
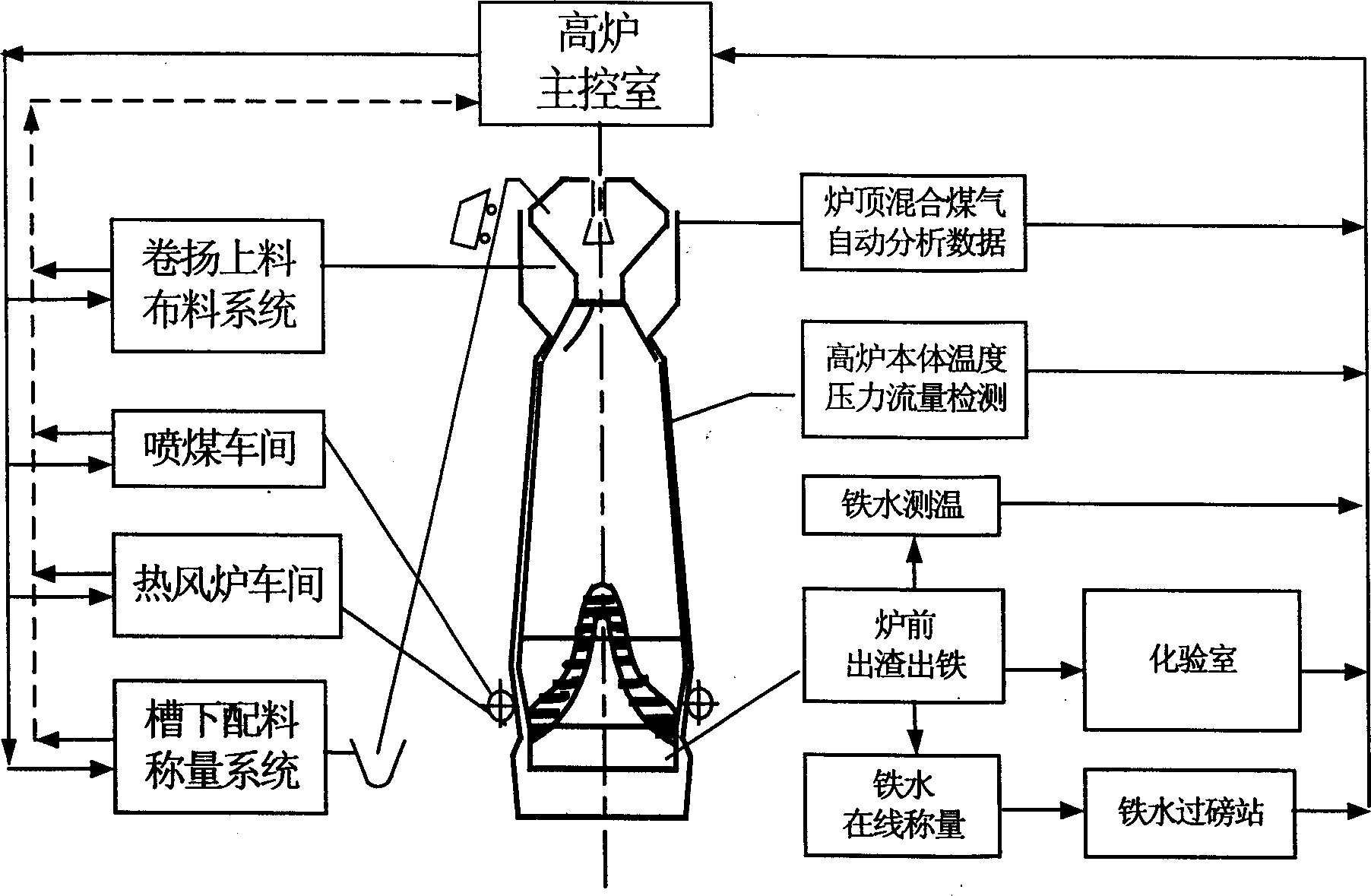
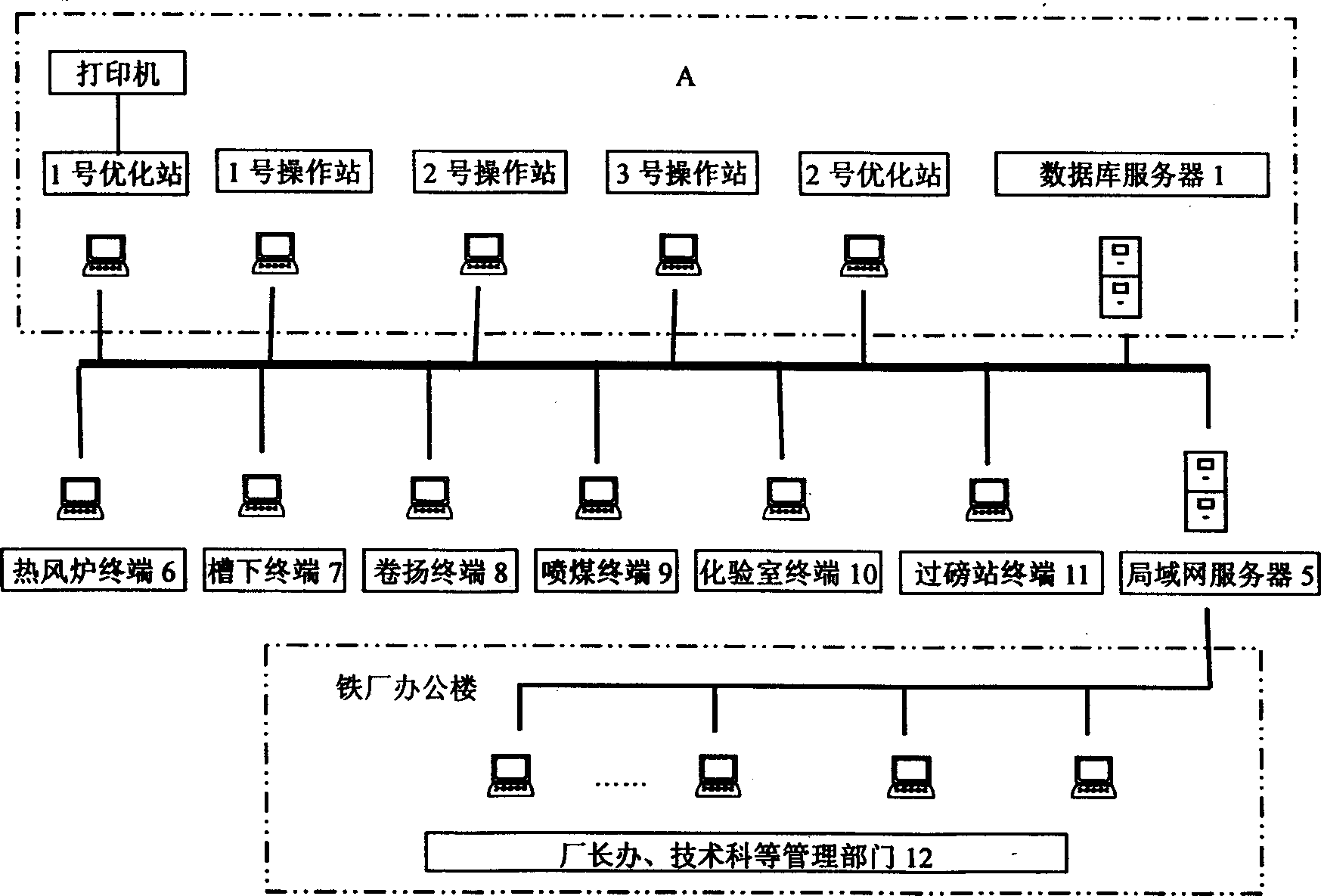
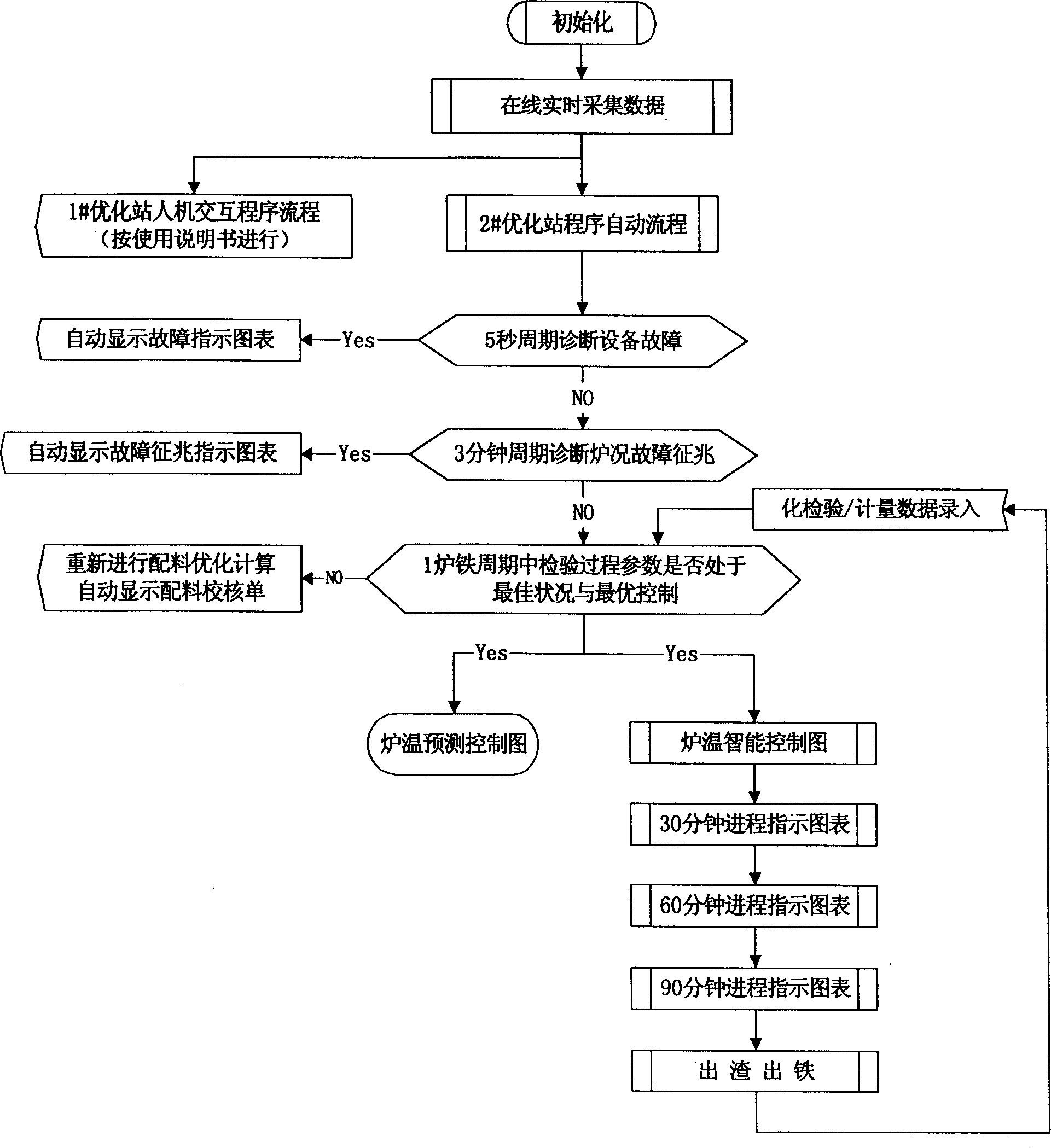
Blast furnace smelt controlling method with intelligent control system
InactiveCN1403593AGuaranteed uptimeRun to keep the blast furnace at optimumBlast furnace detailsMicrocomputerSmelting process
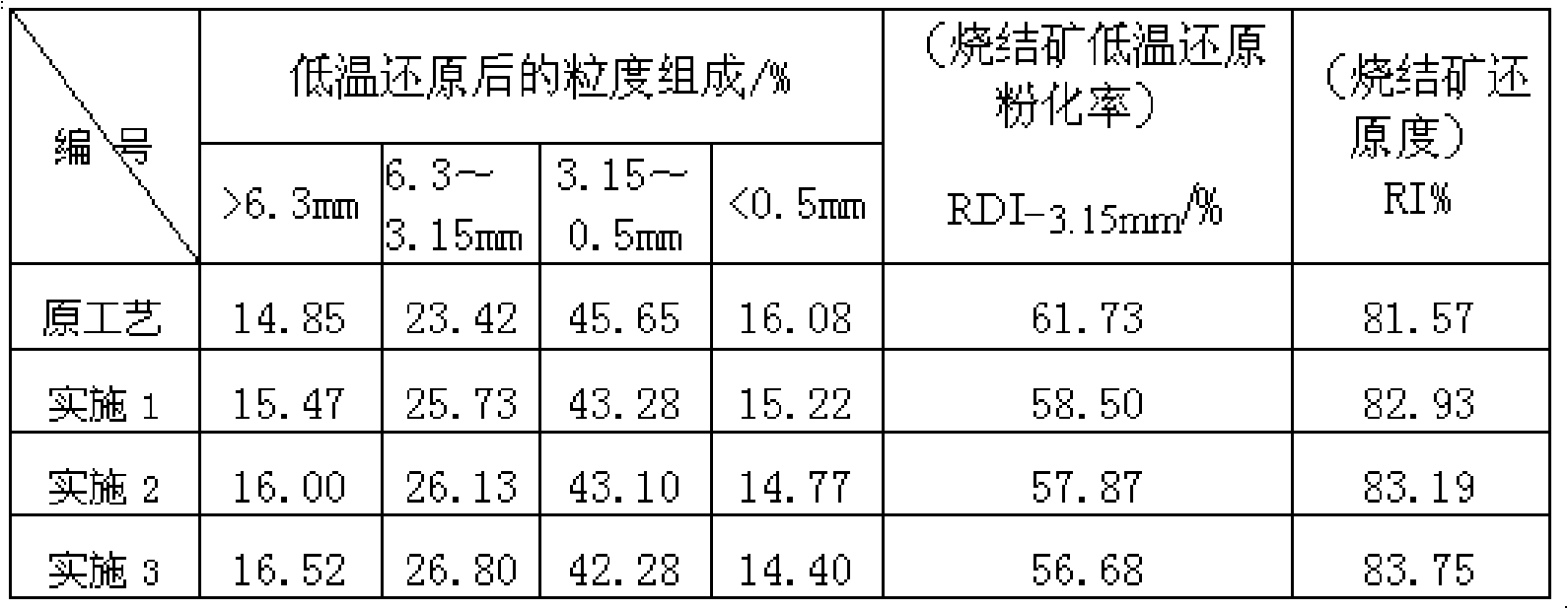
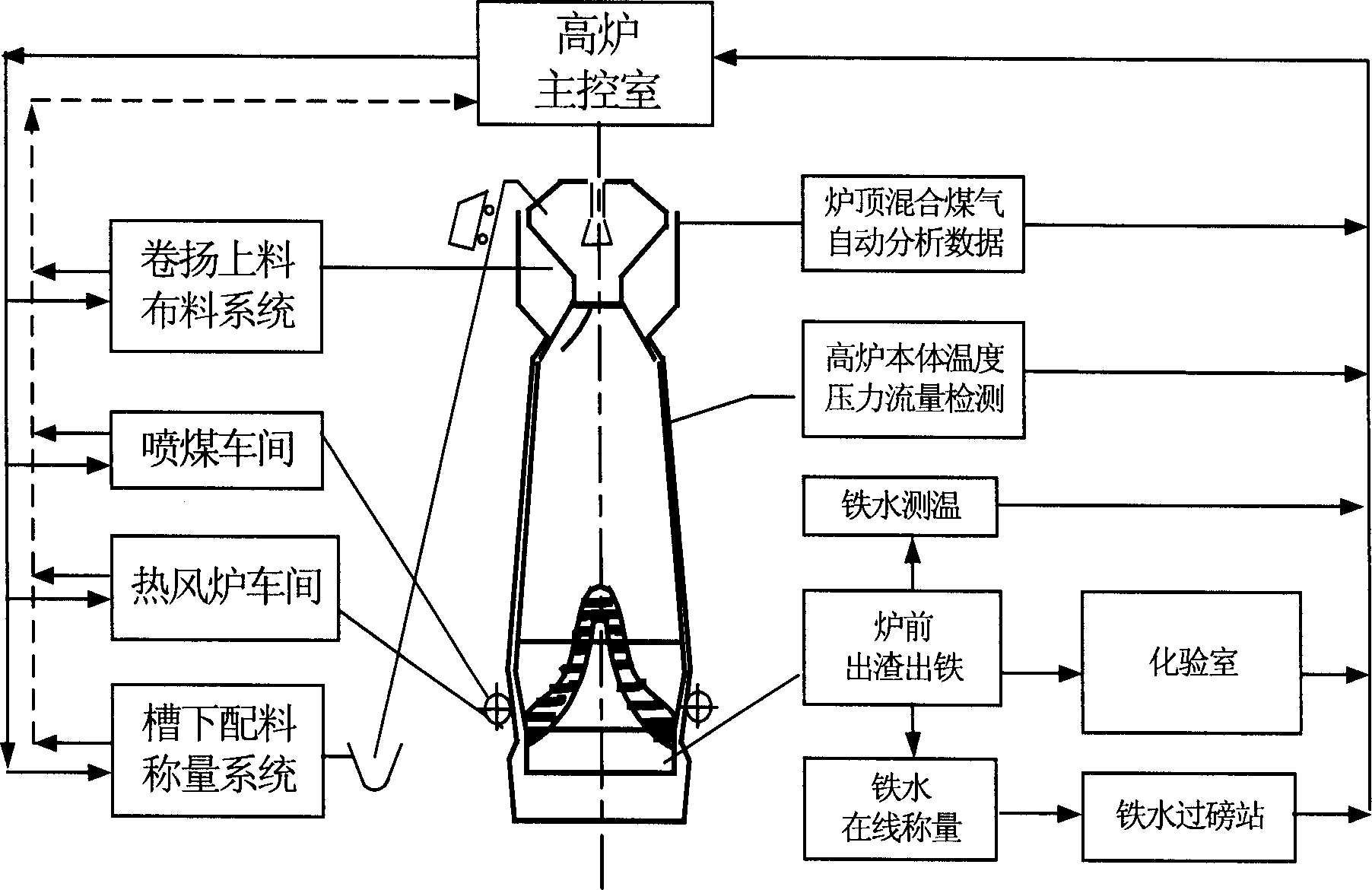
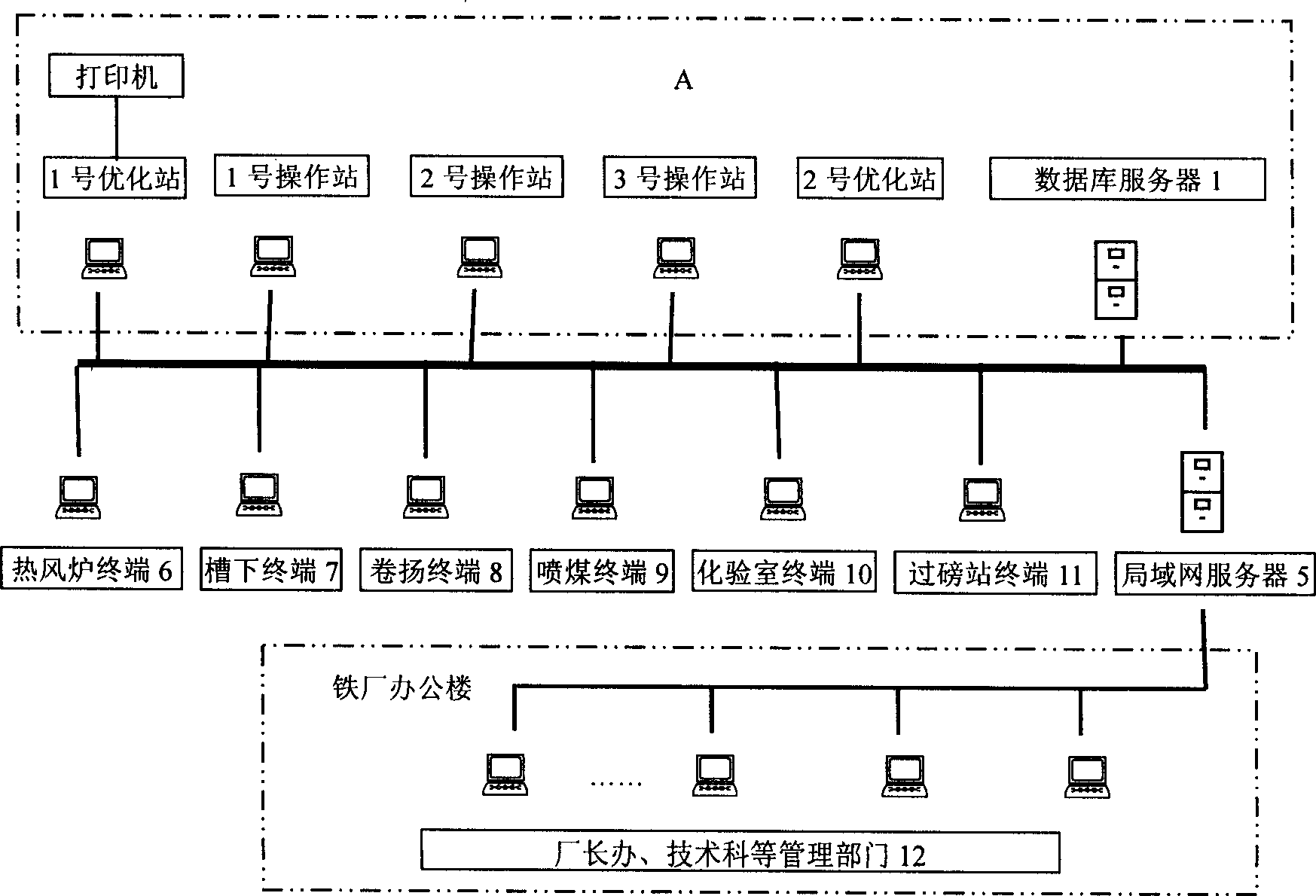
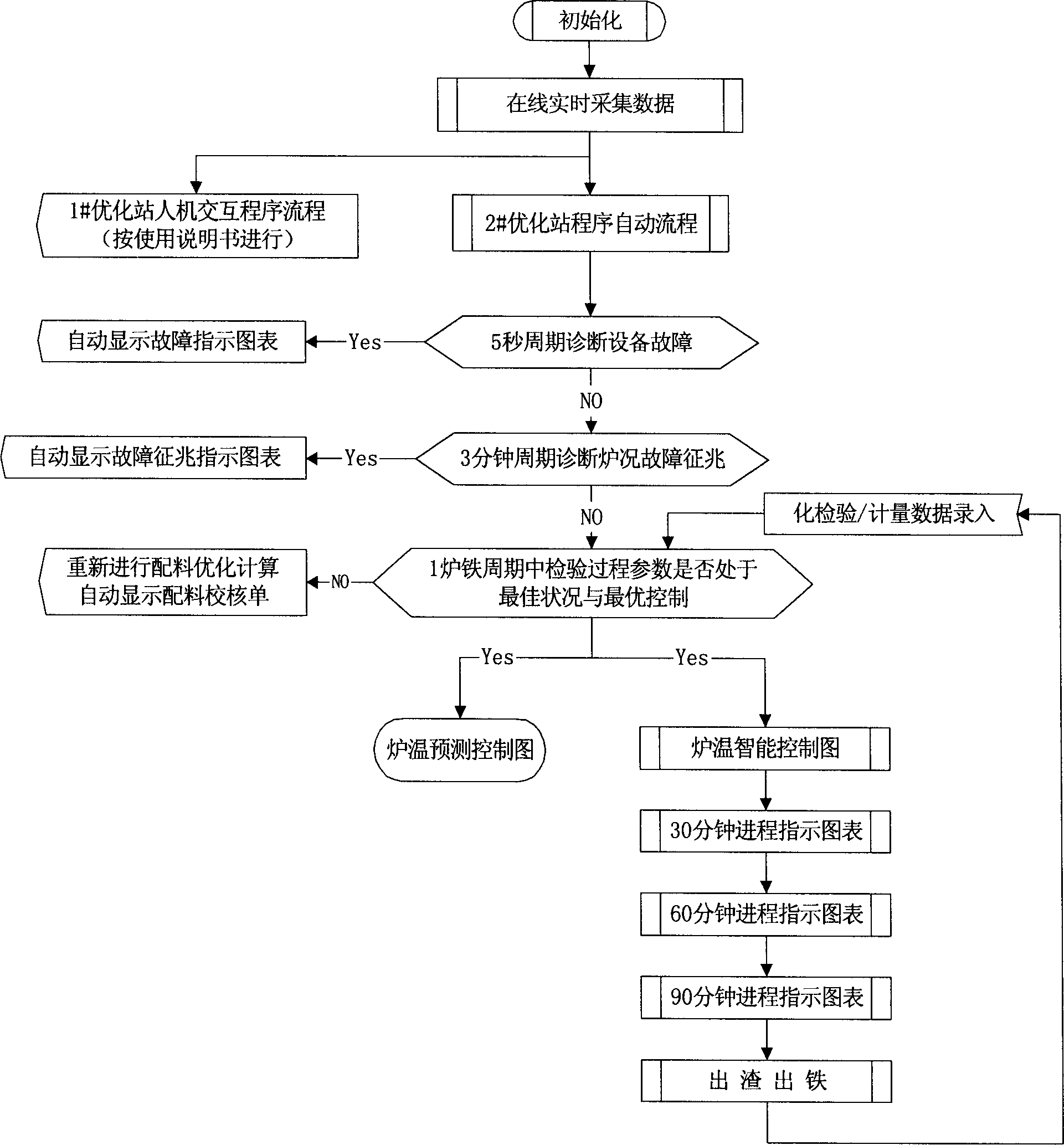
The intelligent control system for blast furnace smelting includes the first and the second optimizing stations in the main control room and several operation stations to constitute microcomputer LAN; and server in the iron smeltery connected to various control step terminals to constitute iron smeltery LAN; and the iron smeltery LAN is connected with the main control room LAN to constitute one network system for real-time acquiring and automatic transmitting of process information. The first optimizing station is provided with intelligent control software module and the second with automatic display module. During operation, the intelligent control software module traces the smelting process via real-time data acquisition and operates automatically according to the data from the LAN, and the operation results are output in man-computer dialogue and simple graphic display mode.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
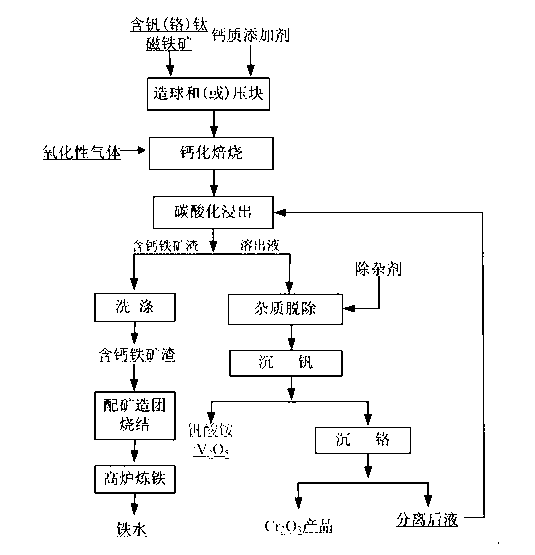
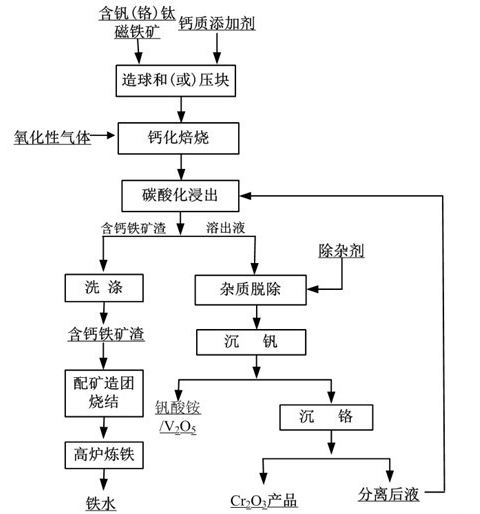
Method for recovering vanadium in vanadium-titanium magnetite ore
ActiveCN102703688ARealize comprehensive utilizationAvoid recyclingProcess efficiency improvementAdhesiveMagnetite
The invention discloses a method for recovering vanadium in vanadium-titanium magnetite ore. The method comprises the process steps of: (1) mixing, pelletizing or briquetting, vanadium-titanium magnetite ore, a calcium additive and an adhesive, drying and oxidizing roasting to obtain roasting clinker; (2) performing carbonation leaching on the roasting clinker by utilizing leaching solution containing CO3<2->, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain calcium-contained iron ore slag and chrome-vanadium-contained dissolving solution; and (3) adding a reagent with NH4+ into the dissolving solution for ammonia settlement, so as to obtain ammonia vanadate, or adding acid liquor into the dissolving solution, and directly acidifying to obtain V2O5. By adopting calcified roasting-carbonation leaching, the vanadium in the vanadium-titanium magnetite ore is recovered, obtained sintered pellets containing the calcium-contained iron ore slag can be directly applied to blast furnace smelting; and therefore, the problem of recovering the vanadium in the vanadium-titanium magnetite ore is effectively solved, and subsequent blast furnace smelting is not influenced. After the vanadium is recovered by using the method, chromium can be recovered from obtained crystallizing mother solution; and therefore, the vanadium-titanium magnetite ore is effectively and comprehensively utilized.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Method for producing high titanium type acid pellet vanadium titanium by chain grate - rotary kiln
This invention discloses a method for producing Ti-rich V-Ti oxidized pellets by chain grate and rotary kiln. The method comprises: mixing vanadic titanomagnetite concentrate with common magnetite concentrate at a weight ratio of 7:3, adding 2.0 wt. % of bentonite, palletizing to obtain 8-16 mm pellets by a disc pelletizer, drying (50-350 deg.C) and pre-heating (500-1000 deg.C) by a chain grate for 12 min, sending dried pellets into a rotary kiln, torrefying at 1150-1300 deg.C and 1.0 r / min for 30-35 min, and cooling torrefied pellets. The obtained Ti-rich V-Ti oxidized pellets have compression strength higher than 1800 N, and TiO2 content of 7.0%, thus can meet the requirement of blast furnace smelting.
Owner:攀枝花钢城集团有限公司球团厂
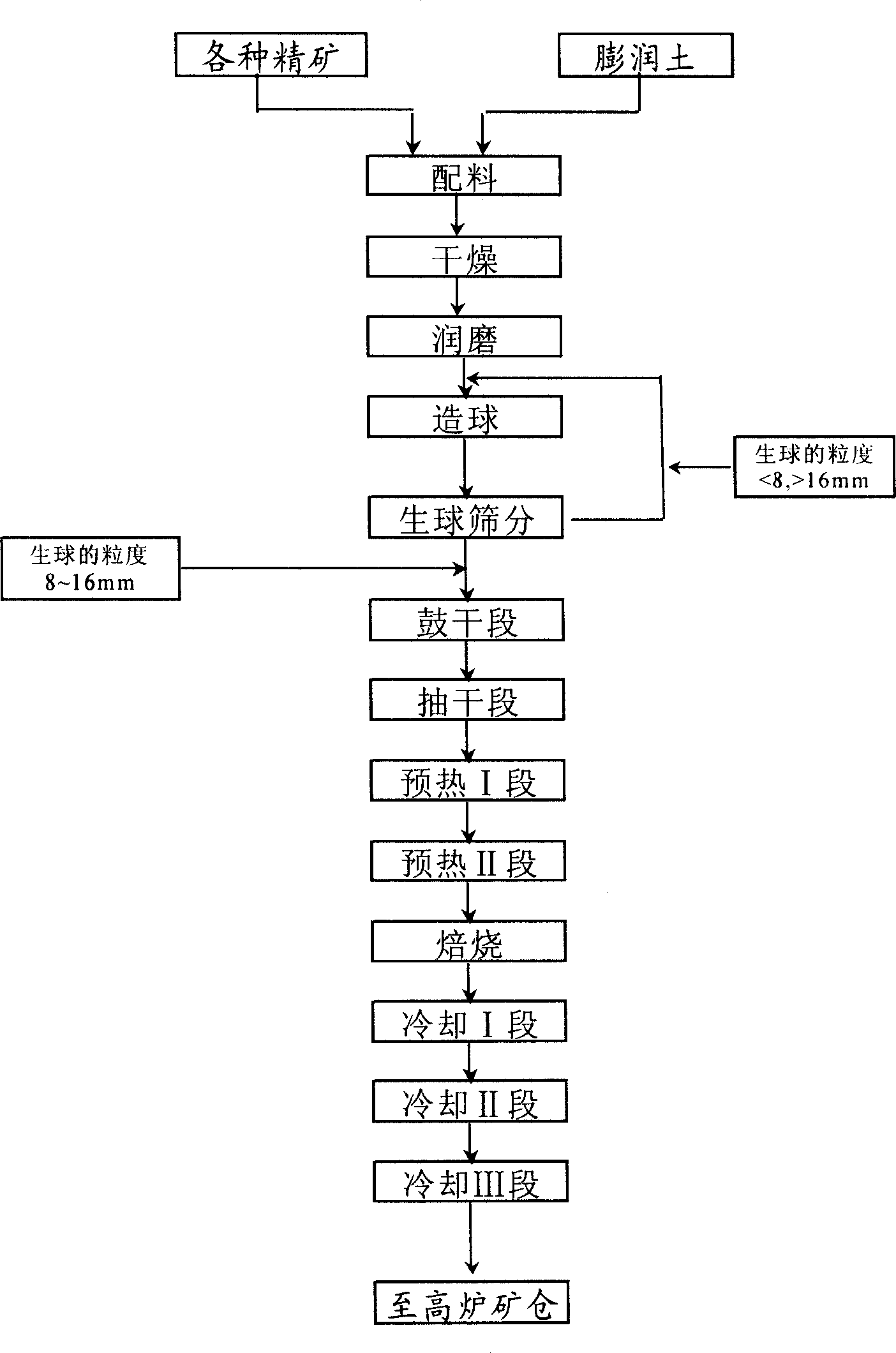
Pelletisation process for iron ore concentrate sintered mix
The invention relates to a granulating method of iron ore concentrate sintering mixture, and belongs to the metallurgical field. The method solves the technical problem that the granulating method of the iron ore concentrate sintering mixture is provided, wherein, the granulating method can increase the quality of sintering minerals. The granulating method of the iron ore concentrate sintering mixture adopts a secondary granulating method for granulating. The granulating method of the iron ore concentrate sintering mixture improves the grain-size composition and the granulation property of the sintering mixture, and increases the ventilation property and the sintering speed of a sinter bed, thereby increasing the sinter output; the granulation of the iron ore concentrate is strengthened, the intensity of the granulating pellets is increased, and the increase of the sinter strength is facilitated; partial high basicity of the iron ore concentrate is formed during the pre-granulating produces, the generation of partial calcium ferrite is promoted, the total content of the calcium ferrite and silicate, the mineral compositions and structure of sintering ore is facilitated to be improved, and the intensity and the finished product rate of the sintering ore are increased; the metallurgical property of the sintering ore is improved, the technical and economic index of blast furnace smelting is increased, and the wide application prospect is realized.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +2
Intelligent blast furnace smelt controlling system
InactiveCN1403594AIncrease the level of intellectual labor automationReduce the intensity of mental workBlast furnace componentsBlast furnace detailsBlast furnace smeltingEngineering
The intelligent control system for blast furnace smelting includes the first and the second optimizing stations in the main control room and several operation stations to constitute main control room LAN as the master's operation platform; and servers in the iron smeltery connected to various control step terminals to constitute iron smeltery LAN; and the iron smeltery LAN is connected with the main control room LAN to constitute one network system for real-time acquiring and automatic transmitting of process information. The first optimizing station is provided with intelligent control software module and the second with automatic display module. During smelting, the intelligent control software module outputs the operation results in man-computer dialogue and simple graphic display mode, so that the master may control to keep the blast furnace operating in optimized state.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Blast-furnace burden distribution method for high-proportion pellets
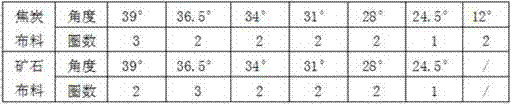
InactiveCN107119163AEfficient control over scrollingEffective control of rolling effectBell-and-hopper arrangementBlast furnace detailsDistribution matrixPresent method
The invention discloses a method for distributing material for a blast furnace with a high proportion of pellets. The process is as follows: the ore to be fed into the furnace includes pellets and sintered ore; the pellets and coke are mixed into the furnace; When the amount of pellets accounts for 30% to 60% of the total ore, the sintered ore is placed at both ends of the cloth stall, and the other ore is placed in the middle of the cloth stall; when the pellets account for more than 60% of the total ore, the sintered ore is placed The stalls on the edge of the furnace throat, and other ores are distributed in other stalls. The method effectively controls the rolling of the pellets by optimizing the material distribution matrix, and stabilizes the forward movement of the blast furnace while increasing the ratio of the pellets into the furnace. This method can effectively control the rolling effect of the pellets in the furnace when the high proportion of pellets is smelted in the blast furnace, which is conducive to stabilizing the two airflows at the edge and center of the furnace, controlling the reasonable operation of the furnace type, and ensuring the stability of the blast furnace. It has the characteristics of strong operability, simple process and easy realization.
Owner:TANGSHAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
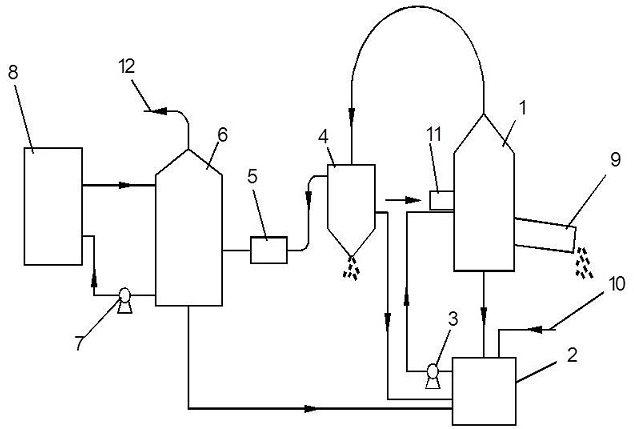
Blast furnace smelting slag water quenching waste steam waste heat recovery system
InactiveCN102424868AImprove waste heat utilization efficiencyIncrease waste heat recoveryLighting and heating apparatusProcess efficiency improvementBlast furnace smeltingWastewater
The present invention provides a blast furnace smelting slag water quenching waste steam waste heat recovery system. The system comprises a blast furnace slag water quenching apparatus, a slag quenching water circulation apparatus and a waste steam waste heat recovery apparatus. The blast furnace slag water quenching apparatus comprises a smelting slag groove, a water quenching apparatus and a slag discharging and conveying belt. The slag quenching water circulation apparatus comprises the water quenching apparatus, a water circulating tank, a water quenching pump and a water supplying pipe. The waste steam waste heat recovery apparatus comprises the water quenching apparatus, a three-phase separator, a fan, a heat exchanger, a hot water pump and a low-temperature user. The method of the present invention is different from the method in the prior art, wherein the recovery of the slag quenching waste water waste heat is adopted to recover the smelting slag waste heat by the method in the prior art, and the waste heat in the waste steam generated from the smelting slag quenching by the recovered water is adopted to recover the smelting slag waste heat by the method of the present invention, the water quality of the waste steam is better than the water quality of the waste water, such that the disadvantages of high hardness of the waste water, equipment scaling, equipment blocking and the like in the prior art are overcome. According to the present invention, the slag quenching waste steam waste heat is effectively recovered; the system has advantages of energy saving and emission reduction, and environmental protection; the collected waste heat can be used to meet the requirements of the low-temperature user.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for comprehensively smelting sefstromite
ActiveCN101906498AHigh recovery rateImprove economyElectric furnaceTunnel kilnBlast furnace smelting
The invention provides a method for comprehensively smelting sefstromite. The method fundamentally solves the problem that the vanadium content in molten iron is difficult to increase so as not to finally extract vanadium, a valuable resource, because the conventional blast furnace smelting cannot utilize one hundred percent sefstromite by directly reducing the one hundred percent sefstromite into vanadium-titanium sponge iron by a tunnel kiln direct reduction method. The method comprises the following steps of: when the vanadium-titanium sponge iron is smelted in an electric furnace, first reducing V2O5 in slag and putting the V2O5 into steel by controlling a reducing atmosphere and then scratching away oxides of difficultly reduced elements such as Si, Al, Ti, Ca, Mg and the like along with the slag to obtain high titanium slag; and oxidizing the vanadium in the molten steel into the slag by oxidizing and blowing to improve the V2O5 content in the slag so as to provide guarantee for subsequent vanadium extraction from the slag and extremely improve the recovery rate and the recovery economic value of the vanadium. The method can also produce high-quality molten steel for developing steel grade with high added value, so the valuable resource, namely the sefstromite can be fully, effectively and rationally utilized.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
Pressing plate type crushing device special for blast furnace smelting
InactiveCN105435927AReduce consumptionSolve outputGrain treatmentsBlast furnace smeltingElectric control
The invention belongs to the technical field of blast furnace smelting equipment, and particularly relates to a pressing plate type crushing device special for blast furnace smelting. The pressing plate type crushing device special for blast furnace smelting is thorough in crushing, simple in structure and high in automation degree. To achieve the technical aim, the pressing plate type crushing device special for blast furnace smelting comprises a base, a conveying device, a support, a fixing plate, a crushing box, an electric push plate, a discharging pipe, an electric control valve, a top plate, a left bearing pedestal, a right bearing pedestal, a lead screw, a servo motor, a nut, a connecting rod, a lifting air cylinder I, an electric mechanical arm, a lifting air cylinder II and a pressing plate. The conveying device is arranged on the right side of the upper end of the base. The defects that an existing iron ore crusher is not even enough in crushing, iron ore of various sizes on a conveying device enters a blast furnace, and consequently fuel consumption is increased, the yield is lowered, and materials are wasted are overcome.
Owner:CHONGQING YUXI STEEL GRP CO LTD
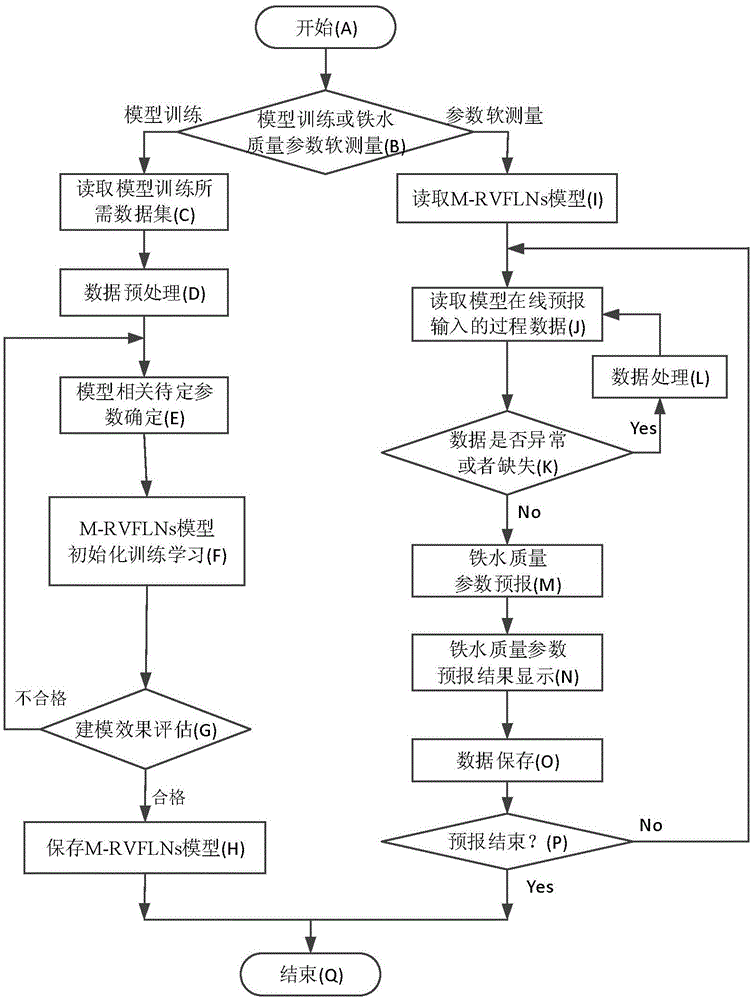
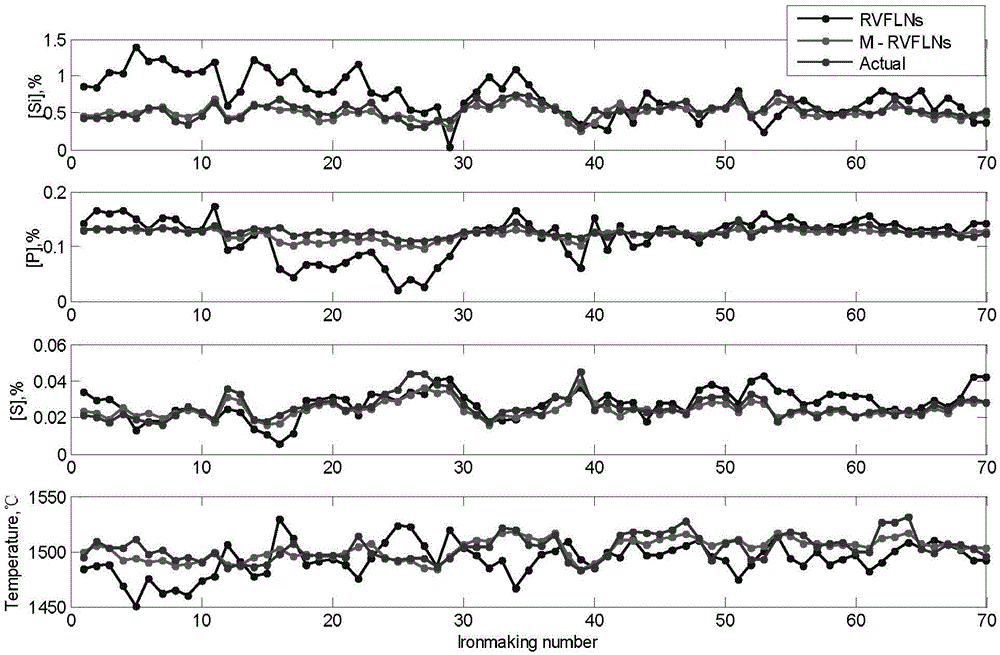
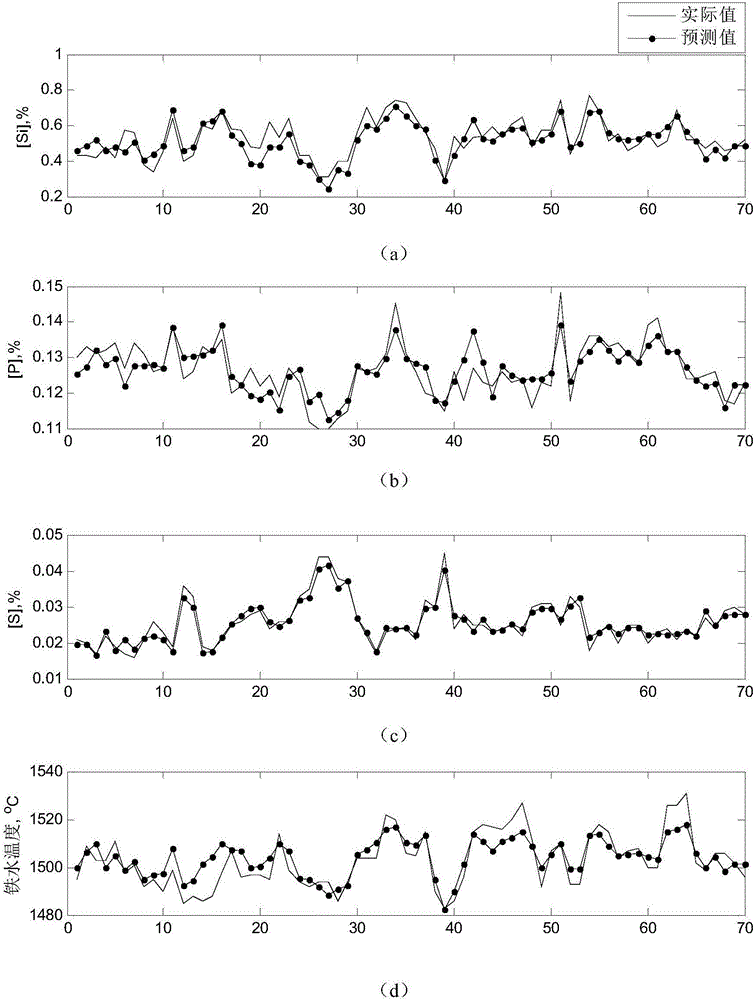
Robust random-weight neural network-based molten-iron quality multi-dimensional soft measurement method
ActiveCN105608492AImplementing Multivariate Robust Soft SensingImplement soft sensingSteel manufacturing process aspectsBlast furnace detailsAutomatic controlPrincipal component analysis
The invention relates to a robust random-weight neural network-based molten-iron quality multi-dimensional soft measurement method which belongs to the blast-furnace smelting automatic control field, in particular to a Cauchy distribution weighted M-estimation random-weight neural network (M-RVFLNs) based method for multi-dimensional parameter-dynamic soft measurement of the molten-iron quality in the blast-furnace smelting process. According to the method of the invention, the principal component analysis (PCA) method is adopted to chose main parameters which affect the blast-furnace molten iron quality as model input variables, a molten-iron quality multi-dimensional dynamic prediction model which has an output self-feedback structure and takes into account input-output data at different moments is constructed, and it is possible to carry out multi-dimensional dynamic soft measurement of the main parameters Si content, P content, S content and molten iron temperature which represent the blast-furnace molten iron quality. The method of the invention comprises the following steps of (1) choosing auxiliary variables and determining model input variables and (2) training and using the M-RVFLNs soft measurement model.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for reclaiming and reusing iron-making dust in blast furnace
InactiveCN1632136AFavorable nodulationHelps eliminate nodulesBlast furnace detailsIron powderBlast furnace smelting
A method for recycling blast furnace ironmaking dust. The bag dust, gravity ash and other iron-containing dust recovered in the blast furnace smelting process are evenly mixed with coal powder, and sprayed into the hearth from the tuyere of the blast furnace. It is required that there is no accumulation in the hearth before injection. , no nodules in the furnace throat, and its process parameters: spray bag dust, the injection amount is 6-10Kg / t iron, hot air temperature> 1000 ℃, blast furnace zinc load <0.15Kg / t iron; spray gravity ash, injection amount is 6Kg / t iron ~ 15Kg / t iron, hot air temperature > 1050°C; spray other iron-containing dust, injection amount < 8Kg / t iron, dust particle size < 0.5mm, hot air temperature > 1050°C; the present invention has the functions of increasing iron, Saving coke, benefiting silicon reduction in molten iron, promoting smooth operation of blast furnace and strengthening smelting, benefiting safe coal injection, reducing nodulation in blast furnace, protecting the environment, and clean production, etc.
Owner:INST OF METALLURGICAL TECH DONGBEI UNIV SHENYANG
High titan type low FeO content sinter and method for preparing same
The invention belongs to the agglomeration field of iron ore, in particular to a high titanium sintering ore with a low FeO content and a preparation method thereof. The technical problem needed to be solved by the invention is to provide a method for preparing the high titanium sintering ore with a low FeO content by taking the v-ti magnetite concentrate ore specially owned by Panzhihua as the material. The invention is mainly characterized in that the sintering material is the high titanium v-ti magnetite concentrate ore; when batching, the carbon addition amount is 2.6 to 3.2 percent; the FeO content of the sintering ore obtained by sintering is 6.5 to 9.5 percent; the FeO content is preferably to be 7.0 to 8.5 percent. The FeO content of the sintering ore is controlled to be 6.5 to 9.5 percent by controlling a fuel mixture ratio with a high precision, thus ensuring the intensity of the sintering ore, improving the performance of the metallurgy and achieving the optimized effect on the aspects of blast furnace metallurgy, cost control and environment protection.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES
Reducing chamber and heating chamber multilayer obturation alternation and fusion gasification combination metal smelting method
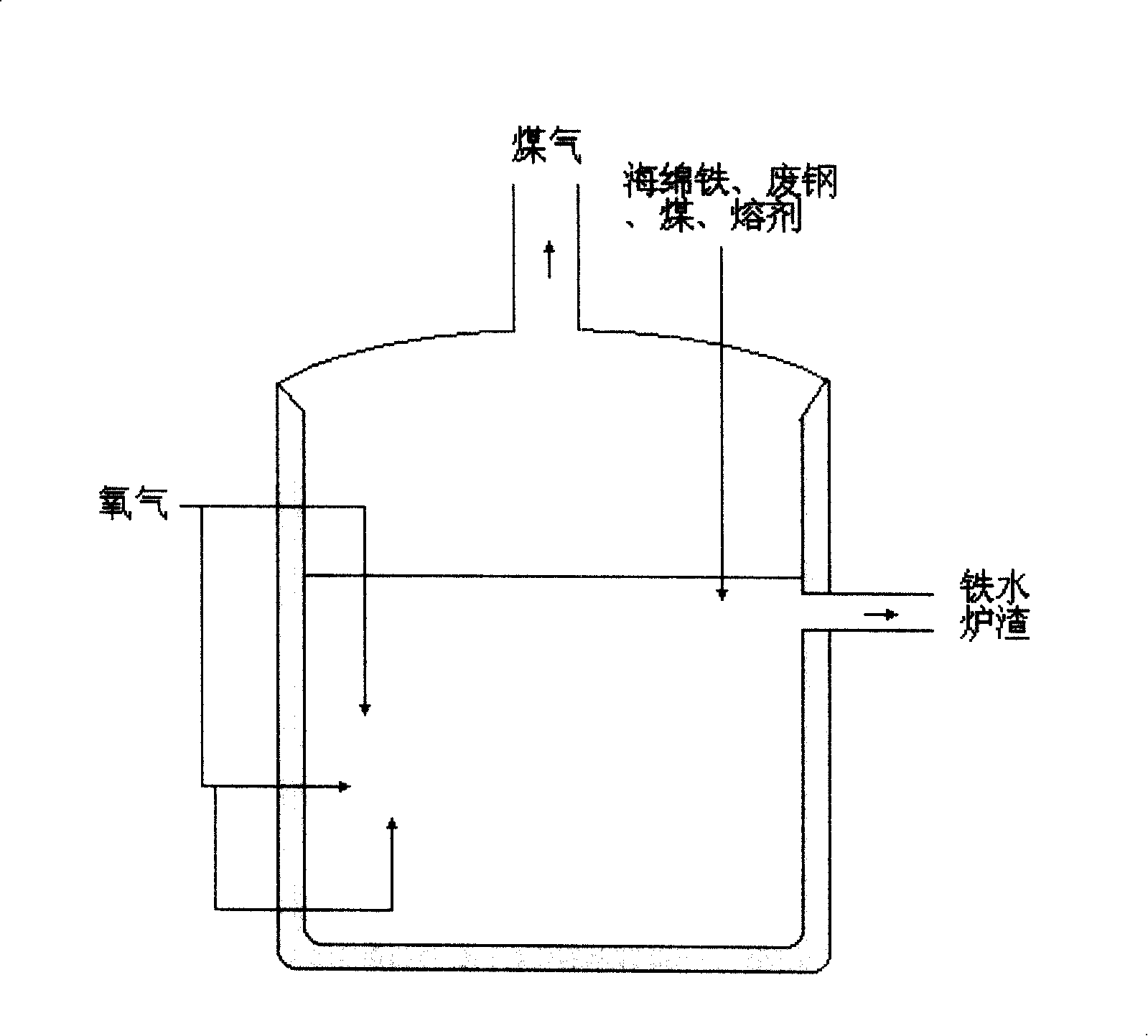
The invention provides a novel metal oxide smelting method, namely, reduction chamber and heating chamber multi-layer sealing space and melting gasification combined smelting method, which aims to solve the problems that coking coal and high-quality iron ore are lacked in blast furnaces and problems existing in various non blast furnaces smelting method. The method is mainly used in smelting iron, which does not need procedures such as coke and sintering and palletizing and the like which pollute, and can smelt powder ore and fine ore, and can use cheap coal and other fuel, and can use cheap iron ore with high harmful element content. The cost to manufacture the invention is evidently lower than the current blast furnaces and non blast furnaces smelting method. The method of smelting metal oxide is divided into two procedures, the first is directly reducing and the second is melting gasification.
Owner:邹明
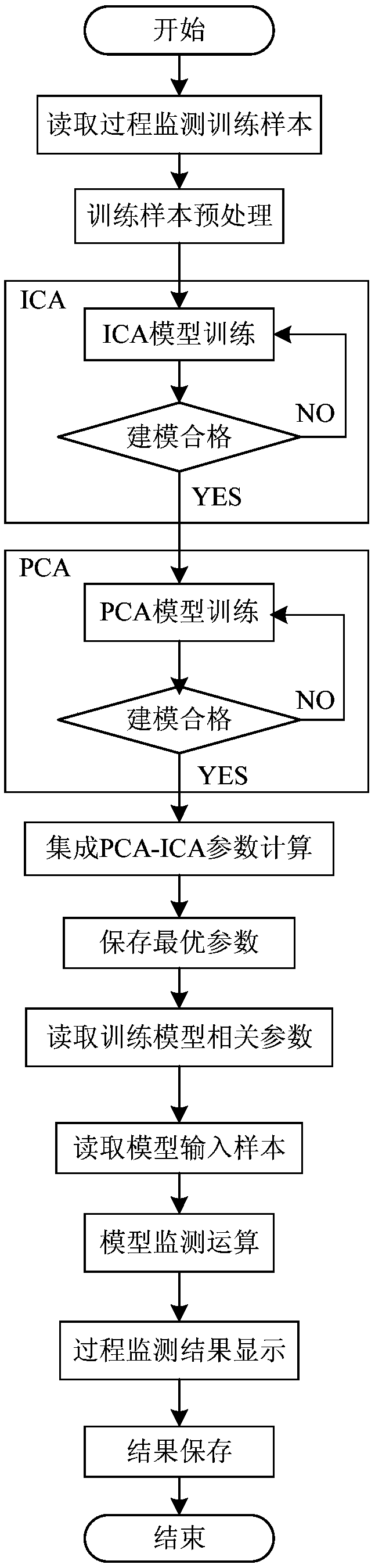
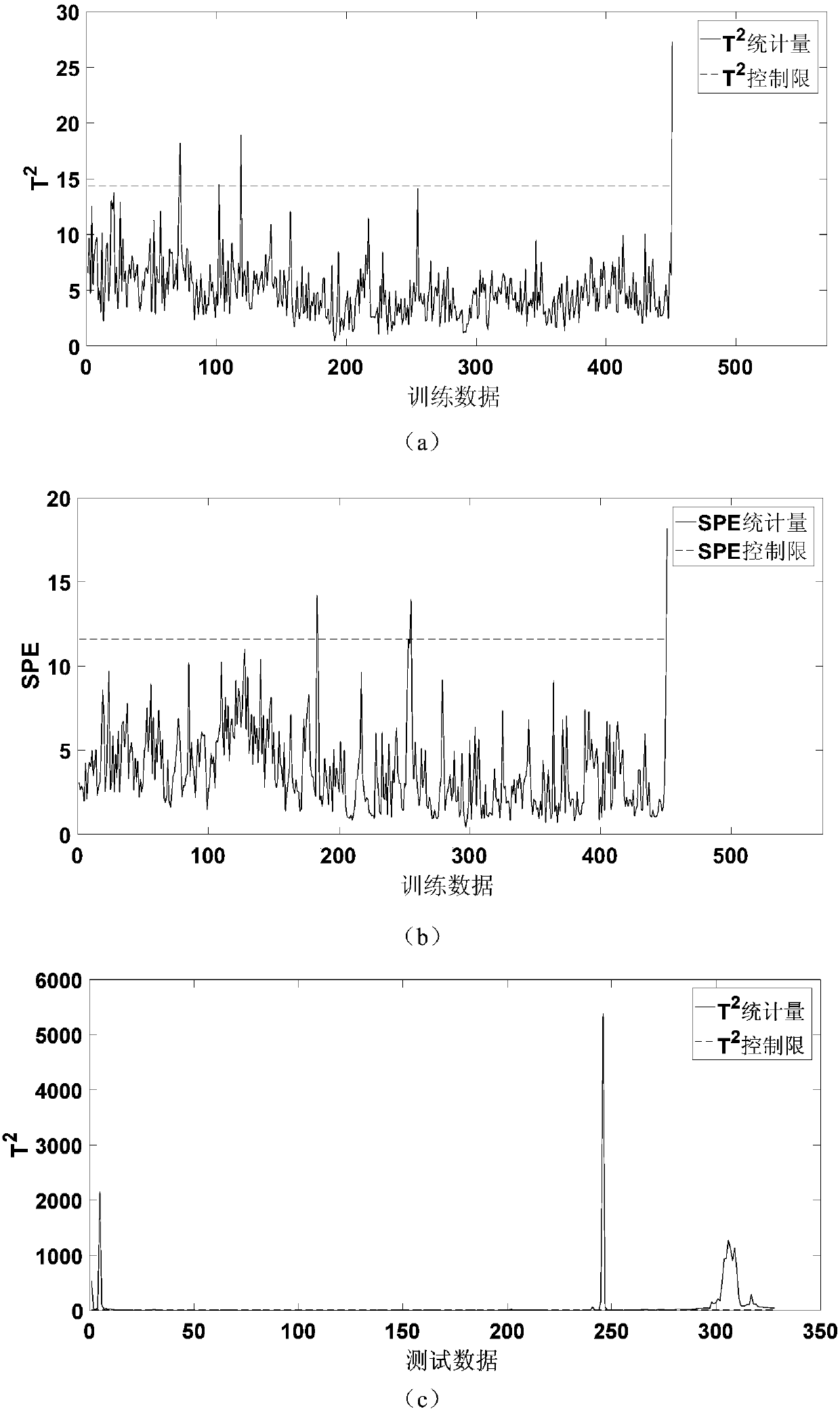
Integrated PCA-ICA blast furnace process monitoring and fault diagnosis method
ActiveCN109062196AEffective monitoringEfficient identificationProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringDiagnosis methodsBlast furnace smelting
The invention provides an integrated PCA-ICA blast furnace process monitoring and a fault diagnosis method, and relates to the technical field of blast furnace smelting process monitoring. The methodincludes the following steps that variable selection is assisted and input variable determination of a blast furnace process monitoring mode is determined; monitoring mode is practiced and monitoringof the integrated PCA-ICA is achieved. According to the integrated PCA-ICA blast furnace process monitoring and the fault diagnosis method, the integrated PCA-ICA process monitoring method is adoptedto monitor a blast furnace process, a novel fault identification index is designed, control limits of corresponding fault identification index are provided in the same time, so that an abnormal operation condition of a blast furnace is monitored and anomaly sources are identified, an inner structure of data is sufficiently analyzed, and thus the abnormal operation condition of the blast furnace ismonitored and the anomaly sources are identified to provide a technical support for ensuring persistent and stable operation of the blast furnace.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for adjusting furnace charge structure before damping-down period of blast furnace for smelting high-titanium schreyerite
ActiveCN104694682AGuaranteed viscosityFast air supplyBlast furnace detailsAir volumeBlast furnace smelting
The invention belongs to the technical field of schreyerite blast furnace smelting, and particularly relates to a method for adjusting a furnace charge structure before a long damping-down period (the damping-down period is longer than five hours and shorter than five days) of a blast furnace for smelting high-titanium schreyerite. The method for adjusting the furnace charge structure before the damping-down period of the blast furnace for smelting the high-titanium schreyerite includes the step that in the smelting period before the damping-down period of the blast furnace, the furnace charge structure is adjusted to enable slag newly generated in the damping-down period of the blast furnace to meet the conditions that the content of TiO2 ranges from 1% to 20%, the binary alkalinity (CaO / SiO2) of the slag ranges from 1.00 to 1.03, the content of CaF2 ranges from 0.50% to 2.0%, and the content of MnO2 ranges from 1.0% to 4%. By means of the method, after damping-down overhauling is completed, the air volume can be rapidly (a period with the length 1 time to 1.5 times that of the damping-down period is needed) recovered to the air volume required by normal production.
Owner:PANGANG GRP XICHANG STEEL & VANADIUM CO LTD
Blast-furnace smelting method for vanadium-titanium magnetite
InactiveCN103361453ALow viscosityEasy to separateBlast furnace detailsMagnetiteBlast furnace smelting
The invention provides a blast-furnace smelting method for vanadium-titanium magnetite. The method comprises the following steps of: in the existence of coke, adding the vanadium-titanium magnetite raw material into a blast furnace, smelting, and blowing fuel and introducing oxygen-containing gas into the blast furnace through a blast-furnace tuyere, wherein the method also comprises the following step of: blowing oxidized powder into the blast furnace through the blast-furnace tuyere. By adopting the blast-furnace smelting method for the vanadium-titanium magnetite, the iron content of iron slag can be reduced obviously.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +2
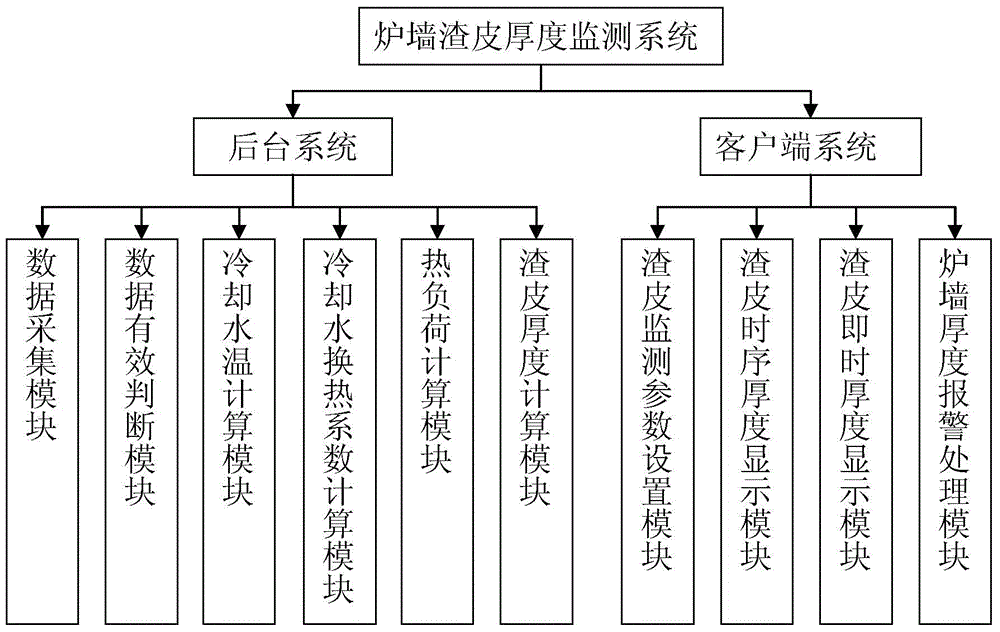
Blast furnace brickwork slag shell thickness monitoring system and method
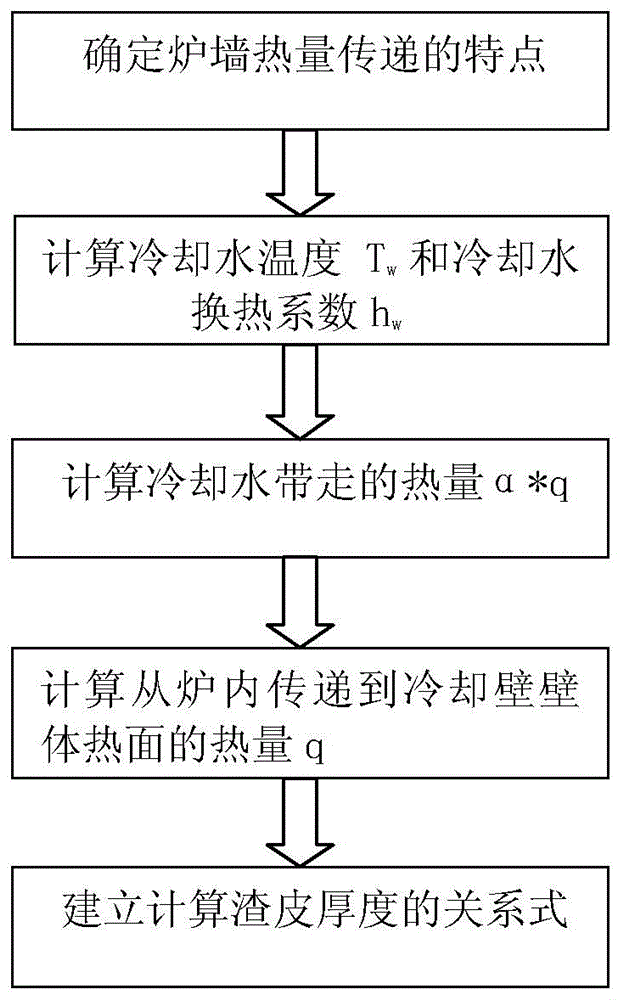
ActiveCN104404187AGuaranteed uptimeExtended service lifeChecking devicesData acquisitionBlast furnace smelting
The invention relates to a blast furnace brickwork slag shell thickness monitoring system and method and belongs to the technical field of blast furnace monitoring. The system comprises a background processing system and a client system, wherein the background processing system comprises a data acquisition module, a data validity judgment module, a cooling water temperature calculating module, a cooling water heat transfer coefficient calculating module, a thermal load calculating module and a slag shell thickness calculating module; the client system comprises a slag shell monitoring and calculating parameter setting module, a slag shell timing sequence thickness display module, a slag shell real-time thickness display module and a brickwork thickness alarm processing module. The method comprises the following steps: determining the characteristics of brickwork heat transfer, calculating the temperature and the heat transfer coefficient of cooling water, calculating the quantity of heat taken away by the cooling water, calculating the heat quantity transferred from the interior of a blast furnace to the hot surface of the wall body of a cooling wall, and establishing the relational expression of calculating the slag shell thickness. According to the system and method, an objective and quantized basis is provided for knowing the brickwork slag shell condition during the blast furnace smelting process, a blast furnace operator is helped to timely know the condition of the brickwork, so that reasonable operating measures are taken, the stable operation of the blast furnace is ensured, and the service life of the blast furnace is prolonged.
Owner:CISDI ENG CO LTD
Method for preparing high titania type high MgO sintering ore
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy of iron and steel, particularly relates to a method for preparing high titania type high MgO sintering ore, aiming to provide a method capable of improving the drum strength of high sintering ore. The method comprises the steps of dosing, mixing material for pellet fabrication, distributing material, igniting and sintering. The high titania type high MgO sinter ore comprises the following ingredients by weight: 48-52 percent of Panzhihua high titania type vanadium-titania magnet ore concentrate, 12-16 percent of Australian ore powder, 7.5-11.5 percent of strong flour, 3.5-5.5 percent of sieving powder, 1-3 percent of gas ash, 1-3 percent of steel slag, 4.3-4.7 percent of coke powder, 3.2-5.5 percent of lime stone, and 2.3-3.8 percent of dolomite. Adding dolomite into the sintering mixture can improve the intensity of the sintering ore and the ratio of finished products, improves the performance of sintering ore metallurgy and the performance of blast furnace slag, achieves the aim of improving sintering and blast furnace smelting technical and economical index, and reduces energy consumption of fuel. The method is simple and easy to operate, and highly flexible by only regulating the structure of sintering materials without altering the field process.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +3
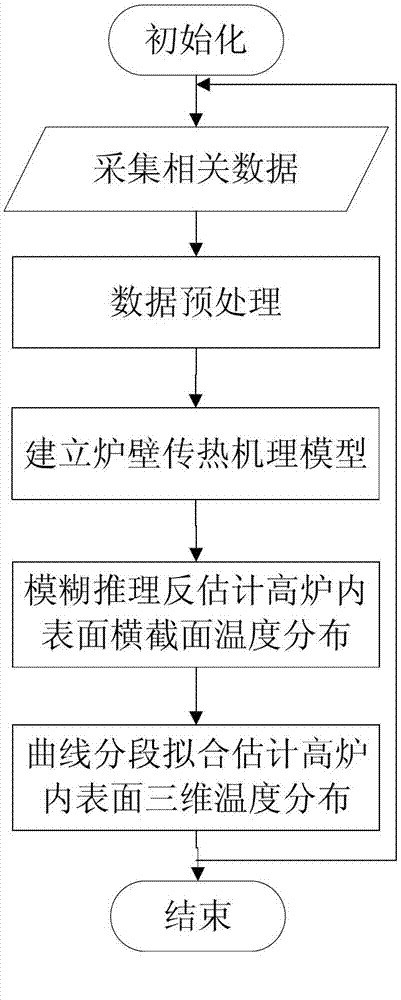
Method for estimating inner surface temperature of blast furnaces
InactiveCN102776303AStable productionImprove smelting qualityBlast furnace detailsProcess efficiency improvementSocial benefitsTemperature curve
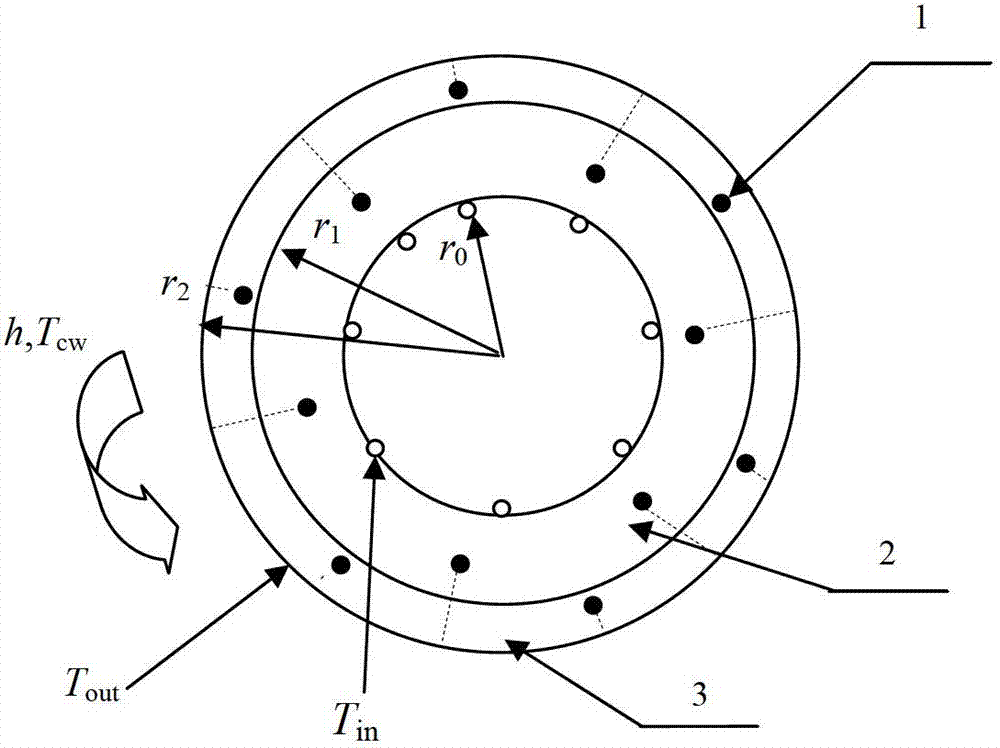
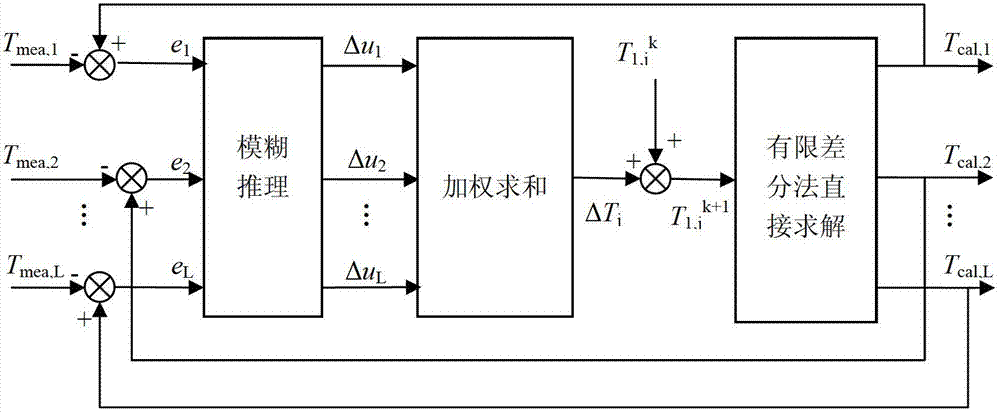
The invention discloses a method for estimating the inner surface temperature of blast furnaces. The method includes measuring the furnace wall temperature and inlet and outlet temperatures of cooling water in the middle of the furnace wall through a thermocouple, analyzing furnace wall heat transfer mechanisms and establishing a two-dimensional steady mechanism model, deducing the two-dimensional temperature distribution on cross sections of different heights of the furnace inner surface by combining the mechanism model and the fuzzy reasoning method, fitting temperature curves piecewise along the axial direction of the blast furnace, combining the curves and estimating the distribution of the three-dimensional temperature distribution of the whole inner surface of the blast furnace. The method for estimating the inner surface temperature of blast furnaces has the advantages of good real-time performance, high temperature estimation accuracy, small deviation, strong adaptability and the like. Changes of the temperature in the furnace can be reflected timely for optimal control, stable production and secure operation of blast furnaces are guaranteed, the blast furnace smelting quality is improved, and good economic benefits and social benefits are provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Magnetic separation method for low-grade chromium-containing vanadium titanium magnetite metalized pellet
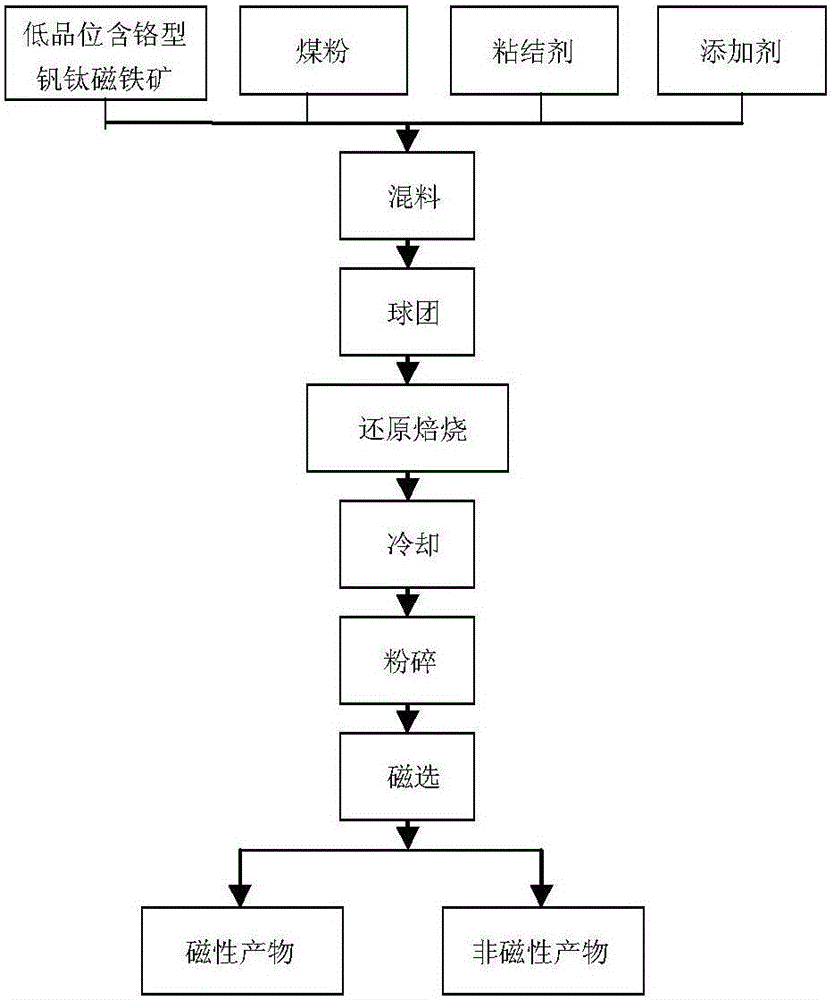
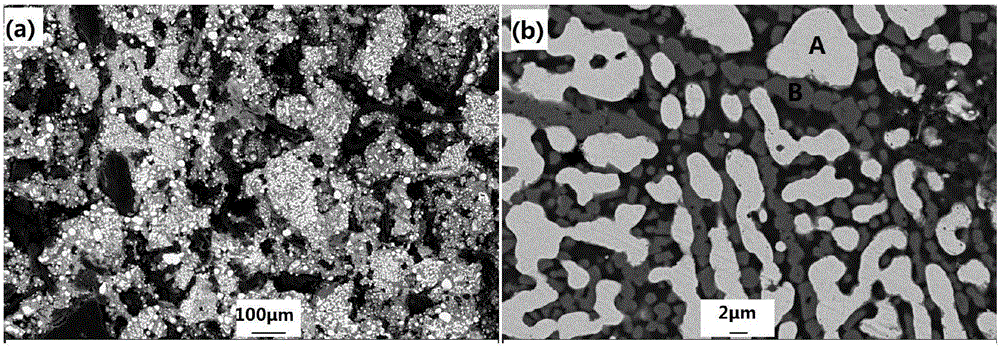
The invention discloses a magnetic separation method for a low-grade chromium-containing vanadium titanium magnetite metalized pellet, belonging to the technical field of non-blast furnace smelting in comprehensive utilization methods of low-grade chromium-containing vanadium titanium magnetite powder. The method is carried out through the following steps of (1) mixing low-grade chromium-containing vanadium titanium magnetite powder, reduced pulverized coal, a binder and an additive by weighing; (2) preparing a pellet from the mixture, and drying; (3) carrying out coal-based pellet self-reduction high-temperature roasting on the dried pellet; (4) cooling the metalized pellet subjected to high-temperature roasting; and (5) smashing the cooled metalized pellet to obtain metalized pellet powder, and then, carrying out magnetic separation by using a magnetic separation tube to obtain an iron-enriched magnetic matter and titanium-enriched nonmagnetic matters. By using the method, the utilization ratios of strategic metal vanadium, titanium and chromium are maximized on the premise that the metallization ratio and iron recovery ratio for coal-based forced reduction of the low-grade chromium-containing vanadium titanium magnetite metalized pellet are increased.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Vanadium-titanium magnetite blast furnace smelting method capable of improving vanadium yield
InactiveCN102220440AReduce typesHigh strengthBlast furnace detailsSmelting processBlast furnace smelting
The invention discloses a vanadium-titanium magnetite blast furnace smelting method capable of improving vanadium yield, belonging to the field of metallurgy, and is mainly used for solving the problem of low vanadium yield during vanadium-titanium magnetite blast furnace smelting. The vanadium-titanium magnetite blast furnace smelting method capable of improving vanadium yield comprises the following steps of: mixing 10-20% of the total addition amount of coke with sinter and adding to a blast furnace together with vanadium-titanium pellets to form an ore layer, wherein the ore layer and coke layer are alternately arranged, the amount of coke in the coke layer is 80-90% of the total addition amount of the coke, the amount of the sinter accounts for 55-65% of the total weight of the ore, and the amount of the vanadium-titanium pellets accounts for 35-45% of the total weight of the ore. The vanadium-titanium magnetite blast furnace smelting method provided by the invention can effectively improve vanadium yield during vanadium-titanium magnetite smelting process, simultaneously accelerate the reduction of iron, improve the smelting intensity and production of the blast furnace, hasan important significance in improving vanadium-titanium ore smelting technology and has a good popularization and application value.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +3
Method for smelting medium titanium slag by blast furnace
InactiveCN101476001AIncrease production levelsImprove breathabilityBlast furnace detailsSteelmakingAlkalinity
The invention belongs to the field of middle titanium slag melting technology, specifically to a middle titanium slag blast furnace smelting method. The technical problems the invention object to resolve is to provide a middle titanium slag melting method in a medium-sized blast furnace, the method can have a better use of schreyerite resources to perform middle titanium slag melting, specifically adopting 25 - 30 parts of all-vanadium-titanium pellet ore, 65 - 70 parts of low-vanadium-titanium magnetite ore and 5 - 10 parts of lump ore as raw materials for smelting in blast furnace. Obtained cast iron satisfies the quality requirements for further steelmaking, the furnace cinder dyadic alkalinity is 1.15 - 1.30, and can be used raw material of the composite powder. The method of the invention uses an appropriate charging stock structure in the blast furnace to reduce the sintering powder and to improve the air permeability, and makes full use of high cost-effective of schreyerite to effectively reduce production costs.
Owner:攀钢集团成都钢铁有限责任公司
Composite low-carbon ironmaking method based on blast furnace blowing coke oven coal gas
InactiveCN110241272AImprove the "cool" phenomenonEffective thermal compensationBlast furnace detailsBlast furnace smeltingCoke oven
The invention provides a composite low-carbon ironmaking method based on blast furnace blowing coke oven coal gas. The method takes a blast furnace as smelting equipment, ore layers and coke layers are taken as furnace charge, the furnace charge is loaded into the blast furnace from the top of the blast furnace, and the ore layers and the coke layers are alternately arranged inside the blast furnace; and the coke oven coal gas is blown at a blast furnace tuyere, meanwhile, two sections of blowing at a furnace top circulating coal gas tuyere and a furnace body are carried out, then blast furnace smelting is carried out by adopting high oxygen enrichment, hot air and coal injection operation, and finally molten iron and furnace slag are obtained. According to the method, the blast furnace smelting efficiency can be improved, the energy conversion and utilization inside the blast furnace can be optimized, the coke ratio can be reduced to the maximum extent, and the emission of carbon dioxide can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Blast furnace smelting process used for high-vanadium-titanium low-MgO furnace slag
InactiveCN102978312AReduce manufacturing costLow production costBlast furnace detailsSteelmakingSmelting process
The invention discloses a blast furnace smelting process used for high-vanadium-titanium low-MgO furnace slag and belongs to the technical field of blast furnace steelmaking. The blast furnace smelting process disclosed by the invention comprises the following step of: smelting after vanadium-titanium sintering ore, acid lump ore, vanadium-titanium pellet and coke cloth are placed into a blast furnace, wherein the vanadium-titanium sintering ore contains 2.2-2.6wt% of MgO and 2.4-2.8wt% of Al2O3; and during smelting, the basicity of the furnace slag is controlled to meet the condition that CaO / SiO2 is equal to 1.28-1.33, the physical thermal of molten iron is more than or equal to 1450 DEG C, and the content of MgO in the blast furnace slag is controlled to be 6.8-8.5%, the content of Al2O3 is controlled to be 11-13% and the content of TiO2 is controlled to be 18-21%. The blast furnace smelting process disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the usage amount of solvent can be reduced, the quantity of slag can be reduced and the TFe grade of charge ore is improved in a high-vanadium-titanium ore smelting process, and the obtained furnace slag has good melting property, liquidity and desulphurization capability; and high-vanadium-titanium magnetic iron ore can be reasonably used, the production cost of a blast furnace is reduced, and the comprehensive economic benefit of an enterprise is increased.
Owner:SICHUAN CHUANWEI GRP CO LTD
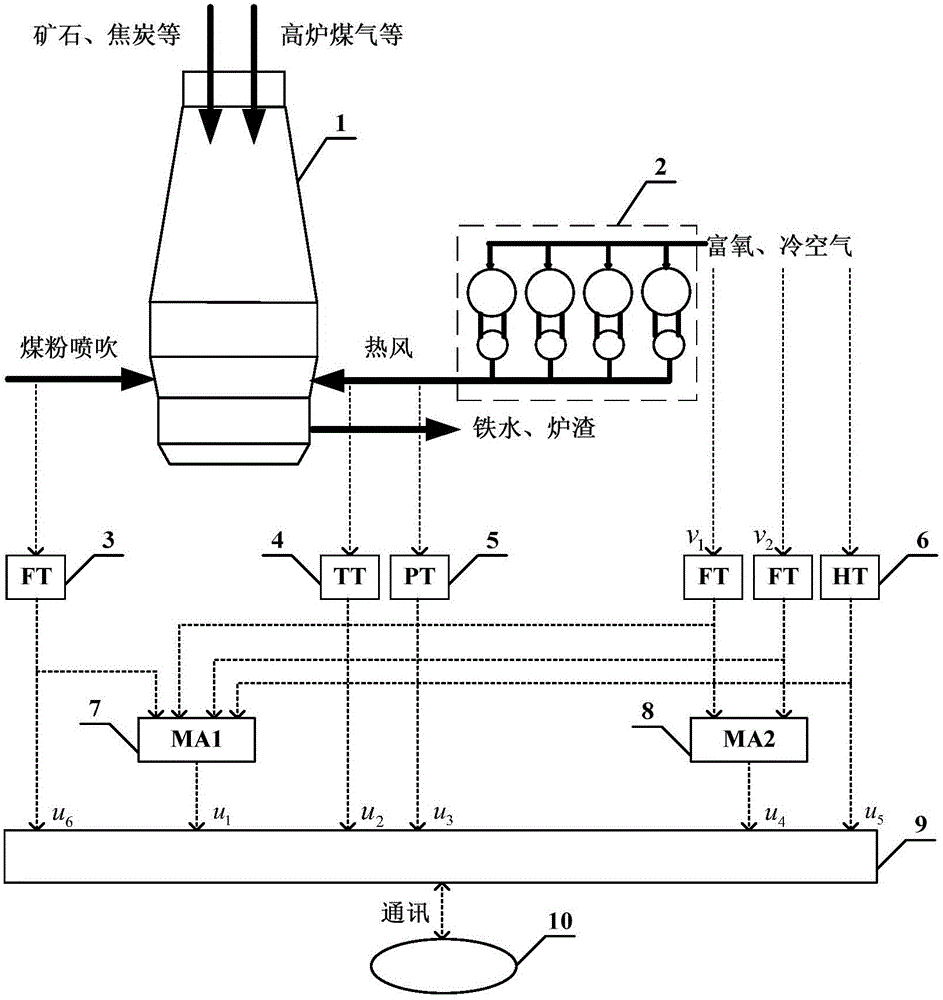
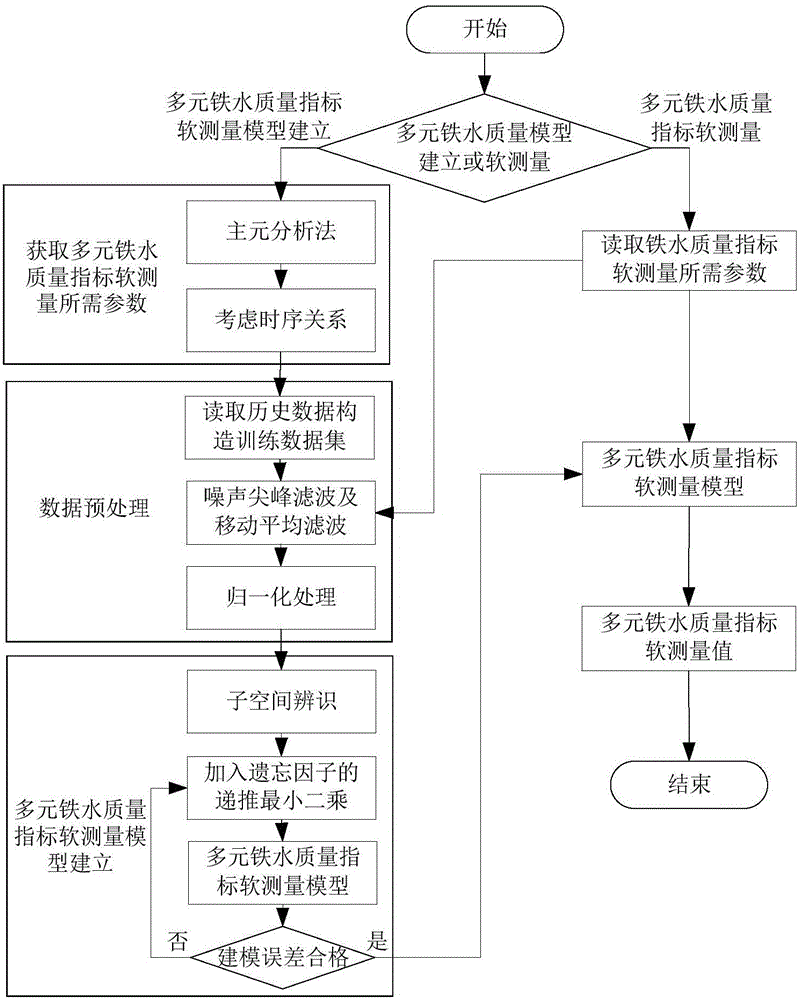
Soft measuring system and method for quality indexes of multielement molten iron of blast furnace
InactiveCN105821170ARealization of dynamic soft sensorSimple structureSteel manufacturing process aspectsForecastingHysteresisNoise removal
Provided are a soft measuring system and method for the quality indexes of multielement molten iron of a blast furnace. The system comprises a data collecting unit, a data preprocessing unit and a soft measuring unit. The method comprises the steps that parameters needed for soft measurement of the quality indexes of multielement molten iron of the blast furnace are acquired; the parameters needed for dynamic soft measurement of the quality indexes of multielement molten iron of the blast furnace are subjected to filtering, noise removal and normalization processing; dynamic soft measurement of multielement molten iron of the blast furnace is carried out through a blast furnace multielement molten iron quality index dynamic soft measurement model; and the parameters needed for soft measurement of the quality indexes of multielement molten iron of the blast furnace obtained after filtering and normalization processing are adopted as input, the current quality indexes of multielement molten iron of the blast furnace are adopted as output, output self-feedback is adopted, and the quality indexes of multielement molten iron of the blast furnace are dynamically predicted through online recurrence. The sequential relationship between the hysteresis characteristic of the blast furnace melting process and input and output variables is considered, the recurrence subspace intelligent modeling technology is adopted, and dynamic online soft measurement of the quality indexes of multielement molten iron of the blast furnace in the smelting process is achieved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
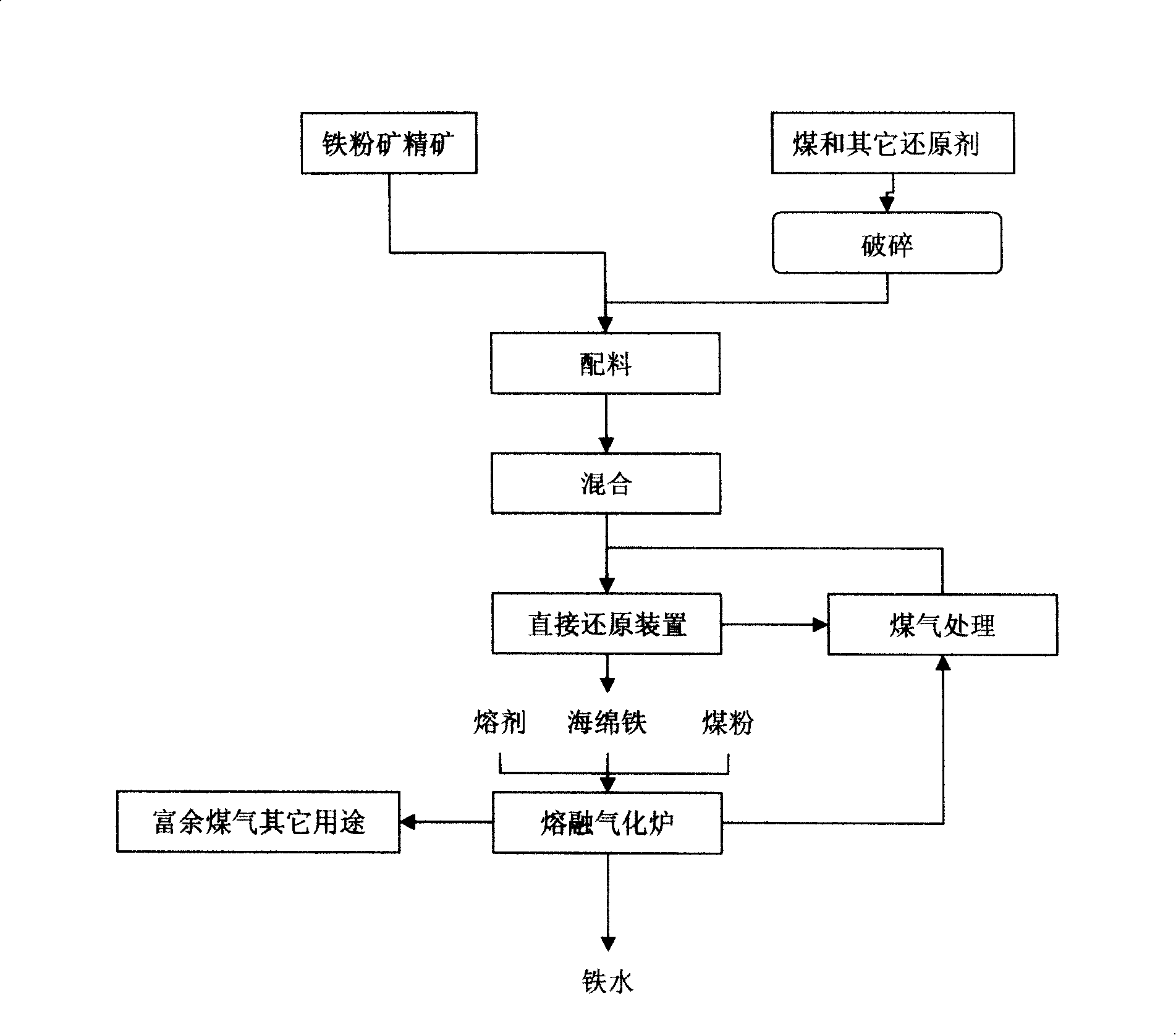
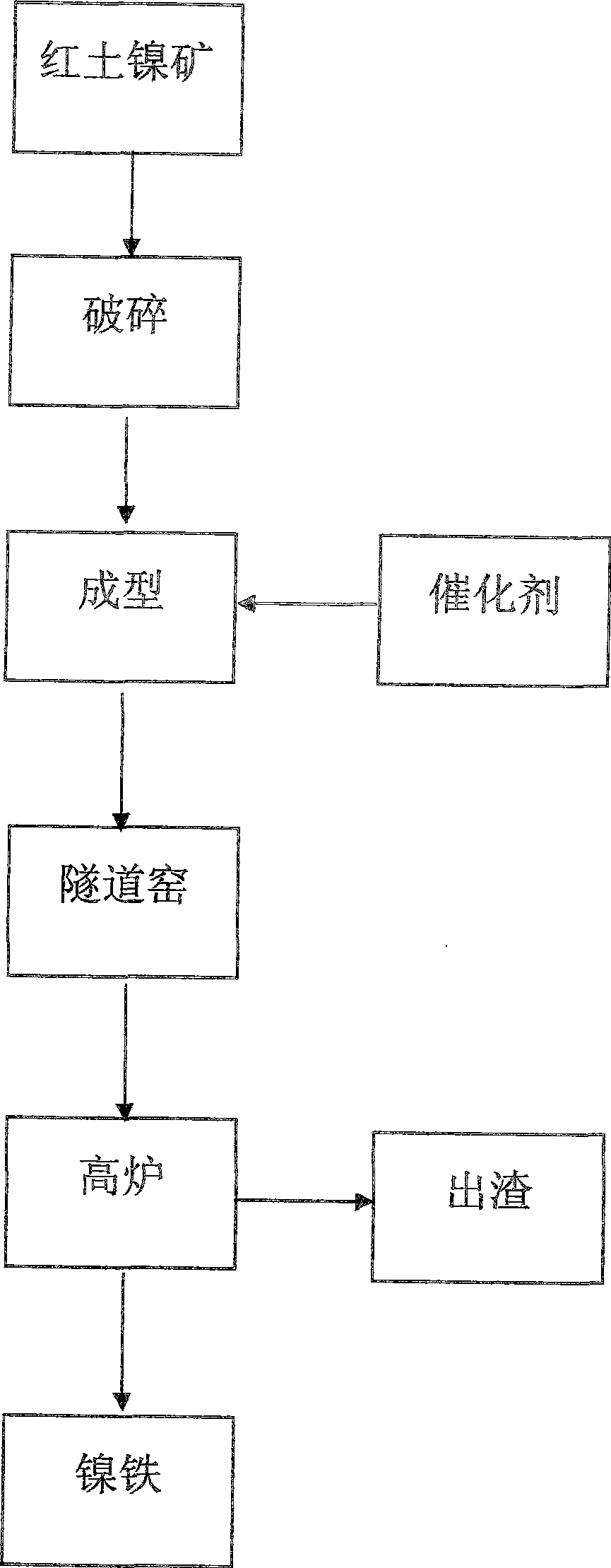
Method for jointly producing ferronickel in tunnel furnace-blast furnace from lateritic nickel
The invention relates to a method for producing ferronickel in tunnel furnace-blast furnace from laterite-nickel ore. The technology is as follows: the laterite-nickel ore powder is crushed to reach a granularity of 0mm to 3mm; a catalyst is added pro rata, blended evenly, and filled into a reduction tank after press forming in an extruder; a reducing agent is added, roasting and reduction are carried out for 4h to 7h at the furnace temperature of 1000 DEG C to 1300 DEG C; the laterite-nickel ore after reduction goes through crushing and magnetic concentration; magnetic concentrating products are pressed to form balls; blast furnace smelting is adopted to obtain high-quality nickel mineral. The method has simple technology, strong adoptability of raw materials and low cost, overcomes the problems of high cost, low quality and few outcome existing in the traditional pyrogenic process for producing ferronickel, realizes a new technology for jointly processing laterite-nickel ore to produce ferronickel in tunnel furnace-blast furnace, reaches the purpose of large output, low energy consumption and high quality of ferronickel, and has notable economic and social benefits.
Owner:毛耐文
Treatment method for metallurgy sintering of abandoned SCR flue gas denitrification catalyst
ActiveCN105907950ARealize green comprehensive utilizationNo secondary pollutionFlue gasBlast furnace smelting
The invention discloses a treatment method for metallurgy sintering of an abandoned SCR flue gas denitrification catalyst. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that the catalyst is broken, wherein the abandoned SCR flue gas denitrification catalyst is broken and ground, and catalyst powder being 100 meshes to 200 meshes is obtained; granulating is conducted, wherein the catalyst powder with the weight percent being 1% to 20% is mixed with iron ore powder, a fluxing agent, fuel, return fines and water, and a sintering mixture is obtained through granulating; and sintering is conducted, wherein the sintering mixture is laid on a bedding material of a sintering machine trolley to be sintered, and sintered ores are formed. By means of the method, the abandoned denitrification catalyst can be treated, the leaching amount of heavy metal of a formed sintered body is relatively low, the environment-friendly requirement is met, and meanwhile parts of the sintered ores can meet the performance requirement and used for blast furnace smelting.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com